Case Study Summarizer #1 — Free Summaries!
Have you ever thought of how many case studies must a student in medicine or business read in their lifetime? Tens, hundreds, or even thousands! As practice shows, the case study’s content is jam-packed with information and broad descriptions that are unnecessary when conducting a review or simply reading the literature.
We offer a Case Study Summarizer to scan any paper in seconds! You will get some valuable insights about our tool that can help with the most extended case studies in a short time! Moreover, we discuss the definition of the case study, its structure, and its main elements. Let’s begin!
- 🧰 How to Use the Tool?

📋 What Is the Case Study Summarizer?
🧩 case study elements & structure, 🧑🏫 how to summarize a case study.
- ✅ 5 Tool’s Benefits
🖇️ References
🧰 how to use the case summarizer.
Our free case study summarizer is so easy to use! Follow these 4 simple steps:
- Enter the text . Paste the text of the case study in the appropriate field of the tool. Ensure that it does not exceed 15,000 characters.
- Adjust settings . You can choose the number of sentences you want in your summary and decide whether to highlight keywords.
- Press the button . Just click the button, and the results will not keep you waiting!
- Copy the result . Your summary will appear in just a few seconds! All you need to do is just copy it in one click.
Do you still have concerns about using our case study summarizer? Then check out its incredible features:
A case study is typically presented as a report, separated into sections with headings and subheadings. It must contain a description of the issue, an explanation of the relevance of the case, and an analysis with conclusions. It ends with implications and recommendations on how to address the issue.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a detailed investigation of one person, group, or event. It aims to learn as much as possible about an individual or a group to generalize the findings on other similar cases. The case study can be employed in various fields, including psychology , medicine , social work, etc.
Here are some case study topics from different professional spheres:
- Medicine : Analysis of the medical and occupational records of a non-smoking individual with lung cancer.
- Business : The decision of Warren Buffett to acquire Precision Castparts Corporation and why that acquisition was a mistake.
- Psychology : The case of Bertha Pappenheim , who suffered from hysteria and contributed to the development of talk therapy to treat mental illness.
Case Study Elements
There are 8 essential elements in any case study. Check the table below to learn more details about each component.
Summarizing is a fundamental skill for everyone since it allows you to distinguish essential information and effectively communicate it to others. In the following paragraphs, we will share a case study summary tutorial.
Executive Summary Case Study
An executive summary is a detailed overview of a report. It saves readers time by summarizing the essential points of the study. It is frequently written to be shared with people who may not have time to read the complete report, for example, CEOs or department heads.
Although the format may vary, the primary elements of an executive summary are as follows:
- An opening statement and some background information .
- The purpose of the report.
- Methodology.
- Summarized and justified recommendations.
How Long Is an Executive Summary?
Your executive summary’s length will vary depending on the text it summarizes. Typically, it takes 10-15% of the full report’s length . Therefore, an executive summary can range from 1 paragraph to 10 pages.
Case Study Summary Guide
Take these 5 steps to write a compelling case study summary:
Step 1 – Read the entire study
Before writing the summary, carefully read the research study from beginning to end.
Step 2 – Highlight the major points
As you read, make notes and underline significant facts, relevant conclusions, and suggested actions.
Step 3 – Divide the document into main sections
Determine what each part of the report is about, and summarize each in a few sentences. You can use the executive summary structure mentioned above to guide your writing.
Step 4 – Be concise
Do not write more than 10% of the length of the original document.
Step 5 – Proofread your summary
Reread your case study summary to ensure it makes sense as an independent piece of writing. Set it aside for a while and look at it with fresh eyes to notice any incoherence and redundant or lacking details.
✒️️ Case Study Summary Example
We have prepared an example of a case study summary for you to see how everything works in practice!
Here is the full report: Akron’s Children’s Hospital: Case Study .
Now, check its summarized version:
Akron Children’s Hospital is a leading pediatric hospital in Northeastern Ohio that faces competition and needs to differentiate itself to attract more patients. To gain insight into the decision-making process of patients' parents, the hospital hired a team of researchers led by Marcus Thomas LLC to conduct business and market analysis.
An observational study was conducted to collect consumer data, including perceptions of the hospital and the criteria used to select it. The problem was that a highly competitive medical industry in Northeastern Ohio resulted in reduced patient volume and financial losses at Akron Children’s Hospital.
The proposed solution was to rethink the hospital’s operations and marketing approach to differentiate it from the competitors and attract more patients. Furthermore, the treatment of certain groups of children had to be improved by increasing the number of specializations available at the hospital.
The organization was recommended to develop an efficient marketing strategy, enhance service delivery, and implement highly innovative medical technologies and procedures.
✅ 5 Benefits of the Case Summarizer You Should Consider
Still in doubt whether our case study summary tool is worth using? Check out its benefits:
- It is time-saving . The online tool is perfect for students in medicine or psychology since it allows for consuming a lot of information in a short time.
- It is easy to use . The interface of our case summarizer is so simple to navigate that even a child can handle it.
- It is unlimited . Try our online summarizer as many times as you need. There are no limitations!
- It is free . You can summarize a case study online in a few minutes without spending money. Such a considerable benefit for prudent students!
- It is accurate . The case summary generator uses essential keywords and phrases to isolate only the most relevant information.
- Executive Summary | USC Libraries
- Case Studies | Carnegie Mellon University
- Writing a Case Study | Monash University
- Guidelines for Writing a Summary | Hunter College
- Executive Summaries | Colorado State University
How to write a case study — examples, templates, and tools

It’s a marketer’s job to communicate the effectiveness of a product or service to potential and current customers to convince them to buy and keep business moving. One of the best methods for doing this is to share success stories that are relatable to prospects and customers based on their pain points, experiences, and overall needs.
That’s where case studies come in. Case studies are an essential part of a content marketing plan. These in-depth stories of customer experiences are some of the most effective at demonstrating the value of a product or service. Yet many marketers don’t use them, whether because of their regimented formats or the process of customer involvement and approval.
A case study is a powerful tool for showcasing your hard work and the success your customer achieved. But writing a great case study can be difficult if you’ve never done it before or if it’s been a while. This guide will show you how to write an effective case study and provide real-world examples and templates that will keep readers engaged and support your business.
In this article, you’ll learn:
What is a case study?
How to write a case study, case study templates, case study examples, case study tools.
A case study is the detailed story of a customer’s experience with a product or service that demonstrates their success and often includes measurable outcomes. Case studies are used in a range of fields and for various reasons, from business to academic research. They’re especially impactful in marketing as brands work to convince and convert consumers with relatable, real-world stories of actual customer experiences.
The best case studies tell the story of a customer’s success, including the steps they took, the results they achieved, and the support they received from a brand along the way. To write a great case study, you need to:
- Celebrate the customer and make them — not a product or service — the star of the story.
- Craft the story with specific audiences or target segments in mind so that the story of one customer will be viewed as relatable and actionable for another customer.
- Write copy that is easy to read and engaging so that readers will gain the insights and messages intended.
- Follow a standardized format that includes all of the essentials a potential customer would find interesting and useful.
- Support all of the claims for success made in the story with data in the forms of hard numbers and customer statements.
Case studies are a type of review but more in depth, aiming to show — rather than just tell — the positive experiences that customers have with a brand. Notably, 89% of consumers read reviews before deciding to buy, and 79% view case study content as part of their purchasing process. When it comes to B2B sales, 52% of buyers rank case studies as an important part of their evaluation process.
Telling a brand story through the experience of a tried-and-true customer matters. The story is relatable to potential new customers as they imagine themselves in the shoes of the company or individual featured in the case study. Showcasing previous customers can help new ones see themselves engaging with your brand in the ways that are most meaningful to them.
Besides sharing the perspective of another customer, case studies stand out from other content marketing forms because they are based on evidence. Whether pulling from client testimonials or data-driven results, case studies tend to have more impact on new business because the story contains information that is both objective (data) and subjective (customer experience) — and the brand doesn’t sound too self-promotional.

Case studies are unique in that there’s a fairly standardized format for telling a customer’s story. But that doesn’t mean there isn’t room for creativity. It’s all about making sure that teams are clear on the goals for the case study — along with strategies for supporting content and channels — and understanding how the story fits within the framework of the company’s overall marketing goals.
Here are the basic steps to writing a good case study.
1. Identify your goal
Start by defining exactly who your case study will be designed to help. Case studies are about specific instances where a company works with a customer to achieve a goal. Identify which customers are likely to have these goals, as well as other needs the story should cover to appeal to them.
The answer is often found in one of the buyer personas that have been constructed as part of your larger marketing strategy. This can include anything from new leads generated by the marketing team to long-term customers that are being pressed for cross-sell opportunities. In all of these cases, demonstrating value through a relatable customer success story can be part of the solution to conversion.
2. Choose your client or subject
Who you highlight matters. Case studies tie brands together that might otherwise not cross paths. A writer will want to ensure that the highlighted customer aligns with their own company’s brand identity and offerings. Look for a customer with positive name recognition who has had great success with a product or service and is willing to be an advocate.
The client should also match up with the identified target audience. Whichever company or individual is selected should be a reflection of other potential customers who can see themselves in similar circumstances, having the same problems and possible solutions.
Some of the most compelling case studies feature customers who:
- Switch from one product or service to another while naming competitors that missed the mark.
- Experience measurable results that are relatable to others in a specific industry.
- Represent well-known brands and recognizable names that are likely to compel action.
- Advocate for a product or service as a champion and are well-versed in its advantages.
Whoever or whatever customer is selected, marketers must ensure they have the permission of the company involved before getting started. Some brands have strict review and approval procedures for any official marketing or promotional materials that include their name. Acquiring those approvals in advance will prevent any miscommunication or wasted effort if there is an issue with their legal or compliance teams.
3. Conduct research and compile data
Substantiating the claims made in a case study — either by the marketing team or customers themselves — adds validity to the story. To do this, include data and feedback from the client that defines what success looks like. This can be anything from demonstrating return on investment (ROI) to a specific metric the customer was striving to improve. Case studies should prove how an outcome was achieved and show tangible results that indicate to the customer that your solution is the right one.
This step could also include customer interviews. Make sure that the people being interviewed are key stakeholders in the purchase decision or deployment and use of the product or service that is being highlighted. Content writers should work off a set list of questions prepared in advance. It can be helpful to share these with the interviewees beforehand so they have time to consider and craft their responses. One of the best interview tactics to keep in mind is to ask questions where yes and no are not natural answers. This way, your subject will provide more open-ended responses that produce more meaningful content.
4. Choose the right format
There are a number of different ways to format a case study. Depending on what you hope to achieve, one style will be better than another. However, there are some common elements to include, such as:
- An engaging headline
- A subject and customer introduction
- The unique challenge or challenges the customer faced
- The solution the customer used to solve the problem
- The results achieved
- Data and statistics to back up claims of success
- A strong call to action (CTA) to engage with the vendor
It’s also important to note that while case studies are traditionally written as stories, they don’t have to be in a written format. Some companies choose to get more creative with their case studies and produce multimedia content, depending on their audience and objectives. Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more.
5. Write your case study
We’ll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few things to keep in mind when writing your case study.
- Be clear and concise. Readers want to get to the point of the story quickly and easily, and they’ll be looking to see themselves reflected in the story right from the start.
- Provide a big picture. Always make sure to explain who the client is, their goals, and how they achieved success in a short introduction to engage the reader.
- Construct a clear narrative. Stick to the story from the perspective of the customer and what they needed to solve instead of just listing product features or benefits.
- Leverage graphics. Incorporating infographics, charts, and sidebars can be a more engaging and eye-catching way to share key statistics and data in readable ways.
- Offer the right amount of detail. Most case studies are one or two pages with clear sections that a reader can skim to find the information most important to them.
- Include data to support claims. Show real results — both facts and figures and customer quotes — to demonstrate credibility and prove the solution works.
6. Promote your story
Marketers have a number of options for distribution of a freshly minted case study. Many brands choose to publish case studies on their website and post them on social media. This can help support SEO and organic content strategies while also boosting company credibility and trust as visitors see that other businesses have used the product or service.
Marketers are always looking for quality content they can use for lead generation. Consider offering a case study as gated content behind a form on a landing page or as an offer in an email message. One great way to do this is to summarize the content and tease the full story available for download after the user takes an action.
Sales teams can also leverage case studies, so be sure they are aware that the assets exist once they’re published. Especially when it comes to larger B2B sales, companies often ask for examples of similar customer challenges that have been solved.
Now that you’ve learned a bit about case studies and what they should include, you may be wondering how to start creating great customer story content. Here are a couple of templates you can use to structure your case study.
Template 1 — Challenge-solution-result format
- Start with an engaging title. This should be fewer than 70 characters long for SEO best practices. One of the best ways to approach the title is to include the customer’s name and a hint at the challenge they overcame in the end.
- Create an introduction. Lead with an explanation as to who the customer is, the need they had, and the opportunity they found with a specific product or solution. Writers can also suggest the success the customer experienced with the solution they chose.
- Present the challenge. This should be several paragraphs long and explain the problem the customer faced and the issues they were trying to solve. Details should tie into the company’s products and services naturally. This section needs to be the most relatable to the reader so they can picture themselves in a similar situation.
- Share the solution. Explain which product or service offered was the ideal fit for the customer and why. Feel free to delve into their experience setting up, purchasing, and onboarding the solution.
- Explain the results. Demonstrate the impact of the solution they chose by backing up their positive experience with data. Fill in with customer quotes and tangible, measurable results that show the effect of their choice.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that invites readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to nurture them further in the marketing pipeline. What you ask of the reader should tie directly into the goals that were established for the case study in the first place.
Template 2 — Data-driven format
- Start with an engaging title. Be sure to include a statistic or data point in the first 70 characters. Again, it’s best to include the customer’s name as part of the title.
- Create an overview. Share the customer’s background and a short version of the challenge they faced. Present the reason a particular product or service was chosen, and feel free to include quotes from the customer about their selection process.
- Present data point 1. Isolate the first metric that the customer used to define success and explain how the product or solution helped to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 2. Isolate the second metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Present data point 3. Isolate the final metric that the customer used to define success and explain what the product or solution did to achieve this goal. Provide data points and quotes to substantiate the claim that success was achieved.
- Summarize the results. Reiterate the fact that the customer was able to achieve success thanks to a specific product or service. Include quotes and statements that reflect customer satisfaction and suggest they plan to continue using the solution.
- Ask for action. Include a CTA at the end of the case study that asks readers to reach out for more information, try a demo, or learn more — to further nurture them in the marketing pipeline. Again, remember that this is where marketers can look to convert their content into action with the customer.
While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success.
Juniper Networks
One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study , which puts the reader in the customer’s shoes. The beginning of the story quickly orients the reader so that they know exactly who the article is about and what they were trying to achieve. Solutions are outlined in a way that shows Adobe Experience Manager is the best choice and a natural fit for the customer. Along the way, quotes from the client are incorporated to help add validity to the statements. The results in the case study are conveyed with clear evidence of scale and volume using tangible data.

The story of Lenovo’s journey with Adobe is one that spans years of planning, implementation, and rollout. The Lenovo case study does a great job of consolidating all of this into a relatable journey that other enterprise organizations can see themselves taking, despite the project size. This case study also features descriptive headers and compelling visual elements that engage the reader and strengthen the content.
Tata Consulting
When it comes to using data to show customer results, this case study does an excellent job of conveying details and numbers in an easy-to-digest manner. Bullet points at the start break up the content while also helping the reader understand exactly what the case study will be about. Tata Consulting used Adobe to deliver elevated, engaging content experiences for a large telecommunications client of its own — an objective that’s relatable for a lot of companies.
Case studies are a vital tool for any marketing team as they enable you to demonstrate the value of your company’s products and services to others. They help marketers do their job and add credibility to a brand trying to promote its solutions by using the experiences and stories of real customers.
When you’re ready to get started with a case study:
- Think about a few goals you’d like to accomplish with your content.
- Make a list of successful clients that would be strong candidates for a case study.
- Reach out to the client to get their approval and conduct an interview.
- Gather the data to present an engaging and effective customer story.
Adobe can help
There are several Adobe products that can help you craft compelling case studies. Adobe Experience Platform helps you collect data and deliver great customer experiences across every channel. Once you’ve created your case studies, Experience Platform will help you deliver the right information to the right customer at the right time for maximum impact.
To learn more, watch the Adobe Experience Platform story .
Keep in mind that the best case studies are backed by data. That’s where Adobe Real-Time Customer Data Platform and Adobe Analytics come into play. With Real-Time CDP, you can gather the data you need to build a great case study and target specific customers to deliver the content to the right audience at the perfect moment.
Watch the Real-Time CDP overview video to learn more.
Finally, Adobe Analytics turns real-time data into real-time insights. It helps your business collect and synthesize data from multiple platforms to make more informed decisions and create the best case study possible.
Request a demo to learn more about Adobe Analytics.
https://business.adobe.com/blog/perspectives/b2b-ecommerce-10-case-studies-inspire-you
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/business-case
https://business.adobe.com/blog/basics/what-is-real-time-analytics

How to Summarize a Case Study Effectively
Saving time and effort with Notta, starting from today!
There are hundreds of marketing methods today, but a written case study remains a tried and tested practice to attract new customers. A few months ago, I started working on the case studies — and that's when I learned so much about what works — and what doesn't.
By the time a reader decides to take a look at your case study, they're seriously considering your offering. It's the time when the prospect will either engage more or lose their interest completely. But before the reader thinks of looking at the case study, they'll need a short, meaningful summary.
But how to summarize a case study that's short, simple, and informative? I've written over 50+ case studies, and each one has a short summary. In this detailed guide, I'll show you some tried and tested methods of summarizing long documents.
What is a Case Study Summary?
A case study summary is a short recap of a detailed case, interview, or other document. It has all of the same traits as that of a good summary: it's clean, short, straightforward, and flows naturally for the reader. But in the business world, a case study has the job of connecting customers with business, and a great summary also does the same.
A lead decides to look at the case study summary only if they're seriously interested in the products/services you offer. After reading, your reader's reaction will likely come down to this: did the case study summary make the benefits seem necessary or just nice to have?
If it's the latter, your prospects will probably avoid reading the detailed case study and pass on the opportunity. That's why the summary should include the key points and highlights from the case study and showcase to customers that your product or service is a necessity for their business growth.

How to Summarize a Case Study (with Guidelines)
I have recently read a statement: 'An educated client is a secure client.' Business typically boils down to two priorities: creating a useful product and then making people realize how it can help them. Both of these things mainly revolve around customer education, and both require a case study summary to get the job done.
Here, I'll reveal some simple steps that will help you summarize a case study.
Read the Case Study
When it comes to summarizing a case study, think about how effective it will be from the reader's perspective. You can even take notes and formulate an information architecture into proper formatting, headers, and bullet points to manage content better.
Understand the Goal
A business case study, for example, is a detailed document that defines how a business and its product helped a client improve sales. You should apply the same story and approach to write a case study summary — ensuring it sticks in the heart and mind of the reader.
Identify the Main Points
A good case study teaches prospects something — related to your products, services, new features, or how you're different. Think about the main points of the case study and why people should bother to read it. One of the biggest keys to a great summary is to speak to the customers' pain points directly and immediately offer the solution.

Write a Clear Summary
Now, write the way you talk — with clear ideas, concise language, and a welcoming tone. You need to hold onto your reader's attention with appropriate words and interesting facts. My number one tip is to be creative — even if the case study is boring. Here, your ultimate goal is to be engaging and creative — and, that too, within the confines of the industry.
Ready to revolutionize your post-meeting workflow? Give Notta's AI Summary Templates a try today and experience the difference for yourself. Simply select the template that best fits your needs, and watch as Notta transforms your raw notes into polished, concise summaries. Your time is precious – let Notta help you make the most of it.
Read and Revise
When you're done writing, read the summary aloud to yourself. Give it some emotions (if you can and if the topic allows you) while ensuring there is no fluff in the summary.
Depending on the type of case study summary , you might include different elements — but here's a general breakdown of the guidelines that you should keep in mind while summarizing.
Length : A good summary should have everything — from an attention-grabbing headline to a detailed explanation of the product, service, concept, or project. But that doesn't mean it can be a seven-page-long document. You must stick to the important facts and keep it pretty short — a few paragraphs or one page maximum .
Problem & Solution: Next, clearly state the problem (or issue) you want to solve and then briefly explain how the information provided in the case study solves it.
End with CTA: You'll need to tell your readers what to do next. For example, add the contact information if you want them to contact you or add links to more articles so they can continue reading.
Example of a Case Study Summary
Let's take a look at one example of how people summarize case studies. The example below is technically one page but packs a lot of information into it.
Here's an example of how to write an executive summary for a case study .
[Introduction]: The case study explains how the leading eCommerce platform (Company X) improved its customer experience with the digital tool. [Challenge]: Digital presence and customer satisfaction were the two key challenges faced by Company X. [Approach]: With the help of AI and automation, Company X implemented a robust CRM system and even launched a mobile app for user interaction. [Solution]: The approach helped the client improve their sales by 20% — in only three months.
Tips for Summarizing a Case Study
One of my responsibilities as a freelancer is creating case studies and sending them to potential clients. They're busy people, so I include a case study summary at the beginning that briefs the ten pages of detailed information into a few bullet points — the must-knows. Here’s how to write a case study summary — faster and better.
Write Great Hook Lines
Any article, blog, interview, email, or summary with an annoying hook line is going to get sent to spam right away. You should check and make sure the hook line is short enough to be read in seconds and grabs the attention of the reader. The point is to place the important or value-added material at the top of the summary.

Keep Things Scannable
People are busy, and only a few of them have the time to read a summary that's packed with text. If you take some time to think about what case study summaries work best, you'll likely find that the most effective ones are pretty brief. Smart formatting (with a strategic design) can keep the summary short while ensuring it has enough substance.
Automate Tasks with AI
With an AI case study summary tool, you can skip the blank-page stage of the summarizing process. These tools can analyze the content and come up with a short, informative summary — freeing up your time for other work. Notta is one of the popular AI note-taking and summarizing apps out there right now.
Whether you want to summarize interviews or voice memos, Notta Web App can help you with the job. It's particularly helpful if you've case studies in audio or video format: just upload the file, and Notta will generate a transcript and well-structured summary with an overview, key chapters, and action items.
Try Notta - the best online transcription & summarization tool. Transcribe and summarize your conversations and meetings quickly with high accuracy.
Start for Free
How Long Should a Case Study Summary Be?
While the exact length of a case study summary will depend on what you're summarizing, it typically ranges from a few paragraphs (2 or 3) to one single page . For example, if you're writing a customer case study with your storytelling skills, it can go as long as one page. But if you are summarizing an interview for the recruiting team, a paragraph or two would help them understand the candidate's skills.
How to Write a Good Case Study?
Even the most trusted marketers or businesses will tell you how much case studies have boosted their business. It's like a customer review that can get you more business — only if you write it properly. If you're new to writing case studies, here are simple steps to make the process a lot easier.
Start your research: Like anything else you write, you'll need to do proper research for a case study. For example, this includes the target audience, the message you're trying to convey, and the value your case study will provide.
Write the key highlights : A good case study summary is typically short and sweet, so don't defeat the whole purpose by adding unnecessary things. You'll need to include only the key highlights that matter the most to the reader.
Choose the format: While you may feel tempted to use all the space you have — don't. Some empty space around the text keeps the summary look uncluttered and easy to read.
Include a social proof: Reading a case study is like reading a review — but it mainly relies on storytelling. Including social proof in the case study will push leads to book their first call, send an email, or even sign up for a newsletter.
Be honest: The goal of your case study isn't to win over every single person reading it — instead, it's to win over the people who'll be your potential customers. Being honest is the key here.
Key Takeaways
It takes some time and effort to learn how to summarize a case study and condense all the important information into only a few paragraphs. If you don’t have enough time, check out my favorite AI note-taker and summarizer , Notta . It’s pretty easy to use — just upload the case study video, and the AI tool will quickly transcribe and summarize the information.
Chrome Extension
Help Center
vs Otter.ai
vs Fireflies.ai
vs Happy Scribe
vs Sonix.ai
Integrations
Microsoft Teams
Google Meet
Google Drive
Audio to Text Converter
Online Video Converter
Online Audio Converter
Online Vocal Remover
YouTube Video Summarizer
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Training and Development
- Beginner Guides
Blog Case Study
How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
By Danesh Ramuthi , Sep 07, 2023

In today’s world, where data is king and persuasion is queen, a killer case study can change the game. Think high-powered meetings at fancy companies or even nailing that college presentation: a rock-solid case study could be the magic weapon you need.
Okay, let’s get real: case studies can be kinda snooze-worthy. But guess what? They don’t have to be!
In this article, you’ll learn all about crafting and presenting powerful case studies. From selecting the right metrics to using persuasive narrative techniques, I will cover every element that transforms a mere report into a compelling case study.
And if you’re feeling a little lost, don’t worry! There are cool tools like Venngage’s Case Study Creator to help you whip up something awesome, even if you’re short on time. Plus, the pre-designed case study templates are like instant polish because let’s be honest, everyone loves a shortcut.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a case study presentation?
Purpose of presenting a case study, how to structure a case study presentation, how long should a case study presentation be, 5 case study presentation templates, tips for delivering an effective case study presentation, common mistakes to avoid in a case study presentation, how to present a case study faqs.
A case study presentation involves a comprehensive examination of a specific subject, which could range from an individual, group, location, event, organization or phenomenon.
They’re like puzzles you get to solve with the audience, all while making you think outside the box.
Unlike a basic report or whitepaper, the purpose of a case study presentation is to stimulate critical thinking among the viewers.
The primary objective of a case study is to provide an extensive and profound comprehension of the chosen topic. You don’t just throw numbers at your audience. You use examples and real-life cases to make you think and see things from different angles.

The primary purpose of presenting a case study is to offer a comprehensive, evidence-based argument that informs, persuades and engages your audience.
Here’s the juicy part: presenting that case study can be your secret weapon. Whether you’re pitching a groundbreaking idea to a room full of suits or trying to impress your professor with your A-game, a well-crafted case study can be the magic dust that sprinkles brilliance over your words.
Think of it like digging into a puzzle you can’t quite crack . A case study lets you explore every piece, turn it over and see how it fits together. This close-up look helps you understand the whole picture, not just a blurry snapshot.
It’s also your chance to showcase how you analyze things, step by step, until you reach a conclusion. It’s all about being open and honest about how you got there.
Besides, presenting a case study gives you an opportunity to connect data and real-world scenarios in a compelling narrative. It helps to make your argument more relatable and accessible, increasing its impact on your audience.
One of the contexts where case studies can be very helpful is during the job interview. In some job interviews, you as candidates may be asked to present a case study as part of the selection process.
Having a case study presentation prepared allows the candidate to demonstrate their ability to understand complex issues, formulate strategies and communicate their ideas effectively.
The way you present a case study can make all the difference in how it’s received. A well-structured presentation not only holds the attention of your audience but also ensures that your key points are communicated clearly and effectively.
In this section, let’s go through the key steps that’ll help you structure your case study presentation for maximum impact.
Let’s get into it.
Open with an introductory overview
Start by introducing the subject of your case study and its relevance. Explain why this case study is important and who would benefit from the insights gained. This is your opportunity to grab your audience’s attention.
Explain the problem in question
Dive into the problem or challenge that the case study focuses on. Provide enough background information for the audience to understand the issue. If possible, quantify the problem using data or metrics to show the magnitude or severity.
Detail the solutions to solve the problem
After outlining the problem, describe the steps taken to find a solution. This could include the methodology, any experiments or tests performed and the options that were considered. Make sure to elaborate on why the final solution was chosen over the others.
Key stakeholders Involved
Talk about the individuals, groups or organizations that were directly impacted by or involved in the problem and its solution.
Stakeholders may experience a range of outcomes—some may benefit, while others could face setbacks.
For example, in a business transformation case study, employees could face job relocations or changes in work culture, while shareholders might be looking at potential gains or losses.
Discuss the key results & outcomes
Discuss the results of implementing the solution. Use data and metrics to back up your statements. Did the solution meet its objectives? What impact did it have on the stakeholders? Be honest about any setbacks or areas for improvement as well.
Include visuals to support your analysis
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in helping your audience grasp complex issues. Utilize charts, graphs, images or video clips to supplement your points. Make sure to explain each visual and how it contributes to your overall argument.
Pie charts illustrate the proportion of different components within a whole, useful for visualizing market share, budget allocation or user demographics.
This is particularly useful especially if you’re displaying survey results in your case study presentation.
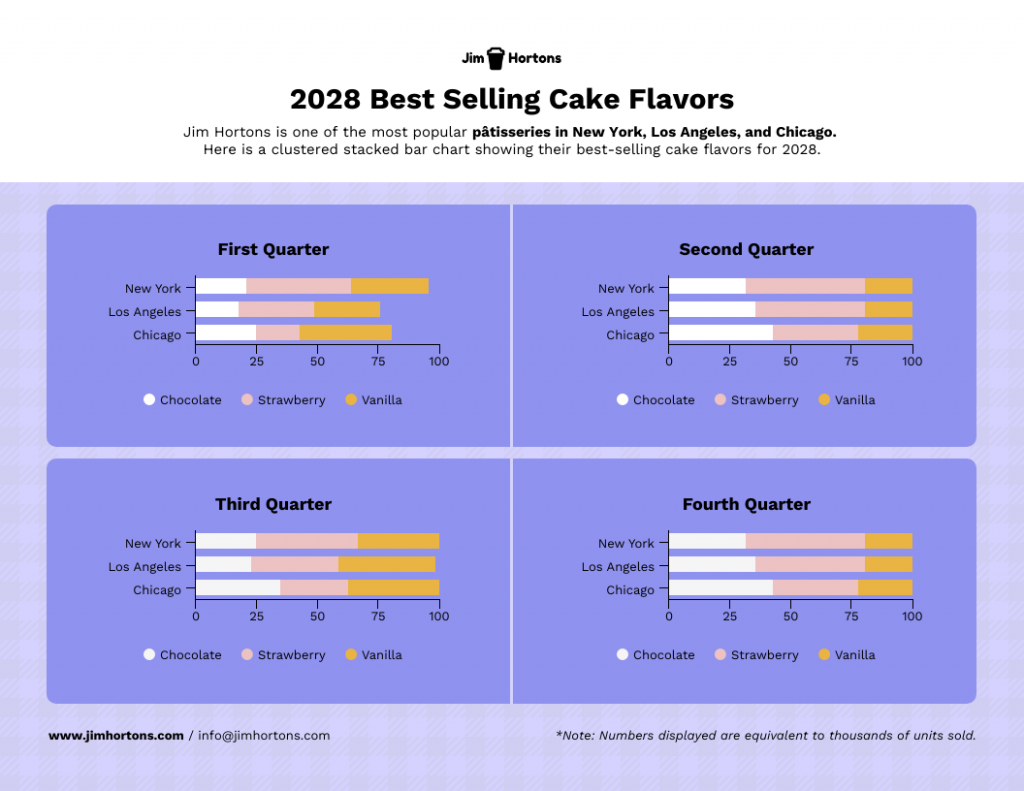
Stacked charts on the other hand are perfect for visualizing composition and trends. This is great for analyzing things like customer demographics, product breakdowns or budget allocation in your case study.
Consider this example of a stacked bar chart template. It provides a straightforward summary of the top-selling cake flavors across various locations, offering a quick and comprehensive view of the data.
Not the chart you’re looking for? Browse Venngage’s gallery of chart templates to find the perfect one that’ll captivate your audience and level up your data storytelling.
Recommendations and next steps
Wrap up by providing recommendations based on the case study findings. Outline the next steps that stakeholders should take to either expand on the success of the project or address any remaining challenges.
Acknowledgments and references
Thank the people who contributed to the case study and helped in the problem-solving process. Cite any external resources, reports or data sets that contributed to your analysis.
Feedback & Q&A session
Open the floor for questions and feedback from your audience. This allows for further discussion and can provide additional insights that may not have been considered previously.
Closing remarks
Conclude the presentation by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the takeaways. Thank your audience for their time and participation and express your willingness to engage in further discussions or collaborations on the subject.

Well, the length of a case study presentation can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the needs of your audience. However, a typical business or academic presentation often lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
This time frame usually allows for a thorough explanation of the case while maintaining audience engagement. However, always consider leaving a few minutes at the end for a Q&A session to address any questions or clarify points made during the presentation.
When it comes to presenting a compelling case study, having a well-structured template can be a game-changer.
It helps you organize your thoughts, data and findings in a coherent and visually pleasing manner.
Not all case studies are created equal and different scenarios require distinct approaches for maximum impact.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences.
Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly.
1) Lab report case study template
Ever feel like your research gets lost in a world of endless numbers and jargon? Lab case studies are your way out!
Think of it as building a bridge between your cool experiment and everyone else. It’s more than just reporting results – it’s explaining the “why” and “how” in a way that grabs attention and makes sense.
This lap report template acts as a blueprint for your report, guiding you through each essential section (introduction, methods, results, etc.) in a logical order.

2) Product case study template
It’s time you ditch those boring slideshows and bullet points because I’ve got a better way to win over clients: product case study templates.
Instead of just listing features and benefits, you get to create a clear and concise story that shows potential clients exactly what your product can do for them. It’s like painting a picture they can easily visualize, helping them understand the value your product brings to the table.
Grab the template below, fill in the details, and watch as your product’s impact comes to life!

3) Content marketing case study template
In digital marketing, showcasing your accomplishments is as vital as achieving them.
A well-crafted case study not only acts as a testament to your successes but can also serve as an instructional tool for others.
With this coral content marketing case study template—a perfect blend of vibrant design and structured documentation, you can narrate your marketing triumphs effectively.

4) Case study psychology template
Understanding how people tick is one of psychology’s biggest quests and case studies are like magnifying glasses for the mind. They offer in-depth looks at real-life behaviors, emotions and thought processes, revealing fascinating insights into what makes us human.
Writing a top-notch case study, though, can be a challenge. It requires careful organization, clear presentation and meticulous attention to detail. That’s where a good case study psychology template comes in handy.
Think of it as a helpful guide, taking care of formatting and structure while you focus on the juicy content. No more wrestling with layouts or margins – just pour your research magic into crafting a compelling narrative.
5) Lead generation case study template
Lead generation can be a real head-scratcher. But here’s a little help: a lead generation case study.
Think of it like a friendly handshake and a confident resume all rolled into one. It’s your chance to showcase your expertise, share real-world successes and offer valuable insights. Potential clients get to see your track record, understand your approach and decide if you’re the right fit.
No need to start from scratch, though. This lead generation case study template guides you step-by-step through crafting a clear, compelling narrative that highlights your wins and offers actionable tips for others. Fill in the gaps with your specific data and strategies, and voilà! You’ve got a powerful tool to attract new customers.
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
So, you’ve spent hours crafting the perfect case study and are now tasked with presenting it. Crafting the case study is only half the battle; delivering it effectively is equally important.
Whether you’re facing a room of executives, academics or potential clients, how you present your findings can make a significant difference in how your work is received.
Forget boring reports and snooze-inducing presentations! Let’s make your case study sing. Here are some key pointers to turn information into an engaging and persuasive performance:
- Know your audience : Tailor your presentation to the knowledge level and interests of your audience. Remember to use language and examples that resonate with them.
- Rehearse : Rehearsing your case study presentation is the key to a smooth delivery and for ensuring that you stay within the allotted time. Practice helps you fine-tune your pacing, hone your speaking skills with good word pronunciations and become comfortable with the material, leading to a more confident, conversational and effective presentation.
- Start strong : Open with a compelling introduction that grabs your audience’s attention. You might want to use an interesting statistic, a provocative question or a brief story that sets the stage for your case study.
- Be clear and concise : Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Get to the point quickly and stay focused on your objectives.
- Use visual aids : Incorporate slides with graphics, charts or videos to supplement your verbal presentation. Make sure they are easy to read and understand.
- Tell a story : Use storytelling techniques to make the case study more engaging. A well-told narrative can help you make complex data more relatable and easier to digest.

Ditching the dry reports and slide decks? Venngage’s case study templates let you wow customers with your solutions and gain insights to improve your business plan. Pre-built templates, visual magic and customer captivation – all just a click away. Go tell your story and watch them say “wow!”
Crafting and presenting a case study is a skillful task that requires careful planning and execution. While a well-prepared case study can be a powerful tool for showcasing your successes, educating your audience or encouraging discussion, there are several pitfalls you should avoid to make your presentation as effective as possible. Here are some common mistakes to watch out for:
Overloading with information
A case study is not an encyclopedia. Overloading your presentation with excessive data, text or jargon can make it cumbersome and difficult for the audience to digest the key points. Stick to what’s essential and impactful.
Lack of structure
Jumping haphazardly between points or topics can confuse your audience. A well-structured presentation, with a logical flow from introduction to conclusion, is crucial for effective communication.
Ignoring the audience
Different audiences have different needs and levels of understanding. Failing to adapt your presentation to your audience can result in a disconnect and a less impactful presentation.
Poor visual elements
While content is king, poor design or lack of visual elements can make your case study dull or hard to follow. Make sure you use high-quality images, graphs and other visual aids to support your narrative.
Not focusing on results
A case study aims to showcase a problem and its solution, but what most people care about are the results. Failing to highlight or adequately explain the outcomes can make your presentation fall flat.
How to start a case study presentation?
Starting a case study presentation effectively involves a few key steps:
- Grab attention : Open with a hook—an intriguing statistic, a provocative question or a compelling visual—to engage your audience from the get-go.
- Set the stage : Briefly introduce the subject, context and relevance of the case study to give your audience an idea of what to expect.
- Outline objectives : Clearly state what the case study aims to achieve. Are you solving a problem, proving a point or showcasing a success?
- Agenda : Give a quick outline of the key sections or topics you’ll cover to help the audience follow along.
- Set expectations : Let your audience know what you want them to take away from the presentation, whether it’s knowledge, inspiration or a call to action.
How to present a case study on PowerPoint and on Google Slides?
Presenting a case study on PowerPoint and Google Slides involves a structured approach for clarity and impact using presentation slides:
- Title slide : Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations.
- Introduction : Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
- Objectives : Clearly state the goals of the case study in a dedicated slide.
- Findings : Use charts, graphs and bullet points to present your findings succinctly.
- Analysis : Discuss what the findings mean, drawing on supporting data or secondary research as necessary.
- Conclusion : Summarize key takeaways and results.
- Q&A : End with a slide inviting questions from the audience.
What’s the role of analysis in a case study presentation?
The role of analysis in a case study presentation is to interpret the data and findings, providing context and meaning to them.
It helps your audience understand the implications of the case study, connects the dots between the problem and the solution and may offer recommendations for future action.
Is it important to include real data and results in the presentation?
Yes, including real data and results in a case study presentation is crucial to show experience, credibility and impact. Authentic data lends weight to your findings and conclusions, enabling the audience to trust your analysis and take your recommendations more seriously
How do I conclude a case study presentation effectively?
To conclude a case study presentation effectively, summarize the key findings, insights and recommendations in a clear and concise manner.
End with a strong call-to-action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
What’s the best way to showcase data in a case study presentation ?
The best way to showcase data in a case study presentation is through visual aids like charts, graphs and infographics which make complex information easily digestible, engaging and creative.
Don’t just report results, visualize them! This template for example lets you transform your social media case study into a captivating infographic that sparks conversation.

Choose the type of visual that best represents the data you’re showing; for example, use bar charts for comparisons or pie charts for parts of a whole.
Ensure that the visuals are high-quality and clearly labeled, so the audience can quickly grasp the key points.
Keep the design consistent and simple, avoiding clutter or overly complex visuals that could distract from the message.
Choose a template that perfectly suits your case study where you can utilize different visual aids for maximum impact.
Need more inspiration on how to turn numbers into impact with the help of infographics? Our ready-to-use infographic templates take the guesswork out of creating visual impact for your case studies with just a few clicks.
Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Congrats on mastering the art of compelling case study presentations! This guide has equipped you with all the essentials, from structure and nuances to avoiding common pitfalls. You’re ready to impress any audience, whether in the boardroom, the classroom or beyond.
And remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Venngage’s Case Study Creator is your trusty companion, ready to elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary. So, let your confidence shine, leverage your newly acquired skills and prepare to deliver presentations that truly resonate.
Go forth and make a lasting impact!

How To Summarize A Case Study
- Success Team
- December 14, 2022
Top-Rated AI Meeting Assistant With Incredible ChatGPT & Qualitative Data Analysis Capabilities
Join 150,000+ individuals and teams who rely on speak ai to capture and analyze unstructured language data for valuable insights. streamline your workflows, unlock new revenue streams and keep doing what you love..
Get a 7-day fully-featured trial!
Case studies are an important research tool used by businesses, marketers, and academics to gain insight into a particular situation or problem. They are often used to analyze customer experiences, product performance, and market trends. Summarizing a case study is a critical skill for any researcher, as it allows them to quickly and effectively convey the key points of the study to their audience. In this article, we’ll discuss the best practices for summarizing a case study and provide tips for making your summary as effective as possible.
What Is A Case Study?
A case study is an in-depth examination of a particular situation or problem. It is used to analyze customer experiences, product performance, and market trends. Case studies are often used to identify potential solutions to a problem or to gain insight into a particular situation. They can also be used to compare different approaches to solving a problem or to evaluate the effectiveness of a particular solution.
Why Summarize A Case Study?
Summarizing a case study is an important skill for any researcher, as it allows them to quickly and effectively convey the key points of the study to their audience. Summarizing a case study can help you make sure that your audience understands the key points of the study and can help you focus on the most important aspects of the study. Additionally, summarizing a case study can help you save time, as it allows you to quickly review the key points of the study without having to read through the entire document.
Tips For Summarizing A Case Study
1. read the entire study.
The first step in summarizing a case study is to read the entire study. This will help you get a better understanding of the key points of the study and will help you identify the most important aspects of the study. Additionally, reading the entire study will help you identify any potential gaps or areas that need further exploration.
2. Identify the Main Points
Once you’ve read the entire study, the next step is to identify the main points of the study. This can be done by looking for key words or phrases that are repeated throughout the study. Additionally, you can look for any conclusions or recommendations that the study makes. Identifying the main points of the study will help you focus your summary and ensure that you are conveying the most important aspects of the study.
3. Write a Clear Summary
Once you’ve identified the main points of the study, the next step is to write a clear and concise summary. This should include a brief overview of the study, the main points of the study, and any conclusions or recommendations that the study makes. Additionally, you should include any key words or phrases that are repeated throughout the study. Writing a clear and concise summary will help ensure that your audience understands the key points of the study.
4. Use SEO Optimization
When summarizing a case study, it’s important to use SEO optimization to ensure that your summary is easily found by search engines. This can be done by including relevant keywords and phrases throughout the summary. Additionally, you should include a meta description that accurately describes the content of the summary. Using SEO optimization will help ensure that your summary is easily found by search engines and will help your summary rank higher in search engine results.
5. Edit and Proofread
Once you’ve written your summary, the next step is to edit and proofread it. This will help ensure that your summary is clear, concise, and free of any errors. Additionally, it will help ensure that your summary conveys the key points of the study accurately and effectively. Editing and proofreading your summary will help ensure that your summary is of the highest quality and will help ensure that your audience understands the key points of the study.
Summarizing a case study is an important skill for any researcher, as it allows them to quickly and effectively convey the key points of the study to their audience. In this article, we’ve discussed the best practices for summarizing a case study and provided tips for making your summary as effective as possible. By following these tips, you can ensure that your summary is clear, concise, and free of any errors. Additionally, you can use SEO optimization to ensure that your summary is easily found by search engines and will help your summary rank higher in search engine results.
How To Use The Best Large Language Models With Speak
Step 1: Create Your Speak Account
To start your transcription and analysis, you first need to create a Speak account . No worries, this is super easy to do!
Get a 7-day trial with 30 minutes of free English audio and video transcription included when you sign up for Speak.
To sign up for Speak and start using Speak Magic Prompts, visit the Speak app register page here .
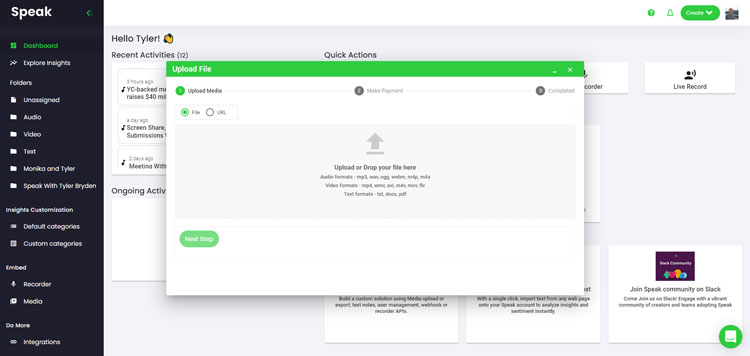
Step 2: Upload Your Language Data
We typically recommend MP4s for video or MP3s for audio.
However, we accept a range of audio, video and text file types.
You can upload your file for transcription in several ways using Speak:
Accepted Audio File Types
Accepted video file types, accepted text file types, csv imports.
You can also upload CSVs of text files or audio and video files. You can learn more about CSV uploads and download Speak-compatible CSVs here .
With the CSVs, you can upload anything from dozens of YouTube videos to thousands of Interview Data.
Publicly Available URLs
You can also upload media to Speak through a publicly available URL.
As long as the file type extension is available at the end of the URL you will have no problem importing your recording for automatic transcription and analysis.
YouTube URLs
Speak is compatible with YouTube videos. All you have to do is copy the URL of the YouTube video (for example, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qKfcLcHeivc ).
Speak will automatically find the file, calculate the length, and import the video.
If using YouTube videos, please make sure you use the full link and not the shortened YouTube snippet. Additionally, make sure you remove the channel name from the URL.
Speak Integrations
As mentioned, Speak also contains a range of integrations for Zoom , Zapier , Vimeo and more that will help you automatically transcribe your media.
This library of integrations continues to grow! Have a request? Feel encouraged to send us a message.
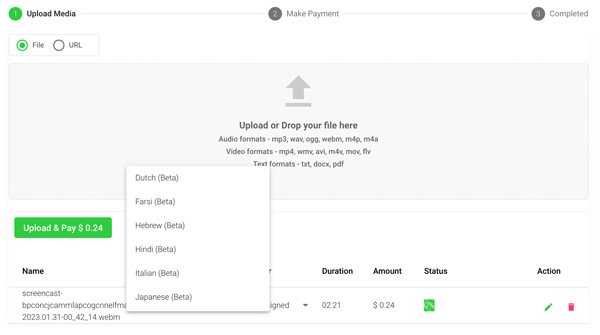
Step 3: Calculate and Pay the Total Automatically
Once you have your file(s) ready and load it into Speak, it will automatically calculate the total cost (you get 30 minutes of audio and video free in the 7-day trial - take advantage of it!).
If you are uploading text data into Speak, you do not currently have to pay any cost. Only the Speak Magic Prompts analysis would create a fee which will be detailed below.
Once you go over your 30 minutes or need to use Speak Magic Prompts, you can pay by subscribing to a personalized plan using our real-time calculator .
You can also add a balance or pay for uploads and analysis without a plan using your credit card .
Step 4: Wait for Speak to Analyze Your Language Data
If you are uploading audio and video, our automated transcription software will prepare your transcript quickly. Once completed, you will get an email notification that your transcript is complete. That email will contain a link back to the file so you can access the interactive media player with the transcript, analysis, and export formats ready for you.
If you are importing CSVs or uploading text files Speak will generally analyze the information much more quickly.
Step 5: Visit Your File Or Folder
Speak is capable of analyzing both individual files and entire folders of data.
When you are viewing any individual file in Speak, all you have to do is click on the "Prompts" button.
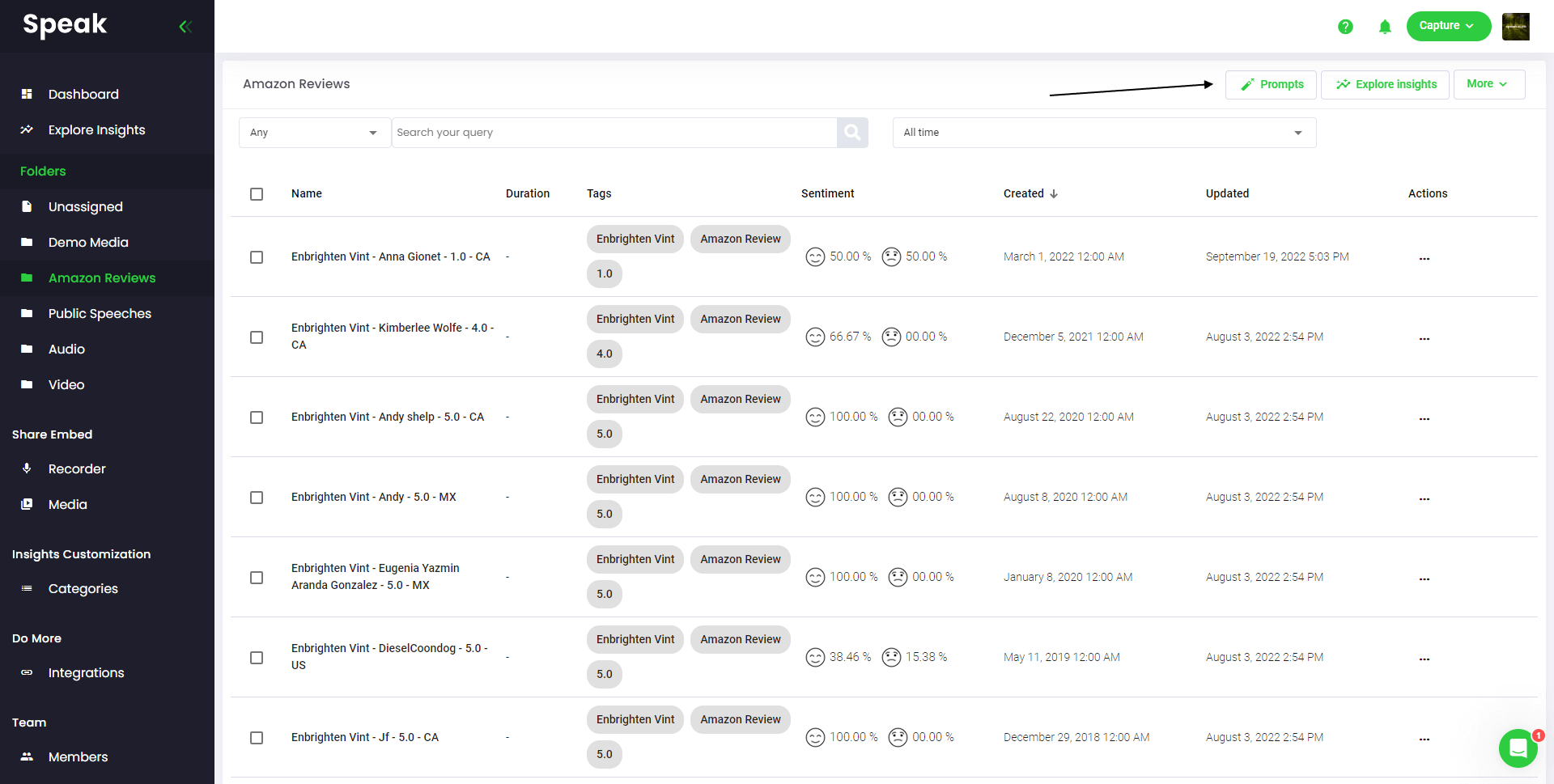
If you want to analyze many files, all you have to do is add the files you want to analyze into a folder within Speak.
You can do that by adding new files into Speak or you can organize your current files into your desired folder with the software's easy editing functionality.
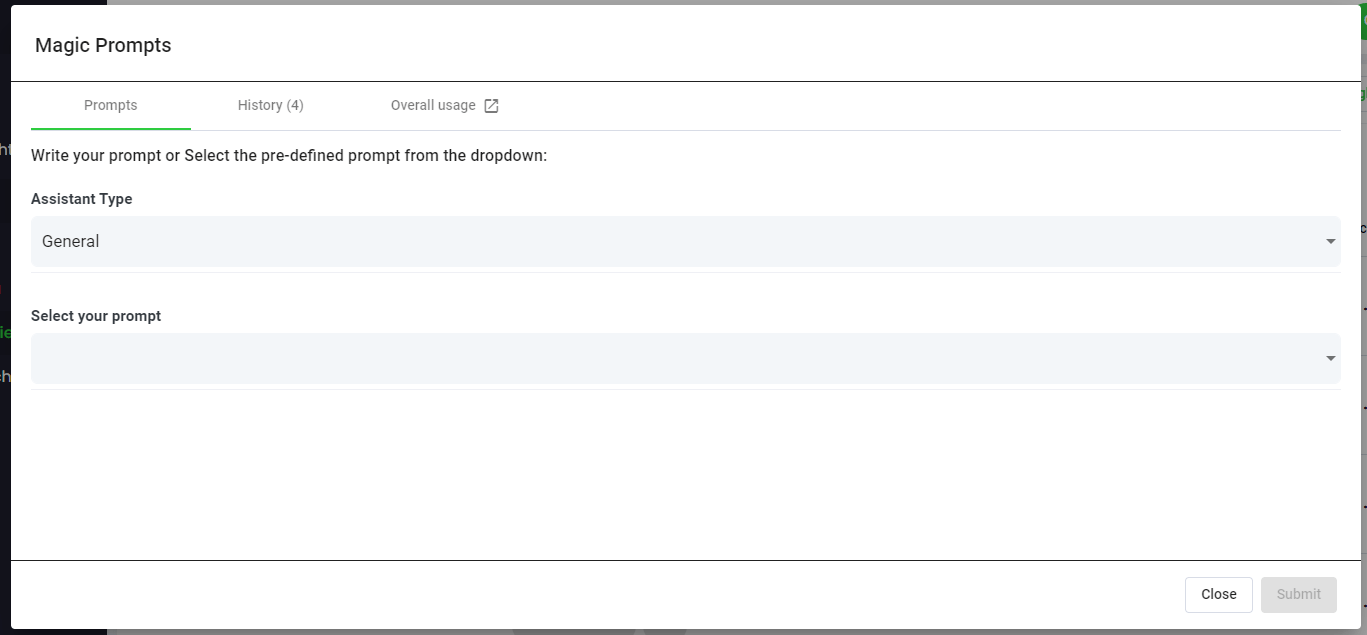
Step 6: Select Speak Magic Prompts To Analyze Your Data
What are magic prompts.
Speak Magic Prompts leverage innovation in artificial intelligence models often referred to as "generative AI".
These models have analyzed huge amounts of data from across the internet to gain an understanding of language.
With that understanding, these "large language models" are capable of performing mind-bending tasks!
With Speak Magic Prompts, you can now perform those tasks on the audio, video and text data in your Speak account.
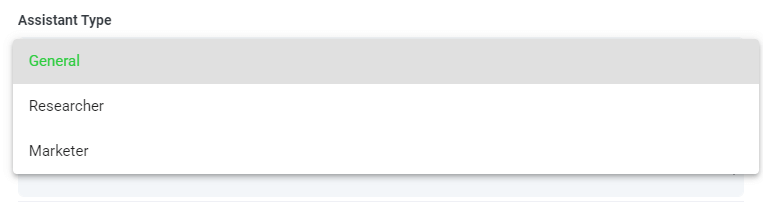
Step 7: Select Your Assistant Type
To help you get better results from Speak Magic Prompts, Speak has introduced "Assistant Type".
These assistant types pre-set and provide context to the prompt engine for more concise, meaningful outputs based on your needs.
To begin, we have included:
Choose the most relevant assistant type from the dropdown.
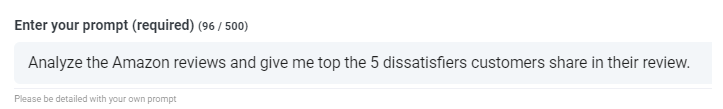
Step 8: Create Or Select Your Desired Prompt
Here are some examples prompts that you can apply to any file right now:
- Create a SWOT Analysis
- Give me the top action items
- Create a bullet point list summary
- Tell me the key issues that were left unresolved
- Tell me what questions were asked
- Create Your Own Custom Prompts
A modal will pop up so you can use the suggested prompts we shared above to instantly and magically get your answers.
If you have your own prompts you want to create, select "Custom Prompt" from the dropdown and another text box will open where you can ask anything you want of your data!

Step 9: Review & Share Responses
Speak will generate a concise response for you in a text box below the prompt selection dropdown.
In this example, we ask to analyze all the Interview Data in the folder at once for the top product dissatisfiers.
You can easily copy that response for your presentations, content, emails, team members and more!
Speak Magic Prompts As ChatGPT For Interview Data Pricing
Our team at Speak Ai continues to optimize the pricing for Magic Prompts and Speak as a whole.
Right now, anyone in the 7-day trial of Speak gets 100,000 characters included in their account.
If you need more characters, you can easily include Speak Magic Prompts in your plan when you create a subscription.
You can also upgrade the number of characters in your account if you already have a subscription.
Both options are available on the subscription page .
Alternatively, you can use Speak Magic Prompts by adding a balance to your account. The balance will be used as you analyze characters.
Completely Personalize Your Plan 📝
Here at Speak, we've made it incredibly easy to personalize your subscription.
Once you sign-up, just visit our custom plan builder and select the media volume, team size, and features you want to get a plan that fits your needs.
No more rigid plans. Upgrade, downgrade or cancel at any time.
Claim Your Special Offer 🎁
When you subscribe, you will also get a free premium add-on for three months!
That means you save up to $50 USD per month and $150 USD in total.
Once you subscribe to a plan, all you have to do is send us a live chat with your selected premium add-on from the list below:
- Premium Export Options (Word, CSV & More)
- Custom Categories & Insights
- Bulk Editing & Data Organization
- Recorder Customization (Branding, Input & More)
- Media Player Customization
- Shareable Media Libraries
We will put the add-on live in your account free of charge!
What are you waiting for?
Refer Others & Earn Real Money 💸
If you have friends, peers and followers interested in using our platform, you can earn real monthly money.
You will get paid a percentage of all sales whether the customers you refer to pay for a plan, automatically transcribe media or leverage professional transcription services.
Use this link to become an official Speak affiliate.
Check Out Our Dedicated Resources📚
- Speak Ai YouTube Channel
- Guide To Building Your Perfect Speak Plan
Book A Free Implementation Session 🤝
It would be an honour to personally jump on an introductory call with you to make sure you are set up for success.
Just use our Calendly link to find a time that works well for you. We look forward to meeting you!
Top-Rated AI Meeting Assistant With Incredible ChatGPT & Qualitative Data Analysis Capabilities

Transcribe and analyze your media like never before.
Automatically generate transcripts, captions, insights and reports with intuitive software and APIs.
All You Wanted to Know About How to Write a Case Study

What do you study in your college? If you are a psychology, sociology, or anthropology student, we bet you might be familiar with what a case study is. This research method is used to study a certain person, group, or situation. In this guide from our dissertation writing service , you will learn how to write a case study professionally, from researching to citing sources properly. Also, we will explore different types of case studies and show you examples — so that you won’t have any other questions left.
What Is a Case Study?
A case study is a subcategory of research design which investigates problems and offers solutions. Case studies can range from academic research studies to corporate promotional tools trying to sell an idea—their scope is quite vast.
What Is the Difference Between a Research Paper and a Case Study?
While research papers turn the reader’s attention to a certain problem, case studies go even further. Case study guidelines require students to pay attention to details, examining issues closely and in-depth using different research methods. For example, case studies may be used to examine court cases if you study Law, or a patient's health history if you study Medicine. Case studies are also used in Marketing, which are thorough, empirically supported analysis of a good or service's performance. Well-designed case studies can be valuable for prospective customers as they can identify and solve the potential customers pain point.
Case studies involve a lot of storytelling – they usually examine particular cases for a person or a group of people. This method of research is very helpful, as it is very practical and can give a lot of hands-on information. Most commonly, the length of the case study is about 500-900 words, which is much less than the length of an average research paper.
The structure of a case study is very similar to storytelling. It has a protagonist or main character, which in your case is actually a problem you are trying to solve. You can use the system of 3 Acts to make it a compelling story. It should have an introduction, rising action, a climax where transformation occurs, falling action, and a solution.
Here is a rough formula for you to use in your case study:
Problem (Act I): > Solution (Act II) > Result (Act III) > Conclusion.
Types of Case Studies
The purpose of a case study is to provide detailed reports on an event, an institution, a place, future customers, or pretty much anything. There are a few common types of case study, but the type depends on the topic. The following are the most common domains where case studies are needed:

- Historical case studies are great to learn from. Historical events have a multitude of source info offering different perspectives. There are always modern parallels where these perspectives can be applied, compared, and thoroughly analyzed.
- Problem-oriented case studies are usually used for solving problems. These are often assigned as theoretical situations where you need to immerse yourself in the situation to examine it. Imagine you’re working for a startup and you’ve just noticed a significant flaw in your product’s design. Before taking it to the senior manager, you want to do a comprehensive study on the issue and provide solutions. On a greater scale, problem-oriented case studies are a vital part of relevant socio-economic discussions.
- Cumulative case studies collect information and offer comparisons. In business, case studies are often used to tell people about the value of a product.
- Critical case studies explore the causes and effects of a certain case.
- Illustrative case studies describe certain events, investigating outcomes and lessons learned.
Need a compelling case study? EssayPro has got you covered. Our experts are ready to provide you with detailed, insightful case studies that capture the essence of real-world scenarios. Elevate your academic work with our professional assistance.

Case Study Format
The case study format is typically made up of eight parts:
- Executive Summary. Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you’re researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences.
- Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
- Case Evaluation. Isolate the sections of the study you want to focus on. In it, explain why something is working or is not working.
- Proposed Solutions. Offer realistic ways to solve what isn’t working or how to improve its current condition. Explain why these solutions work by offering testable evidence.
- Conclusion. Summarize the main points from the case evaluations and proposed solutions. 6. Recommendations. Talk about the strategy that you should choose. Explain why this choice is the most appropriate.
- Implementation. Explain how to put the specific strategies into action.
- References. Provide all the citations.
How to Write a Case Study
Let's discover how to write a case study.

Setting Up the Research
When writing a case study, remember that research should always come first. Reading many different sources and analyzing other points of view will help you come up with more creative solutions. You can also conduct an actual interview to thoroughly investigate the customer story that you'll need for your case study. Including all of the necessary research, writing a case study may take some time. The research process involves doing the following:
- Define your objective. Explain the reason why you’re presenting your subject. Figure out where you will feature your case study; whether it is written, on video, shown as an infographic, streamed as a podcast, etc.
- Determine who will be the right candidate for your case study. Get permission, quotes, and other features that will make your case study effective. Get in touch with your candidate to see if they approve of being part of your work. Study that candidate’s situation and note down what caused it.
- Identify which various consequences could result from the situation. Follow these guidelines on how to start a case study: surf the net to find some general information you might find useful.
- Make a list of credible sources and examine them. Seek out important facts and highlight problems. Always write down your ideas and make sure to brainstorm.
- Focus on several key issues – why they exist, and how they impact your research subject. Think of several unique solutions. Draw from class discussions, readings, and personal experience. When writing a case study, focus on the best solution and explore it in depth. After having all your research in place, writing a case study will be easy. You may first want to check the rubric and criteria of your assignment for the correct case study structure.
Read Also: 'CREDIBLE SOURCES: WHAT ARE THEY?'
Although your instructor might be looking at slightly different criteria, every case study rubric essentially has the same standards. Your professor will want you to exhibit 8 different outcomes:
- Correctly identify the concepts, theories, and practices in the discipline.
- Identify the relevant theories and principles associated with the particular study.
- Evaluate legal and ethical principles and apply them to your decision-making.
- Recognize the global importance and contribution of your case.
- Construct a coherent summary and explanation of the study.
- Demonstrate analytical and critical-thinking skills.
- Explain the interrelationships between the environment and nature.
- Integrate theory and practice of the discipline within the analysis.
Need Case Study DONE FAST?
Pick a topic, tell us your requirements and get your paper on time.
Case Study Outline
Let's look at the structure of an outline based on the issue of the alcoholic addiction of 30 people.
Introduction
- Statement of the issue: Alcoholism is a disease rather than a weakness of character.
- Presentation of the problem: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there.
- Explanation of the terms: In the past, alcoholism was commonly referred to as alcohol dependence or alcohol addiction. Alcoholism is now the more severe stage of this addiction in the disorder spectrum.
- Hypotheses: Drinking in excess can lead to the use of other drugs.
- Importance of your story: How the information you present can help people with their addictions.
- Background of the story: Include an explanation of why you chose this topic.
- Presentation of analysis and data: Describe the criteria for choosing 30 candidates, the structure of the interview, and the outcomes.
- Strong argument 1: ex. X% of candidates dealing with anxiety and depression...
- Strong argument 2: ex. X amount of people started drinking by their mid-teens.
- Strong argument 3: ex. X% of respondents’ parents had issues with alcohol.
- Concluding statement: I have researched if alcoholism is a disease and found out that…
- Recommendations: Ways and actions for preventing alcohol use.
Writing a Case Study Draft
After you’ve done your case study research and written the outline, it’s time to focus on the draft. In a draft, you have to develop and write your case study by using: the data which you collected throughout the research, interviews, and the analysis processes that were undertaken. Follow these rules for the draft:

- Your draft should contain at least 4 sections: an introduction; a body where you should include background information, an explanation of why you decided to do this case study, and a presentation of your main findings; a conclusion where you present data; and references.
- In the introduction, you should set the pace very clearly. You can even raise a question or quote someone you interviewed in the research phase. It must provide adequate background information on the topic. The background may include analyses of previous studies on your topic. Include the aim of your case here as well. Think of it as a thesis statement. The aim must describe the purpose of your work—presenting the issues that you want to tackle. Include background information, such as photos or videos you used when doing the research.
- Describe your unique research process, whether it was through interviews, observations, academic journals, etc. The next point includes providing the results of your research. Tell the audience what you found out. Why is this important, and what could be learned from it? Discuss the real implications of the problem and its significance in the world.
- Include quotes and data (such as findings, percentages, and awards). This will add a personal touch and better credibility to the case you present. Explain what results you find during your interviews in regards to the problem and how it developed. Also, write about solutions which have already been proposed by other people who have already written about this case.
- At the end of your case study, you should offer possible solutions, but don’t worry about solving them yourself.
Use Data to Illustrate Key Points in Your Case Study
Even though your case study is a story, it should be based on evidence. Use as much data as possible to illustrate your point. Without the right data, your case study may appear weak and the readers may not be able to relate to your issue as much as they should. Let's see the examples from essay writing service :
With data: Alcoholism is affecting more than 14 million people in the USA, which makes it the third most common mental illness there. Without data: A lot of people suffer from alcoholism in the United States.
Try to include as many credible sources as possible. You may have terms or sources that could be hard for other cultures to understand. If this is the case, you should include them in the appendix or Notes for the Instructor or Professor.
Finalizing the Draft: Checklist
After you finish drafting your case study, polish it up by answering these ‘ask yourself’ questions and think about how to end your case study:
- Check that you follow the correct case study format, also in regards to text formatting.
- Check that your work is consistent with its referencing and citation style.
- Micro-editing — check for grammar and spelling issues.
- Macro-editing — does ‘the big picture’ come across to the reader? Is there enough raw data, such as real-life examples or personal experiences? Have you made your data collection process completely transparent? Does your analysis provide a clear conclusion, allowing for further research and practice?
Problems to avoid:
- Overgeneralization – Do not go into further research that deviates from the main problem.
- Failure to Document Limitations – Just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study, you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis.
- Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications – Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings.
How to Create a Title Page and Cite a Case Study
Let's see how to create an awesome title page.
Your title page depends on the prescribed citation format. The title page should include:
- A title that attracts some attention and describes your study
- The title should have the words “case study” in it
- The title should range between 5-9 words in length
- Your name and contact information
- Your finished paper should be only 500 to 1,500 words in length.With this type of assignment, write effectively and avoid fluff
Here is a template for the APA and MLA format title page:
There are some cases when you need to cite someone else's study in your own one – therefore, you need to master how to cite a case study. A case study is like a research paper when it comes to citations. You can cite it like you cite a book, depending on what style you need.
Citation Example in MLA Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing, 2008. Print.
Citation Example in APA Hill, L., Khanna, T., & Stecker, E. A. (2008). HCL Technologies. Boston: Harvard Business Publishing.
Citation Example in Chicago Hill, Linda, Tarun Khanna, and Emily A. Stecker. HCL Technologies.
Case Study Examples
To give you an idea of a professional case study example, we gathered and linked some below.
Eastman Kodak Case Study
Case Study Example: Audi Trains Mexican Autoworkers in Germany
To conclude, a case study is one of the best methods of getting an overview of what happened to a person, a group, or a situation in practice. It allows you to have an in-depth glance at the real-life problems that businesses, healthcare industry, criminal justice, etc. may face. This insight helps us look at such situations in a different light. This is because we see scenarios that we otherwise would not, without necessarily being there. If you need custom essays , try our research paper writing services .
Get Help Form Qualified Writers
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. If you’re having trouble with your case study, help with essay request - we'll help. EssayPro writers have read and written countless case studies and are experts in endless disciplines. Request essay writing, editing, or proofreading assistance from our custom case study writing service , and all of your worries will be gone.
Don't Know Where to Start?
Crafting a case study is not easy. You might want to write one of high quality, but you don’t have the time or expertise. Request ' write my case study ' assistance from our service.
Related Articles
.webp)

- Search for:
- Apple Templates
- Software Testing
- White Paper Templates
- Business Process Design
- Software Development
- A-Z (Apple)
- Writing Tips
- Action Plan Writing
- Business Plan Writing
No products in the cart.
Return to shop
Case Study Templates
How to write the executive summary for case studies.
The Executive Summary of your Case Study must make the right impression on your readers. It’s the first section they read. However, the Executive Summary must be the last part of the document you write.
How to Write a Case Study
When writing this section, remember this is your best chance to interest the reader—and get them to take action! For example: call your Sales team and get more information about your products, sign up for a newsletter, download a trial product, or request more information about your product line.
What’s the Purpose of an Executive Summary?
Executive Summaries should give readers a high-level overview of your Case Study.
This is NOT the introduction to your document; rather this sets the scene and describes your company, vision and product offering. In your mind’s eye, see the Executive Summary and the Case Study are two separate documents. Approach each one with a different ‘writer’s hat’.
The tone, style, and language may be different. In general, the Executive Summary will be tightly-written, direct, and high-level. You dive into these points in the case study itself. This applies to in-depth case studies over five pages. Shorter case studies may not require the same background information.
Best Practice: Writing your Executive Summary
Write your Executive Summary as though it were standalone document . It’s usually best to do this when the proposal is finished as you will then have digested the material and have a fuller grasp of the business objectives.
The Executive Summary as a ‘document’ introduces your business, principles, products, and people.
When writing your Case Study’s executive summary provide brief summaries of the following:
- Business operations
- Company’s background
- Competitors
- Customer list
- Financial projections
- Flagship products
- Industry awards
- Key services
- Management team
- Market share
- Marketing and sales objectives
- Office locations
- Partnerships
- Strategic alliances
- Vision Statement
Case study for Architecture projects
Guidelines: Writing the Executive Summary
The Executive Summary should be no more than one or two pages.
I’ve seen very concise and persuasive introductions that were less than three-hundred words. The business writers knew how to introduce the key points, ignore/relegate less important material, and use a writing style that made the reader want to read the rest of the document.
This applies to in-depth case studies over five pages. Shorter case studies may not require the same background information.
Don’t resort to clichés and hackneyed phrases. Your customers read business documents all day. Make sure yours stands out.
Note : This applies to in-depth case studies. Shorter case studies may not require the same background information.
- Company – Describe your company background, with details of your industry position, physical location and number of employees.
- Management – Introduce the key members of the senior management team. Where possible, give their name, position, age, prior employer, experience in similar activities, degrees etc. Use common sense here and move these to a later section in the document if it takes too much space. When writing a Case Study, I often add a section called Pen Portraits and add profiles of the management team in there.
- Product Offering – If you’re discussing a specific product offering, for example, software for selling digital goods online, then outline the three main benefits. Where appropriate, discuss key features, customers, competitors and industry awards.
- Value Proposition – Describe what is unique about this product, for example, if it can it be patented, localized, scaled, used over the web, on mobile devices.
- Financials – This is required if you’re seeking funding, looking for partners, or applying for a grant. Keep it short. Check the figures more than once!
- Funding – Describe your current position, use of funds to date, prior funding. Also break out the investment you’ve received to date, investors’ names, business valuation, and details of the exit strategy. (This section may not apply to all Case Studies.)
- Contact Information – Add your name, position, company, address, phone, fax, email and website address.
What else should go into the Executive Summary?
Anthony James
Username or email address *
Password *
Remember me Log in
Lost your password?
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 1:00 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
Published on November 23, 2020 by Shona McCombes . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Summarizing , or writing a summary, means giving a concise overview of a text’s main points in your own words. A summary is always much shorter than the original text.
There are five key steps that can help you to write a summary:
- Read the text
- Break it down into sections
- Identify the key points in each section
- Write the summary
- Check the summary against the article
Writing a summary does not involve critiquing or evaluating the source . You should simply provide an accurate account of the most important information and ideas (without copying any text from the original).
Table of contents
When to write a summary, step 1: read the text, step 2: break the text down into sections, step 3: identify the key points in each section, step 4: write the summary, step 5: check the summary against the article, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about summarizing.
There are many situations in which you might have to summarize an article or other source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to show you’ve understood the material
- To keep notes that will help you remember what you’ve read
- To give an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
When you’re writing an academic text like an essay , research paper , or dissertation , you’ll integrate sources in a variety of ways. You might use a brief quote to support your point, or paraphrase a few sentences or paragraphs.
But it’s often appropriate to summarize a whole article or chapter if it is especially relevant to your own research, or to provide an overview of a source before you analyze or critique it.
In any case, the goal of summarizing is to give your reader a clear understanding of the original source. Follow the five steps outlined below to write a good summary.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
You should read the article more than once to make sure you’ve thoroughly understood it. It’s often effective to read in three stages:
- Scan the article quickly to get a sense of its topic and overall shape.
- Read the article carefully, highlighting important points and taking notes as you read.
- Skim the article again to confirm you’ve understood the key points, and reread any particularly important or difficult passages.
There are some tricks you can use to identify the key points as you read:
- Start by reading the abstract . This already contains the author’s own summary of their work, and it tells you what to expect from the article.
- Pay attention to headings and subheadings . These should give you a good sense of what each part is about.
- Read the introduction and the conclusion together and compare them: What did the author set out to do, and what was the outcome?
To make the text more manageable and understand its sub-points, break it down into smaller sections.
If the text is a scientific paper that follows a standard empirical structure, it is probably already organized into clearly marked sections, usually including an introduction , methods , results , and discussion .
Other types of articles may not be explicitly divided into sections. But most articles and essays will be structured around a series of sub-points or themes.
Now it’s time go through each section and pick out its most important points. What does your reader need to know to understand the overall argument or conclusion of the article?
Keep in mind that a summary does not involve paraphrasing every single paragraph of the article. Your goal is to extract the essential points, leaving out anything that can be considered background information or supplementary detail.
In a scientific article, there are some easy questions you can ask to identify the key points in each part.
If the article takes a different form, you might have to think more carefully about what points are most important for the reader to understand its argument.
In that case, pay particular attention to the thesis statement —the central claim that the author wants us to accept, which usually appears in the introduction—and the topic sentences that signal the main idea of each paragraph.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Now that you know the key points that the article aims to communicate, you need to put them in your own words.
To avoid plagiarism and show you’ve understood the article, it’s essential to properly paraphrase the author’s ideas. Do not copy and paste parts of the article, not even just a sentence or two.
The best way to do this is to put the article aside and write out your own understanding of the author’s key points.
Examples of article summaries
Let’s take a look at an example. Below, we summarize this article , which scientifically investigates the old saying “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.”
Davis et al. (2015) set out to empirically test the popular saying “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.” Apples are often used to represent a healthy lifestyle, and research has shown their nutritional properties could be beneficial for various aspects of health. The authors’ unique approach is to take the saying literally and ask: do people who eat apples use healthcare services less frequently? If there is indeed such a relationship, they suggest, promoting apple consumption could help reduce healthcare costs.
The study used publicly available cross-sectional data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Participants were categorized as either apple eaters or non-apple eaters based on their self-reported apple consumption in an average 24-hour period. They were also categorized as either avoiding or not avoiding the use of healthcare services in the past year. The data was statistically analyzed to test whether there was an association between apple consumption and several dependent variables: physician visits, hospital stays, use of mental health services, and use of prescription medication.
Although apple eaters were slightly more likely to have avoided physician visits, this relationship was not statistically significant after adjusting for various relevant factors. No association was found between apple consumption and hospital stays or mental health service use. However, apple eaters were found to be slightly more likely to have avoided using prescription medication. Based on these results, the authors conclude that an apple a day does not keep the doctor away, but it may keep the pharmacist away. They suggest that this finding could have implications for reducing healthcare costs, considering the high annual costs of prescription medication and the inexpensiveness of apples.
However, the authors also note several limitations of the study: most importantly, that apple eaters are likely to differ from non-apple eaters in ways that may have confounded the results (for example, apple eaters may be more likely to be health-conscious). To establish any causal relationship between apple consumption and avoidance of medication, they recommend experimental research.
An article summary like the above would be appropriate for a stand-alone summary assignment. However, you’ll often want to give an even more concise summary of an article.
For example, in a literature review or meta analysis you may want to briefly summarize this study as part of a wider discussion of various sources. In this case, we can boil our summary down even further to include only the most relevant information.
Using national survey data, Davis et al. (2015) tested the assertion that “an apple a day keeps the doctor away” and did not find statistically significant evidence to support this hypothesis. While people who consumed apples were slightly less likely to use prescription medications, the study was unable to demonstrate a causal relationship between these variables.
Citing the source you’re summarizing
When including a summary as part of a larger text, it’s essential to properly cite the source you’re summarizing. The exact format depends on your citation style , but it usually includes an in-text citation and a full reference at the end of your paper.
You can easily create your citations and references in APA or MLA using our free citation generators.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
Finally, read through the article once more to ensure that:
- You’ve accurately represented the author’s work
- You haven’t missed any essential information
- The phrasing is not too similar to any sentences in the original.
If you’re summarizing many articles as part of your own work, it may be a good idea to use a plagiarism checker to double-check that your text is completely original and properly cited. Just be sure to use one that’s safe and reliable.
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
A summary is a short overview of the main points of an article or other source, written entirely in your own words. Want to make your life super easy? Try our free text summarizer today!
A summary is always much shorter than the original text. The length of a summary can range from just a few sentences to several paragraphs; it depends on the length of the article you’re summarizing, and on the purpose of the summary.
You might have to write a summary of a source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to prove you understand the material
- For your own use, to keep notes on your reading
- To provide an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
- In a paper , to summarize or introduce a relevant study
To avoid plagiarism when summarizing an article or other source, follow these two rules:
- Write the summary entirely in your own words by paraphrasing the author’s ideas.
- Cite the source with an in-text citation and a full reference so your reader can easily find the original text.
An abstract concisely explains all the key points of an academic text such as a thesis , dissertation or journal article. It should summarize the whole text, not just introduce it.
An abstract is a type of summary , but summaries are also written elsewhere in academic writing . For example, you might summarize a source in a paper , in a literature review , or as a standalone assignment.
All can be done within seconds with our free text summarizer .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, May 31). How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/how-to-summarize/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to paraphrase | step-by-step guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in apa, mla & chicago, the basics of in-text citation | apa & mla examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:42px;color:#F5F4F3;}@media (max-width: 1120px){.css-s5s6ko{margin-right:12px;}} Join us: Learn how to build a trusted AI strategy to support your company's intelligent transformation, featuring Forrester .css-1ixh9fn{display:inline-block;}@media (max-width: 480px){.css-1ixh9fn{display:block;margin-top:12px;}} .css-1uaoevr-heading-6{font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-1uaoevr-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} .css-ora5nu-heading-6{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;color:#0D0E10;-webkit-transition:all 0.3s;transition:all 0.3s;position:relative;font-size:16px;line-height:28px;padding:0;font-size:14px;line-height:24px;font-weight:500;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;color:#F5F4F3;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{border-bottom:0;color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover path{fill:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div{border-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover div:before{border-left-color:#CD4848;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active{border-bottom:0;background-color:#EBE8E8;color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active path{fill:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div{border-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:active div:before{border-left-color:#0D0E10;}.css-ora5nu-heading-6:hover{color:#F5F4F3;} Register now .css-1k6cidy{width:11px;height:11px;margin-left:8px;}.css-1k6cidy path{fill:currentColor;}
- Project planning |
- How to write an executive summary, with ...
How to write an executive summary, with examples

The best way to do that is with an executive summary. If you’ve never written an executive summary, this article has all you need to know to plan, write, and share them with your team.
What is an executive summary?
An executive summary is an overview of a document. The length and scope of your executive summary will differ depending on the document it’s summarizing, but in general an executive summary can be anywhere from one to two pages long. In the document, you’ll want to share all of the information your readers and important stakeholders need to know.
Imagine it this way: if your high-level stakeholders were to only read your executive summary, would they have all of the information they need to succeed? If so, your summary has done its job.
You’ll often find executive summaries of:
Business cases
Project proposals
Research documents
Environmental studies
Market surveys
Project plans
In general, there are four parts to any executive summary:
Start with the problem or need the document is solving.
Outline the recommended solution.
Explain the solution’s value.
Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work.
What is an executive summary in project management?
In project management, an executive summary is a way to bring clarity to cross-functional collaborators, team leadership, and project stakeholders . Think of it like a project’s “ elevator pitch ” for team members who don’t have the time or the need to dive into all of the project’s details.
The main difference between an executive summary in project management and a more traditional executive summary in a business plan is that the former should be created at the beginning of your project—whereas the latter should be created after you’ve written your business plan. For example, to write an executive summary of an environmental study, you would compile a report on the results and findings once your study was over. But for an executive summary in project management, you want to cover what the project is aiming to achieve and why those goals matter.
The same four parts apply to an executive summary in project management:
Start with the problem or need the project is solving. Why is this project happening? What insight, customer feedback, product plan, or other need caused it to come to life?
Outline the recommended solution, or the project’s objectives. How is the project going to solve the problem you established in the first part? What are the project goals and objectives?
Explain the solution’s value. Once you’ve finished your project, what will happen? How will this improve and solve the problem you established in the first part?
Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work. This is another opportunity to reiterate why the problem is important, and why the project matters. It can also be helpful to reference your audience and how your solution will solve their problem. Finally, include any relevant next steps.
If you’ve never written an executive summary before, you might be curious about where it fits into other project management elements. Here’s how executive summaries stack up:
Executive summary vs. project plan
A project plan is a blueprint of the key elements your project will accomplish in order to hit your project goals and objectives. Project plans will include your goals, success metrics, stakeholders and roles, budget, milestones and deliverables, timeline and schedule, and communication plan .
An executive summary is a summary of the most important information in your project plan. Think of the absolutely crucial things your management team needs to know when they land in your project, before they even have a chance to look at the project plan—that’s your executive summary.
Executive summary vs. project overview
Project overviews and executive summaries often have similar elements—they both contain a summary of important project information. However, your project overview should be directly attached to your project. There should be a direct line of sight between your project and your project overview.
While you can include your executive summary in your project depending on what type of project management tool you use, it may also be a stand-alone document.
Executive summary vs. project objectives
Your executive summary should contain and expand upon your project objectives in the second part ( Outline the recommended solution, or the project’s objectives ). In addition to including your project objectives, your executive summary should also include why achieving your project objectives will add value, as well as provide details about how you’re going to get there.
The benefits of an executive summary
You may be asking: why should I write an executive summary for my project? Isn’t the project plan enough?
Well, like we mentioned earlier, not everyone has the time or need to dive into your project and see, from a glance, what the goals are and why they matter. Work management tools like Asana help you capture a lot of crucial information about a project, so you and your team have clarity on who’s doing what by when. Your executive summary is designed less for team members who are actively working on the project and more for stakeholders outside of the project who want quick insight and answers about why your project matters.
An effective executive summary gives stakeholders a big-picture view of the entire project and its important points—without requiring them to dive into all the details. Then, if they want more information, they can access the project plan or navigate through tasks in your work management tool.
How to write a great executive summary, with examples
Every executive summary has four parts. In order to write a great executive summary, follow this template. Then once you’ve written your executive summary, read it again to make sure it includes all of the key information your stakeholders need to know.
1. Start with the problem or need the project is solving
At the beginning of your executive summary, start by explaining why this document (and the project it represents) matter. Take some time to outline what the problem is, including any research or customer feedback you’ve gotten . Clarify how this problem is important and relevant to your customers, and why solving it matters.
For example, let’s imagine you work for a watch manufacturing company. Your project is to devise a simpler, cheaper watch that still appeals to luxury buyers while also targeting a new bracket of customers.
Example executive summary:
In recent customer feedback sessions, 52% of customers have expressed a need for a simpler and cheaper version of our product. In surveys of customers who have chosen competitor watches, price is mentioned 87% of the time. To best serve our existing customers, and to branch into new markets, we need to develop a series of watches that we can sell at an appropriate price point for this market.
2. Outline the recommended solution, or the project’s objectives
Now that you’ve outlined the problem, explain what your solution is. Unlike an abstract or outline, you should be prescriptive in your solution—that is to say, you should work to convince your readers that your solution is the right one. This is less of a brainstorming section and more of a place to support your recommended solution.
Because you’re creating your executive summary at the beginning of your project, it’s ok if you don’t have all of your deliverables and milestones mapped out. But this is your chance to describe, in broad strokes, what will happen during the project. If you need help formulating a high-level overview of your project’s main deliverables and timeline, consider creating a project roadmap before diving into your executive summary.
Continuing our example executive summary:
Our new watch series will begin at 20% cheaper than our current cheapest option, with the potential for 40%+ cheaper options depending on material and movement. In order to offer these prices, we will do the following:
Offer watches in new materials, including potentially silicone or wood
Use high-quality quartz movement instead of in-house automatic movement
Introduce customizable band options, with a focus on choice and flexibility over traditional luxury
Note that every watch will still be rigorously quality controlled in order to maintain the same world-class speed and precision of our current offerings.
3. Explain the solution’s value
At this point, you begin to get into more details about how your solution will impact and improve upon the problem you outlined in the beginning. What, if any, results do you expect? This is the section to include any relevant financial information, project risks, or potential benefits. You should also relate this project back to your company goals or OKRs . How does this work map to your company objectives?
With new offerings that are between 20% and 40% cheaper than our current cheapest option, we expect to be able to break into the casual watch market, while still supporting our luxury brand. That will help us hit FY22’s Objective 3: Expanding the brand. These new offerings have the potential to bring in upwards of three million dollars in profits annually, which will help us hit FY22’s Objective 1: 7 million dollars in annual profit.
Early customer feedback sessions indicate that cheaper options will not impact the value or prestige of the luxury brand, though this is a risk that should be factored in during design. In order to mitigate that risk, the product marketing team will begin working on their go-to-market strategy six months before the launch.
4. Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work
Now that you’ve shared all of this important information with executive stakeholders, this final section is your chance to guide their understanding of the impact and importance of this work on the organization. What, if anything, should they take away from your executive summary?
To round out our example executive summary:
Cheaper and varied offerings not only allow us to break into a new market—it will also expand our brand in a positive way. With the attention from these new offerings, plus the anticipated demand for cheaper watches, we expect to increase market share by 2% annually. For more information, read our go-to-market strategy and customer feedback documentation .
Example of an executive summary
When you put it all together, this is what your executive summary might look like:
![summary in case study [Product UI] Example executive summary in Asana (Project Overview)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/8aa7d41f-aed9-4f82-bb7a-4305cea4404d/inline-project-planning-executive-summary-examples-1-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Common mistakes people make when writing executive summaries
You’re not going to become an executive summary-writing pro overnight, and that’s ok. As you get started, use the four-part template provided in this article as a guide. Then, as you continue to hone your executive summary writing skills, here are a few common pitfalls to avoid:
Avoid using jargon
Your executive summary is a document that anyone, from project contributors to executive stakeholders, should be able to read and understand. Remember that you’re much closer to the daily work and individual tasks than your stakeholders will be, so read your executive summary once over to make sure there’s no unnecessary jargon. Where you can, explain the jargon, or skip it all together.
Remember: this isn’t a full report
Your executive summary is just that—a summary. If you find yourself getting into the details of specific tasks, due dates, and attachments, try taking a step back and asking yourself if that information really belongs in your executive summary. Some details are important—you want your summary to be actionable and engaging. But keep in mind that the wealth of information in your project will be captured in your work management tool , not your executive summary.
Make sure the summary can stand alone
You know this project inside and out, but your stakeholders won’t. Once you’ve written your executive summary, take a second look to make sure the summary can stand on its own. Is there any context your stakeholders need in order to understand the summary? If so, weave it into your executive summary, or consider linking out to it as additional information.
Always proofread
Your executive summary is a living document, and if you miss a typo you can always go back in and fix it. But it never hurts to proofread or send to a colleague for a fresh set of eyes.
In summary: an executive summary is a must-have
Executive summaries are a great way to get everyone up to date and on the same page about your project. If you have a lot of project stakeholders who need quick insight into what the project is solving and why it matters, an executive summary is the perfect way to give them the information they need.
For more tips about how to connect high-level strategy and plans to daily execution, read our article about strategic planning .
Related resources

Unmanaged business goals don’t work. Here’s what does.
How Asana uses work management to drive product development

How Asana uses work management to streamline project intake processes

How Asana uses work management for smoother creative production

How to Write Executive Summary for a Case Study|Business Plan

What is an executive summary?
Executive Summary is the brief introduction to and summary of your business plan (or case study). It should describe your business, the problem it solves, your target market, and the financial highlights.
A good executive summary takes your reader’s attention and lets them know what you’re doing and why they should read the rest of your business plan or proposal. It’s not unusual for investors to make an initial decision simply on the basis of reading the Executive Summary, so it’s important to get it right. We ‘re going to show you how to write an executive summary that sets your business plan apart from the rest.
For example, if a company performs a competitor analysis before deciding whether or not to move in a different strategic direction, a business plan would be put together to articulate the findings and propose further steps. This business plan would be opened with an executive summary.
As such, the executive summary quickly becomes the most important part of any business plan.
Is an executive summary important?
Are you writing a business plan to show it to investors or bankers? Then you need to have a good executive summary. A lot of people will read only the summary, no matter what. Others will first read the summary to decide whether or not to read the rest of the plan. The Executive Summary is essential to the plans that are being written for outsiders.
Now, if you are writing a business plan for internal use only, you may not need to write an executive summary. However, there are some internal plans – such as an annual operational plan or a strategic plan – that can use the summary to highlight the necessary information and to present a digestible version of the overall plan.
How long should an executive summary be?
The general rule is to have as short as possible executive summaries. Your audience has limited time and attention and needs to see your business plan information as quickly as possible.
Try to keep your executive summary under 2 pages, if necessary, even if it can be longer.
Sometimes you may need a longer executive summary
For complex case studies, you may need a more in-depth executive summary to provide readers with an overview of the case study.It may be long, but it effectively introduces the client, outlines their challenge, and describes the solution and the outcome. Sets the stage for further reading.
Guide to write an effective executive summary for Business Plan
1. a product or service description and the problem solved by your company.
Include a brief description of the product or service you are offering and why it is necessary. Your business does not need to address a larger social problem, but it should address customer needs or market opportunities.
2. A description of your target market
Your target market is who you think your clients are going to be. Sometimes the name of the product itself defines the market, such as “Peoria ‘s Best Thai Food” or “Mini Cooper Dashboard Accessory.” If not, a brief description of the target market — your primary audience or the people you think will spend money on your solution — will suffice.
3. Competition
Assuming that your business has competition, briefly describe how your business will be differentiated. Are you competing for a price, quality, or something else? Briefly describe what makes you different from your business here.
4. Financial Overview
If you are an existing company, this may be as simple as highlighting recent annual sales and growth over the last year. For start-ups, it could be a brief description of aspirations, such as the sales forecast target for the next year or three years from now. I often recommend a simple highlights chart, a sales bar chart, and a gross margin for the next three years.
5. Write About Your Team
This is particularly important for startup companies. Investors want to know who’s behind the business idea, and why you and your team are the right people to build the business. It may also be worth highlighting any gaps in your team and how you intend to fill them. If you have potential partners or candidates in mind, briefly mention them and expand their qualifications to your full business plan.
6. Funding Needs
If you’re using your business plan to raise money for your business, your executive summary should show how much money you ‘re looking for. Investors will want to know this in advance, and they won’t have to dig through a business plan to find this detail.
How To Write the Executive Summary for Case Studies?
The term “case study” brings to mind a psychologist who explores the patient’s history and treatment and writes down the details, but in fact, a case study is just as likely to involve an industry or law research report. It identifies a problem or a need, investigates its causes, presents a variety of opinions, and suggests certain actions. This involves a lot of information, which is why you might want to present it along with an executive summary – an additional document, something like a mini-report, which consolidates the most important information.
Remember, when writing this section, this is your best chance to interest the reader — and get them to act! For example: call your sales team and get more information about your products, sign up for a newsletter, download a trial product, or ask for more information about your product line.
- Understanding an Executive Summary: Consider the Executive Summary as a time-saving measure. It’s not necessarily for you, but for the people who will be receiving and reviewing your study. It captures the most important information so that your readers can understand your data and conclusions within a fraction of the time it takes them to read the entire study. For example, if you’re a financial executive building up a business case for the planned IT acquisitions, you ‘d bring your management team together to make their input into the acquisition of funds for specific IT projects. The case explains their own motivations and needs and their desire to be involved in high-level strategic decisions. It must be extremely detailed to be accurate and credible. Top-level management and chief executives have a lot of issues on their plates, so they might postpone reading your full report because it’s sure to be a time-consuming project. If you’re preparing an executive summary to go along with your report, it’s more likely to be read.
- Preparing the Data: You ‘re going to want to include enough details about your research in your executive summary to make it powerful and compelling, but brevity is key. Your summary should answer most – if not all – of the important questions that senior management may have, but be comparatively brief. A good place to start with is a review of your study, taking note of what jumps out to you as the most important data.
- Organizing the Summary: Even if your case study is 300 pages long, you may want to keep your executive summary down to 10 pages or so. If your study is shorter, your summary should be shorter. You might start with an introduction, explaining why you prepared a case study, even if it was because higher-level management asked for it. Explain why the study was needed. Describe how you’ve done your research. Lay out your findings, and then finish with your recommendations. With most executive summaries, quoting the corresponding word-by-word report is a bad idea, but when summarizing a case or research study, it is considered permissible to “cut and paste” parts of your recommendation section.
- Writing the Document: Not every great analytical mind has a gift of words as well. If writing isn’t your strong suit, you might want to consider brainstorming your management team for their ideas or hire a professional writer to draft a summary for you based on your notes. If you feel confident about your abilities, remember that your summary is your first and best chance of achieving your business objectives. Use a language that makes it clear that you believe strongly in your business case. Remember that although you know your area of expertise both inside and outside, your audience, often higher-level management, may have only a general overview of your specific field of expertise.
Download Free executive summary template for case study from HERE
See Also How to write business plan step by step How to calculate business startup costs
You may also like

Navigating the New Era: How Security Firms Are...

The Future of Clinical Trials: Embracing Precision...

Maximizing Efficiency: Tips for Hiring Top Talent in...

The Crucial Role of Mining Scales in Ensuring...

Fostering a Healthy Work Environment: The Importance...

The Rise of Food Carts: Exploring the Global Street...

Protect Your Rights In Legal Cases: A How-To Guide

Building Strong Legal Defense: Mistakes To Avoid When...
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Heart Views
- v.18(3); Jul-Sep 2017
Guidelines To Writing A Clinical Case Report
What is a clinical case report.
A case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports usually describe an unusual or novel occurrence and as such, remain one of the cornerstones of medical progress and provide many new ideas in medicine. Some reports contain an extensive review of the relevant literature on the topic. The case report is a rapid short communication between busy clinicians who may not have time or resources to conduct large scale research.
WHAT ARE THE REASONS FOR PUBLISHING A CASE REPORT?
The most common reasons for publishing a case are the following: 1) an unexpected association between diseases or symptoms; 2) an unexpected event in the course observing or treating a patient; 3) findings that shed new light on the possible pathogenesis of a disease or an adverse effect; 4) unique or rare features of a disease; 5) unique therapeutic approaches; variation of anatomical structures.
Most journals publish case reports that deal with one or more of the following:
- Unusual observations
- Adverse response to therapies
- Unusual combination of conditions leading to confusion
- Illustration of a new theory
- Question regarding a current theory
- Personal impact.
STRUCTURE OF A CASE REPORT[ 1 , 2 ]
Different journals have slightly different formats for case reports. It is always a good idea to read some of the target jiurnals case reports to get a general idea of the sequence and format.
In general, all case reports include the following components: an abstract, an introduction, a case, and a discussion. Some journals might require literature review.
The abstract should summarize the case, the problem it addresses, and the message it conveys. Abstracts of case studies are usually very short, preferably not more than 150 words.
Introduction
The introduction gives a brief overview of the problem that the case addresses, citing relevant literature where necessary. The introduction generally ends with a single sentence describing the patient and the basic condition that he or she is suffering from.
This section provides the details of the case in the following order:
- Patient description
- Case history
- Physical examination results
- Results of pathological tests and other investigations
- Treatment plan
- Expected outcome of the treatment plan
- Actual outcome.
The author should ensure that all the relevant details are included and unnecessary ones excluded.
This is the most important part of the case report; the part that will convince the journal that the case is publication worthy. This section should start by expanding on what has been said in the introduction, focusing on why the case is noteworthy and the problem that it addresses.
This is followed by a summary of the existing literature on the topic. (If the journal specifies a separate section on literature review, it should be added before the Discussion). This part describes the existing theories and research findings on the key issue in the patient's condition. The review should narrow down to the source of confusion or the main challenge in the case.
Finally, the case report should be connected to the existing literature, mentioning the message that the case conveys. The author should explain whether this corroborates with or detracts from current beliefs about the problem and how this evidence can add value to future clinical practice.
A case report ends with a conclusion or with summary points, depending on the journal's specified format. This section should briefly give readers the key points covered in the case report. Here, the author can give suggestions and recommendations to clinicians, teachers, or researchers. Some journals do not want a separate section for the conclusion: it can then be the concluding paragraph of the Discussion section.
Notes on patient consent
Informed consent in an ethical requirement for most studies involving humans, so before you start writing your case report, take a written consent from the patient as all journals require that you provide it at the time of manuscript submission. In case the patient is a minor, parental consent is required. For adults who are unable to consent to investigation or treatment, consent of closest family members is required.
Patient anonymity is also an important requirement. Remember not to disclose any information that might reveal the identity of the patient. You need to be particularly careful with pictures, and ensure that pictures of the affected area do not reveal the identity of the patient.

Case Study Summary

It doesn’t always take an expert to fix a problem. Have you ever had a light in your house that doesn’t go on? Well, it’s not an engineering project , so it wouldn’t take a genius to identify if it’s a busted light bulb or a wiring issue. For these two cases, you can easily solve one problem but might need the help of an electrician for the other. When you encounter a particular situation, basic knowledge can help you to overcome it. And when you’ve dealt with the dilemma, what comes out may be additional knowledge on how to fix similar problems. And sometimes, life just gives you these things to test how well you can handle it. In academic settings, the presentation of these solutions can be considered a case study summary.
To get a firm grip on the principles and characteristics of discipline, you may need to test out what you know through given situations. In the fields of social science, business, and research, these situations are called case studies. And the initial analysis report is called a case study summary. A case executive summary is what the readers first encounter before they decide if the case is worth examining. Your case summary saves readers time in understanding the situation you’ve presented. It holds important information about medical or business case studies that your readers need to take in.
What a Case Study Summary Isn’t
Many may assume that a case study summary is the same as an abstract. They are relatively similar, but they have their key differences. A research executive summary is for those outside the academic spectrum. An abstract is for professors, research analysts, and anyone in the academe. The case study summary is also not the introduction, although it may contain similar content, they don’t share the same purpose. It is also not the preface of the study. Most importantly, it is not just a collection of random highlights within the analysis. The format of a case study summary is for the understanding of the collected data.
10+ Case Study Summary Example
A lot of case studies are hard to understand. Some people even dread the idea of reading the whole research project from start to finish. Thankfully, there is a more natural way to grasp the context of the study. That is through case study summaries. If you are working o a case study, you should be able to write a comprehensive overview of your own. To help you figure out the outline and format of your summary, here are 10+ case study summary examples you can check out.
1. Master Technology Case Study Summary Example
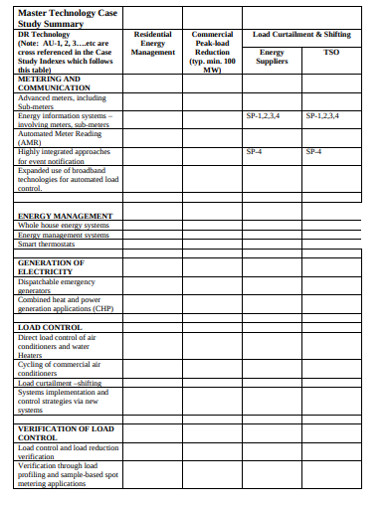
Size: 15 KB
2. Family Case Study Summary Example

Size: 216 KB
3. Case Study Summary Report Example

Size: 277 KB
4. Sample Case Studies Summary Example

Size: 487 KB
5. Case Studies Summary Workshop Example

Size: 356 KB
6. Commissioner Case Study Summary Example

7. Case Study Summary Information Example

Size: 946 KB
8. Formal Case Study Summary Example
Size: 235 KB
9. Academic Case Study Summary Example

Size: 263 KB
10. Corporation Case Studies Summary Example

Size: 573 KB
11. Standard Case Study Summary Example

Size: 193 KB
The Making an Effective Case Study Summary
As a researcher, you wouldn’t want your readers to have a hard time making sense of your case analysis . All the effort you put into making that can go to waste if it isn’t easy to understand. What you need is a compelling case study summary. If your review has the right information, your reader can level with you in no time. Here are some tricks to making a good case study summary.
1. Decide the Need
After writing an entire case study, the last thing you want is more report writing. That is why the first step to making a useful case summary is deciding if there is a need to have one. Some case studies that are considerably easier to understand don’t need case study summaries. But if your decision making says that you need it, then you better start!
2. Decide the Length
The length of the summary doesn’t always reflect how much information it holds. It can, however, determine how well of a writer you are. Your overview can be as concise as you want or as detailed as it needs to be. For as long as your research summary is readable, any length will do.
3. Prepare Data
The next step is conducting data analysis to figure out which data you are going to add to your case study summary. Pick out the most important details and the data most likely to raise questions. Anticipating these questions can help you formulate possible answers to add in your summary.
4. Organize Data
Making sure your data is organized is part and parcel to having a comprehensive case study summary. You can write a short introduction to open your summary and explain the purpose of your study. You then explain your solutions to the problem statement . Make sure no factoid overlaps another to avoid confusion.
5. Format Content
A continuous piece of writing can make a reader hesitate. Format your summary in a way that doesn’t seem too daunting. Divide your content, add a few white spaces. You have to let your readers’ eyes rest when scanning your summary. Don’t make your summary datasheet intimidating to look at.
When handling cases, whether you are a market analyst of a social science researcher, case study summaries are your best friends in data collection.

AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Case Study Executive Summary Template
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Doc
- Get started in seconds
When it comes to presenting your case study to busy executives, you need to make a lasting impression in a short amount of time. ClickUp's Case Study Executive Summary Template is here to help you do just that!
With this template, you can create a concise and impactful executive summary that highlights the most important points of your case study, including:
- A clear description of the problem or situation you addressed
- The approach you took to analyze and solve the problem
- The key findings and insights derived from your study
- Actionable recommendations and outcomes for decision-makers
Say goodbye to lengthy reports and hello to a streamlined and effective executive summary that will capture the attention of even the busiest executives. Try ClickUp's Case Study Executive Summary Template today and start impressing your stakeholders with your concise and compelling case study summaries.
Benefits of Case Study Executive Summary Template
When it comes to presenting a case study to busy executives, an executive summary template can be a game-changer. Here's how it can benefit your organization:
- Saves time by providing a concise overview of the case study's main points and findings
- Allows executives to quickly grasp the problem, approach, analysis, and recommendations of the study
- Facilitates informed decision-making by presenting key information in a clear and organized manner
- Enhances communication and collaboration among team members by providing a structured format for sharing case study insights
Main Elements of Case Study Executive Summary Template
ClickUp's Case Study Executive Summary template is the perfect tool to showcase the highlights and key findings of your case study in an organized and professional manner. Here are the main elements of this template:
- Custom Statuses: Stay on top of the progress of your executive summary by using custom statuses such as In Progress, Review, and Completed.
- Custom Fields: Capture important details about your case study, such as Client Name, Objective, Methodology, Results, and Conclusion, using custom fields. This allows for easy data entry and retrieval.
- Different Views: Choose from various views to work with your executive summary. Use the Doc view to write and format your summary, the Table view to organize data and findings, and the Calendar view to set deadlines and milestones.
With ClickUp's Case Study Executive Summary template, you can streamline the process of creating professional and impactful case study summaries.
How to Use Executive Summary for Case Study
To create a compelling and effective case study executive summary, follow these five steps:
1. Understand the purpose
Before you start writing your executive summary, it's important to understand its purpose. The executive summary is a concise overview of the case study that highlights the key points and findings. It should provide enough information to give the reader a clear understanding of the case study without having to read the entire report.
Use the Docs feature in ClickUp to familiarize yourself with the purpose and structure of an executive summary.
2. Identify the main sections
To create a well-organized executive summary, identify the main sections of your case study that need to be included. This typically includes a brief introduction, the problem or challenge, the solution implemented, the results achieved, and any key takeaways or lessons learned.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to outline the main sections and structure your executive summary.
3. Summarize the key points
In each section of your executive summary, summarize the key points from the corresponding section of the case study. Focus on the most important information and findings, and avoid including unnecessary details. Use clear and concise language to effectively communicate the main points.
Use the tasks feature in ClickUp to create individual sections for each key point and summarize them concisely.
4. Highlight the results and impact
One of the most important aspects of a case study is the results achieved and the impact it had. In your executive summary, highlight the key results and their significance. Use data and metrics to support your claims and provide evidence of the success of the case study.
Use custom fields in ClickUp to track and showcase the specific results and impact of the case study.
5. Review and refine
Once you have completed your case study executive summary, take the time to review and refine it. Look for any areas that can be improved or clarified, and ensure that the summary is cohesive and flows smoothly. Consider seeking feedback from others to get a fresh perspective.
Set a recurring task in ClickUp to review and refine your executive summary periodically to keep it up-to-date and relevant.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Case Study Executive Summary Template
Companies and consultants can use this Case Study Executive Summary Template to quickly summarize the key points of a case study for busy executives or decision-makers.
First, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create effective executive summaries:
- Use the Summary View to provide a concise overview of the case study, including the problem, approach, analysis, and main recommendations or outcomes
- The Key Findings View will help you highlight the most important insights and conclusions from the study
- Use the Recommendations View to outline specific actions or strategies recommended based on the case study findings
- The Visuals View will allow you to include charts, graphs, or other visual representations to support your summary
- Customize the template by adding sections or fields that are relevant to your specific case study
- Update the summary regularly as new information or developments arise
- Share the executive summary with the intended audience in a clear and easily accessible format
Related Templates
- Taxi Drivers Executive Summary Template
- Training And Development Project Executive Summary Template
- Music Producers Executive Summary Template
- A Grant Executive Summary Template
- Facility Administrators Executive Summary Template
Free forever with 100MB storage
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide

How Do We Know Climate Change Is Real?
There is unequivocal evidence that Earth is warming at an unprecedented rate. Human activity is the principal cause.

- While Earth’s climate has changed throughout its history , the current warming is happening at a rate not seen in the past 10,000 years.
- According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change ( IPCC ), "Since systematic scientific assessments began in the 1970s, the influence of human activity on the warming of the climate system has evolved from theory to established fact." 1
- Scientific information taken from natural sources (such as ice cores, rocks, and tree rings) and from modern equipment (like satellites and instruments) all show the signs of a changing climate.
- From global temperature rise to melting ice sheets, the evidence of a warming planet abounds.
The rate of change since the mid-20th century is unprecedented over millennia.
Earth's climate has changed throughout history. Just in the last 800,000 years, there have been eight cycles of ice ages and warmer periods, with the end of the last ice age about 11,700 years ago marking the beginning of the modern climate era — and of human civilization. Most of these climate changes are attributed to very small variations in Earth’s orbit that change the amount of solar energy our planet receives.
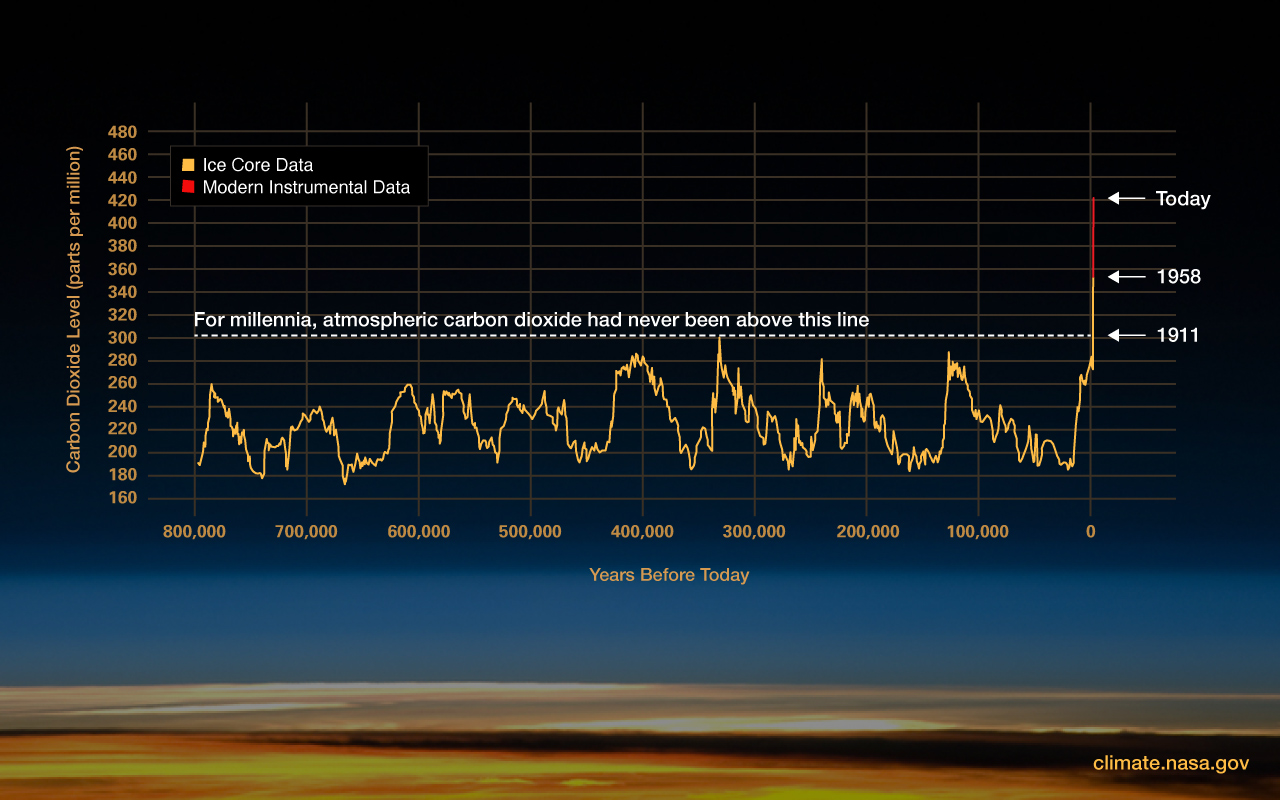
The current warming trend is different because it is clearly the result of human activities since the mid-1800s, and is proceeding at a rate not seen over many recent millennia. 1 It is undeniable that human activities have produced the atmospheric gases that have trapped more of the Sun’s energy in the Earth system. This extra energy has warmed the atmosphere, ocean, and land, and widespread and rapid changes in the atmosphere, ocean, cryosphere, and biosphere have occurred.
Related Reading
Do scientists agree on climate change?
Yes, the vast majority of actively publishing climate scientists – 97 percent – agree that humans are causing global warming and climate change.
Earth-orbiting satellites and new technologies have helped scientists see the big picture, collecting many different types of information about our planet and its climate all over the world. These data, collected over many years, reveal the signs and patterns of a changing climate.
Scientists demonstrated the heat-trapping nature of carbon dioxide and other gases in the mid-19th century. 2 Many of the science instruments NASA uses to study our climate focus on how these gases affect the movement of infrared radiation through the atmosphere. From the measured impacts of increases in these gases, there is no question that increased greenhouse gas levels warm Earth in response.
"Scientific evidence for warming of the climate system is unequivocal." — Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Ice cores drawn from Greenland, Antarctica, and tropical mountain glaciers show that Earth’s climate responds to changes in greenhouse gas levels. Ancient evidence can also be found in tree rings, ocean sediments, coral reefs, and layers of sedimentary rocks. This ancient, or paleoclimate, evidence reveals that current warming is occurring roughly 10 times faster than the average rate of warming after an ice age. Carbon dioxide from human activities is increasing about 250 times faster than it did from natural sources after the last Ice Age. 3
The Evidence for Rapid Climate Change Is Compelling:
Global temperature is rising.
The planet's average surface temperature has risen about 2 degrees Fahrenheit (1 degrees Celsius) since the late 19th century, a change driven largely by increased carbon dioxide emissions into the atmosphere and other human activities. 4 Most of the warming occurred in the past 40 years, with the seven most recent years being the warmest. The years 2016 and 2020 are tied for the warmest year on record. 5
The Ocean Is Getting Warmer
The ocean has absorbed much of this increased heat, with the top 100 meters (about 328 feet) of ocean showing warming of 0.67 degrees Fahrenheit (0.33 degrees Celsius) since 1969. 6 Earth stores 90% of the extra energy in the ocean.
The Ice Sheets Are Shrinking
The Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets have decreased in mass. Data from NASA's Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment show Greenland lost an average of 279 billion tons of ice per year between 1993 and 2019, while Antarctica lost about 148 billion tons of ice per year. 7
Glaciers Are Retreating
Glaciers are retreating almost everywhere around the world — including in the Alps, Himalayas, Andes, Rockies, Alaska, and Africa. 8
Snow Cover Is Decreasing
Satellite observations reveal that the amount of spring snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere has decreased over the past five decades and the snow is melting earlier. 9
Sea Level Is Rising
Global sea level rose about 8 inches (20 centimeters) in the last century. The rate in the last two decades, however, is nearly double that of the last century and accelerating slightly every year. 10
Arctic Sea Ice Is Declining
Both the extent and thickness of Arctic sea ice has declined rapidly over the last several decades. 11
Extreme Events Are Increasing in Frequency
The number of record high temperature events in the United States has been increasing, while the number of record low temperature events has been decreasing, since 1950. The U.S. has also witnessed increasing numbers of intense rainfall events. 12
Ocean Acidification Is Increasing
Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, the acidity of surface ocean waters has increased by about 30%. 13 , 14 This increase is due to humans emitting more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere and hence more being absorbed into the ocean. The ocean has absorbed between 20% and 30% of total anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions in recent decades (7.2 to 10.8 billion metric tons per year). 1 5 , 16
1. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report, WGI, Technical Summary . B.D. Santer et.al., “A search for human influences on the thermal structure of the atmosphere.” Nature 382 (04 July 1996): 39-46. https://doi.org/10.1038/382039a0. Gabriele C. Hegerl et al., “Detecting Greenhouse-Gas-Induced Climate Change with an Optimal Fingerprint Method.” Journal of Climate 9 (October 1996): 2281-2306. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<2281:DGGICC>2.0.CO;2. V. Ramaswamy, et al., “Anthropogenic and Natural Influences in the Evolution of Lower Stratospheric Cooling.” Science 311 (24 February 2006): 1138-1141. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1122587. B.D. Santer et al., “Contributions of Anthropogenic and Natural Forcing to Recent Tropopause Height Changes.” Science 301 (25 July 2003): 479-483. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1084123. T. Westerhold et al., "An astronomically dated record of Earth’s climate and its predictability over the last 66 million years." Science 369 (11 Sept. 2020): 1383-1387. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1094123
2. In 1824, Joseph Fourier calculated that an Earth-sized planet, at our distance from the Sun, ought to be much colder. He suggested something in the atmosphere must be acting like an insulating blanket. In 1856, Eunice Foote discovered that blanket, showing that carbon dioxide and water vapor in Earth's atmosphere trap escaping infrared (heat) radiation. In the 1860s, physicist John Tyndall recognized Earth's natural greenhouse effect and suggested that slight changes in the atmospheric composition could bring about climatic variations. In 1896, a seminal paper by Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius first predicted that changes in atmospheric carbon dioxide levels could substantially alter the surface temperature through the greenhouse effect. In 1938, Guy Callendar connected carbon dioxide increases in Earth’s atmosphere to global warming. In 1941, Milutin Milankovic linked ice ages to Earth’s orbital characteristics. Gilbert Plass formulated the Carbon Dioxide Theory of Climate Change in 1956.
3. IPCC Sixth Assessment Report, WG1, Chapter 2 Vostok ice core data; NOAA Mauna Loa CO2 record O. Gaffney, W. Steffen, "The Anthropocene Equation." The Anthropocene Review 4, issue 1 (April 2017): 53-61. https://doi.org/abs/10.1177/2053019616688022.
4. https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/monitoring https://crudata.uea.ac.uk/cru/data/temperature/ http://data.giss.nasa.gov/gistemp
5. https://www.giss.nasa.gov/research/news/20170118/
6. S. Levitus, J. Antonov, T. Boyer, O Baranova, H. Garcia, R. Locarnini, A. Mishonov, J. Reagan, D. Seidov, E. Yarosh, M. Zweng, " NCEI ocean heat content, temperature anomalies, salinity anomalies, thermosteric sea level anomalies, halosteric sea level anomalies, and total steric sea level anomalies from 1955 to present calculated from in situ oceanographic subsurface profile data (NCEI Accession 0164586), Version 4.4. (2017) NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information. https://www.nodc.noaa.gov/OC5/3M_HEAT_CONTENT/index3.html K. von Schuckmann, L. Cheng, L,. D. Palmer, J. Hansen, C. Tassone, V. Aich, S. Adusumilli, H. Beltrami, H., T. Boyer, F. Cuesta-Valero, D. Desbruyeres, C. Domingues, A. Garcia-Garcia, P. Gentine, J. Gilson, M. Gorfer, L. Haimberger, M. Ishii, M., G. Johnson, R. Killick, B. King, G. Kirchengast, N. Kolodziejczyk, J. Lyman, B. Marzeion, M. Mayer, M. Monier, D. Monselesan, S. Purkey, D. Roemmich, A. Schweiger, S. Seneviratne, A. Shepherd, D. Slater, A. Steiner, F. Straneo, M.L. Timmermans, S. Wijffels. "Heat stored in the Earth system: where does the energy go?" Earth System Science Data 12, Issue 3 (07 September 2020): 2013-2041. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-12-2013-2020.
7. I. Velicogna, Yara Mohajerani, A. Geruo, F. Landerer, J. Mouginot, B. Noel, E. Rignot, T. Sutterly, M. van den Broeke, M. Wessem, D. Wiese, "Continuity of Ice Sheet Mass Loss in Greenland and Antarctica From the GRACE and GRACE Follow-On Missions." Geophysical Research Letters 47, Issue 8 (28 April 2020): e2020GL087291. https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL087291.
8. National Snow and Ice Data Center World Glacier Monitoring Service
9. National Snow and Ice Data Center D.A. Robinson, D. K. Hall, and T. L. Mote, "MEaSUREs Northern Hemisphere Terrestrial Snow Cover Extent Daily 25km EASE-Grid 2.0, Version 1 (2017). Boulder, Colorado USA. NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center. doi: https://doi.org/10.5067/MEASURES/CRYOSPHERE/nsidc-0530.001 . http://nsidc.org/cryosphere/sotc/snow_extent.html Rutgers University Global Snow Lab. Data History
10. R.S. Nerem, B.D. Beckley, J. T. Fasullo, B.D. Hamlington, D. Masters, and G.T. Mitchum, "Climate-change–driven accelerated sea-level rise detected in the altimeter era." PNAS 15, no. 9 (12 Feb. 2018): 2022-2025. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717312115.
11. https://nsidc.org/cryosphere/sotc/sea_ice.html Pan-Arctic Ice Ocean Modeling and Assimilation System (PIOMAS, Zhang and Rothrock, 2003) http://psc.apl.washington.edu/research/projects/arctic-sea-ice-volume-anomaly/ http://psc.apl.uw.edu/research/projects/projections-of-an-ice-diminished-arctic-ocean/
12. USGCRP, 2017: Climate Science Special Report: Fourth National Climate Assessment, Volume I [Wuebbles, D.J., D.W. Fahey, K.A. Hibbard, D.J. Dokken, B.C. Stewart, and T.K. Maycock (eds.)]. U.S. Global Change Research Program, Washington, DC, USA, 470 pp, https://doi.org/10.7930/j0j964j6 .
13. http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/co2/story/What+is+Ocean+Acidification%3F
14. http://www.pmel.noaa.gov/co2/story/Ocean+Acidification
15. C.L. Sabine, et al., “The Oceanic Sink for Anthropogenic CO2.” Science 305 (16 July 2004): 367-371. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1097403.
16. Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate , Technical Summary, Chapter TS.5, Changing Ocean, Marine Ecosystems, and Dependent Communities, Section 5.2.2.3. https://www.ipcc.ch/srocc/chapter/technical-summary/
Header image shows clouds imitating mountains as the sun sets after midnight as seen from Denali's backcountry Unit 13 on June 14, 2019. Credit: NPS/Emily Mesner
Discover More Topics From NASA
Explore Earth Science

Earth Science in Action

Earth Science Data
Facts About Earth

Law Enforcement Deaths by Suicide
Introduction.
Police and correctional officers (hereafter referred to as public safety personnel) routinely confront arduous and psychologically taxing circumstances that can adversely affect their mental and emotional health. In a thorough survey encompassing 2,232 law enforcement officers, Mumford and colleagues (2021) noted that although two-thirds displayed healthy behaviors, approximately one-fourth encountered moderate health challenges, and a minority (6 percent) grappled with more severe health issues. Similarly, a separate study conducted by Drew and Martin (2023) involving 3,994 officers found that 44 percent experienced psychological distress, such as depression and anxiety within the previous four weeks, and nearly a quarter of them experienced moderate to severe distress.
Extensive research highlights the profound repercussions of poor wellness characteristics among public safety personnel, including cognitive dissonance toward society, feelings of isolation, and diminished self-worth, which potentially increase the risk of suicide attempts or deaths by suicide (Civilotti et al., 2022; Newiss et al., 2022; Stogner et al., 2020; Violanti & Steege, 2021). Thoen et al. (2020) reported that 12.4 percent of surveyed police officers expressed a likelihood of future suicide attempts, with 13.2 percent acknowledging suicidal thoughts in the past year. Moreover, compared to the general population, law enforcement officers face a 54 percent higher risk of dying by suicide (Violanti & Steege, 2021), underscoring the critical need for comprehensive wellness programs and support structures within the field.
Despite extensive research into the correlates of public safety personnel deaths by suicide, all police and public safety professions are challenged by the absence of a systematic, national, and comprehensive data collection effort to fully grasp the extent of the problem (Dixon, 2021; Malik et al., 2023; NASEM, 2023). Recognizing the critical need for accurate data in this area, Congress enacted the Law Enforcement Suicide Data Collection (LESDC) Act on June 16, 2020. Part of the LESDC Act mandates the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) to establish a national data collection effort to seek incidental information on suicides, including gestures, ideation, and attempted suicides within the law enforcement community. However, initial federal efforts have been slow and have encountered numerous challenges.
The nonprofit organization First H.E.L.P. (Honor, Educate, Lead, Prevent) has been collecting data systematically since 2016 on deaths by suicide among public safety personnel. In late 2023, the CNA Corporation (hereafter “CNA”) initiated a partnership with First H.E.L.P. to undertake the first comprehensive analysis of its extensive dataset on public safety personnel deaths by suicide. This brief presents an overview of previous research and data collection endeavors related to public safety personnel deaths by suicide. It outlines the methodology employed by First H.E.L.P. for its data collection and offers descriptive insights into public safety personnel deaths by suicide. The results are organized according to the year of occurrence, agency information, geographical distribution, demographic attributes, position details, help-seeking behaviors, life challenges the person encountered before their death, and details about the death event.
Approved for public release. Unlimited distribution.
- Document Number: RM-2024-U-037860-Final
- Publication Date: 3/20/2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
summarize the story by introducing the customer and their pain points. explain what your organization did. highlight the key results, including 1 or 2 statistics that drive home the takeaway message. Write the executive summary first to help you focus the rest of the case study. But don't be too rigid: in the process of reviewing the ...
Executive Summary Case Study. An executive summary is a detailed overview of a report. It saves readers time by summarizing the essential points of the study. It is frequently written to be shared with people who may not have time to read the complete report, for example, CEOs or department heads.
Case study examples. Case studies are proven marketing strategies in a wide variety of B2B industries. Here are just a few examples of a case study: Amazon Web Services, Inc. provides companies with cloud computing platforms and APIs on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis.
Case study formats can include traditional print stories, interactive web or social content, data-heavy infographics, professionally shot videos, podcasts, and more. 5. Write your case study. We'll go into more detail later about how exactly to write a case study, including templates and examples. Generally speaking, though, there are a few ...
A case study summary is a short recap of a detailed case, interview, or other document. It has all of the same traits as that of a good summary: it's clean, short, straightforward, and flows naturally for the reader. But in the business world, a case study has the job of connecting customers with business, and a great summary also does the same
Explain the problem in question. Dive into the problem or challenge that the case study focuses on. Provide enough background information for the audience to understand the issue. If possible, quantify the problem using data or metrics to show the magnitude or severity.
A great case study will contain five essential elements: Without proper preparation, your case study won't have enough details to be strongly relatable, convincing, or reassuring. To help you streamline your process, use the prep section of our free case study template and follow the suggested research method below. Step 1: Set Your Objectives
Tips For Summarizing A Case Study. 1. Read the Entire Study. The first step in summarizing a case study is to read the entire study. This will help you get a better understanding of the key points of the study and will help you identify the most important aspects of the study. Additionally, reading the entire study will help you identify any ...
The five case studies listed below are well-written, well-designed, and incorporate a time-tested structure. 1. Lane Terralever and Pinnacle at Promontory. This case study example from Lane Terralever incorporates images to support the content and effectively uses subheadings to make the piece scannable. 2.
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
Explain what you will examine in the case study. Write an overview of the field you're researching. Make a thesis statement and sum up the results of your observation in a maximum of 2 sentences. Background. Provide background information and the most relevant facts. Isolate the issues.
In your mind's eye, see the Executive Summary and the Case Study are two separate documents. Approach each one with a different 'writer's hat'. The tone, style, and language may be different. In general, the Executive Summary will be tightly-written, direct, and high-level. You dive into these points in the case study itself.
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity.
An article summary like the above would be appropriate for a stand-alone summary assignment. However, you'll often want to give an even more concise summary of an article. For example, in a literature review or meta analysis you may want to briefly summarize this study as part of a wider discussion of various sources. In this case, we can ...
Case Studies. Case studies are in-depth studies of a subject, person, event or organization. They focus on real-world problems and situations and require a deep understanding of the subject. Whether you're writing case studies for academics, projects or business, at a glance, your executive summary should: Describe who the case study is about.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Environmental studies. Market surveys. Project plans. In general, there are four parts to any executive summary: Start with the problem or need the document is solving. Outline the recommended solution. Explain the solution's value. Wrap up with a conclusion about the importance of the work.
A good place to start with is a review of your study, taking note of what jumps out to you as the most important data. Organizing the Summary: Even if your case study is 300 pages long, you may want to keep your executive summary down to 10 pages or so. If your study is shorter, your summary should be shorter.
A case report is a detailed report of the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of an individual patient. Case reports usually describe an unusual or novel occurrence and as such, remain one of the cornerstones of medical progress and provide many new ideas in medicine. Some reports contain an extensive review of the relevant ...
The format of a case study summary is for the understanding of the collected data. 10+ Case Study Summary Example. A lot of case studies are hard to understand. Some people even dread the idea of reading the whole research project from start to finish. Thankfully, there is a more natural way to grasp the context of the study.
Although case studies have been discussed extensively in the literature, little has been written about the specific steps one may use to conduct case study research effectively (Gagnon, 2010; Hancock & Algozzine, 2016).Baskarada (2014) also emphasized the need to have a succinct guideline that can be practically followed as it is actually tough to execute a case study well in practice.
ClickUp's Case Study Executive Summary template is the perfect tool to showcase the highlights and key findings of your case study in an organized and professional manner. Here are the main elements of this template: Custom Statuses: Stay on top of the progress of your executive summary by using custom statuses such as In Progress, Review, and ...
Here's how to create a concise and insightful case study summary with our tool. 1. Enter the Details: Paste your lengthy case study into the field. Select your target audience, tone of voice, and output language. 2. Push to Produce: Hit the button to kick off the AI-powered summarization process. Our AI instantly gets to work.
Case Study Exercise I. A chapter from Microsoft Azure Machine Learning by Sumit Mund, Christina Storm
Our study's findings encourage a more cautious, personalized approach to dietary recommendations, ensuring that they are aligned with an individual's health status and the latest scientific evidence," he continued. "Although the study identified an association between an 8-hour eating window and cardiovascular death, this does not mean ...
Authorities in Tennessee are searching for a 22-year-old college student who vanished after leaving a downtown Nashville bar more than a week ago. Riley Strain, a student at the University of ...
The current warming trend is different because it is clearly the result of human activities since the mid-1800s, and is proceeding at a rate not seen over many recent millennia. 1 It is undeniable that human activities have produced the atmospheric gases that have trapped more of the Sun's energy in the Earth system. This extra energy has warmed the atmosphere, ocean, and land, and ...
Plain language summary Some medications can lead to a condition called drug-induced long QT syndrome (diLQTS), which can be a serious abnormal heart rhythm in some patients. ... KCNE2-I57T and SCN5A-G615E with diLQTS in a large observational case-control study (6,083 self-reported white patients treated with 27 different high-risk QT-prolonging ...
Similarly, a separate study conducted by Drew and Martin (2023) involving 3,994 officers found that 44 percent experienced psychological distress, such as depression and anxiety within the previous four weeks, and nearly a quarter of them experienced moderate to severe distress.