

Narrative History Essay
Narrative history essay generator.

Knowing stories about history is really interesting. You will be able to come across with old traditions and cultures and the people’s way of life in the old times. Sometimes, a good story lies on our most compelling history. History plays a vital role in our lives where we are able to compare how we are living today versus how they used to live before. With all their strategies for survival during the old times, would it be amazing to know everything about it? In this article, you will get to know about narrative history and how to create history essays.
6+ Narrative History Essay Examples
1. narrative reflection of history essay.

Size: 411 KB
2. Narrative History Partnership Essay

Size: 376 KB
3. Narrative Historical Assignment Essay

Size: 442 KB
4. Editable Narrative History Essay

Size: 44 KB
5. Narrative Historical Inquiry Essay

Size: 440 KB
6. Printable Narrative History Essay

Size: 938 KB
7. Narrative History Nature Essay

What is a Narrative History?
A narrative history teaches you how to tell stories about the past. It contains when, where and why it happened, the importance of the event and who are the people involved in it. It basically allows us to understand the events in time. A narrative history focuses on the most substantial moment in the past which focuses on the actions and the causes that contributed to the outcome.
Why Narrative History Matters?
- Narrative history establishes the identity of their authors and readers.
Narrative histories are may be about a story of a family, community, experience of a person, etc. It gives credits to the authors and provides life with the information to the readers.
- Narrative history represent language and literature .
It makes reading available and easy to organize because it allows everyday life to center on historical orientation.
- Narrative history gives people the chance to take action from what they have learned over the past.
The purpose of a narrative history is to make people aware of the past actualities. It allows people living for today to take action as individuals or groups with regards to their historical knowledge.
How to Write a Narrative History Essay
Just like any other essay , creating a narrative history essay should also follow a certain format. Since you are going to tell a story of history, you add more components to the structure itself.
– Know the narrator of the story. Whose voice will perform in the narrative? Usually, the voice will be the author’s but using the 3rd person to describe events. You may also use 1st person to account a communication event or to describe an experience over looking for some historical facts.
The author is known as the one who controls the narrator. All that is happening in the story must not be in the narrator’s account because you should be able to see from different perspectives to undergo observations to see possible errors.
– Make sure that all the sequence of the events are connected to each other. It should have a beginning, middle and end. This contains what you are going to include in the story and take time to know the pace or the tempo of the story.
– Narratives should contain accounts of action. This means that it is the place where the elements of the story would gather.
– A good narrative has characters that is developed from forces on all sides of choice and has a tension between the person and his or her time and the way they resist.
– You have to put in mind that a narrative is not just any writing, rather it responds to accuracy. It should have coherence and fidelity that brings truth to the experience of a reader.
Why is history a narrative?
History is a narrative representation of the past that can be communicated in different methods as a form of expression. It tells stories so that the people living in modern times will be able to know what kind of life they had been living in the old times.
What makes a good historical narrative?
Narrative history should be organized in chronological order. You will not be able to understand the sequence of the events if the stories were not arranged by time.
What is the most important element of a narrative?
The most important element of a narrative is the conflict . It is the part where you are torn between having the idea that an ending would be a tragedy or something happy.
You just have to worry less about writing your narrative history essay. You just have to put the story on your paper, see if you have left out something and work artistically in your work.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write a Narrative History Essay on the impact of a major invention.
Create a Narrative History Essay about a pivotal moment in civil rights history.
Historical Narrative Essay Topics
Clio has taught education courses at the college level and has a Ph.D. in curriculum and instruction.
Table of Contents
The historical narrative essay, essay topics about people, essay topics about places, essay topics about events.
As you teach your students about history and social studies, you may be looking for ways they can express their learning through writing. Similarly, as your students grow in their familiarity with the writing process, you might seek out ways they can extend themselves to writing across the discipline. The historical narrative essay is a wonderful genre for meeting all of these purposes. When students write historical narratives, they focus on historical topics but write about them using a narrative structure that enables broader reflection on themes and ideas. Historical narrative essays often focus on small moments, telling them like stories that can then be used to reflect on bigger themes and ideas from history. The narrative essay topics in this lesson can be modified to get students of all ages and writing abilities focused on the intersection of history and writing.
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account
- Tell a story about a person from history who you believe made a big difference in the world. As you write about this person's life and works, try to focus in on one moment, action, or speech that you think encapsulates something meaningful about the person. You can also reflect on what you personally admire about this person and why you think they are especially important in history.
- Think about a person or group of people whose story you think is often missing or hidden from a bigger picture of history. Write an essay that describes your understanding of that person's or group's experience of a particular time, using a narrative structure to help your readers picture and imagine that person's life and its relevance to history.
- In this essay, write about a person from history who you think of as extremely different from yourself. Describe a story from their life and work that showcases this difference. Reflect in your essay on the person's major characteristics and what makes them a memorable historical figure, considering what you can also learn about yourself from the contrast with this person.
- Imagine that you are spending a day or part of a day in a place that you consider historically significant. Try to tell the story of the place, using all of your senses to enhance your description. Write about what makes the place historically significant and what it makes you think, feel and wonder.
- Tell a story from history with a focus on the geography where it took place. As you write, consider how this story might have unfolded differently given a different climate, landscape, and/or geopolitical situation. Your essay should describe the place alongside the story and should reflect on the importance of place as a historical phenomenon.
- Think of a building or architectural structure that has played an important role in history or culture. Write an essay that tells the history of this structure as though telling a story. Think about the memories that the building holds and the extent to which it, as a place, is also a character in history.
- What is an historical event that you really wish you had been alive to witness? Write about this event from your own point of view as though you had been there, watching from the sidelines. Tell the story of the event, but also reflect on its meaning, the feelings you would have had as a witness, and what might have unfolded differently in history if the event had never occurred.
- Focus in on an historical event that you find shameful, violent, or otherwise negative. Try to tell the story of this event in a way that helps you understand why it happened and what it meant in spite of the shame or otherwise negative feelings it precipitates. Think about what you might have learned from the event or from studying it as part of learning history; consider what humanity as a whole can learn from terrible historical occurrences.
- Write an essay about an event from history that you think shows people at their best. Show what people were involved in the event, what they did that makes you proud or excited, and what happened as a result of this event. Reflect on what it shows about people and their potential overall.
Register to view this lesson
Unlock your education, see for yourself why 30 million people use study.com, become a study.com member and start learning now..
Already a member? Log In
Resources created by teachers for teachers
I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. It’s like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. I feel like it’s a lifeline.
Historical Narrative Essay Topics Related Study Materials
- Related Topics
Browse by Courses
- FTCE General Knowledge Test (GK) (827): Reading Subtest Practice & Study Guide
- AP English Language Syllabus Resource & Lesson Plans
- Technical Writing Syllabus Resource & Lesson Plans
- College Composition Syllabus Resource & Lesson Plans
- GED Reasoning Through Language Arts
- Literacy Instruction in the Elementary School
- GACE Program Admission Assessment Test I Reading (210): Practice & Study Guide
- GACE Reading (617) Prep
- GACE Middle Grades Language Arts (011) Prep
- English 101 Syllabus Resource & Lesson Plans
- The Great Gatsby Study Guide
- Twelfth Night Study Guide
- PARCC ELA - Grade 10: Test Prep & Practice
- Ohio Graduation Test: Study Guide & Practice
- 12th Grade English: Homeschool Curriculum
Browse by Lessons
- Reading the Iliad by Homer | Length & Interpretation
- King Nestor in The Iliad by Homer | Character Traits & Analysis
- Bourriaud's Relational Aesthetics
- The Spanish Tragedy by Thomas Kyd | Summary & Themes
- Death of a Salesman: Characters & Quotes
- Death of a Salesman & The American Dream: Analysis & Criticism
- Death of a Salesman Discussion Questions
- Death of a Salesman Essay Topics
- Biff in Death of a Salesman | Character Traits & Analysis
- Literary Criticism of Death of a Salesman
- Betrayal in Death of a Salesman
- A View From the Bridge by Arthur Miller | Summary & Setting
- A View from the Bridge: Themes & Analysis
- A View from the Bridge: Characters & Quotes
- Note-Taking Techniques & Strategies
Create an account to start this course today Used by over 30 million students worldwide Create an account
Explore our library of over 88,000 lessons
- Foreign Language
- Social Science
- See All College Courses
- Common Core
- High School
- See All High School Courses
- College & Career Guidance Courses
- College Placement Exams
- Entrance Exams
- General Test Prep
- K-8 Courses
- Skills Courses
- Teacher Certification Exams
- See All Other Courses
- Create a Goal
- Create custom courses
- Get your questions answered
The Ultimate Narrative Essay Guide for Beginners

A narrative essay tells a story in chronological order, with an introduction that introduces the characters and sets the scene. Then a series of events leads to a climax or turning point, and finally a resolution or reflection on the experience.
Speaking of which, are you in sixes and sevens about narrative essays? Don’t worry this ultimate expert guide will wipe out all your doubts. So let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Everything You Need to Know About Narrative Essay
What is a narrative essay.
When you go through a narrative essay definition, you would know that a narrative essay purpose is to tell a story. It’s all about sharing an experience or event and is different from other types of essays because it’s more focused on how the event made you feel or what you learned from it, rather than just presenting facts or an argument. Let’s explore more details on this interesting write-up and get to know how to write a narrative essay.
Elements of a Narrative Essay
Here’s a breakdown of the key elements of a narrative essay:
A narrative essay has a beginning, middle, and end. It builds up tension and excitement and then wraps things up in a neat package.
Real people, including the writer, often feature in personal narratives. Details of the characters and their thoughts, feelings, and actions can help readers to relate to the tale.
It’s really important to know when and where something happened so we can get a good idea of the context. Going into detail about what it looks like helps the reader to really feel like they’re part of the story.
Conflict or Challenge
A story in a narrative essay usually involves some kind of conflict or challenge that moves the plot along. It could be something inside the character, like a personal battle, or something from outside, like an issue they have to face in the world.
Theme or Message
A narrative essay isn’t just about recounting an event – it’s about showing the impact it had on you and what you took away from it. It’s an opportunity to share your thoughts and feelings about the experience, and how it changed your outlook.
Emotional Impact
The author is trying to make the story they’re telling relatable, engaging, and memorable by using language and storytelling to evoke feelings in whoever’s reading it.
Narrative essays let writers have a blast telling stories about their own lives. It’s an opportunity to share insights and impart wisdom, or just have some fun with the reader. Descriptive language, sensory details, dialogue, and a great narrative voice are all essentials for making the story come alive.
The Purpose of a Narrative Essay
A narrative essay is more than just a story – it’s a way to share a meaningful, engaging, and relatable experience with the reader. Includes:
Sharing Personal Experience
Narrative essays are a great way for writers to share their personal experiences, feelings, thoughts, and reflections. It’s an opportunity to connect with readers and make them feel something.
Entertainment and Engagement
The essay attempts to keep the reader interested by using descriptive language, storytelling elements, and a powerful voice. It attempts to pull them in and make them feel involved by creating suspense, mystery, or an emotional connection.
Conveying a Message or Insight
Narrative essays are more than just a story – they aim to teach you something. They usually have a moral lesson, a new understanding, or a realization about life that the author gained from the experience.
Building Empathy and Understanding
By telling their stories, people can give others insight into different perspectives, feelings, and situations. Sharing these tales can create compassion in the reader and help broaden their knowledge of different life experiences.
Inspiration and Motivation
Stories about personal struggles, successes, and transformations can be really encouraging to people who are going through similar situations. It can provide them with hope and guidance, and let them know that they’re not alone.
Reflecting on Life’s Significance
These essays usually make you think about the importance of certain moments in life or the impact of certain experiences. They make you look deep within yourself and ponder on the things you learned or how you changed because of those events.
Demonstrating Writing Skills
Coming up with a gripping narrative essay takes serious writing chops, like vivid descriptions, powerful language, timing, and organization. It’s an opportunity for writers to show off their story-telling abilities.
Preserving Personal History
Sometimes narrative essays are used to record experiences and special moments that have an emotional resonance. They can be used to preserve individual memories or for future generations to look back on.
Cultural and Societal Exploration
Personal stories can look at cultural or social aspects, giving us an insight into customs, opinions, or social interactions seen through someone’s own experience.
Format of a Narrative Essay
Narrative essays are quite flexible in terms of format, which allows the writer to tell a story in a creative and compelling way. Here’s a quick breakdown of the narrative essay format, along with some examples:
Introduction
Set the scene and introduce the story.
Engage the reader and establish the tone of the narrative.
Hook: Start with a captivating opening line to grab the reader’s attention. For instance:
Example: “The scorching sun beat down on us as we trekked through the desert, our water supply dwindling.”
Background Information: Provide necessary context or background without giving away the entire story.
Example: “It was the summer of 2015 when I embarked on a life-changing journey to…”
Thesis Statement or Narrative Purpose
Present the main idea or the central message of the essay.
Offer a glimpse of what the reader can expect from the narrative.
Thesis Statement: This isn’t as rigid as in other essays but can be a sentence summarizing the essence of the story.
Example: “Little did I know, that seemingly ordinary hike would teach me invaluable lessons about resilience and friendship.”
Body Paragraphs
Present the sequence of events in chronological order.
Develop characters, setting, conflict, and resolution.
Story Progression : Describe events in the order they occurred, focusing on details that evoke emotions and create vivid imagery.
Example : Detail the trek through the desert, the challenges faced, interactions with fellow hikers, and the pivotal moments.
Character Development : Introduce characters and their roles in the story. Show their emotions, thoughts, and actions.
Example : Describe how each character reacted to the dwindling water supply and supported each other through adversity.
Dialogue and Interactions : Use dialogue to bring the story to life and reveal character personalities.
Example : “Sarah handed me her last bottle of water, saying, ‘We’re in this together.'”
Reach the peak of the story, the moment of highest tension or significance.
Turning Point: Highlight the most crucial moment or realization in the narrative.
Example: “As the sun dipped below the horizon and hope seemed lost, a distant sound caught our attention—the rescue team’s helicopters.”
Provide closure to the story.
Reflect on the significance of the experience and its impact.
Reflection : Summarize the key lessons learned or insights gained from the experience.
Example : “That hike taught me the true meaning of resilience and the invaluable support of friendship in challenging times.”
Closing Thought : End with a memorable line that reinforces the narrative’s message or leaves a lasting impression.
Example : “As we boarded the helicopters, I knew this adventure would forever be etched in my heart.”
Example Summary:
Imagine a narrative about surviving a challenging hike through the desert, emphasizing the bonds formed and lessons learned. The narrative essay structure might look like starting with an engaging scene, narrating the hardships faced, showcasing the characters’ resilience, and culminating in a powerful realization about friendship and endurance.
Different Types of Narrative Essays
There are a bunch of different types of narrative essays – each one focuses on different elements of storytelling and has its own purpose. Here’s a breakdown of the narrative essay types and what they mean.
Personal Narrative
Description : Tells a personal story or experience from the writer’s life.
Purpose: Reflects on personal growth, lessons learned, or significant moments.
Example of Narrative Essay Types:
Topic : “The Day I Conquered My Fear of Public Speaking”
Focus: Details the experience, emotions, and eventual triumph over a fear of public speaking during a pivotal event.
Descriptive Narrative
Description : Emphasizes vivid details and sensory imagery.
Purpose : Creates a sensory experience, painting a vivid picture for the reader.
Topic : “A Walk Through the Enchanted Forest”
Focus : Paints a detailed picture of the sights, sounds, smells, and feelings experienced during a walk through a mystical forest.
Autobiographical Narrative
Description: Chronicles significant events or moments from the writer’s life.
Purpose: Provides insights into the writer’s life, experiences, and growth.
Topic: “Lessons from My Childhood: How My Grandmother Shaped Who I Am”
Focus: Explores pivotal moments and lessons learned from interactions with a significant family member.
Experiential Narrative
Description: Relays experiences beyond the writer’s personal life.
Purpose: Shares experiences, travels, or events from a broader perspective.
Topic: “Volunteering in a Remote Village: A Journey of Empathy”
Focus: Chronicles the writer’s volunteering experience, highlighting interactions with a community and personal growth.
Literary Narrative
Description: Incorporates literary elements like symbolism, allegory, or thematic explorations.
Purpose: Uses storytelling for deeper explorations of themes or concepts.
Topic: “The Symbolism of the Red Door: A Journey Through Change”
Focus: Uses a red door as a symbol, exploring its significance in the narrator’s life and the theme of transition.
Historical Narrative
Description: Recounts historical events or periods through a personal lens.
Purpose: Presents history through personal experiences or perspectives.
Topic: “A Grandfather’s Tales: Living Through the Great Depression”
Focus: Shares personal stories from a family member who lived through a historical era, offering insights into that period.
Digital or Multimedia Narrative
Description: Incorporates multimedia elements like images, videos, or audio to tell a story.
Purpose: Explores storytelling through various digital platforms or formats.
Topic: “A Travel Diary: Exploring Europe Through Vlogs”
Focus: Combines video clips, photos, and personal narration to document a travel experience.
How to Choose a Topic for Your Narrative Essay?
Selecting a compelling topic for your narrative essay is crucial as it sets the stage for your storytelling. Choosing a boring topic is one of the narrative essay mistakes to avoid . Here’s a detailed guide on how to choose the right topic:
Reflect on Personal Experiences
- Significant Moments:
Moments that had a profound impact on your life or shaped your perspective.
Example: A moment of triumph, overcoming a fear, a life-changing decision, or an unforgettable experience.
- Emotional Resonance:
Events that evoke strong emotions or feelings.
Example: Joy, fear, sadness, excitement, or moments of realization.
- Lessons Learned:
Experiences that taught you valuable lessons or brought about personal growth.
Example: Challenges that led to personal development, shifts in mindset, or newfound insights.
Explore Unique Perspectives
- Uncommon Experiences:
Unique or unconventional experiences that might captivate the reader’s interest.
Example: Unusual travels, interactions with different cultures, or uncommon hobbies.
- Different Points of View:
Stories from others’ perspectives that impacted you deeply.
Example: A family member’s story, a friend’s experience, or a historical event from a personal lens.
Focus on Specific Themes or Concepts
- Themes or Concepts of Interest:
Themes or ideas you want to explore through storytelling.
Example: Friendship, resilience, identity, cultural diversity, or personal transformation.
- Symbolism or Metaphor:
Using symbols or metaphors as the core of your narrative.
Example: Exploring the symbolism of an object or a place in relation to a broader theme.
Consider Your Audience and Purpose
- Relevance to Your Audience:
Topics that resonate with your audience’s interests or experiences.
Example: Choose a relatable theme or experience that your readers might connect with emotionally.
- Impact or Message:
What message or insight do you want to convey through your story?
Example: Choose a topic that aligns with the message or lesson you aim to impart to your readers.
Brainstorm and Evaluate Ideas
- Free Writing or Mind Mapping:
Process: Write down all potential ideas without filtering. Mind maps or free-writing exercises can help generate diverse ideas.
- Evaluate Feasibility:
The depth of the story, the availability of vivid details, and your personal connection to the topic.
Imagine you’re considering topics for a narrative essay. You reflect on your experiences and decide to explore the topic of “Overcoming Stage Fright: How a School Play Changed My Perspective.” This topic resonates because it involves a significant challenge you faced and the personal growth it brought about.
Narrative Essay Topics
50 easy narrative essay topics.
- Learning to Ride a Bike
- My First Day of School
- A Surprise Birthday Party
- The Day I Got Lost
- Visiting a Haunted House
- An Encounter with a Wild Animal
- My Favorite Childhood Toy
- The Best Vacation I Ever Had
- An Unforgettable Family Gathering
- Conquering a Fear of Heights
- A Special Gift I Received
- Moving to a New City
- The Most Memorable Meal
- Getting Caught in a Rainstorm
- An Act of Kindness I Witnessed
- The First Time I Cooked a Meal
- My Experience with a New Hobby
- The Day I Met My Best Friend
- A Hike in the Mountains
- Learning a New Language
- An Embarrassing Moment
- Dealing with a Bully
- My First Job Interview
- A Sporting Event I Attended
- The Scariest Dream I Had
- Helping a Stranger
- The Joy of Achieving a Goal
- A Road Trip Adventure
- Overcoming a Personal Challenge
- The Significance of a Family Tradition
- An Unusual Pet I Owned
- A Misunderstanding with a Friend
- Exploring an Abandoned Building
- My Favorite Book and Why
- The Impact of a Role Model
- A Cultural Celebration I Participated In
- A Valuable Lesson from a Teacher
- A Trip to the Zoo
- An Unplanned Adventure
- Volunteering Experience
- A Moment of Forgiveness
- A Decision I Regretted
- A Special Talent I Have
- The Importance of Family Traditions
- The Thrill of Performing on Stage
- A Moment of Sudden Inspiration
- The Meaning of Home
- Learning to Play a Musical Instrument
- A Childhood Memory at the Park
- Witnessing a Beautiful Sunset
Narrative Essay Topics for College Students
- Discovering a New Passion
- Overcoming Academic Challenges
- Navigating Cultural Differences
- Embracing Independence: Moving Away from Home
- Exploring Career Aspirations
- Coping with Stress in College
- The Impact of a Mentor in My Life
- Balancing Work and Studies
- Facing a Fear of Public Speaking
- Exploring a Semester Abroad
- The Evolution of My Study Habits
- Volunteering Experience That Changed My Perspective
- The Role of Technology in Education
- Finding Balance: Social Life vs. Academics
- Learning a New Skill Outside the Classroom
- Reflecting on Freshman Year Challenges
- The Joys and Struggles of Group Projects
- My Experience with Internship or Work Placement
- Challenges of Time Management in College
- Redefining Success Beyond Grades
- The Influence of Literature on My Thinking
- The Impact of Social Media on College Life
- Overcoming Procrastination
- Lessons from a Leadership Role
- Exploring Diversity on Campus
- Exploring Passion for Environmental Conservation
- An Eye-Opening Course That Changed My Perspective
- Living with Roommates: Challenges and Lessons
- The Significance of Extracurricular Activities
- The Influence of a Professor on My Academic Journey
- Discussing Mental Health in College
- The Evolution of My Career Goals
- Confronting Personal Biases Through Education
- The Experience of Attending a Conference or Symposium
- Challenges Faced by Non-Native English Speakers in College
- The Impact of Traveling During Breaks
- Exploring Identity: Cultural or Personal
- The Impact of Music or Art on My Life
- Addressing Diversity in the Classroom
- Exploring Entrepreneurial Ambitions
- My Experience with Research Projects
- Overcoming Impostor Syndrome in College
- The Importance of Networking in College
- Finding Resilience During Tough Times
- The Impact of Global Issues on Local Perspectives
- The Influence of Family Expectations on Education
- Lessons from a Part-Time Job
- Exploring the College Sports Culture
- The Role of Technology in Modern Education
- The Journey of Self-Discovery Through Education
Narrative Essay Comparison
Narrative essay vs. descriptive essay.
Here’s our first narrative essay comparison! While both narrative and descriptive essays focus on vividly portraying a subject or an event, they differ in their primary objectives and approaches. Now, let’s delve into the nuances of comparison on narrative essays.
Narrative Essay:
Storytelling: Focuses on narrating a personal experience or event.
Chronological Order: Follows a structured timeline of events to tell a story.
Message or Lesson: Often includes a central message, moral, or lesson learned from the experience.
Engagement: Aims to captivate the reader through a compelling storyline and character development.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s point of view, using “I” and expressing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Emphasizes a plot with a beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Character Development: Focuses on describing characters, their interactions, emotions, and growth.
Conflict or Challenge: Usually involves a central conflict or challenge that drives the narrative forward.
Dialogue: Incorporates conversations to bring characters and their interactions to life.
Reflection: Concludes with reflection or insight gained from the experience.
Descriptive Essay:
Vivid Description: Aims to vividly depict a person, place, object, or event.
Imagery and Details: Focuses on sensory details to create a vivid image in the reader’s mind.
Emotion through Description: Uses descriptive language to evoke emotions and engage the reader’s senses.
Painting a Picture: Creates a sensory-rich description allowing the reader to visualize the subject.
Imagery and Sensory Details: Focuses on providing rich sensory descriptions, using vivid language and adjectives.
Point of Focus: Concentrates on describing a specific subject or scene in detail.
Spatial Organization: Often employs spatial organization to describe from one area or aspect to another.
Objective Observations: Typically avoids the use of personal opinions or emotions; instead, the focus remains on providing a detailed and objective description.
Comparison:
Focus: Narrative essays emphasize storytelling, while descriptive essays focus on vividly describing a subject or scene.
Perspective: Narrative essays are often written from a first-person perspective, while descriptive essays may use a more objective viewpoint.
Purpose: Narrative essays aim to convey a message or lesson through a story, while descriptive essays aim to paint a detailed picture for the reader without necessarily conveying a specific message.
Narrative Essay vs. Argumentative Essay
The narrative essay and the argumentative essay serve distinct purposes and employ different approaches:
Engagement and Emotion: Aims to captivate the reader through a compelling story.
Reflective: Often includes reflection on the significance of the experience or lessons learned.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s point of view, sharing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Emphasizes a storyline with a beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Message or Lesson: Conveys a central message, moral, or insight derived from the experience.
Argumentative Essay:
Persuasion and Argumentation: Aims to persuade the reader to adopt the writer’s viewpoint on a specific topic.
Logical Reasoning: Presents evidence, facts, and reasoning to support a particular argument or stance.
Debate and Counterarguments: Acknowledge opposing views and counter them with evidence and reasoning.
Thesis Statement: Includes a clear thesis statement that outlines the writer’s position on the topic.
Thesis and Evidence: Starts with a strong thesis statement and supports it with factual evidence, statistics, expert opinions, or logical reasoning.
Counterarguments: Addresses opposing viewpoints and provides rebuttals with evidence.
Logical Structure: Follows a logical structure with an introduction, body paragraphs presenting arguments and evidence, and a conclusion reaffirming the thesis.
Formal Language: Uses formal language and avoids personal anecdotes or emotional appeals.
Objective: Argumentative essays focus on presenting a logical argument supported by evidence, while narrative essays prioritize storytelling and personal reflection.
Purpose: Argumentative essays aim to persuade and convince the reader of a particular viewpoint, while narrative essays aim to engage, entertain, and share personal experiences.
Structure: Narrative essays follow a storytelling structure with character development and plot, while argumentative essays follow a more formal, structured approach with logical arguments and evidence.
In essence, while both essays involve writing and presenting information, the narrative essay focuses on sharing a personal experience, whereas the argumentative essay aims to persuade the audience by presenting a well-supported argument.
Narrative Essay vs. Personal Essay
While there can be an overlap between narrative and personal essays, they have distinctive characteristics:
Storytelling: Emphasizes recounting a specific experience or event in a structured narrative form.
Engagement through Story: Aims to engage the reader through a compelling story with characters, plot, and a central theme or message.
Reflective: Often includes reflection on the significance of the experience and the lessons learned.
First-Person Perspective: Typically narrated from the writer’s viewpoint, expressing personal emotions and thoughts.
Plot Development: Focuses on developing a storyline with a clear beginning, middle, climax, and resolution.
Character Development: Includes descriptions of characters, their interactions, emotions, and growth.
Central Message: Conveys a central message, moral, or insight derived from the experience.
Personal Essay:
Exploration of Ideas or Themes: Explores personal ideas, opinions, or reflections on a particular topic or subject.
Expression of Thoughts and Opinions: Expresses the writer’s thoughts, feelings, and perspectives on a specific subject matter.
Reflection and Introspection: Often involves self-reflection and introspection on personal experiences, beliefs, or values.
Varied Structure and Content: Can encompass various forms, including memoirs, personal anecdotes, or reflections on life experiences.
Flexibility in Structure: Allows for diverse structures and forms based on the writer’s intent, which could be narrative-like or more reflective.
Theme-Centric Writing: Focuses on exploring a central theme or idea, with personal anecdotes or experiences supporting and illustrating the theme.
Expressive Language: Utilizes descriptive and expressive language to convey personal perspectives, emotions, and opinions.
Focus: Narrative essays primarily focus on storytelling through a structured narrative, while personal essays encompass a broader range of personal expression, which can include storytelling but isn’t limited to it.
Structure: Narrative essays have a more structured plot development with characters and a clear sequence of events, while personal essays might adopt various structures, focusing more on personal reflection, ideas, or themes.
Intent: While both involve personal experiences, narrative essays emphasize telling a story with a message or lesson learned, while personal essays aim to explore personal thoughts, feelings, or opinions on a broader range of topics or themes.

A narrative essay is more than just telling a story. It’s also meant to engage the reader, get them thinking, and leave a lasting impact. Whether it’s to amuse, motivate, teach, or reflect, these essays are a great way to communicate with your audience. This interesting narrative essay guide was all about letting you understand the narrative essay, its importance, and how can you write one.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score

- TEFL Internship
- TEFL Masters
- Find a TEFL Course
- Special Offers
- Course Providers
- Teach English Abroad
- Find a TEFL Job
- About DoTEFL
- Our Mission
- How DoTEFL Works
Forgotten Password

- How To Write a Narrative Essay: Guide With Examples
- Learn English
- James Prior
- No Comments
- Updated December 12, 2023
Welcome to the creative world of narrative essays where you get to become the storyteller and craft your own narrative. In this article, we’ll break down how to write a narrative essay, covering the essential elements and techniques that you need to know.

Table of Contents
What is a Narrative Essay?
A narrative essay is a form of writing where the author recounts a personal experience or story. Unlike other types of essays, a narrative essay allows you to share a real-life event or sequence of events, often drawing from personal insights and emotions.
In a narrative essay, you take on the role of a storyteller, employing vivid details and descriptive language to transport the reader into the world of your story. The narrative often unfolds in chronological order, guiding the audience through a journey of experiences, reflections, and sometimes, a lesson learned.
The success of a narrative essay lies in your ability to create a compelling narrative arc. This means establishing a clear beginning, middle, and end. This structure helps build suspense, maintain the reader’s interest, and deliver a cohesive and impactful story. Ultimately, a well-crafted narrative essay not only narrates an event but also communicates the deeper meaning or significance behind the experience, making it a powerful and memorable piece of writing and leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
Types of Narrative Essays
Narrative essays come in various forms, each with unique characteristics. The most common type of narrative essay are personal narrative essays where you write about a personal experience. This can cover a whole range of topics as these examples of personal narrative essays illustrate. As a student in school or college, you’ll often be asked to write these types of essays. You may also need to write them later in life when applying for jobs and describing your past experiences.
However, this isn’t the only type of narrative essay. There are also fictional narrative essays that you can write using your imagination, and various subject specific narrative essays that you might have come across without even realizing it.
So, it’s worth knowing about the different types of narrative essays and what they each focus on before we move on to how to write them.
Here are some common types of narrative essays:
- Focus on a personal experience or event from the author’s life.
- Use the first-person perspective to convey the writer’s emotions and reflections.
- Can take many forms, from science fiction and fantasy to adventure and romance.
- Spark the imagination to create captivating stories.
- Provide a detailed account of the author’s life, often covering a significant timespan.
- Explore key life events, achievements, challenges, and personal growth.
- Reflect on the writer’s experiences with language, reading, or writing.
- Explore how these experiences have shaped the writer’s identity and skills
- Document the author’s experiences and insights gained from a journey or travel.
- Describe places visited, people encountered, and the lessons learned during the trip.
- Explore historical events or periods through a personal lens.
- Combine factual information with the writer’s perspective and experiences.
The narrative essay type you’ll work with often depends on the purpose, audience, and nature of the story being told. So, how should you write narrative essays?
How To Write Narrative Essays
From selecting the right topic to building a captivating storyline, we explore the basics to guide you in creating engaging narratives. So, grab your pen, and let’s delve into the fundamentals of writing a standout narrative essay.
Before we start, it’s worth pointing out that most narrative essays are written in the first-person. Through the use of first-person perspective, you get to connect with the reader, offering a glimpse into your thoughts, reactions, and the significance of the story being shared.
Let’s get into how to create these stories:
Write your plot
If you want to tell a compelling story you need a good plot. Your plot will give your story a structure. Every good story includes some kind of conflict. You should start with setting the scene for readers. After this, you introduce a challenge or obstacle. Readers will keep reading until the end to find out how you managed to overcome it.
Your story should reach a climax where tension is highest. This will be the turning point that leads to a resolution. For example, moving outside of your comfort zone was difficult and scary. It wasn’t easy at first but eventually, you grew braver and more confident. Readers should discover more about who you are as a person through what they read.
A seasoned writer knows how to craft a story that connects with an audience and creates an impact.
Hook readers with your introduction
In your introduction, you will introduce the main idea of your essay and set the context. Ways to make it more engaging are to:
- Use sensory images to describe the setting in which your story takes place.
- Use a quote that illustrates your main idea.
- Pose an intriguing question.
- Introduce an unexpected fact or a statement that grabs attention.
Develop your characters
You need to make readers feel they know any characters you introduce in your narrative essay. You can do this by revealing their personalities and quirks through the actions they take. It is always better to show the actions of characters rather than giving facts about them. Describing a character’s body language and features can also reveal a great deal about the person. You can check out these adjectives to describe a person to get some inspiration.
Use dialogue
Dialogue can bring your narrative essay to life. Most fiction books use dialogue extensively . It helps to move the story along in a subtle way. When you allow characters to talk, what they have to say seems more realistic. You can use similes , metaphors, and other parts of speech to make your story more compelling. Just make sure the dialogue is written clearly with the right punctuation so readers understand exactly who is talking.
Work on the pace of the story
Your story must flow along at a steady pace. If there’s too much action, readers may get confused. If you use descriptive writing, try not to overdo it. The clear, concise language throughout will appeal to readers more than lengthy descriptions.
Build up towards a climax
This is the point at which the tension in your story is the highest. A compelling climax takes readers by surprise. They may not have seen it coming. This doesn’t mean your climax should come out of left field. You need to carefully lead up to it step by step and guide readers along. When you reveal it they should be able to look back and realize it’s logical.
Cut out what you don’t need
Your story will suffer if you include too much detail that doesn’t move your story along. It may flow better once you cut out some unnecessary details. Most narrative essays are about five paragraphs but this will depend on the topic and requirements.
In a narrative essay, you share your experiences and insights. The journey you take your readers on should leave them feeling moved or inspired. It takes practice to learn how to write in a way that causes this reaction. With a good plot as your guide, it’s easier to write a compelling story that flows toward a satisfying resolution.
- Recent Posts
- 113+ American Slang Words & Phrases With Examples - May 29, 2024
- 11 Best Business English Courses Online - May 29, 2024
- How to Teach Business English - May 27, 2024
More from DoTEFL

The Meaning of Population & What is the Mean of Population?
- Updated November 2, 2023

How to Become an English Teacher in Japan
- Anna Deutschman
- Updated February 5, 2024

101 Cause and Effect Essay Topics for Inquisitive Students
47 Online Timers for the Classroom
- Updated October 28, 2023

How to Teach Students to Love Reading
- Updated December 14, 2022

What is an EFL Teacher & What Does EFL Teaching Involve?
- Updated March 7, 2024
- The global TEFL course directory.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 3 great narrative essay examples + tips for writing.
General Education

A narrative essay is one of the most intimidating assignments you can be handed at any level of your education. Where you've previously written argumentative essays that make a point or analytic essays that dissect meaning, a narrative essay asks you to write what is effectively a story .
But unlike a simple work of creative fiction, your narrative essay must have a clear and concrete motif —a recurring theme or idea that you’ll explore throughout. Narrative essays are less rigid, more creative in expression, and therefore pretty different from most other essays you’ll be writing.
But not to fear—in this article, we’ll be covering what a narrative essay is, how to write a good one, and also analyzing some personal narrative essay examples to show you what a great one looks like.
What Is a Narrative Essay?
At first glance, a narrative essay might sound like you’re just writing a story. Like the stories you're used to reading, a narrative essay is generally (but not always) chronological, following a clear throughline from beginning to end. Even if the story jumps around in time, all the details will come back to one specific theme, demonstrated through your choice in motifs.
Unlike many creative stories, however, your narrative essay should be based in fact. That doesn’t mean that every detail needs to be pure and untainted by imagination, but rather that you shouldn’t wholly invent the events of your narrative essay. There’s nothing wrong with inventing a person’s words if you can’t remember them exactly, but you shouldn’t say they said something they weren’t even close to saying.
Another big difference between narrative essays and creative fiction—as well as other kinds of essays—is that narrative essays are based on motifs. A motif is a dominant idea or theme, one that you establish before writing the essay. As you’re crafting the narrative, it’ll feed back into your motif to create a comprehensive picture of whatever that motif is.
For example, say you want to write a narrative essay about how your first day in high school helped you establish your identity. You might discuss events like trying to figure out where to sit in the cafeteria, having to describe yourself in five words as an icebreaker in your math class, or being unsure what to do during your lunch break because it’s no longer acceptable to go outside and play during lunch. All of those ideas feed back into the central motif of establishing your identity.
The important thing to remember is that while a narrative essay is typically told chronologically and intended to read like a story, it is not purely for entertainment value. A narrative essay delivers its theme by deliberately weaving the motifs through the events, scenes, and details. While a narrative essay may be entertaining, its primary purpose is to tell a complete story based on a central meaning.
Unlike other essay forms, it is totally okay—even expected—to use first-person narration in narrative essays. If you’re writing a story about yourself, it’s natural to refer to yourself within the essay. It’s also okay to use other perspectives, such as third- or even second-person, but that should only be done if it better serves your motif. Generally speaking, your narrative essay should be in first-person perspective.
Though your motif choices may feel at times like you’re making a point the way you would in an argumentative essay, a narrative essay’s goal is to tell a story, not convince the reader of anything. Your reader should be able to tell what your motif is from reading, but you don’t have to change their mind about anything. If they don’t understand the point you are making, you should consider strengthening the delivery of the events and descriptions that support your motif.
Narrative essays also share some features with analytical essays, in which you derive meaning from a book, film, or other media. But narrative essays work differently—you’re not trying to draw meaning from an existing text, but rather using an event you’ve experienced to convey meaning. In an analytical essay, you examine narrative, whereas in a narrative essay you create narrative.
The structure of a narrative essay is also a bit different than other essays. You’ll generally be getting your point across chronologically as opposed to grouping together specific arguments in paragraphs or sections. To return to the example of an essay discussing your first day of high school and how it impacted the shaping of your identity, it would be weird to put the events out of order, even if not knowing what to do after lunch feels like a stronger idea than choosing where to sit. Instead of organizing to deliver your information based on maximum impact, you’ll be telling your story as it happened, using concrete details to reinforce your theme.

3 Great Narrative Essay Examples
One of the best ways to learn how to write a narrative essay is to look at a great narrative essay sample. Let’s take a look at some truly stellar narrative essay examples and dive into what exactly makes them work so well.
A Ticket to the Fair by David Foster Wallace
Today is Press Day at the Illinois State Fair in Springfield, and I’m supposed to be at the fairgrounds by 9:00 A.M. to get my credentials. I imagine credentials to be a small white card in the band of a fedora. I’ve never been considered press before. My real interest in credentials is getting into rides and shows for free. I’m fresh in from the East Coast, for an East Coast magazine. Why exactly they’re interested in the Illinois State Fair remains unclear to me. I suspect that every so often editors at East Coast magazines slap their foreheads and remember that about 90 percent of the United States lies between the coasts, and figure they’ll engage somebody to do pith-helmeted anthropological reporting on something rural and heartlandish. I think they asked me to do this because I grew up here, just a couple hours’ drive from downstate Springfield. I never did go to the state fair, though—I pretty much topped out at the county fair level. Actually, I haven’t been back to Illinois for a long time, and I can’t say I’ve missed it.
Throughout this essay, David Foster Wallace recounts his experience as press at the Illinois State Fair. But it’s clear from this opening that he’s not just reporting on the events exactly as they happened—though that’s also true— but rather making a point about how the East Coast, where he lives and works, thinks about the Midwest.
In his opening paragraph, Wallace states that outright: “Why exactly they’re interested in the Illinois State Fair remains unclear to me. I suspect that every so often editors at East Coast magazines slap their foreheads and remember that about 90 percent of the United States lies between the coasts, and figure they’ll engage somebody to do pith-helmeted anthropological reporting on something rural and heartlandish.”
Not every motif needs to be stated this clearly , but in an essay as long as Wallace’s, particularly since the audience for such a piece may feel similarly and forget that such a large portion of the country exists, it’s important to make that point clear.
But Wallace doesn’t just rest on introducing his motif and telling the events exactly as they occurred from there. It’s clear that he selects events that remind us of that idea of East Coast cynicism , such as when he realizes that the Help Me Grow tent is standing on top of fake grass that is killing the real grass beneath, when he realizes the hypocrisy of craving a corn dog when faced with a real, suffering pig, when he’s upset for his friend even though he’s not the one being sexually harassed, and when he witnesses another East Coast person doing something he wouldn’t dare to do.
Wallace is literally telling the audience exactly what happened, complete with dates and timestamps for when each event occurred. But he’s also choosing those events with a purpose—he doesn’t focus on details that don’t serve his motif. That’s why he discusses the experiences of people, how the smells are unappealing to him, and how all the people he meets, in cowboy hats, overalls, or “black spandex that looks like cheesecake leotards,” feel almost alien to him.
All of these details feed back into the throughline of East Coast thinking that Wallace introduces in the first paragraph. He also refers back to it in the essay’s final paragraph, stating:
At last, an overarching theory blooms inside my head: megalopolitan East Coasters’ summer treats and breaks and literally ‘getaways,’ flights-from—from crowds, noise, heat, dirt, the stress of too many sensory choices….The East Coast existential treat is escape from confines and stimuli—quiet, rustic vistas that hold still, turn inward, turn away. Not so in the rural Midwest. Here you’re pretty much away all the time….Something in a Midwesterner sort of actuates , deep down, at a public event….The real spectacle that draws us here is us.
Throughout this journey, Wallace has tried to demonstrate how the East Coast thinks about the Midwest, ultimately concluding that they are captivated by the Midwest’s less stimuli-filled life, but that the real reason they are interested in events like the Illinois State Fair is that they are, in some ways, a means of looking at the East Coast in a new, estranging way.
The reason this works so well is that Wallace has carefully chosen his examples, outlined his motif and themes in the first paragraph, and eventually circled back to the original motif with a clearer understanding of his original point.
When outlining your own narrative essay, try to do the same. Start with a theme, build upon it with examples, and return to it in the end with an even deeper understanding of the original issue. You don’t need this much space to explore a theme, either—as we’ll see in the next example, a strong narrative essay can also be very short.
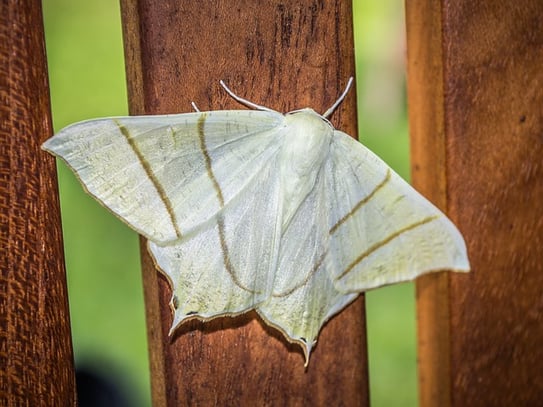

Death of a Moth by Virginia Woolf
After a time, tired by his dancing apparently, he settled on the window ledge in the sun, and, the queer spectacle being at an end, I forgot about him. Then, looking up, my eye was caught by him. He was trying to resume his dancing, but seemed either so stiff or so awkward that he could only flutter to the bottom of the window-pane; and when he tried to fly across it he failed. Being intent on other matters I watched these futile attempts for a time without thinking, unconsciously waiting for him to resume his flight, as one waits for a machine, that has stopped momentarily, to start again without considering the reason of its failure. After perhaps a seventh attempt he slipped from the wooden ledge and fell, fluttering his wings, on to his back on the window sill. The helplessness of his attitude roused me. It flashed upon me that he was in difficulties; he could no longer raise himself; his legs struggled vainly. But, as I stretched out a pencil, meaning to help him to right himself, it came over me that the failure and awkwardness were the approach of death. I laid the pencil down again.
In this essay, Virginia Woolf explains her encounter with a dying moth. On surface level, this essay is just a recounting of an afternoon in which she watched a moth die—it’s even established in the title. But there’s more to it than that. Though Woolf does not begin her essay with as clear a motif as Wallace, it’s not hard to pick out the evidence she uses to support her point, which is that the experience of this moth is also the human experience.
In the title, Woolf tells us this essay is about death. But in the first paragraph, she seems to mostly be discussing life—the moth is “content with life,” people are working in the fields, and birds are flying. However, she mentions that it is mid-September and that the fields were being plowed. It’s autumn and it’s time for the harvest; the time of year in which many things die.
In this short essay, she chronicles the experience of watching a moth seemingly embody life, then die. Though this essay is literally about a moth, it’s also about a whole lot more than that. After all, moths aren’t the only things that die—Woolf is also reflecting on her own mortality, as well as the mortality of everything around her.
At its core, the essay discusses the push and pull of life and death, not in a way that’s necessarily sad, but in a way that is accepting of both. Woolf begins by setting up the transitional fall season, often associated with things coming to an end, and raises the ideas of pleasure, vitality, and pity.
At one point, Woolf tries to help the dying moth, but reconsiders, as it would interfere with the natural order of the world. The moth’s death is part of the natural order of the world, just like fall, just like her own eventual death.
All these themes are set up in the beginning and explored throughout the essay’s narrative. Though Woolf doesn’t directly state her theme, she reinforces it by choosing a small, isolated event—watching a moth die—and illustrating her point through details.
With this essay, we can see that you don’t need a big, weird, exciting event to discuss an important meaning. Woolf is able to explore complicated ideas in a short essay by being deliberate about what details she includes, just as you can be in your own essays.
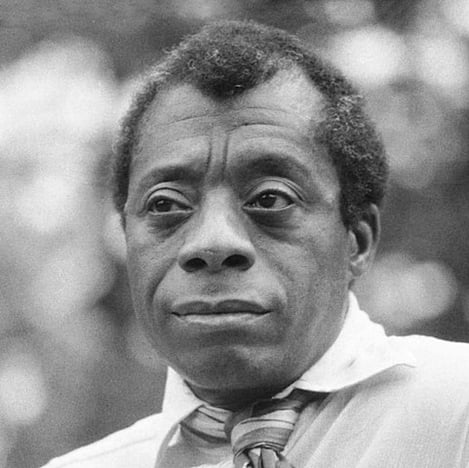

Notes of a Native Son by James Baldwin
On the twenty-ninth of July, in 1943, my father died. On the same day, a few hours later, his last child was born. Over a month before this, while all our energies were concentrated in waiting for these events, there had been, in Detroit, one of the bloodiest race riots of the century. A few hours after my father’s funeral, while he lay in state in the undertaker’s chapel, a race riot broke out in Harlem. On the morning of the third of August, we drove my father to the graveyard through a wilderness of smashed plate glass.
Like Woolf, Baldwin does not lay out his themes in concrete terms—unlike Wallace, there’s no clear sentence that explains what he’ll be talking about. However, you can see the motifs quite clearly: death, fatherhood, struggle, and race.
Throughout the narrative essay, Baldwin discusses the circumstances of his father’s death, including his complicated relationship with his father. By introducing those motifs in the first paragraph, the reader understands that everything discussed in the essay will come back to those core ideas. When Baldwin talks about his experience with a white teacher taking an interest in him and his father’s resistance to that, he is also talking about race and his father’s death. When he talks about his father’s death, he is also talking about his views on race. When he talks about his encounters with segregation and racism, he is talking, in part, about his father.
Because his father was a hard, uncompromising man, Baldwin struggles to reconcile the knowledge that his father was right about many things with his desire to not let that hardness consume him, as well.
Baldwin doesn’t explicitly state any of this, but his writing so often touches on the same motifs that it becomes clear he wants us to think about all these ideas in conversation with one another.
At the end of the essay, Baldwin makes it more clear:
This fight begins, however, in the heart and it had now been laid to my charge to keep my own heart free of hatred and despair. This intimation made my heart heavy and, now that my father was irrecoverable, I wished that he had been beside me so that I could have searched his face for the answers which only the future would give me now.
Here, Baldwin ties together the themes and motifs into one clear statement: that he must continue to fight and recognize injustice, especially racial injustice, just as his father did. But unlike his father, he must do it beginning with himself—he must not let himself be closed off to the world as his father was. And yet, he still wishes he had his father for guidance, even as he establishes that he hopes to be a different man than his father.
In this essay, Baldwin loads the front of the essay with his motifs, and, through his narrative, weaves them together into a theme. In the end, he comes to a conclusion that connects all of those things together and leaves the reader with a lasting impression of completion—though the elements may have been initially disparate, in the end everything makes sense.
You can replicate this tactic of introducing seemingly unattached ideas and weaving them together in your own essays. By introducing those motifs, developing them throughout, and bringing them together in the end, you can demonstrate to your reader how all of them are related. However, it’s especially important to be sure that your motifs and clear and consistent throughout your essay so that the conclusion feels earned and consistent—if not, readers may feel mislead.
5 Key Tips for Writing Narrative Essays
Narrative essays can be a lot of fun to write since they’re so heavily based on creativity. But that can also feel intimidating—sometimes it’s easier to have strict guidelines than to have to make it all up yourself. Here are a few tips to keep your narrative essay feeling strong and fresh.
Develop Strong Motifs
Motifs are the foundation of a narrative essay . What are you trying to say? How can you say that using specific symbols or events? Those are your motifs.
In the same way that an argumentative essay’s body should support its thesis, the body of your narrative essay should include motifs that support your theme.
Try to avoid cliches, as these will feel tired to your readers. Instead of roses to symbolize love, try succulents. Instead of the ocean representing some vast, unknowable truth, try the depths of your brother’s bedroom. Keep your language and motifs fresh and your essay will be even stronger!
Use First-Person Perspective
In many essays, you’re expected to remove yourself so that your points stand on their own. Not so in a narrative essay—in this case, you want to make use of your own perspective.
Sometimes a different perspective can make your point even stronger. If you want someone to identify with your point of view, it may be tempting to choose a second-person perspective. However, be sure you really understand the function of second-person; it’s very easy to put a reader off if the narration isn’t expertly deployed.
If you want a little bit of distance, third-person perspective may be okay. But be careful—too much distance and your reader may feel like the narrative lacks truth.
That’s why first-person perspective is the standard. It keeps you, the writer, close to the narrative, reminding the reader that it really happened. And because you really know what happened and how, you’re free to inject your own opinion into the story without it detracting from your point, as it would in a different type of essay.
Stick to the Truth
Your essay should be true. However, this is a creative essay, and it’s okay to embellish a little. Rarely in life do we experience anything with a clear, concrete meaning the way somebody in a book might. If you flub the details a little, it’s okay—just don’t make them up entirely.
Also, nobody expects you to perfectly recall details that may have happened years ago. You may have to reconstruct dialog from your memory and your imagination. That’s okay, again, as long as you aren’t making it up entirely and assigning made-up statements to somebody.
Dialog is a powerful tool. A good conversation can add flavor and interest to a story, as we saw demonstrated in David Foster Wallace’s essay. As previously mentioned, it’s okay to flub it a little, especially because you’re likely writing about an experience you had without knowing that you’d be writing about it later.
However, don’t rely too much on it. Your narrative essay shouldn’t be told through people explaining things to one another; the motif comes through in the details. Dialog can be one of those details, but it shouldn’t be the only one.

Use Sensory Descriptions
Because a narrative essay is a story, you can use sensory details to make your writing more interesting. If you’re describing a particular experience, you can go into detail about things like taste, smell, and hearing in a way that you probably wouldn’t do in any other essay style.
These details can tie into your overall motifs and further your point. Woolf describes in great detail what she sees while watching the moth, giving us the sense that we, too, are watching the moth. In Wallace’s essay, he discusses the sights, sounds, and smells of the Illinois State Fair to help emphasize his point about its strangeness. And in Baldwin’s essay, he describes shattered glass as a “wilderness,” and uses the feelings of his body to describe his mental state.
All these descriptions anchor us not only in the story, but in the motifs and themes as well. One of the tools of a writer is making the reader feel as you felt, and sensory details help you achieve that.
What’s Next?
Looking to brush up on your essay-writing capabilities before the ACT? This guide to ACT English will walk you through some of the best strategies and practice questions to get you prepared!
Part of practicing for the ACT is ensuring your word choice and diction are on point. Check out this guide to some of the most common errors on the ACT English section to be sure that you're not making these common mistakes!
A solid understanding of English principles will help you make an effective point in a narrative essay, and you can get that understanding through taking a rigorous assortment of high school English classes !

Melissa Brinks graduated from the University of Washington in 2014 with a Bachelor's in English with a creative writing emphasis. She has spent several years tutoring K-12 students in many subjects, including in SAT prep, to help them prepare for their college education.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

Oral History
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you figure out how to use oral histories in essays. It will give you suggestions for how to prepare for and conduct oral history interviews and help you determine, based on your context and purpose, how to integrate raw material into your essay.
Introduction
If we aren’t experts on a particular time or culture, our knowledge of it is often limited to major events and sweeping trends. This doesn’t necessarily help us understand the everyday experience of life in the past or in another culture. However, we do know a great deal about everyday experience in our own time and culture, and a large part of that knowledge comes not from textbooks but from talking to others. We learn about the histories of our families through conversation with those who remember them and about what various cultures value by observing their celebrations and listening to their music, among other things. So if you want to learn about another culture, country, era, etc., why not use a version of this strategy and talk to people who are or were part of it about their experiences and memories?
Oral history involves interviewing a person or group to get an inside perspective into what it was like to live in a particular time or is like to live as the member of a particular group within a society. Interviewing a group of people can create a picture of that experience, and a large project of this kind (such as UNC’s Southern Oral History Project) can be a way of preserving a piece of history. When we interview one person, we gain knowledge of an individual’s experiences, which may or may not be typical of their time and culture. We can also learn more about the experiences of groups from all sections of society, including the ones whose experience is not always thoroughly known or well documented, such as the working class, ethnic or religious minorities, or women.
When professors use oral history projects in classes, they usually ask you to interview only one or two people. The interview stage of the process requires effective question-making and interviewing skills. Usually, the project consists of taking raw material from an interview and shaping it into an essay. This step requires you to make some decisions about how you want to present the material and analytical skill to help you interpret what you learn.
Who uses oral history projects and why
Fields in which you might be assigned an oral history paper include history, anthropology, and other disciplines that study the experiences of specific social groups such as women or ethnic groups. The goals of these fields affect the ways they use this kind of project:
- History : Historians use evidence to understand the experiences of people in the past. Oral history can be a valuable source of evidence for understanding the experiences of individuals or groups within a certain historical period. Oral testimony cannot replace analysis of traditional historical materials (official documents, letters, newspapers, secondary sources, etc.). It can, however, reveal the role of individuals in shaping the past and/or how larger trends impacted the individual. When an oral history essay places the experiences of an individual within the context of a historical period, it can help illuminate both the individual’s experience and the historical period.
- Folklore : Folklorists study culture as it is expressed in everyday life and often use oral history projects to gather materials to preserve and study. Interviewing individuals is one of the primary means of accessing folklore; for example, folklorists use oral histories to learn about a culture’s musical traditions or festivals.
- Anthropology : An archeologist might use oral history to learn more about the lifeways of peoples who have living descendants or to locate sites for archeological excavation. A cultural anthropologist might use oral history as a way to understand how individuals think of themselves in relation to the rest of the world. This technique can help anthropologists understand how culture shapes individuals either consciously or unconsciously, on the one hand, and the ways that individuals contribute to the production of culture, on the other hand.
Fields that study marginalized social groups (such as women, African-Americans, Latino/as): In these fields, conducting and analyzing an interview is a way of uncovering experience that might be underrepresented in mainstream culture. Dominant cultures have a tendency not to notice or acknowledge the experiences of certain subgroups, viewing them as peripheral rather than central—in other words, marginalizing them. Academic fields have emerged to explore the experiences of marginalized groups, and these fields tend to value experiential knowledge. Oral history projects can be a way of accessing such knowledge.
Preparing for the interview
Before the interview, familiarize yourself with the history and characteristics of the culture your interviewee is from. That way, you’ll have a context for what you learn.
Some interviews may be fairly unstructured, with only general guidance from you. For instance, you may just choose some topics to discuss, allowing the interviewee to lead the way. This is appropriate when your goal is relatively broad, such as the preservation of the person’s voice, memories, and perspective, as opposed to using the interview to construct a focused argument. Some interviews, especially those in undergraduate course assignments, are more highly structured and take the shape of a list of questions and responses. This is especially useful when you hope to use the raw material of the interview to make a particular point or are looking to address very focused issues. If you are planning a more structured interview, prepare a list of questions, including some basic ones about aspects of the person’s identity (such as age, level of education, and occupation). In devising your questions, consider the interviewee’s cultural context. Think about what kinds of issues would be most helpful for you to learn about. For instance, learning how the person felt about major life events might help you understand how your interviewee sees their life as a whole. Questions about what it was actually like to live through segregation or the Vietnam War might give you a new perspective on a historical time period. As you ask your questions, work from your list, but be ready to ask follow-up questions in case you don’t understand the response or want to know more. A response to one of your questions may also trigger curiosity about some other issue, so it’s good to be ready to follow whatever path seems most promising. Include open-ended questions, especially “how” and “why” questions, as they will probably yield the richest raw material for your essay; asking yes/no questions is okay for gathering factual information. Ask for examples when you think it would help you (and the readers of your essay) understand the person’s perspective.
Conducting the interview
To conduct the interviewing process in an ethical way, ask the person’s permission to use their comments in your essay; written consent is ideal so you have a record of it. If you are recording a phone conversation, the interviewee’s written consent is required by law. Ask if the interviewee would prefer that you not use their actual name.
Tape record the interview if possible. If you try to work only from notes, you won’t have an exact record of the person’s comments and could end up distorting their meaning. Test your tape recorder, digital voice recorder, or videocamera ahead of time and bring extra batteries if necessary. If you’re recording, try to minimize background noise. In any interview setting, try to select an environment free from distractions, so that both you and the interviewee will be able to concentrate. Choose a spot where you will both feel comfortable. Silence will feel awkward at first, but give your interviewee a chance to think. Don’t move on too quickly just because there is a bit of a pause. Watch for signs of fatigue. If the person you’re interviewing begins to seem tired, take a break or set up another time to finish the interview. Treat the person you’re interviewing with respect, regardless of your own attitudes and opinions. Making assumptions about the person may damage trust and skew the essay you write.
Transcribing oral histories
Sometimes, you may be asked to transcribe your oral history interview or part of it. Transcription is the process of taking a sound file and translating it to text; it creates a written transcript of an oral conversation. One of the goals of transcribing interviews is to give readers a sense of the interview—how was it formatted, was it formal or informal, did the interviewer ask a lot of questions or did the interview subject do most of the talking with just a few prompts, what language and speaking style did the participants use?
A transcript of an oral history interview is, in the words of one style guide, “at best an imperfect representation of an oral interview. The transcriber’s most important task is to render as close a replica to the actual event as possible. Accuracy, not speed, is the transcriber’s goal” (Baylor Style Guide). Therefore, the transcript should reflect, as closely as possible, the words, speech patterns, and thought patterns of the interview subject. Their word choice, grammar, and ideas should be transcribed as accurately as possible. It’s not generally necessary, though, to reproduce a dialect or accent, unless you have specific training in doing so. The same style guide says, “Oral history is not an exercise in literary composition; the transcriber should avoid value judgments about the grammar or vocabulary of an interviewee.”
Transcribing can be a long and very detailed process. It will be easiest if you take detailed notes during the interview about the different questions, topics, and themes that you discuss. Write down any memorable phrases or ideas, so you have some markers for different points in the interview. You will need to listen to the entire portion of the interview to be transcribed several times. Many people find it helpful to listen all the way through a section once, then again, transcribing as much as possible, then a third (or fourth, or fifth!) time in order to fill in all the holes. At the end of this handout, you will find some websites that detail how to transcribe an oral history interview.
When you have a complete transcript, it is common practice to return it to the interviewee for editing—these changes can be noted in various ways or integrated into the document. Interviewees may need to correct things like dates, names, or places. Or they may want to provide more elaboration or clarification on a subject. Though this is standard practice for professional historians, your instructor may or may not expect you to do this.
Turning the raw material into an essay
The process you use will depend on what you want your essay to do. If, for instance, you want your essay merely to showcase an individual’s thoughts on a time or subject, you will simply need to frame the comments of the interviewee and shape them into a narrative. If, on the other hand, your intention is to interpret the interviewee’s comments, using them as evidence for an argument, you will need to make a strong argument while still letting the interviewee’s experience and insights come through. Your essay might use the interviewee’s comments to advance an alternate interpretation of a historical time or culture, confirm a commonly held characterization, or enrich an existing view.
Because oral history papers can vary a great deal according to their aims, make sure to develop a clear sense of your purpose. The assignment itself may specify quite clearly what kind of an oral history project you may do or leave many of the choices up to you. In either case, figuring out what you want your essay to accomplish will help you make definitive decisions about how to write it.
Decisions you’ll need to make about your project
First, determine the overall purpose of your essay. What would you like your essay to do?
A . Transcribe the comments of the individual.
B . Present the experiences and/or perspective of the individual.
C . Place the individual’s experiences and/or perspective within a larger historical or social context.
D . Use the individual’s experiences and/or perspective to make an argument about a larger historical or social context.
(C and D are especially common in undergraduate assignments of this type, but every assignment is different.)
Based on your answer to the above question, choose which section of this handout you’d like to read. If you’re not certain what you’d like your essay to do, read through all of the following sections to get a better sense of what your essay might include.
If you answered A., that you want your essay to transcribe the comments of the individual, consider the following questions and responses
What should you say about the interviewee’s comments?
Introduce the individual, explain the circumstances of the interview, and then literally transcribe your questions and their responses.
How should you structure your essay?
Present the questions and responses in the order you asked the questions. You may also include an introduction that briefly describes the person.
How should you present quotes and use paraphrases?
Transcribe the questions and responses so that paraphrases won’t be necessary. A question and answer format is a clear way to present a transcription (see the “examples” section at the end of this handout).
Should you read and/or incorporate secondary sources?
Whether or not you need to use secondary sources is partially a matter of what the assignment calls for. Secondary sources about the cultural context might help you think of your questions, but you won’t need to include them in your transcription of the responses.
Here is an example of how you might handle one of your interviewee’s comments within the body of the essay. Suppose that your paper is for a women’s studies project in which your instructor has asked you to interview a female family member; you have chosen to interview your grandmother, Lucretia. Suppose that you asked the following question: “How free did you feel in terms of choosing your jobs? If you felt limited, why do you think that might have been?”
If you want your essay to transcribe the interview, you will just present the questions and answers:
[Your name]: How free did you feel in terms of choosing your jobs? If you felt limited, why do you think that might have been? Lucretia: I have always been good at organizing things and getting along with people, so that made it easy for me to find receptionist jobs. But in those times, you didn’t see women executives. That was just how things were; people simply didn’t consider women for those jobs.
If you answered B., that you want your essay to present the experiences and/or perspective of the individual, consider the following questions and responses
Introduce the individual and outline the topics that the interview explored. Then use these topics to help you decide whether you want to organize the essay by the sequence of your questions or by topics that emerged as you reviewed your notes. You may frame the interviewee’s comments by providing transitions and a conclusion that reiterates the central point(s) that the interview revealed.
Your introduction should say a few things about who the person is and name some of the recurring themes or issues to prepare the reader to notice those in the body of the essay. The body of the essay should organize the interviewee’s comments, for instance chronologically or topically, and provide bridges (transitions) between sections.
Frame your quotes will phrases like “Sue Ellen explained . . .” or “Horatio’s view on plum trees is that . . .”; if you use paraphrases, be careful not to change their implications or lose their intent, since your goal is to present rather than interpret. For this approach as well as the next, our handout on quotations might be helpful.
If your assignment asks you to present (“B”) the results in essay form, you will integrate the questions and answers into your text, although sometimes you may find it easier to just paraphrase the question:
While Lucretia does feel that her occupational life offered her some opportunities, she describes feeling a sense of limitation, at least in retrospect: “I have always been good at organizing things and getting along with people, so that made it easy for me to find receptionist jobs. But in those times, you didn’t see women executives. That was just how things were; people simply didn’t consider women for those jobs.”
If you answered C., that you want your essay to place the individual’s experiences and/or perspective within a larger historical or social context, consider the following questions and responses
Analyze the responses to your questions and what they illustrate about their historical or social context. You might consider how your interviewee’s identity (their class, gender, and ethnicity, for instance) relates to the nature of the interviewee’s experience or perspective. For this kind of essay, you’ll need an analytical thesis statement (see our handout on thesis statements ), a plan for how to organize the subtopics that demonstrate your thesis, analysis/interpretation of the interviewee’s comments, and a conclusion that draws your analysis together.
Your introduction should contain and explain a thesis statement that makes a claim about the nature of the historical or social context. Organizing the body paragraphs by topic may be an effective way of explaining how the individual’s experiences fit into the broader historical or social context.
You’ll provide framing phrases as in the previous case, but you’ll also need to include your explanation of the significance of the quotes. A good general guideline is to include at least as much explanation of the quote as the quote is long. Paraphrases are helpful when you need just the content of the comment to make your point—that is, when the language the interviewee uses is not the primary issue. If you’re writing an analytical or argumentative essay, a mixture of paraphrases and quotes will probably serve your purpose best.
Whether or not you need to use secondary sources is partially a matter of what the assignment calls for. But if the assignment doesn’t specify, you’ll probably need to read and perhaps refer explicitly to some secondary sources so that you will have the necessary evidence to create a picture of the broader historical or social context.
If your assignment asks you to place the responses in their social context, you will need to integrate the quotes into text, paired with either the questions themselves or paraphrases, along with some analysis of how the individual’s experiences fit into their social context. You may even include some references to secondary sources, depending on the assignment and your own sense of whether they would strengthen your analysis:
Lucretia describes feeling limited in terms of her occupational life: “I have always been good at organizing things and getting along with people, so that made it easy for me to find receptionist jobs. But in those times, you didn’t see women executives. That was just how things were; people simply didn’t consider women for those jobs.” Her account reveals a sense of how fixed gender roles were in the workplace and seems fairly typical for the time and place, as feminist historian Tammy Ixplox’s scholarship suggests (Ixplox 39).
If you answered D., that you want your essay to use the individual’s experiences and/or perspective to make an argument about a larger historical or social context, consider the following questions and responses
Use the interviewee’s comments as evidence for an argument you want to make about a particular historical or social context. For instance, you might want to argue that working-class women’s experience in 1950s America does not necessarily fit with popularly-held notions of the fifties housewife. Or you might want to show how racism affected one African-American man’s everyday life to demonstrate how insidious racism can be. For these kinds of essays, you may need some supporting research to get a better sense of the historical and social context, so you’ll understand how the individual’s experience relates to broader cultural trends and phenomena. In terms of what the essay will look like, you’ll need a thesis that makes a claim, an organizational plan that reflects the main points you think will best support that thesis, lots of explanation of how the interviewee’s comments illustrate the thesis, and a conclusion that draws your argument together.
You’ll need an introduction with a strong, interpretive thesis statement that the body of the essay explains and demonstrates. The interviewee’s comments will function as evidence for your argument, so each body paragraph should correspond to a point in your argument.
You’ll provide framing phrases as in the previous case, but you’ll also need to include your explanation of the significance of the quotes. A good rule of thumb is to include at least as much explanation of the quote as the quote is long. Paraphrases are helpful when you need just the content of the comment to make your point—that is, when the language the interviewee uses is not the primary issue. If you’re writing an analytical or argumentative essay, a mixture of paraphrases and quotes will probably serve your purpose best.
Whether or not you need to use secondary sources is partially a matter of what the assignment calls for. But if the assignment doesn’t specify, you’ll probably need to read and incorporate some secondary sources to complement or provide a counterpoint to the interviewee’s comments and to support your claims about the larger historical or social context.
If your assignment asks you to make an argument, for example, about how the interviewee’s responses reflect gender issues and roles, you will need to integrate the quotes into your text as evidence for your argument about gender roles, perhaps with reference to secondary sources if appropriate:
Lucretia’s experiences reveal gender roles in the workplace, in which only men tended to fill the executive positions. She describes feeling limited in terms of her occupational life: “I have always been good at organizing things and getting along with people, so that made it easy for me to find receptionist jobs. But in those times, you didn’t see women executives. That was just how things were; people simply didn’t consider women for those jobs.” In her experience, no one questioned these roles, which reveals how ingrained and even internalized social expectations for different genders were at the time. This phenomenon is consistent with feminist historian Tammy Ixplox’s scholarship on this cultural context (Ixplox 39).
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Baylor University. n.d. “Transcribing Style Guide.” Institute for Oral History. Accessed June 24, 2019. https://www.baylor.edu/oralhistory/index.php?id=931752 .
Library of Congress. n.d. “Indexing and Transcribing Your Interviews.” Veterans History Project. Last updated August 2020. http://www.loc.gov/vets/transcribe.html .
Moyer, Judith. 1993. “Step-by-Step Guide to Oral History.” DoHistory . Harvard University. http://dohistory.org/on_your_own/toolkit/oralHistory.html .
Shopes, Linda. 2002. “Making Sense of Oral History.” History Matters: The US Survey Course on the Web. February 2002. http://historymatters.gmu.edu/mse/oral/ .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
Published on September 4, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays.
Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and descriptive essays are about exercising creativity and writing in an interesting way. At university level, argumentative essays are the most common type.
| Essay type | Skills tested | Example prompt |
|---|---|---|
| Has the rise of the internet had a positive or negative impact on education? | ||
| Explain how the invention of the printing press changed European society in the 15th century. | ||
| Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself. | ||
| Describe an object that has sentimental value for you. |
In high school and college, you will also often have to write textual analysis essays, which test your skills in close reading and interpretation.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Argumentative essays, expository essays, narrative essays, descriptive essays, textual analysis essays, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about types of essays.
An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement —a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations ) and analysis.
Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic. This is the most common type of essay at college level—most papers you write will involve some kind of argumentation.
The essay is divided into an introduction, body, and conclusion:
- The introduction provides your topic and thesis statement
- The body presents your evidence and arguments
- The conclusion summarizes your argument and emphasizes its importance
The example below is a paragraph from the body of an argumentative essay about the effects of the internet on education. Mouse over it to learn more.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a topic. It doesn’t require an original argument, just a balanced and well-organized view of the topic.
Expository essays test your familiarity with a topic and your ability to organize and convey information. They are commonly assigned at high school or in exam questions at college level.
The introduction of an expository essay states your topic and provides some general background, the body presents the details, and the conclusion summarizes the information presented.
A typical body paragraph from an expository essay about the invention of the printing press is shown below. Mouse over it to learn more.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
A narrative essay is one that tells a story. This is usually a story about a personal experience you had, but it may also be an imaginative exploration of something you have not experienced.
Narrative essays test your ability to build up a narrative in an engaging, well-structured way. They are much more personal and creative than other kinds of academic writing . Writing a personal statement for an application requires the same skills as a narrative essay.
A narrative essay isn’t strictly divided into introduction, body, and conclusion, but it should still begin by setting up the narrative and finish by expressing the point of the story—what you learned from your experience, or why it made an impression on you.
Mouse over the example below, a short narrative essay responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” to explore its structure.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
A descriptive essay provides a detailed sensory description of something. Like narrative essays, they allow you to be more creative than most academic writing, but they are more tightly focused than narrative essays. You might describe a specific place or object, rather than telling a whole story.
Descriptive essays test your ability to use language creatively, making striking word choices to convey a memorable picture of what you’re describing.
A descriptive essay can be quite loosely structured, though it should usually begin by introducing the object of your description and end by drawing an overall picture of it. The important thing is to use careful word choices and figurative language to create an original description of your object.
Mouse over the example below, a response to the prompt “Describe a place you love to spend time in,” to learn more about descriptive essays.
On Sunday afternoons I like to spend my time in the garden behind my house. The garden is narrow but long, a corridor of green extending from the back of the house, and I sit on a lawn chair at the far end to read and relax. I am in my small peaceful paradise: the shade of the tree, the feel of the grass on my feet, the gentle activity of the fish in the pond beside me.
My cat crosses the garden nimbly and leaps onto the fence to survey it from above. From his perch he can watch over his little kingdom and keep an eye on the neighbours. He does this until the barking of next door’s dog scares him from his post and he bolts for the cat flap to govern from the safety of the kitchen.
With that, I am left alone with the fish, whose whole world is the pond by my feet. The fish explore the pond every day as if for the first time, prodding and inspecting every stone. I sometimes feel the same about sitting here in the garden; I know the place better than anyone, but whenever I return I still feel compelled to pay attention to all its details and novelties—a new bird perched in the tree, the growth of the grass, and the movement of the insects it shelters…
Sitting out in the garden, I feel serene. I feel at home. And yet I always feel there is more to discover. The bounds of my garden may be small, but there is a whole world contained within it, and it is one I will never get tired of inhabiting.
Though every essay type tests your writing skills, some essays also test your ability to read carefully and critically. In a textual analysis essay, you don’t just present information on a topic, but closely analyze a text to explain how it achieves certain effects.
Rhetorical analysis
A rhetorical analysis looks at a persuasive text (e.g. a speech, an essay, a political cartoon) in terms of the rhetorical devices it uses, and evaluates their effectiveness.
The goal is not to state whether you agree with the author’s argument but to look at how they have constructed it.
The introduction of a rhetorical analysis presents the text, some background information, and your thesis statement; the body comprises the analysis itself; and the conclusion wraps up your analysis of the text, emphasizing its relevance to broader concerns.
The example below is from a rhetorical analysis of Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech . Mouse over it to learn more.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
Literary analysis
A literary analysis essay presents a close reading of a work of literature—e.g. a poem or novel—to explore the choices made by the author and how they help to convey the text’s theme. It is not simply a book report or a review, but an in-depth interpretation of the text.
Literary analysis looks at things like setting, characters, themes, and figurative language. The goal is to closely analyze what the author conveys and how.
The introduction of a literary analysis essay presents the text and background, and provides your thesis statement; the body consists of close readings of the text with quotations and analysis in support of your argument; and the conclusion emphasizes what your approach tells us about the text.
Mouse over the example below, the introduction to a literary analysis essay on Frankenstein , to learn more.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
At high school and in composition classes at university, you’ll often be told to write a specific type of essay , but you might also just be given prompts.
Look for keywords in these prompts that suggest a certain approach: The word “explain” suggests you should write an expository essay , while the word “describe” implies a descriptive essay . An argumentative essay might be prompted with the word “assess” or “argue.”
The vast majority of essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Almost all academic writing involves building up an argument, though other types of essay might be assigned in composition classes.
Essays can present arguments about all kinds of different topics. For example:
- In a literary analysis essay, you might make an argument for a specific interpretation of a text
- In a history essay, you might present an argument for the importance of a particular event
- In a politics essay, you might argue for the validity of a certain political theory
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved June 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-types/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write an expository essay, how to write an essay outline | guidelines & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Nieman Foundation
- Fellowships
To promote and elevate the standards of journalism
Journalist’s Trade
March 15, 2002.

Historical Writing and the Revival of Narrative
‘…the line between scholarly and popular writing is now much more difficult to discern.’.

Jill Lepore
Tagged with.
Beginning in 1979, not coincidentally the year the first Pulitzer was awarded for feature writing, British historian Lawrence Stone heralded the revival of narrative in academic history writing. The story was back. Stone defined narrative as the organization of material in a chronologically sequential order and focusing the content into a single, coherent story. Now this represented a departure from common historical writing and should give you a sense of just how inhospitable to plot that genre had become.
Unlike structural or scientific history, which is analytical, narrative history, for Stone, is descriptive. From most historians’ point of view, to call a piece of writing “descriptive” is the worst kind of damnation. But far from lamenting descriptive narratives, Stone celebrated them. Narrative history, he suggested, is by no means lacking in interpretation, so long as it’s directed by what Stone called a “pregnant principle.”
Stories with pregnant principles are hard to write and especially difficult to write artfully. Many narrative histories written by academics take readers on sea-sickening sails that endlessly tack back and forth between story and argument. How to tell a story that does more than describe what happened is not immediately obvious, at least to most academic historians.
RELATED ARTICLE “The Immersion Experience In Historical Narrative” – Jill Lepore In a perceptive essay written in 1992, Cambridge historian Peter Burke suggested that historians ought to borrow the anthropological notion of thick description—a technique that interprets an alien culture through the precise and concrete description of particular practices and events—and write thick narratives that seamlessly integrate story and context. The problem for historians, Burke suggested, is making a narrative thick enough to deal not only with the sequence of events and the conscious intentions of the actors in these events, but also with structures, institutions, modes of thought, whether these structures act as a brake on the events or as an accelerator.
In practice, since the 1960’s thick narratives with pregnant principles have often taken the form of what historians somewhat ambivalently call “micro-histories”: stories about a single, usually very ordinary person, place or event, that seek to reveal the society’s broader structures. This work rests on the central premise that ordinary lives, thickly described, illuminate culture best.
Telling small stories, writing micro-histories, does not inevitably produce important scholarship. Just the opposite, alas, is far likelier. As Peter Burke warned, “The reduction in scale does not thicken a narrative by itself.” When micro-histories are good, they’re breathtakingly brilliant. When they’re bad, they’re pretty much worthless.
Now consider the history of journalism. If 20th century academic historians turned their backs on storytelling in the early part of the century, only to return to it in the late 1970’s, journalists trudged along a similar path. They scorned storytelling in favor of fact-finding, and then changed their minds.
In the late 19th and early 20th century, according to journalist Jon Franklin, the best American writers, reporters included, began their careers and received their literary training writing short stories. The short story in its heyday was the universal school for writers, Franklin argues. The short story demanded the utmost of the writer, both technically and artistically. It served as the great eliminator of mediocre talent. When short story writers turned to reporting, they brought a desk drawer full of literary devices, an economy of prose, an eye for detail, an ear for dialogue, and a keen sense of plot and resolution.
In the 1950’s and 1960’s Franklin asserts, “The quality of journalistic writing was devastated by the demise of the short story apprenticeship. When journalism turned away from literature, newspaper and magazine writing lost its luster. Nonfiction wasn’t as good a training ground as the short story had been because it emphasized subject over form and rewarded reporting skills at the expense of writing technique.”
But when “In Cold Blood” was published in 1965, it melded the accuracy of nonfiction with the dramatic force of fiction and ushered in the new genre of nonfiction—a genre that today dwells in a foggy frontier between journalism and literature.
RELATED ARTICLE “Journalists and historians can learn from each other.” – Adam Hochschild What’s to be gained by comparing the history of history with the history of journalism? A few critical insights. The revival of narrative in historical writing parallels the emergence of narrative journalism. In narrative history’s most celebrated invention, the micro-history, there is a passing resemblance to narrative journalism’s favorite form, the nonfiction short story.
Micro-histories and nonfiction short stories have a good deal in common. Both genres emerged in the 1970’s in response to professional trends, especially prevalent in the 1950’s, that valued accuracy and analysis more than literary flair. Micro-history and the much-vaunted revival of narrative in historical writing were responses to structural or quantitative history. Narrative journalism and the nonfiction short story were reactions against investigative journalism’s emphasis on fact-finding over prose style.
Both micro-histories and nonfiction short stories tend to concern themselves with the everyday experiences of ordinary people; a means of offering broader cultural interpretations, moving from events to structures. Both genres selfconsciously employ the techniques of dramatic fiction, including character development, plotting and conflict resolution. Most micro-historians and narrative journalists aspire to write narratives thickened with the butter of detail and the flour of implication.
Micro-histories and nonfiction short stories also fall prey to the same dangers. Peter Burke considered small stories’ greatest pitfall to be their tendency to focus attention on the sensational. Both academics writing micro-histories and journalists writing nonfiction short stories are drawn to the drama of murder trials, suicides, kidnapping, rapes and other miscellaneous crimes and disasters.
It’s easy to push this parallel too far. Crucial differences separate these two genres. Micro-histories are not non-fiction short stories; they are micro in focus, not in length. Journalists sometimes write about the past, but most narrative journalism, of course, is not historical.
Still, the similarities are intriguing and they raise a key question. If narrative history and narrative journalism use similar devices, consider similar subjects, and are the consequence of related trends in the politics and the arts, why then are historians and journalists not on better terms? It must be said that a great deal of the animosity so commonly expressed by academic historians towards popular history boils down to this: History books are selling like hot cakes, but journalists are making all the money.
To be fair, most historians have few intellectual objections to a rattling good history, so long as the story is told in the service of an argument. Often it isn’t. In 1992 Peter Burke warned that the revival of narrative might lead to a return to pure antiquarianism; to storytelling for its own sake. Part of what grates academic historians is that many popular histories are, from their point of view, actually miscarried micro-histories. That is, they tell a small story but fail to use that story to interpret larger historical structures. At their worst, popular histories are all headlines. They gesture at significance but fail to demonstrate it.
Far from thickly narrating a life, the worst popular histories also tend to rip people out of the past and stick them to the present. These people from different places and times, they’re just like us, only dead. Bad popular history, like bad historical novels and films, manages at once to exoticize the past. Descriptions of clothes, hairstyles, houses and the minutia of daily life are always lovingly recreated while rendering familiar the people who lived in it. Fashions changed, but complicated, historically specific ideas like sovereignty or progress or childhood magically transcend history.
It’s just this kind of writing that [Princeton University historian] Sean Wilentz condemns as passive nostalgic spectacle. But is narrative and are journalists to blame? Since both historians and journalists have embraced narrative, the line between scholarly and popular writing is now much more difficult to discern. Truman Capote is not responsible for David McCullough, but he’s not irrelevant, either.
Much history today is written under the banner of narrative. Does it inevitably render its readers passive? No, but perhaps it should. One kind of passivity, or maybe we should call it enthrallment, is a measure of success. Readers can be nearly paralyzed by compelling stories confidently told. In the hands of a good narrator, readers can be lulled into alternating states of wonder and agreement.
Storytelling is not a necessary evil in the writing of history. It’s a necessary good. Using stories to make historical arguments makes sense, because it gives a writer greater power over her reader. A writer who wants to can pummel his reader into passivity, but a writer who wants to challenge his reader betters his odds to success by telling a story.
Most popular articles from Nieman Foundation
Summer 2004: journalist’s trade introduction, publisher, editor and reporter, the press and the presidency.

How to Write a Narrative Essay Step by Step

Essay writing comes in various styles, many of which do not demand extensive research. One such style is the narrative essay, which combines personal storytelling with academic reflection. Unlike other essay types, narrative essays are not bound by strict requirements or the need for a bibliography. They feature a more flexible structure, creative language, and a singular focus: to tell a story.
This genre provides a special opportunity for writers to connect with readers on a personal level. By sharing personal experiences and reflections, authors engage their audience emotionally while imparting meaningful messages or lessons. In the sections that follow, our custom term paper writing experts will delve into different aspects of narrative writing, from selecting a topic to structuring your essay effectively.
What Is a Narrative Essay
A narrative essay, as the name suggests, is characterized by the presence of a narrative. Unlike argumentative essays, which present and defend a position, or analytical essays, which dissect another text, narrative essays tell a coherent story. Their goal is to convey a point or impart a lesson through personal experiences. These essays are frequently assigned in high school and for college admissions.
An effective narrative essay generally follows a chronological sequence of events and exhibits three main traits:
- Centers on one main idea.
- Utilizes specific details to illustrate that idea.
- Adheres to a clear sequence of events.
Structurally, a narrative essay resembles short stories, featuring vivid descriptions, plots, characters, and discussions. However, there are key differences. These essays focus on a central theme or argument and conclude decisively, whereas short stories often leave readers with a more abstract moral or message.
A narrative essay is typically written in the first person and follows a standard format with an introduction, body, and conclusion. In contrast, short stories can adopt various formats and may not adhere to the same structured approach.
What is the Purpose of a Narrative Essay
No matter what you write — fiction, non-fiction, memoir, biography — grasping narrative writing helps you connect with your reader, giving them a glimpse of your world. Here, we outline its key purposes:
.webp)
- Academic Assignments: They fulfill requirements for school assignments, allowing students to demonstrate their understanding and creativity.
- Self-Reflection: As a key purpose of a narrative essay, this type of writing enables individuals to reflect on personal achievements or significant events, fostering introspection and self-awareness.
- Professional Endeavors: They are used when applying for jobs or scholarships, showcasing one's communication skills, experiences, and character.
- Literary Analysis: Narrative storytelling is employed in analyzing literature, providing a medium to explore themes, characters, and storytelling techniques.
- Cultural Exploration: They facilitate the exploration of different cultures, allowing individuals to share insights and experiences from diverse perspectives.
- Creative Expression: These essays offer a means of expressing oneself creatively, weaving personal narratives into compelling stories.
- Communication of Messages: Through storytelling, narrative writing conveys messages or lessons, engaging readers and imparting wisdom or insights.
- Engagement: Above all, these essays connect with the audience on a personal level, fostering empathy, understanding, and emotional resonance.
Meanwhile, if you’re willing to describe your life in greater depth, our guide on how to write an autobiography might be just what you need!
How to Write a Narrative Essay in 5 Steps
Writing a narrative essay is a unique process compared to other types of school essays. Rather than analyzing topics or defending a position, it focuses on sharing personal experiences through storytelling. By following a few straightforward steps, you can transform your ideas into an engaging narrative.
.webp)
Step 1: Start with a Topic Selection
When crafting a narrative essay, begin by selecting a topic that either relates to your personal experiences or aligns with a given prompt. If a prompt is provided, consider its requirements and brainstorm ideas that fit within its scope.
As you brainstorm, jot down key moments or points you want to include in your essay. Evaluate how each point will fit into the overall structure of your narrative and ensure it adheres to any word count limits.
Think about the tone and style you wish to adopt. Will your essay be reflective, humorous, or something else? Consider incorporating specific stylistic elements, such as repeated phrases or cliffhanger endings, to enhance your storytelling and engage your reader.
Remain flexible throughout this process. As you explore different ideas, be open to tweaking your topic, tone, and style to better suit your narrative.
For more inspiration and to skip the brainstorming phase, check out a ready-made Narrative Essay Topic list!
Step 2: Make a Clear Outline
Once you have your topic, it's time to draft your narrative essay outline. This outline serves as a blueprint, guiding you in crafting a coherent and engaging story. Start by pinpointing the main points you wish to address, such as pivotal moments or insights gained, and allocate each to a separate paragraph to maintain a clear sequence.
Your outline should help you structure the flow of your narrative, planning out the sequence of events and the level of detail to include. For example, if your essay is about a memorable trip, your outline might start with a paragraph setting the scene, followed by paragraphs describing key experiences and interactions, and concluding with reflections on how the trip impacted you.
When outlining your conclusion, think about how to effectively wrap up your story by summarizing the main events and the significance they hold. For a more systematic approach, make sure to check out how to write an essay conclusion .
| Topic: | ||
|---|---|---|
| Introduction | ||
| Challenge Description | ||
| Perseverance and Action | ||
| Reflection and Growth | ||
| Conclusion | ||
Step 3: Write Your Narrative Essay
Using your outline as a guide, now, it's time to start writing a narrative essay. Remember that narrative essays provide you with a creative outlet, so feel free to break away from the constraints of traditional academic writing styles. Captivating the reader and giving your narrative life should be your main goals.
Tip 💡 Use first-person : Infuse your essay with personal authenticity and engagement by embracing pronouns like 'I' and 'me'.
Tip 💡 Employ storytelling techniques : Draw upon the techniques employed in fiction and creative nonfiction, such as dialogue and symbolism, to enrich your narrative and captivate your audience.
Tip 💡 Demonstrate, don't merely state : Instead of blandly presenting facts, immerse your reader in your narrative by employing vivid descriptions and sensory details.
Tip 💡 Remain authentic: Preserve the integrity of your voice and experiences. Candidly share your thoughts and emotions to ensure your narrative essay resonates as genuine and relatable.
Step 4: Don't Forget to Revise
After completing your initial draft, it's essential to revise and polish your essay. Begin by taking a break to refresh your perspective before returning with a clear mind - this is one of the best tips for writing a narrative essay!
When revisiting your essay, carefully review it to ensure logical coherence and flow. Address any inconsistencies or narrative gaps, refining your essay for improved clarity. Pay attention to elements such as tense, point of view, and narrative voice throughout.
Step 5: Proofread Your Writing
Now that you understand how to end a narrative essay, don’t forget to dedicate time to meticulous proofreading to catch any lingering errors or typos. Pay close attention to formatting and citation style, if applicable.
Sharing your essay with trusted individuals such as friends, family, or educators can provide valuable feedback and fresh insights. Incorporate the feedback received, along with your own observations from the revision process, to strengthen the impact and effectiveness of your essay.
Narrative Essay Topics: The List
Let's go back to the topics and give you some handy, ready-made options. Sure, you can think of ideas on your own, but we can lend a hand with these suggestions before you commit to the writing process.
- Reflecting on earning my first degree: a pivotal milestone in my life.
- The most awful dish I’ve ever tasted: my unforgettable tale.
- How a personal experience changed my attitudes and actions.
- The worst exam experience I’ve ever had: a harrowing tale.
- Encountering something eerie: a chilling moment in my life.
- Fond memories of summer vacations during my childhood.
- The story of a heroic act that saved someone's life.
- My top tunes: songs that resonate deeply with me.
- The origins and meanings of my nicknames.
- The superpower I wish I had and why.
- A lecture that profoundly changed my perspective.
- Does my school prioritize digital skills for students?
- Great summer reads for book lovers: my top suggestions.
- The music genres and melodies that reflect my tastes and emotions.
- Passions and interests that drive my aspirations.
- My ultimate guide to spending Sundays efficiently.
- Questions and curiosities about how the world works.
- Values and principles I'd risk my life for.
- How much do I follow global current events?
- Steps I’ve taken to achieve my dream job.
Want to Be Like an Expert Writer?
Order now and let our narrative essay writer turn your experiences into a captivating and unforgettable tale
Narrative Essay Examples
For inspiration on your upcoming essay, check out these excellent samples from our essay writer . Use them as a guide to help craft your own story, ensuring that your unique voice and experiences come through in your work.
If sharing your personal stories is not your cup of tea, you can buy essays online from our expert writers, who will customize the paper to your particular writing style and tone.
Final Recap
Now that you understand what makes a narrative essay tick, you're probably itching to write your own standout piece. Let our skilled research paper writing service lend you a hand! We're here to offer personalized services tailored to your needs. By providing value with flexible pricing and quick turnaround times, we'll bring your narrative to life together!
Unlock Your Potential with Our Essays!
Order now and take the first step towards achieving your academic goals
What Is A Narrative Essay?
How to start a narrative essay, how to write a good narrative essay.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
Added new info on narrative essay
Related Articles
.webp)
Narrative History
Historians have always crafted narratives. War. Peace. Political battles. Feuds in the hollers. Floods on the Mississippi. Hurricanes. Strikes. Assassinations. Voyages to known and unknown places. Trials of the century. Personal quests. Leaders with uncommon touches and tragic flaws. This is the stuff of great narrative and the stuff of narrative history—stories about the past told with verve and drama but also with strong arguments and thick footnotes.
Over the years, historians—and here we’re talking largely about American, university-trained and -based scholars—have produced numerous libraries’ worth of moving tales spiced with telling details set against carefully drawn backdrops and built around scrupulously fleshed-out characters. Just like any good nonfiction instructor, Samuel Morison, one of the 20th century’s most brilliant and widely read historians, urged his Harvard graduate students to read more than academic books and journals. According to a recent article in The New Yorker, Morison told them to study the art of the novel and the grace of the essay. Without this grounding, he feared that his students would write only “dull, solid” monographs. Now Morison wasn’t a self loathing historian, just a realistic one. Each “dull, solid” book and article, he knew, added to the base of historical knowledge, but that was it. No one outside the small cohort of scholars in a subfield would ever read them. For most historians, this was OK. Tenure and promotion came through deeply researched accounts of wars, trials and political campaigns targeted at other academics—not through broadly conceived narratives aimed at large audiences.
The scope of the historical profession narrowed a bit more in the 1960s and 1970s. Borrowing techniques and approaches from social scientists, historians churned out streams of studies tightly focused on the daily lives of ordinary, often forgotten people and on long-term patterns of work, mobility and reproduction that showcased method, data sets and argument over plot, suspense and character development. Some deliberately shied away from artful storytelling, fearful that the hints of play and performance that came with narrative would take away from the veracity and seriousness of the accounts. Better in this professional climate to construct tables and long, discursive footnotes than chiseled characters and in-depth scenes.
Journalists, features writers and biographers quickly stepped into the narrative void left by the historians’ social-scientific turn. Skilled storytellers and diligent researchers like J. Anthony Lukas and Robert A. Caro told gripping tales of race and disappointment, city building and power brokers. Audiences came running. David McCullough recounted the building of the Brooklyn Bridge, and John Barry traced the floodwaters of the Mississippi, and people turned the pages. Doris Kearns Goodwin and Stephen Ambrose—Ambrose started out as a university-based historian but chafed under the academy’s narrative and political constraints, or so he said—retold sprawling national narratives of good and evil, and book-buyers swarmed. Taylor Branch and Edmund Morris buried themselves in the archives and produced gripping, authoritative accounts of the lives of Martin Luther King Jr. and Teddy Roosevelt, and the scribes of The New York Review of Books debated their insights.
Just as Samuel Morison had predicted, strong writers of compelling narratives had, by the 1980s, taken over the popular market for history. Unwilling to concede the past to nonprofessionals, some historians looked to strike back. But they knew that this meant rediscovering their field’s deep narrative traditions. It also meant taking on the big topics. And it meant imitating the narrative strategies deployed so well by journalist-historians like Goodwin and Caro—with, of course, fatter footnotes and longer bibliographies.
Reflecting the trend, in 1989, Princeton professor James M. McPherson crafted “Battle Cry of Freedom,” a vivid, even moving account of the military history of the Civil War. In the following decade, Joseph Ellis of Mount Holyoke College published “American Sphinx,” an elegant look at the private Thomas Jefferson. This triggered a sort of founding fathers revival, as professors—this time with the journalists following—raced to see who would get out the next book on Hamilton, Jefferson and Adams. Others who missed this bandwagon turned their attention to Lincoln and the noble grunts of World War II. As these accounts started to appear on The New York Times’ Best Sellers List, other historians hired agents and looked to capture a slice of this growing audience. But even more, the renewed interest in narrative—and royalty checks—trickled down. Graduate programs from Princeton to North Carolina to Southern California started to offer writing seminars alongside methods classes, featuring the work of Lukas and McPherson as well as of Gay Talese and Philip Roth.
But the grand narrative of the big event and the big leader wasn’t the only thing happening in the history business. The freedom movements of the 1960s rocked the academy. African-Americans, women, Native Americans, Chicanos, gays, lesbians and transgendered people demanded not just equity before the law but also a place in the nation’s past. Yet, including the “others” upset some firmly established master narratives. Things weren’t so clear anymore. Whose story was true, historians wondered? The answer depended on the perspective.
Some historians concluded—with great misgivings—that truth was subjective. It wasn’t that there wasn’t truth but that truth—the past—looked different depending on where you stood. For some historians, this insight freed them from the restrictions of the omnipresent third-person narrative—the detached and commanding position adopted by historians. Some scholars, then, began to experiment with voice and structure. With a novelist’s eye for detail and phrasing, James E. Goodman, in “Stories of Scottsboro,” retold the tragedy of the wrongly accused Scottsboro boys from a multiplicity of angles with each chapter changing perspective. In his follow-up book, “Blackout,” an account of the night the lights went out in New York City in 1977, he retells the event in a frenzy of over 50 short-story blasts. Never does he step in and say which account is true and which is not. The complexity of experience is what matters to him.
Others have injected themselves into their stories. Art historian Eunice Lipton went searching for Manet’s model in “Alias Olympia” and found herself. In “Blood Done Sign My Name,” Timothy B. Tyson recalled a racially charged murder in his southern hometown to reinterpret the Civil Rights Movement and the politics of his minister father. And John Putnam Demos—a Yale professor and highly respected colonial historian—ran into some dead ends in the archives, but rather than give up his stories, he imagined his way into the heads of his characters, writing brief fictions as history in “The Unredeemed Captive.”
Creative nonfiction writers have been slow to pick up on historians’ narrative experiments. But this—and perhaps some advice about conducting research—is perhaps the most valuable thing historians have to offer. Truth is precarious, unstable and elusive, and this—as Goodman, Demos and the others show—is the real drama of the past. The search for truth, the battle for whose truth matters and what truth gets codified into official histories, textbooks and monuments, is the stuff of stories—tense, suspenseful stories—the stuff of both creative nonfiction and narrative history.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
650 Prompts for Narrative and Personal Writing

By Michael Gonchar
- Oct. 20, 2016
Update, Sept. 4, 2019: Check out our newest evergreen collection of “ 550 Prompts for Narrative and Personal Writing ” that includes dozens of new prompts.
Update, Feb. 15, 2019: Learn more about how to use our 1000s of writing prompts by watching our free on-demand webinar: “ Give Them Something to Write About: Teach Across the Curriculum With New York Times-Inspired Daily Prompts. ”
Every school day since 2009 we’ve asked students a question based on an article in The New York Times.
Now, seven years later, and in honor of the Oct. 20 National Day on Writing , we’ve collected 650 of them that invite narrative and personal writing and listed them by category below. Consider it an update of a previous post, and a companion to the list of 301 argumentative writing prompts we published in 2015.
Here is a PDF of all 650 prompts , and we also have a related lesson plan, From ‘Lives’ to ‘Modern Love’: Writing Personal Essays With Help From The New York Times .
Below, a list that touches on everything from sports to travel, education, gender roles, video games, fashion, family, pop culture, social media and more. Like all our Student Opinion questions , each links to a related Times article and includes a series of follow-up questions. All questions published since May 2015 are still open to comment by any student 13 or older.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
We will keep fighting for all libraries - stand with us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
The fiction of narrative : essays on history, literature, and theory, 1957-2007
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
98 Previews
12 Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by station47.cebu on July 24, 2023
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
- Our Writers
- How to Order
- Assignment Writing Service
- Report Writing Service
- Buy Coursework
- Dissertation Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service
- All Essay Services
- Buy Research Paper
- Buy Term Paper
- Buy Dissertation
- Buy Case study
- Buy Presentation
- Buy Personal statement
Narrative Essay
Narrative Essay Examples
10+ Interesting Narrative Essay Examples Plus Writing Tips!

People also read
Narrative Essay - A Complete Writing Guide with Examples
Writing a Personal Narrative Essay: Everything You Need to Know
Best Narrative Essay Topics 2023 for Students
Crafting a Winning Narrative Essay Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
Many students struggle with crafting engaging and impactful narrative essays. They often find it challenging to weave their personal experiences into coherent and compelling stories.
If you’re having a hard time, don't worry!
We’ve compiled a range of narrative essay examples that will serve as helpful tools for you to get started. These examples will provide a clear path for crafting engaging and powerful narrative essays.
So, keep reading and find our expertly written examples!
- 1. Narrative Essay Definition
- 2. Narrative Essay Examples
- 3. Narrative Essay Examples for Students
- 4. Narrative Essay Topics
- 5. Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative Essay Definition
Writing a narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that revolves around personal experiences, aiming to immerse the reader in the author's world. It's a piece of writing that delves into the depths of thoughts and feelings.
In a narrative essay, life experiences take center stage, serving as the main substance of the story. It's a powerful tool for writers to convey a personal journey, turning experiences into a captivating tale. This form of storytelling is an artful display of emotions intended to engage readers, leaving the reader feeling like they are a part of the story.
By focusing on a specific theme, event, emotions, and reflections, a narrative essay weaves a storyline that leads the reader through the author's experiences.
The Essentials of Narrative Essays
Let's start with the basics. The four types of essays are argumentative essays , descriptive essays , expository essays , and narrative essays.
The goal of a narrative essay is to tell a compelling tale from one person's perspective. A narrative essay uses all components you’d find in a typical story, such as a beginning, middle, and conclusion, as well as plot, characters, setting, and climax.
The narrative essay's goal is the plot, which should be detailed enough to reach a climax. Here's how it works:
- It's usually presented in chronological order.
- It has a function. This is typically evident in the thesis statement's opening paragraph.
- It may include speech.
- It's told with sensory details and vivid language, drawing the reader in. All of these elements are connected to the writer's major argument in some way.
Before writing your essay, make sure you go through a sufficient number of narrative essay examples. These examples will help you in knowing the dos and don’ts of a good narrative essay.
It is always a better option to have some sense of direction before you start anything. Below, you can find important details and a bunch of narrative essay examples. These examples will also help you build your content according to the format.
Here is a how to start a narrative essay example:
|
Sample Narrative Essay
The examples inform the readers about the writing style and structure of the narration. The essay below will help you understand how to create a story and build this type of essay in no time.
|
Here is another narrative essay examples 500 words:
|
Narrative Essay Examples for Students
Narrative essays offer students a platform to express their experiences and creativity. These examples show how to effectively structure and present personal stories for education.
Here are some helpful narrative essay examples:
Narrative Essay Examples Middle School
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 7
Narrative Essay Examples for Grade 8
Grade 11 Narrative Essay Examples
Narrative Essay Example For High School
Narrative Essay Example For College
Personal Narrative Essay Example
Descriptive Narrative Essay Example
3rd Person Narrative Essay Example
Narrative Essay Topics
Here are some narrative essay topics to help you get started with your narrative essay writing.
- When I got my first bunny
- When I moved to Canada
- I haven’t experienced this freezing temperature ever before
- The moment I won the basketball finale
- A memorable day at the museum
- How I talk to my parrot
- The day I saw the death
- When I finally rebelled against my professor
Need more topics? Check out these extensive narrative essay topics to get creative ideas!
Narrative Essay Writing Tips
Narrative essays give you the freedom to be creative, but it can be tough to make yours special. Use these tips to make your story interesting:
- Share your story from a personal viewpoint, engaging the reader with your experiences.
- Use vivid descriptions to paint a clear picture of the setting, characters, and emotions involved.
- Organize events in chronological order for a smooth and understandable narrative.
- Bring characters to life through their actions, dialogue, and personalities.
- Employ dialogue sparingly to add realism and progression to the narrative.
- Engage readers by evoking emotions through your storytelling.
- End with reflection or a lesson learned from the experience, providing insight.
Now you have essay examples and tips to help you get started, you have a solid starting point for crafting compelling narrative essays.
However, if storytelling isn't your forte, you can always turn to our essay service for help.
Our writers are specialists who can tackle any type of essay with great skill. With their experience, you get a top-quality, 100% plagiarism-free essay everytime.
So, let our narrative essay writing service make sure your narrative essay stands out. Order now!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Caleb S. has been providing writing services for over five years and has a Masters degree from Oxford University. He is an expert in his craft and takes great pride in helping students achieve their academic goals. Caleb is a dedicated professional who always puts his clients first.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The On-Campus and Online versions of Purdue OWL assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue OWL serves the Purdue West Lafayette and Indianapolis campuses and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
- Follow PetaPixel on YouTube
- Follow PetaPixel on Facebook
- Follow PetaPixel on Twitter
- Follow PetaPixel on Instagram
How to Create a Photo Essay
The photographic essay, also called a photo essay or photo story, is a powerful way for photographers to tell a story with their images. If you are interested in creating your own photo essay, this article will guide you through the whole process, from finding a story to shoot to the basics of crafting your first visual narrative.
Table of Contents
What is a photo essay.
A photo essay tells a story visually. Just like the kind you read, the photo essay offers a complete rendering of a subject or situation using a series of carefully crafted and curated images. Photo stories have a theme, and each image backs up that overarching theme which is defined in the photo essay’s title and is sometimes supported with text.
From documentary to narrative to essay, photo stories are designed to move their audience, to inspire a certain action, awareness, or emotion. Photo stories are not just a collection of cool photos. They must use their visual power to capture viewers’ attention and remain unforgettable.
History of the Photo Story
In the “old days”, that is, before 1948, magazines ran photo stories very different from what we know today. They were staged, preconceived by an editor, not a truthful observation of life. Along came a photographer named W. Eugene Smith, who worked for Life magazine.
Deciding to follow a rural doctor for six weeks, he gathered material for a photo essay that really showed what it was like to be in that doctor’s shoes, always on the go to help his scattered patients. Smith’s piece, “ Country Doctor ,” shook other photographers out of their scripted stupor and revolutionized the way photographers report what they see.
From then on, photojournalism gained life and an audience through the lenses of legends like Robert Capa, Dorothea Lange, David “Chim” Seymour, Gordon Parks, Werner Bischof, and Henri Cartier-Bresson. The Vietnam War provided many examples for photo stories as represented by Philip Jones Griffiths, Catherine Leroy, and many more.
More recently, photo stories have found a sturdy home online thanks to the ease of publishing a series of photos digitally versus in print. Lynsey Addario, Peter Essick, and Adam Ferguson represent a few of the photographers pushing visual storytelling today.
Ways to Find Photo Stories and Themes
Photo stories exist all around, right in the midst of everyday life and in the fray of current events. A good place to begin developing a photo essay is by choosing a general theme.
Topics that Interest You
The best expression comes from the heart, so why not choose a topic that interests you. Maybe it’s a social issue, an environmental one, or just something you’re curious about. Find what moves you and share that with the world.
Personal Experiences
The more you’ve lived, the more you have to tell. This doesn’t necessarily mean age, it can also refer to experiences, big and small. If you know a subject better than most, like what it’s like to recover from a car crash, you’re an expert on the matter and therefore you have a story to tell. Also, consider the things you read and see or watch, like news or history, and incorporate that into your search for a story.
Problem/Solution
Problems abound in the world. But so do solutions. Photojournalists can present either, or both. Have a look at something that’s wrong in society and show why it’s a problem. Or find a problem that’s been resolved and show the struggle it took to get there. Even better, take your time shooting your story — sometimes it can take years — and document how a wrong is righted.
Day-in-the-Life
One of the most popular formats, day-in-the-life photo stories present microcosms of life that relate to the bigger picture. In a similar vein, behind-the-scenes photo stories show viewers what life is really like for others, especially in situations that are difficult or impossible to access. Events represent another simple yet powerful theme for documenting and storytelling with a camera.
Types of Photo Stories
Most photo stories concern people. If it’s about something like the environment, for example, the photo story can showcase the people involved. In either case, the impactful photo story will present the challenges and dilemmas of the human condition, viscerally.
There are three general types of photo stories.
Narrative Story
Narrative deals with complications and their resolution, problems, and solutions. If there appears to be no resolution, at least the struggle to find one can provide material for a photo essay. Some sort of narrative thread must push the story from beginning to middle to end, just like what you see in a good movie.
A good story also requires action, which in this case must be visual. Good stories are page-turners, whether they’re a Kerouac tale or a series of photos demonstrating the difficulties of single parenting. Adventure stories are one good example of photographic narrative storytelling.
The term “photo story” is generally used interchangeably with “photo essay”, but some photographers hold that there are subtle differences between the two. The essay type of photo story implies opinion, they argue. Essays make a point. They are the opposite of facts-only news. A photo story essay makes a case for something, like showing the danger and consequences of illegal fireworks or advocating for the preservation of a forest.
Documentary
On the other hand, documentaries lack opinion. Their purpose is to inform without adding judgment. Documentaries present the facts and let viewers decide. They illustrate something that’s occurring but they don’t always include a narrative story or an opinionated approach. Historical places, current events, and unique lifestyles always make for good documentary photo stories.
How to Craft a Photo Essay
Several elements come into play when putting together a photo essay. Once you’ve found a theme, it’s time to give your project a name. While out shooting, jot down titles that come to mind. Consider the title a magazine headline that explains in few words what the whole story is about.
Choose your photos according to whether or not they relate to and support the photo essay’s title. Reject those photos that don’t. If your collection seems to suggest a different angle, a different title, don’t be afraid to rename it. Sometimes stories develop organically. But if your title can’t assemble and define your selection of photos, maybe it’s too vague. Don’t rush it. Identify the theme, take the photos and the photo essay will take shape.
Certain techniques help tell the photo essay.
A photo essay is composed of a diversity of views, angles, and focal lengths. While masters like Henri Cartier-Bresson could capture a photo essay with a single prime lens, in his case a 50mm, the rest of us are wise to rely on multiple focal lengths. Just like what we see in the movies, a story is told with wide shots that set the scene, medium shots that tell the story, and close-ups that reveal character and emotion.
Unique angles make viewers curious and interested, and they break the monotony of standard photography. Consider working black-and-white into your photo essay. The photo essay lends itself well to reportage exclusively in monochrome, as the legends have demonstrated since W. Eugene Smith.
Visual Consistency
The idea of a photo essay is to create a whole, not a bunch of random parts. Think gestalt. The images must interact with each other. Repetition helps achieve this end. Recurring themes, moods, styles, people, things, and perspectives work to unify a project even if the photos tell different parts of the story.
Text can augment the impact of a photo essay. A photo may be worth a thousand words, but it doesn’t always replace them. Captions can be as short as a complete sentence, as long as a paragraph, or longer. Make sure to take notes in case you want to add captions. Some photo stories, however, function just fine without words.
Tell a Story as a Photographer
Few genres of photography have moved people like the photo essay. Since its inception, the art of visual storytelling has captivated audiences. Photo stories show viewers things they had never seen, have moved masses to action, and have inspired video documentaries. Today, photo stories retain their power and place, in part thanks to the internet. Every photographer should experiment with a photo essay or two.
The method of crafting a photo essay is simple yet complicated, just like life. Careful attention must be paid to the selection of images, the choice of title, and the techniques used in shooting. But follow these guidelines and the photo stories will come. Seek issues and experiences that inspire you and go photograph them with the intention of telling a complete story. The viewing world will thank you.
Image credits: Header photo shows the May 13, 1957 story in LIFE magazine titled, “ The Tough Miracle Man of Vietnam .” Stock photos from Depositphotos

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Narrative history establishes the identity of their authors and readers. Narrative histories are may be about a story of a family, community, experience of a person, etc. It gives credits to the authors and provides life with the information to the readers. Narrative history represent language and literature. It makes reading available and easy ...
Common Types of History Papers History papers come in all shapes and sizes. Some papers are narrative (organized like a story according to chronology, or the sequence of events), and some are analytical (organized like an essay according to the topic's internal logic). Some papers are concerned with history (not just what happened,
this, history essays are more than narrative accounts of the past. The purpose of a history essay is to communicate useful conclusions about past events in a purposeful and persuasive manner. History essays that are mere narratives of historical events without being analytical are, therefore, of limited value. Analytical essays are also called
The narrative essay topics in this lesson can be modified to get students of all ages and writing abilities focused on the intersection of history and writing. To unlock this lesson you must be a ...
Purpose: Reach the peak of the story, the moment of highest tension or significance. Elements: Turning Point: Highlight the most crucial moment or realization in the narrative. Example: "As the sun dipped below the horizon and hope seemed lost, a distant sound caught our attention—the rescue team's helicopters.".
Interactive example of a narrative essay. An example of a short narrative essay, responding to the prompt "Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself," is shown below. Hover over different parts of the text to see how the structure works. Narrative essay example.
History & Literature emphasizes primary source texts such as novels, films, songs, monuments, speeches, poems, archival documents, and other first-hand or original works. Most writing assignments in History & Literature will encourage you to anchor your writing in a primary source base and engage with the context in which it was produced.
When writing a narrative essay, one might think of it as telling a story. These essays are often anecdotal, experiential, and personal—allowing students to express themselves in a creative and, quite often, moving ways. Here are some guidelines for writing a narrative essay. If written as a story, the essay should include all the parts of a ...
Here are some common types of narrative essays: Personal Narrative Essays: Focus on a personal experience or event from the author's life. Use the first-person perspective to convey the writer's emotions and reflections. Fictional Narrative Essays: Can take many forms, from science fiction and fantasy to adventure and romance.
Not every form of essay writing involves meticulous research. One form in particular—the narrative essay—combines personal storytelling with academic argument. Narrative essay authors illustrate universal lessons in their unique experiences of the world. Below, you'll find some tips to guide in this style of narrative writing. <br> ## What Is a Narrative Essay? Narrative essays make an ...
A narrative essay delivers its theme by deliberately weaving the motifs through the events, scenes, and details. While a narrative essay may be entertaining, its primary purpose is to tell a complete story based on a central meaning. Unlike other essay forms, it is totally okay—even expected—to use first-person narration in narrative essays.
When an oral history essay places the experiences of an individual within the context of a historical period, it can help illuminate both the individual's experience and the historical period. Folklore : Folklorists study culture as it is expressed in everyday life and often use oral history projects to gather materials to preserve and study.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
The revival of narrative in historical writing parallels the emergence of narrative journalism. In narrative history's most celebrated invention, the micro-history, there is a passing resemblance to narrative journalism's favorite form, the nonfiction short story. Micro-histories and nonfiction short stories have a good deal in common.
A narrative essay, as the name suggests, is characterized by the presence of a narrative. Unlike argumentative essays, which present and defend a position, or analytical essays, which dissect another text, narrative essays tell a coherent story. ... with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing ...
Historians have always crafted narratives. War. Peace. Political battles. Feuds in the hollers. Floods on the Mississippi. Hurricanes. Strikes. Assassinations. Voyages to known and unknown places. Trials of the century. Personal quests. Leaders with uncommon touches and tragic flaws. This is the stuff of great narrative and the stuff of narrative history—stories about the past […]
Narrative history. Narrative history is the practice of writing history in a story-based form. It tends to entail history-writing based on reconstructing series of short-term events, and ever since the influential work of Leopold von Ranke on professionalising history-writing in the nineteenth century has been associated with empiricism.
Here is a PDF of all 650 prompts, and we also have a related lesson plan, From 'Lives' to 'Modern Love': Writing Personal Essays With Help From The New York Times.. Below, a list that ...
Moreover, as Ankersmit knows, Hayden White had academic and personal connections with at least Danto (both were students of and were influenced by Bossenbrook at Wayne State Uni. versity), Mandelbaum (at Michigan), and Mink. 16. An excellent intellectual history of this transition can be found in John Zammito, A Nice.
The fiction of narrative : essays on history, literature, and theory, 1957-2007 by White, Hayden V., 1928-Publication date 2010 Topics Literature, Modern -- History and criticism -- Theory, etc, Literature and history, Narration (Rhetoric) Publisher Baltimore : Johns Hopkins University Press
Narrative Essay Definition. Writing a narrative essay is a unique form of storytelling that revolves around personal experiences, aiming to immerse the reader in the author's world. It's a piece of writing that delves into the depths of thoughts and feelings. In a narrative essay, life experiences take center stage, serving as the main substance of the story. It's a powerful tool for writers ...
The Online Writing Lab (the Purdue OWL) at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out ...
From documentary to narrative to essay, photo stories are designed to move their audience, to inspire a certain action, awareness, or emotion. ... History of the Photo Story. In the "old days ...