

50 IB Biology IA Ideas

How To Write a Perfect Biology IA
Enter your email to get the guide!
Success! The Guide is on it's way to your inbox now!
80 most common ib biology exam questions.
Enter your email and tell us where to send them!

Great! The Questions are on their way to your inbox!
Pin it on pinterest.

IB Biology IA: 60 Examples and Guidance
Charles Whitehouse
The International Baccalaureate (IB) program offers a variety of assessments for students, including Internal Assessments (IAs), which are pieces of coursework marked by students’ teachers. The Biology IA is an assessment designed to test students' understanding of the material they have learned in their biology course and their ability to conduct independent research.
What is the IA?
The IA consists of a laboratory report that students must complete during their IB biology course. For assessments before May 2025, the report should be 6 to 12 pages in length and should include a research question, a methodology section, data analysis, and a conclusion. From May 2025 , the report should be a maximum of 3,000 words.
What should the IA contain?
The research question for the internal assessment should be a testable question that is related to the biology curriculum. It's essential that the question is relevant to the biology curriculum, specific and clearly defined. The methodology section should explain how the research was conducted, including the materials and methods used. The methodology should be detailed and well-explained, and should include information on the materials and methods used, as well as any ethical considerations.
Data analysis is an important aspect of the IA. Students should present their data in a clear and organized manner, and should use appropriate statistical analysis to interpret their results. They should also make sure to include a discussion of the limitations of their study and the implications of their findings.
The conclusion should summarise the main findings of the study and should relate the results back to the research question. It should also include recommendations for further research.
In addition to the laboratory report, students must also complete a reflective statement. Online tutors recommend that this statement should be around 500 words long, and should reflect on the student’s learning during the internal assessment process. The reflective statement should include a description of the student’s personal learning process, including successes and challenges, as well as an evaluation of their performance on the internal assessment and the skills they have gained through the process.
Have a look at our comprehensive set resources for IB Biology developed by expert IB teachers and examiners!
- IB Biology 2024 Study Notes
- IB Biology 2025 Study Notes
- IB Biology 2024 Questions
- IB Biology 2025 Questions
What are some example research questions?
Here are examples with details of potential research questions, written by expert IB Biology tutors and teachers, that could inspire your Biology IA:
1 - Investigating the effect of different types of sugars on the rate of fermentation by yeast. To investigate the effect of different concentrations of a specific herbicide on the growth rate of a particular plant species, one could set up an experiment in which the plants are grown in soil with varying concentrations of the herbicide. An appropriate range of concentrations and a suitable plant species would need to be chosen, along with control variables such as light, temperature, and watering. The growth rate of the plants could be measured by tracking their height or mass over a set period of time. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of the herbicide on the plant's growth.
2 - How does the pH of a solution affect the activity of an enzyme? To investigate the effect of pH on enzyme activity, one could set up an experiment in which the enzyme is exposed to solutions with varying pH levels. The enzyme's activity could be measured by monitoring the rate of a specific reaction catalyzed by the enzyme. Control variables such as temperature, substrate concentration, and enzyme concentration would need to be kept constant. By comparing the activity of the enzyme at different pH levels, the optimal pH range for the enzyme could be determined.
3 - Can the concentration of vitamin C in different types of fruit juice be determined using titration?
To determine the concentration of vitamin C in different types of fruit juice using titration, a standardized solution of a known concentration of potassium permanganate would be prepared. A sample of the fruit juice would be titrated with the potassium permanganate solution until the endpoint is reached, indicating that all the vitamin C has reacted with the potassium permanganate. The concentration of vitamin C in the fruit juice can then be calculated based on the volume and concentration of the potassium permanganate solution used in the titration. This process would need to be repeated for each type of fruit juice being tested.
4 - Investigating the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis in aquatic plants.
Set up an experiment in which aquatic plants are placed in containers with varying levels of light intensity. The light intensity could be controlled by adjusting the distance between the light source and the plants. The rate of photosynthesis could be measured by tracking the amount of oxygen produced by the plants over a set period of time. Comparing the rates of photosynthesis of the different groups would determine the impact of light intensity on the plant's photosynthetic activity. Control variables such as temperature, water quality, and plant species would need to be kept constant.
5 - How does the concentration of carbon dioxide affect the rate of photosynthesis in terrestrial plants?
Conduct an experiment in which plants are grown under different concentrations of carbon dioxide. The plants would need to be grown in a controlled environment with consistent light, temperature, and watering. The rate of photosynthesis could be measured by monitoring the oxygen production of the plants using a dissolved oxygen probe. The results could then be analyzed to determine how the concentration of carbon dioxide affects the rate of photosynthesis in terrestrial plants.
6 - Can the presence of glucose in urine be determined using Benedict's test?
Collect a urine sample from the individual being tested. Add Benedict's reagent to the sample and heat it in a water bath. If glucose is present in the urine, it will react with the Benedict's reagent and cause a color change. The intensity of the color change can be compared to a color chart to determine the concentration of glucose in the urine. This process would need to be repeated for each urine sample being tested.
7 - Investigating the effect of temperature on the respiration rate of germinating seeds.
Set up an experiment in which germinating seeds are exposed to different temperatures. The respiration rate of the seeds could be measured by monitoring the amount of oxygen consumed or carbon dioxide produced over a set period of time. The experiment would need to control for other variables such as the type of seed, the amount of water and nutrients provided, and the length of time the seeds have been germinating. Comparing the respiration rates of the different groups would determine the effect of temperature on the seeds' respiration rate.
8 - How does the concentration of salt in a solution affect the growth of bacteria?
Prepare a series of solutions with varying concentrations of salt, and inoculate each with a known amount of bacteria. The solutions would need to be incubated at a constant temperature for a set period of time, and the growth of the bacteria could be measured by counting the number of colonies or by using a spectrophotometer to measure the optical density of the solution. Comparing the growth rates of the bacteria in the different salt concentrations would determine the effect of salt on bacterial growth. Control variables such as pH, temperature, and nutrient availability would need to be kept constant.
9 - Can the concentration of nitrogen compounds in soil be determined using colorimetry?
Collect soil samples from different locations and extract the nitrogen compounds using a suitable method such as Kjeldahl digestion. The extracted compounds can then be analyzed using colorimetry, which involves adding a reagent that reacts with the nitrogen compounds and produces a color. The intensity of the color can be measured using a spectrophotometer, and the concentration of nitrogen compounds in the soil can be calculated based on the absorbance of the color. This process would need to be repeated for each soil sample being tested.
10 - Investigating the effect of different types of plant hormones on the growth of seedlings.
Set up an experiment in which seedlings are grown in different concentrations of plant hormones, with control variables such as light, temperature, and watering. The growth rate of the seedlings could be measured by tracking their height or mass over a set period of time. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of the plant hormones on the seedlings' growth. The experiment could also include observations of other plant characteristics such as leaf size and color, root development, and overall health.
Get expert help with your IB Biology
The world's leading online IB Biology tutoring provider trusted by students, parents, and schools globally.
4.92 /5 based on 480 reviews
11 - How does the concentration of salt in water affect the hatching rate of brine shrimp?
Set up multiple containers with different concentrations of salt water and add brine shrimp eggs to each container. The containers should be kept at a consistent temperature and light level. After a set period of time, count the number of hatched brine shrimp in each container and calculate the hatching rate. Comparing the hatching rates of the different containers would determine the effect of salt concentration on the hatching rate of brine shrimp.
12 - Can the rate of mitosis be determined using microscopy techniques?
Collect a sample of cells undergoing mitosis and prepare them for microscopy. Using a microscope, observe the cells and record the time it takes for each cell to complete each stage of mitosis. The rate of mitosis can then be calculated by dividing the time taken for each stage by the total time taken for the entire process. This process would need to be repeated for multiple cells to ensure accuracy and reliability of the results.
13 - Investigating the effect of different types of antibiotics on the growth of bacteria.
Culture bacteria in petri dishes with different concentrations of antibiotics. The growth of the bacteria can be observed and measured over a set period of time. The concentration of antibiotic that inhibits the growth of the bacteria can be determined, and the effectiveness of different types of antibiotics can be compared. Control variables such as temperature, humidity, and nutrient availability would need to be kept constant to ensure accurate results.
14 - How does the concentration of oxygen affect the respiration rate of crickets?
Set up a series of chambers with different concentrations of oxygen, ranging from low to high. Place crickets in each chamber and monitor their respiration rate by measuring the amount of oxygen consumed and carbon dioxide produced over a set period of time. The results can be analyzed to determine the effect of oxygen concentration on the respiration rate of crickets. Control variables such as temperature and humidity would need to be kept constant throughout the experiment.
15 - Can the concentration of glucose in blood be determined using glucose oxidase and spectrophotometry?
A sample of blood would be mixed with glucose oxidase, which converts glucose to hydrogen peroxide. The amount of hydrogen peroxide produced is proportional to the amount of glucose in the sample. A spectrophotometer would then be used to measure the absorbance of the sample at a specific wavelength, which is also proportional to the amount of hydrogen peroxide present. The concentration of glucose in the blood sample can then be calculated based on the absorbance reading and a standard curve generated using known concentrations of glucose. This process would need to be repeated for each blood sample being tested.
16 - Investigating the effect of different types of pesticides on the growth of bean plants.
Set up an experiment in which bean plants are grown in soil treated with varying concentrations of different pesticides. An appropriate range of concentrations and a suitable plant species would need to be chosen, along with control variables such as light, temperature, and watering. The growth rate of the plants could be measured by tracking their height or mass over a set period of time. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of the pesticides on the plant's growth. Additionally, the health of the plants could be assessed by examining their leaves for signs of damage or discoloration.
17 - How does the concentration of light affect the growth of algae?
Set up multiple containers with different concentrations of light, ranging from low to high. In each container, add a sample of algae and monitor their growth over a set period of time. The growth rate of the algae can be measured by tracking their biomass or chlorophyll content. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of light concentration on the growth of algae. Control variables such as temperature, nutrient availability, and water quality would need to be maintained to ensure accurate results.
18 - Can the presence of starch in leaves be determined using iodine solution?
Obtain a sample of the leaf and grind it into a fine powder. Add a few drops of iodine solution to the powder and observe the color change. If the solution turns blue-black, it indicates the presence of starch in the leaf. This process would need to be repeated for multiple leaves from different plants to ensure accuracy and reliability of the results. Control variables such as the age of the leaf and the time of day the sample is taken should also be considered.
19 - Investigating the effect of different types of plant nutrients on the growth of tomatoes.
Set up an experiment in which tomato plants are grown in soil with varying concentrations of different plant nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Control variables such as light, temperature, and watering would need to be maintained. The growth rate of the plants could be measured by tracking their height or mass over a set period of time. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of the plant nutrients on the plant's growth. Additionally, the nutrient content of the tomato plants could be analyzed to determine if there is a correlation between the nutrient concentration in the soil and the nutrient content in the plant.
20 - How does the concentration of carbon dioxide affect the growth of marine plants?
Conduct an experiment in which marine plants are grown in water with varying concentrations of carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide concentration could be controlled by bubbling different amounts of carbon dioxide gas into the water. The growth rate of the plants could be measured by tracking their height, mass, or chlorophyll content over a set period of time. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of carbon dioxide concentration on the plant's growth. Other variables such as light, temperature, and nutrient availability would need to be controlled to ensure that any differences in growth rate are due to the carbon dioxide concentration.
21 - Can the concentration of protein in an egg be determined using the Biuret method?
To determine the concentration of protein in an egg using the Biuret method, the egg would need to be homogenized and the protein extracted. A Biuret reagent would then be added to the protein extract, which would cause a color change if protein is present. The intensity of the color change would be proportional to the concentration of protein in the egg. A standard curve could be created using known concentrations of protein to determine the concentration of protein in the egg sample. This process would need to be repeated for each egg being tested.
22 - Investigating the effect of different types of plant hormones on the root growth of seedlings.
Set up an experiment in which seedlings are grown in soil with different concentrations of plant hormones. An appropriate range of concentrations and a suitable plant species would need to be chosen, along with control variables such as light, temperature, and watering. The root growth of the seedlings could be measured by tracking their length or mass over a set period of time. Comparing the root growth of the different groups would determine the impact of the plant hormones on the seedling's root growth.
23 - How does the concentration of oxygen affect the respiration rate of goldfish?
Set up multiple tanks with goldfish and varying levels of oxygen concentration. The respiration rate of the goldfish can be measured by tracking their oxygen consumption or carbon dioxide production. The experiment would need to be conducted over a set period of time with control variables such as temperature and feeding schedules. Comparing the respiration rates of the different groups would determine the effect of oxygen concentration on the goldfish's respiration rate.
24 - Can the concentration of a specific hormone in blood be determined using ELISA?
ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) involves coating a microplate with a specific antibody that binds to the hormone of interest. The sample of blood is then added to the plate, and any hormone present in the sample will bind to the antibody. A secondary antibody that is linked to an enzyme is then added, which will bind to the hormone-antibody complex. The enzyme will then catalyze a reaction that produces a detectable signal, such as a color change. The intensity of the signal is proportional to the amount of hormone present in the sample, allowing for the concentration of the hormone to be determined. A standard curve can be created using known concentrations of the hormone to accurately quantify the concentration in the sample.
25 - Investigating the effect of different types of pollutants on the growth of watercress.
Set up an experiment in which watercress plants are grown in water contaminated with different types and concentrations of pollutants. The growth rate of the plants could be measured by tracking their height or mass over a set period of time. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of the pollutants on the plant's growth. Control variables such as light, temperature, and watering would need to be kept constant to ensure accurate results. The types and concentrations of pollutants used in the experiment would need to be carefully chosen based on their potential impact on watercress growth and their relevance to real-world pollution scenarios.
26 - How does the concentration of light affect the rate of respiration in germinating seeds?
Set up a series of experiments in which germinating seeds are exposed to different intensities of light. The rate of respiration could be measured by tracking the amount of oxygen consumed or carbon dioxide produced by the seeds over a set period of time. The experiment would need to control for other variables such as temperature and humidity. Comparing the rates of respiration for the different light intensities would determine the impact of light concentration on the rate of respiration in germinating seeds.
27 - Can the concentration of nitrates in water be determined using colorimetry?
Prepare a series of standard solutions of known concentrations of nitrates. A sample of the water would be mixed with a reagent that reacts with nitrates to produce a colored product. The intensity of the color would be measured using a colorimeter, and the concentration of nitrates in the water can be calculated based on the intensity of the color and the concentration of the standard solutions. This process would need to be repeated for each water sample being tested.
28 - Investigating the effect of different types of disinfectants on the growth of bacteria.
Prepare a culture of bacteria and divide it into multiple groups. Each group would be exposed to a different type of disinfectant, while control groups would not be exposed to any disinfectant. The growth rate of the bacteria in each group would be measured over a set period of time, either by counting the number of colonies or by measuring the turbidity of the culture. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the effectiveness of each disinfectant on inhibiting bacterial growth.
29 - How does the concentration of salt in water affect the growth of duckweed?
Set up multiple containers of water with varying concentrations of salt. Add duckweed to each container and monitor their growth over a set period of time. The growth rate of the duckweed can be measured by tracking their surface area or biomass. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of salt concentration on the growth of duckweed. Control variables such as light, temperature, and nutrients should be kept constant across all containers.
30 - Can the concentration of ethanol in different types of alcoholic beverages be determined using gas chromatography?
Use gas chromatography to separate the components of the alcoholic beverage sample. The ethanol would be detected and quantified using a detector such as a flame ionization detector. The concentration of ethanol in each sample can then be calculated based on the peak area or height of the ethanol peak in the chromatogram. This process would need to be repeated for each type of alcoholic beverage being tested.
31 - Investigating the effects of different types of exercise on heart rate and blood pressure.
Recruit a group of participants and randomly assign them to different exercise groups (e.g. running, cycling, weightlifting). Measure their heart rate and blood pressure before and after the exercise session. Repeat this process for each exercise group. Analyze the data to determine if there are any significant differences in the effects of the different types of exercise on heart rate and blood pressure. Control variables such as age, gender, and fitness level should be taken into account.
32 - How does the level of noise pollution affect the behavior and communication of animals?
Conduct a field study in which the behavior and communication of animals in areas with varying levels of noise pollution are observed and recorded. Control variables such as time of day, weather conditions, and animal species would need to be taken into account. The observations could include changes in vocalizations, movement patterns, and social interactions. Comparing the behavior and communication of animals in areas with different levels of noise pollution would determine the impact of noise on their behavior. Statistical analysis could be used to establish correlations between noise levels and changes in animal behavior.
33 - Investigating the effects of different types of fertilizers on plant growth and nutrient uptake.
Set up an experiment in which identical plants are grown in soil with different types of fertilizers. The growth rate of the plants could be measured by tracking their height or mass over a set period of time. Nutrient uptake could be measured by analyzing the nutrient content of the plants at the end of the experiment. Comparing the growth rates and nutrient uptake of the different groups would determine the impact of the fertilizers on plant growth and nutrient uptake. Control variables such as light, temperature, and watering would need to be kept constant.
34 - How does exposure to light pollution affect the migration and behavior of nocturnal animals?
Conduct a field study in which nocturnal animals are observed in areas with varying levels of light pollution. The behavior and migration patterns of the animals could be tracked using GPS or radio telemetry. Data on the animals' activity levels, movement patterns, and habitat use could be collected and compared between areas with different levels of light pollution. This would allow for an assessment of the impact of light pollution on nocturnal animals and their ecosystems.
35 - Investigating the effects of different types of water pollution on aquatic ecosystems and organisms.
Set up multiple tanks or containers with different types and levels of water pollution, such as oil spills, chemical runoff, or excess nutrients. Populate each tank with a variety of aquatic organisms, such as fish, algae, and invertebrates. Monitor the health and behavior of the organisms over a set period of time, noting any changes in growth, reproduction, or mortality rates. Comparing the results from each tank would allow for an assessment of the impact of different types of water pollution on aquatic ecosystems and organisms.
36 - How does exposure to electromagnetic radiation affect the growth and development of plants?
Set up an experiment in which plants are exposed to different levels of electromagnetic radiation, such as UV light or radio waves. The plants would need to be grown in a controlled environment with consistent light, temperature, and watering. The growth rate and development of the plants could be measured by tracking their height, leaf size, and overall health over a set period of time. Comparing the growth and development of the plants exposed to different levels of electromagnetic radiation would determine the impact of the radiation on the plants. Control groups of plants not exposed to radiation would also need to be included for comparison.
37 - Investigating the effects of different types of air pollution on respiratory function and lung health.
Recruit a sample of participants who are exposed to different types of air pollution, such as those who live near busy roads or industrial areas. Conduct lung function tests, such as spirometry, on each participant to establish a baseline measurement of their respiratory health. Repeat the tests after a set period of time to determine any changes in lung function. Comparing the results of participants exposed to different types of air pollution would determine the impact of each type on respiratory function and lung health. Other factors, such as age and smoking status, would need to be controlled for in the analysis.
38 - How does the level of acidity affect the growth and survival of aquatic organisms?
Conduct experiments in which aquatic organisms are exposed to different levels of acidity. The organisms could be placed in tanks with varying pH levels, and their survival and growth rates could be monitored over time. Control variables such as temperature, light, and food availability would need to be kept constant. Comparing the survival and growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of acidity on the organisms. Additionally, other factors such as changes in behavior or reproduction could also be observed and analyzed.
39 - Investigating the effects of different types of food additives on human health and metabolism.
Conduct a literature review to identify the potential health effects of different food additives. Design a study in which participants consume a controlled diet with varying levels of the food additives being tested. Blood and urine samples could be collected at regular intervals to measure changes in metabolism and biomarkers of health. Statistical analysis would be used to determine if there are significant differences in health outcomes between the different groups.
40 - How does the level of UV radiation affect the growth and survival of plants?
Set up an experiment in which plants are grown under different levels of UV radiation. This could be achieved by using UV lamps of varying intensities or by placing the plants at different distances from a natural source of UV radiation, such as the sun. The growth rate, survival rate, and other relevant factors such as leaf size and chlorophyll content could be measured and compared across the different groups. This would help determine the impact of UV radiation on plant growth and survival. Control variables such as temperature, humidity, and watering would need to be carefully monitored and controlled to ensure accurate results.
41 - Investigating the effects of different types of drugs on human physiology and behavior.
Conduct a double-blind, randomized controlled trial with a group of participants who are given different types of drugs. The physiological and behavioral effects of the drugs would be measured through various tests and assessments, such as blood pressure, heart rate, cognitive function, and mood. The results would be analyzed to determine the impact of each drug on the participants' physiology and behavior, and any potential side effects or risks associated with each drug would be identified.
42 - How does the level of carbon dioxide affect the growth and development of plants?
Conduct an experiment in which plants are grown in controlled environments with varying levels of carbon dioxide. The growth rate, height, and biomass of the plants can be measured over a set period of time. The results can be compared to determine the impact of different levels of carbon dioxide on plant growth and development. Other variables such as light, temperature, and watering would need to be controlled to ensure that the results are accurate and reliable.
43 - Investigating the effects of different types of pesticides on non-target organisms and ecosystems.
Conduct a series of experiments in which different non-target organisms are exposed to varying concentrations of the pesticide. The organisms could be chosen based on their ecological importance, such as pollinators or soil microorganisms. The effects of the pesticide on the organisms could be measured by tracking their survival rates, reproductive success, or behavior. Additionally, the impact of the pesticide on the broader ecosystem could be assessed by monitoring changes in the abundance and diversity of other species in the area. Comparing the results of these experiments would provide insight into the potential ecological risks associated with the use of the pesticide.
44 - How does the level of atmospheric pollutants affect the growth and development of plants?
Set up an experiment in which plants are grown in controlled environments with varying levels of atmospheric pollutants, such as nitrogen dioxide or ozone. The growth rate, leaf area, and chlorophyll content of the plants could be measured over a set period of time. Comparing the growth rates and health of the plants exposed to different levels of pollutants would determine the impact of atmospheric pollutants on plant growth and development. Control variables such as light, temperature, and watering would need to be kept constant to ensure accurate results.
45 - Investigating the effects of different types of microorganisms on the digestive system and gut microbiome.
Conduct a study in which different groups of animals are exposed to different types of microorganisms, either through their diet or through direct exposure. The effects on their digestive system and gut microbiome could be measured through various methods such as analyzing fecal samples, measuring changes in gut pH, or monitoring the presence of certain bacteria. Comparing the results from the different groups would determine the impact of the microorganisms on the animals' digestive system and gut microbiome.
46 - How does the level of humidity affect the growth and survival of insects?
Conduct an experiment in which insects are exposed to different levels of humidity in a controlled environment. The survival rate and growth rate of the insects could be measured over a set period of time. The experiment would need to control for other variables such as temperature, food availability, and lighting. Comparing the survival and growth rates of the insects in different humidity levels would determine the impact of humidity on their growth and survival.
47 - Investigating the effects of different types of radiation on the genetic material and DNA replication.
Cultivate a sample of cells in a controlled environment and expose them to different types of radiation, such as gamma rays or UV light. The cells would then be monitored for changes in their genetic material, such as mutations or damage to DNA replication. The results could be compared to a control group that was not exposed to radiation to determine the effects of each type of radiation on the cells. Additional experiments could be conducted to investigate the long-term effects of radiation exposure on the cells.
48 - How does the level of soil salinity affect the growth and survival of plants?
Set up an experiment in which plants are grown in soil with varying levels of salinity. An appropriate range of salinity levels and a suitable plant species would need to be chosen, along with control variables such as light, temperature, and watering. The growth rate and survival rate of the plants could be measured by tracking their height, mass, and number of leaves over a set period of time. Comparing the growth and survival rates of the different groups would determine the impact of soil salinity on the plant's growth and survival. Additionally, the concentration of ions in the soil could be measured to determine the relationship between soil salinity and plant growth.
49 - Investigating the effects of different types of antibiotics on bacterial growth and antibiotic resistance.
Set up a series of petri dishes with agar and bacterial cultures. Each dish would contain a different antibiotic, with varying concentrations. The dishes would be incubated for a set period of time, and the growth of the bacteria would be measured. The results would show which antibiotics were most effective at inhibiting bacterial growth, and whether any resistance had developed. Control variables such as temperature, humidity, and the type of bacteria used would need to be carefully controlled to ensure accurate results.
50 - How does the level of soil pH affect the growth and survival of plants?
Conduct an experiment in which plants are grown in soil with varying pH levels. An appropriate range of pH levels and a suitable plant species would need to be chosen, along with control variables such as light, temperature, and watering. The growth rate of the plants could be measured by tracking their height or mass over a set period of time. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of soil pH on the plant's growth and survival. Other factors such as nutrient availability and toxicity would also need to be considered and controlled for in the experiment.
51 - Investigating the effects of different types of hormones on animal behavior and physiology.
Conduct experiments with different groups of animals, each exposed to a different hormone. The behavior and physiology of the animals would be monitored and recorded over a set period of time. Control variables such as diet, environment, and age would need to be maintained across all groups. Comparing the results of the different groups would determine the effects of each hormone on the animals' behavior and physiology. Statistical analysis could be used to determine the significance of the results.
52 - How does the level of water availability affect the growth and survival of plants?
Conduct an experiment in which plants are grown in different levels of water availability, ranging from drought conditions to optimal watering. The growth rate, survival rate, and overall health of the plants would be monitored over a set period of time. The data collected would be used to determine the impact of water availability on plant growth and survival. Control variables such as light, temperature, and soil type would need to be kept constant to ensure accurate results.
53 - Investigating the effects of different types of plant extracts on bacterial growth and antibiotic resistance.
Prepare bacterial cultures in petri dishes with different concentrations of the plant extracts. The growth of the bacteria can be observed over a set period of time, and the effectiveness of the plant extracts in inhibiting bacterial growth and antibiotic resistance can be determined by comparing the growth rates of the different groups. Control variables such as temperature and nutrient availability would need to be kept constant to ensure accurate results.
54 - How does the level of nutrients affect the growth and development of microorganisms?
Conduct experiments in which microorganisms are grown in nutrient-rich and nutrient-poor environments. The growth rate and development of the microorganisms could be measured by tracking their population size and observing their morphology under a microscope. Comparing the growth rates and morphology of the microorganisms in the different environments would determine the impact of nutrient levels on their growth and development. Control variables such as temperature, pH, and oxygen levels would need to be kept constant.
55 - Investigating the effects of different types of pollution on the reproductive systems and fertility of animals.
Select a suitable animal species and expose them to different types of pollution, such as air pollution or water pollution. The reproductive systems and fertility of the animals could be monitored over a set period of time, and compared to a control group that was not exposed to pollution. The impact of the pollution on the animals' reproductive systems and fertility could be determined by analyzing factors such as the number of offspring produced, the health of the offspring, and any abnormalities or complications observed during pregnancy or birth.
56 - How does the level of light intensity affect the growth and development of microorganisms?
Set up multiple petri dishes with agar and different levels of light intensity, ranging from complete darkness to bright light. Inoculate each dish with the same strain of microorganisms and incubate them for a set period of time. The growth of the microorganisms can be measured by counting the number of colonies or by measuring the turbidity of the culture. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of light intensity on the growth and development of the microorganisms. Control variables such as temperature, nutrient availability, and humidity would need to be maintained throughout the experiment.
57 - Investigating the effects of different types of food on the metabolism and energy balance of humans.
Conduct a randomized controlled trial in which participants are assigned to different groups and given different types of food to eat for a set period of time. The participants' energy intake, metabolism, and weight would be measured before and after the intervention to determine the impact of the different types of food on their energy balance. Other factors such as physical activity levels and sleep patterns would also need to be controlled for to ensure accurate results.
58 - How does the level of nutrients affect the growth and development of plants?
Conduct an experiment in which plants are grown in different nutrient solutions with varying levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. The growth rate, height, and mass of the plants could be measured over a set period of time to determine the impact of the nutrient levels on their growth and development. Control variables such as light, temperature, and watering would need to be kept constant. The results could be analyzed to determine the optimal nutrient levels for plant growth and development.
59 - Investigating the effects of different types of hormones on plant growth and development.
Set up an experiment in which different groups of plants are treated with different types and concentrations of hormones. The growth rate, height, and mass of the plants could be measured over a set period of time. Control variables such as light, temperature, and watering would need to be kept constant. Comparing the growth rates of the different groups would determine the impact of the hormones on the plant's growth and development. Additional measurements such as leaf size, root length, and flower production could also be taken to further analyze the effects of the hormones.
60 - How does the level of water quality affect the growth and survival of aquatic organisms?
Set up multiple aquariums with varying levels of water quality, such as different levels of pollutants or pH. Introduce the same species of aquatic organism into each aquarium and monitor their growth and survival over a set period of time. The growth rate and survival rate of the organisms can be compared between the different aquariums to determine the impact of water quality on their growth and survival. Control variables such as temperature and feeding schedules should be kept consistent across all aquariums.
Remember to come up with your own original IA topic and check it with your teacher. It should be practical to conduct and relevant to the syllabus. Even A-Level Biology tutors say that this is a great opportunity to develop your personal interests, while advancing your knowledge of the Biology curriculum.
How can I prepare for the IA?
To prepare for the IA, students should ensure that they understand the material covered in their biology course and should practice writing lab reports. They should also seek feedback from their teachers on their writing skills and their understanding of the research process. IB tutors provide personalized guidance and can help students understand complex topics and achieve higher grades as well.
TutorChase's IB resources are perfect for students who want to get a 7 in their IB Biology exams and also prepare for the internal assessment. They are completely free, cover all topics in depth, also have IB Biology past papers and are structured by topic so you can easily keep track of your progress.
How is the IA graded?
The IA is worth 20% of the final grade for the IB biology course, whether you are studying at Higher or at Standard Level. It is graded by the student’s teacher, who is trained and certified by the International Baccalaureate organization. The report is then sent to a moderator, who will check that the report adheres to the IB guidelines and that the grade awarded is appropriate.
Online Biology tutors emphasise that it is important for students to be familiar with the assessment criteria for the biology internal assessment. These criteria are used to grade the laboratory report and reflective statement, and include aspects such as the quality of the research question, the methodology used, the data analysis, and the conclusion. Students should also make sure that their report is well-written and properly formatted, and that it includes all the required sections.
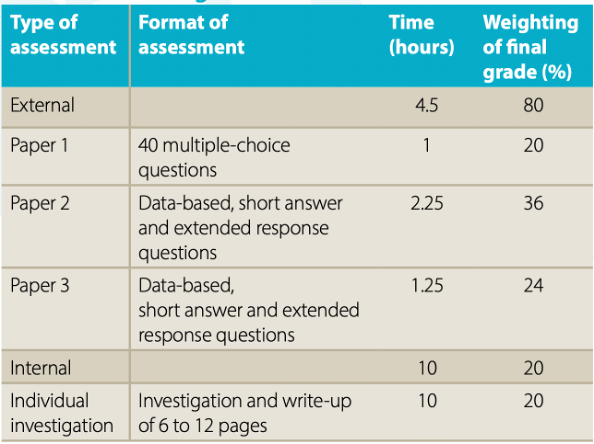
Source: IB Biology Subject Guide, pre-May 2025
In summary, the IA in the IB is an opportunity for students to demonstrate their understanding of the biology curriculum, as well as their ability to conduct independent research. It consists of a laboratory report and a reflective statement, and is worth 20% of the final grade for the course. To prepare for the assessment, students should ensure that they understand the material covered in their IB Biology.
Need help from an expert?
The world’s top online tutoring provider trusted by students, parents, and schools globally.
Study and Practice for Free
Trusted by 100,000+ Students Worldwide
Achieve Top Grades in your Exams with our Free Resources.
Practice Questions, Study Notes, and Past Exam Papers for all Subjects!
Need Expert Help?
If you’re looking for assistance with IB Biology, get in touch with the TutorChase team and we’ll be able to provide you with an expert IB Biology tutor . We’ll be there every step of the way!

Professional tutor and Cambridge University researcher

Written by: Charles Whitehouse
Charles scored 45/45 on the International Baccalaureate and has six years' experience tutoring IB and IGCSE students and advising them with their university applications. He studied a double integrated Masters at Magdalen College Oxford and has worked as a research scientist and strategy consultant.
Related Posts

What are the Hardest IB Subjects?

IB Theory of Knowledge: Knowledge Questions Explained

How to Choose Your IB Subjects

Hire a tutor
Please fill out the form and we'll find a tutor for you
- Select your country
- Afghanistan
- Åland Islands
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bouvet Island
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- Brunei Darussalam
- Burkina Faso
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Congo, The Democratic Republic of the
- Cook Islands
- Cote D'Ivoire
- Czech Republic
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands (Malvinas)
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- French Southern Territories
- Guinea-Bissau
- Heard Island and Mcdonald Islands
- Holy See (Vatican City State)
- Iran, Islamic Republic Of
- Isle of Man
- Korea, Democratic People'S Republic of
- Korea, Republic of
- Lao People'S Democratic Republic
- Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- Liechtenstein
- Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of
- Marshall Islands
- Micronesia, Federated States of
- Moldova, Republic of
- Netherlands
- Netherlands Antilles
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestinian Territory, Occupied
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Puerto Rico
- Russian Federation
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Serbia and Montenegro
- Sierra Leone
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen
- Switzerland
- Syrian Arab Republic
- Taiwan, Province of China
- Tanzania, United Republic of
- Timor-Leste
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- United States Minor Outlying Islands
- Virgin Islands, British
- Virgin Islands, U.S.
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara

Still have questions? Let’s get in touch.
30 IB Biology IA Topic Ideas!

Are you struggling with choosing your topic for your IB Biology IA? Don’t worry, we’ve all been there. Finding a topic is one of the – if not THE – most important part of writing your IA, so we want to make sure that you get it right! Luckily, there are so many great topics to choose from, and we’ve asked some of our top team to note down some topics that might inspire your own incredible research!
NOTE: These topics are purely meant as inspiration and are not to be chosen blindly. Even though many of these topics led to high scores for some of our graduates in the past, it is important that you listen to the advice of your subject teacher before choosing any topic!
Get Support from a Top Tutor Today
At Lanterna we have hundreds of tutors who smashed Biology. They know exactly how to get a 7 in your IA and exam and can give you tips and tricks on how you can do the same. What are you waiting for? Get your own tutor today!
Biology ia ideas with independent variables
1, Look at the genetic similarities and differences between species, kingdoms, phylas, classes, genuses, orders, families, and domains.
2, Testing global warming: How does CO2, water vapour, oxygen, or any other variable affect temperature inside a cutoff bottle exposed to simulated sunlight?
3, Describe how the primary productivity of algae changes with temperature, algae concentration, other aquatic plants, salinity, nutrients, and any other variables you may want to consider.
4, How does varying the gel concentrations of agarose affect DNA migration through a gel?
5, Effect of BMI on skin surface temperature in various body areas on rate of recovery once exposed to cold.
6, How does sudden change in body position affect heart rate and baroreceptor feedback?
7, How do the respiration rates of baker’s yeast and wine yeast in various sugar solutions compare?
8, How do the buffering actions of milk, yogurt, juices, detergents etc. compare?
9, Do our reaction times slow down with age?
10, Can we slow down the decaying times of vegetables? Can temperature, humidity, or exposure to sunlight affect how quickly vegetables decay?
Need inspo for Physics too? Check out some Physics IA ideas here !
11, What is the effect of the salt concentration on germination of different types of seeds?
12, What happens after the best-by date of dairy products?
13, Comparative study between 5 different species of animals using BLAST analysis to determine evolutionary history
14, What is the respective change of allele frequency when initial frequencies are manipulated?
15, Analysing the impact of river pollution on marine life.
16, Determine the effect of glucose concentration on the rate of osmosis.
17, What is the effect of pests on the diversity of plants in a lawn?
18, What is the effect of isotonic drinks on rehydration and recovery after exercise?
19, What is the difference in the CO2 levels exhaled before and after enduring physical exercise?
20, Testing the effectiveness of different types of toothpaste in inhibiting the growth of different types of bacteria.
Grab Free Biology Resources !
21, The effect of temperature / light on fruit ripening
22, Exploring stomatal density in a variety of conditions
23, Testing the effectiveness of toothpaste types
24, Investigating the effect of smoke water on the germination and growth of E.pilularis
25, Exploring the effect of sunlight on biomass
26, Exploring effect of light levels on the predation of the peppered moth
27, Investigating the effect of different light intensities on water weeds
28, How do different antibiotics interact with the process of seed germination?
29, Determining the effect of time on the plasmolysis of potatoes
30, Exploring mollusc shapes with regards to an external variable e.g. location on shore
So there we have it! 30 Biology IA topic ideas to get your lab report started! Still feeling a bit uneasy about the task ahead? Fear not, we have elite Biology tutors who can assist you through the process!
Share article links
Related Articles

- Most Popular
25 IB Chemistry IA Topic Ideas
We all know that scoring superbly on internal assessments is a great way to boost our IB grades. But how do we get started on a lab report and, crucially, what should we write about? In general, keep in mind that for your Chemistry IA we want to measuring how changing one variable has an […]
20 IB Physics IA Topic Ideas!
Choosing where to start with an IA can be the hardest part, and this is definitely true for the Physics IA. We know that our topic has to be somewhat related to the syllabus, but where should we focus? Thankfully, we’ve asked some of our favourite IB graduates for some of the ideas they pursued! […]
25 History IA Topic Ideas!
Are you about to start your History internal assessment? We know the struggle. One of the most difficult parts about the task is finding a good History IA topic because it feels like you can just write about anything. The IB breaks it down into 7 main different types of topics that you can choose, […]
12 Examples and Tips for IB Biology IA
May 4, 2022 | IB subjects

IA is one of the many things IB students struggle with, but some might feel that writing the IA in Biology is especially confusing since it covers broad topics. This post is for those who are having a hard time coming up with a topic, are worried about writing the IA in Biology overall, or are interested in Biology but not so sure about taking it because of IA. An overview of the subject IB Biology can also be seen in a previous post: Exam Strategy for IB Biology (HL/SL) .
1. Overview of Biology IA
Both HL and SL students are expected to write an IA ( Internal Assessment ) in Biology which accounts for 20% of the final grade . The IA in biology is expected to be a 6-12 pages long report about an investigation a student carries out based on their own hypothesis.
1.1 IA Criteria
HL and SL share the same IA criteria and it’s important to understand the criteria before and while carrying out the investigation for your IA. (Reference: Biology Teacher Support Material )
2. Examples of Biology IA Topics
Many IB graduates have kindly answered an online survey by MakeSensei and given examples of IA topics in IB Biology. Some of them are RQs (Research Questions), so you might want to see the pattern of how they make RQs for your future IA.
- What is the effect of exposure to different concentration of sodium chloride solutions for different duration time on the germination percentage, mean germination time, and relative injury rate of Ipomoea aquatica?
- Lactic acid experiment in milk
- What is the effect of sodium chloride concentration (0.0, 0.4, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, and 2.0 %) on the rate of hydrolysis of 1.0 % starch solution by 2.0 % ɑ-amylase (Bacillus subtilis), measured as the rate of decrease in absorbance value (Au s–1), using Spectrophotometer Vis at 434.2nm?
- Protein-digestive enzyme
- What is the effect of fertiliser quantity on evening levels of dissolved oxygen in river water samples over a period of two weeks?
- An Investigation into the Effect of Different Types and Concentrations of Pesticides (Orthoran Acephate, Kadan Safe, Kadan Plus DX) on Seed Germination: Observing Plant Growth of ErucaSativa, Brassica Oleracea, Lepidium Sativum and Perilla Frutescens
- An investigation into the effect of sodium chloride on plant germination and its growth.
- (Title: How to make delicious natto) RQ: What is the effect of pre-soaking time of soybeans, 0.00, 3.00, 6.00, 9.00, and 12.00 hours (±0.05 hours), on the length of threads between separated fermented soybeans (natto) measured by a clear plastic ruler (±0.1cm)?
- Effect of light intensity on the travel activity of a Physella acuta
- Investigating the effect of concentration of the salt solution on germination and growth of cotton and spinach seeds
- Investigating the correlation of the length of knee roots of a mangrove and the number of holes crabs make in the given area
- Effect of temperature on denaturation of albumin protein
3. Tips for Biology IA
3.1 Set Appropriate Independent/Dependent Variables
In order to carry out the investigation with sufficient sample size and trials, there needs to be independent and dependent variables that are both appropriate in terms of the purpose of your investigation. If you want to find out the relationship between X and Y (how X influences Y), then your independent variable should be X and your dependent variable should be Y. Both variables should be measurable , meaning quantitative, to allow various statistical analyses. But having qualitative data is valued in discussion as well.
3.2 The More Data, The Better
It is known that you should have at least 25 samples of data for your Biology IA, but let us explain why. While having multiple trials is necessary for the investigation, each trial should also have multiple samples. Therefore, 5 trials with 5 samples each make up 25 samples in total. Having said that, your sample size is up to you, and having more than 25 samples would only make your data more robust . But make sure you have enough time and energy to process the whole data.
3.3 Use Appropriate Secondary Sources
Doing background research on the field you’re focusing on in IA is required to back up your hypothesis, discussion, and conclusion. A lot of people use secondary sources (sources that are not first-hand) and most often through the internet. But, using Wikipedia or personal blogs would not be appropriate for your IA because they may not be reliable, accurate information. Instead, you might want to use these websites to search for previous academic articles and journals.
- Google Scholar
- The World Factbook (provides you data about the country of your interest)
3.4 Don’t Forget Annotations and Citations
- Annotations
An annotation is a short comment written near an image to give an explanation. Annotations are necessary when the image and its title don’t give enough explanation to specific objects in the image and your word count is limited. For example, when you’re showing your method with an image of instruments, readers might not understand why you chose those instruments to carry out your experiment. To avoid such inconvenience, annotations provide more detailed information than the title and the main text.
A citation is a short version of the reference to your source and it needs to be in-text or footnote. Every time you mention something that is not original or first-hand, you need to put citation(s) to prove where that statement comes from. If you miss citations, it will be considered plagiarism and you could fail the IB. Therefore, citations are important!! You could use Citation Machine to create a reference list and citation for each reference (check which style is preferred by your teacher).
- IB subjects
- Intro to IB

Recent Posts
- 21 IB Graduates Share Tips to Overcome IB Struggles
- 5 Things to Consider When IB Students Choose University
- 5 Tips for Supporting IB Students as a Parent
- 50 IB CAS Ideas by IB Graduates
- 6 Examples and Tips for IB Physics IA
Tiber Tutor
Explored ib biology .

IB Biology Internal Assessment Solved: A Guide to Acing Your Biology IA
What is a Biology IA?
The Biology Internal Assessment (IA) is a take home report on a research question of your choice. It is worth 20% of your final grade and thus it is important to perform well in it. The Biology IA can be daunting. It has a 16-page limit, which might seem like a lot to do, but towards the end of the IA you’ll be wishing you had more pages to work with. This guide is aimed to help you ace the IB Biology IA and to answer any questions you may have.
Choosing a Research Question
The most difficult part of the IA is choosing a research question. There are thousands of topics out there all of which are interesting. However unfortunately when conducting research, you are restricted to scope and the equipment which is available. Well how can you find a topic?
In order to find a topic, I would first choose a syllabus point which sounds appealing to you. Once you have found a syllabus point start googling experiments which have been conducted on that point. They do not have to be identical. DO NOT choose the first experiment you find. I would recommend collecting multiple experiments and read through all of them noting down how it was conducted and whether they had any unanswered questions.
These unanswered questions should be used as motivation when creating a research question. From here you can conduct further research to determine whether it is in the scope or not. If it is then you now have a research question to base your IA off. If it is outside the scope attempt to simplify the question or narrow the focus to that of which you can work with.
Conducting Research
Now that you have your research question it is time to gain background knowledge. Background knowledge is crucial as not only does it enhance your understanding of the topic, but it will be used in your IA to help the reader understand the topic.
When conducting research, the biggest mistake people make is using refutable sources. I would recommend using only published research articles as they have the most evidence to support their claims. This will enhance the reliability of your IA as information you are using is backed up by multiple sources. HOWEVER, it is crucial to ensure that you reference in APA format. We will explore referencing later in the article.
The research you gather should be used in your IA to explain to the reader the reasoning behind your question and to explain any concepts which may be confusing or abstract.
Undergoing the Experiment
Once you have conducted your research you are ready to create your method. The method you create to conduct the experiment is the same method you will place in your report. So, I would recommend that your method is detailed and concise. To ensure this, pretend that you are writing a method to someone who has never conducted an experiment before. This not only makes the method easy to follow for others, but for yourself too, ensuring that the experiment is conducted smoothly.
It is important that you conduct multiple trials. This will be explored in your evaluation as the more trials you conduct the more accurate and reliable your results become. However, when conducting multiple trials, try to conduct them during the same time period as it reduces the number of controlled variables.
Also, keep in mind that there is a possibility that the experiment may not work or that it may have varying results. If that occurs, do not stress, it is completely normal and will give you more to discuss later in the evaluation.
Writing the Report
Now for the fun part. Writing the report. When writing the report there are some sections which are more difficult than others. Below I will explore the sections most students find difficult to complete in a coherent manner.
Background Information
This section involves the most external information. Here you will collate all the information you have gathered on your research question and explore it. One key mistake students make is they do not systematically explore the information. I would recommend inserting subheadings for the various concepts you will explore, ie: 1.1: Photosynthesis, 1.2: electromagnetic spectrum, 1.3 Mentha spicata L, spearmint. Through using subheadings, it becomes easier for the marker to follow the report.
Paraphrase, Paraphrase & Paraphrase. One common mistake students make is that they “dump” information into their report and reference it. AVOID THIS. Instead, I would recommend paraphrasing information, explaining it and its relevance to the report.
Materials, Risks, Environment and Variables
Listing materials is easy and is probably the easiest part of the IA. However, many students do forget to insert the uncertainties for measuring instruments. This is very important as uncertainties must be explored in the weaknesses section for the IA.
Risk assessment should be included in the IA. It ensures that potential hazards which may arise during the experiment have been identified and precautions installed. It also ensures that if someone were to repeat the experiment, they are also aware of the dangers.
The experiments should all be ethical. Hence, environmental considerations should be addressed to show that ethical considerations were taken into account and methods were implemented to ensure the environment was not harmed.
All variables should be discussed in the report. This includes independent, dependent and controlled variables. When listing the variables, it should be discussed how they were controlled and why they should be controlled. This increases personal engagement, as it shows the marker that there was constant reflection being conducted.
Qualitative and Quantitative
When discussing results, both quantitative and qualitative results should be discussed. When discussing quantitative results, I would recommend using tables and graphs. It allows for clear and concise representation of information and allows for easier comparisons and discussions. Averages and standard deviation for the graphs and tables should be explored, as they allow for more accurate and justified conclusions to be drawn. Other tests such as t test, Tukey’s statistical difference test or chi squared test can be used to enhance the IA and discussion of results.
Qualitative analysis consists of differences which can be visually identified. Here you discuss differences in visual representation before the experiment was conducted to after the experiment.
Strength vs Weakness
Strengths: In this section I would recommend listing 2-3 strengths and commenting on how they affected the report or experiment.
Weaknesses: In this section I would recommend listing 5-6 weaknesses, and commenting on how they affected the report or experiment. You should then explore how you can improve this if you were to conduct the experiment again.
Further Questions
At the end of the IA, I would recommend including 2-3 further questions which could be explored if you had the opportunity. This improves personal engagement as it shows the marker that you have reflected on the current experiment and thought about what else you could explore.
Reference List (APA Format)
Ensure all in text references are listed at the end of the IA in APA format and alphabetical order. If this is difficult, I would recommend using the reference tab on a word document. Once you insert the information it converts it to APA format and will list it alphabetically for you.
Remember that the examiners are focusing on the detail of your report and your reflection. If you find that there was an error in the experiment, DISCUSS IT.
Best of luck for the Internal Assessment. You’ve got this!!
- Internal Assessment Guides
Recent Posts
IB Economics Internal Assessment Solved: A Guide to Acing Your Economics IA
IB Sports Science Internal Assessment Solved: A Guide to Acing Your SEHS IA
The Complete IB Physics Internal Assessment Guide

More than 30 IB Biology IA Topic Ideas To Use

An important part of the International Baccalaureate (IB) Biology program is the Internal Assessment (IA). It encourages students to think critically, do original research, and use what they've learned in practical contexts. Yet, deciding on a subject for the IA might be challenging. This article provides a list of 30 potential topics for an IA in IB Biology .
Before we start, IB-Pros offers resources and tutors willing to enhance the quality and effectiveness of your IA project.
Hire Your IB Online Tutor Now
30 Captivating Biology IA Topic Ideas for IB Students
1- look at how temperature affects enzyme function.
This proposed IA topic is about looking into how changes in temperature affect how enzymes work. Proteins called enzymes speed up chemical processes in living things. The optimum temperatures for the activity of various enzymes vary. Students may learn more about the connection between temperature and enzyme activity by doing experiments in which they try out various temperatures and record the results.
2- Investigating how various light wavelengths affect plant development.
For photosynthesis to take place, which is crucial for plant growth and survival, plants need light. Yet, the impacts of various light wavelengths on plant development are distinct. Students can learn more about the relationship between the wavelength of light and how plants grow by doing experiments with different wavelengths of light and watching how the plants grow.
3- Analyzing how various medicines affect bacterial growth
To combat bacterial infections, antibiotics are often prescribed. Antibiotics are drugs that inhibit the development of germs, yet they all work somewhat differently. Seeing how different drugs affect the growth of bacteria can help scientists figure out how well antibiotics work against different types of bacteria.
4 - Examining the impact of various salt concentrations on osmosis in potato cell cultures
Water molecules undergo osmosis as they go from a high-concentration region to a low-concentration region separated by a semipermeable membrane. By changing the concentration of solutes on either side of the membrane, salt may impact the rate of osmosis in potato cells. Students can test the relationship between the amount of salt in potato cells and the rate of osmosis by adding different amounts of salt and watching the rate of osmosis.
5- Investigating the Role of pH in the Photosynthesis of Aquatic Plants
The rate of photosynthesis in aquatic plants may be altered by changing the pH of the water. Students may learn more about how changes in pH affect the photosynthetic rate of aquatic plants by doing their experiments.
6- looking at how varying sugar levels affect yeast fermentation
Yeast cells transform sugar into alcohol and carbon dioxide via a process called yeast fermentation. The concentration of sugar may influence the pace of fermentation. Students may test the correlation between sugar content and yeast fermentation by brewing a batch with varying quantities of sugar and monitoring the pace of fermentation.
7: Researching how physical activity affects blood pressure and the heart rate
By boosting the body's need for oxygen and nutrients, exercise has the potential to raise heart rate and blood pressure. Exercise has been linked to improved cardiovascular health, which students can study by measuring their heart rate and blood pressure before and after a workout.
8- Examining Caffeine's Impact on Reaction Times
As a stimulant, caffeine may influence cognitive processes such as response speed. Students may learn more about how caffeine affects response time by taking a test before and after they consume caffeine.
9. Researching the impact of CO2 levels on insect respiration rates
Insects can't breathe in high amounts of carbon dioxide because it prevents them from exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide. Students can learn more about the link between CO2 levels and how fast insects breathe by doing experiments with different levels of CO2 and watching how the insect breathing rates change.
10 - Investigating the impact of various fertilizers on plant development
Fertilizers are helpful because they give plants the nutrients they need to grow well. However, different fertilizers have different effects on how plants grow. Students can find out how well different fertilizers work by doing experiments with them and watching how plants grow.
11- Studying how changing temperatures affect bacterial development
To thrive, bacteria need to be kept within certain temperature ranges. Students may learn about the correlation between temperature and bacterial growth by doing their experiments at varying temperatures and recording the results.
12 - Analyzing the impact of various antacids on gastric acid
Those who have acid reflux or heartburn often use antacids, which are drugs intended to neutralize stomach acid. The effects of various antacids on stomach acid might vary. Students may learn more about which antacids are best for treating acid reflux by seeing how each one affects stomach acid.
13- Researching the Role of Noise on Plant Development
Sound waves may affect plant development by influencing hormone secretion. Students can look into the link between sound and plant growth by playing different sounds for plants and then watching how they grow.
14- Studying the Impact of Hydrogen Peroxide Concentrations on Catalase Activity
Hydrogen peroxide may be decomposed into harmless water and oxygen with the help of an enzyme called catalase. Hydrogen peroxide concentration may modulate catalase activity rate. Students may learn more about the correlation between hydrogen peroxide levels and catalase activity by doing their experiments.
15—Investigating how changing the pH of saliva affects the amylase enzyme's activity.
The salivary enzyme amylase breaks down carbohydrates into simple sugars. Saliva's pH may affect how active amylase is. Students may learn about the correlation between pH and amylase activity by testing the effects of varying the pH of their experiments. Hire Your IB Online Tutor Now
Read More About:
The A To Z Guide For Structuring Your TOK Essay For Optimal Success
The Extended Essay (EE) In Business Management
The New TOK Exhibition Explained
The Perfect Guide To Earn A 7 In Your IB Psychology IA
The Simple Guide To Effective Time Management In The IB DP
16- Studying how ethanol concentration affects the permeability of beetroot cell membranes (Experiment 16)
Alcohol's propensity to disrupt lipid bilayers may change cell membrane permeability. Students can see if there is a link between ethanol concentration and membrane permeability by watching what happens when ethanol is added to beetroot cells and how the color comes out.
17- Study of the Impact of Light Wavelength on Photosynthesis in Spinach Leaves
The presence or absence of specific light wavelengths may change the rate of photosynthesis. Students can see what happens to spinach leaves when they are exposed to different amounts of light to test how light wavelength affects photosynthesis.
18- Examining how various salt concentrations affect seed germination
By changing the soil's water potential, salt may prevent seeds from germinating. Students can find out how salt concentration affects seed germination by putting seeds in different salt concentrations and watching how fast the seeds grow.
19- Investigating how various water sources affect plant development.
The dissolved minerals and nutrients present in the water may have an impact on plant development. Students may discover which kinds of water are best for fostering plant development by watering plants with each type and then monitoring plant growth.
20- Studying how different light intensities affect the photosynthesis of elodea plants
Given that light is the primary source of energy for the process, the amount of light available may have an impact on the speed of photosynthesis. Students can learn about how the amount of light affects photosynthesis by putting elodea plants in different amounts of light and watching how fast they grow.
Hire Your IB Online Tutor Now
21- The influence of various sugars on yeast fermentation
Various sugars may have varying effects on yeast fermentation. By trying out different sugars and keeping an eye on how fast the yeast ferments, students can find out which sugars work best.
22- Investigating how various salt concentrations influence plant development
Since it changes the soil's water potential, salt may affect plant development. Students may learn about the connection between salt concentration and plant development by doing experiments in which they use varying quantities of salt and then record the results in terms of how much their plants have grown.
Read More About: Is IB Worth It and What Are Its Growing Opportunities
23- Studying how different temperatures affect plants' ability to exhale
The evaporation of water from a plant's leaves is called transpiration. The temperature may affect the rate of transpiration. Students may learn more about the connection between temperature and transpiration by doing experiments in which they are exposed to varying temperatures and record their results.
24. Analyzing how various fertilizers influence plant development
Variations in nutrient content between fertilizer kinds may stunt or promote plant development. Students can learn about how different fertilizers affect the growth of plants by trying them out and comparing the results.
25- A Study of Physical Activity and Blood Pressure
The demand for oxygen and nutrients is increased during exercise, which might affect heart rate. Students may learn more about how exercise affects the heart rate by keeping a heart rate log before and after physical activity.
26- Researching the antibacterial effects of various medications
Antibiotics may inhibit bacterial development in a variety of ways. Students can find out how well different antibiotics work by giving bacteria to them and then watching how the bacteria grow.
27- Examining Caffeine's Impact on Daphnia's Heart Rate
Daphnia is used a lot in laboratories because it is so small and easy to handle. Caffeine may have an impact on Daphnia's heart rate. Daphnia's heart rate may be monitored before and after being exposed to coffee, so students can learn more about the connection between the two.
28- Analyzing the impact of several water types on yeast respiration
The way yeast breathes may be affected by the minerals and nutrients that are dissolved in the water. Students can determine which kinds of water are best for boosting yeast respiration by doing experiments with various types of water and monitoring the rate of respiration in the yeast.
29- Pea plant development as a function of light intensity (Experiment No. 29)
The amount of light a plant receives is important because it determines how much energy it has for photosynthesis. Students may learn about the correlation between light levels and plant development by doing controlled experiments in the classroom.
30- Investigating how various soils affect plant development
Changes in the amounts of nutrients and minerals in different types of soil can affect how plants grow. Students may learn which soils are best for plant development by planting the same kind of plant in each soil type and then comparing the results. Read More About: Comprehensive Overview IB Visual Arts
These suggestions for the IA study are meant as jumping-off points, not as final destinations. Create your research topic and hypothesis with the help of these examples. Keep in mind that IAs that are targeted, well-structured, and make use of relevant scientific approaches and procedures tend to fare the best. I hope your studies go well.

Hire a Tutor & Get Free Trial


Empowering Minds, Exploring Life

Biology IA Examples: Exploring Interesting Projects
Biology Internal Assessments (IAs) are not just a part of the IB curriculum; they’re a golden ticket for students to dive headfirst into the fascinating world of scientific exploration. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through a variety of interesting Biology IA examples that go beyond the classroom, providing students with hands-on experiences that are both educational and fun.
Investigating Enzyme Activity:
Enzymes, those microscopic heroes in our cells, make biochemical reactions happen. For an engaging IA, students can explore how external factors influence enzyme activity. This might involve experimenting with varying temperatures to observe the effects on catalase activity in liver cells. By understanding these nuances, students not only unravel the complexities of enzymes but also gain insights into real-world applications.
Examining Plant Growth Responses:
Plants, often underestimated, are incredible organisms with complex growth responses. In a captivating IA project, students can experiment with different concentrations of plant growth hormones to decipher their impact on bean plant growth. This isn’t just about playing with plants; it’s a chance to uncover the regulatory mechanisms that govern plant development and growth.
Studying Microbial Growth:
Microbes, though tiny, wield substantial power in the biological landscape. IA projects focused on microbial growth open up a realm of possibilities. For example, investigating how antibacterial agents affect the growth of Escherichia coli or studying the influence of environmental factors on mold growth on bread provides valuable insights. These explorations not only contribute to our understanding of microbes but also have practical implications in fields like medicine and food safety.
Investigating Genetic Inheritance:
Genetics , the code of life, is a playground for exciting IA projects. Students can delve into genetic traits using model organisms like fruit flies, unraveling the principles of inheritance. Alternatively, exploring the distribution of blood types in a specific population unveils the intricacies of genetic inheritance. These projects not only enhance genetic literacy but also allow students to actively contribute to ongoing genetic research.
Analyzing the Impact of Environmental Factors
Ecology comes to life in IA projects examining the relationship between organisms and their environment. By experimenting with environmental factors such as pollution or habitat changes, students can uncover their impact on population dynamics. A compelling IA might involve studying the effects of different pollutants on the growth of aquatic microorganisms, providing valuable insights into the delicate balance of ecosystems.
Investigating Human Physiology:
Our own bodies are a treasure trove of mysteries. IA projects in human physiology can focus on systems like the heart, lungs, or senses. For instance, studying the effects of exercise on heart rate or exploring the connection between taste perception and genetic variations offers a window into the intricate workings of the human body. These projects not only deepen our understanding of human biology but also have implications for health and well-being.
Conclusion:
Biology IAs offer more than just grades; they offer a chance for students to actively engage with science. The examples explored in this guide highlight the vast possibilities within the realm of Biology IAs, showcasing how students can not only grasp theoretical concepts but also contribute to the broader scientific community. As students embark on these investigative journeys, they’re not just students – they’re budding scientists uncovering the mysteries of the biological world.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
50 Biology IA Topics: Essential Selections for Learners
What is Biology IA
What are the Essential Components of the IA
Biology IA Topics
How Can I Prepare for a Biology IA
Final words.
I've witnessed firsthand the transformative power of engaging with the right research question in biology. Drawing from years of experience and a deep understanding of the subject, I've curated a list of 50 Biology IA topics to guide students and researchers alike. This compilation is more than just a list; it's a bridge connecting curious minds to the vast and intricate world of biological sciences. Each topic has been carefully selected for its potential to challenge, inspire, and contribute to our growing body of knowledge. Whether you're exploring the microscopic intricacies of cell biology or the complex ecosystems that sustain life on Earth, these topics are designed to foster a profound appreciation for the living world and its phenomena.
What is Biology IA (Internal Assessment) ?
The IA involves the submission of a lab report by students as part of their IB biology curriculum. Until May 2025, the report must be between 6 and 12 pages, encompassing a research question, methodology, data analysis, and a conclusion. Starting from May 2025, the report's length will be capped at 3,000 words.
IA should begin with a research question that is not only testable but also deeply rooted in the biology syllabus. This question must be closely aligned with the curriculum, precisely defined, and specific. In the methodology section, a detailed account of the research process, including the materials and methods utilized, should be provided. This section must be thorough, clearly describing the research steps, resources employed, and any ethical considerations addressed. Analyzing the gathered data is a critical phase of the IA. Students are expected to organize their data neatly and apply suitable statistical methods for analysis, interpreting their findings accurately. They should also discuss any study limitations and the broader significance of their results. The conclusion should encapsulate the study's key outcomes, linking them directly to the initial research question, and suggest areas for future investigation. Moreover, students must submit a reflective statement as part of their IA. This narrative, approximately 500 words, should ponder the student's learning journey throughout the IA process. It should cover the student's personal experiences, highlighting both triumphs and obstacles faced, assess their performance and the competencies developed during the assessment, and provide a thoughtful evaluation of the entire experience. Throughout this process, students may find tools like " essay typer free " helpful in articulating their thoughts and insights effectively.
List of 50 Biology IA Topics
- Deep Dive into the Syllabus: Start by thoroughly understanding the IB Biology syllabus. Knowing the curriculum inside out helps you identify areas that interest you and align with the IA requirements. It also ensures that your research question is relevant and grounded in the course content.
- Practice Lab Report Writing: Enhance your lab report writing skills by practicing regularly. Familiarize yourself with the structure and conventions of scientific writing. Pay special attention to clarity, coherence, and the logical flow of information. Consider reviewing exemplar lab reports and seeking constructive feedback from teachers or peers.
- Seek Feedback Early: Don't wait until your IA is fully developed to seek feedback. Discuss your ideas, research question, and methodology with your biology teacher or an IB tutor early in the process. Regular feedback can help refine your approach, identify potential pitfalls, and ensure your project is on the right track.
- Master Data Analysis Techniques: A significant part of the IA is analyzing the data you've collected. Brush up on your statistical skills and familiarize yourself with software or tools that can aid in data analysis. Understanding how to interpret your results accurately is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions.
- Reflect on Your Learning: The IA is not just about demonstrating your knowledge of biology; it's also an opportunity to reflect on your learning process. Engage in self-reflection throughout your IA journey, noting what you've learned, challenges you've encountered, and how you've overcome them. This reflective practice not only enhances your IA but also contributes to your personal growth as a learner.
- The Effect of pH on Enzyme Activity: Investigate how different pH levels affect the activity of a specific enzyme, such as catalase found in potato cells. You'll need pH buffers, potato extract, hydrogen peroxide, and a spectrophotometer to measure the reaction rate. This experiment explores how enzyme function is influenced by pH, demonstrating the importance of homeostasis in biological systems.
- Photosynthesis Rate under Different Light Colors: Examine how light color affects the rate of photosynthesis using aquatic plants like Elodea. You'll need light sources of different colors, a carbon dioxide indicator solution, and a timer. By measuring oxygen production or CO2 consumption, students can understand how light wavelength influences photosynthetic efficiency.
- The Effect of Temperature on Bacterial Growth: Explore how temperature impacts the growth rate of bacteria such as E. coli. Required materials include bacterial cultures, nutrient agar plates, incubators set at different temperatures, and a colony counter. This experiment highlights the importance of temperature in microbial ecology and food safety.
- Plant Growth in Different Soil Types : Investigate how various soil types affect plant growth. You'll need seeds (such as beans), different types of soil (sand, clay, loam), pots, and a ruler to measure growth. This study can reveal the importance of soil composition on plant health and yield, essential for agriculture and ecology.
- The Impact of Salt Concentration on Seed Germination: Study how varying salt concentrations in water affect the germination rate of seeds like radishes. Materials include seeds, petri dishes, filter paper, and salt solutions of different concentrations. This experiment simulates the effects of soil salinity on plant life, relevant to understanding agricultural challenges and ecosystem responses to salinity.
- Caffeine's Effect on Daphnia Heart Rate : Examine the impact of different caffeine concentrations on the heart rate of Daphnia magna. You'll need a microscope, Daphnia, caffeine solutions, and a stopwatch. This experiment introduces students to the physiological effects of stimulants and the concept of dose-response relationships in pharmacology.
- The Role of Light Intensity on Plant Stomatal Density: Investigate how varying light intensities affect stomatal density in leaf specimens. Necessary materials include leaves from plants grown under different light conditions, a microscope, and clear nail polish for leaf impressions. This study explores how plants adapt to their light environments, affecting gas exchange and water loss.
- Antibiotic Resistance Spread in Bacteria: Explore how antibiotic resistance spreads among bacterial populations. Use antibiotic discs, bacterial cultures, nutrient agar, and an incubator. This experiment demonstrates the mechanism of natural selection and the importance of antibiotic stewardship in healthcare.
- The Effectiveness of Natural vs. Synthetic Antibacterials: Compare the antibacterial efficacy of natural substances (e.g., garlic, honey) versus synthetic antibacterials (e.g., commercial disinfectants). Materials include bacterial cultures, nutrient agar plates, paper discs soaked in antibacterial solutions, and an incubator. This topic highlights the potential of natural substances in fighting bacteria and the concept of antibiotic resistance.
- The Influence of Music on Plant Growth: Investigate the effect of different types of music on plant growth rates. You'll need plants, speakers, and various genres of music. By measuring growth over time, this experiment can explore the intriguing possibility of sound waves affecting plant physiology.
- Osmosis in Potato Tissue: Examine how osmotic balance is affected by salt or sugar solutions using potato strips. Materials include potato strips, various concentrations of salt or sugar solutions, and a balance. This simple yet effective experiment teaches the principles of osmosis and cell membrane permeability.
- The Impact of Different Fertilizers on Algae Growth: Study how various fertilizers influence algae proliferation in water samples. Required materials include water samples, different types of fertilizers, and a light source. This experiment highlights the issue of nutrient pollution and eutrophication in aquatic ecosystems.
- The Role of Mycorrhizal Fungi in Plant Growth: Investigate the impact of mycorrhizal fungi on the growth of plant roots. Materials include plant seedlings, mycorrhizal fungi inoculum, and soil. This study sheds light on the symbiotic relationships in ecosystems and their importance for plant nutrition.
- The Effect of Acid Rain on Plant Growth: E xamine how simulated acid rain (using solutions of different pH levels) affects the growth of plants. Materials include seedlings, pH-adjusted water solutions, and growth measurement tools. This experiment explores environmental stressors on plants and the broader implications of pollution.
- Genetic Diversity in Plant Leaf Morphology: Analyze the genetic diversity within a plant species by comparing leaf morphology. You'll need leaves from various individuals of the same species, a scanner or camera, and image analysis software. This project introduces concepts of genetic variation and its observable effects in populations.
- The Effects of Microplastics on Brine Shrimp Survival: Investigate the survival rate of brine shrimp in water with varying concentrations of microplastics. Use brine shrimp, microplastic particles, and tanks. This study highlights environmental issues and the impact of pollutants on aquatic life.
- Comparing Plant Transpiration Under Different Humidity Levels: Examine how different environmental humidity levels affect plant transpiration rates. Materials include plants, plastic bags to create humidity conditions, and a balance to measure water loss. This experiment explores plant water relations and adaptations to environmental stress.
- The Influence of Mobile Phone Radiation on Seed Germination: Study the effect of electromagnetic radiation from mobile phones on the germination rate of seeds. You'll need seeds, mobile phones, and controlled germination environments. This project investigates the potential impact of technology on biological processes.
- Assessing Vitamin C Degradation in Fruit Juices Over Time: Measure the degradation of vitamin C in various fruit juices stored at different temperatures over time. Use fruit juices, vitamin C test strips or a titration kit. This experiment explores nutrient stability and the factors affecting it.
- The Impact of Exercise on Human Heart Rate Recovery: Analyze how different intensities of exercise affect heart rate recovery in humans. Materials include a heart rate monitor, stopwatch, and volunteers. This study sheds light on cardiovascular fitness and physiological responses to exercise.
- Soil pH and Its Effect on Earthworm Activity: Investigate how varying soil pH levels affect the activity and distribution of earthworms. Materials include soil samples with different pH levels, earthworms, and observation containers. This experiment highlights soil health and biodiversity.
- The Role of Water Temperature in Goldfish Metabolism: Examine how changes in water temperature affect the metabolic rate of goldfish, using water baths, thermometers, and oxygen probes. This study explores ectothermic metabolism and environmental adaptations.
- Investigating the Allelopathic Effects of Plant Extracts on Seed Germination: Study how extracts from certain plants inhibit or promote the germination of seeds from other plants. Use plant extracts, seeds, petri dishes, and filter paper. This experiment delves into plant interactions and chemical ecology.
- The Effects of Different Light Intensities on Daphnia Heart Rate: Analyze how light intensity influences the heart rate of Daphnia magna, using a microscope, light sources with adjustable intensity, and a stopwatch. This explores the effects of environmental stimuli on physiological responses.
- The Efficacy of Various Water Purification Methods on Bacterial Content: Compare the effectiveness of different water purification techniques in reducing bacterial content. Materials include contaminated water samples, purification methods (filtration, boiling, chemical treatment), and agar plates for bacterial culturing. This study is relevant to public health and sanitation.
- The Impact of Aeration on Water Quality and Aquatic Life: Investigate how different levels of water aeration affect the quality of water and the health of aquatic organisms. Use tanks, aerators, water quality test kits, and aquatic plants or animals. This experiment highlights the importance of oxygen in aquatic ecosystems.
- Studying the Biodegradation Rate of Various Organic Materials: Compare the biodegradation rates of different organic materials under the same environmental conditions. Materials include organic substances (food scraps, paper, etc.), soil, and compost bins. This project emphasizes sustainability and waste management.
- The Effect of Light Wavelengths on Algae Photosynthesis: Examine how different wavelengths of light affect the photosynthesis rate of algae, using colored filters, light sources, and a CO2 indicator. This study contributes to understanding photosynthetic efficiency and light energy utilization.
- Insect Biodiversity in Different Habitats: Assess insect biodiversity across various habitats using pitfall traps, sweep nets, and identification guides. This project explores biodiversity, ecosystems, and the importance of conservation.
- The Influence of Sugar Types on Yeast Fermentation: Investigate how different types of sugar (glucose, fructose, sucrose) affect the fermentation rate of yeast, using yeast cultures, sugar solutions, and gas collection methods. This experiment explores cellular respiration and biochemistry.
- Assessing the Impact of Noise Pollution on Plant Growth: Study how different levels of noise pollution affect the growth of plants, using speakers to simulate noise conditions and measuring plant growth parameters. This investigates environmental stressors and plant responses.
- The Role of Antioxidants in Preventing Apple Browning: Examine the effectiveness of various antioxidants (lemon juice, vitamin C solution) in preventing the browning of apple slices, comparing treated and untreated samples. This explores oxidation reactions and food preservation methods.
- The Effect of Different Substrates on Worm Composting Efficiency: Compare the composting efficiency of worms in different substrates (paper, vegetable scraps, mixed organic material), measuring decomposition rate and soil quality. This highlights sustainable waste management and soil health.
- Exploring Plant Cloning Techniques in Potato Tubers: Investigate the efficiency of different plant cloning techniques using potato tubers, focusing on methods like cutting and grafting, and assessing growth success rates. This introduces genetic replication and agricultural practices.
- Studying the Effectiveness of Sunscreen in Blocking UV Radiation: Compare the effectiveness of different SPF sunscreens in blocking UV radiation using UV-sensitive beads or paper, highlighting the importance of sun protection and skin cancer prevention.
- The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Function in Students: Examine the effects of varying degrees of sleep deprivation on cognitive functions such as memory and reaction time in student volunteers, using cognitive tests and questionnaires. This explores human physiology and health science.
- Investigating the Rate of Water Absorption in Different Soil Types: Study how various soil types (clay, sand, loam) absorb water, using soil samples, water, and measuring equipment. This experiment is relevant to agriculture, gardening, and environmental science.
- The Effect of Magnetic Fields on Plant Growth: Explore the influence of different strengths of magnetic fields on the growth and development of plants, using magnets and plant specimens. This investigates electromagnetic effects on biological systems.
- Assessing the Antifungal Properties of Plant Extracts: Examine the antifungal efficacy of various plant extracts against fungal pathogens in plants, using fungal cultures, plant extracts, and agar plates. This study has implications for natural disease management in agriculture.
- The Influence of Carbon Dioxide Levels on Plant Growth: Investigate how varying concentrations of CO2 affect the growth rate of plants, using controlled environments with adjusted CO2 levels. This experiment is relevant to studies on climate change and plant physiology.
- Exploring the Effects of Different Pollutants on Microbial Soil Health: Assess the impact of various pollutants (oil, pesticides, heavy metals) on the microbial health of soil, using soil samples, pollutants, and microbial culture techniques. This highlights environmental pollution and ecosystem health.
- The Role of Salinity in Fish Osmoregulation: Study how different salinity levels in water affect the osmoregulation mechanisms of fish, using aquariums, salinity meters, and fish specimens. This experiment explores marine biology and physiological adaptations.
- Investigating the Effects of Urbanization on Bird Populations: Compare bird species diversity and population numbers in urban versus rural areas, using birdwatching techniques and data analysis. This project examines biodiversity loss and conservation in changing environments.
- The Impact of Different Cooking Methods on Vegetable Nutrient Content: Examine how boiling, steaming, and microwaving affect the nutrient content of vegetables, using cooking equipment, vegetables, and nutrient testing kits. This explores nutrition science and food preparation methods.
- Assessing the Effectiveness of Different Handwashing Techniques: Investigate the bacterial reduction efficacy of various handwashing techniques and products, using bacterial cultures, agar plates, and volunteers. This is crucial for public health and hygiene education.
For optimal preparation for the IA, students must have a solid grasp of the biology course content and hone their lab report writing skills. They should actively seek their teachers' input on their writing abilities and comprehension of the research methodology.
Deep Dive into the Syllabus: Thoroughly understand the IB Biology syllabus. Knowing the curriculum inside out helps you identify areas that interest you and align with the IA requirements. It also ensures that your research question is relevant and grounded in the course content.
Practice Lab Report Writing:
- Enhance your lab report writing skills by practicing regularly.
- Familiarize yourself with the structure and conventions of scientific writing.
- Pay special attention to clarity, coherence, and the logical flow of information.
- Consider reviewing exemplar lab reports and seeking constructive feedback from teachers or peers.
Seek Feedback Early: Don't wait until your IA is fully developed to seek feedback. Discuss your ideas, research question, and methodology with your biology teacher or an IB tutor early in the process. Regular feedback can help refine your approach, identify potential pitfalls, and ensure your project is on the right track.
Master Data Analysis Techniques: A significant part of the IA is analyzing your collected data. Brush up on your statistical skills and familiarize yourself with software or tools to aid data analysis. Understanding how to interpret your results accurately is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions.
Reflect on Your Learning: The IA is not just about demonstrating your knowledge of biology; it's also an opportunity to reflect on your learning process. Engage in self-reflection throughout your IA journey, noting what you've learned, your challenges, and how you've overcome them. This reflective practice not only enhances your IA but also contributes to your personal growth as a learner.
As we wrap up our exploration of these Biology IA topic ideas, I hope you've found inspiration and a starting point for your investigative journey. Each topic offers a unique opportunity to delve into the wonders of the biological world, challenging you to ask questions, seek answers, and contribute to our collective understanding of life's intricacies. Remember, the key to a successful IA lies in choosing a topic that interests you and approaching it with curiosity, diligence, and a scientific mindset. Happy researching, and may your IA journey be as enlightening as it is rewarding!
.webp)
A collection of tips and notes for the International Baccalaureate.
IB Biology Internal Assessment (23/24)
Below I will attach a PDF of my Biology IA (submitted for Biology HL). It scored 23/24 (which, according to the boundaries of the M20 session, was a 7). Unfortunately, I don’t know where I lost the one mark.
Quick disclaimer; my Biology IA was a database IA, so the majority of the tips I’ll share in this post will specifically relate to writing a successful database IA. If you’re looking for tips for an experiment-based IA, I’d recommend you go check my post about my Chemistry IA , where I share some of my experiences with an experiment-based IA as well as a general structure I’d replicate when writing an experiment-based IA.
Across my three sciences (Biology HL, Chemistry HL, Physics SL), I wrote two experiment-based IAs and one database IA. As such, I feel as though I have a pretty solid understanding of the pros and cons of each IA “type” (excluding, of course, a simulation-based IA). In short, I can express the essence of these two IA types in quite a rudimentary table:
As per the above table, one of the downsides of an experiment-based IA is the amount of effort required to complete it. In experiment-based IAs, a lot of time and effort goes into planning your methodology, conducting preliminary trials, conducting the experiment itself etc. However, this hard work has a payoff, given that an advantage of an experiment-based IA is that the analysis and evaluation of your data is pretty straightforward, since there’s so much you could talk about when it comes to the accuracy and precision of your experiment.
On the other hand, a database IA requires a considerably smaller amount of time and effort to plan. Once you find a good data source and set up your primary equations on a spreadsheet, Excel practically does the rest of the work for you. It personally took me about 2 days to find all my data and process it. However, the drawback to a database IA is that it requires a lot of critical thinking and understanding of statistics and data sampling when it comes to the analysis and evaluation (which contribute half of the points you could achieve for your IA). Ultimately, because most people don’t have a good enough understanding of statistics and data sampling, they tend to score poorly in database IAs or shy away from them completely to begin with. In this post, I hope to provide you with a solid understanding of how to successfully complete a database IA, and hopefully my own IA acts as a decent exemplar for all of you to use.
The IA which I wrote was a “correlation-based IA”, which essentially means it explored the correlation between two (biology) related variables. I have not yet seen someone write a database IA that wasn’t correlation-based, so in this post I’ll be focusing on the structure and content of a correlation-based database IA. To do this, I’ll propose a general structure to use when writing a correlation-based database IA, and expand on some of the technical information that you should include in each section.
1. Research Question: In this section, state your research question. If you’re writing a correlation-based database IA, you want to make sure that your research question isn’t too simple, and that you add some unique ‘twist’ to your investigation. For example, instead of just determining the correlation between HDI and mortality rates due to CHD, I decided to specifically look at the distinction between this correlation in developing and developed countries. Some other ‘twists’ you could add to your investigation is to look at your correlation in different age groups, or between men and women.
2. Introduction: In this section, introduce why you ended up choosing to explore your particular research question. This is where I’d sneak in a bit about the connect between the research question and your interests/personal life (I was personally inspired to write my IA after I shadowed a cardiologist at a local hospital). You might also want to mention how answering your research question has important applications in the real world. In my own IA, I made the ‘Introduction’ section part of the ‘Background Information’ section to make sure my IA didn’t exceed the 12 page limit, but if you’re not running out of space I’d recommend making two separate sections.
3. Background Information: In this section, you want to illustrate all the biology knowledge that’s pertinent to your research question. This section is very important in a correlation-based database IA given that it’s one of the only sections where you’re provided an opportunity to discuss the biological background of your investigation. This section also acts as a reminder that your IA is biology-focused, not maths-focused. Additionally, in this section you should discuss other important background information that’s relevant to your investigation. For example, if you’re exploring the correlation between HDI and CHD mortality (as I have done), you’ll want to use the ‘Background Information” section to not only explain the pathogenesis of CHD but also the significance of CHD as a socioeconomic indicator.
4. Hypothesis: This section is pretty self-explanatory; just state your hypothesis. This should ideally be accompanied by a scientific explanation to support your hypothesis. In my case, I referenced a study about the correlation between the HDI and healthcare quality in a country to justify why HDI and CHD mortality should be negatively correlated.
5. Approach to the Research Question: In this section you should illustrate some of your personal engagement with the IA by explaining how you developed your methodology. For a correlation-based database IA, I suggest that three main points should be considered in this section: 1) how you will control confounding variables in your investigation, 2) how you minimised the effects of errors and variability in your data and, 3) how you standardised your variables. Below I further elaborate on these 3 points, using what I hope is a useful analogy.
In its most basic form, a correlation-based database IA is the development of an algorithm to process raw data into a form which allows you to determine whether a correlation exists between two variables. You can think of this algorithm like a machine, where your raw data is the input and the processed data is the output. In the “Approach to the Research Question” section, you essentially outline the three main ‘steps’ of the machine. The diagram below is a helpful guide:

As you see, the first “step” in the database machine is to control the raw data you collect for confounding variables. A confounding variable is a variable that influences both you dependent and independent variable (e.g. a variable that influences both HDI and mortality rates due to CHD). As such, if confounding variables are not controlled for it could lead to spurious correlations in your investigation. Confounding variables can also be variables other than your independent variable that influences your dependent variable, which you should also control (these types of variables are analogous to controlled variables in experiment-based IAs). For instance, lifestyle habits are an example of a variable which may affect both the HDI of a country and the mortality rate due to CHD. Ultimately, to control confounding variables in your experiment you must develop an inclusion criteria. The “Inclusion Criteria” section comes up later in the IA but you can foreshadow its existence in this section already.
The second “step” in the database machine is to take the data you’ve adjusted for confounding and further adjust it, this time for random variability. Random variability in data may be caused for a variety of reasons, and typically these reasons are difficult to identify. However, the existence of random errors in your data may contribute to a spurious correlation, and therefore random variability in data must be accounted for. For example, in my IA I looked at data relating to CHD mortality across different years in different countries. At any one year, there might have been some unknown factor which influenced the CHD mortality in a given country. This factor could be, for example, a sampling error or the introduction of a new procedure to treat CHD. As such, I decided to account for random variability by calculating the mean mortality rate due to CHD.
The last “step” in the database machine is to take the data you’ve adjusted (for confounding and random variability) and standardise it. Standardising data allows you to fairly compare it. For example, in my IA I looked at mortality rates due to CHD, and decided to standardise the mortality rate which I collected by expressing it per 100,000 people in a country’s population. This is important, given that the number of people who die from CHD in any given country is relative to that country’s population. There are, of course, many other ways to standardize data, but for most correlation-based database IAs which I’ve seen (where mortality/survival rates are used), expressing your data per the population is a good way to go.
6. Data sources : In this section of your IA, you should list all of the data sources which you’ve used to carry out your investigation. You should also provide an explanation as to how your chosen data sources are reliable and credible. Generally, if your data sources are well-recognised data-collecting institutions (e.g. the WHO, the World Bank), you can argue that they are also trustworthy and ergo reliable. For population statistics I’d use the World Bank database , mortality rates due to a variety of different diseases are provided by the WHO , and HDI data can be found online on United Nations Development Programme’s website.
7. Variables : In this section, state the final variables which you will explore in the investigation. This includes your independent variable (e.g. HDI) and your dependent variable (e.g. mortality rates due to CHD per 100,00 people). Additionally, state that other variables exist which you need to control (e.g. confounding variables), and that you will design an inclusion criteria in your investigation to control these variables.
8. Inclusion Criteria: In this section you will outline the inclusion criteria which you’ve designed for your investigation. In short, inclusion criteria are characteristics which the raw data you use must have in order to be used in the investigation. These criteria don’t only aim to adjust your data for confounding, but also to control other factors to ensure your results are more accurate and representative. As an example, the inclusion criteria for my own IA were as follows:

As you can see, my inclusion criteria consisted of four variables; location, population, HDI, and socioeconomic organisation, which were presented in a table. Given that my investigation looked at the distinction between developing and developed countries, I created separate inclusion criteria for each. For each inclusion criteria which you design, you need to provide an explanation for how it will enhance the accuracy or representativeness of your results. Below I outline the reason for choosing each of my variables. In your own IA, you should also provide a justification for the inclusion criteria you design.
Location : I chose to limit my chosen countries to European countries in order to limit the effects of confounding variables such as lifestyle and dietary habits. These European countries were those defined by the World Health Organidation, as per their website.This inclusion criteria was the same for both developing and developed countries.
Population : If you are sampling data from individual countries, it is necessary to ensure that the population size of these countries is sufficiently large. The larger the population, the more price and representative your results will be (and vice versa). Naturally, I’m not knowledgeable enough to decide which population size is sufficiently large to have confidence in the precision of my data. As such, I referenced a scientific study by Zhu et al. which stated that a sample size of 2 million is enough to ensure the precision of my data. This inclusion criteria excluded certain European countries, such as Liechtenstein and Monaco, from being included in my investigation.
HDI: According to the United Nations Development Programme, “countries with an HDI score higher than 0.788 are considered to be developed, while countries with an HDI value lower than 0.788 are considered to be developing”. I used this parameter to determine which sampled countries are developing and which are developed.
Socioeconomic organisation: I chose to further limit the eligible countries in my investigation to two socioeconomic organisations in order to limit the effects of confounding variables such as economic and cultural status. The two socioeconomic organisations which I chose were the CEIT (Countries with Economies in Transition) for developing countries and the OECD (Organisation for Economics Co-operation and Development) for developed countries.
As you can see, my inclusion criteria specified that variables such as population and HDI needed to be relevant as of 2000; meaning that an eligible developing country had to have, for example; a HDI smaller than 0.788 since the year 2000. This is because I sampled data from my investigation from the year 2000 onwards (given that this was the scope of raw data which I was able to find). Depending on the time period from which you sample your raw data from, this year would likely be different.
9. Safety, Environmental and Ethical Considerations: In this section, briefly outline which safety, environmental, and ethical precautions are necessary when conducting the experiment. Given the nature of a database IAs, there are no substantial safety and environmental considerations to be made. However, you may want to note that it is necessary to use data ethically and in accordance to guidelines set by your database sources (e.g. abide by copyright laws).
10. Methodology and Trial Investigation: In this section you should conduct a trial investigation to gain insight into the feasibility of the correlation you’re investigating, thus providing a justification for you to proceed and carry out the final investigation. Additionally, I would recommend using the trial investigation to explain the methodology you’ve designed for your IA. This will not only allow you to gain points in the ‘Analysis’ and ‘Communication’ criteria of the IA, but it will also save you space given that you will only need to provide the final results of your investigation later on, seeing as you’ve already explained your methodology beforehand.
In order to carry out a trial investigation, it is necessary to randomly sample your data to ensure that your trial investigation is truly representative of the rest of your data. For my IA, I randomly sampled 5 developing and 5 developed countries and carried out the investigation with their data. The way in which you randomly sample your data will vary per IA. Hereafter, explain your investigation’s methodology and all the different tables and calculation which you’ve used. For every calculation you make in the processing of your data, make sure to include a sample calculation. After processing all of your data and presenting it in a graph, determine which correlation exists in your data and justify why you should go ahead and conduct your final investigation. In my case, I used the R 2 values from my graphs to superficially assess how strong my correlations were, and thus whether I should continue with my final investigation.
(For those of you who don’t know, the R 2 value on a graph represents the proportion of the variance in the dependent variable that is predictable from the independent variable or, in layman terms, the degree of scattering of your data around the fitter trendline. The greater the R 2 value for a graph, the less scattering there is around the trendline, which may suggest a stronger correlation.)
11. Investigation and Results: Given that you’ve already explained your methodology in the previous section of your IA, all you need to do in this section is present the final processed data as well as any final graphs or tables you’ve created. Make sure to state in this section that you utilised the same methodology shown in the trial investigation to conduct the final one. Additionally, you may want to state that the raw data for the final investigation is “available upon request”, just to indicate to the person reading your IA that you actually processed the data yourself.
12. Statistical Testing: This section is, in my opinion, the one where most students miss out on marks for the ‘Evaluation’ criterion of the IA. In a correlation-based database IA, this section is where most students will conduct a statistical test to determine the strength of their correlation. Below I will provide a short description of how to conduct statistical testing for a correlation-based database IA:
Firstly, you need to determine which statistical test you will conduct. The two most frequently used statistical test for correlation are the Pearson’s correlation and Spearman’s correlation. The Pearson’s correlation tests for linear relationships, whereas the Spearman’s correlation tests for monotonic relationships. The difference between these two types of correlations is illustrated in the graphs below:

As you see, a linear relationship is a “straight-line” relationship between two variables, whereas a monotonic relationship is one where the function either always increases or always decreases, not both. Evidently, all linear relationships are monotonic, but not all monotonic relationships are linear. However, it will most probably not be clear whether the processed data in your investigation represents a linear relationship or one that is only monotonic. However, in order to conduct a Pearson’s correlation your data needs to meet certain assumptions, one of which is that your data is normally distributed, given that the test is sensitive to outliers and skewness in the data. As such, if you determine that your data is normally distributed, you should conduct a Pearson’s correlation. If your data is not normally distributed you won’t be able to conduct a Pearson’s correlation and should instead conduct a Spearman’s correlation.
An easy way to test whether your processed data is normally distributed, and thus whether you should conduct a Pearson’s correlation or not, is to conduct a skewness analysis. A skewness analysis is a quick calculation which tells you whether or not you data warrants concern of skewness. In a skewness analysis, you need to determine the value of two variables; the “skewness coefficient” and the “standard error”. Both of these variables can be calculated on Microsoft Excel.
The skewness coefficient is a variable which expresses how skewed your data is, and is a separate value for your independent and dependent variable data. Let’s say you want to calculate the skewness coefficient of your independent variable data. First, paste your data into a column on an Excel sheet. If your data spans from, say, cell E8 to cell E28, type the following equation into Excel in order to calculate the skewness coefficient of your data:
Use the same equation to calculate the skewness coefficient of your dependent variable data.
The standard error is different to the skewness coefficient and is usually the same value for both your independent and dependent variable data. The value of the standard error of your data depends on how many data points each of your variables has. In my investigation I had 31 pairs of data points, and therefore each of my variables (independent and dependent) had 31 data points. The value of the standard error was, therefore, the same for both the independent and dependent variable data. To calculate the standard error of your own data, use the following equation on Excel, where ‘N’ is the number of data points you have:
Finally, in order to assess the skewness of your data, you need to compare the absolute value of the skewness coefficient for each of your variables with twice the value of the standard error. If the value for the skewness coefficient is less than twice its standard error, then there is no concern of skewness in the data and the Pearson’s correlation can be conducted. If the value of the skewness coefficient is greater than twice its standard error, then there is concern of skewness and you need to conduct the Spearman’s correlation.
In short, the results of a skewness analysis can be presented in a table, as follows:

After the skewness analysis you need to conduct your chosen statistical test. I personally conducted the Pearson’s correlation, but I will demonstrate how to conduct both the Pearson’s and Spearman’s correlation below:
Pearson’s correlation: The Pearson’s correlation tests the strength of a linear correlation. The result of the Pearson’s correlation; the Pearson correlation coefficient ( r ), expresses the strength of and direction of a linear correlation (ranging from -1 to 1). The Pearson’s correlation is conducted using the following formula, where r is the Pearson correlation coefficient, x is your independent variable data, y is your dependent variable data, and n is the number of data pairs in your investigation.
As illustrated by the above equation, it is necessary to determine the sum of x, y, xy, x 2 and y 2 . After doing so, plug in your results into the above equation (alongside the value for n ), and the result will be your Pearson correlation coefficient.
Spearman’s correlation: Conducting the Spearman’s correlation is slightly more complex than the Pearson’s correlation. Similarly to the Pearson’s correlation coefficient, the Spearman’s correlation coefficient expresses the strength of and direction of a linear correlation (ranging from -1 to 1). Given that I haven’t personally conducted the Spearman’s correlation for my IA, I’m not very experienced in the process of doing so, but I found a great link which is very clear at describing how to calculate the Spearman’s correlation, which I will link here .
Lastly, after conducting the statistical test of choice, you need to ensure that the results of your statistical test are “statistically significant”; that is to say that the correlation which you’ve determined using the statistical test is caused by something other than chance. To determine statistical significance, you need to compare the result of your statistical test to a certain “critical value” which is based on the degrees of freedom and level of confidence assumed. I defined the two latter terms below:
- degrees of freedom : the number of values in the final calculation of a statistic that are free to vary. The degrees of freedom for an investigation is calculated as the number of data pairs minus 2 (e.g. for my investigation, which had 31 data pairs, there would be 29 degrees of freedom)
- level of confidence : the level of confidence when determining statistical significance refers to the risk that the correlation investigated is due to chance. Typically, a level of confidence of 0.05 is chosen, which denotes a 5% risk that the correlation investigated is due to chance.
You can determine the critical value for your investigation using either this document for the Pearson’s correlation or this document for the Spearman’s correlation. For instance, if you conducted a Pearson’s correlation and had 10 degrees of freedom at a level of confidence of 0.05, your critical value would be 0.576 (with reference to the appropriate document). Ultimately, if the absolute value of the correlation coefficient you have determined is greater than your assigned critical value, the results of your statistical testing are statistically significant, and vice versa.
I know this section was long, but it’s really important to get this part of the IA right in order to score highly. Remember, the statistical testing has three main parts: 1) conduct a skewness analysis to determine which statistical test to conduct, 2) conduct your chosen statistical test and, 3) determine if the results of your statistical test are statistically significant.
13. Analysis and Conclusion : In this section, analyze your final, processed data and provide an answer to your research question (if possible). This section should summarize the data which you’ve collected and how it (hopefully) supports your initial hypothesis. When analyzing the data, take into account the results of your statistical testing as well as the R 2 values from your final graphs.
14. Evaluation of Errors and Improvements: This section is of paramount important to the overall quality of your IA. The more detailed and thoughtful your evaluation of your investigation is, the better. To begin your evaluation, start by pointing out some of the strengths of your investigation. This could be the use of a trial investigation, or the thoroughness of your statistical testing. However, the bulk of the ‘Evaluation’ section should focus on identifying errors in your investigation and suggesting possible improvements to them. I mainly focused on how my methodology failed to take into account certain confounding variables, given that I suggested that these confounding variables were what caused my final correlations to be less than perfect. As such, most of the major errors in my investigation were linked to the nature of my inclusion criteria. Additionally, you may wish to point out some methodological errors in your investigation, such as the way in which you standardised your data, or how you could enhance the precision of your results by reducing the effects of certain random errors.
15. Extensions: In this section, identify any possible extensions to your investigation. It’s important to differentiate between improvements in the previous section and extensions in this one. An improvement involves tweaking your current methodology to ensure a more accurate and precise investigation. An extension, on the other hand, is suggesting an entirely new part of the methodology that would explore another aspect of your investigation. The extension you identify should, however, still be aimed at exploring something in the domain of your research question.
16. Literature: This is the last section of your IA and should include all of the sources which you’ve used, referenced in whichever style you want (I chose Chicago-style citation). Make sure to also reference any images which you’ve included in your IA in this section as well.
I hope this information is useful, and good luck!
Share this:
12 thoughts on “ ib biology internal assessment (23/24) ”.
Thank you so much for this!!! You probably saved my ass, bc I had to write a second biology IA (the first was was too shitty). This is such a good guide, thanks again!!
You don’t know how thankful i am for this like you saved my ass but i still need more helppppppp! My ANOVA test isnt’t working and my R values aren’t matching my data. Please help
Hi! Thank you for the post, it was really helpful. I was just wondering what font, font size and margin size you used? Also, I’m still not sure if the bibliography counts in the page limit but, correct me if I’m wrong, it didn’t seem to count in your IA?
Hi! I’m glad you found the post useful. I used Times New Roman size 11. I’m not really sure what margin size I used – I basically stretched the margins as far as I could because I had quite a lot of words to fit into the 12-page limit. To my knowledge, the bibliography does not count as part of the page limit. All the best!
Thank you so much for replying! The info was really useful 🙂
Hi! I was wondering how exactly you were able to gather your data from these databases? The websites are quite confusing
Hi! You usually need to download an Excel sheet or look through large tables to gather data from databases. For the WHO database, for instance, you can download different Excel sheets depending on what type of data you’re looking for. Hope that helps!
Hello. I just wanted to thank you for your precious advices. They are coming in really handy since I am taking HL biology too.
Hi! I was feeling so stressed because i didnt knew what to do with my ia and this helped a lot. Thank you so much!
Hi. Just wanted to thank you for the useful tips. They really helped me out when writing my database IA
Damn, I find myself on this website a few days before Christmas as the only one from my school doing a DB IA and I gotta admit I was super lost until I found your step-by-step guide Thank you very much.
you might just be the greatest of all time
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
Biology SL IA Samples
Score a home run on your Biology SL with our exclusive collection of Free Sample IAs! Get insider tips and tricks for success.

Evaluación del efecto del uso de agua con diferentes tipos de pH en el crecimiento de las plántulas de Lens culinarius y su longitud de tallo
Explore cómo los diferentes niveles de pH en el agua afectan el crecimiento y la longitud del tallo de las plántulas de Lens Culinarius en este ejemplo de evaluación interna de IB Biology SL.
Effect of acidity, alkalinity & neutrality of the medium on the growth of plants
Discover How Medium Acidity, Alkalinity, And Neutrality Impact Plant Growth. Explore This IB Biology SL Sample IA For Insightful Analysis And Detailed Observations.
Investigation of the effects of concentration & acidity on the rate of absorption of glucose & proteins through osmosis
Explore An IB Biology SL IA Investigating The Effects Of Concentration And Acidity On Glucose And Protein Absorption Rates Through Osmosis. Discover Insightful Findings.
Effect of percentage concentration of lead compounds in rate of photosynthesis
Discover How Lead Concentration Affects Photosynthesis In This IB Biology SL Sample IA, Perfect For Understanding Key Concepts And Excelling In Your Studies.
Effect of australian & malaysian originated daucus carota on the concentration of β-carotene.
Explore The Impact Of Australian And Malaysian Carrots On β-Carotene Levels In This IB Biology SL Sample IA. Discover Key Findings And Methodologies Used In The Study.
Effect of concentration of enzymes on yield of apple juice
Discover How The Concentration Of Enzymes Affects Apple Juice Yield In This Comprehensive IB Biology SL Sample IA. Perfect For Students Seeking Clear, Insightful Examples.
Relationship between vitamin c content & evolution of the genus citrus
Explore How Vitamin C Influences Citrus Evolution With This Sample IB Biology SL IA. Gain Insights Into Key Concepts And Enhance Your Understanding Of The Subject.
Effect of temperature on antioxidation capacity of aloevera juice
Explore The Effect Of Temperature On The Antioxidation Capacity Of Aloe Vera Juice. Dive Into This Comprehensive Sample IA For IB Biology SL And Enhance Your Understanding.
Effect of temperature on the rate of respiration of yeast in aerobic conditions
Discover The Impact Of Temperature On Yeast Respiration In Aerobic Conditions With Our Sample IA For IB Biology SL, Designed To Boost Your Understanding And Grades.
Effects of coffee & caffeine on the growth of plants
Discover How Coffee And Caffeine Impact Plant Growth In Our In-Depth IB Biology SL Investigation Analysis.
Investigating the effect of different light intensities on water weed
Discover How Different Light Intensities Influence Water Weed Growth In This Compelling IB Biology SL Investigation.
Investigating the effect of time on the plasmolysis of potatoes
Discover How Time Influences Potato Plasmolysis In This Captivating IB Biology SL Investigation Sample. Dive Deeper Into Science With Us.
How does the conversion of starch to glucose in nectarines (prunus persica) under two different fruit ripening techniques change over the course of seven days?
Discover How Starch Transforms Into Glucose In Nectarines Over Seven Days With Two Unique Ripening Techniques. Explore Our Findings Now.
What is the effect of temperature on mineral content & ph in alfisols?
Explore How Temperature Impacts Mineral Content And Ph In Alfisols With Our Detailed IB Biology SL Sample IA. Dive Into Scientific Insights Today!
The effect of sunlight on biomass
Discover How Sunlight Transforms Biomass In Our Comprehensive IB Biology SL IA. Dive Into The Intriguing Effects And Enhance Your Understanding Today.
A study on the effect of smoke water on the germination & growth o f eucalyptus pilularis
Discover The Surprising Impact Of Smoke Water On Eucalyptus Pilularis Germination And Growth With This Detailed IB Biology SL Study.

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
Biology IA Topics: 20+ Great Ideas to Get You Started
by Antony W
September 5, 2022

There’s nothing worse than trying to brainstorm and search for Biology IA topics only to come out empty.
The problem is:
There’s a lot to explore in Biology that it proves challenging to determine what topic would be suitable to investigate from the hundreds of possible options. So if you’re having a difficult time figuring out what topic to explore, we can understand.
In this post, we’ll share a list of the best IB Biology IA topics that you can use either for inspiration to help you come up with a topic of your own or as a modified topic for further research.
Biology Internal Assessment Writing Help
Don’t enough time left to complete your Biology IA and don’t know what to do?
Use our Internal Assessment writing service to get professional academic writing help from our team. Our writers are experts in writing IAs, and we guarantee high quality assignments that earn top marks.
IB Biology Internal Assessment (IA) Topics
Coming up with an IB Biology IA topic to explore isn’t difficult if you understand the requirements. Like Physics and Chemistry , your IA in Biology must focus on scientific writing and research in the Biology subject.
Below is a list of 30+ topic ideas for Biology Internal Assessment:
- Assessment of the effect of temperature on the vitamin C content of various juices
- What effect can quick shifts in body posture have on baroreceptor feedback and pulse rate?
- How do detergents, drinks, yogurt, and milk stack up when it comes to buffering?
- How does the ideal pH affect the growth rate of pinto and green beans? Proven Through Experiment
- The temperature dependence of the activation energy released during the decomposition of H2O2 utilizing the catalase enzyme and aluminum inhibitor as catalysts.
- To what extent does organic household waste affect the germination and emergence of tomato seeds?
- Investigating the Role of Carbonated Drink Volume and pH in Tooth Erosion/Decay
- In vitro Studies of Aluminum Chloride's Effects on the Liver Catalase Enzyme's Degradation of Hydrogen Peroxide
- Changes in seashell mass and carbon monoxide (CO) emitted during the reaction as a function of HCL concentration
- Does river pollution threaten the source of water for marine life?
- Fruit ripening as influenced by environmental factors including light and temperature
- How can we evaluate the respiration rates of wine yeast and baker's yeast in various sugar solutions?
- What happens to DNA movement as the concentration of the agarose gel changes?
- Compare the top and bottom 25 nations in terms of HDI and their rates of lung cancer-related mortality using secondary data.
- How does body mass index (BMI) affect the skin's surface temperature and the pace at which it recovers after exposure to cold?
- Hydrogen peroxide breakdown rate influenced by presence of various metal ions (H,O.).
- Using the Silver Nitrate titration method, how much variation exists between the chlorine concentrations (mg / L) of several locally accessible brands of treated water?
- How post-workout use of energy drinks affects cardiovascular function and blood pressure
- How do energy drinks affect blood pressure and heart rate following exercise?
- How do varying amounts of lactases affect the efficiency with which lactose and other disaccharides in milk are digested?
- Is there a correlation between the presence of home furnishings and stunted plant development?
- In terms of the pace of hydrochloric acid neutralization, as assessed by the difference in change in pH levels in 5 minutes, how do cumin and turmeric powder compare to indigestion tablets?
- What effect does zinc chloride concentration have on plaque development?
- What happens to the length of Citrus limon roots as the Oxytetracycline concentration is raised from 5 mg/L to 10 mg/L?
- Is there a correlation between the pH of spoiled milk and the temperature at which it was stored?
- How can the opposing effects of temperature and light intensity on the time it takes for photosynthesis to occur cancel each other out?
- How can the acidity of certain drinks contribute to tooth decay?
- What happens to your heart rate if you suddenly start working out hard, and how much of an effect does warming up have on your maximum heart rate
- How effective are natural antiseptics such as ginger and turmeric compared to store-bought alternatives?
- How potent are synthetic antibacterial treatments in comparison to natural antibacterial remedies?
- What effect does sodium chloride have on bougainvillea seed germination at various concentrations?
- What effect does soil composition have on the propagation of a plant's offshoots?
- How much does the amount of sodium nitrate powder used to preserve meat reduce its quality?
- For what reason does moringa seed and leaf extract (herbal medication) inhibit the growth of dandruff-causing Malassezia yeast (Pittosporum)?
- Which laundry detergent is best in breaking down lipids and getting rid of stains?
- When it comes to radishes, how does the salinity of the water effect their development rate?
- Does Gibberellic acid influence dolly Parton rose germination, and how does it react at various concentrations?
Assessed internally and moderated externally by the IB, Biology IA at SL and HL accounts for 25% and 20% of the final grades respectively. Your teacher will assess your work out of 24 based on well-defined assessment criteria. As such, you should work on a topic that you can explore comprehensively within the scope of the assignment.
Final Thoughts
The IB Biology IA assignment isn’t as lengthy as the extended essay in the same subject, but it can be quite involving. You’ll conduct extensive experiments and the writing process is going to be somewhat longer.
To have an easy time working on the subject, it’s best to choose a topic that interests you, so you can focus on an area that you’ve always wanted to explore.
Given that we’ve shared over30 topic ideas with you, you shouldn’t have a difficult time figuring out what to work on.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.
IBDP Biology
Website by David Faure, Richard Scarr & Lucy Martin
Updated 25 May 2024
Recent posts View all
- Student Access
- My favourites
- Presentation mode
- Teaching materials
- Print this page
How simple could an IA research question be?
Thursday 1 October 2015

- Finding the osmotic potential of onion cells, with a RQ, 'what is the osmotic potential of an onion cell?'
- Investigating amylase using starch and iodine, RQ, 'what is the effect of temperature on amylase?"
What would be the consequence to a student who chose something really simple like this?
I looked through the OCC for supporting evidence and I estimated the maximum grades which would be possible for a very simple piece of work using an IA Investigation - marking sheet
We don't know what the grade boundaries will be yet and applying the mark scheme is still a bit of an art for us all so please take the following notes with a pinch of salt. Do leave a comment if you agree, or disagree about something.
In the frequently asked questions page on the OCC there are some useful responses.
- It is unlikely that investigation will be totally original, but the idea should be new to the student and not simply a copy of something that has already been done in class.
- Students can help each other, as an extra pair of hands but can't use the same data
- Investigations using simple familiar equipment is OK but not a simple expt design: "it is expected that the level of sophistication will be commensurate with diploma level science"
- teacher's must consult with students during the planning pocess to avoid investigations which collect no results, but a limited results set should not have a very negative impact on the student's mark.
The TSM of the OCC has some advice on the different strands of IA assessment from which I have summarised a few points below together with a comment about marking such an investigation. The Inthinking page links contain a short summary of each aspect of assessment of the Investigation.
Personal Engagement
The TSM states "The topic chosen should also be of suitable complexity. If the research question is very basic or the answer self-evident then there is little opportunity to gain full marks for exploration and analysis as the student will not have the opportunity to demonstrate his or her skills."
Exploration
Students must demonstrate the thinking behind their ideas using their subject knowledge. In order to demonstrate focus on the issues at hand.…data must be of sufficient quantity and treatable in an appropriate manner, so that it can generate a conclusion, in order to fulfill the criteria of analysis and evaluation.
An experiment which was too simple or superficial would limit marks in Exploration: the aspect “topic and research question” could not be more than 4, “background information provided” might be 4 and it would probably limit, “Appropriateness of the methodology” mark to 4. This might cap Exploration to a maximum possible mark of 4.
If there is insufficient data then any treatment will be superficial - students should revisit the method before the analysis is arrived at. Alternatively, the use of databases or simulations to provide sufficient material for analysis could help in such situations.
Any treatment of the data must be appropriate to the focus of the investigation in an attempt to answer the research question.
An experiment which was too simple which didn’t have a focussed research question couldn’t really have raw data better than ‘relevant but incomplete’ = 4, Processing couldn’t be “appropriate and sufficient”. This might limit Analysis to <=4.
In the analysis, it may be concluded that there is a positive correlation between x and y; in the evaluation, the student is expected to decide, “Does the conclusion support the original thinking?”
An experiment which is too simple could not have a 4 mark conclusion “relevant to the research question” but it might have a good comparison to theory mark, and also for the strengths weaknesses and improvement suggestions. So evaluations marks would be less affected. Lets be generous and say 5 marks is possible.
Communication
This section is likely to be unaffected by the design of the experiment as it mainly depends on the formal presentation of the report
So to answer the question, "How simple could an IA research question be?"
Yes quite simple if ...
If a student is struggling to achive a grade 4 then a safe simple experiment is a good idea, so long as it meets these criteria.
- The IA should be something new to the student, and not a repeat of something that has been done in class.
- It must collect data either from an experiment or a data base / simulation or both.
Using guessology (in the absence of data) a very simple IA investigation could achieve the following marks: perhaps grade 5.
Not too simple, it needs some complexity if ...
If students are aiming for higher grades then something more complex is necessary otherwise the student will not be able to achieve the higher grades in exploration analysis and evaluation for the reasons outlined above.
These investigations must have:
- a focussed research question which allows a conclusion
- sufficient data for analysis and enough to answer the research question
- a conclusion relevent to the research question.
I'd be really keen to know what other IB teachers think? Please leave a comment below.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this post, we give you 50 IB Biology IA Ideas to help you speed up your research process. Within each topic listed below, we include the basic reasons for investigating each topic, what the possible independent variables and dependent variables are as well as the basic experimental setup! Remember!
All Biology IA Examples. Starting from the May 2025 session, the Biology IA requirements have changed. We created a couple of exemplars to show you how the new IA should look like. It's OK to refer to the old Biology IA exemplars (since the new IA is quite similar) for inspiration/ideas, but make sure to follow the new requirements.
Here are examples with details of potential research questions, written by expert IB Biology tutors and teachers, that could inspire your Biology IA: 1 - Investigating the effect of different types of sugars on the rate of fermentation by yeast. To investigate the effect of different concentrations of a specific herbicide on the growth rate of ...
Selecting an IBxq Biology IA idea has always been challenging! Before we look for IB Biology IA ideas, let's clearly comprehend the IB Biology Diploma Programme Subject, its objectives, partwise breakdown, and what IB expects of you. The IB IAs are essential to one's overall subject performance since they make up 20% of the final score.
Biology ia ideas with independent variables. 1, Look at the genetic similarities and differences between species, kingdoms, phylas, classes, genuses, orders, families, and domains. 2, Testing global warming: How does CO2, water vapour, oxygen, or any other variable affect temperature inside a cutoff bottle exposed to simulated sunlight?
2. Examples of Biology IA Topics. Many IB graduates have kindly answered an online survey by MakeSensei and given examples of IA topics in IB Biology. Some of them are RQs (Research Questions), so you might want to see the pattern of how they make RQs for your future IA. 2.1 For HL
This page contains links to official IB biology example IAs conducted by previous International baccalaureate students. Each biology sample Internal Assessment is marked by an official IB examiner, following the IB biology IA marking rubric. We suggest you use them for good IA ideas, and to explore how to write a biology IA well for your own ...
The IA, at a glance. The Internal Assessment, or IA, is a mandatory assignment of all IB students. It consists of a piece of written coursework that is assessed internally by a teacher, as well as externally moderated by the IB themselves. The IA accounts for 20% of a student's final assessment, and should involve roughly 10 hours of teaching ...
The Biology Internal Assessment (IA) is a take home report on a research question of your choice. It is worth 20% of your final grade and thus it is important to perform well in it. The Biology IA can be daunting. It has a 16-page limit, which might seem like a lot to do, but towards the end of the IA you'll be wishing you had more pages to ...
A good IA does not have to be a very complex and intricate piece of work. A clear research question, consistent structure, and clear personal engagement which demonstrates knowledge will earn the student a good grade. So let's jump into what you are here for. Here is a list of 25 possible topics that serve as great biology IA ideas. To keep ...
Internal Assessment Exploration. Click for a printable summary of IB internal assessment requirements. This criterion assesses the extent to which the student establishes the scientific context for the work, states a clear and focused research question and uses concepts and techniques appropriate to the Diploma Programme level to design an ...
An important part of the International Baccalaureate (IB) Biology program is the Internal Assessment (IA). It encourages students to think critically, do original research, and use what they've learned in practical contexts. Yet, deciding on a subject for the IA might be challenging. This article provides a list of 30 potential topics for an IA in IB Biology.
IA. Biology - HL. 6 (Breakdown) Examiner's summary. Criterion A [2/2]:The student demonstrates a strong personal interest in the topic and research question, justifying its relevance both globally and personally. They also show initiative in designing and conducting the study, with a well-formulated hypothesis and careful consideration of the ...
The Higher Level (HL) Biology Internal Assessment (IA) is a crucial component of the International Baccalaureate (IB) program. It allows students to delve deep into a scientific topic of their choice and showcase their research and analytical skills. In this guide, we will focus on the preliminary pages of the Biology IA, specifically the Title.
Internal Assessment Research Design. This criterion assesses the extent to which the student effectively communicates the methodology (purpose and practice) used to address the research question. Click for the summary of IB internal assessment requirements. Click for a printable score sheet. Command terms indicate the depth of treatment ...
IA projects in human physiology can focus on systems like the heart, lungs, or senses. For instance, studying the effects of exercise on heart rate or exploring the connection between taste perception and genetic variations offers a window into the intricate workings of the human body. These projects not only deepen our understanding of human ...
The IA involves the submission of a lab report by students as part of their IB biology curriculum. Until May 2025, the report must be between 6 and 12 pages, encompassing a research question, methodology, data analysis, and a conclusion. Starting from May 2025, the report's length will be capped at 3,000 words.
Below I will attach a PDF of my Biology IA (submitted for Biology HL). It scored 23/24 (which, according to the boundaries of the M20 session, was a 7). ... Research Question: In this section, state your research question. If you're writing a correlation-based database IA, you want to make sure that your research question isn't too simple ...
Effect of temperature on the rate of respiration of yeast in aerobic conditions. Discover The Impact Of Temperature On Yeast Respiration In Aerobic Conditions With Our Sample IA For IB Biology SL, Designed To Boost Your Understanding And Grades. Biology SL. Free. 5 /7.
IB Biology Internal Assessment (IA) Topics. Coming up with an IB Biology IA topic to explore isn't difficult if you understand the requirements. Like Physics and Chemistry, your IA in Biology must focus on scientific writing and research in the Biology subject. Below is a list of 30+ topic ideas for Biology Internal Assessment:
An experiment which is too simple could not have a 4 mark conclusion "relevant to the research question" but it might have a good comparison to theory mark, and also for the strengths weaknesses and improvement suggestions. So evaluations marks would be less affected. Lets be generous and say 5 marks is possible.
2. apply understanding of DNA, genes and the continuity of life or the continuity of life on Earth to develop research questions. 5. investigate phenomena associated with DNA, genes and the continuity of life or the continuity of life on Earth through research. The student work has the following characteristics: