Reported Speech: Rules, Examples, Exceptions

👉 Quiz 1 / Quiz 2
Advanced Grammar Course

What is reported speech?
“Reported speech” is when we talk about what somebody else said – for example:
- Direct Speech: “I’ve been to London three times.”
- Reported Speech: She said she’d been to London three times.
There are a lot of tricky little details to remember, but don’t worry, I’ll explain them and we’ll see lots of examples. The lesson will have three parts – we’ll start by looking at statements in reported speech, and then we’ll learn about some exceptions to the rules, and finally we’ll cover reported questions, requests, and commands.

So much of English grammar – like this topic, reported speech – can be confusing, hard to understand, and even harder to use correctly. I can help you learn grammar easily and use it confidently inside my Advanced English Grammar Course.
In this course, I will make even the most difficult parts of English grammar clear to you – and there are lots of opportunities for you to practice!

Backshift of Verb Tenses in Reported Speech
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called “backshift.”
Here are some examples in different verb tenses:
Reported Speech (Part 1) Quiz
Exceptions to backshift in reported speech.
Now that you know some of the reported speech rules about backshift, let’s learn some exceptions.
There are two situations in which we do NOT need to change the verb tense.
No backshift needed when the situation is still true
For example, if someone says “I have three children” (direct speech) then we would say “He said he has three children” because the situation continues to be true.
If I tell you “I live in the United States” (direct speech) then you could tell someone else “She said she lives in the United States” (that’s reported speech) because it is still true.
When the situation is still true, then we don’t need to backshift the verb.

He said he HAS three children
But when the situation is NOT still true, then we DO need to backshift the verb.
Imagine your friend says, “I have a headache.”
- If you immediately go and talk to another friend, you could say, “She said she has a headache,” because the situation is still true
- If you’re talking about that conversation a month after it happened, then you would say, “She said she had a headache,” because it’s no longer true.
No backshift needed when the situation is still in the future
We also don’t need to backshift to the verb when somebody said something about the future, and the event is still in the future.
Here’s an example:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Friday .”
- “She said she ‘ll call me on Friday”, because Friday is still in the future from now.
- It is also possible to say, “She said she ‘d (she would) call me on Friday.”
- Both of them are correct, so the backshift in this case is optional.
Let’s look at a different situation:
- On Monday, my friend said, “I ‘ll call you on Tuesday .”
- “She said she ‘d call me on Tuesday.” I must backshift because the event is NOT still in the future.

Review: Reported Speech, Backshift, & Exceptions
Quick review:
- Normally in reported speech we backshift the verb, we put it in a verb tense that’s a little bit further in the past.
- when the situation is still true
- when the situation is still in the future
Reported Requests, Orders, and Questions
Those were the rules for reported statements, just regular sentences.
What about reported speech for questions, requests, and orders?
For reported requests, we use “asked (someone) to do something”:
- “Please make a copy of this report.” (direct speech)
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. (reported speech)
For reported orders, we use “told (someone) to do something:”
- “Go to the bank.” (direct speech)
- “He told me to go to the bank.” (reported speech)
The main verb stays in the infinitive with “to”:
- She asked me to make a copy of the report. She asked me make a copy of the report.
- He told me to go to the bank. He told me go to the bank.
For yes/no questions, we use “asked if” and “wanted to know if” in reported speech.
- “Are you coming to the party?” (direct)
- He asked if I was coming to the party. (reported)
- “Did you turn off the TV?” (direct)
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.” (reported)
The main verb changes and back shifts according to the rules and exceptions we learned earlier.
Notice that we don’t use do/does/did in the reported question:
- She wanted to know did I turn off the TV.
- She wanted to know if I had turned off the TV.
For other questions that are not yes/no questions, we use asked/wanted to know (without “if”):
- “When was the company founded?” (direct)
- She asked when the company was founded.” (reported)
- “What kind of car do you drive?” (direct)
- He wanted to know what kind of car I drive. (reported)
Again, notice that we don’t use do/does/did in reported questions:
- “Where does he work?”
- She wanted to know where does he work.
- She wanted to know where he works.
Also, in questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question:
- “Where were you born?” ([to be] + subject)
- He asked where I was born. (subject + [to be])
- He asked where was I born.

Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Learn more about reported speech:
- Reported speech: Perfect English Grammar
- Reported speech: BJYU’s
If you want to take your English grammar to the next level, then my Advanced English Grammar Course is for you! It will help you master the details of the English language, with clear explanations of essential grammar topics, and lots of practice. I hope to see you inside!
I’ve got one last little exercise for you, and that is to write sentences using reported speech. Think about a conversation you’ve had in the past, and write about it – let’s see you put this into practice right away.
Master the details of English grammar:

More Espresso English Lessons:
About the author.
Shayna Oliveira
Shayna Oliveira is the founder of Espresso English, where you can improve your English fast - even if you don’t have much time to study. Millions of students are learning English from her clear, friendly, and practical lessons! Shayna is a CELTA-certified teacher with 10+ years of experience helping English learners become more fluent in her English courses.
Reported Speech – Rules, Examples & Worksheet
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
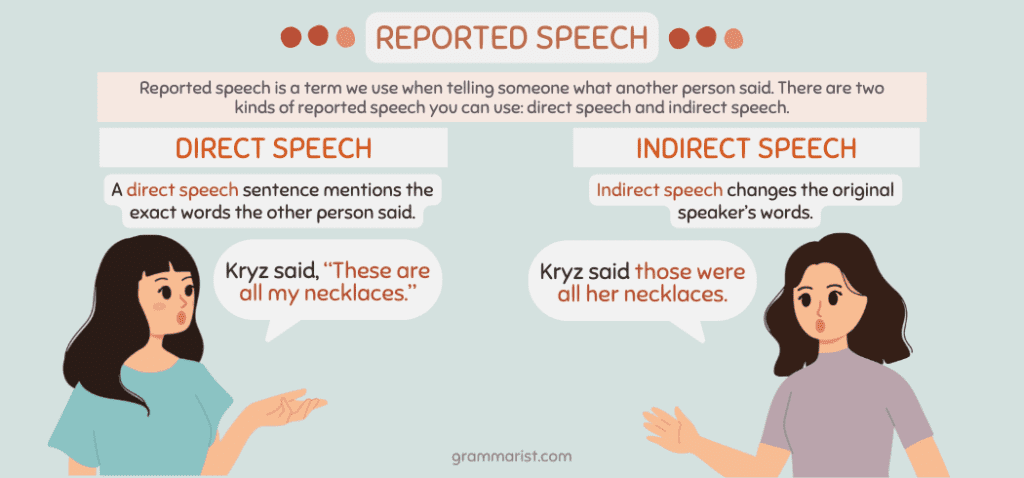
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
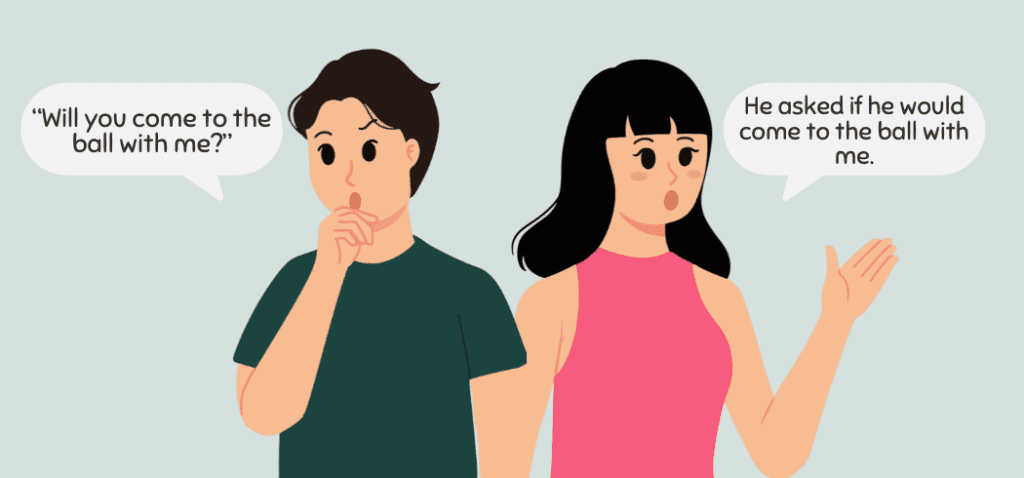
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.

Reported Speech with Examples and Test (PDF)
Reported speech is used when we want to convey what someone else has said to us or to another person. It involves paraphrasing or summarising what has been said , often changing verb tenses , pronouns and other elements to suit the context of the report.
*doesn’t change
Formula of Reported Speech
The formula for reported speech involves transforming direct speech into an indirect form while maintaining the meaning of the original statement. In general, the formula includes:
- Choosing an appropriate reporting verb (e.g., say, tell, mention, explain).
- Changing pronouns and time expressions if necessary.
- Shifting the tense of the verb back if the reporting verb is in the past tense.
- Using reporting clauses like “that” or appropriate conjunctions.
- Adjusting word order and punctuation to fit the structure of the reported speech.
Here’s a simplified formula:
Reporting Verb + Indirect Object + Conjunction + Reported Clause
For example:
- She said (reporting verb) to me (indirect object) that (conjunction) she liked ice cream (reported clause).

Here’s how we use reported speech:
Reporting Verbs: We use verbs like ‘say’ or ‘tell’ to introduce reported speech. If the reporting verb is in the present tense, the tense of the reported speech generally remains the same.
If the reporting verb is in the past tense , the tense of the reported speech often shifts back in time.
Tense Changes: Tense changes are common in reported speech. For example, present simple may change to past simple, present continuous to past continuous, etc. However, some verbs like ‘would’, ‘could’, ‘should’, ‘might’, ‘must’, and ‘ought to’ generally don’t change.
Reported Questions: When reporting questions, we often change them into statements while preserving the meaning. Question words are retained, and the tense of the verbs may change.
Reported Requests and Orders: Requests and orders are reported similarly to statements. Reported requests often use ‘asked me to’ + infinitive, while reported orders use ‘told me to’ + infinitive.
Time Expressions: Time expressions may need to change depending on when the reported speech occurred in relation to the reporting moment. For instance, ‘today’ may become ‘that day’ or ‘yesterday’, ‘yesterday’ might become ‘the day before’, and so forth.
Reported Speech with Examples PDF
Reported Speech PDF – download
Reported Speech Test
Reported Speech A2 – B1 Test – download
You May Also Like

Data Science vs. Machine Learning: What’s the Difference?
Synonyms for ADDITIONALLY with Examples

20+ Example Sentences in Simple Past Tense (PDF)
- I would like books for studying.

Reported speech - 1
Reported speech - 2
Reported speech - 3
Worksheets - handouts
Reported speech
Worksheets - pdf exercises.
- Reported statements - worksheet
- Worksheet - reported questions
- Reported yes/no questions
- Worksheet - reported speech
- Reported speech - exercises pdf
- Indirect speech - exercises
- Reported speech - exercises
- Mixed reported speech 1
- Mixed reported speech 2
- Reported speech 1
- Reported speech 2
- Reported speech 3
- Reported speech 4
- Reported speech 5
- Reported wh- questions
- Reported speech - worksheet
- Reported commands
- Reported questions
- Reported speech 1
- Reported speech 2
- Reported requests and orders
- Reported speech exercise
- Reported questions - worksheet
- Indirect speech - worksheet
- Worksheets pdf - print
- Grammar worksheets - handouts
Grammar - lessons
- Reported speech - grammar notes
- How to use reported speech - lesson
- Tense changes - grammar
Reported Speech Exercises
Perfect english grammar.

Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site:
( Click here to read the explanations about reported speech )
Reported Statements:
- Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Past Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Present Perfect Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Future Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Mixed Tense Reported Statement Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- 'Say' and 'Tell' (quite easy) (in PDF here)
Reported Questions:
- Present Simple Reported Yes/No Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Present Simple Reported Wh Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Mixed Tense Reported Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
Reported Orders and Requests:
- Reported Requests and Orders Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Reported Speech Mixed Exercise 1 (difficult) (in PDF here)
- Reported Speech Mixed Exercise 2 (difficult) (in PDF here)

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech

Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
English Practice Downloadable PDF Grammar and Vocabulary Worksheets
Reported speech (b1).
- RS013 - Reported Speech
- RS012 - Reported Questions and Commands
- RS011 - Reported Speech
- RS010 - Reported Speech
- RS009 - Reported Commands
- RS008 - Reported Questions
- RS007 - Reported Speech
- RS006 - Reported Speech
- RS005 - Reported Speech
- RS004 - Reported Speech
- RS003 - Reported Speech
- RS002 - Reported Speech - Mixed Exercises
- RS001 - Reported Speech - Mixed Exercises
- Adjective - Adverb
- Gerund and Infinitive
- Modal Verbs
- Reported Speech
- Passive Voice
- Definite and Indefinite Articles
- Quantifiers
- Relative Clauses
- Prepositions
- Questions and Negations
- Question Tags
- Language in Use
- Word Formation
- General Vocabulary
- Topical Vocabulary
- Key Word Transformation
News Articles
- Letters and Emails
- Blog Posts and Comments
- Connectives and Linking Phrases
- Phrasal Verbs
- Collocations and Phrases
Vatican releases new norms on alleged supernatural phenomena
By Vatican News
A new document from the Dicastery for the Doctrine of the Faith published on Friday, May 17, has updated the norms for discerning alleged supernatural phenomena . The norms come into force on Sunday, May 19, the feast of Pentecost.
The document is preceded by a detailed presentation by Cardinal Víctor Manuel Fernández, Prefect of the Dicastery, followed by an introduction and six possible conclusions. The procedure allows for faster decisions while respecting popular devotion.
As a rule, the Church’s authority will no longer be engaged to officially define the supernatural nature of a phenomenon, a process that can require large amounts time to thoroughly study an event.
Another new norm involves the explicit involvement of the Dicastery for the Doctrine of the Faith, which must approve the local bishop’s final decision and which has the authority to intervene motu proprio at any time.
Many cases in recent decades have involved the former Holy Office, even when individual bishops have expressed themselves. However, the interventions have usually remained behind the scenes and were never made public.
The Dicastery’s new explicit involvement also relates to the difficulty in circumscribing phenomena, which in some cases reach national and even global dimensions, “meaning that a decision made in one Diocese has consequences also elsewhere.”
Reasons for the new norms
The document originates from the long experience of the last century, which saw cases where the local bishop (or bishops of a region) rapidly declared a phenomenon’s supernatural nature, only for the Holy Office to express a different decision later. Other cases involved a bishop saying one thing and his successor deciding the opposite (regarding the same phenomenon).
Each event also required lengthy discernment periods to evaluate all elements in order to reach a decision on the supernatural nature or non-supernatural nature of the phenomena. These time periods sometimes contrasted with the urgency to give pastoral responses for the good of the faithful.
The Dicastery began revising the norms in 2019, leading to the current text approved by Pope Francis on May 4.
Spiritual fruits and risks
In his presentation, Cardinal Fernández explains that, “many times, these events have led to a great richness of spiritual fruits, growth in faith, devotion, fraternity, and service. In some cases, they have given rise to shrines throughout the world that are at the heart of many people’s popular piety today.”
However, there is also the possibility that “in some events of alleged supernatural origin,” serious issues that harm the faithful may arise. These include cases where from the alleged phenomena, “profit, power, fame, social recognition, or other personal interest” (II, Art. 15, 4°) are derived, even to the point of “exerting control over people or carrying out abuses (II, Art. 16).”
There may be “doctrinal errors, an oversimplification of the Gospel message, or the spread of a sectarian mentality.” There is the possibility of believers “being misled by an event that is attributed to a divine initiative but is merely the product of someone’s imagination, desire for novelty, tendency to fabricate falsehoods (mythomania), or inclination toward lying.”
General guidelines
According to the new norms, the Church will exercise her duties of discernment, based on the following:
“(a) whether signs of a divine action can be ascertained in phenomena that are alleged to be of supernatural origin; (b) whether there is anything that conflicts with faith and morals in the writings or messages of those involved in the alleged phenomena in question; (c) whether it is permissible to appreciate their spiritual fruits, whether they need to be purified from problematic elements, or whether the faithful should be warned about potential risks; (d) whether it is advisable for the competent ecclesiastical authority to realize their pastoral value” (I, 10).
However, “it is not foreseen in these Norms that ecclesiastical authority would give a positive recognition of the divine origin of alleged supernatural phenomena” (I, 11).
Therefore, as a rule, “neither the Diocesan Bishop, nor the Episcopal Conferences, nor the Dicastery will declare that these phenomena are of supernatural origin, even if a Nihil obstat is granted. It remains true, however, that the Holy Father can authorize a special procedure in this regard” (I, 23).
Possible conclusions regarding an alleged phenomenon
The discernment of an alleged supernatural phenomenon may reach the following six conclusions.
- Nihil Obstat : Without expressing any certainty about the supernatural authenticity of the phenomenon itself, many signs of the action of the Holy Spirit are acknowledged. The bishop is encouraged to appreciate the pastoral value and promote the dissemination of the phenomenon, including pilgrimages;
- Prae oculis habeatur : Although important positive signs are recognized, some aspects of confusion or potential risks are also perceived that require the diocesan bishop to engage in a careful discernment and dialogue with the recipients of a given spiritual experience. If there were writings or messages, doctrinal clarification might be necessary;
- Curatur : Various or significant critical elements are noted, but the phenomenon is already spread widely, and verifiable spiritual fruits are connected to it. Therefore, a ban that could upset the faithful is not recommended, but the local bishop is advised not to encourage the phenomenon;
- Sub mandato : The critical issues are not connected to the phenomenon itself but to its improper use by people or groups, such as undue financial gain or immoral acts. The Holy See entrusts the pastoral leadership of the specific place to the diocesan bishop or a delegate;
- Prohibetur et obstruatur : Despite various positive elements, the critical issues and risks associated with this phenomenon appear to be very serious. The Dicastery asks the local bishop to offer a catechesis that can help the faithful understand the reasons for the decision and reorient their legitimate spiritual concerns;
- Declaratio de non supernaturalitate : The Dicastery for the Doctrine of the Faith authorizes the local bishop to declare that the phenomenon is found to be not supernatural based on concrete facts and evidence, such as the confession of an alleged visionary or credible testimonies of fabrication of the phenomenon.
Procedures to follow
The new norms then indicate the procedures to be implemented. It is up to the diocesan bishop to examine cases and submit their judgment to the Dicastery for approval. The bishop is asked to refrain from making public declarations about the authenticity or supernatural nature and to ensure there is no confusion or sensationalism.
If the elements of the case “seem sufficient,” the diocesan bishop will then set up an investigative commission, which should include at least one theologian, one canonist, and an expert chosen based on the nature of the phenomenon.
Positive and negative criteria
The document lays out several positive criteria to evaluate the alleged supernatural phenomenon.
These include: “the credibility and good reputation of the persons who claim to be recipients of supernatural events or to be directly involved in them, as well as the reputation of the witnesses who have been heard...; the doctrinal orthodoxy of the phenomenon and any messages related to it; the unpredictable nature of the phenomenon, by which it is evident that it is not the result of the initiative of the people involved; and, fruits of the Christian life” (II, 14).
The negative criteria involve: “the possibility of a manifest error about the event; potential doctrinal errors...; a sectarian spirit that breeds division in the Church; an overt pursuit of profit, power, fame, social recognition, or other personal interest closely linked to the event; gravely immoral actions…; psychological alterations or psychopathic tendencies in the person that may have exerted an influence on the alleged supernatural event; and, any psychosis, collective hysteria, and other elements traceable to a pathological context” (II, 15).
Finally, “the use of purported supernatural experiences or recognized mystical elements as a means of or a pretext for exerting control over people or carrying out abuses” (II, 16) is considered of particular moral gravity.
Regardless of the final approved determination, the diocesan bishop “must continue to watch over the phenomenon and the people involved, exercising his ordinary power” (II, 24).
Thank you for reading our article. You can keep up-to-date by subscribing to our daily newsletter. Just click here

More upcoming events:

Listen to our podcasts

Subscribe to our newsletters
To get the latest news

Papal audiences

Daily readings

Saint of the day

A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Handwashing
- Hand Hygiene as a Family Activity
- Hand Hygiene FAQs
- Handwashing Facts
- Publications, Data, & Statistics
- Health Promotion Materials
- Global Handwashing Day
- Clean Hands and Spaces: Handwashing and Cleaning in Educational Facilities
- Life is Better with Clean Hands Campaign
- Clinical Safety
- Healthcare Training
- Clean Hands Count Materials
About Hand Hygiene for Patients in Healthcare Settings
- Patients in healthcare settings are at risk of getting infections while receiving treatment for other conditions.
- Cleaning your hands can prevent the spread of germs, including those that are resistant to antibiotics, and protects healthcare personnel and patients.
- Patients and their loved ones can play a role in asking and reminding healthcare personnel to clean their hands.
Your hands can spread germs.
- Hands have good germs that your body needs to stay healthy. Hands can also have bad germs on them that make you sick.
Alcohol-based hand sanitizer kills most of the bad germs that make you sick.
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers kill the good and bad germs, but the good germs quickly come back on your hands.
Alcohol-based hand sanitizer does not create antimicrobial-resistant germs.
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers kill germs quickly and in a different way than antibiotics.
- Using alcohol-based hand sanitizers to clean your hands does not cause antimicrobial resistance.
Steps to take
When patients and visitors should clean their hands.
- Before preparing or eating food.
- Before touching your eyes, nose, or mouth.
- Before and after changing wound dressings or bandages.
- After using the restroom.
- After blowing your nose, coughing, or sneezing.
- After touching hospital surfaces such as bed rails, bedside tables, doorknobs, remote controls, or the phone.
How to clean hands
With an alcohol-based hand sanitizer:.
- Put product on hands and rub hands together.
- Cover all surfaces until hands feel dry.
- This should take around 20 seconds.
With soap and water:
- Wet your hands with warm water. Use liquid soap if possible. Apply a nickel- or quarter-sized amount of soap to your hands.
- Rub your hands together until the soap forms a lather and then rub all over the top of your hands, in between your fingers and the area around and under the fingernails.
- Continue rubbing your hands for at least 15 seconds. Need a timer? Imagine singing the "Happy Birthday" song twice.
- Rinse your hands well under running water.
- Dry your hands using a paper towel if possible. Then use your paper towel to turn off the faucet and to open the door if needed.
Clean Hands Count Campaign Materials
Ask your healthcare provider to clean their hands.
- Wearing gloves alone is not enough for your healthcare provider to prevent the spread of infection.
- "Before you start the exam, would you mind cleaning your hands again?"
- "Would it be alright if you cleaned your hands before changing my bandages?"
- "I didn't see you clean your hands when you came in, would you mind cleaning them again before you examine me?"
- "I'm worried about germs spreading in the hospital. Will you please clean your hands once more before you start my treatment?"
Speak up for clean hands in healthcare settings
- Clean your own hands and ask those around you to do the same.
- Don't be afraid to use your voice: it's okay to ask your healthcare provider to clean their hands.
- "I saw you clean your hands when you arrived some time ago, but would you mind cleaning them again?"
Frequently asked questions
Is there such a thing as too clean.
- Germs are everywhere. They are within and on our bodies and on every surface you touch. But not all germs are bad. We need some of these germs to keep us healthy and our immune system strong.
- Your hands have good germs on them that your body needs to stay healthy. These germs live under the deeper layers of the skin.
- Your hands can also have bad germs on them that make you sick. These germs live on the surface and are easily killed/wiped away by the alcohol-based hand sanitizer.
- Using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer is the preferred way for to keep your hands clean.
Washing with soap and water: 15 versus 20 seconds
- Wash your hands for more than 15 seconds, not exactly 15 seconds.
- The time it takes is less important than making sure you clean all areas of your hands.
- Alcohol-based hand sanitizers are the preferred way to clean your hands in healthcare facilities.
Which one? Soap and water versus alcohol-based hand sanitizer
An alcohol-based hand sanitizer is the preferred method for cleaning your hands when they are not visibly dirty because it:
- Is more effective at killing potentially deadly germs on hands than soap.
- when moving from soiled to clean activities with the same patient or resident.
- when moving between patients or residents in shared rooms or common areas.
- Improves skin condition with less irritation and dryness than soap and water.
Guidelines for Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings Published 2002
Core Infection Prevention and Control Practices for Safe Healthcare Delivery in All Settings
What CDC is doing
CDC's Clean Hands Count campaign offers posters, factsheets, and brochures for healthcare providers and patients.
Keep reading: Clean Hands Count materials
Healthcare personnel
When and how to practice hand hygiene. Learn more .
New Training and Education Resources available for Healthcare Professionals.
Hand Hygiene in Healthcare Settings Video Series link: Education Courses | Hand Hygiene | CDC
Clean Hands
Having clean hands is one of the best ways to avoid getting sick and prevent the spread of germs to others.
For Everyone
Health care providers.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reported Speech. Greg: "I am cooking dinner Maya.". Maya: "Greg said he was cooking dinner.". So most often, the reported speech is going to be in the past tense, because the original statement, will now be in the past! *We will learn about reporting verbs in part 2 of this lesson, but for now we will just use said/told.
1. say can introduce a statement or follow it. Tom said, "I've just heard the news". or "I've just heard the news",Tom said. Inversion of say and noun subject is possible when say follows the statement. "I've just heard the news", said Tom.
English grammar rules Reported speech Reported statements If we want to report what other people said, thought or felt, we can use the direct or indirect (reported) speech. The direct speech: "I like it," he said. "Irene is late," he thought. "I will pass the exam," she hoped. The indirect (reported) speech: He said he liked it. He thought that ...
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
We would like to show you a description here but the site won't allow us.
L1-2 Reported speech handout. Reported Speech. September 2014. Updated Sept 2017. Kindly contributed by Kathy Crockford. Search for Kathy on www.skillsworkshop.org L1‐L2 Functional English & ESOL writing. For related resources and curriculum links visit the download page for this resource at skillsworkshop.
In reported speech there are a lot of verbs we can use. We can use 'tell' with an indirect object, 'told me', 'told him', 'told us' etc. Or we can use verbs such as 'explain', 'admit' 'mention', 'say' and so on. That's all from me, good luck with your grammar challenge! Grammar Challenge bbclearningenglish.com.
Grammar videos: Reported speech We use reported speech when we want to tell someone what someone said. We usually use a reporting verb (e.g. say, tell, ask, etc.) and then change the tense of what was actually said in direct speech. Exactly. Verbs in the present simple change to the past simple; the present (Direct speech: '
5 Lesson 9. Reported Speech Reporting Statements -Tenses 2. Tenses If the sentence starts in the present, there is no backshift of tenses in reported speech. If the sentence starts in the past, there is often backshift of tenses in reported speech. Backshift You must change the tense if the introductory clause is in a past tense (e. g.
We usually follow the rules below. When we are reporting speech, we are usually talking about the past; therefore, we change the verbs into the past. Direct Speech Reported Speech Simple Present: "I eat pizza." Simple Past: He said (that) he ate pizza.
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please. Instead, say request or say. For example: "Please don't interrupt the event," said the host.
a clause has meaning by itself (often it can be a full sentence) 1. Reporting verbswith the same structure as say: rep. verb + clause. *agree *promise *suggest complain *admit explain mention *claim. Direct Speech Reported Speech. "Why don't you go cycling in the countryside tomorrow," Ellen said.
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later. In the direct speech example you can see the modal verb 'will' being used to ask a question. Notice how in reported speech the modal verb 'will' and the reporting verb 'ask' are both written in the past tense. So, 'will' becomes 'would' and 'ask' becomes 'asked'.
7. He asked me, "Do you understand all the rules?" He asked me if I understood all the rules. 8. She asked me, "When will I see you again?" She asked me when she would see me again. 9. My parents said, "We' going on holiday tomorrow." My parents said that they/we were going on holiday the following day. 10. She said, "Wait until I get back!"
Reported Speech (Reporting verb in past tense) "I eat breakfast at 8 AM.". She said (that) she ate breakfast at 8 AM. "We are going to the beach.". They told me (that) they were going to the beach. "He speaks Spanish fluently.". She said (that) he spoke Spanish fluently. "She cooks delicious meals.".
Reported speech 2. Reported requests and orders. Reported speech exercise. Reported questions - worksheet. Indirect speech - worksheet. Worksheets pdf - print. Grammar worksheets - handouts. Grammar - lessons. Reported speech - grammar notes.
Perfect English Grammar. Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site: ( Click here to read the explanations about reported speech ) Reported Statements: Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here) Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy)
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
RS008 - Reported Questions. RS007 - Reported Speech. RS006 - Reported Speech. RS005 - Reported Speech. RS004 - Reported Speech. RS003 - Reported Speech. RS002 - Reported Speech - Mixed Exercises. RS001 - Reported Speech - Mixed Exercises. Adjective and Adverbs - Downloadable PDF Worksheets for English Language Learners - Intermediate Level (B1)
Note: That is often implied in indirect discourse. It is not mandatory to use it, so it is indicated in brackets in this lesson. Introductory verbs To relate someone's words to both direct and indirect speech, you need an introductory verb. The two most frequent are tell and say, but there are many other possible ones like: ask reply warn
Grammar videos: Reported speech We use reported speech when we want to tell someone what someone said. We usually use a reporting verb (e.g. say, tell, ask, etc.) and then change the tense of what was actually said in direct speech. Exactly. Verbs in the present simple change to the past simple; the present (Direct speech: '
A new document from the Dicastery for the Doctrine of the Faith published on Friday, May 17, has updated the norms for discerning alleged supernatural phenomena. The norms come into force on Sunday, May 19, the feast of Pentecost. The document is preceded by a detailed presentation by Cardinal Víctor Manuel Fernández, Prefect of the Dicastery ...
Wet your hands with warm water. Use liquid soap if possible. Apply a nickel- or quarter-sized amount of soap to your hands. Rub your hands together until the soap forms a lather and then rub all over the top of your hands, in between your fingers and the area around and under the fingernails. Continue rubbing your hands for at least 15 seconds.