- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Results Section – Writing Guide and Examples

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Results
Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Results Section in Research
The results section of the research paper presents the findings of the study. It is the part of the paper where the researcher reports the data collected during the study and analyzes it to draw conclusions.
In the results section, the researcher should describe the data that was collected, the statistical analysis performed, and the findings of the study. It is important to be objective and not interpret the data in this section. Instead, the researcher should report the data as accurately and objectively as possible.
Structure of Research Results Section
The structure of the research results section can vary depending on the type of research conducted, but in general, it should contain the following components:
- Introduction: The introduction should provide an overview of the study, its aims, and its research questions. It should also briefly explain the methodology used to conduct the study.
- Data presentation : This section presents the data collected during the study. It may include tables, graphs, or other visual aids to help readers better understand the data. The data presented should be organized in a logical and coherent way, with headings and subheadings used to help guide the reader.
- Data analysis: In this section, the data presented in the previous section are analyzed and interpreted. The statistical tests used to analyze the data should be clearly explained, and the results of the tests should be presented in a way that is easy to understand.
- Discussion of results : This section should provide an interpretation of the results of the study, including a discussion of any unexpected findings. The discussion should also address the study’s research questions and explain how the results contribute to the field of study.
- Limitations: This section should acknowledge any limitations of the study, such as sample size, data collection methods, or other factors that may have influenced the results.
- Conclusions: The conclusions should summarize the main findings of the study and provide a final interpretation of the results. The conclusions should also address the study’s research questions and explain how the results contribute to the field of study.
- Recommendations : This section may provide recommendations for future research based on the study’s findings. It may also suggest practical applications for the study’s results in real-world settings.
Outline of Research Results Section
The following is an outline of the key components typically included in the Results section:
I. Introduction
- A brief overview of the research objectives and hypotheses
- A statement of the research question
II. Descriptive statistics
- Summary statistics (e.g., mean, standard deviation) for each variable analyzed
- Frequencies and percentages for categorical variables
III. Inferential statistics
- Results of statistical analyses, including tests of hypotheses
- Tables or figures to display statistical results
IV. Effect sizes and confidence intervals
- Effect sizes (e.g., Cohen’s d, odds ratio) to quantify the strength of the relationship between variables
- Confidence intervals to estimate the range of plausible values for the effect size
V. Subgroup analyses
- Results of analyses that examined differences between subgroups (e.g., by gender, age, treatment group)
VI. Limitations and assumptions
- Discussion of any limitations of the study and potential sources of bias
- Assumptions made in the statistical analyses
VII. Conclusions
- A summary of the key findings and their implications
- A statement of whether the hypotheses were supported or not
- Suggestions for future research
Example of Research Results Section
An Example of a Research Results Section could be:
- This study sought to examine the relationship between sleep quality and academic performance in college students.
- Hypothesis : College students who report better sleep quality will have higher GPAs than those who report poor sleep quality.
- Methodology : Participants completed a survey about their sleep habits and academic performance.
II. Participants
- Participants were college students (N=200) from a mid-sized public university in the United States.
- The sample was evenly split by gender (50% female, 50% male) and predominantly white (85%).
- Participants were recruited through flyers and online advertisements.
III. Results
- Participants who reported better sleep quality had significantly higher GPAs (M=3.5, SD=0.5) than those who reported poor sleep quality (M=2.9, SD=0.6).
- See Table 1 for a summary of the results.
- Participants who reported consistent sleep schedules had higher GPAs than those with irregular sleep schedules.
IV. Discussion
- The results support the hypothesis that better sleep quality is associated with higher academic performance in college students.
- These findings have implications for college students, as prioritizing sleep could lead to better academic outcomes.
- Limitations of the study include self-reported data and the lack of control for other variables that could impact academic performance.
V. Conclusion
- College students who prioritize sleep may see a positive impact on their academic performance.
- These findings highlight the importance of sleep in academic success.
- Future research could explore interventions to improve sleep quality in college students.
Example of Research Results in Research Paper :
Our study aimed to compare the performance of three different machine learning algorithms (Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, and Neural Network) in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company. We collected a dataset of 10,000 customer records, with 20 predictor variables and a binary churn outcome variable.
Our analysis revealed that all three algorithms performed well in predicting customer churn, with an overall accuracy of 85%. However, the Random Forest algorithm showed the highest accuracy (88%), followed by the Support Vector Machine (86%) and the Neural Network (84%).
Furthermore, we found that the most important predictor variables for customer churn were monthly charges, contract type, and tenure. Random Forest identified monthly charges as the most important variable, while Support Vector Machine and Neural Network identified contract type as the most important.
Overall, our results suggest that machine learning algorithms can be effective in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company, and that Random Forest is the most accurate algorithm for this task.
Example 3 :
Title : The Impact of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
Abstract : This study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use, body image, and self-esteem among young adults. A total of 200 participants were recruited from a university and completed self-report measures of social media use, body image satisfaction, and self-esteem.
Results: The results showed that social media use was significantly associated with body image dissatisfaction and lower self-esteem. Specifically, participants who reported spending more time on social media platforms had lower levels of body image satisfaction and self-esteem compared to those who reported less social media use. Moreover, the study found that comparing oneself to others on social media was a significant predictor of body image dissatisfaction and lower self-esteem.
Conclusion : These results suggest that social media use can have negative effects on body image satisfaction and self-esteem among young adults. It is important for individuals to be mindful of their social media use and to recognize the potential negative impact it can have on their mental health. Furthermore, interventions aimed at promoting positive body image and self-esteem should take into account the role of social media in shaping these attitudes and behaviors.
Importance of Research Results
Research results are important for several reasons, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research results can contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field, whether it be in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, or humanities.
- Developing theories: Research results can help to develop or modify existing theories and create new ones.
- Improving practices: Research results can inform and improve practices in various fields, such as education, healthcare, business, and public policy.
- Identifying problems and solutions: Research results can identify problems and provide solutions to complex issues in society, including issues related to health, environment, social justice, and economics.
- Validating claims : Research results can validate or refute claims made by individuals or groups in society, such as politicians, corporations, or activists.
- Providing evidence: Research results can provide evidence to support decision-making, policy-making, and resource allocation in various fields.
How to Write Results in A Research Paper
Here are some general guidelines on how to write results in a research paper:
- Organize the results section: Start by organizing the results section in a logical and coherent manner. Divide the section into subsections if necessary, based on the research questions or hypotheses.
- Present the findings: Present the findings in a clear and concise manner. Use tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data and make the presentation more engaging.
- Describe the data: Describe the data in detail, including the sample size, response rate, and any missing data. Provide relevant descriptive statistics such as means, standard deviations, and ranges.
- Interpret the findings: Interpret the findings in light of the research questions or hypotheses. Discuss the implications of the findings and the extent to which they support or contradict existing theories or previous research.
- Discuss the limitations : Discuss the limitations of the study, including any potential sources of bias or confounding factors that may have affected the results.
- Compare the results : Compare the results with those of previous studies or theoretical predictions. Discuss any similarities, differences, or inconsistencies.
- Avoid redundancy: Avoid repeating information that has already been presented in the introduction or methods sections. Instead, focus on presenting new and relevant information.
- Be objective: Be objective in presenting the results, avoiding any personal biases or interpretations.
When to Write Research Results
Here are situations When to Write Research Results”
- After conducting research on the chosen topic and obtaining relevant data, organize the findings in a structured format that accurately represents the information gathered.
- Once the data has been analyzed and interpreted, and conclusions have been drawn, begin the writing process.
- Before starting to write, ensure that the research results adhere to the guidelines and requirements of the intended audience, such as a scientific journal or academic conference.
- Begin by writing an abstract that briefly summarizes the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
- Follow the abstract with an introduction that provides context for the research, explains its significance, and outlines the research question and objectives.
- The next section should be a literature review that provides an overview of existing research on the topic and highlights the gaps in knowledge that the current research seeks to address.
- The methodology section should provide a detailed explanation of the research design, including the sample size, data collection methods, and analytical techniques used.
- Present the research results in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and figures to illustrate the findings.
- Discuss the implications of the research results, including how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge on the topic and what further research is needed.
- Conclude the paper by summarizing the main findings, reiterating the significance of the research, and offering suggestions for future research.
Purpose of Research Results
The purposes of Research Results are as follows:
- Informing policy and practice: Research results can provide evidence-based information to inform policy decisions, such as in the fields of healthcare, education, and environmental regulation. They can also inform best practices in fields such as business, engineering, and social work.
- Addressing societal problems : Research results can be used to help address societal problems, such as reducing poverty, improving public health, and promoting social justice.
- Generating economic benefits : Research results can lead to the development of new products, services, and technologies that can create economic value and improve quality of life.
- Supporting academic and professional development : Research results can be used to support academic and professional development by providing opportunities for students, researchers, and practitioners to learn about new findings and methodologies in their field.
- Enhancing public understanding: Research results can help to educate the public about important issues and promote scientific literacy, leading to more informed decision-making and better public policy.
- Evaluating interventions: Research results can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, such as treatments, educational programs, and social policies. This can help to identify areas where improvements are needed and guide future interventions.
- Contributing to scientific progress: Research results can contribute to the advancement of science by providing new insights and discoveries that can lead to new theories, methods, and techniques.
- Informing decision-making : Research results can provide decision-makers with the information they need to make informed decisions. This can include decision-making at the individual, organizational, or governmental levels.
- Fostering collaboration : Research results can facilitate collaboration between researchers and practitioners, leading to new partnerships, interdisciplinary approaches, and innovative solutions to complex problems.
Advantages of Research Results
Some Advantages of Research Results are as follows:
- Improved decision-making: Research results can help inform decision-making in various fields, including medicine, business, and government. For example, research on the effectiveness of different treatments for a particular disease can help doctors make informed decisions about the best course of treatment for their patients.
- Innovation : Research results can lead to the development of new technologies, products, and services. For example, research on renewable energy sources can lead to the development of new and more efficient ways to harness renewable energy.
- Economic benefits: Research results can stimulate economic growth by providing new opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs. For example, research on new materials or manufacturing techniques can lead to the development of new products and processes that can create new jobs and boost economic activity.
- Improved quality of life: Research results can contribute to improving the quality of life for individuals and society as a whole. For example, research on the causes of a particular disease can lead to the development of new treatments and cures, improving the health and well-being of millions of people.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing...

Problem Statement – Writing Guide, Examples and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Implications in Research – Types, Examples and...

- Manuscript Preparation
How to write the results section of a research paper
- 3 minute read
- 67.2K views
Table of Contents
At its core, a research paper aims to fill a gap in the research on a given topic. As a result, the results section of the paper, which describes the key findings of the study, is often considered the core of the paper. This is the section that gets the most attention from reviewers, peers, students, and any news organization reporting on your findings. Writing a clear, concise, and logical results section is, therefore, one of the most important parts of preparing your manuscript.
Difference between results and discussion
Before delving into how to write the results section, it is important to first understand the difference between the results and discussion sections. The results section needs to detail the findings of the study. The aim of this section is not to draw connections between the different findings or to compare it to previous findings in literature—that is the purview of the discussion section. Unlike the discussion section, which can touch upon the hypothetical, the results section needs to focus on the purely factual. In some cases, it may even be preferable to club these two sections together into a single section. For example, while writing a review article, it can be worthwhile to club these two sections together, as the main results in this case are the conclusions that can be drawn from the literature.
Structure of the results section
Although the main purpose of the results section in a research paper is to report the findings, it is necessary to present an introduction and repeat the research question. This establishes a connection to the previous section of the paper and creates a smooth flow of information.
Next, the results section needs to communicate the findings of your research in a systematic manner. The section needs to be organized such that the primary research question is addressed first, then the secondary research questions. If the research addresses multiple questions, the results section must individually connect with each of the questions. This ensures clarity and minimizes confusion while reading.
Consider representing your results visually. For example, graphs, tables, and other figures can help illustrate the findings of your paper, especially if there is a large amount of data in the results.
Remember, an appealing results section can help peer reviewers better understand the merits of your research, thereby increasing your chances of publication.
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper
- Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions.
- The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is best to avoid overinterpreting the results.
- If the research addresses more than one hypothesis, use sub-sections to describe the results. This prevents confusion and promotes understanding.
- Ensure that negative results are included in this section, even if they do not support the research hypothesis.
- Wherever possible, use illustrations like tables, figures, charts, or other visual representations to showcase the results of your research paper. Mention these illustrations in the text, but do not repeat the information that they convey.
- For statistical data, it is adequate to highlight the tests and explain their results. The initial or raw data should not be mentioned in the results section of a research paper.
The results section of a research paper is usually the most impactful section because it draws the greatest attention. Regardless of the subject of your research paper, a well-written results section is capable of generating interest in your research.
For detailed information and assistance on writing the results of a research paper, refer to Elsevier Author Services.

- Research Process
Writing a good review article

Why is data validation important in research?
You may also like.

Page-Turner Articles are More Than Just Good Arguments: Be Mindful of Tone and Structure!

A Must-see for Researchers! How to Ensure Inclusivity in Your Scientific Writing

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
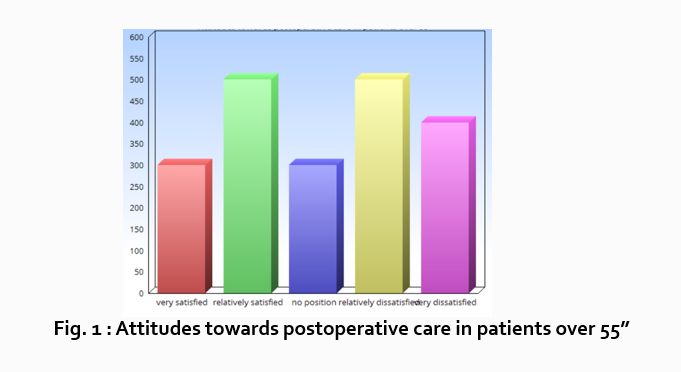
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
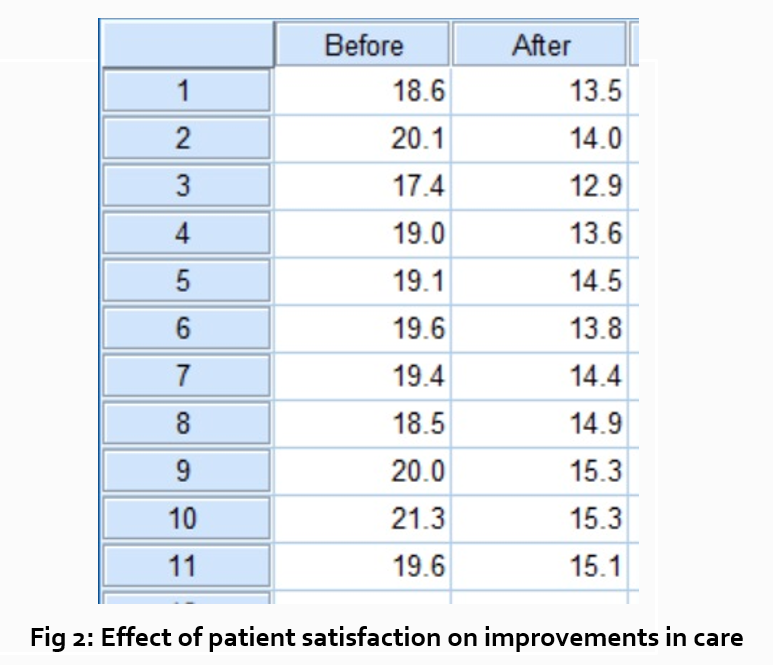
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
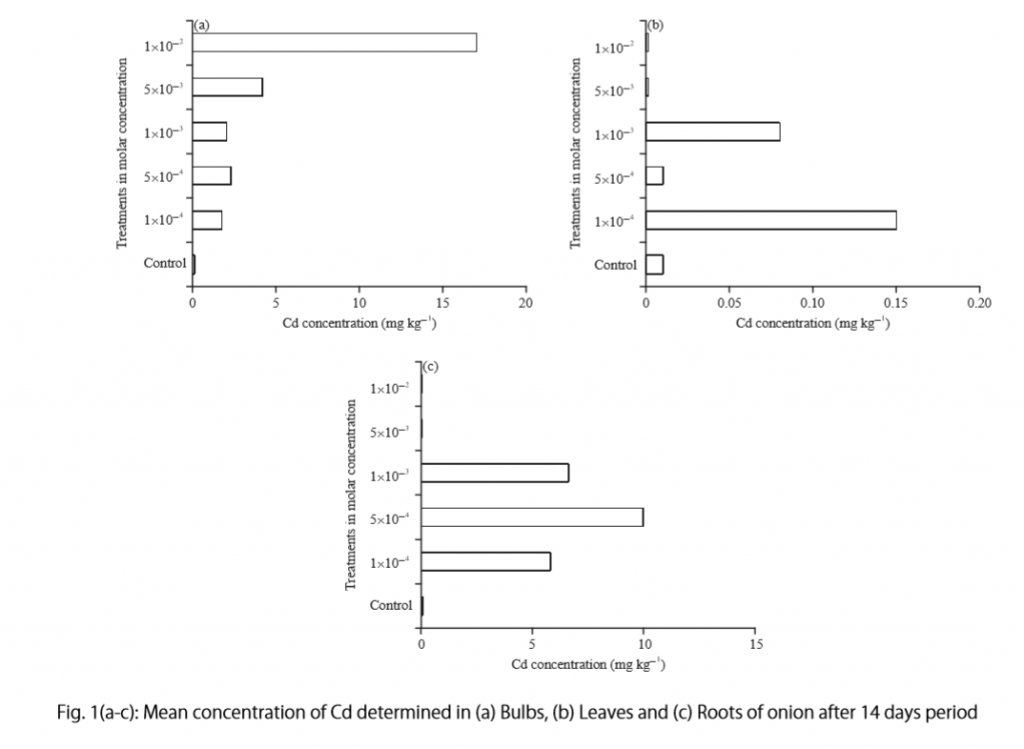
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper.
- Writing a lab report
- INTRODUCTION
Writing a "good" results section
Figures and Captions in Lab Reports
"Results Checklist" from: How to Write a Good Scientific Paper. Chris A. Mack. SPIE. 2018.
Additional tips for results sections.
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web
This is the core of the paper. Don't start the results sections with methods you left out of the Materials and Methods section. You need to give an overall description of the experiments and present the data you found.
- Factual statements supported by evidence. Short and sweet without excess words
- Present representative data rather than endlessly repetitive data
- Discuss variables only if they had an effect (positive or negative)
- Use meaningful statistics
- Avoid redundancy. If it is in the tables or captions you may not need to repeat it
A short article by Dr. Brett Couch and Dr. Deena Wassenberg, Biology Program, University of Minnesota
- Present the results of the paper, in logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary.
- Explain the results and show how they help to answer the research questions posed in the Introduction. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained.
- Avoid: presenting results that are never discussed; presenting results in chronological order rather than logical order; ignoring results that do not support the conclusions;
- Number tables and figures separately beginning with 1 (i.e. Table 1, Table 2, Figure 1, etc.).
- Do not attempt to evaluate the results in this section. Report only what you found; hold all discussion of the significance of the results for the Discussion section.
- It is not necessary to describe every step of your statistical analyses. Scientists understand all about null hypotheses, rejection rules, and so forth and do not need to be reminded of them. Just say something like, "Honeybees did not use the flowers in proportion to their availability (X2 = 7.9, p<0.05, d.f.= 4, chi-square test)." Likewise, cite tables and figures without describing in detail how the data were manipulated. Explanations of this sort should appear in a legend or caption written on the same page as the figure or table.
- You must refer in the text to each figure or table you include in your paper.
- Tables generally should report summary-level data, such as means ± standard deviations, rather than all your raw data. A long list of all your individual observations will mean much less than a few concise, easy-to-read tables or figures that bring out the main findings of your study.
- Only use a figure (graph) when the data lend themselves to a good visual representation. Avoid using figures that show too many variables or trends at once, because they can be hard to understand.
From: https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/imrad-results-discussion
- << Previous: METHODS
- Next: DISCUSSION >>
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 9:33 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 7. The Results
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The results section is where you report the findings of your study based upon the methodology [or methodologies] you applied to gather information. The results section should state the findings of the research arranged in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation. A section describing results should be particularly detailed if your paper includes data generated from your own research.
Annesley, Thomas M. "Show Your Cards: The Results Section and the Poker Game." Clinical Chemistry 56 (July 2010): 1066-1070.
Importance of a Good Results Section
When formulating the results section, it's important to remember that the results of a study do not prove anything . Findings can only confirm or reject the hypothesis underpinning your study. However, the act of articulating the results helps you to understand the problem from within, to break it into pieces, and to view the research problem from various perspectives.
The page length of this section is set by the amount and types of data to be reported . Be concise. Use non-textual elements appropriately, such as figures and tables, to present findings more effectively. In deciding what data to describe in your results section, you must clearly distinguish information that would normally be included in a research paper from any raw data or other content that could be included as an appendix. In general, raw data that has not been summarized should not be included in the main text of your paper unless requested to do so by your professor.
Avoid providing data that is not critical to answering the research question . The background information you described in the introduction section should provide the reader with any additional context or explanation needed to understand the results. A good strategy is to always re-read the background section of your paper after you have written up your results to ensure that the reader has enough context to understand the results [and, later, how you interpreted the results in the discussion section of your paper that follows].
Bavdekar, Sandeep B. and Sneha Chandak. "Results: Unraveling the Findings." Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 63 (September 2015): 44-46; Brett, Paul. "A Genre Analysis of the Results Section of Sociology Articles." English for Specific Speakers 13 (1994): 47-59; Go to English for Specific Purposes on ScienceDirect;Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section. San Francisco Edit; "Reporting Findings." In Making Sense of Social Research Malcolm Williams, editor. (London;: SAGE Publications, 2003) pp. 188-207.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Organization and Approach
For most research papers in the social and behavioral sciences, there are two possible ways of organizing the results . Both approaches are appropriate in how you report your findings, but use only one approach.
- Present a synopsis of the results followed by an explanation of key findings . This approach can be used to highlight important findings. For example, you may have noticed an unusual correlation between two variables during the analysis of your findings. It is appropriate to highlight this finding in the results section. However, speculating as to why this correlation exists and offering a hypothesis about what may be happening belongs in the discussion section of your paper.
- Present a result and then explain it, before presenting the next result then explaining it, and so on, then end with an overall synopsis . This is the preferred approach if you have multiple results of equal significance. It is more common in longer papers because it helps the reader to better understand each finding. In this model, it is helpful to provide a brief conclusion that ties each of the findings together and provides a narrative bridge to the discussion section of the your paper.
NOTE: Just as the literature review should be arranged under conceptual categories rather than systematically describing each source, you should also organize your findings under key themes related to addressing the research problem. This can be done under either format noted above [i.e., a thorough explanation of the key results or a sequential, thematic description and explanation of each finding].
II. Content
In general, the content of your results section should include the following:
- Introductory context for understanding the results by restating the research problem underpinning your study . This is useful in re-orientating the reader's focus back to the research problem after having read a review of the literature and your explanation of the methods used for gathering and analyzing information.
- Inclusion of non-textual elements, such as, figures, charts, photos, maps, tables, etc. to further illustrate key findings, if appropriate . Rather than relying entirely on descriptive text, consider how your findings can be presented visually. This is a helpful way of condensing a lot of data into one place that can then be referred to in the text. Consider referring to appendices if there is a lot of non-textual elements.
- A systematic description of your results, highlighting for the reader observations that are most relevant to the topic under investigation . Not all results that emerge from the methodology used to gather information may be related to answering the " So What? " question. Do not confuse observations with interpretations; observations in this context refers to highlighting important findings you discovered through a process of reviewing prior literature and gathering data.
- The page length of your results section is guided by the amount and types of data to be reported . However, focus on findings that are important and related to addressing the research problem. It is not uncommon to have unanticipated results that are not relevant to answering the research question. This is not to say that you don't acknowledge tangential findings and, in fact, can be referred to as areas for further research in the conclusion of your paper. However, spending time in the results section describing tangential findings clutters your overall results section and distracts the reader.
- A short paragraph that concludes the results section by synthesizing the key findings of the study . Highlight the most important findings you want readers to remember as they transition into the discussion section. This is particularly important if, for example, there are many results to report, the findings are complicated or unanticipated, or they are impactful or actionable in some way [i.e., able to be pursued in a feasible way applied to practice].
NOTE: Always use the past tense when referring to your study's findings. Reference to findings should always be described as having already happened because the method used to gather the information has been completed.
III. Problems to Avoid
When writing the results section, avoid doing the following :
- Discussing or interpreting your results . Save this for the discussion section of your paper, although where appropriate, you should compare or contrast specific results to those found in other studies [e.g., "Similar to the work of Smith [1990], one of the findings of this study is the strong correlation between motivation and academic achievement...."].
- Reporting background information or attempting to explain your findings. This should have been done in your introduction section, but don't panic! Often the results of a study point to the need for additional background information or to explain the topic further, so don't think you did something wrong. Writing up research is rarely a linear process. Always revise your introduction as needed.
- Ignoring negative results . A negative result generally refers to a finding that does not support the underlying assumptions of your study. Do not ignore them. Document these findings and then state in your discussion section why you believe a negative result emerged from your study. Note that negative results, and how you handle them, can give you an opportunity to write a more engaging discussion section, therefore, don't be hesitant to highlight them.
- Including raw data or intermediate calculations . Ask your professor if you need to include any raw data generated by your study, such as transcripts from interviews or data files. If raw data is to be included, place it in an appendix or set of appendices that are referred to in the text.
- Be as factual and concise as possible in reporting your findings . Do not use phrases that are vague or non-specific, such as, "appeared to be greater than other variables..." or "demonstrates promising trends that...." Subjective modifiers should be explained in the discussion section of the paper [i.e., why did one variable appear greater? Or, how does the finding demonstrate a promising trend?].
- Presenting the same data or repeating the same information more than once . If you want to highlight a particular finding, it is appropriate to do so in the results section. However, you should emphasize its significance in relation to addressing the research problem in the discussion section. Do not repeat it in your results section because you can do that in the conclusion of your paper.
- Confusing figures with tables . Be sure to properly label any non-textual elements in your paper. Don't call a chart an illustration or a figure a table. If you are not sure, go here .
Annesley, Thomas M. "Show Your Cards: The Results Section and the Poker Game." Clinical Chemistry 56 (July 2010): 1066-1070; Bavdekar, Sandeep B. and Sneha Chandak. "Results: Unraveling the Findings." Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 63 (September 2015): 44-46; Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Caprette, David R. Writing Research Papers. Experimental Biosciences Resources. Rice University; Hancock, Dawson R. and Bob Algozzine. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers . 2nd ed. New York: Teachers College Press, 2011; Introduction to Nursing Research: Reporting Research Findings. Nursing Research: Open Access Nursing Research and Review Articles. (January 4, 2012); Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section. San Francisco Edit ; Ng, K. H. and W. C. Peh. "Writing the Results." Singapore Medical Journal 49 (2008): 967-968; Reporting Research Findings. Wilder Research, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Human Services. (February 2009); Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Results. Thesis Writing in the Sciences. Course Syllabus. University of Florida.
Writing Tip
Why Don't I Just Combine the Results Section with the Discussion Section?
It's not unusual to find articles in scholarly social science journals where the author(s) have combined a description of the findings with a discussion about their significance and implications. You could do this. However, if you are inexperienced writing research papers, consider creating two distinct sections for each section in your paper as a way to better organize your thoughts and, by extension, your paper. Think of the results section as the place where you report what your study found; think of the discussion section as the place where you interpret the information and answer the "So What?" question. As you become more skilled writing research papers, you can consider melding the results of your study with a discussion of its implications.
Driscoll, Dana Lynn and Aleksandra Kasztalska. Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
- << Previous: Insiderness
- Next: Using Non-Textual Elements >>
- Last Updated: May 30, 2024 9:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Turk J Urol
- v.39(Suppl 1); 2013 Sep
How to clearly articulate results and construct tables and figures in a scientific paper?
The writing of the results section of a scientific paper is very important for the readers for clearly understanding of the study. This review summarizes the rules for writing the results section of a scientific paper and describes the use of tables and figures.
Introduction
Medical articles consist of review articles, case reports, and letters to the editor which are prepared with the intention of publishing in journals related to the medical discipline of the author. For an academician to be able to progress in carreer, and make his/her activities known in the academic environment, require preparation of the protocol of his/her academic research article, and acquiring sufficient information, and experience related to the composition of this article. In this review article, the information related to the writing of the ‘Results’ section, and use of tables, and figures will be presented to the attention of the readers.
Writing the ‘Results’ section
The ‘Results’ section is perhaps the most important part of a research article. In fact the authors will share the results of their research/study with their readers. Renown British biologist Thomas Henry Huxley (1825–1895) indicated his feelings as “The great tragedy of science: the slaying of a beautiful hypothesis by an ugly fact.” which emphasizes the importance of accurately, and impressively written results.
In essence results provide a response for the question” What is found in the research performed?”. Therefore, it is the most vital part of the article. As a priority, while drafting the ‘Results’ section of a manuscript one should not firstly write down methods in the ‘Material and Method’ section. The first sentence should give information about the number of patients who met the inclusion criteria, and thus enrolled in the study. [ 1 ] Besides information about the number of patients excluded from the study, and the reasons for exclusion is very important in that they will enlighten the readers, and reviewers who critically evaluate the manuscript, and also reflect the seriousness of the study. On the other hand, the results obtained should be recorded in chronological order, and without any comments. [ 2 ] In this section use of simple present tense is more appropriate. The findings should be expressed in brief, lucid, and explicable words. The writing style should not be boring for the reader. During writing process of a research article, a generally ill-conceived point is that positive, and significant findings are more important, attractive, and valuable, while negative, and insignificant findings are worthless, and less attractive. A scientific research is not performed to confirm a hypothesis, rather to test it. Not only positive, and significant results are worth writing, on the other hand negative or statistically insignificant result which support fallacy of a widely accepted opinion might be valuable. Therefore, all findings obtained during research should be inclıuded in the ‘Results’ section. [ 1 ]
While writing the ‘Results’ section, the sequence of results, tabulated data, and information which will be illustrated as figures should be definitively indicated. In indicating insignificant changes, do not use expressions as “decreased” or “increased”, these words should be reserved for significant changes. If results related to more than one parameter would be reported, it is appropriate to write the results under the subheading of its related parameter so as to facilitate reading, and comprehension of information. [ 2 ] Only data, and information concerning the study in question should be included in the ‘Results’ section. Results not mentioned in this section should not be included in the ‘Discussion’ and ‘Summary’ sections. Since the results obtained by the authors are cited in the ‘Results’ section, any reference should not be indicated in this section. [ 3 ]
In the ‘Results’ section, numerical expressions should be written in technically appropriate terms. The number of digits (1, 2 or 3 digits) to be written after a comma (in Turkish) or a point (in especially American English) should be determined The number of digits written after the punctuation marks should not be changed all throughout the text. Data should be expressed as mean/median ± standard deviation. Data as age, and scale scores should be indicated together with ranges of values. Absolute numerical value corresponding to a percentage must be also indicated. P values calculated in statistical analysis should be expressed in their absolute values. While writing p values of statistically significant data, instead of p<0.05 the actual level of significance should be recorded. If p value is smaller than 0.001, then it can be written as p <0.01. [ 2 ] While writing the ‘Results’ section, significant data which should be recalled by the readers must be indicated in the main text. It will be appropriate to indicate other demographic numerical details in tables or figures.
As an example elucidating the abovementioned topics a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the Turkish Journal of Urology in the year 2007 (Türk Üroloji Dergisi 2007;33:18–23) is presented below:
“A total of 9 (56.2%) female, and 7 (43.8%) male patients with were included in this study. Mean age of all the patients was 44.3±13.8 (17–65) years, and mean dimensions of the adrenal mass was 4.5±3.4 (1–14) cm. Mean ages of the male, and female patients were 44.1 (30–65), and 42.4 (17–64) years, while mean diameters of adrenal masses were 3.2 (1–5), and 4.5 (1–14) cm (p age =0.963, p mass size =0.206). Surgical procedures were realized using transperitoneal approach through Chevron incision in 1 (6.2%), and retroperitoneal approach using flank incision with removal of the 11. rib in 15 (93.7%) patients. Right (n=6; 37.5%), and left (n=2; 12.5%) adrenalectomies were performed. Two (12.5%) patients underwent bilateral adrenalectomy in the same session because of clinical Cushing’s syndrome persisted despite transsphenoidal hipophysectomy. Mean operative time, and length of the hospital stay were 135 (65–190) min, and 3 (2–6) days, respectively. While resecting 11. rib during retroperitoneal adrenalectomy performed in 1 patient, pleura was perforated for nearly 1.5 cm. The perforated region was drained, and closed intraoperatively with 4/0 polyglyctan sutures. The patient did not develop postoperative pneumothorax. In none of the patients postoperative complications as pneumothorax, bleeding, prolonged drainage were seen. Results of histopathological analysis of the specimens retrieved at the end of the operation were summarized in Table 1 .” Table 1. Histopathological examination results of the patients Histopathological diagnosis Men n (%) Women n (%) Total n (%) Adrenal cortical adenoma 5 (31.3) 6 (37.6) 11 (68.8) Pheochromocytoma 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) 2 (12.6) Ganglioneuroma 1 (6.2) - 1 (6.2) Myelolipoma - 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) Adrenal carcinoma - 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) Total 7 (43.7) 9 (56.2) 16 (100) Open in a separate window
Use of tables, and figures
To prevent the audience from getting bored while reading a scientific article, some of the data should be expressed in a visual format in graphics, and figures rather than crowded numerical values in the text. Peer-reviewers frequently look at tables, and figures. High quality tables, and figures increase the chance of acceptance of the manuscript for publication.
Number of tables in the manuscript should not exceed the number recommended by the editorial board of the journal. Data in the main text, and tables should not be repeated many times. Tables should be comprehensible, and a reader should be able to express an opinion about the results just at looking at the tables without reading the main text. Data included in tables should comply with those mentioned in the main text, and percentages in rows, and columns should be summed up accurately. Unit of each variable should be absolutely defined. Sampling size of each group should be absolutely indicated. Values should be expressed as values±standard error, range or 95% confidence interval. Tables should include precise p values, and level of significance as assessed with statistical analysis should be indicated in footnotes. [ 2 ] Use of abbreviations in tables should be avoided, if abbreviations are required they should be defined explicitly in the footnotes or legends of the tables. As a general rule, rows should be arranged as double-spaced Besides do not use pattern coloring for cells of rows, and columns. Values included in tables should be correctly approximated. [ 1 , 2 ]
As an example elucidating the abovementioned topics a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the Turkish Journal of Urology in the year 2007 (Türk Üroloji Dergisi 2007;33:18–23).is shown in Table 1 .
Most of the readers priorly prefer to look at figures, and graphs rather than reading lots of pages. Selection of appropriate types of graphs for demonstration of data is a critical decision which requires artist’s meticulousness. As is the case with tables, graphs, and figures should also disploay information not provided in the text. Bar, line, and pie graphs, scatter plots, and histograms are some examples of graphs. In graphs, independent variables should be represented on the horizontal, and dependent variables on the vertical axis. Number of subjects in every subgroup should be indicated The labels on each axis should be easily understandable. [ 2 ] The label of the Y axis should be written vertically from bottom to top. The fundamental point in writing explanatory notes for graphs, and figures is to help the readers understand the contents of them without referring to the main text. Meanings of abbreviations, and acronyms used in the graphs, and figures should be provided in explanatory notes. In the explanatory notes striking data should be emphasized. Statistical tests used, levels of significance, sampling size, stains used for analyses, and magnification rate should be written in order to facilitate comprehension of the study procedures. [ 1 , 2 ]
Flow diagram can be utilized in the ‘Results’ section. This diagram facilitates comprehension of the results obtained at certain steps of monitorization during the research process. Flow diagram can be used either in the ‘Results’ or ‘Material and Method’ section. [ 2 , 3 ]
Histopathological analyses, surgical technique or radiological images which are considered to be more useful for the comprehension of the text by the readers can be visually displayed. Important findings should be marked on photos, and their definitions should be provided clearly in the explanatory legends. [ 1 ]
As an example elucidating the abovementioned issues, graphics, and flow diagram in the ‘Results’ section of a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the World Journal of Urology in the year 2010 (World J Urol 2010;28:17–22.) are shown in Figures 1 , and and2 2 .

a The mean SHIM scores of the groups before and after treatment. SHIM sexual health inventory for male. b The mean IPSS scores of the groups before and after treatment. IPSS international prostate symptom score

Flowchart showing patients’ progress during the study. SHIM sexual health inventory for male, IIEF international index of erectile function, IPSS international prostate symptom score, QoL quality of life, Q max maximum urinary flow rate. PRV post voiding residual urine volume
In conclusion, in line with the motto of the famous German physicist Albert Einstein (1879–1955). ‘If you are out to describe the truth, leave elegance to the tailor .’ results obtained in a scientific research article should be expressed accurately, and with a masterstroke of a tailor in compliance with certain rules which will ensure acceptability of the scientific manuscript by the editorial board of the journal, and also facilitate its intelligibility by the readers.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an APA Results Section
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Verywell / Nusha Ashjaee
What to Include in an APA Results Section
- Justify Claims
- Summarize Results
Report All Relevant Results
- Report Statistical Findings
Include Tables and Figures
What not to include in an apa results section.
Psychology papers generally follow a specific structure. One important section of a paper is known as the results section. An APA results section of a psychology paper summarizes the data that was collected and the statistical analyses that were performed. The goal of this section is to report the results of your study or experiment without any type of subjective interpretation.
At a Glance
The results section is a vital part of an APA paper that summarizes a study's findings and statistical analysis. This section often includes descriptive text, tables, and figures to help summarize the findings. The focus is purely on summarizing and presenting the findings and should not include any interpretation, since you'll cover that in the subsequent discussion section.
This article covers how to write an APA results section, including what to include and what to avoid.
The results section is the third section of a psychology paper. It will appear after the introduction and methods sections and before the discussion section.
The results section should include:
- A summary of the research findings.
- Information about participant flow, recruitment, retention, and attrition. If some participants started the study and later left or failed to complete the study, then this should be described.
- Information about any reasons why some data might have been excluded from the study.
- Statistical information including samples sizes and statistical tests that were used. It should report standard deviations, p-values, and other measures of interest.
Results Should Justify Your Claims
Report data in order to sufficiently justify your conclusions. Since you'll be talking about your own interpretation of the results in the discussion section, you need to be sure that the information reported in the results section justifies your claims.
When you start writing your discussion section, you can then look back on your results to ensure that all the data you need are there to fully support your conclusions. Be sure not to make claims in your discussion section that are not supported by the findings described in your results section.
Summarize Your Results
Remember, you are summarizing the results of your psychological study, not reporting them in full detail. The results section should be a relatively brief overview of your findings, not a complete presentation of every single number and calculation.
If you choose, you can create a supplemental online archive where other researchers can access the raw data if they choose.
How long should a results section be?
The length of your results section will vary depending on the nature of your paper and the complexity of your research. In most cases, this will be the shortest section of your paper.
Just as the results section of your psychology paper should sufficiently justify your claims, it should also provide an accurate look at what you found in your study. Be sure to mention all relevant information.
Don't omit findings simply because they failed to support your predictions.
Your hypothesis may have expected more statistically significant results or your study didn't support your hypothesis , but that doesn't mean that the conclusions you reach are not useful. Provide data about what you found in your results section, then save your interpretation for what the results might mean in the discussion section.
While your study might not have supported your original predictions, your finding can provide important inspiration for future explorations into a topic.
How is the results section different from the discussion section?
The results section provides the results of your study or experiment. The goal of the section is to report what happened and the statistical analyses you performed. The discussion section is where you will examine what these results mean and whether they support or fail to support your hypothesis.
Report Your Statistical Findings
Always assume that your readers have a solid understanding of statistical concepts. There's no need to explain what a t-test is or how a one-way ANOVA works. Your responsibility is to report the results of your study, not to teach your readers how to analyze or interpret statistics.
Include Effect Sizes
The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association recommends including effect sizes in your results section so that readers can appreciate the importance of your study's findings.
Your results section should include both text and illustrations. Presenting data in this way makes it easier for readers to quickly look at your results.
Structure your results section around tables or figures that summarize the results of your statistical analysis. In many cases, the easiest way to accomplish this is to first create your tables and figures and then organize them in a logical way. Next, write the summary text to support your illustrative materials.
Only include tables and figures if you are going to talk about them in the body text of your results section.
In addition to knowing what you should include in the results section of your psychology paper, it's also important to be aware of things that you should avoid putting in this section:
Cause-and-Effect Conclusions
Don't draw cause-effect conclusions. Avoid making any claims suggesting that your result "proves" that something is true.
Interpretations
Present the data without editorializing it. Save your comments and interpretations for the discussion section of your paper.
Statistics Without Context
Don't include statistics without narration. The results section should not be a numbers dump. Instead, you should sequentially narrate what these numbers mean.
Don't include the raw data in the results section. The results section should be a concise presentation of the results. If there is raw data that would be useful, include it in the appendix .
Don't only rely on descriptive text. Use tables and figures to present these findings when appropriate. This makes the results section easier to read and can convey a great deal of information quickly.
Repeated Data
Don't present the same data twice in your illustrative materials. If you have already presented some data in a table, don't present it again in a figure. If you have presented data in a figure, don't present it again in a table.
All of Your Findings
Don't feel like you have to include everything. If data is irrelevant to the research question, don't include it in the results section.
But Don't Skip Relevant Data
Don't leave out results because they don't support your claims. Even if your data does not support your hypothesis, including it in your findings is essential if it's relevant.
More Tips for Writing a Results Section
If you are struggling, there are a few things to remember that might help:
- Use the past tense . The results section should be written in the past tense.
- Be concise and objective . You will have the opportunity to give your own interpretations of the results in the discussion section.
- Use APA format . As you are writing your results section, keep a style guide on hand. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association is the official source for APA style.
- Visit your library . Read some journal articles that are on your topic. Pay attention to how the authors present the results of their research.
- Get a second opinion . If possible, take your paper to your school's writing lab for additional assistance.
What This Means For You
Remember, the results section of your paper is all about providing the data from your study. This section is often the shortest part of your paper, and in most cases, the most clinical.
Be sure not to include any subjective interpretation of the results. Simply relay the data in the most objective and straightforward way possible. You can then provide your own analysis of what these results mean in the discussion section of your paper.
Bavdekar SB, Chandak S. Results: Unraveling the findings . J Assoc Physicians India . 2015 Sep;63(9):44-6. PMID:27608866.
Snyder N, Foltz C, Lendner M, Vaccaro AR. How to write an effective results section . Clin Spine Surg . 2019;32(7):295-296. doi:10.1097/BSD.0000000000000845
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
Purdue Online Writing Lab. APA sample paper: Experimental psychology .
Berkeley University. Reviewing test results .
Tuncel A, Atan A. How to clearly articulate results and construct tables and figures in a scientific paper ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):16-19. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.048
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper
Table of Contents
Laura Moro-Martin, freelance scientific writer on Kolabtree, provides expert tips on how to write the results section of a research paper .
You have prepared a detailed −but concise− Methods section . Now it is time to write the Results of your research article. This part of the paper reports the findings of the experiments that you conducted to answer the research question(s). The Results can be considered the nucleus of a scientific article because they justify your claims, so you need to ensure that they are clear and understandable. You are telling a story −of course, a scientific story− and you want the readers to picture that same story in their minds. Let’s see how to avoid that your message ends up as in the ‘telephone game’.
The Results Section: Goals and Structure
Depending on the discipline, journal, and the nature of the study, the structure of the article can differ. We will focus on articles were the Results and Discussion appear in two separate sections, but it is possible in some cases to combine them.
In the Results section, you provide an overall description of the experiments and present the data that you obtained in a logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary. The Results section should simply state your findings without bias or interpretation. For example, in your analysis, you may have noticed a significant correlation between two variables never described before. It is correct to explain this in the Results section. However, speculation about the reasons for this correlation should go in the Discussion section of your paper.
In general, the Results section includes the following elements:
- A very short introductory context that repeats the research question and helps to understand your results.
- Report on data collection, recruitment, and/or participants. For example, in the case of clinical research, it is common to include a first table summarizing the demographic, clinical, and other relevant characteristics of the study participants.
- A systematic description of the main findings in a logical order (generally following the order of the Methods section), highlighting the most relevant results.
- Other important secondary findings, such as secondary outcomes or subgroup analyses (remember that you do not need to mention any single result).
- Visual elements, such as, figures, charts, maps, tables, etc. that summarize and illustrate the findings. These elements should be cited in the text and numbered in order. Figures and tables should be able to stand on its own without the text, which means that the legend should include enough information to understand the non-textual element.
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper: Tips
The first tip −applicable to other sections of the paper too− is to check and apply the requirements of the journal to which you are submitting your work.
In the Results section, you need to write concisely and objectively, leaving interpretation for the Discussion section. As always, ‘learning from others’ can help you. Select a few papers from your field, including some published in your target journal, which you consider ‘good quality’ and well written. Read them carefully and observe how the Results section is structured, the type and amount of information provided, and how the findings are exposed in a logical order. Keep an eye on visual elements, such as figures, tables, and supplementary materials. Understand what works well in those papers to effectively convey their findings, and apply it to your writing.
Your Results section needs to describe the sequence of what you did and found, the frequency of occurrence of a particular event or result, the quantities of your observations, and the causality (i.e. the relationships or connections) between the events that you observed.
To organize the results, you can try to provide them alongside the research questions. In practice, this means that you will organize this section based on the sequence of tables and figures summarizing the results of your statistical analysis. In this way, it will be easier for readers to look at and understand your findings. You need to report your statistical findings, without describing every step of your statistical analysis. Tables and figures generally report summary-level data (for example, means and standard deviations), rather than all the raw data.
Following, you can prepare the summary text to support those visual elements. You need not only to present but also to explain your findings, showing how they help to address the research question(s) and how they align with the objectives that you presented in the Introduction . Keep in mind that results do not speak for themselves, so if you do not describe them in words, the reader may perceive the findings differently from you. Build coherence along this section using goal statements and explicit reasoning (guide the reader through your reasoning, including sentences of this type: ‘In order to…, we performed….’; ‘In view of this result, we ….’, etc.).
In summary, the general steps for writing the Results section of a research article are:
- Check the guidelines of your target journal and read articles that it has published in similar topics to your study.
- Catalogue your findings in relation to the journal requirements, and design figures and tables to organize your data.
- Write the Results section following the order of figures and tables.
- Edit and revise your draft and seek additional input from colleagues or experts.
The Style of the Results Section
‘If you are out to describe the truth, leave elegance to the tailor’, Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann said. Although the scope of the Results section −and of scientific papers in general− is eminently functional, this does not mean that you cannot write well. Try to improve the rhythm to move the reader along, use transitions and connectors between different sections and paragraphs, and dedicate time to revise your writing.
The Results section should be written in the past tense. Although writing in the passive voice may be tempting, the use of the active voice makes the action much more visualizable. The passive voice weakens the power of language and increases the number of words needed to say the same thing, so we recommend using the active voice as much as possible. Another tip to make your language visualizable and reduce sentence length is the use of verbal phrases instead of long nouns. For example, instead of writing ‘As shown in Table 1, there was a significant increase in gene expression’, you can say ‘As shown in Table 1, gene expression increased significantly’.
Get a Second (And Even Third) Opinion
Writing a scientific article is not an individual work. Take advantage of your co-authors by making them check the Results section and adding their comments and suggestions. Not only that, but an external opinion will help you to identify misinterpretations or errors. Ask a colleague that is not directly involved in the work to review your Results and then try to evaluate what your colleague did or did not understand. If needed, seek additional help from a qualified expert.
Common Errors to Avoid While Writing the Results Section
Several mistakes frequently occur when you write the Results section of a research paper. Here we have collected a few examples:
- Including raw results and/or endlessly repetitive data. You do not need to present every single number and calculation, but a summary of the results. If relevant, raw data can be included in supplementary materials.
- Including redundant information. If data are contained in the tables or figures, you do not need to repeat all of them in the Results section. You will have the opportunity to highlight the most relevant results in the Discussion .
- Repeating background information or methods , or introducing several sentences of introductory information (if you feel that more background information is necessary to present a result, consider inserting that information in the Introduction ).
- Results and Methods do not match . You need to explain the methodology used to obtain all the experimental observations.
- Ignoring negative results or results that do not support the conclusions. In addition to posing potential ethical concerns on your work, reviewers will not like it. You need to mention all relevant findings, even if they failed to support your predictions or hypotheses. Negative results are useful and will guide future studies on the topic. Provide your interpretation for negative results in the Discussion .
- Discussing or interpreting the results . Leave that for the Discussion , unless your target journal allows preparing one section combining Results and Discussion .
- Errors in figures/tables are varied and common . Examples of errors include using an excessive number of figures/tables (it is a good idea to select the most relevant ones and move the rest to supplementary materials), very complex figures/tables (hard-to-read figures with many subfigures or enormous tables may confuse your readers; think how these elements will be visualized in the final format of the article), difficult to interpret figures/tables (cryptic abbreviations; inadequate use of colors, axis, scales, symbols, etc.), and figures/tables that are not self-standing (figures/tables require a caption, all abbreviations used need to be explained in the legend or a footnote, and statistical tests applied are frequently reported). Do not include tables and figures that are not mentioned in the body text of your Results .
In summary, the Results section is the nucleus of your paper that justifies your claims. Take time to adequately organize it and prepare understandable figures and tables to convey your message to the reader. Good writing!
- The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. https://abacus.bates.edu/~ganderso/biology/resources/writing/HTWsections.html – methods (accessed on 30th September 2020)
- Organizing Academic Research Papers: 7. The Results. https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185931 (accessed on 30th September 2020)
- Kendra Cherry. How to Write an APA Results Section. https://www.verywellmind.com/how-to-write-a-results-section-2795727 (accessed on 30th September 2020)
- Chapin Rodríguez. Empowering your scientific language by making it “visualizable”. http://creaducate.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/tipsheet36_visualizable-lang-tip-sheet.pdf (accessed on 1st October 2020)
- IMRaD Results Discussion. https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/imrad-results-discussion (accessed on 1st October 2020)
- Writing the Results Section for a Research Paper. https://wordvice.com/writing-the-results-section-for-a-research-paper/ (accessed on 1st October 2020)
- Scott L. Montgomery. The Chicago Guide to Communicating Science , Chapter 9. Second edition, The University of Chicago Press, 2017.
- Hilary Glasman-Deal . Science Research Writing for Non-Native Speakers of English, Unit 2 . Imperial College Press, 2010.
Unlock Corporate Benefits • Secure Payment Assistance • Onboarding Support • Dedicated Account Manager
Sign up with your professional email to avail special advances offered against purchase orders, seamless multi-channel payments, and extended support for agreements.
About Author
Ramya Sriram manages digital content and communications at Kolabtree (kolabtree.com), the world's largest freelancing platform for scientists. She has over a decade of experience in publishing, advertising and digital content creation.
Related Posts
Spotlight: kolabtree’s regulatory medical writer dr. nare simonyan, how healthcare writers can help your business , the benefits of outsourcing in continuing medical education (cme), leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

Organizing Academic Research Papers: 7. The Results
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The results section of the research paper is where you report the findings of your study based upon the information gathered as a result of the methodology [or methodologies] you applied. The results section should simply state the findings, without bias or interpretation, and arranged in a logical sequence. The results section should always be written in the past tense. A section describing results [a.k.a., "findings"] is particularly necessary if your paper includes data generated from your own research.
Importance of a Good Results Section
When formulating the results section, it's important to remember that the results of a study do not prove anything . Research results can only confirm or reject the research problem underpinning your study. However, the act of articulating the results helps you to understand the problem from within, to break it into pieces, and to view the research problem from various perspectives.
The page length of this section is set by the amount and types of data to be reported . Be concise, using non-textual elements, such as figures and tables, if appropriate, to present results more effectively. In deciding what data to describe in your results section, you must clearly distinguish material that would normally be included in a research paper from any raw data or other material that could be included as an appendix. In general, raw data should not be included in the main text of your paper unless requested to do so by your professor.
Avoid providing data that is not critical to answering the research question . The background information you described in the introduction section should provide the reader with any additional context or explanation needed to understand the results. A good rule is to always re-read the background section of your paper after you have written up your results to ensure that the reader has enough context to understand the results [and, later, how you interpreted the results in the discussion section of your paper].
Bates College; Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Results . The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
For most research paper formats, there are two ways of presenting and organizing the results .
- Present the results followed by a short explanation of the findings . For example, you may have noticed an unusual correlation between two variables during the analysis of your findings. It is correct to point this out in the results section. However, speculating as to why this correlation exists, and offering a hypothesis about what may be happening, belongs in the discussion section of your paper.
- Present a section and then discuss it, before presenting the next section then discussing it, and so on . This is more common in longer papers because it helps the reader to better understand each finding. In this model, it can be helpful to provide a brief conclusion in the results section that ties each of the findings together and links to the discussion.
NOTE: The discussion section should generally follow the same format chosen in presenting and organizing the results.
II. Content
In general, the content of your results section should include the following elements:
- An introductory context for understanding the results by restating the research problem that underpins the purpose of your study.
- A summary of your key findings arranged in a logical sequence that generally follows your methodology section.
- Inclusion of non-textual elements, such as, figures, charts, photos, maps, tables, etc. to further illustrate the findings, if appropriate.
- In the text, a systematic description of your results, highlighting for the reader observations that are most relevant to the topic under investigation [remember that not all results that emerge from the methodology that you used to gather the data may be relevant].
- Use of the past tense when refering to your results.
- The page length of your results section is guided by the amount and types of data to be reported. However, focus only on findings that are important and related to addressing the research problem.
Using Non-textual Elements
- Either place figures, tables, charts, etc. within the text of the result, or include them in the back of the report--do one or the other but never do both.
- In the text, refer to each non-textual element in numbered order [e.g., Table 1, Table 2; Chart 1, Chart 2; Map 1, Map 2].
- If you place non-textual elements at the end of the report, make sure they are clearly distinguished from any attached appendix materials, such as raw data.
- Regardless of placement, each non-textual element must be numbered consecutively and complete with caption [caption goes under the figure, table, chart, etc.]
- Each non-textual element must be titled, numbered consecutively, and complete with a heading [title with description goes above the figure, table, chart, etc.].
- In proofreading your results section, be sure that each non-textual element is sufficiently complete so that it could stand on its own, separate from the text.
III. Problems to Avoid
When writing the results section, avoid doing the following :
- Discussing or interpreting your results . Save all this for the next section of your paper, although where appropriate, you should compare or contrast specific results to those found in other studies [e.g., "Similar to Smith [1990], one of the findings of this study is the strong correlation between motivation and academic achievement...."].
- Reporting background information or attempting to explain your findings ; this should have been done in your Introduction section, but don't panic! Often the results of a study point to the need to provide additional background information or to explain the topic further, so don't think you did something wrong. Revise your introduction as needed.
- Ignoring negative results . If some of your results fail to support your hypothesis, do not ignore them. Document them, then state in your discussion section why you believe a negative result emerged from your study. Note that negative results, and how you handle them, often provides you with the opportunity to write a more engaging discussion section, therefore, don't be afraid to highlight them.
- Including raw data or intermediate calculations . Ask your professor if you need to include any raw data generated by your study, such as transcripts from interviews or data files. If raw data is to be included, place it in an appendix or set of appendices that are referred to in the text.
- Be as factual and concise as possible in reporting your findings . Do not use phrases that are vague or non-specific, such as, "appeared to be greater or lesser than..." or "demonstrates promising trends that...."
- Presenting the same data or repeating the same information more than once . If you feel the need to highlight something, you will have a chance to do that in the discussion section.
- Confusing figures with tables . Be sure to properly label any non-textual elements in your paper. If you are not sure, look up the term in a dictionary.
Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Caprette, David R. Writing Research Papers . Experimental Biosciences Resources. Rice University; Hancock, Dawson R. and Bob Algozzine. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers . 2nd ed. New York: Teachers College Press, 2011; Introduction to Nursing Research: Reporting Research Findings. Nursing Research: Open Access Nursing Research and Review Articles. (January 4, 2012); Reporting Research Findings. Wilder Research, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Human Services. (February 2009); Results . The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Results . Thesis Writing in the Sciences. Course Syllabus. University of Florida.
Writing Tip
Why Don't I Just Combine the Results Section with the Discussion Section?
It's not unusual to find articles in social science journals where the author(s) have combined a description of the findings from the study with a discussion about their implications. You could do this. However, if you are inexperienced writing research papers, consider creating two sections for each element in your paper as a way to better organize your thoughts and, by extension, your paper. Think of the results section as the place where you report what your study found; think of the discussion section as the place where you interpret your data and answer the "so what?" question. As you become more skilled writing research papers, you may want to meld the results of your study with a discussion of its implications.
- << Previous: Quantitative Methods
- Next: Using Non-Textual Elements >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website

Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
How to Write an Effective Results Section
Affiliation.
- 1 Rothman Orthopaedics Institute, Philadelphia, PA.
- PMID: 31145152
- DOI: 10.1097/BSD.0000000000000845
Developing a well-written research paper is an important step in completing a scientific study. This paper is where the principle investigator and co-authors report the purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions of the study. A key element of writing a research paper is to clearly and objectively report the study's findings in the Results section. The Results section is where the authors inform the readers about the findings from the statistical analysis of the data collected to operationalize the study hypothesis, optimally adding novel information to the collective knowledge on the subject matter. By utilizing clear, concise, and well-organized writing techniques and visual aids in the reporting of the data, the author is able to construct a case for the research question at hand even without interpreting the data.
- Data Analysis
- Peer Review, Research*
- Publishing*
- Sample Size
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Results Section Of A Research Paper: How To Write It Properly

The results section of a research paper refers to the part that represents the study’s core findings from the methods that the researcher used to collect and analyze data. This section presents the results logically without interpretation or bias from the author.
Thus, this part of a research paper sets up the read for evaluation and analysis of the findings in the discussion section. Essentially, this section breaks down the information into several sentences, showing its importance to the research question. Writing results section in a research paper entails summarizing the gathered data and the performed statistical analysis. That way, the author presents or reports the results without subjective interpretation.
What Is The Results Section Of A Research Paper?
In its simplest definition, a research paper results section is where the researcher reports the findings of a study based on the applied methodology for gathering information. It’s the part where the author states the research findings in a logical sequence without interpreting them. If the research paper has data from actual research, this section should feature a detailed description of the results.
When writing a dissertation, a thesis, or any other academic paper, the result section should come third in sections’ sequence. It should follow the Methods and Materials presentation and the Discussion section comes after it. But most scientific papers present the Results and Discussion sections together. However, the results section answers the question, “What did your research uncover?”
Ideally, this section allows you to report findings in research paper, creating the basis for sufficiently justified conclusions. After writing the study findings in the results section, you interpret them in the subsequent discussion part. Therefore, your results section should report information that will justify your claims. That way, you can look back on the results section when writing the discussion part to ensure that your report supports your conclusions.
What Goes in the Results Section of a Research Paper?
This section should present results in research paper. The findings part of a research paper can differ in structure depending on the study, discipline, and journal. Nevertheless, the results section presents a description of the experiment while presenting the research results. When writing this part of your research paper, you can use graphs and tables if necessary.
However, state the findings without interpreting them. For instance, you can find a correlation between variables when analyzing data. In that case, your results section can explain this correlation without speculating about the causes of this correlation.
Here’s what to include in the results section of research paper:
A brief introductory of the context, repeating the research questions to help the readers understand the results A report about information collection, participants, and recruitment: for instance, you can include a demographic summary with the participants’ characteristics A systematic findings’ description, with a logical presentation highlighting relevant and crucial results A contextual data analysis explaining the meaning in sentences Information corresponding to the primary research questions Secondary findings like subgroup analysis and secondary outcomes Visual elements like charts, figures, tables, and maps, illustrating and summarizing the findings
Ensure that your results section cites and numbers visual elements in an orderly manner. Every table or figure should stand alone without text. That means visual elements should have adequate non-textual content to enable the audiences to understand their meanings.
If your study has a broad scope, several variables, or used methodologies that yielded different results, state the most relevant results only based on the research question you presented in your Introduction section.
The general rule is to leave out any data that doesn’t present your study’s direct outcome or findings. Unless the professor, advisor, university faulty, or your target journal requests you to combine the Results and Discussion sections, omit the interpretations and explanations of the results in this section.
How Long Should A Results Section Be?
The findings section of a research paper ranges between two and three pages, with tables, text, and figures. In most cases, universities and journals insist that this section shouldn’t exceed 1,000 words over four to nine paragraphs, usually with no references.
But a good findings section occupies 5% of the entire paper. For instance, this section should have 500 words if a dissertation has 10,000 words. If the educator didn’t specify the number of words to include in this chapter, use the data you collect to determine its length. Nevertheless, be as concise as possible by featuring only relevant results that answer your research question.
How To Write Results Section Of Research Paper
Perhaps, you have completed researching and writing the preceding sections, and you’re now wondering how to write results. By the time you’re composing this section, you already have findings or answers to your research questions. However, you don’t even know how to start a results section. And your search for guidelines landed you on this page.
Well, every research project is different and unique. That’s why researchers use different strategies when writing this section of their research papers. The scientific or academic discipline, specialization field, target journal, and the author are factors influencing how you write this section. Nevertheless, there’s a general way of writing this section, although it might differ slightly between disciplines. Here’s how to write results section in a research paper.
Check the instructions or guidelines. Check their instructions or guidelines first, whether you’re writing the research paper as part of your coursework or for an academic journal. These guidelines outline the requirements for presenting results in research papers. Also, check the published articles to know how to approach this section. When reviewing the procedures, check content restrictions and length. Essentially, learn everything you can about this section from the instructions or guidelines before you start writing. Reflect on your research findings. With instructions and guidelines in mind, reflect on your research findings to determine how to present them in your research paper. Decide on the best way to show the results so that they can answer the research question. Also, strive to clarify and streamline your report, especially with a complex and lengthy results section. You can use subheadings to avoid peripheral and excessive details. Additionally, consider breaking down the content to make it easy for the readers to understand or remember. Your hypothesis, research question, or methodologies might influence the structure of the findings sections. Nevertheless, a hierarchy of importance, chronological order, or meaningful grouping of categories or themes can be an effective way of presenting your findings. Design your visual presentations. Visual presentations improve the textual report of the research findings. Therefore, decide on the figures and styles to use in your tables, graphs, photos, and maps. However, check the instructions and guidelines of your faculty or journal to determine the visual aids you can use. Also, check what the guidelines say about their formats and design elements. Ideally, number the figures and tables according to their mention in the text. Additionally, your figures and tables should be self-explanatory. Write your findings section. Writing the results section of a research paper entails communicating the information you gathered from your study. Ideally, be as objective and factual as possible. If you gathered complex information, try to simplify and present it accurately, precisely, and clearly. Therefore, use well-structured sentences instead of complex expressions and phrases. Also, use an active voice and past tense since you’ve already done the research. Additionally, use correct spelling, grammar, and punctuation. Take your time to present the findings in the best way possible to focus your readers on your study objectives while preparing them for the coming speculations, interpretations, and recommendations. Edit Your Findings Section. Once you’ve written the results part of your paper, please go through it to ensure that you’ve presented your study findings in the best way possible. Make sure that the content of this section is factual, accurate, and without errors. You’ve taken a considerable amount of time to compose the results scientific paper audiences will find interesting to read. Therefore, take a moment to go through the draft and eliminate all errors.
Practical Tips on How to Write a Results Section of a Research Paper
The results part of a research paper aims to present the key findings objectively in a logical and orderly sequence using text and illustrative materials. A common mistake that many authors make is confusing the information in the discussion and the results sections. To avoid this, focus on presenting your research findings without interpreting them or speculating about them.
The following tips on how to write a results section should make this task easier for you:
Summarize your study results: Instead of reporting the findings in full detail, summarize them. That way, you can develop an overview of the results. Present relevant findings only: Don’t report everything you found during your research. Instead, present pertinent information only. That means taking time to analyze your results to know what your audiences want to know. Report statistical findings: When writing this section, assume that the audiences understand statistical concepts. Therefore, don’t try to explain the nitty-gritty in this section. Remember that your work is to report your study’s findings in this section. Be objective and concise: You can interpret the findings in the discussion sections. Therefore, focus on presenting the results objectively and concisely in this section. Use the suitable format: Use the correct style to present the findings depending on your study field.
Get Professional Help with the Research Section
Maybe you’re pursuing your graduate or undergraduate studies but cannot write the results part of your paper. Perhaps, you’re done researching and analyzing information, but this section proves too tricky for you to write. Well, you’re not alone because many students across the world struggle to present their research findings.
Luckily, our highly educated, talented, and experienced writers are always ready to assist such learners. If you are stuck with the results part of your paper, our professionals can help you . We offer high-quality, custom writing help online. We’re a reliable team of experts with a sterling reputation for providing comprehensive assistance to college, high school, and university learners. We deliver highly informative academic papers after conducting extensive and in-depth research. Contact us saying something like, “please do my thesis” to get quality help with your paper!

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates

- Foundations
- Write Paper
Search form
- Experiments
- Anthropology
- Self-Esteem
- Social Anxiety

- Research Paper >
Writing a Results Section
The next stage of any research paper: writing the results section, announcing your findings to the world.
This article is a part of the guide:
- Outline Examples
- Example of a Paper
- Write a Hypothesis
- Introduction
Browse Full Outline
- 1 Write a Research Paper
- 2 Writing a Paper
- 3.1 Write an Outline
- 3.2 Outline Examples
- 4.1 Thesis Statement
- 4.2 Write a Hypothesis
- 5.2 Abstract
- 5.3 Introduction
- 5.4 Methods
- 5.5 Results
- 5.6 Discussion
- 5.7 Conclusion
- 5.8 Bibliography
- 6.1 Table of Contents
- 6.2 Acknowledgements
- 6.3 Appendix
- 7.1 In Text Citations
- 7.2 Footnotes
- 7.3.1 Floating Blocks
- 7.4 Example of a Paper
- 7.5 Example of a Paper 2
- 7.6.1 Citations
- 7.7.1 Writing Style
- 7.7.2 Citations
- 8.1.1 Sham Peer Review
- 8.1.2 Advantages
- 8.1.3 Disadvantages
- 8.2 Publication Bias
- 8.3.1 Journal Rejection
- 9.1 Article Writing
- 9.2 Ideas for Topics
In theory, this is the easiest part to write, because it is a straightforward commentary of exactly what you observed and found. In reality, it can be a little tricky, because it is very easy to include too much information and bury the important findings.

Too Much Information?
The results section is not for interpreting the results in any way; that belongs strictly in the discussion section. You should aim to narrate your findings without trying to interpret or evaluate them, other than to provide a link to the discussion section.
For example, you may have noticed an unusual correlation between two variables during the analysis of your results. It is correct to point this out in the results section.
Speculating why this correlation is happening, and postulating about what may be happening, belongs in the discussion section .
It is very easy to put too much information into the results section and obscure your findings underneath reams of irrelevance.
If you make a table of your findings, you do not need to insert a graph highlighting the same data. If you have a table of results, refer to it in the text, but do not repeat the figures - duplicate information will be penalized.
One common way of getting around this is to be less specific in the text. For example, if the result in table one shows 23.9%, you could write….
Table One shows that almost a quarter of…..

Tips for Writing a Results Section
Perhaps the best way to use the results section is to show the most relevant information in the graphs, figures and tables.
The text, conversely, is used to direct the reader to those, also clarifying any unclear points. The text should also act as a link to the discussion section, highlighting any correlations and findings and leaving plenty of open questions.
For most research paper formats , there are two ways of presenting and organizing the results. The first method is to present the results and add a short discussion explaining them at the end, before leading into the discussion proper.
This is very common where the research paper is straightforward, and provides continuity. The other way is to present a section and then discuss it, before presenting the next section with a short discussion. This is common in longer papers, and your discussion part of the paper will generally follow the same structure.
Be sure to include negative results - writing a results section without them not only invalidate the paper, but it is extremely bad science. The negative results, and how you handle them, often gives you the makings of a great discussion section, so do not be afraid to highlight them.
Using an Appendix to Streamline Writing the Results Section
If you condense your raw data down, there is no need to include the initial findings in the results, because this will simply confuse the reader.
If you are in doubt about how much to include, you can always insert your raw data into the appendix section, allowing others to follow your calculations from the start. This is especially useful if you have used many statistical manipulations, so that people can check your calculations and ensure that you have not made any mistakes.
In the age of spreadsheets, where the computer program prepares all of the calculations for you, this is becoming less common, although you should specify the program that you used and the version. On that note, it is unnecessary show your working - assume that the reader understands what a Chi Squared test, or a Students t-test is, and can perform it themselves.
Once you have a streamlined and informative results section, you can move onto the discussion section, where you begin to elaborate your findings.
- Psychology 101
- Flags and Countries
- Capitals and Countries
Martyn Shuttleworth (Mar 2, 2009). Writing a Results Section. Retrieved Jun 05, 2024 from Explorable.com: https://explorable.com/writing-a-results-section
You Are Allowed To Copy The Text
The text in this article is licensed under the Creative Commons-License Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) .
This means you're free to copy, share and adapt any parts (or all) of the text in the article, as long as you give appropriate credit and provide a link/reference to this page.
That is it. You don't need our permission to copy the article; just include a link/reference back to this page. You can use it freely (with some kind of link), and we're also okay with people reprinting in publications like books, blogs, newsletters, course-material, papers, wikipedia and presentations (with clear attribution).
Want to stay up to date? Follow us!
Check out the official book.
Learn how to construct, style and format an Academic paper and take your skills to the next level.

(also available as ebook )
Save this course for later
Don't have time for it all now? No problem, save it as a course and come back to it later.
Footer bottom
- Privacy Policy

- Subscribe to our RSS Feed
- Like us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
Training videos | Faqs

Results Section Examples and Writing Tips
Abstract | Introduction | Literature Review | Research question | Materials & Methods | Results | Discussion | Conclusion
In this blog, we look at how to write the results section of a research paper. We will go through plenty of results examples and understand how to construct a great results section for your research paper.
1. What is the purpose of the results section?
The authors report their findings in the results section. This is a relatively easy section to write. You simply have to organize your results and write them up in a logical sequence. You must present your findings without evaluating or interpreting them. You must try to illustrate your data using figures and tables to make it more accessible to the readers.
2. How should I structure my results section?
The results section of a research paper typically contains the following components:
Data pre-processing You can talk about any difficulties you encountered while collecting or processing the data.
Main findings You should present your main findings (both positive and negative) in a logical sequence.
Statistics You must use descriptive statistics and inferential statistics to present your data (mean, SD, CI etc.)
Figures and tables Use figures and tables to summarize large amounts of data in a visually pleasing way.
Trends and patterns Trends and patterns describe the general change in some variable in relation to another variable.
Reanalysis You can talk about any reanalysis of data you had to perform in order to reconfirm your findings.
3. Examples of results section
Let’s look at some examples of the results section. We will be looking at results section examples from different fields and of different formats. We have split this section into multiple components so that it is easy for you to understand.
3.1. An example of a pre-processing passage in the results section
Here is an example of the results section from an engineering research paper where the authors talk about pre-processing. The authors are saying that they performed a series of steps before conducting the actual analysis. They are saying that they filled in the missing data using linear interpolation. And then, they transformed and normalized the data. Finally, they applied data smoothing to remove any noise in the data. As you can see the authors are very transparent and are detailing everything they did to the data before the actual analysis.
The following is a brief summary of the preprocessing steps applied prior to analysis. The data were screened for outliers and such data points were set to missing. Subsequently, the missing data were filled by linear interpolation. The data were transformed using the Box method and then normalized to zero mean and unit standard deviation. The smoothing was applied at the final step to remove the noise in the data. _ Missing data _ Missing data fix _ Data normalization _ Data smoothing
3.2. An example of main findings passage in the results section
While presenting your findings you must clearly explain the following:
This is an example of the results section from a psychology research paper where authors are outlining their main findings. In this paper, the authors are investigating the effects of different types of music on people. The authors say that they found significant differences between classical and pop music in terms of memory recall. And then, they are saying that they did not find any differences in terms of emotional response. Finally, they are saying that they were quite surprised to find that both types of music fatigued the listeners at the same rate.
The results indicate significant differences between classical music and pop music in terms of their effects on memory recall and cognition (p<0.05). However, there was no significant difference across the groups for the emotional response to the music (p>0.05). It was surprising to find that both types of music elicited similar levels of fatigue in both groups (p>0.05). _ What was found? _ What was not found? _ Unexpected results
It is very clear from their tone that the last result was a bit unexpected. You can see that the authors have presented their findings in an unbiased manner without any interpretation. They have listed, the positive, the negative, and the neutral results logically in the text. This is how it should be done.
3.3. An example of using statistics in the results section
The use of relevant statistics is very important while writing your results section. It offers two benefits, number one, it will help you summarize the data in a meaningful way, and number two, it will make your text sound more credible. This results example is from a social sciences research paper investigating the relationship between social media and mental health. I want you to pay specific attention to the descriptive and inferential statistics used throughout the text.
The results of this study indicate significant differences in anxiety levels between high social media usage and moderate social media usage (p<0.05). The average time spent by high social media users (5.2 ± 2.2) was considerably higher than that of moderate social media users (3.2 ± 2.2). The odds of sleep disturbance were significantly greater for high social media users (odds ratio, 2.12; 95% CI, 1.81-2.17) compared to moderate social media users (odds ratio, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.07-1.18). _ p-values _ Standard deviation _ Odds ratio & confidence interval
The authors say that there is a significant difference in anxiety levels between high social media users and moderate social media users. Since the authors have used the word significant, they have specified the p-value of the statistical test they used to ascertain this. Then they are providing the actual values of the amount of time spent by both groups on social media. They have presented the data in the form, mean plus or minus standard deviation, which is the standard scientific way to represent this type of data. In the final statement, they talk about the odds of both groups experiencing sleep disturbances. They have provided the odds ratio along with the confidence intervals.
3.4. An example of using figures and tables in the results section
One of the important components of the results section is figures and tables. Try to present your data in figures and tables wherever necessary.
Here is a results example where authors are using figures and tables to describe their results. In the first couple of lines, they are talking about a trend in their data that relates to the change in temperature over time. They are constantly referring to the figure to get their point across to the readers. And finally, in the last sentence, they are telling the readers that the actual numerical data is provided in the table, and they can refer to it if they want. This is a standard way to use figures and tables in your research paper.
In Figure 1.1, the values are plotted as a function of time. The two peaks in the plot correspond to the maximum and minimum temperature values. The specific values obtained for each experiment are given in Table 2. _ Figure _ Figure info _ Table
3.5. An example of elaborating trends/patterns in the results section
As a researcher, it is your job to identify trends, patterns, and relationships between different variables in your data, and tell your readers about them. Because they can reveal very important evidence that you can use to answer your research questions or prove your hypothesis.
The temperature value increases until it reaches a peak value, then decreases rapidly to zero. This effect was 10 times larger at room temperature. There appears to be a positive association between temperature and time. _ Trend _ Pattern _ Interpreting the evidence
In this example, the author talks about his observation that the temperature changes over time in a certain pattern. Then the author talks about noticing the same behaviour under different conditions. Then based on the evidence, the author concludes that there is a positive association between time and temperature. The passage flows very well. You can clearly understand what the author is trying to say here.
4. Frequently Asked Questions
Most journals require separate results and discussion sections. So, it is very important that you are just reporting and describing your results without interpreting them in your results section. The interpretation of the results must be done in the discussion section.
Do not suppress negative results in your paper. Don’t worry if your experiments did not yield the results that you were expecting. Don’t try to ignore or downplay the result just because it doesn’t support your hypothesis. It doesn’t mean that your research is a failure. Negative results are as good as positive results. Actually, you have discovered a useful piece of evidence that your experiments don’t work
Here is an example of an author reporting negative and moderate results in the paper. This is perfectly fine. The authors have reported their results in the paper with full transparency and honesty. And that is how it should be.
The performance did not improve significantly with the new approach, though some marginal improvement was still achieved in terms of speed. These findings are in contrary to our original hypothesis. _ Moderate results _ Negative results
Most people skim through the paper just going through figures and tables without reading any text in the paper. So, captions should be as short as possible but detailed enough for the readers to understand the figure or table without having to read the text.
The best way to answer this question is if you want to illustrate the trends and patterns in the data, then a figure is the best option. If you want to show the actual values or present a lot of numerical information in your paper. Then, a table might be the best way to go.
The best way to answer this question is if you cannot present your data in your text in one or two lines, then you should consider putting it in a figure or a table.
You should write your results section in the past tense, because you are reporting the results of an experiment that you conducted in the past.
Similar Posts

Introduction Paragraph Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through a few introduction paragraph examples and understand how to construct a great introduction paragraph for your research paper.

How to Create a Research Paper Outline?
In this blog we will see how to create a research paper outline and start writing your research paper.

3 Costly Mistakes to Avoid in the Research Introduction
In this blog, we will discuss three common mistakes that beginner writers make while writing the research paper introduction.

Literature Review Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many literature review examples and understand different ways to present past literature in your paper.

How to Handle Negative Results in your Research Paper?
In this blog, we will see how to effectively communicate negative and unexpected findings in your paper with detailed examples.

Technical Terms, Notations, and Scientific Jargon in Research Papers
In this blog, we will teach you how to use specialized terminology in your research papers with some practical examples.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 2 Share Facebook
- 1 Share Twitter
- 0 Share LinkedIn
- 2 Share Email
How to Write the Results and Discussion: 9 Tips
Do you know how to write the results section of a research paper? How about the discussion section? Here are 9 tips on how to do it.
Writing the results and discussion section could be one difficulty that you encounter when writing your first research manuscript. There is no simple hard and fast rule in doing it, but the following guide can help you start off with confidence.
The results and discussion section are also referred to as the data presentation, analysis, and interpretation section. You present the results, show the analysis, and interpret the outcome of the analysis.
As a takeoff point, it would help if we separate these two terms, i.e., results and discussion, into simply the results and the discussion as separate parts of the paper. In some universities and usually in scientific journals, however, these are taken as one.
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper
As the term connotes, write only the results of your study. What comprises the results? I describe it in the following paragraphs.
1. Graphs, tables, or photographs
We derive the observations from the application of the method or methodology that we use. These can be best presented using tables and graphs as an objective representation of the measurements that you made. Numbers are more definite approximations of reality compared to just mere words. Words are more subjective and replete with misunderstanding.
Be consistent with your units of measurement. If you start off with kg, then use the same unit all throughout your paper.
Never should you manipulate the outcome of your measurements. Be honest in presenting information even if the result is unexpected. Whether the result is positive or negative, present it. This is an objective move.
You may also add photographs whenever needed, but make sure these are relevant, not just whimsical addition to your paper or a means to flaunt your good photography skills ; although it would be helpful to show such skill coupled with relevance. Pictures can speak a thousand words.
Give as much detail as possible in your presentation of the results. Read and reread your statements for clarity. Engage a competent friend or a colleague’s discerning eye for details.
2. Topic sentences or subheadings
It is easy to follow your presentation if you break this into meaningful subtopics based on your stated objectives. A one-to-one correspondence would be great. Say, the first subheading will be about objective one, the second subheading about objective two, and so on.
Notice that in writing this article, it is an easy read to have a subheading for every major thought. This makes for easy reading thus understanding. And the writing becomes logical.
3. Key results
We should state clearly the key results at the beginning of each paragraph. It should serve as the topic sentence (see the TSPU Principle ). Support that statement with more detail, such as presenting the results of statistical analysis.
For example:
There is a significant positive relationship between the number of hours spent by students in answering mathematics questions and their examination score. This result is consistent across all grade levels in the three schools examined. Table 1 shows the correlation coefficients and their corresponding significance level.
How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
After examining several theses of previous years, I noticed that many undergraduate and even graduate students miss this part. They present the results and the analysis, but no discussion is in sight.

So what comprises the discussion? Here’s what should be present in the discussion part:
1. Trends and spatial differences
Trends refer to changes over time. Are your results showing an increasing, decreasing or just plain, constant direction? This trend should be clear in the graph that you presented.
Spatial differences refer to differences in space or location within the same time frame. Is there a significant difference between the two groups examined? Is there a difference in the morphological measurements of one group of animals obtained from one location compared to another group? These are questions that explore spatial differences.
2. Insightful interpretation of results
Insightful interpretation means well thought explanations. That means you will have to ponder deeply the results of your study and make a knowledgeable statement of your interpretation using the body of evidence at hand. This is where you cite evidences obtained by other authors. You either confirm or affirm other people’s work or refute using your own findings.
3. Generalizations
Be on guard in writing your generalizations. Make sure that the data you analyzed can be extrapolated or will allow you to predict somehow the behavior of one variable. If you have enough samples, then you may make a generalization.
How enough is enough, you may ask. If your data has little variability, as indicated by low variances, then it is possible that additional measurements will not change whatever trend you have.
Always match your generalization with whatever results you have. Conversely, do not generalize when you have very few samples. Don’t say 50% when you actually have only two, three, or even four samples described in your study. That’s plain absurd.
4. Exceptions to the rule
In scientific inquiry, not all things or factors are discovered. There are always unknown or unaccounted areas. This is the reason why everything is founded on probability. No one’s 100 percent sure. So you should never say “prove” as a matter of contention. “Prove” means 100% sure which never happens. There are always expected deviants from the norm.
5. Reasons things happen
Things happen because of something else. Reaction arises from action. These are called determining factors.
Are there reasons your results follow a trend? Is it evident in your study? If there is, then say it and explain why so, again based on your observations or evidence.
You may guess, but make it educated, meaning, you have done your homework. You have reviewed the literature and use it as a leverage for advancing your hypothesis or inference.
Does your finding support or refute what has been done so far? Does it support previously advanced hypotheses?
Remember that there is no such thing as a simple explanation of a complex phenomenon. Find one that is most aligned with your findings.
It would be interesting to be on the controversial side as long as you have done your study systematically and bias is reduced to a minimum.
6. The contribution of your work
What are the important things that your study has contributed so far in view of what has been laid out in the body of literature? Why is your work important and what things need to be investigated further?
From your set of questions, if many other questions arise, then your work has helped unravel other areas worthy of investigation. This is just how science works. The mysteries of the universe are uncovered, yet there are still many unknowns.
No human has an absolute understanding of everything. But if your work has the potential to make life better, then it’s a great accomplishment.
Follow these links on how to write the results section of a research paper and how to write the discussion section of a research paper as added readings to help you convey more effectively your research findings.
Kim Kastens, Stephanie Pfirman, Martin Stute, Bill Hahn, Dallas Abbott, and Chris Scholz (n.d.). How to write your thesis. Retrieved May 24, 2015 from http://www.ldeo.columbia.edu/~martins/sen_sem/thesis_org.html
Related Posts

What is a Conceptual Framework? Expounded Definition and Five Purposes
Research findings dispel old myths.
How to Go Viral: 6 Key Concepts from 6,956 Articles
About the author, patrick regoniel.
Dr. Regoniel, a faculty member of the graduate school, served as consultant to various environmental research and development projects covering issues and concerns on climate change, coral reef resources and management, economic valuation of environmental and natural resources, mining, and waste management and pollution. He has extensive experience on applied statistics, systems modelling and analysis, an avid practitioner of LaTeX, and a multidisciplinary web developer. He leverages pioneering AI-powered content creation tools to produce unique and comprehensive articles in this website.
SimplyEducate.Me Privacy Policy

Research Voyage
Research Tips and Infromation
How to Write Results Section of Your Research Paper

Introduction
How to summarize the data preprocessing steps in the results section, how to summarize the research findings in the results section, common phrasal verbs used in results section, what are common mistakes observed in the results section, how long should a results section be of a research paper, should the results of a research paper be given in the introduction or in another section.
- What is the difference between the "discussion" and the "results" section of a research paper?
Does the summary be part of the result section in the research article?
Why do some scientific papers not include a ‘methods and results’ section, how do you introduce a results section, why do researchers need to avoid making speculations in the results section of a research paper.
The result section is the third major part of the research paper and it’s probably the most important part because it contains actual outcomes about your experiment. The other sections contain a plan, hope and interpretations but the result section is the actual truth of your study.
In the result section, one should aim to narrate his/her finding without trying to interpret or evaluate them. Basically, the result section explains any issues you faced during your data collection, the main results of the experiment and any other interesting trends in the data.
With the results, we want to convey our data in the most accessible way, so we usually use visual elements like graphs and tables to make it easier to understand. The facts, figures, and findings are to be presented in a logical manner leading to the hypothesis and following the sequence of the method section. Mention must be made for the negative results as it would substantiate the discussion section later on. Interpretation of the meaning of the results section is done in the discussion section .
How Results Section is Structured?
When structuring the results section, it is important that your information is presented in a logical order.
Now, when it comes to the organization of the result section, as a generic rule
- Always start with textual content, not a Table or Figure
- Make sure you show the Tables and Figures after they are mentioned in the text
- Explain any missing data or problems you had while collecting the data.
The results section gives you the opportunity to:
- Summarize the Data Preprocessing Steps
2. Report on the Findings
3. Summarize the Research Findings
At the beginning of the result section, you can discuss how you have collected, transformed and analyzed your data. This step is usually known as data preprocessing.
The data collection step may involve collecting data from various hardware, software or internet sources.
If your research requires data cleaning, then explain the steps and procedures used for data cleaning. Here, the researchers can describe how they transformed data to facilitate analysis (e.g. converting data from one format to another format). If there was missing data, explain how you have substituted missing values and with what techniques you have substituted your data.
You can mention what software or statistical procedures you have used to analyze and interpret the data. Demonstrate with the help of charts or tables the cleansed data ready to be used for getting results. In a few research papers, you may find these steps appearing at the end of the method section.
How to Present your Research Findings in Research Section?
Second, present your findings in a structured way (such as thematically or chronologically), bringing the readers’ attention to any important, interesting, or significant findings.
Be sure to include a combination of text and visuals. Data illustrations should not be used to substitute or replace text, but to enhance the narrative of your findings.
Resultant data are to be presented either through text, figures, graphs or tables or in a combination of all of the best suited for leading to the hypothesis. Care should be taken to prevent any duplication of the text, figures, graphs, and tables. If any result is presented in figures or graphs, it need not be explained through text. Similarly, any data presented through the graph should not be repeated in the table.
Each table and graph should be clearly labelled and titled. Each different finding should be made in a separate sub-section under the proper sub-heading following the sequence adopted in Method Section.
If you are not comfortable with data analysis then you can take professional services for research data analysis .
Figures
Identify and list the figures which are relevant to your results. For example, if you are working on the problem statement of ” Identifying the pathological issues with pomegranate fruits”, then you can add the figures of pomegranate fruits with good quality and bad quality along with their stage of infection. If you are working on pomegranate cultivar-related issues, put the figures of pomegranate fruits belonging to different cultivars.
The key takeaway here is not to add any figures which may not directly contribute to results. These diagrams may include generic block diagrams, and images conveying generic information like farm fields, plantations etc.
While putting the figures, as much as possible use grayscale images as many users take the photocopies in black and white mode. In certain scenarios you are
In the case of figures, the captions should come below, called Fig. 1, Fig. 2 and so on.
You can visit my article on The Power of Images in Research Papers: How They Enhance the Quality of Your Paper? . This article will help you how images or figures enhances the possibility of selection of your paper to top quality journals and conferences.
Tables are good for showing the exact values or showing much different information in one place. Graphs are good for showing overall trends and are much easier to understand quickly. It also depends on your data.
Tables are labelled at the top as Table 1, Table 2 and so on. Every table must have a caption. It’s good if one can put independent variable conditions on the left side vertically, and the things you have measured horizontally so one can easily compare the measurements across the categories. But you need to decide for each table you make, what is easiest to understand, and what fits on the paper.
Visit article on Best Practices for Designing and Formatting Tables in Research Papers for further details on proper representation of tables at proper places.
You can use various types of graphs in your results like a line graph, bar graph, scatter plot, a line graph with colours, a box with whiskers plot and a histogram.
In general, continuous variables like temperature, growth, age, and time can be better displayed in a line graph on a scatter plot or maybe on histograms.
If you have comparative data that you would like to represent through a chart then a bar chart would be the best option. This type of chart is one of the more familiar options as it is easy to interpret.
These charts are useful for displaying data that is classified into nominal or ordinal categories. In any case, you need to decide which is the best option for each particular example you have, but never put a graph and a table with the same data in your paper.
In the case of graphs, the captions should come below, called Fig. 1, Fig. 2 and so on.
A limited number of professional tools provide you the chance to add some life to your graphs, charts, and figures and present your data in a way that will astound your audience as much as your astounding results.
My article on Maximizing the Impact of Your Research Paper with Graphs and Charts will help you in drawing eye catching and informative graphs and charts for your research paper.
The results section should include a closing paragraph that clearly summarizes the key findings of the study. This paves the way for the discussion section of the research paper, wherein the results are interpreted and put in conversation with existing literature.
Any unusual correlation observed between variables should be noted in the result section. But any speculation about the reason for such an unusual correlation should be avoided. Such speculations are the domains of the discussion section.
Comparisons between samples or controls are to be clearly defined by specifically mentioning the common quality and the degree of difference between the comparable samples or controls. Results should always be presented in the past tense.
Common academic phrases that can be used in the results section of a paper or research article. I have included a table with examples to illustrate how these phrases might be used:

Let’s look at some of the common mistakes which can be observed in the result section.
- One should not include raw data which are not directly related to your objectives. Readers will not be able to interpret your intentions and may unnecessarily collect unwanted data while replicating your experiments.
- Do not just tell the readers to look at the Table and Figure and figure it out by themselves, e.g “The results are shown in the following Tables and Graphs”.
- Do not give too much explanation about Figures and Tables.
“An Optimized Fuzzy Based Short Term Object Motion Prediction for Real-Life Robot Navigation Environment” ( Paper Link )
Object motions with different motion patterns are generated by a simulator in different directions to generate the initial rule base. The rules generated are clustered based on the direction of the motion pattern into the directional space clusters. Table 1 shows the number of rules that remained in each directional space after removing inconsistencies and redundancies.
Our predictor algorithm is tested for a real-life benchmark dataset (EC Funded CAVIAR project/IST 2001 37540) to check for relative error. The data set consists of different human motion patterns observed at INRIA Lab at Grenoble, France and Shop Centre. These motion patterns consist of frames captured at 25 frames/second. A typical scenario of the INRIA Lab and the Shop Centre is shown in the Figure below.

Fig.1: A typical scenario of the INRIA Lab and the Shop Centre
For each test case, the average response time is calculated to find its suitability for a real-life environment. The prediction algorithm is tested by processing the frame data of moving human patterns stored in the database at intervals of 50 frames (02 Seconds).
The navigation environment is presented in the form of a Prediction graph where the x-axis represents the Range parameter and the y-axis represents the Angle parameter. The predicted Angle and Range values are compared with actual values obtained from the real-life environment.
The performance of the predictor is tested when more than one object is sensed by the sensor. The tests are carried out assuming at most 6-8 objects can be visible and can affect the decisions to be made regarding robot traversal.
The results section is an essential component of any research paper, as it provides readers with a detailed understanding of the study’s findings. In this blog post, we discussed three important steps for writing a results section: summarizing the data preprocessing steps, reporting on the findings, and summarizing the research findings.
Firstly, summarizing the data preprocessing steps is crucial in the results section, as it provides readers with an understanding of how the raw data was processed and transformed. This step includes data cleaning, data transformation, and data reduction techniques. By summarizing the data preprocessing steps, readers can understand how the data was prepared for analysis, which is critical for interpreting the study’s findings accurately.
Secondly, reporting on the findings is an important step in the results section. It involves presenting the study’s results in a clear and concise manner, using tables, graphs, and statistical analyses where necessary. This step should be focused on answering the research question or hypothesis and should present the findings in a way that is easily understood by the reader. Reporting on the findings can also include providing detailed interpretations of the results, as well as any potential limitations of the study.
Finally, summarizing the research findings is crucial in the results section, as it provides readers with a concise summary of the study’s main results and conclusions. This step should be written in a clear and straightforward manner, highlighting the most important findings and explaining their significance. Additionally, it should relate the study’s findings to the research question or hypothesis and provide a conclusion that is well-supported by the results.
Overall, the results section of a research paper is a critical component that requires careful attention to detail. By following the guidelines discussed in this blog post, researchers can present their findings in a clear and concise manner, helping readers to understand the research process and the resulting conclusions.
Frequently Asked Questions
An IMRaD paper format suggests around 35% of the text should be dedicated to the results and discussion section. For a research paper of length 10 pages, the results and discussion section should occupy 3-4 pages.
The results of a research paper should be given in a separate section. However, the highlights of the results can be discussed in the introduction section.
What is the difference between the “discussion” and the “results” section of a research paper?
The results section only depicts the results obtained by implementing the methodology used. The results will be in the form of figures, tables, charts or graphs. The discussion section elaborates the analysis of the results obtained in the results section.
The summary can be part of the results section of a research paper. However, the results obtained can be summarized in the form of a table in results section of a research paper.
Survey papers and papers which are focussed on theoretical proofs do not involve separate methods and results sections.
The results section is introduced by the data collection steps and the setting up of equipment in different scenarios for obtaining the results.
Making speculations in the results section may lead to wrong interpretations by the researcher who is planning to replicate the methodology used for obtaining the results. This may further lead to wrong comparative analysis.
Upcoming Events
- Visit the Upcoming International Conferences at Exotic Travel Destinations with Travel Plan
- Visit for Research Internships Worldwide

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Recent Posts
- These Institutes Offer Remote Research/Academic Internships
- How to Include Your Journal in the UGC-CARE List? A Guide for Publishers
- Understanding UGC CARE Journals: A Comprehensive Guide
- Top 10 AI-Based Research Paper Abstract Generators
- EditPad Research Title Generator: Is It Helpful to Create a Title for Your Research?
- All Blog Posts
- Research Career
- Research Conference
- Research Internship
- Research Journal
- Research Tools
- Uncategorized
- Research Conferences
- Research Journals
- Research Grants
- Internships
- Research Internships
- Email Templates
- Conferences
- Blog Partners
- Privacy Policy
Copyright © 2024 Research Voyage
Design by ThemesDNA.com

Originality.ai Ranked Among Top-Tier AI Text Detectors According to the Study — “The Effectiveness of Software Designed to Detect AI-Generated Writing”
Originality.ai ranked among top-tier ai detectors according to the research in "the effectiveness of software designed to detect ai-generated writing.".

The study by William H. Walters, " The Effectiveness of Software Designed to Detect AI-Generated Writing: A Comparison of 16 AI Text Detectors ," provides a comprehensive evaluation of 16 publicly available AI text detectors. Based on the study’s findings, Originality.ai showed remarkable accuracy in identifying AI-generated text.
Key Findings (TL;DR)
- Three AI text detectors — Originality.ai, Copyleaks, and TurnItIn — demonstrated exceptional accuracy across all three sets of documents examined in this study: GPT-3.5 papers, GPT-4 papers, and human-generated papers.
- Although most of the other detectors in the study could distinguish between GPT-3.5 papers and human-generated papers with a reasonably high accuracy they were not as effective at distinguishing between GPT-4 and student-written papers.

Study Details
This study evaluated the accuracy of 16 publicly available AI text detectors in discerning AI-generated from human-generated writing. The evaluated document included 126 essays generated by AI and humans across various domains.
Each detector’s performance was assessed for its overall accuracy, its accuracy with each type of document, its decisiveness, the number of false positives, and the number of false negatives.
Originality.ai was one of the top three highest-performing AI detectors — demonstrating high accuracy with all three sets of documents.
AI Text Detection Tools
- 16 AI detection tools : Originality.ai, Copyleaks, TurnItIn, Scribbr, ZeroGPT, Grammica, GPTZero, Crossplag, OpenAI, IvyPanda, GPT Radar, SEO.ai, Content at Scale, Writer, Sapling, ContentDetector.ai
- Top performers : Originality.ai, Copyleaks, TurnItIn
GPT 3.5 and GPT 4 were each used to generate 42 short papers (literature reviews), similar to the type of papers typically assigned to students in first-year composition courses at US universities. The topics covered social sciences, natural sciences, and the humanities.
The 42 human-written documents were gathered from a set of 178 papers submitted by Manhattan College English 110 (First Year Composition) students during the 2014 to 2015 academic year.
The 2014 to 2015 timeframe was selected because it occurred before the widespread availability of AI tools such as ChatGPT to ensure the papers were written without AI.
This dataset consists of 126 documents divided into the following:
- 42 undergraduate essays generated by ChatGPT-3.5
- 42 generated by ChatGPT-4
- 42 human-written essays from a first-year composition course
Evaluation Criteria
Each detector’s performance was assessed for:
- Its overall accuracy across all 126 documents.
- Its accuracy when tested against each of the three sets of documents.
- Its decisiveness (the relative number of uncertain responses).
- The number of false positives (human-generated papers designated as AI by the detector)
- The number of false negatives (AI-generated papers designated as human by the detector).
The analysis involved four steps:
- Preparing the three sets of documents.
- Selecting the 16 AI text detectors to include in the study.
- Using each detector to evaluate the 126 documents and code the responses as AI, human, or uncertain.
- Evaluating the accuracy of each detector and its ability to identify AI-generated and human-generated text.
Originality.ai’s Performance
Originality.ai excelled at detecting both AI-generated and human-written documents with high accuracy. The study positioned it as a top-tier AI-generated text detection tool with a 97% overall accuracy rate.
All 126 documents
- Correct: 98%
- Incorrect: 0%
- Uncertain: 2%

GPT-3.5 Papers
- Correct: 100%
- Uncertain: 0%

GPT-4 Papers

Human Papers
- Correct: 95%
- Uncertain: 5%

Effectiveness of Originality.ai
- Overall Accuracy : Very high
- Accuracy, GPT-3.5 : Very high
- Accuracy, GPT-4 : Very high
- Decisiveness : High
- False Positives : Few
- False Negatives : Few

Final Thoughts
Originality.ai is positioned as a top-tier AI-generated text detection tool with exceptional accuracy. Its performance is on par with, and sometimes even better than, other leading tools like CopyLeaks and TurnItIn, ensuring the authenticity and integrity of the written content.
Jonathan Gillham
More from the blog, empirical study of ai-generated text detection — results as per an empirical study of ai-generated text detection tools.
Originality.ai exhibited outstanding AI detection capabilities, according to research in An Empirical Study of AI-Generated Text Detection Tools, 2023.
Most Commonly Used ChatGPT Words & Phrases
Are humans as good at detecting AI content as they think? We analyzed 10 million ChatGPT terms to find out! Discover ChatGPT's most common words and phrases.
Worst Google AI Responses Overview
Discover the funniest and most bizarre responses by Google's AI. Check out our top 50 picks and find out what went wrong with each one!
AI Content Detector & Plagiarism Checker for Serious Content Publishers
Improve your content quality by accurately detecting duplicate content and artificially generated text..
AI & Plagiarism Detector for Serious Content Publishers
KNOWLEDGE BASE
© 0000 Originality.ai
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
India election results: Modi claims victory for alliance
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) supporters listen to prime minister Narendra Modi’s victory speech at the party headquarters in New Delhi.
- Copy Link copied
Today’s live coverage has ended, but there’s still plenty to catch up on. Read what you missed below and find more coverage on the AP’s global elections hub.
India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi has claimed victory for his alliance as early results from the staggered, six-week election showed fewer seats for his Bharatiya Janata Party than expected and it appeared unlikely to secure a majority on its own. Final figures are not expected until Wednesday local time, with counting going late into the night.
Here’s what to know:
- Where results stand: After winning a record 303 seats in 2019, Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party appeared unlikely to win more than 240, far short of the 272 needed to form a majority government on its own.
- National Democratic Alliance: The political coalition led by Modi’s party appears on track to win a combined 286 seat majority.
- Modi claims early victory: In a speech to supporters , Modi claimed victory for his alliance , calling the election a big win despite the stronger-than-expected challenge from the opposition.
Across India, supporters of various political parties, leaders and candidates celebrated wins as counting nears its end

Prime Minister Narendra Modi is greeted by supporters as he arrives at Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) headquarters in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
A supporter of Shiv Sena (Uddhav Balasaheb Thackeray) dances as he celebrates with others their party’s lead during the counting of votes in India’s national election in Mumbai, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
Samajwadi Party supporters celebrate their party’s lead during the counting of votes in India’s national election in Lucknow, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Rajesh Kumar Singh)
Congress Party leader Rahul Gandhi, in white shirt, sees his mother and party leader Sonia Gandhi off as she leaves the party headquarters after feeling physical discomfort during a press conference in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri)
Congress Party supporters wait to get a glimpse of the party leader Rahul Gandhi at the party headquarters in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri)
Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK) party supporters celebrate as they follow proceedings of the vote counting at their party headquarters in Chennai, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Mahesh Kumar A.)
Trinamool Congress Party leader and Chief Minister of West Bengal state, Mamata Banerjee, and her nephew and party leader Abhishek Banerjee make a victory sign with their hands as they arrive to address a press conference in Kolkata, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Bikas Das)
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) supporters dance inside the party office after hearing of a candidate’s victory during the counting in India’s national election, in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Hindu nationalist party showed a comfortable lead Tuesday, according to early figures reported by India’s Election Commission, but was facing a stronger challenge from the opposition than had been expected. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
Supporters of Congress Party cheer the party leader Rahul Gandhi, center, as he leaves the party headquarters after addressing a press conference in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri)
A Congress Party supporter carries a flag printed with a portrait of party leader Rahul Gandhi at the party headquarters in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri)
A Samajwadi Party supporter carries portraits of party leader Akhilesh Yadav, right, and Congress Party leader, Rahul Gandhi, as he celebrates his party’s lead during the counting of votes in India’s national election in Lucknow, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Rajesh Kumar Singh)
Workers carry a large cutout portrait of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi at the party headquarters in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)

A man walks past posters with portraits of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) state President K. Annamalai on a street in Chennai, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Mahesh Kumar A.)
After winning a record 303 seats in 2019, the BJP appeared unlikely to win more than 240, far short of the 272 needed to form a majority government on its own, with 194 seats won and the lead in 46 constituencies and counting ongoing.
Modi’s NDA coalition, meantime, was on track to win a combined 286 seat majority, with 225 seats won and leads in 61 races.
The opposition INDIA coalition appeared as if it would win 210 seats.
Final figures were not expected until Wednesday, with counting going late into the night.
The White House on Tuesday commended India for demonstrating its “vibrant democratic process” after close to 970 million Indians went to the polls during its six-week long election.
White House national security spokesperson John Kirby said the turnout demonstrated the Indian electorate’s commitment to democracy.
“So we celebrate that with them,” Kirby told reporters. ”And we applaud the government writ large for successfully completing a truly, massively-sized electoral undertaking.”
Kirby declined to comment about Prime Minister Narendra Modi and his BJP party’s apparent victory, noting that “not all the votes have been tallied and counted.”

Indian President Droupadi Murmu greets the crowd gathered at her temporary residence in New Delhi in 2022 (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
India’s president is its head of state, but the position is largely ceremonial.
Droupadi Murmu, the current president, was elected in 2022 by lawmakers — an electoral college that consists of lawmakers in both houses of Parliament and elected members of the legislative assemblies of all states. She hails from the same political party as Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
The position can be important during times of political uncertainty such as a hung parliament, when the office assumes greater power. The president is bound by the advice of the Cabinet led by the prime minister, who is the chief executive.
Tallies reported by India’s Election Commission showed Modi’s BJP-led National Democratic Alliance, 209 of them going to BJP.
The opposition Congress party is part of the INDIA alliance , which so far had won 177 seats, 81 of them for Congress.
Tallying is ongoing. A total of 272 seats are needed for a majority.
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi during the inauguration of Kashi Vishwanath Dham Corridor, a promenade that connects the sacred Ganges River with the centuries-old temple dedicated to Lord Shiva in Varanasi, India, Monday, Dec. 13, 2021 (AP Photo/Rajesh Kumar Singh)
India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi, who claimed victory for his alliance in an election seen as a referendum on his decade in power, is a popular but polarizing leader who has presided over a fast-growing economy while advancing Hindu nationalism.
Modi, 73, is only the second Indian prime minister to win a third straight term.
To supporters, Modi is a larger-than-life figure who has improved India’s standing in the world, helped make its economy the world’s fifth-largest , and streamlined the country’s vast welfare program, which serves around 60% of the population. To some, he may even be more than human.
But to critics, he’s a cult leader who has eroded India’s democracy and advanced divisive politics targeting the Muslims who make up 14% of the country’s population. They say he has also increasingly wielded strong-arm tactics to subdue political opponents, squeeze independent media and quash dissent.
▶ Read more in our profile of the prime minister.
As Narendra Modi claimed victory for his alliance, congratulations from neighbors began rolling in on X despite the National Democratic Alliance having several seats to win before securing a majority.
Nepalese Prime Minister Pushpa Kamal Dahal: “Congratulations to PM @narendramodi on the electoral success of BJP and NDA in the Loksabha elections for the third consecutive term. We are happy to note the successful completion of the world’s largest democratic exercise with enthusiastic participation of the people of India.”
Bhutanese Prime Minister Tshering Tobgay: “Congratulations to my friend PM @narendramodi ji and NDA for the historic 3rd consecutive win in the world’s biggest elections. As he continues to lead Bharat to great heights, I look forward to working closely with him to further strengthen the relations between our 2 countries.”
Mauritian Prime Minister Pravind Kumar Jugnauth: “Congratulations Prime Minister Modi Ji @narendramodi on your laudable victory for a historic third term. Under your helm, the largest democracy will continue to achieve remarkable progress. Long live the Mauritius-India special relationship.”
Sri Lankan President Ranil Wickremesinghe: I extend my warmest felicitations to the @BJP4India led NDA on its victory, demonstrating the confidence of the Indian people in the progress and prosperity under the leadership of PM @narendramodi. As the closest neighbour Sri Lanka looks forward to further strengthening the partnership with India.”

Prime Minister Narendra Modi is garlanded by senior Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) leaders Rajnath Singh, left, party President JP Nadda, right, and Amit Shah, at the party headquarters in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
Around 33 minutes.
32. The National Democratic Alliance, led by Narendra Modi’s BJP, has claimed 240 seats. It needs 272 to secure a majority and thus a third term for the prime minister.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi says India will will see a “new chapter of big decisions” in his third term in office.
After claiming victory for his coalition alliance despite a lackluster performance from his own party, Modi told a crowd at party headquarters he would not shirk from pushing forward with his agenda.
He said he would advance India’s defense production, jobs for youth, raise exports and help farmers, among other things.
“This country will see a new chapter of big decisions. This is Modi’s guarantee,” he said, speaking in the third person.
His speech is still ongoing.

Prime Minister Narendra Modi greets supporters as he arrives at Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) headquarters in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
Prime Minister Narendra Modi promises “new chapter of big decisions” after declaring victory for his coalition.
But if his BJP is indeed forced to form a coalition, the party would likely “be heavily dependent on the goodwill of its allies, which makes them critical players who we can expect will extract their pound of flesh, both in terms of policymaking as well as government formation,” said Milan Vaishnav, director of the South Asia Program at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.

Prime Minister Narendra Modi claimed victory for his alliance, despite a lackluster performance from his own party as it faced a stronger than expected challenge from the opposition, which pushed back against the leader’s mixed economic record and polarizing politics.
Modi said that his National Democratic Alliance will form the government for the third consecutive time.
“Today’s victory is the victory of the world’s largest democracy,” he said, speaking at his party headquarters.
For the first time since Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party swept to power in 2014, it appeared unlikely that it would secure a majority on its own – but the prime minister’s coalition was still expected to be elected to a third five-year term in the world’s largest democratic exercise .
If Modi does have to rely on coalition support to govern, it would be a stunning blow for the 73-year-old, who had hoped for a landslide victory.
As Prime Minister Narendra Modi claims victory for his alliance, 329 of 543 seats have been decided, according to India’s Election Commission. Counting is expected to continue through the night.

Narendra Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party and its National Democratic Alliance has yet to secure the 272 seats needed for a parliamentary majority, but the prime minister has declared “a very big win.”
India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi swept to power a decade ago on promises to transform India’s economy, and as he seeks a third term as prime minister, it would be hard to argue he hasn’t made strides.
▶ Read more about the growth of India’s economy — and why some feel left behind.

Supporters of National Democratic Alliance watch as their candidates arrive to file nomination papers ahead of national elections in Mumbai, India, Monday, April 29, 2024. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
The National Democratic Alliance, an Indian political coalition, is led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party. It was founded in 1998 and comprises center-right and right-wing political parties.
The coalition’s first chair was former BJP Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee. The coalition ruled from 1998 to 2004, but then was out of power until 2014, when Modi was first elected as the prime minister.
BJP’s key allies in the NDA include more than a dozen regional parties, including the Telugu Desam Party, Janta Dal (United), Pattali Makkal Katchi, the Republican Parry of India (Athwale Group) and Shiv Sena.
The NDA could be key to Modi retaining his position. In the past two elections, the BJP has secured an outright majority, but early figures indicate it might need the coalition to reach that threshold.
More than 12 hours after vote counting started, India’s Election Commission reports that the ruling Bharatiya Janata Party has won 140 seats while the Congress party has won 55.
272 seats are needed to secure a majority. Preliminary results indicate Modi’s BJP will need to rely on its coalition partners to achieve that.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has arrived at Bharatiya Janata Party headquarters in New Delhi, where supporters are spilling out into the road.

Samajwadi Party supporters dance as they celebrate their party’s lead during the counting of votes in India’s national election in Lucknow, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Rajesh Kumar Singh)
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Hindu nationalist party is facing a major upset in India’s most populous state at the hands of a powerful regional group, Samajwadi Party or Socialist Group.
The Samajwadi Party, founded in 1992 and now led by Akhilesh Yadav, has already won 10 seats in Uttar Pradesh state and was leading in another 28 constituencies. It is part of the Congress-led INDIA alliance, which is facing off against the BJP-led National Democratic Alliance.
Modi’s BJP has won in 12 districts (including Modi’s own Varanasi seat) and is leading in 20 constituencies. Exit polls had predicted a landslide victory for the BJP in the state.
“In this election, it seems Lord Ram has deserted the BJP,” Samajwadi spokesperson Rajendra Chaudhry said.

Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, shows the indelible ink mark on his index finger after casting his vote during the third phase of general elections, in Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India, Tuesday, May 7, 2024. (AP Photo/Ajit Solanki)
The 73-year-old is one of India’s most beloved — and polarizing — leaders. He’s already won twice, first in 2014 and then in 2019, and is now seeking a hattrick victory.
His supporters see him as a self-made, strong leader who has improved India’s standing on the global stage, and credit his pro-business policies with making the economy the world’s fifth-largest. At the same time, his rule has seen brazen attacks against minorities, particularly Muslims.
India’s democracy, critics say, is faltering and Modi has increasingly blurred the line between religion and state. But both agree on one thing: Modi has achieved staying power by making Hindu nationalism acceptable — desirable, even — to a nation of 1.4 billion that for decades prided itself on secularism and diversity.
Millions of Indians are voting in a six-week long national election in a referendum on Narendra Modi, the populist prime minister who has championed an assertive brand of Hindu nationalist politics. The voters will cast ballots in the first round of voting across 21 states. Over 970 million voters will elect 543 members for the lower house of Parliament for five years during the staggered elections that will run until June 1. The votes will be counted on June 4. (AP Video by Piyush Nagpal)
Each phase was held on a single day, with voting in several constituencies across multiple states. The staggered polling allowed the government to deploy tens of thousands of troops to prevent violence and transport election officials and voting machines.
People walk past a large poster of the movie “Swatantra Veer Savarkar” displayed outside a cinema hall in Mumbai (AP Photo/Rajanish Kakade)
For more than a century, Bollywood has unified India, a country riven with religious, caste and political divide. It’s been a rare industry where religion has been least influential in deciding the success of filmmakers and actors. Bollywood films have also championed political diversity and religious harmony.
That culture, however, appears to be under threat.
Under Narendra Modi’s Hindu nationalist government, many filmmakers have made movies on bygone Hindu kings extolling their bravery. Boisterous and action-packed movies valorizing the Indian Army have become box office successes. Political dramas and biopics that eulogize Hindu nationalists are the norm.
In most of these films, the stock villains are medieval Muslim rulers, leftist or opposition leaders, free thinkers or rights activists — and neighboring Pakistan.
▶ Read more about how some in the Hindi film industry have embraced Modi.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi says his coalition is on the path to a third straight term in government after India’s marathon election.
“People have placed their faith in NDA, for a third consecutive time! This is a historical feat in India’s history,” Modi on Tuesday said in a post on X, referring to the National Democratic Alliance which his party heads. He said he will continue to work and fulfil the aspirations of the people.
As Modi posted his comment, his coalition had won 128 seats and led in 157 races according to the Election Commission. A total of 272 seats were needed to form a majority government.
For Payal, a resident of the northern city of Lucknow who uses only one name, the election was about the economy and India’s vast number of people living in poverty. “People are suffering, there are no jobs, people are in such a state that their kids are compelled to make and sell tea on the roadside,” Payal said. “This is a big deal for us. If we don’t wake up now, when will we?”
Supporters of Shiv Sena (Uddhav Balasaheb Thackeray) dance as they celebrate their party’s lead during the counting of votes in India’s national election in Mumbai, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
Supporters of Congress Party dance as they celebrate their party’s lead during the counting of votes in India’s national election in Mumbai, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Rafiq Maqbool)
Faces of Trinamool Congress Party supporters smeared with green colour display victory sign as they celebrate the election results in Kolkata, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s Hindu nationalist party showed a comfortable lead Tuesday, according to early figures reported by India’s Election Commission, but was facing a stronger challenge from the opposition than had been expected. (AP Photo/Bikas Das)
Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (DMK) party supporters cheer as they follow proceedings of the vote counting at their party headquarters in Chennai, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. India began counting more than 640 million votes Tuesday in the world’s largest democratic exercise, which was widely expected to return Prime Minister Narendra Modi to a third term after a decade in power. (AP Photo/Mahesh Kumar A.)
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) supporters shout slogans as they celebrate their party’s lead during the counting of votes outside the party office in Srinagar, Indian controlled Kashmir, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Dar Yasin)
Congress party supporters cheer as they follow proceedings of vote counting at their party headquarters in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. India began counting more than 640 million votes Tuesday in the world’s largest democratic exercise, which was widely expected to return Prime Minister Narendra Modi to a third term after a decade in power. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri)
A band plays music as Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) supporters dance inside the party office after hearing of a candidate’s victory during the counting in India’s national election, in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. xPrime Minister Narendra Modi’s Hindu nationalist party showed a comfortable lead Tuesday, according to early figures reported by India’s Election Commission, but was facing a stronger challenge from the opposition than had been expected. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) supporters light firecrackers after hearing of a candidate’s victory during the counting of votes in India’s national election, in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
Across India, supporters of various political parties have been celebrating results as they trickle in with colored powder, fireworks, drums and more.
Hindu nationalism, once a fringe ideology in India, is now mainstream. Nobody has done more to advance this cause than Prime Minister Narendra Modi, one of India’s most beloved and polarizing political leaders.
Hindu nationalism , once a fringe ideology in India , is now mainstream. Nobody has done more to advance this cause than Prime Minister Narendra Modi , one of India’s most beloved and polarizing political leaders.
And no entity has had more influence on his political philosophy and ambitions than a paramilitary, right-wing group founded nearly a century ago and known as the RSS.
▶ Read more about how Hindu nationalism has become mainstream over the past decade.
Aam Aadmi Party leader Arvind Kejriwal greets his supporters from a vehicle during a roadshow in New Delhi, India, Saturday, May 11, 2024. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri)
As votes are being counted, Arvind Kejriwal, 55, is likely keeping track — from jail.
One of India’s most consequential opposition leaders, Kejriwal was arrested in March over alleged corruption charges, and let out on bail in May for a few weeks. He campaigned heavily during this time in his stronghold of New Delhi, India’s capital, as well as a few other cities before heading back to jail.
Kejriwal stormed into Indian politics in 2012 as he launched the anti-corruption Aam Aadmi Party, or Common People’s Party.
Since then, he has emerged as a fierce Modi rival, especially in New Delhi and Punjab state, where his party is in power.
His arrest and the ensuing saga dominated headlines, as he and his party accused Modi’s government of engineering his arrest to keep him out of the race. The government has denied this.
Kejriwal’s AAP is part of a broad alliance of opposition parties called INDIA, the main challenger to Modi’s BJP in this election.

Congress Party leader Rahul Gandhi holds a copy of the Indian Constitution as he addresses a press conference at the party headquarters in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024. (AP Photo/Altaf Qadri)
Rahul Gandhi, the face of the Congress party’s campaign and would-be prime minister, said the preliminary results showed India does not want Narendra Modi.
“People’s clear message to PM Modi and Home Minister Amit Shah is that we don’t want you to run the nation,” Gandhi said at a Congress party press conference around 10 hours into the vote count. “The poorest of this country have defended the constitution of India.”
Flanked by Congress leaders, including mother Sonia Gandhi, the Nehru-Gandhi dynasty scion brandished a copy of the constitution.
Despite a stronger-than-expected showing from Congress’ INDIA alliance thus far, Modi is still expected to secure a third term as prime minister.
The counting is ticking along more than 10 hours after it began, and results have now been called for 103 parliamentary seats out of a total of 543.
Modi’s National Democratic Alliance had won 67 seats, with 62 of them going to his Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party, according to India’s Election Commission. The opposing INDIA coalition had bagged 31 seats, with the main Congress party winning 27 of them. The remaining five seats went to other regional parties.

Congress party leader Shashi Taroor, and contender for the party president position, left, raises hands with newly elected president Mallikarjun Kharge in New Delhi, India, Wednesday, Oct. 19, 2022. (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
India’s opposition Congress party has called its alliance’s strong showing in the polls a “win for democracy” and a “moral and political loss” for Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
Congress party President Mallikarjun Kharge just addressed a press conference in New Delhi, saying that because no party had a clear majority, the mandate was against Modi.
“Our fight has not ended yet. We will continue to fight for the country’s development, for the constitution, for the benefit of the people,” Kharge said.
Modi’s coalition led in a majority of seats Tuesday in India’s general election , according to early figures, but faced a stronger challenge from the opposition than expected after it pushed back against the leader’s mixed economic record and polarizing politics. Modi was still widely expected to be elected to a third five-year term in the world’s largest democratic exercise .
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) supporters celebrate in Srinagar as vote counting is underway in India’s 2024 Lok Sabha election. AP video: Dar Yasin
Some 10 hours into counting , partial tallies reported by India’s Election Commission showed Narendra Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party was ahead in 196 constituencies and had won 45, including one uncontested, of 543 parliamentary seats. The main opposition Congress party led in 83 constituencies and had won 15.
A total of 272 seats are needed for a majority. In 2019, the BJP won 303 seats, while they secured 282 in 2014 when Modi first came to power.
Modi’s party is part of the National Democratic Alliance, whose members led in 236 constituencies and won 50, according to the partial count. The Congress party is part of the INDIA alliance , which led in 211 constituencies and had won 19.
The Election Commission does not release data on the percentage of votes tallied.

India’s general elections are held every five years. There are no specified term limits for lawmakers and thus no limit on how many years a prime minister can serve. Narendra Modi has already been in power for a decade. Should he win a third term and finish it out, he’ll near the record of the longest-serving prime minister, Jawaharlal Nehru.
India employs a first-past-the-post multiparty electoral system. That means for individual contests, whoever receives the most votes wins. To win a parliamentary majority — and thus the premiership — a party or a coalition of parties must secure at least 272 seats (543 seats are up for a vote). India’s electoral system is similar to the U.K.’s.
Congress party supporters celebrate in Mumbai as vote counting is underway in India’s 2024 Lok Sabha election. (AP video: Rafiq Maqbool)
India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi filed his nomination on Tuesday to run for a third term in India’s general election. Modi hopes to retain his seat in the holy Hindu city, his constituency, from where he ran and won, first in 2014 and then again in 2019. (AP video shot by Rajesh Kumar Singh)
Although Narendra Modi is the former chief minister of Gujarat, the incumbent prime minister has retained his seat in Varanasi.
It’s the constituency from which he first ran and won in 2014. Located in Uttar Pradesh, India’s most populous state, Varanasi is a holy Hindu city. It’s about 1,350 kilometers (840 miles) east of Modi’s hometown of Vadnagar in Gujarat state.
A woman shows her index fingers marked with an indelible ink as she poses for a photograph next to a cutout portrait of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi after casting her vote in Varanasi, India (AP Photo/Rajesh Kumar Singh)
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has won his seat from the Hindu holy city of Varanasi, the constituency from where he ran and won, first in 2014 and then again in 2019, India’s election commission reported.
Modi, who won by more than 152,000 votes, secured 54% of total votes. He was pitted against opposition Congress party’s Ajai Rai, who secured 40% of the votes.
The holy city is located on the banks of the revered Ganges River and is part of Uttar Pradesh state, India’s most populous, with around 200 million people.
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in a white waistcoat, and Yogi Adityanath, Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh greet supporters from a vehicle during a roadshow in Varanasi, India, Monday, May 13, 2024. (AP Photo/Rajesh Kumar)
In campaign rallies, Narendra Modi has called Muslims “infiltrators” and said they “have too many children,” referring to a Hindu nationalist trope that Muslims produce more children with the aim of outnumbering Hindus in India. He has also accused the rival Indian National Congress party of scheming to “loot” wealth from the country’s Hindus and redistribute it among Muslims, who comprise 14% of India’s more than 1.4 billion people.
Modi had kicked off his campaign with a focus on economic progress, promising he would make India a developed nation by 2047. But he and the ruling BJP doubled down heavily on their Hindu nationalism platform , with Modi employing some of his most divisive rhetoric in his decade in power.
The Congress party filed a complaint with the Election Commission of India, alleging Modi broke rules that bar candidates from engaging in any activity that aggravates religious tensions.
Analysts say the change in tone came as the BJP targeted a supermajority by consolidating votes among the majority Hindu population — a number that now seems out of reach. They say Modi’s party also ratcheted up polarizing speeches to distract voters from larger issues, like unemployment and economic distress, that the opposition has focused on.
A polling officer applies indelible ink mark on the finger of a voter during the fifth round of multi-phase national elections in Ayodhya, India, Monday, May 20, 2024. (AP Photo/Rajesh Kumar Singh)
Narendra Modi’s BJP have lost their seat in Ayodhya, a deeply symbolic loss for the party after the prime minister opened a grand but controversial Hindu temple there in January.
The BJP candidate, Lallu Singh, lost to a candidate put up by the regional Samajwadi Party, Singh’s poll agent Kamlesh Srivastava told The Associated Press. Singh had held the seat since 2014.
Modi and his party have heavily campaigned on this temple dedicated to Lord Ram, built on the historic ruins of a mosque that was destroyed by Hindu mobs in 1992.
In this photograph released by Indian Government Press Information Bureau, Indian Prime Minister, arrives to lead the opening of a temple dedicated to Hinduism’s Lord Ram in Ayodhya, India, Monday, Jan. 22, 2024. (Press Information Bureau via AP)
Experts said the January opening, where Modi performed rituals inside the temple, marked the unofficial start of his campaign as they hoped it would resonate with his Hindu majority voters. Modi’s government had turned the event into a national occasion by organizing live screenings across the country and closing offices for half a day.
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) supporters celebrate in Delhi as vote counting is underway in India’s 2024 Lok Sabha election. (AP video: Manish Swarup)

Vinod Kumar Vidyarthi waits with sweets outside the BJP party office for the final election results (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
Outside the BJP party office in New Delhi, supporter Vinod Kumar Vidyarthi sported a stole emblazoned with Modi’s likeness and toted a Modi-branded water bottle and sweets.
Despite the sweets, he had strong words regarding the election and the Hindu nationalist party he supports: “Our party will form the government. We had traitors within us. After we form the government, it will be a victory for Hindus and we will chase away all those who betrayed us.”
Polling officers Dekule Kapfo, Neke W Konyak, Neichutuonuo Yhome and Nukutholu Nienu prepare election-related paperwork on the eve of polling (AP Photo/Yirmiyan Arthur)
The Northern Angami constituency of Chedema village is Nagaland’s first to be solely managed by women polling officers. It was the idea of Kumar Ramnikant, the administrative head of Kohima district, in hopes of breaking job stereotypes.
“Women are more systematic. They take every sentence seriously, whereas men have an easy attitude,” said Zhoto Khamo, an officer who has supervised many elections.
▶ Read more about these polling officers and see more photos of the station.
The vote counting is still carrying on, but results have been called for 28 parliamentary seats out of 542 so far.
Narendra Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party has won 19 seats, according to India’s Election Commission, while its main opposition Congress party bagged 4 seats. The rest went to different regional parties.
Vote tallying is expected to take all day, but the count so far shows Modi’s party leading in 225 constituencies with the Congress ahead in 93.
G20 leaders pay their tributes at the Rajghat, a Mahatma Gandhi memorial, in New Delhi, India, Sunday, Sept. 10, 2023. (AP Photo/Kenny Holston, Pool)
The polls are seen as a test for India’s democratic and secular traditions, which critics say have seen a slow erosion under Narendra Modi’s 10-year rule. It also tests the limits of a populist leader who has risen to power by mixing religion with politics on a Hindu-first platform.
India’s clout on the global stage has risen under Modi. It’s seen by Western nations as a counterweight to Chinese aggression in the region even as New Delhi maintains its historic ties with Russia. And its large economy, one of the fastest growing in the world, has only boosted its rise as an emerging global power.
Earthmovers remove burnt debris the day after a fire broke out in an amusement park in Rajkot, India, Sunday, May 26, 2024 (AP Photo/Ajit Solanki)
Early leads from India’s election commission projected Narendra Modi’s ruling Bharatiya Janata Party was leading in 25 of 26 seats in the prime minister’s home state of Gujarat. But party leaders said they were not celebrating victory because of a recent fire at an amusement park in the state that killed 27 people.
A massive fire broke out last month at an amusement park in the state’s Rajkot city. Those killed included children.
“We had decided that there will be no celebratory victory or beating of drums. So we are not celebrating,” said C. R. Patil, a senior leader from Modi’s party.
India’s top opposition leader Rahul Gandhi, center, arrives at the Parliament in New Delhi, India, Monday, Aug.7, 2023 (AP Photo)
The 53-year-old is the scion of modern India’s most powerful political dynasty. He is the great-grandson of the country’s first prime minister, Jawaharlal Nehru. His grandmother and father also held the top job and were each assassinated.
He is the star face for the opposition Congress party, which governed India for nearly 55 years after the country gained independence from the British in 1947. This time, he and his Congress party are leading the main opposition alliance, called INDIA, against Narendra Modi’s BJP.
While his family connections have helped retain some loyal voters, they have also worked against him — especially in the past two elections, where he suffered huge losses against Modi, who refers to Gandhi as an out-of-touch elite, coasting on his surname.
On the campaign trail, Gandhi has called Modi a dictator ruining India’s democracy. He has attacked Modi and the BJP over recent anti-Muslim rhetoric. And his party is hoping to benefit from economic distress, including high unemployment.

A Bharatiya Janta Party supporter prepares to offer prayers to the cut-out of Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi outside their party headquarters in New Delhi, India, Tuesday, June 4, 2024 (AP Photo/Manish Swarup)
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s ruling Hindu nationalist party appears to be falling short of a majority in the early vote count. If these trends hold, it would be a stunning setback to the populist who has never relied on coalition partners to govern.
Modi’s party is still expected to form the government and return as the prime minister for a rare third consecutive term as his National Democratic Alliance was leading in about 290 constituencies — ahead of the 272 seats needed for a majority. Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party alone was leading in 242 seats.
A coalition would, however, diminish Modi’s power as a strongman leader who won his party landslide victories in 2014 and 2019 elections.
In such a scenario, his BJP would likely “be heavily dependent on the goodwill of its allies, which makes them critical players who we can expect will extract their pound of flesh, both in terms of policymaking as well as government formation,” said Milan Vaishnav, director of the South Asia Program at the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace.
“This would be truly, you know, uncharted territory, both for Indians as well as for the prime minister,” Vaishnav said.
Since coming to power in 2014, Modi’s BJP has governed in a coalition government but has always held a majority on its own.
Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) supporters celebrate in Guwahati as party seeks majority for third term in Assam. (AP video: Anupam Nath)
People cross the Brahmaputra river in a boat to reach a polling booth in Morigaon district, Assam, India, on April 26 (AP Photo/Anupam Nath)
As hundreds of millions headed to the polls, they did so amid sweltering heat and unpredictable weather extremes worsened by human-caused climate change. That climate change has led to losses of livelihood, forced migration and increasingly difficult living conditions.
India’s top political parties made promises to address climate change and reduce emissions in their election manifestos — but little of that was evident on the campaign trail.
Here’s a look at what climate change has wrought in the country:
- Western and central India: extreme heat and longer droughts
- Coastal regions: stronger and more frequent cyclones
- Northeastern India: unpredictable and increased flooding
- Himalayas: melting glaciers and intense rain
▶ Read more about how climate change has affected the election.

COMMENTS
Here are a few best practices: Your results should always be written in the past tense. While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analyzed, it should be written as concisely as possible. Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions.
How to Write Results in A Research Paper. Here are some general guidelines on how to write results in a research paper: Organize the results section: Start by organizing the results section in a logical and coherent manner. Divide the section into subsections if necessary, based on the research questions or hypotheses.
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper. Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions. The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is ...
Step 1: Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will ...
Present the results of the paper, in logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary. Explain the results and show how they help to answer the research questions posed in the Introduction. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained. Avoid: presenting results that are never discussed; presenting ...
The results section of a research paper tells the reader what you found, while the discussion section tells the reader what your findings mean. The results section should present the facts in an academic and unbiased manner, avoiding any attempt at analyzing or interpreting the data. Think of the results section as setting the stage for the ...
Wilder Research, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Human Services. (February 2009); Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Results. Thesis Writing in the Sciences. Course Syllabus. University of Florida.
The writing of the results section of a scientific paper is very important for the readers for clearly understanding of the study. This review summarizes the rules for writing the results section of a scientific paper and describes the use of tables and figures. ... As an example elucidating the abovementioned topics a research paper written by ...
Structure your results section around tables or figures that summarize the results of your statistical analysis. In many cases, the easiest way to accomplish this is to first create your tables and figures and then organize them in a logical way. Next, write the summary text to support your illustrative materials.
Build coherence along this section using goal statements and explicit reasoning (guide the reader through your reasoning, including sentences of this type: 'In order to…, we performed….'; 'In view of this result, we ….', etc.). In summary, the general steps for writing the Results section of a research article are:
The results section of the research paper is where you report the findings of your study based upon the information gathered as a result of the methodology [or methodologies] you applied. The results section should simply state the findings, without bias or interpretation, and arranged in a logical sequence. The results section should always be ...
The results section is where you report the main findings of your research. Watch this video to learn how to report your results concisely and objectively in...
The Results section is a vital organ of a scientific paper, the main reason why readers come and read to. " ". nd new information in the paper. However, writing the"Results section demands a rigorous process that discourages. fi ". many researchers, leaving their work unpublished and uncommunicated in reputable journals.
Developing a well-written research paper is an important step in completing a scientific study. This paper is where the principle investigator and co-authors report the purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions of the study. A key element of writing a research paper is to clearly and objectively report the study's findings in the Results section.
The results section of a research paper refers to the part that represents the study's core findings from the methods that the researcher used to collect and analyze data. This section presents the results logically without interpretation or bias from the author. Thus, this part of a research paper sets up the read for evaluation and analysis ...
The next stage of any research paper: writing the results section, announcing your findings to the world. In theory, this is the easiest part to write, because it is a straightforward commentary of exactly what you observed and found. In reality, it can be a little tricky, because it is very easy to include too much information and bury the ...
The results section is only for the results of the research. The results section provides the facts about what you discovered in the course of your research or experiment. The discussion section is where you can get analytical or reflective about exactly what you have discovered. This is the place where you can tell us what the results mean.
Examples of results section. 3.1. An example of a pre-processing passage in the results section. 3.2. An example of main findings passage in the results section. 3.3. An example of using statistics in the results section. 3.4. An example of using figures and tables in the results section.
How to Structure the Results Section: Start with a summary of the research aims and questions so that you can get your readers focused on the core of your study. Use the past tense and active ...
Pictures can speak a thousand words. Give as much detail as possible in your presentation of the results. Read and reread your statements for clarity. Engage a competent friend or a colleague's discerning eye for details. 2. Topic sentences or subheadings.
Results section of research paper contains outcomes about experiments. In the results section, you should narrate research findings without interpretation. ... He loves to educate researchers and research scholars on Research Paper Writing, Thesis Writing, Research Grants, Patenting Research Work and the latest Research-related issues.
A research summary is a crucial piece of writing that serves as an insightful overview of your research on a specific topic. As a researcher, it is essential to provide your reader with a detailed summary of the key findings from your study. When crafting a research summary, it is important to consider the structure of the article and the goal ...
The number of false positives (human-generated papers designated as AI by the detector) The number of false negatives (AI-generated papers designated as human by the detector). The analysis involved four steps: Preparing the three sets of documents. Selecting the 16 AI text detectors to include in the study.
Sue Kay, a Republican in the town of Apex in Wake County, which leans Democratic, said she was "disgusted" by the conviction. "There are businessmen in New York who cheat everyday," Ms ...
India's first general elections since achieving independence from Britain in 1947 took place from late 1951 through early 1952. Women had suffrage from the start. Due to high illiteracy at the time, voters were given blank ballot papers to place in boxes marked with symbols that represent each party, The Associated Press reported at the time.