

Votre exemple de Business Plan rédigé en français

Q ue ce soit pour obtenir un prêt, présenter votre activité à un futur fournisseur ou encore repenser votre projet, un business plan en français peut s'avérer utile . Cependant, cette importante étape d'un projet entrepreneurial n'est pas facile à concevoir. Un business plan exige généralement beaucoup de travail. Il se peut que vous ne soyez ni un expert en finances ou en argumentation commerciale . Il est possible que vous ayez des difficultés avec certains éléments déterminants pour la création de votre business plan. Il peut s'agir par exemple de la structure des tableaux financiers, de la rédaction de l'analyse SWOT, du Business Model Canvas ou de la présentation générale du document. Cependant, la réalisation d'un business plan en français peut être simplifiée . C'est le cas si vous êtes bien informé et si vous utilisez la bonne méthode. Il existe de nombreuses façons de faire de votre business plan un succès. Dans cet article, nous vous détaillons le contenu d'un business plan en français, nous vous dévoilons la méthode pour réussir la rédaction de ce dernier et, dans le cas où vous souhaiteriez vous aider d'un professionnel ou d'un modèle, nous vous indiquons les différents prix pour un business plan en français.
Que doit contenir un business plan en français ?
Dans la mesure où chaque projet est unique, il est impossible de trouver un modèle de plan d'affaires universel qui soit adapté à tous les projets . Cependant, un certain nombre de chapitres et d'éléments doivent être inclus dans le document. Généralement, on retrouvera cette structure pour un business plan en français : - Présentation du marché sur lequel vous vous lancez - Présentation de l’opportunité de marché (que vous avez identifié) - Identification des derniers changements dans les habitudes de consommation - Description des facteurs de succès d'une entreprise comme la vôtre - Présentation de la solution apportée et de la valeur crée - Présentation du porteur de projet - Analyse de vos segments de marché - Analyse de la concurrence - Identification d'avantages concurrentiels - Plan d'actions sur 3 ans - Stratégie marketing pour faire croître son chiffre d'affaires - Plan de recrutement (parfois) - Plan opérationnel (& technologique) - Business Model (synthèse grâce au Business Model Canvas) - Politique de gestion des risques - Prévisionnel financier - Annexes (parfois)

Comment rédiger facilement un business plan en français ?
Quelle longueur pour un business plan en français ? Même si votre projet est passionnant, nul n'aura la patience de parcourir un business plan de 100 pages. Allez droit au but et utilisez les annexes si nécessaire. Un document trop long et qui aborde des détails peu intéressants vous fera passer pour quelqu'un qui n'est pas capable de synthétiser et d'aller à l'essentiel ! Quels sont les règles à respecter pour réussir un business plan en français ? Tout d'abord, il faut savoir qu'un document contenant des fautes d'orthographe ne sera pas pris au sérieux. Par conséquent, il est préférable de faire relire votre business plan par des proches ou des professionnels de la rédaction, avant de le remettre aux mains de potentiels investisseurs. Également, il est peu probable que votre banquier soit un expert concernant votre industrie. Même si vous vous efforcez d'éviter le jargon, il est vraisemblable que certains passages de votre plan d'affaires soient un peu difficiles à comprendre pour votre banquier. Révisez votre document et faites-le relire par un proche qui n'a aucune connaissance de votre projet. S’il n’arrive pas à le comprendre, vous devez réviser et simplifier votre texte. Assurez-vous que le plan d'affaires s'adresse principalement aux autres et non à vous. Quelle présentation pour un business plan en français ? Soignez la forme et la présentation ! À titre d'exemple, chaque page doit avoir la même mise en page (police, logo, titre, couleurs, etc.). Quoi de plus pénible qu'un document confus et difficilement lisible ? En effet, il est important de savoir qu'un document peu esthétique donnera à votre interlocuteur l'impression d'un travail bâclé et n'attirera guère l'attention.
Même si votre projet est passionnant, nul n'aura la patience de parcourir un business plan de 100 pages.

Quel est le tarif d'un business plan en français ?
Comment avoir un business plan en français gratuitement ? Vous pouvez télécharger ci-dessous notre exemple rédigé de business plan en français. Ensuite, vous êtes libres de vous en inspirer et de faire le travail vous-même. C'est une solution gratuite, qui prend du temps, mais qui n'est pas insurmontable. Combien coûte un business plan en français réalisé par un expert-comptable ? Généralement, le tarif peut aller de 300 à 1 500 euros.Vous pouvez solliciter un comptable pour vous accompagner dans cette démarche. Mais ce dernier ne vous aidera que pour la partie financière du business plan. Il faut dire qu’il n’est pas un spécialiste en matière d'entrepreneuriat. Il connaît peu les problématiques relatives au développement d'une jeune entreprise. En outre, il n’est pas un concepteur ou graphiste, et ne sera donc pas en mesure de créer une présentation adaptée. Dois-je faire réaliser mon business plan en français par un étudiant ? Pour les petits projets, il existe de très bonnes alternatives peu coûteuses : les étudiants. En effet, des étudiants d'écoles de commerce et d'IUT ayant un DUT en marketing (ou techniques de commercialisation ou autre) proposent de faire des business plans à prix abordables (entre 300 et 1 000 euros). Vous bénéficiez d'un travail moins rigoureux que s'il était réalisé par une agence, mais à un coût plus avantageux. Cependant, vous n'avez aucune garantie quant à la qualité du business plan que vous allez recevoir. Combien coûte la réalisation d'un business plan en français par un consultant ? Le tarif d'un business plan conçu par un expert diffère selon la complexité du projet et coûte généralement entre 800 et 3 000 euros. Il est évident qu'un projet de création d'une entreprise individuelle dans un domaine standard, comme une pâtisserie, nécessite moins d'investissement qu'un projet de création d'une entreprise industrielle sophistiquée. Par conséquent, les prix des business plans avec ce type de professionnel sont susceptibles de fluctuer. Quel est le meilleur rapport qualité-prix pour un business plan en français ? L'utilisation d'un modèle modifiable, entièrement rédigé, adapté à votre industrie ! C'est le cas de nos modèles de business plans . Le tarif de nos modèles de business plan est fixé à 39,90 € et celui de nos modèles de prévisionnel financier à 59,90 €. Tous nos modèles font 35 pages et sont élaborés par des gens qui font des business plans tous les jours. Ne partez pas de zéro: nos experts ont déjà travaillé pour vous et ont synthétisé le fruit de leurs recherches dans les différents modèles. Nos modèles de business plan contiennent tout ce qu'un business plan doit contenir. Des données de marché aux tendances de l'industrie en passant par l'analyse des concurrents, la proposition de valeur, le Business Model Canvas, ou bien le plan d'action marketing adapté à votre type d'entreprise. Ils vous aideront à mettre votre projet en valeur. Il ne vous reste plus qu'à compléter pour obtenir un business plan complet, sérieux et professionnel . Vous pouvez modifier le modèle (tout est entièrement modifiable) à l'aide de Powerpoint, Keynote ou Google Slides (tous disponibles gratuitement, sur PC et MAC). Ce n'est pas seulement un "exemple" pour s'inspirer, c'est la base de votre futur business plan : personnalisez le reste en ajoutant votre logo, vos photos ou encore votre présentation. Finissez le travail et produisez un business plan de professionnel ! En cas de question, notre support est disponible pour vous.
- le choix d'une sélection entraîne une actualisation complète de la page

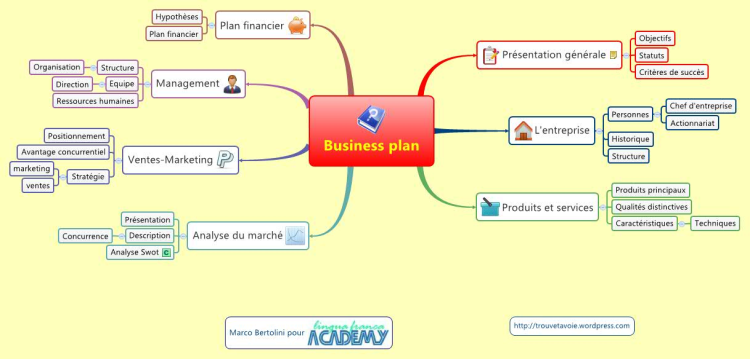
Business plan - French Template - Plan d'affaire - modele en francais
Join Biggerplate FREE to access thousands of mind maps!
Already a member? Login .

Related Mind Maps:
Share this mind map.
To open this mind map, you`ll need Visit Website or compatible mind mapping software installed.
Need help? Please contact us
Another free Xmind Management Mind Map shared on Biggerplate! Register FREE to download thousands of mind map templates and examples!
Register FREE to download this map.
Already registered? Login .
Go Further with Mind Mapping: Upgrade to Biggerplate Plus!
Upcoming webinars:.

Validate your mind mapping software skills with Biggerplate Certification!
Fill out the form below to sign-up for a new account

Start Business in France
My french business visa.
An 8-step roadmap to prepare your visa application.
Included in My French Business Course
1-to-1 coaching.
Get Valerie's support for 4 months to turn your dream project into reality. Meet up every 2 weeks on Zoom and debrief on your progress. Get Valérie's input and collaborate on tougher subjects.
French System & Rules
Know the rules that may impact your project. Get a clear overview of the French legal structures, taxes and business visas. Finally, understand how to choose the right setup for your project.
Templates & Worksheets
Get a personal finance sheet, business plan, financial templates, worksheets, and guides. Tick your checklist, as you confidently progress with your business visa application for France.
Prepare a strong business visa application
Working on your own on a project involving a move to a new country and freelancing can be overwhelming . Especially if you are currently working or looking after your family. Time flies and your project seems to be stuck.
My French Business Visa is an online course and personalised coaching to help you steadily build your business visa application . Let yourself be guided and see progress every week.
My French Business Visa Course is a step-by-step guide to help you structure and prepare your business visa application - Visa profession liberale, visa talent or carte de sejour entrepreneur . Turn your idea into a strong business plan, check the French regulations, choose a legal structure that makes sense, create a financial plan and finally understand French taxes.
With My French Business Visa course, you will go from feeling lost and frustrated with the French system, to being confident about choosing the right setup for you, understanding your business taxes, while having a clear path to follow up to your business registration.
By the end of this course, you will have a structured business project and submitted your business visa or carte de sejour application .
Get support from Valerie to make visible progress with your project and get closer to your moving date for France.
Let's meet before signing up
Course curriculum, objectives & vision.
Vision & Objectives
10 Misions to Prepare your Move
1-to-1 Meetings
BONUS : Retro Planning + Checklist
Business Vision Workshop - Replay
Mundey Young - Business Coach
Finding your business idea
Different ways to find a business idea
Workbook + 💯 business ideas
Reality Check with French system
6 steps reality check
PDF list of regulated activities
Bonus - Personal Budget Sheet
Business Plan & Strategy
BP Workbook + BP Template
Business Overview
Market Analysis
Your Ideal Customer
Your Product & Services
Your Strategy
Business Structure
Legal Structures
Overview : Start here!
Summary of all legal structures
Micro Entrepreneur
Entreprise Individuelle
EURL /& SARL
SASU & SAS
Bonus - My Professional Network
Financial Planning
Financial plan - Part 1
Financial plan - Part 2
Financial plan Example with template
Financial Plan template
Business visa application
Different visas
Documents needed & application process
Using France Visa & DREETS websites
Filling forms Cerfa 13473.01 form
Micro Entrepreneur PO form
Renewing visa & applying for residency
BONUS - Visa / CDS - Letter of intention template
First steps in France
5 Missions Once in France
House Search: Dossier + Tips
House Search Sheet
Download your retro planning
Extra support

About this course
3 x €232,00.
- 9.5 hours of video content

Who is it for?
My French Business 1-to-1 if for you if:
You want to move to France in 6 to 12 months
Your want to freelance or start a business.
You need a visa profession liberale, visa talent or carte de sejour entrepreneur.
You want external support for feedback & progress.
You're ready to commit to your project.
My French Business Visa Course
Pricing options.
Self-Tuition or 1-to-1 Coaching.
Pricing Options
1-to-1 Coaching One Off
About this instructor
Valerie Aston

One-to-One Coaching
All students benefit from unlimited access to My French Business Visa course. One-to-one coaching students also get a call with Valerie every 2 weeks for 4 months.
Yes. Module 2 of My French Business Visa is all about finding the right idea, brainstorming, and deciding which one you're most excited about. You will also get a PDF with 100 business ideas based other expats running a business in France.
It's always good to plan ahead, especially if you need to apply for a business carte de sejour or visa. My French Business Visa explains how the French system works and will help you build your project.
With the 1-to-1 coaching package, you'll have weekly Zoom calls with Valerie to discuss your build your project. Together you will steadily build your business plan, financial plan, business visa or carte de sejour application. You'll get personalised feedback on a weekly basis for 3 months. Sometimes it will be 30 min to touch base and keep you accountable; Sometimes it might be an intensive work session. It's 100% tailor to your needs.
Yes, there is a dedicated module of My French Business Visa covering specific requirements for British citizens and non-European citizens wanting to create a business in France.
Yes. You can pay over 3 months, whichever package you decide to go for: Self-Tuition or 1-to-1 coaching access. There is also a 30-days refund policy.
Yes. Each student joining the MFB Visa Course signs a confidentiality agreement. Any information shared for the live calls or private Facebook group cannot be shared with someone outside the group. Valerie also commits to this rule.
I'm afraid not. Your business plan and financial plan will be 2 key elements to include in your visa request. And we will cover the visa application process in Module 7, but My French Business Visa doesn't include a visa application service (i.e. handled-for-you service).
Absolutely. My French Business Visa has been designed for first-time entrepreneurs with no experience in financial planning, as well as experienced ones. For 1-to-1 coaching students, I will take over this process and we will build your financial plan over our weekly calls.
Interested in the 1-to-1 Coaching?
My French Business course has been designed to make you move forward with your project. With MFB you will:
Turn your idea into a business plan.
Ensure your project meets French rules.
Get a simple business plan and financial plan template.
Understand how French taxes work for your business.
Prepare for your visa/CDS application
Make informed decisions to move your project forward.
I'm in! Pay in 3 instalments
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Sample Business Plans » Food
French Fries Business Plan [Sample Template]
Since the arrival of fast food restaurants, a lot of entrepreneurs have become millionaires. If you are considering becoming a millionaire in the food industry, one of the coolest ways of making money is to open a French fries food production company.
Although this type is profitable, but at the same time you can run at a loss if your business is not well positioned and managed. It is important to state that loads of food related business cum fast food restaurants close shops simple because they failed to conduct detailed market survey and feasibility studies before launching the business.
Your ability to re – strategize and always ramp up your service deliveries will help you stay competitive. It is important to point out that French Fries food business is one the businesses that can’t go out of fashion simply because people eat food on a daily basis.
Depending on the scale you want to start, the startup capital for this type of business can be considered to be moderate. As a matter of fact, you can start your own French fries’ food business and then grow it big within a short period of time by reinvesting your profits back to the business.
If you are ready to take a journey into this industry, then this type of business is what you truly want to do after you must have done your findings. You will also need is to write a good business plan. Below is a sample French fries food restaurant business plan templates that will help you successfully write yours with little or no stress;
A Sample French Fries Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
French fries food business belongs to the Snacks Food Production industry and operators in this industry primarily produces snack foods such as potato and corn chips, pretzels, roasted and salted nuts, nut butters, popcorn and other related snacks.
Most players in this industry do not produce cookies, crackers, bakery products, cereal or granola bars et al. French fries are generally served hot, either soft or crispy, and are usually eaten as part of lunch or dinner or by themselves as a snack, and they generally appear on the menus of fast food restaurants.
If you are a close observer of happenings in the Snack Food Production industry, you will agree that the industry has profited from increased demand over the last half a decade. As the economy, has continued to experience growth, discretionary income levels have ascended.
Hence, renewed consumer spending has increased sales of potato and tortilla chips, along with nuts and seeds. With improvement in the economic conditions, the industry is expected to rake more revenue. Expected increases in per capita disposable income will aid some consumers to trade up to premium brands and product segments, helping drive revenue growth.
In addition, as consumers demand more healthy versions of existing snacks, players in the industry are expected to introduce a wider variety of products. The Snack Food Production industry is a thriving sector of the economy of the united states, United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Canada and in most country of the world.
Statistics has it that in the United States of America, The Snack Food Production industry generates a whooping sum of well over $38 billion annually from more than 2,851 registered snack food production outlets / franchise scattered all around the United States of America.
The industry is responsible for the employment of well over 53,204 people. Experts project The Fast Food Restaurants industry to grow at a 3.6 percent annual rate from 2011 to 2016. ConAgra, Snyder’s Lance and PepsiCo are the leaders in The Fast Food Restaurants industry; they have the lion market share in the industry.
Over and above, the French fries food production line of business is a profitable industry and it is open for any aspiring entrepreneur to come in and establish his or her business; you can chose to start on a small scale in a street corner like the average mom and pop business or you can chose to start on a large scale with several outlets in key cities all across the United States of America.
2. Executive Summary
Golden Fingers French Fries is a standard and registered chain of fast food restaurant that with strong bias in the production of French fries that will be located in one of the busiest roads in Long Beach – California but hope to spread out via franchising to key cities in the United States with the first 5 years of operations.
We are at the final stage of leasing a facility along a major road that is big enough to fit into the design of the kind of fast food restaurant that we intend launching and the facility is located in a corner piece directly opposite the largest residential estate in Long Beach – California.
Golden Fingers French Fries will be involved in the sale of French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks, water, juice, and sodas et al in our restaurant and when customers order for it to be delivered to them in any location around us.
Basically, we will be involved in operating quick-service restaurants, operating fast food services, operating drive-thru and take-out facilities in our chains of fast food outlets that will be scattered all across major cities in the United States and Canada.
We are aware that there are several large and small scale French fries food business scattered all around Long Beach – California, which is why we spent time and resources to conduct our feasibility studies and market survey so as to offer much more than our competitors will be offering.
We have delivery service options for our customers, and our outlet is well secured with the various payment options. Golden Fingers French Fries will ensure that all our customers are given first class treatment whenever they visit any of our chains of fast food outlets.
We have a CRM software that will enable us manage a one on one relationship with our customers no matter how large the numbers of our customers’ base may grow to. We will ensure that we get our customers involved when making some business decisions that directly affect them.
We are aware of the trend in the snacks food production / fast food industry and we are not only going to operate a system where our customers would have to come to our fast food restaurant to make purchase or whatever they want, but we will also operate an online fast food restaurant and our customers can place orders for our foods, snack and drinks online and they will get it delivered to their houses or any location they want us to deliver the goods to within Long Beach – California.
Golden Fingers French Fries is a family business that is owned by Jason Kennedy and his immediate family members. Jason Kennedy is a French fries specialist; he has a B.Sc. in Food Science and a Diploma in Business Administration, with well over 6 years of experience in the restaurant and fast food industry, working for some of the leading brand in the United States.
Although the business is launching out with just one outlet in Long Beach – California, but there is a plan to open other outlets via franchising all around California and in other key cities in the United States of America and Canada.
3. Our Products and Services
Golden Fingers French Fries is in the snacks production industry to service a wide range of clients and of course to make profits, which is why we will ensure we go all the way to make available a wide varieties of French fries and snacks in our outlets always.
We will ensure that we do all that is permitted by the law of the United States to achieve our aim and ambition of starting the business. Our product and service offerings are listed below;
- Operating quick-service restaurants
- Operating fast food services
- Operating drive-thru and take-out facilities
- Potato chips
- Nuts and seeds
- Peanut butter
- Tortilla and corn chips
- Other chips
- Other snacks
- Sale of Chicken and Chips
- Sale of beverages, such as water, juice and sodas
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our vision is to become the leading French fries food production company – brand in Long Beach – California.
- Our mission is to establish chains of fast food restaurants that will make available a wide variety of French fries, snacks and soft drinks at affordable prices to the residence of Long Beach – California and other cities in the United States of America and Canada where we intend opening our chains of French fries food outlets.
Our Business Structure
Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC do not intend to start a fast food restaurant business just like the usual mom and pop business around the street corner; our intention of starting a fast food restaurant business is to build a standard business in Long Beach – California.
Although our French fries food outlet might not be as big as ConAgra, Snyder’s Lance and PepsiCo et al, but will ensure that we put the right structure in place that will support the kind of growth that we have in mind while setting up the business.
We will ensure that we hire people that are qualified, honest, customer centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all the stakeholders (the owners, workforce, and customers). As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our senior management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of ten years or more.
In view of that, we have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
- Chief Executive Officer (Owner)
- Restaurant Manager
- Human Resources and Admin Manager
- Chef / Kitchen Workers
Sales and Marketing Manager
Information Technologist
- Accountants / Cashiers
- Customer Services Executive
- Van Drivers / Deliverers
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Officer – CEO (Chief Florist):
- Heightens management’s effectiveness
- Accountable for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Liable for providing direction for the business
- Creates, communicating, and implementing the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
- Reports to the board
Admin and HR Manager
- In control for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Preserves office supplies by checking stocks; placing and expediting orders; evaluating new products.
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance requirements; calling for repairs.
- Updates job knowledge by participating in educational opportunities; reading professional publications; maintaining personal networks; participating in professional organizations.
- Defines positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Transmits out staff induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Responsible for arranging travel, meetings and appointments
- Manages the smooth running of the daily office activities.
Restaurant Manager:
- Responsible for managing the daily activities in the restaurant (kitchen inclusive)
- Ensures that the restaurant facility is in tip top shape and conducive enough to welcome customers
- Interfaces with third – party providers (vendors)
- Reports to the Chief Executive Officer
- Handle any other duty as assigned by the CEO
Chef / Kitchen Staff
- Responsible for producing French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks as supervised by the kitchen supervisor
- In authority of carrying out all casual or unskilled jobs in the restaurant
- Responsible for packaging French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks meant for delivery
- Handles any other duty as assigned by the restaurant manager
- Manages external research and coordinate all the internal sources of information to retain the organizations’ best customers and attract new ones
- Models demographic information and analyze the volumes of transactional data generated by customer purchases
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts; participates in the structuring and financing of projects; assures the completion of development projects.
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Develops, executes and evaluates new plans for expanding increase sales
- Document all customer contact and information
- Represent the company in strategic meetings
- Manages the organization website
- Handles ecommerce aspect of the business
- Responsible for installing and maintenance of computer software and hardware for the organization
- Manages logistics and supply chain software, Web servers, e-commerce software and POS (point of sale) systems
Accountant / Cashier:
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Provides managements with financial analyses, development budgets, and accounting reports; analyzes financial feasibility for the most complex proposed projects; conducts market research to forecast trends and business conditions.
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensures compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for the organization
- Serves as internal auditor for the organization
Waiters / Waitress
- Promptly attends to customers in a friendly and professional manner
- Ensures that un-occupied tables are always set and ready for customers
- Pulls out chairs for customers as they arrive
- Handle any other duty as assigned by the Chief Operating officer / restaurant manager
Van Drivers / Sandwich Deliverers:
- Delivers customer’s orders promptly
- Deliver correspondence for the restaurant
- Runs errand for the organization
- Any other duty as assigned by the floor / line manager
- Responsible for cleaning the shop facility at all times
- Ensure that toiletries and supplies don’t run out of stock
- Cleans both the interior and exterior of the store facility
- Handle any other duty as assigned by the shop manager.
6. SWOT Analysis
Our intention of starting just one outlet of our fast food restaurant in Long Beach – California is to test run the business for a period of 2 to 5 years to know if we will invest more money, expand the business and then open other outlets all over California and Key Cities in the United States of America and Canada.
We are quite aware that there are several fast food and French fries food outlets all over Long Beach – California and even in the same location where we intend locating ours, which is why we are following the due process of establishing a business.
We know that if a proper SWOT analysis is conducted for our business, we will be able to position our business to maximize our strength, leverage on the opportunities that will be available to us, mitigate our risks and be welled equipped to confront our threats.
French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks employed the services of an expert HR and Business Analyst with bias in fast food line of business to help us conduct a thorough SWOT analysis and to help us create a Business model that will help us achieve our business goals and objectives.
This is the summary of the SWOT analysis that was conducted for Golden Fingers French Fries
Our location, the business model we will be operating on (physical chains of fast food restaurants with active online presence), varieties of payment options, wide varieties of French fries, snacks and soft drinks and our excellent customer service culture will definitely count as a strong strength for Golden Fingers French Fries. So also, we have a management team that has what it takes to grow startup business from survival to profitability within the shortest time – frame.
A major weakness that may count against us is the fact that we are a new French fries food – business and we don’t have the financial capacity to compete with multi – million dollars chains of fast food restaurants with strong bias for French fries like ConAgra, Snyder’s Lance and PepsiCo et al.
- Opportunities:
The fact that we are going to be operating our fast food restaurant in one of the busiest streets in Long Beach – California, provides us with unlimited opportunities to sell our French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks, water, juice, and sodas et al to a large number of people.
We have been able to conduct thorough feasibility studies and market survey and we know what our potential clients will be looking for when they visit our fast food restaurant; we are well positioned to take on the opportunities that will come our way.
Just like any other business, one of the major threats that we are likely going to face is economic downturn. It is a fact that economic downturn affects purchasing / spending power. Another threat that may likely confront us is the arrival of a new French fries food production business or fast food restaurant in same location where ours is located.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
In this era when the online community is growing rapidly, you would do your business a who if you create your own online presence. One of the easiest ways to get people to see you as an expert in your line of business is to blog constantly about French fries and fast foods generally.
You may also want to leverage on social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter, and others to publicize your French fries food outlet. You can as well go ahead to open an online portal where people can place order from French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks, water, juice, and sodas et al.
You must ensure that your delivery system is efficient if you intend to do well with your online fast food business. So also, keeping consumers’ appetites satisfied, fast food restaurants / franchises have created new menu options that capitalize on the trend of increasing awareness of the health risks associated with a high-fat diet.
The industry has also thrived by developing products at price points attractive enough to weather the slow recovery, resulting in strong revenue growth. As a result of this, these trends are expected to continue and contribute to revenue growth going forward.
8. Our Target Market
One thing about French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks, water, juice, and sodas et al is that you can hardly find someone who don’t patronize them. As a matter of fact, most fast food restaurants now have menu designed specifically for veg and others depending on their food preferences.
In view of that, we have positioned our fast food restaurant to service the residence of Long Beach – California and every other location where our chains of fast food outlets will be located in key cities all over the United States of America and Canada.
We have conducted our market research and we have ideas of what our target market would be expecting from us. We are in business to retail our products to the following groups of people;
- Event Planners
- Vegetarians
- Corporate Organizations
- Corporate Executives
- Business People
- Sports Men and Women
Our competitive advantage
A close study of the snacks food production / fast food industry reveals that the market has become much more intensely competitive over the last decade. So , you have to be highly creative, customer centric and proactive if you must survive in this industry.
We are aware of the stiffer competition and we are well prepared to compete favorably with other chains of fast food restaurants in Long Beach – California.
Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC is launching a standard French fries food production business that will indeed become the preferred choice of residence of Long Beach – California and other cities where we intend opening our chains of fast food outlets.
Our fast food outlet is located in a corner piece property on a busy road directly opposite one of the largest residential estates in Long Beach – California. We have enough parking spaces that can accommodate well over 20 cars per time.
One thing is certain, we will ensure that we have a wide variety of French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks, water, juice, and sodas et al available in our shop at all times. It will be difficult for customers to visit our fast food outlets and not make a purchase of French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks, water, juice, and sodas et al.
One of our business goals is to make Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC a one stop fast food restaurant. Our excellent customer service culture, online options, various payment options and highly secured facility will serve as a competitive advantage for us.
Lastly, our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category (startups French fries food production / fast food restaurants) in the snacks food production / fast food industry, meaning that they will be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our aims and objectives.
We will also give good working conditions and commissions to freelance sales agents that we will recruit from time to time.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Golden Fingers French Fries is in operation to operate a standard and secured fast food restaurant business in Long Beach – California. We are in the snacks food production / fast food industry to
10. Sales Forecast
One thing is certain when it comes to fast food restaurant business, if your fast food restaurant is centrally positioned, you will always attract customers cum sales and that will sure translate to increase in revenue generation for the business.
We are well positioned to take on the available market in Long Beach – California and we are quite optimistic that we will meet our set target of generating enough income / profits from the first six month of operations and grow the business and our clientele base.
We have been able to critically examine the snack food production / fast food industry and we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast. The sales projections are based on information gathered on the field and some assumptions that are peculiar to similar startups in Long Beach – California.
Below is the sales projection for Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC, it is based on the location of our business and other factors as it relates to French fries shop start – ups in the United States;
- First Fiscal Year-: $120,000
- Second Fiscal Year-: $250,000
- Third Fiscal Year-: $750,000
N.B: This projection is done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown and there won’t be any major competitor offering same products and customer care services as we do within same location. Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
Before choosing a location for Golden Fingers French Fries, we carried out a detailed market survey and feasibility studies in order for us to be able to be able to penetrate the available market and become the preferred choice for residence of Long Beach – California.
We have detailed information and data that we were able to utilize to structure our business to attract the numbers of customers we want to attract per time. We hired experts who have good understanding of the snacks food production / fast food industry to help us develop
In other to continue to be in business and grow, we must continue to sell our French fries, snacks and drinks which is why we will go all out to empower or sales and marketing team to deliver. In summary, Golden Fingers French Fries will adopt the following sales and marketing approach to win customers over;
- Open our French fries food production outlet in a grand style with a party for all.
- Introduce our French fries food production outlets by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to corporate organizations, schools, event planners, households and key stake holders in Long Beach – California
- Ensure that we have a wide variety of French fries, snacks and soft drinks in our restaurant at all times.
- Make use of attractive hand bills to create awareness and also to give direction to our fast food restaurant
- Position our signage / flexi banners at strategic places around Long Beach – California
- Position our greeters to welcome and direct potential customers
- Create a loyalty plan that will enable us reward our regular customers
- Engage on road shows within our neighborhood to create awareness for our fast food restaurant.
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
Despite the fact that our fast food restaurant is well located, we will still go ahead to intensify publicity for the business. We are going to explore all available means to promote Golden Fingers French Fries.
Golden Fingers French Fries has a long-term plan of opening chains of fast food outlets in various locations all around California and key cities in the United States and Canada which is why we will deliberately build our brand to be well accepted in Long Beach before venturing out.
As a matter of fact, our publicity and advertising strategy is not solely for winning customers over but to effectively communicate our brand. Here are the platforms we intend leveraging on to promote and advertise Golden Fingers French Fries;
- Place adverts on community based newspapers, radio stations and TV stations.
- Encourage the use of word of mouth publicity from our loyal customers
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; YouTube, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Snapchat, Badoo, Google+ and other platforms to promote our business.
- Ensure that our we position our banners and billboards in strategic positions all around Long Beach – California
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas in and around our neighborhood
- Contact corporate organizations, households, religious centers, schools and event planners et al by calling them up and informing them of Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC and the products we sell
- Advertise Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC business in our official website and employ strategies that will help us pull traffic to the site
- Brand all our official cars and delivery vans and ensure that all our staff members and management staff wears our branded shirt or cap at regular intervals
12. Our Pricing Strategy
Pricing is one of the key factors that gives leverage to fast food restaurants, it is normal for consumers to go to places where they can purchase / order French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks, water, juice, and sodas et al at cheaper price which is why big players in the snacks food production / fast food industry will continue to attract loads of consumers.
We know we don’t have the capacity to compete with bigger and well – established chains of snacks food production outlets like ConAgra, Snyder’s Lance and PepsiCo et al, but we will ensure that the prices of all the products that are available in our fast food restaurant are competitive with what is obtainable amongst fast food restaurant within our level.
We are aware that there are contracts for supply of fast foods and soft drinks by government establishments, NGOs, corporate organizations or big religious organization; we will ensure that we abide by the bidding pricing template when we bid for such contracts.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment with cash
- Payment via credit cards / Point of Sale Machines (POS Machines)
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via mobile money transfer
- Payment via bank draft
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our client make payment for the purchase of products without any stress on their part. Our bank account numbers will be made available on our website and promotional materials to clients who may want to deposit cash or make online transfer for our products and services.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
In setting up any business, the amount or cost will depend on the approach and scale you want to undertake. If you intend to go big by renting a place, then you would need a good amount of capital as you would need to ensure that your employees are well taken care of, and that your facility is conducive enough for workers to be creative and productive.
This means that the start-up can either be low or high depending on your goals, vision and aspirations for your business. The tools and equipment that will be used are nearly the same cost everywhere, and any difference in prices would be minimal and can be overlooked.
As for the detailed cost analysis for starting a French fries food outlet / fast food restaurant; it might differ in other countries due to the value of their money. These are the key areas where we will spend our start – up capital;
- The total fee for registering the business in the United States of America – $750.
- Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits as well as the accounting services (software, P.O.S machines and other software) – $1,300.
- Marketing promotion expenses for the grand opening of Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of – $3,580.
- The cost for hiring Business Consultant – $2,500.
- Insurance (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) coverage at a total premium – $2,400.
- The cost for payment of rent for 12 month at $1.76 per square feet in the total amount of $105,600.
- The cost for construction of a fast food restaurant (kitchen inclusive) – $100,000.
- Other start-up expenses including stationery ( $500 ) and phone and utility deposits ( $2,500 ).
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $100,000
- The cost for Start-up inventory (food ingredients, drinks and packaging materials et al) – $80,000
- Storage hardware (bins, rack, shelves, food case) – $3,720
- The cost for counter area equipment (counter top, sink, ice machine, etc.) – $9,500
- Cost for store equipment (cash register, security, ventilation, signage) – $13,750
- Cost of purchase of distribution vans – $50,000
- The cost for the purchase of furniture and gadgets (Computers, Printers, Telephone, TVs, Sound System, tables and chairs et al) – $4,000.
- The cost of Launching a Website – $600
- The cost for our opening party – $10,000
- Miscellaneous – $10,000
We would need an estimate of two hundred and fifty thousand dollars ( $250,000 ) to successfully set up our French fries food outlet in Long Beach – California. Please note that this amount includes the salaries of the entire staff member for the first month of operation and the amount could be more or lower.
Generating Funds / Startup Capital for Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC
Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC is a private business that is solely owned and financed by Jason Kennedy and his immediate family members. They do not intend to welcome any external business partners which is why he has decided to restrict the sourcing of the start – up capital to 3 major sources.
These are the areas we intend generating our start – up capital;
- Generate part of the start – up capital from personal savings
- Source for soft loans from family members and friends
- Apply for loan from my Bank
N.B: We have been able to generate about $100,000 ( Personal savings $80,000 and soft loan from family members $20,000 ) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $150,000 from our bank. All the papers and document have been signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited with the amount.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
The future of a business lies in the numbers of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of the employees, their investment strategy and the business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business (company), then it won’t be too long before the business close shop.
One of our major goals of starting Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without the need for injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running.
We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to retail our French fries / potato chips, nuts and seeds, peanut butter, tortilla and corn chips, other chips, other snacks, water, juice, and sodas et al a little bit cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are well prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
Golden Fingers French Fries®, LLC will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of three years or more. We know that if that is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List / Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check: Completed
- Business Registration: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts: Completed
- Securing Point of Sales (POS) Machines: Completed
- Opening Mobile Money Accounts: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Leasing of facility and remodeling the restaurant (kitchen inclusive): In Progress
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Generating capital from family members: Completed
- Applications for Loan from the bank: In Progress
- Writing of Business Plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents and other relevant Legal Documents: In Progress
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Graphic Designs and Printing of Packaging Marketing / Promotional Materials: In Progress
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of the Needed furniture, racks, shelves, computers, electronic appliances, office appliances and CCTV: In progress
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business both online and around the community: In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement (License): Secured
- Opening party / launching party planning: In Progress
- Compilation of our list of products that will be available in our shop: Completed
- Establishing business relationship with vendors – suppliers of potato, ingredients, coffees and soft drinks: In Progress
More on Food
Download the Business Model Canvas En Francais Template in Word (DOC) - Neos Chronos
Download the business model canvas en francais in word (doc)..
Welcome to Neos Chronos. Your editable Business Model Canvas En Francais (BMC) Template should download automatically - typically your browser will open a pop-up window. If your download does not start automatically, please use the
Manual Download Format: Word (DOC)
button to proceed.
DISCOVER MORE RESOURCES
Beside the Business Model Canvas En Francais (BMC) we have developed a wealth of complimentary business modelling tools, resources and templates for startup founders and enterprise executives who want to introduce lean methods into their businesses. Check our template library and feel free to use them for your work.
Download more resources No cost, no registration required.
We have created our resources in the template library as a service to the entrepreneur community. This is why we provide them under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , unless marked otherwise. Like more than two (2) million people so far, you are free to use and adapt the content for your own purposes as long as you visibly acknowledge Neos Chronos as the source in any derivative work. In practical terms this means that you are free to use and adapt this Business Model Canvas En Francais Template as long as you do not remove our copyright notice, and you do not restrict the rights you received from us when sharing the result with others.
You are welcome to link back to this page if you found it useful. This is the easiest form of attribution and it helps us reach more people.
EXPLORE OUR SERVICES
If you want to make the most out of your brand new Business Model Canvas En Francais Template, then one of the following personalised services may be for you. At Neos Chronos we have helped over 120 startups progress in their entrepreneurial journey and our advisors created over £150 million of sales revenue for the companies they have served.
workshop for startups
LEAN CANVAS
workshop for enterprises
BUSINESS MODEL CANVAS
workshop for all
VALUE PROPOSITION CANVAS
Entrepreneur for a day, credits & references.
All names and trademarks mentioned herein and in the Business Model Canvas En Francais Template are the property of their respective owners. Please observe the Neos Chronos Terms of Use .
- Deciphering Digital Business Models
- How to Create your Strategyzer Business Model Canvas
- How to Create your Value Proposition Canvas
- A Simple Model for Sales Success
- A Primer to Selecting Advisors, Coaches and Mentors
- Startup Equity Dilution Calculator
- Metaverse Startup Ideas and Metaverse Business Opportunities
For more information on how our advisory services can help you accelerate your entrepreneurial journey, please contact us to arrange an introductory meeting or
Book a Discovery Session now! Get to know us. Put us to the test.
Neos Chronos
Neos Chronos are an advisory services firm for startups and large enterprises. We care that enterprise executives solve their hardest strategic issues and avoid disruption, and startup founders accelerate growth and avoid business-critical mistakes.
Download business model templates
Services Insights People News Contact
Site Search Sitemap Resources Privacy Terms of Use
Twitter LinkedIn Facebook Instagram Pinterest
Share This Page
French Entrepreneur Visa Business Plan
How to write a business plan for the french entrepreneur visa application.
Buy The Instant Access Business Plan Template

Are you applying for the entrepreneur / profession libérale visa?
Are you feeling a little lost and confused with the business plan?
How do you write a business plan for the French entrepreneur visa?
Hi, I’m Kate and In September 2021, I successfully applied for the VLS-TS entrepreneur/ profession libérale from the UK.
Actually I successfully applied for three visas- myself and my husband on entrepreneur visas and my son on a VLS-TS visiteur.
I know how tough it can be to find guidance to assist with your application so I’ve pulled some these resources together to help you navigate your application.
I applied via Manchester TLS so any country-specific experience is based on the UK.

Where do I start when applying for the French entrepreneur/profession liberale visa?
Firstly, you need to work out the following:
- What your business will be selling ( click here to know if your profession is regulated- this may mean you need to have your qualifications recognised in France)
- What the structure will be (limited company, self employed, overseas employer) to make sure you’re applying for the correct visa as there a few kinds of French working visa
- If you need assistance then head to Strictly Fiscal France on Facebook where you can ask questions and use the search function in the group to help make your decision
The next step for the VLS-TS entrepreneur/profession liberale
Once you’re sure that the VLS-TS entrepreneur/ profession libérale is the one for you then have a read through my visa pro article from French Property News for a comprehensive overview of the process.
For any extra assistance with the visa application itself then head to Applying for a French CdS (Carte de Séjour) and/or visa Facebook group as I am unable to give advice here.
Update 2023: some business plans need to be submitted for approval via your new prefecture in France for an ‘avis favorable’ before you apply via the TLS centre in the UK or consulate elsewhere. Ensure you search the Facebook group given above for up to date advice on ever changing criteria as this was not part of my process.
The Business Plan for the French Entrepreneur Visa
So now you’re ready to write your business plan?
There is no official template for the business plan which must accompany the visa application however this page is often cited as the next best thing- although I found it difficult to use and overkill for what is needed.
Some general guidance in French can be found here.
How To Write a Successful Business Plan for the French Entrepreneur Visa
I know how writing a business plan can stop you in your tracks.
You need financial projections, operational considerations and more.
Even though you know you can make your business a success in France, you can struggle to get all that down on paper in a way the French consulate will approve of.
I’ve taken the business plan that I wrote for my successful application, and changed the sections into prompts and questions for you to flesh out. You can now purchase it to ensure you have a solid starting block.

Business Plan Template for the French Entrepreneur Visa
This is a template to support your application for the French long stay visa- entrepreneur/profession libérale.
It is suitable for service based businesses ie. consultants, coaches, virtual assistants, therapists, but could be used as a starting point for any other business by adding addtional sections.
This template includes sections such as competitor analysis, proposed services and financial projections.
The notes included in each section are to act as prompts and questions, to allow you to flesh out your business plan in your own words and appropriate to your own business. This gives you the structure and flow, the prompts help you to write your plan which means you can hit the ground running with your business plan instead of staring at a blank piece of paper.
Please note, this is not a complete business plan or a copy of my complete business plan, that would cost £1000+ this is a templated version for you to fill out in your own words using my prompts.
Y ou can also now add on a business plan review at checkout to get my eyes on you r completed plan before you submit it!
How it works

Upon checkout you will receive a link via email. Please check your spam / junk folder if you don’t receive it.

Download your template
Download your template and fill it in using the notes in each section as prompts.

Vive la France!
Use your new business plan to support your application for the French long stay visa- entrepreneur/profession libérale.
When you purchase the French Entrepreneur Visa Business Plan Template, you’ll also get:
NEW Move To France Launchpad !
Your comprehensive PDF planning notebook designed to streamline and organise your relocation to France .
Whether you prefer digital use on your laptop or the convenience of a printed copy, this serves as your go-to resource for planning and executing a smooth transition for you and your family.
Packed with essential sections and prompts, dedicated pages for checklists and ample space for notes and reminders, this tool has been created from real-life experience to plan a hassle-free move to France- all in one place!

Are you ready for your dream move to France?
Buy the template today and you’re one step closer to making it a reality.
You can add a business plan review on at checkout to get my eyes on your plan when you’ve completed it!
Frequently Asked Questions
Once you’ve completed the checkout process you’ll be provided with a login link via email to access the template within my learning management platform.
If you do not see it in your email inbox, please check your spam / junk folders
If you still do not see it please do not panic. Instead, contact [email protected] .Your mailbox may have blocked the message as it contains a link from an unknown sender.
Once you’re insdie the product dashboard, the template is available in two formats: Google Doc and Microsoft Word.
When you click the link to open the document it will ask you to make a copy into your own Google Drive or you can choose to download the Word file to your computer.
This template is suitable for service based businesses ie. consultants, coaches, virtual assistants. But it could be used as a starting point for any other business.
This is a template to support your application for the French long stay visa- entrepreneur/profession libérale. (VLS-TS entreprenuer/prof. liberale)
As per our terms and conditions, you will receive instant access to the product via an automated login link being sent to your email address- therefore you will waive your right to a refund.
It is important that you check that you are happy to purchase this product before doing so.
We are committed to transaprency at Olivier Consultancy. Full terms & conditions can be found at the bottom of this page.
This document is a template document. It is intended for the use of you as the sole client and is not for re-sale or sub license.
At the point of purchase, you are confirming your express consent to receiving the download immediately. In agreeing to receive the download at that point you will lose your right to cancel and your right to a refund.
It is your responsibility to ensure that you can open the file format. If you are unsure, please email hello@olivier-consultancy before you make your purchase.
DISCLAIMER: At no point does this template constitute advice, or guidance and this does not form a client/consultant relationship. This template is for information only and has not been authorised by any French governental or immigration body. This template was used successfully for visa applications in 2021 and is provided by personal experience only.
No responsibility is taken for any visa applications or other, after using this template.
Privacy Overview
Start Business in France

How to get a business visa or carte de sejour entrepreneur for France
Your dream is to move to France for a fresh start and to run a small business which will enable you to enjoy your new lifestyle. Who wouldn't dream of moving to a new country and finding the right balance between work and personal life.
There is just one step between this dream and the reality - it is getting a business visa for non-European citizen or a carte se sejour entrepreneur/profession libérale for English citizen. How do you ensure that you get this business visa or carte de sejour? What can you do to ensure that the French Embassy gives you the golden ticket - a business visa. In this article, I’m sharing my best tips to succeed with your business visa application for France.
Before I go any futher, here are the business visa that you may consider as a non-European citizen: visa commercant (buy-to-resell, ecommerce, shops, tourism), visa profession liberale (consultants, programmers, teachers, coaches), visa Talents (highly skilled, Master's degree + 30KE investment in your business). The first two are my favourites, as they are easier to get, i.e no need to justify a financial investment in your business, provided you have an income to live on.
1 - Keep it simple
This first tip may sound counter intuitive, but it’s the most important one. Keep your project simple. The role of the French Embassy advisors is to look at your business plan and check that you are ticking all the boxes enabling you to carry out your activity. This means rules, regulations, legal structure, link to any existing business. Anything that doesn’t tick the rules, raises a red flag and your visa request is likely to be rejected.
Your dream might be to create a tea-shop or restaurant, but this involves finding premises, signing a leasing contract (pretty tough from abroad), checking the kitchen's health and safety standards, buying some expensive professional equipment. A short term alternative could be to set up as a chef à domicile or traiteur, then once you are up and running in France, look into your long term project.
You might want to create a marketing agency as a French incorporated business, but this means finding a bank to work with (tough from abroad), having draft letters of incorporation. An easier option could be to start freelancing as a micro entrepreneur, then the following year, move up to a French incorporated business.
Keep it simple for the French Embassy to say "Oui" to you.
2 - Have a long term plan
Following on from my first tip, try to project yourself in one year, then 3 to 5 years time. Have a short term plan for your visa application, enabling you to be self-suffisant and earning enough income for your 1st year visa renewal (or have enough savings). Then plan your development once your visa has been renewed. What do you want to achieve or develop? Will it impact the type of visa you may need? For instance switching from a visa profession liberale as a marketing consultant to a visa commercant to create your French incorporated business?
3 - Write a strong business plan
Your business plan has two purposes: 1/ Enabling you to create a vision and strategy for your activity and 2/ Enabling the French Embassy to decide that your business project looks viable. The clearer you are on your offer, ideal customer, competitors, market analysis, strategy and sales projection, the easier it is for them to say yes. Show your experience, expertise and a good understanding of your market.
A good business plan will also include a financial plan, with your projected sales and running expenses over 3 years. Aim to show that your business will generate enough income for you to live from or that you have enough savings. Aim for an income of at least 19,000 euros for a single person, or show some savings or other sources of income (private pension, rental income, divorce alimony).
4 - Check the regulations & taxes with a French business expert
This is probably where most visas get rejected. You applied for a business visa to open a beauty shop, but you have no official qualification. You want to open an equestrian center, but need approval from local authorities before you can do so. If you need help for this step, book a Power Hour with me. I will double check the regulation and best set up for your project.
5 - Show your existing support and forward planning
If you’ve shared your business project with your network or former employers and they are keen to use your services, ask them for their support. Ask for a “lettre d’intention” for each of them. This is basically a letter in which they confirm that they support your initiative and may use your services.
This letter isn’t a contract, meaning that your contact can decide not to work with you in the future. But it shows your ability to gather some momentum and potential customers even before you move to France.
This is a very strong tool for freelancers providing services business to business.
Finally, I would also recommend to make a list of the actions that you have already taken to build your project. You've been to France to check the area, your market, meet some contacts. You've met an accountant, a bank manager or a business advisor. You've taken some French lessons or worked with a business coach, mention it. It shows that you are planning ahead and gives condfidence in your abiility to take action and make things happen. A simple table with the date, contact's company and topic covered will do the job.


Sales & Marketing Plan for a French Restaurant (Example)
- January 9, 2024
- Business Plan , Sales & Marketing Strategy

Establishing and managing a thriving French restaurant demands more than just culinary expertise; it necessitates a well-thought-out approach to sales and marketing strategies. This comprehensive guide is designed to aid in devising a specialized sales and marketing plan tailored to the business plan of a French restaurant .
It begins with a thorough market analysis to comprehend competitors and diner preferences. It then emphasizes creating a unique brand identity and strategic market positioning.
Exploring diverse marketing channels for effective patron engagement, it delves into various sales strategies aimed at boosting revenue generation.

French Restaurant Business Plan

Fully editable 30+ slides Powerpoint presentation business plan template.
Download an expert-built 30+ slides Powerpoint business plan template
Market Analysis
Competitive analysis:.
- Identify Key Competitors : Understanding the landscape within which your French restaurant operates is crucial. Delve deeply into researching your competitors, both direct and indirect. Direct competitors would include other French restaurants in the vicinity, while indirect competitors might encompass upscale dining establishments offering European cuisine or local bistros with unique menus.
- SWOT Analysis : Performing a SWOT analysis for your restaurant is pivotal. Assess your strengths in French culinary expertise, unique recipes, or chef specialties. Identify weaknesses in service, ambiance, or menu variety. Explore opportunities to innovate or expand offerings and anticipate potential threats like changing consumer preferences or economic downturns.
Target Audience Profiling
- Demographics: To effectively target and cater to your audience, delve into detailed demographic and psychographic profiling. Understand the age groups, income levels, and cultural inclinations of your potential patrons
- Customer Preferences: Determine their dining preferences, whether they seek authenticity in French cuisine, a luxurious dining experience, or a casual yet elegant atmosphere.Craft customer personas to visualize your ideal patrons. Consider personas like “Sophisticated Connoisseurs” who value authenticity, “Young Urban Professionals” seeking trendy experiences, or “Families Exploring New Cuisines.”
Branding and Positioning
Brand identity development.
- Brand Story and Values: The essence of your French restaurant lies in its story. Craft a narrative that evokes the charm and richness of French culinary heritage. Share the inspiration behind your restaurant, be it a family legacy of French cooking, a chef’s journey through regional cuisines, or a fascination with French gastronomy.
- Visual Elements: Create a consistent visual identity. From the logo design to the interior decor, ensure elements reflect the essence of France, be it rustic Provencal vibes, chic Parisian elegance, or coastal influences from the French Riviera. This cohesive branding elevates the dining experience and sets the stage for a memorable visit.
Market Positioning Strategy
- Define Your Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Define the Unique Selling Proposition (USP) of your French restaurant. Whether it’s authenticity in traditional French recipes, fusion with local ingredients, a specific dining experience, or a curated wine selection, highlight what sets your restaurant apart.
- Positioning Statement: Craft a positioning statement that succinctly conveys this USP. For instance, “Embracing French Culinary Heritage with a Local Twist” or “An Oasis of Provencal Flavors in the Heart of the City.” This statement becomes the guiding principle for all marketing and operational decisions.
Marketing Channels
Digital marketing.
- Social Media: Utilize various social media platforms (Instagram, Facebook) to showcase enticing French cuisine, share chef’s specialties, and highlight the restaurant’s ambiance. Engage with the audience through comments, stories, and interactive content.
- Website and SEO: Develop a professional website showcasing the menu, chef profiles, ambiance, and special events. Optimize it for local SEO to attract online traffic searching for French dining options in the area.
Local Advertising
Establish strong community ties to enhance local engagement and entice customers to your restaurant.
- Flyers and Local Promotion: Design visually appealing flyers showcasing the uniqueness of your French restaurant. Strategically distribute these flyers in local cafes, boutique shops, cultural centers, and business hubs to capture the attention of potential diners within the vicinity. Highlight special menu items, themed events, or exclusive offers to pique interest.
- Partnerships : Forge partnerships with neighboring businesses that align with your restaurant’s ambiance or values. Collaborate with local wine shops, artisanal bakeries, or art galleries for joint promotions, exclusive wine pairings, or art-themed dining nights.
- Local Event Participation: Engage actively with the local community by participating in neighborhood events, food festivals, or cultural gatherings. Set up a stall or booth offering delectable samples of your French cuisine, allowing attendees to savor the flavors your restaurant offers.
Promotional Activities
- Seasonal Promotions: Create themed dining nights or seasonal promotions like ‘Bastille Day Specials’ or ‘Wine and Cheese Pairing Evenings’ to attract customers seeking unique dining experiences.
- First-Time Visitor Discounts: Incentivize trial visits by offering special discounts for first-time diners. Provide introductory offers like a complimentary appetizer or a discount on the first meal to encourage new customers to experience your French cuisine.
- Loyalty Programs: I mplement a loyalty program rewarding regular patrons. Offer incentives such as a loyalty card, after a certain number of visits.
Sales Channels
In-restaurant upselling.
- Specialty Add-Ons: Train staff to recommend additional offerings that complement the dining experience, such as pairing suggestions for entrees, upgrades to premium wines, or specialty desserts.
- Celebratory Packages: Introduce packages for special occasions like ‘Anniversary Dinners’ or ‘Birthday Celebrations,’ including complimentary desserts or customized menus.
- Additional Offerings: Offer additional services or experiences, such as exclusive chef’s table dinners or dessert pairings, to increase per-customer spending.
Online Booking and Sales
- Online Booking System: Implement an easy-to-use online reservation system on the website and social media platforms. Incentivize online bookings with special offers or priority seating.
- E-Commerce: Introduce e-commerce for selling merchandise, curated wine selections, or gourmet food products associated with the restaurant.
Membership and Loyalty Programs
- Membership Options: Encourage customer loyalty through membership programs offering exclusive perks. Provide VIP access to events, early notifications of new menu launches, or personalized dining experiences reserved for members.
- Loyalty Rewards: Develop a digital loyalty program rewarding patrons with points for every visit or purchase. Offer incentives like discounts, freebies, or special access based on accumulated points. Implement a tiered system to motivate customers to reach higher levels for premium benefits.
Related Posts

Steakhouse Business Plan PDF Example
- May 10, 2024
- Business Plan

Executive Summary of a Steakhouse: Template & Example
- May 6, 2024
- Business Plan , Executive Summary

Bubble Tea Business Plan PDF Example
- March 19, 2024
Privacy Overview
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
How to Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (+ Template and Examples)
Every successful business has one thing in common, a good and well-executed business plan. A business plan is more than a document, it is a complete guide that outlines the goals your business wants to achieve, including its financial goals . It helps you analyze results, make strategic decisions, show your business operations and growth.
If you want to start a business or already have one and need to pitch it to investors for funding, writing a good business plan improves your chances of attracting financiers. As a startup, if you want to secure loans from financial institutions, part of the requirements involve submitting your business plan.
Writing a business plan does not have to be a complicated or time-consuming process. In this article, you will learn the step-by-step process for writing a successful business plan.
You will also learn what you need a business plan for, tips and strategies for writing a convincing business plan, business plan examples and templates that will save you tons of time, and the alternatives to the traditional business plan.
Let’s get started.
What Do You Need A Business Plan For?
Businesses create business plans for different purposes such as to secure funds, monitor business growth, measure your marketing strategies, and measure your business success.
1. Secure Funds
One of the primary reasons for writing a business plan is to secure funds, either from financial institutions/agencies or investors.
For you to effectively acquire funds, your business plan must contain the key elements of your business plan . For example, your business plan should include your growth plans, goals you want to achieve, and milestones you have recorded.
A business plan can also attract new business partners that are willing to contribute financially and intellectually. If you are writing a business plan to a bank, your project must show your traction , that is, the proof that you can pay back any loan borrowed.
Also, if you are writing to an investor, your plan must contain evidence that you can effectively utilize the funds you want them to invest in your business. Here, you are using your business plan to persuade a group or an individual that your business is a source of a good investment.
2. Monitor Business Growth
A business plan can help you track cash flows in your business. It steers your business to greater heights. A business plan capable of tracking business growth should contain:
- The business goals
- Methods to achieve the goals
- Time-frame for attaining those goals
A good business plan should guide you through every step in achieving your goals. It can also track the allocation of assets to every aspect of the business. You can tell when you are spending more than you should on a project.
You can compare a business plan to a written GPS. It helps you manage your business and hints at the right time to expand your business.
3. Measure Business Success
A business plan can help you measure your business success rate. Some small-scale businesses are thriving better than more prominent companies because of their track record of success.
Right from the onset of your business operation, set goals and work towards them. Write a plan to guide you through your procedures. Use your plan to measure how much you have achieved and how much is left to attain.
You can also weigh your success by monitoring the position of your brand relative to competitors. On the other hand, a business plan can also show you why you have not achieved a goal. It can tell if you have elapsed the time frame you set to attain a goal.
4. Document Your Marketing Strategies
You can use a business plan to document your marketing plans. Every business should have an effective marketing plan.
Competition mandates every business owner to go the extraordinary mile to remain relevant in the market. Your business plan should contain your marketing strategies that work. You can measure the success rate of your marketing plans.
In your business plan, your marketing strategy must answer the questions:
- How do you want to reach your target audience?
- How do you plan to retain your customers?
- What is/are your pricing plans?
- What is your budget for marketing?

How to Write a Business Plan Step-by-Step
1. create your executive summary.
The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans . Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.

Generally, there are nine sections in a business plan, the executive summary should condense essential ideas from the other eight sections.
A good executive summary should do the following:
- A Snapshot of Growth Potential. Briefly inform the reader about your company and why it will be successful)
- Contain your Mission Statement which explains what the main objective or focus of your business is.
- Product Description and Differentiation. Brief description of your products or services and why it is different from other solutions in the market.
- The Team. Basic information about your company’s leadership team and employees
- Business Concept. A solid description of what your business does.
- Target Market. The customers you plan to sell to.
- Marketing Strategy. Your plans on reaching and selling to your customers
- Current Financial State. Brief information about what revenue your business currently generates.
- Projected Financial State. Brief information about what you foresee your business revenue to be in the future.
The executive summary is the make-or-break section of your business plan. If your summary cannot in less than two pages cannot clearly describe how your business will solve a particular problem of your target audience and make a profit, your business plan is set on a faulty foundation.
Avoid using the executive summary to hype your business, instead, focus on helping the reader understand the what and how of your plan.
View the executive summary as an opportunity to introduce your vision for your company. You know your executive summary is powerful when it can answer these key questions:
- Who is your target audience?
- What sector or industry are you in?
- What are your products and services?
- What is the future of your industry?
- Is your company scaleable?
- Who are the owners and leaders of your company? What are their backgrounds and experience levels?
- What is the motivation for starting your company?
- What are the next steps?
Writing the executive summary last although it is the most important section of your business plan is an excellent idea. The reason why is because it is a high-level overview of your business plan. It is the section that determines whether potential investors and lenders will read further or not.
The executive summary can be a stand-alone document that covers everything in your business plan. It is not uncommon for investors to request only the executive summary when evaluating your business. If the information in the executive summary impresses them, they will ask for the complete business plan.
If you are writing your business plan for your planning purposes, you do not need to write the executive summary.
2. Add Your Company Overview
The company overview or description is the next section in your business plan after the executive summary. It describes what your business does.
Adding your company overview can be tricky especially when your business is still in the planning stages. Existing businesses can easily summarize their current operations but may encounter difficulties trying to explain what they plan to become.
Your company overview should contain the following:
- What products and services you will provide
- Geographical markets and locations your company have a presence
- What you need to run your business
- Who your target audience or customers are
- Who will service your customers
- Your company’s purpose, mission, and vision
- Information about your company’s founders
- Who the founders are
- Notable achievements of your company so far
When creating a company overview, you have to focus on three basics: identifying your industry, identifying your customer, and explaining the problem you solve.
If you are stuck when creating your company overview, try to answer some of these questions that pertain to you.
- Who are you targeting? (The answer is not everyone)
- What pain point does your product or service solve for your customers that they will be willing to spend money on resolving?
- How does your product or service overcome that pain point?
- Where is the location of your business?
- What products, equipment, and services do you need to run your business?
- How is your company’s product or service different from your competition in the eyes of your customers?
- How many employees do you need and what skills do you require them to have?
After answering some or all of these questions, you will get more than enough information you need to write your company overview or description section. When writing this section, describe what your company does for your customers.

The company description or overview section contains three elements: mission statement, history, and objectives.
- Mission Statement
The mission statement refers to the reason why your business or company is existing. It goes beyond what you do or sell, it is about the ‘why’. A good mission statement should be emotional and inspirational.
Your mission statement should follow the KISS rule (Keep It Simple, Stupid). For example, Shopify’s mission statement is “Make commerce better for everyone.”
When describing your company’s history, make it simple and avoid the temptation of tying it to a defensive narrative. Write it in the manner you would a profile. Your company’s history should include the following information:
- Founding Date
- Major Milestones
- Location(s)
- Flagship Products or Services
- Number of Employees
- Executive Leadership Roles
When you fill in this information, you use it to write one or two paragraphs about your company’s history.
Business Objectives
Your business objective must be SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.) Failure to clearly identify your business objectives does not inspire confidence and makes it hard for your team members to work towards a common purpose.
3. Perform Market and Competitive Analyses to Proof a Big Enough Business Opportunity
The third step in writing a business plan is the market and competitive analysis section. Every business, no matter the size, needs to perform comprehensive market and competitive analyses before it enters into a market.
Performing market and competitive analyses are critical for the success of your business. It helps you avoid entering the right market with the wrong product, or vice versa. Anyone reading your business plans, especially financiers and financial institutions will want to see proof that there is a big enough business opportunity you are targeting.
This section is where you describe the market and industry you want to operate in and show the big opportunities in the market that your business can leverage to make a profit. If you noticed any unique trends when doing your research, show them in this section.
Market analysis alone is not enough, you have to add competitive analysis to strengthen this section. There are already businesses in the industry or market, how do you plan to take a share of the market from them?
You have to clearly illustrate the competitive landscape in your business plan. Are there areas your competitors are doing well? Are there areas where they are not doing so well? Show it.
Make it clear in this section why you are moving into the industry and what weaknesses are present there that you plan to explain. How are your competitors going to react to your market entry? How do you plan to get customers? Do you plan on taking your competitors' competitors, tap into other sources for customers, or both?
Illustrate the competitive landscape as well. What are your competitors doing well and not so well?
Answering these questions and thoughts will aid your market and competitive analysis of the opportunities in your space. Depending on how sophisticated your industry is, or the expectations of your financiers, you may need to carry out a more comprehensive market and competitive analysis to prove that big business opportunity.
Instead of looking at the market and competitive analyses as one entity, separating them will make the research even more comprehensive.
Market Analysis
Market analysis, boarding speaking, refers to research a business carried out on its industry, market, and competitors. It helps businesses gain a good understanding of their target market and the outlook of their industry. Before starting a company, it is vital to carry out market research to find out if the market is viable.

The market analysis section is a key part of the business plan. It is the section where you identify who your best clients or customers are. You cannot omit this section, without it your business plan is incomplete.
A good market analysis will tell your readers how you fit into the existing market and what makes you stand out. This section requires in-depth research, it will probably be the most time-consuming part of the business plan to write.
- Market Research
To create a compelling market analysis that will win over investors and financial institutions, you have to carry out thorough market research . Your market research should be targeted at your primary target market for your products or services. Here is what you want to find out about your target market.
- Your target market’s needs or pain points
- The existing solutions for their pain points
- Geographic Location
- Demographics
The purpose of carrying out a marketing analysis is to get all the information you need to show that you have a solid and thorough understanding of your target audience.
Only after you have fully understood the people you plan to sell your products or services to, can you evaluate correctly if your target market will be interested in your products or services.
You can easily convince interested parties to invest in your business if you can show them you thoroughly understand the market and show them that there is a market for your products or services.
How to Quantify Your Target Market
One of the goals of your marketing research is to understand who your ideal customers are and their purchasing power. To quantify your target market, you have to determine the following:
- Your Potential Customers: They are the people you plan to target. For example, if you sell accounting software for small businesses , then anyone who runs an enterprise or large business is unlikely to be your customers. Also, individuals who do not have a business will most likely not be interested in your product.
- Total Households: If you are selling household products such as heating and air conditioning systems, determining the number of total households is more important than finding out the total population in the area you want to sell to. The logic is simple, people buy the product but it is the household that uses it.
- Median Income: You need to know the median income of your target market. If you target a market that cannot afford to buy your products and services, your business will not last long.
- Income by Demographics: If your potential customers belong to a certain age group or gender, determining income levels by demographics is necessary. For example, if you sell men's clothes, your target audience is men.
What Does a Good Market Analysis Entail?
Your business does not exist on its own, it can only flourish within an industry and alongside competitors. Market analysis takes into consideration your industry, target market, and competitors. Understanding these three entities will drastically improve your company’s chances of success.

You can view your market analysis as an examination of the market you want to break into and an education on the emerging trends and themes in that market. Good market analyses include the following:
- Industry Description. You find out about the history of your industry, the current and future market size, and who the largest players/companies are in your industry.
- Overview of Target Market. You research your target market and its characteristics. Who are you targeting? Note, it cannot be everyone, it has to be a specific group. You also have to find out all information possible about your customers that can help you understand how and why they make buying decisions.
- Size of Target Market: You need to know the size of your target market, how frequently they buy, and the expected quantity they buy so you do not risk overproducing and having lots of bad inventory. Researching the size of your target market will help you determine if it is big enough for sustained business or not.
- Growth Potential: Before picking a target market, you want to be sure there are lots of potential for future growth. You want to avoid going for an industry that is declining slowly or rapidly with almost zero growth potential.
- Market Share Potential: Does your business stand a good chance of taking a good share of the market?
- Market Pricing and Promotional Strategies: Your market analysis should give you an idea of the price point you can expect to charge for your products and services. Researching your target market will also give you ideas of pricing strategies you can implement to break into the market or to enjoy maximum profits.
- Potential Barriers to Entry: One of the biggest benefits of conducting market analysis is that it shows you every potential barrier to entry your business will likely encounter. It is a good idea to discuss potential barriers to entry such as changing technology. It informs readers of your business plan that you understand the market.
- Research on Competitors: You need to know the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and how you can exploit them for the benefit of your business. Find patterns and trends among your competitors that make them successful, discover what works and what doesn’t, and see what you can do better.
The market analysis section is not just for talking about your target market, industry, and competitors. You also have to explain how your company can fill the hole you have identified in the market.
Here are some questions you can answer that can help you position your product or service in a positive light to your readers.
- Is your product or service of superior quality?
- What additional features do you offer that your competitors do not offer?
- Are you targeting a ‘new’ market?
Basically, your market analysis should include an analysis of what already exists in the market and an explanation of how your company fits into the market.
Competitive Analysis
In the competitive analysis section, y ou have to understand who your direct and indirect competitions are, and how successful they are in the marketplace. It is the section where you assess the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, the advantage(s) they possess in the market and show the unique features or qualities that make you different from your competitors.

Many businesses do market analysis and competitive analysis together. However, to fully understand what the competitive analysis entails, it is essential to separate it from the market analysis.
Competitive analysis for your business can also include analysis on how to overcome barriers to entry in your target market.
The primary goal of conducting a competitive analysis is to distinguish your business from your competitors. A strong competitive analysis is essential if you want to convince potential funding sources to invest in your business. You have to show potential investors and lenders that your business has what it takes to compete in the marketplace successfully.
Competitive analysis will s how you what the strengths of your competition are and what they are doing to maintain that advantage.
When doing your competitive research, you first have to identify your competitor and then get all the information you can about them. The idea of spending time to identify your competitor and learn everything about them may seem daunting but it is well worth it.
Find answers to the following questions after you have identified who your competitors are.
- What are your successful competitors doing?
- Why is what they are doing working?
- Can your business do it better?
- What are the weaknesses of your successful competitors?
- What are they not doing well?
- Can your business turn its weaknesses into strengths?
- How good is your competitors’ customer service?
- Where do your competitors invest in advertising?
- What sales and pricing strategies are they using?
- What marketing strategies are they using?
- What kind of press coverage do they get?
- What are their customers saying about your competitors (both the positive and negative)?
If your competitors have a website, it is a good idea to visit their websites for more competitors’ research. Check their “About Us” page for more information.

If you are presenting your business plan to investors, you need to clearly distinguish yourself from your competitors. Investors can easily tell when you have not properly researched your competitors.
Take time to think about what unique qualities or features set you apart from your competitors. If you do not have any direct competition offering your product to the market, it does not mean you leave out the competitor analysis section blank. Instead research on other companies that are providing a similar product, or whose product is solving the problem your product solves.
The next step is to create a table listing the top competitors you want to include in your business plan. Ensure you list your business as the last and on the right. What you just created is known as the competitor analysis table.
Direct vs Indirect Competition
You cannot know if your product or service will be a fit for your target market if you have not understood your business and the competitive landscape.
There is no market you want to target where you will not encounter competition, even if your product is innovative. Including competitive analysis in your business plan is essential.
If you are entering an established market, you need to explain how you plan to differentiate your products from the available options in the market. Also, include a list of few companies that you view as your direct competitors The competition you face in an established market is your direct competition.
In situations where you are entering a market with no direct competition, it does not mean there is no competition there. Consider your indirect competition that offers substitutes for the products or services you offer.
For example, if you sell an innovative SaaS product, let us say a project management software , a company offering time management software is your indirect competition.
There is an easy way to find out who your indirect competitors are in the absence of no direct competitors. You simply have to research how your potential customers are solving the problems that your product or service seeks to solve. That is your direct competition.
Factors that Differentiate Your Business from the Competition
There are three main factors that any business can use to differentiate itself from its competition. They are cost leadership, product differentiation, and market segmentation.
1. Cost Leadership
A strategy you can impose to maximize your profits and gain an edge over your competitors. It involves offering lower prices than what the majority of your competitors are offering.
A common practice among businesses looking to enter into a market where there are dominant players is to use free trials or pricing to attract as many customers as possible to their offer.
2. Product Differentiation
Your product or service should have a unique selling proposition (USP) that your competitors do not have or do not stress in their marketing.
Part of the marketing strategy should involve making your products unique and different from your competitors. It does not have to be different from your competitors, it can be the addition to a feature or benefit that your competitors do not currently have.
3. Market Segmentation
As a new business seeking to break into an industry, you will gain more success from focusing on a specific niche or target market, and not the whole industry.
If your competitors are focused on a general need or target market, you can differentiate yourself from them by having a small and hyper-targeted audience. For example, if your competitors are selling men’s clothes in their online stores , you can sell hoodies for men.
4. Define Your Business and Management Structure
The next step in your business plan is your business and management structure. It is the section where you describe the legal structure of your business and the team running it.
Your business is only as good as the management team that runs it, while the management team can only strive when there is a proper business and management structure in place.
If your company is a sole proprietor or a limited liability company (LLC), a general or limited partnership, or a C or an S corporation, state it clearly in this section.
Use an organizational chart to show the management structure in your business. Clearly show who is in charge of what area in your company. It is where you show how each key manager or team leader’s unique experience can contribute immensely to the success of your company. You can also opt to add the resumes and CVs of the key players in your company.
The business and management structure section should show who the owner is, and other owners of the businesses (if the business has other owners). For businesses or companies with multiple owners, include the percent ownership of the various owners and clearly show the extent of each others’ involvement in the company.
Investors want to know who is behind the company and the team running it to determine if it has the right management to achieve its set goals.

Management Team
The management team section is where you show that you have the right team in place to successfully execute the business operations and ideas. Take time to create the management structure for your business. Think about all the important roles and responsibilities that you need managers for to grow your business.
Include brief bios of each key team member and ensure you highlight only the relevant information that is needed. If your team members have background industry experience or have held top positions for other companies and achieved success while filling that role, highlight it in this section.

A common mistake that many startups make is assigning C-level titles such as (CMO and CEO) to everyone on their team. It is unrealistic for a small business to have those titles. While it may look good on paper for the ego of your team members, it can prevent investors from investing in your business.
Instead of building an unrealistic management structure that does not fit your business reality, it is best to allow business titles to grow as the business grows. Starting everyone at the top leaves no room for future change or growth, which is bad for productivity.
Your management team does not have to be complete before you start writing your business plan. You can have a complete business plan even when there are managerial positions that are empty and need filling.
If you have management gaps in your team, simply show the gaps and indicate you are searching for the right candidates for the role(s). Investors do not expect you to have a full management team when you are just starting your business.
Key Questions to Answer When Structuring Your Management Team
- Who are the key leaders?
- What experiences, skills, and educational backgrounds do you expect your key leaders to have?
- Do your key leaders have industry experience?
- What positions will they fill and what duties will they perform in those positions?
- What level of authority do the key leaders have and what are their responsibilities?
- What is the salary for the various management positions that will attract the ideal candidates?
Additional Tips for Writing the Management Structure Section
1. Avoid Adding ‘Ghost’ Names to Your Management Team
There is always that temptation to include a ‘ghost’ name to your management team to attract and influence investors to invest in your business. Although the presence of these celebrity management team members may attract the attention of investors, it can cause your business to lose any credibility if you get found out.
Seasoned investors will investigate further the members of your management team before committing fully to your business If they find out that the celebrity name used does not play any actual role in your business, they will not invest and may write you off as dishonest.
2. Focus on Credentials But Pay Extra Attention to the Roles
Investors want to know the experience that your key team members have to determine if they can successfully reach the company’s growth and financial goals.
While it is an excellent boost for your key management team to have the right credentials, you also want to pay extra attention to the roles they will play in your company.
Organizational Chart

Adding an organizational chart in this section of your business plan is not necessary, you can do it in your business plan’s appendix.
If you are exploring funding options, it is not uncommon to get asked for your organizational chart. The function of an organizational chart goes beyond raising money, you can also use it as a useful planning tool for your business.
An organizational chart can help you identify how best to structure your management team for maximum productivity and point you towards key roles you need to fill in the future.
You can use the organizational chart to show your company’s internal management structure such as the roles and responsibilities of your management team, and relationships that exist between them.
5. Describe Your Product and Service Offering
In your business plan, you have to describe what you sell or the service you plan to offer. It is the next step after defining your business and management structure. The products and services section is where you sell the benefits of your business.
Here you have to explain how your product or service will benefit your customers and describe your product lifecycle. It is also the section where you write down your plans for intellectual property like patent filings and copyrighting.
The research and development that you are undertaking for your product or service need to be explained in detail in this section. However, do not get too technical, sell the general idea and its benefits.
If you have any diagrams or intricate designs of your product or service, do not include them in the products and services section. Instead, leave them for the addendum page. Also, if you are leaving out diagrams or designs for the addendum, ensure you add this phrase “For more detail, visit the addendum Page #.”
Your product and service section in your business plan should include the following:
- A detailed explanation that clearly shows how your product or service works.
- The pricing model for your product or service.
- Your business’ sales and distribution strategy.
- The ideal customers that want your product or service.
- The benefits of your products and services.
- Reason(s) why your product or service is a better alternative to what your competitors are currently offering in the market.
- Plans for filling the orders you receive
- If you have current or pending patents, copyrights, and trademarks for your product or service, you can also discuss them in this section.
What to Focus On When Describing the Benefits, Lifecycle, and Production Process of Your Products or Services
In the products and services section, you have to distill the benefits, lifecycle, and production process of your products and services.
When describing the benefits of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Unique features
- Translating the unique features into benefits
- The emotional, psychological, and practical payoffs to attract customers
- Intellectual property rights or any patents
When describing the product life cycle of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Upsells, cross-sells, and down-sells
- Time between purchases
- Plans for research and development.
When describing the production process for your products or services, you need to think about the following:
- The creation of new or existing products and services.
- The sources for the raw materials or components you need for production.
- Assembling the products
- Maintaining quality control
- Supply-chain logistics (receiving the raw materials and delivering the finished products)
- The day-to-day management of the production processes, bookkeeping, and inventory.
Tips for Writing the Products or Services Section of Your Business Plan
1. Avoid Technical Descriptions and Industry Buzzwords
The products and services section of your business plan should clearly describe the products and services that your company provides. However, it is not a section to include technical jargons that anyone outside your industry will not understand.
A good practice is to remove highly detailed or technical descriptions in favor of simple terms. Industry buzzwords are not necessary, if there are simpler terms you can use, then use them. If you plan to use your business plan to source funds, making the product or service section so technical will do you no favors.
2. Describe How Your Products or Services Differ from Your Competitors
When potential investors look at your business plan, they want to know how the products and services you are offering differ from that of your competition. Differentiating your products or services from your competition in a way that makes your solution more attractive is critical.
If you are going the innovative path and there is no market currently for your product or service, you need to describe in this section why the market needs your product or service.
For example, overnight delivery was a niche business that only a few companies were participating in. Federal Express (FedEx) had to show in its business plan that there was a large opportunity for that service and they justified why the market needed that service.
3. Long or Short Products or Services Section
Should your products or services section be short? Does the long products or services section attract more investors?
There are no straightforward answers to these questions. Whether your products or services section should be long or relatively short depends on the nature of your business.
If your business is product-focused, then automatically you need to use more space to describe the details of your products. However, if the product your business sells is a commodity item that relies on competitive pricing or other pricing strategies, you do not have to use up so much space to provide significant details about the product.
Likewise, if you are selling a commodity that is available in numerous outlets, then you do not have to spend time on writing a long products or services section.
The key to the success of your business is most likely the effectiveness of your marketing strategies compared to your competitors. Use more space to address that section.
If you are creating a new product or service that the market does not know about, your products or services section can be lengthy. The reason why is because you need to explain everything about the product or service such as the nature of the product, its use case, and values.
A short products or services section for an innovative product or service will not give the readers enough information to properly evaluate your business.
4. Describe Your Relationships with Vendors or Suppliers
Your business will rely on vendors or suppliers to supply raw materials or the components needed to make your products. In your products and services section, describe your relationships with your vendors and suppliers fully.
Avoid the mistake of relying on only one supplier or vendor. If that supplier or vendor fails to supply or goes out of business, you can easily face supply problems and struggle to meet your demands. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships for better business stability.
5. Your Primary Goal Is to Convince Your Readers
The primary goal of your business plan is to convince your readers that your business is viable and to create a guide for your business to follow. It applies to the products and services section.
When drafting this section, think like the reader. See your reader as someone who has no idea about your products and services. You are using the products and services section to provide the needed information to help your reader understand your products and services. As a result, you have to be clear and to the point.
While you want to educate your readers about your products or services, you also do not want to bore them with lots of technical details. Show your products and services and not your fancy choice of words.
Your products and services section should provide the answer to the “what” question for your business. You and your management team may run the business, but it is your products and services that are the lifeblood of the business.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing your Products and Services Section
Answering these questions can help you write your products and services section quickly and in a way that will appeal to your readers.
- Are your products existing on the market or are they still in the development stage?
- What is your timeline for adding new products and services to the market?
- What are the positives that make your products and services different from your competitors?
- Do your products and services have any competitive advantage that your competitors’ products and services do not currently have?
- Do your products or services have any competitive disadvantages that you need to overcome to compete with your competitors? If your answer is yes, state how you plan to overcome them,
- How much does it cost to produce your products or services? How much do you plan to sell it for?
- What is the price for your products and services compared to your competitors? Is pricing an issue?
- What are your operating costs and will it be low enough for you to compete with your competitors and still take home a reasonable profit margin?
- What is your plan for acquiring your products? Are you involved in the production of your products or services?
- Are you the manufacturer and produce all the components you need to create your products? Do you assemble your products by using components supplied by other manufacturers? Do you purchase your products directly from suppliers or wholesalers?
- Do you have a steady supply of products that you need to start your business? (If your business is yet to kick-off)
- How do you plan to distribute your products or services to the market?
You can also hint at the marketing or promotion plans you have for your products or services such as how you plan to build awareness or retain customers. The next section is where you can go fully into details about your business’s marketing and sales plan.
6. Show and Explain Your Marketing and Sales Plan
Providing great products and services is wonderful, but it means nothing if you do not have a marketing and sales plan to inform your customers about them. Your marketing and sales plan is critical to the success of your business.
The sales and marketing section is where you show and offer a detailed explanation of your marketing and sales plan and how you plan to execute it. It covers your pricing plan, proposed advertising and promotion activities, activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success, and the benefits of your products and services.
There are several ways you can approach your marketing and sales strategy. Ideally, your marketing and sales strategy has to fit the unique needs of your business.
In this section, you describe how the plans your business has for attracting and retaining customers, and the exact process for making a sale happen. It is essential to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales plans because you are still going to reference this section when you are making financial projections for your business.
Outline Your Business’ Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

The sales and marketing section is where you outline your business’s unique selling proposition (USP). When you are developing your unique selling proposition, think about the strongest reasons why people should buy from you over your competition. That reason(s) is most likely a good fit to serve as your unique selling proposition (USP).
Target Market and Target Audience
Plans on how to get your products or services to your target market and how to get your target audience to buy them go into this section. You also highlight the strengths of your business here, particularly what sets them apart from your competition.

Before you start writing your marketing and sales plan, you need to have properly defined your target audience and fleshed out your buyer persona. If you do not first understand the individual you are marketing to, your marketing and sales plan will lack any substance and easily fall.
Creating a Smart Marketing and Sales Plan
Marketing your products and services is an investment that requires you to spend money. Like any other investment, you have to generate a good return on investment (ROI) to justify using that marketing and sales plan. Good marketing and sales plans bring in high sales and profits to your company.
Avoid spending money on unproductive marketing channels. Do your research and find out the best marketing and sales plan that works best for your company.
Your marketing and sales plan can be broken into different parts: your positioning statement, pricing, promotion, packaging, advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media, and strategic alliances.
Your Positioning Statement
Your positioning statement is the first part of your marketing and sales plan. It refers to the way you present your company to your customers.
Are you the premium solution, the low-price solution, or are you the intermediary between the two extremes in the market? What do you offer that your competitors do not that can give you leverage in the market?
Before you start writing your positioning statement, you need to spend some time evaluating the current market conditions. Here are some questions that can help you to evaluate the market
- What are the unique features or benefits that you offer that your competitors lack?
- What are your customers’ primary needs and wants?
- Why should a customer choose you over your competition? How do you plan to differentiate yourself from the competition?
- How does your company’s solution compare with other solutions in the market?
After answering these questions, then you can start writing your positioning statement. Your positioning statement does not have to be in-depth or too long.
All you need to explain with your positioning statement are two focus areas. The first is the position of your company within the competitive landscape. The other focus area is the core value proposition that sets your company apart from other alternatives that your ideal customer might consider.
Here is a simple template you can use to develop a positioning statement.
For [description of target market] who [need of target market], [product or service] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [top competition], it [most essential distinguishing feature].
For example, let’s create the positioning statement for fictional accounting software and QuickBooks alternative , TBooks.
“For small business owners who need accounting services, TBooks is an accounting software that helps small businesses handle their small business bookkeeping basics quickly and easily. Unlike Wave, TBooks gives small businesses access to live sessions with top accountants.”
You can edit this positioning statement sample and fill it with your business details.
After writing your positioning statement, the next step is the pricing of your offerings. The overall positioning strategy you set in your positioning statement will often determine how you price your products or services.
Pricing is a powerful tool that sends a strong message to your customers. Failure to get your pricing strategy right can make or mar your business. If you are targeting a low-income audience, setting a premium price can result in low sales.
You can use pricing to communicate your positioning to your customers. For example, if you are offering a product at a premium price, you are sending a message to your customers that the product belongs to the premium category.
Basic Rules to Follow When Pricing Your Offering
Setting a price for your offering involves more than just putting a price tag on it. Deciding on the right pricing for your offering requires following some basic rules. They include covering your costs, primary and secondary profit center pricing, and matching the market rate.
- Covering Your Costs: The price you set for your products or service should be more than it costs you to produce and deliver them. Every business has the same goal, to make a profit. Depending on the strategy you want to use, there are exceptions to this rule. However, the vast majority of businesses follow this rule.
- Primary and Secondary Profit Center Pricing: When a company sets its price above the cost of production, it is making that product its primary profit center. A company can also decide not to make its initial price its primary profit center by selling below or at even with its production cost. It rather depends on the support product or even maintenance that is associated with the initial purchase to make its profit. The initial price thus became its secondary profit center.
- Matching the Market Rate: A good rule to follow when pricing your products or services is to match your pricing with consumer demand and expectations. If you price your products or services beyond the price your customer perceives as the ideal price range, you may end up with no customers. Pricing your products too low below what your customer perceives as the ideal price range may lead to them undervaluing your offering.
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing strategy influences the price of your offering. There are several pricing strategies available for you to choose from when examining the right pricing strategy for your business. They include cost-plus pricing, market-based pricing, value pricing, and more.

- Cost-plus Pricing: This strategy is one of the simplest and oldest pricing strategies. Here you consider the cost of producing a unit of your product and then add a profit to it to arrive at your market price. It is an effective pricing strategy for manufacturers because it helps them cover their initial costs. Another name for the cost-plus pricing strategy is the markup pricing strategy.
- Market-based Pricing: This pricing strategy analyses the market including competitors’ pricing and then sets a price based on what the market is expecting. With this pricing strategy, you can either set your price at the low-end or high-end of the market.
- Value Pricing: This pricing strategy involves setting a price based on the value you are providing to your customer. When adopting a value-based pricing strategy, you have to set a price that your customers are willing to pay. Service-based businesses such as small business insurance providers , luxury goods sellers, and the fashion industry use this pricing strategy.
After carefully sorting out your positioning statement and pricing, the next item to look at is your promotional strategy. Your promotional strategy explains how you plan on communicating with your customers and prospects.
As a business, you must measure all your costs, including the cost of your promotions. You also want to measure how much sales your promotions bring for your business to determine its usefulness. Promotional strategies or programs that do not lead to profit need to be removed.
There are different types of promotional strategies you can adopt for your business, they include advertising, public relations, and content marketing.
Advertising
Your business plan should include your advertising plan which can be found in the marketing and sales plan section. You need to include an overview of your advertising plans such as the areas you plan to spend money on to advertise your business and offers.
Ensure that you make it clear in this section if your business will be advertising online or using the more traditional offline media, or the combination of both online and offline media. You can also include the advertising medium you want to use to raise awareness about your business and offers.
Some common online advertising mediums you can use include social media ads, landing pages, sales pages, SEO, Pay-Per-Click, emails, Google Ads, and others. Some common traditional and offline advertising mediums include word of mouth, radios, direct mail, televisions, flyers, billboards, posters, and others.
A key component of your advertising strategy is how you plan to measure the effectiveness and success of your advertising campaign. There is no point in sticking with an advertising plan or medium that does not produce results for your business in the long run.
Public Relations
A great way to reach your customers is to get the media to cover your business or product. Publicity, especially good ones, should be a part of your marketing and sales plan. In this section, show your plans for getting prominent reviews of your product from reputable publications and sources.
Your business needs that exposure to grow. If public relations is a crucial part of your promotional strategy, provide details about your public relations plan here.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is a popular promotional strategy used by businesses to inform and attract their customers. It is about teaching and educating your prospects on various topics of interest in your niche, it does not just involve informing them about the benefits and features of the products and services you have,

Businesses publish content usually for free where they provide useful information, tips, and advice so that their target market can be made aware of the importance of their products and services. Content marketing strategies seek to nurture prospects into buyers over time by simply providing value.
Your company can create a blog where it will be publishing content for its target market. You will need to use the best website builder such as Wix and Squarespace and the best web hosting services such as Bluehost, Hostinger, and other Bluehost alternatives to create a functional blog or website.
If content marketing is a crucial part of your promotional strategy (as it should be), detail your plans under promotions.
Including high-quality images of the packaging of your product in your business plan is a lovely idea. You can add the images of the packaging of that product in the marketing and sales plan section. If you are not selling a product, then you do not need to include any worry about the physical packaging of your product.
When organizing the packaging section of your business plan, you can answer the following questions to make maximum use of this section.
- Is your choice of packaging consistent with your positioning strategy?
- What key value proposition does your packaging communicate? (It should reflect the key value proposition of your business)
- How does your packaging compare to that of your competitors?
Social Media
Your 21st-century business needs to have a good social media presence. Not having one is leaving out opportunities for growth and reaching out to your prospect.
You do not have to join the thousands of social media platforms out there. What you need to do is join the ones that your customers are active on and be active there.

Businesses use social media to provide information about their products such as promotions, discounts, the benefits of their products, and content on their blogs.
Social media is also a platform for engaging with your customers and getting feedback about your products or services. Make no mistake, more and more of your prospects are using social media channels to find more information about companies.
You need to consider the social media channels you want to prioritize your business (prioritize the ones your customers are active in) and your branding plans in this section.

Strategic Alliances
If your company plans to work closely with other companies as part of your sales and marketing plan, include it in this section. Prove details about those partnerships in your business plan if you have already established them.
Strategic alliances can be beneficial for all parties involved including your company. Working closely with another company in the form of a partnership can provide access to a different target market segment for your company.
The company you are partnering with may also gain access to your target market or simply offer a new product or service (that of your company) to its customers.
Mutually beneficial partnerships can cover the weaknesses of one company with the strength of another. You should consider strategic alliances with companies that sell complimentary products to yours. For example, if you provide printers, you can partner with a company that produces ink since the customers that buy printers from you will also need inks for printing.
Steps Involved in Creating a Marketing and Sales Plan
1. Focus on Your Target Market
Identify who your customers are, the market you want to target. Then determine the best ways to get your products or services to your potential customers.
2. Evaluate Your Competition
One of the goals of having a marketing plan is to distinguish yourself from your competition. You cannot stand out from them without first knowing them in and out.
You can know your competitors by gathering information about their products, pricing, service, and advertising campaigns.
These questions can help you know your competition.
- What makes your competition successful?
- What are their weaknesses?
- What are customers saying about your competition?
3. Consider Your Brand
Customers' perception of your brand has a strong impact on your sales. Your marketing and sales plan should seek to bolster the image of your brand. Before you start marketing your business, think about the message you want to pass across about your business and your products and services.
4. Focus on Benefits
The majority of your customers do not view your product in terms of features, what they want to know is the benefits and solutions your product offers. Think about the problems your product solves and the benefits it delivers, and use it to create the right sales and marketing message.
Your marketing plan should focus on what you want your customer to get instead of what you provide. Identify those benefits in your marketing and sales plan.
5. Focus on Differentiation
Your marketing and sales plan should look for a unique angle they can take that differentiates your business from the competition, even if the products offered are similar. Some good areas of differentiation you can use are your benefits, pricing, and features.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing Your Marketing and Sales Plan
- What is your company’s budget for sales and marketing campaigns?
- What key metrics will you use to determine if your marketing plans are successful?
- What are your alternatives if your initial marketing efforts do not succeed?
- Who are the sales representatives you need to promote your products or services?
- What are the marketing and sales channels you plan to use? How do you plan to get your products in front of your ideal customers?
- Where will you sell your products?
You may want to include samples of marketing materials you plan to use such as print ads, website descriptions, and social media ads. While it is not compulsory to include these samples, it can help you better communicate your marketing and sales plan and objectives.
The purpose of the marketing and sales section is to answer this question “How will you reach your customers?” If you cannot convincingly provide an answer to this question, you need to rework your marketing and sales section.
7. Clearly Show Your Funding Request
If you are writing your business plan to ask for funding from investors or financial institutions, the funding request section is where you will outline your funding requirements. The funding request section should answer the question ‘How much money will your business need in the near future (3 to 5 years)?’
A good funding request section will clearly outline and explain the amount of funding your business needs over the next five years. You need to know the amount of money your business needs to make an accurate funding request.
Also, when writing your funding request, provide details of how the funds will be used over the period. Specify if you want to use the funds to buy raw materials or machinery, pay salaries, pay for advertisements, and cover specific bills such as rent and electricity.
In addition to explaining what you want to use the funds requested for, you need to clearly state the projected return on investment (ROI) . Investors and creditors want to know if your business can generate profit for them if they put funds into it.
Ensure you do not inflate the figures and stay as realistic as possible. Investors and financial institutions you are seeking funds from will do their research before investing money in your business.
If you are not sure of an exact number to request from, you can use some range of numbers as rough estimates. Add a best-case scenario and a work-case scenario to your funding request. Also, include a description of your strategic future financial plans such as selling your business or paying off debts.
Funding Request: Debt or Equity?
When making your funding request, specify the type of funding you want. Do you want debt or equity? Draw out the terms that will be applicable for the funding, and the length of time the funding request will cover.
Case for Equity
If your new business has not yet started generating profits, you are most likely preparing to sell equity in your business to raise capital at the early stage. Equity here refers to ownership. In this case, you are selling a portion of your company to raise capital.
Although this method of raising capital for your business does not put your business in debt, keep in mind that an equity owner may expect to play a key role in company decisions even if he does not hold a major stake in the company.
Most equity sales for startups are usually private transactions . If you are making a funding request by offering equity in exchange for funding, let the investor know that they will be paid a dividend (a share of the company’s profit). Also, let the investor know the process for selling their equity in your business.
Case for Debt
You may decide not to offer equity in exchange for funds, instead, you make a funding request with the promise to pay back the money borrowed at the agreed time frame.
When making a funding request with an agreement to pay back, note that you will have to repay your creditors both the principal amount borrowed and the interest on it. Financial institutions offer this type of funding for businesses.
Large companies combine both equity and debt in their capital structure. When drafting your business plan, decide if you want to offer both or one over the other.
Before you sell equity in exchange for funding in your business, consider if you are willing to accept not being in total control of your business. Also, before you seek loans in your funding request section, ensure that the terms of repayment are favorable.
You should set a clear timeline in your funding request so that potential investors and creditors can know what you are expecting. Some investors and creditors may agree to your funding request and then delay payment for longer than 30 days, meanwhile, your business needs an immediate cash injection to operate efficiently.
Additional Tips for Writing the Funding Request Section of your Business Plan
The funding request section is not necessary for every business, it is only needed by businesses who plan to use their business plan to secure funding.
If you are adding the funding request section to your business plan, provide an itemized summary of how you plan to use the funds requested. Hiring a lawyer, accountant, or other professionals may be necessary for the proper development of this section.
You should also gather and use financial statements that add credibility and support to your funding requests. Ensure that the financial statements you use should include your projected financial data such as projected cash flows, forecast statements, and expenditure budgets.
If you are an existing business, include all historical financial statements such as cash flow statements, balance sheets and income statements .
Provide monthly and quarterly financial statements for a year. If your business has records that date back beyond the one-year mark, add the yearly statements of those years. These documents are for the appendix section of your business plan.
8. Detail Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projections
If you used the funding request section in your business plan, supplement it with a financial plan, metrics, and projections. This section paints a picture of the past performance of your business and then goes ahead to make an informed projection about its future.
The goal of this section is to convince readers that your business is going to be a financial success. It outlines your business plan to generate enough profit to repay the loan (with interest if applicable) and to generate a decent return on investment for investors.
If you have an existing business already in operation, use this section to demonstrate stability through finance. This section should include your cash flow statements, balance sheets, and income statements covering the last three to five years. If your business has some acceptable collateral that you can use to acquire loans, list it in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
Apart from current financial statements, this section should also contain a prospective financial outlook that spans the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and capital expenditure budget.
If your business is new and is not yet generating profit, use clear and realistic projections to show the potentials of your business.
When drafting this section, research industry norms and the performance of comparable businesses. Your financial projections should cover at least five years. State the logic behind your financial projections. Remember you can always make adjustments to this section as the variables change.
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section create a baseline which your business can either exceed or fail to reach. If your business fails to reach your projections in this section, you need to understand why it failed.
Investors and loan managers spend a lot of time going through the financial plan, metrics, and projection section compared to other parts of the business plan. Ensure you spend time creating credible financial analyses for your business in this section.
Many entrepreneurs find this section daunting to write. You do not need a business degree to create a solid financial forecast for your business. Business finances, especially for startups, are not as complicated as they seem. There are several online tools and templates that make writing this section so much easier.
Use Graphs and Charts
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business. Charts and images make it easier to communicate your finances.
Accuracy in this section is key, ensure you carefully analyze your past financial statements properly before making financial projects.
Address the Risk Factors and Show Realistic Financial Projections
Keep your financial plan, metrics, and projection realistic. It is okay to be optimistic in your financial projection, however, you have to justify it.
You should also address the various risk factors associated with your business in this section. Investors want to know the potential risks involved, show them. You should also show your plans for mitigating those risks.
What You Should In The Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection Section of Your Business Plan
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section of your business plan should have monthly sales and revenue forecasts for the first year. It should also include annual projections that cover 3 to 5 years.
A three-year projection is a basic requirement to have in your business plan. However, some investors may request a five-year forecast.
Your business plan should include the following financial statements: sales forecast, personnel plan, income statement, income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and an exit strategy.
1. Sales Forecast
Sales forecast refers to your projections about the number of sales your business is going to record over the next few years. It is typically broken into several rows, with each row assigned to a core product or service that your business is offering.
One common mistake people make in their business plan is to break down the sales forecast section into long details. A sales forecast should forecast the high-level details.
For example, if you are forecasting sales for a payroll software provider, you could break down your forecast into target market segments or subscription categories.

Your sales forecast section should also have a corresponding row for each sales row to cover the direct cost or Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). The objective of these rows is to show the expenses that your business incurs in making and delivering your product or service.
Note that your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) should only cover those direct costs incurred when making your products. Other indirect expenses such as insurance, salaries, payroll tax, and rent should not be included.
For example, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for a restaurant is the cost of ingredients while for a consulting company it will be the cost of paper and other presentation materials.

2. Personnel Plan
The personnel plan section is where you provide details about the payment plan for your employees. For a small business, you can easily list every position in your company and how much you plan to pay in the personnel plan.
However, for larger businesses, you have to break the personnel plan into functional groups such as sales and marketing.
The personnel plan will also include the cost of an employee beyond salary, commonly referred to as the employee burden. These costs include insurance, payroll taxes , and other essential costs incurred monthly as a result of having employees on your payroll.

3. Income Statement
The income statement section shows if your business is making a profit or taking a loss. Another name for the income statement is the profit and loss (P&L). It takes data from your sales forecast and personnel plan and adds other ongoing expenses you incur while running your business.

Every business plan should have an income statement. It subtracts your business expenses from its earnings to show if your business is generating profit or incurring losses.
The income statement has the following items: sales, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), gross margin, operating expenses, total operating expenses, operating income , total expenses, and net profit.
- Sales refer to the revenue your business generates from selling its products or services. Other names for sales are income or revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the total cost of selling your products. Other names for COGS are direct costs or cost of sales. Manufacturing businesses use the Costs of Goods Manufactured (COGM) .
- Gross Margin is the figure you get when you subtract your COGS from your sales. In your income statement, you can express it as a percentage of total sales (Gross margin / Sales = Gross Margin Percent).
- Operating Expenses refer to all the expenses you incur from running your business. It exempts the COGS because it stands alone as a core part of your income statement. You also have to exclude taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Your operating expenses include salaries, marketing expenses, research and development (R&D) expenses, and other expenses.
- Total Operating Expenses refers to the sum of all your operating expenses including those exemptions named above under operating expenses.
- Operating Income refers to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is simply known as the acronym EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Calculating your operating income is simple, all you need to do is to subtract your COGS and total operating expenses from your sales.
- Total Expenses refer to the sum of your operating expenses and your business’ interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
- Net profit shows whether your business has made a profit or taken a loss during a given timeframe.
4. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the money you have in the bank at any given point. It is often confused with the income statement or the profit and loss statement. They are both different types of financial statements. The income statement calculates your profits and losses while the cash flow statement shows you how much you have in the bank.

5. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of the financial health of your business. It contains information about the assets and liabilities of your company, and owner’s or shareholders’ equity.
You can get the net worth of your company by subtracting your company’s liabilities from its assets.

6. Exit Strategy
The exit strategy refers to a probable plan for selling your business either to the public in an IPO or to another company. It is the last thing you include in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
You can choose to omit the exit strategy from your business plan if you plan to maintain full ownership of your business and do not plan on seeking angel investment or virtual capitalist (VC) funding.
Investors may want to know what your exit plan is. They invest in your business to get a good return on investment.
Your exit strategy does not have to include long and boring details. Ensure you identify some interested parties who may be interested in buying the company if it becomes a success.

Key Questions to Answer with Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection
Your financial plan, metrics, and projection section helps investors, creditors, or your internal managers to understand what your expenses are, the amount of cash you need, and what it takes to make your company profitable. It also shows what you will be doing with any funding.
You do not need to show actual financial data if you do not have one. Adding forecasts and projections to your financial statements is added proof that your strategy is feasible and shows investors you have planned properly.
Here are some key questions to answer to help you develop this section.
- What is your sales forecast for the next year?
- When will your company achieve a positive cash flow?
- What are the core expenses you need to operate?
- How much money do you need upfront to operate or grow your company?
- How will you use the loans or investments?
9. Add an Appendix to Your Business Plan
Adding an appendix to your business plan is optional. It is a useful place to put any charts, tables, legal notes, definitions, permits, résumés, and other critical information that do not fit into other sections of your business plan.
The appendix section is where you would want to include details of a patent or patent-pending if you have one. You can always add illustrations or images of your products here. It is the last section of your business plan.
When writing your business plan, there are details you cut short or remove to prevent the entire section from becoming too lengthy. There are also details you want to include in the business plan but are not a good fit for any of the previous sections. You can add that additional information to the appendix section.
Businesses also use the appendix section to include supporting documents or other materials specially requested by investors or lenders.
You can include just about any information that supports the assumptions and statements you made in the business plan under the appendix. It is the one place in the business plan where unrelated data and information can coexist amicably.
If your appendix section is lengthy, try organizing it by adding a table of contents at the beginning of the appendix section. It is also advisable to group similar information to make it easier for the reader to access them.
A well-organized appendix section makes it easier to share your information clearly and concisely. Add footnotes throughout the rest of the business plan or make references in the plan to the documents in the appendix.
The appendix section is usually only necessary if you are seeking funding from investors or lenders, or hoping to attract partners.
People reading business plans do not want to spend time going through a heap of backup information, numbers, and charts. Keep these documents or information in the Appendix section in case the reader wants to dig deeper.
Common Items to Include in the Appendix Section of Your Business Plan
The appendix section includes documents that supplement or support the information or claims given in other sections of the business plans. Common items you can include in the appendix section include:
- Additional data about the process of manufacturing or creation
- Additional description of products or services such as product schematics
- Additional financial documents or projections
- Articles of incorporation and status
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Bank statements
- Business registries
- Client testimonials (if your business is already running)
- Copies of insurances
- Credit histories (personal or/and business)
- Deeds and permits
- Equipment leases
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Industry associations and memberships
- Images of product
- Intellectual property
- Key customer contracts
- Legal documents and other contracts
- Letters of reference
- Links to references
- Market research data
- Organizational charts
- Photographs of potential facilities
- Professional licenses pertaining to your legal structure or type of business
- Purchase orders
- Resumes of the founder(s) and key managers
- State and federal identification numbers or codes
- Trademarks or patents’ registrations
Avoid using the appendix section as a place to dump any document or information you feel like adding. Only add documents or information that you support or increase the credibility of your business plan.
Tips and Strategies for Writing a Convincing Business Plan
To achieve a perfect business plan, you need to consider some key tips and strategies. These tips will raise the efficiency of your business plan above average.
1. Know Your Audience
When writing a business plan, you need to know your audience . Business owners write business plans for different reasons. Your business plan has to be specific. For example, you can write business plans to potential investors, banks, and even fellow board members of the company.
The audience you are writing to determines the structure of the business plan. As a business owner, you have to know your audience. Not everyone will be your audience. Knowing your audience will help you to narrow the scope of your business plan.
Consider what your audience wants to see in your projects, the likely questions they might ask, and what interests them.
- A business plan used to address a company's board members will center on its employment schemes, internal affairs, projects, stakeholders, etc.
- A business plan for financial institutions will talk about the size of your market and the chances for you to pay back any loans you demand.
- A business plan for investors will show proof that you can return the investment capital within a specific time. In addition, it discusses your financial projections, tractions, and market size.
2. Get Inspiration from People
Writing a business plan from scratch as an entrepreneur can be daunting. That is why you need the right inspiration to push you to write one. You can gain inspiration from the successful business plans of other businesses. Look at their business plans, the style they use, the structure of the project, etc.
To make your business plan easier to create, search companies related to your business to get an exact copy of what you need to create an effective business plan. You can also make references while citing examples in your business plans.
When drafting your business plan, get as much help from others as you possibly can. By getting inspiration from people, you can create something better than what they have.
3. Avoid Being Over Optimistic
Many business owners make use of strong adjectives to qualify their content. One of the big mistakes entrepreneurs make when preparing a business plan is promising too much.
The use of superlatives and over-optimistic claims can prepare the audience for more than you can offer. In the end, you disappoint the confidence they have in you.
In most cases, the best option is to be realistic with your claims and statistics. Most of the investors can sense a bit of incompetency from the overuse of superlatives. As a new entrepreneur, do not be tempted to over-promise to get the interests of investors.
The concept of entrepreneurship centers on risks, nothing is certain when you make future analyses. What separates the best is the ability to do careful research and work towards achieving that, not promising more than you can achieve.
To make an excellent first impression as an entrepreneur, replace superlatives with compelling data-driven content. In this way, you are more specific than someone promising a huge ROI from an investment.
4. Keep it Simple and Short
When writing business plans, ensure you keep them simple throughout. Irrespective of the purpose of the business plan, your goal is to convince the audience.
One way to achieve this goal is to make them understand your proposal. Therefore, it would be best if you avoid the use of complex grammar to express yourself. It would be a huge turn-off if the people you want to convince are not familiar with your use of words.
Another thing to note is the length of your business plan. It would be best if you made it as brief as possible.
You hardly see investors or agencies that read through an extremely long document. In that case, if your first few pages can’t convince them, then you have lost it. The more pages you write, the higher the chances of you derailing from the essential contents.
To ensure your business plan has a high conversion rate, you need to dispose of every unnecessary information. For example, if you have a strategy that you are not sure of, it would be best to leave it out of the plan.
5. Make an Outline and Follow Through
A perfect business plan must have touched every part needed to convince the audience. Business owners get easily tempted to concentrate more on their products than on other sections. Doing this can be detrimental to the efficiency of the business plan.
For example, imagine you talking about a product but omitting or providing very little information about the target audience. You will leave your clients confused.
To ensure that your business plan communicates your full business model to readers, you have to input all the necessary information in it. One of the best ways to achieve this is to design a structure and stick to it.
This structure is what guides you throughout the writing. To make your work easier, you can assign an estimated word count or page limit to every section to avoid making it too bulky for easy reading. As a guide, the necessary things your business plan must contain are:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Product or service description
- Target audience
- Market size
- Competition analysis
- Financial projections
Some specific businesses can include some other essential sections, but these are the key sections that must be in every business plan.
6. Ask a Professional to Proofread
When writing a business plan, you must tie all loose ends to get a perfect result. When you are done with writing, call a professional to go through the document for you. You are bound to make mistakes, and the way to correct them is to get external help.
You should get a professional in your field who can relate to every section of your business plan. It would be easier for the professional to notice the inner flaws in the document than an editor with no knowledge of your business.
In addition to getting a professional to proofread, get an editor to proofread and edit your document. The editor will help you identify grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inappropriate writing styles.
Writing a business plan can be daunting, but you can surmount that obstacle and get the best out of it with these tips.
Business Plan Examples and Templates That’ll Save You Tons of Time
1. hubspot's one-page business plan.

The one-page business plan template by HubSpot is the perfect guide for businesses of any size, irrespective of their business strategy. Although the template is condensed into a page, your final business plan should not be a page long! The template is designed to ask helpful questions that can help you develop your business plan.
Hubspot’s one-page business plan template is divided into nine fields:
- Business opportunity
- Company description
- Industry analysis
- Target market
- Implementation timeline
- Marketing plan
- Financial summary
- Funding required
2. Bplan’s Free Business Plan Template

Bplans' free business plan template is investor-approved. It is a rich template used by prestigious educational institutions such as Babson College and Princeton University to teach entrepreneurs how to create a business plan.
The template has six sections: the executive summary, opportunity, execution, company, financial plan, and appendix. There is a step-by-step guide for writing every little detail in the business plan. Follow the instructions each step of the way and you will create a business plan that impresses investors or lenders easily.
3. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

HubSpot’s downloadable business plan template is a more comprehensive option compared to the one-page business template by HubSpot. This free and downloadable business plan template is designed for entrepreneurs.
The template is a comprehensive guide and checklist for business owners just starting their businesses. It tells you everything you need to fill in each section of the business plan and how to do it.
There are nine sections in this business plan template: an executive summary, company and business description, product and services line, market analysis, marketing plan, sales plan, legal notes, financial considerations, and appendix.
4. Business Plan by My Own Business Institute

My Own Business Institute (MOBI) which is a part of Santa Clara University's Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship offers a free business plan template. You can either copy the free business template from the link provided above or download it as a Word document.
The comprehensive template consists of a whopping 15 sections.
- The Business Profile
- The Vision and the People
- Home-Based Business and Freelance Business Opportunities
- Organization
- Licenses and Permits
- Business Insurance
- Communication Tools
- Acquisitions
- Location and Leasing
- Accounting and Cash Flow
- Opening and Marketing
- Managing Employees
- Expanding and Handling Problems
There are lots of helpful tips on how to fill each section in the free business plan template by MOBI.
5. Score's Business Plan Template for Startups

Score is an American nonprofit organization that helps entrepreneurs build successful companies. This business plan template for startups by Score is available for free download. The business plan template asks a whooping 150 generic questions that help entrepreneurs from different fields to set up the perfect business plan.
The business plan template for startups contains clear instructions and worksheets, all you have to do is answer the questions and fill the worksheets.
There are nine sections in the business plan template: executive summary, company description, products and services, marketing plan, operational plan, management and organization, startup expenses and capitalization, financial plan, and appendices.
The ‘refining the plan’ resource contains instructions that help you modify your business plan to suit your specific needs, industry, and target audience. After you have completed Score’s business plan template, you can work with a SCORE mentor for expert advice in business planning.
6. Minimalist Architecture Business Plan Template by Venngage

The minimalist architecture business plan template is a simple template by Venngage that you can customize to suit your business needs .
There are five sections in the template: an executive summary, statement of problem, approach and methodology, qualifications, and schedule and benchmark. The business plan template has instructions that guide users on what to fill in each section.
7. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two free business plan templates, filled with practical real-life examples that you can model to create your business plan. Both free business plan templates are written by fictional business owners: Rebecca who owns a consulting firm, and Andrew who owns a toy company.
There are five sections in the two SBA’s free business plan templates.
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Service Line
- Marketing and Sales
8. The $100 Startup's One-Page Business Plan

The one-page business plan by the $100 startup is a simple business plan template for entrepreneurs who do not want to create a long and complicated plan . You can include more details in the appendices for funders who want more information beyond what you can put in the one-page business plan.
There are five sections in the one-page business plan such as overview, ka-ching, hustling, success, and obstacles or challenges or open questions. You can answer all the questions using one or two sentences.
9. PandaDoc’s Free Business Plan Template

The free business plan template by PandaDoc is a comprehensive 15-page document that describes the information you should include in every section.
There are 11 sections in PandaDoc’s free business plan template.
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Products and services
- Operations plan
- Management organization
- Financial plan
- Conclusion / Call to action
- Confidentiality statement
You have to sign up for its 14-day free trial to access the template. You will find different business plan templates on PandaDoc once you sign up (including templates for general businesses and specific businesses such as bakeries, startups, restaurants, salons, hotels, and coffee shops)
PandaDoc allows you to customize its business plan templates to fit the needs of your business. After editing the template, you can send it to interested parties and track opens and views through PandaDoc.
10. Invoiceberry Templates for Word, Open Office, Excel, or PPT

InvoiceBerry is a U.K based online invoicing and tracking platform that offers free business plan templates in .docx, .odt, .xlsx, and .pptx formats for freelancers and small businesses.
Before you can download the free business plan template, it will ask you to give it your email address. After you complete the little task, it will send the download link to your inbox for you to download. It also provides a business plan checklist in .xlsx file format that ensures you add the right information to the business plan.
Alternatives to the Traditional Business Plan
A business plan is very important in mapping out how one expects their business to grow over a set number of years, particularly when they need external investment in their business. However, many investors do not have the time to watch you present your business plan. It is a long and boring read.
Luckily, there are three alternatives to the traditional business plan (the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck). These alternatives are less laborious and easier and quicker to present to investors.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
The business model canvas is a business tool used to present all the important components of setting up a business, such as customers, route to market, value proposition, and finance in a single sheet. It provides a very focused blueprint that defines your business initially which you can later expand on if needed.

The sheet is divided mainly into company, industry, and consumer models that are interconnected in how they find problems and proffer solutions.
Segments of the Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas was developed by founder Alexander Osterwalder to answer important business questions. It contains nine segments.

- Key Partners: Who will be occupying important executive positions in your business? What do they bring to the table? Will there be a third party involved with the company?
- Key Activities: What important activities will production entail? What activities will be carried out to ensure the smooth running of the company?
- The Product’s Value Propositions: What does your product do? How will it be different from other products?
- Customer Segments: What demography of consumers are you targeting? What are the habits of these consumers? Who are the MVPs of your target consumers?
- Customer Relationships: How will the team support and work with its customer base? How do you intend to build and maintain trust with the customer?
- Key Resources: What type of personnel and tools will be needed? What size of the budget will they need access to?
- Channels: How do you plan to create awareness of your products? How do you intend to transport your product to the customer?
- Cost Structure: What is the estimated cost of production? How much will distribution cost?
- Revenue Streams: For what value are customers willing to pay? How do they prefer to pay for the product? Are there any external revenues attached apart from the main source? How do the revenue streams contribute to the overall revenue?
Lean Canvas
The lean canvas is a problem-oriented alternative to the standard business model canvas. It was proposed by Ash Maurya, creator of Lean Stack as a development of the business model generation. It uses a more problem-focused approach and it majorly targets entrepreneurs and startup businesses.

Lean Canvas uses the same 9 blocks concept as the business model canvas, however, they have been modified slightly to suit the needs and purpose of a small startup. The key partners, key activities, customer relationships, and key resources are replaced by new segments which are:
- Problem: Simple and straightforward number of problems you have identified, ideally three.
- Solution: The solutions to each problem.
- Unfair Advantage: Something you possess that can't be easily bought or replicated.
- Key Metrics: Important numbers that will tell how your business is doing.
Startup Pitch Deck
While the business model canvas compresses into a factual sheet, startup pitch decks expand flamboyantly.
Pitch decks, through slides, convey your business plan, often through graphs and images used to emphasize estimations and observations in your presentation. Entrepreneurs often use pitch decks to fully convince their target audience of their plans before discussing funding arrangements.

Considering the likelihood of it being used in a small time frame, a good startup pitch deck should ideally contain 20 slides or less to have enough time to answer questions from the audience.
Unlike the standard and lean business model canvases, a pitch deck doesn't have a set template on how to present your business plan but there are still important components to it. These components often mirror those of the business model canvas except that they are in slide form and contain more details.

Using Airbnb (one of the most successful start-ups in recent history) for reference, the important components of a good slide are listed below.
- Cover/Introduction Slide: Here, you should include your company's name and mission statement. Your mission statement should be a very catchy tagline. Also, include personal information and contact details to provide an easy link for potential investors.
- Problem Slide: This slide requires you to create a connection with the audience or the investor that you are pitching. For example in their pitch, Airbnb summarized the most important problems it would solve in three brief points – pricing of hotels, disconnection from city culture, and connection problems for local bookings.
- Solution Slide: This slide includes your core value proposition. List simple and direct solutions to the problems you have mentioned
- Customer Analysis: Here you will provide information on the customers you will be offering your service to. The identity of your customers plays an important part in fundraising as well as the long-run viability of the business.
- Market Validation: Use competitive analysis to show numbers that prove the presence of a market for your product, industry behavior in the present and the long run, as well as the percentage of the market you aim to attract. It shows that you understand your competitors and customers and convinces investors of the opportunities presented in the market.
- Business Model: Your business model is the hook of your presentation. It may vary in complexity but it should generally include a pricing system informed by your market analysis. The goal of the slide is to confirm your business model is easy to implement.
- Marketing Strategy: This slide should summarize a few customer acquisition methods that you plan to use to grow the business.
- Competitive Advantage: What this slide will do is provide information on what will set you apart and make you a more attractive option to customers. It could be the possession of technology that is not widely known in the market.
- Team Slide: Here you will give a brief description of your team. Include your key management personnel here and their specific roles in the company. Include their educational background, job history, and skillsets. Also, talk about their accomplishments in their careers so far to build investors' confidence in members of your team.
- Traction Slide: This validates the company’s business model by showing growth through early sales and support. The slide aims to reduce any lingering fears in potential investors by showing realistic periodic milestones and profit margins. It can include current sales, growth, valuable customers, pre-orders, or data from surveys outlining current consumer interest.
- Funding Slide: This slide is popularly referred to as ‘the ask'. Here you will include important details like how much is needed to get your business off the ground and how the funding will be spent to help the company reach its goals.
- Appendix Slides: Your pitch deck appendix should always be included alongside a standard pitch presentation. It consists of additional slides you could not show in the pitch deck but you need to complement your presentation.
It is important to support your calculations with pictorial renditions. Infographics, such as pie charts or bar graphs, will be more effective in presenting the information than just listing numbers. For example, a six-month graph that shows rising profit margins will easily look more impressive than merely writing it.
Lastly, since a pitch deck is primarily used to secure meetings and you may be sharing your pitch with several investors, it is advisable to keep a separate public version that doesn't include financials. Only disclose the one with projections once you have secured a link with an investor.
Advantages of the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck over the Traditional Business Plan
- Time-Saving: Writing a detailed traditional business plan could take weeks or months. On the other hand, all three alternatives can be done in a few days or even one night of brainstorming if you have a comprehensive understanding of your business.
- Easier to Understand: Since the information presented is almost entirely factual, it puts focus on what is most important in running the business. They cut away the excess pages of fillers in a traditional business plan and allow investors to see what is driving the business and what is getting in the way.
- Easy to Update: Businesses typically present their business plans to many potential investors before they secure funding. What this means is that you may regularly have to amend your presentation to update statistics or adjust to audience-specific needs. For a traditional business plan, this could mean rewriting a whole section of your plan. For the three alternatives, updating is much easier because they are not voluminous.
- Guide for a More In-depth Business Plan: All three alternatives have the added benefit of being able to double as a sketch of your business plan if the need to create one arises in the future.
Business Plan FAQ
Business plans are important for any entrepreneur who is looking for a framework to run their company over some time or seeking external support. Although they are essential for new businesses, every company should ideally have a business plan to track their growth from time to time. They can be used by startups seeking investments or loans to convey their business ideas or an employee to convince his boss of the feasibility of starting a new project. They can also be used by companies seeking to recruit high-profile employee targets into key positions or trying to secure partnerships with other firms.
Business plans often vary depending on your target audience, the scope, and the goals for the plan. Startup plans are the most common among the different types of business plans. A start-up plan is used by a new business to present all the necessary information to help get the business up and running. They are usually used by entrepreneurs who are seeking funding from investors or bank loans. The established company alternative to a start-up plan is a feasibility plan. A feasibility plan is often used by an established company looking for new business opportunities. They are used to show the upsides of creating a new product for a consumer base. Because the audience is usually company people, it requires less company analysis. The third type of business plan is the lean business plan. A lean business plan is a brief, straight-to-the-point breakdown of your ideas and analysis for your business. It does not contain details of your proposal and can be written on one page. Finally, you have the what-if plan. As it implies, a what-if plan is a preparation for the worst-case scenario. You must always be prepared for the possibility of your original plan being rejected. A good what-if plan will serve as a good plan B to the original.
A good business plan has 10 key components. They include an executive plan, product analysis, desired customer base, company analysis, industry analysis, marketing strategy, sales strategy, financial projection, funding, and appendix. Executive Plan Your business should begin with your executive plan. An executive plan will provide early insight into what you are planning to achieve with your business. It should include your mission statement and highlight some of the important points which you will explain later. Product Analysis The next component of your business plan is your product analysis. A key part of this section is explaining the type of item or service you are going to offer as well as the market problems your product will solve. Desired Consumer Base Your product analysis should be supplemented with a detailed breakdown of your desired consumer base. Investors are always interested in knowing the economic power of your market as well as potential MVP customers. Company Analysis The next component of your business plan is your company analysis. Here, you explain how you want to run your business. It will include your operational strategy, an insight into the workforce needed to keep the company running, and important executive positions. It will also provide a calculation of expected operational costs. Industry Analysis A good business plan should also contain well laid out industry analysis. It is important to convince potential investors you know the companies you will be competing with, as well as your plans to gain an edge on the competition. Marketing Strategy Your business plan should also include your marketing strategy. This is how you intend to spread awareness of your product. It should include a detailed explanation of the company brand as well as your advertising methods. Sales Strategy Your sales strategy comes after the market strategy. Here you give an overview of your company's pricing strategy and how you aim to maximize profits. You can also explain how your prices will adapt to market behaviors. Financial Projection The financial projection is the next component of your business plan. It explains your company's expected running cost and revenue earned during the tenure of the business plan. Financial projection gives a clear idea of how your company will develop in the future. Funding The next component of your business plan is funding. You have to detail how much external investment you need to get your business idea off the ground here. Appendix The last component of your plan is the appendix. This is where you put licenses, graphs, or key information that does not fit in any of the other components.
The business model canvas is a business management tool used to quickly define your business idea and model. It is often used when investors need you to pitch your business idea during a brief window.
A pitch deck is similar to a business model canvas except that it makes use of slides in its presentation. A pitch is not primarily used to secure funding, rather its main purpose is to entice potential investors by selling a very optimistic outlook on the business.
Business plan competitions help you evaluate the strength of your business plan. By participating in business plan competitions, you are improving your experience. The experience provides you with a degree of validation while practicing important skills. The main motivation for entering into the competitions is often to secure funding by finishing in podium positions. There is also the chance that you may catch the eye of a casual observer outside of the competition. These competitions also provide good networking opportunities. You could meet mentors who will take a keen interest in guiding you in your business journey. You also have the opportunity to meet other entrepreneurs whose ideas can complement yours.
Exlore Further
- 12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
- 13 Sources of Business Finance For Companies & Sole Traders
- 5 Common Types of Business Structures (+ Pros & Cons)
- How to Buy a Business in 8 Steps (+ Due Diligence Checklist)
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
- Look up in Linguee
- Suggest as a translation of "template"
Linguee Apps
▾ dictionary english-french, template noun ( plural: templates ) —, modèle m ( plural: modèles m ), gabarit m ( plural: gabarits m ), patron m ( plural: patrons m ), reporting template n —, standard template n —, template document n —, blank template n —, contract template n —, budget template n —, template form n —, data template n —, website template n —, new template n —, common template n —, form template n —, input template n —, template text n —, html template n —, legal template n —, attached template n —, copy template n —, current template n —, electronic template n —, template system n —, original template n —, measuring template n —, surgical template n —, prescribed template n —, first template n —, template creation n —, specific template n —, template contract n —, document template n —, equivalent template n —, ▾ external sources (not reviewed).
- This is not a good example for the translation above.
- The wrong words are highlighted.
- It does not match my search.
- It should not be summed up with the orange entries
- The translation is wrong or of bad quality.

Writing a Professional Email in French (Sample template included)
Updated: April 24, 2021 by Mylene in Guides and Tips Array ▪ English Français

Writing a formal email in French can be a challenge. Many people send multiple emails per day to recap an important meeting, to relay an important update, or simply to contact someone. If you’re looking for a job, you’ll also have to compose and send a cover letter.
Whether you want to make a good first impression or you want to write emails that get replies, you have to learn the basics. Sounding professional in French is not always easy. The key is to use the right formula for the right situation.
In France, the term “e-mail” is commonly used.
In this article, I’ll give you the sentences you need to write a professional email in French:
- Use the proper greeting
- Introduce yourself
- Be 100% Formal
- How to write “enclosed” for an attached file
- Choose the right object
- Re-read your email
- Useful phrases
- Add your signature
- Infographic
Sample Email in French
How to write a formal email in french, 1. use the proper greeting.
Being polite is important.
If you don’t know the name nor the gender of the recipient (le destinataire), use:
- Madame, Monsieur,
- Mesdames, Messieurs,
If you know the gender but not the name , then only Madame or Monsieur should be used.
Even if you know the recipient’s name , then Madame or Monsieur is still appropriate.
A formal relationship with someone whose title you know :
- Madame la directrice,
- Monsieur le Président,
A formal relationship with someone whose name you know :
- Monsieur Untel,
- Madame Dupont,

2. Introduce yourself
You have to explain the purpose of your email at first.
After the greetings, introduce your reason for writing. For instance, you can refer to an earlier in-person conversation with the recipient (le destinataire). For example:
- Suite à notre entretien du 14 juin: Following up on our interview on June 14th…
- The following phrases are good choices when your letter’s intent is to inquire about employment Je vous propose ma candidature pour le poste: I would like to submit my candidacy for the position
- Je me réfère à votre annonce parue dans: with reference to your post advertised in
- Votre annonce parue dans… a retenu toute mon attention: Your post advertised in… caught my attention
- Je me permets de poser ma candidature pour le poste de… / au poste de: I wish to apply for the post of…
- Je vous serais très reconnaissant/reconnaissante de : I would be very grateful if you could…

3. Be 100% Formal
When writing formal letters, always use “vous” and never “tu”.
When using you in the singular form, tu implies intimacy and informality, whereas vous is used in formal contexts.
Vous is always used when referring to a group.
4. How to write “enclosed” for an attached file
Most official documents have a title, so look for the title to insert the appropriate name of the document .
- Veuillez trouver le document demandé en pièce: Please find the requested document as asked
- Je vous joins mon CV: I enclose my resume
- Veuillez trouver ci-joint mon CV: Please find attached my resume
5. Choose the right objet
However, just like an email in English, you’ll have a subject or in French “objet” which tells the recipient what the email is about. Choose a keyword that is professional . For example:
- Candidature pour le poste de chef de projet: Application for the position of project manager
- Location appartement: Apartment rental
- Demande de renseignements: Information request

A French business email always ends with a formule de politesse, a closing formula .
Some typical formal ending formulas are:
- Je vous prie d’agréer, (repeat the title as you started your letter), l’expression de mes salutations distinguées.: Yours sincerely.
- Je vous prie d’agréer, Madame, Monsieur, l’expression de mes salutations distinguées.
- Je vous prie d’agréer, Madame Intel, l’expression de mes salutations distinguées.
Another formal sentence would be:
- Je vous prie d’agréer, (repeat the title as you started your letter), l’expression de mes salutations dévouées.
- Je vous prie d’agréer, (repeat the salutation), l’expression de mes sentiments distingués.
The following sentence adds an extra thank you at the beginning for some extra respect points.
- Avec mes remerciements, je vous prie de trouver ici, Madame, Monsieur, l’expression de mes sentiments distingués.
If you’re waiting on a response from someone in a formal situation, you can add “waiting for your response” to the beginning of one of these expressions:
- Dans l’attente de votre réponse, je vous prie d’agréer, Monsieur/Madame, l’expression de mes salutations distinguées.

7. Re-read your email
Re-read your email out loud to ensure it makes sense. By reading the whole email, it will save a lot of stress for you, your colleague, and the client. To avoid any complications and awkward situations you have to always read business-related emails very carefully. Keep in mind that he or she may be having a super busy day so you need to be concise and provide all the necessary information.
So proofread your e-mail before sending. Take your time ! Check the list of recipients, title, content, attachments.
8. Useful phrases
You can embellish an email with the following common phrases :
- J’ai une question concernant: I have a question about
- Je serai disponible le: I’m available on
- Je reste à votre entière disposition pour tout renseignement complémentaire: Please do not hesitate to contact me should you need any further information.
- Nous vous remercions de votre compréhension: Thank you for your understanding
9. Add your signature
The signature is a tool to maintain contact with an interlocutor.
It can be found at the very end of your email. This is to provide the recipient with more detailed information and contact details of the sender. There are compulsory information which must appear in the signature, and which are the following:
- First name and name
- Position in the company
- Legal status of the company
- Full company address
- Company Website
- Sender or company phone number and email address
Additionally, you can include links to social media or the company logo in the signature. However, some users have blocked image files in emails for security reasons, it should therefore be ensured that the signature is acceptable without the logo.
5 ways to improve Your Professional email in French
- Be 100% formal
- Use the proper closing

Objet : Candidature – Chef de projets
Madame Intel, Votre annonce pour un poste de chef de projets a retenu toute mon attention.
Mes précédentes expériences m’ont permis de développer des compétences que je souhaite aujourd’hui mettre au service de votre entreprise.
Participer à l’évolution de votre structure serait une très belle opportunité.
En m’appuyant sur mes connaissances, mon sens de l’adaptation et mes expériences dans divers secteurs d’activités je suis convaincue d’avoir les qualités requises pour ce poste.
Je vous laisse le soin de découvrir mon parcours à la lecture de mon CV et j’aurais le plaisir de discuter de ce poste avec vous.
Dans l’attente de vous faire part de mes motivations, veuillez agréer, Madame, l’expression de mes sentiments distingués.
Mylène Bidule
Here how the French version translates to English:
Your job posting for a project manager position caught my attention.
My previous experiences have allowed me to develop skills that I now want to put at the service of your company.
Participating in the evolution of your structure would be a great opportunity.
Based on my knowledge, my adaptability and my experience in various business sectors, I am convinced that I have the qualities required for this position.
I leave it to you to discover my background by reading my resume and I would have the pleasure to discuss this position with you.
Yours sincerely, Mylène Bidule
Keep learning
This guide gives you the flexibility to tweak and the freedom to use any of the suggested sentences. In addition, the template is a good start for you to get inspired when writing a professional email in French. So, hope you’ll find it useful.
I have also published a number of how-to articles that you can check to learn how to think in French or also how to be successful when taking online courses .
How to learn French better: 5 keys for success

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Original text

Writing a business plan is one of the most important steps in starting a new business. But what should be in that plan, and how do you get started?
Download the Microsoft Word template above to help guide you through the process of creating a business plan. It is free to download and does not require any commitments from you. This template can be beneficial to people seeking to start a business, or operate an existing one without having first written a plan. The document will guide you through everything from analyzing the market opportunity to financing and much more.
And don’t forget, SCORE counselors stand ready to help you with writing this plan or any other facet of starting, growing, or running a business.
Copyright © 2024 SCORE Association, SCORE.org
Funded, in part, through a Cooperative Agreement with the U.S. Small Business Administration. All opinions, and/or recommendations expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the SBA.

Free Download
Business Plan Template for Small Businesses
Business planning can feel complicated. it doesn't have to be. start putting pen to paper today with your free business plan template download..
Available formats:
Downloads: 939,350
Our free template includes:
- Fill-in-the-blanks simplicity
You don't need to be an expert. This template makes business planning easy.
All 100% free. We're here to help you succeed in business, no strings attached.
Why you need a business plan
Writing a business plan can seem like a big task, especially if you’re starting a business for the first time and don’t have a financial background. After all, business plans have changed over the years, and what lenders and investors expect now is different than it was even just 10 years ago.
What hasn’t changed is that writing a business plan will help you:
- Develop a strategy for success
- Reduce the risk of starting a business
- Explore new business ideas
- Attract investors and get funding
Learn more about how you can get value out of your business plan .
What is included in this business plan template?
This template includes definitions, guidance, and examples for every business plan component needed to start, fund, and grow your business.
After downloading the full template, you’ll receive instructions on how to fill out each of the following sections.
Executive summary
The brief summary of your business plan introduces everyone to your business, the problem you solve, and what you’re asking from your readers. It’s the first chapter of your business plan and the last thing you write once you have the details from your full plan.
Problem & solution
More than a simple description of your products and services – here you define the problem you’re solving and the value you provide. It’s also your chance to showcase any initial traction that shows you’re on the right track.
Market analysis and target market
A detailed assessment of the market you intend to enter, including the size and value of the market, potential customer segments, and their buying patterns.
Competition
Show that you know who your competitors are, what advantages you have, and how you’re positioning your business to be competitive.
Marketing & sales
Describe how you’ll reach and sell to potential customers with a detailed sales plan and chosen marketing channels.
What makes your business run? Outline the day-to-day workflows and what needs to be set up for your business to deliver a product or service.
Milestones & metrics
Set goals for your business that include the dates and people responsible for accomplishing them. This is what you’ll use to manage responsibilities, track growth, and execute your larger strategy.
Company overview and team
Provide a brief rundown of the legal and structural components of your company, including your history, current team, and gaps you need to fill.
Financial plan
Create well-structured and accurate financial statements to help you pitch to investors, land funding, and achieve long-term success. All without the help of a financial advisor or a degree in accounting.
While not required, this last section of your business plan is a great place to drop in additional documents that support and strengthen the rest of your plan.
How do you write a simple business plan?
If you’re exploring a business idea and don’t plan to pursue funding, then you actually don’t need to write a traditional business plan. Instead, opt for a one-page plan , which is far easier to create but just as effective.
To write a simple one-page business plan, follow the same core sections as a traditional plan. But instead of lengthy paragraphs and multiple pages covering each area of your business, stick with single sentences and bulleted lists.
If a one-page plan sounds like a better option, download our free simple business plan template to get started.
Start your business plan today
Whether you're writing a business plan to validate your business idea, secure funding, or grow your existing business – our template will help you achieve your goals.

Business plan template FAQ
What file formats are available for this business plan template?
You can download and use this business plan template as a Google Doc, .docx (Microsoft Word), or PDF.
Can you print out this template?
This is a printable business plan template that can be downloaded and printed no matter which format you choose.
Why should you start with a business plan template?
Starting with a good business plan template (like this one) includes everything you need to get started. It helps you organize your thoughts, and provides guidance, instructions, and examples to create an investor-ready and SBA-approved business plan format. It really speeds up the planning process. Oh, and it's 100% free!
Is writing a business plan easy?
Using a business plan template can make writing a business plan easier. Additionally, if you focus on just getting your information down quickly, with the expectation that you'll revisit and revise your plan, you can speed up and simplify the process .
Can someone write your business plan for you?
If you're still struggling to write your business plan even when using a template, you can look into hiring a professional business plan writer. We even have a free resource to help you ask just the right questions to make sure you find the right plan writer.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Related Resources

Work With a Professional Plan Writer
Download your template now
Need to validate your idea, secure funding, or grow your business this template is for you..
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Your business plan template is ready
Find a download link in your email too.
Edit in Google Docs
Download as Docx
Download as PDF

Finish your business plan faster
Get an exclusive 14 day free trial to the world's #1 business planning software.

From template to plan in 30 minutes
- Step-by-step guidance
- Crystal clear financials
- Expert advice at your fingertips
- Funding & lender ready formats
- PLUS all the tools to manage & grow

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Simple Business Plan Templates
By Joe Weller | April 2, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve compiled a variety of simple business plan templates, all of which are free to download in PDF, Word, and Excel formats.
On this page, you’ll find a one-page business plan template , a simple business plan for startups , a small-business plan template , a business plan outline , and more. We also include a business plan sample and the main components of a business plan to help get you started.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
This simple business plan template lays out each element of a traditional business plan to assist you as you build your own, and it provides space to add financing information for startups seeking funding. You can use and customize this simple business plan template to fit the needs for organizations of any size.
One-Page Business Plan Template
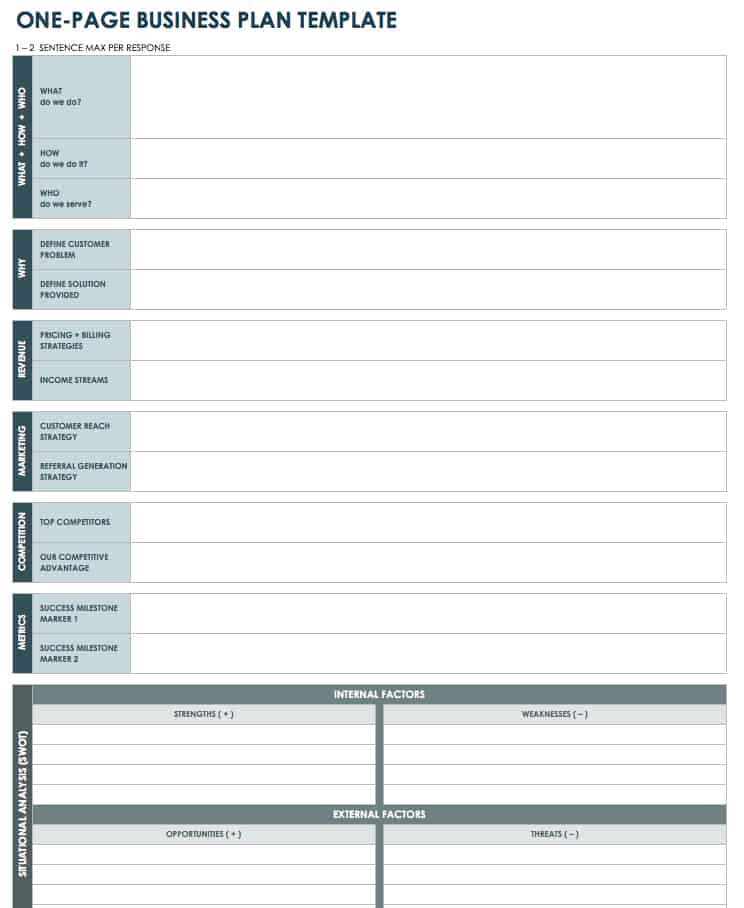
Download One-Page Business Plan Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Use this one-page business plan to document your key ideas in an organized manner. The template can help you create a high-level view of your business plan, and it provides easy scannability for stakeholders. You can use this one-page plan as a reference to build a more detailed blueprint for your business.
For additional single page plans, take a look at " One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide ."
Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template
Download Simple Fill-in-the-Blank Business Plan Template
Use this fill-in-the-blank business plan template to guide you as you build your business plan. Each section comes pre-filled with sample content, with space to add customized verbiage relevant to your product or service.
For additional free, downloadable resources, visit " Free Fill-In-the-Blank Business Plan Templates ."
Simple Business Plan for Startup

Download Startup Business Plan Template — Word
This business plan template is designed with a startup business in mind and contains the essential elements needed to convey key product or service details to investors and stakeholders. Keep all your information organized with this template, which provides space to include an executive summary, a company overview, competitive analysis, a marketing strategy, financial data, and more. For additional resources, visit " Free Startup Business Plan Templates and Examples ."
Simple Small-Business Plan Template

Download Simple Small-Business Plan Template
This template walks you through each component of a small-business plan, including the company background, the introduction of the management team, market analysis, product or service offerings, a financial plan, and more. This template also comes with a built-in table of contents to keep your plan in order, and it can be customized to fit your requirements.
Lean Business Plan Template

Download Lean Business Plan Template
This lean business plan template is a stripped-down version of a traditional business plan that provides only the most essential aspects. Briefly outline your company and industry overview, along with the problem you are solving, as well as your unique value proposition, target market, and key performance metrics. There is also room to list out a timeline of key activities.
Simple Business Plan Outline Template

Download Simple Business Plan Outline Template
Word | PDF
Use this simple business plan outline as a basis to create your own business plan. This template contains 11 sections, including a title page and a table of contents, which details what each section should cover in a traditional business plan. Simplify or expand this outline to create the foundation for a business plan that fits your business needs.
Simple Business Planning Template with Timeline
Download Simple Business Planning Template with Timeline
Excel | Smartsheet
This template doubles as a project plan and timeline to track progress as you develop your business plan. This business planning template enables you to break down your work into phases and provides room to add key tasks and dates for each activity. Easily fill in the cells according to the start and end dates to create a visual timeline, as well as to ensure your plan stays on track.
Simple Business Plan Rubric Template
Download Simple Business Plan Rubric
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Once you complete your business plan, use this business plan rubric template to assess and score each component of your plan. This rubric helps you identify elements of your plan that meet or exceed requirements and pinpoint areas where you need to improve or further elaborate. This template is an invaluable tool to ensure your business plan clearly defines your goals, objectives, and plan of action in order to gain buy-in from potential investors, stakeholders, and partners.
Basic Business Plan Sample
Download Basic Business Plan Sample
This business plan sample serves as an example of a basic business plan that contains all the traditional components. The sample provides a model of what a business plan might look like for a fictional food truck business. Reference this sample as you develop your own business plan.
For additional resources to help support your business planning efforts, check out “ Free Strategic Planning Templates .”
Main Components of a Business Plan
The elements you include in your business plan will depend on your product or service offerings, as well as the size and needs of your business.
Below are the components of a standard business plan and details you should include in each section:
- Company name and contact information
- Website address
- The name of the company or individual viewing the presentation
- Table of Contents
- Company background and purpose
- Mission and vision statement
- Management team introduction
- Core product and service offerings
- Target customers and segments
- Marketing plan
- Competitive analysis
- Unique value proposition
- Financial plan (and requirements, if applicable)
- Business and industry overview
- Historical timeline of your business
- Offerings and the problem they solve
- Current alternatives
- Competitive advantage
- Market size
- Target market segment(s)
- Projected volume and value of sales compared to competitors
- Differentiation from competitors
- Pricing strategy
- Marketing channels
- Promotional plan
- Distribution methods
- Legal structure of your business
- Names of founders, owners, advisors, etc.
- Management team’s roles, relevant experience, and compensation plan
- Staffing requirements and training plans
- Physical location(s) of your business
- Additional physical requirements (e.g., warehouse, specialized equipment, facilities, etc.)
- Production workflow
- Raw materials and sourcing methods
- Projected income statement
- Projected cash flow statement
- Projected balance sheet
- Break-even analysis
- Charts and graphs
- Market research and competitive analysis
- Information about your industry
- Information about your offerings
- Samples of marketing materials
- Other supporting materials
Tips for Creating a Business Plan
It’s easy to feel overwhelmed at the thought of putting together a business plan. Below, you’ll find top tips to help simplify the process as you develop your own plan.
- Use a business plan template (you can choose from the variety above), or refer to the previous section to create a standard outline for your plan.
- Modify your outline to reflect the requirements of your specific business. If you use a standard business plan outline, remove sections that aren’t relevant to you or aren’t necessary to run your business.
- Gather all the information you currently have about your business first, and then use that information to fill out each section in your plan outline.
- Use your resources and conduct additional research to fill in the remaining gaps. (Note: It isn’t necessary to fill out your plan in order, but the executive summary needs to be completed last, as it summarizes the key points in your plan.)
- Ensure your plan clearly communicates the relationship between your marketing, sales, and financial objectives.
- Provide details in your plan that illustrate your strategic plan of action, looking forward three to five years.
- Revisit your plan regularly as strategies and objectives evolve.
- What product or service are we offering?
- Who is the product or service for?
- What problem does our product or service offering solve?
- How will we get the product or service to our target customers?
- Why is our product or service better than the alternatives?
- How can we outperform our competitors?
- What is our unique value proposition?
- When will things get done, and who is responsible for doing them?
- If you need to obtain funding, how will you use the funding?
- When are payments due, and when do payments come in?
- What is the ultimate purpose of your business?
- When do you expect to be profitable?
To identify which type of business plan you should write, and for more helpful tips, take a look at our guide to writing a simple business plan .
Benefits of Using a Business Plan Template
Creating a business plan can be very time-consuming, especially if you aren’t sure where to begin. Finding the right template for your business needs can be beneficial for a variety of reasons.
Using a business plan template — instead of creating your plan from scratch — can benefit you in the following ways:
- Enables you to immediately write down your thoughts and ideas in an organized manner
- Provides structure to help outline your plan
- Saves time and valuable resources
- Helps ensure you don’t miss essential details
Limitations of a Business Plan Template
A business plan template can be convenient, but it has its drawbacks — especially if you use a template that doesn’t fit the specific needs of your business.
Below are some limitations of using a business plan template:
- Each business is unique and needs a business plan that reflects that. A template may not fit your needs.
- A template may restrict collaboration with other team members on different aspects of the plan’s development (sales, marketing, and accounting teams).
- Multiple files containing different versions of the plan may be stored in more than one place.
- You still have to manually create charts and graphs to add to the plan to support your strategy.
- Updates to the plan, spreadsheets, and supporting documents have to be made in multiple places (all documents may not update in real time as changes are made).
Improve Your Business Plan with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Un business plan exige généralement beaucoup de travail. Il se peut que vous ne soyez ni un expert en finances ou en argumentation commerciale. Il est possible que vous ayez des difficultés avec certains éléments déterminants pour la création de votre business plan. Il peut s'agir par exemple de la structure des tableaux financiers, de ...
A French business plan is more than a proposal; it's your business' heartbeat. It paints a vivid picture of what your venture stands for, its financial feasibility, and the promise it holds for profitability. This plan encapsulates your business' raison d'être, outlining objectives, financial projections, and budgetary considerations.
Our Essential Reading articles cover all the bases, from writing your French CV or setting up as an Auto-entrepreneur to running a gite business or navigating the French workplace. From defining your Mission Statement to setting out your five-year plan—a solid business plan is the first step to small business success.
Business plan - French Template - Plan d'affaire - modele en francais Voici un exemple qui peut vous aider pour concevoir le business plan de votre future entreprise. N'oubliez pas que chaque sujet de XMind peut contenir un document Word, Excel, un site web, etc. Et que votre carte peut devenir la structure d'un document Word ou PDF. Bien utile ...
My French Business Visa walks you through an 8-step roadmap to prepare for your business visa for France. From brainstorming ideas, checking French rules, writing your business plan, creating a financial plan, choosing your legal structure, prepare your application. Templates, workbooks, videos & 1-to-1 coaching.
A Sample French Fries Business Plan Template 1. Industry Overview. French fries food business belongs to the Snacks Food Production industry and operators in this industry primarily produces snack foods such as potato and corn chips, pretzels, roasted and salted nuts, nut butters, popcorn and other related snacks.
Beside the Business Model Canvas En Francais (BMC) we have developed a wealth of complimentary business modelling tools, resources and templates for startup founders and enterprise executives who want to introduce lean methods into their businesses. Check our template library and feel free to use them for your work. Download more resources.
Write the financial section of your business plan. Meet an accountant, lawyer or notaire, business advisor. Choose your business legal structure in France. Register your brand name or trademark. Prepare your legal contracts (letters of incorporation, premises, domiciliation) Open a professional bank account. Register your business in France.
When you purchase the French Entrepreneur Visa Business Plan Template, you'll also get: NEW Move To France Launchpad ! Your comprehensive PDF planning notebook designed to streamline and organise your relocation to France .
Check if your activity is regulated in France. Adjust your business idea accordingly. Choose the best legal structure for your project. Write your business plan (template provided). Work on your financial plan (template provided). Understand French taxes. Understand which visa to go for and the application process. Completing My French Business ...
Many translated example sentences containing "business plan template" - French-English dictionary and search engine for French translations. Look up in Linguee; Suggest as a translation of "business plan template" ... in addition to a new business plan template which will be implemented for 2010. ontarionorthland.ca.
3 - Write a strong business plan. Your business plan has two purposes: 1/ Enabling you to create a vision and strategy for your activity and 2/ Enabling the French Embassy to decide that your business project looks viable. The clearer you are on your offer, ideal customer, competitors, market analysis, strategy and sales projection, the easier ...
plan d'affaires m. The director presented the new business plan. Le directeur a présenté le nouveau plan d'affaires. less common: plan d'entreprise m. ·. plan des activités m. ·. plan de développement m.
There are two main ways of creating your French restaurant business plan: Using specialized business planning software, Hiring a business plan writer. Using an online business plan software for your French restaurant's business plan. Using online business planning software is the most efficient and modern way to create a French restaurant ...
728 templates. Create a blank Business Plan. Beige Aesthetic Modern Business Plan A4 Document. Document by Rise & Roar Design. Green Professional Strategic Business Plan Executive Summary. Document by Antler. Startup Business Plan. Document by Maea Studio.
Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product pictures, letters of reference, licenses, permits, patents, legal documents, and other contracts. Example traditional business plans. Before you write your business plan, read the following example business plans written by fictional business owners.
The rest, while still useful, go a bit lighter on guidance in favor of tailoring the plan to a specific industry. Explore: PandaDoc's business plan template library. 5. Canva — Pitch with your plan. Canva is a great option for building a visually stunning business plan that can be used as a pitch tool.
Sales & Marketing Plan for a French Restaurant (Example) Emily. January 9, 2024. Business Plan, Sales & Marketing Strategy. Establishing and managing a thriving French restaurant demands more than just culinary expertise; it necessitates a well-thought-out approach to sales and marketing strategies. This comprehensive guide is designed to aid ...
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
Many translated example sentences containing "template" - French-English dictionary and search engine for French translations. Look up in Linguee; Suggest as a translation of "template" ... the monitoring plan. eur-lex.europa.eu. eur-lex.europa.eu. L'autorité compétente peut imposer à l'exploitant d'aéronefs ...
How to write a formal email in French. 1. Use the proper greeting. Being polite is important. If you don't know the name nor the gender of the recipient (le destinataire), use: Madame, Monsieur, Mesdames, Messieurs, If you know the gender but not the name, then only Madame or Monsieur should be used. Even if you know the recipient's name ...
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
Download the Microsoft Word template above to help guide you through the process of creating a business plan. It is free to download and does not require any commitments from you. This template can be beneficial to people seeking to start a business, or operate an existing one without having first written a plan. The document will guide you ...
To write a simple one-page business plan, follow the same core sections as a traditional plan. But instead of lengthy paragraphs and multiple pages covering each area of your business, stick with single sentences and bulleted lists. If a one-page plan sounds like a better option, download our free simple business plan template to get started.
Download Simple Business Plan Outline Template. Word | PDF. Use this simple business plan outline as a basis to create your own business plan. This template contains 11 sections, including a title page and a table of contents, which details what each section should cover in a traditional business plan.
Edit and Download. Remember to create SMART goals for your marketing plan and strategy. SMART goals are Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant and Time-Bound. In the template above, notice how the target is defined as a percentage. You can also add a deadline to your marketing goal to make it time-bound.