
How To Write A Dissertation Introduction Chapter:
The 7 essential ingredients of an a-grade introduction.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA). Reviewed By Dr Eunice Rautenbach (D. Tech) | March 2020
If you’re reading this, you’re probably at the daunting early phases of writing up the introduction chapter of your dissertation or thesis. It can be intimidating, I know.
In this post, we’ll look at the 7 essential ingredients of a strong dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, as well as the essential things you need to keep in mind as you craft each section. We’ll also share some useful tips to help you optimize your approach.
Overview: How To Write An Introduction Chapter
- Understand the purpose and function of the intro chapter
- Craft an enticing and engaging opening section
- Provide a background and context to the study
- Clearly define the research problem
- State your research aims, objectives and questions
- Explain the significance of your study
- Identify the limitations of your research
- Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis

A quick sidenote:
You’ll notice that I’ve used the words dissertation and thesis interchangeably. While these terms reflect different levels of research – for example, Masters vs PhD-level research – the introduction chapter generally contains the same 7 essential ingredients regardless of level. So, in this post, dissertation introduction equals thesis introduction.
Start with why.
To craft a high-quality dissertation or thesis introduction chapter, you need to understand exactly what this chapter needs to achieve. In other words, what’s its purpose ? As the name suggests, the introduction chapter needs to introduce the reader to your research so that they understand what you’re trying to figure out, or what problem you’re trying to solve. More specifically, you need to answer four important questions in your introduction chapter.
These questions are:
- What will you be researching? (in other words, your research topic)
- Why is that worthwhile? (in other words, your justification)
- What will the scope of your research be? (in other words, what will you cover and what won’t you cover)
- What will the limitations of your research be? (in other words, what will the potential shortcomings of your research be?)
Simply put, your dissertation’s introduction chapter needs to provide an overview of your planned research , as well as a clear rationale for it. In other words, this chapter has to explain the “what” and the “why” of your research – what’s it all about and why’s that important.
Simple enough, right?
Well, the trick is finding the appropriate depth of information. As the researcher, you’ll be extremely close to your topic and this makes it easy to get caught up in the minor details. While these intricate details might be interesting, you need to write your introduction chapter on more of a “need-to-know” type basis, or it will end up way too lengthy and dense. You need to balance painting a clear picture with keeping things concise. Don’t worry though – you’ll be able to explore all the intricate details in later chapters.

Now that you understand what you need to achieve from your introduction chapter, we can get into the details. While the exact requirements for this chapter can vary from university to university, there are seven core components that most universities will require. We call these the seven essential ingredients .
The 7 Essential Ingredients
- The opening section – where you’ll introduce the reader to your research in high-level terms
- The background to the study – where you’ll explain the context of your project
- The research problem – where you’ll explain the “gap” that exists in the current research
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you’ll clearly state what your research will aim to achieve
- The significance (or justification) – where you’ll explain why your research is worth doing and the value it will provide to the world
- The limitations – where you’ll acknowledge the potential limitations of your project and approach
- The structure – where you’ll briefly outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis to help orient the reader
By incorporating these seven essential ingredients into your introduction chapter, you’ll comprehensively cover both the “ what ” and the “ why ” I mentioned earlier – in other words, you’ll achieve the purpose of the chapter.
Side note – you can also use these 7 ingredients in this order as the structure for your chapter to ensure a smooth, logical flow. This isn’t essential, but, generally speaking, it helps create an engaging narrative that’s easy for your reader to understand. If you’d like, you can also download our free introduction chapter template here.
Alright – let’s look at each of the ingredients now.

#1 – The Opening Section
The very first essential ingredient for your dissertation introduction is, well, an introduction or opening section. Just like every other chapter, your introduction chapter needs to start by providing a brief overview of what you’ll be covering in the chapter.
This section needs to engage the reader with clear, concise language that can be easily understood and digested. If the reader (your marker!) has to struggle through it, they’ll lose interest, which will make it harder for you to earn marks. Just because you’re writing an academic paper doesn’t mean you can ignore the basic principles of engaging writing used by marketers, bloggers, and journalists. At the end of the day, you’re all trying to sell an idea – yours is just a research idea.
So, what goes into this opening section?
Well, while there’s no set formula, it’s a good idea to include the following four foundational sentences in your opening section:
1 – A sentence or two introducing the overall field of your research.
For example:
“Organisational skills development involves identifying current or potential skills gaps within a business and developing programs to resolve these gaps. Management research, including X, Y and Z, has clearly established that organisational skills development is an essential contributor to business growth.”
2 – A sentence introducing your specific research problem.
“However, there are conflicting views and an overall lack of research regarding how best to manage skills development initiatives in highly dynamic environments where subject knowledge is rapidly and continuously evolving – for example, in the website development industry.”
3 – A sentence stating your research aims and objectives.
“This research aims to identify and evaluate skills development approaches and strategies for highly dynamic industries in which subject knowledge is continuously evolving.”.
4 – A sentence outlining the layout of the chapter.
“This chapter will provide an introduction to the study by first discussing the background and context, followed by the research problem, the research aims, objectives and questions, the significance and finally, the limitations.”
As I mentioned, this opening section of your introduction chapter shouldn’t be lengthy . Typically, these four sentences should fit neatly into one or two paragraphs, max. What you’re aiming for here is a clear, concise introduction to your research – not a detailed account.
PS – If some of this terminology sounds unfamiliar, don’t stress – I’ll explain each of the concepts later in this post.

#2 – Background to the study
Now that you’ve provided a high-level overview of your dissertation or thesis, it’s time to go a little deeper and lay a foundation for your research topic. This foundation is what the second ingredient is all about – the background to your study.
So, what is the background section all about?
Well, this section of your introduction chapter should provide a broad overview of the topic area that you’ll be researching, as well as the current contextual factors . This could include, for example, a brief history of the topic, recent developments in the area, key pieces of research in the area and so on. In other words, in this section, you need to provide the relevant background information to give the reader a decent foundational understanding of your research area.
Let’s look at an example to make this a little more concrete.
If we stick with the skills development topic I mentioned earlier, the background to the study section would start by providing an overview of the skills development area and outline the key existing research. Then, it would go on to discuss how the modern-day context has created a new challenge for traditional skills development strategies and approaches. Specifically, that in many industries, technical knowledge is constantly and rapidly evolving, and traditional education providers struggle to keep up with the pace of new technologies.
Importantly, you need to write this section with the assumption that the reader is not an expert in your topic area. So, if there are industry-specific jargon and complex terminology, you should briefly explain that here , so that the reader can understand the rest of your document.
Don’t make assumptions about the reader’s knowledge – in most cases, your markers will not be able to ask you questions if they don’t understand something. So, always err on the safe side and explain anything that’s not common knowledge.

#3 – The research problem
Now that you’ve given your reader an overview of your research area, it’s time to get specific about the research problem that you’ll address in your dissertation or thesis. While the background section would have alluded to a potential research problem (or even multiple research problems), the purpose of this section is to narrow the focus and highlight the specific research problem you’ll focus on.
But, what exactly is a research problem, you ask?
Well, a research problem can be any issue or question for which there isn’t already a well-established and agreed-upon answer in the existing research. In other words, a research problem exists when there’s a need to answer a question (or set of questions), but there’s a gap in the existing literature , or the existing research is conflicting and/or inconsistent.
So, to present your research problem, you need to make it clear what exactly is missing in the current literature and why this is a problem . It’s usually a good idea to structure this discussion into three sections – specifically:
- What’s already well-established in the literature (in other words, the current state of research)
- What’s missing in the literature (in other words, the literature gap)
- Why this is a problem (in other words, why it’s important to fill this gap)
Let’s look at an example of this structure using the skills development topic.
Organisational skills development is critically important for employee satisfaction and company performance (reference). Numerous studies have investigated strategies and approaches to manage skills development programs within organisations (reference).
(this paragraph explains what’s already well-established in the literature)
However, these studies have traditionally focused on relatively slow-paced industries where key skills and knowledge do not change particularly often. This body of theory presents a problem for industries that face a rapidly changing skills landscape – for example, the website development industry – where new platforms, languages and best practices emerge on an extremely frequent basis.
(this paragraph explains what’s missing from the literature)
As a result, the existing research is inadequate for industries in which essential knowledge and skills are constantly and rapidly evolving, as it assumes a slow pace of knowledge development. Industries in such environments, therefore, find themselves ill-equipped in terms of skills development strategies and approaches.
(this paragraph explains why the research gap is problematic)
As you can see in this example, in a few lines, we’ve explained (1) the current state of research, (2) the literature gap and (3) why that gap is problematic. By doing this, the research problem is made crystal clear, which lays the foundation for the next ingredient.
#4 – The research aims, objectives and questions
Now that you’ve clearly identified your research problem, it’s time to identify your research aims and objectives , as well as your research questions . In other words, it’s time to explain what you’re going to do about the research problem.
So, what do you need to do here?
Well, the starting point is to clearly state your research aim (or aims) . The research aim is the main goal or the overarching purpose of your dissertation or thesis. In other words, it’s a high-level statement of what you’re aiming to achieve.
Let’s look at an example, sticking with the skills development topic:
“Given the lack of research regarding organisational skills development in fast-moving industries, this study will aim to identify and evaluate the skills development approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK”.
As you can see in this example, the research aim is clearly outlined, as well as the specific context in which the research will be undertaken (in other words, web development companies in the UK).
Next up is the research objective (or objectives) . While the research aims cover the high-level “what”, the research objectives are a bit more practically oriented, looking at specific things you’ll be doing to achieve those research aims.
Let’s take a look at an example of some research objectives (ROs) to fit the research aim.
- RO1 – To identify common skills development strategies and approaches utilised by web development companies in the UK.
- RO2 – To evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies and approaches.
- RO3 – To compare and contrast these strategies and approaches in terms of their strengths and weaknesses.
As you can see from this example, these objectives describe the actions you’ll take and the specific things you’ll investigate in order to achieve your research aims. They break down the research aims into more specific, actionable objectives.
The final step is to state your research questions . Your research questions bring the aims and objectives another level “down to earth”. These are the specific questions that your dissertation or theses will seek to answer. They’re not fluffy, ambiguous or conceptual – they’re very specific and you’ll need to directly answer them in your conclusions chapter .
The research questions typically relate directly to the research objectives and sometimes can look a bit obvious, but they are still extremely important. Let’s take a look at an example of the research questions (RQs) that would flow from the research objectives I mentioned earlier.
- RQ1 – What skills development strategies and approaches are currently being used by web development companies in the UK?
- RQ2 – How effective are each of these strategies and approaches?
- RQ3 – What are the strengths and weaknesses of each of these strategies and approaches?
As you can see, the research questions mimic the research objectives , but they are presented in question format. These questions will act as the driving force throughout your dissertation or thesis – from the literature review to the methodology and onward – so they’re really important.
A final note about this section – it’s really important to be clear about the scope of your study (more technically, the delimitations ). In other words, what you WILL cover and what you WON’T cover. If your research aims, objectives and questions are too broad, you’ll risk losing focus or investigating a problem that is too big to solve within a single dissertation.
Simply put, you need to establish clear boundaries in your research. You can do this, for example, by limiting it to a specific industry, country or time period. That way, you’ll ringfence your research, which will allow you to investigate your topic deeply and thoroughly – which is what earns marks!
Need a helping hand?
#5 – Significance
Now that you’ve made it clear what you’ll be researching, it’s time to make a strong argument regarding your study’s importance and significance . In other words, now that you’ve covered the what, it’s time to cover the why – enter essential ingredient number 5 – significance.
Of course, by this stage, you’ve already briefly alluded to the importance of your study in your background and research problem sections, but you haven’t explicitly stated how your research findings will benefit the world . So, now’s your chance to clearly state how your study will benefit either industry , academia , or – ideally – both . In other words, you need to explain how your research will make a difference and what implications it will have.
Let’s take a look at an example.
“This study will contribute to the body of knowledge on skills development by incorporating skills development strategies and approaches for industries in which knowledge and skills are rapidly and constantly changing. This will help address the current shortage of research in this area and provide real-world value to organisations operating in such dynamic environments.”
As you can see in this example, the paragraph clearly explains how the research will help fill a gap in the literature and also provide practical real-world value to organisations.
This section doesn’t need to be particularly lengthy, but it does need to be convincing . You need to “sell” the value of your research here so that the reader understands why it’s worth committing an entire dissertation or thesis to it. This section needs to be the salesman of your research. So, spend some time thinking about the ways in which your research will make a unique contribution to the world and how the knowledge you create could benefit both academia and industry – and then “sell it” in this section.

#6 – The limitations
Now that you’ve “sold” your research to the reader and hopefully got them excited about what’s coming up in the rest of your dissertation, it’s time to briefly discuss the potential limitations of your research.
But you’re probably thinking, hold up – what limitations? My research is well thought out and carefully designed – why would there be limitations?
Well, no piece of research is perfect . This is especially true for a dissertation or thesis – which typically has a very low or zero budget, tight time constraints and limited researcher experience. Generally, your dissertation will be the first or second formal research project you’ve ever undertaken, so it’s unlikely to win any research awards…
Simply put, your research will invariably have limitations. Don’t stress yourself out though – this is completely acceptable (and expected). Even “professional” research has limitations – as I said, no piece of research is perfect. The key is to recognise the limitations upfront and be completely transparent about them, so that future researchers are aware of them and can improve the study’s design to minimise the limitations and strengthen the findings.
Generally, you’ll want to consider at least the following four common limitations. These are:
- Your scope – for example, perhaps your focus is very narrow and doesn’t consider how certain variables interact with each other.
- Your research methodology – for example, a qualitative methodology could be criticised for being overly subjective, or a quantitative methodology could be criticised for oversimplifying the situation (learn more about methodologies here ).
- Your resources – for example, a lack of time, money, equipment and your own research experience.
- The generalisability of your findings – for example, the findings from the study of a specific industry or country can’t necessarily be generalised to other industries or countries.
Don’t be shy here. There’s no use trying to hide the limitations or weaknesses of your research. In fact, the more critical you can be of your study, the better. The markers want to see that you are aware of the limitations as this demonstrates your understanding of research design – so be brutal.
#7 – The structural outline
Now that you’ve clearly communicated what your research is going to be about, why it’s important and what the limitations of your research will be, the final ingredient is the structural outline.The purpose of this section is simply to provide your reader with a roadmap of what to expect in terms of the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
In this section, you’ll need to provide a brief summary of each chapter’s purpose and contents (including the introduction chapter). A sentence or two explaining what you’ll do in each chapter is generally enough to orient the reader. You don’t want to get too detailed here – it’s purely an outline, not a summary of your research.
Let’s look at an example:
In Chapter One, the context of the study has been introduced. The research objectives and questions have been identified, and the value of such research argued. The limitations of the study have also been discussed.
In Chapter Two, the existing literature will be reviewed and a foundation of theory will be laid out to identify key skills development approaches and strategies within the context of fast-moving industries, especially technology-intensive industries.
In Chapter Three, the methodological choices will be explored. Specifically, the adoption of a qualitative, inductive research approach will be justified, and the broader research design will be discussed, including the limitations thereof.
So, as you can see from the example, this section is simply an outline of the chapter structure, allocating a short paragraph to each chapter. Done correctly, the outline will help your reader understand what to expect and reassure them that you’ll address the multiple facets of the study.
By the way – if you’re unsure of how to structure your dissertation or thesis, be sure to check out our video post which explains dissertation structure .
Keep calm and carry on.
Hopefully you feel a bit more prepared for this challenge of crafting your dissertation or thesis introduction chapter now. Take a deep breath and remember that Rome wasn’t built in a day – conquer one ingredient at a time and you’ll be firmly on the path to success.
Let’s quickly recap – the 7 ingredients are:
- The opening section – where you give a brief, high-level overview of what your research will be about.
- The study background – where you introduce the reader to key theory, concepts and terminology, as well as the context of your study.
- The research problem – where you explain what the problem with the current research is. In other words, the research gap.
- The research aims , objectives and questions – where you clearly state what your dissertation will investigate.
- The significance – where you explain what value your research will provide to the world.
- The limitations – where you explain what the potential shortcomings and limitations of your research may be.
- The structural outline – where you provide a high-level overview of the structure of your document
If you bake these ingredients into your dissertation introduction chapter, you’ll be well on your way to building an engaging introduction chapter that lays a rock-solid foundation for the rest of your document.
Remember, while we’ve covered the essential ingredients here, there may be some additional components that your university requires, so be sure to double-check your project brief!

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

42 Comments
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident enough in undertaking my thesis on the survey;The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction
Glad to hear that. Good luck with your thesis!
Thanks very much for such an insight. I feel confident now undertaking my thesis; The future of facial recognition and learning non verbal interaction.
Thanks so much for this article. I found myself struggling and wasting a lot of time in my thesis writing but after reading this article and watching some of your youtube videos, I now have a clear understanding of what is required for a thesis.
Thank you Derek, i find your each post so useful. Keep it up.
Thank you so much Derek ,for shedding the light and making it easier for me to handle the daunting task of academic writing .
Thanks do much Dereck for the comprehensive guide. It will assist me queit a lot in my thesis.
thanks a lot for helping
i LOVE the gifs, such a fun way to engage readers. thanks for the advice, much appreciated
Thanks a lot Derek! It will be really useful to the beginner in research!
You’re welcome
This is a well written, easily comprehensible, simple introduction to the basics of a Research Dissertation../the need to keep the reader in mind while writing the dissertation is an important point that is covered../ I appreciate the efforts of the author../
The instruction given are perfect and clear. I was supposed to take the course , unfortunately in Nepal the service is not avaialble.However, I am much more hopeful that you will provide require documents whatever you have produced so far.
Thank you very much
Thanks so much ❤️😘 I feel am ready to start writing my research methodology
This is genuinely the most effective advice I have ever been given regarding academia. Thank you so much!
This is one of the best write up I have seen in my road to PhD thesis. regards, this write up update my knowledge of research
I was looking for some good blogs related to Education hopefully your article will help. Thanks for sharing.
This is an awesome masterpiece. It is one of the most comprehensive guides to writing a Dissertation/Thesis I have seen and read.
You just saved me from going astray in writing a Dissertation for my undergraduate studies. I could not be more grateful for such a relevant guide like this. Thank you so much.
Thank you so much Derek, this has been extremely helpful!!
I do have one question though, in the limitations part do you refer to the scope as the focus of the research on a specific industry/country/chronological period? I assume that in order to talk about whether or not the research could be generalized, the above would need to be already presented and described in the introduction.
Thank you again!
Phew! You have genuinely rescued me. I was stuck how to go about my thesis. Now l have started. Thank you.
This is the very best guide in anything that has to do with thesis or dissertation writing. The numerous blends of examples and detailed insights make it worth a read and in fact, a treasure that is worthy to be bookmarked.
Thanks a lot for this masterpiece!
Powerful insight. I can now take a step
Thank you very much for these valuable introductions to thesis chapters. I saw all your videos about writing the introduction, discussion, and conclusion chapter. Then, I am wondering if we need to explain our research limitations in all three chapters, introduction, discussion, and conclusion? Isn’t it a bit redundant? If not, could you please explain how can we write in different ways? Thank you.
Excellent!!! Thank you…
Thanks for this informative content. I have a question. The research gap is mentioned in both the introduction and literature section. I would like to know how can I demonstrate the research gap in both sections without repeating the contents?
I’m incredibly grateful for this invaluable content. I’ve been dreading compiling my postgrad thesis but breaking each chapter down into sections has made it so much easier for me to engage with the material without feeling overwhelmed. After relying on your guidance, I’m really happy with how I’ve laid out my introduction.
Thank you for the informative content you provided
Hi Derrick and Team, thank you so much for the comprehensive guide on how to write a dissertation or a thesis introduction section. For some of us first-timers, it is a daunting task. However, the instruction with relevant examples makes it clear and easy to follow through. Much appreciated.
It was so helpful. God Bless you. Thanks very much
I thank you Grad coach for your priceless help. I have two questions I have learned from your video the limitations of the research presented in chapter one. but in another video also presented in chapter five. which chapter limitation should be included? If possible, I need your answer since I am doing my thesis. how can I explain If I am asked what is my motivation for this research?
Thank you guys for the great work you are doing. Honestly, you have made the research to be interesting and simplified. Even a novice will easily grasp the ideas you put forward, Thank you once again.
Excellent piece!
I feel like just settling for a good topic is usually the hardest part.
Thank you so much. My confidence has been completely destroyed during my first year of PhD and you have helped me pull myself together again
Happy to help 🙂
I am so glad I ran into your resources and did not waste time doing the wrong this. Research is now making so much sense now.
Gratitude to Derrick and the team I was looking for a solid article that would aid me in drafting the thesis’ introduction. I felt quite happy when I came across the piece you wrote because it was so well-written and insightful. I wish you success in the future.
thank you so much. God Bless you
Thank you so much Grad Coach for these helpful insights. Now I can get started, with a great deal of confidence.
It’s ‘alluded to’ not ‘eluded to’.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

1 Chapter 1: The Importance of Research Methods and Becoming an Informed Consumer of Research
Case study : student apprehension regarding research methods.
Research Study
Understanding and Measuring Student Apprehension in Criminal Justice Research Methods Courses 1
Research Question
How do we measure disinterest, relevance argumentation, and math anxiety experienced by students enrolled in research methods courses?
Methodology
It is said that “misery loves company,” so you are not alone in your apprehension and anxiety regarding your research methods course. The problem of student apprehension and anxiety related to taking a research methods course is not new and has been studied for over 25 years. Previously, such apprehension and anxiety appeared to be caused by math anxiety, especially as it applies to statistics. The authors of this article believe that student apprehension goes beyond math anxiety; that math anxiety is too simplistic of an explanation of student fear of research methods courses. Besides math anxiety, the researchers think that apprehension is caused by student indifference to the subject matter and irrelevance of the course because it does not apply to the “real world.” They state that student apprehension in research methods and statistics courses is due to three main factors:
Disinterest (D.);
Relevance Argumentation (RA.), and;
Math Anxiety (MA.).
Taken together, the reconceptualization is known as D.RA.MA., and the combination of these three factors constitutes the D.RA.MA. scale for research methods and statistics courses.
The researchers developed the D.RA.MA. scale by constructing survey questions to measure each factor in the scale (i.e., disinterest, relevance argumentation, and math anxiety). After they developed the survey, they tested it by distributing the survey to three criminal justice classes, totaling 80 students, from a midsized regional comprehensive university in the southern region of the United States. Higher scale scores demonstrate more disinterest, more relevance argumentation, or more math anxiety.
The D.RA.MA. scale consists of 20 survey questions. Ten questions were borrowed from an existing Math Anxiety scale developed by Betz 2 . The researchers then created five items to assess Disinterest and five items intended to measure Relevance Argumentation. The items for the D.RA.MA. scale are illustrated below.
Math Anxiety 3
I usually have been at ease in math classes.
Math does not scare me at all.
I am no good at math.
I don’t think that I could do advanced math.
Generally, I have been secure about attempting math.
For some reason, even though I study, math seems unusually hard for me.
Math has been my worst subject.
My mind goes blank and I am unable to think clearly when working in mathematics.
I think I could handle more difficult math.
I am not the type to do well in mathematics.
Relevance Argumentation 4
I will need research methods for my future work.
I view research methods as a subject that I will rarely use.
Research methods is not really useful for students who intend to work in Criminal Justice.
Knowing research methods will help me earn a living.
Research methods does not reflect the “real world.”
Research Disinterest 5
I am excited about taking research methods.
It would not bother me at all to take more research methods courses.
I expect a research methods class to be boring.
I don’t expect to learn much in research methods.
I really don’t care if I learn anything in research methods, as long as I get the requirement completed.
The Math Anxiety Scale responses for the 80 students ranged from 0 to 30 with a mean of 14, demonstrating a moderate level of math anxiety among the study participants. The responses for Relevance Argumentation ranged from 0 to 12 with a mean of 5.4 while those for Disinterest ranged from 1 to 15 with a mean of 7.0, demonstrating a moderate level of disinterest and relevance argumentation among students regarding research methods. Based on these findings, the study demonstrated that student apprehension regarding research methods courses goes beyond math anxiety and includes two additional factors; disinterest in the subject matter and irrelevance of research methods to the “real world.”
Limitations with the Study Procedure
This research study was designed to develop a broader measure of student apprehension in criminal justice research methods courses. Moving beyond just math anxiety, the researchers accomplished their objective by developing the D.RA.MA. scale; adding disinterest and relevance argumentation to the understanding of student apprehension regarding research methods. As is true for all research, this study is not without limitations. The biggest limitation of this study is the limited sample size. Only 80 students completed the survey. Although this is certainly a good start, similar research (i.e., replication) needs to be completed with larger student samples in different locations throughout the country before the actual quality of the D.RA.MA. scale can be determined.
Impact on Criminal Justice
The D.RA.MA. scale developed in this study identifies disinterest and relevance argumentation, in addition to math anxiety, as part of student apprehension and resistance to research methods. A variety of instructional strategies can be inferred from the D.RA.MA. survey. However, it is important for professors to recognize that no single approach will reduce research methods resistance and apprehension for all students. For example, discussing research methods in a popular culture framework may resonate with students and lead to engaged students who are more interested in the subject matter and identify with the relevance of research methods to criminal justice in general and the future careers of students, in particular. This approach may provide an effective means for combating student disinterest and relevance argumentation in criminal justice research methods courses. At a minimum, it is critical for professors to explain the relevance of research methods to the policies and practices of police, courts, and corrections. Students need to realize that research methods are essential tools for assessing agency policies and practices. Professors will always have D.RA.MA.-plagued students, but recognizing the problem and then developing effective strategies to connect with these students is the challenge all professors face. Experimenting with a multitude of teaching strategies to alleviate the math anxiety, relevance argumentation, and disinterest of criminal justice research methods students will result in more effective teaching and learning.
In This Chapter You Will Learn
What research is and why it is important to be an informed consumer of research
The sources of knowledge development and problems with each
How research methods can dispel myths about crime and the criminal justice system
The steps in the research process
How research has impacted criminal justice operations
Introduction
As noted in the chapter opening case study, it is expected that you have some anxiety and apprehension about taking this criminal justice research methods course. But, you have taken a significant step toward success in this course by opening up your research methods book, so congratulations are in order. You might have opened this book for a number of reasons. Perhaps it is the first day of class and you are ready to get started on the course material. Perhaps you have a quiz or exam soon. Perhaps the book has been gathering dust on your shelf since the first day of class and you are not doing well in your research methods class and are looking for the book to help with course improvement. Perhaps you are taking a research methods class in the future and are seeing if all the chatter among students is true.
No matter how you got here, two things are probably true. First, you are taking this research methods course because it is a requirement for your major. The bottom line is that most of the students who read this text are required to take a research methods course. While you may think studying research methods is irrelevant to your career goals, unnecessary, overly academic, or perhaps even intimidating, you probably must finish this course in order to graduate. Second, you have heard negative comments about this course. The negative comments mention the difficulty of the course and the relevance of the course (e.g., “I am going to be a police officer, so why do I need to take a research methods course?”). If you are like most students we have experienced in our research methods courses in the past, you are not initially interested in this course and are concerned about whether you will do well in it.
If you are concerned about the course, realize that you are not alone because most students are anxious about taking a research methods course. Also realize that your professor is well aware of student anxiety and apprehension regarding research methods. So, relax and do not think about the entire course and the entire book. Take the course content one chapter, one week at a time. One of the advantages of taking a research methods course is that you learn about the process of research methods. Each chapter builds upon the previous chapters, illustrating and discussing more about the research process. This is certainly an advantage, but it is also critical that you understand the initial chapters in this book so you are not confused with the content discussed in later chapters. In addition to anxiety and apprehension over the course material, research methods can be boring if you only read and learn about it with no particular purpose in mind. Although examples are prevalent throughout the book, as you read this material, it is recommended that you think about the relevancy and application of the topics covered in this book to your specific criminal justice interests. As you continue to read the book, think about how you might use the information you are reading in your current position or your intended profession.
The goal of this research methods book is to develop you into an informed consumer of research. Most, if not all, of your fellow classmates will never conduct their own research studies. However, every one of you will be exposed to research findings in your professional and personal lives for the remainder of your lives. You are exposed to research findings in the media (e.g., television, newspapers, and online), in personal interaction with others (e.g., friends and family, doctors, and professors), as well as in class. You should challenge yourself for this semester to keep a journal and document exposure to research in your daily life outside of college whether through the nightly news, newspapers, magazine articles, Internet, personal conversations, or other means. At the end of the semester, you will be amazed at the amount of research you are exposed to in a short period of time. This book is focused on research exposure and assisting you to become an educated consumer of research by providing you the skills necessary to differentiate between good and not so good research. Why should you believe research findings if the study is faulty? Without being an educated consumer of research, you will not be able to differentiate between useful and not useful research. This book is designed to remedy this problem.
This book was written to make your first encounter with research methods relevant and successful while providing you the tools necessary to become an educated consumer of research. Therefore, this book is written with the assumption that students have not had a prior class on research methods. In addition, this book assumes that practical and evaluative knowledge of research methods is more useful than theoretical knowledge of the development of research methods and the relationship between theory and research. Since the focus of this book is on consumerism, not researcher training, practical and evaluative knowledge is more useful than theoretical knowledge.
It is also important to understand that the professors who design academic programs in criminal justice at the associate and bachelor level believe that an understanding of research methods is important for students. That is why, more than likely, this research methods course is a required course in your degree program. These professors understand that a solid understanding of research methods will enrich the qualifications of students for employment and performance in their criminal justice careers.
As previously stated, the basic goal of this book is to make students, as future and possibly even current practitioners in the criminal justice system, better informed and more capable consumers of the results of criminal justice research. This goal is based on the belief that an understanding of research methods allows criminal justice practitioners to be better able to make use of the results of research as it applies to their work-related duties. In fact, thousands of research questions are asked and answered each year in research involving criminal justice and criminological topics. In addition, thousands of articles are published, papers presented at conferences, and reports prepared that provide answers to these questions. The ability to understand research gives practitioners knowledge of the most current information in their respective fields and the ability to use this knowledge to improve the effectiveness of criminal justice agencies.
How Do We Know What We Know? Sources of Knowledge
The reality is the understanding of crime and criminal justice system operations by the public is frequently the product of misguided assumptions, distorted interpretations, outright myths, and hardened ideological positions. 6 This is a bold statement that basically contends that most people’s knowledge of crime and criminal justice is inaccurate. But, how do these inaccuracies occur? Most people have learned what they know about crime and criminal justice system operations through some other means besides scientific research results and findings. Some of that knowledge is based on personal experience and common sense. Much of it is based on the information and images supported by politicians, governmental agencies, and especially the media. This section will discuss the mechanisms used to understand crime and criminal justice operations by the public. It is important to note that although this section will focus on the failings of these knowledge sources, they each can be, and certainly are, accurate at times, and thus are valuable sources of knowledge.
Knowledge from Authority
We gain knowledge from parents, teachers, experts, and others who are in positions of authority in our lives. When we accept something as being correct and true just because someone in a position of authority says it is true, we are using what is referred to as authority knowledge as a means of knowing. Authorities often expend significant time and effort to learn something, and we can benefit from their experience and work.
However, relying on authority as a means of knowing has limitations. It is easy to overestimate the expertise of other people. A person’s expertise is typically limited to a few core areas of significant knowledge; a person is not an expert in all areas. More specifically, criminal justice professors are not experts on all topics related to criminal justice. One professor may be an expert on corrections but know little about policing. If this professor discusses topics in policing in which he is not an expert, we may still assume he is right when he may be wrong. Authority figures may speak on fields they know little about. They can be completely wrong but we may believe them because of their status as an expert. Furthermore, an expert in one area may try to use his authority in an unrelated area. Other times, we have no idea of how the experts arrived at their knowledge. We just know they are experts in the topic area.
As I am writing this, I recall an example of authority knowledge that was wrong during my police academy training in the late 1980s. My academy training was about four years after the U.S. Supreme Court decision in Tennessee v. Garner. 7 In this case, the Court limited the use of deadly force by police to defense of life situations and incidents where the suspect committed a violent offense. Prior to the decision, the police in several states could use deadly force on any fleeing suspect accused of a felony offense. One day, the academy class was practicing mock traffic stops. During one of my mock traffic stops, I received information that the vehicle I stopped was stolen. The driver and passenger exited the vehicle and fled on foot. I did not use deadly force (this was a training exercise so was not real) against the suspects and was chastised by my instructor who insisted that I should have shot the suspects as they were fleeing. Training instructors, just like professors, convey authority knowledge but, in this case, the instructor was wrong. I was not legally authorized to use deadly force in the traffic stop scenario despite the insistence of my instructor to the contrary.
Politicians are sometimes taken as a source of authority knowledge about the law, crime, and criminal justice issues. Since they enact laws that directly impact the operations of the criminal justice system, we may assume they are an authority on crime and criminal justice. More specifically, we may assume that politicians know best about how to reduce crime and increase the effectiveness of the criminal justice system. However, history is rife with laws that sounded good on paper but had no impact on crime. For example, there is little evidence that sex offender registration protects the public from sexual predators or acts as a deterrent to repeat sex offenders even though every state has a law requiring convicted sex offenders to register with local authorities. Perhaps politicians are not the criminal justice experts some perceive them to be.
History is also full of criminal justice authorities that we now see as being misinformed. For example, Cesare Lombroso is the father of the positivist school of criminology. He is most readily recognized for his idea that some individuals are born criminal. He stated that criminals have certain unique biological characteristics, including large protruding jaws, high foreheads, flattened noses, and asymmetrical faces, to name a few. 8 These characteristics were similar to those found in primitive humans. Therefore, Lombroso argued that some individuals were genetic “throwbacks” to a more primitive time and were less evolved than other people and thus, were more likely to be criminals. Lombroso’s research has been discredited because he failed to compare criminals with noncriminals. By studying only criminals, he found characteristics that were common to criminals. However, if Lombroso had studied a group of noncriminals, he would have discovered that these biological characteristics are just as prevalent among noncriminals. This example involves authority knowledge that is supported by research but the research methods used were flawed. The errors of Lombroso seem obvious now, but what do we know today through authority knowledge that is inaccurate or will be proven wrong in the future?
Knowledge from Tradition
In addition to authority knowledge, people often rely on tradition for knowledge. Tradition knowledge relies on the knowledge of the past. Individuals accept something as true because that is the way things have always been so it must be right. A good example of tradition knowledge is preventive/random patrol. Ever since vehicles were brought into the police patrol function, police administrators assumed that having patrol officers drive around randomly in the communities they serve, while they are not answering calls for service, would prevent crime. If you were a patrol officer in the early 1970s and asked your supervisor, “Why do I drive around randomly throughout my assigned area when I am not answering a call for service?” the answer would have been, “That is the way we have always done patrol and random patrol reduces crime through deterrence.” The Kansas City Preventive Patrol Experiment challenged the tradition knowledge that preventive/random patrol reduces crime. The results of the study made it clear that the traditional practice of preventive/random patrol had little to no impact on reducing crime. This allowed police departments to develop other patrol deployment strategies such as directed patrol and “hot spots” policing since preventive patrol was seen as ineffective. The development of effective patrol deployment strategies continues today.
Knowledge from Common Sense
We frequently rely on common sense knowledge for what we know about crime and the criminal justice system because it “just makes sense.” For example, it “just makes sense” that if we send juvenile delinquents on a field trip to prison where they will see first hand the prison environment as well as be yelled at by actual prisoners, they will refrain from future delinquency. That is exactly what the program Scared Straight, originally developed in the 1970s, is designed to do. Scared Straight programs are still in existence today and are even the premise for the television show Beyond Scared Straight on the A&E television network. As originally created, the program was designed to decrease juvenile delinquency by bringing at-risk and delinquent juveniles into prison where they would be “scared straight” by inmates serving life sentences. Participants in the program were talked to and yelled at by the inmates in an effort to scare them. It was believed that the fear felt by the participants would lead to a discontinuation of their delinquent behavior so that they would not end up in prison themselves. This sounds like a good idea. It makes sense, and the program was initially touted as a success due to anecdotal evidence based on a few delinquents who turned their lives around after participation in the program.
However, evaluations of the program and others like it showed that the program was in fact unsuccessful. In the initial evaluation of the Scared Straight program, Finckenauer used a classic experimental design (discussed in Chapter 5), to evaluate the original “Lifer’s Program” at Rahway State Prison in New Jersey where the program was initially developed. 13 Juveniles were randomly assigned to an experimental group that attended the Scared Straight program and a control group that did not participate in the program. Results of the evaluation were not positive. Post-test measures revealed that juveniles who were assigned to the experimental group and participated in the program were actually more seriously delinquent afterwards than those who did not participate in the program. Also using an experimental design with random assignment, Yarborough evaluated the “Juvenile Offenders Learn Truth” (JOLT) program at the State Prison of Southern Michigan at Jackson. 14 This program was similar to that of the “Lifer’s Program,” only with fewer obscenities used by inmates. Post-test measurements were taken at two intervals, three and six months after program completion. Again, results were not positive. Findings revealed no significant differences in delinquency between those juveniles who attended the program and those who did not. Other experiments conducted on Scared Straight- type programs further revealed their inability to deter juveniles from further delinquency. 15 Despite the common sense popularity of these programs, the evaluations showed that Scared Straight programs do not reduce delinquency and, in some instances, may actually increase delinquency. The programs may actually do more harm than good. I guess that begs the question, “Why do we still do these types of programs?”
Scared Straight programs and other widely held common sense beliefs about crime and the criminal justice system are questionable, based on the available research evidence. Common sense is important in our daily lives and is frequently correct, but, at times, it also contains inaccuracies, misinformation, and even prejudice.
CLASSICS IN CJ RESEARCH
Is It Safe to Put Felons on Probation?
Research Study 9
In the mid-1970s, the number of offenders on probation began to significantly increase. By the mid-1980s, probation was the most frequently used sentence in most states and its use was becoming more common for felons, whereas previously, probation was typically limited to misdemeanor crimes and offenses committed by juveniles. Increasing numbers of felony offenders were being placed on probation because judges had no other alternative forms of punishment. Prisons were already operating above capacity due to rising crime rates. Despite the increase in the use of probation in the 1980s, few empirical studies of probation (particularly its use with felony offenders) had been published. In the early 1980s, the Rand Corporation conducted an extensive study of probation to learn more about the offenders sentenced to probation and the effectiveness of probation as a criminal sanction. At the time the study began, over one-third of California’s probation population were convicted felons. 10 This was the first large-scale study of felony probation.
Is it safe to put felons on probation?
Data for the study were obtained from the California Board of Prison Terms (CBPT). The Board had been collecting comprehensive data on all offenders sentenced to prison since 1978 and on a sample of adult males from 17 counties who received probation. From these two data sources, researchers selected a sample of male offenders who had been convicted of the following crimes: robbery, assault, burglary, theft, forgery, and drug offenses. These crimes were selected because an offender could receive either prison or probation if convicted. Approximately 16,500 male felony offenders were included in the study. For each offender, researchers had access to their personal characteristics, information on their crimes, court proceedings, and disposition.
Two main research questions were answered in this study. First, what were the recidivism rates for felony offenders who received probation? When assessing recidivism rates, the study found that the majority of offenders sentenced to probation recidivated during the follow-up period, which averaged 31 months. Overall, 65% of the sample of probationers were re-arrested and 51 % were charged with and convicted of another offense. A total of 18% were convicted of a violent crime.
The second research question asked, what were the characteristics of the probationers who recidivated? Property offenders were more likely to recidivate compared to violent or drug offenders. Researchers also discovered that probationers tended to recidivate by committing the same crime that placed them on probation. Rand researchers included time to recidivism in their analysis and found that property and violent offenders recidivated sooner than drug offenders. The median time to the first filed charge was five months for property offenders and eight months for violent offenders.
The issue of whether or not the findings would generalize to other counties in California and to other states was raised. Data for the study came from probation and prison records from two counties in California. These two counties were not randomly selected, but were chosen because of their large probation populations and the willingness of departments to provide information. Further, the probation departments in these counties had experienced significant budget cuts. Supervision may have become compromised as a result and this could have explained why these counties had high rates of recidivism. Studies of probation recidivism in other states have found recidivism rates to be much lower, suggesting the Rand results may not have applied elsewhere. 11 Several studies examining the effectiveness of probation and the factors correlated with probation outcomes were published after 1985. Much of this research failed to produce results consistent with the Rand study.
The Rand study of felony probation received a considerable amount of attention within the field of corrections. According to one scholar, the study was acclaimed as “the most important criminological research to be reported since World War II.” 12 The National Institute of Justice disseminated the report to criminal justice agencies across the country and even highlighted the study in their monthly newsletter. Today, the study remains one of the most highly cited pieces of corrections research.
According to Rand researchers, these findings raised serious doubts about the effectiveness of probation for felony offenders. Most of the felons sentenced to probation recidivated and researchers were unable to develop an accurate prediction model to improve the courts’ decision-making. The continued use of probation as a sanction for felony offenders appeared to be putting the public at risk. However, without adequate prison space, the courts had no other alternatives besides probation when sentencing offenders.
The researchers made several recommendations to address the limitations of using probation for felony offenders. First, it was recommended that states formally acknowledge that the purpose of probation had changed. Probation was originally used as a means of furthering the goal of rehabilitation in the correctional system. As the United States moved away from that goal in the late 1960s, the expectations of probation changed. Probation was now used as a way to exercise “restrictive supervision” over more serious offenders. Second, probation departments needed to redefine the responsibilities of their probation officers. Probation officers were now expected to be surveillance officers instead of treatment personnel, which required specialized training. In addition, states needed to explore the possibility of broadening the legal authority of its probation officers by allowing them to act as law enforcement officers if necessary. Third, states were advised to adopt a formal client management system that included risk/need assessments of every client. Such a system would help establish uniform, consistent treatment of those on probation and would also help departments allocate their resources efficiently and effectively. Fourth, researchers encouraged states to develop alternative forms of community punishment that offered more public protection than regular probation, which led to the development and use of intensive supervision probation, house arrest, electronic monitoring, day reporting centers, and other intermediate punishments.
Knowledge from Personal Experience
If you personally see something or if it actually happens to you, then you are likely to accept it as true and gain knowledge from the experience. Gaining knowledge through actual experiences is known as personal experience knowledge, and it has a powerful and lasting impact on everyone. Personal experiences are essential building blocks of knowledge and of what we believe to be true. The problem with knowledge gained from personal experiences is that personal experiences can be unique and unreliable, which can distort reality and lead us to believe things that are actually false.
How can events that someone personally experienced be wrong? The events are not wrong. Instead, the knowledge gained from the experience is wrong. For example, the research consistently shows that a person’s demeanor significantly impacts the decision-making of police officers. During a traffic stop, if a person is rude, disrespectful, and uncooperative to the officer, then the driver is more likely to receive a traffic citation than a warning. That is what the research on police discretion shows. However, if a person was rude and uncooperative to a police officer during a traffic stop and was let go without a citation, the person will gain knowledge from this personal experience. The knowledge gained may include that being disrespectful during future traffic stops will get this person out of future tickets. Not likely. The event is not wrong. Instead, the knowledge gained from the experience is wrong because being disrespectful to the police usually leads to more enforcement action taken by the police, not less.
As a student in criminal justice, you have probably experienced something similar in interaction with friends, relatives, and neighbors. Your knowledge of criminal justice that you have developed in your criminal justice classes is trumped by one experience your friend, relative, or neighbor had with the criminal justice system. They believe they are right because they experienced it. However, there are four errors that occur in the knowledge gained from personal experiences: overgeneralization, selective observation, illogical reasoning, and resistance to change.
Overgeneralization happens when people conclude that what they have observed in one or a few cases is true for all cases. For example, you may see that a wealthy businesswomen in your community is acquitted of bribery and may conclude that “wealthy people, especially women, are never convicted in our criminal justice system,” which is an overgeneralization. It is common to draw conclusions about people and society from our personal interactions, but, in reality, our experiences are limited because we interact with just a small percentage of people in society.
The same is true for practitioners in the criminal justice system. Practitioners have a tendency to believe that because something was done a particular way in their agency, it is done that way in all agencies. That may not be true. Although there are certainly operational similarities across criminal justice agencies, there are also nuances that exist across the over 50,000 criminal justice agencies in the United States. Believing that just because it was that way in your agency, it must be that way in all agencies leads to overgeneralization.
Selective observation is choosing, either consciously or unconsciously, to pay attention to and remember events that support our personal preferences and beliefs. In fact, with selective observation, we will seek out evidence that confirms what we believe to be true and ignore the events that provide contradictory evidence. We are more likely to notice pieces of evidence that reinforce and support our ideology. As applied to the criminal justice system, when we are inclined to be critical of the criminal justice system, it is pretty easy to notice its every failing and ignore its successes. For example, if someone believes the police commonly use excessive force, the person is more likely to pay attention to and remember a police brutality allegation on the nightly news than a police pursuit that led to the apprehension of the suspect without incident on the same nightly news. As another example, if you believe treatment efforts on sex offenders are futile, you will pay attention to and remember each sex offender you hear about that recidivates but will pay little attention to any successes. It is easy to find instances that confirm our beliefs, but with selective observation, the complete picture is not being viewed. Therefore, if we only acknowledge the events that confirm our beliefs and ignore those that challenge them, we are falling victim to selective observation.
Besides selective observation, some of our observations may simply be wrong. Consider eyewitness identification. It is a common practice in the criminal justice system, but research has consistently demonstrated inaccuracies in eyewitness identification. The witness feels certain that the person viewed is the person who committed the offense, but sometimes the witness is wrong. Even when our senses of sight, hearing, taste, touch, and smell are fully operational, our minds have to interpret what we have sensed, which may lead to an inaccurate observation.
RESEARCH IN THE NEWS
When Your Criminal Past Isn’t Yours 16
The business of background checks on prospective employees is increasing significantly. According to the Society for Human Resource Management, since the events of September 11, 2001, the percentage of companies that conduct criminal history checks during the hiring process has risen past 90%. Employers spend at least $2 billion a year to look into the pasts of their prospective employees. Problems with the business of background checks were identified through research that included a review of thousands of pages of court filings and interviews with dozens of court officials, data providers, lawyers, victims, and regulators.
The business of background checks is a system weakened by the conversion to digital files and compromised by the significant number of private companies that profit by amassing public records and selling them to employers. The private companies create a system in which a computer program scrapes the public files of court systems around the country to retrieve personal data. Basically, these are automated data-mining programs. Today, half the courts in the United States put criminal records on their public websites. So, the data are there for the taking, but the records that are retrieved typically are not checked for errors—errors that would be obvious to human eyes.
The errors can start with a mistake entered into the logs of a law enforcement agency or a court file. The biggest culprits, though, are companies that compile databases using public information. In some instances, their automated formulas misinterpret the information provided them. Other times, records wind up assigned to the wrong people with a common name. Furthermore, when a government agency erases a criminal conviction after a designated period of good behavior, many of the commercial databases don’t perform the updates required to purge offenses that have been removed from public record. It is clear that these errors can have substantial ramifications, including damaged reputations and loss of job opportunities.
Illogical reasoning occurs when someone jumps to premature conclusions or presents an argument that is based on invalid assumptions. Premature conclusions occur when we feel we have the answer based on a few pieces of evidence and do not need to seek additional information that may invalidate our conclusion. Think of a detective who, after examining only a few pieces of evidence, quickly narrows in on a murder suspect. It is common for a detective to assess the initial evidence and make an initial determination of who committed the murder. However, it is hoped that the detective will continue to sort through all the evidence for confirmation or rejection of his original conclusion regarding the murder suspect. Illogical reasoning by jumping to premature conclusions is common in everyday life. We look for evidence to confirm or reject our beliefs and stop when a small amount of evidence is present; we jump to conclusions. If a person states, “I know four people who have dropped out of high school, and each one of them ended up addicted to drugs, so all dropouts abuse drugs,” the person is jumping to conclusions.
Illogical reasoning also occurs when an argument, based on invalid assumptions, is presented. Let’s revisit the Scared Straight example previously discussed. Program developers assumed that brief exposure to the harsh realities of prison would deter juveniles from future delinquency. The Scared Straight program is an example of illogical reasoning. Four hours of exposure to prison life is not going to counteract years of delinquency and turn a delinquent into a nondelinquent. The program is based on a false assumption and fails to recognize the substantial risk factors present in the lives of most delinquents that must be mediated before the juvenile can live a crime-free lifestyle. A fear of prison, developed through brief exposure, is not enough to counteract the risk factors present in the lives of most delinquents. Although the Scared Straight program sounds good, it is illogical to assume that a brief experience with prison life will have a stronger impact on the decisions made by delinquents than peer support for delinquency, drug abuse, lack of education, poor parental supervision, and other factors that influence delinquency.
Resistance to change is the reluctance to change our beliefs in light of new, accurate, and valid information to the contrary. Resistance to change is common and it occurs for several reasons. First, even though our personal experience may be counter to our belief system, it is hard to admit we were wrong after we have taken a position on an issue. Even when the research evidence shows otherwise, people who work within programs may still believe they are effective. As previously stated, even though the research evidence shows otherwise, Scared Straight programs still exist and there is even a television show devoted to the program. Second, too much devotion to tradition and the argument that this is the way it has always been done inhibits change and hinders our ability to accept new directions and develop new knowledge. Third, uncritical agreement with authority inhibits change. Although authority knowledge is certainly an important means of gaining knowledge, we must critically evaluate the ideas, beliefs, and statements of those in positions of authority and be willing to challenge those statements where necessary. However, people often accept the beliefs of those in positions of authority without question, which hinders change.
Knowledge from Media Portrayals
Television shows, movies, websites, newspapers, and magazine articles are important sources of information. This is especially true for information about crime and the criminal justice system since most people have not had much contact with criminals or the criminal justice system. Instead of gaining knowledge about the criminal justice system through personal experience, most people learn about crime and the operations of the criminal justice system through media outlets. Since the primary goal of many of these media outlets is to entertain, they may not accurately reflect the reality of crime and criminal justice. Despite their inaccuracies, the media has a substantial impact on what people know about crime and the criminal justice system. Most people know what they know about crime and criminal justice through the media, and this knowledge even has an impact on criminal justice system operations.
An example of the potential impact of the media on the actual operations of the criminal justice system involves the CSI: Crime Scene Investigation television shows. The shows have been criticized for their unrealistic portrayal of the role of forensic science in solving criminal cases. Critics claim that CSI viewers accept what they see on the show as an accurate representation of how forensic science works. When summoned for jury duty, they bring with them unrealistic expectations of the forensic evidence they will see in trial. When the expected sophisticated forensic evidence is not presented in the real trial, the juror is more likely to vote to acquit the defendant. This phenomenon is known as the CSI Effect. Has the research shown that the CSI Effect exists and is impacting the criminal justice system? Most of the research shows that the CSI Effect does not exist and thus does not impact juror decision-making, but other research has shown that viewers of CSI have higher expectations related to evidence presented at trial. 17
There are several instances in which media attention on a particular topic created the idea that a major problem existed when it did not. An example is Halloween sadism. Halloween sadism is the practice of giving contaminated treats to children during trick or treating. 18 In 1985, Joel Best wrote an article entitled, “The Myth of the Halloween Sadist.” 19 His article reviewed press coverage of Halloween sadism in the leading papers in the three largest metropolitan areas ( New York Times, Los Angeles Times, and Chicago Tribune ) from 1958–1984. Although the belief in Halloween sadism is widespread, Best found few reported incidents and few reports of children being injured by Halloween sadism. Follow-ups on these reported incidents led to the conclusion that most of these reports were hoaxes. Best concluded, “I have been unable to find a substantiated report of a child being killed or seriously injured by a contaminated treat picked up in the course of trick or treating.” 20 Since 1985, Best has kept his research up to date and has come to the same conclusion. Halloween sadism is an urban legend; it is a story that is told as true, even though there is little or no evidence that the events in the story ever occurred.
Dispelling Myths: The Power of Research Methods
In the prior section, sources of knowledge were discussed along with the limitations of each. A researcher (e.g., criminologist), ideally, takes no knowledge claim for granted, but instead relies on research methods to discover the truth. In the attempt to generate new knowledge, a researcher is skeptical of knowledge that is generated by the sources discussed in the prior section, and this skepticism leads to the questioning of conventional thinking. Through this process, existing knowledge claims are discredited, modified, or substantiated. Research methods provide the researcher with the tools necessary to test current knowledge and discover new knowledge.
Although knowledge developed through research methods is by no means perfect and infallible, it is definitely a more systematic, structured, precise, and evidence-based process than the knowledge sources previously discussed. However, researchers should not dismiss all knowledge from the prior sources discussed, because, as mentioned, these sources of knowledge are sometimes accurate and certainly have their place in the development of knowledge. Researchers should guard against an elitist mind-set in which all knowledge, unless it is research-based knowledge, is dismissed.
To further discuss the importance of research methods in the development of knowledge, this section will discuss myths about crime and criminal justice. Myths are beliefs that are based on emotion rather than rigorous analysis. Take the myth of the Halloween sadist previously discussed. Many believe that there are real examples of children being harmed by razor blades, poison, or other nefarious objects placed in Halloween candy. This belief has changed the practices of many parents on Halloween; not allowing their children to trick-or-treat in their neighborhood and forbidding them from going to the doors of strangers. After careful analysis by Best, there is not a single, known example of children being seriously injured or killed by contaminated candy given by strangers. The Halloween sadist is a myth but it is still perpetuated today, and as the definition states, it is a belief based upon emotion rather than rigorous analysis. People accept myths as accurate knowledge of reality when, in fact, the knowledge is false.
The power of research is the ability to dispel myths. If someone were to assess the research literature on a myth or do their own research, she would find that the knowledge based on the myth is wrong. Perceived reality is contradicted by the facts developed through research. But that does not mean that the myth still doesn’t exist. It is important to keep in mind that the perpetuation and acceptance of myths by the public, politicians, and criminal justice personnel has contributed to the failure of criminal justice practices and policies designed to reduce crime and improve the operations of the criminal justice system. In this section, a detailed example of a myth about crime, police, courts, and corrections will be presented to demonstrate how the myth has been dispelled through research. In addition, several additional myths about crime, police, courts, and corrections will be briefly presented.
The Health Benefits of Alcohol Consumption 21
The press release from Oregon State University is titled “Beer Compound Shows Potent Promise in Prostate Cancer Battle.” The press release leads to several newspaper articles throughout the country written on the preventative nature of drinking beer on prostate cancer development with titles such as “Beer Protects Your Prostate” and “Beer May Help Men Ward Off Prostate Cancer.” By the titles alone, this sounds great; one of the main ingredients in beer appears to thwart prostate cancer.
The study that generated these headlines was conducted by a group of researchers at Oregon State University using cultured cells with purified compounds in a laboratory setting. The research showed that xanthohumol, a compound found in hops, slowed the growth of prostate cancer cells and also the growth of cells that cause enlarged prostates. But you would have to drink more than 17 pints of beer to consume a medically effective dose of xanthohumol, which is almost a case of beer. In addition, although the research is promising, further study is necessary to determine xanthohumol’s true impact on prostate cancer.
These are the types of headlines that people pay attention to and want to believe as true, even if disproven by later research. People want to believe that there are health benefits to alcohol consumption. You have probably heard about the health benefits of drinking red wine, but here is something you should consider. Recently, the University of Connecticut released a statement describing an extensive research misconduct investigation involving a member of its faculty. The investigation was sparked by an anonymous allegation of research irregularities. The comprehensive report of the investigation, which totals approximately 60,000 pages, concludes that the professor is guilty of 145 counts of fabrication and falsification of data. The professor had gained international notoriety for his research into the beneficial properties of resveratrol, which is found in red wine, especially its impact on aging. Obviously, this throws his research conclusions, that red wine has a beneficial impact on the aging process, into question.
Myths about Crime—Drug Users Are Violent
The myth of drug users as violent offenders continues to be perpetuated by media accounts of violent drug users. The public sees drug users as violent offenders who commit violent crimes to get money for drugs or who commit violent crimes while under the intoxicating properties of drugs. The public also recognizes the violent nature of the drug business with gangs and cartels using violence to protect their turf. In May 2012, extensive media attention was given to the case of the Miami man who ate the face of a homeless man for an agonizing 18 minutes until police shot and killed the suspect. The police believed that the suspect was high on the street drug known as “bath salts.” This horrific case definitely leaves the image in the public’s mind about the relationship between violence and drug use.
In recent years, media reports have focused on the relationship between methamphetamine use and violence; before then it was crack cocaine use and violence. 32 However, media portrayals regarding the violent tendencies of drug users date back to the 1930s and the release of Reefer Madness. In 1985, Goldstein suggested that drugs and violence could be related in three different ways:
1. violence could be the direct result of drug ingestion;
2. violence could be a product of the instability of drug market activity; and
3. violence could be the consequence of people having a compulsive need for drugs or money for drugs. 33
So, what does the research show? Studies have found that homicides related to crack cocaine were usually the product of the instability of drug market activity (i.e., buying and selling drugs can be a violent activity) and rarely the result of drug ingestion. 34 After an extensive review of research studies on alcohol, drugs, and violence, Parker and Auerhahn concluded, “Despite a number of published statements to the contrary, we find no significant evidence suggesting that drug use is associated with violence. There is substantial evidence to suggest that alcohol use is significantly associated with violence of all kinds.” 35 The reality is not everyone who uses drugs becomes violent and users who do become violent do not do so every time they use drugs; therefore, the relationship between violence and drug use is a myth.
MYTHS ABOUT CRIME
Some additional myths about crime that research does not support include:
•Crime statistics accurately show what crimes are being committed and what crimes are most harmful. 22
•Most criminals—especially the dangerous ones—are mentally ill. 23
•White-collar crime is only about financial loss and does not hurt anyone. 24
•Serial murderers are middle-aged, white males. 25
•Criminals are significantly different from noncriminals. 26
•People are more likely to be a victim of violent crime committed by a stranger than by someone they know. 27
•Older adults are more likely to be victimized than people in any other age group. 28
•Sex offender registration protects the public from sexual predators. 29
•Juvenile crime rates are significantly increasing. 30
•Only the most violent juveniles are tried as adults. 31
Myths about Police—Female Police Officers Do Not Perform as Well as Males
Female police officers still face the myth that they cannot perform as well as male police officers. Throughout history, females have faced significant difficulties even becoming police officers. In the past, it was common for police agencies to require all police applicants to meet a minimum height requirement to be considered for employment. The minimum height requirement was 5′8″ for most agencies, which limited the ability of females to successfully meet the minimum standards to become a police officer. Even if women could meet the minimum height requirements, they were typically faced with a physical-abilities test that emphasized upper body strength (e.g., push-ups and bench presses). Women failed these tests more often than men, and thus were not eligible to be police officers. Minimum height requirements are no longer used in law enforcement, but the perception that female police officers are not as good as males still exists. Today, the myth that women cannot be effective police officers is based largely on the belief that the need to demonstrate superior physical strength is a daily, common occurrence in law enforcement along with the belief that police work is routinely dangerous, violent, and crime-related.
So, what does the research show? On occasion, it is useful for police officers to be able to overpower suspects by demonstrating superior physical strength, but those types of activities are rare in law enforcement. In addition, it is fairly rare for a police officer to have to deal with a dangerous and violent encounter or even an incident involving a crime. The Police Services Study conducted in the 1970s analyzed 26,418 calls for service in three metropolitan areas and found that only 19% of calls for service involve crime and only 2% of the total calls for service involve violent crime. 43 This research study was among the first to assess the types of calls for service received by police agencies.
Despite the belief that women do not make good police officers, consistent research findings show that women are extremely capable as police officers, and in some respects, outperform their male counterparts. 44 Research has demonstrated several advantages to the hiring, retention, and promotion of women in law enforcement. First, female officers are as competent as their male counterparts. Research does not show any consistent differences in how male and female patrol officers perform their duties. Second, female officers are less likely to use excessive force. Research has shown that female patrol officers are less likely to be involved in high-speed pursuits, incidents of deadly force, and the use of excessive force. Female officers are more capable at calming potentially violent situations through communication and also demonstrate heightened levels of caution. Third, female officers can help implement community-oriented policing. Studies have shown that female officers are more supportive of the community-policing philosophy than are their male counterparts. Fourth, female officers can improve law enforcement’s response to violence against women. Studies have shown that female officers are more patient and understanding in handling domestic violence calls, and female victims of domestic violence are more likely to provide positive evaluations of female officers than their male counterparts. 52
MYTHS ABOUT POLICE
Some additional myths about the police that research does not support include:
•Police target minorities for traffic stops and arrests. 36
•Most crimes are solved through forensic science. 37
•COMPSTAT reduces crime. 38
•Intensive law enforcement efforts at the street level will lead to the control of illicit drug use and abuse. 39
•Police work primarily entails responding to crimes in progress or crimes that have just occurred. 40
•Police presence reduces crime. 41
•Detectives are most responsible for solving crimes and arresting offenders. 42
Myths about Courts—The Death Penalty Is Administered Fairly
According to a recent Gallup poll, 52% of Americans say the death penalty is applied fairly in the United States, the lowest mark in almost 40 years. 53 The issue of fairness and the death penalty typically concerns whether the punishment is equally imposed on offenders who are equally deserving based on legal factors (i.e., similar offense, similar prior criminal history, similar aggravating circumstances, and similar mitigating circumstances). 54 Unfairness can be shown if similarly situated offenders are more or less likely to receive death sentences based on age, gender, and race.
So, what does the research show? First, has research shown that a defendant’s age influences his or her chances of being sentenced to death? A study of about 5,000 homicides, controlling for legally relevant variables, found that defendants over the age of 25 were more than twice as likely to receive the death penalty in comparison to those 25 years of age or younger. 55
Second, has research shown that a defendant’s gender influences his or her chance of being sentenced to death? Capital punishment is almost exclusively reserved for male defendants. On December 31, 2010, there were 3,158 prisoners under a sentence of death in the United States: 58 were women, or 1.8%. 56 However, women account for 10–12% of all murders in the United States. 57 One research study found that male defendants were 2.6 times more likely than females to receive a death sentence after controlling for legally relevant factors. 58
Third, has research shown that a defendant’s race influences his or her chance of being sentenced to death? Most of the research on the biased nature of the death penalty has focused on racial inequities in the sentence. Although some research has shown that a defendant’s race has an impact on the likelihood of receiving a death sentence, a significant amount of research has shown that the race of the victim has the most substantial impact on death sentences. The research evidence clearly shows that offenders who murder white victims are more likely to receive a death sentence than offenders who murder black victims. 59 When assessing the race of both the victim and offender, the composition most likely to receive the death penalty is when a black offender murders a white victim. 60
MYTHS ABOUT COURTS
Some additional myths about courts that research does not support include:
•Many criminals escape justice because of the exclusionary rule. 45
•Subjecting juvenile offenders to harsh punishments can reduce crime committed by juveniles. 46
•Public opinion is overwhelmingly in favor of imprisonment and harsh punishment for offenders. 47
•The death penalty brings closure and a sense of justice to the family and friends of murder victims. 48
•Insanity is a common verdict in criminal courts in the United States. 49
•Eyewitness identification is reliable evidence. 50
•Most people who commit crimes based on hatred, bias, or discrimination face hate crime charges and longer sentencing. 51
Myths about Corrections—Imprisonment Is the Most Severe Form of Punishment
It seems clear that besides the death penalty, the most severe punishment available in our criminal justice system is to lock up offenders in prison. On a continuum, it is perceived that sentence severity increases as one moves from fines, to probation, to intermediate sanctions such as boot camps, and finally, to incarceration in prison. The public and politicians support this perception as well.
So, what does the research show? What do criminals think is the most severe form of punishment? A growing body of research has assessed how convicted offenders perceive and experience the severity of sentences in our criminal justice system. 61 Research suggests that alternatives to incarceration in prison (i.e., probation and intermediate sanctions) are perceived by many offenders as more severe due to a greater risk of program failure (e.g., probation revocation). In comparison, serving prison time is easier. 62
For example, one study found that about one-third of nonviolent offenders given the option of participating in an Intensive Supervision Probation (ISP) program, chose prison instead because the prospects of working every day and submitting to random drug tests was more punitive than serving time in prison. 73 Prisoners also stated that they would likely be caught violating probation conditions (i.e., high risk of program failure) and be sent to prison anyway. 74 In another research study involving survey responses from 415 inmates serving a brief prison sentence for a nonviolent crime, prison was considered the eighth most severe sanction, with only community service and probation seen as less punitive. Electronic monitoring (seventh), intensive supervision probation (sixth), halfway house (fifth), intermittent incarceration (fourth), day reporting (third), county jail (second), and boot camp (first) were all rated by inmates as more severe sanctions than prison. 75
MYTHS ABOUT CORRECTIONS
Some additional myths about corrections that research does not support include:
•Punishing criminals reduces crime. 63
•Prisons are too lenient in their day-to-day operations (prisons as country clubs). 64
•Prisons can be self-supporting if only prisoners were forced to work. 65
•Private prisons are more cost effective than state-run prisons. 66
•Focus of community corrections is rehabilitation rather than punishment. 67
•Correctional rehabilitation does not work. 68
•Drug offenders are treated leniently by the criminal justice system. 69
•Most death row inmates will be executed eventually. 70
•If correctional sanctions are severe enough, people will think twice about committing crimes. 71
•Sexual violence against and exploitation of inmates of the same gender are primarily the result of lack of heterosexual opportunities. 72
What is Research and Why is It Important to be an Informed Consumer of Research?
We probably should have started the chapter with the question “What is research?” but we wanted to initially lay a foundation for the question with a discussion of the problems with how knowledge is developed and the power of research in discovering the truth. Research methods are tools that allow criminology and criminal justice researchers to systematically study crime and the criminal justice system. The study of research methods is the study of the basic rules, appropriate techniques, and relevant procedures for conducting research. Research methods provide the tools necessary to approach issues in criminal justice from a rigorous standpoint and challenge opinions based solely on nonscientific observations and experiences. Similarly, research is the scientific investigation of an issue, problem, or subject utilizing research methods. Research is a means of knowledge development that is designed to assist in discovering answers to research questions and leads to the creation of new questions.
How Is Knowledge Development through Research Different?
Previously, sources of knowledge development were discussed, including authority, tradition, common sense, personal experience, and media portrayals. The problems generated by each knowledge source were also discussed. Research is another source of knowledge development, but it is different than those previously discussed in several ways. First, research relies on logical and systematic methods and observations to answer questions. Researchers use systematic, well-established research practices to seek answers to their questions. The methods and observations are completed in such a way that others can inspect and assess the methods and observations and offer feedback and criticism. Researchers develop, refine, and report their understanding of crime and the criminal justice system more systematically than the public does through casual observation. Those who conduct scientific research employ much more rigorous methods to gather the information/knowledge they are seeking.
Second, in order to prove that a research finding is correct, a researcher must be able to replicate the finding using the same methods. Only through replication can we have confidence in our original finding. For researchers, it may be important to replicate findings many times over so that we are assured our original finding was not a coincidence or chance occurrence. The Minneapolis Domestic Violence Experiment is an example of this and will be discussed in detail in Chapter 5. In the experiment, the researchers found that arrests for domestic violence lead to fewer repeat incidences in comparison to separation of the people involved and mediation. Five replication studies were conducted and none were able to replicate the findings in the Minneapolis study. In fact, three of the replications found that those arrested for domestic violence had higher levels of continued domestic violence, so arrest did not have the deterrent effect found in the Minneapolis study.
Third, research is objective. Objectivity indicates a neutral and nonbiased perspective when conducting research. Although there are examples to the contrary, the researcher should not have a vested interest in what findings are discovered from the research. The researcher is expected to remain objective and report the findings of the study regardless of whether the findings support their personal opinion or agenda. In addition, research ensures objectivity by allowing others to examine and be critical of the methodology, findings, and results of research studies.
It should be clear that using research methods to answer questions about crime and the criminal justice system will greatly reduce the errors in the development of knowledge previously discussed. For example, research methods reduces the likelihood of overgeneralization by using systematic procedures for selecting individuals or groups to study that are representative of the individuals or groups that we wish to generalize. This is the topic of Chapter 3, which covers sampling procedures. In addition, research methods reduces the risk of selective observation by requiring that we measure and observe our research subjects systematically.
Being an Informed Consumer of Research
Criminal justice and criminological research is important for several reasons. First, it can provide better and more objective information. Second, it can promote better decision-making. Today, more than ever, we live in a world driven by data and in which there is an increasing dependence on the assessment of data when making decisions. As well as possible, research ensures that our decisions are based on data and not on an arbitrary or personal basis. Third, it allows for the objective assessment of programs. Fourth, it has often been the source of innovation within criminal justice agencies. Fifth, it can be directly relevant to criminal justice practice and have a significant impact on criminal justice operations.
Before we apply research results to practices in the criminal justice system, and before we even accept those research results as reasonable, we need to be able to know whether or not they are worthwhile. In other words, should we believe the results of the study? Research has its own limitations, so we need to evaluate research results and the methods used to produce them, and we do so through critical evaluation. Critical evaluation involves identifying both positive and negative aspects of the research study—both the good and the bad. Critical evaluation involves comparing the methodology used in the research with the standards established in research methods.
Through critical evaluation, consumers of research break studies down into their essential elements. What are the research questions and hypotheses? What were the independent and dependent variables? What research design was used? Was probability sampling used? What data-gathering procedures were employed? What type of data analysis was conducted and what conclusions were made? These are some of the questions that are asked by informed consumers of research. The evaluation of research ranges from the manner in which one obtains an idea to the ways in which one writes about the research results, and understanding each step in the research process is useful in our attempts to consume research conducted by others. Located between these two activities are issues concerning ethics, sampling, research design, data analyses, and interpretations.
The research design and procedures are typically the most critically evaluated aspects of research and will likewise receive the greatest amount of attention in this text. Informed consumers of research don’t just take the results of a research study at face value because the study is in an academic journal or written by someone with a Ph.D. Instead, informed consumers critically evaluate research. Taking what is learned throughout this text, critical evaluation of research is covered in Chapter 8, and upon completing this text, it is hoped that you will be an informed consumer of research and will put your research knowledge to use throughout your career.
Although many students will never undertake their own research, all will be governed by policies based upon research and exposed to research findings in their chosen professional positions. Most government agencies, including the criminal justice system, as well as private industry, routinely rely on data analysis. Criminal justice students employed with these agencies will be challenged if not prepared for quantitative tasks. Unfortunately, it is not unusual to find students as well as professionals in criminal justice who are unable to fully understand research reports and journal articles in their own field.
Beyond our criminal justice careers, we are all exposed to and use research to help us understand issues and to make personal decisions. For example, we know that cigarette smoking causes lung cancer and has other significant health impacts, so we don’t smoke. Your doctor tells you that your cholesterol is too high and you need to limit your red meat intake because research shows that consumption of red meat raises cholesterol; so, you quit eating red meat. That is why not all the examples in this text are criminal justice research examples. Some come from the medical field while others come from psychology and other disciplines. This is to remind you that you are probably exposed to much more research than you thought on day one of this class.
Overall, knowledge of research methods will allow you to more appropriately consider and consume information that is important to your career in criminal justice. It will help you better understand the process of asking and answering a question systematically and be a better consumer of the kind of information that you really need to be the best criminal justice professional you can. Once familiar with research methods, your anxiety about reviewing technical reports and research findings can be minimized. As discussed in the next section, research methods involve a process and once you understand the process, you can apply your knowledge to any research study, even those in other disciplines.
The Research Process
One of the nice things about studying research methods is it is about learning a process. Research methods can be seen as a sequential process with the first step being followed by the second step, and so on. There are certainly times when the order of the steps may be modified, but researchers typically follow the same process for each research study they complete regardless of the research topic (as depicted in Figure 2.1 in Chapter 2). Very simply, a research problem or question is identified, and a methodology is selected, developed, and implemented to answer the research question. This sequential process is one of the advantages of understanding research methods, because once you understand the process, you can apply that process to any research question that interests you. In addition, research methods are the same across disciplines. So, sampling is the same in business as it is in health education and as it is in criminal justice. Certainly the use of a particular method will be more common in one discipline in comparison to another, but the protocol for implementing the method to complete the research study is the same. For example, field research (discussed in Chapter 6) is used much more frequently in anthropology than in criminal justice. However, the research protocol to implement field research is the same whether you are studying an indigenous Indian tribe in South America in anthropology or a group of heroin users in St. Louis in criminal justice.
Some authors have presented the research process as a wheel or circle, with no specific beginning or end. Typically, the research process begins with the selection of a research problem and the development of research questions or hypotheses (discussed further in Chapter 2). It is common for the results of previous research to generate new research questions and hypotheses for the researcher. This suggests that research is cyclical, a vibrant and continuous process. When a research study answers one question, the result is often the generation of additional questions, which plunges the researcher right back into the research process to complete additional research to answer these new questions.
In this section, a brief overview of the research process will be presented. The chapters that follow address various aspects of the research process, but it is critical that you keep in mind the overall research process as you read this book, which is why is it presented here. Although you will probably not be expected to conduct a research study on your own, it is important for an educated consumer of research to understand the steps in the research process. The steps are presented in chronological order and appear neatly ordered. In practice, the researcher can go back and forth between the steps in the research process.
Step 1: Select a Topic and Conduct a Literature Review
The first step in the research process is typically the identification of a problem or topic that the researcher is interested in studying. Research topics can arise from a wide variety of sources, including the findings of a current study, a question that a criminal justice agency needs to have answered, or the result of intellectual curiosity. Once the researcher has identified a particular problem or topic, the researcher assesses the current state of the literature related to the problem or topic. The researcher will often spend a considerable amount of time in determining what the existing literature has to say about the topic. Has the topic already been studied to the point that the questions in which the researcher is interested have been sufficiently answered? If so, can the researcher approach the subject from a previously unexamined perspective? Many times, research topics have been previously explored but not brought to completion. If this is the case, it is certainly reasonable to examine the topic again. It is even appropriate to replicate a previous study to determine whether the findings reported in the prior research continue to be true in different settings with different participants. This step in the research process is also discussed in Chapter 2.
Step 2: Develop a Research Question
After a topic has been identified and a comprehensive literature review has been completed on the topic, the next step is the development of a research question or questions. The research question marks the beginning of your research study and is critical to the remaining steps in the research process. The research question determines the research plan and methodology that will be employed in the study, the data that will be collected, and the data analysis that will be performed. Basically, the remaining steps in the process are completed in order to answer the research question or questions established in this step. The development of research questions is discussed in more detail in Chapter 2.
Step 3: Develop a Hypothesis
After the research questions have been established, the next step is the formulation of hypotheses, which are statements about the expected relationship between two variables. For example, a hypothesis may state that there is no relationship between heavy metal music preference and violent delinquency. The two variables stated in the hypothesis are music preference and violent delinquency. Hypothesis development is discussed in more detail in Chapter 2.
Step 4: Operationalize Concepts
Operationalization involves the process of giving the concepts in your study a working definition and determining how each concept in your study will be measured. For example, in Step 3, the variables were music preference and violent delinquency. The process of operationalization involves determining how music preference and violent delinquency will be measured. Operationalization is further discussed in Chapter 2.
Step 5: Develop the Research Plan and Methodology
The next step is to develop the methodology that will be employed to answer the research questions and test the hypotheses. The research methodology is the blueprint for the study, which outlines how the research is to be conducted. The research questions will determine the appropriate methodology for the study. The research design selected should be driven by the research questions asked. In other words, the research questions dictate the methods used to answer them. The methodology is basically a research plan on how the research questions will be answered and will detail:
1. What group, subjects, or population will be studied and selected? Sampling will be discussed in Chapter 3.
2 . What research design will be used to collect data to answer the research questions? Various research designs will be covered in Chapters 4–7.
You need to have familiarity with all research designs so that you can become an educated consumer of research. A survey cannot answer all research questions, so knowing a lot about surveys but not other research designs will not serve you well as you assess research studies. There are several common designs used in criminal justice and criminology research. Brief descriptions of several common research designs are presented below, but each is discussed in detail in later chapters.
Survey research is one of the most common research designs employed in criminal justice research. It obtains data directly from research participants by asking them questions and is often conducted through self-administered questionnaires and personal interviews. For example, a professor might have her students complete a survey during class to understand the relationship between drug use and self-esteem. Survey research is discussed in Chapter 4.
Experimental designs are used when researchers are interested in determining whether a program, policy, practice, or intervention is effective. For example, a researcher may use an experimental design to determine if boot camps are effective at reducing juvenile delinquency. Experimental design is discussed in Chapter 5.
Field research involves researchers studying individuals or groups of individuals in their natural environment. The researcher is observing closely or acting as part of the group under study and is able to describe in depth not only the subject’s behaviors, but also consider the motivations that drive those behaviors. For example, if a researcher wanted to learn more about gangs and their activities, he may “hang out” with a gang in order to observe their behavior. Field research is discussed in Chapter 6.
A case study is an in-depth analysis of one or a few illustrative cases. This design allows the story behind an individual, a particular offender, to be told and then information from cases studies can be extrapolated to a larger group. Often these studies require the review and analysis of documents such as police reports and court records and interviews with the offender and others. For example, a researcher may explore the life history of a serial killer to try and understand why the offender killed. Case studies are discussed in Chapter 6.
Secondary data analysis occurs when researchers obtain and reanalyze data that was originally collected for a different purpose. This can include reanalyzing data collected from a prior research study, using criminal justice agency records to answer a research question, or historical research. For example, a researcher using secondary data analysis may analyze inmate files from a nearby prison to understand the relationship between custody level assignment and disciplinary violations inside prison. Secondary data analysis is discussed in Chapter 7.
Content analysis requires the assessment of content contained in mass communication outlets such as newspapers, television, magazines, and the like. In this research design, documents, publications, or presentations are reviewed and analyzed. For example, a researcher utilizing content analysis might review true crime books involving murder to see how the characteristics of the offender and victim in the true crime books match reality as depicted in the FBI’s Supplemental Homicide Reports. Content analysis is discussed in Chapter 7.
Despite the options these designs offer, other research designs are available and will be discussed later in the text. Ultimately, the design used will depend on the nature of the study and the research questions asked.
Step 6: Execute the Research Plan and Collect Data
The next step in the research process is the collection of the data based on the research design developed. For example, if a survey is developed to study the relationship between gang membership and violent delinquency, the distribution and collection of surveys from a group of high school students would occur in this step. Data collection is discussed in several chapters throughout this text.
Step 7: Analyze Data
After the data have been collected, the next phase in the research process involves analyzing the data through various and appropriate statistical techniques. The most common means for data analysis today is through the use of a computer and statistically oriented software. Data analysis and statistics are discussed in Chapter 9.
Step 8: Report Findings, Results, and Limitations
Reporting and interpreting the results of the study make up the final step in the research process. The findings and results of the study can be communicated through reports, journals, books, or computer presentations. At this step, the results are reported and the research questions are answered. In addition, an assessment is made regarding the support or lack of support for the hypotheses tested. It is also at this stage that the researcher can pose additional research questions that may now need to be answered as a result of the research study. In addition, the limitations of the study, as well as the impact those limitations may have on the results of the study, will be described by the researcher. All research has limitations, so it is incumbent on the researcher to identify those limitations for the reader. The process of assessing the quality of research will be discussed in Chapter 8.
Research in Action: Impacting Criminal Justice Operations
Research in the criminal justice system has had significant impacts on its operations. The following sections provide an example of research that has significantly impacted each of the three main components of the criminal justice system: police, courts, and corrections. The purpose of this section is to demonstrate that research has aided the positive development and progression of the criminal justice system.
Police Research Example 76
The efforts of criminal justice researchers in policing have been important and have created the initial and critical foundation necessary for the further development of effective and productive law enforcement. One seminal study asked: How important is it for the police to respond quickly when a citizen calls? The importance of rapid response was conveyed in a 1973 National Commission on Productivity Report despite the fact that there was very little empirical evidence upon which to base this assumption. In fact, the Commission stated “there is no definitive relationship between response time and deterrence, but professional judgment and logic do suggest that the two are related in a strong enough manner to make more rapid response important.” 77 Basically the Commission members were stating that we don’t have any research evidence that response times are important, but we “know” that they are. Police departments allocated substantial resources to the patrol function and deployed officers in an effort to improve response time through the use of the 9-1-1 telephone number, computer-assisted dispatch, and beat assignment systems. Officers were typically assigned to a patrol beat. When the officers were not answering calls for service, they remained in their assigned beats so they could immediately respond to an emergency.
The data for the project were collected as part of a larger experiment on preventive patrol carried out in Kansas City, Missouri, between October 1972 and September 1973. 78 To determine the impact of response time, researchers speculated that the following variables would be influenced by response time: 1) the outcome of the response, 2) citizen satisfaction with response time, and 3) citizen satisfaction with the responding officer. Several data sources were used in the study. First, surveys were completed after all citizen-initiated calls (excluding automobile accidents) that involved contact with a police officer. The survey instrument consisted of questions to assess the length of time to respond to a call and the outcome of the call (i.e., arrest). Over 1,100 surveys were completed. Second, a follow-up survey was mailed to citizens whom the police had contacted during their response. These surveys asked questions to assess citizen satisfaction with response time and outcome. Over 425 of these surveys were returned.
The data collected during the study showed that response time did not determine whether or not the police made an arrest or recovered stolen property. This was the most surprising finding from the study because it challenged one of the basic underlying principles of police patrol. Researchers attributed the lack of significance to the fact that most citizens waited before calling the police. Rapid response simply did not matter in situations where citizens delayed in reporting the crime.
Rapid response time was not only believed to be important in determining the outcome of a response (i.e., more likely to lead to an arrest), it was also considered an important predictor of citizen satisfaction. Data from the study showed that when the police arrived sooner than expected, citizens were more satisfied with response time. However, subsequent research has shown that citizens are also satisfied with a delayed response as long as the dispatcher sets a reasonable expectation for when the patrol officer will arrive. Response time was also the best predictor of how satisfied a citizen was with the responding officer. It was further revealed that citizens became dissatisfied with the police when they were not informed of the outcome (i.e., someone was arrested). Again, these findings indicate the need for dispatchers and patrol officers to communicate with complainants regarding when they should expect an officer to arrive and the outcome of the call.
Based on the results of the response time study, the researchers concluded that rapid response was not as important as police administrators had thought. Response time was not related to an officer’s ability to make an arrest or recover stolen property. Results from the response time study challenged traditional beliefs about the allocation of patrol in our communities. Based on tradition knowledge, as previously discussed, rapidly responding to calls for service is what the police had always done since they started using patrol vehicles. In addition, common sense, as previously discussed, played a role in the practice of rapid response to calls for service; it just made sense that if a patrol officer arrives sooner, she will be more likely to make an arrest.
Prior to the research, police departments operated under the assumption that rapid response was a crucial factor in the ability of an officer to solve a crime and an important predictor of citizen satisfaction. In response to the research on rapid response, many police departments changed the way they responded to calls for service. Many departments adopted a differential police response approach. Differential police response protocols allow police departments to prioritize calls and rapidly dispatch an officer only when an immediate response is needed (i.e., crimes in progress). For crimes in progress, rapid response is critical and may reduce the injuries sustained by the victim as well, but these emergency calls usually account for less than 2% of all 9-1-1 calls for police service. For nonemergency calls, an officer is either dispatched at a later time when the officer is available or a report is taken over the phone or through some other means. Differential police response has been shown to save departments money and give patrol officers more time to engage in community-oriented and proactive policing activities. The benefits for a department are not at the expense of the public. In fact, a study by Robert Worden found a high degree of citizen satisfaction with differential police response. 79
Courts Research Example 80
Research on the courts component of the criminal justice system, while far from complete, has produced direct effects on the operations of the criminal justice system. The study reviewed in this section asked the following research question: Are jurors able to understand different legal rules for establishing a defendant’s criminal responsibility? The study described below explored the issue of criminal responsibility as it applies to the insanity defense in the United States. For several years, the M ’ Naghten rule was the legal rule applied in all courts of the United States. Under M ’ Naghten, criminal responsibility was absent when the offender did not understand the nature of his actions due to failure to distinguish “right” from “wrong.” This is known as the “right/wrong test” for criminal responsibility. The case of Durham v. United States was heard in the U.S. Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia and offered an alternative test for criminal responsibility and insanity. The legal rule emerging from Durham was that criminal responsibility was absent if the offense was a product of mental disease or defect. This ruling provided psychiatrists with a more important role at trial because of the requirement that the behavior be linked to a mental disorder that only a psychiatrist could officially determine.
At the time of Simon’s 1967 study, most courts across the country still followed the M ’ Naghten rule. Questions arose, however, regarding whether juries differed in their understanding of M ’ Naghten versus Durham and, in turn, whether this resulted in differences in their ability to make informed decisions regarding criminal responsibility in cases involving the insanity defense. The study was designed to determine the effect of different legal rules on jurors’ decision-making in cases where the defense was insanity. There was a question of whether there was a difference between the rules to the extent that jurors understood each rule and could capably apply it.
Simon conducted an experimental study on jury deliberations in cases where the only defense was insanity. 81 Utilizing a mock jury approach, Simon took the transcripts of two actual trials with one reflecting the use of the M ’ Naghten rule and the other the Durham rule. Both cases were renamed and the transcripts were edited to constitute a trial of 60–90 minutes in length. These edited transcripts were then recorded, with University of Chicago Law School faculty as the attorneys, judges, and witnesses involved in each case. Groups of 12 jurors listened to each trial with instruction provided at the end regarding the particular rule of law ( M ’ Naghten or Durham) for determining criminal responsibility. Each juror submitted a written statement with his or her initial decision on the case before jury deliberations, and the juries’ final decisions after deliberation were also reported.
Simon found significant differences in the verdicts across the two groups ( M ’ Naghten rule applied and Durham rule applied) even when the case was the same. For the M ’ Naghten version of the case, the psychiatrists stated that the defendant was mentally ill yet knew right from wrong during the crime. These statements/instructions should have led to a guilty verdict on the part of the mock jury. As expected, the M ’ Naghten juries delivered guilty verdicts in 19 of the 20 trials, with one hung jury. For the Durham version of the case, the psychiatrists stated that the crime resulted from the defendant’s mental illness, which should have lead to acquittal. However, the defendant was acquitted in only five of the 26 Durham trials. Twenty-six groups of 12 jurors were exposed to the Durham version of the trial and the case was the same each time. Simon interpreted these results as suggesting that jurors were unambiguous in their interpretations and applications of M ’ Naghten (due to the consistency in guilty verdicts), but they were less clear on the elements of Durham and how to apply it (reflected by the mix of guilty, not guilty, and hung verdicts). 82
After Simon’s study, most states rejected the Durham test. Recall her finding that the Durham rule produced inconsistent verdicts. She interpreted this finding as Durham being no better than providing no guidance to jurors on how to decide the issue of insanity. The observation helped to fuel arguments against the use of Durham, which, in turn, contributed to its demise as a legal rule. Today, only New Hampshire uses a version of the Durham rule in insanity cases.
WHAT RESEARCH SHOWS: IMPACTING CRIMINAL JUSTICE OPERATIONS
The Punishment Cost of Being Young, Black, and Male
Steffensmeier, Ulmer, and Kramer 83 hypothesized that African Americans overall were not likely to be treated more harshly than white defendants by the courts because it was only particular subgroups of minority defendants that fit with court actors’ stereotypes of “more dangerous” offenders. In particular, they argued that younger African American males not only fulfilled this stereotype more than any other age, race, and gender combination, they were also more likely to be perceived by judges as being able to handle incarceration better than other subgroups.
In order to test their hypotheses, the researchers examined sentencing data from Pennsylvania spanning four years (1989–1992). Almost 139,000 cases were examined. The sentences they examined included whether a convicted defendant was incarcerated in prison or jail, and the length of incarceration in prison or jail. The researchers found that offense severity and prior record were the most important predictors of whether a convicted defendant was incarcerated and the length of incarceration. The authors found that the highest likelihood of incarceration and the longest sentences for males were distributed to African Americans aged 18–29 years. Their analysis of females revealed that white females were much less likely than African American females to be incarcerated, regardless of the age group examined. Taken altogether, the analysis revealed that African American males aged 18–29 years maintained the highest odds of incarceration and the longest sentences relative to any other race, sex, and age group.
Overall, this research showed that judges focused primarily on legal factors (offense severity and prior record) when determining the sentences of convicted offenders. These are the factors we expect judges to consider when making sentencing decisions. However, the research also found that judges base their decisions in part on extralegal factors, particularly the interaction of a defendant’s age, race, and gender. This research expanded our knowledge beyond the impact of singular factors on sentencing to expose the interaction effects of several variables (race, gender, and age). Court personnel are aware of these interaction effects based on this study, and others that followed, as well as their personal experiences in the criminal justice system. Identification and recognition of inequities in our justice system (in this case that young, African American males are punished more severely in our justice system) is the first step in mitigating this inequity.
Corrections Research Example 84
Although the research in corrections is far from complete, it has contributed greatly to the development of innovative programs and the professional development of correctional personnel. The contributions of academic and policy-oriented research can be seen across the whole range of correctional functions from pretrial services through probation, institutional corrections, and parole.
Rehabilitation remained the goal of our correctional system until the early 1970s, when the efficacy of rehabilitation was questioned. Violent crime was on the rise, and many politicians placed the blame on the criminal justice system. Some believed the system was too lenient on offenders. Interest in researching the effectiveness of correctional treatment remained low until 1974 when an article written by Robert Martinson and published in Public Interest titled “What Works? Questions and Answers about Prison Reform” generated enormous political and public attention to the effectiveness of correctional treatment. 85
Over a six-month period, Martinson and his colleagues reviewed all of the existing literature on correctional treatment published in English from 1945 to 1967. Each of the articles was evaluated according to traditional standards of social science research. Only studies that utilized an experimental design, included a sufficient sample size, and could be replicated were selected for review. A total of 231 studies examining a variety of different types of treatment were chosen, including educational and vocational training, individual and group counseling, therapeutic milieus, medical treatment, differences in length and type of incarceration, and community corrections. All of the treatment studies included at least one measure of offender recidivism, such as whether or not offenders were rearrested or violated their parole. The recidivism measures were used to examine the success or failure of a program in terms of reducing crime.
After reviewing all 231 studies, Martinson reported that there was no consistent evidence that correctional treatment reduced recidivism. Specifically, he wrote, “with few and isolated exceptions, the rehabilitative efforts that have been reported so far have had no appreciable effect on recidivism.” 86 Martinson further indicated that the lack of empirical support for correctional treatment could be a consequence of poorly implemented programs. If the quality of the programs were improved, the results may have proved more favorable, but this conclusion was for the most part ignored by the media and policy-makers.
Martinson’s report became commonly referred to as “nothing works” and was subsequently used as the definitive study detailing the failures of rehabilitation. The article had implications beyond questioning whether or not specific types of correctional treatment reduced recidivism. The entire philosophy of rehabilitation was now in doubt because of Martinson’s conclusion that “our present strategies … cannot overcome, or even appreciably reduce, the powerful tendencies of offenders to continue in criminal behavior.” 87
Martinson’s article provided policy makers the evidence to justify spending cuts on rehabilitative programs. Furthermore, it allowed politicians to respond to growing concerns about crime with punitive, get-tough strategies. States began implementing strict mandatory sentences that resulted in more criminals being sent to prison and for longer periods of time. Over the next several years, Martinson’s article was used over and over to support abandoning efforts to treat offenders until rehabilitation became virtually nonexistent in our correctional system.
Chapter Summary
This chapter began with a discussion of sources of knowledge development and the problems with each. To depict the importance of research methods in knowledge development, myths about crime and the criminal justice system were reviewed along with research studies that have dispelled myths. As the introductory chapter in this text, this chapter also provided an overview of the steps in the research process from selecting a topic and conducting a literature review at the beginning of a research study to reporting findings, results, and limitations at the end of the study. Examples of actual research studies in the areas of police, courts, and corrections were also provided in this chapter to demonstrate the research process in action and to illustrate how research has significantly impacted practices within the criminal justice system. In addition, this chapter demonstrated the critical importance of becoming an informed consumer of research in both your personal and professional lives.
Critical Thinking Questions
1. What are the primary sources of knowledge development, and what are the problems with each?
2. How is knowledge developed through research methods different from other sources of knowledge?
3. What myths about crime and criminal justice have been dispelled through research? Give an example of a research study that dispelled a myth.
4. Why is it important to be an informed consumer of research?
5. What are the steps in the research process, and what activities occur at each step?
authority knowledge: Knowledge developed when we accept something as being correct and true just because someone in a position of authority says it is true
case study: An in-depth analysis of one or a few illustrative cases
common sense knowledge: Knowledge developed when the information “just makes sense”
content analysis: A method requiring the analyzing of content contained in mass communication outlets such as newspapers, television, magazines, and the like
CSI Effect: Due to the unrealistic portrayal of the role of forensic science in solving criminal cases in television shows, jurors are more likely to vote to acquit a defendant when the expected sophisticated forensic evidence is not presented
differential police response: Methods that allow police departments to prioritize calls and rapidly dispatch an officer only when an immediate response is needed (i.e., crimes in progress)
experimental designs: Used when researchers are interested in determining whether a program, policy, practice, or intervention is effective
field research: Research that involves researchers studying individuals or groups of individuals in their natural environment
Halloween sadism: The practice of giving contaminated treats to children during trick or treating
hypotheses: Statements about the expected relationship between two concepts
illogical reasoning: Occurs when someone jumps to premature conclusions or presents an argument that is based on invalid assumptions
myths: Beliefs that are based on emotion rather than rigorous analysis
operationalization: The process of giving a concept a working definition; determining how each concept in your study will be measured
overgeneralization: Occurs when people conclude that what they have observed in one or a few cases is true for all cases
personal experience knowledge: Knowledge developed through actual experiences
research: The scientific investigation of an issue, problem, or subject utilizing research methods
research methods: The tools that allow criminology and criminal justice researchers to systematically study crime and the criminal justice system and include the basic rules, appropriate techniques, and relevant procedures for conducting research
resistance to change: The reluctance to change our beliefs in light of new, accurate, and valid information to the contrary
secondary data analysis: Occurs when researchers obtain and reanalyze data that were originally collected for a different purpose
selective observation: Choosing, either consciously or unconsciously, to pay attention to and remember events that support our personal preferences and beliefs
survey research: Obtaining data directly from research participants by asking them questions, often conducted through self-administered questionnaires and personal interviews
tradition knowledge: Knowledge developed when we accept something as true because that is the way things have always been, so it must be right
variables: Concepts that have been given a working definition and can take on different values
1 Briggs, Lisa T., Stephen E. Brown, Robert B. Gardner, and Robert L. Davidson. (2009). “D.RA.MA: An extended conceptualization of student anxiety in criminal justice research methods courses.” Journal of Criminal Justice Education 20 (3), 217–226.
2 Betz, N. E. (1978). “Prevalence, distribution, and correlates of math anxiety in college students. Journal of Counseling Psychology 25 (5), 441–448.
3 Briggs, et al., 2009, p. 221.
4 Ibid, p. 221.
5 Ibid, p. 221.
6 Kappeler, Victor E., and Gary W. Potter. (2005). The mythology of crime and criminal justice. Prospect Heights, IL: Waveland.
7 Tennessee v. Gamer, 471 U.S. 1 (1985).
8 Lombroso-Ferrero, Gina. (1911). Criminal man, according to the classification of Cesare Lombroso. New York: Putnam.
9 This study was included in Amy B. Thistlethwaite and John D. Wooldredge. (2010). Forty studies that changed criminal justice: Explorations into the history of criminal justice research. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
10 Petersilia, J., S. Turner, J. Kahan, and J. Peterson. (1985). Granting felons probation: Public risks and alternatives. Santa Monica, CA: Rand.
11 Vito, G. (1986). “Felony probation and recidivism: Replication and response.” Federal Probation 50, 17–25.
12 Conrad, J. (1985). “Research and development in corrections.” Federal Probation 49, 69–71.
13 Finckenauer, James O. (1982). Scared straight! and the panacea phenomenon. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
14 Yarborough, J.C. (1979). Evaluation of JOLT (Juvenile Offenders Learn Truth) as a deterrence program. Lansing, MI: Michigan Department of Corrections.
15 Petrosino, Anthony, Carolyn Turpin-Petrosino, and James O. Finckenauer. (2000). “Well-meaning programs can have harmful effects! Lessons from experiments of programs such as Scared Straight,” Crime & Delinquency 46, 354–379.
16 Robertson, Jordan. “I’m being punished for living right”: Background check system is haunted by errors. December 20, 2011. http://finance.yahoo.com/news /ap-impact-criminal-past-isnt-182335059.html. Retrieved on December 29, 2011.
17 Shelton, D. E. (2008). “The ‘CSI Effect’: Does it really exist?” NIJ Journal 259 [NCJ 221501].
18 Best, Joel. (2011). “Halloween sadism: The evidence.” http://dspace.udel.edu:8080/dspace/bitstream/handle/ 19716/726/Halloween%20sadism.revised%20thru%20201l.pdf?sequence=6. Retrieved on May 7, 2012.
19 Best, Joel. (1985, November). “The myth of the Halloween sadist. Psychology Today 19 (11), p. 14.
21 “Beer compound shows potent promise in prostate cancer battle.” Press release from Oregon State University May 30, 2006. http://oregonstate.edu/ua/ncs/archives/2006/ may/beer-compound-shows-potent-promise-prostate-cancer-battle. Retrieved on January 6, 2012; Colgate, Emily C., Cristobal L. Miranda, Jan F. Stevens, Tammy M. Bray, and Emily Ho. (2007). “Xanthohumol, a prenylflavonoid derived from hops induces apoptosis and inhibits NF-kappaB activation in prostate epithelial cells,” Cancer Letters 246, 201–209; “Health benefits of red wine exaggerated” http://health.yahoo.net/articles /nutrition/health-benefits-red-wine-exaggerated. Retrieved on January 14, 2012; “Scientific journals notified following research misconduct investigation.” January 11, 2012. http://today.uconn.edu/blog/2012/01/scientific-journals -notified-following-research-misconduct-investigation/. Retrieved on January 14, 2012.
22 Pepinsky, Hal. “The myth that crime and criminality can be measured.” 3–11 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
23 Bullock, Jennifer L., and Bruce A. Arrigo. “The myth that mental illness causes crime.” 12–19 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
24 Friedrichs, David O. “The myth that white-collar crime is only about financial loss.” 20–28 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
25 Kuhns III, Joseph B., and Charisse T. M. Coston. “The myth that serial murderers are disproportionately white males.” 37–44 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
26 Longmire, Dennis R., Jacqueline Buffington-Vollum, and Scott Vollum. “The myth of positive differentiation in the classification of dangerous offenders.” 123–131 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
27 Masters, Ruth E., Lori Beth Way, Phyllis B. Gerstenfeld, Bernadette T. Muscat, Michael Hooper, John P. J. Dussich, Lester Pincu, and Candice A. Skrapec. (2013). CJ realities and challenges, 2nd ed. New York: McGraw-Hill.
32 Brownstein, Henry H. “The myth of drug users as violent offenders.” 45–53 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
33 Goldstein, P. (1985). “The drugs/violence nexus: A tripartite conceptual framework.” Journal of Drug Issues 15, 493–506.
34 Goldstein, P, H. Brownstein, and P. Ryan. (1992). “Drug-related homicide in New York City: 1984 and 1988.” Crime & Delinquency 38, 459–476.
35 Parker, R., and K. Auerhahn. (1998). “Alcohol, drugs, and violence.” Annual Review of Sociology 24, 291–311, p. 291.
36 Buerger, Michael. “The myth of racial profiling.” 97–103 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
37 Cordner, Gary, and Kathryn E. Scarborough. “The myth that science solves crimes.” 104–110 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
38 Willis, James J., Stephen D. Mastrofski, and David Weisburd. “The myth that COMPSTAT reduces crime and transforms police organizations.” 111–119 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
39 Masters, et al., 2013.
43 Scott, Eric J. (1981). Calls for service: Citizen demand and initial police response. Washington, DC: Government Printing Office.
44 Lersch, Kim. “The myth of policewomen on patrol.” 89–96 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
45 Janikowski, Richard. “The myth that the exclusionary rule allows many criminals to escape justice.” 132–139 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
46 Bishop, Donna M. “The myth that harsh punishments reduce juvenile crime.” 140–148 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
47 Immarigeon, Russ. “The myth that public attitudes are punitive.” 149–157 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
48 Acker, James R. “The myth of closure and capital punishment.” 167–175 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
49 Masters, et al., 2013.
52 Lersch, 2006.
53 Newport, Frank. “In U.S., support for death penalty falls to 39-year low.” October 13, 2011. http://www.gallup .com/poll/150089/support-death-penalty-falls-year-low.aspx. Retrieved on April 16, 2012.
54 Applegate, Brandon. “The myth that the death penalty is administered fairly.” 158–166 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
55 Williams, M. R., and J. E. Holcomb. (2001). “Racial disparity and death sentences in Ohio.” Journal of Criminal Justice 29, 207–218.
56 Snell, Tracy L. (2011, December). Capital punishment, 2010—statistical tables. Washington, DC: Bureau of Justice Statistics.
57 Applegate, 2006.
58 Williams and Holcomb, 2001.
59 Applegate, 2006.
61 Wood, Peter B. “The myth that imprisonment is the most severe form of punishment.” 192–200 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
63 Michalowski, Raymond. “The myth that punishment reduces crime.” 179–191 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
64 McShane, Marilyn, Frank P. Williams III, and Beth Pelz. “The myth of prisons as country clubs.” 201–208 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
65 Parker, Mary. “The myth that prisons can be self-supporting.” 209–213 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
66 Blakely, Curtis, and John Ortiz Smykla. “Correctional privatization and the myth of inherent efficiency.” 214–220 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
67 Jones, G. Mark. “The myth that the focus of community corrections is rehabilitation.” 221–226 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
68 Cullen, Francis T., and Paula Smith. “The myth that correctional rehabilitation does not work.” 227–238 in Bohm, Robert M., and Jeffrey T. Walker. (2006). Demystifying crime and criminal justice. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
69 Masters, et al., 2013.
73 Petersilia, Joan. (1990). “When probation becomes more dreaded than prison. Federal Probation 54, 23–27.
75 Wood, P. B., and H. G. Grasmick. (1999). “Toward the development of punishment equivalencies: Male and female inmates rate the severity of alternative sanctions compared to prison.” Justice Quarterly 16, 19–50.
76 Example is excerpted from Amy B. Thistlethwaite and John D. Wooldredge. (2010). Forty studies that changed criminal justice: Explorations into the history of criminal justice research. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall. This is an excellent book that demonstrates the impact research has had on criminal justice operations.
77 National Commission on Productivity. (1973). Opportunities for improving productivity in police services. Washington, DC: United States Government Printing Office, p. 19.
78 Pate, T., A. Ferrara, R. Bowers, and J. Lorence. (1976). Police response time: Its determinants and effects. Washington, DC: Police Foundation.
79 Worden, R. (1993). “Toward equity and efficiency in law enforcement: Differential police response. American Journal of Police 12, 1–32.
80 Example is excerpted from Amy B. Thistlethwaite and John D. Wooldredge. (2010). Forty studies that changed criminal justice: Explorations into the history of criminal justice research. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
81 Simon, R. (1967). The jury and the defense of insanity. Boston: Little, Brown.
83 Steffensmeier, D., J. Ulmer, & J. Kramer. (1998). “The interaction of race, gender, and age in criminal sentencing: The punishment cost of being young, black, and male. Criminology 36, 763–797.
84 Example is excerpted from Amy B. Thistlethwaite and John D. Wooldredge. (2010). Forty studies that changed criminal justice: Explorations into the history of criminal justice research. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
85 Martinson, R. (1974). “What works? Questions and answers about prison reform.” The Public Interest 10, 22–54.
86 Ibid, p. 25.
87 Ibid, p. 49.
Applied Research Methods in Criminal Justice and Criminology by University of North Texas is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 1: Introduction to Research Methods
Learning Objectives
At the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Define the term “research methods”.
- List the nine steps in undertaking a research project.
- Differentiate between applied and basic research.
- Explain where research ideas come from.
- Define ontology and epistemology and explain the difference between the two.
- Identify and describe five key research paradigms in social sciences.
- Differentiate between inductive and deductive approaches to research.
Welcome to Introduction to Research Methods. In this textbook, you will learn why research is done and, more importantly, about the methods researchers use to conduct research. Research comes in many forms and, although you may feel that it has no relevance to you and/ or that you know nothing about it, you are exposed to research multiple times a day. You also undertake research yourself, perhaps without even realizing it. This course will help you to understand the research you are exposed to on a daily basis, and how to be more critical of the research you read and use in your own life and career.
This text is intended as an introduction. A plethora of resources exists related to more detailed aspects of conducting research; it is not our intention to replace any of these more comprehensive resources. Keep notes and build your own reading list of articles as you go through the course. Feedback helps to improve this open-source textbook, and is appreciated in the development of the resource.
Research Methods, Data Collection and Ethics Copyright © 2020 by Valerie Sheppard is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

Chapter 1: What is Research and Research Writing?

Write here, write now.
Developing your skills as a writer will make you more successful in ALL of your classes. Knowing how to think critically, organize your ideas, be concise, ask questions, perform research and back up your claims with evidence is key to almost everything you will do at university.
Writing is life
Solid writing skills will help you wow your family and friends with your well-articulated ideas, ace job interviews, build confidence in yourself, and feel part of a community of writers.
Beyond University
Whether you go on to graduate school, teach, work for the government or a non-profit, start your own business or your own heavy metal band, becoming a stronger writer will give you a solid foundation you can keep building on.
This chapter:
- Defines research and gives examples
- Describes the writing process
- Introduces writing using research
- Introduces simple research writing
- Prompts you to think about research and writing meaningful to you
Kimmerer, Robin Wall. Braiding Sweetgrass : Indigenous Wisdom, Scientific Knowledge, and the Teachings of Plants . Milkweed Editions, 2013.
From “ Why Writing Matters “ . Writing Place: A Scholarly Writing Textbook by Lindsay Cuff. CC BY-NC-SA 4.0. 2023.
Reading and Writing Research for Undergraduates Copyright © 2023 by Stephanie Ojeda Ponce is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Chapter 1: Home
- Narrowing Your Topic
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Quantitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative & Quantitative Research Support with the ASC This link opens in a new window
- Library Research Consultations This link opens in a new window
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2023 1:37 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1006886

- Terms and Conditions
- Join the OMT Division

Organization and Management Theory OMT

UN PRME Global Tour - UN PRME African Chapter Research Paper Development Program – May 23, 2024
Kathleen rehbein 2 days ago, caiwei zhang 4 hours ago, 1. un prme global tour - un prme african chapter research paper development program – may 23, 2024.
Dear Academy Colleagues:
We are happy to invite you to participate in an online workshop which is part of the UN PRME World Tour Research Paper Development Program 2022-2024!! Are you interested in learning more about publishing (in general) and conducting research in an African context? Are you an early or mid-career scholar who would like to get feedback on your manuscript? This is a great chance to get feedback from experienced senior scholars!
The following power points provide more detail about the expert speakers who are part of the first part of the workshop, Editor's and Research panels. Anyone can attend this part of the workshop; you just need to register. These exciting panels are followed by a manuscript development workshop, more details are provided for both these events in the links in the PowerPoint slides listed below.
Kelly Alexander, Gordon Institute of Business Science, University of Pretoria
Jill Bogie, Gordon Institute of Business Science, University of Pretoria
Collins Ntim, University of Southampton
Kathleen Rehbein, University of Marquette

2. RE: UN PRME Global Tour - UN PRME African Chapter Research Paper Development Program – May 23, 2024
Hi Kathleen ,
Thank you for sharing this. Do you mind attaching the link for information and registration? This link doesn't seem to work. Thank you so much!
New Best Answer
Community tags.
- Divisions and Interest Groups
- Entrepreneurship
- Organization and Management Theory
- Organizational Behavior
- Technology and Innovation Management
- Annual Meeting
- Connect @ AOM
- Strategy
- Request info
- Majors & Degrees
- Prospective Students
- Current Undergraduate Students
- Current Graduate Students
- Online Students
- Alumni and Friends
- Faculty and Staff
Gulf Park Campus Health Center Invites Campus Community to Monthly 1-Mile Walk and Talk Gathering
Thu, 04/18/2024 - 08:17am | By: Gabriela Shinskie
The University of Southern Mississippi (USM) Gulf Park Health Center (GPHC) invites members of campus community to lace up their walking shoes and join in the monthly “Strutt Your Stuff Walk and Talk,” a 1-mile walk around the school’s beautiful beachfront campus with GPHC nurse practitioner Connie Richardson.
The walks take place on the first Wednesday of every month, beginning at 12:15 p.m. with participants meeting at the GPHC.
“The walk is an opportunity to hold a conversation about general medical problems and to get outside and move in a relaxed setting,” said Richardson.
Richardson was inspired by a program called “Walk with the Doc”. She credits the beautiful coastal spring weather for inspiration to get outside and take a break from school and work. Participants can ask Richardson general health questions during the walk.
The first walk took place April 3, where participants asked questions about bone health, screenings, and blood pressure. Richardson is hoping to continue facilitating conversations about women’s health and other health concerns, while also emphasizing the importance of taking time each day to exercise.
“There are multiple benefits to walking outside, including improving one’s mental health, getting vitamin D [from sunlight], improving metabolism, gaining muscle mass, and benefiting serotonin levels in the brain,” Richardson explained.
Studies have shown that walking a minimum of 4,000 steps a day significantly reduces early death. Setting a goal of 2,300 steps a day also reduces risks of cardiovascular disease.
The next gathering will take place Wednesday, May 1. Learn more about the GPHC and how to participate at the next Strutt Your Stuff Walk and Talk.
Categories: Coastal USM Nursing and Health Professions
Recent News Articles
Ato fraternity gives back to usm's dubard school, lucas recipient of mississippi pinnacle award for lifetime achievement, usm fraternity and sorority life chapter president spotlight: pi kappa phi's kane palazzo.
Language selection
- Français fr
Chapter 4: Economic Growth for Every Generation
On this page:, 4.1 boosting research, innovation, and productivity, 4.2 attracting investment for a net-zero economy, 4.3 growing businesses to create more jobs.
- 4.4 A Strong Workforce for a Strong Economy
Impacts report
Find out more about the expected gender and diversity impacts for each measure in Chapter 4: Economic Growth for Every Generation
To ensure every Canadian succeeds in the 21 st century, we must grow our economy to be more innovative and productive. One where every Canadian can reach their full potential, where every entrepreneur has the tools they need to grow their business, and where hard work pays off. Building the economy of the future is about creating jobs: jobs in the knowledge economy, jobs in manufacturing, jobs in mining and forestry, jobs in the trades, jobs in clean energy, and jobs across the economy, in all regions of the country.
To do this, the government's economic plan is investing in the technologies, incentives, and supports critical to increasing productivity, fostering innovation, and attracting more private investment to Canada. This is how we'll build an economy that unlocks new pathways for every generation to earn their fair share.
The government is targeting investments to make sure Canada continues to lead in the economy of the future, and these are already generating stronger growth and meaningful new job opportunities for Canadians. New jobs—from construction to manufacturing to engineering—in clean technology, in clean energy, and in innovation, are just the start. All of this, helping to attract further investment to create more opportunities, will raise Canada's productivity and competitiveness. This will create more good jobs, and in turn, raise the living standards of all Canadians.
We are at a pivotal moment where we can choose to renew and redouble our investments in the economy of the future, to build an economy that is more productive and more competitive—or risk leaving an entire generation behind. We will not make that mistake. We owe it to our businesses, to our innovators, and most of all, to the upcoming generations of workers, to make sure that the Canadian economy is positioned to thrive in a changing world.
Canada has the best-educated workforce in the world. We are making investments to ensure every generation of workers has the skills the job market, and the global economy, are looking for—and this will help us attract private investment to grow the economy (Chart 4.1). Building on our talented workforce, we are delivering, on a priority basis, our $93 billion suite of major economic investment tax credits to drive growth, secure the future of Canadian businesses in Canada, and create good jobs for generations to come.
In the first three quarters of 2023, Canada had the highest level of foreign direct investment (FDI) on a per capita basis among G7 countries, and ranked third globally in total FDI, after the U.S. and Brazil (Chart 4.2).
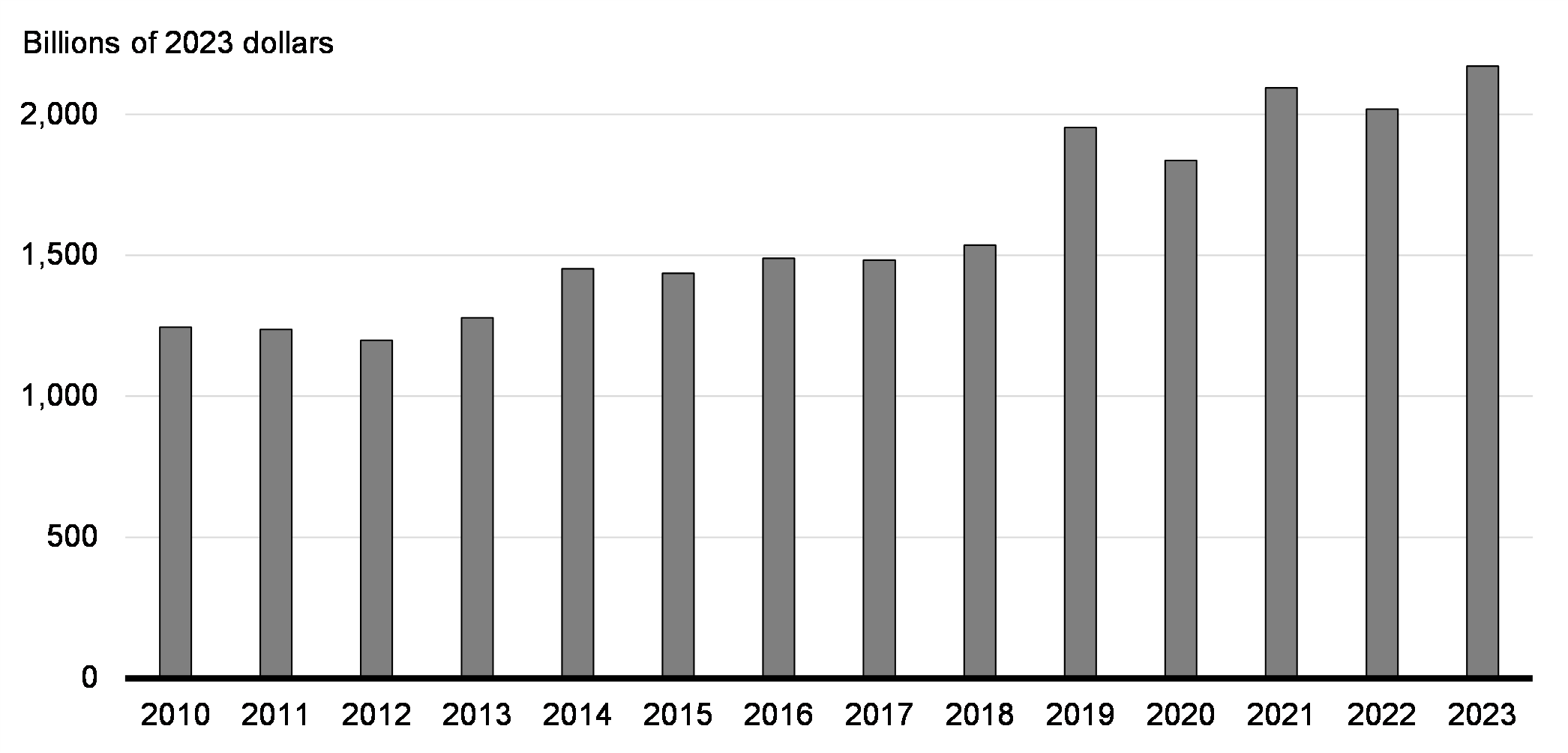
The Canadian economy is adding new, high-paying jobs, in high-growth sectors, like clean tech, clean electricity, and scientific research and development (Chart 4.4). Budget 2024 will continue this momentum by making strategic investments that create opportunities for workers today—driving productivity and economic growth for generations to come.
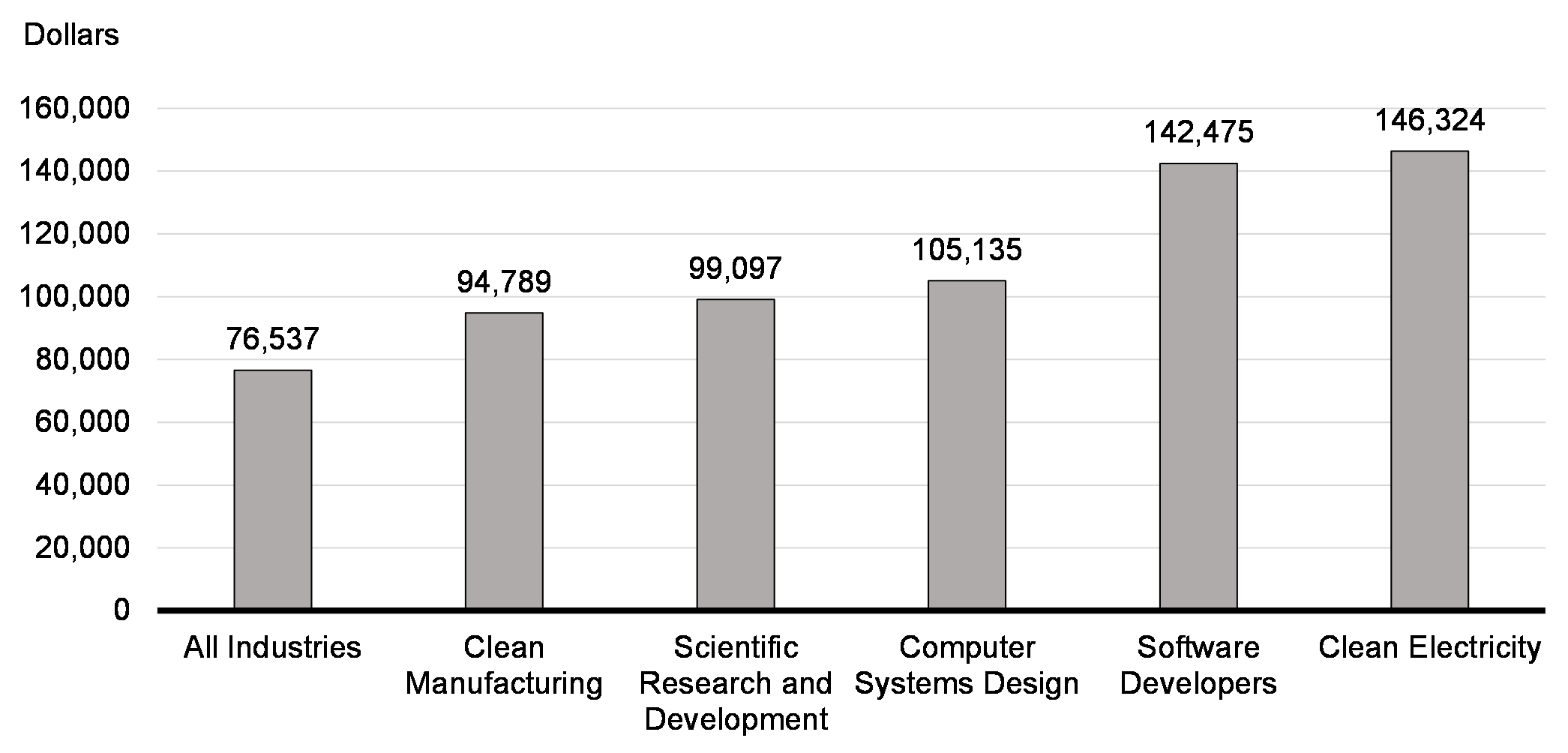
Canada's skilled hands and brilliant minds are our greatest resource. Capitalizing on their ideas, innovations, and hard work is an essential way to keep our place at the forefront of the world's advanced economies. Our world-class innovators, entrepreneurs, scientists, and researchers are solving the most pressing challenges of today, and their discoveries help launch the businesses of tomorrow.
Canadian researchers, entrepreneurs, and companies are the driving force of this progress—from scientific discovery to bringing new solutions to market. They also train and hire younger Canadians who will become the next generation of innovators. New investments to boost research and innovation, including enhancing support for graduate students and post-doctoral fellows, will ensure Canada remains a world leader in science and new technologies, like artificial intelligence.
By making strategic investments today in innovation and research, and supporting the recruitment and development of talent in Canada, we can ensure Canada is a world leader in new technologies for the next generation. In turn, this will drive innovation, growth, and productivity across the economy.
Key Ongoing Actions
- Supporting scientific discovery, developing Canadian research talent, and attracting top researchers from around the planet to make Canada their home base for their important work with more than $16 billion committed since 2016.
- Supporting critical emerging sectors, through initiatives like the Pan-Canadian Artificial Intelligence Strategy, the National Quantum Strategy, the Pan-Canadian Genomics Strategy, and the Biomanufacturing and Life Sciences Strategy.
- Nearly $2 billion to fuel Canada's Global Innovation Clusters to grow these innovation ecosystems, promote commercialization, support intellectual property creation and retention, and scale Canadian businesses.
- Investing $3.5 billion in the Sustainable Canadian Agricultural Partnership to strengthen the innovation, competitiveness, and resiliency of the agriculture and agri-food sector.
- Flowing up to $333 million over the next decade to support dairy sector investments in research, product and market development, and processing capacity for solids non-fat, thus increasing its competitiveness and productivity.
Strengthening Canada's AI Advantage
Canada's artificial intelligence (AI) ecosystem is among the best in the world. Since 2017, the government has invested over $2 billion towards AI in Canada. Fuelled by those investments, Canada is globally recognized for strong AI talent, research, and its AI sector.
Today, Canada's AI sector is ranked first in the world for growth of women in AI, and first in the G7 for year-over-year growth of AI talent. Every year since 2019, Canada has published the most AI-related papers, per capita, in the G7. Our AI firms are filing patents at three times the average rate in the G7, and they are attracting nearly a third of all venture capital in Canada. In 2022-23, there were over 140,000 actively engaged AI professionals in Canada, an increase of 29 per cent compared to the previous year. These are just a few of Canada's competitive advantages in AI and we are aiming even higher.
To secure Canada's AI advantage, the government has already:
- Established the first national AI strategy in the world through the Pan-Canadian Artificial Intelligence Strategy;
- Supported access to advanced computing capacity, including through the recent signing of a letter of intent with NVIDIA and a Memorandum of Understanding with the U.K. government; and,
- Scaled-up Canadian AI firms through the Strategic Innovation Fund and Global Innovation Clusters program.

AI is a transformative economic opportunity for Canada and the government is committed to doing more to support our world-class research community, launch Canadian AI businesses, and help them scale-up to meet the demands of the global economy. The processing capacity required by AI is accelerating a global push for the latest technology, for the latest computing infrastructure.
Currently, most compute capacity is located in other countries. Challenges accessing compute power slows down AI research and innovation, and also exposes Canadian firms to a reliance on privately-owned computing, outside of Canada. This comes with dependencies and security risks. And, it is a barrier holding back our AI firms and researchers.
We need to break those barriers to stay competitive in the global AI race and ensure workers benefit from the higher wages of AI transformations; we must secure Canada's AI advantage. We also need to ensure workers who fear their jobs may be negatively impacted by AI have the tools and skills training needed in a changing economy.
To secure Canada's AI advantage Budget 2024 announces a monumental increase in targeted AI support of $2.4 billion, including:
- $2 billion over five years, starting in 2024-25, to launch a new AI Compute Access Fund and Canadian AI Sovereign Compute Strategy, to help Canadian researchers, start-ups, and scale-up businesses access the computational power they need to compete and help catalyze the development of Canadian-owned and located AI infrastructure.
- $200 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, to boost AI start-ups to bring new technologies to market, and accelerate AI adoption in critical sectors, such as agriculture, clean technology, health care, and manufacturing. This support will be delivered through Canada's Regional Development Agencies.
- $100 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, for the National Research Council's AI Assist Program to help Canadian small- and medium-sized businesses and innovators build and deploy new AI solutions, potentially in coordination with major firms, to increase productivity across the country.
- $50 million over four years, starting in 2025-26, to support workers who may be impacted by AI, such as creative industries. This support will be delivered through the Sectoral Workforce Solutions Program, which will provide new skills training for workers in potentially disrupted sectors and communities.
The government will engage with industry partners and research institutes to swiftly implement AI investment initiatives, fostering collaboration and innovation across sectors for accelerated technological advancement.
Safe and Responsible Use of AI
AI has tremendous economic potential, but as with all technology, it presents important considerations to ensure its safe development and implementation. Canada is a global leader in responsible AI and is supporting an AI ecosystem that promotes responsible use of technology. From development through to implementation and beyond, the government is taking action to protect Canadians from the potentially harmful impacts of AI.
The government is committed to guiding AI innovation in a positive direction, and to encouraging the responsible adoption of AI technologies by Canadians and Canadian businesses. To bolster efforts to ensure the responsible use of AI:
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $50 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, to create an AI Safety Institute of Canada to ensure the safe development and deployment of AI. The AI Safety Institute will help Canada better understand and protect against the risks of advanced and generative AI systems. The government will engage with stakeholders and international partners with competitive AI policies to inform the final design and stand-up of the AI Safety Institute.
- Budget 2024 also proposes to provide $5.1 million in 2025-26 to equip the AI and Data Commissioner Office with the necessary resources to begin enforcing the proposed Artificial Intelligence and Data Act .
- Budget 2024 proposes $3.5 million over two years, starting in 2024-25, to advance Canada's leadership role with the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence, securing Canada's leadership on the global stage when it comes to advancing the responsible development, governance, and use of AI technologies internationally.
Using AI to Keep Canadians Safe
AI has shown incredible potential to toughen up security systems, including screening protocols for air cargo. Since 2012, Transport Canada has been testing innovative approaches to ensure that air cargo coming into Canada is safe, protecting against terrorist attacks. This included launching a pilot project to screen 10 to 15 per cent of air cargo bound for Canada and developing an artificial intelligence system for air cargo screening.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $6.7 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, to Transport Canada to establish the Pre-Load Air Cargo Targeting Program to screen 100 per cent of air cargo bound for Canada. This program, powered by cutting-edge artificial intelligence, will increase security and efficiency, and align Canada's air security regime with those of its international partners.
Incentivizing More Innovation and Productivity
Businesses that invest in cutting-edge technologies are a key driver of Canada's economic growth. When businesses make investments in technology—from developing new patents to implementing new IT systems—it helps ensure Canadian workers put their skills and knowledge to use, improves workplaces, and maximizes our workers' potential and Canada's economic growth.
The government wants to encourage Canadian businesses to invest in the capital—both tangible and intangible—that will help them boost productivity and compete productively in the economy of tomorrow.
- To incentivize investment in innovation-enabling and productivity-enhancing assets, Budget 2024 proposes to allow businesses to immediately write off the full cost of investments in patents, data network infrastructure equipment, computers, and other data processing equipment. Eligible investments, as specified in the relevant capital cost allowance classes, must be acquired and put in use on or after Budget Day and before January 1, 2027. The cost of this measure is estimated at $725 million over five years, starting in 2024-25.
Boosting R&D and Intellectual Property Retention
Research and development (R&D) is a key driver of productivity and growth. Made-in-Canada innovations meaningfully increase our gross domestic product (GDP) per capita, create good-paying jobs, and secure Canada's position as a world-leading advanced economy.
To modernize and improve the Scientific Research and Experimental Development (SR&ED) tax incentives, the federal government launched consultations on January 31, 2024, to explore cost-neutral ways to enhance the program to better support innovative businesses and drive economic growth. In these consultations, which closed on April 15, 2024, the government asked Canadian researchers and innovators for ways to better deliver SR&ED support to small- and medium-sized Canadian businesses and enable the next generation of innovators to scale-up, create jobs, and grow the economy.
- Budget 2024 announces the government is launching a second phase of consultations on more specific policy parameters, to hear further views from businesses and industry on specific and technical reforms. This includes exploring how Canadian public companies could be made eligible for the enhanced credit. Further details on the consultation process will be released shortly on the Department of Finance Canada website.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $600 million over four years, starting in 2025-26, with $150 million per year ongoing for future enhancements to the SR&ED program. The second phase of consultations will inform how this funding could be targeted to boost research and innovation.
On January 31, 2024, the government also launched consultations on creating a patent box regime to encourage the development and retention of intellectual property in Canada. The patent box consultation closed on April 15, 2024. Submissions received through this process, which are still under review, will help inform future government decisions with respect to a patent box regime.
Enhancing Research Support
Since 2016, the federal government has committed more than $16 billion in research, including funding for the federal granting councils—the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC), the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC).
This research support enables groundbreaking discoveries in areas such as climate change, health emergencies, artificial intelligence, and psychological health. This plays a critical role in solving the world's greatest challenges, those that will have impacts for generations.
Canada's granting councils already do excellent work within their areas of expertise, but more needs to be done to maximize their effect. The improvements we are making today, following extensive consultations including with the Advisory Panel on the Federal Research Support System, will strengthen and modernize Canada's federal research support.
- To increase core research grant funding and support Canadian researchers, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $1.8 billion over five years, starting in 2024-25, with $748.3 million per year ongoing to SSHRC, NSERC, and CIHR.
- To provide better coordination across the federally funded research ecosystem, Budget 2024 announces the government will create a new capstone research funding organization. The granting councils will continue to exist within this new organization, and continue supporting excellence in investigator-driven research, including linkages with the Health portfolio. This new organization and structure will also help to advance internationally collaborative, multi-disciplinary, and mission-driven research. The government is delivering on the Advisory Panel's observation that more coordination is needed to maximize the impact of federal research support across Canada's research ecosystem.
- To help guide research priorities moving forward, Budget 2024 also announces the government will create an advisory Council on Science and Innovation. This Council will be made up of leaders from the academic, industry, and not-for-profit sectors, and be responsible for a national science and innovation strategy to guide priority setting and increase the impact of these significant federal investments.
- Budget 2024 also proposes to provide a further $26.9 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, with $26.6 million in remaining amortization and $6.6 million ongoing, to the granting councils to establish an improved and harmonized grant management system.
The government will also work with other key players in the research funding system—the provinces, territories, and Canadian industry—to ensure stronger alignment, and greater co-funding to address important challenges, notably Canada's relatively low level of business R&D investment.
More details on these important modernization efforts will be announced in the 2024 Fall Economic Statement.
World-Leading Research Infrastructure
Modern, high-quality research facilities and infrastructure are essential for breakthroughs in Canadian research and science. These laboratories and research centres are where medical and other scientific breakthroughs are born, helping to solve real-world problems and create the economic opportunities of the future. World-leading research facilities will attract and train the next generation of scientific talent. That's why, since 2015, the federal government has made unprecedented investments in science and technology, at an average of $13.6 billion per year, compared to the average from 2009-10 to 2015-16 of just $10.8 billion per year. But we can't stop here.
To advance the next generation of cutting-edge research, Budget 2024 proposes major research and science infrastructure investments, including:
- $399.8 million over five years, starting in 2025-26, to support TRIUMF, Canada's sub-atomic physics research laboratory, located on the University of British Columbia's Vancouver campus. This investment will upgrade infrastructure at the world's largest cyclotron particle accelerator, positioning TRIUMF, and the partnering Canadian research universities, at the forefront of physics research and enabling new medical breakthroughs and treatments, from drug development to cancer therapy.
- $176 million over five years, starting in 2025‑26, to CANARIE, a national not-for-profit organization that manages Canada's ultra high-speed network to connect researchers, educators, and innovators, including through eduroam. With network speeds hundreds of times faster, and more secure, than conventional home and office networks, this investment will ensure this critical infrastructure can connect researchers across Canada's world-leading post-secondary institutions.
- $83.5 million over three years, starting in 2026-27 to extend support to Canadian Light Source in Saskatoon. Funding will continue the important work at the only facility of its kind in Canada. A synchrotron light source allows scientists and researchers to examine the microscopic nature of matter. This specialized infrastructure contributes to breakthroughs in areas ranging from climate-resistant crop development to green mining processes.
- $45.5 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, to support the Arthur B. McDonald Canadian Astroparticle Physics Research Institute, a network of universities and institutes that coordinate astroparticle physics expertise. Headquartered at Queen's University in Kingston, Ontario, the institute builds on the legacy of Dr. McDonald's 2015 Nobel Prize for his work on neutrino physics. These expert engineers, technicians, and scientists design, construct, and operate the experiments conducted in Canada's underground and underwater research infrastructure, where research into dark matter and other mysterious particles thrives. This supports innovation in areas like clean technology and medical imaging, and educates and inspires the next wave of Canadian talent.
- $30 million over three years, starting in 2024-25, to support the completion of the University of Saskatchewan's Centre for Pandemic Research at the Vaccine and Infectious Disease Organization in Saskatoon. This investment will enable the study of high-risk pathogens to support vaccine and therapeutic development, a key pillar in Canada's Biomanufacturing and Life Sciences Strategy. Of this amount, $3 million would be sourced from the existing resources of Prairies Economic Development Canada.
These new investments build on existing federal research support:
- The Strategic Science Fund, which announced the results of its first competition in December 2023, providing support to 24 third-party science and research organizations starting in 2024-25;
- Canada recently concluded negotiations to be an associate member of Horizon Europe, which would enable Canadians to access a broader range of research opportunities under the European program starting this year; and,
- The steady increase in federal funding for extramural and intramural science and technology by the government which was 44 per cent higher in 2023 relative to 2015.

Investing in Homegrown Research Talent
Canada's student and postgraduate researchers are tackling some of the world's biggest challenges. The solutions they come up with have the potential to make the world a better place and drive Canadian prosperity. They are the future Canadian academic and scientific excellence, who will create new innovative businesses, develop new ways to boost productivity, and create jobs as they scale-up companies—if they get the support they need.
To build a world-leading, innovative economy, and improve our productive capacity, the hard work of top talent must pay off; we must incentivize our top talent to stay here.
Federal support for master's, doctoral, and post-doctoral students and fellows has created new research opportunities for the next generation of scientific talent. Opportunities to conduct world-leading research are critical for growing our economy. In the knowledge economy, the global market for these ideas is highly competitive and we need to make sure talented people have the right incentives to do their groundbreaking research here in Canada.
- To foster the next generation of research talent, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $825 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, with $199.8 million per year ongoing, to increase the annual value of master's and doctoral student scholarships to $27,000 and $40,000, respectively, and post-doctoral fellowships to $70,000. This will also increase the number of research scholarships and fellowships provided, building to approximately 1,720 more graduate students or fellows benefiting each year. To make it easier for students and fellows to access support, the enhanced suite of scholarships and fellowship programs will be streamlined into one talent program.
- To support Indigenous researchers and their communities, Budget 2024 also proposes to provide $30 million over three years, starting in 2024-25, to support Indigenous participation in research, with $10 million each for First Nation, Métis, and Inuit partners.
Boosting Talent for Innovation
Advanced technology development is a highly competitive industry and there is a global race to attract talent and innovative businesses. Canada must compete to ensure our economy is at the forefront of global innovation.
To spur rapid growth in innovation across Canada's economy, the government is partnering with organizations whose mission it is to train the next generation of innovators. This will ensure innovative businesses have the talent they need to grow, create jobs at home, and drive Canada's economic growth.
- Budget 2024 announces the government's intention to work with Talent for Innovation Canada to develop a pilot initiative to build an exceptional research and development workforce in Canada. This industry-led pilot will focus on attracting, training, and deploying top talent across four key sectors: bio-manufacturing; clean technology; electric vehicle manufacturing; and microelectronics, including semiconductors.
Advancing Space Research and Exploration
Canada is a leader in cutting-edge innovation and technologies for space research and exploration. Our astronauts make great contributions to international space exploration missions. The government is investing in Canada's space research and exploration activities.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $8.6 million in 2024-25 to the Canadian Space Agency for the Lunar Exploration Accelerator Program to support Canada's world-class space industry and help accelerate the development of new technologies. This initiative empowers Canada to leverage space to solve everyday challenges, such as enhancing remote health care services and improving access to healthy food in remote communities, while also supporting Canada's human space flight program.
- Budget 2024 announces the establishment of a new whole-of-government approach to space exploration, technology development, and research. The new National Space Council will enable the level of collaboration required to secure Canada's future as a leader in the global space race, addressing cross-cutting issues that span commercial, civil, and defence domains. This will also enable the government to leverage Canada's space industrial base with its world-class capabilities, workforce, and track record of innovation and delivery.
Accelerating Clean Tech Intellectual Property Creation and Retention
Canadian clean technology companies are turning their ideas into the solutions that the world is looking for as it races towards net-zero. Encouraging these innovative companies to maintain operations in Canada and retain ownership of their intellectual property secures the future of their workforce in Canada, helping the clean economy to thrive in Canada.
As part of the government's National Intellectual Property Strategy, the not-for-profit organization Innovation Asset Collective launched the patent collective pilot program in 2020. This pilot program is helping innovative small- and medium-sized enterprises in the clean tech sector with the creation and retention of intellectual property.
- To ensure that small- and medium-sized clean tech businesses benefit from specialized intellectual property support to grow their businesses and leverage intellectual property, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $14.5 million over two years, starting in 2024-25, to Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada for the Innovation Asset Collective.
Find out more about the expected gender and diversity impacts for each measure in section 4.1 Boosting Research, Innovation, and Productivity
In the 21 st century, a competitive economy is a clean economy. There is no greater proof than the $2.4 trillion worth of investment made around the world, last year, in net-zero economies. Canada is at the forefront of the global race to attract investment and seize the opportunities of the clean economy, with the government announcing a net-zero economic plan that will invest over $160 billion. This includes an unprecedented suite of major economic investment tax credits, which will help attract investment through $93 billion in incentives by 2034-35.
All told, the government's investments will crowd in more private investment, securing Canadian leadership in clean electricity and innovation, creating economic growth and more good-paying jobs across the country.
Investors at home and around the world are taking notice of Canada's plan. In defiance of global economic headwinds, last year public markets and private equity capital flows into Canada's net-zero economy grew—reaching $14 billion in 2023, according to RBC. Proof that Canada's investments are working—driving new businesses to take shape, creating good jobs, and making sure that we have clean air and clean water for our kids, grandkids, and for generations to come.

Earlier this year, BloombergNEF ranked Canada's attractiveness to build electric vehicle (EV) battery supply chains first in the world, surpassing China which has held the top spot since the ranking began. From resource workers mining the critical minerals for car batteries, to union workers on auto assembly lines, to the truckers that get cars to dealerships, Canada's advantage in the supply chain is creating high-skilled, good-paying jobs across the country, for workers of all ages.

This first place ranking of Canada's EV supply chains is underpinned by our abundant clean energy, high labour standards, and rigorous standards for consultation and engagement with Indigenous communities. That's what Canada's major economic investment tax credits are doing—seizing Canada's full potential, and doing it right.
By 2050, clean energy GDP could grow fivefold—up to $500 billion, while keeping Canada on track to reach net-zero by 2050. Proof, once again, that good climate policy is good economic policy.

Helping innovative Canadian firms scale-up is essential to increasing the pace of economic growth in Canada. Already, the Cleantech Group's 2023 list of the 100 most innovative global clean technology companies featured 12 Canadian companies, the second highest number of any country, behind only the U.S. The government is investing in clean technology companies to ensure their full capabilities are unlocked.
Budget 2024 announces the next steps in the government's plan to attract even more investment to Canada to create good-paying jobs and accelerate the development and deployment of clean energy and clean technology.
- Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage investment tax credit;
- Clean Technology investment tax credit;
- Clean Hydrogen investment tax credit;
- Clean Technology Manufacturing investment tax credit; and
- Clean Electricity investment tax credit.
- Since the federal government launched the Canada Growth Fund last year, $1.34 billion of capital has been committed to a world-leading geothermal energy technology company, the world's first of its kind carbon contract for difference; and to clean tech entrepreneurs and innovators through a leading Canadian-based climate fund.
- Working with industry, provinces, and Indigenous partners to build an end-to-end electric vehicle battery supply chain, including by securing major investments in 2023.
- Building major clean electricity and clean growth infrastructure projects with investments of at least $20 billion from the Canada Infrastructure Bank.
- $3.8 billion for Canada's Critical Minerals Strategy, to secure our position as the world's supplier of choice for critical minerals and the clean technologies they enable.
- $3 billion to recapitalize the Smart Renewables and Electrification Pathways Program, which builds more clean, affordable, and reliable power, and to support innovation in electricity grids and spur more investments in Canadian offshore wind.
A New EV Supply Chain Investment Tax Credit
The automotive industry is undergoing a major transformation. As more and more electric vehicles are being produced worldwide, it is essential that Canada's automotive industry has the support it needs to retool its assembly lines and build new factories to seize the opportunities of the global switch to electric vehicles. With our world-class natural resource base, talented workforce, and attractive investment climate, Canada will be an electric vehicle supply chain hub for all steps along the manufacturing process. This is an opportunity for Canada to secure its position today at the forefront of this growing global supply chain and secure high-quality jobs for Canadian workers for a generation to come.
Businesses that manufacture electric vehicles and their precursors would already be able to claim the 30 per cent Clean Technology Manufacturing investment tax credit on the cost of their investments in new machinery and equipment, as announced in Budget 2023. Providing additional support to these businesses so they choose Canada for more than one stage in the manufacturing process would secure more jobs for Canadians and help cement Canada's position as a leader in this sector.
- electric vehicle assembly;
- electric vehicle battery production; and,
- cathode active material production.
For a taxpayer's building costs in any of the specified segments to qualify for the tax credit, the taxpayer (or a member of a group of related taxpayers) must claim the Clean Technology Manufacturing investment tax credit in all three of the specified segments, or two of the three specified segments and hold at least a qualifying minority interest in an unrelated corporation that claims the Clean Technology Manufacturing tax credit in the third segment. The building costs of the unrelated corporation would also qualify for the new investment tax credit.
The EV Supply Chain investment tax credit would apply to property that is acquired and becomes available for use on or after January 1, 2024. The credit would be reduced to 5 per cent for 2033 and 2034, and would no longer be in effect after 2034.
The EV Supply Chain investment tax credit is expected to cost $80 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, and an additional $1.02 billion from 2029-30 to 2034-35.
The design and implementation details of the EV Supply Chain investment tax credit will be provided in the 2024 Fall Economic Statement . Its design would incorporate elements of the Clean Technology Manufacturing investment tax credit, where applicable.
Delivering Major Economic Investment Tax Credits
To seize the investment opportunities of the global clean economy, we are delivering our six major economic investment tax credits. These will provide businesses and other investors with the certainty they need to invest and build in Canada. And they are already attracting major, job-creating projects, ensuring we remain globally competitive.
From new clean electricity projects that will provide clean and affordable energy to Canadian homes and businesses, to carbon capture projects that will decarbonize heavy industry, our major economic investment tax credits are moving Canada forward on its track to achieve a net-zero economy by 2050.
In November 2023, the government introduced Bill C-59 to deliver the first two investment tax credits and provide businesses with the certainty they need to make investment decisions in Canada today. Bill C-59 also includes labour requirements to ensure workers are paid prevailing union wages and apprentices have opportunities to gain experience and succeed in the workforce. With the support and collaboration of Parliamentarians, the government anticipates Bill C-59 receiving Royal Assent before June 1, 2024.
- Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage investment tax credit: would be available as of January 1, 2022;
- Clean Technology investment tax credit: would be available as of March 28, 2023; and,
- Clean Hydrogen investment tax credit; and,
The government will soon introduce legislation to deliver the next two investment tax credits:
- Clean Hydrogen investment tax credit: available as of March 28, 2023; and,
- Clean Technology Manufacturing investment tax credit: available as of January 1, 2024.
As a priority, the government will work on introducing legislation for the remaining investment tax credits, including the new EV Supply Chain investment tax credit, as well as proposed expansions and enhancements:
- Clean Electricity investment tax credit: would be available as of the day of Budget 2024, for projects that did not begin construction before March 28, 2023;
- The expansion of the Clean Technology investment tax credit would be available as of November 21, 2023; and,
- The expansion of the Clean Electricity investment tax credit would be available from the day of Budget 2024, for projects that did not begin construction before March 28, 2023.
- Clean Technology Manufacturing investment tax credit enhancements to provide new clarity and improve access for critical minerals projects. Draft legislation will be released for consultation in summer 2024 and the government targets introducing legislation in fall 2024.
- The EV Supply Chain investment tax credit : would be available as of January 1, 2024.
Given that the major economic investment tax credits will be available, including retroactively, from their respective coming into force dates, businesses are already taking action to break ground on projects that will reduce emissions, create jobs, and grow the economy. Passing the major economic investment tax credits into law will secure a cleaner, more prosperous future for Canadians today, and tomorrow.

Implementing the Clean Electricity Investment Tax Credit
As the economy grows, Canada's electricity demand is expected to double by 2050 (Chart 4.7). To meet this increased demand with a clean, reliable, and affordable grid, our electricity capacity must increase by 1.7 to 2.2 times compared to current levels (Chart 4.8). Investing in clean electricity today will reduce Canadians' monthly energy costs by 12 per cent (Chart 4.9) and create approximately 250,000 good jobs by 2050 (Chart 4.10).

Canada already has one of the cleanest electricity grids in the world, with 84 per cent of electricity produced by non-emitting sources of generation. Quebec, British Columbia, Manitoba, Newfoundland and Labrador, and Yukon are already clean electricity leaders and generate nearly all of their electricity from non-emitting hydropower—and have more untapped clean electricity potential. Other regions of Canada will require major investments to ensure clean, reliable electricity grids, and the federal government is stepping up to support provinces and territories with these investments.
In Budget 2023, the government announced the new Clean Electricity investment tax credit to deliver broad-based support to implement clean electricity technologies and accelerate progress towards a Canada-wide net-zero electricity grid.
- Low-emitting electricity generation systems using energy from wind, solar, water, geothermal, waste biomass, nuclear, or natural gas with carbon capture and storage.
- Stationary electricity storage systems that do not use fossil fuels in operation, such as batteries and pumped hydroelectric storage.
- Transmission of electricity between provinces and territories.
- The Clean Electricity investment tax credit would be available to certain taxable and non-taxable corporations, including corporations owned by municipalities or Indigenous communities, and pension investment corporations.
- Provided that a provincial and territorial government satisfies additional conditions, outlined below, the tax credit would also be available to provincial and territorial Crown corporations investing in that province or territory.
- Robust labour requirements to pay prevailing union wages and create apprenticeship opportunities will need to be met to receive the full 15 per cent tax credit.
The Clean Electricity investment tax credit is expected to cost $7.2 billion over five years starting in 2024-25, and an additional $25 billion from 2029-30 to 2034-35.
The Clean Electricity investment tax credit would apply to property that is acquired and becomes available for use on or after the day of Budget 2024 for projects that did not begin construction before March 28, 2023. The credit would no longer be in effect after 2034. Similar rules would apply for provincial and territorial Crown corporations, with modifications outlined below.
Provincial and Territorial Crown Corporations
The federal government is proposing that, for provincial and territorial Crown corporations to access to the Clean Electricity investment tax credit within a jurisdiction, the government of that province or territory would need to:
- Work towards a net-zero electricity grid by 2035; and,
- Provincial and territorial Crown corporations passing through the value of the Clean Electricity investment tax credit to electricity ratepayers in their province or territory to reduce ratepayers' bills.
- Direct provincial and territorial Crown corporations claiming the credit to publicly report, on an annual basis, on how the tax credit has improved ratepayers' bills.
If a provincial or territorial government satisfies all the conditions by March 31, 2025, then provincial or territorial Crown corporations investing in that jurisdiction would be able to access the Clean Electricity investment tax credit for property that is acquired and becomes available for use on or after the day of Budget 2024 for projects that did not begin construction before March 28, 2023.
If a provincial or territorial government does not satisfy all the conditions by March 31, 2025, then provincial or territorial Crown corporations investing in that jurisdiction would not be able to access the Clean Electricity investment tax credit until all the conditions have been satisfied. In this case, the Clean Electricity investment tax credit would apply to property that is acquired and becomes available for use from the date when the conditions are deemed to have been satisfied for projects that did not begin construction before March 28, 2023.
The Department of Finance Canada will consult with provinces and territories on the details of these conditions before legislation is introduced this fall.
Additional design and implementation details for the tax credit can be found in the Budget Tax Measures Supplementary Information, under "Clean Electricity investment tax credit."
Delivering Clean Electricity with Indigenous, Northern, and Remote Communities
The government has announced significant measures to advance clean electricity projects nationwide. These initiatives include the Clean Electricity investment tax credit, the Smart Renewables and Electrification Pathways Program, and strategic financing through the Canada Infrastructure Bank. Understanding the energy goals and challenges in Indigenous, Northern, and remote communities—such as moving away from diesel—the government has offered unique assistance for projects in these areas, including for planning and feasibility stages. Recent federal investments to support projects with these communities include:
- Up to $535 million in Canada Infrastructure Bank financing and $50 million in funding from the Smart Renewables and Electrification Pathways Program for the 250-MW Oneida Energy storage project in Ontario, which is the largest battery storage project in the country.
- $173 million in Canada Infrastructure Bank financing and $50 million in funding from the Smart Renewables and Electrification Pathways Program for the Bekevar Wind Power project, an Indigenous-led wind power project in Saskatchewan.
- $14.4 million in funding to explore the feasibility of the Kivalliq Hydro Fibre Link, an innovative project that would connect northern Manitoba to southeastern Nunavut to provide electricity and internet access to five communities and one existing mine, helping to transition Northern communities off of diesel and connect them to the rest of Canada.
- $9 million in funding from the Smart Renewables and Electrification Pathways Program for the Salay Prayzaan Solar project, which is 100 per cent owned by the Métis Nation of Alberta.
Implementing the Major Economic Investment Tax Credits
The government's suite of major economic investment incentives is unprecedented in Canadian history, and the government is delivering these supports on a priority basis to attract investment, create good-paying jobs, and grow the economy, while continuing to make progress in the fight against climate change.
To deliver the major economic investment tax credits, without delay, the government is boosting resources to the Canada Revenue Agency, Natural Resources Canada, and the Department of Finance Canada, which each have a role to play in delivering these support measures. To this end:
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide the Canada Revenue Agency up to $90.9 million over 11 years, starting in 2024-25, to administer the new major economic investment tax credits.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide Natural Resources Canada $7.4 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, to provide expert technical advice on engineering and scientific matters related to the major economic investment tax credits and to support the administration of certain investment tax credits with the Canada Revenue Agency.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide the Department of Finance Canada $21.4 million over 11 years, starting in 2024-25, to complete the implementation, including legislation, of the major economic investment tax credits, ensure ongoing evaluation and response to emerging issues, and propose appropriate legislative amendments to the Income Tax Act and Income Tax Regulations .
The Canada Growth Fund
The Canada Growth Fund is a $15 billion arm's length public investment vehicle launched by the federal government to attract private capital and invest in Canadian projects and businesses, which is led by Canada's world-leading public sector pension professionals. The Canada Growth Fund investments in clean energy and clean technology are already building Canada's strong, clean economy and creating good-paying jobs across the country:
- On October 25, 2023, the Canada Growth Fund made its first investment—a $90 million investment in a groundbreaking geothermal energy company, Calgary's Eavor Technologies Inc., that is creating meaningful employment opportunities for Albertans and securing the Canadian future of a company at the leading-edge of the global economy.
- The Canada Growth Fund's second investment was announced on December 20, 2023—a $200 million direct investment, plus complementary carbon contract offtake agreement, in a world-leading carbon capture and sequestration company, Calgary's Entropy Inc. to support the reduction of up to one million tonnes of carbon per year. This major investment will support 1,200 good jobs for Albertans and grow the company's Canadian-based activities.
- The Canada Growth Fund's third investment was announced on March 25, 2024—a $50 million commitment into the Idealist Climate Impact Fund, a clean tech investment fund led by the Montréal-based Idealist Capital. The clean tech fund will manage equity investments into innovative entrepreneurs and businesses that are creating good-paying jobs and accelerating the energy transition.
Carbon Contracts for Difference
A price on pollution is the foundation of Canada's plan to build a prosperous net-zero economy. It is a system that is fair and that promotes market-driven solutions. The government recognizes the substantial demand from industry and other stakeholders for carbon contracts for difference (CCFDs) as a tool to accelerate investment in decarbonization and clean growth technologies by providing certainty around carbon pricing.
The 2023 Fall Economic Statement announced that the Canada Growth Fund will be the principal federal entity to issue CCFDs, including allocating, on a priority basis, up to $7 billion to issue all forms of contracts for difference and offtake agreements. The Canada Growth Fund is fulfilling this important role as a federal issuer of CCFDs. Building on its initial success, the Canada Growth Fund is assessing the opportunity to expand its carbon contract offerings and is developing approaches that can best serve the different carbon credit markets across Canada:
- Budget 2024 announces that the Canada Growth Fund is developing an expanded range of CCFD offerings tailored to different markets and their unique risks and opportunities. The Canada Growth Fund will continue offering bespoke CCFDs and carbon offtake agreements, with a focus on provinces contributing significantly to greenhouse gas emissions reductions.
- Building on the insights gained from these transactions, Budget 2024 announces the Canada Growth Fund will explore ways to broaden its approach, for example, by developing off-the-shelf contracts for certain jurisdictions and ways to offer these contracts on a competitive basis for a set amount of emissions reductions.
- The Canada Growth Fund has around $6 billion remaining to continue issuing, on a priority basis, all forms of CCFDs and carbon offtake agreements. Budget 2024 announces the government will ensure that the Canada Growth Fund continues to have the resources it needs to fulfill its role as federal issuer of CCFDs. The government is also evaluating options to enhance the Canada Growth Fund's capacity to offer CCFDs, including by exploring the possibility of a government backstop of certain CCFD liabilities of the Canada Growth Fund.
CCFDs can help develop robust carbon credit markets, and the federal government has taken action to ensure their success. For example, in 2022, Environment and Climate Change Canada worked with Alberta to ensure that their TIER market was sufficiently stringent so that the projected demand for carbon credits exceeded projected supply, ensuring robust credit demand even as more major decarbonization projects get built and more credits are generated.
Credit markets are largely the responsibility of provinces, and there are opportunities to improve how these markets function. For example, commitments to maintain their industrial carbon pricing systems over the long-term, tighten the stringency of systems as necessary to avoid an oversupply of credits, publishing the price of carbon credits, and recommitting to maintain a price signal of $170 per tonne by 2030 could help improve carbon price expectations for investors. Increased credit price transparency would greatly improve market functioning and provide greater investment certainty, unlocking more decarbonization projects. It would also facilitate the Canada Growth Fund's efforts to develop off-the-shelf CCFDs and deliver more deals, much quicker across provincial carbon markets.
- Budget 2024 announces that Environment and Climate Change Canada will work with provinces and territories to improve the functioning of carbon credit markets, in order to help unlock additional decarbonization projects throughout Canada.
Getting Major Projects Done
Putting Canada on a path to net-zero requires significant and sustained private sector investment in clean electricity, critical minerals, and other major projects. For these investments to be made, Canada's regulatory system must be efficient and quicker—it shouldn't take over a decade to open a new mine and secure our critical minerals supply chains.
To that end, Budget 2023 announced an intention to develop a plan to improve the efficiency of the impact assessment and permitting processes for major projects. The Ministerial Working Group on Regulatory Efficiency for Clean Growth Projects was launched to coordinate this work, and drive positive, pro-growth culture change throughout government, to ensure major project approvals come quicker. New major projects create thousands of new, good-paying jobs for Canadians, and the government is focused on getting more done.
- Provide $9 million over three years, starting in 2024-25, to the Privy Council Office's Clean Growth Office to implement the recommendations of the Ministerial Working Group and reduce interdepartmental inefficiencies, including preventing fixation on well-studied and low-risk impacts, ensuring new permitting timelines are upheld throughout departments, and improving data sharing between departments to reduce redundant studies.
- Launch work to establish a new Federal Permitting Coordinator within the Privy Council Office's Clean Growth Office.
- Set a target of five years or less to complete federal impact assessment and permitting processes for federally designated projects, and a target of two years or less for permitting of non-federally designated projects;
- Issue a Cabinet Directive to drive culture change , achieve new targets, and set out clear federal roles and responsibilities within and across departments with the objective of getting clean growth projects built in a timely and predictable manner;
- Build a Federal Permitting Dashboard that reports on the status of large projects which require permits, to improve predictability for project proponents, and increase the federal government's transparency and accountability to Canadians; and,
- Set a three-year target for nuclear project reviews , by working with the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission and Impact Assessment Agency of Canada, and consider how the process can be better streamlined and duplications reduced between the two agencies.
- Amend the Impact Assessment Act to respond to the October 2023 Supreme Court of Canada decision that ruled that elements of the Act are unconstitutional. The proposed amendments will ensure the Act is constitutionally sound, facilitating efficient project reviews while advancing Canada's clean growth and protecting the environment. An amended Act will provide certainty for businesses and investors through measures that include increasing flexibility in substitution of assessments to allow for collaboration and avoid interjurisdictional duplication, clarifying when joint federal-provincial review panels are possible, and allowing for earlier Agency screening decisions as to whether a full impact assessment is required after the Planning phase. The amended Act will remain consistent with the United Nations Declaration on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples Act ;
- Enhance coordination across orders of government using the tools available under the Impact Assessment Act and permitting coordination mechanisms, to reduce duplication and minimize the burden of regulatory processes on project proponents and Indigenous groups; and,
- Engage Northern Premiers, Indigenous communities, industry, and other partners to discuss transformative changes to their unique project review frameworks, to ensure the North is also prepared to assess and build clean growth projects.
- Advance Indigenous participation in major projects, through the Indigenous Loan Guarantee Program detailed in Chapter 6, which will provide more opportunities for Indigenous communities to benefit from the significant number of natural resource and energy projects proposed to take place in their territories;
- Work to establish a Crown Consultation Coordinator to ensure efficient and meaningful Crown consultation with Indigenous peoples on the issuance of federal regulatory permits to projects that do not undergo federal impact assessments. The government will consult First Nations, Inuit, Métis, and Modern Treaty and Self-Governing Indigenous partners on the design of the Crown Consultation Coordinator. The Impact Assessment Agency of Canada will continue to be the Crown consultation body for all federal decisions related to projects that undergo federal impact assessments; and,
- Improve Indigenous capacity for consultation by advancing the co-development and implementation of consultation protocol agreements and resource centres, led by Crown-Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada.
More details on the Ministerial Working Group's recommendations will be published in an Action Plan in spring 2024. Additionally, further analysis of opportunities for improving the efficiency of the impact assessment process will be undertaken as part of the five-year review of the Impact Assessment Act's designated project list, which will occur later this year, following coming into force of the amended Act. This review will be undertaken in consultation with the public, including with Indigenous partners.
Getting major projects built means more jobs, in more regions across Canada, and more opportunities for the next generation of workers.
Securing the Canadian Biofuels Industry
Biofuels and biogas are renewable energy sources sustainably made from plants or biowaste, such as canola crops and landfill emissions. Not only do they generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, they also represent a unique opportunity for the Canadian economy. The industry supports agriculture and forestry jobs and can help decarbonize key sectors like marine, aviation, rail, and heavy industry. Canada's Clean Fuel Regulations , in place since 2022, are helping drive the production and adoption of specific biofuels in Canada.
The government is proposing new measures to support biofuels production in Canada, with a focus on renewable diesel, sustainable aviation fuel, and renewable natural gas, aiming to capitalize on the increasing demand for these fuels and strengthen Canada's position in the market. Budget 2024 announces:
- The government's intention to disburse up to $500 million per year from Clean Fuel Regulations compliance payment revenues to support biofuels production in Canada, subject to sufficient compliance payments being made to the federal government. More details will be announced in the 2024 Fall Economic Statement .
- The government will also retool the Clean Fuels Fund to deliver funding faster, and extend the Fund for an additional four years, until 2029-30. With reprofiled funding proposed through this extension, a total of $776.3 million will be available to be deployed from 2024-25 to 2029-30 to support clean fuel projects. The program will shift to a continuous intake process, and streamlined negotiations and decision-making processes will expedite delivery. By the end of this year, Natural Resources Canada will launch another call for proposals under the extended Clean Fuels Fund.
- The Canada Infrastructure Bank will invest at least $500 million in biofuels production under its green infrastructure investment stream.
Advancing Nuclear Energy, Nuclear Research, and Environmental Remediation
Non-emitting, nuclear energy is one of the key tools in helping the world reach net-zero emissions by 2050. Canada stands out as one of the few countries to have developed and deployed its own nuclear technology, the CANDU. And the robust Canadian supply chains built around CANDU not only generate high-skilled jobs and foster research and development but also play a role in creating affordable and clean electricity. Canada's nuclear sector also produces medical isotopes essential for radiation therapy and diagnosing heart disease.
Canada is a Global Nuclear Energy Leader
Over the last few years, the government has announced significant investments and action to advance nuclear energy:
Large Reactors:
- Canada has committed up to $3 billion in export financing to Romania to support the construction of two new CANDU reactors, reducing Romania's reliance on Russian energy while boosting their own energy security and their neighbours', all while supporting Canadian jobs. Canadian supply chains will participate in the construction and maintenance of these reactors over their multi-decade operating life.
- The government announced $50 million in funding to support Bruce Power's large nuclear expansion.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs):
- The Canada Infrastructure Bank announced a $970 million investment to support Ontario Power Generation in building the first grid-scale SMR among G7 nations at Darlington.
- The Strategic Innovation Fund has committed $94.7 million to accelerate the development of three different next generation SMR designs.
- The government announced $74 million in funding to support SaskPower's SMR development.
- The government announced $120.6 million to enable the deployment of SMRs through various activities such as building regulatory capacity.
Major Economic Investment Tax Credits:
- The Clean Electricity and Clean Technology Manufacturing investment tax credits announced in Budget 2023 would support investments in nuclear electricity generation, nuclear power supply chains, and nuclear fuel production, which are part of the solution for a clean economy transition.
Sustainable Finance:
- The government updated its Green Bond Framework to make certain nuclear energy expenditures eligible.
Budget 2024 is announcing new measures to help get nuclear projects built in a timely, predictable, and responsible fashion.
Canadian Nuclear Laboratories conducts nuclear science research that helps advance clean energy and medical technologies, as well as environmental remediation and waste management of historic nuclear sites. This work is overseen by Atomic Energy of Canada Limited, a Crown corporation responsible for enabling nuclear science and technology and ensuring environmental protection at nuclear sites.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $3.1 billion over 11 years, starting in 2025-26, with $1.5 billion in remaining amortization, to Atomic Energy of Canada Limited to support Canadian Nuclear Laboratories' ongoing nuclear science research, environmental protection, and site remediation work.
Canada-U.S. Energy Transformation Task Force
On March 24, 2023, the Canada-U.S. Energy Transformation Task Force was launched by Prime Minister Trudeau and President Biden, as a one-year joint initiative to support our collective energy security and economic growth as we transition to a clean energy future. Canada is pleased to announce the renewal of the Energy Transformation Task Force for an additional year.
Since its creation, the Energy Transformation Task Force has driven significant progress towards more secure and resilient Canada-U.S. supply chains for critical minerals, nuclear fuels, and green steel and aluminum.
Canada is a global leader in the supply of responsibly sourced critical minerals. The government is investing $3.8 billion through the Canadian Critical Minerals Strategy to further develop Canadian value chains for critical minerals needed for our green and digital economy, including the new Critical Mineral Exploration Tax Credit. The Strategy will be further enabled by enhancements to the Clean Technology Manufacturing investment tax credit, and Canada's new Electric Vehicle Supply Chain investment tax credit.
Canada is building on our strong partnership with the U.S. on critical minerals, underpinned by the Canada-U.S. Joint Action Plan on Critical Minerals Collaboration. Under the Energy Transformation Task Force, we have redoubled efforts to address issues of mutual concern such as bolstering supply security for critical minerals. Our government will continue to work in close collaboration with industry partners and our allies to support cross-border priority critical mineral projects that advance our shared interests.
Nuclear energy will play a key role in achieving net-zero greenhouse gas emissions. Canada is a Tier-1 nuclear nation with over 70 years of technological leadership, including our own national reactor technology, and a strong domestic supply chain that includes the world's largest deposit of high-grade natural uranium. Our government is taking action to support the growth of nuclear energy, including through the Clean Electricity investment tax credit, the Clean Technology Manufacturing investment tax credit, the Strategic Innovation Fund, the Canada Infrastructure Bank, and an updated Green Bond Framework that includes certain nuclear expenditures.
At COP28, the government and likeminded partners reaffirmed their commitment to triple nuclear energy capacity and promote public-private investment to strengthen supply chains and reduce reliance on non-allied countries for nuclear fuel needed for advanced and conventional nuclear energy. Through the Energy Transformation Task Force, Canada will continue to engage industry and international partners with a view to announcing concrete measures later this spring to bolster North American nuclear fuel supply chains.
Canadian steel and aluminum—among the greenest in the world—are important pillars of integrated North American manufacturing supply chains and key products to support the net-zero transition. We have invested significantly to further decarbonize our steel and aluminum sectors and to maintain their competitiveness in the green economy. As well, earlier this year, our government announced actions to increase the transparency of steel import data that will help provide more details on the origins of imported steel and align our practice with the U.S. We will continue to collaborate with the U.S. to promote common approaches for trade in low emissions green steel and aluminum goods.
Canada will continue to advance its work in partnership with the U.S., to reduce our shared exposure to production and supply chains controlled by non-likeminded countries, including by attracting investment in EV supply chains, solar, and more.
Clean Growth Hub
The Clean Growth Hub is the federal government's main source of information and advice on federal funding and other supports for clean technology projects in Canada. It directly supports up to 1,100 companies and organizations every year, ranging from emerging small businesses to Canada's world-leading clean tech companies.
Together, Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada and Natural Resources Canada partner with 16 other departments and agencies to offer this one-stop shop to help businesses seeking to invest in Canada and create net-zero growth navigate the federal government's numerous clean economy programs and incentives—unlocking new investment and creating good jobs for Canadian workers.
- To continue supporting clean technology stakeholders to identify and access relevant support and advice, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $6.1 million over two years, starting in 2024-25, for the Clean Growth Hub.
Made-in-Canada Sustainable Investment Guidelines
The government recognizes the importance of promoting credible climate investment and combating greenwashing, to protect the integrity and fairness of the clean economy. This is critical for fostering investor confidence and mobilizing the private investment that Canada needs to help achieve a net-zero by 2050 economy.
As announced in the 2023 Fall Economic Statement, the Department of Finance Canada is working with Environment and Climate Change Canada and Natural Resources Canada to undertake next steps, in consultation with regulatory agencies, the financial sector, industry, and independent experts, to develop a taxonomy that is aligned with reaching net-zero by 2050.
This work is being informed by the Sustainable Finance Action Council's Taxonomy Roadmap Report, which provided the government with recommendations on the design of a taxonomy to identify economic activities that the financial sector could label as "green" or "transition." The government will provide an update on the development of a Canadian taxonomy later this year.
Find out more about the expected gender and diversity impacts for each measure in section 4.2 Attracting Investment for a Net-Zero Economy
Small- and medium-sized businesses are an integral engine of Canada's economy, and they employ about 64 per cent of Canadian workers. Entrepreneurs, local small business, start-ups, growing medium-sized businesses—everywhere in Canada, there are people with good ideas, ready to grow their businesses and create good jobs. The government is ensuring Canada's investment climate sets businesses up for success.
For economic growth to reach the pace that is needed, existing businesses need support to stay competitive and scale-up. The government is taking action to help businesses scale-up their technological innovations, and implement productivity-raising technology across the economy. By cutting red tape, new and existing businesses can grow faster. Boosting access to financing from financial Crown corporations and encouraging Canada's large public pension funds to put their investments to work here at home will unlock new growth opportunities for Canadian businesses.
Through Budget 2024, the government is making it easier for new businesses to start-up and for existing businesses to grow by cutting red tape, and providing the tools businesses need to scale-up. The government is also taking steps to have Canadian public institutions and Crown corporations put their capital to work here at home and seize opportunities to increase Canada's growth and productivity.
The federal government has set up a range of programs and initiatives to help small and medium businesses thrive, and foster economic growth, including:
- Supporting small- and medium-sized businesses to hire 55,000 first year apprentices in construction and manufacturing Red Seal Trades through a grant of $5,000 towards upfront costs, such as salaries and training.
- Maintaining the lowest marginal effective tax rate (METR) in the G7, and a 5.2 percentage point competitive advantage over the average U.S. METR, to ensure Canada is a competitive place to do business.
- Secured commitments with Visa and Mastercard to lower credit card interchange fees for small businesses while protecting reward programs for consumers. These reductions are expected to save eligible Canadian small businesses approximately $1 billion over five years.
- Budget 2022 cut taxes for Canada's growing small businesses by more gradually phasing out their access to the small business tax rate.
- Ongoing support for small- and medium-sized businesses through Canada's seven Regional Development Agencies, including over $3.7 billion since 2018 to help businesses scale-up and innovate through the Regional Economic Growth through Innovation program.
- Almost $7 billion since 2018 for the Women Entrepreneurship Strategy to help women-owned businesses access the financing, networks, and expertise they need to start-up, scale-up, and access new markets.
- Enhancements to the Canada Small Business Financing Program, increasing annual financing to small businesses by an estimated $560 million.
- Up to $265 million for the Black Entrepreneurship Program to help Black business owners and entrepreneurs succeed and grow their businesses.
- $150 million investment in the Indigenous Growth Fund, to help recruit other investors, and in turn provide a long-term source of capital to support continued success for Indigenous businesses.
- $49 billion in interest-free, partially forgivable loans of up to $60,000 to nearly 900,000 small businesses and not-for-profit organizations through the Canada Emergency Business Account (CEBA).
National Regulatory Alignment
Barriers to internal trade are preventing Canada from reaching its economic potential. These barriers, most commonly the 13 different sets of regulations for each province and territory, hold back businesses from trading across provincial and territorial borders, restrict workers from moving between provinces and territories, and can increase costs for businesses as they work to overcome regulatory hurdles.
By addressing barriers to internal trade, including harmonizing regulations between provinces and territories, we can create more opportunities for Canadian businesses to grow and make life more affordable for all Canadians through greater competition and consumer choice. According to the International Monetary Fund, Canada could increase its gross domestic product (GDP) per capita by as much as 4 per cent—or $2,900 per capita estimated in 2023 dollars through the reduction of internal trade barriers for interprovincial trade of goods.
In 2022, the federal government launched the Federal Action Plan to Strengthen Internal Trade , which is guiding work with the provinces and territories to cut red tape. This includes a rigorous assessment of remaining federal exceptions in the Canadian Free Trade Agreement (CFTA) and important investments in trade data and research.
Two significant milestones have now been reached, with further actions upcoming in 2024:
- The removal and streamlining of one third of all federal exceptions in the CFTA. This means the removal of 14 exceptions related to procurement that will provide Canadian businesses more opportunities to compete to deliver government goods and services. By the end of 2024, the federal government will publicly release the rationale for all remaining exceptions, and encourages provinces and territories to do the same.
- The launch of the new Canadian Internal Trade Data and Information Hub on April 3, 2024. The Hub is an open and accessible data platform that will provide governments, businesses, and workers with timely, free information to help them make choices about where to invest and where to work. The Hub will help shine a light on where labour mobility barriers are highest and where unnecessary red tape costs businesses time and money.
The federal government is committed to working with provinces and territories to ensure goods, services, and workers move seamlessly across the country by advancing the mutual recognition of regulatory standards and eliminating unnecessary red tape for full labour mobility in the construction, health, and child care sectors.
- Budget 2024 announces that the government will launch the first-ever Canadian Survey on Interprovincial Trade in June 2024, to engage thousands of Canadian businesses on the challenges they face when buying, selling, and investing across provincial and territorial borders. The survey's insights will help identify top interprovincial barriers so that they can be eliminated.
As detailed in Chapter 1, the federal government is also leveraging federal housing financing to encourage provinces and territories to align their building codes, including to support modular housing construction, to make it easier to build more homes, faster.
The federal government will announce further progress to align the regulatory environment across the country in due course.
The New Canada Carbon Rebate for Small Businesses
Canada's small- and medium-sized businesses keep main streets flourishing across the country, create jobs, and deliver the dream of entrepreneurship. It is essential that these businesses thrive so they can continue being the bedrock of our communities and our economy.
Pollution has a cost, one which will only rise this century as climate change causes intensifying natural disasters and more severe health effects, as detailed in Chapter 5. Canada's carbon pricing system includes a federal backstop for provinces and territories that don't put their own system in place. It's a system designed to be fair and affordable—for households, Indigenous communities, farmers, and businesses—while reducing the pollution that is causing climate change.
The government is delivering on its commitment to return proceeds from the price on pollution to small- and medium-sized businesses, by announcing an accelerated and automated return process to provide direct refunds to small- and medium-sized businesses in the provinces where the federal fuel charge applies—the new Canada Carbon Rebate for Small Businesses.
- Proceeds would be returned directly to eligible corporations through direct payments from the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA), separately from CRA tax refunds.
- To receive their proceed return for each fuel charge year, corporations would be required to have filed their tax return for 2023 by July 15, 2024.
- The proposal would return proceeds for future fuel charge years, including 2024-25, in a similar manner each year.
Environment and Climate Change Canada continues to consult with Indigenous governments on how best to directly return fuel charge proceeds to their communities, and will announce next steps soon. The share of fuel charge proceeds allocated to Indigenous governments will double to 2 per cent of direct proceeds beginning this year.
Unlocking New Opportunity Through Financial Crown Corporations
Canada's financial Crown corporations support economic growth by helping businesses get the financing they need to grow; helping farmers and agri-businesses invest in new equipment and technology and support their operations; and helping companies sell their products around the world.
Canadians expect the government to make the most of their tax dollars. That is why in the 2023 Fall Economic Statement the government announced it would be reviewing the operations of the Business Development Bank of Canada, Export Development Canada, and Farm Credit Canada. Based on this review:
- The amended Framework has also introduced a target solvency rating for financial Crown corporations in cases where the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions has no legislative supervisory role. The amended Framework can be found in the: Capital and Dividend Policy Framework for Financial Crown Corporations .
- The Business Development Bank of Canada should increase financing for promising new and high-growth businesses and accelerate reorientation of its venture capital investments toward emerging and higher-risk sectors to help attract more private capital.
- Export Development Canada should leverage its full toolkit and authorities, including by updating internal risk management guidance to facilitate greater risk taking across its portfolio. Recognizing that success for Canadian exporters in highly competitive markets and sectors at times requires additional targeted support, Export Development Canada should also create a new stretch capital envelope to maximize potential for exporters in areas of strategic importance for Canada by taking on greater risk in deploying its capital. Having Export Development Canada take on more higher-risk, higher-impact transactions itself will reduce the need for direct support through the Canada Account. Further implementation details, including the scale and scope of the envelope, will be identified over the coming months.
- Farm Credit Canada should continue to pursue opportunities to support agri-food and agribusiness, including through venture capital investment, and further deployment of technologies to mitigate climate change. The government intends to amend the Farm Credit Canada Act to require regular legislative reviews that ensure Farm Credit Canada's activities are aligned with the sector's needs.
In focusing their mandate on driving economic growth and productivity, these Crown corporations are also expected to prioritize new financing, insurance, and advisory support to under-financed business owners, as well as increase their public reporting and engagement with Canadians. The performance incentives of senior leaders are expected to align with their organizations taking on increased risk appetite in support of economic growth objectives. For Export Development Canada, performance incentives should also encourage alignment of business activities with countries that have free trade agreements with Canada.
Investing in Canadian Start-Ups
Venture capital financing gives Canadian entrepreneurs the resources they need to start-up, scale-up, and become the next generation of Canadian anchor companies. Financing can help take new ideas from lab to market, while creating high-quality, middle-class jobs.
The Venture Capital Catalyst Initiative (VCCI) strengthens Canada's venture capital ecosystem by co-investing with the private market, discovering and nurturing the next generation of globally recognized Canadian companies, and generating returns for private and public investors alike. Since 2016, the government has invested $821 million through VCCI, delivering support to over 300 companies across Canada.
- Building on this momentum, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $200 million over two years, starting 2026-27, on a cash basis, to increase access to venture capital for equity-deserving entrepreneurs, and to invest in underserved communities and outside key metropolitan hubs.
Encouraging Pension Funds to Invest in Canada
Keeping Canada's vibrant economy strong for future generations of Canadians requires significant capital investments in our businesses, industries, and communities. Attracting higher levels of investment into Canada from all sources, including foreign and domestic private and institutional investors will raise Canada's productivity and increase living standards for all Canadians.
Pension plans are a critical pillar in Canada's retirement income system that ensures Canadians can enjoy a secure and dignified retirement. Canadian pension funds hold over $3 trillion in assets, which are invested both at home and abroad to provide secure retirement income for plan members and retirees.
The government believes that encouraging pension funds to invest in Canada more would help grow the Canadian economy and provide the stable long-term returns needed to deliver strong pensions for Canadians. In the 2023 Fall Economic Statement , the government committed to improving transparency around pension funds' investments and to working collaboratively with Canadian pension funds to create an environment that encourages and identifies more domestic investment opportunities for pension funds and other responsible institutional investors.
Canadian pension funds rely on their strong governance practices and diversified portfolios to deliver Canadians' pensions, with assets including public and private equity, infrastructure, real estate, and bonds. Canada's own economy is full of investment opportunities in these asset classes that could provide valuable contributions to pension fund portfolios. Opening up more opportunities for investment by pension funds in these domestic assets would help one of Canada's largest pools of savings contribute to the growth of the Canadian economy.
Further engagement with industry experts and pension funds will guide the government's way forward on ways to make more domestic investments available that meet the needs of pension funds.
- digital infrastructure and AI investment;
- physical infrastructure;
- airport facilities;
- venture capital investments;
- building more homes, including on public lands; and,
- the removal of the 30 per cent rule for domestic investments.
To support investments in airport facilities, the Minister of Transport will release a policy statement this summer that highlights existing flexibilities under the governance model for Canada's National Airport System airports to attract capital, including from pension funds.
- Following up on the 2023 Fall Economic Statement , Budget 2024 also proposes to amend the Pension Benefits Standards Act, 1985 to enable and require the Office of the Superintendent of Financial Institutions to publicly release information related to the plan investments of large federally regulated pension plans.
The information to be disclosed would be set out in regulations and would include the distribution of plan investments by jurisdiction and, within each jurisdiction, by asset class.
The government will continue to engage with provinces and territories to discuss similar disclosures by Canada's largest pension plans in a simple and uniform format.
Boosting Regional Economic Growth
To build a brighter future for communities across the country, Canada's Regional Development Agencies help businesses and innovators grow to fuel economic growth and create good middle class jobs. Through the Regional Economic Growth through Innovation program, businesses can access funding to scale-up, implement new technologies, improve productivity, and find new markets, helping to develop prosperous and inclusive communities across the country.
- To create jobs and boost regional economic growth, Budget 2024 proposes to provide an additional $158.5 million over two years, starting in 2024-25, on a cash basis, to Canada's Regional Development Agencies for the Regional Economic Growth through Innovation program. A portion of this funding will be dedicated to housing innovation.
This support builds on the $200 million that Regional Development Agencies will deliver to businesses for AI adoption.
Cutting Red Tape to Boost Innovation
For innovative businesses to scale-up new ideas, they need certainty that they will be able to bring their product to market. But existing regulation can often be too outdated to fit the needs of new technologies.
To ensure regulation keeps pace with the speed of new innovations, rather than hold innovation back, the government is advancing work on regulatory "sandboxes" to create temporary rules to enable testing of products, services, or new regulatory approaches.
- Budget 2024 announces the government's intent to introduce amendments to the Red Tape Reduction Act to broaden the use of regulatory sandboxes across government. The changes will enable innovation by offering limited exemptions to existing legislation and regulations, streamlining the regulatory system, and reforming regulations to modern business realities.
Supporting the Canadian Chamber of Commerce's Business Data Lab
Since 2022, the Canadian Chamber of Commerce has collaborated with Statistics Canada to provide Canadian businesses with insights and information through the Business Data Lab. This initiative provides access to real-time information and analysis, that helps Canadian businesses stay informed, and make decisions that help them stay strong and support workers.
- To advance this work, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $7.2 million over three years, starting in 2024-25, to support the Canadian Chamber of Commerce's Business Data Lab.
Find out more about the expected gender and diversity impacts for each measure in section 4.3 Growing Businesses to Create More Jobs
4.4 A Strong Workforce for a Strong Economy
Building an economy that is fair for everyone means making sure that every generation can seize the opportunities of the government's investments to grow the economy and create jobs.
Investing in new jobs and skills support for younger Canadians will help them get that first good job or start their first business. Strengthening labour laws and safeguarding the rights of workers will help ensure more jobs are good jobs. Skills and education investments for the next generation of workers will lead to higher productivity and benefit businesses in Canada and looking to invest in Canada who can tap into a robust, highly skilled workforce.
The federal government's generational job-creating investments today lay the groundwork for a brighter tomorrow, where good job opportunities are available to everyone.
- Helping over one million Canadians each year upgrade their skills or find new jobs by investing nearly $3 billion annually in Canada's Labour Market Development Agreements and Workforce Development Agreements with provinces and territories.
- Supporting a trades workforce that is skilled, inclusive, certified, and productive through the Canadian Apprenticeship Strategy.
- Equipping close to 105,000 Canadian workers with the skills they need by increasing access to union-led training through the Union Training and Innovation Program since 2019-20, and supporting over 45,000 apprentices through interest-free Canada Apprentice Loans since 2018-19.
- Introducing labour requirements for prevailing union wages and apprenticeship opportunities in most major economic investment tax credits to ensure Canadian workers thrive in the growing clean economy.
- Ensuring workers have time to recover when they get sick, by providing ten days of paid sick leave for all federally regulated workers.
- Banning the use of replacement workers during a strike or lockout in federally regulated workplaces to protect workers' right to strike and support a fairer collective bargaining process during labour disputes.
Empowering Young Entrepreneurs
Futurpreneur Canada is a national not-for-profit organization that provides young entrepreneurs with access to financing, mentorship, and other business supports to help them launch and grow their business. For over two decades, Futurpreneur Canada's programs and offerings, supported by $161.5 million in federal funding, have helped over 17,700 young entrepreneurs to launch more than 13,900 businesses across the country, supporting thousands of jobs since its inception.
- To empower young entrepreneurs, Budget 2024 proposes to provide $60 million over five years, starting in 2024-25, for Futurpreneur Canada. Futurpreneur Canada will match this federal investment with funding received from other orders of government and private sector partners.
By 2029, Futurpreneur Canada estimates this investment will enable an estimated 6,250 additional youth-owned businesses to launch and scale-up their businesses.
Futurpreneur Helps Young Entrepreneurs Scale-up Their Businesses
Sarah is a recent university graduate who wants to launch a sustainable clothing manufacturing company, but is unsure where to begin. She learns about Futurpreneur Canada. After visiting their website, she finds resources to help develop and test her business model, write a business plan and even attends a webinar to answer her questions. Now, Sarah feels confident and prepared to launch her business, but is having difficulty securing financing.
She decides to apply to Futurpreneur's Startup Program to take advantage of their financing and mentorship offering. Futurpreneur helps her finalize her business plan and cash flow, collects the necessary documentation, reviews her application and determines her business is a good fit, and provides her with financing and mentoring to help launch her business and start making sales.
Sarah is matched with an experienced business mentor who will provide her with guidance and reassurance over the next two years and receives financing of up to $20,000 from Futurpreneur and up to $40,000 from BDC to help start her business. She is also connected to various networking events with experts and other young entrepreneurs to build her business network and gain peer advice.
Investing in a Strong Workforce for a Strong Economy
Investments since Budget 2017 in skills training measures include:
Labour Market Transfer Agreements: Annual investment of nearly $3 billion enabling provinces and territories to deliver training and employment supports tailored to their unique labour market needs.
Union-based training: Over $200 million through Budget 2022 and Fall Economic Statement 2022 to expand the Union Training and Innovation Program to train more than 30,000 additional apprentices and journeypersons.
Employer-led training: Budget 2021 announced the Sectoral Workforce Solutions Program to help key sectors of the economy, including the construction sector, implement solutions to address their current and emerging workforce needs. Budget 2021 also announced $250 million for the Upskilling for Industry Initiative to support more than 15,000 workers. Budget 2024 proposes $50 million over four years to provide skills training for workers in sectors disrupted by AI, and $10 million over two years to train more early childhood educators, building up the talent needed for the expansion of affordable, high-quality child care.
Apprenticeship Service: Launched the Apprenticeship Service to help first year apprentices in construction and manufacturing Red Seal trades connect with opportunities at small and medium-sized employers. Budget 2024 proposes to provide $90 million over two years for the Apprenticeship Service to help create placements in the residential construction sector.
Skilled Trades Awareness and Readiness Program: Budget 2018 announced the Skilled Trades Awareness and Readiness Program to help Canadians explore the trades and make informed career choices. Budget 2024 proposes $10 million over two years to continue to encourage Canadians to explore and prepare for careers in the skilled trades.
Sustainable Jobs Training Fund: Recently launched the Sustainable Jobs Training Fund to help workers upgrade or gain new skills for jobs in the low-carbon economy.
Indigenous-led training: $99.4 million per year through the co-developed Indigenous Skills and Employment Training (ISET) Program to help Indigenous people improve their skills and find employment.
Financial support for adult learners: About $250 million per year for the Canada Training Credit, which covers up to 50 per cent of eligible training fees.
Affordability for Apprentices: Eliminated Elimination of interest on Canada Apprentice Loans, which provides up to $4,000 per period of technical training for tuition, tools, equipment, living expenses and forgone wages.
Apprenticeship Requirements for Clean Economy Investment Tax Credits: to access the highest tax credit rates, projects must dedicate at least 10 per cent of labour hours performed by covered workers to apprentices. This provides apprentices with the crucial hours they need to complete their training.
Establishing a Right to Disconnect
Everyone needs some downtime; it is essential for well-being and mental health. As the nature of work in many industries has become increasingly digital, workers are finding it increasingly difficult to disconnect from their devices and inboxes after hours and on weekends. This has particularly impacted Millennial and Gen Z workers, many of whom have worked their whole careers without firm separation between work and personal time.
The government is taking action to restore work-life balance for the many workers in federally regulated industries, including but not limited to financial services, telecommunications, and transportation, by moving forward with a right disconnect from work, outside of their working hours.
- This is expected to benefit up to 500,000 employees in federally regulated sectors.
Further, on the topic of worker misclassification, Employment and Social Development Canada and the Canada Revenue Agency will enter into necessary data-sharing agreements to facilitate inspections and enforcement.
Modernizing the Employment Equity Act
Through the Employment Equity Act , the government promotes and improves equality and diversity in federally regulated workplaces. Since the introduction of the Employment Equity Act , continued progress has been made to address inequalities, but some workers are still facing barriers to employment and many federal workplaces fail to reflect the full diversity of Canada's population. That is why, in 2021, the government launched an arm's length Task Force to review the Act and advise on how to modernize the federal employment equity framework.
- Following the recommendations of the Task Force, Budget 2024 announces the government's intention to propose legislative amendments to modernize the Employment Equity Act , including by expanding designated equity groups.
Examining Critical Port Operations
Labour disputes and work stoppages at Canadian ports can lead to serious economic impacts by disrupting supply chains. To protect port workers and resolve the structural issues underlying port labour disputes, in 2023, the government launched the first phase of a formal review in collaboration with industrial relations experts.
- Budget 2024 proposes to provide $3.1 million over two years, starting in 2024-25, to enable the Labour Program at Employment and Social Development Canada to complete the second phase of its review, which will explore long-term solutions to minimize labour disputes, respect the collective bargaining process, and secure the stability of Canada's supply chains. This funding would be sourced from existing departmental resources.
Extending Temporary Support for Seasonal Workers
Many seasonal workers—including in fishing and tourism sectors in Atlantic Canada and Quebec—rely on Employment Insurance for the support they need between work seasons. To address gaps in Employment Insurance support between seasons, the government introduced temporary rules in 2018 to provide up to five additional weeks—for a maximum of 45 weeks—to eligible seasonal workers in 13 economic regions. This support is set to expire in October 2024.
- Budget 2024 proposes to extend this support for seasonal workers in targeted regions until October 2026. The cost of this measure is estimated at $263.5 million over four years, starting in 2024-25.
Find out more about the expected gender and diversity impacts for each measure in section 4.4 A Strong Workforce for a Strong Economy
Page details

SUNY Canton students boast their concrete knowledge
C ANTON, N.Y. (WWTI) — SUNY Canton students are showing off their concrete knowledge developed through research into applications using the fiberglass-reinforced building material.
Led by Associate Professor Saeid Haji Ghasemali, Ph.D., who teaches in the Civil and Environmental Engineering Technology program, students in the American Concrete Institute student chapter have presented their findings on innovative building techniques at several conferences. They’ve also cemented new accolades for the college’s Canino School of Engineering Technology.
“ Our students participated in the Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer (GFRP) poster session at the American Concrete Institute (ACI) convention in New Orleans, ” Haji Ghasemali said. “ They were the only undergraduates among a group of graduate students from different universities. Their active involvement truly stood out and showed their dedication and talent. ”
According to the faculty member, the judges were astounded by the quality of research conducted by SUNY Canton’s undergraduate students. The quality of their work rivaled that of graduate-level research, earning recognition from the judging panel. Civil and Environmental Engineering Technology major Cameron J. Hodson of Auburn, the SUNY Canton ACI Chapter President received a certificate and accolades for the presentation.
Previously, the students won first place for their “Sustainable Structural Enhancement of Lightweight Concrete Beams with GFRP” poster presentation during the NYS 2024 Green Building Conference in Syracuse. The recent accomplishments contributed to the relatively new student group clinching the 2023 ACI Student Chapter Award. “ This prestigious recognition underscores SUNY Canton’s dedication to expanding research in this field ,” Haji Ghasemali said.
Civil and Environmental Engineering Technology student members of SUNY Canton’s ACI Student Chapter include:
- Waleed Safdar of Brooklyn;
- Nathan A. Upton of Syracuse;
- Ronald J. Wood-Terrance of Bombay;
- Brendan A. Morrow of Wetaskiwin, Alberta;
- Gabriel Murphy of Canton;
- Lucas Roy of Sainte-Anne-De-Bellevue, Quebec;
- Mathew Greene of Waddington;
- Patience V. Dawson of Brooklyn;
- Caprice A. Pramana of Woodside;
- Emma L. Kielmeier of Pyrites;
- Timothy J. McLellan of Ogdensburg;
- Logan S. McCargar of West Stockholm; and
- Jad M. Kouram of Ogdensburg.
The student chapter first emerged to make a remarkable showing at ACI’s Fiber Reinforced Polymer Competition in November. The students earned a second-place national finish and secured eighth place internationally. Additional information is available on SUNY Canton’s website .
For the latest news, weather, sports, and streaming video, head to WWTI - InformNNY.com.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It shows that on the pre-test majority of the. respondents had a low range score in Endurance Dimension of AQ® (49 or. 27.07%) and the rest got a below average score (61 or 33.70%), 47 or 25.97%. got an average score, 19 or 10.48% got an above average score and 5 or 2.76%. got a high score.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Typically, chapter one of a research project proposal or thesis includes the following components: Study background. Statement of the problem. Purpose of the study. Research question (s) Significance of the study. Definition of terms.
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 introduces the research problem and the evidence supporting the existence of the problem. It outlines an initial review of the literature on the study topic and articulates the purpose of the study. The definitions of any technical terms necessary for the reader to understand are essential.
CHAPTER The Selection of a 1 Research Approach Introducing Key Terms in this Chapter Research has its own language, and it is important to understand key terms to use in a study. The title of this book uses the term, research approaches. Research approaches (or methodologies) are procedures for research that
Craft an enticing and engaging opening section. Provide a background and context to the study. Clearly define the research problem. State your research aims, objectives and questions. Explain the significance of your study. Identify the limitations of your research. Outline the structure of your dissertation or thesis.
In PhD studies, the purpose usually involves applying a theory to solve the problem. In other words, the purpose tells the reader what the goal of the study is, and what your study will accomplish, through which theoretical lens. The purpose statement also includes brief information about direction, scope, and where the data will come from.
Research methods defined. Research methods comprise a systematic process of inquiry applied in such a manner as to learn something about our social world (Saylor Academy, 2012). The key message in the preceding statement is that undertaking research is a systematic process, i.e. there is a system, or a right way, to do research.
nings of the study, significance/need of the study, objectives, and research questions and/or hypothesis. to be tested. In essence, chapter one prepares the. reader for what is coming in the next chapters of a thesis or dissertation. Therefore, careful attention to detail is a must for writing introduction/chapter one.
Chapter 1 Step 1 • Develop a Good Research Question 11 You might think this would be easy to do, but it's not. Even the most seasoned researchers have to spend a lot of time on this step. An Example: Mass Transit Let's take an example. Maybe you're interested in mass transit. You know: the
1 Answer to this question. Answer: The Introduction section sets the context for your research work, explains the research problem, and indicates the purpose behind the study. The Introduction also highlights how your research contributes to knowledge in your field and builds on previous similar studies.
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION. 1. The purpose of this qualitative grounded theory study was to identify what motivates. women to stay in or return to science, technology, engineering, and math professions. (STEM), leading to a motivation model. As illustrated in the literature review, research has. abbreviations. introduce introduce you can use Once ...
Chapter 1. A Complete Dissertation 7 purpose, or it does not stand alone as a document. Chapter 2: Literature Review This chapter situates the study in the con-text of previous research and scholarly mate - rial pertaining to the topic, presents a critical synthesis of empirical literature according to relevant themes or variables, justifies how
Summary. The importance of research aims and objectives cannot be over-stressed. It is vital to have a very clear understanding of what the research is about and what you are actually trying to achieve. You need to know this. And you need to be able to communicate it to others. Carrying out a research project is rather like going on a journey.
There are certainly times when the order of the steps may be modified, but researchers typically follow the same process for each research study they complete regardless of the research topic (as depicted in Figure 2.1 in Chapter 2). Very simply, a research problem or question is identified, and a methodology is selected, developed, and ...
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
6 Chapter 1 Uncertainty and Curiosity Research does not start with a thesis statement. It starts with a question. And though research is recursive,* which means that you will move back and forth between various stages in your research and writing process, developing an effective question might in itself be the most important part of the research
Chapter 1 The Selection of a Research Approach Chapter 2 Review of the Literature Chapter 3 The Use of Theory Chapter 4 Writing Strategies and Ethical Considerations This book is intended to help researchers develop a plan or proposal for a research study. Part I addresses
Chapter 1: Introduction to Research Methods. Learning Objectives. At the end of this chapter, you will be able to: Define the term "research methods". List the nine steps in undertaking a research project. Differentiate between applied and basic research. Explain where research ideas come from. Define ontology and epistemology and explain ...
1.2 Defining Research Methodology. It is an essential process of any scientific study, which serves as a framework for processing and achieving the predicted outcomes of the study. It is commonly defined as a systematic and organized process of collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting information to answer specific questions or solve ...
Chapter 1: What is Research and Research Writing? Writing is a journey—it is seldom a straight line. Writing is thinking. It's witnessing, observing, and sharing. Writing is powerful—it can change the world by communicating a new discovery or challenging someone's pre-existing beliefs, and it can also change you.
system research problem in a dynamic environment with the implementation of a real world application. This subproblem is discussed in Chapter 4. 1.5 Hypothesis Hypothesis 1: The theory of productive efficiency can be extended into the dynamical realm by incorporating certain concepts within a SD framework.
Chapter 1: Home; Narrowing Your Topic; Problem Statement; Purpose Statement; Alignment; Conceptual Framework; Theoretical Framework; Quantitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window; Qualitative Research Questions This link opens in a new window; Qualitative & Quantitative Research Support with the ASC This link opens in a new window; Library Research Consultations This link ...
Dear Academy Colleagues: We are happy to invite you to participate in an online workshop which is part of the UN PRME World Tour Research Paper Development Program 2022-2024!! Are you interested in learning more about publishing (in general) and conducting research in an African context?
Gulf Park Campus Health Center Invites Campus Community to Monthly 1-Mile Walk and Talk Gathering. Thu, 04/18/2024 - 08:17am | By: Gabriela Shinskie. The University of Southern Mississippi (USM) Gulf Park Health Center (GPHC) invites members of campus community to lace up their walking shoes and join in the monthly "Strutt Your Stuff Walk and Talk," a 1-mile walk around the school's ...
Chapter 4 - Net Fiscal Impact: 0: 2,898: 453: 1,717: 831: 1,680: 7,578: Note: Numbers may not add due to rounding. A glossary of abbreviations used in this table can be found at the end of Annex 1. 1 Does not include funding to be disbursed through Clean Fuel Regulations compliance payment revenues. 2 Measure reimbursed by increased Employment ...
CANTON, N.Y. (WWTI) — SUNY Canton students are showing off their concrete knowledge developed through research into applications using the fiberglass-reinforced building material. Led by ...
The Special Education Research Center shall carry out research activities under this part consistent with the mission described in section 9567(b) of this title, such as activities that— (1) improve services provided under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act [20 U.S.C. 1400 et seq.] in order to improve—