
18 Qualitative Research Examples

Qualitative research is an approach to scientific research that involves using observation to gather and analyze non-numerical, in-depth, and well-contextualized datasets.
It serves as an integral part of academic, professional, and even daily decision-making processes (Baxter & Jack, 2008).
Methods of qualitative research encompass a wide range of techniques, from in-depth personal encounters, like ethnographies (studying cultures in-depth) and autoethnographies (examining one’s own cultural experiences), to collection of diverse perspectives on topics through methods like interviewing focus groups (gatherings of individuals to discuss specific topics).
Qualitative Research Examples
1. ethnography.
Definition: Ethnography is a qualitative research design aimed at exploring cultural phenomena. Rooted in the discipline of anthropology , this research approach investigates the social interactions, behaviors, and perceptions within groups, communities, or organizations.
Ethnographic research is characterized by extended observation of the group, often through direct participation, in the participants’ environment. An ethnographer typically lives with the study group for extended periods, intricately observing their everyday lives (Khan, 2014).
It aims to present a complete, detailed and accurate picture of the observed social life, rituals, symbols, and values from the perspective of the study group.
Example of Ethnographic Research
Title: “ The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity “
Citation: Evans, J. (2010). The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity. Peter Lang.
Overview: This study by Evans (2010) provides a rich narrative of young adult male identity as experienced in everyday life. The author immersed himself among a group of young men, participating in their activities and cultivating a deep understanding of their lifestyle, values, and motivations. This research exemplified the ethnographic approach, revealing complexities of the subjects’ identities and societal roles, which could hardly be accessed through other qualitative research designs.
Read my Full Guide on Ethnography Here
2. Autoethnography
Definition: Autoethnography is an approach to qualitative research where the researcher uses their own personal experiences to extend the understanding of a certain group, culture, or setting. Essentially, it allows for the exploration of self within the context of social phenomena.
Unlike traditional ethnography, which focuses on the study of others, autoethnography turns the ethnographic gaze inward, allowing the researcher to use their personal experiences within a culture as rich qualitative data (Durham, 2019).
The objective is to critically appraise one’s personal experiences as they navigate and negotiate cultural, political, and social meanings. The researcher becomes both the observer and the participant, intertwining personal and cultural experiences in the research.
Example of Autoethnographic Research
Title: “ A Day In The Life Of An NHS Nurse “
Citation: Osben, J. (2019). A day in the life of a NHS nurse in 21st Century Britain: An auto-ethnography. The Journal of Autoethnography for Health & Social Care. 1(1).
Overview: This study presents an autoethnography of a day in the life of an NHS nurse (who, of course, is also the researcher). The author uses the research to achieve reflexivity, with the researcher concluding: “Scrutinising my practice and situating it within a wider contextual backdrop has compelled me to significantly increase my level of scrutiny into the driving forces that influence my practice.”
Read my Full Guide on Autoethnography Here
3. Semi-Structured Interviews
Definition: Semi-structured interviews stand as one of the most frequently used methods in qualitative research. These interviews are planned and utilize a set of pre-established questions, but also allow for the interviewer to steer the conversation in other directions based on the responses given by the interviewee.
In semi-structured interviews, the interviewer prepares a guide that outlines the focal points of the discussion. However, the interview is flexible, allowing for more in-depth probing if the interviewer deems it necessary (Qu, & Dumay, 2011). This style of interviewing strikes a balance between structured ones which might limit the discussion, and unstructured ones, which could lack focus.
Example of Semi-Structured Interview Research
Title: “ Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review “
Citation: Puts, M., et al. (2014). Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review. Annals of oncology, 25 (3), 564-577.
Overview: Puts et al. (2014) executed an extensive systematic review in which they conducted semi-structured interviews with older adults suffering from cancer to examine the factors influencing their adherence to cancer treatment. The findings suggested that various factors, including side effects, faith in healthcare professionals, and social support have substantial impacts on treatment adherence. This research demonstrates how semi-structured interviews can provide rich and profound insights into the subjective experiences of patients.
4. Focus Groups
Definition: Focus groups are a qualitative research method that involves organized discussion with a selected group of individuals to gain their perspectives on a specific concept, product, or phenomenon. Typically, these discussions are guided by a moderator.
During a focus group session, the moderator has a list of questions or topics to discuss, and participants are encouraged to interact with each other (Morgan, 2010). This interactivity can stimulate more information and provide a broader understanding of the issue under scrutiny. The open format allows participants to ask questions and respond freely, offering invaluable insights into attitudes, experiences, and group norms.
Example of Focus Group Research
Title: “ Perspectives of Older Adults on Aging Well: A Focus Group Study “
Citation: Halaweh, H., Dahlin-Ivanoff, S., Svantesson, U., & Willén, C. (2018). Perspectives of older adults on aging well: a focus group study. Journal of aging research .
Overview: This study aimed to explore what older adults (aged 60 years and older) perceived to be ‘aging well’. The researchers identified three major themes from their focus group interviews: a sense of well-being, having good physical health, and preserving good mental health. The findings highlight the importance of factors such as positive emotions, social engagement, physical activity, healthy eating habits, and maintaining independence in promoting aging well among older adults.
5. Phenomenology
Definition: Phenomenology, a qualitative research method, involves the examination of lived experiences to gain an in-depth understanding of the essence or underlying meanings of a phenomenon.
The focus of phenomenology lies in meticulously describing participants’ conscious experiences related to the chosen phenomenon (Padilla-Díaz, 2015).
In a phenomenological study, the researcher collects detailed, first-hand perspectives of the participants, typically via in-depth interviews, and then uses various strategies to interpret and structure these experiences, ultimately revealing essential themes (Creswell, 2013). This approach focuses on the perspective of individuals experiencing the phenomenon, seeking to explore, clarify, and understand the meanings they attach to those experiences.
Example of Phenomenology Research
Title: “ A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology: current state, promise, and future directions for research ”
Citation: Cilesiz, S. (2011). A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology: Current state, promise, and future directions for research. Educational Technology Research and Development, 59 , 487-510.
Overview: A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology by Sebnem Cilesiz represents a good starting point for formulating a phenomenological study. With its focus on the ‘essence of experience’, this piece presents methodological, reliability, validity, and data analysis techniques that phenomenologists use to explain how people experience technology in their everyday lives.
6. Grounded Theory
Definition: Grounded theory is a systematic methodology in qualitative research that typically applies inductive reasoning . The primary aim is to develop a theoretical explanation or framework for a process, action, or interaction grounded in, and arising from, empirical data (Birks & Mills, 2015).
In grounded theory, data collection and analysis work together in a recursive process. The researcher collects data, analyses it, and then collects more data based on the evolving understanding of the research context. This ongoing process continues until a comprehensive theory that represents the data and the associated phenomenon emerges – a point known as theoretical saturation (Charmaz, 2014).
Example of Grounded Theory Research
Title: “ Student Engagement in High School Classrooms from the Perspective of Flow Theory “
Citation: Shernoff, D. J., Csikszentmihalyi, M., Shneider, B., & Shernoff, E. S. (2003). Student engagement in high school classrooms from the perspective of flow theory. School Psychology Quarterly, 18 (2), 158–176.
Overview: Shernoff and colleagues (2003) used grounded theory to explore student engagement in high school classrooms. The researchers collected data through student self-reports, interviews, and observations. Key findings revealed that academic challenge, student autonomy, and teacher support emerged as the most significant factors influencing students’ engagement, demonstrating how grounded theory can illuminate complex dynamics within real-world contexts.
7. Narrative Research
Definition: Narrative research is a qualitative research method dedicated to storytelling and understanding how individuals experience the world. It focuses on studying an individual’s life and experiences as narrated by that individual (Polkinghorne, 2013).
In narrative research, the researcher collects data through methods such as interviews, observations , and document analysis. The emphasis is on the stories told by participants – narratives that reflect their experiences, thoughts, and feelings.
These stories are then interpreted by the researcher, who attempts to understand the meaning the participant attributes to these experiences (Josselson, 2011).
Example of Narrative Research
Title: “Narrative Structures and the Language of the Self”
Citation: McAdams, D. P., Josselson, R., & Lieblich, A. (2006). Identity and story: Creating self in narrative . American Psychological Association.
Overview: In this innovative study, McAdams et al. (2006) employed narrative research to explore how individuals construct their identities through the stories they tell about themselves. By examining personal narratives, the researchers discerned patterns associated with characters, motivations, conflicts, and resolutions, contributing valuable insights about the relationship between narrative and individual identity.
8. Case Study Research
Definition: Case study research is a qualitative research method that involves an in-depth investigation of a single instance or event: a case. These ‘cases’ can range from individuals, groups, or entities to specific projects, programs, or strategies (Creswell, 2013).
The case study method typically uses multiple sources of information for comprehensive contextual analysis. It aims to explore and understand the complexity and uniqueness of a particular case in a real-world context (Merriam & Tisdell, 2015). This investigation could result in a detailed description of the case, a process for its development, or an exploration of a related issue or problem.
Example of Case Study Research
Title: “ Teacher’s Role in Fostering Preschoolers’ Computational Thinking: An Exploratory Case Study “
Citation: Wang, X. C., Choi, Y., Benson, K., Eggleston, C., & Weber, D. (2021). Teacher’s role in fostering preschoolers’ computational thinking: An exploratory case study. Early Education and Development , 32 (1), 26-48.
Overview: This study investigates the role of teachers in promoting computational thinking skills in preschoolers. The study utilized a qualitative case study methodology to examine the computational thinking scaffolding strategies employed by a teacher interacting with three preschoolers in a small group setting. The findings highlight the importance of teachers’ guidance in fostering computational thinking practices such as problem reformulation/decomposition, systematic testing, and debugging.
Read about some Famous Case Studies in Psychology Here
9. Participant Observation
Definition: Participant observation has the researcher immerse themselves in a group or community setting to observe the behavior of its members. It is similar to ethnography, but generally, the researcher isn’t embedded for a long period of time.
The researcher, being a participant, engages in daily activities, interactions, and events as a way of conducting a detailed study of a particular social phenomenon (Kawulich, 2005).
The method involves long-term engagement in the field, maintaining detailed records of observed events, informal interviews, direct participation, and reflexivity. This approach allows for a holistic view of the participants’ lived experiences, behaviours, and interactions within their everyday environment (Dewalt, 2011).
Example of Participant Observation Research
Title: Conflict in the boardroom: a participant observation study of supervisory board dynamics
Citation: Heemskerk, E. M., Heemskerk, K., & Wats, M. M. (2017). Conflict in the boardroom: a participant observation study of supervisory board dynamics. Journal of Management & Governance , 21 , 233-263.
Overview: This study examined how conflicts within corporate boards affect their performance. The researchers used a participant observation method, where they actively engaged with 11 supervisory boards and observed their dynamics. They found that having a shared understanding of the board’s role called a common framework, improved performance by reducing relationship conflicts, encouraging task conflicts, and minimizing conflicts between the board and CEO.
10. Non-Participant Observation
Definition: Non-participant observation is a qualitative research method in which the researcher observes the phenomena of interest without actively participating in the situation, setting, or community being studied.
This method allows the researcher to maintain a position of distance, as they are solely an observer and not a participant in the activities being observed (Kawulich, 2005).
During non-participant observation, the researcher typically records field notes on the actions, interactions, and behaviors observed , focusing on specific aspects of the situation deemed relevant to the research question.
This could include verbal and nonverbal communication , activities, interactions, and environmental contexts (Angrosino, 2007). They could also use video or audio recordings or other methods to collect data.
Example of Non-Participant Observation Research
Title: Mental Health Nurses’ attitudes towards mental illness and recovery-oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units: A non-participant observation study
Citation: Sreeram, A., Cross, W. M., & Townsin, L. (2023). Mental Health Nurses’ attitudes towards mental illness and recovery‐oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units: A non‐participant observation study. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing .
Overview: This study investigated the attitudes of mental health nurses towards mental illness and recovery-oriented practice in acute inpatient psychiatric units. The researchers used a non-participant observation method, meaning they observed the nurses without directly participating in their activities. The findings shed light on the nurses’ perspectives and behaviors, providing valuable insights into their attitudes toward mental health and recovery-focused care in these settings.
11. Content Analysis
Definition: Content Analysis involves scrutinizing textual, visual, or spoken content to categorize and quantify information. The goal is to identify patterns, themes, biases, or other characteristics (Hsieh & Shannon, 2005).
Content Analysis is widely used in various disciplines for a multitude of purposes. Researchers typically use this method to distill large amounts of unstructured data, like interview transcripts, newspaper articles, or social media posts, into manageable and meaningful chunks.
When wielded appropriately, Content Analysis can illuminate the density and frequency of certain themes within a dataset, provide insights into how specific terms or concepts are applied contextually, and offer inferences about the meanings of their content and use (Duriau, Reger, & Pfarrer, 2007).
Example of Content Analysis
Title: Framing European politics: A content analysis of press and television news .
Citation: Semetko, H. A., & Valkenburg, P. M. (2000). Framing European politics: A content analysis of press and television news. Journal of Communication, 50 (2), 93-109.
Overview: This study analyzed press and television news articles about European politics using a method called content analysis. The researchers examined the prevalence of different “frames” in the news, which are ways of presenting information to shape audience perceptions. They found that the most common frames were attribution of responsibility, conflict, economic consequences, human interest, and morality.
Read my Full Guide on Content Analysis Here
12. Discourse Analysis
Definition: Discourse Analysis, a qualitative research method, interprets the meanings, functions, and coherence of certain languages in context.
Discourse analysis is typically understood through social constructionism, critical theory , and poststructuralism and used for understanding how language constructs social concepts (Cheek, 2004).
Discourse Analysis offers great breadth, providing tools to examine spoken or written language, often beyond the level of the sentence. It enables researchers to scrutinize how text and talk articulate social and political interactions and hierarchies.
Insight can be garnered from different conversations, institutional text, and media coverage to understand how topics are addressed or framed within a specific social context (Jorgensen & Phillips, 2002).
Example of Discourse Analysis
Title: The construction of teacher identities in educational policy documents: A critical discourse analysis
Citation: Thomas, S. (2005). The construction of teacher identities in educational policy documents: A critical discourse analysis. Critical Studies in Education, 46 (2), 25-44.
Overview: The author examines how an education policy in one state of Australia positions teacher professionalism and teacher identities. While there are competing discourses about professional identity, the policy framework privileges a narrative that frames the ‘good’ teacher as one that accepts ever-tightening control and regulation over their professional practice.
Read my Full Guide on Discourse Analysis Here
13. Action Research
Definition: Action Research is a qualitative research technique that is employed to bring about change while simultaneously studying the process and results of that change.
This method involves a cyclical process of fact-finding, action, evaluation, and reflection (Greenwood & Levin, 2016).
Typically, Action Research is used in the fields of education, social sciences , and community development. The process isn’t just about resolving an issue but also developing knowledge that can be used in the future to address similar or related problems.
The researcher plays an active role in the research process, which is normally broken down into four steps:
- developing a plan to improve what is currently being done
- implementing the plan
- observing the effects of the plan, and
- reflecting upon these effects (Smith, 2010).
Example of Action Research
Title: Using Digital Sandbox Gaming to Improve Creativity Within Boys’ Writing
Citation: Ellison, M., & Drew, C. (2020). Using digital sandbox gaming to improve creativity within boys’ writing. Journal of Research in Childhood Education , 34 (2), 277-287.
Overview: This was a research study one of my research students completed in his own classroom under my supervision. He implemented a digital game-based approach to literacy teaching with boys and interviewed his students to see if the use of games as stimuli for storytelling helped draw them into the learning experience.
Read my Full Guide on Action Research Here
14. Semiotic Analysis
Definition: Semiotic Analysis is a qualitative method of research that interprets signs and symbols in communication to understand sociocultural phenomena. It stems from semiotics, the study of signs and symbols and their use or interpretation (Chandler, 2017).
In a Semiotic Analysis, signs (anything that represents something else) are interpreted based on their significance and the role they play in representing ideas.
This type of research often involves the examination of images, sounds, and word choice to uncover the embedded sociocultural meanings. For example, an advertisement for a car might be studied to learn more about societal views on masculinity or success (Berger, 2010).
Example of Semiotic Research
Title: Shielding the learned body: a semiotic analysis of school badges in New South Wales, Australia
Citation: Symes, C. (2023). Shielding the learned body: a semiotic analysis of school badges in New South Wales, Australia. Semiotica , 2023 (250), 167-190.
Overview: This study examines school badges in New South Wales, Australia, and explores their significance through a semiotic analysis. The badges, which are part of the school’s visual identity, are seen as symbolic representations that convey meanings. The analysis reveals that these badges often draw on heraldic models, incorporating elements like colors, names, motifs, and mottoes that reflect local culture and history, thus connecting students to their national identity. Additionally, the study highlights how some schools have shifted from traditional badges to modern logos and slogans, reflecting a more business-oriented approach.
15. Qualitative Longitudinal Studies
Definition: Qualitative Longitudinal Studies are a research method that involves repeated observation of the same items over an extended period of time.
Unlike a snapshot perspective, this method aims to piece together individual histories and examine the influences and impacts of change (Neale, 2019).
Qualitative Longitudinal Studies provide an in-depth understanding of change as it happens, including changes in people’s lives, their perceptions, and their behaviors.
For instance, this method could be used to follow a group of students through their schooling years to understand the evolution of their learning behaviors and attitudes towards education (Saldaña, 2003).
Example of Qualitative Longitudinal Research
Title: Patient and caregiver perspectives on managing pain in advanced cancer: a qualitative longitudinal study
Citation: Hackett, J., Godfrey, M., & Bennett, M. I. (2016). Patient and caregiver perspectives on managing pain in advanced cancer: a qualitative longitudinal study. Palliative medicine , 30 (8), 711-719.
Overview: This article examines how patients and their caregivers manage pain in advanced cancer through a qualitative longitudinal study. The researchers interviewed patients and caregivers at two different time points and collected audio diaries to gain insights into their experiences, making this study longitudinal.
Read my Full Guide on Longitudinal Research Here
16. Open-Ended Surveys
Definition: Open-Ended Surveys are a type of qualitative research method where respondents provide answers in their own words. Unlike closed-ended surveys, which limit responses to predefined options, open-ended surveys allow for expansive and unsolicited explanations (Fink, 2013).
Open-ended surveys are commonly used in a range of fields, from market research to social studies. As they don’t force respondents into predefined response categories, these surveys help to draw out rich, detailed data that might uncover new variables or ideas.
For example, an open-ended survey might be used to understand customer opinions about a new product or service (Lavrakas, 2008).
Contrast this to a quantitative closed-ended survey, like a Likert scale, which could theoretically help us to come up with generalizable data but is restricted by the questions on the questionnaire, meaning new and surprising data and insights can’t emerge from the survey results in the same way.
Example of Open-Ended Survey Research
Title: Advantages and disadvantages of technology in relationships: Findings from an open-ended survey
Citation: Hertlein, K. M., & Ancheta, K. (2014). Advantages and disadvantages of technology in relationships: Findings from an open-ended survey. The Qualitative Report , 19 (11), 1-11.
Overview: This article examines the advantages and disadvantages of technology in couple relationships through an open-ended survey method. Researchers analyzed responses from 410 undergraduate students to understand how technology affects relationships. They found that technology can contribute to relationship development, management, and enhancement, but it can also create challenges such as distancing, lack of clarity, and impaired trust.
17. Naturalistic Observation
Definition: Naturalistic Observation is a type of qualitative research method that involves observing individuals in their natural environments without interference or manipulation by the researcher.
Naturalistic observation is often used when conducting research on behaviors that cannot be controlled or manipulated in a laboratory setting (Kawulich, 2005).
It is frequently used in the fields of psychology, sociology, and anthropology. For instance, to understand the social dynamics in a schoolyard, a researcher could spend time observing the children interact during their recess, noting their behaviors, interactions, and conflicts without imposing their presence on the children’s activities (Forsyth, 2010).
Example of Naturalistic Observation Research
Title: Dispositional mindfulness in daily life: A naturalistic observation study
Citation: Kaplan, D. M., Raison, C. L., Milek, A., Tackman, A. M., Pace, T. W., & Mehl, M. R. (2018). Dispositional mindfulness in daily life: A naturalistic observation study. PloS one , 13 (11), e0206029.
Overview: In this study, researchers conducted two studies: one exploring assumptions about mindfulness and behavior, and the other using naturalistic observation to examine actual behavioral manifestations of mindfulness. They found that trait mindfulness is associated with a heightened perceptual focus in conversations, suggesting that being mindful is expressed primarily through sharpened attention rather than observable behavioral or social differences.
Read my Full Guide on Naturalistic Observation Here
18. Photo-Elicitation
Definition: Photo-elicitation utilizes photographs as a means to trigger discussions and evoke responses during interviews. This strategy aids in bringing out topics of discussion that may not emerge through verbal prompting alone (Harper, 2002).
Traditionally, Photo-Elicitation has been useful in various fields such as education, psychology, and sociology. The method involves the researcher or participants taking photographs, which are then used as prompts for discussion.
For instance, a researcher studying urban environmental issues might invite participants to photograph areas in their neighborhood that they perceive as environmentally detrimental, and then discuss each photo in depth (Clark-Ibáñez, 2004).
Example of Photo-Elicitation Research
Title: Early adolescent food routines: A photo-elicitation study
Citation: Green, E. M., Spivak, C., & Dollahite, J. S. (2021). Early adolescent food routines: A photo-elicitation study. Appetite, 158 .
Overview: This study focused on early adolescents (ages 10-14) and their food routines. Researchers conducted in-depth interviews using a photo-elicitation approach, where participants took photos related to their food choices and experiences. Through analysis, the study identified various routines and three main themes: family, settings, and meals/foods consumed, revealing how early adolescents view and are influenced by their eating routines.
Features of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a research method focused on understanding the meaning individuals or groups attribute to a social or human problem (Creswell, 2013).
Some key features of this method include:
- Naturalistic Inquiry: Qualitative research happens in the natural setting of the phenomena, aiming to understand “real world” situations (Patton, 2015). This immersion in the field or subject allows the researcher to gather a deep understanding of the subject matter.
- Emphasis on Process: It aims to understand how events unfold over time rather than focusing solely on outcomes (Merriam & Tisdell, 2015). The process-oriented nature of qualitative research allows researchers to investigate sequences, timing, and changes.
- Interpretive: It involves interpreting and making sense of phenomena in terms of the meanings people assign to them (Denzin & Lincoln, 2011). This interpretive element allows for rich, nuanced insights into human behavior and experiences.
- Holistic Perspective: Qualitative research seeks to understand the whole phenomenon rather than focusing on individual components (Creswell, 2013). It emphasizes the complex interplay of factors, providing a richer, more nuanced view of the research subject.
- Prioritizes Depth over Breadth: Qualitative research favors depth of understanding over breadth, typically involving a smaller but more focused sample size (Hennink, Hutter, & Bailey, 2020). This enables detailed exploration of the phenomena of interest, often leading to rich and complex data.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research
Qualitative research centers on exploring and understanding the meaning individuals or groups attribute to a social or human problem (Creswell, 2013).
It involves an in-depth approach to the subject matter, aiming to capture the richness and complexity of human experience.
Examples include conducting interviews, observing behaviors, or analyzing text and images.
There are strengths inherent in this approach. In its focus on understanding subjective experiences and interpretations, qualitative research can yield rich and detailed data that quantitative research may overlook (Denzin & Lincoln, 2011).
Additionally, qualitative research is adaptive, allowing the researcher to respond to new directions and insights as they emerge during the research process.
However, there are also limitations. Because of the interpretive nature of this research, findings may not be generalizable to a broader population (Marshall & Rossman, 2014). Well-designed quantitative research, on the other hand, can be generalizable.
Moreover, the reliability and validity of qualitative data can be challenging to establish due to its subjective nature, unlike quantitative research, which is ideally more objective.
Compare Qualitative and Quantitative Research Methodologies in This Guide Here
In conclusion, qualitative research methods provide distinctive ways to explore social phenomena and understand nuances that quantitative approaches might overlook. Each method, from Ethnography to Photo-Elicitation, presents its strengths and weaknesses but they all offer valuable means of investigating complex, real-world situations. The goal for the researcher is not to find a definitive tool, but to employ the method best suited for their research questions and the context at hand (Almalki, 2016). Above all, these methods underscore the richness of human experience and deepen our understanding of the world around us.
Angrosino, M. (2007). Doing ethnographic and observational research. Sage Publications.
Areni, C. S., & Kim, D. (1994). The influence of in-store lighting on consumers’ examination of merchandise in a wine store. International Journal of Research in Marketing, 11 (2), 117-125.
Barker, C., Pistrang, N., & Elliott, R. (2016). Research Methods in Clinical Psychology: An Introduction for Students and Practitioners. John Wiley & Sons.
Baxter, P. & Jack, S. (2008). Qualitative case study methodology: Study design and implementation for novice researchers. The Qualitative Report, 13 (4), 544-559.
Berger, A. A. (2010). The Objects of Affection: Semiotics and Consumer Culture. Palgrave Macmillan.
Bevan, M. T. (2014). A method of phenomenological interviewing. Qualitative health research, 24 (1), 136-144.
Birks, M., & Mills, J. (2015). Grounded theory: A practical guide . Sage Publications.
Bryman, A. (2015) . The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Research. Sage Publications.
Chandler, D. (2017). Semiotics: The Basics. Routledge.
Charmaz, K. (2014). Constructing grounded theory. Sage Publications.
Cheek, J. (2004). At the margins? Discourse analysis and qualitative research. Qualitative Health Research, 14(8), 1140-1150.
Clark-Ibáñez, M. (2004). Framing the social world with photo-elicitation interviews. American Behavioral Scientist, 47(12), 1507-1527.
Creswell, J. W. (2013). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative and Mixed Methods Approaches. Sage Publications.
Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2017). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches. Sage publications.
Crowe, S., Cresswell, K., Robertson, A., Huby, G., Avery, A., & Sheikh, A. (2011). The case study approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 11(100), 1-9.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). The Sage Handbook of Qualitative Research. Sage.
Dewalt, K. M., & Dewalt, B. R. (2011). Participant observation: A guide for fieldworkers. Rowman Altamira.
Doody, O., Slevin, E., & Taggart, L. (2013). Focus group interviews in nursing research: part 1. British Journal of Nursing, 22(1), 16-19.
Durham, A. (2019). Autoethnography. In P. Atkinson (Ed.), Qualitative Research Methods. Oxford University Press.
Duriau, V. J., Reger, R. K., & Pfarrer, M. D. (2007). A content analysis of the content analysis literature in organization studies: Research themes, data sources, and methodological refinements. Organizational Research Methods, 10(1), 5-34.
Evans, J. (2010). The Everyday Lives of Men: An Ethnographic Investigation of Young Adult Male Identity. Peter Lang.
Farrall, S. (2006). What is qualitative longitudinal research? Papers in Social Research Methods, Qualitative Series, No.11, London School of Economics, Methodology Institute.
Fielding, J., & Fielding, N. (2008). Synergy and synthesis: integrating qualitative and quantitative data. The SAGE handbook of social research methods, 555-571.
Fink, A. (2013). How to conduct surveys: A step-by-step guide . SAGE.
Forsyth, D. R. (2010). Group Dynamics . Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Fugard, A. J. B., & Potts, H. W. W. (2015). Supporting thinking on sample sizes for thematic analyses: A quantitative tool. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 18 (6), 669–684.
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research. Aldine de Gruyter.
Gray, J. R., Grove, S. K., & Sutherland, S. (2017). Burns and Grove’s the Practice of Nursing Research E-Book: Appraisal, Synthesis, and Generation of Evidence. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Greenwood, D. J., & Levin, M. (2016). Introduction to action research: Social research for social change. SAGE.
Harper, D. (2002). Talking about pictures: A case for photo elicitation. Visual Studies, 17 (1), 13-26.
Heinonen, T. (2012). Making Sense of the Social: Human Sciences and the Narrative Turn. Rozenberg Publishers.
Heisley, D. D., & Levy, S. J. (1991). Autodriving: A photoelicitation technique. Journal of Consumer Research, 18 (3), 257-272.
Hennink, M. M., Hutter, I., & Bailey, A. (2020). Qualitative Research Methods . SAGE Publications Ltd.
Hsieh, H. F., & Shannon, S. E. (2005). Three Approaches to Qualitative Content Analysis. Qualitative Health Research, 15 (9), 1277–1288.
Jorgensen, D. L. (2015). Participant Observation. In Emerging Trends in the Social and Behavioral Sciences: An Interdisciplinary, Searchable, and Linkable Resource. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Jorgensen, M., & Phillips, L. (2002). Discourse Analysis as Theory and Method . SAGE.
Josselson, R. (2011). Narrative research: Constructing, deconstructing, and reconstructing story. In Five ways of doing qualitative analysis . Guilford Press.
Kawulich, B. B. (2005). Participant observation as a data collection method. Forum: Qualitative Social Research, 6 (2).
Khan, S. (2014). Qualitative Research Method: Grounded Theory. Journal of Basic and Clinical Pharmacy, 5 (4), 86-88.
Koshy, E., Koshy, V., & Waterman, H. (2010). Action Research in Healthcare . SAGE.
Krippendorff, K. (2013). Content Analysis: An Introduction to its Methodology. SAGE.
Lannon, J., & Cooper, P. (2012). Humanistic Advertising: A Holistic Cultural Perspective. International Journal of Advertising, 15 (2), 97–111.
Lavrakas, P. J. (2008). Encyclopedia of survey research methods. SAGE Publications.
Lieblich, A., Tuval-Mashiach, R., & Zilber, T. (2008). Narrative research: Reading, analysis and interpretation. Sage Publications.
Mackey, A., & Gass, S. M. (2015). Second language research: Methodology and design. Routledge.
Marshall, C., & Rossman, G. B. (2014). Designing qualitative research. Sage publications.
McAdams, D. P., Josselson, R., & Lieblich, A. (2006). Identity and story: Creating self in narrative. American Psychological Association.
Merriam, S. B., & Tisdell, E. J. (2015). Qualitative Research: A Guide to Design and Implementation. Jossey-Bass.
Mick, D. G. (1986). Consumer Research and Semiotics: Exploring the Morphology of Signs, Symbols, and Significance. Journal of Consumer Research, 13 (2), 196-213.
Morgan, D. L. (2010). Focus groups as qualitative research. Sage Publications.
Mulhall, A. (2003). In the field: notes on observation in qualitative research. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 41 (3), 306-313.
Neale, B. (2019). What is Qualitative Longitudinal Research? Bloomsbury Publishing.
Nolan, L. B., & Renderos, T. B. (2012). A focus group study on the influence of fatalism and religiosity on cancer risk perceptions in rural, eastern North Carolina. Journal of religion and health, 51 (1), 91-104.
Padilla-Díaz, M. (2015). Phenomenology in educational qualitative research: Philosophy as science or philosophical science? International Journal of Educational Excellence, 1 (2), 101-110.
Parker, I. (2014). Discourse dynamics: Critical analysis for social and individual psychology . Routledge.
Patton, M. Q. (2015). Qualitative research & evaluation methods: Integrating theory and practice . Sage Publications.
Polkinghorne, D. E. (2013). Narrative configuration in qualitative analysis. In Life history and narrative. Routledge.
Puts, M. T., Tapscott, B., Fitch, M., Howell, D., Monette, J., Wan-Chow-Wah, D., Krzyzanowska, M., Leighl, N. B., Springall, E., & Alibhai, S. (2014). Factors influencing adherence to cancer treatment in older adults with cancer: a systematic review. Annals of oncology, 25 (3), 564-577.
Qu, S. Q., & Dumay, J. (2011). The qualitative research interview . Qualitative research in accounting & management.
Ali, J., & Bhaskar, S. B. (2016). Basic statistical tools in research and data analysis. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia, 60 (9), 662–669.
Rosenbaum, M. S. (2017). Exploring the social supportive role of third places in consumers’ lives. Journal of Service Research, 20 (1), 26-42.
Saldaña, J. (2003). Longitudinal Qualitative Research: Analyzing Change Through Time . AltaMira Press.
Saldaña, J. (2014). The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers. SAGE.
Shernoff, D. J., Csikszentmihalyi, M., Shneider, B., & Shernoff, E. S. (2003). Student engagement in high school classrooms from the perspective of flow theory. School Psychology Quarterly, 18 (2), 158-176.
Smith, J. A. (2015). Qualitative Psychology: A Practical Guide to Research Methods . Sage Publications.
Smith, M. K. (2010). Action Research. The encyclopedia of informal education.
Sue, V. M., & Ritter, L. A. (2012). Conducting online surveys . SAGE Publications.
Van Auken, P. M., Frisvoll, S. J., & Stewart, S. I. (2010). Visualising community: using participant-driven photo-elicitation for research and application. Local Environment, 15 (4), 373-388.
Van Voorhis, F. L., & Morgan, B. L. (2007). Understanding Power and Rules of Thumb for Determining Sample Sizes. Tutorials in Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 3 (2), 43–50.
Wodak, R., & Meyer, M. (2015). Methods of Critical Discourse Analysis . SAGE.
Zuber-Skerritt, O. (2018). Action research for developing educational theories and practices . Routledge.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Chapter 1. Introduction
“Science is in danger, and for that reason it is becoming dangerous” -Pierre Bourdieu, Science of Science and Reflexivity
Why an Open Access Textbook on Qualitative Research Methods?
I have been teaching qualitative research methods to both undergraduates and graduate students for many years. Although there are some excellent textbooks out there, they are often costly, and none of them, to my mind, properly introduces qualitative research methods to the beginning student (whether undergraduate or graduate student). In contrast, this open-access textbook is designed as a (free) true introduction to the subject, with helpful, practical pointers on how to conduct research and how to access more advanced instruction.
Textbooks are typically arranged in one of two ways: (1) by technique (each chapter covers one method used in qualitative research); or (2) by process (chapters advance from research design through publication). But both of these approaches are necessary for the beginner student. This textbook will have sections dedicated to the process as well as the techniques of qualitative research. This is a true “comprehensive” book for the beginning student. In addition to covering techniques of data collection and data analysis, it provides a road map of how to get started and how to keep going and where to go for advanced instruction. It covers aspects of research design and research communication as well as methods employed. Along the way, it includes examples from many different disciplines in the social sciences.
The primary goal has been to create a useful, accessible, engaging textbook for use across many disciplines. And, let’s face it. Textbooks can be boring. I hope readers find this to be a little different. I have tried to write in a practical and forthright manner, with many lively examples and references to good and intellectually creative qualitative research. Woven throughout the text are short textual asides (in colored textboxes) by professional (academic) qualitative researchers in various disciplines. These short accounts by practitioners should help inspire students. So, let’s begin!
What is Research?
When we use the word research , what exactly do we mean by that? This is one of those words that everyone thinks they understand, but it is worth beginning this textbook with a short explanation. We use the term to refer to “empirical research,” which is actually a historically specific approach to understanding the world around us. Think about how you know things about the world. [1] You might know your mother loves you because she’s told you she does. Or because that is what “mothers” do by tradition. Or you might know because you’ve looked for evidence that she does, like taking care of you when you are sick or reading to you in bed or working two jobs so you can have the things you need to do OK in life. Maybe it seems churlish to look for evidence; you just take it “on faith” that you are loved.
Only one of the above comes close to what we mean by research. Empirical research is research (investigation) based on evidence. Conclusions can then be drawn from observable data. This observable data can also be “tested” or checked. If the data cannot be tested, that is a good indication that we are not doing research. Note that we can never “prove” conclusively, through observable data, that our mothers love us. We might have some “disconfirming evidence” (that time she didn’t show up to your graduation, for example) that could push you to question an original hypothesis , but no amount of “confirming evidence” will ever allow us to say with 100% certainty, “my mother loves me.” Faith and tradition and authority work differently. Our knowledge can be 100% certain using each of those alternative methods of knowledge, but our certainty in those cases will not be based on facts or evidence.
For many periods of history, those in power have been nervous about “science” because it uses evidence and facts as the primary source of understanding the world, and facts can be at odds with what power or authority or tradition want you to believe. That is why I say that scientific empirical research is a historically specific approach to understand the world. You are in college or university now partly to learn how to engage in this historically specific approach.
In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries in Europe, there was a newfound respect for empirical research, some of which was seriously challenging to the established church. Using observations and testing them, scientists found that the earth was not at the center of the universe, for example, but rather that it was but one planet of many which circled the sun. [2] For the next two centuries, the science of astronomy, physics, biology, and chemistry emerged and became disciplines taught in universities. All used the scientific method of observation and testing to advance knowledge. Knowledge about people , however, and social institutions, however, was still left to faith, tradition, and authority. Historians and philosophers and poets wrote about the human condition, but none of them used research to do so. [3]
It was not until the nineteenth century that “social science” really emerged, using the scientific method (empirical observation) to understand people and social institutions. New fields of sociology, economics, political science, and anthropology emerged. The first sociologists, people like Auguste Comte and Karl Marx, sought specifically to apply the scientific method of research to understand society, Engels famously claiming that Marx had done for the social world what Darwin did for the natural world, tracings its laws of development. Today we tend to take for granted the naturalness of science here, but it is actually a pretty recent and radical development.
To return to the question, “does your mother love you?” Well, this is actually not really how a researcher would frame the question, as it is too specific to your case. It doesn’t tell us much about the world at large, even if it does tell us something about you and your relationship with your mother. A social science researcher might ask, “do mothers love their children?” Or maybe they would be more interested in how this loving relationship might change over time (e.g., “do mothers love their children more now than they did in the 18th century when so many children died before reaching adulthood?”) or perhaps they might be interested in measuring quality of love across cultures or time periods, or even establishing “what love looks like” using the mother/child relationship as a site of exploration. All of these make good research questions because we can use observable data to answer them.
What is Qualitative Research?
“All we know is how to learn. How to study, how to listen, how to talk, how to tell. If we don’t tell the world, we don’t know the world. We’re lost in it, we die.” -Ursula LeGuin, The Telling
At its simplest, qualitative research is research about the social world that does not use numbers in its analyses. All those who fear statistics can breathe a sigh of relief – there are no mathematical formulae or regression models in this book! But this definition is less about what qualitative research can be and more about what it is not. To be honest, any simple statement will fail to capture the power and depth of qualitative research. One way of contrasting qualitative research to quantitative research is to note that the focus of qualitative research is less about explaining and predicting relationships between variables and more about understanding the social world. To use our mother love example, the question about “what love looks like” is a good question for the qualitative researcher while all questions measuring love or comparing incidences of love (both of which require measurement) are good questions for quantitative researchers. Patton writes,
Qualitative data describe. They take us, as readers, into the time and place of the observation so that we know what it was like to have been there. They capture and communicate someone else’s experience of the world in his or her own words. Qualitative data tell a story. ( Patton 2002:47 )
Qualitative researchers are asking different questions about the world than their quantitative colleagues. Even when researchers are employed in “mixed methods” research ( both quantitative and qualitative), they are using different methods to address different questions of the study. I do a lot of research about first-generation and working-college college students. Where a quantitative researcher might ask, how many first-generation college students graduate from college within four years? Or does first-generation college status predict high student debt loads? A qualitative researcher might ask, how does the college experience differ for first-generation college students? What is it like to carry a lot of debt, and how does this impact the ability to complete college on time? Both sets of questions are important, but they can only be answered using specific tools tailored to those questions. For the former, you need large numbers to make adequate comparisons. For the latter, you need to talk to people, find out what they are thinking and feeling, and try to inhabit their shoes for a little while so you can make sense of their experiences and beliefs.
Examples of Qualitative Research
You have probably seen examples of qualitative research before, but you might not have paid particular attention to how they were produced or realized that the accounts you were reading were the result of hours, months, even years of research “in the field.” A good qualitative researcher will present the product of their hours of work in such a way that it seems natural, even obvious, to the reader. Because we are trying to convey what it is like answers, qualitative research is often presented as stories – stories about how people live their lives, go to work, raise their children, interact with one another. In some ways, this can seem like reading particularly insightful novels. But, unlike novels, there are very specific rules and guidelines that qualitative researchers follow to ensure that the “story” they are telling is accurate , a truthful rendition of what life is like for the people being studied. Most of this textbook will be spent conveying those rules and guidelines. Let’s take a look, first, however, at three examples of what the end product looks like. I have chosen these three examples to showcase very different approaches to qualitative research, and I will return to these five examples throughout the book. They were all published as whole books (not chapters or articles), and they are worth the long read, if you have the time. I will also provide some information on how these books came to be and the length of time it takes to get them into book version. It is important you know about this process, and the rest of this textbook will help explain why it takes so long to conduct good qualitative research!
Example 1 : The End Game (ethnography + interviews)
Corey Abramson is a sociologist who teaches at the University of Arizona. In 2015 he published The End Game: How Inequality Shapes our Final Years ( 2015 ). This book was based on the research he did for his dissertation at the University of California-Berkeley in 2012. Actually, the dissertation was completed in 2012 but the work that was produced that took several years. The dissertation was entitled, “This is How We Live, This is How We Die: Social Stratification, Aging, and Health in Urban America” ( 2012 ). You can see how the book version, which was written for a more general audience, has a more engaging sound to it, but that the dissertation version, which is what academic faculty read and evaluate, has a more descriptive title. You can read the title and know that this is a study about aging and health and that the focus is going to be inequality and that the context (place) is going to be “urban America.” It’s a study about “how” people do something – in this case, how they deal with aging and death. This is the very first sentence of the dissertation, “From our first breath in the hospital to the day we die, we live in a society characterized by unequal opportunities for maintaining health and taking care of ourselves when ill. These disparities reflect persistent racial, socio-economic, and gender-based inequalities and contribute to their persistence over time” ( 1 ). What follows is a truthful account of how that is so.
Cory Abramson spent three years conducting his research in four different urban neighborhoods. We call the type of research he conducted “comparative ethnographic” because he designed his study to compare groups of seniors as they went about their everyday business. It’s comparative because he is comparing different groups (based on race, class, gender) and ethnographic because he is studying the culture/way of life of a group. [4] He had an educated guess, rooted in what previous research had shown and what social theory would suggest, that people’s experiences of aging differ by race, class, and gender. So, he set up a research design that would allow him to observe differences. He chose two primarily middle-class (one was racially diverse and the other was predominantly White) and two primarily poor neighborhoods (one was racially diverse and the other was predominantly African American). He hung out in senior centers and other places seniors congregated, watched them as they took the bus to get prescriptions filled, sat in doctor’s offices with them, and listened to their conversations with each other. He also conducted more formal conversations, what we call in-depth interviews, with sixty seniors from each of the four neighborhoods. As with a lot of fieldwork , as he got closer to the people involved, he both expanded and deepened his reach –
By the end of the project, I expanded my pool of general observations to include various settings frequented by seniors: apartment building common rooms, doctors’ offices, emergency rooms, pharmacies, senior centers, bars, parks, corner stores, shopping centers, pool halls, hair salons, coffee shops, and discount stores. Over the course of the three years of fieldwork, I observed hundreds of elders, and developed close relationships with a number of them. ( 2012:10 )
When Abramson rewrote the dissertation for a general audience and published his book in 2015, it got a lot of attention. It is a beautifully written book and it provided insight into a common human experience that we surprisingly know very little about. It won the Outstanding Publication Award by the American Sociological Association Section on Aging and the Life Course and was featured in the New York Times . The book was about aging, and specifically how inequality shapes the aging process, but it was also about much more than that. It helped show how inequality affects people’s everyday lives. For example, by observing the difficulties the poor had in setting up appointments and getting to them using public transportation and then being made to wait to see a doctor, sometimes in standing-room-only situations, when they are unwell, and then being treated dismissively by hospital staff, Abramson allowed readers to feel the material reality of being poor in the US. Comparing these examples with seniors with adequate supplemental insurance who have the resources to hire car services or have others assist them in arranging care when they need it, jolts the reader to understand and appreciate the difference money makes in the lives and circumstances of us all, and in a way that is different than simply reading a statistic (“80% of the poor do not keep regular doctor’s appointments”) does. Qualitative research can reach into spaces and places that often go unexamined and then reports back to the rest of us what it is like in those spaces and places.
Example 2: Racing for Innocence (Interviews + Content Analysis + Fictional Stories)
Jennifer Pierce is a Professor of American Studies at the University of Minnesota. Trained as a sociologist, she has written a number of books about gender, race, and power. Her very first book, Gender Trials: Emotional Lives in Contemporary Law Firms, published in 1995, is a brilliant look at gender dynamics within two law firms. Pierce was a participant observer, working as a paralegal, and she observed how female lawyers and female paralegals struggled to obtain parity with their male colleagues.
Fifteen years later, she reexamined the context of the law firm to include an examination of racial dynamics, particularly how elite white men working in these spaces created and maintained a culture that made it difficult for both female attorneys and attorneys of color to thrive. Her book, Racing for Innocence: Whiteness, Gender, and the Backlash Against Affirmative Action , published in 2012, is an interesting and creative blending of interviews with attorneys, content analyses of popular films during this period, and fictional accounts of racial discrimination and sexual harassment. The law firm she chose to study had come under an affirmative action order and was in the process of implementing equitable policies and programs. She wanted to understand how recipients of white privilege (the elite white male attorneys) come to deny the role they play in reproducing inequality. Through interviews with attorneys who were present both before and during the affirmative action order, she creates a historical record of the “bad behavior” that necessitated new policies and procedures, but also, and more importantly , probed the participants ’ understanding of this behavior. It should come as no surprise that most (but not all) of the white male attorneys saw little need for change, and that almost everyone else had accounts that were different if not sometimes downright harrowing.
I’ve used Pierce’s book in my qualitative research methods courses as an example of an interesting blend of techniques and presentation styles. My students often have a very difficult time with the fictional accounts she includes. But they serve an important communicative purpose here. They are her attempts at presenting “both sides” to an objective reality – something happens (Pierce writes this something so it is very clear what it is), and the two participants to the thing that happened have very different understandings of what this means. By including these stories, Pierce presents one of her key findings – people remember things differently and these different memories tend to support their own ideological positions. I wonder what Pierce would have written had she studied the murder of George Floyd or the storming of the US Capitol on January 6 or any number of other historic events whose observers and participants record very different happenings.
This is not to say that qualitative researchers write fictional accounts. In fact, the use of fiction in our work remains controversial. When used, it must be clearly identified as a presentation device, as Pierce did. I include Racing for Innocence here as an example of the multiple uses of methods and techniques and the way that these work together to produce better understandings by us, the readers, of what Pierce studied. We readers come away with a better grasp of how and why advantaged people understate their own involvement in situations and structures that advantage them. This is normal human behavior , in other words. This case may have been about elite white men in law firms, but the general insights here can be transposed to other settings. Indeed, Pierce argues that more research needs to be done about the role elites play in the reproduction of inequality in the workplace in general.
Example 3: Amplified Advantage (Mixed Methods: Survey Interviews + Focus Groups + Archives)
The final example comes from my own work with college students, particularly the ways in which class background affects the experience of college and outcomes for graduates. I include it here as an example of mixed methods, and for the use of supplementary archival research. I’ve done a lot of research over the years on first-generation, low-income, and working-class college students. I am curious (and skeptical) about the possibility of social mobility today, particularly with the rising cost of college and growing inequality in general. As one of the few people in my family to go to college, I didn’t grow up with a lot of examples of what college was like or how to make the most of it. And when I entered graduate school, I realized with dismay that there were very few people like me there. I worried about becoming too different from my family and friends back home. And I wasn’t at all sure that I would ever be able to pay back the huge load of debt I was taking on. And so I wrote my dissertation and first two books about working-class college students. These books focused on experiences in college and the difficulties of navigating between family and school ( Hurst 2010a, 2012 ). But even after all that research, I kept coming back to wondering if working-class students who made it through college had an equal chance at finding good jobs and happy lives,
What happens to students after college? Do working-class students fare as well as their peers? I knew from my own experience that barriers continued through graduate school and beyond, and that my debtload was higher than that of my peers, constraining some of the choices I made when I graduated. To answer these questions, I designed a study of students attending small liberal arts colleges, the type of college that tried to equalize the experience of students by requiring all students to live on campus and offering small classes with lots of interaction with faculty. These private colleges tend to have more money and resources so they can provide financial aid to low-income students. They also attract some very wealthy students. Because they enroll students across the class spectrum, I would be able to draw comparisons. I ended up spending about four years collecting data, both a survey of more than 2000 students (which formed the basis for quantitative analyses) and qualitative data collection (interviews, focus groups, archival research, and participant observation). This is what we call a “mixed methods” approach because we use both quantitative and qualitative data. The survey gave me a large enough number of students that I could make comparisons of the how many kind, and to be able to say with some authority that there were in fact significant differences in experience and outcome by class (e.g., wealthier students earned more money and had little debt; working-class students often found jobs that were not in their chosen careers and were very affected by debt, upper-middle-class students were more likely to go to graduate school). But the survey analyses could not explain why these differences existed. For that, I needed to talk to people and ask them about their motivations and aspirations. I needed to understand their perceptions of the world, and it is very hard to do this through a survey.
By interviewing students and recent graduates, I was able to discern particular patterns and pathways through college and beyond. Specifically, I identified three versions of gameplay. Upper-middle-class students, whose parents were themselves professionals (academics, lawyers, managers of non-profits), saw college as the first stage of their education and took classes and declared majors that would prepare them for graduate school. They also spent a lot of time building their resumes, taking advantage of opportunities to help professors with their research, or study abroad. This helped them gain admission to highly-ranked graduate schools and interesting jobs in the public sector. In contrast, upper-class students, whose parents were wealthy and more likely to be engaged in business (as CEOs or other high-level directors), prioritized building social capital. They did this by joining fraternities and sororities and playing club sports. This helped them when they graduated as they called on friends and parents of friends to find them well-paying jobs. Finally, low-income, first-generation, and working-class students were often adrift. They took the classes that were recommended to them but without the knowledge of how to connect them to life beyond college. They spent time working and studying rather than partying or building their resumes. All three sets of students thought they were “doing college” the right way, the way that one was supposed to do college. But these three versions of gameplay led to distinct outcomes that advantaged some students over others. I titled my work “Amplified Advantage” to highlight this process.
These three examples, Cory Abramson’s The End Game , Jennifer Peirce’s Racing for Innocence, and my own Amplified Advantage, demonstrate the range of approaches and tools available to the qualitative researcher. They also help explain why qualitative research is so important. Numbers can tell us some things about the world, but they cannot get at the hearts and minds, motivations and beliefs of the people who make up the social worlds we inhabit. For that, we need tools that allow us to listen and make sense of what people tell us and show us. That is what good qualitative research offers us.
How Is This Book Organized?
This textbook is organized as a comprehensive introduction to the use of qualitative research methods. The first half covers general topics (e.g., approaches to qualitative research, ethics) and research design (necessary steps for building a successful qualitative research study). The second half reviews various data collection and data analysis techniques. Of course, building a successful qualitative research study requires some knowledge of data collection and data analysis so the chapters in the first half and the chapters in the second half should be read in conversation with each other. That said, each chapter can be read on its own for assistance with a particular narrow topic. In addition to the chapters, a helpful glossary can be found in the back of the book. Rummage around in the text as needed.
Chapter Descriptions
Chapter 2 provides an overview of the Research Design Process. How does one begin a study? What is an appropriate research question? How is the study to be done – with what methods ? Involving what people and sites? Although qualitative research studies can and often do change and develop over the course of data collection, it is important to have a good idea of what the aims and goals of your study are at the outset and a good plan of how to achieve those aims and goals. Chapter 2 provides a road map of the process.
Chapter 3 describes and explains various ways of knowing the (social) world. What is it possible for us to know about how other people think or why they behave the way they do? What does it mean to say something is a “fact” or that it is “well-known” and understood? Qualitative researchers are particularly interested in these questions because of the types of research questions we are interested in answering (the how questions rather than the how many questions of quantitative research). Qualitative researchers have adopted various epistemological approaches. Chapter 3 will explore these approaches, highlighting interpretivist approaches that acknowledge the subjective aspect of reality – in other words, reality and knowledge are not objective but rather influenced by (interpreted through) people.
Chapter 4 focuses on the practical matter of developing a research question and finding the right approach to data collection. In any given study (think of Cory Abramson’s study of aging, for example), there may be years of collected data, thousands of observations , hundreds of pages of notes to read and review and make sense of. If all you had was a general interest area (“aging”), it would be very difficult, nearly impossible, to make sense of all of that data. The research question provides a helpful lens to refine and clarify (and simplify) everything you find and collect. For that reason, it is important to pull out that lens (articulate the research question) before you get started. In the case of the aging study, Cory Abramson was interested in how inequalities affected understandings and responses to aging. It is for this reason he designed a study that would allow him to compare different groups of seniors (some middle-class, some poor). Inevitably, he saw much more in the three years in the field than what made it into his book (or dissertation), but he was able to narrow down the complexity of the social world to provide us with this rich account linked to the original research question. Developing a good research question is thus crucial to effective design and a successful outcome. Chapter 4 will provide pointers on how to do this. Chapter 4 also provides an overview of general approaches taken to doing qualitative research and various “traditions of inquiry.”
Chapter 5 explores sampling . After you have developed a research question and have a general idea of how you will collect data (Observations? Interviews?), how do you go about actually finding people and sites to study? Although there is no “correct number” of people to interview , the sample should follow the research question and research design. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. Chapter 5 explains why this is so and what qualities instead make a good sample for qualitative research.
Chapter 6 addresses the importance of reflexivity in qualitative research. Related to epistemological issues of how we know anything about the social world, qualitative researchers understand that we the researchers can never be truly neutral or outside the study we are conducting. As observers, we see things that make sense to us and may entirely miss what is either too obvious to note or too different to comprehend. As interviewers, as much as we would like to ask questions neutrally and remain in the background, interviews are a form of conversation, and the persons we interview are responding to us . Therefore, it is important to reflect upon our social positions and the knowledges and expectations we bring to our work and to work through any blind spots that we may have. Chapter 6 provides some examples of reflexivity in practice and exercises for thinking through one’s own biases.
Chapter 7 is a very important chapter and should not be overlooked. As a practical matter, it should also be read closely with chapters 6 and 8. Because qualitative researchers deal with people and the social world, it is imperative they develop and adhere to a strong ethical code for conducting research in a way that does not harm. There are legal requirements and guidelines for doing so (see chapter 8), but these requirements should not be considered synonymous with the ethical code required of us. Each researcher must constantly interrogate every aspect of their research, from research question to design to sample through analysis and presentation, to ensure that a minimum of harm (ideally, zero harm) is caused. Because each research project is unique, the standards of care for each study are unique. Part of being a professional researcher is carrying this code in one’s heart, being constantly attentive to what is required under particular circumstances. Chapter 7 provides various research scenarios and asks readers to weigh in on the suitability and appropriateness of the research. If done in a class setting, it will become obvious fairly quickly that there are often no absolutely correct answers, as different people find different aspects of the scenarios of greatest importance. Minimizing the harm in one area may require possible harm in another. Being attentive to all the ethical aspects of one’s research and making the best judgments one can, clearly and consciously, is an integral part of being a good researcher.
Chapter 8 , best to be read in conjunction with chapter 7, explains the role and importance of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) . Under federal guidelines, an IRB is an appropriately constituted group that has been formally designated to review and monitor research involving human subjects . Every institution that receives funding from the federal government has an IRB. IRBs have the authority to approve, require modifications to (to secure approval), or disapprove research. This group review serves an important role in the protection of the rights and welfare of human research subjects. Chapter 8 reviews the history of IRBs and the work they do but also argues that IRBs’ review of qualitative research is often both over-inclusive and under-inclusive. Some aspects of qualitative research are not well understood by IRBs, given that they were developed to prevent abuses in biomedical research. Thus, it is important not to rely on IRBs to identify all the potential ethical issues that emerge in our research (see chapter 7).
Chapter 9 provides help for getting started on formulating a research question based on gaps in the pre-existing literature. Research is conducted as part of a community, even if particular studies are done by single individuals (or small teams). What any of us finds and reports back becomes part of a much larger body of knowledge. Thus, it is important that we look at the larger body of knowledge before we actually start our bit to see how we can best contribute. When I first began interviewing working-class college students, there was only one other similar study I could find, and it hadn’t been published (it was a dissertation of students from poor backgrounds). But there had been a lot published by professors who had grown up working class and made it through college despite the odds. These accounts by “working-class academics” became an important inspiration for my study and helped me frame the questions I asked the students I interviewed. Chapter 9 will provide some pointers on how to search for relevant literature and how to use this to refine your research question.
Chapter 10 serves as a bridge between the two parts of the textbook, by introducing techniques of data collection. Qualitative research is often characterized by the form of data collection – for example, an ethnographic study is one that employs primarily observational data collection for the purpose of documenting and presenting a particular culture or ethnos. Techniques can be effectively combined, depending on the research question and the aims and goals of the study. Chapter 10 provides a general overview of all the various techniques and how they can be combined.
The second part of the textbook moves into the doing part of qualitative research once the research question has been articulated and the study designed. Chapters 11 through 17 cover various data collection techniques and approaches. Chapters 18 and 19 provide a very simple overview of basic data analysis. Chapter 20 covers communication of the data to various audiences, and in various formats.
Chapter 11 begins our overview of data collection techniques with a focus on interviewing , the true heart of qualitative research. This technique can serve as the primary and exclusive form of data collection, or it can be used to supplement other forms (observation, archival). An interview is distinct from a survey, where questions are asked in a specific order and often with a range of predetermined responses available. Interviews can be conversational and unstructured or, more conventionally, semistructured , where a general set of interview questions “guides” the conversation. Chapter 11 covers the basics of interviews: how to create interview guides, how many people to interview, where to conduct the interview, what to watch out for (how to prepare against things going wrong), and how to get the most out of your interviews.
Chapter 12 covers an important variant of interviewing, the focus group. Focus groups are semistructured interviews with a group of people moderated by a facilitator (the researcher or researcher’s assistant). Focus groups explicitly use group interaction to assist in the data collection. They are best used to collect data on a specific topic that is non-personal and shared among the group. For example, asking a group of college students about a common experience such as taking classes by remote delivery during the pandemic year of 2020. Chapter 12 covers the basics of focus groups: when to use them, how to create interview guides for them, and how to run them effectively.
Chapter 13 moves away from interviewing to the second major form of data collection unique to qualitative researchers – observation . Qualitative research that employs observation can best be understood as falling on a continuum of “fly on the wall” observation (e.g., observing how strangers interact in a doctor’s waiting room) to “participant” observation, where the researcher is also an active participant of the activity being observed. For example, an activist in the Black Lives Matter movement might want to study the movement, using her inside position to gain access to observe key meetings and interactions. Chapter 13 covers the basics of participant observation studies: advantages and disadvantages, gaining access, ethical concerns related to insider/outsider status and entanglement, and recording techniques.
Chapter 14 takes a closer look at “deep ethnography” – immersion in the field of a particularly long duration for the purpose of gaining a deeper understanding and appreciation of a particular culture or social world. Clifford Geertz called this “deep hanging out.” Whereas participant observation is often combined with semistructured interview techniques, deep ethnography’s commitment to “living the life” or experiencing the situation as it really is demands more conversational and natural interactions with people. These interactions and conversations may take place over months or even years. As can be expected, there are some costs to this technique, as well as some very large rewards when done competently. Chapter 14 provides some examples of deep ethnographies that will inspire some beginning researchers and intimidate others.
Chapter 15 moves in the opposite direction of deep ethnography, a technique that is the least positivist of all those discussed here, to mixed methods , a set of techniques that is arguably the most positivist . A mixed methods approach combines both qualitative data collection and quantitative data collection, commonly by combining a survey that is analyzed statistically (e.g., cross-tabs or regression analyses of large number probability samples) with semi-structured interviews. Although it is somewhat unconventional to discuss mixed methods in textbooks on qualitative research, I think it is important to recognize this often-employed approach here. There are several advantages and some disadvantages to taking this route. Chapter 16 will describe those advantages and disadvantages and provide some particular guidance on how to design a mixed methods study for maximum effectiveness.
Chapter 16 covers data collection that does not involve live human subjects at all – archival and historical research (chapter 17 will also cover data that does not involve interacting with human subjects). Sometimes people are unavailable to us, either because they do not wish to be interviewed or observed (as is the case with many “elites”) or because they are too far away, in both place and time. Fortunately, humans leave many traces and we can often answer questions we have by examining those traces. Special collections and archives can be goldmines for social science research. This chapter will explain how to access these places, for what purposes, and how to begin to make sense of what you find.
Chapter 17 covers another data collection area that does not involve face-to-face interaction with humans: content analysis . Although content analysis may be understood more properly as a data analysis technique, the term is often used for the entire approach, which will be the case here. Content analysis involves interpreting meaning from a body of text. This body of text might be something found in historical records (see chapter 16) or something collected by the researcher, as in the case of comment posts on a popular blog post. I once used the stories told by student loan debtors on the website studentloanjustice.org as the content I analyzed. Content analysis is particularly useful when attempting to define and understand prevalent stories or communication about a topic of interest. In other words, when we are less interested in what particular people (our defined sample) are doing or believing and more interested in what general narratives exist about a particular topic or issue. This chapter will explore different approaches to content analysis and provide helpful tips on how to collect data, how to turn that data into codes for analysis, and how to go about presenting what is found through analysis.
Where chapter 17 has pushed us towards data analysis, chapters 18 and 19 are all about what to do with the data collected, whether that data be in the form of interview transcripts or fieldnotes from observations. Chapter 18 introduces the basics of coding , the iterative process of assigning meaning to the data in order to both simplify and identify patterns. What is a code and how does it work? What are the different ways of coding data, and when should you use them? What is a codebook, and why do you need one? What does the process of data analysis look like?
Chapter 19 goes further into detail on codes and how to use them, particularly the later stages of coding in which our codes are refined, simplified, combined, and organized. These later rounds of coding are essential to getting the most out of the data we’ve collected. As students are often overwhelmed with the amount of data (a corpus of interview transcripts typically runs into the hundreds of pages; fieldnotes can easily top that), this chapter will also address time management and provide suggestions for dealing with chaos and reminders that feeling overwhelmed at the analysis stage is part of the process. By the end of the chapter, you should understand how “findings” are actually found.
The book concludes with a chapter dedicated to the effective presentation of data results. Chapter 20 covers the many ways that researchers communicate their studies to various audiences (academic, personal, political), what elements must be included in these various publications, and the hallmarks of excellent qualitative research that various audiences will be expecting. Because qualitative researchers are motivated by understanding and conveying meaning , effective communication is not only an essential skill but a fundamental facet of the entire research project. Ethnographers must be able to convey a certain sense of verisimilitude , the appearance of true reality. Those employing interviews must faithfully depict the key meanings of the people they interviewed in a way that rings true to those people, even if the end result surprises them. And all researchers must strive for clarity in their publications so that various audiences can understand what was found and why it is important.
The book concludes with a short chapter ( chapter 21 ) discussing the value of qualitative research. At the very end of this book, you will find a glossary of terms. I recommend you make frequent use of the glossary and add to each entry as you find examples. Although the entries are meant to be simple and clear, you may also want to paraphrase the definition—make it “make sense” to you, in other words. In addition to the standard reference list (all works cited here), you will find various recommendations for further reading at the end of many chapters. Some of these recommendations will be examples of excellent qualitative research, indicated with an asterisk (*) at the end of the entry. As they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. A good example of qualitative research can teach you more about conducting research than any textbook can (this one included). I highly recommend you select one to three examples from these lists and read them along with the textbook.
A final note on the choice of examples – you will note that many of the examples used in the text come from research on college students. This is for two reasons. First, as most of my research falls in this area, I am most familiar with this literature and have contacts with those who do research here and can call upon them to share their stories with you. Second, and more importantly, my hope is that this textbook reaches a wide audience of beginning researchers who study widely and deeply across the range of what can be known about the social world (from marine resources management to public policy to nursing to political science to sexuality studies and beyond). It is sometimes difficult to find examples that speak to all those research interests, however. A focus on college students is something that all readers can understand and, hopefully, appreciate, as we are all now or have been at some point a college student.
Recommended Reading: Other Qualitative Research Textbooks
I’ve included a brief list of some of my favorite qualitative research textbooks and guidebooks if you need more than what you will find in this introductory text. For each, I’ve also indicated if these are for “beginning” or “advanced” (graduate-level) readers. Many of these books have several editions that do not significantly vary; the edition recommended is merely the edition I have used in teaching and to whose page numbers any specific references made in the text agree.
Barbour, Rosaline. 2014. Introducing Qualitative Research: A Student’s Guide. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A good introduction to qualitative research, with abundant examples (often from the discipline of health care) and clear definitions. Includes quick summaries at the ends of each chapter. However, some US students might find the British context distracting and can be a bit advanced in some places. Beginning .
Bloomberg, Linda Dale, and Marie F. Volpe. 2012. Completing Your Qualitative Dissertation . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Specifically designed to guide graduate students through the research process. Advanced .
Creswell, John W., and Cheryl Poth. 2018 Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among Five Traditions . 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. This is a classic and one of the go-to books I used myself as a graduate student. One of the best things about this text is its clear presentation of five distinct traditions in qualitative research. Despite the title, this reasonably sized book is about more than research design, including both data analysis and how to write about qualitative research. Advanced .
Lareau, Annette. 2021. Listening to People: A Practical Guide to Interviewing, Participant Observation, Data Analysis, and Writing It All Up . Chicago: University of Chicago Press. A readable and personal account of conducting qualitative research by an eminent sociologist, with a heavy emphasis on the kinds of participant-observation research conducted by the author. Despite its reader-friendliness, this is really a book targeted to graduate students learning the craft. Advanced .
Lune, Howard, and Bruce L. Berg. 2018. 9th edition. Qualitative Research Methods for the Social Sciences. Pearson . Although a good introduction to qualitative methods, the authors favor symbolic interactionist and dramaturgical approaches, which limits the appeal primarily to sociologists. Beginning .
Marshall, Catherine, and Gretchen B. Rossman. 2016. 6th edition. Designing Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Very readable and accessible guide to research design by two educational scholars. Although the presentation is sometimes fairly dry, personal vignettes and illustrations enliven the text. Beginning .
Maxwell, Joseph A. 2013. Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach . 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A short and accessible introduction to qualitative research design, particularly helpful for graduate students contemplating theses and dissertations. This has been a standard textbook in my graduate-level courses for years. Advanced .
Patton, Michael Quinn. 2002. Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. This is a comprehensive text that served as my “go-to” reference when I was a graduate student. It is particularly helpful for those involved in program evaluation and other forms of evaluation studies and uses examples from a wide range of disciplines. Advanced .
Rubin, Ashley T. 2021. Rocking Qualitative Social Science: An Irreverent Guide to Rigorous Research. Stanford : Stanford University Press. A delightful and personal read. Rubin uses rock climbing as an extended metaphor for learning how to conduct qualitative research. A bit slanted toward ethnographic and archival methods of data collection, with frequent examples from her own studies in criminology. Beginning .
Weis, Lois, and Michelle Fine. 2000. Speed Bumps: A Student-Friendly Guide to Qualitative Research . New York: Teachers College Press. Readable and accessibly written in a quasi-conversational style. Particularly strong in its discussion of ethical issues throughout the qualitative research process. Not comprehensive, however, and very much tied to ethnographic research. Although designed for graduate students, this is a recommended read for students of all levels. Beginning .
Patton’s Ten Suggestions for Doing Qualitative Research
The following ten suggestions were made by Michael Quinn Patton in his massive textbooks Qualitative Research and Evaluations Methods . This book is highly recommended for those of you who want more than an introduction to qualitative methods. It is the book I relied on heavily when I was a graduate student, although it is much easier to “dip into” when necessary than to read through as a whole. Patton is asked for “just one bit of advice” for a graduate student considering using qualitative research methods for their dissertation. Here are his top ten responses, in short form, heavily paraphrased, and with additional comments and emphases from me:
- Make sure that a qualitative approach fits the research question. The following are the kinds of questions that call out for qualitative methods or where qualitative methods are particularly appropriate: questions about people’s experiences or how they make sense of those experiences; studying a person in their natural environment; researching a phenomenon so unknown that it would be impossible to study it with standardized instruments or other forms of quantitative data collection.
- Study qualitative research by going to the original sources for the design and analysis appropriate to the particular approach you want to take (e.g., read Glaser and Straus if you are using grounded theory )
- Find a dissertation adviser who understands or at least who will support your use of qualitative research methods. You are asking for trouble if your entire committee is populated by quantitative researchers, even if they are all very knowledgeable about the subject or focus of your study (maybe even more so if they are!)
- Really work on design. Doing qualitative research effectively takes a lot of planning. Even if things are more flexible than in quantitative research, a good design is absolutely essential when starting out.
- Practice data collection techniques, particularly interviewing and observing. There is definitely a set of learned skills here! Do not expect your first interview to be perfect. You will continue to grow as a researcher the more interviews you conduct, and you will probably come to understand yourself a bit more in the process, too. This is not easy, despite what others who don’t work with qualitative methods may assume (and tell you!)
- Have a plan for analysis before you begin data collection. This is often a requirement in IRB protocols , although you can get away with writing something fairly simple. And even if you are taking an approach, such as grounded theory, that pushes you to remain fairly open-minded during the data collection process, you still want to know what you will be doing with all the data collected – creating a codebook? Writing analytical memos? Comparing cases? Having a plan in hand will also help prevent you from collecting too much extraneous data.
- Be prepared to confront controversies both within the qualitative research community and between qualitative research and quantitative research. Don’t be naïve about this – qualitative research, particularly some approaches, will be derided by many more “positivist” researchers and audiences. For example, is an “n” of 1 really sufficient? Yes! But not everyone will agree.
- Do not make the mistake of using qualitative research methods because someone told you it was easier, or because you are intimidated by the math required of statistical analyses. Qualitative research is difficult in its own way (and many would claim much more time-consuming than quantitative research). Do it because you are convinced it is right for your goals, aims, and research questions.
- Find a good support network. This could be a research mentor, or it could be a group of friends or colleagues who are also using qualitative research, or it could be just someone who will listen to you work through all of the issues you will confront out in the field and during the writing process. Even though qualitative research often involves human subjects, it can be pretty lonely. A lot of times you will feel like you are working without a net. You have to create one for yourself. Take care of yourself.
- And, finally, in the words of Patton, “Prepare to be changed. Looking deeply at other people’s lives will force you to look deeply at yourself.”
- We will actually spend an entire chapter ( chapter 3 ) looking at this question in much more detail! ↵
- Note that this might have been news to Europeans at the time, but many other societies around the world had also come to this conclusion through observation. There is often a tendency to equate “the scientific revolution” with the European world in which it took place, but this is somewhat misleading. ↵
- Historians are a special case here. Historians have scrupulously and rigorously investigated the social world, but not for the purpose of understanding general laws about how things work, which is the point of scientific empirical research. History is often referred to as an idiographic field of study, meaning that it studies things that happened or are happening in themselves and not for general observations or conclusions. ↵
- Don’t worry, we’ll spend more time later in this book unpacking the meaning of ethnography and other terms that are important here. Note the available glossary ↵
An approach to research that is “multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives." ( Denzin and Lincoln 2005:2 ). Contrast with quantitative research .
In contrast to methodology, methods are more simply the practices and tools used to collect and analyze data. Examples of common methods in qualitative research are interviews , observations , and documentary analysis . One’s methodology should connect to one’s choice of methods, of course, but they are distinguishable terms. See also methodology .
A proposed explanation for an observation, phenomenon, or scientific problem that can be tested by further investigation. The positing of a hypothesis is often the first step in quantitative research but not in qualitative research. Even when qualitative researchers offer possible explanations in advance of conducting research, they will tend to not use the word “hypothesis” as it conjures up the kind of positivist research they are not conducting.
The foundational question to be addressed by the research study. This will form the anchor of the research design, collection, and analysis. Note that in qualitative research, the research question may, and probably will, alter or develop during the course of the research.
An approach to research that collects and analyzes numerical data for the purpose of finding patterns and averages, making predictions, testing causal relationships, and generalizing results to wider populations. Contrast with qualitative research .
Data collection that takes place in real-world settings, referred to as “the field;” a key component of much Grounded Theory and ethnographic research. Patton ( 2002 ) calls fieldwork “the central activity of qualitative inquiry” where “‘going into the field’ means having direct and personal contact with people under study in their own environments – getting close to people and situations being studied to personally understand the realities of minutiae of daily life” (48).
The people who are the subjects of a qualitative study. In interview-based studies, they may be the respondents to the interviewer; for purposes of IRBs, they are often referred to as the human subjects of the research.
The branch of philosophy concerned with knowledge. For researchers, it is important to recognize and adopt one of the many distinguishing epistemological perspectives as part of our understanding of what questions research can address or fully answer. See, e.g., constructivism , subjectivism, and objectivism .
An approach that refutes the possibility of neutrality in social science research. All research is “guided by a set of beliefs and feelings about the world and how it should be understood and studied” (Denzin and Lincoln 2005: 13). In contrast to positivism , interpretivism recognizes the social constructedness of reality, and researchers adopting this approach focus on capturing interpretations and understandings people have about the world rather than “the world” as it is (which is a chimera).
The cluster of data-collection tools and techniques that involve observing interactions between people, the behaviors, and practices of individuals (sometimes in contrast to what they say about how they act and behave), and cultures in context. Observational methods are the key tools employed by ethnographers and Grounded Theory .
Research based on data collected and analyzed by the research (in contrast to secondary “library” research).
The process of selecting people or other units of analysis to represent a larger population. In quantitative research, this representation is taken quite literally, as statistically representative. In qualitative research, in contrast, sample selection is often made based on potential to generate insight about a particular topic or phenomenon.
A method of data collection in which the researcher asks the participant questions; the answers to these questions are often recorded and transcribed verbatim. There are many different kinds of interviews - see also semistructured interview , structured interview , and unstructured interview .
The specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. Contrast population.
The practice of being conscious of and reflective upon one’s own social location and presence when conducting research. Because qualitative research often requires interaction with live humans, failing to take into account how one’s presence and prior expectations and social location affect the data collected and how analyzed may limit the reliability of the findings. This remains true even when dealing with historical archives and other content. Who we are matters when asking questions about how people experience the world because we, too, are a part of that world.
The science and practice of right conduct; in research, it is also the delineation of moral obligations towards research participants, communities to which we belong, and communities in which we conduct our research.
An administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated. The IRB is charged with the responsibility of reviewing all research involving human participants. The IRB is concerned with protecting the welfare, rights, and privacy of human subjects. The IRB has the authority to approve, disapprove, monitor, and require modifications in all research activities that fall within its jurisdiction as specified by both the federal regulations and institutional policy.
Research, according to US federal guidelines, that involves “a living individual about whom an investigator (whether professional or student) conducting research: (1) Obtains information or biospecimens through intervention or interaction with the individual, and uses, studies, or analyzes the information or biospecimens; or (2) Obtains, uses, studies, analyzes, or generates identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens.”
One of the primary methodological traditions of inquiry in qualitative research, ethnography is the study of a group or group culture, largely through observational fieldwork supplemented by interviews. It is a form of fieldwork that may include participant-observation data collection. See chapter 14 for a discussion of deep ethnography.
A form of interview that follows a standard guide of questions asked, although the order of the questions may change to match the particular needs of each individual interview subject, and probing “follow-up” questions are often added during the course of the interview. The semi-structured interview is the primary form of interviewing used by qualitative researchers in the social sciences. It is sometimes referred to as an “in-depth” interview. See also interview and interview guide .
A method of observational data collection taking place in a natural setting; a form of fieldwork . The term encompasses a continuum of relative participation by the researcher (from full participant to “fly-on-the-wall” observer). This is also sometimes referred to as ethnography , although the latter is characterized by a greater focus on the culture under observation.
A research design that employs both quantitative and qualitative methods, as in the case of a survey supplemented by interviews.
An epistemological perspective that posits the existence of reality through sensory experience similar to empiricism but goes further in denying any non-sensory basis of thought or consciousness. In the social sciences, the term has roots in the proto-sociologist August Comte, who believed he could discern “laws” of society similar to the laws of natural science (e.g., gravity). The term has come to mean the kinds of measurable and verifiable science conducted by quantitative researchers and is thus used pejoratively by some qualitative researchers interested in interpretation, consciousness, and human understanding. Calling someone a “positivist” is often intended as an insult. See also empiricism and objectivism.
A place or collection containing records, documents, or other materials of historical interest; most universities have an archive of material related to the university’s history, as well as other “special collections” that may be of interest to members of the community.
A method of both data collection and data analysis in which a given content (textual, visual, graphic) is examined systematically and rigorously to identify meanings, themes, patterns and assumptions. Qualitative content analysis (QCA) is concerned with gathering and interpreting an existing body of material.
A word or short phrase that symbolically assigns a summative, salient, essence-capturing, and/or evocative attribute for a portion of language-based or visual data (Saldaña 2021:5).
Usually a verbatim written record of an interview or focus group discussion.
The primary form of data for fieldwork , participant observation , and ethnography . These notes, taken by the researcher either during the course of fieldwork or at day’s end, should include as many details as possible on what was observed and what was said. They should include clear identifiers of date, time, setting, and names (or identifying characteristics) of participants.
The process of labeling and organizing qualitative data to identify different themes and the relationships between them; a way of simplifying data to allow better management and retrieval of key themes and illustrative passages. See coding frame and codebook.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
A detailed description of any proposed research that involves human subjects for review by IRB. The protocol serves as the recipe for the conduct of the research activity. It includes the scientific rationale to justify the conduct of the study, the information necessary to conduct the study, the plan for managing and analyzing the data, and a discussion of the research ethical issues relevant to the research. Protocols for qualitative research often include interview guides, all documents related to recruitment, informed consent forms, very clear guidelines on the safekeeping of materials collected, and plans for de-identifying transcripts or other data that include personal identifying information.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
Qualitative research: methods and examples
Last updated
13 April 2023
Reviewed by
Qualitative research involves gathering and evaluating non-numerical information to comprehend concepts, perspectives, and experiences. It’s also helpful for obtaining in-depth insights into a certain subject or generating new research ideas.
As a result, qualitative research is practical if you want to try anything new or produce new ideas.
There are various ways you can conduct qualitative research. In this article, you'll learn more about qualitative research methodologies, including when you should use them.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a broad term describing various research types that rely on asking open-ended questions. Qualitative research investigates “how” or “why” certain phenomena occur. It is about discovering the inherent nature of something.
The primary objective of qualitative research is to understand an individual's ideas, points of view, and feelings. In this way, collecting in-depth knowledge of a specific topic is possible. Knowing your audience's feelings about a particular subject is important for making reasonable research conclusions.
Unlike quantitative research , this approach does not involve collecting numerical, objective data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is used extensively in education, sociology, health science, history, and anthropology.
- Types of qualitative research methodology
Typically, qualitative research aims at uncovering the attitudes and behavior of the target audience concerning a specific topic. For example, “How would you describe your experience as a new Dovetail user?”
Some of the methods for conducting qualitative analysis include:
Focus groups
Hosting a focus group is a popular qualitative research method. It involves obtaining qualitative data from a limited sample of participants. In a moderated version of a focus group, the moderator asks participants a series of predefined questions. They aim to interact and build a group discussion that reveals their preferences, candid thoughts, and experiences.
Unmoderated, online focus groups are increasingly popular because they eliminate the need to interact with people face to face.
Focus groups can be more cost-effective than 1:1 interviews or studying a group in a natural setting and reporting one’s observations.
Focus groups make it possible to gather multiple points of view quickly and efficiently, making them an excellent choice for testing new concepts or conducting market research on a new product.
However, there are some potential drawbacks to this method. It may be unsuitable for sensitive or controversial topics. Participants might be reluctant to disclose their true feelings or respond falsely to conform to what they believe is the socially acceptable answer (known as response bias).
Case study research
A case study is an in-depth evaluation of a specific person, incident, organization, or society. This type of qualitative research has evolved into a broadly applied research method in education, law, business, and the social sciences.
Even though case study research may appear challenging to implement, it is one of the most direct research methods. It requires detailed analysis, broad-ranging data collection methodologies, and a degree of existing knowledge about the subject area under investigation.
Historical model
The historical approach is a distinct research method that deeply examines previous events to better understand the present and forecast future occurrences of the same phenomena. Its primary goal is to evaluate the impacts of history on the present and hence discover comparable patterns in the present to predict future outcomes.
Oral history
This qualitative data collection method involves gathering verbal testimonials from individuals about their personal experiences. It is widely used in historical disciplines to offer counterpoints to established historical facts and narratives. The most common methods of gathering oral history are audio recordings, analysis of auto-biographical text, videos, and interviews.
Qualitative observation
One of the most fundamental, oldest research methods, qualitative observation , is the process through which a researcher collects data using their senses of sight, smell, hearing, etc. It is used to observe the properties of the subject being studied. For example, “What does it look like?” As research methods go, it is subjective and depends on researchers’ first-hand experiences to obtain information, so it is prone to bias. However, it is an excellent way to start a broad line of inquiry like, “What is going on here?”
Record keeping and review
Record keeping uses existing documents and relevant data sources that can be employed for future studies. It is equivalent to visiting the library and going through publications or any other reference material to gather important facts that will likely be used in the research.
Grounded theory approach
The grounded theory approach is a commonly used research method employed across a variety of different studies. It offers a unique way to gather, interpret, and analyze. With this approach, data is gathered and analyzed simultaneously. Existing analysis frames and codes are disregarded, and data is analyzed inductively, with new codes and frames generated from the research.
Ethnographic research
Ethnography is a descriptive form of a qualitative study of people and their cultures. Its primary goal is to study people's behavior in their natural environment. This method necessitates that the researcher adapts to their target audience's setting.
Thereby, you will be able to understand their motivation, lifestyle, ambitions, traditions, and culture in situ. But, the researcher must be prepared to deal with geographical constraints while collecting data i.e., audiences can’t be studied in a laboratory or research facility.
This study can last from a couple of days to several years. Thus, it is time-consuming and complicated, requiring you to have both the time to gather the relevant data as well as the expertise in analyzing, observing, and interpreting data to draw meaningful conclusions.
Narrative framework
A narrative framework is a qualitative research approach that relies on people's written text or visual images. It entails people analyzing these events or narratives to determine certain topics or issues. With this approach, you can understand how people represent themselves and their experiences to a larger audience.
Phenomenological approach
The phenomenological study seeks to investigate the experiences of a particular phenomenon within a group of individuals or communities. It analyzes a certain event through interviews with persons who have witnessed it to determine the connections between their views. Even though this method relies heavily on interviews, other data sources (recorded notes), and observations could be employed to enhance the findings.
- Qualitative research methods (tools)
Some of the instruments involved in qualitative research include:
Document research: Also known as document analysis because it involves evaluating written documents. These can include personal and non-personal materials like archives, policy publications, yearly reports, diaries, or letters.
Focus groups: This is where a researcher poses questions and generates conversation among a group of people. The major goal of focus groups is to examine participants' experiences and knowledge, including research into how and why individuals act in various ways.
Secondary study: Involves acquiring existing information from texts, images, audio, or video recordings.
Observations: This requires thorough field notes on everything you see, hear, or experience. Compared to reported conduct or opinion, this study method can assist you in getting insights into a specific situation and observable behaviors.
Structured interviews : In this approach, you will directly engage people one-on-one. Interviews are ideal for learning about a person's subjective beliefs, motivations, and encounters.
Surveys: This is when you distribute questionnaires containing open-ended questions
- What are common examples of qualitative research?
Everyday examples of qualitative research include:
Conducting a demographic analysis of a business
For instance, suppose you own a business such as a grocery store (or any store) and believe it caters to a broad customer base, but after conducting a demographic analysis, you discover that most of your customers are men.
You could do 1:1 interviews with female customers to learn why they don't shop at your store.
In this case, interviewing potential female customers should clarify why they don't find your shop appealing. It could be because of the products you sell or a need for greater brand awareness, among other possible reasons.
Launching or testing a new product
Suppose you are the product manager at a SaaS company looking to introduce a new product. Focus groups can be an excellent way to determine whether your product is marketable.
In this instance, you could hold a focus group with a sample group drawn from your intended audience. The group will explore the product based on its new features while you ensure adequate data on how users react to the new features. The data you collect will be key to making sales and marketing decisions.
Conducting studies to explain buyers' behaviors
You can also use qualitative research to understand existing buyer behavior better. Marketers analyze historical information linked to their businesses and industries to see when purchasers buy more.
Qualitative research can help you determine when to target new clients and peak seasons to boost sales by investigating the reason behind these behaviors.
- Qualitative research: data collection
Data collection is gathering information on predetermined variables to gain appropriate answers, test hypotheses, and analyze results. Researchers will collect non-numerical data for qualitative data collection to obtain detailed explanations and draw conclusions.
To get valid findings and achieve a conclusion in qualitative research, researchers must collect comprehensive and multifaceted data.
Qualitative data is usually gathered through interviews or focus groups with videotapes or handwritten notes. If there are recordings, they are transcribed before the data analysis process. Researchers keep separate folders for the recordings acquired from each focus group when collecting qualitative research data to categorize the data.
- Qualitative research: data analysis
Qualitative data analysis is organizing, examining, and interpreting qualitative data. Its main objective is identifying trends and patterns, responding to research questions, and recommending actions based on the findings. Textual analysis is a popular method for analyzing qualitative data.
Textual analysis differs from other qualitative research approaches in that researchers consider the social circumstances of study participants to decode their words, behaviors, and broader meaning.
Learn more about qualitative research data analysis software
- When to use qualitative research
Qualitative research is helpful in various situations, particularly when a researcher wants to capture accurate, in-depth insights.
Here are some instances when qualitative research can be valuable:
Examining your product or service to improve your marketing approach
When researching market segments, demographics, and customer service teams
Identifying client language when you want to design a quantitative survey
When attempting to comprehend your or someone else's strengths and weaknesses
Assessing feelings and beliefs about societal and public policy matters
Collecting information about a business or product's perception
Analyzing your target audience's reactions to marketing efforts
When launching a new product or coming up with a new idea
When seeking to evaluate buyers' purchasing patterns
- Qualitative research methods vs. quantitative research methods
Qualitative research examines people's ideas and what influences their perception, whereas quantitative research draws conclusions based on numbers and measurements.
Qualitative research is descriptive, and its primary goal is to comprehensively understand people's attitudes, behaviors, and ideas.
In contrast, quantitative research is more restrictive because it relies on numerical data and analyzes statistical data to make decisions. This research method assists researchers in gaining an initial grasp of the subject, which deals with numbers. For instance, the number of customers likely to purchase your products or use your services.
What is the most important feature of qualitative research?
A distinguishing feature of qualitative research is that it’s conducted in a real-world setting instead of a simulated environment. The researcher is examining actual phenomena instead of experimenting with different variables to see what outcomes (data) might result.
Can I use qualitative and quantitative approaches together in a study?
Yes, combining qualitative and quantitative research approaches happens all the time and is known as mixed methods research. For example, you could study individuals’ perceived risk in a certain scenario, such as how people rate the safety or riskiness of a given neighborhood. Simultaneously, you could analyze historical data objectively, indicating how safe or dangerous that area has been in the last year. To get the most out of mixed-method research, it’s important to understand the pros and cons of each methodology, so you can create a thoughtfully designed study that will yield compelling results.
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 21 December 2023
Last updated: 16 December 2023
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 15 February 2024
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 10 April 2023
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods 101:
The “big 6” methods + examples.
By: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (D.Tech) | May 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Qualitative data analysis methods. Wow, that’s a mouthful.
If you’re new to the world of research, qualitative data analysis can look rather intimidating. So much bulky terminology and so many abstract, fluffy concepts. It certainly can be a minefield!
Don’t worry – in this post, we’ll unpack the most popular analysis methods , one at a time, so that you can approach your analysis with confidence and competence – whether that’s for a dissertation, thesis or really any kind of research project.
What (exactly) is qualitative data analysis?
To understand qualitative data analysis, we need to first understand qualitative data – so let’s step back and ask the question, “what exactly is qualitative data?”.
Qualitative data refers to pretty much any data that’s “not numbers” . In other words, it’s not the stuff you measure using a fixed scale or complex equipment, nor do you analyse it using complex statistics or mathematics.
So, if it’s not numbers, what is it?
Words, you guessed? Well… sometimes , yes. Qualitative data can, and often does, take the form of interview transcripts, documents and open-ended survey responses – but it can also involve the interpretation of images and videos. In other words, qualitative isn’t just limited to text-based data.
So, how’s that different from quantitative data, you ask?
Simply put, qualitative research focuses on words, descriptions, concepts or ideas – while quantitative research focuses on numbers and statistics . Qualitative research investigates the “softer side” of things to explore and describe , while quantitative research focuses on the “hard numbers”, to measure differences between variables and the relationships between them. If you’re keen to learn more about the differences between qual and quant, we’ve got a detailed post over here .
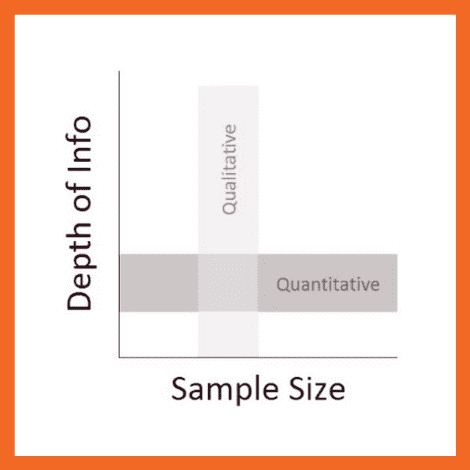
So, qualitative analysis is easier than quantitative, right?
Not quite. In many ways, qualitative data can be challenging and time-consuming to analyse and interpret. At the end of your data collection phase (which itself takes a lot of time), you’ll likely have many pages of text-based data or hours upon hours of audio to work through. You might also have subtle nuances of interactions or discussions that have danced around in your mind, or that you scribbled down in messy field notes. All of this needs to work its way into your analysis.
Making sense of all of this is no small task and you shouldn’t underestimate it. Long story short – qualitative analysis can be a lot of work! Of course, quantitative analysis is no piece of cake either, but it’s important to recognise that qualitative analysis still requires a significant investment in terms of time and effort.
Need a helping hand?
In this post, we’ll explore qualitative data analysis by looking at some of the most common analysis methods we encounter. We’re not going to cover every possible qualitative method and we’re not going to go into heavy detail – we’re just going to give you the big picture. That said, we will of course includes links to loads of extra resources so that you can learn more about whichever analysis method interests you.
Without further delay, let’s get into it.
The “Big 6” Qualitative Analysis Methods
There are many different types of qualitative data analysis, all of which serve different purposes and have unique strengths and weaknesses . We’ll start by outlining the analysis methods and then we’ll dive into the details for each.
The 6 most popular methods (or at least the ones we see at Grad Coach) are:
- Content analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Grounded theory (GT)
- Interpretive phenomenological analysis (IPA)
Let’s take a look at each of them…
QDA Method #1: Qualitative Content Analysis
Content analysis is possibly the most common and straightforward QDA method. At the simplest level, content analysis is used to evaluate patterns within a piece of content (for example, words, phrases or images) or across multiple pieces of content or sources of communication. For example, a collection of newspaper articles or political speeches.
With content analysis, you could, for instance, identify the frequency with which an idea is shared or spoken about – like the number of times a Kardashian is mentioned on Twitter. Or you could identify patterns of deeper underlying interpretations – for instance, by identifying phrases or words in tourist pamphlets that highlight India as an ancient country.
Because content analysis can be used in such a wide variety of ways, it’s important to go into your analysis with a very specific question and goal, or you’ll get lost in the fog. With content analysis, you’ll group large amounts of text into codes , summarise these into categories, and possibly even tabulate the data to calculate the frequency of certain concepts or variables. Because of this, content analysis provides a small splash of quantitative thinking within a qualitative method.
Naturally, while content analysis is widely useful, it’s not without its drawbacks . One of the main issues with content analysis is that it can be very time-consuming , as it requires lots of reading and re-reading of the texts. Also, because of its multidimensional focus on both qualitative and quantitative aspects, it is sometimes accused of losing important nuances in communication.
Content analysis also tends to concentrate on a very specific timeline and doesn’t take into account what happened before or after that timeline. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing though – just something to be aware of. So, keep these factors in mind if you’re considering content analysis. Every analysis method has its limitations , so don’t be put off by these – just be aware of them ! If you’re interested in learning more about content analysis, the video below provides a good starting point.
QDA Method #2: Narrative Analysis
As the name suggests, narrative analysis is all about listening to people telling stories and analysing what that means . Since stories serve a functional purpose of helping us make sense of the world, we can gain insights into the ways that people deal with and make sense of reality by analysing their stories and the ways they’re told.
You could, for example, use narrative analysis to explore whether how something is being said is important. For instance, the narrative of a prisoner trying to justify their crime could provide insight into their view of the world and the justice system. Similarly, analysing the ways entrepreneurs talk about the struggles in their careers or cancer patients telling stories of hope could provide powerful insights into their mindsets and perspectives . Simply put, narrative analysis is about paying attention to the stories that people tell – and more importantly, the way they tell them.
Of course, the narrative approach has its weaknesses , too. Sample sizes are generally quite small due to the time-consuming process of capturing narratives. Because of this, along with the multitude of social and lifestyle factors which can influence a subject, narrative analysis can be quite difficult to reproduce in subsequent research. This means that it’s difficult to test the findings of some of this research.
Similarly, researcher bias can have a strong influence on the results here, so you need to be particularly careful about the potential biases you can bring into your analysis when using this method. Nevertheless, narrative analysis is still a very useful qualitative analysis method – just keep these limitations in mind and be careful not to draw broad conclusions . If you’re keen to learn more about narrative analysis, the video below provides a great introduction to this qualitative analysis method.
QDA Method #3: Discourse Analysis
Discourse is simply a fancy word for written or spoken language or debate . So, discourse analysis is all about analysing language within its social context. In other words, analysing language – such as a conversation, a speech, etc – within the culture and society it takes place. For example, you could analyse how a janitor speaks to a CEO, or how politicians speak about terrorism.
To truly understand these conversations or speeches, the culture and history of those involved in the communication are important factors to consider. For example, a janitor might speak more casually with a CEO in a company that emphasises equality among workers. Similarly, a politician might speak more about terrorism if there was a recent terrorist incident in the country.
So, as you can see, by using discourse analysis, you can identify how culture , history or power dynamics (to name a few) have an effect on the way concepts are spoken about. So, if your research aims and objectives involve understanding culture or power dynamics, discourse analysis can be a powerful method.
Because there are many social influences in terms of how we speak to each other, the potential use of discourse analysis is vast . Of course, this also means it’s important to have a very specific research question (or questions) in mind when analysing your data and looking for patterns and themes, or you might land up going down a winding rabbit hole.
Discourse analysis can also be very time-consuming as you need to sample the data to the point of saturation – in other words, until no new information and insights emerge. But this is, of course, part of what makes discourse analysis such a powerful technique. So, keep these factors in mind when considering this QDA method. Again, if you’re keen to learn more, the video below presents a good starting point.
QDA Method #4: Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis looks at patterns of meaning in a data set – for example, a set of interviews or focus group transcripts. But what exactly does that… mean? Well, a thematic analysis takes bodies of data (which are often quite large) and groups them according to similarities – in other words, themes . These themes help us make sense of the content and derive meaning from it.
Let’s take a look at an example.
With thematic analysis, you could analyse 100 online reviews of a popular sushi restaurant to find out what patrons think about the place. By reviewing the data, you would then identify the themes that crop up repeatedly within the data – for example, “fresh ingredients” or “friendly wait staff”.
So, as you can see, thematic analysis can be pretty useful for finding out about people’s experiences , views, and opinions . Therefore, if your research aims and objectives involve understanding people’s experience or view of something, thematic analysis can be a great choice.
Since thematic analysis is a bit of an exploratory process, it’s not unusual for your research questions to develop , or even change as you progress through the analysis. While this is somewhat natural in exploratory research, it can also be seen as a disadvantage as it means that data needs to be re-reviewed each time a research question is adjusted. In other words, thematic analysis can be quite time-consuming – but for a good reason. So, keep this in mind if you choose to use thematic analysis for your project and budget extra time for unexpected adjustments.

QDA Method #5: Grounded theory (GT)
Grounded theory is a powerful qualitative analysis method where the intention is to create a new theory (or theories) using the data at hand, through a series of “ tests ” and “ revisions ”. Strictly speaking, GT is more a research design type than an analysis method, but we’ve included it here as it’s often referred to as a method.
What’s most important with grounded theory is that you go into the analysis with an open mind and let the data speak for itself – rather than dragging existing hypotheses or theories into your analysis. In other words, your analysis must develop from the ground up (hence the name).
Let’s look at an example of GT in action.
Assume you’re interested in developing a theory about what factors influence students to watch a YouTube video about qualitative analysis. Using Grounded theory , you’d start with this general overarching question about the given population (i.e., graduate students). First, you’d approach a small sample – for example, five graduate students in a department at a university. Ideally, this sample would be reasonably representative of the broader population. You’d interview these students to identify what factors lead them to watch the video.
After analysing the interview data, a general pattern could emerge. For example, you might notice that graduate students are more likely to read a post about qualitative methods if they are just starting on their dissertation journey, or if they have an upcoming test about research methods.
From here, you’ll look for another small sample – for example, five more graduate students in a different department – and see whether this pattern holds true for them. If not, you’ll look for commonalities and adapt your theory accordingly. As this process continues, the theory would develop . As we mentioned earlier, what’s important with grounded theory is that the theory develops from the data – not from some preconceived idea.
So, what are the drawbacks of grounded theory? Well, some argue that there’s a tricky circularity to grounded theory. For it to work, in principle, you should know as little as possible regarding the research question and population, so that you reduce the bias in your interpretation. However, in many circumstances, it’s also thought to be unwise to approach a research question without knowledge of the current literature . In other words, it’s a bit of a “chicken or the egg” situation.
Regardless, grounded theory remains a popular (and powerful) option. Naturally, it’s a very useful method when you’re researching a topic that is completely new or has very little existing research about it, as it allows you to start from scratch and work your way from the ground up .

QDA Method #6: Interpretive Phenomenological Analysis (IPA)
Interpretive. Phenomenological. Analysis. IPA . Try saying that three times fast…
Let’s just stick with IPA, okay?
IPA is designed to help you understand the personal experiences of a subject (for example, a person or group of people) concerning a major life event, an experience or a situation . This event or experience is the “phenomenon” that makes up the “P” in IPA. Such phenomena may range from relatively common events – such as motherhood, or being involved in a car accident – to those which are extremely rare – for example, someone’s personal experience in a refugee camp. So, IPA is a great choice if your research involves analysing people’s personal experiences of something that happened to them.
It’s important to remember that IPA is subject – centred . In other words, it’s focused on the experiencer . This means that, while you’ll likely use a coding system to identify commonalities, it’s important not to lose the depth of experience or meaning by trying to reduce everything to codes. Also, keep in mind that since your sample size will generally be very small with IPA, you often won’t be able to draw broad conclusions about the generalisability of your findings. But that’s okay as long as it aligns with your research aims and objectives.
Another thing to be aware of with IPA is personal bias . While researcher bias can creep into all forms of research, self-awareness is critically important with IPA, as it can have a major impact on the results. For example, a researcher who was a victim of a crime himself could insert his own feelings of frustration and anger into the way he interprets the experience of someone who was kidnapped. So, if you’re going to undertake IPA, you need to be very self-aware or you could muddy the analysis.

How to choose the right analysis method
In light of all of the qualitative analysis methods we’ve covered so far, you’re probably asking yourself the question, “ How do I choose the right one? ”
Much like all the other methodological decisions you’ll need to make, selecting the right qualitative analysis method largely depends on your research aims, objectives and questions . In other words, the best tool for the job depends on what you’re trying to build. For example:
- Perhaps your research aims to analyse the use of words and what they reveal about the intention of the storyteller and the cultural context of the time.
- Perhaps your research aims to develop an understanding of the unique personal experiences of people that have experienced a certain event, or
- Perhaps your research aims to develop insight regarding the influence of a certain culture on its members.
As you can probably see, each of these research aims are distinctly different , and therefore different analysis methods would be suitable for each one. For example, narrative analysis would likely be a good option for the first aim, while grounded theory wouldn’t be as relevant.
It’s also important to remember that each method has its own set of strengths, weaknesses and general limitations. No single analysis method is perfect . So, depending on the nature of your research, it may make sense to adopt more than one method (this is called triangulation ). Keep in mind though that this will of course be quite time-consuming.
As we’ve seen, all of the qualitative analysis methods we’ve discussed make use of coding and theme-generating techniques, but the intent and approach of each analysis method differ quite substantially. So, it’s very important to come into your research with a clear intention before you decide which analysis method (or methods) to use.
Start by reviewing your research aims , objectives and research questions to assess what exactly you’re trying to find out – then select a qualitative analysis method that fits. Never pick a method just because you like it or have experience using it – your analysis method (or methods) must align with your broader research aims and objectives.

Let’s recap on QDA methods…
In this post, we looked at six popular qualitative data analysis methods:
- First, we looked at content analysis , a straightforward method that blends a little bit of quant into a primarily qualitative analysis.
- Then we looked at narrative analysis , which is about analysing how stories are told.
- Next up was discourse analysis – which is about analysing conversations and interactions.
- Then we moved on to thematic analysis – which is about identifying themes and patterns.
- From there, we went south with grounded theory – which is about starting from scratch with a specific question and using the data alone to build a theory in response to that question.
- And finally, we looked at IPA – which is about understanding people’s unique experiences of a phenomenon.
Of course, these aren’t the only options when it comes to qualitative data analysis, but they’re a great starting point if you’re dipping your toes into qualitative research for the first time.
If you’re still feeling a bit confused, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research process to help you develop your best work.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

84 Comments
This has been very helpful. Thank you.
Thank you madam,
Thank you so much for this information
I wonder it so clear for understand and good for me. can I ask additional query?
Very insightful and useful
Good work done with clear explanations. Thank you.
Thanks so much for the write-up, it’s really good.
Thanks madam . It is very important .
thank you very good
This has been very well explained in simple language . It is useful even for a new researcher.
Great to hear that. Good luck with your qualitative data analysis, Pramod!
This is very useful information. And it was very a clear language structured presentation. Thanks a lot.
Thank you so much.
very informative sequential presentation
Precise explanation of method.
Hi, may we use 2 data analysis methods in our qualitative research?
Thanks for your comment. Most commonly, one would use one type of analysis method, but it depends on your research aims and objectives.
You explained it in very simple language, everyone can understand it. Thanks so much.
Thank you very much, this is very helpful. It has been explained in a very simple manner that even a layman understands
Thank nicely explained can I ask is Qualitative content analysis the same as thematic analysis?
Thanks for your comment. No, QCA and thematic are two different types of analysis. This article might help clarify – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/nhs.12048
This is my first time to come across a well explained data analysis. so helpful.
I have thoroughly enjoyed your explanation of the six qualitative analysis methods. This is very helpful. Thank you!
Thank you very much, this is well explained and useful
i need a citation of your book.
Thanks a lot , remarkable indeed, enlighting to the best
Hi Derek, What other theories/methods would you recommend when the data is a whole speech?
Keep writing useful artikel.
It is important concept about QDA and also the way to express is easily understandable, so thanks for all.
Thank you, this is well explained and very useful.
Very helpful .Thanks.
Hi there! Very well explained. Simple but very useful style of writing. Please provide the citation of the text. warm regards
The session was very helpful and insightful. Thank you
This was very helpful and insightful. Easy to read and understand
As a professional academic writer, this has been so informative and educative. Keep up the good work Grad Coach you are unmatched with quality content for sure.
Keep up the good work Grad Coach you are unmatched with quality content for sure.
Its Great and help me the most. A Million Thanks you Dr.
It is a very nice work
Very insightful. Please, which of this approach could be used for a research that one is trying to elicit students’ misconceptions in a particular concept ?
This is Amazing and well explained, thanks
great overview
What do we call a research data analysis method that one use to advise or determining the best accounting tool or techniques that should be adopted in a company.
Informative video, explained in a clear and simple way. Kudos
Waoo! I have chosen method wrong for my data analysis. But I can revise my work according to this guide. Thank you so much for this helpful lecture.
This has been very helpful. It gave me a good view of my research objectives and how to choose the best method. Thematic analysis it is.
Very helpful indeed. Thanku so much for the insight.
This was incredibly helpful.
Very helpful.
very educative
Nicely written especially for novice academic researchers like me! Thank you.
choosing a right method for a paper is always a hard job for a student, this is a useful information, but it would be more useful personally for me, if the author provide me with a little bit more information about the data analysis techniques in type of explanatory research. Can we use qualitative content analysis technique for explanatory research ? or what is the suitable data analysis method for explanatory research in social studies?
that was very helpful for me. because these details are so important to my research. thank you very much
I learnt a lot. Thank you
Relevant and Informative, thanks !
Well-planned and organized, thanks much! 🙂
I have reviewed qualitative data analysis in a simplest way possible. The content will highly be useful for developing my book on qualitative data analysis methods. Cheers!
Clear explanation on qualitative and how about Case study
This was helpful. Thank you
This was really of great assistance, it was just the right information needed. Explanation very clear and follow.
Wow, Thanks for making my life easy
This was helpful thanks .
Very helpful…. clear and written in an easily understandable manner. Thank you.
This was so helpful as it was easy to understand. I’m a new to research thank you so much.
so educative…. but Ijust want to know which method is coding of the qualitative or tallying done?
Thank you for the great content, I have learnt a lot. So helpful
precise and clear presentation with simple language and thank you for that.
very informative content, thank you.
You guys are amazing on YouTube on this platform. Your teachings are great, educative, and informative. kudos!
Brilliant Delivery. You made a complex subject seem so easy. Well done.
Beautifully explained.
Thanks a lot
Is there a video the captures the practical process of coding using automated applications?
Thanks for the comment. We don’t recommend using automated applications for coding, as they are not sufficiently accurate in our experience.
content analysis can be qualitative research?
THANK YOU VERY MUCH.
Thank you very much for such a wonderful content
do you have any material on Data collection
What a powerful explanation of the QDA methods. Thank you.
Great explanation both written and Video. i have been using of it on a day to day working of my thesis project in accounting and finance. Thank you very much for your support.
very helpful, thank you so much
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Qualitative Research Questions: Gain Powerful Insights + 25 Examples
We review the basics of qualitative research questions, including their key components, how to craft them effectively, & 25 example questions.
Einstein was many things—a physicist, a philosopher, and, undoubtedly, a mastermind. He also had an incredible way with words. His quote, "Everything that can be counted does not necessarily count; everything that counts cannot necessarily be counted," is particularly poignant when it comes to research.
Some inquiries call for a quantitative approach, for counting and measuring data in order to arrive at general conclusions. Other investigations, like qualitative research, rely on deep exploration and understanding of individual cases in order to develop a greater understanding of the whole. That’s what we’re going to focus on today.
Qualitative research questions focus on the "how" and "why" of things, rather than the "what". They ask about people's experiences and perceptions , and can be used to explore a wide range of topics.
The following article will discuss the basics of qualitative research questions, including their key components, and how to craft them effectively. You'll also find 25 examples of effective qualitative research questions you can use as inspiration for your own studies.
Let’s get started!
What are qualitative research questions, and when are they used?
When researchers set out to conduct a study on a certain topic, their research is chiefly directed by an overarching question . This question provides focus for the study and helps determine what kind of data will be collected.
By starting with a question, we gain parameters and objectives for our line of research. What are we studying? For what purpose? How will we know when we’ve achieved our goals?
Of course, some of these questions can be described as quantitative in nature. When a research question is quantitative, it usually seeks to measure or calculate something in a systematic way.
For example:
- How many people in our town use the library?
- What is the average income of families in our city?
- How much does the average person weigh?
Other research questions, however—and the ones we will be focusing on in this article—are qualitative in nature. Qualitative research questions are open-ended and seek to explore a given topic in-depth.
According to the Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry , “Qualitative research aims to address questions concerned with developing an understanding of the meaning and experience dimensions of humans’ lives and social worlds.”
This type of research can be used to gain a better understanding of people’s thoughts, feelings and experiences by “addressing questions beyond ‘what works’, towards ‘what works for whom when, how and why, and focusing on intervention improvement rather than accreditation,” states one paper in Neurological Research and Practice .
Qualitative questions often produce rich data that can help researchers develop hypotheses for further quantitative study.
- What are people’s thoughts on the new library?
- How does it feel to be a first-generation student at our school?
- How do people feel about the changes taking place in our town?
As stated by a paper in Human Reproduction , “...‘qualitative’ methods are used to answer questions about experience, meaning, and perspective, most often from the standpoint of the participant. These data are usually not amenable to counting or measuring.”
Both quantitative and qualitative questions have their uses; in fact, they often complement each other. A well-designed research study will include a mix of both types of questions in order to gain a fuller understanding of the topic at hand.
If you would like to recruit unlimited participants for qualitative research for free and only pay for the interview you conduct, try using Respondent today.
Crafting qualitative research questions for powerful insights
Now that we have a basic understanding of what qualitative research questions are and when they are used, let’s take a look at how you can begin crafting your own.
According to a study in the International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education, there is a certain process researchers should follow when crafting their questions, which we’ll explore in more depth.
1. Beginning the process
Start with a point of interest or curiosity, and pose a draft question or ‘self-question’. What do you want to know about the topic at hand? What is your specific curiosity? You may find it helpful to begin by writing several questions.
For example, if you’re interested in understanding how your customer base feels about a recent change to your product, you might ask:
- What made you decide to try the new product?
- How do you feel about the change?
- What do you think of the new design/functionality?
- What benefits do you see in the change?
2. Create one overarching, guiding question
At this point, narrow down the draft questions into one specific question. “Sometimes, these broader research questions are not stated as questions, but rather as goals for the study.”
As an example of this, you might narrow down these three questions:
into the following question:
- What are our customers’ thoughts on the recent change to our product?
3. Theoretical framing
As you read the relevant literature and apply theory to your research, the question should be altered to achieve better outcomes. Experts agree that pursuing a qualitative line of inquiry should open up the possibility for questioning your original theories and altering the conceptual framework with which the research began.
If we continue with the current example, it’s possible you may uncover new data that informs your research and changes your question. For instance, you may discover that customers’ feelings about the change are not just a reaction to the change itself, but also to how it was implemented. In this case, your question would need to reflect this new information:
- How did customers react to the process of the change, as well as the change itself?
4. Ethical considerations
A study in the International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education stresses that ethics are “a central issue when a researcher proposes to study the lives of others, especially marginalized populations.” Consider how your question or inquiry will affect the people it relates to—their lives and their safety. Shape your question to avoid physical, emotional, or mental upset for the focus group.
In analyzing your question from this perspective, if you feel that it may cause harm, you should consider changing the question or ending your research project. Perhaps you’ve discovered that your question encourages harmful or invasive questioning, in which case you should reformulate it.
5. Writing the question
The actual process of writing the question comes only after considering the above points. The purpose of crafting your research questions is to delve into what your study is specifically about” Remember that qualitative research questions are not trying to find the cause of an effect, but rather to explore the effect itself.
Your questions should be clear, concise, and understandable to those outside of your field. In addition, they should generate rich data. The questions you choose will also depend on the type of research you are conducting:
- If you’re doing a phenomenological study, your questions might be open-ended, in order to allow participants to share their experiences in their own words.
- If you’re doing a grounded-theory study, your questions might be focused on generating a list of categories or themes.
- If you’re doing ethnography, your questions might be about understanding the culture you’re studying.
Whenyou have well-written questions, it is much easier to develop your research design and collect data that accurately reflects your inquiry.
In writing your questions, it may help you to refer to this simple flowchart process for constructing questions:
Download Free E-Book
25 examples of expertly crafted qualitative research questions
It's easy enough to cover the theory of writing a qualitative research question, but sometimes it's best if you can see the process in practice. In this section, we'll list 25 examples of B2B and B2C-related qualitative questions.
Let's begin with five questions. We'll show you the question, explain why it's considered qualitative, and then give you an example of how it can be used in research.
1. What is the customer's perception of our company's brand?
Qualitative research questions are often open-ended and invite respondents to share their thoughts and feelings on a subject. This question is qualitative because it seeks customer feedback on the company's brand.
This question can be used in research to understand how customers feel about the company's branding, what they like and don't like about it, and whether they would recommend it to others.
2. Why do customers buy our product?
This question is also qualitative because it seeks to understand the customer's motivations for purchasing a product. It can be used in research to identify the reasons customers buy a certain product, what needs or desires the product fulfills for them, and how they feel about the purchase after using the product.
3. How do our customers interact with our products?
Again, this question is qualitative because it seeks to understand customer behavior. In this case, it can be used in research to see how customers use the product, how they interact with it, and what emotions or thoughts the product evokes in them.
4. What are our customers' biggest frustrations with our products?
By seeking to understand customer frustrations, this question is qualitative and can provide valuable insights. It can be used in research to help identify areas in which the company needs to make improvements with its products.
5. How do our customers feel about our customer service?
Rather than asking why customers like or dislike something, this question asks how they feel. This qualitative question can provide insights into customer satisfaction or dissatisfaction with a company.
This type of question can be used in research to understand what customers think of the company's customer service and whether they feel it meets their needs.
20 more examples to refer to when writing your question
Now that you’re aware of what makes certain questions qualitative, let's move into 20 more examples of qualitative research questions:
- How do your customers react when updates are made to your app interface?
- How do customers feel when they complete their purchase through your ecommerce site?
- What are your customers' main frustrations with your service?
- How do people feel about the quality of your products compared to those of your competitors?
- What motivates customers to refer their friends and family members to your product or service?
- What are the main benefits your customers receive from using your product or service?
- How do people feel when they finish a purchase on your website?
- What are the main motivations behind customer loyalty to your brand?
- How does your app make people feel emotionally?
- For younger generations using your app, how does it make them feel about themselves?
- What reputation do people associate with your brand?
- How inclusive do people find your app?
- In what ways are your customers' experiences unique to them?
- What are the main areas of improvement your customers would like to see in your product or service?
- How do people feel about their interactions with your tech team?
- What are the top five reasons people use your online marketplace?
- How does using your app make people feel in terms of connectedness?
- What emotions do people experience when they're using your product or service?
- Aside from the features of your product, what else about it attracts customers?
- How does your company culture make people feel?
As you can see, these kinds of questions are completely open-ended. In a way, they allow the research and discoveries made along the way to direct the research. The questions are merely a starting point from which to explore.
This video offers tips on how to write good qualitative research questions, produced by Qualitative Research Expert, Kimberly Baker.
Wrap-up: crafting your own qualitative research questions.
Over the course of this article, we've explored what qualitative research questions are, why they matter, and how they should be written. Hopefully you now have a clear understanding of how to craft your own.
Remember, qualitative research questions should always be designed to explore a certain experience or phenomena in-depth, in order to generate powerful insights. As you write your questions, be sure to keep the following in mind:
- Are you being inclusive of all relevant perspectives?
- Are your questions specific enough to generate clear answers?
- Will your questions allow for an in-depth exploration of the topic at hand?
- Do the questions reflect your research goals and objectives?
If you can answer "yes" to all of the questions above, and you've followed the tips for writing qualitative research questions we shared in this article, then you're well on your way to crafting powerful queries that will yield valuable insights.
Download Free E-Book
.png?width=2500&name=Respondent_100+Questions_Banners_1200x644%20(1).png)
Asking the right questions in the right way is the key to research success. That’s true for not just the discussion guide but for every step of a research project. Following are 100+ questions that will take you from defining your research objective through screening and participant discussions.
Fill out the form below to access free e-book!
Recommend Resources:
- How to Recruit Participants for Qualitative Research
- The Best UX Research Tools of 2022
- 10 Smart Tips for Conducting Better User Interviews
- 50 Powerful Questions You Should Ask In Your Next User Interview
- How To Find Participants For User Research: 13 Ways To Make It Happen
- UX Diary Study: 5 Essential Tips For Conducing Better Studies
- User Testing Recruitment: 10 Smart Tips To Find Participants Fast
- Qualitative Research Questions: Gain Powerful Insights + 25
- How To Successfully Recruit Participants for A Study (2022 Edition)
- How To Properly Recruit Focus Group Participants (2022 Edition)
- The Best Unmoderated Usability Testing Tools of 2022
50 Powerful User Interview Questions You Should Consider Asking
We researched the best user interview questions you can use for your qualitative research studies. Use these 50 sample questions for your next...
Understanding Why High-Quality Research Needs High-Quality Participants
Why are high-quality participants essential to your research? Read here to find out who they are, why you need them, and how to find them.
A Guide to Usability Testing Questions (Including 100 Examples)
Asking the right questions in the right way is the key to the success of your UX research project. With tips and 100+ question examples, Respondent...
Research Paper Guide
Types Of Qualitative Research
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
16 min read
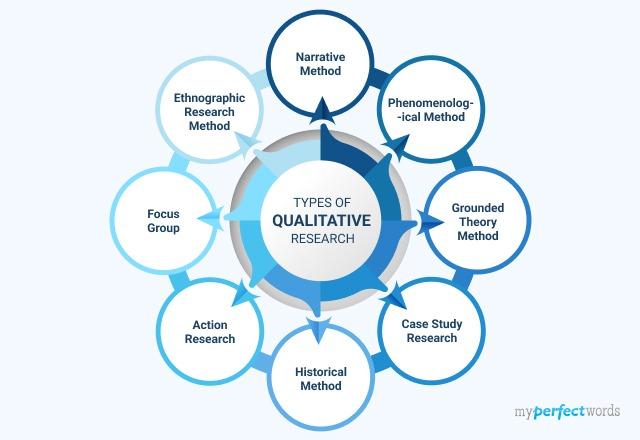
People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Are you overwhelmed by the multitude of qualitative research methods available? It's no secret that choosing the right approach can leave you stuck at the starting line of your research.
Selecting an unsuitable method can lead to wasted time, resources, and potentially skewed results. But with so many options to consider, it's easy to feel lost in the complexities of qualitative research.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explain the types of qualitative research, their unique characteristics, advantages, and best use cases for each method.
Let's dive in!

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
- 1. What is Qualitative Research?
- 2. Types of Qualitative Research Methods
- 3. Types of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
What is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is a robust and flexible methodology used to explore and understand complex phenomena in-depth.
Unlike quantitative research , qualitative research dives into the rich and complex aspects of human experiences, behaviors, and perceptions.
At its core, this type of research question seek to answer for:
- Why do people think or behave a certain way?
- What are the underlying motivations and meanings behind actions?
- How do individuals perceive and interpret the world around them?
This approach values context, diversity, and the unique perspectives of participants.
Rather than seeking generalizable findings applicable to a broad population, qualitative research aims for detailed insights, patterns, and themes that come from the people being studied.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research possesses the following characteristics:
- Subjective Perspective: Qualitative research explores subjective experiences, emphasizing the uniqueness of human behavior and opinions.
- In-Depth Exploration: It involves deep investigation, allowing a comprehensive understanding of specific phenomena.
- Open-Ended Questions: Qualitative research uses open-ended questions to encourage detailed, descriptive responses.
- Contextual Understanding: It emphasizes the importance of understanding the research context and setting.
- Rich Descriptions: Qualitative research produces rich, descriptive findings that contribute to a nuanced understanding of the topic.
Types of Qualitative Research Methods
Researchers collect data on the targeted population, place, or event by using different types of qualitative research analysis.
Each qualitative research method offers a distinct perspective, enabling researchers to reveal concealed meanings, patterns, and valuable insights.
Below are the most commonly used qualitative research types for writing a paper.
Ethnographic Research Method
Ethnography, a subfield of anthropology, provides a scientific approach to examining human societies and cultures. It ranks among the most widely employed qualitative research techniques.
In ethnographic field notes, researchers actively engage with the environment and live alongside the focus group.
This immersive interaction allows researchers to gain insights into the objectives, motivations, challenges, and distinctive cultural attributes of the individuals under study.
Key cultural characteristics that ethnography helps to illustrate encompass:
- Geographical Location
- Religious Practices
- Tribal Systems
- Shared Experiences
Unlike traditional survey and interview-based research methods, ethnographers don't rely on structured questioning.
Instead, they become observers within the community, emphasizing participant observation over an extended period. However, it may also be appropriate to complement observations with interviews of individuals who possess knowledge of the culture.
Ethnographic research can present challenges if the researcher is unfamiliar with the social norms and language of the group being studied.
Furthermore, interpretations made by outsiders may lead to misinterpretations or confusion. Therefore, thorough validation of data is essential before presenting findings.
Narrative Method
The narrative research design unfolds over an extended period to compile data, much like crafting a cohesive story. Similar to a narrative structure, it begins with a starting point and progresses through various life situations.
In this method, researchers engage in in-depth interviews and review relevant documents. They explore events that have had a significant impact on an individual's personality and life journey. Interviews may occur over weeks, months, or even years, depending on the depth and scope of the narrative being studied.
The outcome of narrative research is the presentation of a concise story that captures essential themes, conflicts, and challenges. It provides a holistic view of the individual's experiences, both positive and negative, which have shaped their unique narrative.
Phenomenological Method
The term "phenomenological" pertains to the study of phenomena, which can encompass events, situations, or experiences.
This method is ideal for examining a subject from multiple perspectives and contributing to existing knowledge, with a particular focus on subjective experiences.
Researchers employing the phenomenological method use various data collection techniques, including interviews, site visits, observations, surveys, and document reviews.
These methods help gather rich and diverse data about the phenomenon under investigation.
A central aspect of this technique is capturing how participants experience events or activities, delving into their subjective viewpoints. Ultimately, the research results in the creation of a thematic database that validates the findings and offers insights from the subject's perspective.
Grounded Theory Method
A grounded theory approach differs from a phenomenological study in that it seeks to explain, provide reasons for, or develop theories behind an event or phenomenon.
It serves as a means to construct new theories by systematically collecting and analyzing data related to a specific phenomenon.
Researchers employing the grounded theory method utilize a variety of data collection techniques, including observation, interviews, literature review , and the analysis of relevant documents.
The focus of content analysis is not individual behaviors but a specific phenomenon or incident.
This method typically involves various coding techniques and large sample sizes to identify themes and develop more comprehensive theories.
Case Study Research
The case study approach entails a comprehensive examination of a subject over an extended period, with a focus on providing detailed insights into the subject, which can be an event, person, business, or place.
Data for case studies is collected from diverse sources, including interviews, direct observation, historical records, and documentation.
Case studies find applications across various disciplines, including law, education, medicine, and the sciences. They can serve both descriptive and explanatory purposes, making them a versatile research methodology .
Researchers often turn to the case study method when they want to explore:
- 'How' and 'why' research questions
- Behaviors under observation
- Understanding a specific phenomenon
- The contextual factors influencing the phenomena
Historical Method
The historical method aims to describe and analyze past events, offering insights into present patterns and the potential to predict future scenarios.
Researchers formulate research questions based on a hypothetical idea and then rigorously test this idea using multiple historical resources.
Key steps in the historical method include:
- Developing a research idea
- Identifying appropriate sources such as archives and libraries
- Ensuring the reliability and validity of these sources
- Creating a well-organized research outline
- Systematically collecting research data
The analysis phase involves critically assessing the collected data, accepting or rejecting it based on credibility, and identifying any conflicting evidence.
Ultimately, the outcomes of the historical method are presented in the form of a biography or a scholarly paper that provides a comprehensive account of the research findings.
Action Research
Action research is a dynamic research approach focused on addressing practical challenges in real-world settings while simultaneously conducting research to improve the situation.
It follows a cyclic process, starting with the identification of a specific issue or problem in a particular context.
The key steps in action research include:
- Planning and implementing actions to address the issue
- Collecting data during the action phase to understand its impact
- Reflecting on the data and analyzing it to gain insights
- Adjusting the action plan based on the analysis
This process may be iterative, with multiple cycles of action and reflection.
The outcomes of action research are practical solutions and improved practices that directly benefit the context in which the research is conducted. Additionally, it leads to a deeper and more nuanced understanding of the issue under investigation.
Focus Groups
Focus groups are a qualitative research method used to gather in-depth insights and perspectives on a specific topic or research question.
This approach involves assembling a small group of participants who possess relevant knowledge or experiences related to the research focus.
Key steps in the focus group method include:
- Selecting participants
- Moderating the discussion
- Structuring the conversation around open-ended questions
- Collecting data through audio or video recordings and note-taking
The discussion is dynamic and interactive, encouraging participants to share their thoughts, experiences, and opinions.
The analysis phase involves reviewing the data collected from the focus group discussion to identify common themes, patterns, and valuable insights. Focus groups provide rich qualitative data that offer a deeper and more nuanced understanding of the research topic or question.
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Types of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research employs different data analysis methods, each suited to specific research goals:
- Thematic Analysis: Identifies recurring themes or concepts within data.
- Content Analysis: Systematically categorizes and quantifies text or media content.
- Narrative Analysis: Focuses on storytelling and narrative elements in data.
- Grounded Theory Analysis: Develops or refines theories based on data.
- Discourse Analysis: Examines language and communication patterns.
- Framework Analysis: Organizes data using predefined categories.
- Visual Analysis: Interprets visual data like photos or videos.
- Cross-case Analysis: Compares patterns across multiple cases.
The choice depends on research questions and data type, enhancing understanding and insights.
Benefits of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers valuable advantages, including:
- Flexibility: Adaptable to various research questions and settings.
- Holistic Approach: Explores multiple dimensions of phenomena.
- Theory Development: Contributes to theory creation or refinement.
- Participant Engagement: Fosters active participant involvement.
- Complements Quantitative Research: Provides a comprehensive understanding.
All in all, different types of qualitative research methodology can assist in understanding the behavior and motivations of people. Similarly, it will also help in generating original ideas and formulating a better research problem.
However, not everyone can write a good research paper. Thus, if you get stuck at any stage, you can get professional help.
MyPerfectWords.com is the best custom writing paper service , where you can hire a professional writer.
We assure you that you will receive high-quality paper at the most reasonable rates.
Contact our team with your " pay for my research paper " queries. We are available 24/7!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
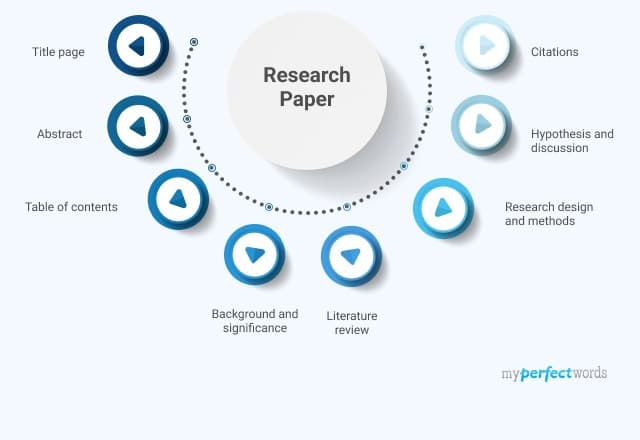
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Qualitative Data Analysis: What is it, Methods + Examples

In a world rich with information and narrative, understanding the deeper layers of human experiences requires a unique vision that goes beyond numbers and figures. This is where the power of qualitative data analysis comes to light.
In this blog, we’ll learn about qualitative data analysis, explore its methods, and provide real-life examples showcasing its power in uncovering insights.
What is Qualitative Data Analysis?
Qualitative data analysis is a systematic process of examining non-numerical data to extract meaning, patterns, and insights.
In contrast to quantitative analysis, which focuses on numbers and statistical metrics, the qualitative study focuses on the qualitative aspects of data, such as text, images, audio, and videos. It seeks to understand every aspect of human experiences, perceptions, and behaviors by examining the data’s richness.
Companies frequently conduct this analysis on customer feedback. You can collect qualitative data from reviews, complaints, chat messages, interactions with support centers, customer interviews, case notes, or even social media comments. This kind of data holds the key to understanding customer sentiments and preferences in a way that goes beyond mere numbers.
Importance of Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis plays a crucial role in your research and decision-making process across various disciplines. Let’s explore some key reasons that underline the significance of this analysis:
In-Depth Understanding
It enables you to explore complex and nuanced aspects of a phenomenon, delving into the ‘how’ and ‘why’ questions. This method provides you with a deeper understanding of human behavior, experiences, and contexts that quantitative approaches might not capture fully.
Contextual Insight
You can use this analysis to give context to numerical data. It will help you understand the circumstances and conditions that influence participants’ thoughts, feelings, and actions. This contextual insight becomes essential for generating comprehensive explanations.

Theory Development
You can generate or refine hypotheses via qualitative data analysis. As you analyze the data attentively, you can form hypotheses, concepts, and frameworks that will drive your future research and contribute to theoretical advances.
Participant Perspectives
When performing qualitative research, you can highlight participant voices and opinions. This approach is especially useful for understanding marginalized or underrepresented people, as it allows them to communicate their experiences and points of view.
Exploratory Research
The analysis is frequently used at the exploratory stage of your project. It assists you in identifying important variables, developing research questions, and designing quantitative studies that will follow.
Types of Qualitative Data
When conducting qualitative research, you can use several qualitative data collection methods , and here you will come across many sorts of qualitative data that can provide you with unique insights into your study topic. These data kinds add new views and angles to your understanding and analysis.
Interviews and Focus Groups
Interviews and focus groups will be among your key methods for gathering qualitative data. Interviews are one-on-one talks in which participants can freely share their thoughts, experiences, and opinions.
Focus groups, on the other hand, are discussions in which members interact with one another, resulting in dynamic exchanges of ideas. Both methods provide rich qualitative data and direct access to participant perspectives.
Observations and Field Notes
Observations and field notes are another useful sort of qualitative data. You can immerse yourself in the research environment through direct observation, carefully documenting behaviors, interactions, and contextual factors.
These observations will be recorded in your field notes, providing a complete picture of the environment and the behaviors you’re researching. This data type is especially important for comprehending behavior in their natural setting.
Textual and Visual Data
Textual and visual data include a wide range of resources that can be qualitatively analyzed. Documents, written narratives, and transcripts from various sources, such as interviews or speeches, are examples of textual data.
Photographs, films, and even artwork provide a visual layer to your research. These forms of data allow you to investigate what is spoken and the underlying emotions, details, and symbols expressed by language or pictures.
When to Choose Qualitative Data Analysis over Quantitative Data Analysis
As you begin your research journey, understanding why the analysis of qualitative data is important will guide your approach to understanding complex events. If you analyze qualitative data, it will provide new insights that complement quantitative methodologies, which will give you a broader understanding of your study topic.
It is critical to know when to use qualitative analysis over quantitative procedures. You can prefer qualitative data analysis when:
- Complexity Reigns: When your research questions involve deep human experiences, motivations, or emotions, qualitative research excels at revealing these complexities.
- Exploration is Key: Qualitative analysis is ideal for exploratory research. It will assist you in understanding a new or poorly understood topic before formulating quantitative hypotheses.
- Context Matters: If you want to understand how context affects behaviors or results, qualitative data analysis provides the depth needed to grasp these relationships.
- Unanticipated Findings: When your study provides surprising new viewpoints or ideas, qualitative analysis helps you to delve deeply into these emerging themes.
- Subjective Interpretation is Vital: When it comes to understanding people’s subjective experiences and interpretations, qualitative data analysis is the way to go.
You can make informed decisions regarding the right approach for your research objectives if you understand the importance of qualitative analysis and recognize the situations where it shines.
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods and Examples
Exploring various qualitative data analysis methods will provide you with a wide collection for making sense of your research findings. Once the data has been collected, you can choose from several analysis methods based on your research objectives and the data type you’ve collected.
There are five main methods for analyzing qualitative data. Each method takes a distinct approach to identifying patterns, themes, and insights within your qualitative data. They are:
Method 1: Content Analysis
Content analysis is a methodical technique for analyzing textual or visual data in a structured manner. In this method, you will categorize qualitative data by splitting it into manageable pieces and assigning the manual coding process to these units.
As you go, you’ll notice ongoing codes and designs that will allow you to conclude the content. This method is very beneficial for detecting common ideas, concepts, or themes in your data without losing the context.
Steps to Do Content Analysis
Follow these steps when conducting content analysis:
- Collect and Immerse: Begin by collecting the necessary textual or visual data. Immerse yourself in this data to fully understand its content, context, and complexities.
- Assign Codes and Categories: Assign codes to relevant data sections that systematically represent major ideas or themes. Arrange comparable codes into groups that cover the major themes.
- Analyze and Interpret: Develop a structured framework from the categories and codes. Then, evaluate the data in the context of your research question, investigate relationships between categories, discover patterns, and draw meaning from these connections.
Benefits & Challenges
There are various advantages to using content analysis:
- Structured Approach: It offers a systematic approach to dealing with large data sets and ensures consistency throughout the research.
- Objective Insights: This method promotes objectivity, which helps to reduce potential biases in your study.
- Pattern Discovery: Content analysis can help uncover hidden trends, themes, and patterns that are not always obvious.
- Versatility: You can apply content analysis to various data formats, including text, internet content, images, etc.
However, keep in mind the challenges that arise:
- Subjectivity: Even with the best attempts, a certain bias may remain in coding and interpretation.
- Complexity: Analyzing huge data sets requires time and great attention to detail.
- Contextual Nuances: Content analysis may not capture all of the contextual richness that qualitative data analysis highlights.
Example of Content Analysis
Suppose you’re conducting market research and looking at customer feedback on a product. As you collect relevant data and analyze feedback, you’ll see repeating codes like “price,” “quality,” “customer service,” and “features.” These codes are organized into categories such as “positive reviews,” “negative reviews,” and “suggestions for improvement.”
According to your findings, themes such as “price” and “customer service” stand out and show that pricing and customer service greatly impact customer satisfaction. This example highlights the power of content analysis for obtaining significant insights from large textual data collections.
Method 2: Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis is a well-structured procedure for identifying and analyzing recurring themes in your data. As you become more engaged in the data, you’ll generate codes or short labels representing key concepts. These codes are then organized into themes, providing a consistent framework for organizing and comprehending the substance of the data.
The analysis allows you to organize complex narratives and perspectives into meaningful categories, which will allow you to identify connections and patterns that may not be visible at first.
Steps to Do Thematic Analysis
Follow these steps when conducting a thematic analysis:
- Code and Group: Start by thoroughly examining the data and giving initial codes that identify the segments. To create initial themes, combine relevant codes.
- Code and Group: Begin by engaging yourself in the data, assigning first codes to notable segments. To construct basic themes, group comparable codes together.
- Analyze and Report: Analyze the data within each theme to derive relevant insights. Organize the topics into a consistent structure and explain your findings, along with data extracts that represent each theme.
Thematic analysis has various benefits:
- Structured Exploration: It is a method for identifying patterns and themes in complex qualitative data.
- Comprehensive knowledge: Thematic analysis promotes an in-depth understanding of the complications and meanings of the data.
- Application Flexibility: This method can be customized to various research situations and data kinds.
However, challenges may arise, such as:
- Interpretive Nature: Interpreting qualitative data in thematic analysis is vital, and it is critical to manage researcher bias.
- Time-consuming: The study can be time-consuming, especially with large data sets.
- Subjectivity: The selection of codes and topics might be subjective.
Example of Thematic Analysis
Assume you’re conducting a thematic analysis on job satisfaction interviews. Following your immersion in the data, you assign initial codes such as “work-life balance,” “career growth,” and “colleague relationships.” As you organize these codes, you’ll notice themes develop, such as “Factors Influencing Job Satisfaction” and “Impact on Work Engagement.”
Further investigation reveals the tales and experiences included within these themes and provides insights into how various elements influence job satisfaction. This example demonstrates how thematic analysis can reveal meaningful patterns and insights in qualitative data.
Method 3: Narrative Analysis
The narrative analysis involves the narratives that people share. You’ll investigate the histories in your data, looking at how stories are created and the meanings they express. This method is excellent for learning how people make sense of their experiences through narrative.
Steps to Do Narrative Analysis
The following steps are involved in narrative analysis:
- Gather and Analyze: Start by collecting narratives, such as first-person tales, interviews, or written accounts. Analyze the stories, focusing on the plot, feelings, and characters.
- Find Themes: Look for recurring themes or patterns in various narratives. Think about the similarities and differences between these topics and personal experiences.
- Interpret and Extract Insights: Contextualize the narratives within their larger context. Accept the subjective nature of each narrative and analyze the narrator’s voice and style. Extract insights from the tales by diving into the emotions, motivations, and implications communicated by the stories.
There are various advantages to narrative analysis:
- Deep Exploration: It lets you look deeply into people’s personal experiences and perspectives.
- Human-Centered: This method prioritizes the human perspective, allowing individuals to express themselves.
However, difficulties may arise, such as:
- Interpretive Complexity: Analyzing narratives requires dealing with the complexities of meaning and interpretation.
- Time-consuming: Because of the richness and complexities of tales, working with them can be time-consuming.
Example of Narrative Analysis
Assume you’re conducting narrative analysis on refugee interviews. As you read the stories, you’ll notice common themes of toughness, loss, and hope. The narratives provide insight into the obstacles that refugees face, their strengths, and the dreams that guide them.
The analysis can provide a deeper insight into the refugees’ experiences and the broader social context they navigate by examining the narratives’ emotional subtleties and underlying meanings. This example highlights how narrative analysis can reveal important insights into human stories.
Method 4: Grounded Theory Analysis
Grounded theory analysis is an iterative and systematic approach that allows you to create theories directly from data without being limited by pre-existing hypotheses. With an open mind, you collect data and generate early codes and labels that capture essential ideas or concepts within the data.
As you progress, you refine these codes and increasingly connect them, eventually developing a theory based on the data. Grounded theory analysis is a dynamic process for developing new insights and hypotheses based on details in your data.
Steps to Do Grounded Theory Analysis
Grounded theory analysis requires the following steps:
- Initial Coding: First, immerse yourself in the data, producing initial codes that represent major concepts or patterns.
- Categorize and Connect: Using axial coding, organize the initial codes, which establish relationships and connections between topics.
- Build the Theory: Focus on creating a core category that connects the codes and themes. Regularly refine the theory by comparing and integrating new data, ensuring that it evolves organically from the data.
Grounded theory analysis has various benefits:
- Theory Generation: It provides a one-of-a-kind opportunity to generate hypotheses straight from data and promotes new insights.
- In-depth Understanding: The analysis allows you to deeply analyze the data and reveal complex relationships and patterns.
- Flexible Process: This method is customizable and ongoing, which allows you to enhance your research as you collect additional data.
However, challenges might arise with:
- Time and Resources: Because grounded theory analysis is a continuous process, it requires a large commitment of time and resources.
- Theoretical Development: Creating a grounded theory involves a thorough understanding of qualitative data analysis software and theoretical concepts.
- Interpretation of Complexity: Interpreting and incorporating a newly developed theory into existing literature can be intellectually hard.
Example of Grounded Theory Analysis
Assume you’re performing a grounded theory analysis on workplace collaboration interviews. As you open code the data, you will discover notions such as “communication barriers,” “team dynamics,” and “leadership roles.” Axial coding demonstrates links between these notions, emphasizing the significance of efficient communication in developing collaboration.
You create the core “Integrated Communication Strategies” category through selective coding, which unifies new topics.
This theory-driven category serves as the framework for understanding how numerous aspects contribute to effective team collaboration. This example shows how grounded theory analysis allows you to generate a theory directly from the inherent nature of the data.
Method 5: Discourse Analysis
Discourse analysis focuses on language and communication. You’ll look at how language produces meaning and how it reflects power relations, identities, and cultural influences. This strategy examines what is said and how it is said; the words, phrasing, and larger context of communication.
The analysis is precious when investigating power dynamics, identities, and cultural influences encoded in language. By evaluating the language used in your data, you can identify underlying assumptions, cultural standards, and how individuals negotiate meaning through communication.
Steps to Do Discourse Analysis
Conducting discourse analysis entails the following steps:
- Select Discourse: For analysis, choose language-based data such as texts, speeches, or media content.
- Analyze Language: Immerse yourself in the conversation, examining language choices, metaphors, and underlying assumptions.
- Discover Patterns: Recognize the dialogue’s reoccurring themes, ideologies, and power dynamics. To fully understand the effects of these patterns, put them in their larger context.
There are various advantages of using discourse analysis:
- Understanding Language: It provides an extensive understanding of how language builds meaning and influences perceptions.
- Uncovering Power Dynamics: The analysis reveals how power dynamics appear via language.
- Cultural Insights: This method identifies cultural norms, beliefs, and ideologies stored in communication.
However, the following challenges may arise:
- Complexity of Interpretation: Language analysis involves navigating multiple levels of nuance and interpretation.
- Subjectivity: Interpretation can be subjective, so controlling researcher bias is important.
- Time-Intensive: Discourse analysis can take a lot of time because careful linguistic study is required in this analysis.
Example of Discourse Analysis
Consider doing discourse analysis on media coverage of a political event. You notice repeating linguistic patterns in news articles that depict the event as a conflict between opposing parties. Through deconstruction, you can expose how this framing supports particular ideologies and power relations.
You can illustrate how language choices influence public perceptions and contribute to building the narrative around the event by analyzing the speech within the broader political and social context. This example shows how discourse analysis can reveal hidden power dynamics and cultural influences on communication.
How to do Qualitative Data Analysis with the QuestionPro Research suite?
QuestionPro is a popular survey and research platform that offers tools for collecting and analyzing qualitative and quantitative data. Follow these general steps for conducting qualitative data analysis using the QuestionPro Research Suite:
- Collect Qualitative Data: Set up your survey to capture qualitative responses. It might involve open-ended questions, text boxes, or comment sections where participants can provide detailed responses.
- Export Qualitative Responses: Export the responses once you’ve collected qualitative data through your survey. QuestionPro typically allows you to export survey data in various formats, such as Excel or CSV.
- Prepare Data for Analysis: Review the exported data and clean it if necessary. Remove irrelevant or duplicate entries to ensure your data is ready for analysis.
- Code and Categorize Responses: Segment and label data, letting new patterns emerge naturally, then develop categories through axial coding to structure the analysis.
- Identify Themes: Analyze the coded responses to identify recurring themes, patterns, and insights. Look for similarities and differences in participants’ responses.
- Generate Reports and Visualizations: Utilize the reporting features of QuestionPro to create visualizations, charts, and graphs that help communicate the themes and findings from your qualitative research.
- Interpret and Draw Conclusions: Interpret the themes and patterns you’ve identified in the qualitative data. Consider how these findings answer your research questions or provide insights into your study topic.
- Integrate with Quantitative Data (if applicable): If you’re also conducting quantitative research using QuestionPro, consider integrating your qualitative findings with quantitative results to provide a more comprehensive understanding.
Qualitative data analysis is vital in uncovering various human experiences, views, and stories. If you’re ready to transform your research journey and apply the power of qualitative analysis, now is the moment to do it. Book a demo with QuestionPro today and begin your journey of exploration.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 7 Focus Group Software for Comprehensive Research
Apr 17, 2024

Top 7 DEI Software Solutions to Empower Your Workplace
Apr 16, 2024

The Power of AI in Customer Experience — Tuesday CX Thoughts

Employee Lifecycle Management Software: Top of 2024
Apr 15, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 30 January 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organisation?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography, action research, phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasise different aims and perspectives.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves ‘instruments’ in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analysing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organise your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorise your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analysing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasise different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analysing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analysing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalisability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalisable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labour-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 30). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 15 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari

83 Qualitative Research Questions & Examples

Qualitative research questions help you understand consumer sentiment. They’re strategically designed to show organizations how and why people feel the way they do about a brand, product, or service. It looks beyond the numbers and is one of the most telling types of market research a company can do.
The UK Data Service describes this perfectly, saying, “The value of qualitative research is that it gives a voice to the lived experience .”
Read on to see seven use cases and 83 qualitative research questions, with the added bonus of examples that show how to get similar insights faster with Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence.

What is a qualitative research question?
A qualitative research question explores a topic in-depth, aiming to better understand the subject through interviews, observations, and other non-numerical data. Qualitative research questions are open-ended, helping to uncover a target audience’s opinions, beliefs, and motivations.
How to choose qualitative research questions?
Choosing the right qualitative research questions can be incremental to the success of your research and the findings you uncover. Here’s my six-step process for choosing the best qualitative research questions.
- Start by understanding the purpose of your research. What do you want to learn? What outcome are you hoping to achieve?
- Consider who you are researching. What are their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs? How can you best capture these in your research questions ?
- Keep your questions open-ended . Qualitative research questions should not be too narrow or too broad. Aim to ask specific questions to provide meaningful answers but broad enough to allow for exploration.
- Balance your research questions. You don’t want all of your questions to be the same type. Aim to mix up your questions to get a variety of answers.
- Ensure your research questions are ethical and free from bias. Always have a second (and third) person check for unconscious bias.
- Consider the language you use. Your questions should be written in a way that is clear and easy to understand. Avoid using jargon , acronyms, or overly technical language.

Types of qualitative research questions
For a question to be considered qualitative, it usually needs to be open-ended. However, as I’ll explain, there can sometimes be a slight cross-over between quantitative and qualitative research questions.
Open-ended questions
These allow for a wide range of responses and can be formatted with multiple-choice answers or a free-text box to collect additional details. The next two types of qualitative questions are considered open questions, but each has its own style and purpose.
- Probing questions are used to delve deeper into a respondent’s thoughts, such as “Can you tell me more about why you feel that way?”
- Comparative questions ask people to compare two or more items, such as “Which product do you prefer and why?” These qualitative questions are highly useful for understanding brand awareness , competitive analysis , and more.
Closed-ended questions
These ask respondents to choose from a predetermined set of responses, such as “On a scale of 1-5, how satisfied are you with the new product?” While they’re traditionally quantitative, adding a free text box that asks for extra comments into why a specific rating was chosen will provide qualitative insights alongside their respective quantitative research question responses.
- Ranking questions get people to rank items in order of preference, such as “Please rank these products in terms of quality.” They’re advantageous in many scenarios, like product development, competitive analysis, and brand awareness.
- Likert scale questions ask people to rate items on a scale, such as “On a scale of 1-5, how satisfied are you with the new product?” Ideal for placement on websites and emails to gather quick, snappy feedback.
Qualitative research question examples
There are many applications of qualitative research and lots of ways you can put your findings to work for the success of your business. Here’s a summary of the most common use cases for qualitative questions and examples to ask.
Qualitative questions for identifying customer needs and motivations
These types of questions help you find out why customers choose products or services and what they are looking for when making a purchase.
- What factors do you consider when deciding to buy a product?
- What would make you choose one product or service over another?
- What are the most important elements of a product that you would buy?
- What features do you look for when purchasing a product?
- What qualities do you look for in a company’s products?
- Do you prefer localized or global brands when making a purchase?
- How do you determine the value of a product?
- What do you think is the most important factor when choosing a product?
- How do you decide if a product or service is worth the money?
- Do you have any specific expectations when purchasing a product?
- Do you prefer to purchase products or services online or in person?
- What kind of customer service do you expect when buying a product?
- How do you decide when it is time to switch to a different product?
- Where do you research products before you decide to buy?
- What do you think is the most important customer value when making a purchase?
Qualitative research questions to enhance customer experience
Use these questions to reveal insights into how customers interact with a company’s products or services and how those experiences can be improved.
- What aspects of our product or service do customers find most valuable?
- How do customers perceive our customer service?
- What factors are most important to customers when purchasing?
- What do customers think of our brand?
- What do customers think of our current marketing efforts?
- How do customers feel about the features and benefits of our product?
- How do customers feel about the price of our product or service?
- How could we improve the customer experience?
- What do customers think of our website or app?
- What do customers think of our customer support?
- What could we do to make our product or service easier to use?
- What do customers think of our competitors?
- What is your preferred way to access our site?
- How do customers feel about our delivery/shipping times?
- What do customers think of our loyalty programs?
Qualitative research question example for customer experience
- 🙋♀️ Question: What is your preferred way to access our site?
- 🤓 Insight sought: How mobile-dominant are consumers? Should you invest more in mobile optimization or mobile marketing?
- 🤯 Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: While using this type of question is ideal if you have a large database to survey when placed on a site or sent to a limited customer list, it only gives you a point-in-time perspective from a limited group of people.
- 💡 A new approach: You can get better, broader insights quicker with Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence. To fully inform your research, you need to know preferences at the industry or market level.
- ⏰ Time to insight: 30 seconds
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb offers multiple ways to answer this question without going through a lengthy qualitative research process.
First, I’m going to do a website market analysis of the banking credit and lending market in the finance sector to get a clearer picture of industry benchmarks.
Here, I can view device preferences across any industry or market instantly. It shows me the device distribution for any country across any period. This clearly answers the question of how mobile dominate my target audience is , with 59.79% opting to access site via a desktop vs. 40.21% via mobile
I then use the trends section to show me the exact split between mobile and web traffic for each key player in my space. Let’s say I’m about to embark on a competitive campaign that targets customers of Chase and Bank of America ; I can see both their audiences are highly desktop dominant compared with others in their space .
Qualitative question examples for developing new products or services
Research questions like this can help you understand customer pain points and give you insights to develop products that meet those needs.
- What is the primary reason you would choose to purchase a product from our company?
- How do you currently use products or services that are similar to ours?
- Is there anything that could be improved with products currently on the market?
- What features would you like to see added to our products?
- How do you prefer to contact a customer service team?
- What do you think sets our company apart from our competitors?
- What other product or service offerings would like to see us offer?
- What type of information would help you make decisions about buying a product?
- What type of advertising methods are most effective in getting your attention?
- What is the biggest deterrent to purchasing products from us?
Qualitative research question example for service development
- 🙋♀️ Question: What type of advertising methods are most effective in getting your attention?
- 🤓 Insight sought: The marketing channels and/or content that performs best with a target audience .
- 🤯 Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: When using qualitative research surveys to answer questions like this, the sample size is limited, and bias could be at play.
- 💡 A better approach: The most authentic insights come from viewing real actions and results that take place in the digital world. No questions or answers are needed to uncover this intel, and the information you seek is readily available in less than a minute.
- ⏰ Time to insight: 5 minutes
- ✅ How it’s done: There are a few ways to approach this. You can either take an industry-wide perspective or hone in on specific competitors to unpack their individual successes. Here, I’ll quickly show a snapshot with a whole market perspective.

Using the market analysis element of Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence, I select my industry or market, which I’ve kept as banking and credit. A quick click into marketing channels shows me which channels drive the highest traffic in my market. Taking direct traffic out of the equation, for now, I can see that referrals and organic traffic are the two highest-performing channels in this market.
Similarweb allows me to view the specific referral partners and pages across these channels.

Looking closely at referrals in this market, I’ve chosen chase.com and its five closest rivals . I select referrals in the channel traffic element of marketing channels. I see that Capital One is a clear winner, gaining almost 25 million visits due to referral partnerships.

Next, I get to see exactly who is referring traffic to Capital One and the total traffic share for each referrer. I can see the growth as a percentage and how that has changed, along with an engagement score that rates the average engagement level of that audience segment. This is particularly useful when deciding on which new referral partnerships to pursue.
Once I’ve identified the channels and campaigns that yield the best results, I can then use Similarweb to dive into the various ad creatives and content that have the greatest impact.

These ads are just a few of those listed in the creatives section from my competitive website analysis of Capital One. You can filter this list by the specific campaign, publishers, and ad networks to view those that matter to you most. You can also discover video ad creatives in the same place too.
In just five minutes ⏰
- I’ve captured audience loyalty statistics across my market
- Spotted the most competitive players
- Identified the marketing channels my audience is most responsive to
- I know which content and campaigns are driving the highest traffic volume
- I’ve created a target list for new referral partners and have been able to prioritize this based on results and engagement figures from my rivals
- I can see the types of creatives that my target audience is responding to, giving me ideas for ways to generate effective copy for future campaigns
Qualitative questions to determine pricing strategies
Companies need to make sure pricing stays relevant and competitive. Use these questions to determine customer perceptions on pricing and develop pricing strategies to maximize profits and reduce churn.
- How do you feel about our pricing structure?
- How does our pricing compare to other similar products?
- What value do you feel you get from our pricing?
- How could we make our pricing more attractive?
- What would be an ideal price for our product?
- Which features of our product that you would like to see priced differently?
- What discounts or deals would you like to see us offer?
- How do you feel about the amount you have to pay for our product?
Get Faster Answers to Qualitative Research Questions with Similarweb Today
Qualitative research question example for determining pricing strategies.
- 🙋♀️ Question: What discounts or deals would you like to see us offer?
- 🤓 Insight sought: The promotions or campaigns that resonate with your target audience.
- 🤯 Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Consumers don’t always recall the types of ads or campaigns they respond to. Over time, their needs and habits change. Your sample size is limited to those you ask, leaving a huge pool of unknowns at play.
- 💡 A better approach: While qualitative insights are good to know, you get the most accurate picture of the highest-performing promotion and campaigns by looking at data collected directly from the web. These analytics are real-world, real-time, and based on the collective actions of many, instead of the limited survey group you approach. By getting a complete picture across an entire market, your decisions are better informed and more aligned with current market trends and behaviors.
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb’s Popular Pages feature shows the content, products, campaigns, and pages with the highest growth for any website. So, if you’re trying to unpack the successes of others in your space and find out what content resonates with a target audience, there’s a far quicker way to get answers to these questions with Similarweb.

Here, I’m using Capital One as an example site. I can see trending pages on their site showing the largest increase in page views. Other filters include campaign, best-performing, and new–each of which shows you page URLs, share of traffic , and growth as a percentage. This page is particularly useful for staying on top of trending topics , campaigns, and new content being pushed out in a market by key competitors.
Qualitative research questions for product development teams
It’s vital to stay in touch with changing consumer needs. These questions can also be used for new product or service development, but this time, it’s from the perspective of a product manager or development team.
- What are customers’ primary needs and wants for this product?
- What do customers think of our current product offerings?
- What is the most important feature or benefit of our product?
- How can we improve our product to meet customers’ needs better?
- What do customers like or dislike about our competitors’ products?
- What do customers look for when deciding between our product and a competitor’s?
- How have customer needs and wants for this product changed over time?
- What motivates customers to purchase this product?
- What is the most important thing customers want from this product?
- What features or benefits are most important when selecting a product?
- What do customers perceive to be our product’s pros and cons?
- What would make customers switch from a competitor’s product to ours?
- How do customers perceive our product in comparison to similar products?
- What do customers think of our pricing and value proposition?
- What do customers think of our product’s design, usability, and aesthetics?
Qualitative questions examples to understand customer segments
Market segmentation seeks to create groups of consumers with shared characteristics. Use these questions to learn more about different customer segments and how to target them with tailored messaging.
- What motivates customers to make a purchase?
- How do customers perceive our brand in comparison to our competitors?
- How do customers feel about our product quality?
- How do customers define quality in our products?
- What factors influence customers’ purchasing decisions ?
- What are the most important aspects of customer service?
- What do customers think of our customer service?
- What do customers think of our pricing?
- How do customers rate our product offerings?
- How do customers prefer to make purchases (online, in-store, etc.)?
Qualitative research question example for understanding customer segments
- 🙋♀️ Question: Which social media channels are you most active on?
- 🤓 Insight sought: Formulate a social media strategy . Specifically, the social media channels most likely to succeed with a target audience.
- 🤯 Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Qualitative research question responses are limited to those you ask, giving you a limited sample size. Questions like this are usually at risk of some bias, and this may not be reflective of real-world actions.
- 💡 A better approach: Get a complete picture of social media preferences for an entire market or specific audience belonging to rival firms. Insights are available in real-time, and are based on the actions of many, not a select group of participants. Data is readily available, easy to understand, and expandable at a moment’s notice.
- ✅ How it’s done: Using Similarweb’s website analysis feature, you can get a clear breakdown of social media stats for your audience using the marketing channels element. It shows the percentage of visits from each channel to your site, respective growth, and specific referral pages by each platform. All data is expandable, meaning you can select any platform, period, and region to drill down and get more accurate intel, instantly.

This example shows me Bank of America’s social media distribution, with YouTube , Linkedin , and Facebook taking the top three spots, and accounting for almost 80% of traffic being driven from social media.
When doing any type of market research, it’s important to benchmark performance against industry averages and perform a social media competitive analysis to verify rival performance across the same channels.
Qualitative questions to inform competitive analysis
Organizations must assess market sentiment toward other players to compete and beat rival firms. Whether you want to increase market share , challenge industry leaders , or reduce churn, understanding how people view you vs. the competition is key.
- What is the overall perception of our competitors’ product offerings in the market?
- What attributes do our competitors prioritize in their customer experience?
- What strategies do our competitors use to differentiate their products from ours?
- How do our competitors position their products in relation to ours?
- How do our competitors’ pricing models compare to ours?
- What do consumers think of our competitors’ product quality?
- What do consumers think of our competitors’ customer service?
- What are the key drivers of purchase decisions in our market?
- What is the impact of our competitors’ marketing campaigns on our market share ? 10. How do our competitors leverage social media to promote their products?
Qualitative research question example for competitive analysis
- 🙋♀️ Question: What other companies do you shop with for x?
- 🤓 Insight sought: W ho are your competitors? Which of your rival’s sites do your customers visit? How loyal are consumers in your market?
- 🤯 Challenges with traditional qualitative research methods: Sample size is limited, and customers could be unwilling to reveal which competitors they shop with, or how often they around. Where finances are involved, people can act with reluctance or bias, and be unwilling to reveal other suppliers they do business with.
- 💡 A better approach: Get a complete picture of your audience’s loyalty, see who else they shop with, and how many other sites they visit in your competitive group. Find out the size of the untapped opportunity and which players are doing a better job at attracting unique visitors – without having to ask people to reveal their preferences.
- ✅ How it’s done: Similarweb website analysis shows you the competitive sites your audience visits, giving you access to data that shows cross-visitation habits, audience loyalty, and untapped potential in a matter of minutes.

Using the audience interests element of Similarweb website analysis, you can view the cross-browsing behaviors of a website’s audience instantly. You can see a matrix that shows the percentage of visitors on a target site and any rival site they may have visited.

With the Similarweb audience overlap feature, view the cross-visitation habits of an audience across specific websites. In this example, I chose chase.com and its four closest competitors to review. For each intersection, you see the number of unique visitors and the overall proportion of each site’s audience it represents. It also shows the volume of unreached potential visitors.

Here, you can see a direct comparison of the audience loyalty represented in a bar graph. It shows a breakdown of each site’s audience based on how many other sites they have visited. Those sites with the highest loyalty show fewer additional sites visited.
From the perspective of chase.com, I can see 47% of their visitors do not visit rival sites. 33% of their audience visited 1 or more sites in this group, 14% visited 2 or more sites, 4% visited 3 or more sites, and just 0.8% viewed all sites in this comparison.
How to answer qualitative research questions with Similarweb
Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence drastically improves market research efficiency and time to insight. Both of these can impact the bottom line and the pace at which organizations can adapt and flex when markets shift, and rivals change tactics.
Outdated practices, while still useful, take time . And with a quicker, more efficient way to garner similar insights, opting for the fast lane puts you at a competitive advantage.
With a birds-eye view of the actions and behaviors of companies and consumers across a market , you can answer certain research questions without the need to plan, do, and review extensive qualitative market research .
Wrapping up
Qualitative research methods have been around for centuries. From designing the questions to finding the best distribution channels, collecting and analyzing findings takes time to get the insights you need. Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence drastically improves efficiency and time to insight. Both of which impact the bottom line and the pace at which organizations can adapt and flex when markets shift.
Similarweb’s suite of digital intelligence solutions offers unbiased, accurate, honest insights you can trust for analyzing any industry, market, or audience.
- Methodologies used for data collection are robust, transparent, and trustworthy.
- Clear presentation of data via an easy-to-use, intuitive platform.
- It updates dynamically–giving you the freshest data about an industry or market.
- Data is available via an API – so you can plug into platforms like Tableau or PowerBI to streamline your analyses.
- Filter and refine results according to your needs.
Are quantitative or qualitative research questions best?
Both have their place and purpose in market research. Qualitative research questions seek to provide details, whereas quantitative market research gives you numerical statistics that are easier and quicker to analyze. You get more flexibility with qualitative questions, and they’re non-directional.
What are the advantages of qualitative research?
Qualitative research is advantageous because it allows researchers to better understand their subject matter by exploring people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations in a particular context. It also allows researchers to uncover new insights that may not have been discovered with quantitative research methods.
What are some of the challenges of qualitative research?
Qualitative research can be time-consuming and costly, typically involving in-depth interviews and focus groups. Additionally, there are challenges associated with the reliability and validity of the collected data, as there is no universal standard for interpreting the results.
Related Posts

What is a Niche Market? And How to Find the Right One

The Future of UK Finance: Top Trends to Watch in 2024

From AI to Buy: The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Retail
How to Conduct a Social Media Competitor Analysis: 5 Quick Steps

Industry Research: The Data-Backed Approach
How to Do a Competitive Analysis: A Complete Guide
Wondering what similarweb can do for you.
Here are two ways you can get started with Similarweb today!

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods
Published on April 12, 2019 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on June 22, 2023.
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge.
Common quantitative methods include experiments, observations recorded as numbers, and surveys with closed-ended questions.
Quantitative research is at risk for research biases including information bias , omitted variable bias , sampling bias , or selection bias . Qualitative research Qualitative research is expressed in words . It is used to understand concepts, thoughts or experiences. This type of research enables you to gather in-depth insights on topics that are not well understood.
Common qualitative methods include interviews with open-ended questions, observations described in words, and literature reviews that explore concepts and theories.
Table of contents
The differences between quantitative and qualitative research, data collection methods, when to use qualitative vs. quantitative research, how to analyze qualitative and quantitative data, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative and quantitative research.
Quantitative and qualitative research use different research methods to collect and analyze data, and they allow you to answer different kinds of research questions.
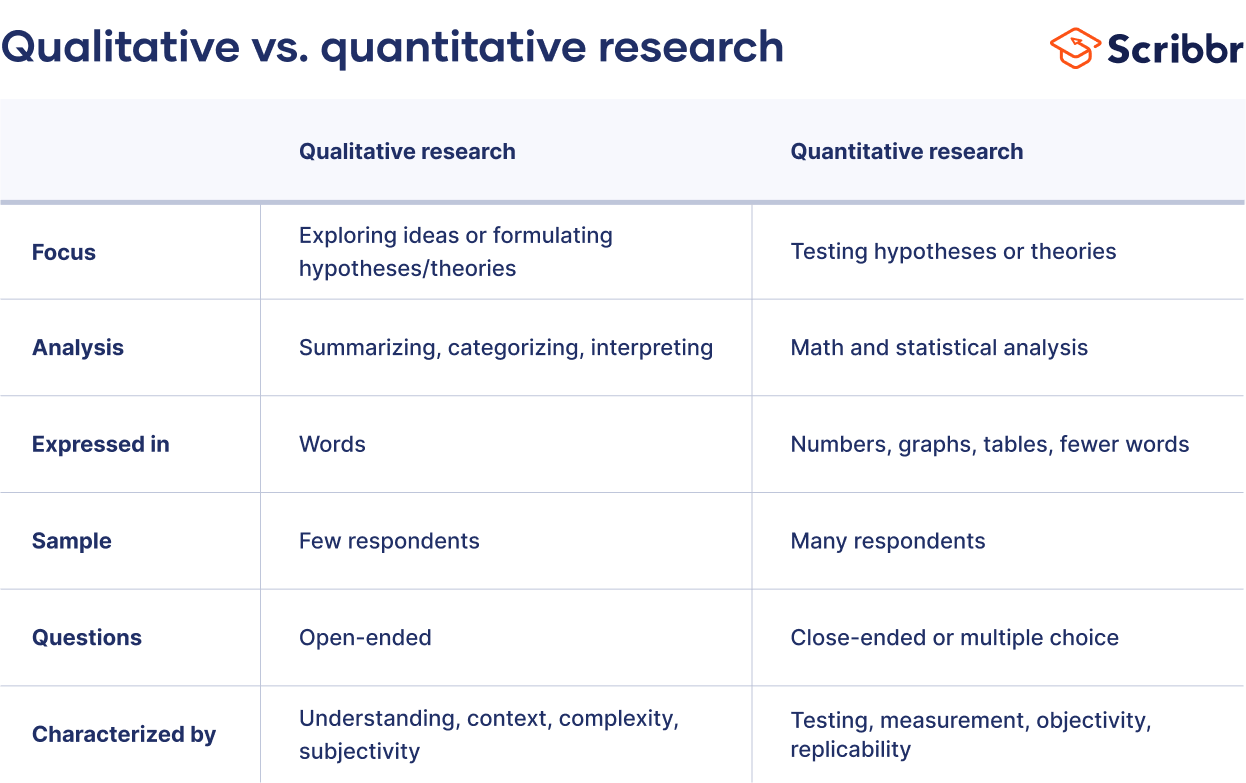
Quantitative and qualitative data can be collected using various methods. It is important to use a data collection method that will help answer your research question(s).
Many data collection methods can be either qualitative or quantitative. For example, in surveys, observational studies or case studies , your data can be represented as numbers (e.g., using rating scales or counting frequencies) or as words (e.g., with open-ended questions or descriptions of what you observe).
However, some methods are more commonly used in one type or the other.
Quantitative data collection methods
- Surveys : List of closed or multiple choice questions that is distributed to a sample (online, in person, or over the phone).
- Experiments : Situation in which different types of variables are controlled and manipulated to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Observations : Observing subjects in a natural environment where variables can’t be controlled.
Qualitative data collection methods
- Interviews : Asking open-ended questions verbally to respondents.
- Focus groups : Discussion among a group of people about a topic to gather opinions that can be used for further research.
- Ethnography : Participating in a community or organization for an extended period of time to closely observe culture and behavior.
- Literature review : Survey of published works by other authors.
A rule of thumb for deciding whether to use qualitative or quantitative data is:
- Use quantitative research if you want to confirm or test something (a theory or hypothesis )
- Use qualitative research if you want to understand something (concepts, thoughts, experiences)
For most research topics you can choose a qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods approach . Which type you choose depends on, among other things, whether you’re taking an inductive vs. deductive research approach ; your research question(s) ; whether you’re doing experimental , correlational , or descriptive research ; and practical considerations such as time, money, availability of data, and access to respondents.
Quantitative research approach
You survey 300 students at your university and ask them questions such as: “on a scale from 1-5, how satisfied are your with your professors?”
You can perform statistical analysis on the data and draw conclusions such as: “on average students rated their professors 4.4”.
Qualitative research approach
You conduct in-depth interviews with 15 students and ask them open-ended questions such as: “How satisfied are you with your studies?”, “What is the most positive aspect of your study program?” and “What can be done to improve the study program?”
Based on the answers you get you can ask follow-up questions to clarify things. You transcribe all interviews using transcription software and try to find commonalities and patterns.
Mixed methods approach
You conduct interviews to find out how satisfied students are with their studies. Through open-ended questions you learn things you never thought about before and gain new insights. Later, you use a survey to test these insights on a larger scale.
It’s also possible to start with a survey to find out the overall trends, followed by interviews to better understand the reasons behind the trends.
Qualitative or quantitative data by itself can’t prove or demonstrate anything, but has to be analyzed to show its meaning in relation to the research questions. The method of analysis differs for each type of data.
Analyzing quantitative data
Quantitative data is based on numbers. Simple math or more advanced statistical analysis is used to discover commonalities or patterns in the data. The results are often reported in graphs and tables.
Applications such as Excel, SPSS, or R can be used to calculate things like:
- Average scores ( means )
- The number of times a particular answer was given
- The correlation or causation between two or more variables
- The reliability and validity of the results
Analyzing qualitative data
Qualitative data is more difficult to analyze than quantitative data. It consists of text, images or videos instead of numbers.
Some common approaches to analyzing qualitative data include:
- Qualitative content analysis : Tracking the occurrence, position and meaning of words or phrases
- Thematic analysis : Closely examining the data to identify the main themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying how communication works in social contexts
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2023, June 22). Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved April 17, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-quantitative-research/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, what is quantitative research | definition, uses & methods, what is qualitative research | methods & examples, mixed methods research | definition, guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Patient Cent Res Rev
- v.11(1); Spring 2024
- PMC11000705

Research Frameworks: Critical Components for Reporting Qualitative Health Care Research
Qualitative health care research can provide insights into health care practices that quantitative studies cannot. However, the potential of qualitative research to improve health care is undermined by reporting that does not explain or justify the research questions and design. The vital role of research frameworks for designing and conducting quality research is widely accepted, but despite many articles and books on the topic, confusion persists about what constitutes an adequate underpinning framework, what to call it, and how to use one. This editorial clarifies some of the terminology and reinforces why research frameworks are essential for good-quality reporting of all research, especially qualitative research.
Qualitative research provides valuable insights into health care interactions and decision-making processes – for example, why and how a clinician may ignore prevailing evidence and continue making clinical decisions the way they always have. 1 The perception of qualitative health care research has improved since a 2016 article by Greenhalgh et al. highlighted the higher contributions and citation rates of qualitative research than those of contemporaneous quantitative research. 2 The Greenhalgh et al. article was subsequently supported by an open letter from 76 senior academics spanning 11 countries to the editors of the British Medical Journal . 3 Despite greater recognition and acceptance, qualitative research continues to have an “uneasy relationship with theory,” 4 which contributes to poor reporting.
As an editor for the Journal of Patient-Centered Research and Reviews , as well as Human Resources for Health , I have seen several exemplary qualitative articles with clear and coherent reporting. On the other hand, I have often been concerned by a lack of rigorous reporting, which may reflect and reinforce the outdated perception of qualitative research as the “soft option.” 5 Qualitative research is more than conducting a few semi-structured interviews, transcribing the audio recordings verbatim, coding the transcripts, and developing and reporting themes, including a few quotes. Qualitative research that benefits health care is time-consuming and labor-intensive, requires robust design, and is rooted in theory, along with comprehensive reporting. 6
What Is “Theory”?
So fundamental is theory to qualitative research that I initially toyed with titling this editorial, “ Theory: the missing link in qualitative health care research articles ,” before deeming that focus too broad. As far back as 1967, Merton 6 warned that “the word theory threatens to become meaningless.” While it cannot be overstated that “atheoretical” studies lack the underlying logic that justifies researchers’ design choices, the word theory is so overused that it is difficult to understand what constitutes an adequate theoretical foundation and what to call it.
Theory, as used in the term theoretical foundation , refers to the existing body of knowledge. 7 , 8 The existing body of knowledge consists of more than formal theories , with their explanatory and predictive characteristics, so theory implies more than just theories . Box 1 9 – 12 defines the “building blocks of formal theories.” 9 Theorizing or theory-building starts with concepts at the most concrete, experiential level, becoming progressively more abstract until a higher-level theory is developed that explains the relationships between the building blocks. 9 Grand theories are broad, representing the most abstract level of theorizing. Middle-range and explanatory theories are progressively less abstract, more specific to particular phenomena or cases (middle-range) or variables (explanatory), and testable.
The Building Blocks of Formal Theories 9
The importance of research frameworks.
Researchers may draw on several elements to frame their research. Generally, a framework is regarded as “a set of ideas that you use when you are forming your decisions and judgements” 13 or “a system of rules, ideas, or beliefs that is used to plan or decide something.” 14 Research frameworks may consist of a single formal theory or part thereof, any combination of several theories or relevant constructs from different theories, models (as simplified representations of formal theories), concepts from the literature and researchers’ experiences.
Although Merriam 15 was of the view that every study has a framework, whether explicit or not, there are advantages to using an explicit framework. Research frameworks map “the territory being investigated,” 8 thus helping researchers to be explicit about what informed their research design, from developing research questions and choosing appropriate methods to data analysis and interpretation. Using a framework makes research findings more meaningful 12 and promotes generalizability by situating the study and interpreting data in more general terms than the study itself. 16
Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks
The variation in how the terms theoretical and conceptual frameworks are used may be confusing. Some researchers refer to only theoretical frameworks 17 , 18 or conceptual frameworks, 19 – 21 while others use the terms interchangeably. 7 Other researchers distinguish between the two. For example, Miles, Huberman & Saldana 8 see theoretical frameworks as based on formal theories and conceptual frameworks derived inductively from locally relevant concepts and variables, although they may include theoretical aspects. Conversely, some researchers believe that theoretical frameworks include formal theories and concepts. 18 Others argue that any differences between the two types of frameworks are semantic and, instead, emphasize using a research framework to provide coherence across the research questions, methods and interpretation of the results, irrespective of what that framework is called.
Like Ravitch and Riggan, 22 I regard conceptual frameworks (CFs) as the broader term. Including researchers’ perspectives and experiences in CFs provides valuable sources of originality. Novel perspectives guard against research repeating what has already been stated. 23 The term theoretical framework (TF) may be appropriate where formal published and identifiable theories or parts of such theories are used. 24 However, existing formal theories alone may not provide the current state of relevant concepts essential to understanding the motivation for and logic underlying a study. Some researchers may argue that relevant concepts may be covered in the literature review, but what is the point of literature reviews and prior findings unless authors connect them to the research questions and design? Indeed, Sutton & Straw 25 exclude literature reviews and lists of prior findings as an adequate foundation for a study, along with individual lists of variables or constructs (even when the constructs are defined), predictions or hypotheses, and diagrams that do not propose relationships. One or more of these aspects could be used in a research framework (eg, in a TF), and the literature review could (and should) focus on the theories or parts of theories (constructs), offer some critique of the theory and point out how they intend to use the theory. This would be more meaningful than merely describing the theory as the “background” to the study, without explicitly stating why and how it is being used. Similarly, a CF may include a discussion of the theories being used (basically, a TF) and a literature review of the current understanding of any relevant concepts that are not regarded as formal theory.
It may be helpful for authors to specify whether they are using a theoretical or a conceptual framework, but more importantly, authors should make explicit how they constructed and used their research framework. Some studies start with research frameworks of one type and end up with another type, 8 , 22 underscoring the need for authors to clarify the type of framework used and how it informed their research. Accepting the sheer complexity surrounding research frameworks and lamenting the difficulty of reducing the confusion around these terms, Box 2 26 – 31 and Box 3 offer examples highlighting the fundamental elements of theoretical and conceptual frameworks while acknowledging that they share a common purpose.
Examples of How Theoretical Frameworks May Be Used
Examples of how conceptual frameworks may be used, misconceptions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research’s “uneasy relationship with theory” 4 may be due to several misconceptions. One possible misconception is that qualitative research aims to build theory and thus does not need theoretical grounding. The reality is that all qualitative research methods, not just Grounded Theory studies focused on theory building, may lead to theory construction. 16 Similarly, all types of qualitative research, including Grounded Theory studies, should be guided by research frameworks. 16
Not using a research framework may also be due to misconceptions that qualitative research aims to understand people’s perspectives and experiences without examining them from a particular theoretical perspective or that theoretical foundations may influence researchers’ interpretations of participants’ meanings. In fact, in the same way that participants’ meanings vary, qualitative researchers’ interpretations (as opposed to descriptions) of participants’ meaning-making will differ. 32 , 33 Research frameworks thus provide a frame of reference for “making sense of the data.” 34
Studies informed by well-defined research frameworks can make a world of difference in alleviating misconceptions. Good qualitative reporting requires research frameworks that make explicit the combination of relevant theories, theoretical constructs and concepts that will permeate every aspect of the research. Irrespective of the term used, research frameworks are critical components of reporting not only qualitative but also all types of research.
Acknowledgments
In memory of Martie Sanders: supervisor, mentor, and colleague. My deepest gratitude for your unfailing support and guidance. I feel your loss.
Conflicts of Interest: None.
- What is Field Research: Meaning, Examples, Pros & Cons

Introduction
Field research is a method of research that deals with understanding and interpreting the social interactions of groups of people and communities by observing and dealing with people in their natural settings.
The field research methods involve direct observation, participant observation, and qualitative interviews.
Let’s take a deeper look at field research, what it entails, some examples as well as the pros and cons of field research.
What is Field Research
Field research can be defined as a qualitative method of data collection focused on observing, relating, and understanding people while they are in their natural environment. It is somewhat similar to documentaries on Nat Geo wild where the animals are observed in their natural habitat.
Similarly, social scientists, who are sometimes called men watchers carry out interviews and observe people from a distance to see how they act in a social environment and react to situations around them.
Field research usually begins in a specific setting and the end game is to study, observe and analyze the subject within that setting. It looks at the cause and effect as well as the correlation between the participants and their natural setting. Due to the presence of multiple variables, it is sometimes difficult to properly analyze the results of field research.
Field research adopts a wide range of social research methods, such as limited participation, direct observation, document analysis, surveys, and informal interviews. Although field research is generally considered qualitative research , it often involves multiple elements of quantitative research.
Methods of Field Research
There are 5 different methods of conducting Field Research and they are as follows;
1. Direct Observation
In this method of research, the researcher watches and records the activities of groups of people or individuals as they go about their daily activities. Direct observation can be structured or unstructured.
Structured here means that the observation takes place using a guide or process developed before that time.
Unstructured, on the other hand, means that the researcher conducted the observation, watching people and events, and taking notes as events progressed, without the aid of any predetermined technique.
Some other features of direct observation include the following;
- The observer does not attempt to actively engage the people being observed in conversations or interviews, rather he or she blends into the crowd and carries out their observation.
- Data collected include field notes, videos, photographs, rating scales, etc.
- Direct observation most times occurs in the open, usually public settings, that requires no permission to gain entry. Conducting direct observation in a private setting would raise ethical concerns.
- The outcome of direct observation is not in any way influenced by the researcher.
2. Participant Observation
This research method has an understanding with a group of individuals, to take part in their daily routines and their scheduled events. In this case, the researcher dwells among the group or community being observed for as long as is necessary to build trust and evoke acceptance.
Data from the participant’s observation take the following varying forms;
- Field notes are the primary source of data. These notes are taken during the researcher’s observations and from the events they experienced and later developed the notes into formal field notes.
- A diary is used to record special intimate events that occur within the setting.
- The process of participant observation is intent on developing relationships with the members which breed conversations that are sometimes formal or informal. Formal here refers to deliberate depth interviews, while informal could stem from everyday conversations that give insight into the study.
Data from these events can be part of the field notes or separate interview transcripts.
The method of participant observation aims to make the people involved comfortable enough to share what they know freely without any inhibition.
3. Ethnography
Ethnography is a form of field research that carries out observation through social research, social perspective, and the cultural values of a social setting. In this scenario, the observation is carried out objectively, hence the researcher may choose to live within a social environment of a cultural group and silently observe and record their daily routines and behavior.
4. Qualitative Interviews
Qualitative interviews are a type of field research method that gets information by asking direct questions from individuals to gather data on a particular subject. Qualitative interviews are usually conducted via 3 methods namely;
- Informal Interviews
- Semi Structured Interviews
- Standardized Open ended Interviews
Let’s take a look at each of them briefly along with their advantages and disadvantages.
This kind of interview is often conversational and occurs during participant and direct observations.
The interview is triggered, most times spontaneously by conversing with a member of the group on the areas of interest and as the conversation progresses, the researcher fluidly introduces the specific question.
- Semi-Structured Interviews
In this scenario, the researcher already has a list of prepared questions, that are open-ended and can evoke as much information as possible. The researcher can venture into other topics as the interview progresses, using a call-and-response style.
This method of field research can adopt a mix of one-on-one interviews or focus groups.
- Standardized, Open-Ended Interviews
These are scripted interviews with the questions prepped and written before the interview following a predetermined order. It is similar to a survey and the questions are open-ended to gather detailed information from the respondents and sometimes it involves multiple interviewers.
5. Case Study
A case study research is a detailed analysis of a person, situation, or event. This method may seem a bit complex, however, it is one of the easiest ways of conducting research. difficult to operate, however, it is one of the simplest ways of researching as it involves only a detailed study of an individual or a group of people or events. Every aspect of the subject life and history is analyzed to identify patterns and causes of behavior.
Steps to Conduct Field Research
Due to the nature of field research, the tight timelines, and the associated costs involved, planning and implementing can be a bit overwhelming. We have put together steps to adopt that would make the whole process hitch free for you.
Set Up The Right Team : To begin your field research, the first step is to have the right team. The role of the researcher and the team members has to be well defined from the start, with the relevant milestones agreed upon to measure progress.
Recruiting People for the Study : The success of field research largely depends on the people being studied. Evaluate the individuals selected for the research to be sure that they tick all the boxes required for successful research in the area of study that is being researched.
Data Collection Methodology : The methodology of data collection adopted must be suited to the area or kind of research being conducted. It could be one of the methods or a combination of two or more methods.
Visit The Site: A prior visit to the site is essential to the success of the field research. This should be done to also help determine the best methodology that would be suitable for the location.
Data Analysis: Analyzing the data gathered is important to validate the hypothesis of the field research.
Communicating Results : Once the data is analyzed, communicate the results to the stakeholders involved in the research so that the relevant action required based on the results can be decided and carried out promptly.
Reasons to Conduct Field Research
Field research has been widely used in the 20th century in the social sciences. However, it can be time-consuming and costly to implement. Despite this fact, there exist a lot of reasons to conduct field research.
Here are 4 major reasons to conduct field research:
Solves the problem of lack of data : Field research fixes the issue of gaps in data, especially in cases where there is very little or no data about a topic. In cases like this, the only way to validate any hypothesis is through primary research and data. Conducting field research solves the problem of data lapses and provides material evidence to support any findings.
Understanding the context of the study : In many cases, the data collected is appropriate, however for a deep understanding of the data gathered there is a need for field research to help understand other factors in the study. For instance, if data show that students from rich homes generally do well academically.
Conducting field research can bring to the fore other factors like, discipline, well-equipped teachers, motivation from their forebears to excel in whatever they do, etc. but field research is still conducted.
Increasing data quality: Since this research, method employs the use of multiple tools to collect data and varying methodologies, the quality of data is higher.
Collecting ancillary data : Field research puts the researchers in a position of being at the center of the data collection process, in terms of location, one on one relationship with the participants, etc. This exposes them to new lines of thought that would have hitherto been overlooked and they can now collect data, that was not planned for at the beginning of the study.
Examples of Field Research
1. Interprete social metrics in a slum By employing the use of observation methods and formal interviews, researchers can now understand the social indicators and social hierarchy that exist in a slum.
Financial independence and the way the slum is run daily are part of the study and data collected from these areas can give insight into the way a slum operates differently from structured societies.
2. Understand the impact of sports on a child’s development This method of field research takes years to conduct and the sample size can be quite huge. Data collected and analyzed from this study provides insight into how children from different physical locations and backgrounds are influenced by sports and the impact of sporting activities on a child’s development.
3. The study of animal migration patterns Field research is used immensely to study flora and fauna. A major use case is scientists observing and studying animal migration patterns alongside the change of seasons and its influence on animal migration patterns.
Field research takes time and uses months and sometimes years to help gather data that show how to safely expedite the passage of animals.
Advantages of Field Research
Field research and the various methodology employed have their pros and cons.
Let’s take a look at some of them.
- Provide context to the data being analyzed in terms of settings, interactions, or individuals.
- The source of data does not require or involve verbal interactions, and there is no intrusion of anyone’s personal, space because everything is done quietly, from a distance.
- The researcher develops a deep and detailed understanding of a setting and the members within the setting.
- It is carried out in a real-world and natural environment which eliminates tampering with variables.
- The study is conducted in a comfortable environment, hence data can be gathered even about an ancillary topic, that would have been undiscovered in other circumstances.
- The researcher’s deep understanding of the research subjects due to their proximity to them makes the research thorough and precise.
- It helps the researcher to be flexible and respond to individual differences while capturing emerging information. Allows the researcher to be responsive to individual differences and to capture emerging information.
Disadvantages of Field Research
- The researcher might not be able to capture all that is being said and there is the risk of losing information.
- The quality of the information derived is dependent, on the researcher’s skills.
- Significant interactions and events may occur when an observer is not present.
- Some topics cannot easily be interpreted by mere observation.g., attitudes, emotions, affection).
- The reliability of observations can be complex due to the presence of multiple observers with different interpretations.
- It requires a lot of time (and resources)and can take years to complete.
- The researcher may lose objectivity as they spend more time among the members of the group.
- It is a subjective and interpretive method that is solely dependent on the researcher’s ability.
Field research helps researchers to gain firsthand experience and knowledge about the events, processes, and people, being studied. No other method provides this kind of close-up view of the everyday life of people and events. It is a very detailed method of research and is excellent for understanding the role of social context in shaping the lives, perspectives, and experiences of people. Alongside this, it may uncover aspects of a person that might never have been discovered.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- Data Collection
- field research
- qualitative research
- Angela Kayode-Sanni

You may also like:
Research Summary: What Is It & How To Write One
Introduction A research summary is a requirement during academic research and sometimes you might need to prepare a research summary...

Projective Techniques In Surveys: Definition, Types & Pros & Cons
Introduction When you’re conducting a survey, you need to find out what people think about things. But how do you get an accurate and...
The McNamara Fallacy: How Researchers Can Detect and to Avoid it.
Introduction The McNamara Fallacy is a common problem in research. It happens when researchers take a single piece of data as evidence...
Unit of Analysis: Definition, Types & Examples
Introduction A unit of analysis is the smallest level of analysis for a research project. It’s important to choose the right unit of...
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..
Manufacturing Using 3D-Technology: Qualitative Study Plan Research Paper
Problem background.
The problem to be resolved through this research is that shipping spare parts, hardware, tools, and equipment to space has been an expensive and time-consuming venture. For instance, annually, over 7000 pounds of hardware and spare parts are sent to the International Space Station (ISS). However, the latter fails to factor in the 29,000 pounds of spaceflight hardware stored aboard the ISS and another 39,000 pounds stored terrestrially on Earth (Ngo et al., 2018). Currently, with flights to and from the ISS scheduled often, resupply missions create the logistics of transporting hardware, tools, and parts more accessible than ever to low Earth Orbit (LEO).
The current literature does not sufficiently resolve the resupply missions in the space industry from the perspective of the follower. Nonetheless, when considering the enormous distances between celestial bodies like the earth, Mars, and Moon, resupply missions to future Martian and Lunar outposts are expected to be time consuming and logistical issue. In order to address the problem of shipping these products, additive manufacturing using 3D printing technology known as in-space manufacturing (ISM) has been recommended as a solution to the problem (Ngo et al., 2018). There are many international and national space organizations, private sector firms, and universities actively researching the possibility of utilizing ISM for the production of tools, parts, and human organs for utilization during long-time spaceflight, particularly to Mars, Moon, and beyond.
Intent /Objective of this Study
The long-term aim of this research is to establish a formalized ISM or additive manufacturing using 3D-Technology. The ISM offers a solution for flexible and sustainable missions both in transit and on the surface via on-demand repair, fabrication, and recycling abilities for habitats, critical systems, and mission logistics and maintenance. The objective of the current research is to offer a detailed review of industry practices and literature in correlation with resupply missions for spaceflight to Mars, the Moon, and beyond. Specifically, the research provides a comprehensive review of sources and features of resupply missions commonly found in spaceflight projects. Further, the study will develop an ISM system for easier resupplying missions and frameworks.
Research Question
Are maximum resupply missions for spaceflight achieved after developing the ISM?
Research Hypothesis
Maximum resupply missions for spaceflight are achieved after developing the ISM.
Problem Prevalence
The problem is moderately prevalent in the existing current research since it is of prime interest for the field, but only in a narrowly focused set of specializations. A study suggests that spacecraft power systems experience the problem of degradation over time, decreasing the amount of power accessible for use as the mission progresses (Trujillo et al., 2017). In other words, efficient and effective utilization of space-based resources is essential for future missions of NASA science and exploration. In addition, the literature points towards a possibility of interference with an array of international and national operating assets and a serious threat to in-space staff (Antonsen et al., 2022). Such issues are due to the ever-increasing prevalence of Micrometeoroid and Orbital Debris (MMOD) (Antonsen et al., 2022). Existing capacities are inadequate for extraction, forming stocks, refining, transporting in-situ materials for ISM, fuelling, servicing, and repair (Dervay et al., 2021). Therefore, it is evident that the current research addresses the problem extensively but within a limited set of interests, such as operations, risk management, and energy security.
Current Efforts
When it comes to the researchers’ efforts at the moment, the key focus is put on expanding design limitations and improving accessibilities. In the case of the latter, it will allow the professionals to have improved access to and exploration of space (Trujillo et al., 2017). For example, a study to examine the commercial feasibility of many potential applications of ISM via a sequence of case studies revealed that ISM has the potential to be a paradigm-shifting in technology (Trujillo et al., 2017). In addition, the design limitations are important to consider as well since the ISM is able to change the paradigm of space system design (Moraguez & De Weck, 2020). Researchers are trying to achieve it by supporting the fabrication and repair of components that are unencumbered by launch-associated design limitations (Moraguez & De Weck, 2020). This is especially true due to the fact that there are nowhere the signs of an exponential increase of debris pieces discovered at present (Pardini & Anselmo, 2021). Thus, the current efforts are specifically focused on addressing accessibilities and design limitations.
Leading Recommendations
The leading recommendations in the field include 3D printing and astrometry, which are essentially extensions of in-space manufacturing. A study found that ground-based optical BepiColombo astrometry is an example of how the framework can be implemented in practice, which forms the basis of the recommendation (Micheli et al., 2021). The answer lies in the communication process between the send and receiver, which allows for more efficient in-space manufacturing effort coordination. 3D printing in virtual reality is another mode of the ISM, where the mapping techniques can be used to optimize both the printing process as well as the recovery (Somavarapu & Guzzetti, 2021). A less prospective recommendation is electrodynamic tethering, which wants to use propellant-less Jovian spacecraft captures (Casanova-Álvarez et al., 2021). Thus, both 3D printing and astrometry show promise in advancing the ISM, but technological challenges still persist.
Similarities in the Research Approach
A preliminary literature review reveals that past studies are similar to the research being undertaken by the team because it focuses on ways of addressing spaceflight resupply missions’ problems. In terms of modeling and resolving the problems, different methods have been recommended; for example, network-based optimization; and visualization techniques and databases are applied to visualize and communicate the problems (Ngo et al., 2018). However, what is missing from past research is a detailed and structured method for implementing and managing the problems and benefits of ISM in space projects.
Data Collection and Analysis Plan
The data used to evaluate the problem will be based on ISM development and its benefits in relation to LEO. The data collection for this research will come from scholarly, peer-reviewed articles, websites of government-financed space organizations like the European Space Agency and NASA, and books. In addition, websites from reputable firms in the space sector like SpaceX, Boeing, and Blue Origin (Ngo et al., 2018). In addition, data will be collected sparingly from articles from sources like Spaceflightnow, Space.com, and Space Daily.
Further, there are many scholarly articles, books, and reputable data from the space industry at disposal, but the in-space manufacturing site of NASA is a useful source. The data collected can then be analyzed using content analysis, in which a researcher identifies the frequency with which the concept or words in the articles or books are shared (Sekaran & Bougie, 2019). Research has to group large amounts of text into codes and summarize them into categories and tabulate the data to attain the frequency of some variables or concepts.
Antonsen, E. L., Myers, J. G., Boley, L., Arellano, J., Kerstman, E., Kadwa, B., Buckland, D. M., & Van Baalen, M. (2022). Estimating medical risk in human spaceflight . npj Microgravity , 8 (1). Web.
Casanova-Álvarez, M., Navarro-Medina, F., & Tommasini, D. (2021). Conceptual design of Electrodynamic multi tether system for self-propelled Jovian capture . Acta Astronautica , 184 , 299-307. Web.
Dervay, J. P., Brandt, K. E., & Sanders, R. (2021). Spaceflight medical operations . Human Spaceflight Operations: Lessons Learned from 60 Years in Space , 3 (4), 457-492. Web.
Micheli, M., Koschny, D., Conversi, L., Budnik, F., Gray, B., Santana-Ros, T., Reszelewski, R., Żołnowski, M., Gȩdek, M., Gendre, B., Coward, D., Molotov, I. E., Rumyantsev, V., Liakos, A., & Schmalz, S. (2021). Optical observations of the BepiColombo spacecraft as a proxy for a potential threatening asteroid . Acta Astronautica , 184 , 251-258. Web.
Moraguez, M., & De Weck, O. (2020). Benefits of in-space manufacturing technology development for human Spaceflight . 2020 IEEE Aerospace Conference . (6th ed., pp. 235-267). Facet. Web.
Ngo, T., Kashani, A., Imbalzano, G., Nguyen, K., & Hui, D. (2018). Additive manufacturing 3Dprinting): A review of materials, methods, applications and challenges . Composites Part B: Engineering, 143 , 172-196. Web.
Pardini, C., & Anselmo, L. (2021). Evaluating the impact of space activities in low earth orbit . Acta Astronautica , 184 (3), 11-22. Web.
Sekaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2019). Research methods for business: A skill building approach (3 rd ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
Somavarapu, D. H., & Guzzetti, D. (2021). Toward immersive spacecraft trajectory design: Mapping user drawings to natural periodic orbits . Acta Astronautica , 184 , 208-221. Web.
Trujillo, A. E., Moraguez, M. T., Owens, A., Wald, S. I., & De Weck, O. (2017). Feasibility analysis of commercial in-space manufacturing applications . AIAA SPACE and Astronautics Forum and Exposition . Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, April 17). Manufacturing Using 3D-Technology: Qualitative Study Plan. https://ivypanda.com/essays/manufacturing-using-3d-technology-qualitative-study-plan/
"Manufacturing Using 3D-Technology: Qualitative Study Plan." IvyPanda , 17 Apr. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/manufacturing-using-3d-technology-qualitative-study-plan/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Manufacturing Using 3D-Technology: Qualitative Study Plan'. 17 April.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Manufacturing Using 3D-Technology: Qualitative Study Plan." April 17, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/manufacturing-using-3d-technology-qualitative-study-plan/.
1. IvyPanda . "Manufacturing Using 3D-Technology: Qualitative Study Plan." April 17, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/manufacturing-using-3d-technology-qualitative-study-plan/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Manufacturing Using 3D-Technology: Qualitative Study Plan." April 17, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/manufacturing-using-3d-technology-qualitative-study-plan/.
- The Impact of In-Space Manufacturing on Production
- Privatization of Human Space Flight
- Challenger and Columbia Spaceflight Accidents
- Hydrogen Power and Fuel Cell Efficiency
- ACME Mexico ISM Plan
- Buddhism, Sikhism and Baha’ism
- George Patton: General and Military Innovator
- Spacecraft Exploration: NASA and ESA
- People with Disabilities: The Systemic Ableism
- Information System Management in Sally Beauty, Inc.
- New Technologies: Advancements and Challenges
- Tech Trends: Computer Vision vs. Virtual Twins
- Blockchain: Exploring Innovation
- Researchers Who Altered Evolution of Transistors and Software
- Blockchain Technology, Fraud and Accountability
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 17.4.2024 in Vol 26 (2024)
This is a member publication of University College London (Jisc)
Twitter Analysis of Health Care Workers’ Sentiment and Discourse Regarding Post–COVID-19 Condition in Children and Young People: Mixed Methods Study
Authors of this article:

Original Paper
- Macarena Chepo 1 * , RN, BSN, MPH, PhD ;
- Sam Martin 2, 3 * , MSc, PhD ;
- Noémie Déom 2 , MSc ;
- Ahmad Firas Khalid 4 , MD, PhD ;
- Cecilia Vindrola-Padros 2 , BA, MA, PhD
1 School of Nursing, Universidad Andrés Bello, Santiago, Chile
2 Department of Targeted Intervention, University College London, London, United Kingdom
3 Oxford Vaccine Group, Churchill Hospital, University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
4 Canadian Institutes of Health Research Health System Impact Fellowship, Centre for Implementation Research, Ottawa Hospital Research Institute, Otawa, ON, Canada
*these authors contributed equally
Corresponding Author:
Sam Martin, MSc, PhD
Department of Targeted Intervention
University College London
Charles Bell House 43-45
Foley Street
London, W1W 7TY
United Kingdom
Phone: 44 (0)20 3108 3232
Email: [email protected]
Background: The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant global impact, with millions of cases and deaths. Research highlights the persistence of symptoms over time (post–COVID-19 condition), a situation of particular concern in children and young people with symptoms. Social media such as Twitter (subsequently rebranded as X) could provide valuable information on the impact of the post–COVID-19 condition on this demographic.
Objective: With a social media analysis of the discourse surrounding the prevalence of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people, we aimed to explore the perceptions of health care workers (HCWs) concerning post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people in the United Kingdom between January 2021 and January 2022. This will allow us to contribute to the emerging knowledge on post–COVID-19 condition and identify critical areas and future directions for researchers and policy makers.
Methods: From a pragmatic paradigm, we used a mixed methods approach. Through discourse, keyword, sentiment, and image analyses, using Pulsar and InfraNodus, we analyzed the discourse about the experience of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people in the United Kingdom shared on Twitter between January 1, 2021, and January 31, 2022, from a sample of HCWs with Twitter accounts whose biography identifies them as HCWs.
Results: We obtained 300,000 tweets, out of which (after filtering for relevant tweets) we performed an in-depth qualitative sample analysis of 2588 tweets. The HCWs were responsive to announcements issued by the authorities regarding the management of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom. The most frequent sentiment expressed was negative. The main themes were uncertainty about the future, policies and regulations, managing and addressing the COVID-19 pandemic and post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people, vaccination, using Twitter to share scientific literature and management strategies, and clinical and personal experiences.
Conclusions: The perceptions described on Twitter by HCWs concerning the presence of the post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people appear to be a relevant and timely issue and responsive to the declarations and guidelines issued by health authorities over time. We recommend further support and training strategies for health workers and school staff regarding the manifestations and treatment of children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition.
Introduction
More than 3 years after the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic [ 1 ], the social, political, and economic impact of this phenomenon has been more than significant, considering >700 million worldwide cases and nearly 7 million people’s deaths [ 2 ]. Given the scale of the phenomenon, it is imperative for all countries to thoroughly examine the lessons gleaned from the pandemic, particularly regarding a matter that has raised significant concern among the populace: the long-term effects experienced by individuals who have had COVID-19, spanning weeks, months, or even years after their initial infection [ 3 ]. This phenomenon, referred to as post–COVID-19 condition (or more commonly “long COVID”), warrants careful consideration and analysis [ 4 ].
There is increasing information regarding the clinical manifestation of this condition, particularly in the adult population. The worldwide prevalence has been estimated at approximately 50% to 70% in individuals hospitalized during acute COVID-19 infection and 10% to 12% in vaccinated cases [ 5 ]. While children and young people have a low likelihood of severe COVID-19 infection [ 6 ], the information available to date indicates that the presence of post–COVID-19 condition in this group may be as disabling as in adults, reaching a prevalence rate of 23.4% (range 3.7%-66.5%) [ 7 ].
An agreed definition by the World Health Organization indicates that post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people is a condition that occurs “in individuals with a history of confirmed or probable SARS-CoV-2 infection when experiencing symptoms lasting at least two months which initially occurred within three months of acute COVID-19” [ 8 ]. Post–COVID-19 condition strongly impacts daily functioning and can develop or continue after COVID-19 infection and may fluctuate or relapse over time [ 4 , 8 , 9 ].
Among the symptoms most frequently attributable to post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people are fatigue, altered smell or anosmia, and anxiety [ 8 ]. However, other symptoms have also been reported, such as sleep disturbances, difficulty in concentrating, abdominal pain, myalgia or arthralgia, earache or ringing in ears, mood swings, persistent chest pain, stomach pain, light sensitivity, diarrhea, heart palpitations, and skin lesions [ 8 , 10 ]. One of England’s most significant studies is the Children and Young People With Long COVID study by Stephenson et al [ 11 ]. This national research matched longitudinal and cohort studies in adolescent individuals aged 11 to 17 years and found the presence of symptoms in 35.4% of the adolescent individuals who tested positive at baseline and 8.3% who of the adolescent individuals who tested negative at baseline. A total of 3 months after testing, 66.5% of those who tested positive and 53.3% of those who tested negative had any symptoms [ 11 ]. However, Stephenson et al [ 12 ] recently indicated that in a 6-month follow-up, the prevalence of specific symptoms reported at the time of the polymerase chain reaction testing decreased over time, where, for example, the prevalence of chills, fever, myalgia, cough, and sore throat among those who tested positive decreased from 10% to 25% to <3%.
As research on the symptoms, prevalence, and treatment of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people continues, it is essential to add to the literature by developing studies that determine the condition’s impact on this group, considering that they are experiencing a range of unwanted symptoms that disrupt their quality of life and that of their families.
Considering that listening to the voices of families and health workers could be helpful to broaden the knowledge achieved in post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people, a powerful tool could be social media, such as Twitter (subsequently rebranded as X). With >3729 million daily active users, Twitter has become one of the most important social platforms in the world [ 13 ]. People used Twitter during the COVID-19 pandemic for different purposes, such as world leaders communicating with citizens [ 14 , 15 ], organizations monitoring movement [ 16 ], scientists studying public discourse around the pandemic [ 17 , 18 ], and researchers performing sentiment analysis [ 19 - 21 ]. In the case of physicians and health care workers (HCWs), Twitter has been used to share and evaluate scientific evidence, guidelines, and technical advice [ 22 - 24 ] and track the course and burden of disease [ 25 ].
Using the social media monitoring platform Pulsar [ 26 ], we aimed to explore HCWs’ perceptions concerning post–COVID condition in children and young people in the United Kingdom between January 2021 and January 2022. We aimed to contribute to the emerging knowledge on post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people and identify critical areas and future directions for researchers and policy makers.
We considered a mixed methods approach to be a pragmatic research paradigm. We analyzed data by conducting a Collaborative and Digital Analysis of Big Qualitative Data in Time Sensitive Contexts (LISTEN) [ 27 ]. This mixed methods analysis consisted of iterative cycles intercalating team discussion and using digital text and discourse analytics tools to analyze related social media data [ 27 ]. We used the LISTEN method to perform quantitative and qualitative analyses of Twitter posts, extracted through the Pulsar platform [ 26 ], related to the experience of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people in the United Kingdom (eg, phrases, words, hashtags, videos, and images), published between January 1, 2021, and January 31, 2022. We created an advanced Boolean search for keywords mentioning “long COVID” and corelated words, hashtags, and symptoms; furthermore, we filtered for user accounts who identified as HCWs in their Twitter biography description ( Multimedia Appendix 1 ).
Quantitative analysis of all tweets included the following: (1) engagement analysis, where we specifically measured reactions to posts, for example, a retweet, a share, or a comment or quote made toward a tweet; (2) sentiment and emotion analysis, where we measured the positive or negative sentiment in the words and tone of each post within the context of post–COVID-19 condition and HCW’s roles ( Multimedia Appendix 2 ); (3) emotion analysis, where we measured the emotions expressed in the tweets, classified as sadness, anger, disgust, fear, and joy; (4) frequency analysis, where we observed the frequency of keywords and themes in the data set; (5) segmentation analysis, where we measured the key connections or relationships between keywords and their frequent use in the same context; (6) demographic analysis, where we measured the occupation, gender (man or woman or nonbinary or unknown), and city of origin related to the users posting tweets; and (7) analyses, where we evaluated the most influential accounts and the most mentioned websites.
Big qualitative analysis was carried out through thematic discourse analysis of the data sample, using InfraNodus [ 28 ], specifically analyzing the key themes and topics of concern expressed throughout the data set. A codebook was constructed based on the mapping of themes agreed upon by 3 researchers (ND, SM, and MC; Multimedia Appendix 3 ).
The principal investigators (ND, AFK, SM, and MC) interpreted and analyzed the data collected, following the recommendations for rigorous research provided by Creswell and Poth [ 29 ]. Using the LISTEN method [ 27 ], we aimed to show that the integration of qualitative insights through thematic analysis with the quantitative backing of topic modeling can offer a comprehensive view of the discourse. This mixed methods approach allows us to capture the richness of qualitative data while leveraging the objectivity of quantitative measures. Our initial data harvest of the larger corpus data from the Pulsar platform captured 300,000 tweets; this data harvest helped to underpin the software’s sentiment analysis modeling of this specific data set, providing a robust quantitative foundation. The addition of further qualitative data analyses from a smaller qualitative sample allowed for an in-depth understanding of nuanced conversations, particularly when exploring new or complex phenomena such as post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people, with the provision of insights into the context, subtext, and sentiment behind the tweets offering valuable snapshots of public perception and discourse. We used an iterative mixed methods approach, iterating between team discussions and using digital analytics tools to discern relevant themes from the Twitter data corpus. Specifically, we used InfraNodus for thematic analysis, which incorporates a topic modeling script for analyzing and identifying key topics of concern with a data set and provides a structured and objective interpretation of the data. The coding process involved 3 independent researchers (MC, SM, and ND), each with expertise in health care, social network analysis, and digital global health. When initial coding disagreements arose, we meticulously tagged any queries and discussed the posts in question. These instances led to 3 structured meetings wherein the research team deliberated collaboratively to resolve conflicting interpretations. This approach resulted in an 81.99% (2122/2588) initial intercoder agreement rate for the tweets analyzed. For the remaining instances where consensus was not initially reached, the majority rule was applied to finalize theme codings. To quantify the reliability of our coding procedure, with 81.99% (2122/2588) of the tweets coded identically, we used the Cohen κ score, which provides a measure of interrater agreement adjusted for chance. Including the calculation of all variations, this score was calculated to be approximately κ=0.70, indicating good agreement among the coders.
Ethical Considerations
The study only collected data from publicly accessible social networks that have been anonymized by various means, particularly by replacing all usernames and links with anonymous text and summaries of tweets that have been edited, retaining the original message, avoiding direct quotations being identifiable, and ensuring that no information is provided on the identity of the individuals who posted the content studied on the platform.
Internet research requires researchers to carefully consider guidelines to determine whether ethics approval and informed consent are needed [ 30 ]. On the basis of the terms set out by the Research Ethics Committee at the University College London [ 31 ], the study was considered exempt from formal ethics approval for the following reasons: (1) study involving information freely available in the public domain, such as published biographies, newspaper accounts of an individual’s activities, and published minutes of a meeting, that although is considered personal under the Data Protection Act, would not require ethics review; and (2) study involving anonymized records and data sets in the public domain, such as data sets available through the Office for National Statistics or the UK Data Archive where appropriate permissions have already been obtained and it is not possible to identify individuals from the information provided.
Therefore, we anonymized all records and data sets collected during the study to make identification impossible. We removed social media usernames from the data samples. No direct or easily traceable quotes have been included. These measures align with best practices [ 32 - 35 ]. While this study was beyond the scope of the human ethics committee, we adhered to the principles of ethics: beneficence, nonmaleficence, autonomy, and justice [ 36 ]. We collected and analyzed data through secure encrypted servers via the Meltwater and InfraNodus platforms.
Audience Analysis
During the period from January 2021 to January 2022, we obtained 300,000 tweets from 936 accounts. After filtering for relevant posts (refer to inclusion and exclusion criteria in Multimedia Appendix 1 ), we analyzed a sample of 2588 tweets using mixed methods analysis. In terms of gender (man, woman, nonbinary, or unknown), 32.88% (851/2588) were female individuals, 23.49% (608/2588) were male individuals, and 43.59% (1128/2588) were unknown. According to the description given in the user’s biography, the most frequently self-reported terms were “NHS” (582/2588, 22.49%), “health” (230/2588, 8.89%), “medical” (168/2588, 6.49%), “nurse” (166/2588, 6.41%), “clinical” (160/2588, 6.18%), “mum” (158/2588, 6.11%), “doctor” (145/2588, 5.6%), and “GP” (145/2588, 5.6%). In terms of city, tweets came mainly from London (958/2588, 37.02%), Newcastle upon Tyne (326/2588, 12.6%), Redcar (160/2588, 6.18%), Manchester (140/2588, 5.41%), and Bradford (111/2588, 4.29%).
Regarding profession described in the user’s biography, the most frequently mentioned roles were nurses (176/2588, 6.8%); medical roles, for example, paramedic and nursing assistant (173/2588, 6.68%); clinical roles, for example, surgeon, physiotherapist, and anesthesiologist (160/2588, 6.18%); general practitioners (GPs), for example, hospital GP or local surgery GP (142/2588, 5.49%); and physician (140/2588, 5.41%). The most frequent organization affiliated with was the National Health Service (587/2588, 22.68%).
Most Influential Accounts
One of the accounts that generated the highest number of mentions and, therefore, some of the most influence, as they were the ones that talked the most about post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people, was the account for @longcovidkids (593/2588, 22.91% tweets), related to the most shared website longcovidkids.org [ 37 ] , an international UK-based charity for families and children living with post–COVID-19 condition. Although the account was created in October 2020, it was first mentioned in our data collection timeline on January 1, 2021. It offers web support services, funding, and research participation and represents children and young people living with post–COVID-19 condition in expert forums, research panels, health organizations, and parliamentary groups. The other most shared web pages were theguardian.com (the United Kingdom) [ 38 ], bbc.co.uk (the United Kingdom) [ 39 ], peoplewith.com (the United States) [ 40 ], and ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (the United States) [ 41 ]. This shows that in the United Kingdom, there was a mixed influence of UK and US link resources linked to HCW Twitter users in the United Kingdom.
Keyword Analysis
The volume of social media engagement in the discussion about the post–COVID-19 condition experience in children and young people in the United Kingdom reached 1400 posts, 1550 engagements, and 1.9 million impressions. Overall, comments were very responsive to government decisions regarding the vaccination program and school closures ( Multimedia Appendix 4 ). During the first peak of comments in January 2021, the amount of discourse expanded leading up to March 2021, when there were different announcements of school closures, and the guidelines were delivered regarding the priority groups of the vaccination program (frontline HCW and people aged >80 years first). The highest engagement was between June and July 2021, which coincides with the government announcement regarding the availability of vaccines for people aged >18 years. The third peak of comments occurred in September 2021, the same month the authorities announced the extension of the vaccination program to children aged 12 to 15 years.
Top Keywords Analysis
The top words in posts associated with children and young people’s experience of post–COVID-19 condition in the United Kingdom were “Children” (352/2588, 13.6%), “kids” (160/2588, 6.18%), “people” (158/2588, 6.11%), “Young” (148/2588, 5.72%), and “schools” (83/2588, 3.21%). The top hashtags were #longcovid (1387/2588, 53.59%), #longcovidkids (448/2588, 17.31%), #covid19 (370/2588, 14.3%), and #covid (176/2588, 6.8%).
Sentiment and Emotions Analysis
According to sentiment analysis, 99.38% (2572/2588) of the posts reflected negative sentiments and 0.62% (16/2588) reflected positive sentiments. Negative sentiments were mainly associated with comments on hospitalization figures related to the COVID-19 pandemic, criticism of pandemic mitigation policies, and vaccination of children and young people. Furthermore, positive sentiments mainly concerned acknowledgments around decreasing numbers of community support groups.
The primary emotions identified were as follows:
- Sadness (1752/2588, 67.7%), such as in the following tweet:
@[Username] Really upset, after my tough on-call last night. Hospitalisations are still going up, and Gov announcement minismises the effect of long-COVID in adults and children. It’s so hard to keep spirits up today. But we’ll try and continue doing our best in the NHS.
- Joy (367/2588, 14.18%), such as in the following tweet:
@[Username] It’s been an amazing day! [...] I’ve been able to share the experience I’ve gained treating children and adolescents with Long COVID over the last year.
- Fear (233/2588, 9%), as seen in the following tweet:
@[Username] It’s really urgent that young people get the message that they need to get vaccinated. Long COVID is ruining many people’s lives! It’s not a lie or hypochondria, there are real, physiological changes, please understand!
Segmentation Analysis
This analysis revealed the critical clusters of conversation around the main topics of concern within the discourse network around post–COVID-19 condition. Comments were distributed in 4 key conversation segments as follows:
- People, schools, and prevention (1734/2588, 67%): Most of the comments related to measures taken in terms of COVID-19 prevention in schools, concern about the risk of exposure, and sharing experiences of infection in schools.
- Health, adults, and impact (401/2588, 15.49%): Comments mainly reflected concerns and uncertainty about the long-term effect of post–COVID-19 condition on both children and young people and adults.
- Cases, virus, and risk (326/2588, 12.6%): Comments reflected worries about the associated risks and long-term consequences attributable to post–COVID-19 condition (in both adults and children and young people) and the constant mutation of the virus, which will create a permanent risk in the population.
- Months, distress, and symptoms (106/2588, 4.1%): Some HCWs used Twitter to share how children and young people experience post–COVID-19 condition and the extent of these symptoms. Some HCWs exemplified certain typical manifestations, such as fatigue.
Discourse Analysis by Theme
To better understand the topics discussed from the segmentation analysis, we performed a discourse analysis of the key co-occurring themes and topics of concern shared within discussions regarding post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people. The following themes emerged ( Textbox 1 ): concern or uncertainty for the future, school attendance, mask protection from COVID-19, vaccine uptake, infection rates, policy (support or skepticism), understanding and visualizing symptoms, child mental health, access to care, community support, and research ( Figures 1 and 2 ).
- Concern for the future or uncertainty (615/2588, 23.76% tweets): Most comments showed a concern for the future, focusing on shared statistics regarding the rate and spread of infection in children and young people and how this would affect future health outcomes. Furthermore, this group expressed concern regarding political decisions; the presence of illness in loved ones; the eventual overload and response capacity of the health system in the face of an increase in post–COVID-19 condition cases; and the need for training of health care workers (HCWs) to deal with comorbid, potentially long-term symptoms ( Figure 1 A).
- Schools (460/2588, 17.77% tweets): Comments aimed to promote vaccination policies for schoolchildren and flexible measures regarding teachers’ work and attendance, considering cases of people with prolonged symptoms. In addition, several tweets expressed dissatisfaction with school risk mitigation measures, such as the use of face masks and air filters ( Figure 1 B).
- Vaccine (386/2588, 14.9% tweets): Most tweets from this group showed their disapproval of the constant changes in the government’s decisions regarding schools and priority groups for vaccination. Between March and June 2021, the first set of tweets criticized the lack of priority in the vaccination program for schoolchildren and other at-risk groups (such as teachers). Once the authorities announced a vaccination program for schoolchildren aged 12 to 15 years ( Multimedia Appendix 4 ), most comments promoted vaccination for this group. A few comments (78/2588, 3.01%) shared concerns about the vaccine’s efficacy for children, based on the experiences of COVID-19 reinfection in adults despite having received the recommended initial doses. However, to a lesser extent (26/2588, 1%), there was a refusal to vaccinate children, citing fear of possible adverse effects. Nonetheless, it is worth noting that the community frequently refuted such comments ( Figure 1 C).
- Share statistics (334/2588, 12.91% tweets): Frequently, HCWs shared statistical data, such as the number of affected children and young people, the number of post–COVID-19 condition cases, and hospital admissions and deaths. Some of these data were used to validate the existence of the post–COVID-19 phenomenon or to express concern about it ( Figure 1 D).
- Policy (316/2588, 12.21% tweets): The comments were responsive to the policies emanating from the authorities over time ( Multimedia Appendix 4 ). There were 5 main criticisms, including changes in school closure or opening policies; HCWs question why the authorities ignore the evidence of post–COVID-19 cases in children and young people, leading them to question whether decision makers have sufficient training to control the pandemic adequately; the failure to include teachers and school workers in the COVID-19 vaccination program as well as the younger population; the lack of mitigation measures in schools, such as improvements in ventilation systems and mandatory use of masks; and the herd immunity as a plan in the government’s hidden agenda , that is, to promote work and activate the economy ( Figure 1 E).
- “Proof” (280/2588, 10.82% tweets): Most tweets in this group argued regarding the existence of children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition through pictures; statistics; scientific papers; and personal, family, and professional experiences ( Figure 1 F).
- Signs and symptoms (189/2588, 7.3% tweets): Among the symptoms described, chronic fatigue and exhaustion were the most frequent symptoms, which prevent normal activities. Other symptoms were respiratory: dyspnea, chronic cough, and shortness of breath; gastrointestinal: acute or intense abdominal pain, nausea, bloating, gastroparesis, and change in smell or taste; muscular: severe joint pain, “painful foot” and difficulty with physical activity; mental health: anxiety and low mood; topical: rash, skin rashes, and redness and pain in the eyes; and nonspecific symptoms, such as chest pain, heart palpitations, constant high body temperature, precocious puberty, hormonal changes, and erectile dysfunction ( Figure 2 A).
- Face masks (119/2588, 4.6% tweets): Face masks were widely promoted, especially in schools, because HCWs considered them as a practical and straightforward strategy to control the pandemic ( Figure 2 B).
- Skepticism (101/2588, 3.9% tweets): Comments showed reticence toward post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people. Some of the arguments focused on a perceived lack of clarity in the clinical manifestations and stressed the need to better differentiate the post–COVID-19 condition from other related symptomatologies, such as mood disorders (eg, depression and anxiety due to confinement). In contrast, several arguments agreed on the need for more scientific evidence, arguing that post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people are isolated. Other users claimed not to know of such cases instead of calling post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people SMS text message an exaggeration. In addition, several arguments favored releasing restrictions for children and young people, particularly arguments related to the use of masks, because of possible associated risks, for example, hypoxia ( Figure 2 C).
- Mental health (54/2588, 2.09% tweets): Symptoms attributable to mental health problems in children and young people were also a concern. For instance, HCWs mentioned sadness, fear of infecting their family, anxiety regarding sick parents, stress, night terrors, self-harm, and suicidal ideation. Furthermore, users discussed a perceived lack of specific support for children and young people and their families in situations such as hospitalization; prolonged COVID-19 condition; admission to intensive care; and death of a family member, schoolmate, or teacher, all situations that triggered permanent stress in these groups ( Figure 2 D).
- Community support or asking for advice (93/2588, 3.59% tweets): Some HCWs used Twitter to ask for guidance on a specific issue or share experiences of having post–COVID-19 condition or caring for children and young people or family members. Furthermore, they shared informative infographics provided by experts regarding post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people ( Figure 2 E).
- Access to health care or treatment (72/2588, 2.78% tweets): Some HCWs mentioned the lack of specialist (cardiology) support, concerns regarding prolonged National Health Service burnout, and criticisms regarding how follow-up was carried out concerning the relative symptomatology of children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition. At the same time, opening new centers for children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition generated different reactions. On the one hand, some HCWs recognized it as a substantial development, but on the other hand, some HCWs recognized it as proof of the existence of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people, which raised concerns for the future ( Figure 2 F).
- Research (52/2588, 2% tweets): Under this theme, tweets largely promoted study on post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people or highlighted the need for further study on the subject ( Figure 2 G).
- Images (57/2588, 2.2% tweets): Images shared were primarily from scientific studies, including infographics (from organizations such as National Health Service or @LongCovidKids) and visualization of children and young people’s symptoms, such as rashes, COVID-19 toe, and joint pain. Most infographics shared by organizations (and not individuals), such as the organization LongCovidKids, were related to statistics, such as the number of children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition or the quantification of the type of symptoms experienced. Shared photographs tended to show the more “visually recognizable” symptoms of post–COVID-19 condition, such as skin lesions, rashes, or inflammation. The less visible symptoms, such as chronic fatigue and neurological issues, were represented with photographs of children and young people lying, sleeping under blankets, or duvets or on hospital beds ( Figure 2 H).

Principal Findings
Our primary objective was to explore HCWs’ perceptions concerning post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people in the United Kingdom between January 2021 and January 2022. Our findings indicated that comments made by HCWs on Twitter were responsive to announcements issued by authorities regarding the management of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom and associated regulations on the operation of schools. The most frequent feelings and emotions were negative, mainly sadness. In turn, we identified relevant themes for HCWs, such as uncertainty or concern about the future; policies; and regulations for the prevention, management, and addressing both COVID-19 and post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people; vaccination; and the use of Twitter as a strategy to share scientific literature, management strategies, and clinical and personal experiences.
Concern from HCWs regarding the policies for addressing the COVID-19 pandemic in the children and young people in the United Kingdom (including vaccination and schools) was a recurring theme in our findings. Furthermore, concern regarding the side effects of the COVID-19 vaccine and how the vaccine might interact with preexisting physiological symptoms of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people was a topic of discussion. Similarly, the constant change in policy making in the United Kingdom, as public health bodies and governments have tried to understand and adapt to the emergence of post–COVID-19 condition, have added to the strength of this ongoing debate [ 42 ]. The lack of up-to-date evidence on post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people prompted HCWs to rely on Twitter during the pandemic to communicate relevant information. Twitter has a broad audience reach; is used as a communication tool by politicians, health bodies, and other key influences; and facilitates real-time updates [ 43 ]. During the pandemic, HCWs, primarily those in frontline roles and local response coordination, have often been challenged to become credible spokespersons for pandemic information [ 44 ]. Such credibility directly influences public confidence and decision-making, ultimately determining the success or failure of a public health intervention [ 43 ].
Furthermore, failures in risk communication could explain the presence of uncertainty and negative feelings associated with school regulations. When people are upset, distressed, or fearful, they often do not trust the authority, decrease the perceived validity of the communication received, and find information processing difficult [ 45 ]. In this regard, Fotheringham et al [ 46 ] indicated that during 2020, school leaders in the United Kingdom faced pressures and challenges related to translating and enacting school policies, particularly with the perceived lack of agency shared by the government concerning being able to translate centrally issued guidelines. In turn, Tomson et al [ 47 ] reported that the pandemic has negatively impacted the well-being of leaders in all types of schools and across all demographic groups, affecting their ability to think clearly and solve work-related problems. Given that the protection and care of children and young people health during the COVID-19 pandemic ultimately rests with school leaders, the search for support strategies that focus on the needs of these groups becomes an urgent necessity.
Findings in Relation to Other Studies
Using Twitter’s information, this is one of the first studies to capture health professionals’ perceptions of prolonged COVID-19 in the children and young people in the United Kingdom. However, other studies have addressed post–COVID-19 condition on this social network. Callard and Peregov [ 48 ] reviewed how, through social platforms such as Twitter, patients made the persistence and heterogeneity of COVID-19 symptoms visible, thus catapulting the inclusion of post–COVID-19 condition as a relevant phenomenon in clinical and policy debates. In contrast, other authors in the last 2 years have explored on various platforms (including Twitter) the persistence of symptoms and emotional impact after months of suspected and confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 [ 49 - 55 ], including the period of vaccination. Furthermore, others have explored web discussions regarding this phenomenon [ 56 ]. Several of these authors agree on a perceived lack of support and specific resources from governmental bodies, a lack of information or clarity in the instructions given, and the absence of formal mechanisms to allow the voices of patients and the community to be heard. The above point is critical as it highlights the gap between the needs of the population and the response provided by policy makers, which not only translates into a gap in access to health services but also limits citizen participation in decision-making on the issues that affect their own health and increases distrust toward regulations and instructions issued by the government.
Implications for Policy and Practice
Several policy recommendations and implications are targeted at various stakeholders to consider while implementing future policy guidelines to address post–COVID-19 health care delivery. First, policy makers should consider investing appropriate resources to collect data regarding post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people, specifically on the impact of COVID-19 on the mental health of children and young people. This implies working closely with researchers to streamline data collection and reporting on post–COVID-19 condition. Second, policy makers should consider providing a basic level of psychosocial support with access to quality mental health and psychosocial support services for HCWs, school staff, parents, and children and young people experiencing post–COVID-19 condition. This implies strengthening health systems, community-based programming, and mobilization. Policies must include documenting the impact of mental health and psychosocial support interventions and innovative approaches to be more widely disseminated and scaled up across different contexts and target population groups. Third, to address the criticism around frequent changes in school closure and opening policies, decision makers should develop clear, easy-to-understand school mitigation plans informed by the best available evidence. The plans should incorporate teachers, school workers, and parents to ensure all voices are included in the policy plan. Fourth, policy makers should adopt a shared decision-making approach incorporating HCWs in the decision-making process for managing the COVID-19 pandemic. Finally, government decision makers should set post–COVID-19 pandemic recovery policies informed from a health equity perspective and how this affects children and young people living with post–COVID-19 condition, factoring in childhood, family income, housing, domestic violence, access to health care, and racism.
In terms of the needed clearer road map for recommendations to support training strategies for HCWs and school staff regarding post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people, we have outlined the following 10 steps.
Step 1: Data Collection and Analysis
Our study underlines the critical need for comprehensive data on post–COVID-19 condition’s impact on the mental health of children and young people. As a first step, it is recommended that policy makers should allocate resources for the systematic collection and analysis of data on post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people, particularly focusing on mental health outcomes. These data should be used to identify the most prevalent symptoms and the most effective treatment strategies. In this context, it is recommended that experts emphasize the importance of early detection and medical consultation for mental health issues in children and young people diagnosed with post–COVID-19 condition, including mood changes, irritability, social withdrawal, memory problems, difficulty in concentrating, anxiety, depression, posttraumatic stress, school absenteeism, and suicidal ideation [ 57 , 58 ]. This entails working closely with researchers to streamline data collection and reporting on post–COVID-19 condition.
Step 2: Psychosocial Support Framework
It has been noted that globally, programs for managing post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people are heterogeneous, ranging from the use of physiotherapy, pediatric occupational therapy, and psychological support to interventions aimed at lifestyle modifications [ 59 ]. This diversity could impact differential outcomes in the treatment, recovery, and timely and effective rehabilitation of children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition. Upon analyzing the wider literature and the social media data in this study, it is recommended that a basic level of psychosocial support should be established. This would involve ensuring access to quality mental health services for HCWs, school staff, parents, and children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition. This framework should be integrated into the health system and community-based programming, emphasizing the mobilization of resources and strengthening of support networks. It is suggested that the psychosocial support framework should facilitate access to quality mental health services and support networks that are robust and responsive. Community engagement gleaned from further Twitter discourse analysis should be a helpful guide in the development of these services to ensure they meet the real and expressed needs of children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition. Practical examples of basic psychosocial support include using web support services; individual or group therapy sessions; school-based emotional support programs; and counseling sessions aimed at parents, family members, or school staff.
Step 3: Educational Mitigation Plans
The frequent policy changes around school closures highlight the necessity for stable and clear educational mitigation plans. It is recommended that these plans should be directly informed by the evidence collected and further analysis of sentiments and emotions surrounding post–COVID-19 condition in schools. Incorporating the viewpoints of teachers, parents, and school staff, as identified in our thematic analysis, will ensure that the mitigation strategies are comprehensive, feasible, and sensitive to the psychosocial impact on children and young people. School staff and policy makers should collaborate to develop clear, evidence-informed educational mitigation plans. These plans should be straightforward and involve teachers, school workers, and parents in their creation, ensuring a unified approach that considers the voices of all stakeholders.
Step 4: Shared Decision-Making in Health Care
In health care settings, the adoption of a shared decision-making model is crucial, enabling HCWs to actively contribute to the formulation of COVID-19 and post–COVID-19 policies. This inclusive approach ensures that frontline workers can provide valuable insights toward policy development. To facilitate this, the establishment of advisory committees composed of representatives from HCWs is recommended. This committee can convene regularly to deliberate on key decisions pertaining to the COVID-19 pandemic management, including prevention measures, resource distribution, and vaccination strategies. Such collaborative groups have demonstrated effectiveness in identifying priority needs within the context of a pandemic [ 60 ].
Step 5: Health Equity in Policy Setting
Post–COVID-19 recovery policies should be set with a health equity lens. This means considering factors such as family income, housing, domestic violence, access to health care, and racism and how these factors affect children and young people living with post–COVID-19 condition. Our findings emphasize the importance of framing post–COVID-19 recovery policies through a lens of health equity. The concerns raised by HCWs regarding the socioeconomic impacts, such as family income and access to health care, underline the need for policies that address not just the medical aspects of post–COVID-19 condition but also the social determinants of health. An equitable approach will ensure that children and young people from diverse backgrounds receive appropriate support.
Step 6: Documenting and Disseminating Interventions
It is vital to document the impact of mental health and psychosocial support interventions. In this context, it is crucial to implement innovative strategies to disseminate unbiased information about post–COVID-19 condition among health care professionals and educators working with children and young people, ensuring it reaches different contexts and populations. These strategies may include creating interactive multimedia resources, such as videos and mobile apps; organizing webinars; actively using social media; and forming web support groups. These groups will provide a space where patients, health care professionals, and educators can share their experiences and knowledge regarding post–COVID-19 condition. These actions will not only help reduce isolation and social stigma but also strengthen support for these groups considered vulnerable [ 61 ].
Step 7: Developing a Clear Communication Strategy
Policy makers must develop a clear communication strategy to address frequent policy changes and mitigate confusion. This strategy should be informed by the data collected and analysis conducted in Step 1. The data reveal a palpable sense of uncertainty and frustration due to frequent policy shifts, underscoring the need for a clear and consistent communication strategy. This strategy should be grounded in the evidence gathered from the health care community’s discourse and aim to minimize confusion by providing timely, transparent, and reliable information regarding post–COVID-19 policies and support services.
Step 8: Training and Support Strategies
On the basis of the findings of the comprehensive data analysis, specific training and support strategies should be developed for HCWs and school staff. These strategies should be focused on the practical aspects of identifying and managing post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people. For instance, training sessions could include practical workshops on recognizing post–COVID-19 symptoms in children and adolescents, conducting diagnostic assessments, and implementing appropriate treatment and support interventions.
Step 9: Continuous Feedback and Policy Adaptation
The continuous evolution of the post–COVID-19 phenomenon demands an iterative approach to policy making. On the basis of our study, we recommend establishing feedback mechanisms with HCWs and school staff to monitor the reception and effectiveness of implemented policies. This feedback, coupled with ongoing research, should inform policy adaptations to ensure they remain aligned with the evolving landscape of post–COVID-19 condition and its impact on children and young people.
Step 10: Evaluation and Research
Finally, there should be a commitment to ongoing evaluation and research. This will involve not only monitoring the implementation of the abovementioned steps but also supporting new research to fill any remaining gaps in understanding the long-term effects of COVID-19 on children and young people.
This sequence of steps is designed to be iterative and responsive, ensuring that the recommendations from the study are translated into concrete actions that adapt to emerging data and research findings.
Strengths and Limitations
A key strength of this study is that our social media analysis of post–COVID-19 condition contributes toward an emerging understanding of reported experiential, emotional, and practical dimensions of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people specifically and questions of vaccine hesitancy in children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition. This is one of the few studies to collect HCWs’ perceptions regarding post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people in the United Kingdom using information from Twitter. We identify key areas that need considering attention and focus, such as the provision of psychosocial support with access to quality mental health resources to alleviate the impact of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people and the development of clear post–COVID-19 pandemic recovery guidelines that are informed by health equity perspective, and how this affects children and young people living with post–COVID-19 condition.
One of the limitations this study acknowledges is the definition of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people. When data were collected, the lack of consensus on the definition of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people forced us to formulate a definition of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people based on the available literature. Furthermore, this study is limited to the perceptions of people who used descriptors in their web biography attributable to HCWs; therefore, our results only represent some HCWs in the United Kingdom and those in other countries. In turn, this research collected data from Twitter only; therefore, further inquiry into HCWs’ perceptions of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people required expanding to other data sources or social networks and including languages other than English. We acknowledge that demographic factors, geographic location, and individual daily activities of social media users can significantly influence language use and word choice, introducing potential biases in tweet-based data. Such biases are inherent in any analysis of social media content and can affect the generalizability of findings. For instance, our study relies on Twitter data, which do not encompass the full spectrum of global or the UK public opinion on post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people. While Twitter serves as a valuable platform for capturing real-time sentiments and experiences, it is not fully representative of all demographics and geographic regions. Our results may reflect the perspectives of more vocal or active social media users, which may not correspond to the silent majority or those without access to social media. In addition, the absence of geotagged information for many users limits our ability to conduct a more nuanced spatial analysis of the sentiments expressed.
Furthermore, our study is built upon the recognition that social media data may overrepresent certain demographic groups while underrepresenting others, such as the older population or those without reliable internet access. This skew can influence the apparent prevalence of certain views or experiences of post–COVID-19 condition. Moreover, individuals’ patterns of daily life, reflected in their social media use and content, contribute additional layers of complexity and potential bias to the discourse analyzed.
Consistent with scholarly precedents on the subject [ 62 , 63 ], our study acknowledges these biases as intrinsic limitations of social media–based research. Although our analysis did not control for these factors, we recognize their potential impact on our results. Future studies would benefit from incorporating a broader array of data sources, including interviews or focus groups, to provide a more representative and comprehensive understanding of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people. This approach would complement our Twitter-based findings and help mitigate the biases inherent in social media data.
Conclusions
More than a year after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, the perceptions described on Twitter by HCWs concerning the presence of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people appear to be a relevant and timely issue as well as very responsive to the declarations and guidelines issued by the health authorities over time. The most prominent group within the discourse studied was the activist or lobbying organization @LongCovidKids, which shared the most tweets and images over the period studied. We recommend that future research focus on how web health activism is organized and carried out for children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition. Such a strategy would allow for a better understanding of the scope and impact of this phenomenon and how it can influence decision-making. Furthermore, we suggest different mitigation strategies, support, and training of HCWs and school staff regarding manifestations and treatment of post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people across all demographic areas.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Rapid Research Evaluation and Assessment Lab, Department of Targeted Intervention, University College London, London, United Kingdom, whose support has been essential for developing this project.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
Filters used for the search strategy on Twitter.
Sentiment analysis framework: attitudes toward post–COVID-19 condition in children and young people.
Theme codebook: examples of tweets that fit into main themes tagged for mention of children and young people with post–COVID-19 condition.
Timeline of national governmental policies and guidelines regarding children and young people.
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) Global research and innovation forum. Global Research Collaboration for Infectious Disease Preparedness. Feb 12, 2020. URL: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-public-health-emergency-of-international-concern-(pheic)-global-research-and-inno vation-forum [accessed 2022-06-06]
- Johns Hopkins University of Medicine. COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). Coronavirus Resource Center. Jan 22, 2020. URL: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html [accessed 2023-06-09]
- Nature Editorial. Long COVID and kids: more research is urgently needed. Nature. Feb 08, 2022;602(7896):183. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Long COVID or post-COVID conditions. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. URL: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/long-term-effects/index.html [accessed 2023-06-09]
- Davis HE, McCorkell L, Vogel JM, Topol E. Long COVID: major findings, mechanisms and recommendations. Nat Rev Microbiol. Mar 13, 2023;21(3):133-146. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Zimmermann P, Curtis N. Why is COVID-19 less severe in children? A review of the proposed mechanisms underlying the age-related difference in severity of SARS-CoV-2 infections. Arch Dis Child. Dec 01, 2020;106(5):429-439. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Zheng YB, Zeng N, Yuan K, Tian SS, Yang YB, Gao N, et al. Prevalence and risk factor for long COVID in children and adolescents: a meta-analysis and systematic review. J Infect Public Health. Mar 07, 2023;16(5):660-672. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- World Health Organization. A clinical case definition for post COVID-19 condition in children and adolescents by expert consensus. World Health Organization. Feb 16, 2023. URL: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-Post -COVID-19-condition-CA-Clinical-case-definition-2023-1 [accessed 2024-03-26]
- Stephenson T, Allin B, Nugawela MD, Rojas N, Dalrymple E, Pinto Pereira S, CLoCk Consortium, et al. Long COVID (post-COVID-19 condition) in children: a modified Delphi process. Arch Dis Child. Jun 17, 2022;107(7):674-680. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Esposito S, Principi N, Azzari C, Cardinale F, Di Mauro G, Galli L, et al. Italian intersociety consensus on management of long Covid in children. Ital J Pediatr. Mar 09, 2022;48(1):1-9. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Stephenson T, Pinto Pereira SM, Shafran R, de Stavola BL, Rojas N, McOwat K, CLoCk Consortium, et al. Physical and mental health 3 months after SARS-CoV-2 infection (long COVID) among adolescents in England (CLoCk): a national matched cohort study. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. Feb 08, 2022;6(4):230-239. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Stephenson T, Pinto Pereira SM, Nugawela MD, McOwat K, Simmons R, Chalder T, et al. CLoCk Consortium. Long COVID-six months of prospective follow-up of changes in symptom profiles of non-hospitalised children and young people after SARS-CoV-2 testing: a national matched cohort study (The CLoCk) study. PLoS One. Mar 6, 2023;18(3):e0277704. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Twitter users, stats, data and trends. Data Reportal. May 11, 2023. URL: https://datareportal.com/essential-twitter-stats#:~ :text=Based [accessed 2023-06-09]
- Rufai SR, Bunce C. World leaders' usage of Twitter in response to the COVID-19 pandemic: a content analysis. J Public Health (Oxf). Aug 18, 2020;42(3):510-516. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Haman M. The use of Twitter by state leaders and its impact on the public during the COVID-19 pandemic. Heliyon. Nov 2020;6(11):e05540. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Huang X, Li Z, Jiang Y, Li X, Porter D. Twitter reveals human mobility dynamics during the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS One. Nov 10, 2020;15(11):e0241957. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Wicke P, Bolognesi MM. Framing COVID-19: how we conceptualize and discuss the pandemic on Twitter. PLoS One. Sep 30, 2020;15(9):e0240010. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chang CH, Monselise M, Yang CC. What are people concerned about during the pandemic? detecting evolving topics about COVID-19 from Twitter. J Healthc Inform Res. Jan 17, 2021;5(1):70-97. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Xue J, Chen J, Hu R, Chen C, Zheng C, Su Y, et al. Twitter discussions and emotions about the COVID-19 pandemic: machine learning approach. J Med Internet Res. Nov 25, 2020;22(11):e20550. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Boon-Itt S, Skunkan Y. Public perception of the COVID-19 pandemic on Twitter: sentiment analysis and topic modeling study. JMIR Public Health Surveill. Nov 11, 2020;6(4):e21978. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Valdez D, Ten Thij M, Bathina K, Rutter LA, Bollen J. Social media insights into US mental health during the COVID-19 pandemic: longitudinal analysis of Twitter data. J Med Internet Res. Dec 14, 2020;22(12):e21418. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Rashid MA, Yip SW, Gill D, Arfeen Z. Sharing is caring: an analysis of #FOAMed Twitter posts during the COVID-19 pandemic. Postgrad Med J. Mar 14, 2022;98(1157):199-204. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ghosh P, Schwartz G, Narouze S. Twitter as a powerful tool for communication between pain physicians during COVID-19 pandemic. Reg Anesth Pain Med. Feb 21, 2021;46(2):187-188. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Burgos LM, Gil Ramirez A, Utengen A, Thamman R. Use of Twitter during COVID-19 pandemic: an opportunity for continuing medical education in cardiology. Medicina (B Aires). 2020;80 Suppl 6:122-123. [ FREE Full text ] [ Medline ]
- Margus C, Brown N, Hertelendy AJ, Safferman MR, Hart A, Ciottone GR. Emergency physician Twitter use in the COVID-19 pandemic as a potential predictor of impending surge: retrospective observational study. J Med Internet Res. Jul 14, 2021;23(7):e28615. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Pulsar TRAC- Audience intelligence platform and social listening tool. Pulsar. URL: https://www.pulsarplatform.com/solutions/pulsar-trac/ [accessed 2022-03-01]
- Vera San Juan N, Aceituno D, Djellouli N, Sumray K, Regenold N, Syversen A, et al. Mental health and well-being of healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic in the UK: contrasting guidelines with experiences in practice. BJPsych Open. Dec 10, 2020;7(1):e15. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Paranyushkin D. InfraNodus: generating insight using text network analysis. In: Proceedings of the World Wide Web Conference. 2019. Presented at: WWW '19; May 13-17, 2019; San Francisco, CA. [ CrossRef ]
- Creswell JW, Poth CN. Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches 4th Edition. Thousand Oaks, CA. SAGE Publications, Inc; 2017.
- Eysenbach G, Till JE. Ethical issues in qualitative research on internet communities. BMJ. Nov 10, 2001;323(7321):1103-1105. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- UCL research ethics. University College London. URL: https://www.ucl.ac.uk/research-ethics/do-i-need-ethical-approval# When [accessed 2023-06-12]
- Martin S, Kilich E, Dada S, Kummervold PE, Denny C, Paterson P, et al. "Vaccines for pregnant women…?! Absurd" - Mapping maternal vaccination discourse and stance on social media over six months. Vaccine. Sep 29, 2020;38(42):6627-6637. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kummervold PE, Martin S, Dada S, Kilich E, Denny C, Paterson P, et al. Categorizing vaccine confidence with a transformer-based machine learning model: analysis of nuances of vaccine sentiment in Twitter discourse. JMIR Med Inform. Oct 08, 2021;9(10):e29584. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ahmed W, Bath PA, Demartini G. Using Twitter as a data source: an overview of ethical, legal, and methodological challenges. In: Woodfield K, editor. The Ethics of Online Research. Bingley, UK. Emerald Publishing Limited; Dec 12, 2017.
- Ayers JW, Caputi TL, Nebeker C, Dredze M. Don't quote me: reverse identification of research participants in social media studies. NPJ Digit Med. Aug 2, 2018;1(1):30. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Varkey B. Principles of clinical ethics and their application to practice. Med Princ Pract. Jun 4, 2021;30(1):17-28. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Long Covid Kids homepage. Long Covid Kids. URL: https://es.longcovidkids.org/ [accessed 2023-06-12]
- The Guardian homepage. The Guardian. URL: https://www.theguardian.com/uk [accessed 2023-06-12]
- Welcome to the BBC. BBC. URL: https://www.bbc.com/ [accessed 2023-06-12]
- People with health. PeopleWith. URL: https://peoplewith.com/ [accessed 2023-06-12]
- Welcome to NCBI. National Institutes of Health National Library of Medicine. URL: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ [accessed 2023-06-12]
- Edobor M. Trust and public discourse during the Covid‐19 pandemic. IPPR Progress Rev. Feb 15, 2021;27(4):354-360. [ CrossRef ]
- Nielsen RK, Fletcher R, Kalogeropoulos A, Simon F. Communications in the coronavirus crisis: lessons for the second wave. Reuters Institute for the Study of Journalism. Oct 27, 2020. URL: https://reutersinstitute.politics.ox.ac.uk/communications-coronavirus-crisis-lessons-second-wave [accessed 2024-03-26]
- Zohar T, Negev M, Sirkin M, Levine H. Trust in COVID-19 policy among public health professionals in Israel during the first wave of the pandemic: a cross-sectional study. Isr J Health Policy Res. Apr 11, 2022;11(1):20. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Enria L, Waterlow N, Rogers NT, Brindle H, Lal S, Eggo RM, et al. Trust and transparency in times of crisis: results from an online survey during the first wave (April 2020) of the COVID-19 epidemic in the UK. PLoS One. Feb 16, 2021;16(2):e0239247. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Fotheringham P, Harriott T, Healy G, Arenge G, Wilson E. Pressures and influences on school leaders navigating policy development during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Brit Educ Res J. Jul 30, 2021;48(2):201-227. [ CrossRef ]
- Thomson P, Greany T, Martindale N. The trust deficit in England: emerging research evidence about school leaders and the pandemic. J Educ Admin History. Sep 13, 2021;53(3-4):296-300. [ CrossRef ]
- Callard F, Perego E. How and why patients made long COVID. Soc Sci Med. Jan 2021;268:113426. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Davis HE, Assaf GS, McCorkell L, Wei H, Low RJ, Re'em Y, et al. Characterizing long COVID in an international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact. EClinicalMedicine. Aug 2021;38:101019. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Miyake E, Martin S. Long Covid: online patient narratives, public health communication and vaccine hesitancy. Digit Health. Nov 29, 2021;7:20552076211059649. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Matharaarachchi S, Domaratzki M, Katz A, Muthukumarana S. Discovering long COVID symptom patterns: association rule mining and sentiment analysis in social media tweets. JMIR Form Res. Sep 07, 2022;6(9):e37984. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bhattacharyya A, Seth A, Rai S. The effects of long COVID-19, its severity, and the need for immediate attention: analysis of clinical trials and Twitter data. Front Big Data. Dec 15, 2022;5:1051386. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Samannodi M, Alwafi H, Naser AY, Al Qurashi AA, Qedair JT, Salawati E, et al. Determinants of post-COVID-19 conditions among SARS-CoV-2-infected patients in Saudi Arabia: a web-based cross-sectional study. Diseases. Aug 23, 2022;10(3):55. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Santarossa S, Rapp A, Sardinas S, Hussein J, Ramirez A, Cassidy-Bushrow AE, et al. Understanding the #longCOVID and #longhaulers conversation on Twitter: multimethod study. JMIR Infodemiology. 2022;2(1):e31259. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Déguilhem A, Malaab J, Talmatkadi M, Renner S, Foulquié P, Fagherazzi G, et al. Identifying profiles and symptoms of patients with long COVID in France: data mining infodemiology study based on social media. JMIR Infodemiology. Nov 22, 2022;2(2):e39849. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Awoyemi T, Ebili U, Olusanya A, Ogunniyi KE, Adejumo AV. Twitter sentiment analysis of long COVID syndrome. Cureus. Jun 2022;14(6):e25901. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Malone LA, Morrow A, Chen Y, Curtis D, de Ferranti SD, Desai M, et al. Multi-disciplinary collaborative consensus guidance statement on the assessment and treatment of postacute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC) in children and adolescents. PM R. Oct 2022;14(10):1241-1269. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Shachar-Lavie I, Shorer M, Segal H, Fennig S, Ashkenazi-Hoffnung L. Mental health among children with long COVID during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur J Pediatr. Apr 14, 2023;182(4):1793-1801. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Brackel CL, Noij LC, Vijverberg SJ, Legghe CL, Maitland-van der Zee AH, van Goudoever JB, et al. International care programs for pediatric post-COVID condition (long COVID) and the way forward. Pediatr Res. Jan 29, 2024. (forthcoming). [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ripp J, Peccoralo L, Charney D. Attending to the emotional well-being of the health care workforce in a New York City health system during the COVID-19 pandemic. Acad Med. Aug 2020;95(8):1136-1139. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Buonsenso D, Camporesi A, Morello R, De Rose C, Fracasso M, Chieffo DP, et al. Social stigma in children with long COVID. Children (Basel). Sep 07, 2023;10(9):1518. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Mitchell L, Frank MR, Harris KD, Dodds PS, Danforth CM. The geography of happiness: connecting twitter sentiment and expression, demographics, and objective characteristics of place. PLoS One. May 29, 2013;8(5):e64417. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Padilla JJ, Kavak H, Lynch CJ, Gore RJ, Diallo SY. Temporal and spatiotemporal investigation of tourist attraction visit sentiment on Twitter. PLoS One. Jun 14, 2018;13(6):e0198857. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
Abbreviations
Edited by A Mavragani; submitted 20.06.23; peer-reviewed by R Gore, A Wahbeh; comments to author 02.11.23; revised version received 14.02.24; accepted 08.03.24; published 17.04.24.
©Macarena Chepo, Sam Martin, Noémie Déom, Ahmad Firas Khalid, Cecilia Vindrola-Padros. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 17.04.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://www.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 17.4.2024 in Vol 4 (2024)
Evaluating the Disease-Related Experiences of TikTok Users With Lupus Erythematosus: Qualitative and Content Analysis
Authors of this article:

There are no citations yet available for this article according to Crossref .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative Research Examples. 1. Ethnography. Definition: Ethnography is a qualitative research design aimed at exploring cultural phenomena. Rooted in the discipline of anthropology, this research approach investigates the social interactions, behaviors, and perceptions within groups, communities, or organizations.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc. Qualitative research question examples
Examples of Qualitative Research. You have probably seen examples of qualitative research before, but you might not have paid particular attention to how they were produced or realized that the accounts you were reading were the result of hours, months, even years of research "in the field." A good qualitative researcher will present the ...
Examples of Qualitative Research. Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research: Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors ...
Qualitative research: methods and examples. Qualitative research is an excellent way to gain insight into real-world problems. This research type can explain various aspects of individuals in a target group, such as their traits, behaviors, and motivations. Qualitative research involves gathering and evaluating non-numerical information to ...
Qualitative research is defined as an exploratory method that aims to understand complex phenomena, often within their natural settings, by examining subjective experiences, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. Learn more about qualitative research methods, types, examples and best practices.
Qualitative research is defined as a market research method that focuses on obtaining data through open-ended and conversational communication. This method is about "what" people think and "why" they think so. For example, consider a convenience store looking to improve its patronage.
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data. The findings of qualitative research are expressed in words and help in understanding individuals' subjective perceptions about an event, condition, or subject. This type of research is exploratory and is used to generate hypotheses or theories ...
QDA Method #1: Qualitative Content Analysis. Content analysis is possibly the most common and straightforward QDA method. At the simplest level, content analysis is used to evaluate patterns within a piece of content (for example, words, phrases or images) or across multiple pieces of content or sources of communication. For example, a collection of newspaper articles or political speeches.
Researchers in social sciences and humanities often use qualitative research methods, especially in specific areas of study like anthropology, history, education, and sociology. Qualitative methods are also applicable in business, technology, and marketing spaces. For example, product managers use qualitative research to understand how target ...
25 examples of expertly crafted qualitative research questions. It's easy enough to cover the theory of writing a qualitative research question, but sometimes it's best if you can see the process in practice. In this section, we'll list 25 examples of B2B and B2C-related qualitative questions. Let's begin with five questions.
Types of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research. Qualitative research employs different data analysis methods, each suited to specific research goals: Thematic Analysis: Identifies recurring themes or concepts within data. Content Analysis: Systematically categorizes and quantifies text or media content.
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] ... (qualitative research). In this example, the researcher has used qualitative research methods (interviews and focus groups) to generate a list of ideas of both why teens start to smoke as well as factors that may have prevented ...
Qualitative data analysis is a systematic process of examining non-numerical data to extract meaning, patterns, and insights. In contrast to quantitative analysis, which focuses on numbers and statistical metrics, the qualitative study focuses on the qualitative aspects of data, such as text, images, audio, and videos.
Qualitative research is a behavioral research method that seeks to understand the undertones, motivations, and subjective interpretations inherent in human behavior. It involves gathering nonnumerical data, such as text, audio, and video, allowing you to explore nuances and patterns that quantitative data can't capture.
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive, allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.. Qualitative research example If you want to generate new ideas for online teaching strategies, a qualitative approach would make the most sense. You can use this type of research to explore exactly what teachers and students struggle ...
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history. Qualitative research question examples
The UK Data Service describes this perfectly, saying, "The value of qualitative research is that it gives a voice to the lived experience .". Read on to see seven use cases and 83 qualitative research questions, with the added bonus of examples that show how to get similar insights faster with Similarweb Digital Research Intelligence.
February 2015. by Erin E. Toolis and Phillip L. Hammack. Lifetime Activism, Marginality, and Psychology: Narratives of Lifelong Feminist Activists Committed to Social Change (PDF, 93KB) August 2014. by Anjali Dutt and Shelly Grabe. Qualitative Inquiry in the History of Psychology (PDF, 82KB) February 2014. by Frederick J. Wertz.
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge. Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions.
Qualitative data in a workplace. Here are examples of how people in various industries may use qualitative observations to perform their work: 11. Scientist: "The solution turned red when we added vinegar." 12. Psychologist: "The child was lethargic and disinterested in her toys.". 13.
QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PAPER 45 research problem. For example, the purpose of this study is to examine the prevalence of the use of synthetic marijuana use among preteens which will lead to a prevention and intervention model to be used in community centers citywide. Significance of the Study
Qualitative research provides valuable insights into health care interactions and decision-making processes - for example, why and how a clinician may ignore prevailing evidence and continue making clinical decisions the way they always have.1 The perception of qualitative health care research has improved since a 2016 article by Greenhalgh et al. highlighted the higher contributions and ...
This paper, on qualitative thematic analysis (QTA) in social change research, falls somewhere between a reflective piece and a how-to guide. Using two examples from my own previous research, I discuss why QTA in the field of social change or social justice, which often analyzes the words of vulnerable, marginalized, or underserved populations, is so fraught, so contested, and so often dismissed.
Introduction. Field research is a method of research that deals with understanding and interpreting the social interactions of groups of people and communities by observing and dealing with people in their natural settings. The field research methods involve direct observation, participant observation, and qualitative interviews.
The long-term aim of this research is to establish a formalized ISM or additive manufacturing using 3D-Technology. The ISM offers a solution for flexible and sustainable missions both in transit and on the surface via on-demand repair, fabrication, and recycling abilities for habitats, critical systems, and mission logistics and maintenance.
Results: We obtained 300,000 tweets, out of which (after filtering for relevant tweets) we performed an in-depth qualitative sample analysis of 2588 tweets. The HCWs were responsive to announcements issued by the authorities regarding the management of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom. The most frequent sentiment expressed was negative.
A Health Literacy Assessment Tool for Patient Care and Research The Newest Vital Sign (NVS) is a valid and reliable screening tool available in English and Spanish that identifies patients at risk for low health literacy. It is easy and quick to administer, requiring just three minutes. In clinical settings, the test allows providers to appropriately adapt their communication practices to the ...
Background: Lupus erythematosus (LE) is an autoimmune condition that is associated with significant detriments to quality of life and daily functioning. TikTok, a popular social networking platform for sharing short videos, provides a unique opportunity to understand experiences with LE within a nonclinical sample, a population that is understudied in LE research.