- Sample Business Plans
- Education & Training

School Business Plan
High demand and a recurring revenue model make starting a school business a lucrative and rewarding profession.
Anyone can start a new business, but you need a detailed business plan when it comes to raising funding, applying for loans, and scaling it like a pro!
Need help writing a business plan for your school business? You’re at the right place. Our school business plan template will help you get started.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our free school business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write A School Business Plan?
Writing a school business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and summarizes each section of your plan.
Here are a few key components to include in your executive summary:
- Introduce your Business: Start your executive summary by briefly introducing your business to your readers.This section may include the name of your school business, its location, when it was founded, the type of school business (E.g., private schools, charter schools, virtual schools), etc.
- Market Opportunity: Summarize your market research, including market size, growth potential, and marketing trends. Highlight the opportunities in the market and how your business will fit in to fill the gap.
- Educational programs & services: Highlight the school services you offer your clients. The USPs and differentiators you offer are always a plus.For instance, you may include education programs, extracurricular activities, special education services, etc as your services.
- Marketing & Sales Strategies: Outline your sales and marketing strategies—what marketing platforms you use, how you plan on acquiring students, etc.
- Financial Highlights: Briefly summarize your financial projections for the initial years of business operations. Include any capital or investment requirements, associated startup costs, projected revenues, and profit forecasts.
- Call to Action: Summarize your executive summary section with a clear CTA, for example, inviting angel investors to discuss the potential business investment.
Ensure your executive summary is clear, concise, easy to understand, and jargon-free.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
The business overview section of your business plan offers detailed information about your business. The details you add will depend on how important they are to your business. Yet, business name, location, business history, and future goals are some of the foundational elements you must consider adding to this section:
- Public schools
- Private schools
- Charter schools
- Magnet schools
- Virtual or online schools
- Boarding schools
- International schools
- Religious schools
- Describe the legal structure of your school, whether it is a sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, or others.
- Explain where your business is located and why you selected the place.
- Owners: List the names of your school’s founders or owners. Describe what shares they own and their responsibilities for efficiently managing the business.
- Mission Statement: Summarize your business’ objective, core principles, and values in your mission statement. This statement needs to be memorable, clear, and brief.
This section should provide a thorough understanding of your business, its history, and its future plans. Keep this section engaging, precise, and to the point.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should offer a thorough understanding of the industry with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. You should include the following components in this section.
- Target market: Start this section by describing your target market. Define your ideal customer and explain what types of services they prefer. Creating a buyer persona will help you easily define your target market to your readers.For instance, families looking for additional education or extracurricular activities are the ideal market for private schools generally.
- Market size and growth potential: Describe your market size and growth potential and whether you will target a niche or a much broader market.For instance, the US education industry is to be $3.12 trillion by 2030, so it is crucial to define the segment of your target market and its growth potential.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify and analyze your direct and indirect competitors. Identify their strengths and weaknesses, and describe what differentiates your school from them. Point out how you have a competitive edge in the market.
- Market Trends: Analyze emerging trends in the industry, such as technology disruptions, changes in customer behavior or preferences, etc. Explain how your business will cope with all the trends.For instance, personalized learning or STEM education is getting important; explain how you plan on dealing with this potential growth opportunity.
- Regulatory Environment: List regulations and licensing requirements that may affect your school business, such as education laws & regulations, government accreditation, teacher certificate & licensing, health & safety regulations, etc.
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your school business plan::
- Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data.
- Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible.
- Illustrate your points with charts and graphs.
- Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind.
4. Products And Services
The product and services section should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to students. To write this section should include the following:
- Education programs
- Extracurricular activities
- Counseling & Guidance
- Special education services
- Transportation services
- Food services
- Testing and assessments
- Describe specialized programs: Highlight any specialized programs or services your school provides in this section. Extracurricular activities, artistic initiatives, sports teams, STEM efforts, language immersion programs, and advanced placement courses may fall under this category.
- Student leadership programs: If your school has a vibrant student leadership program that encourages students to grow as leaders, participate in volunteer work in the community, and actively contribute to the improvement, then mention it here.
- Additional Services: Mention if your school business offers any additional services. You may include services like, after-school programs, school transportation, food services, parent education & involvement, etc.
In short, this section of your school plan must be informative, precise, and client-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Writing the sales and marketing strategies section means a list of strategies you will use to attract and retain your clients. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Define your business’s USPs depending on the market you serve, the equipment you use, and the unique services you provide. Identifying USPs will help you plan your marketing strategies.For example, specialized programs, educational philosophies, experienced faculty, or a strong track record of academic achievements could be some of the great USPs for school business.
- Pricing Strategy: Describe your pricing strategy—how you plan to price your services and stay competitive in the local market. You can mention any discounts you plan on offering to attract new students.
- Marketing Strategies: Discuss your marketing strategies to market your services. You may include some of these marketing strategies in your business plan—social media marketing, Google ads, brochures, content marketing, and print marketing.
- Sales Strategies: Outline the strategies you’ll implement to maximize your sales. Your sales strategies may include targeted marketing, personalized sales approach, referral programs, conversion strategies, etc.
- Customer Retention: Describe your customer retention strategies and how you plan to execute them. For instance excellent services, alumni engagement, parental engagement, etc.
Overall, this section of your school business plan should focus on customer acquisition and retention.
Have a specific, realistic, and data-driven approach while planning sales and marketing strategies for your school business, and be prepared to adapt or make strategic changes in your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section of your business plan should outline the processes and procedures involved in your business operations, such as staffing requirements and operational processes. Here are a few components to add to your operations plan:
- Staffing & Training: Mention your business’s staffing requirements, including the number of employees or teachers needed. Include their qualifications, the training required, and the duties they will perform.
- Operational Process: Outline the processes and procedures you will use to run your school business. Your operational processes may include enrollment process, staffing & human resources, classroom management, finance & budgeting, etc.
- Equipment & Software: Include the list of equipment and software required for school, such as whiteboards & projectors, student information systems, learning management systems, communication & collaboration tools, etc.Explain how these technologies help you maintain quality standards and improve the efficiency of your business operations.
Adding these components to your operations plan will help you lay out your business operations, which will eventually help you manage your business effectively.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of your school business’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
- Founders/CEO: Mention the founders and CEO of your school, and describe their roles and responsibilities in successfully running the business.
- Key managers: Introduce your management and key members of your team, and explain their roles and responsibilities.It should include, key executives(e.g. principal), senior management, and other department managers (e.g. operations manager, admission manager, facilities manager) involved in the school business operations, including their education, professional background, and any relevant experience in the industry.
- Organizational structure: Explain the organizational structure of your management team. Include the reporting line and decision-making hierarchy.
- Compensation Plan: Describe your compensation plan for the management and staff. Include their salaries, incentives, and other benefits.
- Advisors/Consultants: Mentioning advisors or consultants in your business plans adds credibility to your business idea.So, if you have any advisors or consultants, include them with their names and brief information consisting of roles and years of experience.
This section should describe the key personnel for your school, highlighting how you have the perfect team to succeed.
8. Financial Plan
Your financial plan section should provide a summary of your business’s financial projections for the first few years. Here are some key elements to include in your financial plan:
- Profit & loss statement: Describe details such as projected revenue, operational costs, and service costs in your projected profit and loss statement . Make sure to include your business’s expected net profit or loss.
- Cash flow statement: The cash flow for the first few years of your operation should be estimated and described in this section. This may include billing invoices, payment receipts, loan payments, and any other cash flow statements.
- Balance Sheet : Create a projected balance sheet documenting your school business’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Break-even point: Determine and mention your business’s break-even point—the point at which your business costs and revenue will be equal.This exercise will help you understand how much revenue you need to generate to sustain or be profitable.
- Financing Needs: Calculate costs associated with starting a school business, and estimate your financing needs and how much capital you need to raise to operate your business. Be specific about your short-term and long-term financing requirements, such as investment capital or loans.
Be realistic with your financial projections, and make sure you offer relevant information and evidence to support your estimates.
9. Appendix
The appendix section of your plan should include any additional information supporting your business plan’s main content, such as market research, legal documentation, financial statements, and other relevant information.
- Add a table of contents for the appendix section to help readers easily find specific information or sections.
- In addition to your financial statements, provide additional financial documents like tax returns, a list of assets within the business, credit history, and more. These statements must be the latest and offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
- Provide data derived from market research, including stats about the industry, user demographics, and industry trends.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Include any additional documentation related to your business plan, such as product brochures, marketing materials, operational procedures, etc.
Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your school business plan should only include relevant and important information supporting your plan’s main content.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This sample school business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful school plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our school business plan pdf .
Related Posts
After-School Program Business Plan
Preschool Business Plan
400+ Business Plan Template Example
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
Business Plan Cover Page Design Idea
How to Create Business Plan Outline
Frequently asked questions, why do you need a school business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful school business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your school.
How to get funding for your school business?
There are several ways to get funding for your school business, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are:
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting a lot of people to invest in your business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought startup options.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
Where to find business plan writers for your school business?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and ideas better than you, so we recommend you write your school business plan and outline your vision as you have in your mind.
What is the easiest way to write your school business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any school business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software .
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

School Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
School Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your school business plan.
We have helped over 5,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their schools.
Sample Private School Business Plan
Below is a school business plan template to help you create each section of your own education business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Southside Academy, located in St. Paul, Minnesota, is a private school that has been providing quality education to the community’s school children since 2017. Southside Academy teaches elementary, middle school, and high school students in a wide range of subjects including mathematics, science, and history. We aim to provide a welcoming and inviting environment where every student can reach their highest potential.
We promote academic, artistic, and athletic excellence in a close-knit learning environment, with a challenging curriculum that cultivates intellectual curiosity. Furthermore, we offer a low teacher-to-child ratio, where teachers can build close connections with their students as they help them excel. We develop confident, continual learners by establishing behavioral supports and the social culture needed for students to achieve social, emotional, and academic success.
Service Offering
Southside Academy offers a premium private education at an affordable tuition fee. We provide a challenging education where students can explore their true potential and a safe space where they can freely discover and express themselves. Our students range from 1st grade to 12th grade and we teach a wide variety of subjects including:
- Basic Mathematics
- Physical Education
Customer Focus
Southside Academy primarily serves families within a 5-mile radius of the school’s location. The area is home to thousands of middle and upper-class families looking for high-quality education for their children. Before the school was built, the area was underserved and many children had to travel far to attend quality private schools.
Management Team
Southside Academy’s founder is Mike Brown who has been working as a teacher for more than 20 years. Mike has taught at several public schools in the region but saw a great demand for private education. He noticed that the current location of the school was underserved and set out to create a school to serve this population. Mike Brown has successfully led Southside Academy as its principal since the school’s inception and will continue to do so for the foreseeable future.
Mike Brown is supported by a team that has experience teaching students, managing finances, and running businesses. Specifically, our team has solid experience in being effective teachers, connecting to different types of students, and achieving key goals.
Success Factors
Southside Academy is able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Location: Southside Academy’s location is near the center of town, giving members of our community easy access for parents and their children.
- Passionate and Skillful Teachers: Southside Academy hires teachers with strong academic backgrounds who are skillful in handling all types of children.
- Low teacher-to-student ratio: We provide a low teacher-to-student ratio so that every student gets personal attention from teachers to reach their highest potential.
- Affordable, quality education: Most of the schools in the area offer their services at a very expensive price. Our fees will be moderately low so that good education is accessible to all families.
Financial Highlights
Southside Academy is currently seeking additional donations of $600,000 in order to fulfill our mission. The breakdown of the funding may be seen below:
- Salaries: $200,000
- School Materials (books, toys, desks, chairs, etc): $180,000
- Administrative Expenses: $120,000 to pay for lease costs, ongoing operational expenses, and marketing.
- Working capital: $100,000
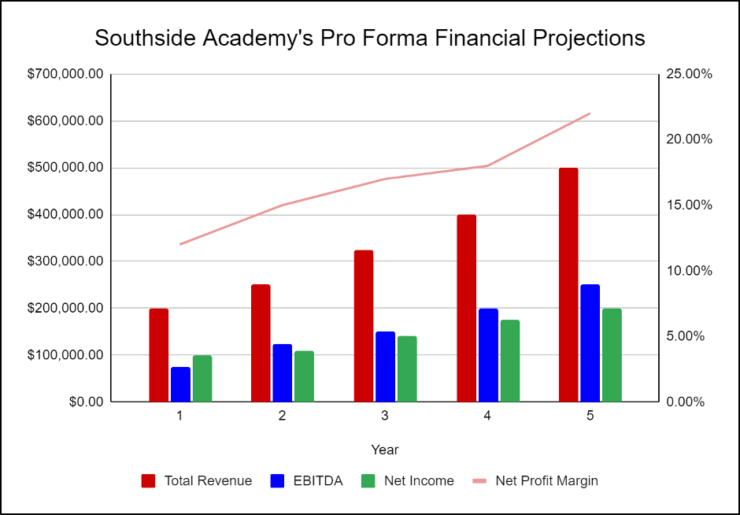
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Southside Academy.
Company Overview
Who is southside academy, southside academy’s history.
Southside Academy started as an idea from a group of school teachers, including Mike Brown. The teachers were university pals who are passionate about teaching and children. They have seen the gaps in education in St. Paul, Minnesota, and wanted to create a school that elevates the academic environment for the children of this area.
Their plans to build a school started in 2015, but it was only until April 2016 that they finally completed all the paperwork and met the legal requirements. Since then, Southside Academy has achieved the following milestones:
- Found a location and built the school
- Developed the school’s name, logo, and website
- Determined curriculum
- Hired teachers and other key employees
Southside Academy’s Services
Industry analysis.
Education is an essential foundation for a thriving society. It’s more important than ever before that every child has access to affordable, high-quality education. While public schools are an essential option for many low-income families, the education provided by private schools often results in higher test scores and more students moving on to top-tier universities.
The private school industry has experienced steady growth in the past five years. The key industry drivers are economic growth, the rise in numbers of K-12 students, an increase in the number of families with both parents working, and government initiatives to support education.
According to Polaris Market Research, this growth is expected to continue with a forecasted compound annual growth rate of 6.6% from now until 2030. This shows that Southside Academy has great potential to keep growing and expanding. We will have ample opportunities to grow our curriculum and offer services to students that help them reach their highest potential.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Southside Academy serves the families and children of St. Paul, Minnesota. The area is mostly populated by young couples and new families that have disposable income and can pay a premium for their children’s education.
The precise demographics of the town in which our location resides are as follows:
| Total | Percent | |
|---|---|---|
| Total population | 1,680,988 | 100% |
| Male | 838,675 | 49.9% |
| Female | 842,313 | 50.1% |
| 20 to 24 years | 114,872 | 6.8% |
| 25 to 34 years | 273,588 | 16.3% |
| 35 to 44 years | 235,946 | 14.0% |
| 45 to 54 years | 210,256 | 12.5% |
| 55 to 59 years | 105,057 | 6.2% |
| 60 to 64 years | 87,484 | 5.2% |
| 65 to 74 years | 116,878 | 7.0% |
| 75 to 84 years | 52,524 | 3.1% |
Customer Segmentation
We primarily target the following three customer segments:
- Young children
- Young couples
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Southside Academy faces competition from other schools with similar profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Waters Independent School
Founded in 1968, Waters Independent School is a non-profit and tax-exempt independent school system. The school is governed by an independent Board of Trustees and offers preschool through eighth-grade programs. WIS is accredited by the state’s Council of Independent Schools (FCIS).
Waters Independent School has small class sizes with low student-to-teacher ratios. Further, WIS’ Programs include a strong academic foundation coupled with programs in the arts, physical education, media/technology, foreign language, and extracurricular areas.
Hill Preparatory School
Founded in 1923, Hill Preparatory School is a private, non-sectarian, coeducational, college preparatory day school. It offers PK-12 programs in a safe, student-centered environment. HPS supports its students through the challenges of the school year with one-on-one attention from dedicated faculty, robust services like The Learning Center and the College Center, and the most advanced educational technology. The campus spans 28 acres and has a new 60,000+ square foot facility.
Future Leaders Preparatory School
Founded in 1968, Future Leaders Prep is a private school for PreK3-8th grade. FLPS offers preschool, elementary school, and middle school programs and offers the International Baccalaureate program of study for all students. Teachers are endorsed in gifted education through a master’s level grant with [local University]’s College of Education Gifted Program. In addition to the school, Future Leaders offers community programs such as music, dance, art, and theater lessons through the Community School of the Arts, youth sports in the Community School for Sports, and the 7-week summer camp.
Competitive Advantage
There are many schools in St. Paul, Minnesota but none of them provides the same quality of education that Southside Academy provides, specifically the following:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
The Southside Academy brand will focus on the school’s unique value proposition:
- Providing premium education at an affordable price
- Providing a supportive and challenging place for children to learn
- Giving parents the assurance that their children will reach their full potential
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Southside Academy is as follows:
Social Media
Southside Academy will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. The school will utilize social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media platforms. It will use targeted marketing to appeal to the target demographics.
Publications
The school will place print advertisements in key local publications, including newspapers, area magazines, and business newsletters. Additionally, Southside Academy will print brochures and place them in specific locations frequented by target individuals.
Website/SEO
Southside Academy will invest heavily in developing a professional website that displays all of the features and benefits of Southside Academy. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the school’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Direct Mail
Southside Academy will blanket neighborhoods with direct mail pieces. These pieces will provide general information on Southside Academy and incentives to enroll.
Southside Academy prices its tuition at a moderate price so our students and their families feel they are getting great value when choosing our school.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Southside Academy.
Operation Functions:
- Mike Brown is the school Principal. He manages the teachers, directs the direction of education, and serves as the head of the school.
- Mike is joined by Amanda Johnson who acts as the Administrative Assistant for the school. She helps Mike with the operations of the school as well as the marketing and administrative functions.
- Mike has hired an extensive team of highly qualified educators. Together, they teach dozens of subjects, including biology, chemistry, social studies, and mathematics. Every teacher that works for Southside Academy is passionate about education and pushing their students to reach their highest potential.
Milestones:
Southside Academy expects to achieve the following milestones in the following six months:
- 3/202X Kickoff of promotional campaign to attract new students
- 4/202X Start donation campaign
- 5/202X Hire new teachers for the upcoming year
- 6/202X Achieve donation/funding goal
- 7/202X Finalize list of incoming students for next year
- 8/202X Start next school year
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Southside Academy’s revenues come from student tuition fees and donations from both individuals and corporations.
The major costs for the company will be staffing, marketing expenses, location maintenance, equipment, and materials.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Southside Academy is currently seeking additional fundraising and capital of $600,000 in order to fulfill our mission. The breakdown of the funding may be seen below:
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and to pay off the startup business loan.
- Year 1: 200
- Year 2: 300
- Year 3: 400
- Year 4: 500
- Year 5: 600
- Tuition rate per year: $10,000
Financial Statements
Income statement.
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |
Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
School Business Plan FAQs
What is a school business plan.
A school business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your school business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your School business plan using our School Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of School Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of school businesses, some examples include: private K-12 school, charter school, virtual schools, independent schools, primary school, secondary education, or preschool.
How Do You Get Funding for Your School Business Plan?
School businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a School Business?
Starting a school business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A School Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed school business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your school business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your school business is in compliance with local laws.
3, Register Your School Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your school business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your school business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary School Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your school business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your school business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful school business:
- How to Start a School
Other Helpful Business Plan Templates
Nonprofit Business Plan Template

Item added to your cart
How to write a business plan for your private school project.

Starting a private school is a great way to provide students with an alternative education option that is tailored to their individual needs and interests.
It also allows for greater autonomy and flexibility in curriculum design and implementation, allowing for more personalized learning experiences.
But, before that, you need a business plan.
Creating a business plan before beginning a project is essential for success. It helps to identify potential risks and opportunities, as well as providing a roadmap for the project.
In short, a good business plan will help ensure the profitability of your private school project .
What should be covered when creating a business plan for a private school? How can it be effectively planned? What are the essential financial measures to include? What steps should I take to ensure an efficient process when writing a business plan?
Good news, you can find all the answers to these questions in the forthcoming article!
One last thing: you can avoid starting your business plan from scratch.
Feel free to download our professional business plan for a private school and tailor it to suit your project.

Designing a business plan for a private school
Is a business plan recommended for your private school project.
Yes, you should create a business plan for your private school project.
Crafting a well-structured business plan will help you to:
- gain knowledge of the private school market
- keep up with the industry's changing trends
- discover what makes a private school competitive
- understand parents' educational preferences and expectations
- come up with a winning value proposition for your independent educational institution
- examine competitor market share
- find solid competitive advantages for your private school project
- find a business model that will lead to a positive bottom line
- implement a winning strategy on the short and the long-term
- assess potential risks involved in starting a private school, such as regulatory compliance, student safety, and educational quality
Our team has created a business plan for a private school that is designed to make it easier for you to achieve all the elements listed.
How to outline a business plan for a private school?
If done well, your business plan will be a full package of content, metrics and financial data. It must be presented in a structured format, to make easy to read and digest.
When we built our business plan for a private school , we made sure to structure it propertly.
You'll come across 5 sections (Opportunity, Project, Market Research, Strategy and Finances).
1. Market Opportunity
The section number one is called "Market Opportunity".
Access relevant data and metrics for the private school project, assisting you in analyzing the opportunities and challenges within the education and schooling sector.
The data here is always fresh; we update it twice a year.
2. Project Presentation
The "Project" section is where you outline your private school project. You can describe the educational philosophy, curriculum offerings, extracurricular activities, facilities, teaching staff qualifications, admission process, and the unique value proposition that sets your school apart in providing quality education.
Remember to introduce yourself at the end of this section.
Discuss your passion for education, your vision for the private school, and how you plan to create an enriching and nurturing learning environment for students. Highlight your qualified faculty, your innovative curriculum, and your dedication to providing personalized attention and holistic development opportunities through your private school project.
We wrote some content in our business plan. Change it to fit your concept.
3. Market Research
The next item on the list is the "Market Research" section.
The purpose of this section is to introduce the market segments for your private school project.
It includes a competition study, outlining other private schools in the area. Your school's unique educational programs and competitive advantages are also highlighted. A customized SWOT analysis is included.
4. Strategy
Within the "Strategy" section, a detailed plan spanning three years is presented, highlighting the initiatives and actions necessary to make your private school project highly profitable.
Additionally, you'll find a marketing strategy, a plan to manage risks, and a completed Business Model Canvas, tailored to a private school, in this section.
5. Finances
In the end, the section labeled "Finances" allows you to showcase the financial details and values of your project.

How to elaborate the Executive Summary for a private school?
The Executive Summary serves as a compact introduction to the business plan of your private school project.
Don't go beyond 2 pages; ensure you include only the critical information.
This document is designed to make the reader excited about your business plan.
In the Executive Summary of your private school project, answer these questions: what is your private school project about? who is your target market? are there other private schools in the area? what sets your school apart from them? how much funding do you require?
How to do the market analysis for a private school?
The market study of your private school project helps you understand external factors such as parent preferences for education, competition within the private school sector, and emerging trends in educational practices.
By conducting an extensive market study, a private school can understand parent and student needs, offer quality education and comprehensive programs, optimize pricing strategies, and execute targeted marketing campaigns, ultimately leading to a larger student base, increased enrollment, and a prominent position in the private education sector.
Here is what what we've put in the "Market Research" section of our business plan for a private school :
- key insights and trends in private schools, including private school enrollment rates, education quality, and the impact of specialized private school programs
- a list of potential market segments for a private school
- the competitive review
- the competitive advantages to target for a private school

The key points of the business plan for a private school
What's the business model of a private school, business model of a private school.
a private school's business model revolves around providing education services to students in a private setting. Revenue is generated through tuition fees, potentially offering additional services such as extracurricular activities or specialized programs.
The business model focuses on offering a high-quality and comprehensive curriculum, hiring qualified educators, providing modern facilities and resources, marketing to target parents and students, and building strong relationships with parents and the local community.
Success depends on establishing a positive reputation for academic excellence, attracting and retaining students, meeting regulatory requirements, effective marketing strategies, and delivering a holistic and enriching educational experience.
Business model ≠ Business plan
Avoid confusing "business plan" with "business model."
A business model is a framework that outlines how a company creates value, delivers products or services, and generates revenue.
In a business plan, you employ the Business Model Canvas as a practical tool to outline the key aspects of your business model.
Rest assured, there is a Business Model Canvas (already completed) in our business plan for a private school .
How do you identify the market segments of a private school?
Segmenting the market for your private school project involves dividing your potential students and families into different groups based on their educational needs, preferences, and demographics.
These categories may include factors such as grade levels, curriculum types, extracurricular programs, or families seeking specific educational approaches (e.g., Montessori, STEM, arts-focused).
By segmenting your market, you can offer a private school experience that caters to each segment's specific requirements. For example, you might provide elementary, middle, and high school programs for students of different grade levels, offer a comprehensive curriculum that encompasses a range of subjects and learning areas, specialize in specific educational approaches or philosophies such as Montessori, STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics), or an arts-focused curriculum, or focus on offering a variety of extracurricular programs and enrichment activities that align with the interests and talents of students.
Market segmentation allows you to effectively target your marketing efforts, communicate the unique benefits of your private school, and provide a nurturing and stimulating educational environment that meets the unique needs and preferences of each student segment and their families.
In the business plan for a private school , you will find a comprehensive market segmentation that will help you identify your potential customers.
How to conduct a competitor analysis for a private school?
Without surprise, you won't be the only private school project in your area. There are other educational initiatives working towards establishing quality private schools.
Develop a solid business plan by conducting an extensive competitor analysis that evaluates their strengths and weaknesses.
Address their weaknesses (such as inadequate curriculum design, lack of extracurricular activities, or poor student support services).
Why is it crucial to notice these aspects? Because these weaknesses can impact the success of private school projects.
By focusing on these areas, you can offer a comprehensive and well-rounded education curriculum, provide qualified and dedicated teaching staff, and create a nurturing and inclusive school environment, positioning your private school project as a preferred choice for parents and students seeking quality education and holistic development.
It's what we call competitive advantages—building them is essential for a standout business.
Here are some examples of competitive advantages for a high school: experienced and dedicated teaching staff, diverse educational programs, supportive learning environment.
How to draft a SWOT analysis for a high school?
A SWOT analysis can help identify potential opportunities and threats that can affect the success of the private school project.
As you can guess, there is indeed a completed and editable SWOT matrix in our business plan for a private school
The strengths for a private school
S stands for Strengths in SWOT, representing the project's valuable strengths or advantages.
For a private school, possible strengths could include a highly qualified teaching staff, a rigorous academic curriculum, a diverse student body, and a strong emphasis on extracurricular activities.
The weaknesses for a private school
The "W" symbolizes Weaknesses, indicating the specific areas or aspects of the project that require attention.
For a private school, potential weaknesses could include inadequate funding, lack of qualified teachers, insufficient resources, and limited parental involvement.
The opportunities for a private school
The "O" in SWOT stands for Opportunities, which are positive external factors that can help the project succeed.
In the case of a private school, potential opportunities include creating an innovative curriculum, increasing student engagement, expanding the school's reach through technology, and developing community partnerships.
The threats for a private school
When we refer to the "T" in SWOT, we're referring to Threats, which are the external risks or detrimental factors that can impact the project's performance.
How to develop a marketing plan for a high school?
A marketing strategy is a necessary component of a business plan as it describes how a business will engage customers and generate sales.
A well-crafted marketing strategy will attract parents seeking quality education for their children to your private school project.
Parents won't enroll their children in your private school project without effective marketing; showcasing the quality of education, extracurricular activities, and nurturing environment is crucial.
Are you implementing effective marketing strategies for your private school project? Consider hosting open houses or informational sessions for parents, showcasing your school's unique educational programs, and utilizing targeted advertising campaigns in local communities.
Don't worry if you have no clue about marketing and communication.
How to build a solid financial plan for a high school?
A successful business plan must include detailed financial information, such as income and expense projections, cash flow statements, and a break-even analysis.
In the process of developing your business plan, you'll need to determine the expected revenue for your private school project.
The revenue forecast should be based on reliable information and reflect current market conditions.
Our financial plan for a private school is straightforward and equipped with automated checks, enabling you to validate and adjust your assumptions easily. This way, we make sure you're building solid financial projections.
It goes without saying that you'll have to develop a provisional budget for your private school project. Don't overlook any expense. By the way, we've listed them all in our financial plan!
The break-even analysis is central in the financial plan as it will tell you whether your private school project will be profitable or not.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.
How to Write Schools Business Plan? Guide & Template
In today’s dynamic educational landscape, running a school isn’t just about providing quality education; it’s also about managing resources efficiently and ensuring sustainable growth. A well-thought-out business plan is the cornerstone of any successful educational institution. In this article, we’ll delve into the nuances of creating an effective schools business plan, exploring its importance, the funding avenues available, and the advantages it offers.
Download Now => Free School Business Plan Template
What is a Schools Business Plan?
A schools business plan is a strategic document outlining the objectives, operational structure, financial forecasts, and growth strategies for an educational institution. It serves as a roadmap, guiding administrators, investors, and stakeholders on the path towards achieving educational excellence and financial sustainability.
Why Do You Need a Business Plan for a Schools?
Strategic Direction: A business plan helps define the school’s mission, vision, and core values, providing clarity on its purpose and direction. Financial Planning: It facilitates financial forecasting and budgeting, ensuring prudent resource allocation and long-term financial stability. Risk Management: By identifying potential risks and challenges, a business plan enables proactive mitigation strategies, safeguarding the institution’s interests. Accountability: It fosters accountability among stakeholders by clearly articulating roles, responsibilities, and performance metrics.
Source of Funding for Schools Business
Funding a schools business can be sourced from various avenues, including:
- Government Grants: Funding allocated by governmental bodies for education.
- Private Investors: Individuals or organizations investing in the school.
- Tuition Fees: Revenue generated from student tuition and fees.
- Fundraising Events: Organizing events to raise funds from the community.
- Corporate Sponsorship: Partnering with businesses for financial support.
How to Write a Schools Business Plan?
Creating a schools business plan involves the following steps:
- Executive Summary: Provide a concise overview of the institution’s mission, objectives, and key strategies.
- Market Analysis: Evaluate the competitive landscape, target demographics, and demand for educational services.
- Operational Plan: Outline the organizational structure, staffing requirements, and day-to-day operations.
- Financial Projections: Prepare detailed financial forecasts, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
- Marketing Strategy: Define promotional tactics to attract students, engage parents, and enhance the school’s reputation.
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks and develop contingency plans to mitigate them.
Advantages of Starting a Schools Business
- Fulfillment of Educational Needs: Contributing to the community by providing quality education and fostering intellectual growth.
- Financial Sustainability: Generating revenue streams that support the institution’s growth and development.
- Autonomy and Flexibility: Having the freedom to innovate and adapt to changing educational trends and student needs.
- Positive Impact: Making a difference in the lives of students, families, and society at large by nurturing future leaders and citizens.
In the competitive landscape of education, a well-crafted schools business plan is indispensable for achieving sustainable growth and excellence. By outlining clear objectives, securing funding, and implementing effective strategies, educational institutions can not only thrive but also make a lasting impact on the community and future generations.
Schools Business Plan FAQs
How do I write a business plan for a private school?
To write a business plan for a private school, include an overview of your educational philosophy and curriculum, student demographic and market projections, competitor landscape and how you’ll differentiate, multi-year financial forecasts and capital requirements, ownership structure, leadership team and governance plans.
How do I write a business proposal for school?
Key elements to cover in a school business proposal are the student needs your model addresses, specifics of your academic program and curriculum, introductions to school leadership and operations team, projected expenses and revenue tied to student enrollment forecasts, key performance indicators to evaluate success.
How do you write an academic business plan?
When developing an academic-focused business plan include your credentials, educational programming details and research support, target student profiles tied to curriculum, how instruction will be delivered and assessed for quality, staffing requirements for growth, and enrollment expansion plans driving budget forecasts.
How long does it take to write a school business plan?
A thorough school business plan containing all key components like market sizing, competitor benchmarking, leadership overviews, detailed financial models factoring expenses like staffing, facilities and materials can typically take between 50–200 hours to thoughtfully write and refine.

Written by Ivan Smith
Hello, I'm Ivan Smith, a graduate with a Bachelor of Business Administration in Marketing. Currently, I'm actively engaged in practicing business plan writing.
Text to speech

School Business Plan Template [Updated 2024]
School Business Plan
If you want to start a school or expand your current school, you need a business plan.
The following school business plan template gives you the key elements to include in a winning business plan. In addition to this template, a well-crafted plan will include market research to help you better understand the school industry, market trends, your competitive advantage and your target market. It will also help you craft a smart marketing strategy and a strong financial plan.
You can download our business plan template (including a full, customizable financial model) to your computer here.
Below are links to each of the key components of an education business plan to help you launch a successful school. This can be used for a variety of school business plans, including a private school business plan, a charter school, public schools, independent schools, virtual schools, primary or secondary education.
- Executive Summary – The executive summary provides an overview of your business opportunity and summarizes the business plan.
- Company Overview – The company overview includes information about your business concept, academic and extracurricular activities offered, and legal structure.
- Industry Analysis – The industry analysis includes market research that supports your business and provides insights into market trends and the education industry.
- Customer Analysis – The customer analysis provides an overview of your target customers.
- Competitive Analysis – The competitive analysis should identify your direct and indirect competitors and highlight your competitive advantage.
- Marketing Plan – The marketing plan includes your marketing strategy, pricing strategy, examples of marketing materials, and search engine optimization plan.
- Operations Plan – The operations plan includes information on your school’s day-to-day operations and processes.
- Management Team – The management team section includes a profile of the organizational structure, school leaders, their experience and responsibilities.
- Financial Plan – The financial plan includes financial projections, a cash flow statement, profit and loss statement and balance sheet.
Download our business plan template (including a full financial projections model and financial statements).
Comments are closed.
School Business Plan Home I. Executive Summary II. Company Overview III. Industry Analysis IV. Customer Analysis V. Competitive Analysis VI. Marketing Plan VII. Operations Plan VIII. Management Team IX. Financial Plan

Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

Ultimate School Business Plan Template: Plan for Success

Craft your school business plan with a comprehensive template that sets a strong foundation for success. Ensure your educational venture thrives with strategic planning and clear objectives.
Creating a successful school business plan is a critical step in establishing a flourishing educational institution. It serves as a roadmap guiding your school towards its goals, helping to secure funding, attract key staff, and set student achievement targets. A well-crafted business plan outlines the vision, mission, and the actionable steps you need to take to address the challenges of the evolving educational landscape.
It’s vital to articulate your unique value proposition, analyze your intended market, and lay out a realistic financial forecast. With precise planning and attention to detail, your school’s business plan can inspire confidence among stakeholders and serve as a beacon for your educational aspirations. By capably anticipating future needs and demonstrating a deep understanding of your school’s potential, your business plan becomes an indispensable tool in your school’s journey towards excellence.
The Essentials Of A School Business Plan
Starting an educational institution requires a solid foundation, and that foundation is your school business plan . Like a blueprint guiding a builder, this plan lights the path for a school’s success. From defining goals to allocating resources, every aspect needs careful consideration. Here’s what you need to know about crafting a robust business plan for your school.
Core Components
An effective school business plan includes several core elements:
- Executive Summary: An overview of your school’s aim, model, and unique offerings.
- Market Analysis : Insight into the educational landscape, potential competition, and target audience.
- Organizational Structure: Outlines management, staffing, and operational logistics.
- Services or Programs: Detailed curriculum and extracurricular activities offered.
- Marketing Plan: Strategies to attract students and build your school’s reputation.
- Financial Projection : Expected income, costs, and forecasts for sustainability and growth.
Importance Of A Clear Mission Statement
Your school’s mission statement is its heartbeat. It clarifies your school’s purpose and guides decisions. A powerful mission statement is clear, concise, and reflects your school’s core values. It unifies your team and resonates with families, giving your school a distinct identity.
| Tips for a Powerful Mission Statement | |
|---|---|
| State precisely what your school aims to achieve. | |
| Create an emotional connection with your audience. | |
| Set achievable goals that reflect your capabilities. | |
| Keep it short to ensure it’s memorable and effective. | |
Market Analysis And Positioning
A sound business plan for a school is incomplete without a detailed market analysis and strategic positioning. This crucial section sheds light on the environment your school will operate in. Understanding your target market and the competitive landscape are steps that cannot be overlooked. A deep dive into these areas will guide your school’s approach to capturing market share and securing a unique place in the educational landscape.
Identifying Your Target Market
Knowing who your school is designed to serve is the first step to success. Consider the following to accurately define your audience:
- Demographics: Age range, socioeconomic status, location
- Educational needs: Special programs, curricular focus
- Parental preferences: School values, extracurricular activities
Use surveys, community data, and trend analysis to gather information . This data forms the backbone of your marketing strategy.
Competitive Landscape Evaluation
Understanding the competition is as important as knowing your students. Address these aspects to assess your competition:
| Local Public School | No tuition, established community presence | Limited resources, large class sizes | 45% |
| Nearby Private Academy | Strong academic record, exclusive offerings | Higher tuition, less diverse student body | 20% |
A thorough analysis helps identify gaps in the market and areas for potential growth . Your school can carve a niche by addressing these opportunities.
Curriculum Design And Educational Programs
Crafting a curriculum is like drawing a map for a journey to knowledge. It outlines every step of the learning path. Schools must create programs that engage students, meet standards, and foster skills for the future. A business plan for a school is incomplete without a well-planned curriculum.
Developing Your Educational Model
The heart of a school lies in its educational model . This model guides the teaching and learning processes. It must reflect the school’s values and objectives. Elements include teaching styles, assessment methods, and learning outcomes.
Your model should address various learning styles , ensuring no student falls behind. Consider these aspects:
- Project-based learning
- Technology integration
- Collaborative activities
- Individual assessments
Flexibility is crucial in adapting to educational trends and student needs.
Consider the skills that employers seek. Are students ready for tomorrow’s challenges?
Specialty Programs And Niche Education
Specialty programs set a school apart. They draw interest and add value to the education provided. Focus on niches that cater to specific interests or industries.
| Program Type | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| STEM | Builds critical thinking and problem-solving skills | Robotics, coding, environmental science |
| Arts | Enhances creativity and self-expression | Creative writing, theater, music production |
| Language Immersion | Improves communication and cultural awareness | Spanish immersion, Mandarin courses |
Understand the community when selecting specialty programs. Are there local industries that could benefit from specific skills?
Partner with businesses and universities for real-world experiences. This adds great value to educational programs.
Operational Strategies And Management Structure
A well-constructed school business plan relies on robust Operational Strategies and Management Structure . This section is the blueprint for day-to-day operations, shaping how the school functions. It ensures the institution runs smoothly, addresses student needs effectively, and meets educational standards.
Defining Organizational Roles
Clearly defined roles are the backbone of any thriving educational institution. They streamline responsibilities, enhance accountability, and foster a strong chain of command. Below is a brief look at key positions in a school’s organizational structure.
| Overall school leadership, policy implementation, staff supervision | |
| Assist the principal, discipline, student affairs | |
| Educate students, plan lessons, evaluate progress | |
| Maintain records, manage logistics, facilitate communication | |
| Provide additional student services, maintain facilities |
Building An Effective Team
Crafting a team with a shared vision for success is paramount. An effective team works towards common goals, supports each other, and places student achievement at the forefront.
- Hire qualified staff with a passion for education.
- Encourage ongoing training to keep skills sharp.
- Promote teamwork through regular meetings and team-building activities.
- Set clear expectations and provide constructive feedback.
- Recognize achievements to maintain high morale and motivation.
Financial Planning And Projections
Embarking on the journey of establishing a school requires meticulous financial planning. Crafting a detailed business plan sets the foundation for a prosperous educational institution. The ‘Financial Planning and Projections’ section is a pivotal element. It outlines the fiscal roadmap and serves as an assurance to stakeholders and investors. It demonstrates the feasibility and the financial foresight of your educational venture.
Start-up Costs And Budgeting
Deploying a transparent framework for start-up costs and budgeting is essential. This planning ensures that no expense goes unnoticed. An exhaustive list of initial costs sets the tone for budget allocations . Essential aspects to include:
- Facility purchase or lease
- Renovation and equipment
- Curriculum development
- Licensing and legal fees
- Marketing and promotion
- Staff recruitment and training
Establish realistic budget plans by itemizing and projecting these costs in a clearly formatted table . This step helps in managing funds efficiently from the outset.
| Item | Cost |
|---|---|
| Facility Lease | $100,000 |
| Equipment | $50,000 |
| Curriculum Development | $20,000 |
Revenue Streams And Tuition Modelling
Pinpointing how your school will generate income is a cornerstone of your business plan. Traditionally, tuition fees are the main revenue stream for most schools. Layering multiple revenue streams provides financial stability. Incorporate strategies such as:
- Annual tuition rates
- Enrollment fees
- Fundraising events
- Grants and scholarships
Develop dynamic tuition models that offer flexibility while maintaining revenue goals. These models should reflect the cost of delivering top-notch education balanced with market demands. Factor in discounts, payment plans, and financial aid options to ensure inclusivity.
| Grade Level | Tuition Fee |
|---|---|
| Elementary | $8,000 |
| Middle School | $10,000 |
| High School | $12,000 |
By carefully projecting and planning the financial aspects, your school business plan will reflect a well-thought-out strategy promising a successful path forward.
Marketing Plan For School Enrollment
The school’s future begins with a solid marketing plan for enrollment. Crafting the right strategy attracts students and builds the educational community. Let’s explore key methods for promoting your school and drawing in new learners.
Building Brand Awareness
A school’s brand reflects its values, mission, and the quality of education it provides. Build recognition and trust with a consistent and compelling message.
- Launch a user-friendly website with engaging content about the school ethos.
- Utilize social media to showcase school events, achievements, and testimonials.
- Organize school tours and open houses for families to experience the environment.
- Engage with local businesses and the community to build partnerships.
- Feature in the local media through news stories, interviews, and expert articles.
Strategies For Student Recruitment
Effective recruitment strategies help schools connect with potential students and their families.
| Strategy | Details | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Create ads focused on specific demographics. | Increase in inquiries from interested families. | |
| Encourage current families to refer friends. | Grow enrollment through word-of-mouth. | |
| Participate in local events to gain visibility. | Strengthen community presence and attract local students. | |
| Use email and SEO to reach wider audiences. | Broaden reach and attract online prospects. |
Combine personal touch with digital outreach to maximize student recruitment.
Risk Assessment And Mitigation
No school business plan is complete without evaluating risks. Risk Assessment and Mitigation are crucial for preparing for the unexpected. This section highlights how to recognize potential issues and action plans to tackle them efficiently. A well-crafted risk strategy ensures your school can navigate challenges and succeed long-term.
Understanding Potential Pitfalls
Identifying risks is the first step to protection. Below are common challenges a school might face:
- Natural disasters: Weather events can disrupt operations.
- Financial uncertainties: Changes in funding can affect budgeting.
- Legal changes: New regulations may require quick adaptation.
- Technology failures: Systems can experience downtime.
- Safety concerns: Incidents can occur on campus.
By understanding these, schools can create specific strategies to address each risk.
Developing A Crisis Management Plan
Create a reactive strategy when challenges strike. Essential components include:
| Assign roles for quick action during crises. | |
| Plan clear messaging to stakeholders. | |
| Define steps for various scenarios. | |
| Prepare staff with regular drills. | |
| Detail post-crisis return to normalcy. |
A plan that covers these areas can reduce impact and aid a swifter recovery.
Measuring Success And Implementing Feedback
Measuring Success and Implementing Feedback is a key chapter in your school’s business plan. A school must track its progress and understand what works. It also needs to know ways to get better. These are like a report card but for your school plan. They show where the school shines and needs polish. Here is how to set goals and check them, with ways to fix any issues.
Key Performance Indicators
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) help schools see their wins and challenges. Choosing the right KPIs makes sure schools focus on what matters. They can be about student scores, teacher happiness, or how many new students join. Well-picked KPIs provide a clear picture of where the school is heading. Look at these every term and compare them to your goals.
- Enrollment Rates: How many new students are joining?
- Graduation Rates: How many students finish their studies?
- Student Performance: Do students do well in tests and projects?
- Faculty Retention: Do teachers stay year after year?
- Parent Satisfaction: Are parents happy with the school?
Continuous Improvement Cycle
The Continuous Improvement Cycle is a loop that never ends. It tells schools to:
- Make a plan.
- Carry out the plan.
- Check how it went.
- Act on what you learn.
This circle helps schools get better all the time. It needs feedback from students, teachers, and parents. Schools use this feedback to fix problems and try new things. Here’s a simple table that shows the cycle:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| Decide what you want to change or make better. | |
| Put your plans into action in the real world. | |
| Use KPIs to see if your plan worked. | |
| Use what you learned to make your plan even better. |
Keeping the cycle going means your school keeps learning. It stays ready for new changes. It makes the school a great place for everyone.
Long-term Vision And Expanding Your School
Crafting the ultimate school business plan demands a clear long-term vision. It is not just about starting strong but also about ensuring that your school can grow and scale effectively over the years. Let’s explore how you can set your school on a path of sustainable expansion and achieve lasting success.
Future Growth Opportunities
Identifying potential avenues for growth is essential to your school’s long-term health. Imagine where your school might be in five, ten, or even twenty years.
- Assess community needs for education.
- Analyse trends in learning and technology.
- Expand course offerings to stay relevant .
- Explore additional campus locations .
These steps create a dynamic blueprint for growth that can adapt with time.
Sustainability And Scaling Up
A sustainable school business plan balances quality and scalability . Your strategic initiatives should foster a robust educational environment while allowing for measured growth.
| Area of Focus | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Financial Health | Develop diverse and . |
| Operational Efficiency | Implement systems and technologies that . |
| Staff and Faculty Development | Invest in continual for staff. |
With sustainable practices, your school can thrive in the long run and scale up responsibly.
Legal Considerations And Compliance
Starting a school is a bold step towards shaping young minds. It’s critical to understand the legal side . This will keep your school within laws. Every country has laws for education. A good business plan knows these laws well.
Education Laws And Accreditation
Your school must meet education standards . These vary by place. To operate legally , knowing and following these laws is a must. Accreditation shows quality. This attracts parents and students.
- Research local education laws.
- Find the right accreditation bodies.
- Prepare documents for approval.
Health And Safety Regulations
Students’ well-being is priority. Health and safety rules keep them safe . Your school needs clear safety plans. Regular training and drills are part of this.
- Check health and safety laws.
- Write a practical safety policy.
- Train staff on first aid and emergency responses.
Technology Integration In The Education Business
The landscape of education constantly evolves with technology . Schools need to embrace these changes to stay ahead. A comprehensive school business plan should reflect this. Integrating cutting-edge technology prepares students for the future. Educational institutions must leverage digital tools. They should also adapt to emerging trends in educational technology (EdTech). This is vital for their long-term success.
Leveraging Digital Tools
Embracing digital tools transforms the learning experience. It creates interactive and personalized classrooms. Here’s how to leverage them in your school:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) organize courses and track progress.
- Interactive whiteboards make lessons engaging.
- Digital libraries offer vast resources at one click.
- Communication platforms connect teachers, students, and parents.
Adapting To Emerging Edtech Trends
EdTech is fast-paced, making adaptation key. Schools must be alert to new trends:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) for personalized learning paths.
- Virtual Reality (VR) for immersive educational experiences.
- Gamification boosts engagement and learning retention.
- Coding and Robotics prepare students for future careers.
Tips For Crafting A Persuasive Executive Summary
Creating a standout executive summary for your school business plan can grab attention immediately. Think of it like the trailer to a blockbuster movie. It needs to excite and captivate. The executive summary should shine a spotlight on your business’s strengths and spark investor interest. Let’s explore how to make every word count.
Key Elements To Include
To ensure your executive summary is impactful, focus on these critical components:
- Mission Statement: Clearly define your school’s purpose and guiding principles.
- Business Objectives: Lay out specific, measurable goals that will gauge success.
- Unique Value Proposition: Highlight what sets your school apart from the competition.
- Leadership and Management Team: Showcase the experience and skills your team brings to the table.
- Market Analysis: Summarize key findings that affirm the demand for your school.
- Operational Strategy: Outline how your school will run efficiently and effectively.
- Financial Projections: Provide a snapshot of projected revenues, expenses, and profits.
Tailoring Your Message To Investors
Investors seek clarity and value. Remember these tips to align your summary with their expectations:
- Know your audience. Speak directly to what they value most in an educational investment.
- Be concise. Deliver compelling information without unnecessary details.
- Use confident language. Show investors your strong belief in the school’s future success.
- Visual data. Incorporate easy-to-understand charts to demonstrate growth potential.
- Call to action. End with a clear invitation for investors to engage further with your plan.
Your executive summary is not just the first section of your business plan; it’s the part that makes the first and lasting impression. Nail it with precision and passion to pave the way for your school’s success story.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you write an ultimate business plan.
To write an ultimate business plan, start with an executive summary, detail your company description, conduct a market analysis, outline organization and management, describe your products/services, develop a sales and marketing strategy, and present financial projections and funding requests.
What Are The 6 Components Of Successful Business Plan?
The six key components of a successful business plan are: executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization and management structure, sales strategies, and financial projections.
How Do You Write A Business Plan For A School Project?
Begin with a clear executive summary outlining objectives and mission. Detail the school’s structure, educational programs, and target market. Include a marketing plan and financial projections. Finish with an overview of the management team and operational plan. Keep language concise and jargon-free for readability.
What Are The 7 Things In A Business Plan?
A business plan typically includes these seven components: executive summary, company description, market analysis, organization and management, service or product line, marketing and sales strategy, and financial projections.
Crafting a robust business plan is the foundation of a successful school venture. Our ultimate template guides you through every crucial step. Stay ahead in the educational sector by implementing this strategic blueprint. Embrace the journey to success with confidence – your comprehensive school business plan awaits.
Start planning, start succeeding!

Private School Financial Model
This is a financial model template for a new private school startup business. The Excel model allows forecasting the cash flows over the next 10 years... read more
- Excel Model – $44.95 Version 9.1
- PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 9.0

Day Care Financial Model Excel Template
Discover Daycare Financial Model. Spend less time on Cash Flow forecasting and more time on your products. A sophisticated 5-year daycare pr... read more
- Excel - Multi-User – $129.00 Version 1
- Excel - Single-User – $99.00 Version 1
- Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

3 Statement Financial Modeling with DCF & Relative Valuation – Self Learning Kit
Financial Modeling Tutorial guides user via step by step approach on how to build financial models with DCF valuation

Pre-School Care Financial Model Excel Template
Get the Best Pre-School Care Financial Projection Template. Creates a financial summary formatted for your Pitch Deck. Ready to Raise Capital. F... read more
- Excel - Multi-User – $129.00
- Excel - Single-User – $99.00
- Free Demo – $0.00

Child Care Financial Model Excel Template
Try Child Care Pro Forma Projection. Simple-to-use yet very sophisticated planning tool. Get reliable results with minimal experience. A sophist... read more

Financial Plan for the Startup of a University and School
The University and School Financial Model aim to plan the operations, financial feasibility, and profitability of starting up a University and School.... read more
- Premium Excel Version – $119.95 Version 1
- Basic Excel Version – $89.95 Version 2
- PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 1
Language School Financial Model
The purpose of the model is to forecast the cash flows in form of a financial model in Excel when starting a new language school or to value an existi... read more
- PDF Preview – $0.00
- Excel Version – $34.95

In-Home Daycare Financial Model Excel Template
Purchase In-Home Daycare Financial Plan. Spend less time on Cash Flow forecasting and more time on your products. Highly versatile and user-frie... read more

Babysitting Financial Model Excel Template
Discover Babysitting Financial Projection Template. Use this Excel to plan effectively, manage Cash Flows and foresight your growth for 5 years.... read more

Martial Arts School Financial Model Excel Template
Order Martial Arts School Financial Model Template. Enhance your pitches and impress potential investors with the expected financial metrics. A ... read more

Public-Private Partnership (PPP) Financial Model
Financial Model presenting development and operating scenarios of various projects under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) agreement.
- Excel Financial Model – $119.00 Version 1
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

Driving School Financial Model Excel Template
Discover Driving School Financial Model. Fortunately, you can solve Cash Flow shortfalls with a bit of effort. The driving school financial proj... read more

Dance Studio Financial Model Excel Template
Get Dance Studio Financial Model. Requesting a loan without a financial model for paying it back is a common way to land in the rejection pile. ... read more

Flight School Financial Model Excel Template
Check Flight School Pro-forma Template. Solid package of print-ready reports: P&L and Cash Flow statement, and a complete set of ratios. Fli... read more

E-Learning Institute Financial Model – Dynamic 10 Year Forecast
Financial Model providing a dynamic up to 10-year financial forecast for an E-Learning Institute.
- Financial Model - Standard Version – $89.00 Version 1
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $109.00 Version 1

Dance Studio Financial Model – 5 Year Financial Forecast
Provides an advanced 5-year financial plan for a startup or operating Dance Studio and is a flexible tool for owners to forecast the company’s finan... read more
- Financial Model - Standard Version – $69.00 Version 1
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $89.00 Version 1

Scuba Diving Center – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing an advanced 5-year financial plan for a startup Scuba Diving Center.
- Financial Model - Standard Version – $79.00 Version 1
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $99.00 Version 1

Start Up Nursery School Financial Model
Start Up Nursery School Financial Model presents the case of an investment in a nursery school and its operations. The model generates the three finan... read more
- Excel Model – $79.00
- Free PDF – $0.00

Education Startup/Existing Business Financial Projection 3 Statement Model
3 statement 8 year rolling financial projection Excel model for an existing or startup Education institution/business
- Full Excel Model – $59.00
- PDF Example – $0.00

Student Loan – Graduated Repayment Calculator
This is a full Graduated Repayment Plan student loan calculator that has used the same algorithm as the government to show you repayment schedules ove... read more
Sky Diving Center – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing an advanced 5-year financial plan for a startup Sky Diving Center.

Driving School – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing an advanced 5-year financial plan for a startup or operating Driving School.

Dance School Financial Model Excel Template
Get the Best Dance School Pro Forma Projection. Enhance your pitch decks and impress potential investors with a proven, strategy template. Five-... read more

Childcare Center Financial Plan
The Childcare Center business model template aims to forecast the financial feasibility and profitability of starting a childcare business. This fina... read more
- Premium Excel – $119.95 Version 1
- Basic Excel – $89.95 Version 1

Family Service Financial Model Excel Template
Get Your Family Service Financial Model. Create fully-integrated financial projection for 5 years. With 3 way financial statements inside. Five ... read more

Beauty School Financial Model Excel Template
Order Your Beauty School Financial Model. There's power in Cash Flow Projections and the insight they can provide your business. Five-year horiz... read more

Music School Financial Model Excel Template
Try Music School Financial Model. Excel template - robust and powerful. This is your solid foundation to plan your business model. Five-year fin... read more

Baby Swimming School – Dynamic 10 Year Financial Model
Financial model providing a dynamic 10-Year Financial Plan for a Baby Swimming School for children up to 4 Years old.

Dog Obedience School Financial Model Excel Template
Order Dog Obedience School Financial Model Template. Use this Excel to plan effectively, manage Cash Flows and foresight your growth for 5 years... read more

Online Coaching Platform/Marketplace Financial Model Template
This Online Coaching Model is a perfect tool for financial feasibility study on launching a Online Coaching platform.

Foreign Languages School Financial Model Excel Template
Check Our Foreign Languages School Pro Forma Projection. Spend less time on Cash Flow forecasting and more time on your products. Highly versati... read more

Dog Kennel Financial Model Excel Template
Dog Kennel Pro Forma Template Excel - well-tested, robust, and powerful Get you solid foundation to plan your business model. Shop Now Creates 5-year ... read more

Online Tutoring Services Financial Model (10+ Yrs DCF and Valuation)
The Online Tutoring Services Financial Model is a comprehensive tool designed to analyze the financial aspects of an online tutoring platform or busin... read more
- Free PDF – $0.00 Version 1
- Excel Model – $79.00 Version 1

Fight School Financial Model Excel Template
Check Our Fight School Financial Plan. Sources & Uses, Profit & Loss, Cash Flow statements, KPIs and 30+ graphs Inside The fight school ... read more

Online Classes Subscription Financial Model Excel Template
Order Your Online Classes Subscription Financial Plan. This well-tested, robust, and powerful template is your solid foundation to plan a succes... read more

Infant Care Financial Model Excel Template
Impress bankers and investors with a proven, solid Infant Care Financial Projection Template. Generates 5-year infant care financial model excel... read more

Private School Financial Model – Dynamic 10 Year Forecast
Financial Model providing a dynamic up to 10-year financial forecast for a startup or existing Private School.
- Excel Financial Model – $109.00 Version 1

Nursery School Financial Model – 5 Year Forecast
Financial Model providing a 5 Year Financial Forecast for a startup Nursery School.
- Financial Model - Light Version – $79.00 Version 1

Baby Minding Financial Model Excel Template
Get Baby Minding Financial Model Template. Simple-to-use yet very sophisticated planning tool. Get reliable results with minimal experience. Fiv... read more
Education Financial Model Templates Bundle
This is a collection of financial model templates for businesses in the Education Industry as well as its related sectors.

E-Learning Marketplace – Dynamic 10 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing a dynamic up to 10-year financial forecast for an E-Learning Marketplace business.
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $119.00 Version 1

Summer Camp Financial Model Excel Template
Summer Camp Budget Template There's power in Cash Flow Projections and the insight they can provide your business . Buy Now The Summer Camp p&l te... read more

Dog Daycare Financial Model Excel Template
Dog Daycare Budget Template Create fully-integrated financial projection for 5 years With 3 way financial statements inside. Buy Now Creates 5-year Do... read more

Foreign Languages School – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing an advanced 5-year financial plan for a startup or operating Foreign Languages School.
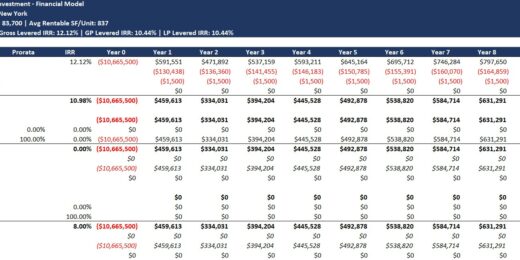
Student Housing Real Estate Investment Model with Returns & Waterfall
Pro Forma Models created this financial model to calculate and analyze the pro forma indicative return from a student housing real estate investment. ... read more
- Excel Model – $50.00 Version 1

Private School Financial Model – 10+ Year DCF & Valuation
A financial model for a private school business serves as a comprehensive tool to forecast and analyze the financial performance of the institution.
- Excel Model – $79.00 Version 2

Tutoring Service Financial Model Excel Template
Tutoring Service Pro Forma Template Excel - well-tested, robust and powerful Get you solid foundation to plan your business model. Shop Now The Tutori... read more

Speech Therapy Center – 5 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing an advanced 5-year financial plan for a startup or operating Speech Therapy Center offering therapy sessions for pre-schoole... read more

Feasibility Studies & Financial Template for a Training Center
Through the template, you can prepare a complete feasibility study for a training center in various fields, in addition to more than 40 financial and ... read more
- Excel Model – $60.00 Version 1.3

Online Course Provider Multichannel Financial Plan
The Online Course Provider – Multichannel Financial Model aims to plan the financial feasibility and profitability of the business of an online cour... read more
- Premium Excel – $149.95 Version 1
- Basic Excel – $109.95 Version 1
- PDF Demo Versions – $0.00 Version 1
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

How to Start a School

Starting Your Own School
Anyone can start a school. All you need is an idea and the drive to make it happen. But there are a few things you need to know before you get started. In this article, we will outline the steps you need to take, the permits and licenses you need, and how to find funding.
Importantly, a critical step in starting a school is to complete your business plan. To help you out, you should download Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template here .
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here
14 Steps to Starting a School
Choose the name for your school.
The first step to starting a new school is to choose your school’s business name.
This is a very important choice since your business name is your brand and will last for the lifetime of your business. Ideally you choose a name that is meaningful and memorable. Here are some tips for choosing a name for your school:
- Make sure the name is available . Check your desired name against trademark databases and your state’s list of registered business names to see if it’s available. Also check to see if a suitable domain name is available.
- Keep it simple . The best names are usually ones that are easy to remember, pronounce and spell.
- Think about marketing . Come up with a name that reflects the desired brand and/or focus of your school.
Develop Your School Business Plan
One of the most important steps in starting a school is to develop your business plan. The purpose of a business plan is to ensure that you fully understand your market and your strategy. The plan also provides you with a roadmap to follow and if needed, to present to funding sources to raise capital for your school.
Your business plan should include the following sections:
- Executive Summary – this section should summarize your entire business plan so readers can quickly understand the key details of your school.
- Company Overview – this section tells the reader about the history of your school and what type of school you operate. For example, are you a private school, religious school, charter school, boarding school, Montessori school, or a type of trade school such as a cosmetology school or welding school? You should also include information about the grade levels of your students.
- Industry Analysis – here you will document key information about the education industry. Conduct market research and document how big the industry is and what trends are affecting it.
- Customer Analysis – in this section, you will document who your ideal or target students are and their demographics. For example, how old are they? Where do they live? What do they find important when paying for educational services like the ones you will offer?
- Competitive Analysis – here you will document the key direct and indirect competitors you will face and how you will build competitive advantage ({i.e., small class size, new facilities, low tuition fees, unique mission or curriculum, etc.)
- Marketing Plan – your marketing plan should address the 4Ps: Product, Price, Promotions and Place.
- Product : Determine and document what products/services you will offer
- Prices : Document the prices of your products/services
- Place : Where will your school be located and how will that location help you increase sales?
- Promotions : What promotional methods will you use to attract students to your school? For example, you might decide to use pay-per-click advertising, public relations, search engine optimization and/or social media marketing.
- Operations Plan – here you will determine the key processes you will need to run your day-to-day operations. You will also determine your staffing and faculty needs. Finally, in this section of your plan, you will create a projected growth timeline showing the milestones you hope to achieve in the coming years.
- Administrative Team – this section details the background and key qualifications of your school’s administrative team, key staff members and faculty members and their job descriptions.
- Financial Plan – finally, the financial plan answers questions including the following:
- What startup costs will you incur?
- How will your school make money?
- What are your projected sales and expenses for the next five years?
- Do you need to raise funding to launch your school?
Choose the Legal Structure for Your School
Next you need to choose a legal structure for your school and register it and your business name with the Secretary of State in each state where you operate your school.
Below are the five most common legal structures:
1) Sole proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is a business entity in which the owner of the school and the business are the same legal person. The owner of a sole proprietorship is responsible for all debts and obligations of the business. There are no formalities required to establish a sole proprietorship, and it is easy to set up and operate. The main advantage of a sole proprietorship is that it is simple and inexpensive to establish. The main disadvantage is that the owner is liable for all debts and obligations of the business.
2) Partnerships
A partnership is a legal structure that is popular among small businesses. It is an agreement between two or more people who want to start a school together. The partners share in the profits and losses of the business.
The advantages of a partnership are that it is easy to set up, and the partners share in the profits and losses of the business. The disadvantages of a partnership are that the partners are jointly liable for the debts of the business, and disagreements between partners can be difficult to resolve.
3) Limited Liability Company (LLC)
A limited liability company, or LLC, is a type of business entity that provides limited liability to its owners. This means that the owners of an LLC are not personally responsible for the debts and liabilities of the business. The advantages of an LLC for a school include flexibility in management, pass-through taxation (avoids double taxation as explained below), and limited personal liability. The disadvantages of an LLC include lack of availability in some states and self-employment taxes.
4) C Corporation
A C Corporation is a business entity that is separate from its owners. It has its own tax ID and can have shareholders. The main advantage of a C Corporation for a school is that it offers limited liability to its owners. This means that the owners are not personally responsible for the debts and liabilities of the business. The disadvantage is that C Corporations are subject to double taxation. This means that the corporation pays taxes on its profits, and the shareholders also pay taxes on their dividends.
5) S Corporation
An S Corporation is a type of corporation that provides its owners with limited liability protection and allows them to pass their business income through to their personal income tax returns, thus avoiding double taxation. There are several limitations on S Corporations including the number of shareholders they can have among others.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
Secure startup funding for your school (if needed).
In developing your business plan, you might have determined that you need to raise funding to launch your new school.
Secure a Location for Your School
Having the right space can be important for your school, particularly if you’d like to meet clients there.
To find the right physical space, consider:
- Driving around to find the right areas while looking for “for lease” signs
- Contacting a commercial real estate agent
- Doing commercial real estate searches online
- Telling others about your needs and seeing if someone in your network has a connection that can help you find the right space
Incorporate Your Business at the Guaranteed Lowest Price
We are proud to have partnered with Business Rocket to help you incorporate your business at the lowest price, guaranteed.
Not only does BusinessRocket have a 4.9 out of 5 rating on TrustPilot (with over 1,000 reviews) because of their amazing quality…but they also guarantee the most affordable incorporation packages and the fastest processing time in the industry.
Register Your School with the IRS
Next, you need to register your school with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) which will result in the IRS issuing you an Employer Identification Number (EIN).
Most banks will require you to have an EIN in order to open up an account. In addition, in order to hire employees, you will need an EIN since that is how the IRS tracks your payroll tax payments.
Open a Business Bank Account
It is important to establish a bank account in your school’s name. This process is fairly simple and involves the following steps:
- Identify and contact the bank you want to use
- Gather and present the required documents (generally include your company’s Articles of Incorporation, driver’s license or passport, and proof of address)
- Complete the bank’s application form and provide all relevant information
- Meet with a banker to discuss your school’s needs and establish a relationship with them
Get a Business Credit Card
You should get a business credit card for your school to help you separate personal and school-related expenses.
You can either apply for a business credit card through your bank or apply for one through a credit card company.
When you’re applying for a business credit card, you’ll need to provide some information about your school. This includes the name of your school, the address of your school, and the type of school you’re running. You’ll also need to provide some information about yourself, including your name, Social Security number, and date of birth.
Get the Required Business Licenses and Permits
Every state, county and city has different business license and permit requirements.
Nearly all states, counties and/or cities have license requirements including:
- General Business License : getting your Articles of Incorporation as discussed above
- Sales Tax License or Tax-Exempt Status : for selling products and/or taxable services or to establish if you are a nonprofit organization
- Zoning Approval : typically at the city or county level, this provides authorization for construction or use of a school building or land for a particular purpose
- Food Service, Processing and/or Warehouse Licensing : to ensure safe food preparation
- Health Facility Licensing & Certification : to ensure safe rendering of healthcare services
- Fire Department Approval : a process by which the local fire department reviews and approves the installation of a fire alarm system.
Get Business Insurance for Your School
Other business insurance policies that you should consider for your school include:
- General liability insurance : This covers accidents and injuries that occur on your property. It also covers damages caused by your employees or products.
- Commercial auto insurance : If a vehicle is used in your business, this type of insurance will cover if a vehicle is damaged or stolen.
- Workers’ compensation insurance : If you have employees, this type of policy works with your general liability policy to protect against workplace injuries and accidents. It also covers medical expenses and lost wages.
- Commercial property insurance : This covers damage to your property caused by fire, theft, or vandalism.
- Business interruption insurance : This covers lost income and expenses if your business is forced to close due to a covered event.
- Professional liability insurance : This protects your school against claims of professional negligence.

Buy or Lease the Right School Equipment
The equipment and tools you need will depend on the type of school you start. In general, you will need to buy or lease:
- Classroom furniture and equipment, such as desks, chairs, measuring tools and other items that are necessary for your students
- Lab instruments and equipment, such as microscopes, telescopes, beakers and other supplies that are required to perform experiments in science classes
- Teaching aids for your elementary school teachers
- Office equipment, including computers, printers and other tools that are useful for administration
- Laptop or desktop computers for your students to use in the classroom
Develop Your School Marketing Materials
Marketing materials will be required to attract and retain students to your school.
The key marketing materials you will need are as follows:
- Logo : Spend some time developing a good logo for your school. Your logo will be printed on company stationery, business cards, marketing materials and so forth. The right logo can increase customer trust and awareness of your brand.
- Website : Likewise, a professional school website provides potential students with information about the products and/or services you offer, your company’s history, and contact information. Importantly, remember that the look and feel of your website will affect how students and families perceive your school.
- Social Media Accounts : establish social media accounts in your company’s name. Accounts on Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn and/or other social media networks will help students and others find and interact with your school.
Purchase and Setup the Software Needed to Run Your School
Most schools need accounting software and student information systems to manage and track their student enrollment, grades, and schedules.
For accounting, you will need software that can generate invoices and track inventory and expenses. Your software should also allow you to create purchase orders and track vendor discounts. While there are many different software options available, some of the most popular programs for accounting include QuickBooks and Xero.
Most schools require their teachers to use a student information system (SIS). An SIS is a centralized database that manages class rosters, attendance records, grades, and more.
The right SIS will make your job as a school administrator easier, improve the efficiency of record keeping and reporting, and provide valuable insights into your students’ learning experiences.
Open for Learning
How much does it cost to start a school.
In general, the costs for starting a new school can range from $200,000 to $1,000,000 depending on the type of school you are starting.
The cost of starting a school will generally include:
- Inventory and equipment rentals for traditional lab-based classes
- Curriculum design and books
- Marketing expenses
- Licenses and permits
- Business insurance
- Administrative overhead (salaries for your administration team, staff and faculty, computers, software licenses)
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

34+ SAMPLE School Business Plan in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
School business plan | ms word | google docs | apple pages, 34+ sample school business plan, what is a school business plan, benefits of a school business plan, how to write a school business plan, why are the mission statement and vision statement important, what is the use of school business plan.

Preschool Business Plan Template

Music School Business Plan Template

School Business Plan Template

Free Basic School Business Plan Template

Bible School Business Plan Template

High School Business Plan Template

Middle School Business Plan Template

One Page School Business Plan Template

School Business Continuity Plan Template
Middle School Business Plan Assignment

Sample Primary School Business Plan
School Business Plan in PDF

Senior High School Business Plan

Non-Profit School Business Plan

Sample Kindergarten School Business Plan

Park Primary School Business Plan

School Business Plan Executive Summary
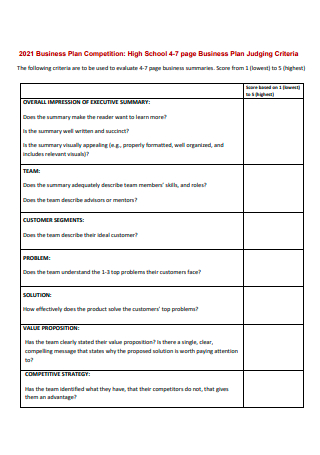
School Business Plan for Students

School Budget Business Plan

Sample School Funding Business Plan

School Project Business Plan

School Vocational Business Plan

School of Creative Music Education Business Plan

Nursery and Primary School Business Plan

Temple Community After School Program Business Plan

Sample Preschool Business Plan
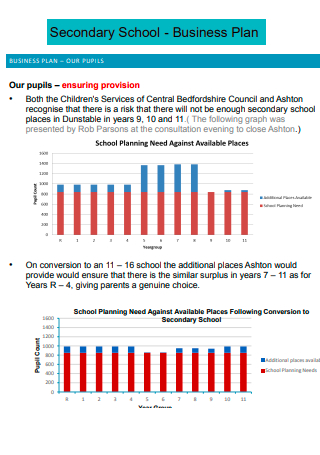
Secondary School Business Plan

Public School Business Plan

Sample Senior School Business Plan

School Education Business Plan

School Self Assessment and Review Business Plan

School Business Continuity Management Plan
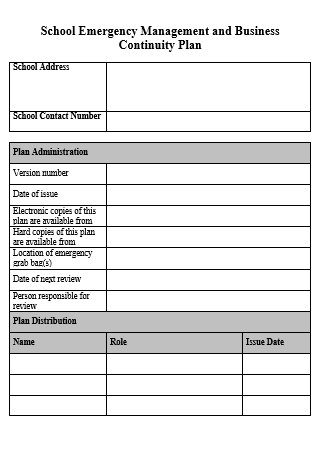
School Emergency Management and Business Continuity Plan

New School Business Plan
Step 1: school overview, step 2: executive summary, step 3: school services.
- Literacy services
- Numeracy services
- Meeting accreditation standards
- Foundations in science and mathematics
- Foundations in geography and history
- Giving extracurricular activities
- Giving books and school materials
Step 4: Mission Statement and Vision Statement
Step 5: job description, step 6: swot analysis.
- Strengths – What is the ace of your school against your competitors?
- Weaknesses – On what aspects are your school lacking?
- Opportunities – Where does your school excel in teaching?
- Threats – What can make a student leave your school?
Step 7: Market Research
Step 8: sales plan, step 9: publicity plan, step 10: school budget, share this post on your network, you may also like these articles.
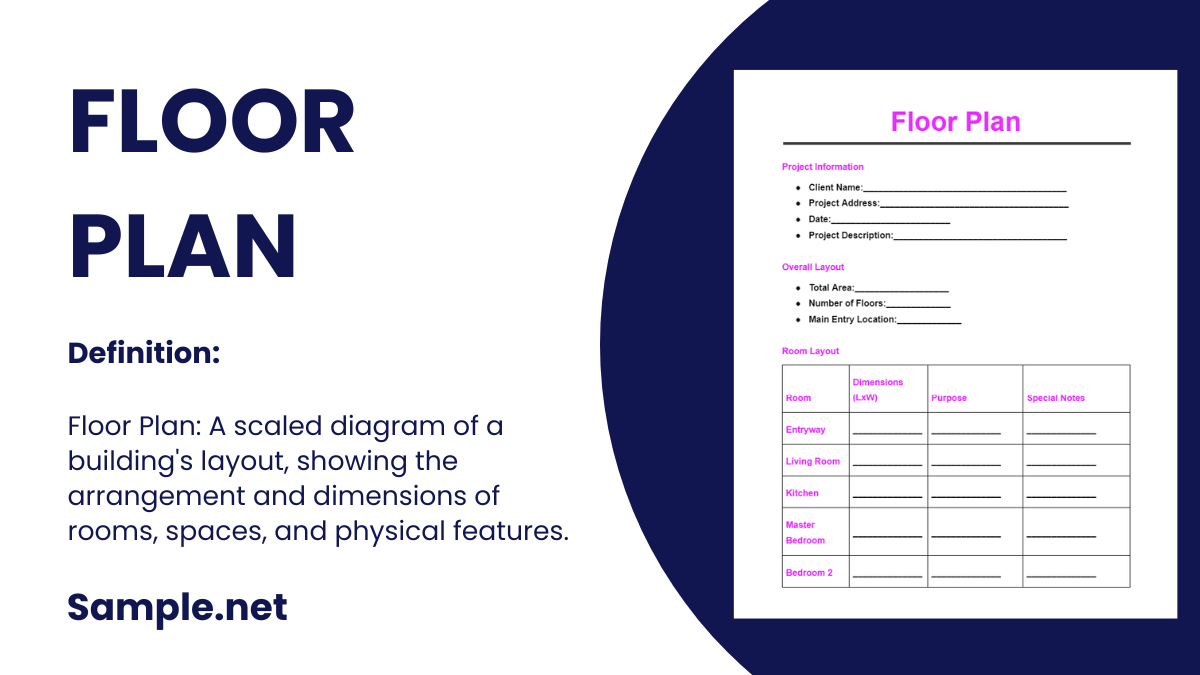
In this comprehensive guide, we explore the essentials of creating an effective Floor Plan. Whether you are designing a new home, renovating an existing space, or planning an office…
Nursing Care Plan

In this comprehensive guide, we explore the essentials of creating an effective Nursing Care Plan. Whether you are a nursing student, a new graduate, or an experienced nurse, this…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
How to write a business plan for a private secondary school?

Putting together a business plan for a private secondary school can be daunting - especially if you're creating a business for the first time - but with this comprehensive guide, you'll have the necessary tools to do it confidently.
We will explore why writing one is so important in both starting up and growing an existing private secondary school, as well as what should go into making an effective plan - from its structure to content - and what tools can be used to streamline the process and avoid errors.
Without further ado, let us begin!
In this guide:
Why write a business plan for a private secondary school?
- What information is needed to create a business plan for a private secondary school?
- How do I build a financial forecast for a private secondary school?
The written part of a private secondary school business plan
- What tool should I use to write my private secondary school business plan?
Being clear on the scope and goals of the document will make it easier to understand its structure and content. So before diving into the actual content of the plan, let's have a quick look at the main reasons why you would want to write a private secondary school business plan in the first place.
To have a clear roadmap to grow the business
It's rarely business as usual for small businesses. The economy follows cycles where years of growth are followed by recessions, and the business environment is always changing with new technologies, new regulations, new competitors, and new consumer behaviours appearing all the time...
In this context, running a business without a clear roadmap is like driving blindfolded: it's dangerous at best. That's why writing a business plan for a private secondary school is essential to create successful and sustainable businesses.
To write an effective business plan, you will need to take stock of where you are (if you are already in business) and where you want the business to go in the next three to five years.
Once you know where you want your private secondary school to be, you'll have to identify:
- what resources (human, equipment, and capital) are needed to get there,
- at what pace the business needs to progress to get there in time,
- and what risks you'll face along the way.
Going through this process regularly is beneficial, both for startups and existing companies, as it helps make informed decisions about how best to allocate resources to ensure the long-term success of the business.
To get visibility on future cash flows
If your small private secondary school runs out of cash: it's game over. That's why we often say "cash is king", and it's crucial to have a clear view of your private secondary school's future cash flows.
So, how can you achieve this? It's simple - you need to have an up-to-date financial forecast.
The good news is that your private secondary school business plan already includes a financial forecast (which we'll discuss further in this guide). Your task is to ensure it stays current.
To accomplish this, it's essential to regularly compare your actual financial performance with what was planned in your financial forecast. Based on your business's current trajectory, you can make adjustments to the forecast.
By diligently monitoring your private secondary school's financial health, you'll be able to spot potential financial issues, like unexpected cash shortfalls, early on and take corrective actions. Moreover, this practice will enable you to recognize and capitalize on growth opportunities, such as excess cash flow enabling you to expand to new locations.
To secure financing
Crafting a comprehensive business plan for your private secondary school, whether you're starting up or already established, is paramount when you're seeking financing from banks or investors.
Given how fragile small businesses are, financiers will want to ensure that you have a clear roadmap in place as well as command and control of your future cash flows before entertaining the idea of funding you.
For banks, the information in your business plan will be used to assess your borrowing capacity - which is defined as the maximum amount of debt your business can afford alongside your ability to repay the loan. This evaluation helps them decide whether to extend credit to your business and under what terms (interest rate, duration, repayment options, collateral, etc.).
Similarly, investors will thoroughly review your plan to determine if their investment can yield an attractive return. They'll be looking for evidence that your private secondary school has the potential for healthy growth, profitability, and consistent cash flow generation over time.
Now that you understand the importance of creating a business plan for your private secondary school, let's delve into the necessary information needed to craft an effective plan.
Need a convincing business plan?
The Business Plan Shop makes it easy to create a financial forecast to assess the potential profitability of your projects, and write a business plan that’ll wow investors.
Information needed to create a business plan for a private secondary school
Drafting a private secondary school business plan requires research so that you can project sales, investments and cost accurately in your financial forecast, and convince the reader that there is a viable commercial opportunity to be seized.
Below, we'll focus on three critical pieces of information you should gather before starting to write your plan.
Carrying out market research for a private secondary school
Before you begin writing your business plan for a private secondary school, conducting market research is a critical step in ensuring precise and realistic financial projections.
Market research grants you valuable insights into your target customer base, competitors, pricing strategies, and other crucial factors that can impact the success of your business.
In the course of this research, you may stumble upon trends that could impact your private secondary school.
You may find that potential students are increasingly interested in extracurricular activities. Market research could reveal that students may be looking for a school that provides a variety of activities, such as sports teams, clubs, or other experiential learning opportunities. Additionally, market research could indicate that parents may be looking for a school that provides a high-quality education, with a focus on technology and innovation. This could mean that students are interested in being equipped with the skills necessary to succeed in a rapidly changing world.
Such market trends play a pivotal role in revenue forecasting, as they provide essential data regarding potential customers' spending habits and preferences.
By integrating these findings into your financial projections, you can provide investors with more accurate information, enabling them to make well-informed decisions about investing in your private secondary school.
Developing the marketing plan for a private secondary school
Before delving into your private secondary school business plan, it's imperative to budget for sales and marketing expenses.
To achieve this, a comprehensive sales and marketing plan is essential. This plan should provide an accurate projection of the necessary actions to acquire and retain customers.
Additionally, it will outline the required workforce to carry out these initiatives and the corresponding budget for promotions, advertising, and other marketing endeavours.
By budgeting accordingly, you can ensure that the right resources are allocated to these vital activities, aligning them with the sales and growth objectives outlined in your business plan.
The staffing and capital expenditure requirements of a private secondary school
Whether you are starting or expanding a private secondary school, it is important to have a clear plan for recruitment and capital expenditures (investment in equipment and real estate) in order to ensure the success of the business.
Both the recruitment and investment plans need to be coherent with the timing and level of growth planned in your forecast, and require appropriate funding.
Staffing costs for a private secondary school might include the salaries of the headmaster, teachers, administrative staff, custodial staff, and cafeteria workers. Equipment costs might include the purchase of textbooks, scientific equipment, computers, furniture, and other supplies.
In order to create a realistic financial forecast, you will also need to consider the other operating expenses associated with running the business on a day-to-day basis (insurance, bookkeeping, etc.).
Once you have all the necessary information to create a business plan for your private secondary school, it is time to start creating your financial forecast.
What goes into your private secondary school's financial forecast?
The financial forecast of your private secondary school will enable you to assess the profitability potential of your business in the coming years and how much capital is required to fund the actions planned in the business plan.
The four key outputs of a financial forecast for a private secondary school are:
- The profit and loss (P&L) statement ,
- The projected balance sheet ,
- The cash flow forecast ,
- And the sources and uses table .
Let's take a closer look at each of these.
The projected P&L statement
Your private secondary school forecasted P&L statement enables the reader of your business plan to get an idea of how much revenue and profits your business is expected to make in the near future.
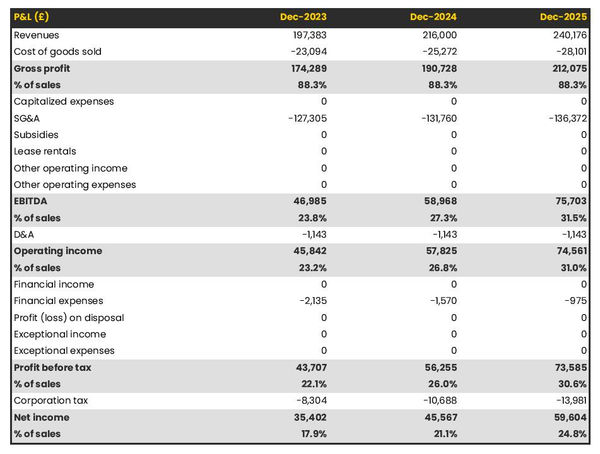
Ideally, your reader will want to see:
- Growth above the inflation level
- Expanding profit margins
- Positive net profit throughout the plan
Expectations for an established private secondary school will of course be different than for a startup. Existing businesses which have reached their cruising altitude might have slower growth and higher margins than ventures just being started.
The projected balance sheet of your private secondary school
Your private secondary school's forecasted balance sheet enables the reader of your plan to assess your financial structure, working capital, and investment policy.
It is composed of three types of elements: assets, liabilities and equity:
- Assets: represent what the business owns and uses to produce cash flows. It includes resources such as cash, equipment, and accounts receivable (money owed by clients).
- Liabilities: represent funds advanced to the business by lenders and other creditors. It includes items such as accounts payable (money owed to suppliers), taxes due and loans.
- Equity: is the combination of what has been invested by the business owners and the cumulative profits and losses generated by the business to date (which are called retained earnings). Equity is a proxy for the value of the owner's stake in the business.
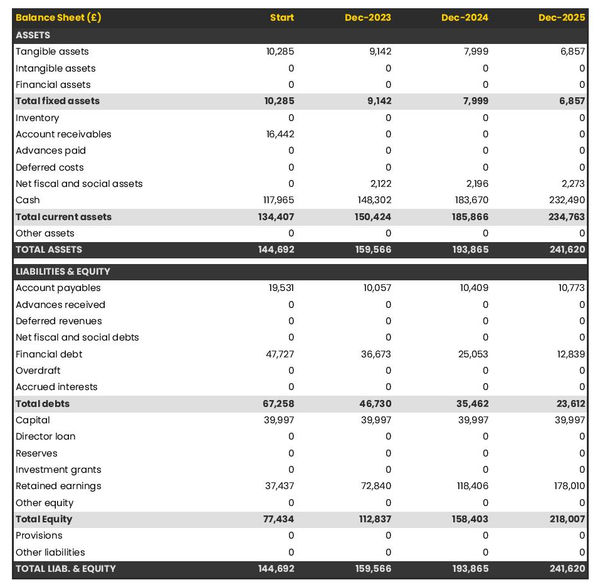
Your private secondary school's balance sheet will usually be analyzed in conjunction with the other financial statements included in your forecast.
Two key points of focus will be:
- Your private secondary school's liquidity: does your business have sufficient cash and short-term assets to pay what it owes over the next 12 months?
- And its solvency: does your business have the capacity to repay its debt over the medium-term?
The cash flow forecast
As we've seen earlier in this guide, monitoring future cash flows is the key to success and the only way of ensuring that your private secondary school has enough cash to operate.
As you can expect showing future cash flows is the main role of the cash flow forecast in your private secondary school business plan.
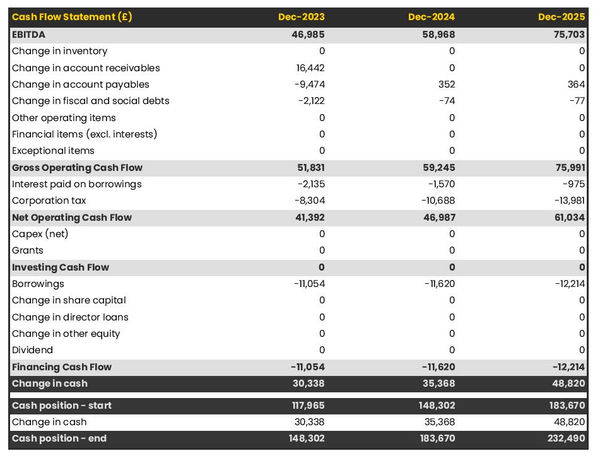
It is best practice to organise the cash flow statement by nature in order to show the cash impact of the following areas:
- Cash flow generated from operations: the operating cash flow shows how much cash is generated or consumed by the business's commercial activities
- Cash flow from investing activities: the investing cash flow shows how much cash is being invested in capital expenditure (equipment, real estate, etc.) either to maintain the business's equipment or to expand its capabilities
- Cash flow from financing activities: the financing cash flow shows how much cash is raised or distributed to financiers
Looking at the cash flow forecast helps you to make sure that your business has enough cash to keep running, and can help you anticipate potential cash shortfalls.
Your private secondary school business plan will normally include both yearly and monthly cash flow forecasts so that the readers can view the impact of seasonality on your business cash position and generation.
The initial financing plan
The sources and uses table or initial financing plan is a key component of your business plan when starting a private secondary school.
It shows where the capital needed to set up the business will come from (sources) and how it will be spent (uses).
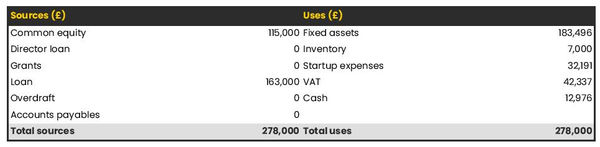
This table helps size the investment required to set up the private secondary school, and understand how risks will be distributed between the business owners, and the financiers.
The sources and uses table also highlights what the starting cash position will be. This is key for startups as the business needs to have sufficient funding to sustain operations until the break-even point is reached.
Now that you have a clear understanding of what will go into the financial forecast of your private secondary school business plan, let's have a look at the written part of the plan.
The written part of a private secondary school business plan is composed of 7 main sections:
- The executive summary
- The presentation of the company
- The products and services
- The market analysis
- The strategy
- The operations
- The financial plan
Throughout these sections, you will seek to provide the reader with the details and context needed for them to form a view on whether or not your business plan is achievable and your forecast a realistic possibility.
Let's go through the content of each section in more detail!
1. The executive summary
The first section of your private secondary school's business plan is the executive summary which provides, as its name suggests, an enticing summary of your plan which should hook the reader and make them want to know more about your business.
When writing the executive summary, it is important to provide an overview of the business, the market, the key financials, and what you are asking from the reader.
Start with a brief introduction of the business, its name, concept, location, how long it has been in operation, and what makes it unique. Mention any services or products you plan to offer and who you sell to.
Then you should follow with an overview of the addressable market for your private secondary school, current trends, and potential growth opportunities.
You should then include a summary of your key financial figures such as projected revenues, profits, and cash flows.
Finally, you should detail any funding requirements in the ask section.
2. The presentation of the company
The second section in your private secondary school's business plan should focus on the structure and ownership, location, and management team of the company.
The structure and ownership part provides an overview of the legal structure of the business, who the owners are and how much each has invested and owns. If you are seeking financing it is important that the reader gets a clear picture of which legal entity is receiving the funds, and who controls the business.
The location part should give an overview of the premises from which the company is operating, and why that location is of particular interest (catchment area, accessibility, amenities nearby, etc.).
When describing the location of your private secondary school to a third party financier, you could emphasize the potential of the local market. You may point out the benefits of a major city nearby, such as potential access to a highly-educated workforce, businesses, and other resources. You could also mention the potential for a robust transportation network, which could help your school attract students from a wider region. Additionally, you might mention the potential of the area to attract students from outside of the area, as the local geography and climate could be attractive to prospective students.
Finally, you should introduce the management team. Explain each member's role, background, and experience.
It is also important to emphasize any past successes that the members of the management team have achieved, and how long they've been working together, as this will help potential lenders or investors understand why they should trust in their leadership.
3. The products and services section
The products and services section of your business plan should include a detailed description of what your company offers, who are the target customers, and what distribution channels are part of your go-to-market.
For example, your private secondary school might offer its customers a range of classes such as Advanced Placement (AP) courses, foreign language classes, and a variety of extracurricular activities. Additionally, the school might provide services such as guidance counseling, college admissions assistance, and mentoring programs. All of these offerings would help to ensure that students are well prepared for life after graduation.
4. The market analysis
When presenting your market analysis in your private secondary school business plan, you should detail the customers' demographics and segmentation, target market, competition, barriers to entry, and any regulations that may apply.
The goal of this section is to help the reader understand how big and attractive your market is, and demonstrate that you have a solid understanding of the industry.
You should start with the demographics and segmentation subsection, which gives an overview of the addressable market for your private secondary school, the main trends in the marketplace, and introduces the different customer segments and their preferences in terms of purchasing habits and budgets.
The target market section should follow and zoom on the customer segments your private secondary school is targeting, and explain how your products and services meet the specific needs of these customers.
For example, your target market might include affluent families who are willing to invest in their children's education and want them to attend a private school. These parents might value the quality of education, the smaller class sizes, and the extracurricular activities that a private school can offer. They would be likely to be willing to pay a premium for these features.
Then comes the competition subsection, where you should introduce your main competitors and explain what differentiates you from them.
Finally, you should finish your market analysis by giving an overview of the main regulations applicable to your private secondary school.
5. The strategy section
When you write the strategy section of your private secondary school business plan, remember to cover key elements such as your competitive edge, pricing strategy, sales & marketing plan, milestones, and risks and mitigants.
In the competitive edge subsection, elaborate on what makes your company stand out from competitors. This becomes especially important if you're a startup, aiming to carve a place for yourself amidst established players in the marketplace.
The pricing strategy subsection should demonstrate how you plan to maintain profitability while offering competitive prices to attract customers.
Outline your sales & marketing plan, detailing how you'll reach out to new customers and retain existing ones through loyalty programs or special offers.
For the milestones subsection, outline your company's achievements to date and your main objectives for the future, complete with specific dates to set clear expectations for progress.
Lastly, the risks and mitigants subsection should address the main risks that could affect your plan's execution. Explain the measures you've put in place to minimize these risks, assuring potential investors or lenders.
Your private secondary school may face a variety of risks. For example, it could be at risk of financial losses if there is a decrease in enrollment numbers. Additionally, it might be vulnerable to cyber-attacks if its online systems are not properly secured. Adequate security measures and contingency plans should be in place to protect the school from these potential risks.
6. The operations section
The operations of your private secondary school must be presented in detail in your business plan.
Begin by addressing your staff, specifying the main roles and your recruitment plan to support the anticipated growth. Outline the qualifications and experience needed for each role and discuss your recruitment strategies, which may involve using job boards, referrals, or headhunters.
Next, clearly state your private secondary school's operating hours, allowing the reader to gauge the adequacy of your staffing levels. Additionally, mention any considerations for varying opening times during peak seasons and your approach to handling customer queries outside regular operating hours.
The key assets and intellectual property (IP) required to run your business should also be highlighted. If you rely on licenses, trademarks, physical structures like equipment or property, or lease agreements, ensure they are well-documented in this section.
Your private secondary school might have two key assets and forms of intellectual property: its proprietary curriculum and its brand. The curriculum could be a unique blend of traditional and innovative teaching methods that are tailored to the specific needs and goals of the school. It may also include a variety of resources to support students in their learning. Additionally, the school may have cultivated its own brand and image that differentiate it from other educational institutions. This might include a recognizable logo, mascot, mission statement, and other distinguishing characteristics.
Finally, provide a comprehensive list of suppliers you intend to collaborate with, along with a breakdown of their services and main commercial terms, such as price, payment terms, break clauses and contract duration. Investors often seek insight into the reasons behind your supplier choices, which may include a preference for higher-quality products or established relationships from past ventures.
7. The presentation of the financial plan
The financial plan section is where we will include the financial forecast we talked about earlier in this guide.
Now that you have a clear idea of the content of a private secondary school business plan, let's look at some of the tools you can use to create yours.
What tool should I use to write my private secondary school's business plan?
In this section, we will be reviewing the two main solutions for creating a private secondary school business plan:
- Using specialized online business plan software,
- Outsourcing the plan to the business plan writer.
Using an online business plan software for your private secondary school's business plan
Using online business planning software is the most efficient and modern way to create a private secondary school business plan.
There are several advantages to using specialized software:
- You can easily create your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the financial calculations for you without errors
- You are guided through the writing process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan
- You can access a library of dozens of complete business plan samples and templates for inspiration
- You get a professional business plan, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank or investors
- You can easily track your actual financial performance against your financial forecast
- You can create scenarios to stress test your forecast's main assumptions
- You can easily update your forecast as time goes by to maintain visibility on future cash flows
- You have a friendly support team on standby to assist you when you are stuck
If you're interested in using this type of solution, you can try The Business Plan Shop for free by signing up here .
Hiring a business plan writer to write your private secondary school's business plan
Outsourcing your private secondary school business plan to a business plan writer can also be a viable option.
Business plan writers are experienced in writing business plans and adept at creating financial forecasts without errors. Furthermore, hiring a consultant can save you time and allow you to focus on the day-to-day operations of your business.
However, hiring business plan writers is expensive as you are paying for the software used by the consultant, plus their time, and their profit margin of course.
From experience, you need to budget at least £1.5k ($2.0k) excluding tax for a complete business plan, more if you need to make changes after the initial version (which happens frequently after the initial meetings with lenders or investors).
You also need to be careful when seeking investment. Investors want their money to be used to grow the business, not spent on consulting fees. Therefore, the amount you spend on business plan writing services (and other consulting services such as legal services) needs to be negligible relative to the amount raised.
The other drawback is that you usually don't own the business plan itself: you just get the output, while the actual document is saved in the consultant's business plan software - which makes it difficult to maintain the document up to date without hiring the consultant on a retainer.
For these reasons, outsourcing the private secondary school business plan to a business plan writer should be considered carefully, weighing both the advantages and disadvantages of hiring outside help.
Ultimately, it may be the right decision for some businesses, while others may find it beneficial to write their business plan using online software.
Why not create your private secondary school's business plan using Word or Excel?
Using Microsoft Excel and Word (or their Google, Apple, or open-source equivalents) to write a private secondary school business plan is not advisable. Allow me to explain the reasons.
Firstly, creating an accurate and error-free financial forecast on Excel or any spreadsheet demands technical expertise in accounting principles and financial modelling. Without a degree in finance and accounting and significant financial modelling experience, it's unlikely that the reader will fully trust your numbers.
Secondly, relying on spreadsheets is inefficient. While it may have been the go-to option in the past, technology has evolved, and software now performs such tasks much faster and more accurately.
The second reason is that it is inefficient. Building forecasts on spreadsheets was the only option in the early 2000s, nowadays technology has advanced and software can do it much faster and much more accurately.
And with the rise of AI, software is also becoming smarter at helping us detect mistakes in our forecasts and helping us analyse the numbers to make better decisions.
Moreover, software offers ease in comparing actuals versus forecasts and maintaining up-to-date forecasts for clear visibility on future cash flows, as we discussed earlier in this guide. Such tasks are cumbersome when using spreadsheets.
Now, let's address the written part of your private secondary school business plan. While it may be less prone to errors, using software can significantly boost productivity. Word processors lack instructions and examples for each section of your business plan. They also won't automatically update your numbers when changes occur in your forecast, and they lack automated formatting capabilities.
In summary, while some entrepreneurs may consider Word or Excel for their business plan, it's far from the best or most efficient solution when compared to specialized software.
- A business plan has 2 complementary parts: a financial forecast showcasing the expected growth, profits and cash flows of the business; and a written part which provides the context needed to judge if the forecast is realistic and relevant.
- Having an up-to-date business plan is the only way to keep visibility on your private secondary school's future cash flows.
- Using business plan software is the modern way of writing and maintaining business plans.
We hope that this practical guide gave you insights on how to write the business plan for your private secondary school. Do not hesitate to get in touch with our team if you still have questions.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- In-depth business plan structure
- How to write the structure and ownership section of your business plan?
- Is it worth using a business plan writer?
- Business plan cover page tips
- Key steps to write a business plan?
- Free business plan template
Know someone who owns or wants to start a private secondary school? Share this article with them!

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here
| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |
Business Plan Executive Summary Example & Template

Updated: Jun 3, 2024, 1:03pm

Table of Contents
Components of an executive summary, how to write an executive summary, example of an executive summary, frequently asked questions.
A business plan is a document that you create that outlines your company’s objectives and how you plan to meet those objectives. Every business plan has key sections such as management and marketing. It should also have an executive summary, which is a synopsis of each of the plan sections in a one- to two-page overview. This guide will help you create an executive summary for your business plan that is comprehensive while being concise.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
The executive summary should mimic the sections found in the business plan . It is just a more concise way of stating what’s in the plan so that a reader can get a broad overview of what to expect.
State the company’s mission statement and provide a few sentences on what the company’s purpose is.
Company History and Management
This section describes the basics of where the company is located, how long it has been in operation, who is running it and what their level of experience is. Remember that this is a summary and that you’ll expand on management experience within the business plan itself. But the reader should know the basics of the company structure and who is running the company from this section.
Products or Services
This section tells the reader what the product or service of the company is. Every company does something. This is where you outline exactly what you do and how you solve a problem for the consumer.
This is an important section that summarizes how large the market is for the product or service. In the business plan, you’ll do a complete market analysis. Here, you will write the key takeaways that show that you have the potential to grow the business because there are consumers in the market for it.
Competitive Advantages
This is where you will summarize what makes you better than the competitors. Identify key strengths that will be reasons why consumers will choose you over another company.
Financial Projections
This is where you estimate the sales projections for the first years in business. At a minimum, you should have at least one year’s projections, but it may be better to have three to five years if you can project that far ahead.
Startup Financing Requirements
This states what it will cost to get the company launched and running. You may tackle this as a first-year requirement or if you have made further projections, look at two to three years of cost needs.
The executive summary is found at the start of the business plan, even though it is a summary of the plan. However, you should write the executive summary last. Writing the summary once you have done the work and written the business plan will be easier. After all, it is a summary of what is in the plan. Keep the executive summary limited to two pages so that it doesn’t take someone a long time to peruse what the summary says.
Start A Limited Liability Company Online Today with ZenBusiness
Click to get started.
It might be easier to write an executive summary if you know what to expect. Here is an example of an executive summary that you can use as a template.

Bottom Line
Writing an executive summary doesn’t need to be difficult if you’ve already done the work of writing the business plan itself. Take the elements from the plan and summarize each section. Point out key details that will make the reader want to learn more about the company and its financing needs.
How long is an executive summary?
An executive summary should be one to two pages and no more. This is just enough information to help the reader determine their overall interest in the company.
Does an executive summary have keywords?
The executive summary uses keywords to help sell the idea of the business. As such, there may be enumeration, causation and contrasting words.
How do I write a business plan?
If you have business partners, make sure to collaborate with them to ensure that the plan accurately reflects the goals of all parties involved. You can use our simple business plan template to get started.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best LLC Services
- Best Registered Agent Services
- Best Trademark Registration Services
- Top LegalZoom Competitors
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Plan Software
- ZenBusiness Review
- LegalZoom LLC Review
- Northwest Registered Agent Review
- Rocket Lawyer Review
- Inc. Authority Review
- Rocket Lawyer vs. LegalZoom
- Bizee Review (Formerly Incfile)
- Swyft Filings Review
- Harbor Compliance Review
- Sole Proprietorship vs. LLC
- LLC vs. Corporation
- LLC vs. S Corp
- LLP vs. LLC
- DBA vs. LLC
- LegalZoom vs. Incfile
- LegalZoom vs. ZenBusiness
- LegalZoom vs. Rocket Lawyer
- ZenBusiness vs. Incfile
- How To Start A Business
- How to Set Up an LLC
- How to Get a Business License
- LLC Operating Agreement Template
- 501(c)(3) Application Guide
- What is a Business License?
- What is an LLC?
- What is an S Corp?
- What is a C Corp?
- What is a DBA?
- What is a Sole Proprietorship?
- What is a Registered Agent?
- How to Dissolve an LLC
- How to File a DBA
- What Are Articles Of Incorporation?
- Types Of Business Ownership
Next Up In Business
- Best Online Legal Services
- How To Write A Business Plan
- Member-Managed LLC Vs. Manager-Managed LLC
- Starting An S-Corp
- LLC Vs. C Corp
- How Much Does It Cost To Start An LLC?

What Is SNMP? Simple Network Management Protocol Explained
What Is A Single-Member LLC? Definition, Pros And Cons
What Is Penetration Testing? Definition & Best Practices
What Is Network Access Control (NAC)?
What Is Network Segmentation?

How To Start A Business In Louisiana (2024 Guide)
Kimberlee Leonard has 22 years of experience as a freelance writer. Her work has been featured on US News and World Report, Business.com and Fit Small Business. She brings practical experience as a business owner and insurance agent to her role as a small business writer.
Cassie is a deputy editor collaborating with teams around the world while living in the beautiful hills of Kentucky. Focusing on bringing growth to small businesses, she is passionate about economic development and has held positions on the boards of directors of two non-profit organizations seeking to revitalize her former railroad town. Prior to joining the team at Forbes Advisor, Cassie was a content operations manager and copywriting manager.
All Formats
Table of Contents
Plan template bundle, education business plan template bundle, 25+ school business plan templates in doc | pdf, 1. bible school business plan template, 2. school business plan template, 3. music school business plan template, 4. simple middle school business plan template, 5. free self-sufficient school business plan template, 6. free primary school business plan template, 7. free basic school business plan worksheet, 8. free sample primary school business plan template, 9. free school admission business plan template, 10. free basic primary school business plan, 11. community school business plan with executive summary, 12. free preschool daycare / childcare business plan, 13. free students secondary school business plan, 14. free business plan for charter schools template, 15. free independent public school business plan, 16. free draft quarterly school project business plan, 17. hospitality school business planner with introduction, 18. free senior high school business plan template, 19. nursery & primary kindergarten kids school business plan, 20. free school management & business continuity plan, 21. free school education improvement business plan, 22. free school business continuity plan form, 23. free charter school business plan outline, 24. free private school business plan template, 25. free school business lesson plan template, how to create a highly effective preschool business plan, step 1: create the cover page, step 2: create a summary of what you want to build, step 3: give an analysis of the market, step 4: propose how you wish to achieve your goals, step 5: calculate and estimate the costs, what is a perfect business plan, how to make the perfect business plan, step 1: make a proper analysis, step 2: mention purpose, step 3: make a government outline, step 4: try to make an execution, step 5: keep your financial statement, step 6: follow the appendix, plan templates.
A business plan helps you with a new project, product, service, or system when managing a company. Students, teachers, and administrative members can also improve their education for secondary school, primary school, or other preschool kids. Moreover, you can also launch a new course for your private high school and secondary school subjects like music, art, and any lesson. We understand that the content and research take time, so we provide you with school business plan templates .

- Google Docs

- Apple Pages

More in Plan Templates
School Cash Management Policy Template
Business plan template, school improvement plan template, sample school marketing plan template, editable school marketing plan template, school training plan template, preschool lesson plan template, school operational plan template, school communication plan template, private school strategic plan template.
- 7+ Financial Plan Templates
- 10+ Operational Plan Templates
- 9+ Training Plan Templates
- 5+ Shooting Schedule Template
- 11+ School Counselor Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | Word
- 9+ Interdisciplinary Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Business Continuity Plan Templates in Google Docs | Ms Word | Pages | PDF
- 18+ Compensation Plan Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Executive Bonus Plan Templates in PDF
- 8+ Facility Management Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Diversity Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 11+ Audit Corrective Action Plan Templates in MS Word | Excel | PDF
- 9+ Recruitment Agency Marketing Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Recruitment Marketing Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Student Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.
Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Educational Software K-12 Business Plan
Start your own educational software k-12 business plan
Curriculum Companion Suites
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Introduction Curriculum Companion Suites (CSS) is a medium-sized software development and consulting firm focused on making the educational process more efficient and effective for K-12 schools. CCS software serves as a virtual teaching assistant for the educational process. Students can follow along with curriculum electronically through a central computer terminal at the front of the classroom.
The Company CCS keys to success are the company’s commitment to market awareness and future potential direction of the educational process, and CCS’ relationships with a large number of educational institutions and districts.
Curriculum Companion Suites is a start-up company comprised of six executives and seventy-six employees. The executives represent all functional areas, with 70 years of combined experience in the software development industry. Two majority shareholders, Andrew Christiansen and David Fields, own 80% of the company. Other investors own a minority stake. At the moment, the company does not have plans for going public, as most of the financing is raised internally. CSS is incorporated in the state of Oregon by the two majority shareholders.
Products CCS offers a suite of educational software for each grade level, from kindergarten through 12th grade. These suites are developed in collaboration with major curriculum publishers with whom CCS has established strategic partnerships.
CCS provides full installation, initial and ongoing consulting support. These services are provided as part of each software package purchase.
The Market The competitive marketplace includes only a handful of direct competitors within the learning information systems vendors segment, providing software products and installation and systems integration services to kindergarten through senior high (K-12) schools in the United States. CCS competes primarily against more traditional methods of education, training and testing, including pencil and paper testing. In addition, CCS competes with other companies offering educational software products to schools, such as International Business Machines Corporation, Apple Computer, Inc., and Mattel, Inc.
Educational institutions and school districts have not been active in searching out technical enhancements to the educational process. Rather, companies such as CCS have often utilized a more “push” type of marketing strategy. The educational community has had to be “educated” themselves on the opportunities of utilizing technical infrastructures to enhance learning processes.
Since only a handful of other companies are competing directly with CCS in this market, the company plans to develop a healthy level of market share, with a goal of 10% at the end of three years.
The target market for CCS is the urban/metropolitan educational market, as this market presents the highest level of opportunity in terms of revenues. Additionally, software installations and customizations in this market are much more feasible in terms of technical logistics and efficiencies. Thus, profitability is by far more likely in this market.
Relationships have been established with a large number of educational institutions and school districts across the U.S. Significant investments have been made by CCS to research and understand the specific needs and potential enhancements to the current educational process.
Financial Considerations CCS expects to raise a substantial amount of owner capital, and borrow a comparable amount in a guaranteed SBA 10-year loan. This provides the bulk of the current financing required.
CCS intends to deliver generous sales in the first year, with steady grown in the second and third years of the plan.
1.1 Mission
Curriculum Companion Suites aims to offer software curriculum suites to K-12 schools within the U.S. market. CCS will focus on providing solutions to enhance the educational capabilities of schools.

1.2 Keys to Success
CCS keys to success include:
- The company’s commitment to being keenly alert to the current educational environment and future potential direction of the educational process.
- CCS’ relationships with a large number of educational institutions and districts.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Curriculum Companion Suites is a start-up comprised of six executives. These executives represent all functional areas, with 70 years of combined experience in the software development industry. Two majority shareholders, Andrew Christiansen and David Fields, own 80% of the company. The bulk of outside financing will come from a 10-year Small Business Administration (SBA) loan.
2.1 Company Ownership
CSS is incorporated in the state of Oregon by Andrew Christiansen and David Fields. Other investors own a minority stake. At the moment, the company does not have plans for going public, as most of the financing is raised internally.
CSS is a start-up company that was registered in the year 2000.
2.2 Start-up Summary
Of the total start-up expenses, the lion’s share has been spent on software licenses. Estimated start-up cash requirements should be sufficient to cover ongoing expenses in the first months of operation. Christiansen and Fields have each invested heavily, with the rest of investment coming from minority shareholders. The company has also secured a 10-year SBA loan and a one-year loan from its bank. Following is a chart and table summarizing projected initial start-up costs.

| Start-up | |
| Requirements | |
| Start-up Expenses | |
| Legal | $3,000 |
| Software Licenses | $20,000 |
| Other | $1,000 |
| Total Start-up Expenses | $24,000 |
| Start-up Assets | |
| Cash Required | $180,000 |
| Other Current Assets | $75,000 |
| Long-term Assets | $100,000 |
| Total Assets | $355,000 |
| Total Requirements | $379,000 |
| Start-up Funding | |
| Start-up Expenses to Fund | $24,000 |
| Start-up Assets to Fund | $355,000 |
| Total Funding Required | $379,000 |
| Assets | |
| Non-cash Assets from Start-up | $175,000 |
| Cash Requirements from Start-up | $180,000 |
| Additional Cash Raised | $0 |
| Cash Balance on Starting Date | $180,000 |
| Total Assets | $355,000 |
| Liabilities and Capital | |
| Liabilities | |
| Current Borrowing | $50,000 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $150,000 |
| Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills) | $1,000 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $201,000 |
| Capital | |
| Planned Investment | |
| Andrew Christiansen | $60,000 |
| David Fields | $60,000 |
| Other | $58,000 |
| Additional Investment Requirement | $0 |
| Total Planned Investment | $178,000 |
| Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses) | ($24,000) |
| Total Capital | $154,000 |
| Total Capital and Liabilities | $355,000 |
| Total Funding | $379,000 |
CCS offers a suite of educational software for each grade level, from Kindergarten through 12th grade. These suites are developed in collaboration with major curriculum publishers with whom CCS has established strategic partnerships.
CCS provides full installation, initial, and ongoing consulting support. These services are provided as part of each software package purchase.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
CCS has a focus on K-12 schools within the U.S. market, especially schools who:
- already own educational packages from large curriculum publishers who are CCS strategic partners
- owns software that has been recently developed by CSS.
The following chart and table summarize the total market potential for CSS products.

| Market Analysis | |||||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |||
| Potential Customers | Growth | CAGR | |||||
| Urban K-12 Schools | 5% | 2,500 | 2,625 | 2,756 | 2,894 | 3,039 | 5.00% |
| Rural K-12 Schools | 5% | 1,500 | 1,575 | 1,654 | 1,737 | 1,824 | 5.01% |
| Total | 5.01% | 4,000 | 4,200 | 4,410 | 4,631 | 4,863 | 5.01% |
4.1 Market Segmentation
Metropolitan Schools
Metropolitan schools often have larger student populations, with more classes, requiring more extensive and comprehensive software packages. The installations are consequently more extensive in nature.
Rural Schools
Rural schools often have relatively smaller student populations, and fewer classes. Additional customization during installations is usually necessary, as the infrastructure for computer networks is either substandard or nonexistent.
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy

4.3 Market Needs
CCS’s research has found that educators, as well as parents of K-12 children believe that the educational process is in need of significant improvements. Children, for the most part, have been found to strongly prefer an educational environment where they can learn “hands on” using the computer in conjunction with teacher facilitation, as opposed to teacher facilitation only.
4.4 Service Business Analysis
Major competition to CSS comes not from other software developers but from traditional book publishers. In fact, one of the goals of the company is to educate its clientele about the possibilities and features of the specially-designed software that assists in the educational process. The tool CSS provides teachers with will help them become more effective and efficient in classrooms. The company believes that the novelty and added value its products provide to educators will be key buying decision criteria for the customers.
4.5 Competition and Buying Patterns
Only a handful of other companies are competing directly with CCS in this market. CCS plans to develop a healthy level of market share, with a goal of 10% at the end of three years. With the exponential increase in computer and Internet usage among the public in the last five years, this is a relatively new market. CCS has taken a lead primarily due to its intense efforts both in research and development, as well as in establishing relationships in the educational community.
The competitive marketplace includes only a handful of direct competitors within the learning information systems vendors segment, providing software products and installation and systems integration services to kindergarten through senior high (K-12) schools in the United States. Typical learning information systems consist of computer software and related training designed to improve student academic performance by increasing the quality, quantity, and timeliness of performance data available to educators and by facilitating increased student practice of essential skills.
There are a number of competing products covering a wide range of educational requirements. These include:
- Accelerated reading products–software for motivating and monitoring increased literature-based reading practice.
- Accelerated math–software aimed to increase a student’s competency across this discipline utilizing the latest techniques.
- Professional development training for educators.
- Test-generation software.
Software products offered by competitors also aim to improve student academic performance by intensifying skills practice and increasing the quality, quantity and timeliness of information available to educators.
CCS competes primarily against more traditional methods of education, training and testing, including pencil and paper testing. In addition, CCS competes with other companies offering educational software products to schools, such as International Business Machines Corporation, Apple Computer, Inc., and Mattel, Inc. Many other companies, including Microsoft Corporation and Walt Disney Company, provide educational software products.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
CCS intends to succeed by offering K-12 schools a technological tool to assist teachers in making the educational process more efficient and effective.
5.1 Competitive Edge
CCS’ competitive edge is its new ideas and first to market technologies.
5.2 Sales Strategy
The table and charts shows the level of sales CCS intends to deliver in the first year through the third year of the plan. Detailed monthly sales for the first year are in the appendix.

| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Unit Sales | |||
| Software Systems | 240 | 276 | 317 |
| Installation & Customization | 240 | 276 | 317 |
| Other Consulting | 120 | 138 | 159 |
| Total Unit Sales | 600 | 690 | 794 |
| Unit Prices | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Software Systems | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 |
| Installation & Customization | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 |
| Other Consulting | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 |
| Sales | |||
| Software Systems | $6,000,000 | $6,900,000 | $7,935,000 |
| Installation & Customization | $3,600,000 | $4,140,000 | $4,761,000 |
| Other Consulting | $600,000 | $690,000 | $793,500 |
| Total Sales | $10,200,000 | $11,730,000 | $13,489,500 |
| Direct Unit Costs | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Software Systems | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 |
| Installation & Customization | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 |
| Other Consulting | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | |||
| Software Systems | $480,000 | $552,000 | $634,800 |
| Installation & Customization | $2,400,000 | $2,760,000 | $3,174,000 |
| Other Consulting | $240,000 | $276,000 | $317,400 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $3,120,000 | $3,588,000 | $4,126,200 |
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Andrew B. Christiansen has extensive experience in business planning and finance, including tenures as chief financial officer with ABC Conglomerate and DEF International. David E. Fields brings in experience in the area of marketing, advertising, and communications.
6.1 Personnel Plan
CSS will focus on strong product development and marketing. These are the areas where most of the investments and training will go. The table below, and in the appendix, outlines the company’s personnel plan for the next years.
| Personnel Plan | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Product Development | $900,000 | $945,000 | $992,250 |
| Installation Technicians | $875,000 | $918,750 | $964,688 |
| Administrative | $595,000 | $624,750 | $655,988 |
| Sales & Marketing | $900,000 | $945,000 | $992,250 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total People | 82 | 86 | 90 |
| Total Payroll | $3,270,000 | $3,433,500 | $3,605,175 |
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
CCS expects to raise its own capital, and to acquire a guaranteed the SBA 10-year loan. This provides the bulk of the current financing required.
7.1 Break-even Analysis
CCS’s Break-even Analysis is based on the average of the first-year figures for total sales by units, and by operating expenses. These are presented as per-unit revenue, per-unit cost, and fixed costs. These conservative assumptions make for a more accurate estimate of real risk.

| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Units Break-even | 27 |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $466,023 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Per-Unit Revenue | $17,000.00 |
| Average Per-Unit Variable Cost | $5,200.00 |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $323,475 |
7.2 Projected Profit and Loss
The projected Profit and Loss for CCS is presented in the accompanying table. The three yearly totals are shown here, with year one monthlies in the appendix.

| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | $10,200,000 | $11,730,000 | $13,489,500 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $3,120,000 | $3,588,000 | $4,126,200 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $3,120,000 | $3,588,000 | $4,126,200 |
| Gross Margin | $7,080,000 | $8,142,000 | $9,363,300 |
| Gross Margin % | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $3,270,000 | $3,433,500 | $3,605,175 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $96,000 | $150,000 | $265,000 |
| Depreciation | $24,000 | $27,600 | $31,740 |
| Utilities | $1,200 | $1,500 | $1,700 |
| Payroll Taxes | $490,500 | $515,025 | $540,776 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $3,881,700 | $4,127,625 | $4,444,391 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $3,198,300 | $4,014,375 | $4,918,909 |
| EBITDA | $3,222,300 | $4,041,975 | $4,950,649 |
| Interest Expense | $18,700 | $16,400 | $14,000 |
| Taxes Incurred | $808,144 | $999,494 | $1,246,664 |
| Net Profit | $2,371,456 | $2,998,481 | $3,658,244 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 23.25% | 25.56% | 27.12% |
7.3 Projected Cash Flow
The cash flow projection shows that provisions for ongoing expenses are adequate to meet CCS’s needs as the business generates cash flow sufficient to support operations.

| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $3,468,000 | $3,988,200 | $4,586,430 |
| Cash from Receivables | $5,628,700 | $7,576,305 | $8,712,751 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $9,096,700 | $11,564,505 | $13,299,181 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $190,000 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $9,286,700 | $11,564,505 | $13,299,181 |
| Expenditures | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $3,270,000 | $3,433,500 | $3,605,175 |
| Bill Payments | $4,171,394 | $5,201,383 | $6,118,402 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $7,441,394 | $8,634,883 | $9,723,577 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $12,000 | $12,000 | $12,000 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $12,000 | $12,000 | $12,000 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $135,000 | $225,000 | $295,000 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $7,600,394 | $8,883,883 | $10,042,577 |
| Net Cash Flow | $1,686,306 | $2,680,622 | $3,256,604 |
| Cash Balance | $1,866,306 | $4,546,928 | $7,803,532 |
7.4 Projected Balance Sheet
Following is the projected Balance Sheet for CCS. Again, three years of annuals are shown below, with first year monthlies in the appendix.
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $1,866,306 | $4,546,928 | $7,803,532 |
| Accounts Receivable | $1,103,300 | $1,268,795 | $1,459,114 |
| Other Current Assets | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $3,044,606 | $5,890,723 | $9,337,646 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $235,000 | $460,000 | $755,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $24,000 | $51,600 | $83,340 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $211,000 | $408,400 | $671,660 |
| Total Assets | $3,255,606 | $6,299,123 | $10,009,306 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $364,149 | $433,185 | $509,124 |
| Current Borrowing | $38,000 | $26,000 | $14,000 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $402,149 | $459,185 | $523,124 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $138,000 | $126,000 | $114,000 |
| Total Liabilities | $540,149 | $585,185 | $637,124 |
| Paid-in Capital | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($24,000) | $2,347,456 | $5,345,938 |
| Earnings | $2,371,456 | $2,998,481 | $3,658,244 |
| Total Capital | $2,715,456 | $5,713,938 | $9,372,182 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $3,255,606 | $6,299,123 | $10,009,306 |
| Net Worth | $2,715,456 | $5,713,938 | $9,372,182 |
7.5 Business Ratios
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 15.00% | 15.00% | 9.70% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Accounts Receivable | 33.89% | 20.14% | 14.58% | 21.50% |
| Other Current Assets | 2.30% | 1.19% | 0.75% | 45.70% |
| Total Current Assets | 93.52% | 93.52% | 93.29% | 70.20% |
| Long-term Assets | 6.48% | 6.48% | 6.71% | 29.80% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 12.35% | 7.29% | 5.23% | 42.40% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 4.24% | 2.00% | 1.14% | 19.20% |
| Total Liabilities | 16.59% | 9.29% | 6.37% | 61.60% |
| Net Worth | 83.41% | 90.71% | 93.63% | 38.40% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 100.00% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 46.04% | 43.87% | 42.17% | 79.40% |
| Advertising Expenses | 0.59% | 0.85% | 1.48% | 1.30% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | 31.36% | 34.22% | 36.46% | 2.20% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | 7.57 | 12.83 | 17.85 | 1.51 |
| Quick | 7.57 | 12.83 | 17.85 | 1.16 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 16.59% | 9.29% | 6.37% | 61.60% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | 117.09% | 69.97% | 52.33% | 3.50% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | 97.67% | 63.47% | 49.00% | 9.20% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | 23.25% | 25.56% | 27.12% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | 87.33% | 52.48% | 39.03% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | 6.10 | 6.10 | 6.10 | n.a |
| Collection Days | 57 | 56 | 56 | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 12.45 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 28 | 28 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 3.13 | 1.86 | 1.35 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.07 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 0.74 | 0.78 | 0.82 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $2,642,456 | $5,431,538 | $8,814,522 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 171.03 | 244.78 | 351.35 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
| Assets to Sales | 0.32 | 0.54 | 0.74 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 12% | 7% | 5% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 4.83 | 10.07 | 15.06 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 3.76 | 2.05 | 1.44 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Unit Sales | |||||||||||||
| Software Systems | 0% | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Installation & Customization | 0% | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Other Consulting | 0% | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Total Unit Sales | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | |
| Unit Prices | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Software Systems | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | $25,000.00 | |
| Installation & Customization | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | $15,000.00 | |
| Other Consulting | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | $5,000.00 | |
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Software Systems | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 | |
| Installation & Customization | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | $300,000 | |
| Other Consulting | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | $50,000 | |
| Total Sales | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | |
| Direct Unit Costs | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Software Systems | 0.00% | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 |
| Installation & Customization | 0.00% | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 | $10,000.00 |
| Other Consulting | 0.00% | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 | $2,000.00 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | |||||||||||||
| Software Systems | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | $40,000 | |
| Installation & Customization | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 | |
| Other Consulting | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | $20,000 | |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | |
| Personnel Plan | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Product Development | 0% | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 |
| Installation Technicians | 0% | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 | $72,917 |
| Administrative | 0% | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 | $49,583 |
| Sales & Marketing | 0% | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 |
| Other | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total People | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | 82 | |
| Total Payroll | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | |
| General Assumptions | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Current Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Tax Rate | 30.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Cost of Sales | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | $260,000 | |
| Gross Margin | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | $590,000 | |
| Gross Margin % | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | 69.41% | |
| Expenses | |||||||||||||
| Payroll | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Depreciation | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | |
| Utilities | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | |
| Payroll Taxes | 15% | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 | $40,875 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | $323,475 | |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | $266,525 | |
| EBITDA | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | $268,525 | |
| Interest Expense | $1,650 | $1,633 | $1,617 | $1,600 | $1,583 | $1,567 | $1,550 | $1,533 | $1,517 | $1,500 | $1,483 | $1,467 | |
| Taxes Incurred | $79,463 | $66,223 | $66,227 | $66,231 | $66,235 | $66,240 | $66,244 | $66,248 | $66,252 | $66,256 | $66,260 | $66,265 | |
| Net Profit | $185,413 | $198,669 | $198,681 | $198,694 | $198,706 | $198,719 | $198,731 | $198,744 | $198,756 | $198,769 | $198,781 | $198,794 | |
| Net Profit/Sales | 21.81% | 23.37% | 23.37% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.38% | 23.39% | 23.39% | |
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Sales | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | $289,000 | |
| Cash from Receivables | $0 | $18,700 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | $561,000 | |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $289,000 | $307,700 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 0.00% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $190,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $289,000 | $497,700 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | $850,000 | |
| Expenditures | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Spending | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | $272,500 | |
| Bill Payments | $14,003 | $389,646 | $376,831 | $376,818 | $376,806 | $376,793 | $376,781 | $376,768 | $376,756 | $376,743 | $376,731 | $376,718 | |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $286,503 | $662,146 | $649,331 | $649,318 | $649,306 | $649,293 | $649,281 | $649,268 | $649,256 | $649,243 | $649,231 | $649,218 | |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | $15,000 | |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $288,503 | $664,146 | $651,331 | $666,318 | $666,306 | $666,293 | $666,281 | $666,268 | $666,256 | $666,243 | $666,231 | $666,218 | |
| Net Cash Flow | $497 | ($166,446) | $198,669 | $183,682 | $183,694 | $183,707 | $183,719 | $183,732 | $183,744 | $183,757 | $183,769 | $183,782 | |
| Cash Balance | $180,497 | $14,051 | $212,721 | $396,402 | $580,096 | $763,803 | $947,522 | $1,131,254 | $1,314,998 | $1,498,755 | $1,682,524 | $1,866,306 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $180,000 | $180,497 | $14,051 | $212,721 | $396,402 | $580,096 | $763,803 | $947,522 | $1,131,254 | $1,314,998 | $1,498,755 | $1,682,524 | $1,866,306 |
| Accounts Receivable | $0 | $561,000 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 | $1,103,300 |
| Other Current Assets | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 | $75,000 |
| Total Current Assets | $255,000 | $816,497 | $1,192,351 | $1,391,021 | $1,574,702 | $1,758,396 | $1,942,103 | $2,125,822 | $2,309,554 | $2,493,298 | $2,677,055 | $2,860,824 | $3,044,606 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $100,000 | $100,000 | $100,000 | $100,000 | $115,000 | $130,000 | $145,000 | $160,000 | $175,000 | $190,000 | $205,000 | $220,000 | $235,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $2,000 | $4,000 | $6,000 | $8,000 | $10,000 | $12,000 | $14,000 | $16,000 | $18,000 | $20,000 | $22,000 | $24,000 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $100,000 | $98,000 | $96,000 | $94,000 | $107,000 | $120,000 | $133,000 | $146,000 | $159,000 | $172,000 | $185,000 | $198,000 | $211,000 |
| Total Assets | $355,000 | $914,497 | $1,288,351 | $1,485,021 | $1,681,702 | $1,878,396 | $2,075,103 | $2,271,822 | $2,468,554 | $2,665,298 | $2,862,055 | $3,058,824 | $3,255,606 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $1,000 | $377,085 | $364,270 | $364,258 | $364,246 | $364,234 | $364,222 | $364,210 | $364,198 | $364,186 | $364,174 | $364,161 | $364,149 |
| Current Borrowing | $50,000 | $49,000 | $48,000 | $47,000 | $46,000 | $45,000 | $44,000 | $43,000 | $42,000 | $41,000 | $40,000 | $39,000 | $38,000 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $51,000 | $426,085 | $412,270 | $411,258 | $410,246 | $409,234 | $408,222 | $407,210 | $406,198 | $405,186 | $404,174 | $403,161 | $402,149 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $150,000 | $149,000 | $148,000 | $147,000 | $146,000 | $145,000 | $144,000 | $143,000 | $142,000 | $141,000 | $140,000 | $139,000 | $138,000 |
| Total Liabilities | $201,000 | $575,085 | $560,270 | $558,258 | $556,246 | $554,234 | $552,222 | $550,210 | $548,198 | $546,186 | $544,174 | $542,161 | $540,149 |
| Paid-in Capital | $178,000 | $178,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 | $368,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) | ($24,000) |
| Earnings | $0 | $185,413 | $384,081 | $582,763 | $781,456 | $980,163 | $1,178,881 | $1,377,613 | $1,576,356 | $1,775,113 | $1,973,881 | $2,172,663 | $2,371,456 |
| Total Capital | $154,000 | $339,413 | $728,081 | $926,763 | $1,125,456 | $1,324,163 | $1,522,881 | $1,721,613 | $1,920,356 | $2,119,113 | $2,317,881 | $2,516,663 | $2,715,456 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $355,000 | $914,497 | $1,288,351 | $1,485,021 | $1,681,702 | $1,878,396 | $2,075,103 | $2,271,822 | $2,468,554 | $2,665,298 | $2,862,055 | $3,058,824 | $3,255,606 |
| Net Worth | $154,000 | $339,413 | $728,081 | $926,763 | $1,125,456 | $1,324,163 | $1,522,881 | $1,721,613 | $1,920,356 | $2,119,113 | $2,317,881 | $2,516,663 | $2,715,456 |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Sample Business Plans » Education
How to Write a School Supplies Business Plan [Sample Template]
Are you about starting a school supplies company? If YES, here is a complete sample school supplies business plan template & feasibility report you can use FREE. School supplies businesses sell and distribute teaching materials to schools, parents, teachers and students. These stores frequently carry a wide selection of educational materials and decorations for classroom teachers such as books, pencils, pens, etc.
With this type of business, you can choose to own a store/warehouse if you have the financial capacity to or you can choose to operate without a store. The bottom line is that you must own your own distribution truck/van, you should know how to source for school supplies and how to get them delivered to your customers.
Come to think of it, starting a school supplies business is profitable, it is a very easy business to start and it is not so capital intensive especially if you get the goods on trust from the production companies. Getting the right products that people want to buy and good networking and stock keeping records are the secrets of running a school supplies business.
So, if you have decided to start a school supplies business, then you should ensure that you carry out thorough feasibility studies and also market survey. This will enable you locate the business in a location with the right demography, network with school supplies retailers and then hit the ground running.
Business plan is yet another very important business document that you should not take for granted while launching your own school supplies business. Below is a sample school supplies business plan template that will give you the needed guide to write yours with ease.
A Sample School Supplies Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
Businesses in the School Supplies Wholesaling industry are involved in the sale and distribution of office tools, writing implements, stamps and stencils, stationery and loose-leaf paper, notebooks, binders and organizers and other related items.
If you have been keeping close tabs with happenings in the School Supplies Wholesaling industry, you would have noticed that the industry has struggled over the five years to 2018 with low demand and declining supply-chain relevance.
The School Supplies Wholesaling industry is a thriving sector of the economy of the united states of America and they generate a whooping over billion annually from more than 508 registered and licensed School Supplies Wholesaling businesses scattered all around the United States of America.
The industry is responsible for the employment of over 2,698 people. Experts project the industry to grow at a -2.0 percent annual rate within 2013 and 2018. It is important to state that the company holding the largest market share in the School Supplies Wholesaling industry is School Specialty Inc.
A recent report released by IBISWorld shows that over the past five years, the School Supplies Wholesaling industry has declined by -2.0 percent to reach revenue of $2bn in 2018. In the same timeframe, the number of businesses has declined by -0.2 percent and the number of employees has declined by -3.0 percent.
It is a fact that an estimated two-thirds of the United States’ gross domestic product (GDP) comes from retail consumption of which the School Supplies Wholesaling industry contributes greatly. This is why the United States of America’s economy is measured with the yardstick of how well the retailing business is fairing there.
When there is an unstable economy, purchasing power drops and it impacts the retailing / distribution industry negatively which may result in the closure of some of these businesses.
School supplies business is indeed a profitable business venture and it is open for any aspiring entrepreneur to come in and establish his or her business; you can choose to start on a small scale without a store/warehouse or you can choose to start on a large scale with standard store/warehouse, dozens of distribution trucks and a strong online presence.
2. Executive Summary
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC is a registered distribution company that will be involved in the distribution of teaching resources to schools and retail centers. Our warehouse and store will be located around Los Angeles Unified – California which happens to be the district with the second highest number of schools (646,683 schools) in the whole of the United States.
We have been able to lease a warehouse facility that is big enough to fit into the kind of school supplies company that we intend launching and the facility is centrally located in the heart of town with easy delivery network.
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC will distribute a wide range of school supplies at affordable prices from different brands. We will engage in the sale and distribution of office tools, writing implements, stamps and stencils, stationery and loose-leaf paper, notebooks, binders, organizers and other related items.
We are aware that there are several school supplies companies all around Los Angeles- California which is why we spent time and resources to conduct our feasibility studies and market survey so as to offer much more than our competitors will be offering. We have robust distribution network; strong online presence and our distributors are armed with the various payment options available in the United States.
Our customer care is going to be second to none in the whole of Los Angeles Unified – California and our deliveries will be highly reliable. We know that our customers are the reason why we are in business which is why we will go the extra mile to get them satisfied when they patronize our products.
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC will ensure that all our customers are given first class treatment whenever they visit our warehouse or order school supplies from us. We have a CRM software that will enable us manage a one on one relationship with our customers no matter how large the numbers of our customers’ base and distribution network may grow to.
We will ensure that we get our customers involved in the selection of brands and also when making some business decisions that directly affect them.
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC will at all times demonstrate her commitment to sustainability, both individually and as a firm, by actively participating in our communities and integrating sustainable business practices wherever possible. We will ensure that we hold ourselves accountable to the highest standards by meeting our client’s needs precisely and completely.
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC is a family business that is owned by Regina Trent and her immediate family members. Regina Trent has a B.Sc. in Business Administration with over 8 years’ experience in the retailing and distribution industry, working for some of the leading brand in the United States.
Although the business is launching out with focusing on Los Angeles Unified – California, but there is a plan to expand our distribution network all across the state of California.
3. Our Products and Services
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC is in the School Supplies Wholesaling industry and we will be involved in the distribution of a wide range of products from top manufacturing brands in the United States. Our products and services offerings are listed below;
- Writing implements, stamps and stencils
- Stationery (Pencil box, Crayons, Colored pencils, Washable markers, Ballpoint pens, Pencil sharpener, Erasers, Glue sticks, Ruler, Blunt-tipped scissors, Plastic folders, Assorted construction paper, Wide-ruled notebook or pad, Index cards, Loose-leaf paper)
- Notebooks, binders and organizers
- Lunchbox or bag
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our vision is to become the leading brand in the school supplies line of business in the whole of Los Angeles Unified – California.
- Our mission is to establish a highly reliable school supplies business brand that will distribute a wide range of teaching resources to schools and retail centers in Los Angeles Unified and other cities in California where we intend launching out.
Our Business Structure
Our intention of starting a school supplies business is to build a standard retail and distribution business in Los Angeles Unified – California. We will ensure that we put the right structure in place that will support the kind of growth that we have in mind while setting up the business.
We will make sure that we hire people that are qualified, honest, customer centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all our stakeholders. As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our senior management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of ten years or more.
In view of that, we have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions that will be made available at Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC;
- Chief Executive Officer (Owner)
- Warehouse Manager
- Human Resources and Admin Manager
Merchandize Manager
Sales and Marketing Manager
Information Technologist
- Accountants/Cashiers
- Customer Services Executive
- Drivers/Distributors
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Officer – CEO:
- Increases management’s effectiveness by recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results and developing incentives
- Creating, communicating, and implementing the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
- Reports to the board
Admin and HR Manager
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Maintains office supplies by checking stocks; placing and expediting orders; evaluating new products.
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance requirements; calling for repairs.
- Defining job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carrying out induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Responsible for arranging travel, meetings and appointments
- Oversee the smooth running of the daily office activities.
Warehouse Manager:
- Responsible for organizing the safe and efficient receipt, storage and dispatch of warehoused goods
- In charge of planning, coordinating and monitoring the receipt, order assembly and dispatch of goods
- In charge of coordinating the use of automated and computerized systems where necessary
- Responsible for keeping stock control systems up to date and making sure inventories are accurate
- Responsible for producing regular reports and statistics on a daily, weekly and monthly basis
- Ensures that proper records of goods are kept and warehouse does not run out of products
- Ensure that the warehouse facility is in tip top shape and goods are properly arranged and easy to locate
- Supervise the workforce in the warehouse floor.
- Manage vendor relations, market visits, and the ongoing education and development of the organizations’ buying teams
- Responsible for the purchase of office tools, writing implements, stamps and stencils, stationery and loose-leaf paper, notebooks, binders and organizers and other related items for the organizations
- Ensures that the organization operates within stipulated budget.
- Manage external research and coordinate all the internal sources of information to retain the organizations’ best customers and attract new ones
- Model demographic information and analyze the volumes of transactional data generated by customer purchases
- Identify, prioritize, and reach out to new partners, and business opportunities et al
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Document all customer contact and information
- Represent the company in strategic meetings
- Help increase sales and growth for the company
- Manage the organization website
- Handles ecommerce aspect of the business
- Responsible for installing and maintenance of computer software and hardware for the organization
- Manage logistics and supply chain software, Web servers, e-commerce software and POS (point of sale) systems
- Manage the organization’s CCTV
- Handles any other technological and IT related duties.
Accountant/Cashier:
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Provides managements with financial analyses, market research to forecast trends and business conditions.
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensuring compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for the organization
- Serves as internal auditor for the organization
Client Service Executive
- Ensures that all contacts with clients (e-mail, walk-In center, SMS or phone) provides the client with a personalized customer service experience of the highest level
- Through interaction with customers on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s products and services
- Manages administrative duties assigned by the human resources and admin manager in an effective and timely manner
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the organizations’ products, promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to customers when they make enquiries
Distribution Truck Drivers
- Assist in loading and unloading stock
- Maintain a logbook of their driving activities to ensure compliance with federal regulations governing the rest and work periods for operators.
- Keep a record of vehicle inspections and make sure the truck is equipped with safety equipment
- Assist the transport and logistics manager in planning their route according to a distribution schedule.
- Local-delivery drivers may be required to sell products or services to stores and businesses on their route, obtain signatures from recipients and collect cash.
- Inspect vehicles for mechanical items and safety issues and perform preventative maintenance
- Comply with truck driving rules and regulations (size, weight, route designations, parking, break periods etc.) as well as with company policies and procedures
- Collect and verify delivery instructions
- Report defects, accidents or violations
6. SWOT Analysis
Our intention of starting out in Los Angeles Unified and distribute our goods only within the are is to test run the business for a period of 2 to 5 years to know if we will invest more money and then expand all around the state of California.
We are quite aware that there are several school supplies companies all over Los Angeles Unified and even in the same location where we intend locating ours, which is why we are following the due process of establishing a business.
We know that if a proper SWOT analysis is conducted for our business, we will be able to position our business to maximize our strength, leverage on the opportunities that will be available to us, mitigate our risks and be equipped to confront our threats.
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC employed the services of an expert HR and Business Analyst with bias in retailing and distribution to help us conduct a thorough SWOT analysis and to help us create a Business model that will help us achieve our business goals and objectives. This is the summary of the SWOT analysis that was conducted for Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC;
Our location, the business model we will be operating (robust distribution network), varieties of payment options, wide range of products from top brands and our excellent customer service culture will definitely count as a strong strength for Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC. So, also our management team has what it takes to grow a business from startup to profitability with a record time.
A major weakness that may count against us is the fact that we are a new school supplies business and we don’t have the financial capacity to compete with leaders in the industry for now.
- Opportunities:
The fact that we are going to be operating our school supplies business in Los Angeles Unified – California provides us with unlimited opportunities to supply our school supplies to a large number of schools and retail facilities. We have been able to conduct thorough feasibility studies and market survey and we know what our potential clients will be looking for when they patronize our products and services; we are well positioned to take on the opportunities that will come our way.
Just like any other business, one of the major threats that we are likely going to face is economic downturn. It is a fact that economic downturn affects purchasing / spending power. Another threat that may likely confront us is the arrival of a similar business in same location where ours is located. We are not ignoring the fact that unfavorable government policies can also affect our business.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
A broader trend toward ecommerce has been particularly pronounced in this industry, which resulted into encouraging more consumers to circumvent retailers and the wholesalers that supply them. In addition to that, brick-and-mortar retail sales have increasingly shifted to big-box department and discount stores who also retail school supplies.
They have been able to overtime make use of their purchasing power to source products directly from manufacturers, internalizing distribution functions and eliminating independent wholesalers from the school supply chain.
It is now a common phenomenon for distribution companies to leverage on technology to effectively predict consumer demand patterns and to strategically position their business to meet their needs; in essence, the use of technology has helped businesses like school supplies to maximize supply chain efficiencies.
8. Our Target Market
The school supplies wholesaling industry has a wide range of customers. In view of that, we have positioned our school supplies company to service schools and retail centers in Los Angeles Unified – California and every other location we will cover.
We have conducted our market research and we have ideas of what our target market would be expecting from us. We are in business to retail (distribute) a wide range of school supplies from different production companies to the following businesses;
- Retailers of school supplies
Our competitive advantage
A close study of the school supplies industry reveals that the market has become much more intensely competitive over the last decade. As a matter of fact, you have to be highly creative, customer centric and proactive if you must survive in this industry. We are aware of the stiff competition and we are prepared to compete favorably with other leading school supplies businesses in and around Los Angeles Unified – California.
One thing is certain; we will ensure that we have a wide range of products available in our warehouse at all times. One of our business goals is to make Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC a one stop school supplies company. Our excellent customer service culture, timely and reliable delivery services, online presence, and various payment options will serve as a competitive advantage for us.
Lastly, our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category (startups school supplies businesses) in the industry meaning that they will be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our aims and objectives. We will also give good working conditions and commissions to freelance sales agents that we will recruit from time to time.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC is in business to retail (distribute) a wide range of school supplies from top production companies to schools in Los Angeles Unified – California. We are in the school supplies wholesaling industry to maximize profits and we are going to go all the way out to ensure that we achieve or business goals and objectives.
We will generate income for the business by retailing and distributing;
10. Sales Forecast
One thing is certain when it comes to school supplies business, if your business is centrally positioned coupled with effective and reliable distribution network, you will always attract sales and that will sure translate to increase in revenue generation for the business.
We are well positioned to take on the available market in Los Angeles Unified – California and we are quite optimistic that we will meet our set target of generating enough income / profits from our first six months of operation and grow the business and our clientele base.
We have been able to examine the school supplies wholesaling industry, we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast.
Below are the sales projections for Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC, it is based on the location of our business, the list of school supplies and other factors as it relates to school supplies startups in the United States;
- First Fiscal Year: $240,000
- Second Fiscal Year: $350,000
- Third Fiscal Year: $600,000
N.B : This projection was done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown and there won’t be any major competitor offering same products and customer care services as we do within same location. Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
Before choosing a location for Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC, we conducted a thorough market survey and feasibility studies in order for us to be able to penetrate the available market and become the preferred choice for schools, teachers, students and parents in Los Angeles Unified – California.
We hired experts who have good understanding of the retailing and distribution industry to help us develop marketing strategies that will help us achieve our business goal of winning a larger percentage of the available market in Los Angeles Unified – California.
In summary, Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC will adopt the following sales and marketing approach to win customers over;
- Open our business in a grand style with a party for all.
- Introduce our business by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to small – scale school supplies retailers, schools, teachers, students, households and key stakeholders in Los Angeles Unified – California
- Ensure that we have a wide range of school supplies from different brands within and outside the United States at all times.
- Make use of attractive hand bills to create awareness business
- Position our signage / flexi banners at strategic places around Los Angeles Unified – California
- Create a loyalty plan that will enable us reward our regular customers
- Engage on roadshows within our neighborhood to create awareness for our school supplies business.
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
Despite the fact that our school supplies business is well structured and well located, we will still go ahead to intensify publicity for the business.
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC has a long-term plan of opening distribution channels all around the state of California which is why we will deliberately build our brand to be well accepted in Los Angeles Unified School District area before venturing out.
Here are the platforms we intend leveraging on to promote and advertise Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC;
- Place adverts on community – based newspapers, radio and TV stations
- Encourage the use of word of mouth publicity from our loyal customers
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; YouTube, Instagram, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Google+ and other platforms to promote our business.
- Ensure that our we position our banners and billboards in strategic positions all around Los Angeles Unified – California
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas in and around schools within Los Angeles Unified school district areas
- Brand all our official cars and distribution vans/trucks and ensure that all our staff members wear our branded shirt or cap at regular intervals.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
Pricing is one of the key factors that gives leverage to distribution companies and retailers, it is normal for retailers to purchase products from distribution companies where they can goods at cheaper price. We will work towards ensuring that all our goods are distributed at highly competitive prices compared to what is obtainable in the United States of America.
We also have plans in place to discount our goods once in a while and also to reward our loyal customers from time to time.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment with cash
- Payment via credit cards
- Payment via POS machines
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via bank draft
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our client make payment for our products without any stress on their part. Our bank account numbers will be made available on our website and promotional materials
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
From our market research and feasibility studies, we were able to come up with the following financial projections and costing as it relates to establishing a standard school supplies business in the United States of America;
- The total fee for registering the business in the United States of America – $750.
- Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits as well as the accounting services (software, P.O.S machines and other software) – $3,300.
- Marketing promotion expenses for the grand opening of Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of $3,580.
- The cost for hiring business consultant – $2,500.
- The cost for insurance (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) coverage at a total premium – $2,400.
- The cost for payment of rent for 12 months at $1.76 per square feet warehouse facility in the total amount of $105,600.
- The total cost for warehouse facility remodeling (construction of racks and shelves) – $20,000.
- Other start-up expenses including stationery ($500) and phone and utility deposits ($2,500).
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $60,000
- The cost for Start-up inventory (stocking with a wide range of office tools, writing implements, stamps and stencils, stationery and loose-leaf paper, notebooks, binders, organizers and other related items) – $100,000
- The cost for store equipment (cash register, security, ventilation, signage) – $13,750
- The cost of purchase and installation of CCTVs – $5,000
- The cost for the purchase of furniture and gadgets (Computers, Printers, Telephone, TVs, Sound System, tables and chairs et al) – $4,000.
- The cost for the purchase of distribution vans / trucks – $25,000
- The cost of launching a website – $600
- The cost for our opening party – $7,000
- Miscellaneous – $10,000
We would need an estimate of $350,000 to successfully set up our school supplies business in Los Angeles Unified – California.
Generating Funds/Startup Capital for Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC is a private business that is solely owned and financed by Regina Trent and her immediate family members. They do not intend to welcome any external business partner which is why she has decided to restrict the sourcing of the startup capital to 3 major sources.
- Generate part of the startup capital from personal savings
- Source for soft loans from family members and friends
- Apply for loan from the bank
N.B: We have been able to generate about $100,000 (Personal savings $80,000 and soft loan from family members $10,000) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $250,000 from our bank. All the papers and documents have been signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited with the amount.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
The future of a business lies in the number of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of their employees, their investment strategy and business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business (company), then it won’t be too long before the business close shop.
One of our major goals of starting Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running. We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to distribute our school supplies a little bit cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner.
We know that if we diligently put in place all that is stated above, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List/Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check: Completed
- Business Registration: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts: Completed
- Securing Point of Sales (POS) Machines: Completed
- Opening Mobile Money Accounts: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Leasing of warehouse facility and remodeling the facility: In Progress
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Generating capital from family members: Completed
- Applications for Loan from the bank: In Progress
- Writing of Business Plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents and other relevant Legal Documents: In Progress
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Printing of Promotional Materials: In Progress
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of furniture, racks, shelves, computers, electronic appliances, office appliances and CCTV: In progress
- Purchase of distribution vans: Completed
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business both online and around the community: In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement (License): Secured
- Opening party/launching party planning: In Progress
- Compilation of our list of products that will be distribute: Completed
- Establishing business relationship with school supplies manufacturing companies within and outside of the United States of America: In Progress
More on Education

- Payments & Billing
- Onboarding & Registration
- Reporting & Analytics
- After School Programs
- Conferences
- Group Tours
- Testimonials

What to Include in Your After-School Program Business Plan

To start a successful afterschool program, you first need an effective business strategy, which starts with a good business plan
A high-quality afterschool program business plan is essential. It provides a comprehensive overview of your program by running it through multiple types of analyses, approaches, and perspectives.
After all, just like any other business, an after-school program has a leadership structure, offers a service to paying customers, has competition to outperform, and a budget to adhere to.
A business plan should consider how all these factors come together to form a cohesive and effective structure.
In this article, we go over the elements comprising a typical business plan and the most optimal way to approach writing each of them.
Elements of an After-School Program Business Plan
So, which elements should you include in your after-school business plan?
Of course, there is no single definitive answer. Business plans are used by private companies and organizations alike, regardless of size, and they can be tailored to internal or external use.
However, there are still many common components most business plans will include.
These elements form the basic business strategy stress test, which will help you polish your after-school program ideas .
Executive Summary
To start, your after-school program business plan must include an executive summary.
An executive summary is to a business plan what the business plan is to the business itself—a brief and clear synopsis of the most relevant information, written to entice the reader to invest.
The main purpose of an executive summary is to grab the reader’s attention. It should be clear and concise and serve as a highlight reel of the strongest points from the remaining sections of a business plan.
It usually includes the following:
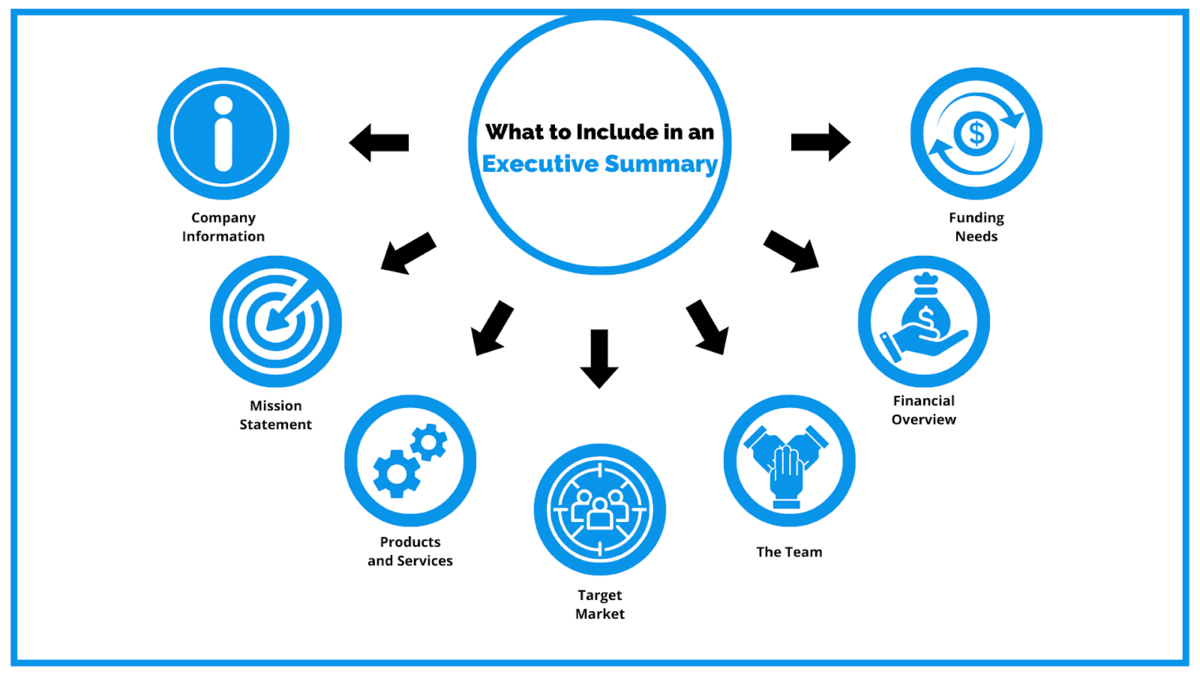
Illustration: Regpack
Because you need to flesh your ideas out before summing them up, the executive summary should be the last section you write.
However, it is the first one people will read.
Therefore, you need to make a strong first impression.
Remember, investors often have dozens of business plans to pick from. If they are not hooked by the end of the executive summary, they can easily decide to move on to the next one.
In short, the starting page of your after-school program business plan should contain an executive summary, a short and to-the-point representation of the business plan and its main ideas.
Business Description
The next element to include in your after-school program business plan is the business description.
This section should briefly convey to the reader what the program is about and what its purpose is.
For the first part, provide basic information such as the program’s name, business model, industry, key personnel, history, and planned opening date.
Next, write your program’s short-term and long-term goals.
Whether you strive for 60 sign-ups in a month or two student groups by the end of the year, it is important to choose goals that fit the acronym SMART—smart, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-bound.
Your objectives should align with your program’s mission, vision, and value statements. These make up the essence of your program and the driving force behind it.
The mission statement has to sum up the purpose of your after-school program in one to two sentences.
Here’s a good example from Urban Youth Harp Ensemble:

Source: Urban Youth Harp Ensemble
A business description should also include a vision statement. This is an aspirational description of the program’s desired academic enrichment in society.
In the case above, it might be: “To raise a musically literate generation.”
All in all, a business plan should include a description of what your after-school program does, why it exists, and its plans for academic achievement.
Description of Services
After defining what your after-school program is generally about, it is important to provide a detailed description of its services.
Begin by defining the educational focus of the program. Are you planning to teach one subject in depth, provide various extracurricular activities, offer homework assistance, or present professional development skills?
Or do you envision a less-focused, more entertaining environment to keep children busy while their parents work?
Elaborate with more specific details about the service.
For example, the students’ age, the location, and the size, length, and frequency of the classes. Include anything you think would be relevant to a person interested in the program.
Take a look at a service section from the Trackers organization:
Source: Trackers After School Basecamp
Ultimately, a good service description is necessary for an after-school program business plan because it provides a clear plan of the program’s real-world application process.
Organizational Structure
The next section to include in your after-school program business plan is the organizational structure.
List out all the people involved or required to run the program. Begin with yourself.
Write your name and position in the program, then provide a short biography, listing relevant skills and a background check.
Do the same for the other team members . In case you don’t have any partners or employees yet, name and describe the positions you plan to fill with future candidates. Also, add your proposed salaries for each position and include them in your financial projections.
When applicable, highlight your or the staff’s experience compatible with your program, like in this example:
Source: Workshop Houston
Workshop Huston offers creative, artistic programs for their students, which is reflected here—the CEO is a musician, and the program director is a multimedia artist.
The involvement of experts gives the program stronger legs to stand on, making it more possible for an interested party to invest or enroll .
In summary, the organizational structure is an overview of the job positions that make up the inner workings of your after-school program, providing insight into the people who fill those positions and their skills.
Operations Plan
The operations plan is the logistical strategy for your after-school program, making it a key element to include in your business plan.
In it, describe in practical terms what your program’s day-to-day operations look like.
Specify what it takes to run the program in terms of finances and resources, and your plan on securing them.
In other words, explain your idea of how to manage the program for it to stay operational and achieve set goals.
The type of questions the operations plan needs to cover include:
- What is the weekly schedule?
- How many groups of students will there be?
- Which teacher will be running which group?
- What will be the staff-to-child ratio?
- Does the program require props or materials, and where will you get them?
- What does the registration process look like for students and parents?
- Will the program be for high school or middle school students?
Also, don’t forget to research city and state legal requirements for working with children. You can usually find it on your state’s government website.
Ensuring you have a compliant system in place will protect the children from potentially dangerous conditions and help you avoid fines or even closure.
In conclusion, an operations plan should be included in your business plan to explain how you intend to fulfill the various requirements of running your after-school program .
Market Analysis
This section of the business plan should provide an overview of the market conditions for your after-school program.
To begin, do in-depth research into the state of the industry and the competition.
Look into the number of programs on a local and national level and extrapolate any noticeable trends regarding growth in recent years. Are after-school programs on the rise or decline?
Find out how your city or state compares to the others in the number of programs to assess the need for one in your area.
If you’re unsure where to find the answers, the Afterschool Alliance offers a lot of useful resources to help you start:
Source: The Afterschool Alliance
Find after-school programs in the vicinity and do a so-called SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats) analysis. Do the same program evaluation for your own, and then compare the results.
To have a chance of succeeding, you have to stand out from your competitors by utilizing your strengths and compensating for your weaknesses.
Once you define the competition’s weak spots, you can carve out a place in the market by offering a better value for money, providing unique enrichment activities, or catering to a specific niche audience.
Overall, the market analysis should illustrate how your program plans to succeed in the context of direct competition and the industry as a whole.
Marketing Strategy
After an exhaustive analysis of the market conditions, your business plan should map out the marketing strategy for the after-school program.
Research different marketing channels to decide which one best fits your needs.
You can pass out flyers, take out ads in the paper, use social media advertising, or use legacy media to market your program. You should come to a decision based on your budget and the target audience.
There are many free and paid solutions that can help you efficiently spread the word, each with its upsides and downsides.
For example, a radio commercial on the local station during rush hour is expensive, but it could also reach many working parents in the area.
Social media is cheap and allows you to market to target audiences, but, depending on where you live, it’s possible that relatively few working adults use it.
All in all, your business plan needs a marketing strategy that can reach the most amount of people by using the limited resources available to the program.
Pricing Strategy
The pricing strategy for your after-school program is vital for its financial stability and eventual success in the real world.
The pricing strategy is firstly informed by market analysis.
For example, if comparable programs in your vicinity charge an average 100$ per week, you should either price gauge them or match their price, but stay in a 100$ ballpark.
If necessary, seek the advice of a financial expert who can carefully go over your projected costs and earnings and set a balanced price.
Next, you have to figure out how you will manage payments. Are you going to charge on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis?
When deciding on payment management, consider using a registration service like Regpack for your program.
Regpack offers an automated billing feature that is easy to set up and simple to use.
Source: Regpack
This is a practical solution that saves you time and energy in collecting payments.
In conclusion, the pricing strategy of an after-school program should outline how much you intend to charge for the service and your method of managing payments.
Financial Plan
In the last section of the business plan, you need to provide all the financial information regarding your after-school program.
Since you are just starting out , this data will be largely theoretical. However, mention the numbers you do have, such as your starting budget proposal, expenses, and any additional investments you have so far.
For the rest, use the financial estimations from previous sections to come up with projected earnings and expenses.
To approximate expenses, add up all the costs of running the program. These include the salaries, the rent for the location, the cost of marketing, and the price of materials you will need.
A simple way to calculate projected earnings is by multiplying the number of students by the monthly price of admission per student.
By juxtaposing earnings with expenses, you can make a better case for the sustainability or growth of your program.
To sum up, a financial plan should contain all the costs and expenses for operating an after-school program, and make reasonable goals and projections based on the numbers.
Your after-school program business plan provides detailed insight into your program services, operational strategies, business goals, funding sources, and finances.
It should include every piece of information that is pertinent to the program’s success in the market and the enrichment opportunities for the students.
The research you do will help you sharpen up your business strategy and convince others of your after-school program’s potential.
Therefore, whether you are looking for investors or just hammering out your plans, write a business plan that follows the route outlined in the article, and by the time you’re finished writing, you will have a stronger after-school program for your school district.

Asaf, Founder and CEO of Regpack, has extensive experience as an entrepreneur and investor. Asaf has built 3 successful companies to date, all with an exit plan or that have stayed in profitability and are still functional. Asaf specializes in product development for the web, team building and in bringing a company from concept to an actualized unit that is profitable.
Related posts

What is Regpack?
Regpack is an online registration software that creates intelligent application processes with integrated payment processing.
We will be contacting you shortly!
How can I help you move forward?
Select a time for your FREE Demo
Thank you! We will get back to you in no time :)
Thanks! We got the information. We really look forward to connecting again. Talk soon.
What do you want to build today?
ONLINE CLASSES
TRIPS AND TOURS
AFTER SCHOOL PROGRAMS
EDUCATIONAL TOURS
APPLICATIONS

See a website experience built just for you!
What industry are you in.

Private School Business Plan [Sample Template]
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business Plans » Education Sector » Schooling

Are you about starting a private school (nursery, primary or high school)? If YES, here’s a complete sample private school business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE.
Okay, so we have considered all the requirements for starting a private school. We also took it further by analyzing and drafting a sample private school marketing plan template backed up by actionable guerrilla marketing ideas for private schools. So let’s proceed to the business planning section.
Suggested for You
- Preschool Business Plan [Sample Template]
- DJ School Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Nursery School Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Music School Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Language School Business Plan [Sample Template]
One of the best things that can happen to anyone is to have a private school. This is one very lucrative business that will continue to rake in money for its owners. As an aspiring entrepreneur who is looking towards starting a business, you should ensure that whatever business you intend to start, you make sure that it is located in an appropriate place.
For example; if you want to start a private school, it will be a wrong business judgment if you decide to site the school close to an industrial area or close to a market. Aspiring entrepreneurs therefore are urged as a matter of necessity to ensure that they carry out a thorough market research and feasibility study of the industry they intend to go into before investing their hard earned money and time.
It is known fact that the demand for private schools is driven by the fact that most public cum government owned schools cannot accommodate every students or potential students in a given geographical location. In some cases, students with special needs cannot cope in public schools hence the need for private schools.
If you think starting a private school business sounds like what you want to do. Then you may want to use the business plan below as a guide.
A Sample Private School Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
Private schools which is also known in the united states as independent schools, non-governmental, or non – state schools are schools that are not administered by either the local, state or the federal governments; hence, they have the right to select their students and are funded in whole or in part by charging their students tuition fees, rather than relying on mandatory taxation through public (government) funding.
Some private schools have structure in place that offer scholarships to some students, which makes the cost cheaper, depending on a talent such as sport scholarship, art scholarship, academic scholarship the student may be brining to the private school, financial need, or tax credit scholarships that might be available.
The Private Schools industry comprises of primary that is kindergarten through sixth grade and secondary that is seventh through 12th grade) educational institutions that are predominantly funded through enrollment and tuition fees from students and of course from other private sources.
Recent reports released by IBISWORLD shows that the revenue for the Private Schools industry is expected to increase, as the economy continues to recover. The indicated that during the five years to 2016, enrollment decreased, which was a trend attributable to rising costs and competition from charter schools.
However, going forward, in the next five years, household income is anticipated to increase, making it easier for families to afford private-school tuition. Additionally, enrollment declines will lesson, resulting in more stable demand for private schools
In the United States of America and of course in most countries of the world, The Private Schools industry is indeed a large and thriving industry. Statistics has it that The Private Schools industry in the United States of America, is worth $52 billion, with an estimated growth rate of 0.1 percent.
There are about 25,742 registered and licensed (accredited) Private schools scattered all around the United States of America and they are responsible for employing about 644,320 people.
Aside from Catholic schools, which is the second largest sector after government schools, with around 21 percent of secondary enrollments, no other private school can boast of dominating the market; every player in the industry can comfortably compete in the industry.
It is important to state that the barriers to entry into the Private Schools industry are high. As a matter of fact, the private school industry is an industry in which it is pretty difficult for new entrants to establish themselves. So also, the reputation of the private school is of utmost importance, as private schools that have a good history of getting students into prestigious colleges often have the best reputations hence good enrollments.
With this, it is obvious that a new entrant into the private school industry cannot offer this. Reputation indeed is imperative to parents’ decisions when shopping for private school for their wards. This is so because the quality of education cannot be assessed until well after it is complete.
As a major marketing tool, schools need to show parents a track record of admission to elite colleges and universities. Even though this might seem like a saturated industry, the industry is still pretty much open for aspiring school proprietors and proprietress to still come in and compete.
As a matter of fact, if you conduct your research and feasibility studies very well before starting your own private school couple with impressive profile of your faculty members, you are likely going to struggle less to make headway in the industry.
2. Executive Summary
Rolland Gyros International Private School is an international private school that will be located in a well – populated residential estate in Ashville – North Carolina, United States of America.
We are a standard private school that is composed of primary (kindergarten through sixth grade) and secondary (seventh through 12th grade) educational institution that will be predominantly funded through tuition fees and levies from students and of course from other private sources.
Rolland Gyros International Private School is a client-focused and result driven private school that provides broad-based learning approaches and experience at an affordable fee that won’t in any way put a hole in the pockets of our clients (students and parents alike).
We will offer standard and professional teaching services in a highly secured and conducive learning environment to all our students that is primary (kindergarten through sixth grade) and secondary (seventh through 12th grade). We will ensure that we work hard to meet and surpass all our students’ expectations and educational goals whenever they enroll in our tutorial college.
At Rolland Gyros International Private School, our students’ overall best interest would always come first, and everything we do is guided by our values and professional ethics. We will ensure that we hire professional educationist cum teachers in various subjects who are well experienced and passionate in imparting knowledge to students at various learning ladder.
Rolland Gyros International Private School will at all time demonstrate her commitment to sustainability, both individually and as an educational organization, by actively participating in our communities and integrating sustainable business practices wherever possible.
We will ensure that we hold ourselves accountable to the highest standards by meeting our students’ needs precisely and completely. We will cultivate a working environment that provides a human, sustainable approach to earning a living, and living in our world, for our partners, employees and for our students.
We have plans to offer learning platforms to people with both learning disability and physical disability (especially the blind, the dumb and the deaf).
Our overall business goal is to position our private school to become the leading tutorial brand in the educational industry in the whole of Ashville – North Carolina, and also to be amongst the top 30 private schools in the United States of America within the first 12 years of operations.
This might look too tall a dream but we are optimistic that this will surely come to pass because we have done our research and feasibility studies and we are enthusiastic and confident that Ashville is the right place to launch our private school.
Rolland Gyros International Private School is founded by Dr. (Mrs.) Irene Rolland Gyros and family. She is an educationist per excellence and she has won many awards in the education sector in the United States.
Dr. (Mrs.) Irene Rolland Gyros has both the academic qualifications and experience to run a private school that can favorably compete with other leading private schools not only in Ashville – North Carolina, but also throughout the United States and Canada.
3. Our Products and Services
Rolland Gyros International Private School is going to offer varieties of educational services within the scope of the education board in the United States of America.
Our intention of starting our private school is to soundly educate people in various subjects and of course to make profits from the education cum private schools industry and we will do all that is permitted by the law in the US to achieve our aim and business goal. Our service offerings are listed below;
- Teaching basic literacy and numeracy
- Establishing foundations in science, mathematics, geography, history and other social sciences
- Constantly working hard to meet regulatory accreditation standards
- Administering private funding efforts
- Providing access to extracurricular activities
- Retailing of Educational Books and Materials
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our vision is to build a highly competitive private school that will become the number one choice for both parents and students in the whole of Ashville – North Carolina.
- Our vision reflects our values: integrity, service, excellence and teamwork.
- Our mission is to provide professional and conducive learning environment to students at different level of learning.
- Our overall business goal is to position Rolland Gyros International Private School to become the leading private school brand in the educational cum private school industry in the whole of Ashville – North Carolina, and also to be amongst the top 30 private schools in the United States of America within the first 12 years of operations.
Our Business Structure
It is a known fact that, the success of any business is to a larger extent dependent on the business structure of the organization and the people who occupy the available roles in the organization. Rolland Gyros International Private School will build a solid business structure that can support the growth of our private school.
We will ensure that we hire competent hands (teaching and non – teaching staff members) to help us build the private school of our dream.
The fact that we want to become one of the leading private school brand in the industry in the whole of the United States of America makes it highly necessary for our organization to deliberately build a well – structured business from the onset.
We will work hard to ensure that we only attract people with the right mindset to help us achieve our business goals and objectives in record time. Below is the business structure that we will build Rolland Gyros International Private School;
- Head of The Private School(School Proprietress)
School Administrator
Tutors for Various Subjects – Secondary (seventh through 12th grade)
Tutors for Various Subjects – Primary (kindergarten through sixth grade)
- Accountant / Bursar
- Client Service Executive / Front Desk Officer
Security Officers
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Head of the Tutorial College / School Coordinator:
- Responsible for providing direction for the college
- Creates, communicates, and implements the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for handling high profile clients and deals
- Responsible for fixing fees and signing business deals (partnership)
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the tutorial college
- Coordinates all arms of the tutorial school (tutorial center, adult education, home tutors and special education)
- Evaluates the success of the tutorial college
- Reports to the board of the tutorial college
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the tutorial school
- Designs job descriptions with KPI to drive performance management for tutors (teachers)
- Regularly hold meetings with key stakeholders (parents and member of the school board) to review the effectiveness of the schools’ Policies, Procedures and Processes
- Maintains office supplies by checking stocks; placing and expediting orders; evaluating new products.
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance requirements; calling for repairs.
- Defines job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carries out staff induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Responsible for arranging travel, meetings and appointments
- Updates job knowledge by participating in educational opportunities; reading professional publications; maintaining personal networks; participating in professional organizations.
- Oversees the smooth running of the daily activities of the private school.
- Effectively teach subject / subjects as assigned by the school administrator
- Accesses the progress of students under their care
- Ensures that students abide by the rules and regulations of the private school
- Contributes his / her quota towards growing the private school
- Receives complaints from parents and channel it to the appropriate quarters
- Handle any other duty as assigned by the school administrator.
- Ensure that students abide by the rules and regulations of the school administrator
- Handles any other duty as assigned by the school administrator.
Marketing Executive
- Identifies, prioritizes, and reaches out to new students, and business opportunities et al
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts; participates in the structuring and financing of projects; assures the completion of development projects.
- Writes winning proposal documents, negotiate fees and rates in line with organizations’ policy
- Responsible for handling business research, market surveys and feasibility studies for clients
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Develops, executes and evaluates new plans for expanding increase sales
- Documents all customer contact and information
- Represents the company in strategic meetings
- Helps to increase sales and growth for the school
School Bursar (Accountant)
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Provides managements with financial analyses, development budgets, and accounting reports; analyzes financial feasibility for the most complex proposed projects; conducts market research to forecast trends and business conditions.
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting for one or more properties.
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensures compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for Rolland Gyros International Private School
- Serves as internal auditor for Rolland Gyros International Private School
Client Service Executive
- Welcomes / receive parents and students by greeting them in person or on the telephone; answering or directing inquiries.
- Ensures that all contacts with parents and students (e-mail, walk-In center, SMS or phone) provides the parents and students with a personalized customer service experience of the highest level
- Through interaction with parents and students on the phone, uses every opportunity to build parent’s interest in the schools’ products and services
- Manages administrative duties assigned by the HR and Admin Manager in an effective and timely manner
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the organizations’ products, promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to parents and students when they make enquiries
- Receives parcels / documents for Rolland Gyros International Private School
- Distribute mails in the organization
- Handles any other duties as assigned by the School Administrator.
- Responsible for cleaning the school facility at all times
- Ensures that toiletries and supplies don’t run out of stock
- Cleans both the interior and exterior of the schools facility
- Handles any other duty as assigned by the school administrator
- Ensures that the school facility is secured at all time
- Controls traffic and organize parking
- Gives security tips to staff members from time to time
- Patrols around the building on a 24 hours basis
- Submits security reports weekly
- Any other duty as assigned by the school administrator
6. SWOT Analysis
Rolland Gyros International Private School engaged the services of a core professional in the area of business consulting and structuring with bias in the education sector to assist us in building a well – structured private school that can favorably compete in the highly competitive education cum private schools industry in the United States.
Part of what the team of business consultant did was to work with the management of our organization in conducting a SWOT analysis for Rolland Gyros International Private School. Here is a summary from the result of the SWOT analysis that was conducted on behalf of Rolland Gyros International Private School;
As a private school, our core strength lies in the power of our team; our workforce. We have a team with excellent qualifications and experience in the educational sector. We are well positioned in a community with the right demography and we know we will attract loads of students from the first day we open our doors and welcome students for enrollment.
As a new private school in Ashville – North Carolina, it might take some time for our organization to break into the market and gain acceptance via reputation in the already saturated education cum private schools industry; that is perhaps our major weakness.
- Opportunities:
The opportunities in the education cum private schools industry is massive considering the number of parents who would want their wards to perform excellently well in their education and go ahead to be admitted in Ivy league colleges.
As a standard and international private school, Rolland Gyros International Private School is ready to take advantage of any opportunity that comes her way.
Every business faces a threat or challenge at any part of the life cycle of the business. These threats can be external or internal. This shows the importance of a business plan, because most threats or challenges are to be anticipated and plans put in place to cushion what effect they might bring to the private school.
Some of the threats that we are likely going to face as a private school operating in the United States of America are unfavorable government policies that might affect private schools, the arrival of a competitor within our location of operations and global economic downturn which usually affects spending / purchasing power.
There is hardly anything we can do as regards these threats other than to be optimistic that things will continue to work for our good.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
The trend in the private school line of business is that the key to attracting students is the educational performance and the pass rate of their students in national exams.
Any private school that has good records will always thrive. The demand for private schools is driven by the fact that most public cum government owned schools cannot accommodate every students or potential students in a given geographical location.
In some cases, students with special needs cannot cope in public schools hence the need for private schools. The economic downturn hasn’t really affected this industry, especially in countries that believe in the efficacy of education.
The areas you would need to spend heavily on is in ensuring that your school is up to standard, your advertisements, and on insurance policy cover. Lastly, it is trendier to find private schools engaging in extra – curricular activities and as a matter of fact, a private school that thrives in sports can leverage on that to attract students who are sports inclined.
8. Our Target Market
As a standard and international private school, Rolland Gyros International Private School is going to offer varieties of educational services within the scope of the education board in the United States of America. Our intention of starting our private school is to soundly educate people in various subjects and of course to make profits from the education cum private schools industry
Our target market as a private school cuts across people (students) of different class and people from different culture background whether African, White, Caucasian, Latinos, Indians, and Asians. We are coming into the education cum private schools industry with a business concept that will enable us work with the students at different learning stages residing in and around Ashville – North Carolina.
Our competitive advantage
Indeed the private schools industry is highly competitive and the entry barriers are high. As a matter of fact, the private school industry is an industry in which it is pretty difficult for new entrants to establish themselves. So also, the reputation of the private school is of utmost importance, as private schools that have a good history of getting students into prestigious colleges often have the best reputations hence good enrollments.
As a major marketing tool, schools need to show parents a track record of admission to elite colleges and universities. We are quite aware that to be highly competitive in the education cum private schools industry means that you should be able to deliver consistent quality service, your students should be able to experience remarkable difference and improvement and you should be able to meet the expectations of both students and parents alike.
Rolland Gyros International Private School might be a new entrant into the education cum private schools industry in the United States of America, but the management staffs and owners of the private school are considered gurus. They are people who are core professionals, licensed and highly qualified educationist / teachers at various levels of learning in the United States. These are part of what will count as a competitive advantage for us.
Lastly, our employees (teaching and non – teaching staff members) will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category (startups private school in the United States) in the industry meaning that they will be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our business aims and objectives.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Rolland Gyros International Private School is established with the aim of maximizing profits in the education cum private schools industry and we are going to go all the way to ensure that we do all it takes to attract students on a regular basis. Rolland Gyros International Private School will generate income by offering the following tutorial services;
- Teaching High school students various subjects in our private school
10. Sales Forecast
One thing is certain, there would always be parents and students who would need the services of private schools to be able to achieve their educational goals and as such the services of private schools will always be needed.
We are well positioned to take on the available market in Ashville – North Carolina and we are quite optimistic that we will meet our set target of generating enough income / profits from the first six month of operations and grow the private school and our student base.
We have been able to critically examine the private schools cum education market in the United States of America and we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast.
The sales projection is based on information gathered on the field and some assumptions that are peculiar to similar startups in Ashville – North Carolina. Below is the sales projection for Rolland Gyros International Private School, it is based on the location of our tutorial center and of course the wide range of tutorial services that we will be offering;
- First Fiscal Year-: $250,000
- Second Fiscal Year-: $450,000
- Third Fiscal Year-: $750,000
N.B : This projection is done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown and natural disasters within the period stated above. So, there won’t be any major competitor (private school) offering same additional services as we do within same location. Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
We are mindful of the fact that there is stiffer competition amongst private schools in the United States of America; hence we have been able to hire some of the best marketing experts to handle our sales and marketing concerns. Our sales and marketing team will be recruited base on their vast experience in the industry and they will be trained on a regular basis so as to be well equipped to meet their targets and the overall goal of the private school.
We will also ensure that our students’ excellent results from national exams and other exams speaks for us in the marketplace; we want to build a standard and first – class private school that will leverage on word of mouth advertisement from satisfied clients (both individuals and corporate organizations).
Our goal is to grow our private school to become one of the top 30 private schools in the United States of America which is why we have mapped out strategy that will help us take advantage of the available market and grow to become a major force to reckon with not only in Ashville – North Carolina but also in other cities in the United States of America.
Rolland Gyros International Private School is set to make use of the following marketing and sales strategies to attract clients;
- Introduce our private school by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to schools, parents / household and key stake holders in Ashville – North Carolina.
- Print out fliers and business cards and strategically drop them in schools, libraries and even student organizations.
- Creating a website, allows parents to be able to look you up, and also allows you to post general study tips, giving you an added advantage.
- Use friends and family to spread word about our private school
- Introduce Rolland Gyros International Private School to learning specialists, school coaches, school administrators, teachers, guidance counselors especially as they are with students everyday
- Post information about Rolland Gyros International Private School on bulletin boards in places like schools, libraries, and local coffee shops.
- Placing a small or classified advertisement in the newspaper, or local publication about Rolland Gyros International Private School
- Using tutorial referral networks such as agencies that will help match students with Rolland Gyros International Private School
- Joining relevant association or body that will enable you network and meet others in same industry.
- Advertising online by using an advertising platform such as Google Adwords, that will allow us place text advertisements alongside on websites with related contents, and along results from search engines.
- Advertise our private school in relevant educational magazines, newspapers, TV stations, and radio station.
- Attend relevant educational expos, seminars, and business fairs et al
- Engage direct marketing approach
- Encourage word of mouth marketing from loyal and satisfied clients
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
We are aware of the potency of a good publicity strategy hence we have been able to work with our brand and publicity consultants to help us map out publicity and advertising strategies that will help us walk our way into the heart of our target market.
We are set to become the number one choice for both parents and students in the whole of Ashville – North Carolina which is why we have made provisions for effective publicity and advertisement of our private school. Below are the platforms we intend to leverage on to promote and advertise Rolland Gyros International Private School;
- Place adverts on both print (community based newspapers and magazines) and electronic media platforms
- Sponsor relevant community based events / programs
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; Instagram, Facebook , twitter, YouTube, Google + et al to promote our brand
- Install our Bill Boards on strategic locations all around Ashville – North Carolina.
- Engage in road show from time to time in targeted neighborhoods in and around Ashville – North Carolina
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas in and around Ashville – North Carolina
- Passing general information via our school’s social media handles like twitter, Facebook, Google hangouts etc.
- Ensure that all our teaching and non – teaching staff members wear our branded shirts and all our vehicles are well branded with our schools’ logo et al.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
Private schools in the United States of America and of course in all the parts of the world charge students per tem / per session and students have the options of either paying their tuitions before resumption or during the school session.
Private schools generally charge students based on loads of factors, locations, services offerings and extra – curricular activities et al At Rolland Gyros International Private School we will keep our fees below the average market rate for all of our students by keeping our overhead low and by collecting payment in advance.
In addition, we will also offer special discounted rates to all our students at regular intervals. We are aware that there are some students that would need special assistance, we will offer flat rate for such services that will be tailored to take care of such students’ needs.
- Payment Options
At Rolland Gyros International Private School, our payment policy will be all inclusive because we are quite aware that different people prefer different payment options as it suits them. Here are the payment options that we will make available to our clients;
- Payment by via bank transfer
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via bank draft
- Payment via mobile money
- Payment with cash
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will help us achieve our plans with little or no itches.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
In setting up a private school business, the amount or cost will depend on the approach and scale you want to undertake.
If you intend to go big by acquiring a large facility, then you would need a higher amount of capital as you would need to ensure that your employees are taken care of, and that your private school’s environment is conducive enough for the students to learn.
This means that the start-up can either be low or high depending on your goals, vision and aspirations for your business. The materials and equipment that will be used are nearly the same cost everywhere, and any difference in prices would be minimal and can be overlooked.
As for the detailed cost analysis for starting a private school business; it might differ in other countries due to the value of their money. However, this is what it would cost us to start Rolland Gyros International Private School in the United of America;
- Business incorporation fees in the United States of America will cost – $750.
- The budget for Liability insurance, permits and license will cost – $3,500
- Acquiring a large facility that will accommodate the number of block of closes, playing field, staff offices and parking lots et al (Re – Construction of the facility inclusive) will cost – $350,000.
- Equipping the classes and office (computers, printers, projectors, markers, pens and pencils, furniture, telephones, filing cabinets, and electronics) will cost – $50,000
- Launching an official Website will cost – $500
- The budget for the payment of salaries for the first three months of operations: $120,000
- Additional Expenditure such as Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions will cost – $15,000
Going by the market survey and feasibility studies conducted, we came to the conclusion that we will need an average of $750,000 to start a small scale but standard private school in the United States of America.
Generating Funding / Startup Capital for Rolland Gyros International Private School
Rolland Gyros International Private School is a family business that will be owned and managed by Dr. (Mrs.) Irene Rolland Gyros and her immediate family.
They are the sole financial of the private school which is why they decided to restrict the sourcing of the start – up capital for the private school to just three major sources. These are the areas we intend generating our start – up capital;
- Generate part of the start – up capital from personal savings and sale of his stocks
- Generate part of the start – up capital from friends and other extended family members
- Generate a larger chunk of the startup capital from the bank (loan facility).
N.B: We have been able to generate about $250,000 (Personal savings $200,000 and soft loan from family members $50,000 ) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $500,000 from our bank. All the papers and document has been duly signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
It is a known fact that the future of any business lies in the numbers of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of the employees, their investment strategy and of course the business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business (company), then it won’t be too long before the business close shop.
One of our major goals of starting Rolland Gyros International Private School is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without the need for injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running.
We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers (students and parents alike) over is to ensure that we offer nothing less than the best, to offer quality education to all our students so much so that they can favorably compete with students all over the United States and gain admission to Ivy League colleges.
Rolland Gyros International Private School will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner of our business strategy.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of three years or more as determined by the board of the organization. We know that if that is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Marketing Plan. Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a school business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of school that you documented in your company overview.
Writing a school business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan: 1. Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan.
Sample Private School Business Plan. Below is a school business plan template to help you create each section of your own education business plan. Executive Summary Business Overview. Southside Academy, located in St. Paul, Minnesota, is a private school that has been providing quality education to the community's school children since 2017.
Additional Expenditure such as Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions will cost - $15,000. Going by the market survey and feasibility studies conducted, we came to the conclusion that we will need an average of $750,000 to start a small scale but standard private school in the United States of America.
The Executive Summary serves as a compact introduction to the business plan of your private school project. Don't go beyond 2 pages; ensure you include only the critical information. This document is designed to make the reader excited about your business plan.
Creating a schools business plan involves the following steps: Executive Summary: Provide a concise overview of the institution's mission, objectives, and key strategies. Market Analysis ...
This can be used for a variety of school business plans, including a private school business plan, a charter school, public schools, independent schools, virtual schools, primary or secondary education. Executive Summary - The executive summary provides an overview of your business opportunity and summarizes the business plan.
STAFFING PLAN. Aspire's staffing plan will augment the current core team with additional capacity to strengthen and plan expansion in Phase One, and to execute effectively in Phase Two and beyond. Most new hires will bring deep function-specific experience and expertise, in both education and business.
Writing a business plan is like a rite of passage for you to become a legitimate school owner or administrator. A business plan will serve as your written guide to making your educational institution a reality. To help you, we'll walk you through the six steps in writing a winning school business plan. Start with the Executive Summary
The Financial Model serves as a cornerstone component of the School Business Plan. The attached "School Financial Template" is the required format for budget submis-sion. The template is meant to be a starting point; the assumptions and line items should be adjusted to reflect your school's specific market and model. Additionally,
A sound business plan for a school is incomplete without a detailed market analysis and strategic positioning. This crucial section sheds light on the environment your school will operate in. Understanding your target market and the competitive landscape are steps that cannot be overlooked. A deep dive into these areas will guide your school's approach to capturing market share and securing ...
The purpose of a business plan is to ensure that you fully understand your market and your strategy. The plan also provides you with a roadmap to follow and if needed, to present to funding sources to raise capital for your school. Your business plan should include the following sections: Executive Summary - this section should summarize your ...
The benefits of a school business plan, the steps on how to write a school business plan, and FAQs on school business plan. ... You can use a good story in delivering the executive summary. Step 3: School Services. Your school surely offers educational services. You need to enumerate them so that the audience will be informed of your services.
1. The executive summary. The first section of your private secondary school's business plan is the executive summary which provides, as its name suggests, an enticing summary of your plan which should hook the reader and make them want to know more about your business.
The objective of this chapter is to help you write an Executive Summary for your business plan . When you've finished reading this chapter you will be able to clearly identify: Why your Business Plan needs and Executive Summary What the Executive Summary should contain As mentioned in the introduction, your Business Plan serves several roles.
Table of Contents. A business plan is a document that you create that outlines your company's objectives and how you plan to meet those objectives. Every business plan has key sections such as ...
25+ School Business Plan Templates in DOC | PDF. A business plan helps you with a new project, product, service, or system when managing a company. Students, teachers, and administrative members can also improve their education for secondary school, primary school, or other preschool kids. Moreover, you can also launch a new course for your ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
School Business Plan - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. 1) The document provides an overview of a private school business plan for Rolland Gyros International Private School located in Ashville, North Carolina. 2) The private school will provide primary and secondary education and will be funded through tuition fees, aiming to ...
Introduction. Curriculum Companion Suites (CSS) is a medium-sized software development and consulting firm focused on making the educational process more efficient and effective for K-12 schools. CCS software serves as a virtual teaching assistant for the educational process. Students can follow along with curriculum electronically through a ...
Marketing promotion expenses for the grand opening of Regina Trent® School Supplies Company, LLC in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of $3,580. The cost for hiring business consultant - $2,500.
The next section to include in your after-school program business plan is the organizational structure. List out all the people involved or required to run the program. Begin with yourself. Write your name and position in the program, then provide a short biography, listing relevant skills and a background check.
Additional Expenditure such as Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions will cost - $15,000. Going by the market survey and feasibility studies conducted, we came to the conclusion that we will need an average of $750,000 to start a small scale but standard private school in the United States of America.
Elon Musk may seek to join Trump's government efficiency commission, raising concerns about conflicts of interest and federal spending cuts.
Montgomery County Superintendent Thomas Taylor outlines entry plan, goals for improving school safety, academic performance and trust in the district.