Since $1.60 per gallon is above the equilibrium price, the quantity demanded would be lower at 550 gallons and the quantity supplied would be higher at 640 gallons. (These results are due to the laws of demand and supply, respectively.) The outcome of lower Qd and higher Qs would be a surplus in the gasoline market of 640 – 550 = 90 gallons.
To make it easier to analyze complex problems. Ceteris paribus allows you to look at the effect of one factor at a time on what it is you are trying to analyze. When you have analyzed all the factors individually, you add the results together to get the final answer.
- An improvement in technology that reduces the cost of production will cause an increase in supply. Alternatively, you can think of this as a reduction in price necessary for firms to supply any quantity. Either way, this can be shown as a rightward (or downward) shift in the supply curve.
- An improvement in product quality is treated as an increase in tastes or preferences, meaning consumers demand more paint at any price level, so demand increases or shifts to the right. If this seems counterintuitive, note that demand in the future for the longer-lasting paint will fall, since consumers are essentially shifting demand from the future to the present.
- An increase in need causes an increase in demand or a rightward shift in the demand curve.
- Factory damage means that firms are unable to supply as much in the present. Technically, this is an increase in the cost of production. Either way you look at it, the supply curve shifts to the left.
- More fuel-efficient cars means there is less need for gasoline. This causes a leftward shift in the demand for gasoline and thus oil. Since the demand curve is shifting down the supply curve, the equilibrium price and quantity both fall.
- Cold weather increases the need for heating oil. This causes a rightward shift in the demand for heating oil and thus oil. Since the demand curve is shifting up the supply curve, the equilibrium price and quantity both rise.
- A discovery of new oil will make oil more abundant. This can be shown as a rightward shift in the supply curve, which will cause a decrease in the equilibrium price along with an increase in the equilibrium quantity. (The supply curve shifts down the demand curve so price and quantity follow the law of demand. If price goes down, then the quantity goes up.)
- When an economy slows down, it produces less output and demands less input, including energy, which is used in the production of virtually everything. A decrease in demand for energy will be reflected as a decrease in the demand for oil, or a leftward shift in demand for oil. Since the demand curve is shifting down the supply curve, both the equilibrium price and quantity of oil will fall.
- Disruption of oil pumping will reduce the supply of oil. This leftward shift in the supply curve will show a movement up the demand curve, resulting in an increase in the equilibrium price of oil and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity.
- Increased insulation will decrease the demand for heating. This leftward shift in the demand for oil causes a movement down the supply curve, resulting in a decrease in the equilibrium price and quantity of oil.
- Solar energy is a substitute for oil-based energy. So if solar energy becomes cheaper, the demand for oil will decrease as consumers switch from oil to solar. The decrease in demand for oil will be shown as a leftward shift in the demand curve. As the demand curve shifts down the supply curve, both equilibrium price and quantity for oil will fall.
- A new, popular kind of plastic will increase the demand for oil. The increase in demand will be shown as a rightward shift in demand, raising the equilibrium price and quantity of oil.
Step 1. Draw the graph with the initial supply and demand curves. Label the initial equilibrium price and quantity.
Step 2. Did the economic event affect supply or demand? Jet fuel is a cost of producing air travel, so an increase in jet fuel price affects supply.
Step 3. An increase in the price of jet fuel caused an increase in the cost of air travel. We show this as an upward or leftward shift in supply.
Step 4. A leftward shift in supply causes a movement up the demand curve, increasing the equilibrium price of air travel and decreasing the equilibrium quantity.
Step 2. Did the economic event affect supply or demand? A tariff is treated like a cost of production, so this affects supply.
Step 3. A tariff reduction is equivalent to a decrease in the cost of production, which we can show as a rightward (or downward) shift in supply.
Step 4. A rightward shift in supply causes a movement down the demand curve, lowering the equilibrium price and raising the equilibrium quantity.
A price ceiling (which is below the equilibrium price) will cause the quantity demanded to rise and the quantity supplied to fall. This is why a price ceiling creates a shortage.
A price ceiling is just a legal restriction. Equilibrium is an economic condition. People may or may not obey the price ceiling, so the actual price may be at or above the price ceiling, but the price ceiling does not change the equilibrium price.
A price ceiling is a legal maximum price, but a price floor is a legal minimum price and, consequently, it would leave room for the price to rise to its equilibrium level. In other words, a price floor below equilibrium will not be binding and will have no effect.
Assuming that people obey the price ceiling, the market price will be below equilibrium, which means that Qd will be more than Qs. Buyers can only buy what is offered for sale, so the number of transactions will fall to Qs. This is easy to see graphically. By analogous reasoning, with a price floor the market price will be above the equilibrium price, so Qd will be less than Qs. Since the limit on transactions here is demand, the number of transactions will fall to Qd. Note that because both price floors and price ceilings reduce the number of transactions, social surplus is less.
Because the losses to consumers are greater than the benefits to producers, so the net effect is negative. Since the lost consumer surplus is greater than the additional producer surplus, social surplus falls.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-microeconomics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Steven A. Greenlaw, David Shapiro
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Microeconomics 2e
- Publication date: Sep 15, 2017
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-microeconomics-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-microeconomics-2e/pages/chapter-3
© Jun 15, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Almost 2024, I hope my site still help you guys

Friday, October 2, 2015
Micro & macro. chapter 2 【thinking like an economist】.

2 comments:

thank you x1000000000. You dont understand how much you have helped me. Thank you.
this is also an amazing study guide. i feel like this should be password protected, would actually fail without this
- Study Guides
- Homework Questions

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Economics Chapter 2 Homework. The production possibilities frontiers depicted in the diagram to the right illustrate. Click the card to flip 👆. both the labor force and capital stock increasing. Click the card to flip 👆. 1 / 38.
52 terms. Isabel_Abdul-Ahad. Preview. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following is not generally considered to be a resource (factor of production)?, Which of the following best demonstrates the concept of scarcity?, Each individual must make choices because and more.
Originally, when the price of bus tickets was 50 cents per trip, this opportunity cost was 0.50/2 = .25 burgers. The reason for this is that at the original prices, one burger ($2) costs the same as four bus tickets ($0.50), so the opportunity cost of a burger is four bus tickets, and the opportunity cost of a bus ticket is .25 (the inverse of ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The production possibilities frontiers depicted in the diagram to the right illustrate, In the diagram to the right, point G indicates an, Suppose the economy whose PPF is shown on the right experiences economic growth. 1.) Use the 3-point curved line drawing tool to show how growth affects the trade-offs the country faces ...
1P. Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 3. Comparative advantage is specializing work according to the comparative advantage, producing good with lower opportunity cost. Opportunity cost is the cost of the next best alternative. Step 2 of 3. The table below summarizes the given information in the question, a fixed time of 60 mins is taken:
Access MindTap Economics for Mankiw's Principles of Economics, 8th Edition, [Instant Access] 8th Edition Chapter 2 solutions now. Our solutions are written by Chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality!
CH2. Problem. 1P. Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 4. a. Production possibility curve: The production possibility curve with consumer goods on X-axis and investment goods on Y-axis is shown as follows: Suppose production of investment goods increases from I 1 to I 2, then firm has to decrease the production of consumer goods from C 1 to C 2.
Studying ECON 201 Principles Of Microeconomics at Drexel University? On Studocu you will find 113 lecture notes, 21 practice materials, 18 assignments and much more ... Chapter 2 Thinking like an Economist. 3 pages 2018/2019 91% (33) 2018/2019 91% (33) Save. ... Econs 501 homework 1 - micro. 2 pages 2016/2017 None. 2016/2017 None. Save ...
Econ macro Ch 2 HW - Chapter 2 Homework. Chapter 2 Homework. Course. Economic Theory: Macroeconomics (ECON-606) 20 Documents. Students shared 20 documents in this course. University University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee. Academic year: 2020/2021. Uploaded by: Anonymous Student.
traditional economy. an economic system that relies on habit, custom, or ritual to decide the three economic questions. market. any arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to exchange things. specialization. the concentration of the productive efforts of individuals and businesses on a limited number of activities. free market economy.
ECON 2301 - Principles of Macroeconomics Homework 2/ Professor - Question 1 - 5 points You are given with the following data for the country of Morocco in the year 2017 - a. What is the GDP of Morocco in 2017 using the expenditure approach? (2) Answer a. We can use the following formula to calculate GDP, GDP= C + I + G +Zn
Economics is associated with the optimal choices in the conditions of scarcity. This is true when the resources are limited in comparison to their availability. While making choices the concept of opportunity cost is essential, since it helps in deciding the value of the good produced by using the given resources. Step 3 of 3.
2. A tax increase on consumer income will cause consumption to fall, pushing the AD curve left, and is a possible solution to inflation. A surge in military spending is an increase in government spending. This will cause the AD curve to shift to the right. If real GDP is less than potential GDP, then this spending would pull the economy out of ...
Introduction to Demand and Supply; 3.1 Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium in Markets for Goods and Services; 3.2 Shifts in Demand and Supply for Goods and Services; 3.3 Changes in Equilibrium Price and Quantity: The Four-Step Process; 3.4 Price Ceilings and Price Floors; 3.5 Demand, Supply, and Efficiency; Key Terms; Key Concepts and Summary; Self-Check Questions; Review Questions
Q-Chat. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A national market lets buyers and sellers conduct transactions around the world., The market price is the typical price at which a good or service sells in a market., A volume discount means that a buyer gets a lower price for purchasing sooner. and more.
Econ 201: Homework PS# Chapter 2. Question 1. Refer to Table 1 below. What is the opportunity cost to Ecoville of increasing the production of socks from 400 to 600? Table 1. Ecoville's Production Possibilities Socks Glasses 800 0 600 600 400 1, 200 1, 0 1, The Opportunity cost is 500 glasses (1,100 - 600)
View Homework Help - ECON Chapter 2 Homework.docx from ECON 108 at Eastern Michigan University. ECON 108 Chapter 2 Name: Emily Bobo Date Due: 1/27/2021 Time Due: 11:59 PM 1. (Shifting Demand) Using
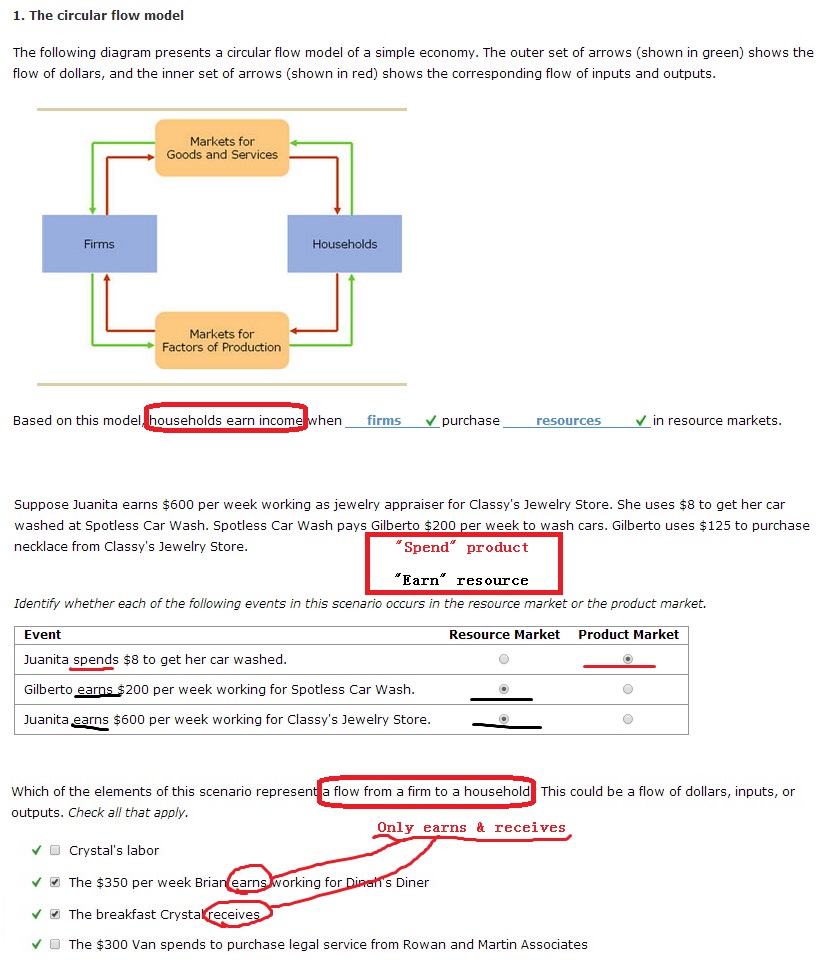
Friday, October 2, 2015. Micro & Macro. Chapter 2 【Thinking Like an Economist】. 1. The circular flow model. The following diagram presents a circular flow model of a simple economy. The outer set of arrows (shown in green) shows the flow of dollars, and the inner set of arrows (shown in red) shows the corresponding flow of inputs and ...
Assume that both mean and median incomes are $40,000 in 2000 and that median income remains constant through 2010. 1.) Using the line drawing tool, draw a line representing median income from 2000 to 2010. Label your line appropriately. 2.) Using the line drawing tool, draw a line for mean income to represent a rising degree of income ...
Take learning further. MyLab ® Economics merges dynamic study tools with the content you rely on. Easily customize your course to add a personal touch. With MyLab Economics, students explore core economic concepts and how they relate to the world around them. Channel your teaching style.
Item:Graded Homework - Chapter 2 Score:100% (Calculated) Due:Thursday, February 6, 2020 11:59 PM Submitted:Thursday, January 30, 2020 4:44 PM Answers: 1. The importance of an economic model is that it allows us to: avoid opportunity costs. build a complex and accurate model of the economy. build an accurate mathematical model of the economy.
Step-by-step solution. a. Opportunity cost: Opportunity cost refers to the value of forgone goods and services to get the other goods and services. They should consider the opportunity cost of waiting in order to decide how high to make their bribe. Opportunity cost of waiting is the value of money that they can earn instead of waiting there.
At Quizlet, we're giving you the tools you need to take on any subject without having to carry around solutions manuals or printing out PDFs! Now, with expert-verified solutions from Economics 22nd Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Economics includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as ...
Econ 335: Assignment 2 Due: Friday, March 8 th by 11:59 PM Chapter 5 Questions 1. As a result of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) in 1994, the United States and Canada shifted toward free trade with Mexico. Note: according to the data about factor endowments in class, the US and Canada are relatively abundant in skilled labor and relatively scarce in unskilled labor.