
- My presentations

Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer
Published by Rudy Brewer Modified over 9 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer"— Presentation transcript:

How Much Do I Remember? Are you ready to play.....

Basic Computer Vocabulary

Computer Skills Preparatory Year Presented by:

Computer Basics Whats that thingamagige?. Parts of a computer.

Chapter 1:Introduction to the world of computers

McGraw-Hill/Irwin ©2008 The McGraw-Hill Companies, All Rights Reserved Plug-in B3 HARDWARE & SOFTWARE.

1 Jordan University of Science & Technology Faculty of Computer & Information Technology Department of Computer Science & Information Systems cs98.

An Overview of the Computer System

Hardware. Basic Computer System Central Processing Unit Input Devices Output Devices Backing Storage Devices.

Introduction to Computers

Computer Systems – Hardware

What Is A Computer System?

1 Hardware - devices for Input. 2 Hardware - devices for Input Processing.

1 System Software “Background software”, manages the computer’s internal resources.

1 Introduction to Computers Prof. Sokol Computer and Information Science Brooklyn College.

Computer Parts There are many parts that work together to make a computer work.

Introduction to Computers Essential Understanding of Computers and Computer Operations.

MIS 175 Spring Learning Objectives When you finish this chapter, you will: –Recognize major components of an electronic computer. –Understand how.

Computer Skills CIS-100 CH 1.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

lesson 1-Introduction to computers.pptx

Related Papers
chitra devi
Kinoti Kaburuki
G G Rajput Rajput
SUBHAJIT PANDA
Computer, any of a class of devices capable of solving problems by processing information in discrete form. It operates on data, including magnitudes, letters, and symbols, that are expressed in binary code — i.e., using only the two digits 0 and 1. By counting, comparing, and manipulating these digits or their combinations according to a set of instructions held in its memory, a digital computer can perform such tasks as to control industrial processes and regulate the operations of machines; analyze and organize vast amounts of business data; and simulate the behaviour of dynamic systems (e.g., global weather patterns and chemical reactions) in scientific research. A typical computer system has four basic functional elements : (1) Input-output equipment, (2) Main memory, (3) Control unit, and (4) Arithmetic-logic unit.
Mahendra Pratap
Emma Greening
THE CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT & OPERATING SYSTEMS
Santino Madut Uchalla
Subhash shetty
A computer is a device that can be instructed to carry out arbitrary sequences of arithmetic or logical operations automatically. The ability of computers to follow generalized sets of operations, called programs, enables them to perform an extremely wide range of tasks. Such computers are used as control systems for a very wide variety of industrial and consumer devices. This includes simple special purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls , factory devices such as industrial robots and computer assisted design, but also in general purpose devices like personal computers and mobile devices such as smartphones. The Internet is run on computers and it connects millions of other computers. Since ancient times, simple manual devices like the abacus aided people in doing calculations. Early in the Industrial Revolution, some mechanical devices were built to automate long tedious tasks, such as guiding patterns for looms. More sophisticated electrical machines did specialized analog calculations in the early 20th century. The first digital electronic calculating machines were developed during World War II. The speed, power, and versatility of computers has increased continuously and dramatically since then. Conventionally, a modern computer consists of at least one processing element, typically a central processing unit (CPU), and some form of memory. The processing element carries out arithmetic and logical operations, and a sequencing and control unit can change the order of operations in response to stored information. Peripheral devices include input devices (keyboards, mice, joystick, etc.), output devices (monitor screens, printers, etc.), and input/output devices that perform both functions (e.g., the 2000s-era touchscreen). Peripheral devices allow information to be retrieved from an external source and they enable the result of operations to be saved and retrieved.- source = Wekipeda
osheen sharma
The central processing unit (CPU, occasionally central processor unit) is the hardware within a computer system which carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The term has been in use in the computer industry at least since the early 1960s. The form, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over the course of their history, but their fundamental operation remains much the same. A computer as shown below performs basically five major operations or functions irrespective of their size and make. These are 1) it accepts data or instructions by way of input, 2) it stores data, 3) it can process data as required by the user, 4) it gives results in the form of output, and 5) it controls all operations inside a computer. We discuss below each of these operations. 1. Input: In computing, an input device is any peripheral (piece of computer hardware equipment) used to provide data and control signals to an information processing system such as a computer or other information appliance. 2. Storage: Storage Devices are the data storage devices that are used in the computers to store the data. The computer has many types of data storage devices. Some of them can be classified as the removable data Storage Devices and the others as the non removable data Storage Devices. The memory is of two types; one is the primary memory and the other one is the secondary memory. The primary memory is the volatile memory and the secondary memory is the non volatile memory. The volatile memory is the kind of the memory that is erasable and the non volatile memory is the one where in the contents cannot be erased. Basically when we talk about the data storage devices it is generally assumed to be the secondary memory.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
The EMBO Journal
C. Von Kobbe
Yahya M. Bah
Oscar Romero Cruz
2016 IEEE International Conference on Recent Trends in Electronics, Information & Communication Technology (RTEICT)
barkha rani
Saidah Manan
Juan Felipe Medina Mendieta
The Indigenous World
International Work Group for Indigenous Affairs (IWGIA)
New Trends in Mathematical Science
عبد الغاني تيايبية
Revista Brasileira de Ciência do Solo
Paulo Valente Ferreira Neto
Restinanda Putri Mulia
Applied ergonomics
Neil Osborne
Ceria: Jurnal Program Studi Pendidikan Anak Usia Dini
Irmawati Irma
U.S. Utility-Scale Solar Gains Another Major New Entrant
Svante Kumlin
Revista chilena de historia natural
Eduardo Peña
Scleroderma, myositis and related syndromes
Simona Rednic
Journal of Power Sources
Carla Fonseca
Frontiers in immunology
Frank Grosveld
saifudeen abdulrahman
Working Papers em Lingüística
Aparecida Isquerdo
Revista Brasileira de Reumatologia
Veselin Skrabic
rtytrewer htytrer
Mahnaz Nouri
Journal of Environmental Management
sneha sagarkar
International Journal of Humanities Social Sciences and Education (IJHSSE)
Mojeed Oladele
See More Documents Like This
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Computer Fundamentals and Programming in C
Reema Thareja, Assistant Professor, Institute of Information Technology and Management
© Oxford University Press 2012. All rights reserved.
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
1 st gen-1940-56
2 nd gen 1956-63
3 rd -64-71
4 th —72-89
5 th -mordern day
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SOFTWARE
- A computer is a machine that takes instructions and performs computations based on those instructions.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COMPUTERS
GENERATION OF COMPUTERS
The word generation means the state of improvement in the product development process. Similarly, computer generation refers to the different advancements of new computer technology.
First Generation (1940-1956) Vacuum Tubes
The first generation computers used very large number of vacuum tubes for circuitry and magnetic drums for memory.
UNIVAC and ENIAC computers are prime examples of first-generation computing devices.
Advantages: Fastest calculating device of their time
Disadvantages:
1. Dissipate a lot of heat
2. Consume a lot of electricity
3. Very bulky in size
4. These computers were frequently down due to hardware failures.
5. These computers needed constant maintenance because of low mean time between failures
6. Limited commercial use because these computers were difficult to program
7. Very expensive
Second Generation (1956-1963) Transistors
- The second generation computers were manufactured using transistors.
- While first generation computers were programmed using machine language, second generation computers moved towards symbolic, or assembly languages, which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words.
- At this time, high-level programming languages like COBOL, FORTRAN, ALGOL and SNOBOL were also being developed.
- Second generation computers were first to store instructions in memory, which moved from a magnetic drum to magnetic core technology.
- Second generation computers were first developed for the atomic energy industry.
Advantages:
1. Consumed less electricity and thus dissipated less heat as compared to first generation computers
2. Faster, cheaper smaller and more reliable than first generation computers
3. Could be programmed using assembly language and high level languages
4. These computers had faster primary memory and a larger secondary memory
1. Second generation computers were manufactured using transistors that had to be assembled manually. This made commercial production of computers difficult and expensive.
Third Generation (1964-1971) Integrated Circuits
- The development of the integrated circuit was the hallmark of the third generation of computers.
- These computers had few megabytes of main memory and magnetic disks which could store few tens of megabytes of data per disk drive.
- High level programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN were standardized by ANSI
- Some more high level programming languages like PL/I PASCAL and BASIC were introduced at this time.
- Third generation computers were the first to implement time sharing operating systems.
- Input to these computers could now be provided using keyboards and mouse.
- Faster than second generation computers and could perform 1 million transactions per second.
2. Smaller, cheaper and more reliable than their predecessors
3. These computers had faster and larger primary memory and secondary storage
4. They were widely used for scientific as well as business applications
5. During this generation of computers, standardization of existing high level languages and invention of new high level languages was done
6. These computers had time sharing operating system which allowed interactive use of computer by one or more users simultaneously thereby improving the productivity of the users.
Fourth Generation (1971-1989) Microprocessors
- The microprocessor started the fourth generation of computers with thousands of integrated circuits built onto a single silicon chip.
- Semi-conductor memories were used which were very fast, even the hard disks became cheaper, smaller in size and larger in capacity.
- For input, floppy disks (in addition to magnetic tapes) were used to port data and programs from one computer to another.
- During this period many new operating systems were developed like MS-DOS MS-Windows UNIX and Apple’s proprietary operating system.
- Development of GUIs, the mouse and handheld devices.
- In this period, several word processing packages, spreadsheet packages and graphics packages were introduced.
1. Smaller, cheaper, faster and more reliable
2. Consumed less electricity and therefore dissipated less heat
3. They had faster and larger primary memory and secondary storage
4. They could be used as general purpose computers.
5. GUIs enabled people to learn to work with computers very easily. So the use of computers in both office and home became widespread.
6. Networks allowed sharing of resources thereby efficient utilization of computer hardware and software
Fifth Generation (Present and Beyond) Artificial Intelligence
- The fifth generation computers are completely based on a new concept of artificial intelligence.
- Although such computers are still in development, there are certain applications like voice recognition which is widely being used today.
- In the fifth generation of computers the aim is to develop devices that respond to natural language input and are capable of learning and self-organization.
- The two most common are LISP and Prolog.
CLASSIFICATION OF COMPUTERS
Computers can be broadly classified into four categories based on their speed, amount of data that they can hold and price.
Computers can be broadly classified into four categories based on their speed, amount of data that they can hold, and price .
Classification of Computers
Super Computer
Mini Computers
Mainframe Computers
Micro Computers
Intelligent Terminal
Dumb Terminal
Workstation
Cellular Telephones
H/PC Pro Devices
APPLICATIONS OF COMPUTERS
- Word Processing
- Digital Audio or Video Composition
- Desktop Publishing
- Traffic Control
- Legal System
- Retail Business
- Travel and Tourism
- Business and Industry
- Weather Forecasting
- Online Banking
- Industry and Engineering
- Decision Support Systems
- Expert Systems
BASIC ORGANIZATION OF A COMPUTER
A computer is an electronic device which basically performs five major operations which includes:
1) accepts data or instructions (input)
2) stores data
3) process data
4) displays results (output) and
5) controls and co-ordinates all operations inside a computer
CONTROL UNIT
ARITHMETIC LOGIC UNIT
Data and instructions
Flow of data and instructions
Control exercised by control unit

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is PowerPoint: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
What is PowerPoint? This blog provides the essence of PowerPoint, a versatile presentation software by Microsoft. Discover its features, uses, and the art of crafting compelling slideshows. Whether you're a student, professional, or simply curious, explore the power of PowerPoint and learn how to create impactful presentations effortlessly.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals (ERP) MB920
- Microsoft Access Training
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Fundamentals (CRM) MB910
- Microsoft Word Course
- Microsoft Dynamics 365 Marketing MB220

According to Glassdoor , a PowerPoint designer's average salary in the UK is about £37,811 annually. In this blog, you will learn What is PowerPoint, its key features, its benefits, and how to use it, as well as learn some tips for creating effective presentations.
Table of contents
1) What is PowerPoint?
2) Understanding the PowerPoint Interface
3) Key Features of PowerPoint
4) How to use PowerPoint to create a presentation?
5) Benefits of PowerPoint
6) Tips for Creating Effective PowerPoint Presentations
7) Conclusion
What is PowerPoint?
PowerPoint is a versatile and popular presentation software developed by Microsoft (MS). It is a part of the Microsoft Office Suite and offers various features and tools to create visually appealing and engaging presentations. MS PowerPoint allows users to combine text, graphics, multimedia elements, and animations to convey information effectively .
Evolution of PowerPoint

Understanding the PowerPoint Interface
The PowerPoint interface provides a user-friendly environment for creating and editing presentations. Familiarising yourself with its essential components will help you navigate the software efficiently. Here's a breakdown of the MS PowerPoint interface:
1) Ribbon : The Ribbon is located at the top of the MS PowerPoint window and consists of multiple tabs, such as Home, Insert, Design, Transitions, and more.
2) Slides pane : The Slides pane is on the left side of the PowerPoint window. It displays thumbnail images of your presentation slides, allowing you to navigate and rearrange them easily. You can add, delete, duplicate, or hide slides from this pane.
3) Notes pane : The Notes pane is located below the Slides pane. It provides space for adding speaker notes or additional information related to each slide.
4) Slide area : The Slide area occupies the central part of the PowerPoint window. It displays the selected slide, where you can add and arrange content such as text, images, charts, and multimedia elements .
5) Task panes : Task panes are additional panels on the PowerPoint window's right side. They offer various functionalities such as formatting options, slide layouts, animations, etc. Task panes can be opened or closed based on your specific needs.
Understanding the MS PowerPoint interface will help you navigate the software effectively and make the most of its features. Whether you are creating slides, adding content, or applying formatting, having a good grasp of the interface ensures a smooth and productive experience .
Key Features of PowerPoint
When it comes to creating captivating and professional presentations, MS PowerPoint stands out as versatile and feature-rich software. Its array of tools and functionalities enables users to bring their imagination and ideas to life. Moreover, it also helps engage their audience effectively .
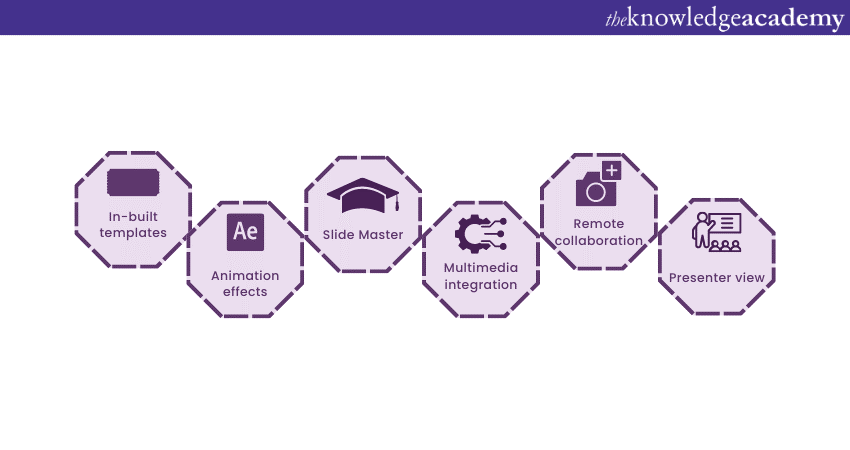
1) Slide Templates : PowerPoint provides a collection of pre-designed templates that make it easy to create visually appealing slides.
2) Slide Master : The Slide Master feature allows users to define the overall layout, font styles, and colour scheme for the entire presentation .
3) Animations and transitions : PowerPoint offers various animation effects and slide transitions to add visual interest and captivate the audience .
4) Multimedia integration : Users can embed images, videos, and audio files directly into their presentations, enhancing the overall impact .
5) Collaboration tools : MS PowerPoint allows multiple users to work on a presentation simultaneously, making it ideal for team projects and remote collaboration .
6) Presenter View : The Presenter View feature gives presenters access to speaker notes, a timer, and a preview of upcoming slides, enabling a seamless presentation experience .
These features collectively contribute to PowerPoint's versatility and make it a powerful tool for developing engaging and impactful presentations.
How to use PowerPoint to create a presentation?
Creating a presentation in PowerPoint is a straightforward process. Whether it's simple animations or explainer videos learning H ow to use PowerPoint is an extremely valuable skill. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to create a presentation:
1) Launch PowerPoint and choose a template or start with a blank slide.
2) Add slides by clicking "New Slide" or using the shortcut key (Ctrl + M).
3) Customise slide content by entering text and inserting visuals.
4) Rearrange slides for a logical flow by dragging them in the slide navigation pane.
5) Apply slide transitions for visual effects in the "Transitions" tab.
6) Add animations to objects in the "Animations" tab.
7) Preview your presentation by clicking "Slide Show".
8) Save your presentation and choose a format (.pptx or .pdf).
9) Share your presentation via email, cloud storage, or collaboration tools.
By following these steps, you can create a well-structured and visually appealing presentation in Microsoft PowerPoint. Remember to keep your content concise, use engaging visuals, and practice your presentation skills to deliver an impactful presentation .
Benefits of PowerPoint
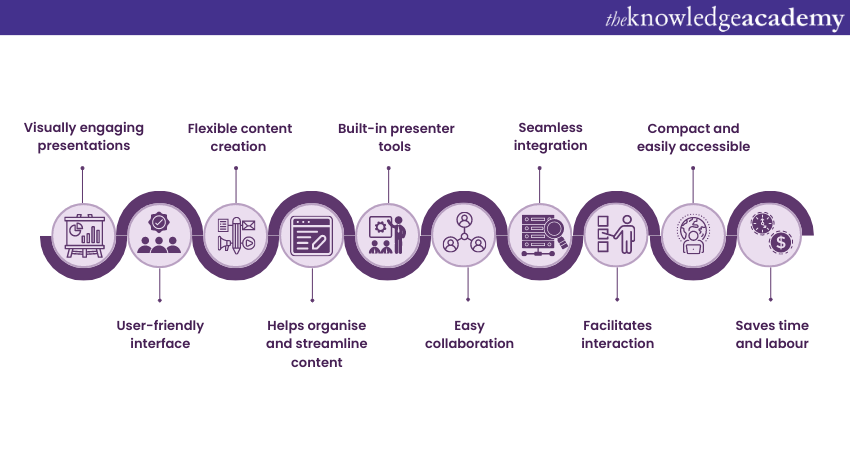
1) Visual appeal : Microsoft PowerPoint allows you to create visually appealing presentations with its wide range of design tools and features. You can use templates, themes, and customisable layouts to make your slides visually engaging and professional .
2) Easy to use : PowerPoint has a user-friendly interface, making it accessible to users of all levels. The intuitive tools and straightforward navigation make it easy to create, edit, and deliver presentations efficiently .
3) Flexibility : PowerPoint provides flexibility in terms of content creation. You can include various types of content, such as text, images, charts, graphs, videos, and audio files, to enhance your message and engage your audience effectively.
4) Organisation and structure : PowerPoint offers features to help you organise and structure your content. You can create multiple slides, use slide masters for consistent formatting, and arrange the sequence of slides to create a logical flow .
5) Presenter tools : PowerPoint includes built-in presenter tools that aid in delivering presentations smoothly. You can use presenter view to see your notes and upcoming slides while your audience sees only the presentation. Additionally, features like slide transitions and animations add visual interest and help you control the flow of information .
6) Collaboration and sharing : PowerPoint allows for easy collaboration and sharing of presentations. Several users can simultaneously work on the same presentation, making it convenient for team projects. You can also share your presentations via email, cloud storage, or online platforms, ensuring easy access for viewers .
7) Integration with other tools : PowerPoint can seamlessly integrate with other Microsoft Office applications, such as Word and Excel. You can import data and charts from Excel or copy and paste content between different Office applications, saving time and effort .
8) Presenter-audience interaction : PowerPoint provides features that facilitate interaction between the presenter and the audience. You can include interactive elements like hyperlinks, buttons, and quizzes to engage your audience and make your presentations more dynamic.
9) Portable and accessible : PowerPoint presentations can be saved in various formats, such as .pptx or .pdf, making them easily accessible on different devices. This portability allows you to deliver presentations on laptops, tablets, or even projectors without compatibility issues .
10) Time and effort savings : PowerPoint simplifies the process of creating presentations, saving you time and effort. The pre-designed templates, slide layouts, and formatting options enable you to create professional-looking presentations efficiently .
Unleash your creativity to deliver captivating presentations that leave a lasting impact with our Microsoft PowerPoint Masterclass – Sign up now!
Tips for Creating Effective PowerPoint Presentations
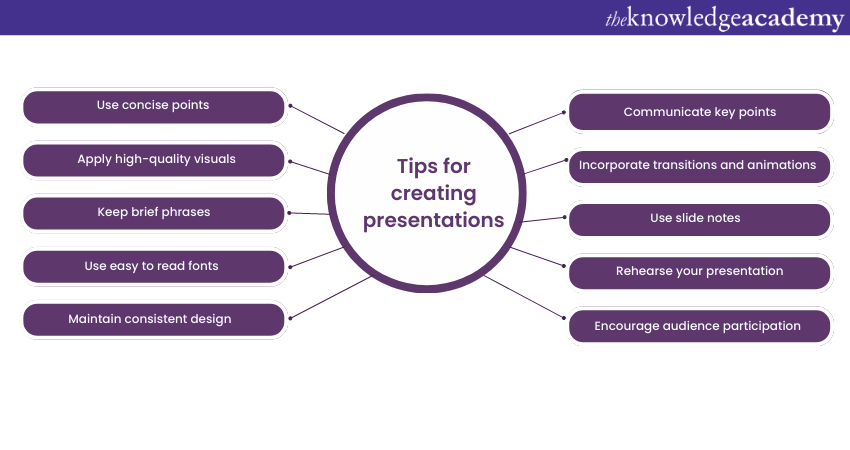
1) Simplicity is key : Keep your slides clean and uncluttered. Use concise bullet points and simple visuals to convey your message effectively .
2) Visuals matter : Incorporate relevant, high-quality visuals such as images, charts, and diagrams to enhance understanding and engagement .
3) Limit text : Avoid overwhelming your audience with excessive text on slides. Use brief phrases or keywords to communicate key points .
4) Choose legible fonts : Opt for clear and readable fonts that are easy to read, even from a distance. Maintain consistency in font styles throughout your presentation .
5) Consistent design : Maintain a consistent design theme, including colours, fonts, and layout, to create a visually appealing and professional presentation.
6) Emphasise important points : Use visual hierarchy techniques, such as font size, colour, and formatting, to draw attention to essential information .
7) Use transitions and animations sparingly : Incorporate slide transitions and animations thoughtfully, focusing on enhancing content and transitions without distracting the audience .
8) S lide notes for guidance : Utilise the slide notes feature to include additional details, explanations, or reminders for a well-prepared and confident presentation.
9) Practice and time yourself : Rehearse your presentation to ensure smooth delivery and stay within the allocated time. Practice helps you refine your content and delivery.
10) Engage the audience : Encourage audience participation through interactive elements, questions, or discussions to foster engagement and make your presentation more memorable.
By implementing these tips, you can create effective MS PowerPoint presentations that capture attention, communicate information clearly, and engage your audience effectively.
Conclusion
We hope this blog has helped you understand What is PowerPoint and how it can help you. It offers powerful features with a user-friendly interface for creating visually appealing presentations. With its tools for organising information, incorporating text and visuals, and delivering impactful content, PowerPoint is a valuable tool for beginners to communicate their ideas effectively .
Master the art of effective communication and productivity and unlock your potential with our comprehensive Microsoft Office Training – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming office applications resources batches & dates.
Thu 11th Apr 2024
Thu 16th May 2024
Thu 6th Jun 2024
Thu 4th Jul 2024
Thu 8th Aug 2024
Thu 5th Sep 2024
Thu 10th Oct 2024
Thu 7th Nov 2024
Thu 5th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel & Certification Course
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
- School Guide
- Class 9 Syllabus
- Maths Notes Class 9
- Science Notes Class 9
- History Notes Class 9
- Geography Notes Class 9
- Political Science Notes Class 9
- NCERT Soln. Class 9 Maths
- RD Sharma Soln. Class 9
- Math Formulas Class 9
- BCA 1st Semester Syllabus (2023)
Fundamentals of IT & Computers
- Basics of Computer and its Operations
- Characteristics of Computer System
- Types of Computers
- Number System and Base Conversions
- What is Algorithm | Introduction to Algorithms
- What is a Flowchart and its Types?
- What is an Operating System?
- DOS Full Form
- Types of Operating Systems
- Commonly Used Operating System
- Difference between Word Processor and Text Editor
- Introduction to Microsoft Word
- Introduction to MS Excel
Introduction to Microsoft PowerPoint
C programming.
- C Programming Language Tutorial
- Operators in C
- Control Structures in Programming Languages
- C if else if ladder
- Nested switch case
- Introduction to Divide and Conquer Algorithm - Data Structure and Algorithm Tutorials
- Understanding Time Complexity with Simple Examples
- What is PseudoCode: A Complete Tutorial
- Arithmetic Operators in C
- C Functions
- Parameter Passing Techniques in C
- Difference Between Call by Value and Call by Reference in C
- Scope rules in C
Basic Mathematics
- Determinant of a Matrix
- Mathematics | Limits, Continuity and Differentiability
- Advanced Differentiation
- Chain Rule Derivative - Theorem, Proof, Examples
- Taylor Series
- Relative Minima and Maxima
- Beta Function
- Gamma Function
- Reduction Formula
- Vector Algebra
Business Communication
- What is Communication?
- Communication and its Types
- BCA 2nd Semester Syllabus (2023)
- BCA 3rd Semester Syllabus (2023)
- BCA 4th Semester Syllabus (2023)
- BCA 5th Semester Syllabus (2023)
- BCA 6th Semester Subjects and Syllabus (2023)
- BCA Full Form
- Bachelor of Computer Applications: Curriculum and Career Opportunity
Information can be displayed using an electronic presentation application. This information is usually presented as a slide show — the data is displayed on a slide that may be viewed on a computer monitor or projected onto a screen using an LCD projector. A presentation might consist of multiple slides that are exhibited one after the other. The presentation tool in MS Office is MS PowerPoint. Microsoft PowerPoint is a popular presentation application, although there are alternatives such as Corel Presentations OpenOffice.org, Impress, etc.
Three major components of a presentation program are:
(i) An editor that allows text to be input and formatted (ii) a means for inserting visual pictures, audio, and video (iii) and a slide-show system to display the final content.
How to open MS PowerPoint
In Windows 8/above:
Step 1: Press Windows + c to open the search bar
Step 2: Type PowerPoint & click on the MS Office version you are having in your system. MS Office window will pop up.
In Windows 7 or below:
Step 1: Go to the program section in the windows start menu. Step 2: Go to MS Office & click on it. A drop-down list is seen Step 3: Click on MS PowerPoint & MS PowerPoint window will pop up.
Creating a Presentation
Once your MS PowerPoint Window pops up, you can create & save the file by:
Step 1: Click on the Microsoft button on the top left.
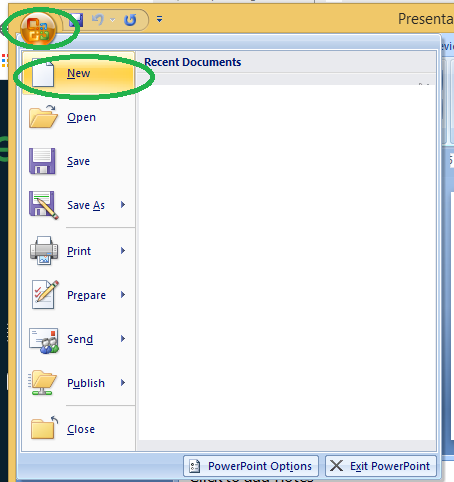
Step 2: Click on new , a new Presentation window will pop up.
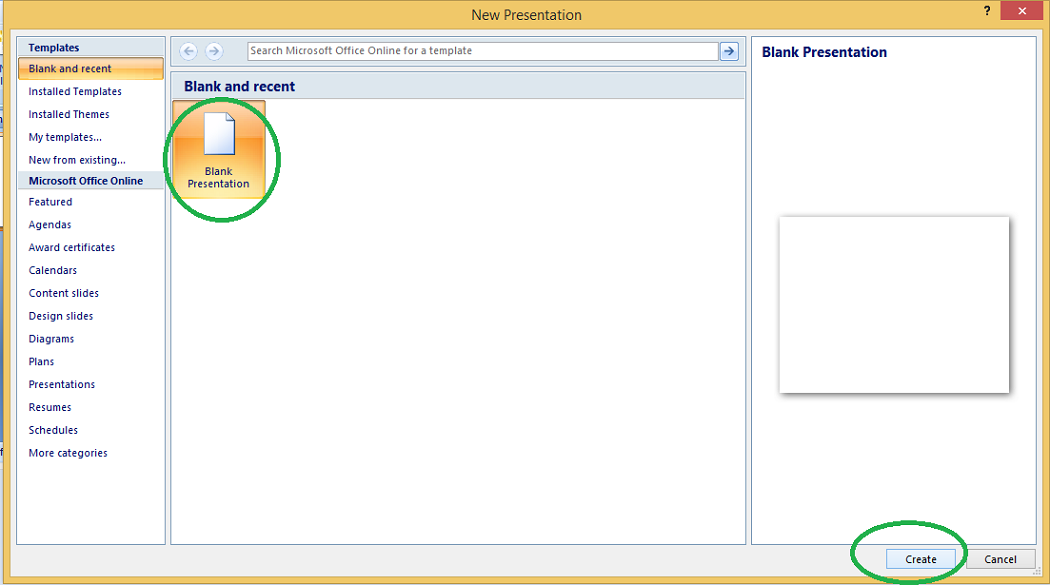
Step 3: Click on Create & a new presentation will be created.
Note: Shortcut for New: Ctrl +n

Saving a Presentation
Once you have created a presentation, it can be easily saved with the help of following steps:
Step 1: Click on the Microsoft icon
Step 2: Click on the Save button
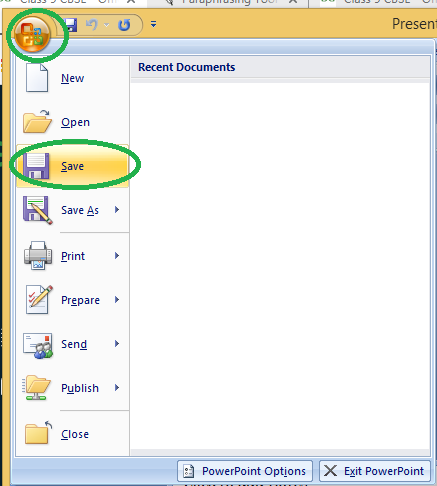
Step 3: A new Window for Save As will pop up.
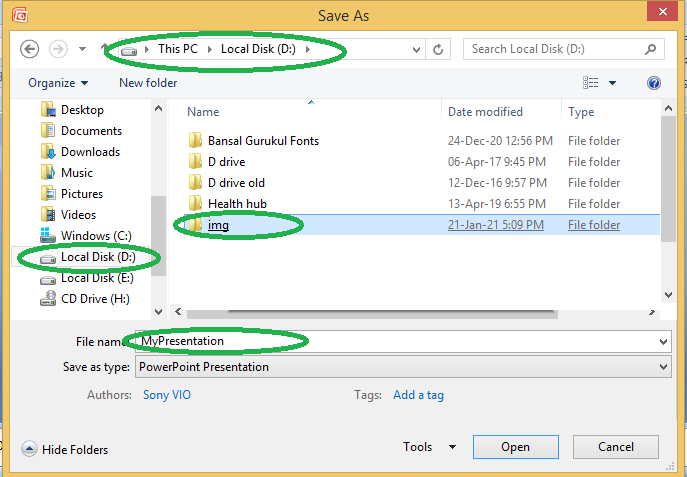
Step 4: Select the drive (by clicking on it: Example: Local Drive (D)) in which you want to save the presentation. Then your drive will open up, select the folder in which you want to save the presentation (Example: img folder here) & then give the required name to your presentation (Example: MyPresentation here). Your presentation is created & saved with the provided name.
Note: Shortcut for save: Ctrl + s
Basic Elements of a PowerPoint Window/Slide
You can see various bars in the presentation window. They are:
(i) Title Bar: This shows the name/title given by you to the current presentation. If user do not save the presentation by any name, default name given by MS PowerPoint appears in this bar. (ii) Menu Bar: Contains menu items like insert, views, design, animations, etc. (iii) Office Button: MS Office button on the left-most top. (iv) Formatting Toolbar: Have tools like Bold, Italic, Underline, Font shape & size etc. to format your data.
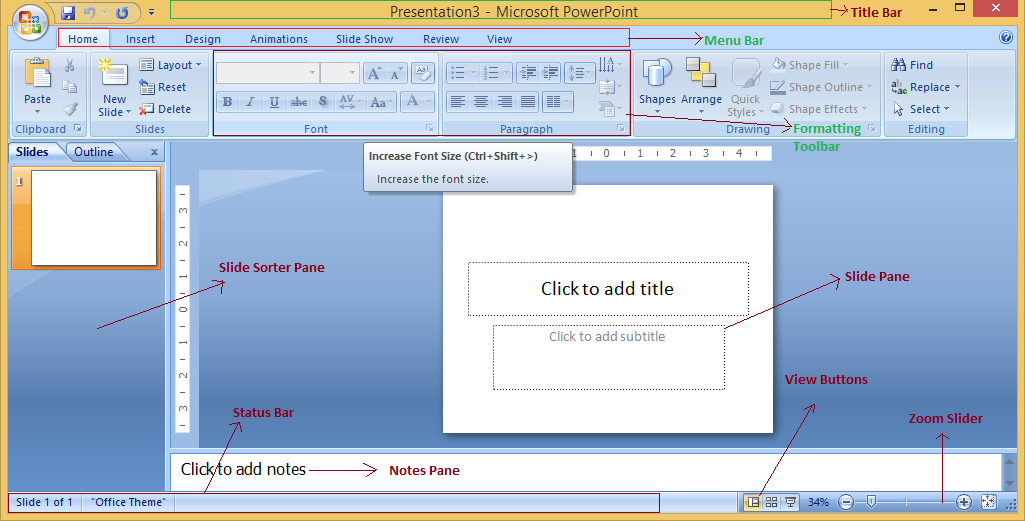
(v) Zoom Slider: To zoom in or zoom out your presentation. (vi) Slide Sorter Pane: This allows us to choose which slides will be shown in which sequence during the slide show. (vii) Notes Pane: This allows us to type notes that we may require later when preparing for the presentation, but they will not be displayed during the slide show. (viii) View Buttons: Provides different views of your presentation like : normal, slide show & slide sorter. (ix) Slide Pane: This is where we type, format, and otherwise design the slide.
Concept of Slide Shows
After preparing the presentation, it’s time for the slide show. Steps for slide show are:
Step 1. Click on the view Option on the top Menu Toolbar Step 2. Click on the slide show option.
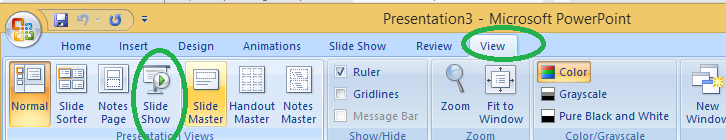
Step 3. The slide show will start (Press Esc key (escape) to come out of slide show)
Note: Shortcut for the slide show is: F5
Sample Questions
Question 1. How to print a Presentation through an attached printer?
Step 1: Click on the Microsoft icon Step 2: Click On Print & a window for Print & Preview the document will pop up. Step 3: Click on Print . Then a window for Print will pop up. Step 4: Select the printer by which you want to take out print of the document. Select the page range (Print of all or some or current page) & number of copies you want. Step 5: Click on OK. You will get print of your Presentation.
Note: Shortcut for print is Ctrl + p.
Question 2. What will you do for closing a Presentation?
The procedure is as follows: 1. Go to Office Button 2. Click on close (last option in the list).
Question 3. Give shortcuts to create, print, close & save a presentation.
1. Ctrl + N – Create a New presentation. 2. Ctrl + S – Save a presentation. 3. Alt + F4 – Close a presentation. 4. Ctrl + P – Print a presentation.
Question 4. What is MS PowerPoint?
PowerPoint (PPT) is a powerful and simple-to-use presentation graphics software tool for creating professional-looking electronic slide shows. A PowerPoint presentation, or PPT, is a collection of slides that exhibit a graphical and visual interpretation of data in order to deliver information in a more creative and dynamic way.
Question 5. In a slide, what kind of elements can be added?
In a slide, we can add: -Graphs -Clip Art -Tables -Media Clips -Pictures -Charts -Videos etc.
Please Login to comment...
- School Learning
- School Programming
- 10 Best Free Social Media Management and Marketing Apps for Android - 2024
- 10 Best Customer Database Software of 2024
- How to Delete Whatsapp Business Account?
- Discord vs Zoom: Select The Efficienct One for Virtual Meetings?
- 30 OOPs Interview Questions and Answers (2024)
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Introduction to PowerPoint
- Computer Science

Microsoft PowerPoint is essentially a graphics presentation software application that comes in the same package of software as MS Access, MS Excel, MS Word, and MS Paint, issued by Microsoft Office . It is a software that helps the user in formulating and arranging their data and information in the form of slides, which enhances the clarity and communication of the subject, along with adding a visual aspect to the data which makes it more appealing and presentable.
Thus, it can be used for presenting business ideas and plans, and visually presenting the data also makes learning with the data a lot easier, thus can be used by teachers in schools for making learning fun and uncomplicated.
Meaning of PowerPoint
PowerPoint is a software that is designed to make graphical presentations in the form of individual pages also known as slides.
Features of PowerPoint
Some of the features available in Microsoft PowerPoint are stated below.
Customising Colour Schemes
Adding Animations
Creating and Adding tables
Adding images
Adding and Managing Hyperlinks
Creating Custom Shows
Creating and Importing Charts
Easy exporting to MS Word
How to Start PowerPoint?
To start powerpoint:.
Click on Start

Click the following in sequence stated: All Programs->Microsoft Office->Microsoft Office PowerPoint
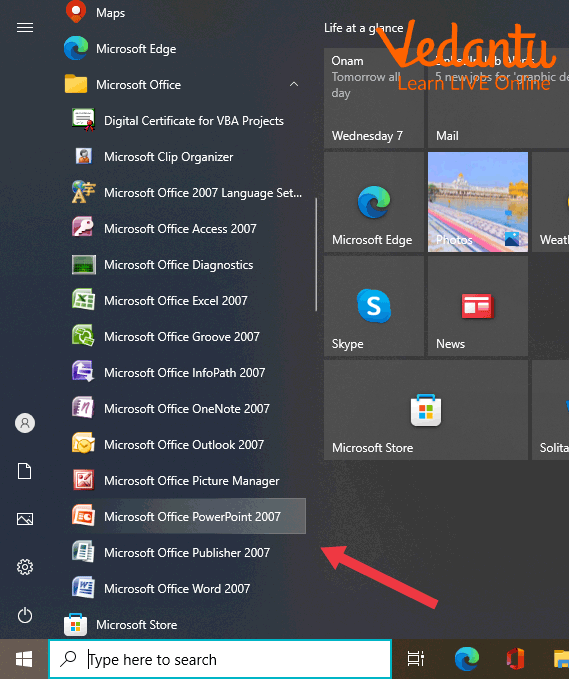
Starting PowerPoint
The Microsoft Office PowerPoint window will appear, starting the software.
How to Open a Blank Presentation?
By default, when we open PowerPoint for the first time, it opens to a new presentation but for future purposes, if we want to open a new presentation, we can do so by following the below-given steps.
Click on New Presentation link on Getting Started pane on the left which results in the appearance of a new window.
Select on Blank Presentation, when the new presentation appears along with it a Layout pane on the right will also appear.
Select any desired layout from the list.
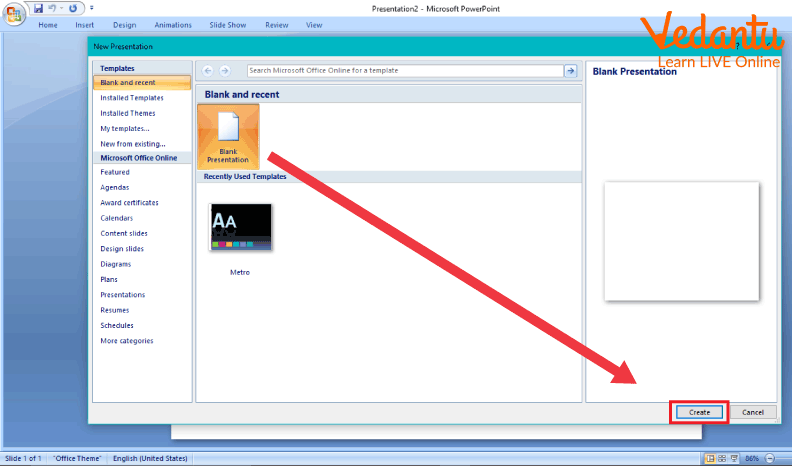
Opening a New Presentation
Uses of PowerPoint
Uses of PowerPoint in Education:
Since PowerPoint offers the feature of adding images and animations, learning by visualisation makes the learning experience more fun and simplified, and researchers state that visual information is retained for a longer amount of time thus it makes the whole process more beneficial.
Uses of PowerPoint in Business:
Business is mainly about creating a well-laid out roadmap and planning for the project at hand and then executing it. With PowerPoint we can assure a more organised output with a solid structure.
Uses of PowerPoint for Government and Citizen Services:
PowerPoint is also a good option, from other software bundled within MS Office, for storing records and since it's also printable, it provides easy access to the records for government and citizen services to the seekers.
MS Office PowerPoint is an application for making graphical presentations thus adding a visual aspect to our data, enhancing its concept, and leading to easier communication. The software offers various features like Customising colour schemes, adding graphics, images, and animation, etc. Thus it serves as a salient software under MS Offices.
Sample Questions
1. How can we view or run a presentation?
Ans: To run a presentation, either click on the F5 key or select Play from Beginning on the Slideshow Pane.
2. How can we add a blank slide to our presentation?
Ans: For adding a new slide in the same presentation simply click on the Slide icon on the Insert tab and choose the type of slide you want to add from the drop-down menu which unfolds on the screen.
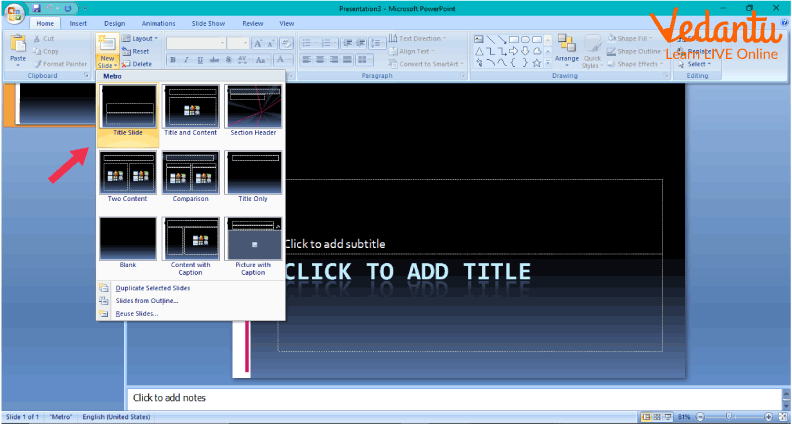
Adding a New Slide
Practice Questions
State whether the following statements are True or False :
In PowerPoint we can use animations.
PowerPoint cannot be used to store records.
PowerPoint allows us to graphically represent data.
We can not export data from PowerPoint to Word.
False
Fill in the blanks with the appropriate answers:
We can add _______, ________ and _________ which gives our presentation a visual aspect.
PowerPoint is a software designed and issued by _______
PowerPoint presents information in the form of individual sheets termed as ________.
Graphics, images, animations
Microsoft Offices

FAQs on Introduction to PowerPoint
1. What is the difference between the transition effect and the animation effect in MS Office PowerPoint?
Transition effects are used on transitioning from one slide to another, whereas Animation effects can be used on the text or the images on the slide.
2. Can we insert sound in a presentation?
Yes we can also insert sound in our presentation.
3. Is Microsoft Office PowerPoint a software?
Yes MS Office PowerPoint is a software application issued by MS Offices.

Introduction to Computer Network
Nov 06, 2019
380 likes | 498 Views
Introduction to Computer Network. Dr. Rania R Ziedan. Agenda. Introduction Network types Network topology Network connection models OSI model. Computer network. A collection of computing devices that are connected in various ways in order to communicate and share resources or files
Share Presentation
- client server
- physical topology
- client server model
- fully connected mesh network

Presentation Transcript
Introduction to Computer Network Dr. Rania R Ziedan
Agenda • Introduction • Network types • Network topology • Network connection models • OSI model
Computer network • A collection of computing devices that are connected in various ways in order to communicate and share resources or files • Wired network: the connections between computers in a network are made using physical wires or cables • Wireless network: the connections between computers in a network are made using radio waves or infrared signals
Computer network • Each computer in the network is known as: node or host • Data transfer rate: is the speed with which data is moved from one place on a network to another, which is a key feature in computer networks
Network Types • Local Area Network (LAN): two or more computers connected together, the computers are physically near each other (for example: in the same building) • LANs are inexpensive to install • LANs provide higher speeds
Network Types • Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): usually span tens of kilometers (for example: in the same city) • The cost of installation and operation is higher. • MANs use high-speed connections such as fiber optics to achieve higher speeds
Network Types • Wide Area Network (WAN): is a connection of LANs (for example : the Internet) • WANs span a larger area than a single city. • These use long distance telecommunication networks for connection, thereby increasing the cost.
The Internet • It is a large group of computers that are connected to each other and used to send information quickly between computers around the world
Physical topology of a network • The term physical topology refers to the way in which a network is laid out physically. • The topology of a network is the geometric representation of the relationship of all the links and linking devices • There are four basic topologies possible: mesh, star, bus, and ring
Physical topology of a network • Mesh Topology • In a mesh topology, every device has a dedicated point-to-point link to every other device. • The term dedicated means that the link carries traffic only between the two devices it connects. • The number of physical links in a fully connected mesh network with n nodes n(n-1)/2 • The mesh topology used in the connection of telephone regionaloffices in which each regional office needs to be connected to every other regional office.
Physical topology of a network • Mesh Topology • Advantages: • Each link can carry its own data load, thus eliminating the traffic problems that can occur with shared links. • A mesh topology is robust. If one link becomes unusable, it does not incapacitate the entire system. • Every message travels along a dedicated line, only the intended recipient sees it. Physical boundaries prevent other users from gaining access to messages. • Point-to-point links make fault identification and fault isolation easy. Traffic can be routed to avoid links with suspected problems. • Disadvantage: • The amount of cabling and the number of I/O ports required.
Physical topology of a network • Star Topology • Each device has a dedicated point-to-point link only to a central controller, usually called a hub. • A star topology does not allow direct traffic between devices. • The controller acts as an exchange: If one device wants to send data to another, it sends the data to the controller, which then relays the data to the other connected device. • The star topology is used in local-area networks (LANs)
Physical topology of a network • Star Topology • Advantages: • less expensive than a mesh topology, each device needs only one link and one I/O port to connect it to any number of others. • Easy to install and reconfigure. • Robustness, if one link fails, only that link is affected, all other links remain active. • As long as the hub is working, it can be used to monitor link problems and bypass defective links • Disadvantage: • the dependency of the whole topology on one single point, the hub. If the hub goes down, the whole system is dead
Physical topology of a network • Bus Topology • A bus topology is multipoint connection. • One long cable acts as a backbone to link all the devices in a network. • Nodes are connected to the bus cable by drop lines and taps. • There is a limit on the number of taps a bus can support and on the distance between those taps. As a signal travels along the backbone, some of its energy is transformed into heat. Therefore, it becomes weaker and weaker as it travels farther and farther. • Bus topology was the one of the first topologies used in the design of early local area networks. • The cable has two end terminals that dampen the signal so that it does not keep moving from one end of the network to the other.
Physical topology of a network • Bus Topology • Advantages: • Ease of installation • Bus uses less cabling than mesh or star topologies. • Disadvantages: • Difficult reconnection and fault isolation. • Difficult to add new devices. • Signal reflection at the taps can cause degradation in quality. This degradation can be controlled by limiting the number and spacing of devices connected to a given length of cable. • Adding new devices may therefore require modification or replacement of the backbone. • In addition, a fault or break in the bus cable stops all transmission, even between devices on the same side of the problem. The damaged area reflects signals back in the direction of origin, creating noise in both directions.
Physical topology of a network • Ring Topology • Each device has a dedicated point-to-point connection with only the two devices on either side of it. • A signal is passed along the ring in one direction, from device to device, until it reaches its destination. • Each device in the ring incorporates a repeater. When a device receives a signal intended for another device, its repeater regenerates the bits and passes them along
Physical topology of a network • Ring Topology • Advantages: • easy to install and reconfigure • Fault isolation is simplified. • Generally in a ring, a signal is always circulating . If one device does not receive a signal within a specified period, it can issue an alarm. The alarm alerts the network operator to the problem and its location. • To add or delete a device requires changing only two connections. The only constraints are media and traffic considerations (maximum ring length and number of devices). • Disadvantages: • Unidirectional traffic • a break in the ring can disable the entire network. • This weakness can be solved by using a dual ring or a switch capable of closing off the break.
Network connection models • Networks can also be classified according to the roles that the networked computers play in the network’s operation. • Peer-to-peer, • server-based, • and client-based.
Network connection models Peer-to-peer model all computers are considered equal. Each computer controls its own information and is capable of functioning as either a client or a server depending upon the requirement. • Peer-to-peer networks are inexpensive and easy to install. • They are popular as home networks and for use in small companies. • Most operating systems come with built-in peer-to-peer networking capability. • The maximum number of peers that can operate on a peer-to-peer network is ten. • Each peer shares resources and allows others open access to them. • Shares can be document folders, printers, peripherals, and any other resource that they control on their computers.
Network connection models Peer-to-peer network
Network connection models • client-server model is a software that consists of two parts, client systems and server systems, both communicate over a computer network
Network connection models • The client-server relationship describes the relation between the client and how it makes a service request to the server, and how the server can accept these requests, process them, and return the requested information to the client
Page request How the Web Works? • WWW use classical client / server architecture • HTTP is text-based request-response protocol HTTP HTTP Server response Server running Web Server Software (IIS, Apache, etc.) Client running a Web Browser
Client/Server • There are two types of servers: • File serverA computer that stores and manages files for multiple users on a network • Web serverA computer that responds to requests for web pages (from the browser client)
Web servers and browsers • web server: software that listens for web page requests • Apache • Microsoft Internet Information Server (IIS) (part of Windows) • web browser: fetches/displays documents from web servers • Mozilla Firefox • Microsoft Internet Explorer (IE) • Apple Safari • Google Chrome • Opera
OSI Architecture The OSI 7-layer Model OSI – Open Systems Interconnection
Description of Layers • Physical Layer • Handles the transmission of raw bits over a communication link • Data Link Layer • Collects a stream of bits into a larger aggregate called a frame • Network adaptor and device drivers in OS implement the protocol in the datalink layer • Frames are actually delivered to hosts • Network Layer • Handles routing between nodes within a packet-switched network • Unit of data exchanged between nodes in this layer is called a packet The lower three layers are implemented on all network nodes
Description of Layers • Transport Layer • Implements a process-to-process channel • Unit of data exchanges in this layer is called a message • Session Layer • Provides a name space that is used to tie together the potentially different transport streams that are part of a single application • Presentation Layer • Concerned about the format of data exchanged between peers • Application Layer • Standardize common type of exchanges The transport layer and the higher layers typically run only on end-hosts and not on the intermediate switches and routers
Summary • A computer network consists of two or more computers that are connected and are able to communicate. • The basic purpose of networks is to enable effective communication, share resources, and facilitate centralized management of data. • Networks can be classified according to their geographical boundaries or their component roles. • The topology of a network is the geometric representation of the relationship of all the links and linking devices
Questions???
- More by User

15-349 Introduction to Computer and Network Security
15-349 Introduction to Computer and Network Security. Iliano Cervesato 7 September 2008 – Beyond Encryption. Where we are. Course intro Cryptography Intro to crypto Modern crypto Symmetric encryption Asymmetric encryption Beyond encryption Cryptographic protocols Attacking protocols
605 views • 36 slides

15-349 Introduction to Computer and Network Security. Iliano Cervesato 14 September 2008 – Attacking Cryptographic Protocols. Where we are. Course intro Cryptography Intro to crypto Modern crypto Symmetric encryption Asymmetric encryption Beyond encryption Cryptographic protocols
412 views • 30 slides

15-349 Introduction to Computer and Network Security. Iliano Cervesato 26 August 2008 – Modern Cryptography. Where we are. Course intro Cryptography Intro to crypto Modern crypto Symmetric encryption Asymmetric encryption Beyond encryption Cryptographic protocols Attacking protocols
375 views • 23 slides

Computer and Network Security Introduction
Computer and Network Security Introduction. Dr. Ron Rymon Efi Arazi School of Computer Science IDC, Herzliya. 2010/11. Today’s Lecture. Introduction A Few Nightmare Scenarios Statistics and Impact Course Plan and Administrativia Models of Computer Security.
582 views • 37 slides

15-349 Introduction to Computer and Network Security. Iliano Cervesato 24 August 2008 – Introduction to Cryptography. Where we are. Course intro Cryptography Intro to crypto Modern crypto Symmetric encryption Asymmetric encryption Beyond encryption Cryptographic protocols
450 views • 31 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER & NETWORK SECURITY
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER & NETWORK SECURITY. Instructor: Dania Alomar. Why S tudy Security ?. Security threats are real… And need protection against Keeping information secure from modification and unauthorized access. Keeping it available is getting increasingly difficult.
1.07k views • 15 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER . Lecture #10 COMPUTER SOFTWARE. By Shahid Naseem (Lecturer). COMPUTER SOFTWARE. A set of instructions given to the computer to solve a particular problem is called software. Software is also called computer program.
549 views • 12 slides

Introduction to Computer
Introduction to Computer . Waqas Ali Sahito Lecturer Department of Computer Science. Subject Distribution. Theory 100 Marks Paper marks = 75 Sessional Marks = 25 Practical 50 Marks Objective = 10 Viva = 20 Sessional Marks = 20 Sessional Marks.
677 views • 41 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER . Lecture #12 FILES FORMAT. By Shahid Naseem (Lecturer). FILES. A collection of data or information that has a name , called the filename .
1.06k views • 15 slides

By Kiramat Rahman Department of Computer & Software Technology. Introduction to Computer. Input / Output (I/O) devices Commonly used input devices Commonly used output devices Other concepts related to I/O devices. Outline. Provide means of communication between a computer
878 views • 61 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER. EVOLUTION OF THE COMPUTER. EVOLUTION OF THE COMPUTER. The history and evolution of computer are divided into two eras : before 1940 after 1940. BEFORE 1940. In the beginning, human do calculation by fingers, stones, small woods etc.
532 views • 8 slides

Introduction to Computer. By: Maria Mullen. Objectives. Identify and use computer hardware Identify the pieces that make up the desktop Open and close desired programs Switch back and forth between open windows Create and save a document Print a document.
721 views • 23 slides

Introduction to computer
Introduction to computer. Submitted by : aashish.c ashish.m Abhijeet.g Ankit.j abhay.j . CONTENT. WHAT IS COMPUTER? WHY COMPUTER? COMPUTER COMPONENT DATA & INFORMATION
843 views • 32 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER. Lecture #15 ARRAYS. By Shahid Naseem (Lecturer). ARRAYS DEFINITION. An array is a sequence of objects of same data type. The objects in an array are also called “elements of array”.
340 views • 16 slides

INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER. Lecture #9 OPERATING SYSTEM. By Shahid Naseem (Lecturer). LECTURE OUTLINES. DATA. A collection of raw (unprepared or unprocessed) facts ( things, people, objects, events) and figures, collected for a specific purpose is called data.
365 views • 19 slides

Introduction to Computer and Network Architectures (Networks)
Introduction to Computer and Network Architectures (Networks). Module introduction. Staff. Ivailo Chakarov- Module leader/tutor/Cisco Academy Director/Part man/part labrador [email protected]. Module content. Module assessment. The assessment for Networks part of the module is:
275 views • 8 slides

Introduction to Network
Introduction to Network. What is a Network?. A network consists of 2 or more computers connected together, and they can communicate and share resources (e.g. information). How many kinds of Networks?. Depending on one ’ s perspective, we can classify networks in different ways.
410 views • 26 slides

15-349 Introduction to Computer and Network Security. Iliano Cervesato 2 September 2008 – Public-key Encryption. Where we are. Course intro Cryptography Intro to crypto Modern crypto Symmetric encryption Asymmetric encryption Beyond encryption Cryptographic protocols
407 views • 27 slides

Introduction to COMPUTER
Introduction to COMPUTER. February 22, 2010. ADB Grant 0133-CAM: Public Financial Management in Rural Development Ministries (Component 1). AN INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY.
818 views • 31 slides

Introduction To Computer
Introduction To Computer. Hardware. Mr. Garel. St. BACHS. What is a Computer?. a computer can be. defined as a machine for processing and storing information electronically. it must have a way for us to get information into the machine, and some way to get it out afterwards so we can
802 views • 13 slides

Introduction to Computer. Computers are everywhere!. Computers are showing up everywhere you look, and even in places you can't see. Computers check out your groceries, pump your gas, dispense money at the ATM, turn the heat on and off, control the way your car runs. They're everywhere!.
1.14k views • 64 slides

305171 Computer Programming Rattapoom Waranusast Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Faculty of Engineering, Naresuan University. Introduction to Computer. What is computer?. A COMPUTER is an electronic device that can: Receive information Perform processes
1.67k views • 66 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Download ppt "Chapter 1: Introduction to Computer". Computer A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions stored in its own memory that can accept data (input), process the data according to specified rules, produce information (output), and store the information for future use.
These are 1) it accepts data or instructions by way of input, 2) it stores data, 3) it can process data as required by the user, 4) it gives results in the form of output, and 5) it controls all operations inside a computer. We discuss below each of these operations. 1. Input: In computing, an input device is any peripheral (piece of computer ...
A computer is an electronic device which basically performs five major operations which includes: 1) accepts data or instructions (input) 2) stores data. 3) process data. 4) displays results (output) and. 5) controls and co-ordinates all operations inside a computer. .
Computer Basics 1. Computer Basic 1 includes two lessons: Lesson 1: Introduction to Computers Lesson 2: Common Computer Terminology. Lesson 1 - Introduction to Computer Objectives. After completing lesson 1, you will be able to: Describe the importance of computers in today's world. Download Presentation.
Step 1.When you start the computer, certain operating system files are loaded into RAM from the hard disk. The operating system displays the user interface on the screen. Operating system interface Operating system instructions Step 2.When you start a Web browser, the program's instructions are loaded into RAM from the hard disk.
Introduction to computer fundamentals. The Computer Defined. A computer is an electronic device that processes data, converting it into information that is useful to people. Analog and Digital Computer. Analog systems represent data as variable points along a continuous spectrum of values. Download Presentation.
Introduction to Computers By Prof. KUMAR GANDHI MEERA'S CLASSES. Introduction to Computers Project on: Use of Computers in Movies & Animation. N/A. Introduction A computer is an electronic machine which converts data into meaningful information. Process or Input Convert Data Data Into Information Meaningful Informatio A SYMBOLIC REPRESENTATION ...
Everything you do on your computer will rely on both hardware and software. For example, right now you may be viewing this lesson that is in a PowerPoint presentation software and the instructor is using a 9/5/2023 mouse or the keyboard (hardware) to click from page to page. 6
Intel's 64-Bit History. 2001: Intel Attempts Radical Shift from IA32 to IA64. Totally different architecture (Itanium, AKA "Itanic") Executes IA32 code only as legacy. Performance disappointing. 2003: AMD Steps in with Evolutionary Solution. x86-64 (now called "AMD64") Intel Felt Obligated to Focus on IA64.
Introduction to Microsoft PowerPoint 17 3. Next, return to your presentation and select the "Location" slide. 4. In the ribbon, at the top of your screen, click on the "Insert" tab. This option will allow us to add items that have been saved to the computer to our PowerPoint presentation. 5.
Introduction to Computers. Introduction to Computers. Seminar I. Parts of the Computer. Personal Computer a PC (any non-Mac computer) has four major pieces of hardware--keyboard, mouse, monitor, central processing unit (CPU). Macs have the same four components, but use different software for the operating system. 1.07k views • 32 slides
Benefits of PowerPoint. PowerPoint is a very popular presentation software and for a good reason. It offers numerous benefits for users, from easy collaboration to ease of use. These are some of the key benefits of PowerPoint. 1) Visual appeal: Microsoft PowerPoint allows you to create visually appealing presentations with its wide range of ...
Creating a Presentation. Once your MS PowerPoint Window pops up, you can create & save the file by: Step 1: Click on the Microsoft button on the top left. Step 2: Click on new, a new Presentation window will pop up. Step 3: Click on Create & a new presentation will be created. Note: Shortcut for New: Ctrl +n.
A computer is an electronic device, operating under the control of instructions (software) stored in its own memory unit, that can accept data (input), manipulate data (process), and produce information (output) from the processing. Generally, the term is used to describe a collection of devices that function together as a system.
MS Office PowerPoint is an application for making graphical presentations thus adding a visual aspect to our data, enhancing its concept, and leading to easier communication. The software offers various features like Customising colour schemes, adding graphics, images, and animation, etc. Thus it serves as a salient software under MS Offices.
Open Educational Resources. OpenStax Releases Free, Interactive Computer Science Textbook. By Rhea Kelly; 04/02/24; OpenStax, the Rice University-based provider of free, peer-reviewed, openly licensed course materials, has expanded its content library with a new computer science textbook: Introduction to Python Programming.. Now available from OpenStax, the world's leading provider of free ...
380 likes | 488 Views. Introduction to Computer Network. Dr. Rania R Ziedan. Agenda. Introduction Network types Network topology Network connection models OSI model. Computer network. A collection of computing devices that are connected in various ways in order to communicate and share resources or files. Download Presentation.