

151+ Good Banking And Finance Research Topics For Students [2024 Updated]
Are you curious about Banking and Finance Research Topics? In this blog, we explore various banking and finance-related research topics. What drives the banking sector’s resilience in the face of challenges? How do financial markets influence our economic well-being?
Let’s find the good topics of personal finance, corporate decision-making, risk management, and more. From the fundamental principles of accounting to the latest trends in fintech, this collection of research topics spans various fields, offering a comprehensive view of the ever-evolving finance domain.
Discover the impact of digital currencies, the role of central banks, and the effectiveness of credit scoring models. Explore the importance of real estate finance and know the behavioral aspects influencing investment decisions. We also examine the intersection of finance with emerging technologies and its role in sustainable development.
Whether you are a student researching finance or the banking sector with good research ideas about economic difficulties. These Banking and Finance Research Topics provide a gateway to understanding the pivotal role finance plays in our global society. Let’s know all about them here.
Table of Contents
What Is Banking And Finance Research Topics?
Banking and finance research topics refer to specific questions that researchers investigate related to financial systems and institutions. These topics help explore how banks, investments, financial markets, and economic policies work.
Some examples of banking and finance research topics include:
- How new technologies like mobile apps are changing banking
- What causes stock market prices to rise and fall
- How government regulations impact financial institutions
- Why do people make certain financial decisions?
- Ways to improve risk management for banks
- The future of cryptocurrencies as an investment
- How fintech companies are competing with traditional banks
Researching these topics aims to gain a deeper understanding of the financial world. The knowledge can then be used to inform better policies, practices, and decisions related to banking and finance.
How To Find Banking And Finance Research Topics For Students?
Here are some tips for students on finding good banking and finance research topics:

- Look at current events in the banking and finance industries for inspiration. Pay attention to what’s happening with major banks, new technologies, economic policies, financial crises, and industry trends.
- Review finance publications, academic journals, magazines, and websites to discover recent research studies related to banking and see what knowledge gaps they identify that require further investigation.
- Browse research paper databases for sample banking and finance essays to find potential topics or note areas requiring additional up-to-date research.
- Align topics with your existing interests and course curriculum. If you enjoy technology, explore fintech questions. If macroeconomics fascinates you, investigate the implications of monetary policies.
- Consider meaningful real-life research questions, like how underprivileged groups are financially underserved or how developing nations can gain affordable banking access.
- Brainstorm ideas and get input from professors who will guide you in refining topics based on viability, available data sources, analytical methods, and relevance to the current finance field.
List of Good Banking And Finance Research Topics
Here are the most interesting banking and finance research topics:
Good Banking And Finance Research Topics For Students
- Comparative analysis of traditional banking vs. online banking.
- The impact of mergers and acquisitions on bank performance.
- Assessing the role of central banks in ensuring financial stability.
- Investigating the effectiveness of bank stress tests in predicting financial crises.
- Analyzing the factors influencing customer satisfaction in banking services.
- The role of blockchain technology in enhancing banking security.
- Examining the impact of interest rate fluctuations on bank profitability.
- Evaluating the role of government intervention in preventing bank failures.
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of Islamic banking.
- The impact of Basel III regulations on banking risk management.
Best Banking And Finance Sector Research Topics For MBA Students
- The role of the stock market in economic development.
- Examining the factors affecting stock market volatility.
- Impact of high-frequency trading on financial markets.
- Exploring the relationship between corporate governance and stock prices.
- The role of derivatives in managing financial market risks.
- Analyzing the impact of macroeconomic indicators on stock prices.
- The role of insider trading in financial markets.
- Investigating the efficiency of emerging financial markets.
- The impact of market sentiment on stock prices.
- Analyzing the role of financial analysts in shaping market perceptions.
Personal Finance-Related Research Topics
- The impact of financial literacy on personal finance management.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of budgeting tools in personal finance.
- The role of behavioral economics in understanding individual investment decisions.
- Investigating the factors influencing retirement savings decisions.
- The impact of socio-economic factors on household debt levels.
- Assessing the effectiveness of financial planning in achieving financial goals.
- The role of technology in personal financial management.
- Analyzing the impact of tax policies on personal savings.
- The relationship between education and income levels in personal finance.
- Investigating the role of psychological biases in personal investment decisions.
Corporate Banking And Finance Research Topics
- The impact of capital structure on firm profitability.
- Evaluating the role of financial leverage in corporate decision-making.
- Analyzing the factors influencing dividend payout policies.
- The impact of corporate governance on firm performance.
- Investigating the relationship between CEO compensation and firm performance.
- The role of working capital management in corporate finance.
- Analyzing the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on multinational corporations.
- The influence of financial disclosure on investor decisions.
- Evaluating the impact of corporate social responsibility on shareholder value.
- The role of venture capital in financing innovation and startups.
Risk Management Research Topics For College Students
- The impact of credit risk on financial institutions.
- Analyzing the role of derivatives in hedging financial risks.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of value-at-risk (VaR) models in risk management.
- The impact of operational risk on financial institutions.
- Exploring the relationship between risk-taking and financial performance.
- Analyzing the role of insurance in managing financial risks.
- The impact of climate change on financial risk assessment.
- Evaluating the role of stress testing in assessing systemic risk.
- The influence of cyber threats on financial institutions’ risk management.
- The role of artificial intelligence in enhancing risk management practices.
Accounting and Auditing Research Topics
- Analyzing the impact of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) on financial reporting quality.
- Evaluating the role of forensic accounting in fraud detection.
- The impact of audit quality on financial statement reliability.
- Investigating the role of auditor independence in ensuring financial transparency.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of fair value accounting in financial reporting.
- The influence of accounting conservatism on financial decision-making.
- Evaluating the impact of accounting information on investment decisions.
- The role of big data analytics in modern accounting practices.
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of sustainability reporting.
- The impact of earnings management on financial statement reliability.
Financial Regulation and Policy Research Topics
- The role of government intervention in preventing financial crises.
- Evaluating the impact of Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of Basel III in regulating global banking.
- The role of regulatory bodies in promoting financial market integrity.
- Investigating the impact of tax policies on corporate financial decisions.
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of cross-border financial regulation.
- The role of ethics in financial decision-making and regulation.
- Evaluating the impact of monetary policy on inflation and economic growth.
- The influence of political factors on financial regulation.
- The impact of regulatory changes on financial innovation.
Real Estate Finance Related Research Topics
- Analyzing the factors influencing real estate prices and investment.
- The impact of interest rate changes on real estate markets.
- Evaluating the role of mortgage-backed securities in real estate finance.
- The influence of housing policies on real estate market dynamics.
- The role of real estate crowdfunding in property financing.
- Analyzing the impact of urbanization on real estate development.
- The role of sustainability in real estate investment decisions.
- Evaluating the impact of economic downturns on real estate values.
- The influence of demographic trends on real estate market dynamics.
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of real estate finance in emerging markets.
Behavioral Finance Research Paper Topics
- Investigating the role of behavioral biases in investment decisions.
- The impact of overconfidence on financial decision-making.
- Analyzing the influence of social networks on investment behavior.
- Evaluating the role of emotions in financial decision-making.
- The impact of financial news and media on investor sentiment.
- Investigating the role of heuristics in shaping financial perceptions.
- Analyzing the impact of market bubbles on investor behavior.
- The influence of framing effects on investment choices.
- Evaluating the role of financial education in mitigating behavioral biases.
- The impact of cultural factors on individual investment decisions.
Financial Technology (Fintech) Research Topics
- Analyzing the impact of robo-advisors on traditional investment advisory services.
- The role of blockchain in reshaping payment systems.
- Evaluating the potential of cryptocurrencies as a mainstream means of exchange.
- The impact of artificial intelligence on credit scoring models.
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of regulating fintech startups.
- The role of big data analytics in personalized financial services.
- Evaluating the impact of open banking on financial innovation.
- The influence of cybersecurity threats on fintech adoption.
- Analyzing the role of regulatory sandboxes in fostering fintech innovation.
- The impact of fintech on financial inclusion in developing economies.
Economics and Finance Sector Related Research Topics
- Investigating the relationship between economic indicators and financial markets.
- The impact of trade policies on exchange rates and international finance.
- Analyzing the role of economic sanctions in shaping financial landscapes.
- Evaluating the impact of globalization on financial stability.
- The role of monetary policy in addressing economic inequality.
- Analyzing the impact of economic recessions on financial decision-making.
- The influence of political instability on financial markets.
- The impact of demographic trends on economic and financial dynamics.
- Evaluating the role of economic forecasting in financial decision-making.
- The relationship between economic growth and financial development.
Sustainable Banking And Finance Research Topics
- Analyzing the impact of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors on investment decisions.
- The role of green finance in promoting sustainable development.
- Evaluating the impact of carbon pricing on financial markets.
- The influence of sustainable investing on corporate decision-making.
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of integrating sustainability into financial reporting.
- The role of impact investing in addressing social and environmental issues.
- Evaluating the impact of climate change on financial risk assessment.
- The influence of corporate sustainability on shareholder value.
- The role of green bonds in financing environmentally friendly projects.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of sustainable finance policies in achieving global goals.
Recent Banking And Finance Research Topics
- Investigating the potential of decentralized finance (DeFi) in traditional banking services.
- The impact of quantum computing on financial modeling and risk management.
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs).
- The role of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in financial services.
- The impact of 5G technology on financial transactions and services.
- Evaluating the potential of tokenization in transforming financial markets.
- Analyzing the role of artificial intelligence in credit scoring and lending decisions.
- The influence of geopolitical factors on global financial markets.
- The impact of regulatory technology (RegTech) in compliance and risk management.
- The role of smart contracts in streamlining financial transactions.
Cross-Border Finance Research Paper Topics
- Investigating the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on cross-border investments.
- The role of currency unions in promoting cross-border trade and investments.
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of cross-border banking operations.
- Evaluating the impact of trade agreements on cross-border financial flows.
- The influence of political and economic integration on cross-border finance.
- Analyzing the role of international financial institutions in cross-border finance.
- The impact of capital controls on cross-border investments.
- The role of cross-border financial services in promoting global economic integration.
- Evaluating the impact of cross-border financial regulations on multinational corporations.
- The influence of cross-border financial crimes on international cooperation.
Financial Education and Literacy Research Topics
- Investigating the impact of financial education programs on students’ financial literacy.
- The role of technology in enhancing financial education and literacy.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of workplace financial wellness programs.
- Analyzing the impact of cultural factors on financial literacy levels.
- The influence of family background on financial literacy.
- The impact of early financial education on long-term financial behavior.
- Analyzing the relationship between financial literacy and retirement planning.
- The role of schools and universities in promoting financial literacy.
- The influence of gender on financial literacy and decision-making.
- Evaluating the impact of online resources on improving financial literacy.
Banking and Finance in Developing Economies
- Analyzing the challenges and opportunities of financial inclusion in developing economies.
- The role of microfinance in poverty alleviation and economic development.
- Evaluating the impact of foreign aid on financial stability in developing countries.
- The influence of corruption on financial development in developing economies.
- Analyzing the role of remittances in shaping economic landscapes in developing countries.
- The impact of informal financial services on rural communities.
- Evaluating the role of government policies in promoting financial development.
- The influence of economic and political instability on financial systems in developing countries.
- The role of international financial institutions in supporting economic growth in developing economies.
- Analyzing the impact of technology adoption on financial inclusion in developing regions.
What Are Some Good Topics In The Area Of Finance And Accounting For A Ph.D. Research?
Here are some current Banking And Finance research topics for students:
| Finance Topics | Accounting Topics |
|---|---|
| 1. Impact of Cryptocurrencies on Financial Markets | 1. Analysis of Accounting Information Systems |
| 2. Role of Behavioral Finance in Investment Decision-Making | 2. Forensic Accounting and Fraud Detection |
| 3. Corporate Governance and Firm Performance | 3. The Role of Auditing in Corporate Governance |
| 4. Financial Regulation and Market Stability | 4. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Reporting |
| 5. Asset Pricing Models and Risk Management | 5. Accounting for Business Combinations and Mergers |
| 6. Venture Capital and Innovation Financing | 6. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) vs. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) |
| 7. Islamic Finance and Banking | 7. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Reporting |
| 8. Impact of Central Bank Policies on Financial Markets | 8. Management Accounting in Decision-Making |
| 9. Real Estate Finance and Investment | 9. Taxation and its Impact on Financial Statements |
| 10. Financial Derivatives and Hedging Strategies | 10. Corporate Governance in Family-Owned Businesses |
| 11. Private Equity and Leveraged Buyouts | 11. Accounting for Intangible Assets |
| 12. Behavioral Aspects of Credit Risk Assessment | 12. Governmental Accounting and Financial Reporting |
| 13. FinTech Innovations in Banking and Finance | 13. Internal Controls and Risk Management |
| 14. Cross-Border Mergers and Acquisitions | 14. Fair Value Accounting and its Implications |
| 15. Impact of Macroeconomic Factors on Stock Prices | 15. Accounting for Derivatives and Hedge Accounting |
| 16. Green Finance and Sustainable Investment | 16. Accounting for Revenue Recognition |
| 17. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Corporate Hedging | 17. Performance Measurement and Balanced Scorecard |
| 18. Behavioral Finance in Corporate Finance | 18. Accounting Information and Market Efficiency |
| 19. Sovereign Wealth Funds and Portfolio Management | 19. Corporate Disclosure and Transparency |
| 20. Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and Startup Funding | 20. Accounting for Leases and Lease Financing |
Recent Project Topics On Banking And Finance PDF
Here are the most recent project topics on banking and finance pdf:
These Are the best Banking and Finance Research Topics. These topics serve as gateways to understanding the nature of banking, finance, and other research topics. As you find a good research topic, consider your interests and the current trends shaping the financial domain. Whether it’s the impact of technology on banking, the dynamics of stock markets, or the role of sustainable finance.
Engage with your coursework, delve into academic journals, and attend seminars to find the latest understandings and potential research questions. Consulting with professors and advisors offers valuable guidance, helping refine your focus. Keep an eye on industry reports and financial news for inspiration, considering contemporary challenges and emerging trends.
Remember, your research can contribute to understanding financial systems and inform real-world practices. Choose a topic that not only captivates your interest but also addresses relevant issues, and you’ll find yourself good banking and finance research topics. Happy exploring!
Related Posts

149+ Most Interesting Civil Engineering Research Topics For Undergraduates

189+ Top-Rated Quantitative Research Topics For Accounting Students [Updated 2024]
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Open access
- Published: 18 June 2021
Financial technology and the future of banking
- Daniel Broby ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5482-0766 1
Financial Innovation volume 7 , Article number: 47 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
48k Accesses
58 Citations
5 Altmetric
Metrics details
This paper presents an analytical framework that describes the business model of banks. It draws on the classical theory of banking and the literature on digital transformation. It provides an explanation for existing trends and, by extending the theory of the banking firm, it illustrates how financial intermediation will be impacted by innovative financial technology applications. It further reviews the options that established banks will have to consider in order to mitigate the threat to their profitability. Deposit taking and lending are considered in the context of the challenge made from shadow banking and the all-digital banks. The paper contributes to an understanding of the future of banking, providing a framework for scholarly empirical investigation. In the discussion, four possible strategies are proposed for market participants, (1) customer retention, (2) customer acquisition, (3) banking as a service and (4) social media payment platforms. It is concluded that, in an increasingly digital world, trust will remain at the core of banking. That said, liquidity transformation will still have an important role to play. The nature of banking and financial services, however, will change dramatically.
Introduction
The bank of the future will have several different manifestations. This paper extends theory to explain the impact of financial technology and the Internet on the nature of banking. It provides an analytical framework for academic investigation, highlighting the trends that are shaping scholarly research into these dynamics. To do this, it re-examines the nature of financial intermediation and transactions. It explains how digital banking will be structurally, as well as physically, different from the banks described in the literature to date. It does this by extending the contribution of Klein ( 1971 ), on the theory of the banking firm. It presents suggested strategies for incumbent, and challenger banks, and how banking as a service and social media payment will reshape the competitive landscape.
The banking industry has been evolving since Banca Monte dei Paschi di Siena opened its doors in 1472. Its leveraged business model has proved very scalable over time, but it is now facing new challenges. Firstly, its book to capital ratios, as documented by Berger et al ( 1995 ), have been consistently falling since 1840. This trend continues as competition has increased. In the past decade, the industry has experienced declines in profitability as measured by return on tangible equity. This is partly the result of falling leverage and fee income and partly due to the net interest margin (connected to traditional lending activity). These trends accelerated following the 2008 financial crisis. At the same time, technology has made banks more competitive. Advances in digital technology are changing the very nature of banking. Banks are now distributing services via mobile technology. A prolonged period of very low interest rates is also having an impact. To sustain their profitability, Brei et al. ( 2020 ) note that many banks have increased their emphasis on fee-generating services.
As Fama ( 1980 ) explains, a bank is an intermediary. The Internet is, however, changing the way financial service providers conduct their role. It is fundamentally changing the nature of the banking. This in turn is changing the nature of banking services, and the way those services are delivered. As a consequence, in order to compete in the changing digital landscape, banks have to adapt. The banks of the future, both incumbents and challengers, need to address liquidity transformation, data, trust, competition, and the digitalization of financial services. Against this backdrop, incumbent banks are focused on reinventing themselves. The challenger banks are, however, starting with a blank canvas. The research questions that these dynamics pose need to be investigated within the context of the theory of banking, hence the need to revise the existing analytical framework.
Banks perform payment and transfer functions for an economy. The Internet can now facilitate and even perform these functions. It is changing the way that transactions are recorded on ledgers and is facilitating both public and private digital currencies. In the past, banks operated in a world of information asymmetry between themselves and their borrowers (clients), but this is changing. This differential gave one bank an advantage over another due to its knowledge about its clients. The digital transformation that financial technology brings reduces this advantage, as this information can be digitally analyzed.
Even the nature of deposits is being transformed. Banks in the future will have to accept deposits and process transactions made in digital form, either Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC) or cryptocurrencies. This presents a number of issues: (1) it changes the way financial services will be delivered, (2) it requires a discussion on resilience, security and competition in payments, (3) it provides a building block for better cross border money transfers and (4) it raises the question of private and public issuance of money. Braggion et al ( 2018 ) consider whether these represent a threat to financial stability.
The academic study of banking began with Edgeworth ( 1888 ). He postulated that it is based on probability. In this respect, the nature of the business model depends on the probability that a bank will not be called upon to meet all its liabilities at the same time. This allows banks to lend more than they have in deposits. Because of the resultant mismatch between long term assets and short-term liabilities, a bank’s capital structure is very sensitive to liquidity trade-offs. This is explained by Diamond and Rajan ( 2000 ). They explain that this makes a bank a’relationship lender’. In effect, they suggest a bank is an intermediary that has borrowed from other investors.
Diamond and Rajan ( 2000 ) argue a lender can negotiate repayment obligations and that a bank benefits from its knowledge of the customer. As shall be shown, the new generation of digital challenger banks do not have the same tradeoffs or knowledge of the customer. They operate more like a broker providing a platform for banking services. This suggests that there will be more than one type of bank in the future and several different payment protocols. It also suggests that banks will have to data mine customer information to improve their understanding of a client’s financial needs.
The key focus of Diamond and Rajan ( 2000 ), however, was to position a traditional bank is an intermediary. Gurley and Shaw ( 1956 ) describe how the customer relationship means a bank can borrow funds by way of deposits (liabilities) and subsequently use them to lend or invest (assets). In facilitating this mediation, they provide a service whereby they store money and provide a mechanism to transmit money. With improvements in financial technology, however, money can be stored digitally, lenders and investors can source funds directly over the internet, and money transfer can be done digitally.
A review of financial technology and banking literature is provided by Thakor ( 2020 ). He highlights that financial service companies are now being provided by non-deposit taking contenders. This paper addresses one of the four research questions raised by his review, namely how theories of financial intermediation can be modified to accommodate banks, shadow banks, and non-intermediated solutions.
To be a bank, an entity must be authorized to accept retail deposits. A challenger bank is, therefore, still a bank in the traditional sense. It does not, however, have the costs of a branch network. A peer-to-peer lender, meanwhile, does not have a deposit base and therefore acts more like a broker. This leads to the issue that this paper addresses, namely how the banks of the future will conduct their intermediation.
In order to understand what the bank of the future will look like, it is necessary to understand the nature of the aforementioned intermediation, and the way it is changing. In this respect, there are two key types of intermediation. These are (1) quantitative asset transformation and, (2) brokerage. The latter is a common model adopted by challenger banks. Figure 1 depicts how these two types of financial intermediation match savers with borrowers. To avoid nuanced distinction between these two types of intermediation, it is common to classify banks by the services they perform. These can be grouped as either private, investment, or commercial banking. The service sub-groupings include payments, settlements, fund management, trading, treasury management, brokerage, and other agency services.
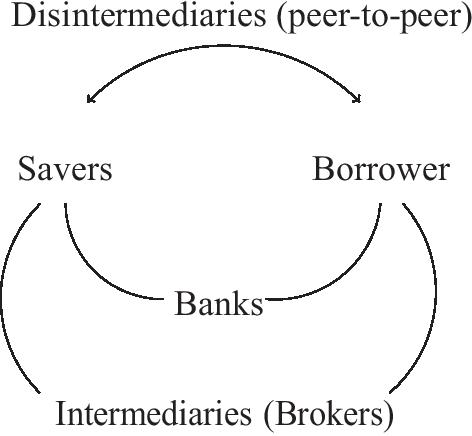
How banks act as intermediaries between lenders and borrowers. This function call also be conducted by intermediaries as brokers, for example by shadow banks. Disintermediation occurs over the internet where peer-to-peer lenders match savers to lenders
Financial technology has the ability to disintermediate the banking sector. The competitive pressures this results in will shape the banks of the future. The channels that will facilitate this are shown in Fig. 2 , namely the Internet and/or mobile devices. Challengers can participate in this by, (1) directly matching borrows with savers over the Internet and, (2) distributing white labels products. The later enables banking as a service and avoids the aforementioned liquidity mismatch.
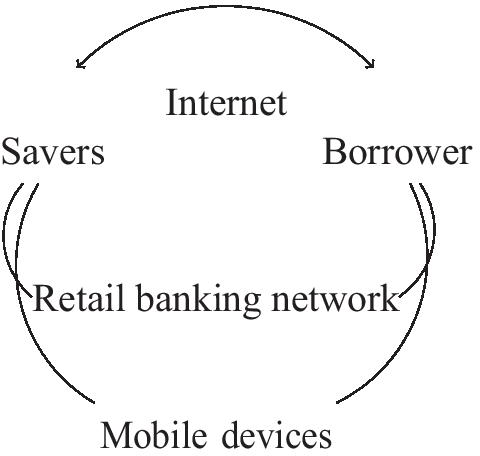
The strategic options banks have to match lenders with borrowers. The traditional and challenger banks are in the same space, competing for business. The distributed banks use the traditional and challenger banks to white label banking services. These banks compete with payment platforms on social media. The Internet heralds an era of banking as a service
There are also physical changes that are being made in the delivery of services. Bricks and mortar branches are in decline. Mobile banking, or m-banking as Liu et al ( 2020 ) describe it, is an increasingly important distribution channel. Robotics are increasingly being used to automate customer interaction. As explained by Vishnu et al ( 2017 ), these improve efficiency and the quality of execution. They allow for increased oversight and can be built on legacy systems as well as from a blank canvas. Application programming interfaces (APIs) are bringing the same type of functionality to m-banking. They can be used to authorize third party use of banking data. How banks evolve over time is important because, according to the OECD, the activity in the financial sector represents between 20 and 30 percent of developed countries Gross Domestic Product.
In summary, financial technology has evolved to a level where online banks and banking as a service are challenging incumbents and the nature of banking mediation. Banking is rapidly transforming because of changes in such technology. At the same time, the solving of the double spending problem, whereby digital money can be cryptographically protected, has led to the possibility that paper money will become redundant at some point in the future. A theoretical framework is required to understand this evolving landscape. This is discussed next.
The theory of the banking firm: a revision
In financial theory, as eloquently explained by Fama ( 1980 ), banking provides an accounting system for transactions and a portfolio system for the storage of assets. That will not change for the banks of the future. Fama ( 1980 ) explains that their activities, in an unregulated state, fulfil the Modigliani–Miller ( 1959 ) theorem of the irrelevance of the financing decision. In practice, traditional banks compete for deposits through the interest rate they offer. This makes the transactional element dependent on the resulting debits and credits that they process, essentially making banks into bookkeeping entities fulfilling the intermediation function. Since this is done in response to competitive forces, the general equilibrium is a passive one. As such, the banking business model is vulnerable to disruption, particularly by innovation in financial technology.
A bank is an idiosyncratic corporate entity due to its ability to generate credit by leveraging its balance sheet. That balance sheet has assets on one side and liabilities on the other, like any corporate entity. The assets consist of cash, lending, financial and fixed assets. On the other side of the balance sheet are its liabilities, deposits, and debt. In this respect, a bank’s equity and its liabilities are its source of funds, and its assets are its use of funds. This is explained by Klein ( 1971 ), who notes that a bank’s equity W , borrowed funds and its deposits B is equal to its total funds F . This is the same for incumbents and challengers. This can be depicted algebraically if we let incumbents be represented by Φ and challengers represented by Γ:
Klein ( 1971 ) further explains that a bank’s equity is therefore made up of its share capital and unimpaired reserves. The latter are held by a bank to protect the bank’s deposit clients. This part is also mandated by regulation, so as to protect customers and indeed the entire banking system from systemic failure. These protective measures include other prudential requirements to hold cash reserves or other liquid assets. As shall be shown, banking services can be performed over the Internet without these protections. Banking as a service, as this phenomenon known, is expected to increase in the future. This will change the nature of the protection available to clients. It will change the way banks transform assets, explained next.
A bank’s deposits are said to be a function of the proportion of total funds obtained through the issuance of the ith deposit type and its total funds F , represented by α i . Where deposits, represented by Bs , are made in the form of Bs (i = 1 *s n) , they generate a rate of interest. It follows that Si Bs = B . As such,
Therefor it can be said that,
The importance of Eq. 3 is that the balance sheet can be leveraged by the issuance of loans. It should be noted, however, that not all loans are returned to the bank in whole or part. Non-performing loans reduce the asset side of a bank’s balance sheet and act as a constraint on capital, and therefore new lending. Clearly, this is not the case with banking as a service. In that model, loans are brokered. That said, with the traditional model, an advantage of financial technology is that it facilitates the data mining of clients’ accounts. Lending can therefore be more targeted to borrowers that are more likely to repay, thereby reducing non-performing loans. Pari passu, the incumbent bank of the future will therefore have a higher risk-adjusted return on capital. In practice, however, banking as a service will bring greater competition from challengers and possible further erosion of margins. Alternatively, some banks will proactively engage in partnerships and acquisitions to maintain their customer base and address the competition.
A bank must have reserves to meet the demand of customers demanding their deposits back. The amount of these reserves is a key function of banking regulation. The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision mandates a requirement to hold various tiers of capital, so that banks have sufficient reserves to protect depositors. The Committee also imposes a framework for mitigating excessive liquidity risk and maturity transformation, through a set Liquidity Coverage Ratio and Net Stable Funding Ratio.
Recent revisions of theory, because of financial technology advances, have altered our understanding of banking intermediation. This will impact the competitive landscape and therefor shape the nature of the bank of the future. In this respect, the threat to incumbent banks comes from peer-to-peer Internet lending platforms. These perform the brokerage function of financial intermediation without the use of the aforementioned banking balance sheet. Unlike regulated deposit takers, such lending platforms do not create assets and do not perform risk and asset transformation. That said, they are reliant on investors who do not always behave in a counter cyclical way.
Financial technology in banking is not new. It has been used to facilitate electronic markets since the 1980’s. Thakor ( 2020 ) refers to three waves of application of financial innovation in banking. The advent of institutional futures markets and the changing nature of financial contracts fundamentally changed the role of banks. In response to this, academics extended the concept of a bank into an entity that either fulfills the aforementioned functions of a broker or a qualitative asset transformer. In this respect, they connect the providers and users of capital without changing the nature of the transformation of the various claims to that capital. This transformation can be in the form risk transfer or the application of leverage. The nature of trading of financial assets, however, is changing. Price discovery can now be done over the Internet and that is moving liquidity from central marketplaces (like the stock exchange) to decentralized ones.
Alongside these trends, in considering what the bank of the future will look like, it is necessary to understand the unregulated lending market that competes with traditional banks. In this part of the lending market, there has been a rise in shadow banks. The literature on these entities is covered by Adrian and Ashcraft ( 2016 ). Shadow banks have taken substantial market share from the traditional banks. They fulfil the brokerage function of banks, but regulators have only partial oversight of their risk transformation or leverage. The rise of shadow banks has been facilitated by financial technology and the originate to distribute model documented by Bord and Santos ( 2012 ). They use alternative trading systems that function as electronic communication networks. These facilitate dark pools of liquidity whereby buyers and sellers of bonds and securities trade off-exchange. Since the credit crisis of 2008, total broker dealer assets have diverged from banking assets. This illustrates the changed lending environment.
In the disintermediated market, banking as a service providers must rely on their equity and what access to funding they can attract from their online network. Without this they are unable to drive lending growth. To explain this, let I represent the online network. Extending Klein ( 1971 ), further let Ψ represent banking as a service and their total funds by F . This state is depicted as,
Theoretically, it can be shown that,
Shadow banks, and those disintermediators who bypass the banking system, have an advantage in a world where technology is ubiquitous. This becomes more apparent when costs are considered. Buchak et al. ( 2018 ) point out that shadow banks finance their originations almost entirely through securitization and what they term the originate to distribute business model. Diversifying risk in this way is good for individual banks, as banking risks can be transferred away from traditional banking balance sheets to institutional balance sheets. That said, the rise of securitization has introduced systemic risk into the banking sector.
Thus, we can see that the nature of banking capital is changing and at the same time technology is replacing labor. Let A denote the number of transactions per account at a period in time, and C denote the total cost per account per time period of providing the services of the payment mechanism. Klein ( 1971 ) points out that, if capital and labor are assumed to be part of the traditional banking model, it can be observed that,
It can therefore be observed that the total service charge per account at a period in time, represented by S, has a linear and proportional relationship to bank account activity. This is another variable that financial technology can impact. According to Klein ( 1971 ) this can be summed up in the following way,
where d is the basic bank decision variable, the service charge per transaction. Once again, in an automated and digital environment, financial technology greatly reduces d for the challenger banks. Swankie and Broby ( 2019 ) examine the impact of Artificial Intelligence on the evaluation of banking risk and conclude that it improves such variables.
Meanwhile, the traditional banking model can be expressed as a product of the number of accounts, M , and the average size of an account, N . This suggests a banks implicit yield is it rate of interest on deposits adjusted by its operating loss in each time period. This yield is generated by payment and loan services. Let R 1 depict this. These can be expressed as a fraction of total demand deposits. This is depicted by Klein ( 1971 ), if one assumes activity per account is constant, as,
As a result, whether a bank is structured with traditional labor overheads or built digitally, is extremely relevant to its profitability. The capital and labor of tradition banks, depicted as Φ i , is greater than online networks, depicted as I i . As such, the later have an advantage. This can be shown as,
What Klein (1972) failed to highlight is that the banking inherently involves leverage. Diamond and Dybving (1983) show that leverage makes bank susceptible to run on their liquidity. The literature divides these between adverse shock events, as explained by Bernanke et al ( 1996 ) or moral hazard events as explained by Demirgu¨¸c-Kunt and Detragiache ( 2002 ). This leverage builds on the balance sheet mismatch of short-term assets with long term liabilities. As such, capital and liquidity are intrinsically linked to viability and solvency.
The way capital and liquidity are managed is through credit and default management. This is done at a bank level and a supervisory level. The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision applies capital and leverage ratios, and central banks manage interest rates and other counter-cyclical measures. The various iterations of the prudential regulation of banks have moved the microeconomic theory of banking from the modeling of risk to the modeling of imperfect information. As mentioned, shadow and disintermediated services do not fall under this form or prudential regulation.
The relationship between leverage and insolvency risk crucially depends on the degree of banks total funds F and their liability structure L . In this respect, the liability structure of traditional banks is also greater than online networks which do not have the same level of available funds, depicted as,
Diamond and Dybvig ( 1983 ) observe that this liability structure is intimately tied to a traditional bank’s assets. In this respect, a bank’s ability to finance its lending at low cost and its ability to achieve repayment are key to its avoidance of insolvency. Online networks and/or brokers do not have to finance their lending, simply source it. Similarly, as brokers they do not face capital loss in the event of a default. This disintermediates the bank through the use of a peer-to-peer environment. These lenders and borrowers are introduced in digital way over the internet. Regulators have taken notice and the digital broker advantage might not last forever. As a result, the future may well see greater cooperation between these competing parties. This also because banks have valuable operational experience compared to new entrants.
It should also be observed that bank lending is either secured or unsecured. Interest on an unsecured loan is typically higher than the interest on a secured loan. In this respect, incumbent banks have an advantage as their closeness to the customer allows them to better understand the security of the assets. Berger et al ( 2005 ) further differentiate lending into transaction lending, relationship lending and credit scoring.
The evolution of the business model in a digital world
As has been demonstrated, the bank of the future in its various manifestations will be a consequence of the evolution of the current banking business model. There has been considerable scholarly investigation into the uniqueness of this business model, but less so on its changing nature. Song and Thakor ( 2010 ) are helpful in this respect and suggest that there are three aspects to this evolution, namely competition, complementary and co-evolution. Although liquidity transformation is evolving, it remains central to a bank’s role.
All the dynamics mentioned are relevant to the economy. There is considerable evidence, as outlined by Levine ( 2001 ), that market liberalization has a causal impact on economic growth. The impact of technology on productivity should prove positive and enhance the functioning of the domestic financial system. Indeed, market liberalization has already reshaped banking by increasing competition. New fee based ancillary financial services have become widespread, as has the proprietorial use of balance sheets. Risk has been securitized and even packaged into trade-able products.
Challenger banks are developing in a complementary way with the incumbents. The latter have an advantage over new entrants because they have information on their customers. The liquidity insurance model, proposed by Diamond and Dybvig ( 1983 ), explains how such banks have informational advantages over exchange markets. That said, financial technology changes these dynamics. It if facilitating the processing of financial data by third parties, explained in greater detail in the section on Open Banking.
At the same time, financial technology is facilitating banking as a service. This is where financial services are delivered by a broker over the Internet without resort to the balance sheet. This includes roboadvisory asset management, peer to peer lending, and crowd funding. Its growth will be facilitated by Open Banking as it becomes more geographically adopted. Figure 3 illustrates how these business models are disintermediating the traditional banking role and matching burrowers and savers.
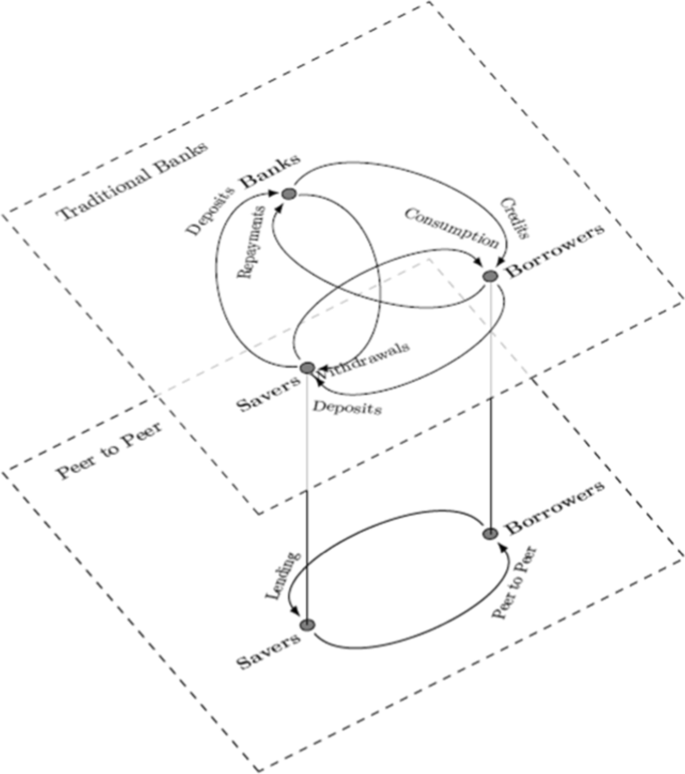
The traditional view of banks ecosystem between savers and borrowers, atop the Internet which is matching savers and borrowers directly in a peer-to-peer way. The Klein ( 1971 ) theory of the banking firm does not incorporate the mirrored dynamics, and as such needs to be extended to reflect the digital innovation that impacts both borrowers and severs in a peer-to-peer environment
Meanwhile, the banking sector is co-evolving alongside a shadow banking phenomenon. Lenders and borrowers are interacting, but outside of the banking sector. This is a concern for central banks and banking regulators, as the lending is taking place in an unregulated environment. Shadow banking has grown because of financial technology, market liberalization and excess liquidity in the asset management ecosystem. Pozsar and Singh ( 2011 ) detail the non-bank/bank intersection of shadow banking. They point out that shadow banking results in reverse maturity transformation. Incumbent banks have blurred the distinction between their use of traditional (M2) liabilities and market-based shadow banking (non-M2) liabilities. This impacts the inter-generational transfers that enable a bank to achieve interest rate smoothing.
Securitization has transformed the risk in the banking sector, transferring it to asset management institutions. These include structured investment vehicles, securities lenders, asset backed commercial paper investors, credit focused hedge and money market funds. This in turn has led to greater systemic risk, the result of the nature of the non-traded liabilities of securitized pooling arrangements. This increased risk manifested itself in the 2008 credit crisis.
Commercial pressures are also shaping the banking industry. The drive for cost efficiency has made incumbent banks address their personally costs. Bank branches have been closed as technology has evolved. Branches make it easier to withdraw or transfer deposits and challenger banks are not as easily able to attract new deposits. The banking sector is therefore looking for new point of customer contact, such as supermarkets, post offices and social media platforms. These structural issues are occurring at the same time as the retail high street is also evolving. Banks have had an aggressive roll out of automated telling machines and a reduction in branches and headcount. Online digital transactions have now become the norm in most developed countries.
The financing of banks is also evolving. Traditional banks have tended to fund illiquid assets with short term and unstable liquid liabilities. This is one of the key contributors to the rise to the credit crisis of 2008. The provision of liquidity as a last resort is central to the asset transformation process. In this respect, the banking sector experienced a shock in 2008 in what is termed the credit crisis. The aforementioned liquidity mismatch resulted in the system not being able to absorb all the risks associated with subprime lending. Central banks had to resort to quantitative easing as a result of the failure of overnight funding mechanisms. The image of the entire banking sector was tarnished, and the banks of the future will have to address this.
The future must learn from the mistakes of the past. The structural weakness of the banking business model cannot be solved. That said, the latest Basel rules introduce further risk mitigation, improved leverage ratios and increased levels of capital reserve. Another lesson of the credit crisis was that there should be greater emphasis on risk culture, governance, and oversight. The independence and performance of the board, the experience and the skill set of senior management are now a greater focus of regulators. Internal controls and data analysis are increasingly more robust and efficient, with a greater focus on a banks stable funding ratio.
Meanwhile, the very nature of money is changing. A digital wallet for crypto-currencies fulfills much the same storage and transmission functions of a bank; and crypto-currencies are increasing being used for payment. Meanwhile, in Sweden, stores have the right to refuse cash and the majority of transactions are card based. This move to credit and debit cards, and the solving of the double spending problem, whereby digital money can be crypto-graphically protected, has led to the possibility that paper money could be replaced at some point in the future. Whether this might be by replacement by a CBDC, or decentralized digital offering, is of secondary importance to the requirement of banks to adapt. Whether accommodating crytpo-currencies or CBDC’s, Kou et al. ( 2021 ) recommend that banks keep focused on alternative payment and money transferring technologies.
Central banks also have to adapt. To limit disintermediation, they have to ensure that the economic design of their sponsored digital currencies focus on access for banks, interest payment relative to bank policy rate, banking holding limits and convertibility with bank deposits. All these developments have implications for banks, particularly in respect of funding, the secure storage of deposits and how digital currency interacts with traditional fiat money.
Open banking
Against the backdrop of all these trends and changes, a new dynamic is shaping the future of the banking sector. This is termed Open Banking, already briefly mentioned. This new way of handling banking data protocols introduces a secure way to give financial service companies consensual access to a bank’s customer financial information. Figure 4 illustrates how this works. Although a fairly simple concept, the implications are important for the banking industry. Essentially, a bank customer gives a regulated API permission to securely access his/her banking website. That is then used by a banking as a service entity to make direct payments and/or download financial data in order to provide a solution. It heralds an era of customer centric banking.
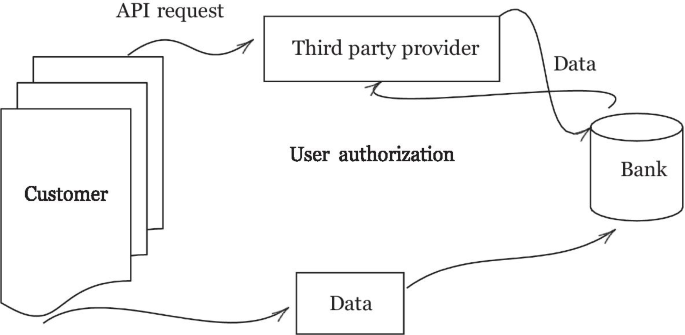
How Open Banking operates. The customer generates data by using his bank account. A third party provider is authorized to access that data through an API request. The bank confirms digitally that the customer has authorized the exchange of data and then fulfills the request
Open Banking was a response to the documented inertia around individual’s willingness to change bank accounts. Following the Retail Banking Review in the UK, this was addressed by lawmakers through the European Union’s Payment Services Directive II. The legislation was designed to make it easier to change banks by allowing customers to delegate authority to transfer their financial data to other parties. As a result of this, a whole host of data centric applications were conceived. Open banking adds further momentum to reshaping the future of banking.
Open Banking has a number of quite revolutionary implications. It was started so customers could change banks easily, but it resulted in some secondary considerations which are going to change the future of banking itself. It gives a clear view of bank financing. It allows aggregation of finances in one place. It also allows can give access to attractive offerings by allowing price comparisons. Open Banking API’s build a secure online financial marketplace based on data. They also allow access to a larger market in a faster way but the third-party providers for the new entrants. Open Banking allows developers to build single solutions on an API addressing very specific problems, like for example, a cash flow based credit rating.
Romānova et al. ( 2018 ) undertook a questionnaire on the Payment Services Directive II. The results suggest that Open Banking will promote competitiveness, innovation, and new product development. The initiative is associated with low costs and customer satisfaction, but that some concerns about security, privacy and risk are present. These can be mitigated, to some extent, by secure protocols and layered permission access.
Discussion: strategic options
Faced with these disruptive trends, there are four strategic options for market participants to con- sider. There are (1) a defensive customer retention strategy for incumbents, (2) an aggressive customer acquisition strategy for challenger banks (3) a banking as a service strategy for new entrants, and (4) a payments strategy for social media platforms.
Each of these strategies has to be conducted in a competitive marketplace for money demand by potential customers. Figure 5 illustrates where the first three strategies lie on the tradeoff between money demand and interest rates. The payment strategy can’t be modeled based on the supply of money. In the figure, the market settles at a rate L 2 . The incumbent banks have the capacity to meet the largest supply of these loans. The challenger banks have a constrained function but due to a lower cost base can gain excess rent through higher rates of interest. The peer-to-peer bank as a service brokers must settle for the market rate and a constrained supply offering.
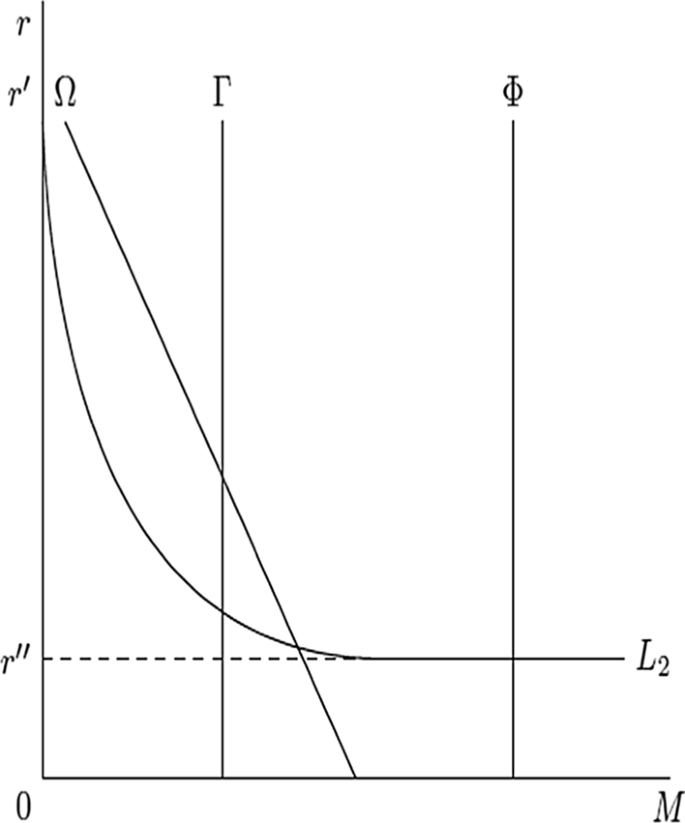
The money demand M by lenders on the y axis. Interest rates on the y axis are labeled as r I and r II . The challenger banks are represented by the line labeled Γ. They have a price and technology advantage and so can lend at higher interest rates. The brokers are represented by the line labeled Ω. They are price takers, accepting the interest rate determined by the market. The same is true for the incumbents, represented by the line labeled Φ but they have a greater market share due to their customer relationships. Note that payments strategy for social media platforms is not shown on this figure as it is not affected by interest rates
Figure 5 illustrates that having a niche strategy is not counterproductive. Liu et al ( 2020 ) found that banks performing niche activities exhibit higher profitability and have lower risk. The syndication market now means that a bank making a loan does not have to be the entity that services it. This means banks in the future can better shape their risk profile and manage their lending books accordingly.
An interesting question for central banks is what the future Deposit Supply function will look like. If all three forms: open banking, traditional banking and challenger banks develop together, will the bank of the future have the same Deposit Supply function? The Klein ( 1971 ) general formulation assumes that deposits are increasing functions of implicit and explicit yields. As such, the very nature of central bank directed monetary policy may have to be revisited, as alluded to in the earlier discussion on digital money.
The client retention strategy (incumbents)
The competitive pressures suggest that incumbent banks need to focus on customer retention. Reichheld and Kenny ( 1990 ) found that the best way to do this was to focus on the retention of branch deposit customers. Obviously, another way is to provide a unique digital experience that matches the challengers.
Incumbent banks have a competitive advantage based on the information they have about their customers. Allen ( 1990 ) argues that where risk aversion is observable, information markets are viable. In other words, both bank and customer benefit from this. The strategic issue for them, therefore, becomes the retention of these customers when faced with greater competition.
Open Banking changes the dynamics of the banking information advantage. Borgogno and Colangelo ( 2020 ) suggest that the access to account (XS2A) rule that it introduced will increase competition and reduce information asymmetry. XS2A requires banks to grant access to bank account data to authorized third payment service providers.
The incumbent banks have a high-cost base and legacy IT systems. This makes it harder for them to migrate to a digital world. There are, however, also benefits from financial technology for the incumbents. These include reduced cost and greater efficiency. Financial technology can also now support platforms that allow incumbent banks to sell NPL’s. These platforms do not require the ownership of assets, they act as consolidators. The use of technology to monitor the transactions make the processing cost efficient. The unique selling point of such platforms is their centralized point of contact which results in a reduction in information asymmetry.
Incumbent banks must adapt a number of areas they got to adapt in terms of their liquidity transformation. They have to adapt the way they handle data. They must get customers to trust them in a digital world and the way that they trust them in a bricks and mortar world. It is no coincidence. When you go into a bank branch that is a great big solid building great big facade and so forth that is done deliberately so that you trust that bank with your deposit.
The risk of having rising non-performing loans needs to be managed, so customer retention should be selective. One of the puzzles in banking is why customers are regularly denied credit, rather than simply being charged a higher price for it. This credit rationing is often alleviated by collateral, but finance theory suggests value is based on the discounted sum of future cash flows. As such, it is conceivable that the bank of the future will use financial technology to provide innovative credit allocation solutions. That said, the dual risks of moral hazard and information asymmetries from the adoption of such solutions must be addressed.
Customer retention is especially important as bank competition is intensifying, as is the digitalization of financial services. Customer retention requires innovation, and that innovation has been moving at a very fast rate. Until now, banks have traditionally been hesitant about technology. More recently, mergers and acquisitions have increased quite substantially, initiated by a need to address actual or perceived weaknesses in financial technology.
The client acquisition strategy (challengers)
As intermediaries, the challenger banks are the same as incumbent banks, but designed from the outset to be digital. This gives them a cost and efficiency advantage. Anagnostopoulos ( 2018 ) suggests that the difference between challenger and traditional banks is that the former address its customers problems more directly. The challenge for such banks is customer acquisition.
Open Banking is a major advantage to challenger banks as it facilitates the changing of accounts. There is widespread dissatisfaction with many incumbent banks. Open Banking makes it easier to change accounts and also easier to get a transaction history on the client.
Customer acquisition can be improved by building trust in a brand. Historically, a bank was physically built in a very robust manner, hence the heavy architecture and grand banking halls. This was done deliberately to engender a sense of confidence in the deposit taking institution. Pure internet banks are not able to do this. As such, they must employ different strategies to convey stability. To do this, some communicate their sustainability credentials, whilst others use generational values-based advertising. Customer acquisition in a banking context is traditionally done by offering more attractive rates of interest. This is illustrated in Fig. 5 by the intersect of traditional banks with the market rate of interest, depicted where the line Γ crosses L 2 . As a result of the relationship with banking yield, teaser rates and introductory rates are common. A customer acquisition strategy has risks, as consumers with good credit can game different challenger banks by frequently changing accounts.
Most customer acquisition, however, is done based on superior service offering. The functionality of challenger banking accounts is often superior to incumbents, largely because the latter are built on legacy databases that have inter-operability issues. Having an open platform of services is a popular customer acquisition technique. The unrestricted provision of third-party products is viewed more favorably than a restricted range of products.
The banking as a service strategy (new entrants)
Banking from a customer’s perspective is the provision of a service. Customers don’t care about the maturity transformation of banking balance sheets. Banking as a service can be performed without recourse to these balance sheets. Banking products are brokered, mostly by new entrants, to individuals as services that can be subscribed to or paid on a fee basis.
There are a number banking as a service solutions including pre-paid and credit cards, lending and leasing. The banking as a service brokers are effectively those that are aggregating services from others using open banking to enable banking as a service.
The rise of banking as a service needs to be understood as these compete directly with traditional banks. As explained, some of these do this through peer-to-peer lending over the internet, others by matching borrows and sellers, conducting mediation as a loan broker. Such entities do not transform assets and do not have banking licenses. They do not have a branch network and often don not have access to deposits. This means that they have no insurance protection and can be subject to interest rate controls.
The new genre of financial technology, banking as a service provider, conduct financial services transformation without access to central bank liquidity. In a distributed digital asset world, the assets are stored on a distributed ledger rather than a traditional banking ledger. Financial technology has automated credit evaluation, savings, investments, insurance, trading, banking payments and risk management. These banking as a service offering are only as secure as the technology on which they are built.
The social media payment strategy (disintermediators and disruptors)
An intermediation bank is a conceptual idea, one created solely on a social networking site. Social media has developed a market for online goods and services. Williams ( 2018 ) estimates that there are 2.46 billion social media users. These all make and receive payments of some kind. They demand security and functionality. Importantly, they have often more clients than most banks. As such, a strategy to monetize the payments infrastructure makes sense.
All social media platforms are rich repositories of data. Such platforms are used to buy and sell things and that requires payments. Some platforms are considering evolving their own digital payment, cutting out the banks as middlemen. These include Facebook’s Diem (formerly Libra), a digital currency, and similar developments at some of the biggest technology companies. The risk with social media payment platform is that there is systemic counter-party protection. Regulators need to address this. One way to do this would be to extend payment service insurance to such platforms.
Social media as a platform moves the payment relationship from a transaction to a customer experience. The ability to use consumer desires in combination with financial data has the potential to deliver a number of new revenue opportunities. These will compete directly with the banks of the future. This will have implications for (1) the money supply, (2) the market share of traditional banks and, (3) the services that payment providers offer.
Further research
Several recommendations for research derive from both the impact of disintermediation and the four proposed strategies that will shape banking in the future. The recommendations and suggestions are based on the mentioned papers and the conclusions drawn from them.
As discussed, the nature of intermediation is changing, and this has implications for the pricing of risk. The role of interest rates in banking will have to be further reviewed. In a decentralized world based on crypto currencies the central banks do not have the same control over the money supply, This suggest the quantity theory of money and the liquidity preference theory need to be revisited. As explained, the Internet reduces much of the friction costs of intermediation. Researchers should ask how this will impact maturity transformation. It is also fair to ask whether at some point in the future there will just be one big bank. This question has already been addressed in the literature but the Internet facilities the possibility. Diamond ( 1984 ) and Ramakrishnan and Thakor ( 1984 ) suggested the answer was due to diversification and its impact on reducing monitoring costs.
Attention should be given by academics to the changing nature of banking risk. How should regulators, for example, address the moral hazard posed by challenger banks with weak balance sheets? What about deposit insurance? Should it be priced to include unregulated entities? Also, what criteria do borrowers use to choose non-banking intermediaries? The changing risk environment also poses two interesting practical questions. What will an online bank run look like, and how can it be averted? How can you establish trust in digital services?
There are also research questions related to the nature of competition. What, for example, will be the nature of cross border competition in a decentralized world? Is the credit rationing that generates competition a static or dynamic phenomena online? What is the value of combining consumer utility with banking services?
Financial intermediaries, like banks, thrive in a world of deficits and surpluses supported by information asymmetries and disconnectedness. The connectivity of the internet changes this dynamic. In this respect, the view of Schumpeter ( 1911 ) on the role of financial intermediaries needs revisiting. Lenders and borrows can be connected peer to peer via the internet.
All the dynamics mentioned change the nature of moral hazard. This needs further investigation. There has been much scholarly research on the intrinsic riskiness of the mismatch between banking assets and liabilities. This mismatch not only results in potential insolvency for a single bank but potentially for the whole system. There has, for example, been much debate on the whether a bank can be too big to fail. As a result of the riskiness of the banking model, the banks of the future will be just a liable to fail as the banks of the past.
This paper presented a revision of the theory of banking in a digital world. In this respect, it built on the work of Klein ( 1971 ). It provided an overview of the changing nature of banking intermediation, a result of the Internet and new digital business models. It presented the traditional academic view of banking and how it is evolving. It showed how this is adapted to explain digital driven disintermediation.
It was shown that the banking industry is facing several documented challenges. Risk is being taken of balance sheet, securitized, and brokered. Financial technology is digitalizing service delivery. At the same time, the very nature of intermediation is being changed due to digital currency. It is argued that the bank of the future not only has to face these competitive issues, but that technology will enhance the delivery of banking services and reduce the cost of their delivery.
The paper further presented the importance of the Open Banking revolution and how that facilitates banking as a service. Open Banking is increasing client churn and driving banking as a service. That in turn is changing the way products are delivered.
Four strategies were proposed to navigate the evolving competitive landscape. These are for incumbents to address customer retention; for challengers to peruse a low-cost digital experience; for niche players to provide banking as a service; and for social media platforms to develop payment platforms. In all these scenarios, the banks of the future will have to have digital strategies for both payments and service delivery.
It was shown that both incumbents and challengers are dependent on capital availability and borrowers credit concerns. Nothing has changed in that respect. The risks remain credit and default risk. What is clear, however, is the bank has become intrinsically linked with technology. The Internet is changing the nature of mediation. It is allowing peer to peer matching of borrowers and savers. It is facilitating new payment protocols and digital currencies. Banks need to evolve and adapt to accommodate these. Most of these questions are empirical in nature. The aim of this paper, however, was to demonstrate that an understanding of the banking model is a prerequisite to understanding how to address these and how to develop hypotheses connected with them.
In conclusion, financial technology is changing the future of banking and the way banks intermediate. It is facilitating digital money and the online transmission of financial assets. It is making banks more customer enteric and more competitive. Scholarly investigation into banking has to adapt. That said, whatever the future, trust will remain at the core of banking. Similarly, deposits and lending will continue to attract regulatory oversight.
Availability of data and materials
Diagrams are my own and the code to reproduce them is available in the supplied Latex files.
Adrian T, Ashcraft AB (2016) Shadow banking: a review of the literature. In: Banking crises. Palgrave Macmillan, London, pp 282–315
Allen F (1990) The market for information and the origin of financial intermediation. J Financ Intermed 1(1):3–30
Article Google Scholar
Anagnostopoulos I (2018) Fintech and regtech: impact on regulators and banks. J Econ Bus 100:7–25
Berger AN, Herring RJ, Szegö GP (1995) The role of capital in financial institutions. J Bank Finance 19(3–4):393–430
Berger AN, Miller NH, Petersen MA, Rajan RG, Stein JC (2005) Does function follow organizational form? Evidence from the lending practices of large and small banks. J Financ Econ 76(2):237–269
Bernanke B, Gertler M, Gilchrist S (1996) The financial accelerator and the flight to quality. The review of economics and statistics, pp1–15
Bord V, Santos JC (2012) The rise of the originate-to-distribute model and the role of banks in financial intermediation. Federal Reserve Bank N Y Econ Policy Rev 18(2):21–34
Google Scholar
Borgogno O, Colangelo G (2020) Data, innovation and competition in finance: the case of the access to account rule. Eur Bus Law Rev 31(4)
Braggion F, Manconi A, Zhu H (2018) Is Fintech a threat to financial stability? Evidence from peer-to-Peer lending in China, November 10
Brei M, Borio C, Gambacorta L (2020) Bank intermediation activity in a low-interest-rate environment. Econ Notes 49(2):12164
Buchak G, Matvos G, Piskorski T, Seru A (2018) Fintech, regulatory arbitrage, and the rise of shadow banks. J Financ Econ 130(3):453–483
Demirgüç-Kunt A, Detragiache E (2002) Does deposit insurance increase banking system stability? An empirical investigation. J Monet Econ 49(7):1373–1406
Diamond DW (1984) Financial intermediation and delegated monitoring. Rev Econ Stud 51(3):393–414
Diamond DW, Dybvig PH (1983) Bank runs, deposit insurance, and liquidity. J Polit Econ 91(3):401–419
Diamond DW, Rajan RG (2000) A theory of bank capital. J Finance 55(6):2431–2465
Edgeworth FY (1888) The mathematical theory of banking. J Roy Stat Soc 51(1):113–127
Fama EF (1980) Banking in the theory of finance. J Monet Econ 6(1):39–57
Gurley JG, Shaw ES (1956) Financial intermediaries and the saving-investment process. J Finance 11(2):257–276
Klein MA (1971) A theory of the banking firm. J Money Credit Bank 3(2):205–218
Kou G, Akdeniz ÖO, Dinçer H, Yüksel S (2021) Fintech investments in European banks: a hybrid IT2 fuzzy multidimensional decision-making approach. Financ Innov 7(1):1–28
Levine R (2001) International financial liberalization and economic growth. Rev Interna Tional Econ 9(4):688–702
Liu FH, Norden L, Spargoli F (2020) Does uniqueness in banking matter? J Bank Finance 120:105941
Pozsar Z, Singh M (2011) The nonbank-bank nexus and the shadow banking system. IMF working papers, pp 1–18
Ramakrishnan RT, Thakor AV (1984) Information reliability and a theory of financial intermediation. Rev Econ Stud 51(3):415–432
Reichheld FF, Kenny DW (1990) The hidden advantages of customer retention. J Retail Bank 12(4):19–24
Romānova I, Grima S, Spiteri J, Kudinska M (2018) The payment services directive 2 and competitiveness: the perspective of European Fintech companies. Eur Res Stud J 21(2):5–24
Modigliani F, Miller MH (1959) The cost of capital, corporation finance, and the theory of investment: reply. Am Econ Rev 49(4):655–669
Schumpeter J (1911) The theory of economic development. Harvard Econ Stud XLVI
Song F, Thakor AV (2010) Financial system architecture and the co-evolution of banks and capital markets. Econ J 120(547):1021–1055
Swankie GDB, Broby D (2019) Examining the impact of artificial intelligence on the evaluation of banking risk. Centre for Financial Regulation and Innovation, white paper
Thakor AV (2020) Fintech and banking: What do we know? J Financ Intermed 41:100833
Vishnu S, Agochiya V, Palkar R (2017) Data-centered dependencies and opportunities for robotics process automation in banking. J Financ Transf 45(1):68–76
Williams MD (2018) Social commerce and the mobile platform: payment and security perceptions of potential users. Comput Hum Behav 115:105557
Download references
Acknowledgements
There are no acknowldgements.
There was no funding associated with this paper.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Financial Regulation and Innovation, Strathclyde Business School, Glasgow, UK
Daniel Broby
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The author confirms the contribution is original and his own. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Daniel Broby .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
I declare I have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Broby, D. Financial technology and the future of banking. Financ Innov 7 , 47 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40854-021-00264-y
Download citation
Received : 21 January 2021
Accepted : 09 June 2021
Published : 18 June 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40854-021-00264-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Cryptocurrencies
- P2P Lending
- Intermediation
- Digital Payments
JEL Classifications

Research Topics & Ideas: Finance
120+ Finance Research Topic Ideas To Fast-Track Your Project
If you’re just starting out exploring potential research topics for your finance-related dissertation, thesis or research project, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll help kickstart your research topic ideation process by providing a hearty list of finance-centric research topics and ideas.
PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . To develop a suitable education-related research topic, you’ll need to identify a clear and convincing research gap , and a viable plan of action to fill that gap.
If this sounds foreign to you, check out our free research topic webinar that explores how to find and refine a high-quality research topic, from scratch. Alternatively, if you’d like hands-on help, consider our 1-on-1 coaching service .
Overview: Finance Research Topics
- Corporate finance topics
- Investment banking topics
- Private equity & VC
- Asset management
- Hedge funds
- Financial planning & advisory
- Quantitative finance
- Treasury management
- Financial technology (FinTech)
- Commercial banking
- International finance

Corporate Finance
These research topic ideas explore a breadth of issues ranging from the examination of capital structure to the exploration of financial strategies in mergers and acquisitions.
- Evaluating the impact of capital structure on firm performance across different industries
- Assessing the effectiveness of financial management practices in emerging markets
- A comparative analysis of the cost of capital and financial structure in multinational corporations across different regulatory environments
- Examining how integrating sustainability and CSR initiatives affect a corporation’s financial performance and brand reputation
- Analysing how rigorous financial analysis informs strategic decisions and contributes to corporate growth
- Examining the relationship between corporate governance structures and financial performance
- A comparative analysis of financing strategies among mergers and acquisitions
- Evaluating the importance of financial transparency and its impact on investor relations and trust
- Investigating the role of financial flexibility in strategic investment decisions during economic downturns
- Investigating how different dividend policies affect shareholder value and the firm’s financial performance
Investment Banking
The list below presents a series of research topics exploring the multifaceted dimensions of investment banking, with a particular focus on its evolution following the 2008 financial crisis.
- Analysing the evolution and impact of regulatory frameworks in investment banking post-2008 financial crisis
- Investigating the challenges and opportunities associated with cross-border M&As facilitated by investment banks.
- Evaluating the role of investment banks in facilitating mergers and acquisitions in emerging markets
- Analysing the transformation brought about by digital technologies in the delivery of investment banking services and its effects on efficiency and client satisfaction.
- Evaluating the role of investment banks in promoting sustainable finance and the integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria in investment decisions.
- Assessing the impact of technology on the efficiency and effectiveness of investment banking services
- Examining the effectiveness of investment banks in pricing and marketing IPOs, and the subsequent performance of these IPOs in the stock market.
- A comparative analysis of different risk management strategies employed by investment banks
- Examining the relationship between investment banking fees and corporate performance
- A comparative analysis of competitive strategies employed by leading investment banks and their impact on market share and profitability
Private Equity & Venture Capital (VC)
These research topic ideas are centred on venture capital and private equity investments, with a focus on their impact on technological startups, emerging technologies, and broader economic ecosystems.
- Investigating the determinants of successful venture capital investments in tech startups
- Analysing the trends and outcomes of venture capital funding in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, or clean energy
- Assessing the performance and return on investment of different exit strategies employed by venture capital firms
- Assessing the impact of private equity investments on the financial performance of SMEs
- Analysing the role of venture capital in fostering innovation and entrepreneurship
- Evaluating the exit strategies of private equity firms: A comparative analysis
- Exploring the ethical considerations in private equity and venture capital financing
- Investigating how private equity ownership influences operational efficiency and overall business performance
- Evaluating the effectiveness of corporate governance structures in companies backed by private equity investments
- Examining how the regulatory environment in different regions affects the operations, investments and performance of private equity and venture capital firms

Asset Management
This list includes a range of research topic ideas focused on asset management, probing into the effectiveness of various strategies, the integration of technology, and the alignment with ethical principles among other key dimensions.
- Analysing the effectiveness of different asset allocation strategies in diverse economic environments
- Analysing the methodologies and effectiveness of performance attribution in asset management firms
- Assessing the impact of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria on fund performance
- Examining the role of robo-advisors in modern asset management
- Evaluating how advancements in technology are reshaping portfolio management strategies within asset management firms
- Evaluating the performance persistence of mutual funds and hedge funds
- Investigating the long-term performance of portfolios managed with ethical or socially responsible investing principles
- Investigating the behavioural biases in individual and institutional investment decisions
- Examining the asset allocation strategies employed by pension funds and their impact on long-term fund performance
- Assessing the operational efficiency of asset management firms and its correlation with fund performance
Hedge Funds
Here we explore research topics related to hedge fund operations and strategies, including their implications on corporate governance, financial market stability, and regulatory compliance among other critical facets.
- Assessing the impact of hedge fund activism on corporate governance and financial performance
- Analysing the effectiveness and implications of market-neutral strategies employed by hedge funds
- Investigating how different fee structures impact the performance and investor attraction to hedge funds
- Evaluating the contribution of hedge funds to financial market liquidity and the implications for market stability
- Analysing the risk-return profile of hedge fund strategies during financial crises
- Evaluating the influence of regulatory changes on hedge fund operations and performance
- Examining the level of transparency and disclosure practices in the hedge fund industry and its impact on investor trust and regulatory compliance
- Assessing the contribution of hedge funds to systemic risk in financial markets, and the effectiveness of regulatory measures in mitigating such risks
- Examining the role of hedge funds in financial market stability
- Investigating the determinants of hedge fund success: A comparative analysis
Financial Planning and Advisory
This list explores various research topic ideas related to financial planning, focusing on the effects of financial literacy, the adoption of digital tools, taxation policies, and the role of financial advisors.
- Evaluating the impact of financial literacy on individual financial planning effectiveness
- Analysing how different taxation policies influence financial planning strategies among individuals and businesses
- Evaluating the effectiveness and user adoption of digital tools in modern financial planning practices
- Investigating the adequacy of long-term financial planning strategies in ensuring retirement security
- Assessing the role of financial education in shaping financial planning behaviour among different demographic groups
- Examining the impact of psychological biases on financial planning and decision-making, and strategies to mitigate these biases
- Assessing the behavioural factors influencing financial planning decisions
- Examining the role of financial advisors in managing retirement savings
- A comparative analysis of traditional versus robo-advisory in financial planning
- Investigating the ethics of financial advisory practices

The following list delves into research topics within the insurance sector, touching on the technological transformations, regulatory shifts, and evolving consumer behaviours among other pivotal aspects.
- Analysing the impact of technology adoption on insurance pricing and risk management
- Analysing the influence of Insurtech innovations on the competitive dynamics and consumer choices in insurance markets
- Investigating the factors affecting consumer behaviour in insurance product selection and the role of digital channels in influencing decisions
- Assessing the effect of regulatory changes on insurance product offerings
- Examining the determinants of insurance penetration in emerging markets
- Evaluating the operational efficiency of claims management processes in insurance companies and its impact on customer satisfaction
- Examining the evolution and effectiveness of risk assessment models used in insurance underwriting and their impact on pricing and coverage
- Evaluating the role of insurance in financial stability and economic development
- Investigating the impact of climate change on insurance models and products
- Exploring the challenges and opportunities in underwriting cyber insurance in the face of evolving cyber threats and regulations
Quantitative Finance
These topic ideas span the development of asset pricing models, evaluation of machine learning algorithms, and the exploration of ethical implications among other pivotal areas.
- Developing and testing new quantitative models for asset pricing
- Analysing the effectiveness and limitations of machine learning algorithms in predicting financial market movements
- Assessing the effectiveness of various risk management techniques in quantitative finance
- Evaluating the advancements in portfolio optimisation techniques and their impact on risk-adjusted returns
- Evaluating the impact of high-frequency trading on market efficiency and stability
- Investigating the influence of algorithmic trading strategies on market efficiency and liquidity
- Examining the risk parity approach in asset allocation and its effectiveness in different market conditions
- Examining the application of machine learning and artificial intelligence in quantitative financial analysis
- Investigating the ethical implications of quantitative financial innovations
- Assessing the profitability and market impact of statistical arbitrage strategies considering different market microstructures
Treasury Management
The following topic ideas explore treasury management, focusing on modernisation through technological advancements, the impact on firm liquidity, and the intertwined relationship with corporate governance among other crucial areas.
- Analysing the impact of treasury management practices on firm liquidity and profitability
- Analysing the role of automation in enhancing operational efficiency and strategic decision-making in treasury management
- Evaluating the effectiveness of various cash management strategies in multinational corporations
- Investigating the potential of blockchain technology in streamlining treasury operations and enhancing transparency
- Examining the role of treasury management in mitigating financial risks
- Evaluating the accuracy and effectiveness of various cash flow forecasting techniques employed in treasury management
- Assessing the impact of technological advancements on treasury management operations
- Examining the effectiveness of different foreign exchange risk management strategies employed by treasury managers in multinational corporations
- Assessing the impact of regulatory compliance requirements on the operational and strategic aspects of treasury management
- Investigating the relationship between treasury management and corporate governance
Financial Technology (FinTech)
The following research topic ideas explore the transformative potential of blockchain, the rise of open banking, and the burgeoning landscape of peer-to-peer lending among other focal areas.
- Evaluating the impact of blockchain technology on financial services
- Investigating the implications of open banking on consumer data privacy and financial services competition
- Assessing the role of FinTech in financial inclusion in emerging markets
- Analysing the role of peer-to-peer lending platforms in promoting financial inclusion and their impact on traditional banking systems
- Examining the cybersecurity challenges faced by FinTech firms and the regulatory measures to ensure data protection and financial stability
- Examining the regulatory challenges and opportunities in the FinTech ecosystem
- Assessing the impact of artificial intelligence on the delivery of financial services, customer experience, and operational efficiency within FinTech firms
- Analysing the adoption and impact of cryptocurrencies on traditional financial systems
- Investigating the determinants of success for FinTech startups

Commercial Banking
These topic ideas span commercial banking, encompassing digital transformation, support for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and the evolving regulatory and competitive landscape among other key themes.
- Assessing the impact of digital transformation on commercial banking services and competitiveness
- Analysing the impact of digital transformation on customer experience and operational efficiency in commercial banking
- Evaluating the role of commercial banks in supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)
- Investigating the effectiveness of credit risk management practices and their impact on bank profitability and financial stability
- Examining the relationship between commercial banking practices and financial stability
- Evaluating the implications of open banking frameworks on the competitive landscape and service innovation in commercial banking
- Assessing how regulatory changes affect lending practices and risk appetite of commercial banks
- Examining how commercial banks are adapting their strategies in response to competition from FinTech firms and changing consumer preferences
- Analysing the impact of regulatory compliance on commercial banking operations
- Investigating the determinants of customer satisfaction and loyalty in commercial banking
International Finance
The folowing research topic ideas are centred around international finance and global economic dynamics, delving into aspects like exchange rate fluctuations, international financial regulations, and the role of international financial institutions among other pivotal areas.
- Analysing the determinants of exchange rate fluctuations and their impact on international trade
- Analysing the influence of global trade agreements on international financial flows and foreign direct investments
- Evaluating the effectiveness of international portfolio diversification strategies in mitigating risks and enhancing returns
- Evaluating the role of international financial institutions in global financial stability
- Investigating the role and implications of offshore financial centres on international financial stability and regulatory harmonisation
- Examining the impact of global financial crises on emerging market economies
- Examining the challenges and regulatory frameworks associated with cross-border banking operations
- Assessing the effectiveness of international financial regulations
- Investigating the challenges and opportunities of cross-border mergers and acquisitions
Choosing A Research Topic
These finance-related research topic ideas are starting points to guide your thinking. They are intentionally very broad and open-ended. By engaging with the currently literature in your field of interest, you’ll be able to narrow down your focus to a specific research gap .
When choosing a topic , you’ll need to take into account its originality, relevance, feasibility, and the resources you have at your disposal. Make sure to align your interest and expertise in the subject with your university program’s specific requirements. Always consult your academic advisor to ensure that your chosen topic not only meets the academic criteria but also provides a valuable contribution to the field.
If you need a helping hand, feel free to check out our private coaching service here.
thank you for suggest those topic, I want to ask you about the subjects related to the fintech, can i measure it and how?
Please guide me on selecting research titles
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

A RESEARCH PROPOSAL ON THE IMPACT OF INTERNET BANKING ON CUSTOMER RETENTION

Related Papers
International Journal of Business and Management
Sundas Saeed , Dr Ali Iftikhar Choudhary , Asad Humayon
Banks are the back bone of the every country. Development of an economy depends on the efficient networking of banking system. This study argues on service quality impact in the internet banking. It explains the relationship between the customer service quality and customer satisfaction. The purpose of this study is to understand that which service quality factors of internet banking can give the higher customer satisfaction level. This conceptual paper justifies the soundness of relationships through intense literature review. Based on our findings from previous literature, management can establish a sequential priority to improve customer service quality in online banking service. Five service quality dimensions namely, Reliability, Privacy, Reputation, Empathy and Website design plays a vital role to fill the gap between customer expectations and customer perceptions regarding the internet banking services.
kazi omar siddiqi
Dr. Mohammad Mahtab Alam
The purpose of this study is to find out the Customer satisfaction of internet banking users which leads to make more loyal customer and hence loyalty leads to the attracting more customer, expansion of business and increase in net profit. The finding of the study shows that there is a significant variation in the level of satisfaction among internet banking users. The satisfaction of an Internet banking users depends upon Reliability, Responsiveness, Security, Ease of use and Tangible. Study also suggests that in which segment there is a need of big push to improve the overall satisfaction of the customers.
Syed Ali Raza , Dr. Tehseen Jawaid
Purpose – This study aims to determine the effects of service quality dimensions on customer satisfaction in Pakistan by using the SERVQUAL model. Design/methodology/approach – A survey research questionnaire of 30 items has been adopted, and the data of 400 respondents were collected from the users of Internet banking of different banks located in Karachi city of Pakistan. Findings – The reliability analysis shows that all dimensions are reliable. Results of the factor analysis confirm the grouping of adopted questioner. At last, the regression analysis indicates a significant positive relationship between assurance, tangibility, reliability and responsiveness with customer satisfaction. Conversely, empathy shows a positive but insignificant effect on the customer satisfaction. Practical implications – It is recommended that the management of online banks has to focus on making the design and content of the Web sites more visually appealing to grab the attention of existing customers, as well as to attract new customers. The management has to take effective measures to further enhance the security and safety of online bank accounts, so that customers can maintain long-term relationships with the usage of online banking. Online banks have to provide more reliable services to the customers at heart to make the customers more comfortable and confident. The management should develop more effective systems to quickly solve the issues of customers. Originality/value – This paper makes a unique contribution to the literature with reference to Pakistan, being a pioneering attempt to investigate the customer satisfac
Journal of Internet Banking and Commerce
Md.Salamun Rashidin
The aim of the present study is twofold; firstly, to measure the differences in e-services of foreign and local commercial banks and secondly, to find out the critical dimension of e-SERVQUAL for online banking. The study used comparative approach; local commercial and foreign banks in Pakistan. For this purpose, the study targeted local (MCB and HBL) and foreign (Standard Charted and Alfalah) banks. A total of 195 responses were received through a mean of questionnaire based on a five - point Likert scale from Sahiwal. The study performed reliability analysis, regression and Pearson chi-square. The reliability of all dimensions was tested with a Cronbach alpha that was greater than.7. The results of the chi-square showed that no difference is found with respect to any dimension in e-services of both local and foreign banks in Pakistan. The findings of the regression analysis showed that e-service quality was affected by 66.2% due to dimensions of e-SERVQUAL. The "reliability" and "privacy" have highest impact on e-service quality than all other dimensions, so banks should pay more attention on these dimensions because that is critical to online banking.
13th Annual International Conference - Convergence 2018 on the theme "Applied and/or Interdisciplinary Research: Emerging Economy Perspectives"
Dr. Nazrul Islam , Rasel Mustafi
Bangladesh is a densely populated country of the world. More than 170 million people live in this country. Mobile banking is a very important and new phenomenon in Bangladesh. In recent years, mobile banking has got highest importance by the customers in the country as it provides immense scope for consumers for banking transactions at any time with the option to access bank's facilities anywhere of the country. It is a subset of electronic banking, the use of which is increasing day by day in Bangladesh. Hence, this paper aims at indentifying the factors that influence the customer experience in mobile banking in Bangladesh. This study is based on a survey of 231 mobile banking customers of nine private commercial banks of Bangladesh. Literature review identified some factors related to mobile banking like convenient and responsive system, transaction speed and accuracy, reliability, transaction security in ATM booth and technological difficulty that affect customers' experience in mobile banking systems etc. Both descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze the data. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the present situation of the mobile banking systems in Bangladesh. Inferential statistics like factor analysis, multiple regression analysis and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) were used to identify the relationships between the overall experience of the mobile banking customers and the specific factor(s) that affect customers experience in mobile banking. Results show that the convenient and responsive system, transaction security in ATM booth and technological difficulty are significant factors that affect the customers experience in mobile banking of Bangladesh. This study suggests that the policymakers should focus on the convenient and responsive system of mobile banking, transaction security in ATM booth and technological difficulty factors that affect customers experience in doing mobile banking for the improvement of the mobile banking services in Bangladesh.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- How it works

Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Banking and Finance Dissertation Topics – Selected for Business Students
Published by Owen Ingram at January 2nd, 2023 , Revised On August 16, 2023
Looking for an interesting banking and finance research idea for your dissertation? Your search for the best finance and banking dissertation topics ends right here because, a t ResearchProspect, we help students choose the most authentic and relevant topic for their dissertation projects.
Bank taxes, financial management, financial trading, credit management, market analysis for private investors, economic research methods, the economics of money and banking, international trade and multinational business, the wellbeing of people and society, principles and practices of banking, management and cost accounting, governance and ethics in banking, investment banking, introductory econometrics, and capital investment management are among the many topics covered in banking and finance.
Without further ado, here is our selection of the besting banking and finance thesis topics and ideas.
Other Useful Links:
- Law Dissertation Topics
- Human Rights Law Dissertation Topics
- Business Law Dissertation Topics
- Employmeny Law Dissertation Topics
- Contract Law Dissertation Topics
- Commercial Law Dissertation Topics
- EU Law Dissertation Ideas
- Sports Law Dissertation Topics
- Medical Law Dissertation Topics
- Maritime Law Dissertation Topics
The following dissertation topics for banking will assist students in achieving the highest possible grades in their dissertation on banking finance:
List of Banking and Finance Dissertation Topics
- A Comprehensive Analysis of the Economic Crisis as It Relates to Banking and Finance
- A Critical Review of Standard Deviation in Business
- The Political and Economic Risks Involving National Bank Transactions
- A Study of Corporate Developments in European Countries Regarding Banking and Finance
- Security Measures Implemented in Financial Institutions Around the World
- Banking and Finance Approaches from Around the World
- An in-depth study of the World Trade Organization’s role in banking and finance
- A Study of the Relationship Between Corporate Strategy and Capital Structures
- Contrasting global, multinational banks with regional businesses
- Preventing Repetitive Economic Collapse in National and Global Finances
- The Motivations for Becoming International Expats All Over the World
- The Difference Between Islamic Banking and Other Religious Denominations in Banking and Financial Habits
- How Can Small-Scale Industries Survive the Global Banking Demands?
- A Study of the Economic Crisis’s Impact on Banking and Finance
- The Impact of the International Stock Exchange on Domestic Bank Transactions
- A 2025 Projected Report on World Trade and Banking Statistics
- How Can We Address the Issue of the Government’s Financial Deficit in Banking?
- A Comparison of Contemporary and Classic Business Models and Companies’ Banking and Financial Habits
- Which of the following should be the principal area of money investment that has arrived at the bank in the form of deposits?
- How to strike a balance between investing money in various plans to generate a profit and managing depositor trust
- What are banks’ responsibilities to their depositors, and how may such liabilities be managed without jeopardising depositor trust?
- How the new banking financing laws enacted by governments throughout the world are better protecting depositors’ rights?
- What is the terminology related to banking finance, which oversees the investment of deposited funds as well as the banks’ responsibilities to depositors?
- Explain the most recent developments in research related to the topic of banking finance
- How research in the banking finance industry assists governments and banking authorities in properly managing their finances?
- What is the most recent credit rating software that assists in determining the rewards and dangers of investing bank funds in the stock market?
- How banking finance assists the world’s top banks in managing consumer expectations and profit?
- The negative impact of a manager’s poor management of a bank’s banking financing
- Is it feasible to conduct a banking firm without the assistance of banking finance management?
- What are the most significant aspects of banking financing that allow businesses to develop without constraints?
The importance of banking finance cannot be overstated. These are only a few of the most extensive subjects on which you may write a banking and finance dissertation. Remember that if you want to succeed in your studies, you must be able to offer reliable numbers and facts on the history and current state of banking and finance throughout the world. Otherwise, you will very certainly be unable to justify your study effectively. We hope you can take some inspiration and ideas from the above banking and finance dissertation topics .
Need professional dissertation help? Click here .
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find banking and finance dissertation topics.
To find banking and finance dissertation topics:
- Follow industry news and trends.
- Study regulatory changes.
- Explore emerging technologies.
- Analyze financial markets.
- Investigate risk management.
- Consider ethical and global aspects.
You May Also Like
The Law of the EU has gained a growing amount of academic attention, especially since the UK decided to leave the union. Concerns are growing about how EU law will continue to impact the UK constitution.
Need interesting and manageable psychology dissertation topics or thesis? Here are the trending psychology dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
Need interesting and manageable Mental Health dissertation topics or thesis? Here are the trending Mental Health dissertation titles so you can choose the most suitable one.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Google Meet
- Mobile Dialer

Resent Search

Management Assignment Writing

Technical Assignment Writing

Finance Assignment Writing

Medical Nursing Writing

Resume Writing

Civil engineering writing

Mathematics and Statistics Projects

CV Writing Service

Essay Writing Service

Online Dissertation Help

Thesis Writing Help

RESEARCH PAPER WRITING SERVICE

Case Study Writing Service

Electrical Engineering Assignment Help

IT Assignment Help

Mechanical Engineering Assignment Help

Homework Writing Help

Science Assignment Writing

Arts Architecture Assignment Help

Chemical Engineering Assignment Help

Computer Network Assignment Help

Arts Assignment Help

Coursework Writing Help

Custom Paper Writing Services

Personal Statement Writing

Biotechnology Assignment Help
C Programming Assignment Help

MBA Assignment Help

English Essay Writing

MATLAB Assignment Help

Narrative Writing Help

Report Writing Help

Get Top Quality Assignment Assistance

Online Exam Help

Macroeconomics Homework Help

Change Management Assignment Help

Operation management Assignment Help

Strategy Assignment Help

Human Resource Management Assignment Help

Psychology Assignment Writing Help
Algebra Homework Help

Best Assignment Writing Tips

Statistics Homework Help

CDR Writing Services

TAFE Assignment Help

Auditing Assignment Help

Literature Essay Help

Online University Assignment Writing

Economics Assignment Help

Programming Language Assignment Help

Political Science Assignment Help

Marketing Assignment Help

Project Management Assignment Help

Geography Assignment Help

Do My Assignment For Me

Business Ethics Assignment Help

Pricing Strategy Assignment Help

The Best Taxation Assignment Help

Finance Planning Assignment Help

Solve My Accounting Paper Online

Market Analysis Assignment

4p Marketing Assignment Help

Corporate Strategy Assignment Help

Project Risk Management Assignment Help

Environmental Law Assignment Help

History Assignment Help

Geometry Assignment Help

Physics Assignment Help

Clinical Reasoning Cycle

Forex Assignment Help

Python Assignment Help

Behavioural Finance Assignment Help

PHP Assignment Help

Social Science Assignment Help

Capital Budgeting Assignment Help

Trigonometry Assignment Help

Java Programming Assignment Help

Corporate Finance Planning Help

Sports Science Assignment Help

Accounting For Financial Statements Assignment Help

Robotics Assignment Help

Cost Accounting Assignment Help

Business Accounting Assignment Help

Activity Based Accounting Assignment Help

Econometrics Assignment Help

Managerial Accounting Assignment Help

R Studio Assignment Help

Cookery Assignment Help

Solidworks assignment Help

UML Diagram Assignment Help

Data Flow Diagram Assignment Help

Employment Law Assignment Help

Calculus Assignment Help

Arithmetic Assignment Help

Write My Assignment

Business Intelligence Assignment Help

Database Assignment Help

Fluid Mechanics Assignment Help

Web Design Assignment Help

Student Assignment Help

Online CPM Homework Help

Chemistry Assignment Help

Biology Assignment Help

Corporate Governance Law Assignment Help

Auto CAD Assignment Help

Public Relations Assignment Help

Bioinformatics Assignment Help

Engineering Assignment Help

Computer Science Assignment Help

C++ Programming Assignment Help

Aerospace Engineering Assignment Help

Agroecology Assignment Help

Finance Assignment Help

Conflict Management Assignment Help

Paleontology Assignment Help

Commercial Law Assignment Help

Criminal Law Assignment Help

Anthropology Assignment Help

Biochemistry Assignment Help

Get the best cheap assignment Help

Online Pharmacology Course Help

Urgent Assignment Help

Paying For Assignment Help

HND Assignment Help

Legitimate Essay Writing Help

Best Online Proofreading Services

Need Help With Your Academic Assignment

Assignment Writing Help In Canada

Assignment Writing Help In UAE

Online Assignment Writing Help in the USA

Assignment Writing Help In Australia

Assignment Writing Help In the UK

Scholarship Essay Writing Help

University of Huddersfield Assignment Help

Ph.D. Assignment Writing Help

Law Assignment Writing Help

Website Design and Development Assignment Help

University of Greenwich Assignment Assistance in the UK
90 Finance Research Proposal Topics
Research papers are an academic type of writing that requires the ability to find the results of a subject and analyse those results to make conclusions and recommendations. In the realm of finance, there are numerous things one could investigate. The management of risk Corporate and organizational governance, investment and many more are just the beginning of the things this field of study covers. Before we dive into the most common topics of finance research papers, it is essential to know about the basics of finance.
What is Finance?
Simply put financial management is the administration of money. However, this type of management encompasses activities like forecasting, savings and lending, borrowing and investing. Finance is a leading area to a swath of different activities related to investing, money credit, capital markets leverage or debit, and banking. Finance-related careers have for quite a while been rewarding because it gives you an advantage over virtually all other courses available. However, in this vast array of subjects, where do students in finance have resources available for writing research papers on finance ? There are several websites that concentrate on topics for finance research papers online.
Select the most appropriate research topic for the Finance Research Proposal
It is critical to choose your subject carefully and remove any irrelevant information. When selecting a research topic, consider its relevance to the current application, its relationship to previous research , the type of issue, and other factors. Additionally, you must ensure that the subject is focused on a specific issue that you will address during your research analysis.
- When you are deciding on your research paper, it is crucial to choose the subject you are fascinated by.
- Find a question with no answer within the area of your research and conduct additional study to discover a feasible solution.
- Before you begin writing your essay, be sure you've completed some preliminary research to make sure you have enough research materials to write about your topic .
- Conduct a search online and discover which topics could be an issue that you must tackle.
- Be sure you're taking a look at current, up-to-date and current information so that you can ensure your report is current.
- Check out a variety of financial theses and papers to get a concept of your chosen subject;
- Find a general view on your topic of financial research and then use the information to focus on one specific aspect.
- Discuss your subject with your friends or others who have written essays. It is also possible to consult with your professors as well.
List of New Finance-Related Topics to Write About in 2024
We have compiled an array of interesting topics for writing about. They are divided into groups. This will allow you to select the most relevant topic for your audience and be sure to write it down completely. Enjoy doing your research.
Innovative Finance Research Topics
Perhaps you're planning to write a fascinating business essay. You'll have to pick some of the most popular topics for finance papers and then create a persuasive essay. This is our list of 10 topics we think are the fascinating.
- A comparative study of the benefits and setbacks of mergers and acquisitions
- Potential solutions Possible solutions Capital Asset Pricing Model
- The future of commerce as well as the consequences of manipulating commodities
- Behavioral Finance for Public Budgeting: Understanding How Biases Influence Policy Decisions
- Stability for retail investors by implementing the Systematic Investment Strategy
- US economic growth and taxation of income
- How will the American economy function in conjunction with the current banking system?
- Analysis of financial statements and ratio analysis are they a real element?
- Blockchain Technology for Public Financial Management: Enhancing Transparency, Efficiency, and Auditability
- Multilevel Marketing and it's application across different economies around the world
- The similarities and differences between traditional finance and behavioral
- Customer satisfaction with e-banking
- The most effective risk management strategies for manufacturing - thorough analysis
- Impact Investing and Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Blending Financial Returns with Social Impact in Public Projects
- Risks that could be posed to the banking sector, and how to mitigate them?
- The latest technology that is behind commercial banking
Research Topics on Finance for MBA
The following list of research subjects in finance will inspire your professors and view finance from a different view.
- An analysis of the investment potential of your selected company
- Capital management - a detailed report
- Considerations for saving taxes and financial strategies
- Life insurance investment and the participation of investors in these investments
- An analysis of the comparison between the traditional product and UIL
- The Future of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
- The Growing Influence of Social Media on Financial Markets
- The Role of Behavioral Finance in Mitigating Investment Biases
- The Future of Work and its Implications for Retirement Planning
- The Impact of Fintech on Financial Inclusion in Developing Economies
New Topics Related to Public Finance
Topics in public finance are financial research topics that cover the tax system, borrowing by the government as well as other aspects.
- Budgeting for government and accounting
- The economic austerity is a result of finance and education in the government
- The concept and practice of the taxation by the government
- How can the government get money by borrowing?
- The revenue collection plan of the government
- Accounting and budgeting for the government
- The Impact of Tax Policy on Income Inequality: Evaluating Distributional Effects
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs) for Infrastructure Development: A Comparative Analysis
- The Role of Financial Literacy in Promoting Public Financial Wellness
- The Rise of Social Impact Bonds: Innovative Financing for Social Programs
Research Topics for International Research in Finance
Because business transactions are taking place globally, and local commerce is no longer the only alternative, it is essential to study international business.
- The Rise of Fintech in Emerging Markets
- Blockchain Technology for Cross-Border Payments
- The Impact of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) on International Monetary Cooperation
- The Role of Sovereign Wealth Funds (SWFs) in International Investment Strategies
- How can we help prevent the onset of global economic crisis?
- Does the banking industry have the ability to lessen the consequences of the financial crisis?
- Can a country get the goal of providing healthcare to homeless people?
- Which areas of healthcare require more money?
- The issues with the high cost of medications in the US
- Sustainable Investment Strategies in Developing Countries
Topics in Research on Healthcare Finance
Here are a few of the most important issues in the field of healthcare finance:
- Which is better, free or paid healthcare?
- Big Data Analytics for Healthcare Cost Management: Identifying Fraud, Waste, and Abuse
- Financial Modeling for Emerging Health Technologies
- Precision Medicine and Personalized Healthcare Financing
- Social Impact Bonds (SIBs) for Public Health Initiatives
- Wearable Technologies and Health Data Collection: Monetizing Health Data for Improved Risk Assessment and Personalized Insurance Products
- Is financing healthcare a privilege or a right?
- Health policies throughout America U.S. through history
- What can countries in the first world do to enhance healthcare?
- What impact has the government had on health care?
- Are we able to achieve universal healthcare for all?
Topics in Corporate Finance
Corporate finance is the process of the organization of capital, financing, and making choices on every investment. Following is a list of finance research topics that will help you avoid errors in this field.
- ESG Factors into Corporate Investment and Financing Decisions
- Alternative Funding Sources for Startups and SMEs: Beyond Traditional Venture Capital and Bank Loans
- Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A) with Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain Assets
- Social Impact Investing within Corporate Strategies: Balancing Financial Returns with Social Responsibility
- The Future of Corporate Debt Structuring: The Impact of Sustainable Bonds, Green Finance, and ESG-Linked Loans
- Human Capital Management as an Investment: Optimizing Workforce Engagement and Skills Development for Long-Term Value Creation
- Potential solutions to ethical issues in the field of corporate finance
- Understanding the investment trends of small and medium-sized firms
- Mutual funds and investment A thorough analysis of its various streams
- How can equity investors deal with the potential risk
- What are the possible advantages and disadvantages of SWIFT and how will it function?
Topics in Business Finance
Every decision we make in the business world has financial consequences. We must therefore be aware of the basics of writing finance-related topics that need analysis, management valuation, management, etc.
- The establishment of business entities and the use of business finance
- Modernization of business and the role of finance in business
- Selling our life insurance Do we have a tax incentive that is effective in this case?
- Who are the people who mutual funds affect in the private and public sectors?
- Diverse investment options for various types of financials - Do you have an investment option you prefer?
- The preferences and choices of investors - A thorough analysis
- The investor's perspective regarding taking a stake in private insurers
- Corporate entities and raising their accountability
- Business finance and ethical issues
- Taxes on small and medium-sized business payment

Personal Financial Topics
Personal finances are a vulnerable field because we all want to attend to our finances in a way that is appropriate. Below are some fascinating problems in this area:
- Strategies for saving money while in a financial bind - A assessment
- The impact of inflation and the rise in the rate of interest on personal finances
- Employers and employees working at home - what are the advantages?
- Is health insurance that is free or affordable healthcare a right that everyone should have?
- What are the most effective ways to save money if you're in a pinch?
- Credit scored - a comprehensive analysis
- The importance of car and credit loans
- How do taxes affect financial decisions?
- What are the most effective ways to effectively manage credit?
- The mobile banking industry and its problems
New Research Topics For Indian Students
- Microfinance Beyond Microloans: Expanding Financial Services for Women Entrepreneurs in India
- The Impact of Aadhaar on Financial Inclusion and Credit Scoring in India
- The Future of Pension Systems in India
- Financial Planning for Millennials in India
- The Growth of Impact Investing in India
- The Role of Social Media Influencers on Investment Decisions of Indian Youth
- Financial Literacy for Small Businesses in India: Developing Culturally Relevant Educational Programs
- The Impact of Behavioral Finance on Individual Investment Choices in India
- Green Bonds and Sustainable Infrastructure Development in India
- The Future of Cashless Transactions in India
Totally New Topics for Research Proposals in Finance in 2024
- The Rise of Fintech in Unbanked Populations: Financial Inclusion Strategies in Fragile States
- The difference between traditional and behavioral finance.
- The impact of budget management on organizational performance
- The Impact of Resource Nationalism on Foreign Investment Flows
- The Geopolitical Risks of Digital Currencies
- The Financialization of Water Resources
- The Financialization of Cybersecurity
- An analysis of the use of financial state in evaluating a company's performance.
- Ethics concerns in corporate finance and how they can be addressed
- Transparency and clarity are improving in corporate organizations.
- Investment management: pros and cons management
- Sustainability and green governance in industries that could pollute the earth.
- How do corporate governance and institutional ownership affect green patent Generation?
- The implementation of risk-management strategies.
- Microfinancing and the alleviation of poverty
- The transformation of the banking industry due to information technology (IT)
- The management of massive credit at commercial banks in both developed and developing countries
- Mobile banking in both developed and developing countries
- A review of credit management practices and bank lending practices in both developed and developing countries.
- Electronic banking is a relationship that influences the satisfaction of customers
- Examining the effects of loan defaults and loan defaults on the financial viability of banks
- Internal controls in accounting firms
- Corporate Social Responsibility is a key issue in the banking systems of today
- The combination of cryptocurrency and banks in a demonetized global
- Security concerns with online banking and transactions online
- Examine the differences between traditional finance and behavioral finance.
- Study of the effect of budgetary control on the effectiveness of an organization.
- A critical analysis of the usage of financial statements to evaluate the efficiency of an organization.
- What are the ethical issues associated with finance in corporations, and how can they be addressed easily?
- Audit independence: improving transparency and accountability within corporate companies
- Credit management and issues related to bad debts at commercial banks of [Country Name].[Country Name].
- Opportunities and challenges of mobile bank banking within [Country NameProspects and challenges of mobile banking in [Country Name].
- Evaluation of lending practices at banks and credit management in [Country Name].The evaluation of credit management practices and lending practices in [Country Name].
- The impact of electronic banking on the satisfaction of customers.
- An analysis of loan defaults and the impact it has on the bank profitability.
How to Write a Perfect Finance Research Paper
Gathering and utilizing the correct financial information is vital in the production of clear financial reports and research papers on finance for academic and corporate goals. These data can range from the financial history of a business, the trends of an asset's performance on its market, or shifts in the market for investment. But, before collecting and analyzing the data it is essential to choose a subject to avoid wasting time by focusing on a faulty subject. How can you be sure the finance research essay you write is done to perfection? Here are some steps to make sure that you adhere to when writing an essay or research paper on finance: an essay on finance:
Pick a relevant Research Paper Area
This article is designed to provide most popular topics for finance research papers. When choosing a successful study paper subject, it's crucial to know the subject you're dealing with. If you don't know the subject you're writing about can result in you taking many dead-end routes and wasting valuable time. Once you have a clear understanding of the topic you must determine the relevancy of the topic and the subject you're writing your research paper on. Also, you can brainstorm ideas for subjects that could be suitable to research for your financial paper and based on these ideas you'll end with a suitable topic.
Plan your writing
It is commonly advised that if you are planning to chop off a branch, invest longer sharpening the axe. Writing effectively requires the steps you take to plan the actions for your research paper prior to you actually begin writing. This will ensure that you're more productive and will ensure that as you write, you are spending less time. In writing a research paper, you'll employ a variety of approaches to writing. It could involve observation, summarizing, or analyzing, arguing, and analyzing. Being mindful of the purpose of your paper is vital during this stage. This is where you will collect ideas for your finance essay.
Editing and writing
The process of writing the finance research paper is at the heart of the procedure. It is not much to be said regarding the writing process if you have prepared well and settled on a topic that is suitable in the study paper. But, every writer is bound to make mistakes. When writing, there will be mistakes made on paper. Additionally, ideas can change, or new ideas may pop out. The reason for the process of editing your financial research document is to polish your paper into the most polished version possible. Here are some tips to follow during how to edit and proofread your work.
- Don't edit your essay immediately after writing. It is best to let it for a few days or for a long period of time prior to beginning your editing and proofreading.
- If you can, ask someone to assist you with proofreading and editing your work. This could be from a friend or family member or even a colleague from class.
- When editing, make sure to edits, do it on chapters that are based on chapter. This will help you lessen the burden as your finance research papers may be quite a lengthy document.
- Use different methods in your editing. Examining for grammatical errors and checking for a flow of logic, ensuring the correct reference usage and many more.
- After editing, read the entire document to ensure that there wasn't anything that was overlooked.
In the final draft of this paper, you will not just exhume data, but also confidence.
Frequently asked questions
What is finance .
Financial management is simply the management of funds. However, this form of management also includes borrowing, investing, and operations like predicting and lending. A wide range of distinct activities relating to investment, money credit, capital markets leverage or debit, and banking fall under the umbrella of finance.
What is the best topic for finance project ?
role of retail credit in bank credit's long-term expansion. Retail bank credit's contribution to the economy's sustained expansion. The role of ECGC guarantees in export credit. An analysis of corporate banking and project finance, including credit for infrastructure.
What are the current research topics in finance ?
Finance-related research topics for students.
- the variations and parallels between conventional finance and behavioral finance.
- e-banking customer satisfaction.
- A thorough review of the best risk management strategies for the manufacturing sector.
- Identification and evaluation of the financial risks associated with a derivatives market.
What are the topics for finance internship ?
General Financial
- Studies on capital budgeting.
- Economic Analysis.
- Ratio evaluation
- Risk assessment.
- Inventory Control.
- Analysis of financial performance.
- studies on venture capital finance.
- Tax preparation.
Which project is best for MBA finance ?
Beginner MBA Finance Projects
- The value of capital budgeting.
- corporate investment analysis.
- portfolio management, including techniques.
- an examination of a company's cost modeling.
- the mechanism for controlling the budget and inventory.
- Public understanding and familiarity with wealth management.
What can be the topics for mba Finance summer internship project in a CA firm ?
corporate finance, international taxation, mergers, and acquisitions, etc
How do I prepare for a finance internship ?
Refresh your knowledge of technical financial topics and abilities. Refresh your memory of typical finance issues or procedures that you could be asked to use on the day of your interview. Candidates seeking internships at Wall Street institutions are frequently required to verbally describe financial practices.
What are the articles related to finance ?
According to Article 280 of the Constitution, the President appoints the Finance Commission, which has as its primary responsibility to make suggestions on how to tax income should be divided between the Union and the States and among the States themselves.
What are some research proposal topics in accounting and finance ?
Five Interesting Topics for Accounting Research Papers
- Software for accounting is required.
- newest accounting software innovations.
- Accounting ethics dilemmas.
- Best accounting techniques' historical prospects.
- Benefits of quick information for contemporary accountants.
What is the best topic for internship ?
Topics for Internship.
- Any State's e-governance.
- Analyze any given service across all States.
- Internet adoption and methods to boost it.
- Internet safety.
- Social media: good or bad?
- Social media's impact on Indian culture
- Social media is eroding our culture's foundation.
What is the best topic in finance ?
Accounting businesses' internal controls. Concerns about corporate social responsibility in contemporary banking systems. combining banks and cryptocurrencies in a demonetized environment. Cybersecurity concerns have an impact on online transactions and banking.
What is the objective of a finance internship ?
Learn everything you can about the company's cash management procedures. Learn everything you can about the company's treasury operations. Learn about the company's corporate budgeting procedure. Discover the company's internal and external financial reporting practices.
What is research proposal with example ?
A research proposal is essentially a formal, organized document that outlines your intended research subject, your reason for choosing it as a topic for study, and your methodology (i.e. your practical approach).
How long is a research proposal ?
2,500 words
How do you start a research proposal example ?
A succinct description of your desired research, no more than 100 words, should be included in the proposal. This might be a few phrases outlining the issue you want to look at or the main issue you want to tackle. Explain the general context in which your study will be conducted.

Top 10 Best Universities Ranking list in India 2022

Generic Conventions: Assignment Help Services

Research Paper Topics For Medical

Top 5 Resources for Writing Excellent Academic Assignments

How to Write a Literature Review for Academic Purposes

Tips for Writing a killer introduction to your assignment

How To Write A Compelling Conclusion For Your University Assignment

Research Papers Topics For Social Science

Best 150 New Research Paper Ideas For Students

7 Best Plagiarism Checkers for Students And Teachers in 2024
Enquiry form.
Open banking: an early review
Journal of Internet and Digital Economics
ISSN : 2752-6356
Article publication date: 5 July 2024
This paper offers an overview of the burgeoning literature on open banking, focusing on its implications for the financial sector.
Design/methodology/approach
The paper reviews the recent developments in the nascent literature of open banking. In particular, it discusses the following issues. (1) the extent to which open banking fosters competition, drives innovation and enhances financial inclusion; (2) the impact of institutional arrangements on the outcomes of open banking initiatives and (3) the critical role of government in promoting open banking and regulating banking activities.
The paper concludes with a discussion on potential directions for future research. First, open banking introduces significant challenges to the traditional banking model. Furthermore, the interplay between open banking and financial risk presents an area ripe for exploration. Lastly, the importance of consumer education in the context of open banking cannot be overstated.
Originality/value
Open innovation enables financial institutions generate productive innovations as well as provide customers with significantly better services, by getting access to previously restricted customer data. However, currently non-bank and fintech lenders often face significant barriers in accessing comprehensive customer data, which restricts their capacity to support non-standard credit models. More emphasis is required to be assigned to research on the economic impact of open banking.
- Open banking
- Bank regulation
- Regulatory arbitrage
- Financial innovation
Xie, C. and Hu, S. (2024), "Open banking: an early review", Journal of Internet and Digital Economics , Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/JIDE-03-2024-0009
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2024, Chengbo Xie and Sijia Hu
Published in Journal of Internet and Digital Economics . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) licence. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this licence may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
1. Introduction
Open Innovation means that valuable ideas can come from inside or out- side the company and can go to market from inside or outside the company as well.
Contrary to the traditional model of closed innovation, which relies exclusively on internal research and development efforts for innovation, open innovation posits a paradigm shift. The underlying premise of open innovation is the recognition that valuable ideas and innovations often originate outside established organizations, particularly from startups. This necessitates the adoption of inbound open innovation strategies to assimilate external knowledge, and outbound open innovation strategies to leverage internally developed innovations that are not being utilized to their full potential. Since the publication of Chesbrough (2003) , the concept of open innovation has gained significant attention across both academic research and practical business applications [1] . This paper aims to introduce and examine a specific transformation within the banking sector that embodies the principles of open innovation: open banking.
Imagine you want to use a financial product offered by an organization other than your bank. This product could be anything you feel would help you, such as an app that gives you a full picture of your financial status, including expenses, savings, and investments or it could be a mortgage or line of credit. But for this product to be fully useful to you, it needs in- formation from your bank, such as the amount of money you have coming in and going out of your accounts, how many accounts you have, how you spend your money, how much interest you have earned or paid, etc. You then instruct your bank to share this information with this other institution or app. Should you wish to stop using this product, you can instruct your bank to stop sharing your data at any given point in time, with no strings attached. This concept is called open banking.
From the perspective of open innovation, newcomers to the banking industry, such as fintech companies, are more likely to generate productive innovations compared to incumbent entities like traditional commercial banks, mainly because those companies have more advanced data processing technologies. However, as summarized by Babina et al. (2024a , b) , non-bank and fintech lenders often face significant barriers in accessing comprehensive customer data. This limitation restricts their capacity to support non-standard credit models, leading them to frequently rely on standardized models for originating residential mortgages. In contrast, traditional banks can leverage their extensive customer data to employ more customized, non-standard credit models. Thus, should non-banks and fintech companies gain access to previously restricted customer data, they could provide customers with significantly better services.
In this paper, we will review the recent developments in the nascent literature of open banking. In particular, we will discuss the following issues.
In Section 2 , we ask whether customer data should be shared among financial intermediaries. An examination of whether customer data should be disseminated among financial intermediaries is imperative, necessitating a comprehensive analysis of the benefits and drawbacks associated with data sharing practices within financial institutions. Numerous instances exist where augmented access to data significantly enhances the services offered by fintech companies, provides a better chance of valuable information production, reduces forecast errors or potentially elevates the competitive dynamics within the banking sector. However, there are circumstances where confidentiality is preferable, as the generation of information might infringe upon the “no questions asked” state posited by Holmstrom (2015) , thereby inducing unnecessary information asymmetry. This principle highlights the potential inefficiency when private data are unnecessarily disclosed, suggesting that carefully deciding when and what customer data to share (or not to share) among financial intermediaries is crucial. Moreover, open banking challenges traditional relationship banking by opening data access and diminishing banks’ competitive edge from exclusive customer information. Simultaneously, it could alter the reliance on collateral in financial transactions. These developments necessitate an in-depth examination of their impact on social welfare.
In Section 3 , we ask whether open banking is the optimal solution for data sharing. The open banking framework empowers customers by granting them the rights to their data, presenting a notable departure from traditional models. This approach directly addresses the question of data ownership, which is a thriving literature. In a frictionless environment, the Coase theorem posits that the specific allocation of data ownership is immaterial to achieving efficiency, as parties are theoretically able to negotiate the transfer of rights to those who can most effectively harness the data. This suggests that, in an ideal scenario, data would seamlessly flow towards those entities capable of deriving the greatest value from it. Nonetheless, in the practical context of real-world frictions, the ownership of data could be crucial. If banks are allowed to retain exclusive control over data, they may be motivated to hoard this valuable resource, thus avoiding competition and fostering a data monopoly. This consideration strongly supports the argument forgiving data ownership to consumers themselves. Yet, this approach is not without challenges, particularly when customer data are highly correlated, potentially leading to a coordination dilemma. Such a situation is fraught with the risk of individuals underselling their data due to concerns that others may do so first, precipitating a race to the bottom. This dilemma is characterized by the risk of individuals selling their data at suboptimal prices due to fears that others might preemptively do the same, leading to a race to the bottom. Thus, it requires comprehensive analysis in determining the optimal allocation of data ownership, especially in the context of advocating for open banking as a model for facilitating data sharing.
In Section 4 , we seek the role of government: can government policies enhance efficiency and mitigate the challenges associated with open banking? As previously discussed, financial intermediaries typically exhibit minimal motivation to share data with competing institutions, indicating a potential need for government intervention to promote an open banking ecosystem. Moreover, the prospect of open data access raises significant concerns regarding the current regulation practice, including excessive risk taking and regulatory arbitrage. Additionally, similar to the discussions on credit registries, the choice between utilizing private versus public agencies for data sharing can markedly affect the open banking framework’s effectiveness and security. Therefore, government policies and regulatory measures are crucial not only in facilitating data sharing among financial entities but also in establishing the optimal infrastructure for such exchanges to safeguard consumer interests and ensure system-wide efficiency.
Section 5 concludes the paper by summarizing key findings and proposing avenues for future research. As it continues to evolve, the burgeoning literature on open banking and its implications presents numerous opportunities for further investigation. There remains a lot of intriguing research questions to explore and theoretical predictions to empirically test. This section will outline potential directions for future research, highlighting areas where the current body of knowledge can be expanded to deepen our understanding of open banking’s impact on the financial sector and beyond.
2. Open banking: is data sharing welfare improving?
Open banking fundamentally empowers bank customers with the autonomy to choose whether their data is shared with alternative financial service providers. At its core, open banking is designed to facilitate data sharing, embodying a classic narrative in information economics. By granting lenders access to more comprehensive data about borrowers, including credit and payment histories, open banking enables a more accurate assessment of credit risk. This enhanced information access aims to mitigate the adverse selection problem, a challenge where lenders are unable to distinguish between high-risk and low-risk borrowers due to imperfect information. This theory, pioneered by Jaffee and Russell (1976) and Stiglitz and Weiss (1981) , posits that such information asymmetries can lead to credit rationing, where potential borrowers are denied access to credit not because of their creditworthiness, but due to the lenders’ inability to accurately assess risk. Open banking seeks to address these inefficiencies by improving information flow between parties, potentially reducing the incidence of credit rationing in the financial sector.
In particular, aligned with the principles of open innovation, empirical research has underscored the efficiency gains non-bank financial institutions and fintech companies bring to the credit market. Fuster et al . (2019) demonstrate that fintech firms incur lower processing costs than traditional lenders, without incurring higher default rates. Similarly, Tang (2019) and Gopal and Schnabl (2022) provide evidence of the complementary role played by P2P lending platforms and fintech companies, particularly in the origination of small loans. Thus, granting non-bank and fintech entities access to traditional bank customer data – a core idea of open banking – is anticipated to further enhance financial service accessibility. Supporting this idea, Babina et al. (2024a , b) present empirical evidence from the UK, illustrating how open banking facilitates consumer access to a broader array of financial services, including financial advice and credit. Notably, their findings also suggest that open banking aids SMEs informing new relationships with fintech lenders. Complementarily, Nam (2023) uses loan data from a leading German fintech lender to show that open banking and data sharing contribute to more efficient credit allocation and the mitigation of adverse selection.
Theoretically, aligning with empirical observations, Babina et al. (2024a , b) study the role of open banking as a catalyst for innovation, drawing on concepts from both industrial organization (IO) and finance literature. Using a calibrated model, their analysis reveals that open banking facilitates welfare improvements through the dual channels of market entry and product improvements when shared data is used for advice. Furthermore, when data sharing is used for credit, it fosters additional market entry and stimulates competition by mitigating adverse selection issues. However, this positive impact is somewhat moderated by increased costs borne by consumers who are either privacy-sensitive or inherently more expensive to serve, indicating a nuanced trade-off between the broad benefits of open banking and its implications for specific consumer segments.
Other theoretical works provide ambiguous predictions. He et al . (2023) and Goldstein et al . (2022) contribute to this discussion by building on the model proposed by Broecker (1990) , which highlights how credit market lenders employ independent but imperfect screening tests to evaluate a borrower’s repayment capability. A key aspect of Broecker’s model is the “winner’s curse” problem, suggesting that a lender acquiring a borrower may have missed negative signals detected by other lenders, with the curse being less severe for lenders possessing better screening abilities.
Expanding on this model, He et al . (2023) distinguish between banks and fintech companies based on their screening capabilities. They argue that in a traditional banking environment, banks enjoy a screening advantage due to their exclusive access to customer data, while fintech firms, despite their technological edge, are limited by the absence of such data. Open banking’s data-sharing provisions could significantly enhance fintech companies’ screening abilities, narrowing the competitive gap with banks. This narrowing fosters increased competition; however, an overcorrection could lead to dominance by fintech firms, creating a situation of reduced competition and potentially worse-off borrowers.
Goldstein et al . (2022) conducts similar analysis under the assumption that lenders possess identical data-analytic capabilities, arriving at similar conclusions as well. Yet, the distinction lies in the focus areas: He et al . (2023) underscore the significance of customer choice in data sharing, whereas Goldstein et al . (2022) delve into how open banking intersects with aspects of maturity transformation. This nuanced difference highlights the complicated impacts of open banking on the credit market, suggesting areas for further empirical investigation.
All these analyses presume that intensifying competition is good for the financial system. However, a large strand of literature focuses the possibility that bank com-petition may result in financial instability (See, e.g. Keeley, 1990 ). This is because the increase in competition would cause bank charter values to decline, which in turn forces banks to increase asset risks and reduce bank capital. Right now, the literature on open banking is silent on this issue. However, it may produce novel insights if one can combine financial instability with the current open banking trend as policymakers would definitely be interested in it.
While existing analyses predominantly posit that heightened competition, as facilitated by open banking, benefits the financial system, a significant body of literature suggests that increased bank competition may lead to financial instability (e.g. Keeley, 1990 ). The rationale is that escalated competition diminishes bank charter values, compelling banks to adopt riskier asset strategies and reduce their bank capital. Currently, discussions on open banking largely overlooks this potential linkage to financial instability [2] . Bridging this gap by integrating concerns of financial stability with the emerging trends in open banking could yield critical insights. Such an investigation is not only academically valuable but also of interest to policymakers, who are tasked with balancing the dual objectives of fostering innovation and ensuring system-wide stability.
The seminal works of Diamond and Dybvig (1983) and Diamond (1984) have initiated extensive research into the unique functions of commercial banks relative to other financial intermediaries. This body of literature underscores the irreplaceable role that banks play in critical financial intermediation processes, such as underwriting, monitoring and balance sheet lending. Recent studies by Gopal and Schnabl (2022) and Buchak et al . (2018) reaffirm that, despite the rapid evolution of fin-tech companies and other non-banking entities, these institutions struggle to fully substitute for banks in these key areas.
Regarding this, Babina et al. (2024a , b) contend that the importance of data in relationship banking implies that removing banks’ exclusive control over customer data could fundamentally alter the dynamics of relationship banking. Another aspect of particular interest is the potential tension between the concept of data sharing inherent in open banking and the traditional banking function of confidentiality. Kaplan (2006) and Dang et al . (2017) contribute to this discussion by suggesting that banks sometimes benefit from keeping detailed asset information confidential to avoid the creation of unnecessary asymmetric information, particularly when private information production is feasible. Thus, the emerging trend of open banking, with its emphasis on data sharing, might inadvertently conflict with the critical role of banks as guardians of sensitive information, raising questions about the balance between transparency and the efficient functioning of financial markets.
3. The institution of open banking
The open banking framework represents a significant shift from traditional banking models, primarily by empowering customers with control over their own data. This paradigm shift is at the forefront of ongoing discussions within the literature on data ownership. As highlighted by Jones and Tonetti (2020) , data distinguishes itself from other assets due to its non-rivalrous nature; it can be utilized simultaneously by multiple parties without diminishing its value. This feature suggests that the potential benefits derived from data access could be substantial, underscoring the importance of who holds the control rights over data. In particular, they show that allocating data control rights to consumers is more efficient, as firms might otherwise hoard data to inhibit market entry. Thus, giving data property rights to consumers can take more advantages of non-rival data, which is consistent with the idea of open banking.
Farboodi and Veldkamp (2021) developed a theoretical model of a data economy where the use of customer-generated data plays a pivotal role in minimizing forecast errors. In such an economy, larger firms, capable of processing extensive transaction data, are positioned to benefit more from data utilization. This prediction is empirically supported by Babina et al. (2024a , b) , who find that larger firms gain greater advantages from AI investments. Given that banks are substantial entities in the financial sector, these findings highlight a viable method to diminish the competitive disparities between traditional banks and fintech companies: by enabling customer data sharing with fintech firms. This strategy, central to the open banking initiative, aims to level the playing field and ensure fair competition within the financial industry.
On the other hand, there are situations where it is not efficient to let customers control data. Acemoglu et al . (2022) consider a model where one customer’s data reveals information about others. This creates an externality that the leakage of one user’s data weakens other users’ incentives to protect their data and privacies. This externality depresses the price of data and leads to excessive data sharing and lower welfare. Parlour et al . (2022) compare two different ways of payment data sharing: firms selling data to the lender or consumers owning the data and choosing whether to port their data to the lender. A similar data externality arises when consumers own the data, making everyone shares the data for free. Thus, policies that aim to give consumers more direct, and potentially stricter, control of their data may have the unintended, opposite effect.
On the contrary, there are circumstances where granting customers control over their data may not lead to optimal outcomes. Acemoglu et al . (2022) present a model illustrating how an individual customer’s data can inadvertently reveal information about others, generating an externality. This leakage can diminish other users’ incentives to safeguard their data and privacy, consequently depressing data prices and fostering excessive data sharing, ultimately resulting in reduced welfare. Similarly, Parlour et al . (2022) explore two mechanisms of payment data sharing: direct sales of data by firms to lenders versus consumer ownership of data with the option to port it to lenders. They find that consumer ownership introduces a negative externality, leading to widespread data sharing at zero price. Therefore, policies designed to enhance consumer control over data might result in unintended opposite effect by encouraging pervasive data sharing due to these externalities.
In the framework of open banking, the right to share or withhold data with other financial institutions rests with the customers, underscoring the significance of consumer choice. Brunnermeier and Payne (2022) demonstrate that when agents lacking collateral opt for information portability choices contrary to those preferred by lending platforms, the latter may cease offering uncollateralized lending. Contrary to prevalent beliefs, this mechanism suggests that open banking might actually restrict access to uncollateralized credit. Furthermore, He et al . (2023) make a distinction between sharing credit-quality data and customer preference data. In scenarios where fintech companies’ access and utilize customer preference data, they gain insights into privacy-sensitive information, enabling them to engage in precision marketing. This capability allows fintech firms not only to tailor their offerings more effectively but also to exclude potentially risky borrowers. If significant, such a mechanism under open banking could enhance screening processes, thereby elevating overall welfare by mitigating risk and aligning products more closely with consumer preferences.
4. The role of government
In this section, we review the existing research on the role of government in advancing open banking initiatives. The reluctance of financial intermediaries to voluntarily share data with competitors positions the government as a crucial force pushing for the open banking transformation. Babina et al. (2024a , b) note that open banking policies have been embraced by 49 countries, with numerous others taking preliminary steps toward implementation, underscoring the government’s critical role in the open banking ecosystem. Leveraging an extensive dataset, their research investigates the political and economic factors driving open banking policies. They find significant diversity in policy approaches, suggesting that the formulation of optimal open banking regulations is influenced by a myriad of factors specific to each financial system. Particularly, they identify consumer trust in data sharing with fintech companies as the main driver of open banking policy adoption. The trust from consumer is indicative of people’s readiness to engage in data sharing, a key element for the success of open banking system.
In addition, the transition to open banking introduces several regulatory challenges. First, as outlined in Section 2 , the advent of open banking generally increases competition within the banking sector, potentially leading to excessive risk-taking by banks. This may necessitate more stringent regulatory measures to curb such activities. Second, as documented by Buchak et al . (2018) , regulatory disparities have contributed to the rise of shadow banking entities, including fintech companies. The open banking transformation, by enhancing the appeal of fintech firms, could further amplify this development. Third, the variance in open banking policies across countries provides opportunities for regulatory arbitrage, complicating efforts to maintain a consistent regulatory environment. Fourth, Philippon (2019) contends that the rise of fintech companies, which rely heavily on big data technologies, may undermine the effectiveness of existing regulations designed to protect minorities. Together, these factors underscore the need for a nuanced approach to regulatory adaptation in response to the evolving landscape of open banking.
Furthermore, in instances where the efficiency benefits of open banking are not guaranteed, it is crucial for the government to recognize such situations and, where feasible, rectify the inefficiencies. Brunnermeier and Payne (2022) suggest that the introduction of a fully interoperable public ledger by the government could serve as a remedy for inefficiencies arising from privately operated open banking systems. Conversely, in scenarios described by He et al . (2023) and Parlour et al . (2022) , where the efficiency outcomes are contingent upon the magnitude of underlying economic forces, policymakers need to be careful to formulate policies.
Finally, open banking shares similarities with credit registries, making it insightful to draw lessons from the literature on credit registries. In terms of the role of government, a crucial question is whether data sharing should be facilitated through a centralized agency, such as a credit bureau, or via private credit score companies. Djankov et al . (2007) present evidence supporting the effectiveness of public credit registries in poor French legal origin countries. Conversely, as highlighted by Babina et al. (2024a , b) and Nam (2023) , significant differences exist between credit registries and open banking: (1) open banking provides a broader spectrum of information; (2) it offers customers the autonomy to choose whether to share their data, along with easier access to their information and (3) it extends the utility of data beyond lending to encompass a wider range of applications. These distinctions amplify the privacy concerns associated with open banking (See, e.g. Brunnermeier and Payne (2022) ), suggesting that privacy protection will pose a novel challenge for governments in the era of open banking (See, e.g. Acquisti et al . (2016) , Abowd and Schmutte (2019) , Jones and Tonetti (2020) and Bian et al . (2021) for general discussion on privacy).
5. Conclusion
As highlighted by Vives (2019) , disruptive technologies such as big data and blockchain have profoundly altered the landscape of the financial system. Fintech companies and other non-bank entities, leveraging these innovative technologies, have not only emerged as formidable competitors but also as potential collaborators with traditional commercial banks. Vives (2019) emphasizes the challenge for regulators in ensuring a level playing field. This paper reviews the burgeoning literature on open banking, a concept aimed at maintaining equality between commercial banks and fintech companies in terms of data access, while also encouraging areas for potential collaboration. As an evolving area of study, open banking research has begun addressing a broad spectrum of foundational questions, including competition, data ownership and government regulation. However, the field continues to confront numerous unresolved challenges.
First, open banking introduces significant challenges to the traditional banking model, particularly in how banks have addressed the free-rider problem by keeping customer information confidential. This strategy has enabled banks to conduct thorough customer screening without sharing the fruits of their labor with competitors. However, the rise of open banking, advocating for more transparent data sharing, might compel banks to either scale back their screening efforts, considering the potential for competitors to benefit from their diligence, or to selectively share information, thus protecting their competitive advantage.
Furthermore, the interplay between open banking and financial risk presents an area ripe for exploration. The redistribution of access to sensitive financial information could have profound implications for risk assessment, fraud prevention and the overall stability of the financial system. Therefore, both theoretical frameworks that address these new dynamics and empirical research that provides evidence from the real-world implementation of open banking are essential for a comprehensive understanding of its impact. Second, while initial empirical studies by Fang and Zhu (2023) , Nam (2023) and Babina et al. (2024a , b) have started to explore the implications of open banking, echoing the theoretical insights of He et al . (2023) , Brunnermeier and Payne (2022) , Goldstein et al . (2022) and Parlour et al . (2022) , there is still much ground to cover in empirical research on open banking. Moving forward, a surge in empirical investigations is expected, focusing on the nuanced economic impacts of open banking, including its effect on market competition, innovation and financial inclusion. Additionally, cross country analyses and policy assessments will be pivotal in distilling best practices and tailoring open banking frameworks to meet diverse regulatory and market needs. This burgeoning area of research promises to shed light on the operational realities of open banking, offering valuable insights.
Lastly, the importance of consumer education in the context of open banking cannot be overstated. As financial ecosystems evolve to become more interconnected and data-driven, consumers stand at the crossroads of innovation and vulnerability. Thus, efforts to enhance consumer awareness and digital literacy will be key to helping individuals make informed decisions about their financial data, ensuring they can use open banking safely. This includes understanding the implications of data sharing, recognizing the potential for privacy breaches and knowing the rights and protections available to them.
See Chesbrough (2003) for case studies about companies’ transformation from closed innovation paradigm to open innovation paradigm such as IBM and Intel. See Chesbrough (2011 , 2019) for examples such as smart cities and smart villages utilizing the idea of open innovation.
See Cevik (2024) for an empirical study on the relationship between fintech and financial stability.
Abowd , J.M. and Schmutte , I.M. ( 2019 ), “ An economic analysis of privacy protection and statistical accuracy as social choices ”, American Economic Review , Vol. 109 No. 1 , pp. 171 - 202 , doi: 10.1257/aer.20170627 .
Acemoglu , D. , Makhdoumi , A. , Malekian , A. and Ozdaglar , A. ( 2022 ), “ Too much data: prices and inefficiencies in data markets ”, American Economic Journal: Microeconomics , Vol. 14 No. 4 , pp. 218 - 256 , doi: 10.1257/mic.20200200 .
Acquisti , A. , Taylor , C. and Wagman , L. ( 2016 ), “ The economics of privacy ”, Journal of Economic Literature , Vol. 54 No. 2 , pp. 442 - 492 , doi: 10.1257/jel.54.2.442 .
Babina , T. , Bahaj , S.A. , Buchak , G. , De Marco , F. , Foulis , A.K. , Gornall , W. , Mazzola , F. and Yu , T. ( 2024a ), Customer Data Access and Fintech Entry: Early Evidence from Open Banking , doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4716658 .
Babina , T. , Fedyk , A. , He , A. and Hodson , J. ( 2024b ), “ Artificial intelligence, firm growth, and product innovation ”, Journal of Financial Economics , Vol. 151 , 103745 , doi: 10.1016/j.jfineco.2023.103745 .
Bian , B. , Ma , X. and Tang , H. ( 2021 ), “ The supply and demand for data privacy: evidence from mobile apps ”, available at : https://ssrn.com/abstract=3987541
Broecker , T. ( 1990 ), “ Credit-worthiness tests and interbank competition ”, Econometrica , Vol. 58 No. 2 , pp. 429 - 452 , doi: 10.2307/2938210 .
Brunnermeier , M. and Payne , J. ( 2022 ), “ Platforms, tokens, and interoperability ”, Unpublished Working Paper .
Buchak , G. , Matvos , G. , Piskorski , T. and Seru , A. ( 2018 ), “ Fintech, regulatory arbitrage, and the rise of shadow banks ”, Journal of Financial Economics , Vol. 130 No. 3 , pp. 453 - 483 , doi: 10.1016/j.jfineco.2018.03.011 .
Cevik , S. ( 2024 ), “ The dark side of the Moon? Fintech and financial stability ”, International Review of Economics , Vol. 71 No. 2 , pp. 421 - 433 .
Chesbrough , H.W. ( 2003 ), Open Innovation: The New Imperative for Creating and Profiting from Technology , Harvard Business Review Press , Cambridge, MA .
Chesbrough , H. ( 2011 ), Open Services Innovation : Rethinking Your Business to Grow and Compete in a New Era , John Wiley & Sons , Hoboken, NJ .
Chesbrough , H. ( 2019 ), Open Innovation Results: Going beyond the Hype and Getting Down to Business , Oxford University Press , Oxford .
Dang , T.V. , Gorton , G. , Holmström , B. and Ordoñez , G. ( 2017 ), “ Banks as secret keepers ”, American Economic Review , Vol. 107 No. 4 , pp. 1005 - 1029 , doi: 10.1257/aer.20140782 .
Diamond , D.W. ( 1984 ), “ Financial intermediation and delegated monitoring ”, The Review of Economic Studies , Vol. 51 No. 3 , pp. 393 - 414 , doi: 10.2307/2297430 .
Diamond , D.W. and Dybvig , P.H. ( 1983 ), “ Bank runs, deposit insurance, and liquidity ”, Journal of Political Economy , Vol. 91 No. 3 , pp. 401 - 419 , doi: 10.1086/261155 .
Djankov , S. , McLiesh , C. and Shleifer , A. ( 2007 ), “ Private credit in 129 countries ”, Journal of Financial Economics , Vol. 84 No. 2 , pp. 299 - 329 , doi: 10.1016/j.jfineco.2006.03.004 .
Fang , J. and Zhu , J. ( 2023 ), “ The impact of open banking on traditional lending in the BRICS ”, Finance Research Letters , Vol. 58 , 104300 , doi: 10.1016/j.frl.2023.104300 .
Farboodi , M. and Veldkamp , L. ( 2021 ), “ A model of the data economy (No. w28427) ”, National Bureau of Economic Research .
Fuster , A. , Plosser , M. , Schnabl , P. and Vickery , J. ( 2019 ), “ The role of technology in mortgage lending ”, The Review of Financial Studies , Vol. 32 No. 5 , pp. 1854 - 1899 , doi: 10.1093/rfs/hhz018 .
Goldstein , I. , Huang , C. and Yang , L. ( 2022 ), “ Open banking under maturity transformation ”, available at: SSRN .
Gopal , M. and Schnabl , P. ( 2022 ), “ The rise of finance companies and fin- tech lenders in small business lending ”, The Review of Financial Studies , Vol. 35 No. 11 , pp. 4859 - 4901 , doi: 10.1093/rfs/hhac034 .
He , Z. , Huang , J. and Zhou , J. ( 2023 ), “ Open banking: credit market competition when borrowers own the data ”, Journal of Financial Economics , Vol. 147 No. 2 , pp. 449 - 474 , doi: 10.1016/j.jfineco.2022.12.003 .
Holmstrom , B. ( 2015 ), “ Understanding the role of debt in the financial system ”, SSRN Scholarly Paper ID 2552018, Social Science Research Network, Rochester, NY .
Jaffee , D.M. and Russell , T. ( 1976 ), “ Imperfect information, uncertainty, and credit rationing* ”, The Quarterly Journal of Economics , Vol. 90 No. 4 , pp. 651 - 666 , doi: 10.2307/1885327 .
Jones , C.I. and Tonetti , C. ( 2020 ), “ Nonrivalry and the economics of data ”, American Economic Review , Vol. 110 No. 9 , pp. 2819 - 2858 , doi: 10.1257/aer.20191330 .
Kaplan , T.R. ( 2006 ), “ Why banks should keep secrets ”, Economic Theory , Vol. 27 No. 2 , pp. 341 - 357 , doi: 10.1007/s00199-004-0597-y .
Keeley , M.C. ( 1990 ), “ Deposit insurance, risk, and market power in banking ”, The American Economic Review , Vol. 80 No. 5 , pp. 1183 - 1200 .
Nam , R.J. ( 2023 ), “ Open banking and customer data sharing: implications for Fintech borrowers ”, available at: SSRN .
Parlour , C.A. , Rajan , U. and Zhu , H. ( 2022 ), “ When FinTech competes for payment flows ”, The Review of Financial Studies , Vol. 35 No. 11 , pp. 4985 - 5024 , doi: 10.1093/rfs/hhac022 .
Philippon , T. ( 2019 ), “ On Fintech and financial inclusion (No. w26330) ”, National Bureau of Economic Research .
Srinivas , V. , Schoeps , J.-T. and Jain , A. ( 2019 ), “ Executing the open banking strategy in the United States ”, available at: https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/industry/financial-services/open-banking-model-strategy-united-states.html
Stiglitz , J.E. and Weiss , A. ( 1981 ), “ Credit rationing in markets with imperfect information ”, The American Economic Review , Vol. 71 No. 3 , pp. 393 - 410 .
Tang , H. ( 2019 ), “ Peer-to-Peer lenders versus banks: substitutes or complements? ”, The Review of Financial Studies , Vol. 32 No. 5 , pp. 1900 - 1938 , doi: 10.1093/rfs/hhy137 .
Vives , X. ( 2019 ), “ Digital disruption in banking ”, Annual Review of Financial Economics , Vol. 11 No. 1 , pp. 243 - 272 , doi: 10.1146/annurev-financial-100719-120854 .
Further reading
Leong , E. ( 2020 ), “ Open banking: the changing nature of regulating banking data-a case study of Australia and Singapore ”, Banking and Finance Law Review , 35.3 , pp. 443 - 469 .
Nanaeva , Z. , Aysan , A.F. and Shirazi , N.S. ( 2021 ), “ Open banking in Europe: the effect of the revised payment services directive on Solarisbank and Insha ”, Journal of Payments Strategy and Systems , Vol. 15 No. 4 , pp. 432 - 444 .
Corresponding author
Related articles, all feedback is valuable.
Please share your general feedback
Report an issue or find answers to frequently asked questions
Contact Customer Support
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Samples >
- Essay Types >
- Research Proposal Example
Banking Industry Research Proposals Samples For Students
8 samples of this type
WowEssays.com paper writer service proudly presents to you an open-access collection of Banking Industry Research Proposals intended to help struggling students tackle their writing challenges. In a practical sense, each Banking Industry Research Proposal sample presented here may be a guide that walks you through the essential stages of the writing procedure and showcases how to compose an academic work that hits the mark. Besides, if you require more visionary help, these examples could give you a nudge toward an original Banking Industry Research Proposal topic or encourage a novice approach to a threadbare theme.
In case this is not enough to quench the thirst for efficient writing help, you can request personalized assistance in the form of a model Research Proposal on Banking Industry crafted by an expert from scratch and tailored to your particular requirements. Be it a plain 2-page paper or a profound, extended piece, our writers specialized in Banking Industry and related topics will deliver it within the pre-agreed timeframe. Buy cheap essays or research papers now!
Problem Of Study Research Proposal Sample
Information technology on international banking performance.
THE IMPACT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ON INTERATIONAL BANKING PERFORMANCE: COMPARATIVE CASE STUDY ANALYSIS OF NIGERIA, UNITED KINGDOM AND BRAZIL BANKING INDUSTRY
INTRODUCTION
Good research proposal on the relationship between equity prices and banking industry performance in the united kingdom, introduction, research proposal on role of managing innovation and projects in banking industry.
Don't waste your time searching for a sample.
Get your research proposal done by professional writers!
Just from $10/page
Role Of Managing Innovation And Projects In Banking Industry Research Proposal Example
Advanced entrepreneurship – chase bank atm machines research proposal template for faster writing, problem statement academic research proposal example.
The Relationship between Motivation, Organizational stressors and Job Satisfaction in the U.S.A Banking Industry
Free Research Proposal On The Effects Of Technology Applications On The Reserve Bank Of Australia
Chapter one: introduction, the effects of training and development on employee performance in the banking sector research proposal sample.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
BANKING SECTOR IN ETHIOPIA: ORIGIN AND PRESENT STATE
- EPH - International Journal of Business & Management Science 9(2):1-13
- CC BY-NC-ND 4.0

- Kotebe University of Education
- This person is not on ResearchGate, or hasn't claimed this research yet.
Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Seid Muhammed
- Prihoda Emese

- Ratinder Kaur
- J Bank Regul

- AFR J BUS MANAGE

- Ronald L. Moy

- Franco Modigliani
- Michael G. Ferri
- Int J Afr Hist Stud
- Charles Schaefer

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

Browser Update Recommended.
Our website has detected that you are using an outdated browser that will prevent you from accessing certain features. An upgrade is recommended to improve you browsing experience.

- Publications
Publication Details
By signing the Paris Agreement, South Africa committed to transform its economy to contribute to keeping global temperature rises well below 2°C. This transformation will inevitably impact financial institutions and could represent a systemic risk for the financial sector. According to central bank and academic research, an orderly transition should not jeopardise financial stability – but understanding transition risks for the banking sector, monitoring them and, when necessary, implementing macroprudential measures is necessary to ensure this stability. This paper is a step towards achieving this outcome. It presents the main transition risks for the South African banking sector, highlighting that the coal value chain is central to these risks. It assesses the banking system’s exposure to transition risks in the corporate sector, showing that they are material and widespread. It concludes by suggesting some macroprudential policy options that could address these risks.
10 Considerations for Fintechs Partnering with Community Banks
Fintech flash.

As banking and technology become more integrated, banks are increasingly partnering with fintechs to expand their customer offerings. The rapid rise of these partnerships has generated questions for both banks and fintechs on how to manage resulting regulatory and financial risks.
On May 3, the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, and the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (collectively, “the agencies”) released final joint guidance for community banks on managing risks associated with third-party partnerships. 1 This guidance builds on previous interagency guidance for all banks entering into third-party partnerships, which we discussed in our June 2023 Fintech Flash .
Herein, we discuss the implications of this guidance for fintechs seeking to enter into partnerships with community banks.
Trends and Challenges for Fintech–Bank Partnerships
Although technology-driven banking services have been prevalent for decades, customer demand for digital access to banks surged during the COVID-19 pandemic. In part to meet this demand, banks turned to fintechs to facilitate digital offerings, commonly entering into banking-as-a-service (BaaS) partnerships, in which fintechs manage user experience while the bank holds the resulting deposits. In April 2024, we detailed considerations for fintechs entering into such partnerships.
These partnerships can blur the lines between fintechs and banks from the customer perspective, inviting regulatory scrutiny. In 2023, banks with BaaS partnerships accounted for 13.5% of prompt corrective action directives, cease and desist orders, consent orders, and formal agreements with federal banking regulators. 2 As a result, some banks have ended their relationships with third-party partners or more carefully considered fintech partnerships.
At the same time, partnerships with community banks present opportunities for fintechs. Community banks recovered well overall from the COVID-19 pandemic, and they hold a steady deposit base that is largely insured. 3 However, community banks often lack the resources and personnel that may give larger banks a leg up in developing digital tools.
Fintechs can bridge this gap by developing these tools at scale and then partnering with community banks to implement them in ways that serve the bank’s needs. The agencies’ joint guidance provides a five-stage road map for community banks seeking to enter into such partnerships: (1) planning, (2) due diligence and third-party selection, (3) contract negotiation, (4) ongoing monitoring, and (5) termination. Below, we provide key takeaways from the guidance that fintechs can use to increase the odds of developing a successful third-party partnership with a community bank, particularly at the due diligence and third-party selection stage.
Key Takeaways for Fintechs
- Develop a pitch. Before a community bank begins to seek out potential partners, they must define the underlying activity that the partner will perform. Given that some community banks may not have a history of partnering with fintechs or the resources to conduct an extensive search, a fintech can get a leg up by developing a clear marketing pitch for why its product will suit the bank’s needs.
- Demonstrate expertise in the subject area. A community bank seeking a partnership will look for partners that can show expertise in the given subject area. A fintech should be able to provide a bank with a detailed proposal describing the proposed product, its past implementation (if applicable), and suggested modifications to meet the bank’s needs. A fintech should have experienced staff on hand to help draft these proposals, tailor the proposals to the bank, negotiate appropriate contract terms, and develop an implementation plan.
- Show an ability to comply with applicable legal requirements. Community banks will look to a potential partner’s ability to comply with applicable legal requirements, including those relating to anti–money laundering and combatting the financing of terrorism, as well as consumer protection laws such as the Electronic Fund Transfer Act, the Truth in Lending Act, and the Equal Credit Opportunity Act. Fintechs should make sure they have relevant policies and procedures covering compliance with all applicable laws and regulations, a demonstrated history of compliance, and the necessary staff for compliance training and monitoring.
- Demonstrate the ability to recover from disruptions. As part of the diligence process, community banks may investigate the performance of potential partners during past periods of financial stress or operational disruptions. Given that community banks may be especially risk-sensitive, fintechs seeking to partner with them should detail recovery efforts from any past disruptions and have a business continuity plan in place.
- Seek to minimize, address, and track customer complaints. Community banks may ask potential partners about their customer complaint history, including the volume and nature of customer complaints. Fintechs seeking to partner with community banks should aim to minimize customer complaint volume, address complaints promptly, and track complaint status in a centralized database.
- Have handy references and be aware of negative PR. As an initial step, community banks may ask for references and conduct internet searches to see if negative information exists about potential partners. Fintechs seeking to partner with community banks should have references on hand and be ready to promptly counter negative information, given that community banks with limited resources may move on to the next candidate if they discover issues.
- Maintain a robust information security program. As part of a partnership, a fintech operating a customer-facing interface may be tasked with storing and transmitting a bank’s customer information. Given that community banks may be especially litigation-averse and may not have extensive IT resources, fintechs seeking to partner with them should demonstrate an ability to keep customer information secure and integrate their infrastructure with the bank’s.
- Develop template contract terms. Once they have selected a fintech partner, community banks will seek to ensure that the partnership contract adequately addresses considerations including performance benchmarks, information-sharing, intellectual property, and data retention. Fintechs can simplify the contract-drafting process by having available template contract terms that can be tailored to the specific needs of the community bank partner.
- Disclose operational changes. Once a community bank has entered into a third-party partnership, it may seek to keep abreast of operational changes at the partner, such as mergers, divestitures, or leadership changes. Fintechs should consider preemptively disclosing such changes to their partners to build trust and ensure a successful partnership.
- Consider contingency plans. Inevitably, some partnerships will fail. Just as community banks will evaluate the risks of and develop a plan for termination of the partnership, fintechs should similarly plan for termination. Fintechs should consider contractual and legal liability for breach of partnership terms and ensure that termination of the partnership could be done in an orderly manner with limited risk to overall operations.
If you are considering entering into a bank partnership, Goodwin’s fintech team has experience guiding fintechs in all types of bank partnerships, including those involving lending, alternative finance, payments, deposits, insurance, broker-dealers, and investment advisers. For specific recommendations relating to a partnership or if you would like additional information about any of the issues discussed in this Flash, please reach out to Danielle Reyes or the Goodwin lawyer with whom you typically consult.
Goodwin’s Fintech Team We practice in every fintech vertical, including lending, alternative finance (e.g., merchant cash advances, earned wage access, and factoring), payments, deposits, insurance, broker-dealers, and investment advisers. In addition to doing product and service development regulatory work, we assist our fintech clients that choose to deliver their solutions through banks in entering into bank partnership and platform agreements.
[1] Third-Party Risk Management, A Guide for Community Banks , Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, and Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, May 2024. [2] Yizhu Wang and Thomas Mason, “Small group of bank-as-a-service banks logs big number of enforcement actions,” S&P Global, January 23, 2024. [3] Alex Graf, “Community banks’ deposit bases hold steady, seen as ‘safe haven,’” S&P Global, March 24, 2023.
This informational piece, which may be considered advertising under the ethical rules of certain jurisdictions, is provided on the understanding that it does not constitute the rendering of legal advice or other professional advice by Goodwin or its lawyers. Prior results do not guarantee a similar outcome.

Danielle Reyes

Andrew Kliewer

Josh Burlingham
Related content, cta update: fincen clarifies boi reporting requirements for dissolved reporting companies, are you ready for mica implementation, fdic approves ilc with traditional bank business model (but don’t rush to submit your application just yet), fdic approves final revised rule to strengthen resolution planning for large banks, occ revises comptroller’s handbook booklet for retail nondeposit investment products, new york governor signs llc transparency act, cfpb launches process to recognize open banking standards, form shl: what you need to know, elevate your expertise: insights into the ucc & efta for payments professionals webinar, goodwin leads the h1 2024 league table rankings, goodwin advises pinova capital on the financing of the acquisition of neuromedex, orrstown financial services completes acquisition of codorus valley bancorp, goodwin’s market leading financial services practice welcomes partner crystal kaldjob in washington, dc, amid ongoing regional growth, goodwin relocates singapore office, goodwin advises rantum capital on financing for the acquisition of lyocontract, goodwin advises emeram on financing for the acquisition of provital, financial services, consumer financial services.
- Public Safety
- Nation & World
State Pier proposal: Train New Bedford kids for a future in offshore wind industry.

NEW BEDFORD — There are New Bedford kids in middle school today who will be retiring from the offshore wind industry decades from now.
That's the prediction of Andrew B. Saunders, president of New Bedford Foss Marine Terminal LLC .
The 61-year-old New Bedford native, who jokes he's a recovering attorney, made the remark during a meeting in May hosted by MassDevelopment to air redevelopment proposals for the eight-acre New Bedford State Pier.
Foss Marine Terminal's proposal to expand its warehouse operation and develop a training center is one of seven under consideration by MassDevelopment.
The proposals could be approved together, separately or denied altogether. A decision deadline has not been announced.
Servedwell: Could a restaurant on New Bedford State Pier bring 200,000 people downtown? What to know.
MassDevelopment, the state’s development finance agency and land bank, manages the state-owned property.
Supplement nearby New Bedford Foss Marine Terminal
The nearby 29-acre New Bedford Foss Marine Terminal is being developed to provide a shore base to support offshore wind construction, then operation and maintenance of the completed projects for decades to come.
The terminal property is located at the former Cannon Street-power-station-Sprague-Eversource site.
"We purchased a 29-acre facility with a private-public partnership with the city of New Bedford, basically knocked everything down. We're turning it in to an offshore wind staging base," Saunders said.
BASE: New Bedford State Pier proposal makes fishing a destination attraction. What to know.
Saunders said Foss Marine's proposal for State Pier will supplement its warehouse operations.
That entails acquiring control of building 1 on State Pier — Saunders stresses that building 1 is not the cold storage warehouse building.
He said the 28,000-square-foot first floor includes 6,000 square feet occupied by Seastreak ferries.
Training center would occupy entire second floor
The Foss proposal takes that into consideration. They would want only 22,000 square feet for the warehouse operation.
The building's 28,000-square-foot second floor would be developed into a basic technical training facility where people can learn how to work in the offshore wind business, he said.
Cuttyhunk: New Bedford State Pier's Cuttyhunk Ferry is a 'lifeline' to tiny Cuttyhunk Island
That's where PACE — People Acting in Community Endeavors — comes in.
Pam Keuchler, PACE executive director, said the anti-poverty action agency serving Greater New Bedford will work in coordination with Foss to provide the training center.
Workforce development provided by PACE
One of the service's offered by PACE is workforce development, she said.
The training provided will give people an opportunity for careers in offshore wind, including people who otherwise wouldn't get the chance at "viable, longstanding careers."
Keuchler added, "We've developed a pre-employment program that is connected to several of the industry representatives that allows folks to then be prepared to go into a variety of training programs."
Saunders said Foss had put PACE in touch with contacts providing similar training in the United Kingdom.
'Tremendous opportunity' for local residents
He added, "There is a tremendous opportunity for the citizens of this area to become trained in this industry. No one is trained currently."
Cruise Lines: New Bedford State Pier park facility proposed by American Cruise Lines
That requires the kind of capacity that would be provided under the Foss proposal, he said.
Those trained in the industry must be recertified every two years.
"Every time someone gets trained you need capacity to train them two years later," he said.
Extensive New Bedford waterfront background
While he jokes about no longer practicing law, his background includes having been general counsel for the New Bedford Harbor Development Commission.
"So I know extremely well about the ideas that people have used to develop the Port," Saunders said.
He also has the practical background, having been involved in the New Bedford waterfront community throughout his life.
Seastreak: Seastreak ferry business thrives at New Bedford's pier. It's making its case to the state
He's worked on fishing boats and on tugboats, he said.
Proposal calls for 270 linear feet of dockage
The Foss proposal includes 270 linear feet of dockage on the east face.
Saunders said they've agreed not to have any garbage or noxious cargos go across that particular dock.
They have also committed to allowing transient dockage of fishing vessels on that east face to allow gear change, "which is very, very critical."
- Personal Finance
- Today's Paper
- Budget 2024
- Olympics 2024
- Partner Content
- Entertainment
- Social Viral
CDSL, Kaveri Seeds in focus post Budget 2024 proposals: SAMCO Securities
India budget 2024 impact: shares of kaveri seeds and mangalam seeds zoomed up to 13 per cent after fm nirmala sitharaman proposed measures for the sector..
)
Listen to This Article
More from this section, poonawalla fincorp shares fall on q1fy25 results; good time to buy, jana small finance bank stock tanks 7% after q1fy25 earnings; check details, cyient dlm stock price falls 4% on profit booking after strong q1fy25 show, this renewable energy solutions provider stock has zoomed 625% in 15 months, oil india stock gains 3% on signing pact with norway's dolphin drilling, budget 2024 live: fiscal deficit narrows to 4.9%; govt eyes below 4.5% figure for fy26, says fm, budget 2024: hostels, skilling among initiatives for women in workforce, budget 2024 stock market news live: indices flat; sitharaman keeps capex outlay at rs 11.11 trillion, union budget 2024: kaveri seed up 14%; govt to release high yielding crops, fm took leaf out of our nyay patra with its internship programme: congress.
Don't miss the most important news and views of the day. Get them on our Telegram channel
First Published: Jul 23 2024 | 12:10 PM IST
Explore News
- Suzlon Energy Share Price Adani Enterprises Share Price Adani Power Share Price IRFC Share Price Tata Motors Share Price Tata Steel Share Price Yes Bank Share Price Infosys Share Price SBI Share Price Tata Power Share Price
- Latest News Company News Market News India News Politics News Cricket News Personal Finance Technology News World News Industry News Education News Opinion Shows Economy News Lifestyle News Health News
- Today's Paper About Us T&C Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Disclaimer Investor Communication GST registration number List Compliance Contact Us Advertise with Us Sitemap Subscribe Careers BS Apps
- ICC T20 World Cup 2024 Budget 2024 Budget 2024 Live Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP)

- Commercial Lending
- Community Banking
- Compliance and Risk
- Cybersecurity
- Human Resources
- Mutual Funds
- Retail and Marketing
- Tax and Accounting
- Wealth Management
- Magazine Archive
- Newsletter Archive
- Sponsored Archive
- Podcast Archive

ABA, associations seek more time for comment on mortgage servicing proposal

The proposed rule would result in a major overhaul of the existing default servicing framework. Public comments on the proposal are currently due Sept. 9. In their letter , the associations said that while updates to the CFPB’s servicing regulations are needed, the 60-day comment period does not provide enough time to sufficiently address potentially complex issues. They asked for at least another 30 days.
“With the goal of developing thoughtful comments on each issue in the rulemaking that will help the bureau achieve its stated objectives and given the extensive set of policy changes that servicing stakeholders are now confronting, stakeholders need more time than has been allotted,” the associations said. “We are aware that the CFPB is not constrained from granting such an extension by any statutory deadline or other federal mandate that requires a 60-day comment period.”
Related Posts

ABA, associations: Banks cannot fight financial scams on their own
Banks are only one contributor to the overall safety and security of the payments ecosystem and cannot single-handedly prevent criminals from defrauding consumers or financial institutions, ABA and three bankers associations said in a joint statement to lawmakers.

ABA recommends ‘good government’ improvements to agencies’ surveys
ABA and three financial trade associations urged the White House Office of Management and Budget to publish key information about agencies' proposed surveys in time for the public to provide fulsome feedback.

House Financial Services Committee seeks ‘leading role’ in overseeing financial AI policy
In a new report, a bipartisan working group formed by the House Financial Services Committee said the committee should “play a leading role” in overseeing the adoption of AI technologies in the financial services and housing sectors.

Financial Stability Board chair warns of ‘uneven’ progress in nonbank regulation
Recent incidents have shown that nonbank entities can create or amplify risk throughout the global financial system, but the pace of agreed-upon reforms has been “uneven” across nations “and we may already be losing momentum,” Klaas Knot, chair...

Banking agencies propose rule to align AML/CFT requirements
Four federal agencies proposed a joint rule that would align each agency's Bank Secrecy Act compliance program requirements with proposed anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism requirements proposed by the FinCEN.

ABA Data Bank: Used vehicle prices fall during economic recovery
Vehicle production and inventories have largely recovered from pandemic-related disruptions, helping to offset the cost of higher financing rates and auto insurance for car buyers.
SPONSORED CONTENT
Visibility and Control

What’s Your Bank’s Digital Maturity?

Sealing The Deal: Learn About Electronic Notarization in This Comprehensive Webinar Series

Digital Account Opening Best Practices That Will Boost Your Deposit Game
Podcast: m&a outlook with paul davis, podcast: understanding how monetary policy shapes sofr, podcast: banking and the american founding era.
American Bankers Association 1333 New Hampshire Ave NW Washington, DC 20036 1-800-BANKERS (800-226-5377) www.aba.com About ABA Privacy Policy Contact ABA

© 2024 American Bankers Association. All rights reserved.
Facility for Rare Isotope Beams
At michigan state university, frib issues third call for proposals for frib beam time.
FRIB issued its third call for proposals today. The FRIB science program commenced in May 2022, delivering successful experiments approved in the first call for proposals. The third call invites scientific users the world over to submit proposals for additional research and new ideas using FRIB capabilities.
With this call, FRIB invites proposals for beam time to be considered at the third meeting of the FRIB Program Advisory Committee (PAC3) in January 2025. The PAC is a group of international experts who review proposals for non-proprietary beam time requests submitted to FRIB. The PAC makes recommendations to the FRIB Laboratory Director about beam-time allocation.
All proposals for review by FRIB PAC3 need to be submitted online by 11 p.m. EST on 9 October 2024 to allow for scientific and technical review of the proposals prior to the PAC3 meeting.
FRIB is a U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC) user facility , supporting the mission of the DOE-SC Office of Nuclear Physics . FRIB is open to all interested researchers, subject to applicable laws and DOE-SC regulations. Beam time for non-proprietary experiments is granted based on a merit review of proposals. There is no charge for users who are doing non-proprietary work, with the understanding that they are expected to publish their results.
FRIB PAC3 will consider proposals for experiments using fast, stopped, and reaccelerated rare-isotope beams from the FRIB linear accelerator (linac). Newly offered for PAC3:
- Additional primary beams from the FRIB linac and increased primary beam intensity (see the FRIB beams page )
- The S2 vault is an experimental area that will house the Sweeper magnet and the MoNA/LISA neutron array. The S2 beamline will also have space for auxiliary instruments and may be used as a general-purpose beamline.
Detailed information regarding proposal preparation can be found in the Call for Proposals .
FRIB supports a community of 1,800 scientists from around the world, enabling them to make discoveries about how the universe formed, while advancing innovation in medicine, nuclear security, environmental science, and more. They are organized in an independent FRIB Users Organization, and include scientists, postdoctoral research associates, and graduate students from universities, national laboratories, and industry.
FRIB PAC3 timeline
- 18 July 2024: Call for Proposals for FRIB PAC3 meeting
- 11 September 2024: Last date for rare isotope beam rate requests
- 9 October 2024: Proposals submitted online by 11 p.m. EST
- January 2025: FRIB PAC3 meeting
- January 2025 - List of approved experiments posted to the FRIB website and spokespersons notified
Michigan State University operates the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) as a user facility for the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science (DOE-SC), supporting the mission of the DOE-SC Office of Nuclear Physics. Hosting what is designed to be the most powerful heavy-ion accelerator, FRIB enables scientists to make discoveries about the properties of rare isotopes in order to better understand the physics of nuclei, nuclear astrophysics, fundamental interactions, and applications for society, including in medicine, homeland security, and industry.
The U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of today’s most pressing challenges. For more information, visit energy.gov/science.
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.

COMMENTS
Best Banking And Finance Sector Research Topics For MBA Students. The role of the stock market in economic development. Examining the factors affecting stock market volatility. Impact of high-frequency trading on financial markets. Exploring the relationship between corporate governance and stock prices. The role of derivatives in managing ...
The research questions that these dynamics pose need to be investigated within the context of the theory of banking, hence the need to revise the existing analytical framework. Banks perform payment and transfer functions for an economy. The Internet can now facilitate and even perform these functions. ... The banking sector is therefore ...
This review covered the themes that include investment, profit, competition, credit risk analysis, banking crime, and fintech. This report also signifies the importance, use of big data, and its function in the banking and financial sector. This study has also discussed the future research scope in the banking industry's big data analytics.
The first cycle (Fig. 1) aimed to provide an initial overview of research on the subject and conduct a preliminary analysis of the literature to refine the search criteria for the content review.As proposed by Vashar et al. (Varsha, Chakraborty & Kar, 2024), this preliminary review mapping aids researchers in assessing whether they can delve into a substantial body of material or if they must ...
"Customers became a center for all banking activities due to increased competition for greater market share. Focusing on customer satisfaction has been the key to increasing service quality according to customers' expectations in the banking sector" (Zairi, 2000). Hanson (2000) suggested that the level of service quality is an indication of
3 Impacts of Digitalization on Banks and Banking 39. content by users. Digital banks now communicate with customers via blogs and 212. receive feedback in this way. For instance, ICICI in India ...
All J AMI's publications related to the banking sector and banks can be roughly. divided into following groups: 1) Estimation and ranking of efficiency and competitiveness of the banks; 2 ...
joint work with my supervisor Jan Bartholdy. Section 3, 4 and 5 are descriptions of the preliminary ideas for future research to be contained in the PhD thesis within the ove. all subject of Empirical Studies in Banking. The appendix describes my current progress of. gramme.2 Deposit Insurance and.
Business, 137 00 Prague, Czech Republic; miroslav [email protected]. * Correspondence: fl[email protected]; Tel.: +49- (0)151-4053-2978. Abstract: The digitalisation of banks is seen as the ...
thesis examines the current level of customer satisfaction of PAO "Sberbank." It seeks d. fferent factors that can dissatisfy c. stomers or have a direct influence on them. The research problem goes as follows:To understand the most the most important service quali.
Investment Banking. The list below presents a series of research topics exploring the multifaceted dimensions of investment banking, with a particular focus on its evolution following the 2008 financial crisis. Analysing the evolution and impact of regulatory frameworks in investment banking post-2008 financial crisis
Example Of Cash Flow Research Proposal. The owner of the business will support the business using his own cash until the business can manage to sustain its operation. Therefore, this means that the business will need the owner's support until it breakeven. The breakeven value of the restaurant is $758,333.33.
The fifth chapter is consisting of conclusion and recommendation about the study. Page |2 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Introduction of the study: In general sense we mean "Bank" as a financial institution that deals with money. Now-a day‟s banking sector is modernizing and expanding its hand in different financial events every day.
• To help the investors for choosing to make their investments in banking sector. • To calculate the risk-return stock of banking sector. • Comparative analysis of 6 selected banks. 6. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY The process used to collect information and data for the purpose for making business decisions. The methodology may include ...
Your search for the best finance and banking dissertation topics ends right here because, a t ResearchProspect, we help students choose the most authentic and relevant topic for their dissertation projects. Bank taxes, financial management, financial trading, credit management, market analysis for private investors, economic research methods ...
Totally New Topics for Research Proposals in Finance in 2024. The Rise of Fintech in Unbanked Populations: Financial Inclusion Strategies in Fragile States. The difference between traditional and behavioral finance. The impact of budget management on organizational performance.
The research stated that mobile banking services in Ethiopia has been stared in 2013 by mobile banking development in Ethiopia is not full-fledged in terms of exhaustively utilizing all the mobile services one can get. Currently, of all the types of mobile banking services, most customers of the bank use notification or alarm inquiry.
This research may help the Ethiopian banking industry by recommending possible solutions and strategies to the problems in Ethiopia banking sector. Scope and limitation of the study; The study will focus on investigate the major challenges and prospects of the banking industry of Ethiopia at the time of coronavirus (covid19) pandemic.
(1) the extent to which open banking fosters competition, drives innovation and enhances financial inclusion; (2) the impact of institutional arrangements on the outcomes of open banking initiatives and (3) the critical role of government in promoting open banking and regulating banking activities.,The paper concludes with a discussion on ...
8 samples of this type. WowEssays.com paper writer service proudly presents to you an open-access collection of Banking Industry Research Proposals intended to help struggling students tackle their writing challenges. In a practical sense, each Banking Industry Research Proposal sample presented here may be a guide that walks you through the ...
The banking sector in Ethiopia is an integral part of the financial sector in particular and the economy as a whole. Its contribution to the country's macroeconomic stability and growth objectives ...
By signing the Paris Agreement, South Africa committed to transform its economy to contribute to keeping global temperature rises well below 2°C. This transformation will inevitably impact financial institutions and could represent a systemic risk for the financial sector. According to central bank and academic research, an orderly transition should not jeopardise financial stability - but ...
A fintech should be able to provide a bank with a detailed proposal describing the proposed product, its past implementation (if applicable), and suggested modifications to meet the bank's needs. A fintech should have experienced staff on hand to help draft these proposals, tailor the proposals to the bank, negotiate appropriate contract ...
He said the 28,000-square-foot first floor includes 6,000 square feet occupied by Seastreak ferries. Training center would occupy entire second floor
The Finance Minister's allocation of Rs 26,000 crore for highway development in Bihar, including the construction of a two-lane bridge over the Ganga and the development of highways like the Patna-Purnea Expressway and Buxar-Bhagalpur Expressway, will greatly benefit highway construction companies such as KNR Construction, and PNC Infratech, etc.
The American Bankers Association and seven financial sector associations today requested that the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau extend by at least 30 days the comment period for its proposed rule to amend Regulation X's mortgage servicing provisions. ... Public comments on the proposal are currently due Sept. 9. ... The OCC will ...
National Bank of Kuwait (International) PLC's ratings are based on potential support from its parent, National Bank of Kuwait S.A.K.P. (NBK; A+/Stable). This reflects NBK's strong ability - as indicated by its ratings - and willingness to provide support to NBKI.
FRIB issued its third call for proposals today. The FRIB science program commenced in May 2022, delivering successful experiments approved in the first call for proposals. The third call invites scientific users the world over to submit proposals for additional research and new ideas using FRIB capabilities.With this call, FRIB invites proposals for beam time to be considered at the third ...
King Charles III on Tuesday delivered a speech outlining the legislative agenda planned for the new Parliamentary session by the UK's first Labour government in 14 years. Prime Minister Keir ...
Dubai Islamic Bank (Public Joint Stock Company)'s Issuer Default Ratings are driven by potential support from United Arab Emirates (AA-/Stable) authorities, if needed, as reflected in its Government Support Ratin. The GSR reflects the authorities' strong ability to, and record of, supporting the banking system.