Forgot password? New user? Sign up
Existing user? Log in
- Number Theory
- Probability
- Everyday Math
- Classical Mechanics
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Computer Science
- Quantitative Finance
Take a guided, problem-solving based approach to learning Calculus. These compilations provide unique perspectives and applications you won't find anywhere else.

Calculus Fundamentals
What's inside.
- Introduction
- Computing Limits
- Derivatives
- Computing Derivatives
- Linear Approximation and Applications
- Introduction to Calculus
Multivariable Calculus
- Vector Bootcamp
- Multivariable Functions
- Limits with Many Variables
- Optimization
- Multiple Integrals
Differential Equations I
- First-Order Separable Equations
- Advanced First-Order Equations
- Basics of Linear Systems
- Higher-Order Equations
Community Wiki
Browse through thousands of Calculus wikis written by our community of experts.
Sequences and Limits
- Arithmetic Progressions
- Geometric Progressions
- Arithmetic-Geometric Progression
- Telescoping Series - Sum
- Telescoping Series - Product
- Convergence Tests
- Harmonic Number
- Absolutely Convergent
- Sums Of Divergent Series
- Limits of Sequences
- Infimum/Supremum
- Nested Functions
- Dedekind Cuts
- Limits of Functions
- Limits by Substitution
- Limits by Factoring
- Limits by Rationalization
- When Does A Limit Exist?
- Continuous Functions
- Epsilon-Delta Definition of a Limit
- Squeeze Theorem
- Extreme Value Theorem
- Intermediate Value Theorem
- Is infinity at the end of the real number line?
- If F(x) is the antiderivative of f(x), is it true that \(\int_a^b\)f(x)dx=F(b)-F(a)?
- Do local extrema occur if and only if f'(x) = 0?
- Is Infinity / Infinity = 1?
- Is infinity times zero = zero?
- What is 1 divided by 0?
- If the limit of a sequence is 0, does the series converge?
Differentiation
- Average and Instantaneous Rate of Change
- Tangent Line to a Curve
- Derivative by First Principle
- Derivatives of Polynomials
- Derivatives of Rational Functions
- Derivatives of Exponential Functions
- Derivatives of Logarithmic Functions
- Partial Derivatives
- Applying Differentiation Rules To Logarithmic Functions
- Product Rule
- Quotient Rule
- Differentiation of Inverse Functions
- Applying Differentiation Rules to Trigonometric Functions
- Calculus With Inverse Trigonometric Functions
- Differentiation Rules
- Higher-order Derivatives
- Increasing / Decreasing Functions
- Inflection Points
- Implicit Differentiation
- Differentiable Function
- Mean Value Theorem
- Rolle's Theorem
Applications of Differentiation
- Indeterminate Forms
- L'Hôpital's Rule
- Related Rates of Change
- Extrema (Local and Absolute)
- Critical Points
- Second Derivative Test
- Lagrange Multipliers
- Vertical Asymptotes
- Average Velocity
- Instantaneous Velocity
- Taylor Series
- Maclaurin Series
- Taylor Series Approximation
- Taylor Series Manipulation
- Interval and Radius of Convergence
- Taylor Series - Error Bounds
- Power Series
- Small-Angle Approximation
- Fourier Series
- Taylor's Theorem (with Lagrange Remainder)
- Analytic Continuation
- Integration
- Line Integral
- Integration of Algebraic Functions
- Integration of Exponential Functions
- Integration of Trigonometric Functions
- Integration of Rational Functions
- Integration of Logarithmic Functions
- Integration of Radical Functions
- Definite Integrals
- Riemann Sums
- Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
- Improper Integrals
- Multiple Integral
- \(u\)-Substitution
- Trigonometric Substitution in Integration
- Integration by Parts
- Differentiation Under the Integral Sign
- Integration Tricks
- Lebesgue Integration
- Stokes' Theorem
- Green’s Theorem
- Area between curves
- Gamma Function
- Beta Function
- Digamma Function
- Riemann Zeta Function
- Cauchy Integral Formula
- Isolated Singularities and Residue Theorem
Applications of Integration
- Disc Method
- Shell Method
- Pappus's Centroid Theorems
Parametric Equations Calculus
- Parametric Equations
- Polar Coordinates
- Converting Polar Coordinates to Cartesian
- Polar Curves
- Parametric Derivative
- Parametric Equations - Velocity and Acceleration
- Polar Equations - Area
- Differential Equations
- Separable Differential Equations
- Homogeneous Linear Differential Equations
- Euler's Method
- Differential Equations - Euler's Method - Small Step Size
- Logistic Differential Equations
- Bernoulli Equation
- Systems of Linear Differential Equations
- Chaos Theory
Numerical Methods
- Root Approximation - Bisection
- Newton Raphson Method
- Integral Approximation - Trapezium Rule
- Integral Approximation - Simpson's Rule
- Chebyshev's Formula
Problem Loading...
Note Loading...
Set Loading...
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 1: Limits and continuity
Unit 2: derivatives: definition and basic rules, unit 3: derivatives: chain rule and other advanced topics, unit 4: applications of derivatives, unit 5: analyzing functions, unit 6: integrals, unit 7: differential equations, unit 8: applications of integrals.
Calculus Questions, Answers and Solutions
Calculus questions with detailed solutions are presented. The questions are about important concepts in calculus.
Calculus Concepts Questions
- Questions and Answers on Functions . A set of questions on the concepts of a function, in calculus, are presented along with their answers and solutions.
- Properties of the Graphs of Functions . Questions designed to help you gain deep understanding of the properties of the graphs of functions which are of major importance in calculus.
- Optimization Problems for Calculus 1 with detailed solutions.
- Calculus 1 Practice Question with detailed solutions.
- Antiderivatives in Calculus . Questions on the concepts and properties of antiderivatives in calculus are presented.
- Fundamental Theorems of Calculus . Questions on the two fundamental theorems of calculus are presented.
- Questions and Answers on Derivatives in Calculus . A set of questions on the concepts of the derivative of a function in calculus are presented with their answers and solutions.
- Computation and Properties of the Derivative in Calculus . Questions on the computation and properties of the derivative of a function in calculus are presented. These questions have been designed to help you gain deep understanding of the properties of the first derivative. Answers to the questions are also presented.
- Applications of Derivatives . Questions and answers on the applications of the first derivative are presented. These questions have been designed to help you understand the applications of derivatives in calculus.
- Critical Numbers of Functions . Questions on the critical numbers of functions are presented. The present questions have been designed to help you better understand the concept of a critical number of a function as defined in calculus. Answers to these questions are also presented.
- Questions and Answers on Limits in Calculus . A set of questions on the concepts of the limit of a function in calculus are presented along with their answers.
- Questions and Answers on Continuity of Functions . Questions on the concepts of continuity and continuous functions in calculus are presented along with their answers.
Calculus Analytical Questions
- Questions on Inverse Functions with Solutions . Questions on inverse functions are presented along with detailed solutions and explanations.
- Express a Function as the Sum of an Even and an Odd Functions . Show that any function f may be expressed as the sum of an even and an odd functions.
- Derivative of Even and Odd Functions . Questions, with answers, explanations and proofs, on derivatives of even and odd functions are presented.
- Calculus Questions with Answers (1) . The uses of the first and second derivative to determine the intervals of increase and decrease of a function, the maximum and minimum points, the interval(s) of concavity and points of inflections are discussed.
- Calculus Questions with Answers (2) . The behaviors and properties of functions, first derivatives and second derivatives are studied graphically .discussed.
- Calculus Questions with Answers (3) . Approximate graphically the first derivative of a function from its graph. Questions are presented along with solutions.
- Calculus Questions with Answers (4) . Calculus questions, on differentiable functions, with detailed solutions are presented. We first present two important theorems on differentiable functions that are used to discuss the solutions to the questions.
- Calculus Questions with Answers (5) . Calculus questions, on tangent lines, are presented along with detailed solutions.
- Questions with Answers on the Second Fundamental Theorem of Calculus . Questions with detailed solutions on the second theorem of calculus are presented.
- Questions on Functions (with Solutions) . Several questions on functions are presented and their detailed solutions discussed.
- Questions on Composite Functions with Solutions . Questions on composite functions are presented along with their detailed solutions.
- Questions on Concavity and Inflection Points . Questions with detailed solutions on concavity and inflection point of graphs of functions.
- Derivatives in Calculus: Questions with Solutions . Questions on derivatives of functions are presented and their detailed solutions discussed.
More References and links on Calculus
- Calculus Tutorials and Problems .
- Solve equations and inequalities
- Simplify expressions
- Factor polynomials
- Graph equations and inequalities
- Advanced solvers
- All solvers
- Arithmetics
- Determinant
- Percentages
- Scientific Notation
- Inequalities
The calculus section of QuickMath allows you to differentiate and integrate almost any mathematical expression.
What is calculus?
Calculus is a vast topic, and it forms the basis for much of modern mathematics. The two branches of calculus are differential calculus and integral calculus.
Differential calculus is the study of rates of change of functions. At school, you are introduced to differential calculus by learning how to find the derivative of a function in order to determine the slope of the graph of that function at any point.
Integral calculus is often introduced in school in terms of finding primitive functions (indefinite integrals) and finding the area under a curve (definite integrals).
Differentiate
The differentiate command allows you to find the derivative of an expression with respect to any variable. In the advanced section, you also have the option of specifying arbitrary functional dependencies within your expression and finding higher order derivatives. The differentiate command knows all the rules of differential calculus, including the product rule, the quotient rule and the chain rule.
Go to the Differentiate page
The integrate command can be used to find either indefinite or definite integrals. If an indefinite integral (primitive function) is sought but cannot be found for a particular function, QuickMath will let you know. Definite integrals will always be given in their exact form when possible, but failing this QuickMath will use a numerical method to give you an approximate value.
Go to the Integrate page
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Integrals were evaluated in the previous tutorial by identifying the integral with an appropriate area and then using methods from geometry to find the area. This procedure will succeed only for very simple integrals. The main result of this section, the fundamental theorem of calculus, includes a very important formula for evaluating integrals. This theorem shows us how to evaluate integrals by first evaluating antiderivatives. The theorem establishes an amazing relationship between the integral, which may be interpreted as an area, and the antiderivative, which is inversely related to the derivative; that is, it relates area and the derivative.
Let f be a continuous function on [a, b ], and define a function F by

The following theorem is called the fundamental theorem and is a consequence of Theorem 1 . The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus

0 = F (a) = G (a) + c

Math Topics
More solvers.
- Add Fractions
- Simplify Fractions
Practice Test
For the following exercises, determine whether each of the following relations is a function.
y = 2 x + 8 y = 2 x + 8
{ ( 2 , 1 ) , ( 3 , 2 ) , ( − 1 , 1 ) , ( 0 , − 2 ) } { ( 2 , 1 ) , ( 3 , 2 ) , ( − 1 , 1 ) , ( 0 , − 2 ) }
For the following exercises, evaluate the function f ( x ) = − 3 x 2 + 2 x f ( x ) = − 3 x 2 + 2 x at the given input.
f ( −2 ) f ( −2 )
f ( a ) f ( a )
Show that the function f ( x ) = − 2 ( x − 1 ) 2 + 3 f ( x ) = − 2 ( x − 1 ) 2 + 3 is not one-to-one.
Write the domain of the function f ( x ) = 3 − x f ( x ) = 3 − x in interval notation.
Given f ( x ) = 2 x 2 − 5 x , f ( x ) = 2 x 2 − 5 x , find f ( a + 1 ) − f ( 1 ) . f ( a + 1 ) − f ( 1 ) .
Graph the function f ( x ) = { x + 1 if − 2 < x < 3 − x if x ≥ 3 f ( x ) = { x + 1 if − 2 < x < 3 − x if x ≥ 3
Find the average rate of change of the function f ( x ) = 3 − 2 x 2 + x f ( x ) = 3 − 2 x 2 + x by finding f ( b ) − f ( a ) b − a . f ( b ) − f ( a ) b − a .
For the following exercises, use the functions f ( x ) = 3 − 2 x 2 + x and g ( x ) = x f ( x ) = 3 − 2 x 2 + x and g ( x ) = x to find the composite functions.
( g ∘ f ) ( x ) ( g ∘ f ) ( x )
( g ∘ f ) ( 1 ) ( g ∘ f ) ( 1 )
Express H ( x ) = 5 x 2 − 3 x 3 H ( x ) = 5 x 2 − 3 x 3 as a composition of two functions, f f and g , g , where ( f ∘ g ) ( x ) = H ( x ) . ( f ∘ g ) ( x ) = H ( x ) .
For the following exercises, graph the functions by translating, stretching, and/or compressing a toolkit function.
f ( x ) = x + 6 − 1 f ( x ) = x + 6 − 1
f ( x ) = 1 x + 2 − 1 f ( x ) = 1 x + 2 − 1
For the following exercises, determine whether the functions are even, odd, or neither.
f ( x ) = − 5 x 2 + 9 x 6 f ( x ) = − 5 x 2 + 9 x 6
f ( x ) = − 5 x 3 + 9 x 5 f ( x ) = − 5 x 3 + 9 x 5
f ( x ) = 1 x f ( x ) = 1 x
Graph the absolute value function f ( x ) = − 2 | x − 1 | + 3. f ( x ) = − 2 | x − 1 | + 3.
Solve | 2 x − 3 | = 17. | 2 x − 3 | = 17.
Solve − | 1 3 x − 3 | ≥ 17. − | 1 3 x − 3 | ≥ 17. Express the solution in interval notation.
For the following exercises, find the inverse of the function.
f ( x ) = 3 x − 5 f ( x ) = 3 x − 5
f ( x ) = 4 x + 7 f ( x ) = 4 x + 7
For the following exercises, use the graph of g g shown in Figure 1 .
On what intervals is the function increasing?
On what intervals is the function decreasing?
Approximate the local minimum of the function. Express the answer as an ordered pair.
Approximate the local maximum of the function. Express the answer as an ordered pair.
For the following exercises, use the graph of the piecewise function shown in Figure 2 .
Find f ( 2 ) . f ( 2 ) .
Find f ( −2 ) . f ( −2 ) .
Write an equation for the piecewise function.
For the following exercises, use the values listed in Table 1 .
Find F ( 6 ) . F ( 6 ) .
Solve the equation F ( x ) = 5. F ( x ) = 5.
Is the graph increasing or decreasing on its domain?
Is the function represented by the graph one-to-one?
Find F − 1 ( 15 ) . F − 1 ( 15 ) .
Given f ( x ) = − 2 x + 11 , f ( x ) = − 2 x + 11 , find f − 1 ( x ) . f − 1 ( x ) .
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/precalculus/pages/1-introduction-to-functions
- Authors: Jay Abramson
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Precalculus
- Publication date: Oct 23, 2014
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/precalculus/pages/1-introduction-to-functions
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/precalculus/pages/1-practice-test
© Dec 8, 2021 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
- Problem Generator
- Mobile Apps
- All Products
- Preferences
- My Apps (API)

Game Central
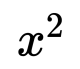
Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language

Get step-by-step solutions to your math problems

Try Math Solver

Get step-by-step explanations
Graph your math problems
Practice, practice, practice

Get math help in your language
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Additional menu
Khan Academy Blog
Free Math Worksheets — Over 100k free practice problems on Khan Academy
Looking for free math worksheets.
You’ve found something even better!
That’s because Khan Academy has over 100,000 free practice questions. And they’re even better than traditional math worksheets – more instantaneous, more interactive, and more fun!
Just choose your grade level or topic to get access to 100% free practice questions:
Kindergarten, basic geometry, pre-algebra, algebra basics, high school geometry.
- Trigonometry
Statistics and probability
High school statistics, ap®︎/college statistics, precalculus, differential calculus, integral calculus, ap®︎/college calculus ab, ap®︎/college calculus bc, multivariable calculus, differential equations, linear algebra.
- Addition and subtraction
- Place value (tens and hundreds)
- Addition and subtraction within 20
- Addition and subtraction within 100
- Addition and subtraction within 1000
- Measurement and data
- Counting and place value
- Measurement and geometry
- Place value
- Measurement, data, and geometry
- Add and subtract within 20
- Add and subtract within 100
- Add and subtract within 1,000
- Money and time
- Measurement
- Intro to multiplication
- 1-digit multiplication
- Addition, subtraction, and estimation
- Intro to division
- Understand fractions
- Equivalent fractions and comparing fractions
- More with multiplication and division
- Arithmetic patterns and problem solving
- Quadrilaterals
- Represent and interpret data
- Multiply by 1-digit numbers
- Multiply by 2-digit numbers
- Factors, multiples and patterns
- Add and subtract fractions
- Multiply fractions
- Understand decimals
- Plane figures
- Measuring angles
- Area and perimeter
- Units of measurement
- Decimal place value
- Add decimals
- Subtract decimals
- Multi-digit multiplication and division
- Divide fractions
- Multiply decimals
- Divide decimals
- Powers of ten
- Coordinate plane
- Algebraic thinking
- Converting units of measure
- Properties of shapes
- Ratios, rates, & percentages
- Arithmetic operations
- Negative numbers
- Properties of numbers
- Variables & expressions
- Equations & inequalities introduction
- Data and statistics
- Negative numbers: addition and subtraction
- Negative numbers: multiplication and division
- Fractions, decimals, & percentages
- Rates & proportional relationships
- Expressions, equations, & inequalities
- Numbers and operations
- Solving equations with one unknown
- Linear equations and functions
- Systems of equations
- Geometric transformations
- Data and modeling
- Volume and surface area
- Pythagorean theorem
- Transformations, congruence, and similarity
- Arithmetic properties
- Factors and multiples
- Reading and interpreting data
- Negative numbers and coordinate plane
- Ratios, rates, proportions
- Equations, expressions, and inequalities
- Exponents, radicals, and scientific notation
- Foundations
- Algebraic expressions
- Linear equations and inequalities
- Graphing lines and slope
- Expressions with exponents
- Quadratics and polynomials
- Equations and geometry
- Algebra foundations
- Solving equations & inequalities
- Working with units
- Linear equations & graphs
- Forms of linear equations
- Inequalities (systems & graphs)
- Absolute value & piecewise functions
- Exponents & radicals
- Exponential growth & decay
- Quadratics: Multiplying & factoring
- Quadratic functions & equations
- Irrational numbers
- Performing transformations
- Transformation properties and proofs
- Right triangles & trigonometry
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry (Advanced)
- Analytic geometry
- Conic sections
- Solid geometry
- Polynomial arithmetic
- Complex numbers
- Polynomial factorization
- Polynomial division
- Polynomial graphs
- Rational exponents and radicals
- Exponential models
- Transformations of functions
- Rational functions
- Trigonometric functions
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry
- Trigonometric equations and identities
- Analyzing categorical data
- Displaying and comparing quantitative data
- Summarizing quantitative data
- Modeling data distributions
- Exploring bivariate numerical data
- Study design
- Probability
- Counting, permutations, and combinations
- Random variables
- Sampling distributions
- Confidence intervals
- Significance tests (hypothesis testing)
- Two-sample inference for the difference between groups
- Inference for categorical data (chi-square tests)
- Advanced regression (inference and transforming)
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Scatterplots
- Data distributions
- Two-way tables
- Binomial probability
- Normal distributions
- Displaying and describing quantitative data
- Inference comparing two groups or populations
- Chi-square tests for categorical data
- More on regression
- Prepare for the 2020 AP®︎ Statistics Exam
- AP®︎ Statistics Standards mappings
- Polynomials
- Composite functions
- Probability and combinatorics
- Limits and continuity
- Derivatives: definition and basic rules
- Derivatives: chain rule and other advanced topics
- Applications of derivatives
- Analyzing functions
- Parametric equations, polar coordinates, and vector-valued functions
- Applications of integrals
- Differentiation: definition and basic derivative rules
- Differentiation: composite, implicit, and inverse functions
- Contextual applications of differentiation
- Applying derivatives to analyze functions
- Integration and accumulation of change
- Applications of integration
- AP Calculus AB solved free response questions from past exams
- AP®︎ Calculus AB Standards mappings
- Infinite sequences and series
- AP Calculus BC solved exams
- AP®︎ Calculus BC Standards mappings
- Integrals review
- Integration techniques
- Thinking about multivariable functions
- Derivatives of multivariable functions
- Applications of multivariable derivatives
- Integrating multivariable functions
- Green’s, Stokes’, and the divergence theorems
- First order differential equations
- Second order linear equations
- Laplace transform
- Vectors and spaces
- Matrix transformations
- Alternate coordinate systems (bases)
Frequently Asked Questions about Khan Academy and Math Worksheets
Why is khan academy even better than traditional math worksheets.
Khan Academy’s 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don’t need to be graded, and don’t require a printer.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets look like?
Here’s an example:
What are teachers saying about Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets?
“My students love Khan Academy because they can immediately learn from their mistakes, unlike traditional worksheets.”
Is Khan Academy free?
Khan Academy’s practice questions are 100% free—with no ads or subscriptions.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets cover?
Our 100,000+ practice questions cover every math topic from arithmetic to calculus, as well as ELA, Science, Social Studies, and more.
Is Khan Academy a company?
Khan Academy is a nonprofit with a mission to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere.
Want to get even more out of Khan Academy?
Then be sure to check out our teacher tools . They’ll help you assign the perfect practice for each student from our full math curriculum and track your students’ progress across the year. Plus, they’re also 100% free — with no subscriptions and no ads.
Get Khanmigo
The best way to learn and teach with AI is here. Ace the school year with our AI-powered guide, Khanmigo.
For learners For teachers For parents
Differential Calculus Questions
Differential calculus questions with solutions are provided for students to practise differentiation questions. Differential calculus is a branch of Calculus in mathematics that studies the instantaneous rate of change in a function corresponding to a given input value. Geometrically, it represents the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at a given particular point, provided that the function exists and is differentiable at that point. The derivative of a real-valued function at a given point in its domain represents the closest linear approximation of that function at that point.
Learn more about differential calculus in maths .

In the above figure, y = f(x) is a continuous and differentiable function between x and x + h, then derivative of y, dy/dx is the slope of the tangent to the graph of y at x.
Then, the derivative of a function is defined as:
Derivatives of Some Functions in Differential Calculus
Some rules of differential calculus.
Let us study some essential rules that we are going to require while differentiating any function.
- Differential of addition or subtraction of functions
- Differential of product of functions
- Quotient rule of differentiation
- Chain rule of differentiation
Let y = f(u) and u = g(x), then
Watch the Video on Theorems of Differentiation
Differential Calculus Questions with Solutions
Solve the following differential calculus question and check your solution with the one given here. Practising these questions will improve your understanding of differentiation and help you score better in examinations. These questions are provided keeping in view the syllabus of Classes XI and XII.
Question 1:
Differentiate the following functions with respect to x:
(ii) cos x 3
(iii) x 3 + tan x
(i) Let f(x) = sin 4x, put 4x = t, then
(ii) Let f(x) = cos x 3 , put x 3 = u, then
(iii) Let h(x) = x 3 + tan x, then
Question 2:
If f(x) = [cos x –sin x]/[cos x + sin x], then prove that f’(x) + [f(x)] 2 = –1.
Divide both the denominator and numerator by cos x, and we get
f(x) = [1 – tan x]/[1 + tan x] = tan ( 𝜋/4 – x)
And [f(x)] 2 = tan 2 ( 𝜋/4 – x)
f’(x) + [f(x)] 2 = –sec 2 ( 𝜋/4 – x) + tan 2 ( 𝜋/4 – x) = –sec 2 ( 𝜋/4 – x) + sec 2 ( 𝜋/4 – x) –1 = –1
∴ f’(x) + [f(x)] 2 = –1
Question 3:
Differentiate with respect to x: (2x + 1)/(2x + 3)
Let y = (2x + 1)/(2x + 3) = 1 – 2/(2x + 3)
Question 4:
If y = tan –1 [(4x)/(1 + 5x 2 )] + tan –1 [(2 + 3x)/(3 – 2x)], find dy/dx.
Differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get
Question 5:
Differentiate the following function:
Differentiating with respect to x, we get
Also check:
- Maxima and Minima
- Application of Derivatives
- Increasing and Decreasing Function
- Linear Approximations
Question 6:
Find the differential of the following exponential and logarithmic functions:
(i) 5 x – 3 cos x + log x
(ii) e x sec x
(iii) 3 x /(2 + sin x)
(i) Let y = 5 x – 3 cos x + log x
dy/dx = 5 x log 5 + 3 sin x + 1/x.
(ii) Let y = e x sec x
dy/dx = d/dx [e x sec x] = sin x {d/dx (e x } + e x {d/dx (sec x)}
= e x sec x + e x. sec x tan x
= e x sec x (tan x + 1)
(iii) Let y = 3 x /(2 + sin x)
Question 7:
Differentiate x 3 /(1 – x 3 ) with respect to x 3 .
Let y = x 3 /(1 – x 3 ) and put t = x 3 , thus we have to find the value of dy/dt
And dt/dx = 3x 2
Question 8:
Differentiate with respect to x:
Taking logarithm on both sides, we get
Check out: Derivative calculator
Question 9:
Given function
Prove that differential of y with respect to x is
Taking logarithms on both sides, we get
log y = y x log x, again taking logarithm on both sides, we have
log (log y) = x log y + log (log x)
Let us differentiate both sides with respect x; we get
Question 10:
If x = sin u and y = sin bu, where b is any real constant. Prove that
First, we shall determine dx/du and dy/du. Thus, differentiating both x and y with respect to u, we get
On squaring both sides, we get,
Differentiating both sides of (i) with respect to x, we get
Dividing both sides by 2(dy/dx), we get,
Recommended Video

Practice Questions on Differential Calculus Questions
1. Find the differential of the following functions with respect to x.
2. Find the derivative of sin (sin x 3 ) at x = 𝜋/2.
3. Find the second order derivative with respect to x of the function x 3 + 24xy + y 3 = 8.
4. If y = 𝛼e ax + 𝛽e –ax , prove that y” – a 2 y = 0.
5. Differentiate with respect to x: tan (x x ).
Download BYJU’S – The Learning App to solve more practice questions on various concepts of higher mathematics with proper explanations, solved examples and video lessons. Register yourself today!
- Share Share
Solver Title
Generating PDF...
- Pre Algebra Order of Operations Factors & Primes Fractions Long Arithmetic Decimals Exponents & Radicals Ratios & Proportions Percent Modulo Number Line Mean, Median & Mode
- Algebra Equations Inequalities System of Equations System of Inequalities Basic Operations Algebraic Properties Partial Fractions Polynomials Rational Expressions Sequences Power Sums Interval Notation Pi (Product) Notation Induction Logical Sets Word Problems
- Pre Calculus Equations Inequalities Scientific Calculator Scientific Notation Arithmetics Complex Numbers Polar/Cartesian Simultaneous Equations System of Inequalities Polynomials Rationales Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Coordinate Geometry Plane Geometry Solid Geometry Conic Sections Trigonometry
- Calculus Derivatives Derivative Applications Limits Integrals Integral Applications Integral Approximation Series ODE Multivariable Calculus Laplace Transform Taylor/Maclaurin Series Fourier Series Fourier Transform
- Functions Line Equations Functions Arithmetic & Comp. Conic Sections Transformation
- Linear Algebra Matrices Vectors
- Trigonometry Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify
- Statistics Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Average Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability Mid-Range Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal Distribution
- Physics Mechanics
- Chemistry Chemical Reactions Chemical Properties
- Finance Simple Interest Compound Interest Present Value Future Value
- Economics Point of Diminishing Return
- Conversions Roman Numerals Radical to Exponent Exponent to Radical To Fraction To Decimal To Mixed Number To Improper Fraction Radians to Degrees Degrees to Radians Hexadecimal Scientific Notation Distance Weight Time Volume
- Pre Algebra
- Pre Calculus
- Linear Algebra
- Trigonometry
- Conversions

Most Used Actions
Number line.
- x^{2}-x-6=0
- -x+3\gt 2x+1
- line\:(1,\:2),\:(3,\:1)
- prove\:\tan^2(x)-\sin^2(x)=\tan^2(x)\sin^2(x)
- \frac{d}{dx}(\frac{3x+9}{2-x})
- (\sin^2(\theta))'
- \lim _{x\to 0}(x\ln (x))
- \int e^x\cos (x)dx
- \int_{0}^{\pi}\sin(x)dx
- \sum_{n=0}^{\infty}\frac{3}{2^n}
- Is there a step by step calculator for math?
- Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of math problems, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and linear algebra. It shows you the solution, graph, detailed steps and explanations for each problem.
- Is there a step by step calculator for physics?
- Symbolab is the best step by step calculator for a wide range of physics problems, including mechanics, electricity and magnetism, and thermodynamics. It shows you the steps and explanations for each problem, so you can learn as you go.
- How to solve math problems step-by-step?
- To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem.
- Practice, practice, practice Math can be an intimidating subject. Each new topic we learn has symbols and problems we have never seen. The unknowing...
Please add a message.
Message received. Thanks for the feedback.
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Computation and Language
Title: large language models are unconscious of unreasonability in math problems.
Abstract: Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate substantial capabilities in solving math problems. However, they tend to produce hallucinations when given questions containing unreasonable errors. In this paper, we study the behavior of LLMs when faced with unreasonable math problems and further explore their potential to address these problems. First, we construct the Unreasonable Math Problem (UMP) benchmark to examine the error detection ability of LLMs. Experiments show that LLMs are able to detect unreasonable errors, but still fail in generating non-hallucinatory content. In order to improve their ability of error detection and correction, we further design a strategic prompt template called Critical Calculation and Conclusion(CCC). With CCC, LLMs can better self-evaluate and detect unreasonable errors in math questions, making them more reliable and safe in practical application scenarios.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Netflix's hit sci-fi series '3 Body Problem' is based on a real math problem that is so complex it's impossible to solve
- The three-body problem is a centuries-old physics question that puzzled Isaac Newton .
- It describes the orbits of three bodies, like planets or stars, trapped in each other's gravity.
- The problem is unsolvable and led to the development of chaos theory.

While Netflix's "3 Body Problem" is a science-fiction show, its name comes from a real math problem that's puzzled scientists since the late 1600s.
In physics, the three-body problem refers to the motion of three bodies trapped in each other's gravitational grip — like a three-star system.
It might sound simple enough, but once you dig into the mathematics, the orbital paths of each object get complicated very quickly.
Two-body vs. three- and multi-body systems
A simpler version is a two-body system like binary stars. Two-body systems have periodic orbits, meaning they are mathematically predictable because they follow the same trajectory over and over. So, if you have the stars' initial positions and velocities, you can calculate where they've been or will be in space far into the past and future.
However, "throwing in a third body that's close enough to interact leads to chaos," Shane Ross, an aerospace and ocean engineering professor at Virginia Tech, told Business Insider. In fact, it's nearly impossible to precisely predict the orbital paths of any system with three bodies or more.
While two orbiting planets might look like a ven diagram with ovular paths overlapping, the paths of three bodies interacting often resemble tangled spaghetti. Their trajectories usually aren't as stable as systems with only two bodies.
All that uncertainty makes what's known as the three-body problem largely unsolvable, Ross said. But there are certain exceptions.
The three-body problem is over 300 years old
The three-body problem dates back to Isaac Newton , who published his "Principia" in 1687.
In the book, the mathematician noted that the planets move in elliptical orbits around the sun. Yet the gravitational pull from Jupiter seemed to affect Saturn's orbital path.
Related stories
The three-body problem didn't just affect distant planets. Trying to understand the variations in the moon's movements caused Newton literal headaches, he complained.
But Newton never fully figured out the three-body problem. And it remained a mathematical mystery for nearly 200 years.
In 1889, a Swedish journal awarded mathematician Henri Poincaré a gold medal and 2,500 Swedish crowns, roughly half a year's salary for a professor at the time, for his essay about the three-body problem that outlined the basis for an entirely new mathematical theory called chaos theory .
According to chaos theory, when there is uncertainty about a system's initial conditions, like an object's mass or velocity, that uncertainty ripples out, making the future more and more unpredictable.
Think of it like taking a wrong turn on a trip. If you make a left instead of a right at the end of your journey, you're probably closer to your destination than if you made the mistake at the very beginning.
Can you solve the three-body problem?
Cracking the three-body problem would help scientists chart the movements of meteors and planets, including Earth, into the extremely far future. Even comparatively small movements of our planet could have large impacts on our climate, Ross said.
Though the three-body problem is considered mathematically unsolvable, there are solutions to specific scenarios. In fact, there are a few that mathematicians have found.
For example, three bodies could stably orbit in a figure eight or equally spaced around a ring. Both are possible depending on the initial positions and velocities of the bodies.
One way researchers look for solutions is with " restricted " three-body problems, where two main bodies (like the sun and Earth) interact and a third object with much smaller mass (like the moon) offers less gravitational interference. In this case, the three-body problem looks a lot like a two-body problem since the sun and Earth comprise the majority of mass in the system.
However, if you're looking at a three-star system, like the one in Netflix's show "3 Body Problem," that's a lot more complicated.
Computers can also run simulations far more efficiently than humans, though due to the inherent uncertainties, the results are typically approximate orbits instead of exact.
Finding solutions to three-body problems is also essential to space travel, Ross said. For his work, he inputs data about the Earth, moon, and spacecraft into a computer. "We can build up a whole library of possible trajectories," he said, "and that gives us an idea of the types of motion that are possible."
- Main content
- For a new problem, you will need to begin a new live expert session.
- You can contact support with any questions regarding your current subscription.
- You will be able to enter math problems once our session is over.
- I am only able to help with one math problem per session. Which problem would you like to work on?
- Does that make sense?
- I am currently working on this problem.
- Are you still there?
- It appears we may have a connection issue. I will end the session - please reconnect if you still need assistance.
- Let me take a look...
- Can you please send an image of the problem you are seeing in your book or homework?
- If you click on "Tap to view steps..." you will see the steps are now numbered. Which step # do you have a question on?
- Please make sure you are in the correct subject. To change subjects, please exit out of this live expert session and select the appropriate subject from the menu located in the upper left corner of the Mathway screen.
- What are you trying to do with this input?
- While we cover a very wide range of problems, we are currently unable to assist with this specific problem. I spoke with my team and we will make note of this for future training. Is there a different problem you would like further assistance with?
- Mathway currently does not support this subject. We are more than happy to answer any math specific question you may have about this problem.
- Mathway currently does not support Ask an Expert Live in Chemistry. If this is what you were looking for, please contact support.
- Mathway currently only computes linear regressions.
- We are here to assist you with your math questions. You will need to get assistance from your school if you are having problems entering the answers into your online assignment.
- Have a great day!
- Hope that helps!
- You're welcome!
- Per our terms of use, Mathway's live experts will not knowingly provide solutions to students while they are taking a test or quiz.
Please ensure that your password is at least 8 characters and contains each of the following:
- a special character: @$#!%*?&

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Calculus 1 Practice Question with detailed solutions. Optimization Problems for Calculus 1 with detailed solutions. Linear Least Squares Fitting. Use partial derivatives to find a linear fit for a given experimental data. Minimum Distance Problem. The first derivative is used to minimize the distance traveled.
Question 10: Find the area between the circle 4x 2 + 4y 2 = 9 and the parabola y 2 = 4x. Solution: Now, 4x 2 + 4y 2 = 9 represents a circle whose centre is at (0,0) and radius is 3/2 and y 2 = 4x represents a rightward parabola, whose vertex is at (0, 0). Now, let us find the points of intersection.
Take a guided, problem-solving based approach to learning Calculus. These compilations provide unique perspectives and applications you won't find anywhere else.
Free math problem solver answers your calculus homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. ... We are here to assist you with your math questions. You will need to get assistance from your school if you are having problems entering the answers into your online assignment.
Unit 1: Limits and continuity. 0/3500 Mastery points. Limits intro Estimating limits from graphs Estimating limits from tables Formal definition of limits (epsilon-delta) Properties of limits Limits by direct substitution Limits using algebraic manipulation Strategy in finding limits. Squeeze theorem Types of discontinuities Continuity at a ...
Beginning Differential Calculus : Problems on the limit of a function as x approaches a fixed constant ; limit of a function as x approaches plus or minus infinity ; limit of a function using the precise epsilon/delta definition of limit ; limit of a function using l'Hopital's rule . Problems on the continuity of a function of one variable
Questions, with answers, explanations and proofs, on derivatives of even and odd functions are presented. Calculus Questions with Answers (1). The uses of the first and second derivative to determine the intervals of increase and decrease of a function, the maximum and minimum points, the interval (s) of concavity and points of inflections are ...
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Let f be continuous on [a. b ], and suppose G is any antiderivative of f on [a, b], that is. G' (x) = f (x) for x in [a. b]. Then, To verify the fundamental theorem, let F be given by , as in Formula (1). Then by Theorem 1, F is an antiderivative of f. Since G is also an antiderivative of f, we know that ...
Calculus: 1001 Practice Problems For Dummies (+ Free Online Practice) Solving calculus problems is a great way to master the various rules, theorems, and calculations you encounter in a typical Calculus class. This Cheat Sheet provides some basic formulas you can refer to regularly to make solving calculus problems a breeze (well, maybe not a ...
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) ... Symbolab is the best calculus calculator solving derivatives, integrals, limits, series, ODEs, and more. ... properties, and application of integrals. This can be used to solve problems in a wide range of fields, including physics, engineering, and economics. Show more; Why users love our Calculus Calculator.
Only Wolfram Problem Generator directly integrates the popular and powerful Step-by-step Solutions from Wolfram|Alpha. You can use a single hint to get unstuck, or explore the entire math problem from beginning to end. Online practice problems for math, including arithmetic, algebra, calculus, linear algebra, number theory, and statistics.
7.1 Solving Trigonometric Equations with Identities; 7.2 Sum and Difference Identities; 7.3 Double-Angle, Half-Angle, and Reduction Formulas; 7.4 Sum-to-Product and Product-to-Sum Formulas; 7.5 Solving Trigonometric Equations; 7.6 Modeling with Trigonometric Functions
Wolfram for Education. Wolfram Demonstrations. Mathematica. MathWorld. Online practice problems with answers for students and teachers. Pick a topic and start practicing, or print a worksheet for study sessions or quizzes.
Get math help in your language. Works in Spanish, Hindi, German, and more. Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
Online math solver with free step by step solutions to algebra, calculus, and other math problems. Get help on the web or with our math app.
Khan Academy's 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don't need to be graded, and don't require a printer. Math Worksheets. Khan Academy. Math worksheets take forever to hunt down across the internet. Khan Academy is your one-stop-shop for practice from arithmetic to calculus. Math worksheets can vary in quality from ...
Differential calculus questions with solutions are provided for students to practise differentiation questions. Differential calculus is a branch of Calculus in mathematics that studies the instantaneous rate of change in a function corresponding to a given input value. Geometrically, it represents the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at a given particular point, provided ...
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Is there a step by step calculator for math? ... To solve math problems step-by-step start by reading the problem carefully and understand what you are being asked to find. Next, identify the relevant information, define the variables, and plan a strategy for solving the problem. ...
Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate substantial capabilities in solving math problems. However, they tend to produce hallucinations when given questions containing unreasonable errors. In this paper, we study the behavior of LLMs when faced with unreasonable math problems and further explore their potential to address these problems. First, we construct the Unreasonable Math Problem (UMP ...
While Netflix's "3 Body Problem" is a science-fiction show, its name comes from a real math problem that's puzzled scientists since the late 1600s. In physics, the three-body problem refers to the ...
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations. Mathway. Visit Mathway on the web. ... We are here to assist you with your math questions. You will need to get assistance from your school if you are having problems entering the answers into your online assignment.