

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
✍️Essay on Natural Resources: Samples in 100, 150 and 200 Words

- Updated on
- Nov 2, 2023

Wondering about how the resources provided by our planet Earth are depleting? Well, that’s true. We have come to the stage where we should start working towards saving our planet. We humans have used our resources in a humongous quantity. Therefore, it’s time we start working towards saving our planet for our future generations. Today we will provide you with a few samples of essay on natural resources which will help you write on this topic easily.
Table of Contents
- 1 What are Natural Resources?
- 2 Types of Natural Resources
- 3 Essay on Natural Resources in 100 Words
- 4 Essay on Natural Resources in 150 Words
- 5 Essay on Natural Resources in 200 Words
What are Natural Resources?
Natural Resources are resources which are present in nature independent of human actions.
These are the resources that are created naturally by the environment, without any help from humans. Soil, stone, sunlight, air, plants, animals, fossil fuels, etc. are all natural resources.
In simple language, natural resources are naturally occurring materials which are useful to humankind. They can also be useful in a variety of ways such as in technological, economic or social contexts. These resources include building, clothing materials, food, water, fertilisers and geothermal energy. Natural resources were traditionally within the purview of the natural sciences.
Also Read: Essay on Save Environment: Samples in 100, 200, 300 Words
Also Read: How to Prepare for UPSC in 6 Months?
Types of Natural Resources
Speaking of the type of natural resources, there are mainly two types of natural resources. These include Renewable and Non-renewable resources.
Renewable Resources: These are those resources which are endlessly available to humans for several uses. These resources are trees, wind, and water.
Non-Renewable Resources: These resources are available to humans in infinite quantities as they are not renewable and their supply may eventually run out. Minerals and fossil fuels are a few examples.
Also Read: Essay on the Importance of the English Language for Students
Essay on Natural Resources in 100 Words
Natural resources are parts of the natural world that are useful to humans. Renewable resources are those that can be swiftly replenished, these include soil, water, and air., Non-renewable resources are those that need time to recover, such as minerals, oil, natural gas, etc.
One should note that the survival of all life on Earth depends on natural resources. However, the usage of natural resources in excess use can cause ecosystem disruption. Many nations are taking action these days to protect their natural resources. Natural resources shouldn’t be used for purposes outside our needs. In order to preserve non-renewable resources, we should utilise renewable resources more frequently than non-renewable ones.
Essay on Natural Resources in 150 Words
The organic aspects of nature that contribute to our way of life are known as natural resources. For survival, we rely on natural resources. Natural resources include things like air, water, soil, minerals, crops, etc. Resources like minerals, oil, and other resources are found in non-living organisms and take eons to regenerate.
The distribution of natural resources is not even. Resources like these are also the primary driver of international trade relations for many nations. However, with time, these natural resources have now been overused by the human mankind beyond their limits.
However, the unrestricted exploitation of natural resources is a challenge for all nations these days. To control this, a lot of nations are emphasising garbage recycling and employing more renewable resources than non-renewable ones.
Sustainable development is the use of natural resources for current requirements without wasting them while keeping an eye on the future. It refers to the wise use of natural resources without sacrificing what coming generations will need.
Also Read: Essay on Unity in Diversity in 100 to 200 Words
Essay on Natural Resources in 200 Words
Natural resources are materials found in the environment that humans use to survive. From the very start, humans have been dependent on these resources. While some of these resources can be restored more rapidly than others, some require more time. Resources like sunlight, water, air, and other renewable resources are readily available and have higher recovery rates than consumption rates.
On the other hand, the formation and processing of non-renewable resources, such as minerals, oil, and natural gas, take a long time. Even the usage rate of these non-renewable resources is higher as compared to the renewable resources. While some natural resources are used immediately, others must first undergo processing.
Even while renewable resources are available in huge quantities, they should also be used responsibly. Both renewable and non-renewable resources require time to be created and processed. Therefore, it is very important for humans to use these resources in a limited quantity and leave some for future generations.
With time, humans are using these resources excessively. With the ever-increasing population, humans have already created a huge impact on the environment. To begin, humans are continuously polluting the air, water and noise. Buildings are being constructed on more land. The land is becoming less valuable in this way. Humans are soon becoming the biggest reason behind depleting natural resources, such as land, water, and air.
Therefore, we mustn’t undervalue these resources. The moment has come for us to recognise the importance of using these resources sustainably.
Related Articles
Natural Resources are substances which are naturally obtained from nature. Here are the 5 natural resources: Coal, Oil, Natural Gas, Sand, Gems, and Metals.
Renewable resources are natural resources that can be replenished or regenerated at a rate comparable to the rate at which they are consumed or harvested. For example: Solar energy, Wind energy, Biomass, Geothermal energy, etc.
Conserving and saving natural resources is essential for sustainable development and the preservation of the environment. Here are some easy tips to save natural resources: Implementing the 3Rs in daily life; Adopting energy-efficient practices such as using energy-saving appliances; Reducing water wastage by fixing leaks, using water-efficient appliances, and practising mindful water usage in daily activities, etc.
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay-writing page and follow Leverage Edu !
Malvika Chawla
Malvika is a content writer cum news freak who comes with a strong background in Journalism and has worked with renowned news websites such as News 9 and The Financial Express to name a few. When not writing, she can be found bringing life to the canvasses by painting on them.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
it is awesome 👌 every doubt of mine gets clear 😀 thank you very much

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Natural Resources Essay | Essay on Natural Resources for Students and Children in English
February 13, 2024 by Prasanna
Natural Resources Essay: Our survival has always wholly depended on the natural resources of the Earth. The natural resources are the blessing of Mother Nature that has provided us with abundant elements to make our life comfortable and prosperous. Natural resources are all those things that are readily present in the environment like air, water, sunlight, wood, coal, etc. Most of these natural resources are present on Earth’s surface (or reach Earth’s surface like sunlight). Still, some natural resources are also hidden below the Earth’s surface, which we have eventually reached and used to benefit us.
To help students regarding essay writing on the topic ‘Natural Resources’, we have provided samples for long and short essays on the theme. Additionally, we have offered ten points about the subject matter that will help the students in framing the essay and act as guidelines.
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Long and Short Essays on Natural Resources for Students and Kids in English
We are providing a short essay on Natural Resources for students of classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6; we are also providing a long essay sample for classes 7, 8, 9, and 10. Along with the essays, ten pointers on the topic are also being given by us so that students can use them as a reference while structuring their essays.
Long Essay on Natural Resources 500 words in English
Human life is unimaginable without natural resources, and it is precise because of these resources that any form of life sustained on this planet with comfort. Natural resources are anything and everything obtained from nature and used by us, starting from elemental air, water, and sunlight to even organic elements like fossil fuels, minerals, timber, etc.
Natural resources that are obtained from living organisms or are eventually formed because of living organisms are called Biotic elements, like forests, birds, animals, fishes, or other marine organisms, fossil fuels (because they are formed because of the decay of organic materials), etc. Natural resources that refer to the non-living elements of nature are called Abiotic resources. Examples of abiotic resources are sunlight, wind, tide, soil, minerals, etc.
Natural elements are present everywhere around the world but not equally distributed. Humans have learned efficient ways in which they can use the natural resources present in their region for their benefit. Like in India, a variety of soil and humid weather has allowed the prosperous growth of agriculture. The areas of the country that are surrounded by sea eventually developed advanced skills in fishing.
Some examples of how we use our natural resources are, using of water for drinking and production of hydro-electric power, sunlight is necessary for plant growth and also providing us heat and vitamins, plants are our primary source of oxygen and food, coal is used for electricity production and as a fuel for vehicles, etc.
With trade and commerce came globalization, and now we are dynamically evolving to find ways in which we can modify methods of using natural resources to create products to serve us better. But we have to remember that not all resources are unlimitedly present in our ecosystem. If we are not careful about the consumption of these resources, then they will eventually exhaust, then we might not have an alternative to survive without those.
The resources like solar, wind, hydro, geothermal, and biomass are called renewable resources because they are present abundantly in the world and are self-replenishing in nature. And the resources like fossil fuels, iron, freshwater, coal, nuclear elements, etc. that took million years for the formation and can eventually perish (cannot be reproduced) are called non-renewable resources.
Hence, it is essential to preserve resources so that they can be present in the future for us and our succeeding generation’s use and benefit. Everyone needs to know natural resources because our survival depends on those. We also need to educate and make people aware of the hazardous effect of the absence of these resources. We should preach and practice the ways of Essay on Conservation of Natural Resources .

Short Essay on Natural Resources 150 words in English
Natural resources are the blessings of nature to its children, living beings that have not only made our survival possible but also made our life comfortable and nourished. Some examples of natural resources are sunlight, air, timber, coal, plants, food, animals, water, natural gases, etc. The natural resources can be classified as Biotic (forest, animals, birds, fish, fossil fuels, etc.) and Abiotic or Non-living (water, minerals, air, soil, sunlight, etc.) resources.
Even though many natural resources are present in the environment in abundance, some resources can ultimately perish. These are called Renewable and Non-Renewable resources, respectively. Hence, we should be careful about our non-renewable natural resources so that they do not exhaust.
We can obtain this by differentiating our necessities from luxuries and spend natural resources in a calculated manner. It is our responsibility as the responsible citizens of this planet to be concerned about the conservation of these natural resources and contribute to the cause by doing our part in saving. we will soonly update Natural Resources Essay in Hindi, Urdu, Kannada and Marathi.
10 Lines on Natural Resources Essay in English
- With the increase in population, there is a higher demand for natural resources.
- Economically richer countries tend to spend or waste more natural resources than the poorer countries.
- With industrialization, the demand for natural resources has skyrocketed the charts from comparing them to the time before.
- Recycling of one-ton paper can save almost 4000kW of energy, 17 trees, and 2 barrels of oil.
- The three Rs that help save natural resources are Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle.
- The energy developed from renewable resources is the fastest-growing energy source, and it is estimated that by 2040 the renewable energy will generate an equal amount of energy as to coal and natural gas.
- Using renewable resources responsibly can reduce the emission of several greenhouse gases that are typically released from fossil fuel.
- Despite being covered by 70% of water, the Earth is less than 1% of the water that is consumable and available for human use.
- The production of renewable energy from wind, sunlight, geothermal heat, waves, etc. does not require the use of much freshwater.
- It is estimated that the global water demand for manufacturing from 2000 to 2050 is to increase by 40%.
FAQ’s on Natural Resources Essay
Question 1. Why is it necessary to conserve our natural resources?
Answer: Natural resources are the primary source of our daily needs. Reckless use of natural resources will eventually exhaust them, and this will affect us and harm more to our future generation. For the sake of us and our environment, we need to understand and implement the ways of conservation of natural resources.
Question 2. What are the types of natural resources present in our environment?
Answer: There are two types of natural resources present in the environment; they are Non-renewable and Renewable resources.
Question 3. Can animals be considered as natural resources?
Answer: Yes, animals are considered as natural resources. Animals are the kind of biological natural resources.
Question 4. Is gold a natural resource?
Answer: Yes, gold is also a natural resource and is classified as a mineral. Minerals like metals are known as abiotic natural resources.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education
Conserving Earth
Earth’s natural resources include air, water, soil, minerals, plants, and animals. Conservation is the practice of caring for these resources so all living things can benefit from them now and in the future.
Biology, Ecology, Earth Science, Geography, Geology, Conservation
Loading ...
Earth ’s natural resources include air , water , soil , minerals , fuels , plants, and animals. Conservation is the practice of caring for these resources so all living things can benefit from them now and in the future. All the things we need to survive , such as food , water, air, and shelter , come from natural resources. Some of these resources, like small plants, can be replaced quickly after they are used. Others, like large trees, take a long time to replace. These are renewable resources . Other resources, such as fossil fuels , cannot be replaced at all. Once they are used up, they are gone f orever . These are nonrenewable resources . People often waste natural resources. Animals are overhunted . Forests are cleared, exposing land to wind and water damage. Fertile soil is exhausted and lost to erosion because of poor farming practices. Fuel supplies are depleted . Water and air are polluted . If resources are carelessly managed, many will be used up. If used wisely and efficiently , however, renewable resources will last much longer. Through conservation, people can reduce waste and manage natural resources wisely. The population of human beings has grown enormously in the past two centuries. Billions of people use up resources quickly as they eat food, build houses, produce goods, and burn fuel for transportation and electricity . The continuation of life as we know it depends on the careful use of natural resources. The need to conserve resources often conflicts with other needs. For some people, a wooded area may be a good place to put a farm. A timber company may want to harvest the area’s trees for construction materials. A business may want to build a factory or shopping mall on the land. All these needs are valid, but sometimes the plants and animals that live in the area are forgotten. The benefits of development need to be weighed against the harm to animals that may be forced to find new habitats , the depletion of resources we may want in the future (such as water or timber), or damage to resources we use today. Development and conservation can coexist in harmony. When we use the environment in ways that ensure we have resources for the future, it is called sustainable development . There are many different resources we need to conserve in order to live sustainably. Forests A forest is a large area covered with trees grouped so their foliage shades the ground. Every continent except Antarctica has forests, from the evergreen -filled boreal forests of the north to mangrove forests in tropical wetlands . Forests are home to more than two-thirds of all known land species . Tropical rainforests are especially rich in biodiversity . Forests provide habitats for animals and plants. They store carbon , helping reduce global warming . They protect soil by reducing runoff . They add nutrients to the soil through leaf litter . They provide people with lumber and firewood. Deforestation is the process of clearing away forests by cutting them down or burning them. People clear forests to use the wood, or to make way for farming or development. Each year, Earth loses about 14.6 million hectares (36 million acres) of forest to deforestation—an area about the size of the U.S. state of New York. Deforestation destroys wildlife habitats and increases soil erosion. It also releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere , contributing to global warming. Deforestation accounts for 15 percent of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions. Deforestation also harms the people who rely on forests for their survival, hunting and gathering, harvesting forest products, or using the timber for firewood. About half of all the forests on Earth are in the tropics —an area that circles the globe near the Equator . Although tropical forests cover fewer than 6 percent of the world’s land area, they are home to about 80 percent of the world’s documented species. For example, more than 500 different species of trees live in the forests on the small U.S. island of Puerto Rico in the Caribbean Sea. Tropical forests give us many valuable products, including woods like mahogany and teak , rubber , fruits, nuts, and flowers. Many of the medicines we use today come from plants found only in tropical rainforests. These include quinine , a malaria drug; curare , an anesthetic used in surgery; and rosy periwinkle , which is used to treat certain types of cancer . Sustainable forestry practices are critical for ensuring we have these resources well into the future. One of these practices is leaving some trees to die and decay naturally in the forest. This “ deadwood ” builds up soil. Other sustainable forestry methods include using low-impact logging practices, harvesting with natural regeneration in mind, and avoiding certain logging techniques , such as removing all the high-value trees or all the largest trees from a forest. Trees can also be conserved if consumers recycle . People in China and Mexico, for example, reuse much of their wastepaper, including writing paper, wrapping paper, and cardboard. If half the world’s paper were recycled, much of the worldwide demand for new paper would be fulfilled, saving many of Earth’s trees. We can also replace some wood products with alternatives like bamboo , which is actually a type of grass. Soil Soil is vital to food production. We need high-quality soil to grow the crops that we eat and feed to livestock . Soil is also important to plants that grow in the wild. Many other types of conservation efforts, such as plant conservation and animal conservation, depend on soil conservation. Poor farming methods, such as repeatedly planting the same crop in the same place, called monoculture , deplete nutrients in the soil. Soil erosion by water and wind increases when farmers plow up and down hills. One soil conservation method is called contour strip cropping . Several crops, such as corn, wheat, and clover , are planted in alternating strips across a slope or across the path of the prevailing wind . Different crops, with different root systems and leaves, help slow erosion.
Harvesting all the trees from a large area, a practice called clearcutting , increases the chances of losing productive topsoil to wind and water erosion. Selective harvesting —the practice of removing individual trees or small groups of trees—leaves other trees standing to anchor the soil. Biodiversity Biodiversity is the variety of living things that populate Earth. The products and benefits we get from nature rely on biodiversity. We need a rich mixture of living things to provide foods, building materials, and medicines, as well as to maintain a clean and healthy landscape . When a species becomes extinct , it is lost to the world forever. Scientists estimate that the current rate of extinction is 1,000 times the natural rate. Through hunting, pollution , habitat destruction, and contribution to global warming, people are speeding up the loss of biodiversity at an alarming rate. It’s hard to know how many species are going extinct because the total number of species is unknown. Scientists discover thousands of new species every year. For example, after looking at just 19 trees in Panama, scientists found 1,200 different species of beetles—80 percent of them unknown to science at the time. Based on various estimates of the number of species on Earth, we could be losing anywhere from 200 to 100,000 species each year. We need to protect biodiversity to ensure we have plentiful and varied food sources. This is true even if we don’t eat a species threatened with extinction because something we do eat may depend on that species for survival. Some predators are useful for keeping the populations of other animals at manageable levels. The extinction of a major predator might mean there are more herbivores looking for food in people’s gardens and farms. Biodiversity is important for more than just food. For instance, we use between 50,000 to 70,000 plant species for medicines worldwide. The Great Barrier Reef , a coral reef off the coast of northeastern Australia, contributes about $6 billion to the nation’s economy through commercial fishing , tourism , and other recreational activities. If the coral reef dies, many of the fish, shellfish , marine mammals , and plants will die, too. Some governments have established parks and preserves to protect wildlife and their habitats. They are also working to abolish hunting and fishing practices that may cause the extinction of some species. Fossil Fuels Fossil fuels are fuels produced from the remains of ancient plants and animals. They include coal , petroleum (oil), and natural gas . People rely on fossil fuels to power vehicles like cars and airplanes, to produce electricity, and to cook and provide heat. In addition, many of the products we use today are made from petroleum. These include plastics , synthetic rubber, fabrics like nylon , medicines, cosmetics , waxes, cleaning products, medical devices, and even bubblegum.
Fossil fuels formed over millions of years. Once we use them up, we cannot replace them. Fossil fuels are a nonrenewable resource. We need to conserve fossil fuels so we don’t run out. However, there are other good reasons to limit our fossil fuel use. These fuels pollute the air when they are burned. Burning fossil fuels also releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to global warming. Global warming is changing ecosystems . The oceans are becoming warmer and more acidic , which threatens sea life. Sea levels are rising, posing risks to coastal communities. Many areas are experiencing more droughts , while others suffer from flooding . Scientists are exploring alternatives to fossil fuels. They are trying to produce renewable biofuels to power cars and trucks. They are looking to produce electricity using the sun, wind, water, and geothermal energy — Earth’s natural heat. Everyone can help conserve fossil fuels by using them carefully. Turn off lights and other electronics when you are not using them. Purchase energy-efficient appliances and weatherproof your home. Walk, ride a bike, carpool , and use public transportation whenever possible. Minerals Earth’s supply of raw mineral resources is in danger. Many mineral deposits that have been located and mapped have been depleted. As the ores for minerals like aluminum and iron become harder to find and extract , their prices skyrocket . This makes tools and machinery more expensive to purchase and operate. Many mining methods, such as mountaintop removal mining (MTR) , devastate the environment. They destroy soil, plants, and animal habitats. Many mining methods also pollute water and air, as toxic chemicals leak into the surrounding ecosystem. Conservation efforts in areas like Chile and the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern United States often promote more sustainable mining methods. Less wasteful mining methods and the recycling of materials will help conserve mineral resources. In Japan, for example, car manufacturers recycle many raw materials used in making automobiles. In the United States, nearly one-third of the iron produced comes from recycled automobiles. Electronic devices present a big problem for conservation because technology changes so quickly. For example, consumers typically replace their cell phones every 18 months. Computers, televisions, and mp3 players are other products contributing to “ e-waste .” The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimates that Americans generated more than three million tons of e-waste in 2007. Electronic products contain minerals as well as petroleum-based plastics. Many of them also contain hazardous materials that can leach out of landfills into the soil and water supply. Many governments are passing laws requiring manufacturers to recycle used electronics. Recycling not only keeps materials out of landfills, but it also reduces the energy used to produce new products. For instance, recycling aluminum saves 90 percent of the energy that would be required to mine new aluminum.
Water Water is a renewable resource. We will not run out of water the way we might run out of fossil fuels. The amount of water on Earth always remains the same. However, most of the planet’s water is unavailable for human use. While more than 70 percent of Earth’s surface is covered by water, only 2.5 percent of it is freshwater . Out of that freshwater, almost 70 percent is permanently frozen in the ice caps covering Antarctica and Greenland. Only about 1 percent of the freshwater on Earth is available for people to use for drinking, bathing, and irrigating crops. People in many regions of the world suffer water shortages . These are caused by depletion of underground water sources known as aquifers , a lack of rainfall due to drought, or pollution of water supplies. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 2.6 billion people lack adequate water sanitation . More than five million people die each year from diseases caused by using polluted water for drinking, cooking, or washing. About one-third of Earth’s population lives in areas that are experiencing water stress . Most of these areas are in developing countries. Polluted water hurts the environment as well as people. For instance, agricultural runoff—the water that runs off of farmland—can contain fertilizers and pesticides . When this water gets into streams , rivers , and oceans, it can harm the organisms that live in or drink from those water sources. People can conserve and protect water supplies in many ways. Individuals can limit water use by fixing leaky faucets, taking shorter showers, planting drought-resistant plants, and buying low-water-use appliances. Governments, businesses, and nonprofit organizations can help developing countries build sanitation facilities. Farmers can change some of their practices to reduce polluted runoff. This includes limiting overgrazing , avoiding over-irrigation, and using alternatives to chemical pesticides whenever possible. Conservation Groups Businesses, international organizations , and some governments are involved in conservation efforts. The United Nations (UN) encourages the creation of national parks around the world. The UN also established World Water Day, an event to raise awareness and promote water conservation. Governments enact laws defining how land should be used and which areas should be set aside as parks and wildlife preserves. Governments also enforce laws designed to protect the environment from pollution, such as requiring factories to install pollution-control devices. Finally, governments often provide incentives for conserving resources, using clean technologies, and recycling used goods. Many international organizations are dedicated to conservation. Members support causes such as saving rain forests, protecting threatened animals, and cleaning up the air. The International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an alliance of governments and private groups founded in 1948. The IUCN works to protect wildlife and habitats. In 1980, the group proposed a world conservation strategy . Many governments have used the IUCN model to develop their own conservation plans. In addition, the IUCN monitors the status of endangered wildlife, threatened national parks and preserves, and other environments around the world. Zoos and botanical gardens also work to protect wildlife. Many zoos raise and breed endangered animals to increase their populations. They conduct research and help educate the public about endangered species . For instance, the San Diego Zoo in the U.S. state of California runs a variety of research programs on topics ranging from disease control in amphibians to heart-healthy diets for gorillas. Scientists at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, in London, England, work to protect plant life around the world. Kew’s Millennium Seed Bank , for example, works with partners in 54 countries to protect biodiversity through seed collection. Kew researchers are also exploring how DNA technology can help restore damaged habitats. Individuals can do many things to help conserve resources. Turning off lights, repairing leaky faucets, and recycling paper, aluminum cans, glass, and plastic are just a few examples. Riding bikes, walking, carpooling, and using public transportation all help conserve fuel and reduce the amount of pollutants released into the environment. Individuals can plant trees to create homes for birds and squirrels. At grocery stores, people can bring their own reusable bags. And people can carry reusable water bottles and coffee mugs rather than using disposable containers. If each of us would conserve in small ways, the result would be a major conservation effort.
Tree Huggers The Chipko Movement, which is dedicated to saving trees, was started by villagers in Uttar Pradesh, India. Chipko means hold fast or embrace. The villagers flung their arms around trees to keep loggers from cutting them down. The villagers won, and Uttar Pradesh banned the felling of trees in the Himalayan foothills. The movement has since expanded to other parts of India.
Thirsty Food People require about 2 to 4 liters of drinking water each day. However, a day's worth of food requires 2,000 to 5,000 liters of water to produce. It takes more water to produce meat than to produce plant-based foods.
Tiger, Tiger Tigers are dangerous animals, but they have more to fear from us than we have to fear from them. Today there are only about 3,200 tigers living in the wild. Three tiger subspecies the Bali, Caspian, and Javan tigers have gone extinct in the past century. Many organizations are working hard to protect the remaining tigers from illegal hunting and habitat loss.
Articles & Profiles
Media credits.
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrators
Educator reviewer, last updated.
October 19, 2023
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

Essay on Natural Resources
Natural resources are the treasures that Mother Earth has bestowed upon us. They include water, air, soil, minerals, and all living things. In this essay, we will delve into the importance of these resources, their sustainable use, and the vital role they play in our lives and the health of our planet.
let’s talk about the importance of natural resources
Our lives depend on these resources more than we realize. For example, fresh water is essential for drinking, agriculture, and industry. According to statistics, 2.2 billion people lack access to safe drinking water, highlighting the critical need for its preservation.
Natural resources fuel our economy
Many industries, such as agriculture, mining, and forestry, rely on natural resources to thrive. Experts emphasize the importance of sustainable practices in these industries to ensure the long-term availability of resources.
Biodiversity is a natural resource
Our ecosystems, which include plants, animals, and microorganisms, provide us with food, medicine, and clean air. The loss of biodiversity can have devastating effects, as experts warn of the potential consequences for our health and well-being.
Natural resources support renewable energy
The sun, wind, and water are valuable sources of renewable energy that reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. By harnessing these resources, we can combat climate change and protect our environment.
Soil is a crucial natural resource
It is the foundation of agriculture, providing nutrients for crops. Soil erosion, often caused by unsustainable farming practices, threatens our ability to grow food. Sustainable farming is essential to protecting this vital resource.
The air we breathe is a natural resource
Clean air is essential for our health, and pollution poses a significant threat. Experts stress the importance of reducing emissions and protecting our atmosphere for future generations.
Minerals are essential for modern life.
They are used in everything from construction to technology. Mining, however, can have environmental impacts, making it crucial to balance resource extraction with conservation efforts.
Forests are a valuable natural resource
They provide habitat for wildlife, absorb carbon dioxide, and offer recreational opportunities. Sustainable forestry practices are necessary to ensure the health of our forests.
The oceans are rich natural resources.
They provide food and support biodiversity. However, overfishing and pollution endanger marine ecosystems. Experts call for responsible fishing and marine conservation efforts.
The importance of conserving natural resources cannot be overstated.
Sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and conserving energy, are crucial to protecting our environment. Every individual can make a difference by adopting eco-friendly habits.
Conclusion of Essay on Natural Resources
In conclusion, natural resources are the lifeblood of our planet, supporting our existence, economy, and well-being. It is our responsibility to use these resources wisely and sustainably, ensuring they are available for future generations. By valuing and conserving our natural resources, we can secure a brighter and healthier future for ourselves and the Earth we call home.
Also Check: List of 500+ Topics for Writing Essay

Essay on Natural Resources

Wealth of Nature
Natural resources, the abundant treasures bestowed upon our planet, encompass everything from air and water to minerals and biodiversity. These resources, essential for sustaining life, economic development, and environmental balance, face unprecedented threats. The unrelenting pace of exploitation and the onslaught of pollution have raised alarms about their depletion. Understanding their significance in driving economies, supporting ecosystems, and fostering life, exploring measures to conserve and sustainably manage these invaluable assets is imperative.

Classification of Natural Resources
Natural resources are typically classified into two main categories.
Watch our Demo Courses and Videos
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.
Renewable Resources
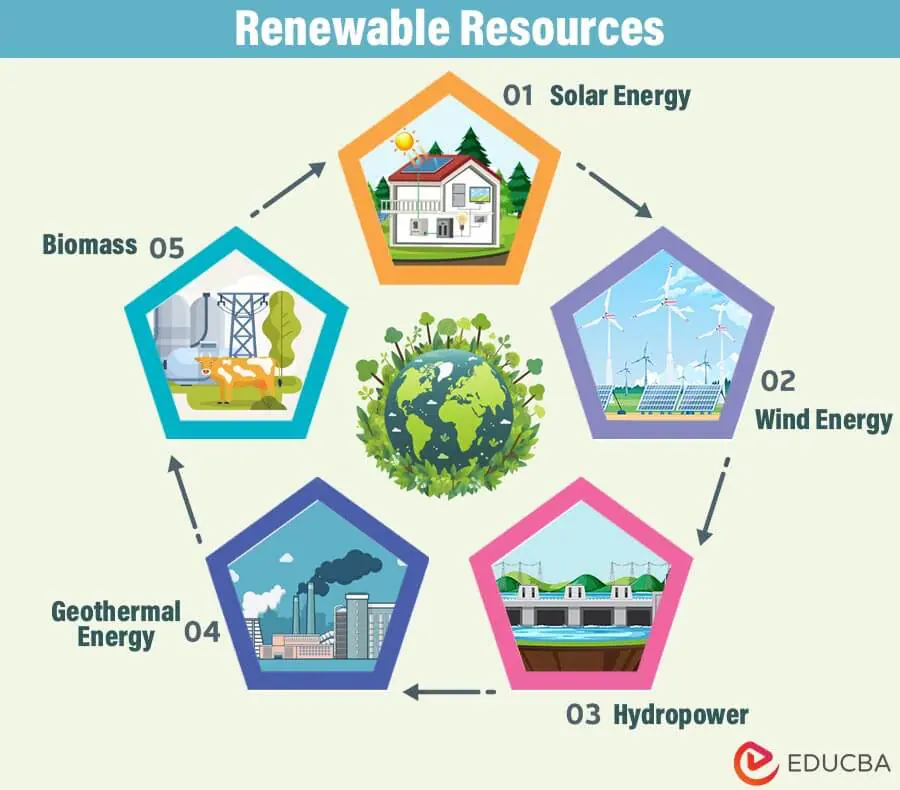
Renewable resources, also known as green or sustainable resources, are elements of the Earth that can be naturally replenished over relatively short periods. These resources are pivotal in sustaining life, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to non-renewable resources. Understanding the intricacies of renewable resources is crucial for adopting responsible and eco-friendly practices.
Let’s delve into the details of some key renewable resources:
1. Solar Energy:
- Source: Derived from the sun’s rays that radiate vast amounts of energy.
- Capture Technology: Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic cells, convert sunlight into electricity.
- Applications: Used for residential and commercial power generation, water heating, and space exploration.
- Advantages: Solar energy is abundant, clean, and widely distributed. It has a minimal environmental impact and reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
2. Wind Energy:
- Source: Energy harnessed from the movement of air masses on Earth.
- Capture Technology: Wind turbines convert kinetic energy from the wind into electrical power.
- Applications: Wind farms for electricity generation, both onshore and offshore.
- Advantages: Environmentally friendly, with no direct emissions. Wind energy reduces greenhouse gas emissions and lessens dependence on finite fossil fuels.
3. Hydropower:
- Source: Energy obtained from the gravitational force of flowing water.
- Capture Technology: Dams and turbines convert the kinetic energy of moving water into electricity.
- Applications: Large-scale hydropower plants for electricity generation and smaller-scale projects.
- Advantages: Dependable and Adaptable, offering a steady and regulated energy supply. Another source of sustainable energy is hydropower.
4. Biomass:
- Source: Organic materials such as wood, crop residues, and waste.
- Capture Technology: Biomass is burned or converted into biofuels to produce heat or electricity.
- Applications: Used for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. Biofuels are utilized as an alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
- Advantages: Biomass is carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide it absorbs during growth balances the carbon dioxide it releases during combustion.
5. Geothermal Energy:
- Source: Heat generated within the Earth’s interior.
- Capture Technology: Geothermal power plants convert heat from the Earth’s interior into electricity.
- Applications: Electricity generation and direct use for heating buildings or spas.
- Advantages: Geothermal energy is reliable and constant, with minimal environmental impact. It provides a continuous and sustainable source of power.
Non-renewable Resources
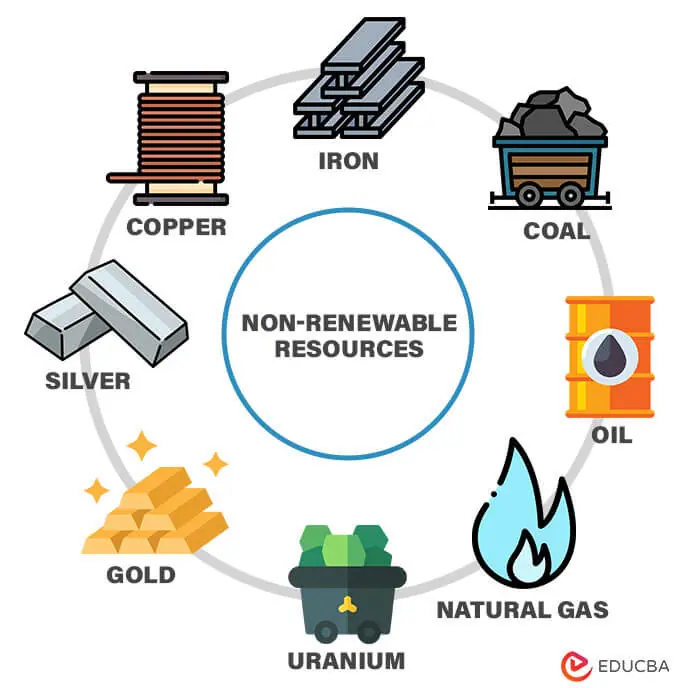
Non-renewable resources are Earth’s treasures with limited and finite availability, formed over geological timescales. Unlike renewable resources, non-renewable resources are not replenished on human timescales, and their extraction and utilization raise concerns about depletion, environmental impact, and sustainability.
Let’s explore some key non-renewable resources in detail:
1. Fossil Fuels:
- Types: Coal, oil (petroleum), and natural gas.
- Formation: Originated from ancient plant and animal remains buried and exposed to pressure and heat for millions of years.
- Extraction: Extracted through coal mining, oil drilling, and natural gas fracking.
- Applications: Used for electricity generation, transportation, heating, and various industrial processes.
- Challenges: Depletion concerns as extraction rates exceed natural replenishment. Fossil fuel combustion produces greenhouse gasses, which worsen air pollution and contribute to climate change.
2. Minerals and Metals:
- Types: Precious metals (gold, silver), base metals (copper, aluminum), and industrial minerals (iron, limestone).
- Formation: Result of geological processes and often extracted through mining.
- Applications: Used in construction, manufacturing, electronics, and various industries.
- Challenges: Limited availability and environmental impact associated with mining activities, including habitat disruption, soil erosion, and water pollution.
3. Nuclear Fuels:
- Type: Uranium, a radioactive metal.
- Formation: Mined from the Earth’s crust.
- Applications: Primary fuel for nuclear power plants, generating electricity through nuclear fission.
- Challenges: Limited uranium reserves, concerns about nuclear accidents, radioactive waste disposal, and nuclear proliferation.
The Importance of Natural Resources
Understanding the importance of natural resources is vital for promoting sustainable practices and ensuring the well-being of present and future generations.
- GDP Contribution: Natural resources are central to economic development, contributing significantly to nations’ Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Agriculture, forestry, mining, and energy extraction are pivotal for economic growth.
- Employment Opportunities: Many livelihoods are directly linked to natural resource extraction, processing, and utilization. From farmers cultivating crops to workers in mining operations, these resources provide employment opportunities worldwide.
- Energy Production: Important energy sources that power industrial processes, transportation, and electricity production include coal, oil, and natural gas. They have historically powered economic development and technological progress.
- Environmental Balance: Natural habitats and ecosystems are crucial for biodiversity, supporting various plant and animal species. Preserving these environments is essential for maintaining ecological balance and preventing species extinction.
- Agriculture and Food Security: Arable land, freshwater, and fertile soil are fundamental for agriculture. These resources support the cultivation of crops, ensuring food security for the global population.
- Industrial and Technological Advancements: Natural resources serve as raw materials for technological advancements, enabling the creation of new products, medicines, and materials.
Distribution of natural resources around the world
Geological, climatic, and biological variables influence the global distribution of natural resources. Here’s an overview of significant natural resources and their distribution:
Fossil Fuels:
- Oil: Concentrated in regions like the Middle East (Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Iran), Russia, Venezuela, and the United States.
- Natural Gas: Abundant in regions including Russia, the Middle East, the United States, Iran, and Qatar.
- Coal: Widely distributed, with significant reserves in the United States, Russia, China, India, and Australia.
Minerals and Metals:
- Iron Ore: Predominantly found in Australia, Brazil, China, India, and Russia.
- Copper: Major deposits in Chile, Peru, China, the United States, and the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Gold: Concentrated in countries like China, Russia, Australia, the United States, and Canada.
- Rare Earth Elements: China holds significant reserves, while other deposits exist in countries like Australia, Russia, and the United States.
Agricultural Resources:
- Arable Land: Unevenly distributed, with fertile regions in countries like the United States, India, Brazil, China, and Russia.
- Water Resources: Vary widely, with countries like Brazil, Russia, Canada, Indonesia, and China holding significant freshwater reserves.
- Key Crops: Production hubs vary—corn in the United States, wheat in Russia and the United States, rice in China and India, and soybeans in Brazil and the United States.
Forests and Timber:
- Tropical Forests: Concentrated in regions like the Amazon Basin (Brazil), Congo Basin (Central Africa), and Southeast Asia (Indonesia, Malaysia).
- Temperate Forests: Predominantly found in countries like Russia, Canada, the United States, and Scandinavia.
Renewable Energy Sources:
- Solar and Wind Energy: Available globally but often more viable in regions with abundant sunlight (deserts) or consistent wind patterns (coastal areas or plains).
- Hydropower: Concentrated in countries like China, Brazil, the United States, Canada, and Russia with ample rivers and suitable topography.
- Marine Resources: Abundant in coastal regions and oceans, with major fishing nations including China, Indonesia, Peru, India, and the United States.
Depletion of Natural Resources
Let’s delve into the ramifications of the depletion of natural resources:
Loss of Biodiversity:
- Habitat Destruction: Many ecosystems are lost due to agriculture, urbanization, and resource extraction from forests, marshes, and other natural habitats. This phenomenon contributes to the extinction of plant and animal species.
- Disruption of Ecological Balance: Depleting one component of an ecosystem can have cascading effects, affecting species that depend on the depleted resource and disrupting the intricate web of interdependencies.
Climate Change:
- Fossil Fuel Depletion: By releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, the exploitation and burning of fossil fuels contribute to climate change. Extreme weather events and the global warming dilemma are made worse by the depletion of these non-renewable resources.
- Deforestation: The depletion of forests reduces their capacity to sequester carbon dioxide, contributing to the greenhouse gas buildup in the atmosphere.
Water Scarcity:
- Over-extraction of Aquifers: Depleting groundwater resources through excessive pumping for agriculture and urban use leads to lowered water tables, increased salinity, and a decline in freshwater availability.
- River Depletion: Rivers can alter their natural flow patterns by dams and diversions for irrigation or hydropower, impacting aquatic ecosystems and communities dependent on these water sources.
Soil Degradation:
- Overfarming and Deforestation: Intensive agricultural practices, deforestation, and improper land management contribute to soil erosion, nutrient depletion, and loss of soil fertility.
- Desertification: Overexploitation of land in arid and semi-arid regions can lead to desertification, rendering once-productive land barren and unsuitable for agriculture.
Resource Conflict:
- Competition for Limited Resources: Depletion of resources, particularly non-renewable ones, can lead to heightened competition and conflicts between nations and communities vying for access to these finite assets.
- Social and Economic Disparities: The unequal distribution of natural resources can exacerbate social and economic disparities, leading to conflicts over resource ownership and access.
Economic Impact:
- Dependency on Non-renewable Resources: Economies heavily reliant on non-renewable resources may encounter difficulties as these resources become scarce, resulting in economic downturns and job losses.
- Disruption of Supply Chains: Depletion of key resources can disrupt global supply chains, affecting industries and markets dependent on these inputs.
Sustainable Practices for Natural Resource Management
Here are several key sustainable practices:
- Conservation and Preservation: Natural resources, including forests, water, soil, and wildlife, must be used and protected responsibly. Preservation seeks to protect ecosystems in their natural state and minimize human interference. Both strategies aim to maintain biodiversity, ecosystem services, and natural habitats.
- Sustainable Agriculture: Implementing agroecology, organic farming, crop rotation, and integrated pest management reduces reliance on harmful chemicals and promotes soil health, biodiversity, and long-term productivity. It also includes practices like precision farming that optimize resource use through data-driven approaches.
- Sustainable Forestry: Adopting sustainable logging practices, such as selective harvesting, reforestation, and reduced-impact logging, ensures the regeneration of forests while preserving biodiversity and ecosystem functions. Forest certification programs, like Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification, promote responsible forest management.
- Water Resource Management: Efficient water use through drip irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and water recycling minimizes waste and ensures adequate water supply for agriculture, industry, and communities. Watershed management approaches also protect water sources and maintain water quality.
- Waste Management and Recycling: Implementing waste reduction strategies and recycling programs and promoting the circular economy minimizes resource depletion, decreases pollution, and maximizes the value extracted from materials, reducing the need for virgin resources.
- Ecosystem-Based Approaches: Preserving and rejuvenating ecosystems like wetlands, mangroves, and coral reefs is vital for sustaining natural resources. This practice safeguards habitats, controls water flow, captures carbon, and fosters biodiversity.
Global Trends in Natural Resource Consumption
Global natural resource consumption trends show how people use Earth’s resources worldwide, driven by population growth, technology, and changing consumption. These trends significantly impact the environment, economies, and societies, making it essential to understand them.
- Population Growth: The ever-increasing global population directly influences resource demands. More people translate to higher needs for food, water, energy, shelter, and raw materials. This growth amplifies pressure on resources, particularly in regions experiencing rapid urbanization and industrialization.
- Industrialization and Technology: Advancements in technology and industrial processes have transformed resource extraction, manufacturing, and energy production. Technology enhances efficiency and intensifies resource consumption due to increased manufacturing, energy demands, and complex supply chains.
- Urbanization: The migration of populations from rural areas to cities leads to concentrated resource consumption. Urban areas require massive amounts of resources for infrastructure, housing, transportation, and services, significantly impacting local and global resource demands.
- Changing Consumption Patterns: Evolving lifestyles and consumer behaviors, often influenced by economic growth and cultural shifts, affect resource consumption. Shifts in dietary preferences, increased use of disposable goods, and a culture of rapid obsolescence contribute to resource depletion.
- Resource Intensive Industries: Certain sectors, such as agriculture, mining, and manufacturing, heavily rely on natural resources. Their expansion to meet growing demands exacerbates resource depletion, ecosystem degradation, and pollution.
- Global Trade and Supply Chains: Globalization has led to intricate networks of trade and supply chains, enabling resource sourcing from various regions. This interconnectedness magnifies the environmental footprint of resource extraction and transportation.
Initiatives taken by the government
Governments worldwide undertake various initiatives to address natural resource management and environmental challenges:
- Legislation and Policies: Governments enact laws and policies to regulate resource extraction, land use, pollution control, and conservation efforts. Examples include the Clean Air Act (US), the Water Framework Directive (EU), and the National Green Tribunal (India).
- Protected Areas: Governments establish and manage national parks, marine sanctuaries, and reserves to preserve biodiversity and critical habitats. Notable examples include the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park (Australia), Serengeti National Park (Tanzania), and Yellowstone National Park (US).
- International Agreements: Governments and the Convention on Biological Diversity enter international agreements like the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement to coordinate actions related to sustainable development, biodiversity conservation, and climate change mitigation.
- Investment in Renewable Energy: To lessen dependency on fossil fuels, governments promote renewable energy sources, including hydroelectric, wind, and solar power, through tax breaks, infrastructure development, and subsidies.
- Environmental Education and Awareness: Governments promote environmental education in schools, public awareness campaigns, and community engagement programs to foster a culture of sustainability and responsible resource management.
- Research and Innovation Funding: Governments allocate funds for research grants, technological innovations, and initiatives to develop sustainable practices, clean technologies, and conservation efforts.
- International Aid and Assistance: Governments provide aid and assistance to developing nations for capacity-building, technology transfer, and sustainable development projects related to natural resource management.
- Regulating Industries: Governments implement regulations and standards for industries regarding waste management, emissions, and sustainable practices to reduce environmental impact.
Case Studies
Here are a few detailed examples:
1. Costa Rica’s Conservation Efforts:
- Background: Agriculture and logging in the 20th century caused extensive deforestation in Costa Rica, posing a threat to its biodiversity and ecosystems.
- Initiatives: The country implemented policies focused on conservation and sustainable practices. It established a national park system, incentivized reforestation through payment for environmental services (PES), and promoted ecotourism.
- Results: The forest cover significantly increased as a result of these activities. By 2020, about 52% of the country’s land area was covered by forests, marking a reversal of deforestation trends. The emphasis on conservation also bolstered the tourism sector, contributing to economic growth.
2. Water Management in Singapore:
- Background: Singapore faced water scarcity due to its limited land area and dependence on neighboring countries for water supply.
- Initiatives: The nation invested in diverse water management strategies. These strategies include NEWater (recycled wastewater for drinking), desalination plants, and the development of reservoirs like Marina Barrage for water catchment.
- Results: Singapore achieved water self-sufficiency, reducing reliance on external sources. The innovative approaches to water management have made the country resilient to droughts and geopolitical uncertainties regarding water access.
3. Sustainable Fisheries in Iceland:
- Background: Overfishing threatened Iceland’s marine ecosystems and fishing industry.
- Initiatives: Iceland implemented a quota-based fisheries management system in the 1980s. It allocated quotas based on scientific assessments of fish stocks, promoted responsible fishing practices, and enforced strict regulations to prevent overfishing.
- Results: The fisheries management system led to the recovery of fish stocks and sustained the fishing industry. Iceland’s approach is lauded globally as a model for sustainable fisheries management.
4. Renewable Energy Transition in Germany:
- Background: Germany aimed to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and nuclear energy, transitioning towards renewable sources.
- Initiatives: The country implemented policies that encouraged the adoption of renewable energy, including the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), feed-in tariffs, and investments in solar, wind, and biomass energy.
- Results: Germany became a global leader in renewable energy production, with renewables contributing significantly to its energy mix. However, challenges related to grid infrastructure, costs, and intermittency persist.
5. Community-Based Conservation in Namibia:
- Background: Namibia faced threats to wildlife due to poaching and conflicts between communities and wildlife.
- Initiatives: Local communities were given the opportunity to manage wildlife and benefit from conservation-related activities, like ecotourism and sustainable hunting, through the establishment of community conservancies.
- Results: Community involvement reduced poaching, habitat preservation, and economic benefits for local populations. This approach empowered communities to become stewards of their natural resources.
The intricate tapestry of natural resources weaves the fabric of our existence. Urgent action is imperative to balance our insatiable demands with sustainable practices, ensuring a legacy of abundance for future generations. We can safeguard the Earth’s vitality by embracing conservation, sustainable technologies, and global cooperation. Our collective responsibility is to nurture and protect these invaluable resources, fostering a harmonious coexistence between humanity and the planet that sustains us.

*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Web Development & many more.
Forgot Password?
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy

Explore 1000+ varieties of Mock tests View more
Submit Next Question
🚀 Limited Time Offer! - 🎁 ENROLL NOW

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center

natural resource
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Open Washington Pressbooks - SFCC Introduction to Geography - Natural Resource Geography
- Social Science LibreTexts - Types of Natural Resources
- NeoK12 - Educational Videos and Games for School Kids - Natural Resource

natural resource , any biological, mineral , or aesthetic asset afforded by nature without human intervention that can be used for some form of benefit, whether material (economic) or immaterial. What is considered a “resource” (or, for that matter, “natural”) has varied over time and from one society to another. Examples of assets that can be considered natural resources include forests , surface water and groundwater , and the fertile lands or the soil and minerals within them (rather than the crops that grow on them), as well as energy resources (such as petroleum , natural gas , and heated water [that is, geothermal energy ]) contained within layers of rock .

The practice of natural resource management considers the ways in which societies manage the supply of or access to the natural resources upon which they rely for their survival and development. Under some definitions, only those natural resources that can renew themselves and whose exploitation relies on their regenerative capacities properly necessitate management. For example, petroleum (oil) is not usually considered a subject of natural resource management, whereas forests are. The management of renewable natural resources seeks to balance the demands of exploitation with a respect for regenerative capacities. In contrast, the use, regulation, and protection of nonrenewable resources tend to fall under the auspices of natural resources law , which is made up of a complex body of national and local laws that have both statutory and common-law components.
- About Project
- Testimonials
Business Management Ideas

Essay on Depletion of Natural Resources
List of essays on depletion of natural resources, essay on depletion of natural resources – 10 lines on the depletion of natural resources written in english (essay 1 – 150 words), essay on depletion of natural resources – short essay for children (essay 2 – 250 words), essay on depletion of natural resources – causes and prevention (essay 3 – 300 words), essay on depletion of natural resources – for school students (class 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12 standard) (essay 4 – 400 words), essay on depletion of natural resources (essay 5 – 500 words), essay on depletion of natural resources – causes and conservation (essay 6 – 600 words), essay on depletion of natural resources – for college and university students (essay 7 – 750 words).
- Essay on Depletion of Natural Resources – Long Essay for Competitive Exams like IAS, IPS, UPSC and Civil Services (Essay 8 – 1000 Words)
Audience: The below given essays are exclusively written for school students (Class 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12 Standard) and college students. Furthermore, those students preparing for competitive exams like IAS, IPS and UPSC can also increase their knowledge by studying these essays.
Depletion of natural resources will eventually lead to a world with lesser elements to survive and makes human life a hardship. Natural resources are the ones that maintain equilibrium in the environment and life.
Natural resources like air, water, solar energy, soil, minerals, coal, etc., are those basic elements that we, living beings, use to lead a normal life. Depletion of natural resources will completely stun the day to day life of a human being as well as fellow living things.
The depletion of natural resources occurs when we vigorously use the available ones at a rapid speed. Some of these non-renewable resources like coal, minerals, etc., take millions of years to form and thus their rapid use will result in depletion of these natural resources. Unsustainable use of these natural resources due to the demand and increase in population has also resulted in depletion of natural resources.
Switching to the renewable sources is one of the many ways to save natural resources from depletion. In order to save this depletion of natural resources, we humans should find out and execute more sustainable and nonpolluting ways to use these natural resources.
Introduction:
Natural resources are provided by Mother Nature to enable the survival of living things and the sustenance of the ecosystem. Depletion of natural resources is the increased consumption of resources that overlaps the replenishment of those resources. The depletion of natural resources occurs due to significant increase in the dependents of the natural resources without an increase in the sources of resources. It can be a devastating problem to the ecosystem because the resources necessary for survival and depletion will cause significant loss of living things
Causes of Depletion of Natural Resources:
Increased population of species that are dependent on the same natural resources cause faster consumption of those resources and results in depletion. The other cause is unnecessary consumption of resources and wastefulness.
Environmental pollution also causes depletion of natural resources through contamination. When natural resources are contaminated, they will be no longer fit for consumption. Deforestation is a major cause of depletion of natural resources. Deforestation results in loss of habitat, food and destruction of the ecosystem. Drought is brought about by deforestation. Drought is an extreme of depletion of water in the environment.
Consequences of Depletion of Natural Resources:
There will be a loss of biodiversity due to death and extinction of living organisms. Natural disasters like drought will also occur upon depletion of natural resources.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the depletion of natural resources is a serious concern because of the adverse effects it has on the ecosystem. Controlled consumption of resources is to be encouraged.
Depletion of natural resources is undoubtedly the product of massive urbanization and industrialization. It occurs due to the continuous, extensive, and irresponsible use by humans disregarding future consequences.
What are the causes of depletion of natural resources?
1. As the earth population exceeds 7 billion, the overpopulation is one of the significant reasons for depletion of natural resources.
2. Wastage and overconsumption tend to contribute to the reasons why natural resources will exhaust in the future.
3. Deforestation leads to the destruction of the earth’s ecosystem, one of the critical reasons for the depletion of natural resources.
4. Mining of minerals and oils also account for resource depletion.
5. Erosion, pollution, and contamination of resources sum up why natural resources will be scarce shortly.
What are the natural resources that might get depleted in the future?
The following natural resources might get a hit and will get exhausted in the near future if we continue to exploit it without any consideration for the future generation and existence of the planet earth.
Water, the essential natural resources will be at stake after 2025, as scientists apprehend that almost 1.8 billion people will have no water to drink. Although the earth’s crust is covered with 70% water, only 2.5 % is drinkable as it comes from the ice-capped mountains and streams while the rest are saline water containing wastes.
Although it’s one of the most important natural resources we have, scientists predict that the available coal deposit will be able to meet the world’s requirement for just another 188 years. With that said, if the demand increases, this timeframe will squeeze.
The present hydrocarbon content of the world, 188 million tonnes is enough to meet the demand but only up to the next 46 years. When the stock finishes, transportation will be hampered.
4. Natural Gas:
The reserve of natural gas will serve till the next 58.6 years which is not enough to meet the world’s demand.
5. Seafood:
Fishermen report that the catch they depend upon for their living is gradually decreasing. If not cultured naturally, some stock of seafood will actually diminish soon.
How to prevent the depletion of natural resources?
Well, the answer is embracing a nature-friendly lifestyle and shifting to renewable and sustainable energy resources like solar power, wind, and hydropower, we can at least slow down the depletion of natural resources.
Depletion of natural resources can be described as a situation where natural resources are consumed faster than they can be replaced or replenished. Natural resources are not always available in infinite quantity. Though they are replaceable, this process takes a long time.
For instance, it takes hundreds of years to replace crude oil reserves. It also takes many years to grow a tree into maturity. The important question now becomes – are we consuming these resources at the same rate at which we use them? The answer to that is definitely negative.
Though natural resources can be renewable and nonrenewable, depletion of natural resources affects both.
The causes of depletion of natural resources could sometimes be man-made and in other cases, unavoidable. We would, however, concern ourselves with only the man-made causes of natural resources depletion.
The following are some of the apparent causes of depletion of natural resources:
1. Overpopulation:
This is a situation whereby the number of people living in a place falls below the number of resources available in that community. The implication is that natural resources get consumed faster than they can be produced.
2. Deforestation:
One might be quick to assume that deforestation only affects trees. This is however far from the truth. Deforestation reduces animal life expectancy and more importantly, it destroys our ecosystem thereby affecting other natural resources.
3. Pollution:
Pollution of various kinds damages natural resources making it difficult for the resources to be produced in good condition. For instance, soil pollution affects plant life making it difficult for trees to grow.
Though we extract natural resources from the ground through mining for human consumption. Every time we get something from the ground, we hasten up the depletion process.
Prevention of Depletion of Natural Resources
Below are some of the efforts that can help curb the excesses of natural resources depletion.
1. Protecting The Trees – This involves several coordinated efforts aimed at reducing the number of tree cutting. It includes sensitizing the populace about the dangers of tree cutting and encouraging them to plant more trees.
2. Recycle – Recycling reduces waste and also reduces the number of toxic materials in our land water and air. Less toxicity leads to less depletion.
3. Reduce the consumption of fossil fuel products.
Depletion of natural resources affects everyone. The food we eat, the water we drink, the fuel we consume all comes from the natural resources. If we lose these resources life becomes difficult for everyone. So we need to be cautious and promote sustainable use of natural resources.
In ancient times, people used energy only for daily activities, such as lighting, guarding, and cooking. But as the development took place, in terms of industrial revolution and urbanization, animals were domesticated for household and farming activities and later as the industrial revolution took place, humans used a lot of power drawn from the natural resources. Initially, it was thought that the natural resources are found generally in abundance but of late, it is found that the availability of natural resources are depleting in quantity and can’t be replenished quickly. This is precisely the depletion of natural resources.
Depletion of Natural Resources:
Earth has two types of natural resources, those that can be replenished despite continuous usage like sunlight, tidal energy, etc. These are renewable resources of energy and those that can’t be replenished are called non – renewable resources. Explosive growth in the human population had led to population overconsumption. Humans’ activities have harmed the nature to that extent that now nature cannot replenish the resources at the rate of the resources being consumed. This leads to the depletion of natural resources.
The major causes of depletion of natural resources are:
1. Population explosion – The increased growth of population demand supply of energy and resources for their survival. The demand for energy supply is taken care of by the natural resources and the technologies invented to harness the natural resources’ benefits. To quench the demand, natural resources are depleted.
2. Environmental pollution – Extensive activities on earth by humans have caused polluted environment. The production of uncountable pollutants by us not only makes the environment hazardous, but also the pollution of various natural resources like air, water, soil, and land, thereby leading to the depletion of natural resources available in the environment.
3. Deforestation – The forest is a rich habitat and the powerhouse of the earth’s ecosystem. The industrial revolution and urbanization by clearing the forested areas deplete the biological resources of the earth.
4. Population over consumption – The demand of resources for a population becomes higher than it actually requires. This is because the human population uses resources and energy as a desired demand commodity to live a very sophisticated life.
5. Natural calamities –Calamities like Tsunami, storms, earthquake deplete a whole lot of natural resources. Fortunately or unfortunately, this is the only cause that humans have no control on, to save the resources from depletion.
6. Climatic change – Global warming is a phenomenon that the environmentalists are talking about. Global warming brings about changes in the climatic cycle which can’t be tolerated by the biological species in the environment. This alters the survivability of various species and leads to extinction of many threatened or near-threatened species.
Prevention of Depletion of Natural Resources:
It has become evidently clear that we are facing a threat in terms of natural resources. With the current higher rate of depletion of the natural resources, it is feared that in a few years, we may not have resources to be utilized for our survival. We must know that nature has its own balancing concept. But as we have been continuously abusing nature, a serious imbalance is in effect.
We must be responsible to take up the arduous task of conserving the natural resources. Planting trees, minimizing energy wastage, conserving water and avoiding the wastage of water, conserving electricity at home and workplace, use of alternative and cleaner energy, replacement of the extraneous energy using equipment with eco–friendly and efficient energy conserving gadgets and equipment, are few steps that we can start doing at local levels to prevent and conserve the natural resources from depletion.
As we understand that the depletion of natural resources is a very serious concern in terms of human survival and environmental sustainability, it’s high time that we take necessary steps to avoid the natural resources from depletion.
Natural Resources:
Depletion of natural resources is the cause of serious concern for the world. Natural resources, as the name suggests, are the materials and sources of energy which are found naturally on earth. There are two major types of natural resources.
The first one is known as the non-renewable or conventional sources of energy. Depletion of natural resources is applicable to this category. Examples are coal, oil, petroleum, minerals, etc. Whereas the second type of natural resources is renewable or nonconventional. The depletion of natural resources in this category is not possible. These include solar energy, wind, energy, hydro power, etc. Both have their own benefits but since the beginning, an excessive dependency and consumption of the non-renewable resources have led to the depletion of natural resources.
Our earth takes years to produce fossil fuels such as coals, oils, petroleum etc. But the exhaustion has happened at a rapid rate. As a result of this depletion of natural resources, we are now falling short of these reserves of energy.
Depletion of natural resources has befallen us for a number of reasons. And when we talk about the depletion of natural resources, it also includes the shrinking of forest areas and vegetation. The biggest cause of depletion of natural resources is industrialization.
Lots of trees are cut to make space for setting up the industries. Industries also consume a lot of coals, oils, and other fossil fuels, adding further to the depletion of natural resources. The humongous growth of human population has direct and indirect roles in the depletion of natural resources.
Large portions of land are required to build houses and other amenities for the people. And to feel the population, farmers often end up clearing the forests for growing crops there. This replacement of vegetation with crop fields is another cause of depletion of natural resources.
Implications of Depletion of Natural Resources:
Deforestation alone means various kinds of depletion of natural resources. For instance, soil erosion is a consequence of it, causing floods, drought, and landslides. Shrinking greenery poses a threat to the wildlife and leads to their extinction.
Depletion of natural resources expands to oceans and seas also. Drilling of ocean beds for oils and other fossil fuels interferes with the functioning of marine life. Moreover, excessive use of coals, petroleum, and mineral oils, has created enormous pollution over the years.
The pollution touches its peak by making a hole in the protective ozone layer of the earth. The depletion of natural resources is an indication that we have badly exhausted and exploited the earth’s surface and stripped of its valuable stores.
Conservation of Natural Resources:
The severe depletion of natural resources has brought to us a point where it has become necessary for us to come up with some long-term and effective measures to nourish back our planet. Shifting to the consumption of renewable and green sources of energy is one such step.
By controlling the pollution and putting a check on our reckless and toxic ways of life would significantly curb further depletion of natural resources. Every one of us should plant trees and make the earth healthier.
Some simple measures can have a huge impact on the current situation of mother earth. By reducing the wastage, reusing the day to day things, and recycling the biodegradable materials, we can save our planet from dying.
Human beings are dependent on nature, but nature is not dependent on humankind. It is the right time to pay back to nature what we have harnessed from it for millions of years.
Depletion of natural resources has long been a concern for people as well as the governments all over the world. Natural resources are vital for our survival. However, there has been a steady decline in the availability of natural resources for human use over the last decade.
There are many causes which have led to the depletion in natural resources. First and foremost is the increase in human population. With an ever-increasing population, the demand for natural resources has also increased substantially. This has led to excess usage of natural resources than the speed at which they are replenished in nature.
Mining is another human activity which has led to depletion of natural resources. We have been suing mining techniques to extract various metals, fossil fuels and other minerals from the earth. But, we have been indifferent of the thought as to how much should we extract in a given period. With hardly any monitoring in place by the government, illegal mining has been on the rise. This has led to over-extraction of the natural resources, thereby depleting them. Although laws are in place to catch and punish the offenders, the execution of the same is still a challenge for the government.
Another important factor which has led to the depletion of natural resources is the increase in pollution levels in air, water and land. The waters of the rivers are so polluted now that they cannot be used for various purposes such as drinking and bathing. So, although the resource is available, we are not in a position to use it for our own use. Additionally, pollution levels in water, air and land have made it difficult for the survival of others species as well which are important to maintain balance in the ecosystem.
The effects of depletion of natural resources are all but harmful for the life on the earth. Depletion of natural resources has altered the ecosystem of the earth. Change of climatic conditions has been noticed over the last decade. Many species have become extinct because they were not able to adapt themselves to the changing environment.
Additionally, it has also led to global warming. There has been a constant increase in the average temperature of the earth. This, in turn, poses a threat to the coastal regions of the world as the water levels have been rising up steadily.
Due to change in climatic conditions, there have been altered patterns of rains in different regions affecting the yield of crops. This has led to price rise as the demand is more than what is being produced in the fields. Also, India is a country where half of the population is dependent on agriculture. Damage of crops has affected the farmers and there has been an increase in farmer suicides as well.
Remedies Available:
There are plenty of natural resources available to us. We put them to use as per our own requirements. For instance, we use fossil fuels such as coal and petroleum to generate electricity, drive vehicles; we use water to rotate turbines in a hydropower station. Similarly, we use sunlight as well to some extent to trap and the solar energy and generate electricity. Depletion of natural resources is actually a concern only for the resources which cannot be replenished easily, for example, coal and petroleum.
On the other hand, resources such as wind and sunlight are available in plenty and shall not be exhausted no matter how much we use them. This is the key to our remedy to minimise the depletion of natural resources. We should switch over to the resources which can easily be replenished. On the other hand, we should minimise the use of fossil fuels.
It is true that there would be no life on earth if we do have the natural resources available to us. However, at the same time, it is also true that it is we who have to ensure that we utilise the resources carefully. Depletion of natural resources is surely an environmental concern that we all should be serious about. There was a time when we switched from cleaner to fossil fuels. Now is the time perhaps to go back in history and rewind our life.
We should think of the solutions available to us such switching to cleaner resources which can easily be replenished in nature. Moreover, the use of resources such as fossil fuels which are on the verge of extinction should be minimised. But, execution of the same is not an easy task. Only a collective effort of people, as well as governments all over the world, can perhaps save the earth and reduce the depletion of natural resources.
Essay on Depletion of Natural Resources – Long Essay for Competitive Exams like IAS, IPS, UPSC and Civil Services (Essay 8 – 100 0 Words)
Depletion of natural resources can be said to be the consumption and use of a particular natural resource a lot faster than the rate of replenishment of the natural resources. We can commonly divide natural resources into non-renewable resources and renewable resources. Anytime either one of the two forms of natural resources is used beyond the rate of their replacement; we can consider it to be the depletion of natural resources. Natural resources depletion usually occurs in reference to fossil fuels consumption, water usage, mining, fishing and farming. Defaunation is a term that is used to describe the depletion of the populations of wildlife.
Causes of the Depletion of Natural Resources:
1. Soil erosion
2. Agricultural practices like slash and burn
3. Contamination and pollution if resources
4. Overpopulation
5. Unnecessary, excessive or overconsumption resources use
6. Mining for minerals and fossil fuels
7. Deforestation
8. Aquifer depletion
Depletion of Minerals:
We need minerals to help provide us with housing, clothing and food. A study carried out by the geological survey of the United States discovered a trend that is long-term during the nineteenth century on resources that are non-renewable like minerals that supply greater ratio of all the raw materials put into the non-food, non-fuel economy sector. A good example can be said to be the increased consumption of gravel, sand and crushed stone that are employed in construction.
Mineral exploitation on a large scale started during the period of industrial revolution in England around 1760 and it has rapidly grown since then. Advancements in technology have made it easier for humans to access grades that are lower and dig deeper with various forms of ore. All forms of industrial basic metals like bauxite, iron and copper and also minerals of rare earth usually encounter limitation in production output periodically.
Some minerals that are believed to start declining in production in twenty years include:
ii. Copper (2024)
iii. Gasoline (2023)
Some minerals that are believed to start declining in production in this century include:
i. Iron (2068)
ii. Coal (2060)
iii. Aluminium (2057)
Depletion of Oil:
Peak oil period is believed to be the particular period in time when we reach the rate that is the maximum for the extraction of petroleum globally. After the peak oil period, the theory of peak oil posits that there will be a decline in the long term of the production rate of oil. A report in 2005 by Hirsch put forward that the prices of predictions that are petroleum derived will increase significantly all over the world as a result of the combination of decreased supply and increased demand, and the most significant one is going to be the price and availability of fuel that is liquid for transportation.
It was concluded by the report that there is going to be a problem of risk management that is unprecedented as a result of the oil production of the world that is peaking. There will be a sharp increase in the prices of fuel that is liquid and there will be volatility in the price. If there is no timely mitigation, there will be unprecedented political, social and economic costs.
Deforestation:
Deforestation can be said to be the process of forest clearing through the burning or cutting of plants and trees that are in an area that is forested. Deforestation has led to the destruction of about half of all of the areas of forests that at one point in time covered the earth. Deforestation happens as a result of a variety of reasons and there are a lot of negative effects of deforestation on our atmosphere and also on the quality land surrounding and in the forested area.
Causes of Deforestation:
One major cause of deforestation can be said to be the clearing of forests for reasons that are agricultural. With the increase in the population of areas that are developing especially those that are near the forests, there is usually more need of lands that are needed for farming. A lot of people usually see the forest as being without value just because the resources of the forest are not in use, for people like this; the profits of deforesting usually outweigh the profits of keeping the forest. As a result of this, it is of utmost importance that developing countries know the value of forests economically.
Depletion of Water:
A vital resource that we need in order to survive each day in life is water. Studies have shown that man can only last about a week if he does not take any water at all. The success and prosperity of people and nations historically has depended heavily on the availability of water. One type of water source that is a resource that is non-renewable is groundwater. Groundwater is about 98% of the fresh water that is available on the earth.
Groundwater can be used in supplying aquifers and wells for public, agricultural and private use. Only about 6% of all the groundwater is replenished about every fifty years.
Renewable Natural Resources:
We can get renewable energy from renewable natural resources. We have two major sources of energy that is renewable which are wind power and solar energy. A lot of research is ongoing on how we can get different alternatives that can replace the depletion of resources that are non-renewable.
We have a lot of major causes and things that give rise to the depletion of natural resources in our planet earth. We are beginning to really see that depletion of natural resources is a thing and there is the need for us to be careful about our consumption of these natural resources.
There is a need for us to learn how to find a balance between resources preservation and economic development. If we fail to do this and exhaust all of our natural resources, there would not be any more natural resources for us to exploit and use to meet all of our needs.
Depletion , Natural Resources
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
Like this post? Don’t forget to share it!
Here are a few recommended articles for you to read next:
- Essay on Natural Resources
- Essay on My School
- Essay on Solar Energy
- Essay on Biodiversity
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life
Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Conservation of Natural Resources Essay

Essay On Conservation of Natural Resource
Natural resources are the resources that occur naturally on Earth. It is an indispensable part of our lives. Natural resources consist of air, water, sunlight, coal, petroleum, natural gas, fossil fuels, oil, etc. However, humans have exploited these resources for their economic gains. Over usage of natural resources has caused depletion resulting in a huge impending threat to the existence of the human race. Conservation of nature means taking care and protecting these resources like forests, water bodies, natural gases, minerals, and fuels so that they continue to be available in abundance.
Long Essay On Conservation of Natural Resource
Conservation of nature means taking care and protecting these resources like forests, water bodies, natural gases, minerals, and fuels so that they continue to be available in abundance. Conservation refers to saving the resources for the use of the upcoming generation. There are enough natural resources which nature has provided to us. It is our duty to save them for our successors. For saving these natural resources we have to gain enough knowledge about that and should work in that direction.
Natural resources are categorized into renewable and non-renewable. Renewable resources can be replenished naturally. These include air, water, and sunlight. Non-renewable resources consist of coal, natural gas, and oil. These resources cannot be replenished by natural resources easily to keep up with consumption. It takes hundreds of years to recycle these resources. The usage of natural resources has been pivotal for the evolution of mankind. But his progress and development have led to the exploitation of these natural resources. This demands a responsible behavior of conserving the resources to ensure sustainability .If we do not use these resources judiciously then it can create an imbalance in the environment. Global warming, floods, climate change, famine, and drought are some of the consequences we will have to face in the future. So, conservation of natural resources has become the need of the hour.
Water is the most important and valuable natural resource on Earth. It sustains all life. We use water for drinking, generating electricity, in agriculture for irrigation of crops, in many industries for manufacturing processes. Scarcity of water would cause loss of vegetation and to all plant life, erosion of soil. Forests determine natural vegetation for mankind. It is the major natural resource that helps in economic development. Their use in fuel, timber, and industrial raw material cannot be undermined. Moreover, forests help in the control of soil erosion and control floods
Fossil fuel is the most important natural commodity for everyday activities. Coal, oil, and natural gas produce a lot of energy. Governments and agencies of various countries are employing different measures to conserve nature. Children should be educated about the implications of the exploitation of the environment. Recycling and reusing of water will help reduce the rate of depletion of freshwater from the planet. Farmers must use modern techniques in agriculture like sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation, dry farming, and rotational grazing, to save water. They should start the practice of rainwater harvesting. Conservation of natural resources is the need of the present and it is our duty to conserve them.
Alternative resources or renewable resources like solar energy or water energy should be used. Saving electricity can be a step to conserve natural resources such as water, coal, natural gases, and biomass. Basic practices like switching off fans, lights, geysers, and air conditioners must become a habit. The use of solar-powered lights and cars, using public transport, and regular car-pooling will reduce the depletion of coal, oil, and gas. Increase the use of biogas and biofuels. Paper is made from wood, which is a renewable natural source. Trees are being cut at a very high speed but take time to grow. To reduce the usage of paper, modern technology must be used. This will help in reducing the carbon footprint in the atmosphere. We must plant more and more trees to prevent deforestation.
Dumping of industrial wastes into water bodies must be prevented to protect marine life. The practice of crop rotation techniques can be implemented to increase soil fertility. Burning fossil fuel emits a large amount of carbon dioxide that is responsible for the greenhouse effect. This must be controlled. It is important to realize that natural resources are limited and it is our social responsibility to protect and take care of nature. We need to rationally use these natural resources to maintain the environment and secure our future. Farmers must use modern techniques in agriculture like sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation, dry farming, and rotational grazing, to save water. They should start the practice of rainwater harvesting.
What is Biodiversity Conservation?
Biodiversity refers generally to the richness of organisms. It can be defined as the variability of the species in a particular area. The conservation of biodiversity is essential for the balance of nature. We can divide conservation into two types based on their site of conservation.
These types are :
In situ Conservation
Ex-situ conservation
There are different types of conservation in environmental science. These are classified under two categories which are mentioned here. In- situ is generally a Latin word. In means inside and ex means outside. In situ is a type of conservation in which we conserve any of the species in its home itself. While ex situ refers to the type of conservation in which we conserve any of the species out of its residence.
In-Situ Conservation
In in-situ conservation, we conserve any of the particular species in their natural habitat. It can also be called on-site conservation of genetic resources. It has various advantages over ex-situ conservation. It does not require any advanced technology for conservation. As we are storing any of the species into its natural habitat, it is also cost-effective. Moreover, scientific research is also possible in an in-situ environment. It is also easily adaptable. Wildlife sanctuaries and national parks are some examples of in-situ conservation.
Ex-Situ Conservation
Ex-situ conservation is when we conserve any of the species out of the site of his residence. In other terms, it is the mode of conservation in which we conserve any particular species out of its habitat. It helps to rescue the threatened species. In an ex-situ conservation, we can send a particular species to that area where proper natural resources are available for its conservation. Zoo, aquarium, zoological gardens, and botanical gardens are some examples of ex-situ conservation.
The advantages of ex-situ conversions is that it is an efficient way to increase the reproduction of threatened species and requires low maintenance.
Conservation of natural resources is the need of the future generation. It is our duty to conserve them for the future. Conservation of biodiversity is the most essential for the upcoming generations. It is important to conserve natural resources to maintain the ecosystem and sustainability of these resources for our future generation. Sustainable development is a theory which states that we should use our resources in such a way that it can also be conserved for our successors.

FAQs on Conservation of Natural Resources Essay
1. What are the types of Natural Resources?
There are two types of natural resources - Renewable resources and non-renewable resources. Renewable sources of energy are those which are inexhaustible in nature and keep producing more and more. Renewable sources of energy are present in nature with enough concentration . Other than renewable resources, non renewable sources of energy are present in limited quantities in nature and can end up due to their overuse.
2. Why is it important to conserve natural resources?
It is important to conserve natural resources to maintain the ecosystem and sustainability of these resources for our future generation. The concept of sustainable development is that we use our resources taking care of future generations. Using the resources in a sustainable manner can conserve the resources for our upcoming generations. For ecological balance , it is necessary that we keep balance in the nature of resources. As the natural resources are present in nature in limited quantities, their conservation is necessary.
3. How do we reduce the consumption of fuel?
Use of solar powered cars, public transport, car-pooling, maintenance of vehicles periodically can reduce the consumption of fuel. We can also try non- conventional sources of energy. For example, we can produce electricity by hydropower plants and wind energy plants. Using non conventional sources of energy will reduce our dependence on fossil- fuels. Now, most of the countries are committing zero carbon emission and so implementation of new techniques for energy production becomes necessary in today's world.
4. What modern techniques should farmers adopt to save water?
To save water, farmers should practice modern techniques like sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation, rotational grazing, dry farming and rain water harvesting. These techniques not only reduce the water consumption but also are more effective for farming. Water harvesting is also one of the most effective techniques for saving water. It also fulfills our goal to attain sustainable development. Especially, in the areas of water shortage, water harvesting techniques can be very useful for farmers to grow the crop of their choice.
5. What are differences between in-situ and ex-situ conservation ?
In - situ conservation refers to the conservation of various species inside their own natural habitat. While , ex situ conservation involves the conservation of species outside of their habitat. In situ conservation requires less technological advancements and is more effective in increasing population of species. While, ex situ conservation involves less maintenance. Wildlife sanctuaries and national parks are examples of in-situ conservation, while aquarium and zoological parks are examples of ex-situ conservation.
You can read on various topics about environmental science on Vedantu platform and also can download PDF.

Essay on Natural Resources
Natural resources and its importance for human life is an important issue for people on earth. Now it is necessary to have knowledge about the need and importance of natural resources as well as spread complete awareness by focusing on its hazardous effects due to the unavailability of these resources. We have provided here some essays on natural resources with detailed knowledgeable information. Essays are divided in two categories; long and short essay on natural resources.
Sample Essay on Natural Resources for Students
Essay 1 (400 words).
Natural resources are those precious gifts for us that are much important for living on this earth. These are air, water, land, trees, wood, soil, minerals, petroleum, metals and sunshine. These resources cannot be created or produced by human being but just can be modified in different manner so that we can use it in better way.
Types of Resources:
Natural resources are mainly divided in two types of categories, these are: Renewal Resources and Non Renewal resources
- Renewal Resources: Renewal resources are those resources which can be regained and reformed after consumption like water, air, sunlight, land, wood, soil, plants and animals. Some are limited in quantity; these are water, plants, animals and fresh air. Without making managed system of consuming these renewal resources we would not be able to get it back in future for the use of our coming generations.
- Non renewal resources: Natural resources that cannot be reproduced and are available in fixed amount on earth are referred as Non Renewal resources. On the earth, they are found below the land like minerals, metals, petroleum and coal. All these are in limited stock and very useful and important for living life.
Different resources are used for different purposes:
- Air is used for wind energy.
- Water is used for drinking and producing hydroelectric energy.
- Plants and trees give us vegetables, fruits, cotton, wood and by using wood we can make paper, furniture and house too.
- Animals give us milk and their skin is used for making lather clothes, shoes, purses, belts, etc.
- Sunlight is used for making us warm and produces solar energy.
- Oil is used as fuel for transportation and electricity.
- Minerals and metals are used for making coins, steel, and jewelry.
- Coal is used to make electricity.
Conclusion:
Natural resources are too much essential for survival on this earth. Without them we cannot imagine our human life. All resources are either directly or indirectly connected with others.
Some resources are produced from other resources for example oxygen and wood are produced by plants and trees; energy can be produced from wind, water and sunlight in different forms. Various secrets of natural resources are still hidden behind the nature and the earth. No one can get the actual source of it. We should follow preservation method for using these resources in such manner that they could always be available for us in future for many centuries coming ahead.
Essay 2 (600 words)
Introduction
Resources obtained from nature are called natural resources and are very essential for survival on earth for human being. Natural resources are air, water, sunlight, forest, land, rock, soil, petroleum, metal and minerals. Land, sunlight, wind and rock have unlimited availability on the earth.
Apart from these resources, other natural resources are divided in two categories:
- Renewal Resources: Renewal resources are those which can be reproduced and regenerated by the efforts of people and some kind of extra care. These resources are plants, fresh air, water, land and animals.
- Non Renewal Resources: Non renewal resources are those which are limited in quantity and never be regained either from earth or by human efforts. These resources are petroleum, coal, minerals and metals.
Apart from these two categories of natural resources, other categories are also defined to differentiate Natural Resources:
Biotic and abiotic resources:
- Biotic resources : These resources are those natural resources which are obtained from global system and have life-like plants, trees and animals.
- Abiotic resources : These resources are those natural resources which are non living like, air, water, land, soil, minerals and metals.
This whole world or universe depends on natural resources in different manner. A human life cannot be imagined or possible without these resources. Different resources have their individual importance in a human life like we need oxygen in air for taking breath and only trees produce oxygen by taking carbon dioxide from air. Sunlight gives us heat that is must for our daily requirements.
Plants require land, soil and water to grow and changes in form of fruitful trees. Tree gives us fresh air, fruits, vegetables, wood, etc. By using wood we make paper and different types of furniture. Water is most essential resource after oxygen for human being. Water animals like fish is used to fulfil starvation of many people and other big water animals.
Other natural resources like petroleum, minerals, coal, etc are used for different types of purposes. Different types of energy can be produced by different resources like solar energy can be produced by sun light, hydro electric energy is produced by using water, wind energy is produced by wind, electricity is produced by coal and water is boiled by burning coal to produce electricity.
Minerals and metals are found deep under the ground and used to make coins, gold, steel and many other things that are needed for our daily routine life. Petroleum, the essential resource given by nature is refined and converted into fuel for transportation.
Availability of Natural resources:
Some of these resources are available on the earth since ancient time even from starting of the civilization like air, water, sunlight, land, plants and animals. Rest resources like metals, minerals, coal and petroleum are found due to the efforts of human after civilization. Different types of energy, wood, cotton cloths, leather materials and expensive ornaments were developed using technologies by human as per the need.
Some non renewal resources are very limited and rarely found on this earth like petroleum and metals, some specific places are reserved on earth from where these resources are obtained. In India, around hundred types of minerals are produced at different places which are very important for financial profits at national level, as we export these minerals to other countries and import some other minerals which are not found in India. In case of petroleum, each country has its different percentage of production of petroleum and do import or export of petroleum according to their consumption need.
Effects of destroying natural resources:
Resources that are found in a natural form and are not produced by human being are natural resources. Use and consumption of these resources matters a lot for future of human life. In current situation forest are left in very few quantities because of the increased population (people cut trees to get wood, paper and land for making building over there).
Animals are also killed for the personal need of human-like enjoying food and making leather goods from skin of different animals. If we still do not understand the importance of forests and animals, result will be hazardous for all. Without fresh air and water, human life will be impossible in future. Thus, to avoid this critical situation, we need to grow plants and limit our consumption of resources like water, electricity, oil, etc.
Related Information:
10 Lines on Natural Resources
More Information:
10 Lines on Conservation of Natural Resources
10 Lines on Natural Resource Depletion
Related Posts
Essay on tiger, essay on books, essay on good manners, essay on time is money, essay on fashion, essay on generation gap, essay on unemployment, essay on necessity is the mother of invention, essay on union is strength, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Essay on Natural Resources For Students and Children in 1000 Words
In this article you will read an essay on natural resources for students and children in 1000 words. It includes types, classification, importance, effects and conservation of natural reaources.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Natural Resources
Do we all care about our natural resources? The answer is no. As long as pollution and other environmental problems don’t get worse, these things might run out.
What are Natural Resources?
Without things like air, sunlight, and water, life on our planet would be impossible.Other natural resources are just as important and have become an important part of our lives, too.
Types of Natural resources
1. renewable natural resources.
An animal is a renewable natural resource, too, because it can be bred and bred so that it can be replaced by a new animal when it gets older.
2. Non-renewable natural resources
Minerals are classified as non-renewable because, although they are naturally formed in the rock cycle, the periods of their formation last for thousands of years. It’s the same with some animals, mostly endangered species, because they’re close to extinction and can’t be replaced.
3. Natural resources as stock
Air: Air is used to generate wind energy. Windmills are used to make them and apply them for a variety of purposes, such as pumping water, grinding grain, etc.
Coal: This is another natural resource used to generate electricity.
Importance of Natural Resources
Everyone should be given an equal opportunity to use resources for the benefit of humanity. You should not spend available resources selfishly without considering your fellow people.
Water is life , and every drop is valuable in a similar way. Wood should be used so as not to damage the forest’s resources more than needed. Sustainable lifestyles should be the goal of resource balance.
Effects of development on the ecosystem
The disease spreads through the environment. Human activity has weakened the protective ozone layer. Overuse of natural resources such as land, water, minerals, coal, oil, etc., has reduced them.
Conservation of Natural Resources
To protect water. Keep the taps closed when not in use. Use less water-consuming toilets. watering plants to do during evening trips. Use of drip irrigation systems and sprinkler irrigation, etc.
Saving energy
Caution in using fuel, prevent misuse, protecting the soil, soil erosion prevention:.
In short, these natural resources are significant for our existence as well as for the development of the country. Maintaining these resources will help open up new opportunities that are necessary for the country’s economic growth.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply, copyright protection, important links.


Essay on Natural Resources
Students are often asked to write an essay on Natural Resources in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Natural Resources
What are natural resources.
Natural resources are things found in nature that humans use. These include water, trees, coal, and gas. We use them for food, building homes, making clothes, and creating energy.
Types of Natural Resources
There are two main types: renewable and non-renewable. Renewable resources, like sunlight and wind, never run out. Non-renewable ones, like oil, can be used up.
Importance of Conservation
It’s important to save natural resources. If we use too much, there may not be enough for future people. We can save by recycling and using less.
We face problems like pollution and overuse. To fix these, we must be careful and find new ways to use resources without harm.
250 Words Essay on Natural Resources
Natural resources are things we find in nature that help us live. They are not made by humans. Instead, they come from the earth, water, and air. Examples include water, trees, oil, and minerals like gold and iron.
We can put natural resources into two groups. The first group is called renewable resources. These are things like sunlight, wind, and plants. They can come back or grow again even after we use them. The second group is non-renewable resources. These are things like coal and oil. Once we use them up, they are gone forever because they take a very long time to form.
Why Are They Important?
Natural resources are important because they are the things we need to live. We use them for food, to build houses, and to make clothes. We also use them to make power for our homes and cars.
Using Resources Carefully
It is important to use natural resources carefully. If we use too much, there might not be enough left for people in the future. We should try to use more renewable resources because they can come back. We should also recycle things like paper and plastic so we don’t have to use more resources to make new ones.
Natural resources are a big part of our lives. We need to make sure we use them in a good way. This means not using too much and choosing resources that can be used again. This way, we can take care of the earth and have enough resources for everyone now and in the future.
500 Words Essay on Natural Resources
We can put natural resources into two main groups: renewable and nonrenewable. Renewable resources are those that can be used over and over again. They include sunlight, wind, and water. Trees and plants are also renewable because they can grow back after we cut them down, as long as we take care of the land.
Nonrenewable resources are different. They do not come back once we use them. These include things like oil, natural gas, and minerals. Once they are gone, they are gone forever. It takes millions of years for the Earth to make more, so we must use them wisely.
Why Are Natural Resources Important?
Using natural resources carefully.
Another way to be careful is to use more renewable resources. For example, instead of using oil to make electricity, we can use wind or solar power. This helps because even if we use a lot of wind or sunlight, there will always be more the next day.
Protecting Our Natural Resources
In conclusion, natural resources are very important. They are the building blocks of our life on Earth. We must use them wisely and protect them so they can last a long time. By doing this, we make sure that we, and all the animals and plants we share the Earth with, can live well now and in the future. It is our job to take care of these precious gifts from nature.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Natural Resources, Geography, and Climate
- First Online: 01 January 2023
Cite this chapter

- Leonid Limonov 2 , 3 &
- Denis Kadochnikov 2 , 4
484 Accesses
The size of Russia’s territory exceeds 17 million square kilometres, or one-eighth of the Earth’s surface. It stretches for about ten thousand kilometres from east to west and for more than four thousand kilometres from north to south. The maritime area under the country’s jurisdiction extends for more than eight million square kilometres.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

The State of the World’s Natural Resources

Mammal Habitats in Europe: Geology, Vegetation, and Climate

Fattakhov, R. V., Nizamutdinov, M. M., & Oreshnikov, V. V. (2019). Analysing and modelling of trends in the development of the territorial: Settlement system in Russia. Ekonomika Regiona [Economy of Region], 15 (2), 436–450 (in Russian).
Google Scholar
Federal Agency for Fishery—Rosrybolovstvo. (2020). Data on the fish catch and harvesting of other aquatic biological resources for January-December 2019 (in Russian). https://fish.gov.ru/wp-content/uploads/documents/otraslevaya_deyatelnost/ekonomika_otrasli/statistika_analitika/2020/f407-01-12_2019.pdf
Federal Service for State Registration, Cadastre and Cartography—Rosreestr. (2019). Data on the state and structure of lands in the Russian Federation on 01.01.2019 (in Russian). https://rosreestr.gov.ru/site/activity/gosudarstvennoe-upravlenie-v-sfere-ispolzovaniya-i-okhrany-zemel/gosudarstvennyy-monitoring-zemel/sostoyanie-zemel-rossii/gosudarstvennyy-natsionalnyy-doklad-o-sostoyanii-i-ispolzovanii-zemel-v-rossiyskoy-federatsii
Federal State Statistics Service of the Russian Federation (2020). Russian statistical yearbook 2020 . Moscow.
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (2020). The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 2020: Sustainability in action. Rome . https://doi.org/10.4060/ca9229en
Article Google Scholar
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (2021). Food and agriculture data . http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/RL
Lappo, G. M. (2012). Goroda Rossii. Vzgljad geografa (Cities of Russia. Geographer’s view) . Novyj hronograf (in Russian).
Ministry of Natural Resources and Ecology of the Russian Federation. (2018). The strategy for the development of the mineral resource base of the Russian Federation until 2035 (Adopted by the Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No 2914-r on 22.12.2018) (in Russian). http://www.mnr.gov.ru/docs/strategiya_razvitiya_mineralno_syrevoy_bazy_rossiyskoy_federatsii_do_2035_goda/strategiya_razvitiya_mineralno_syrevoy_bazy_rossiyskoy_federatsii_do_2035_goda/
Ministry of Natural Resources and Ecology of the Russian Federation. (2019). On the state and the utilization of water resources of the Russian Federation in 2018: The state report . Moscow (in Russian).
Ministry of Natural Resources and Ecology of the Russian Federation. (2020). On the state and the utilization of mineral resources of the Russian Federation in 2019: State report . Moscow (in Russian).
Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation. (2008). The transport strategy of the Russian Federation for the period of up to 2030 (Adopted by the Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation No 1734-r on 22.11.2008) (in Russian). https://mintrans.gov.ru/documents/3/1009
Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation. (2021). The report on the implementation of the Transport Strategy of the Russian Federation for the period of up to 2030. The reporting year 2020 (in Russian). https://mintrans.gov.ru/documents/11/11430
Pivovarov, Y. (2001). Urbanization in Russia in the XX century: Ideas and reality. Social Sciences and Contemporary World, 6 , 101–113 (in Russian).
Schepaschenko, D., Moltchanova, E., Fedorov, S., et al. (2021). Russian forest sequesters substantially more carbon than previously reported. SciRep, 11 , 12825. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92152-9
Soloviev, D. A. (2020). Russia’s hydropower complex: New opportunities and prospects for development. Energy Policy, 1 (143), 26–35 (in Russian).
Stepanov, N. (2019). Arctic and the development of the Northern Sea route in the institutional modernization of Russian economy. Federalism, 1 , 5–23 (in Russian).
Streletskiy DA, Suter LJ, Shiklomanov NI, Porfiriev, B. N., & Eliseev, D. O. (2019). Assessment of climate change impacts on buildings, structures and infrastructure in the Russian regions on permafrost. Environmental Research Letters, 14 (2), 025003. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aaf5e6
Vampilova, L. B., & Manakov, A. G. (2012). Natural and cultural indications of historical-geographical zoning of Russia. Izvestiya RAN (Akad. Nauk SSSR). Seriya Geograficheskaya, 6 , 7–16 (in Russian).
Zvorykina, Y. V., & Teteryatnikov, K. S. (2019). The Northern Sea Route as a tool of Arctic development. Russian Economic Journal, 4 , 21–44 (in Russian). https://doi.org/10.33983/0130-9757-2019-4-21-44
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
International Centre for Social and Economic Research ‘Leontief Centre’, St. Petersburg, Russia
Leonid Limonov & Denis Kadochnikov
The Higher School of Economics, St. Petersburg, Russia
Leonid Limonov
St. Petersburg State University, St. Petersburg, Russia
Denis Kadochnikov
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Leonid Limonov .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Bruegel, Brussels, Belgium
Marek Dabrowski
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Limonov, L., Kadochnikov, D. (2023). Natural Resources, Geography, and Climate. In: Dabrowski, M. (eds) The Contemporary Russian Economy. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17382-0_1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-17382-0_1
Published : 01 January 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-17381-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-17382-0
eBook Packages : Economics and Finance Economics and Finance (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Nature Essay for Students and Children
500+ words nature essay.
Nature is an important and integral part of mankind. It is one of the greatest blessings for human life; however, nowadays humans fail to recognize it as one. Nature has been an inspiration for numerous poets, writers, artists and more of yesteryears. This remarkable creation inspired them to write poems and stories in the glory of it. They truly valued nature which reflects in their works even today. Essentially, nature is everything we are surrounded by like the water we drink, the air we breathe, the sun we soak in, the birds we hear chirping, the moon we gaze at and more. Above all, it is rich and vibrant and consists of both living and non-living things. Therefore, people of the modern age should also learn something from people of yesteryear and start valuing nature before it gets too late.

Significance of Nature
Nature has been in existence long before humans and ever since it has taken care of mankind and nourished it forever. In other words, it offers us a protective layer which guards us against all kinds of damages and harms. Survival of mankind without nature is impossible and humans need to understand that.
If nature has the ability to protect us, it is also powerful enough to destroy the entire mankind. Every form of nature, for instance, the plants , animals , rivers, mountains, moon, and more holds equal significance for us. Absence of one element is enough to cause a catastrophe in the functioning of human life.
We fulfill our healthy lifestyle by eating and drinking healthy, which nature gives us. Similarly, it provides us with water and food that enables us to do so. Rainfall and sunshine, the two most important elements to survive are derived from nature itself.
Further, the air we breathe and the wood we use for various purposes are a gift of nature only. But, with technological advancements, people are not paying attention to nature. The need to conserve and balance the natural assets is rising day by day which requires immediate attention.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conservation of Nature
In order to conserve nature, we must take drastic steps right away to prevent any further damage. The most important step is to prevent deforestation at all levels. Cutting down of trees has serious consequences in different spheres. It can cause soil erosion easily and also bring a decline in rainfall on a major level.

Polluting ocean water must be strictly prohibited by all industries straightaway as it causes a lot of water shortage. The excessive use of automobiles, AC’s and ovens emit a lot of Chlorofluorocarbons’ which depletes the ozone layer. This, in turn, causes global warming which causes thermal expansion and melting of glaciers.
Therefore, we should avoid personal use of the vehicle when we can, switch to public transport and carpooling. We must invest in solar energy giving a chance for the natural resources to replenish.
In conclusion, nature has a powerful transformative power which is responsible for the functioning of life on earth. It is essential for mankind to flourish so it is our duty to conserve it for our future generations. We must stop the selfish activities and try our best to preserve the natural resources so life can forever be nourished on earth.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Why is nature important?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Nature is an essential part of our lives. It is important as it helps in the functioning of human life and gives us natural resources to lead a healthy life.” } }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How can we conserve nature?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “We can take different steps to conserve nature like stopping the cutting down of trees. We must not use automobiles excessively and take public transport instead. Further, we must not pollute our ocean and river water.” } } ] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Virtual Tour
Experience University of Idaho with a virtual tour. Explore now
- Discover a Career
- Find a Major
- Experience U of I Life
More Resources
- Admitted Students
- International Students
Take Action
- Find Financial Aid
- View Deadlines
- Find Your Rep

Helping to ensure U of I is a safe and engaging place for students to learn and be successful. Read about Title IX.
Get Involved
- Clubs & Volunteer Opportunities
- Recreation and Wellbeing
- Student Government
- Student Sustainability Cooperative
- Academic Assistance
- Safety & Security
- Career Services
- Health & Wellness Services
- Register for Classes
- Dates & Deadlines
- Financial Aid
- Sustainable Solutions
- U of I Library

- Upcoming Events
Review the events calendar.
Stay Connected
- Vandal Family Newsletter
- Here We Have Idaho Magazine
- Living on Campus
- Campus Safety
- About Moscow

The largest Vandal Family reunion of the year. Check dates.
Benefits and Services
- Vandal Voyagers Program
- Vandal License Plate
- Submit Class Notes
- Make a Gift
- View Events
- Alumni Chapters
- University Magazine
- Alumni Newsletter

SlateConnect
U of I's web-based retention and advising tool provides an efficient way to guide and support students on their road to graduation. Login to SlateConnect.
Common Tools
- Administrative Procedures Manual (APM)
- Class Schedule
- OIT Tech Support
- Academic Dates & Deadlines
- U of I Retirees Association
- Faculty Senate
- Staff Council
Graduate Admissions
Office of graduate admissions.
820 Idaho Avenue Morrill Hall, Room 205 Moscow, ID 83843
University of Idaho 875 Perimeter Drive MS 3019 Moscow, ID 83844-3019
Phone: 208-885-4001
Email: [email protected]
Web: More Contact Information
Master of Natural Resources (M.N.R.)
Requirements.
Education Level: Bachelor's GPA: 3.0 GRE: No TOEFL/IELTS: 79/6.5 Number of References: 2 Other Req.: Yes, see below
Availabilities
Terms: Fall, Spring or Summer Location: Moscow, Online Thesis Option: Non-thesis Deadlines: View Other Requirements below Expedited Admission: Yes (Former U of I only) Online Option: Yes
Program Contacts
Director of Graduate Studies Leda Kobziar
Env. Ed. and Sci. Comm. (MOSS) Leslie Dorsey Phone: 208-885-1085
College of Natural Resources: Graduate Studies Office Phone: 208-885-1505
Other Requirements
Master natural resources specific .
Domestic Students:
- Fall semester (Aug. to Dec.) – June 15
- Spring semester (Jan. to May) – Nov. 15
- Summer session (May to Aug.) – March 15
International Students: View U of I deadlines
Specialization Areas:
- Fire Ecology & Management — Summer, Fall, Spring admission at Moscow * or Online
- Fish & Wildlife Science & Management Option — Summer, Fall, Spring admission at Moscow* or Online
- Integrated Natural Resources — Summer, Fall, Spring admission at Moscow * or Online
- Environmental Education & Science Communication (part of the McCall Outdoor Science School) — Fall admission only, located at the McCall Field Campus, McCall Idaho, only (select "Moscow" in the online application system)
- Restoration Ecology & Habitat Management — Summer, Fall, Spring admission at Moscow* or Online
* Admission with pending English Proficiency available for programs held at Moscow.
Looking for Natural Resources (M.S. or Ph.D.)?
» View the Natural Resources page.
Grade Point Average (GPA)
Applicants must have a minimum overall Grade Point Average (GPA) of 3.00 on a 4.00 grade scale equivalent to U.S. bachelor’s degree. If your GPA meets the minimum admission requirements, the department of major will determine if your overall academic record and test scores meet department requirements.
Note: If you do not meet the minimum 3.00 GPA, your application can be considered for admission if you:
- Earned an undergraduate GPA of 3.0 or higher for your last 60 semester credits or 90 quarter credits.
- Worked in the program specific profession for 5+ years.
- Obtained a letter of support from a faculty member in the department.
- Wrote a detailed statement/essay describing your professional experience and potential to succeed academically
Degree Levels and Equivalents
All graduate school applicants must satisfy the following criteria to be considered for graduate admission to the University of Idaho: Have earned a bachelor's degree from a college or university accredited by a recognized accrediting body, a ministry of education, or an official quality assurance organization in another country. The bachelor's degree should consist of four years of study, equivalent to 120 semester credit hours or 180 quarter hours.
An official academic record from all post-secondary education institutions attended is required. This may take some time so start this early in your application process.
In the instance that official records cannot be obtained, unofficial records may be used to consider your application. These documents are typically issued to the student and may be considered official after further review. This applies to cases where it is impossible to obtain the official records, and will be considered only on a case by case basis.
Domestic Applicants
Students must have a bachelor’s degree from a college or university accredited by a regional accrediting association. If the degree is from a recognized but not regionally accredited institution, the application will be reviewed by the department and by the College of Graduate Studies.
International Applicants
For information about equivalency and required academic credentials by country of education page, use the Degree Equivalency Guide .
The University of Idaho recommends, and reserves the right to require, a professional credential evaluation by an outside, independent party. Reasons for outside review include, but are not limited to, verification of document authenticity, potential transfer credits and the wish to expedite the processing of an application file. You are responsible for supplying the correct academic records and paying for the evaluation service. You will need to request a course-by-course evaluation. Transferring Internationally earned credits requires a course-by-course professional credential evaluation .
The preferred provider of transcript evaluations is:
- World Education Services, Inc.
There is a list of the five services from which the University of Idaho will accept evaluations.
- Visit our professional credential evaluation page .
Precise, word-for-word, English translations are required for all foreign language documents.
English Proficiency
The most common and widely accepted test is the TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language).
Our institution code for the TOEFL is 4843.
The following are acceptable as proof of English Language Proficiency:
- TOEFL (Test of English as a Foreign Language): minimum overall score of 79
- IELTS (International English Language Testing System): minimum overall score of 6.5
- MELAB (Michigan English Language Assessment Battery): Minimum overall score of 77
- PTE A (Pearson Test of English Academic): Minimum overall score of 58
- U of I American Language & Culture Program (ALCP) with score of a Level 6/Advanced Pass
- U.S. Education Earned Bachelor, or higher, degree at accredited U.S. institution
- Duolingo English Test: Minimum Overall 110 (as of Spring 2024 admission, the minimum required score will be 115)
A waiver for this requirement is automatically granted to applicants whose education is from countries where English is an official/native language. For more information, visit our English language countries page .
- All tests must have been taken within two years of the semester.
- Some graduate programs have a higher requirement. If so, you will need to take the TOEFL, or equivalent test, and obtain the higher score prior to be granted regular admission.
- Some graduate programs allow admission to be granted to applicants who qualify academically, but have not yet achieved U of I minimum English language requirements. To view information and a list of programs accepting students on this admission, visit our international requirements webpage .
Quick Application Guide
For the best user experience:
- Desktop or laptop advised, mobile devices are not recommended
- Have recommender names and email addresses
- Have electronic versions of your required documents
- Be ready to complete an online application fee
Provide Academic & Personal Information
- Program applying
- Academic background
- English proficiency (if applicable)
- GRE (if applicable)
- Your Contact Information
- Answer varying questions
- Three (3) recommender names and emails
- Resume or Curriculum Vitae (CV)
- Statement of Purpose
- Program Specific Materials (if required)
- Transcript Scans (if applicable)
- Provide payment information
Popular Links
- Graduate Application Status Portal
- Contact Graduate Admissions
- U of I Graduate Priority Deadlines
- Graduate Admissions FAQs
Recommendation for admission is based on the department's decision. Final admission is determined by the College of Graduate Studies.
Important notes to keep in mind » Learn More
Scholarships and Costs
Visit the following pages to learn more:
- Scholarships and Costs (General Annual)
- Tuition and Fees (Semester Breakdown)
- Idaho Residency for Tuition Purposes
Note: Environmental Education and Science Communication (@MOSS) has a unique fee structure. Please visit this tuition and fees page for more information.
Letters of Recommendation
The number of letters is up to the academic department/program. Individual programs may require 1 to 3 letters of recommendation. Please gather the names and email addresses of your recommenders. You will need to enter this information to complete an online application. Remember to inform recommenders in advance that they will receive an invitation to upload their letter of support directly to your application.
- Please use your references institutional email address
- Preferably, letters of recommendation should be issued on the university or company letterhead
- Preferably, your recommendations should come from teaching or research faculty in an area related to your anticipated field of study or a company supervisor who has worked with you and can articulate your merits
For more information, visit our documental resources page .
Submitting Documents
Include your full name on ALL materials and ensure uploads are LEGIBLE .
Any change in specific degree, major or semester before enrollment requires a new application (including uploaded material) and a non-refundable fee.
To be considered official , all academic records and test scores (ie. transcripts, degree certificates, GRE, TOEFL) must be sent directly from the institution and/or testing center to Graduate Admissions. When these items are submitted by applicants or educational consultants/agencies, approved or not, they are considered unofficial .
Direct mailing address is:
Graduate Admissions University of Idaho 875 Perimeter Drive MS 3019 Moscow, ID 83844-3019
Additional items that applicants upload into the application include (if required):
- Resume/Curriculum Vitae (required)
- Statement of Purpose (required)
- Scans of Official Transcripts (optional, see below)
- Personal Information Form (some programs)
- Writing Sample (some programs)
- Portfolio (some programs)
Note: Failure to adhere to these requirements could delay your credential evaluation and/or admission to the University of Idaho. For more information or assistance, visit our documental resources page .
Unofficial Transcripts
- Applicants may upload scanned copies of official transcripts and translations via the online application. Only scans of high quality (600 dpi or higher, front and back with grading keys/scales) from the University Registrar’s office, also known as original documents from your institution, are acceptable. These scans may be used to determine your acceptance into the program. However, the official transcript documents will ultimately be required .
Official Transcripts
- Transferring Internationally earned credits requires a course-by-course professional credential evaluation .
- U.S. Institutions: Academic transcripts from each college or university attended must be received by Graduate Admissions directly from the awarding institution in the officially sealed envelope bearing the institution’s official seal, stamp, and/or appropriate signature.
- Graduate Admissions accepts electronic transcripts from U.S. higher education institutions.
- Current or former U of I students: If you have or are currently attending the U of I, you do not need to order U of I transcripts. Graduate Admissions will secure them for you.
Test Scores
- ETS Institution Code (U of I): 4843
- The GRE is only required for some graduate programs.
- Department code (if needed and not supplied): 5199
- A waiver for English language proficiency requirement is automatically granted to students whose education is from countries where English is an official/native language.
- Department code (if needed and not supplied): 99
International
Complete and return the following to Graduate Admissions regardless of your source(s) of funding:
- Certificate of Financial Responsibility Form
- Copy of passport for applicant and all accompanying dependents requiring a Certificate of Eligibility (I-20)
- Current I-20
All students currently in F-1 status at any type of institution (college, university, intensive English institute) in the U.S. who plan to transfer to the University of Idaho must complete the transfer procedure through SEVIS. For more information, see the "Student Visa and SEVIS Information" drop-down below.
Student Visa and SEVIS Information
The U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services regulations require that every student verify the availability of funds to pay for educational and living expenses before an I-20 or DS-2019 form to obtain a visa to enter the U.S. can be issued.
Immigration regulations require that international students holding F-1 or J-1 student visas be certified as full-time students during the academic year. F-1 graduate students are required to be enrolled in nine credit hours and are allowed to take up to three credits of online coursework toward this requirement. J-1 visa holders are also required to enroll in nine credit hours, but are not allowed to take online classes toward the nine credit requirement.
- Additional documents are required for international students , see the "International" section of the "Submitting Documents" drop-down above.
- Not all programs are eligible for an F-1 or J-1. View the "Program Specific" drop-down or contact the program for information.
- All students currently in F-1 status at any type of institution (college, university, intensive English institute) in the U.S. who plan to transfer to the University of Idaho must complete the transfer procedure through SEVIS.
SEVIS Record Transfer Request (PDF Form)
Transfer Procedure:
- Receive admission to the University of Idaho
- Notify your current school of your intentions to transfer
- Complete Part I of this form (only after you have been admitted and choose to attend U of I)
- Have an international student advisor at your current institution complete Part II
- After you and your current school have determined the date to have your SEVIS record electronically released to the University of Idaho, promptly return this form
- After the release date, the University of Idaho will produce an I-20.
- What Are The Major Natural Resources Of Russia?

The Russian Federation is the largest country in the world. The country's vast territory makes it the richest nation in terms of natural resource wealth. The nation is a leading producer of coal, diamonds, aluminum, asbestos, gemstones, diamonds, lime, lead, gypsum, iron ore, bauxite, gallium, boron, mica, natural gas, potash, platinum, oil, rare earth metals, pig iron, peat, nitrogen, cadmium, arsenic, magnesium, molybdenum, phosphate, sulfur, titanium sponge, silicon, uranium, tellurium, vanadium, tungsten, cobalt, graphite, silver, vermiculite, selenium, rhenium, copper, and gold.
Platinum and Palladium
The country produced an estimated 91.16 tons of palladium and 25.9 tons of platinum in the year 2014. The commodities are obtained from various locations in the country including the Kondyor alluvial deposit found in Khabarovskiy which is about 621.3 miles from the city of Khabarovsk. The Kondyor mine produced an estimated 4.08 tons of platinum in the year 2014. The Yorgalan deposit located close to the Kondyor deposit has an estimated 14 tons of platinum reserves. The Norilsk-1 deposit is located on the Taymyr Peninsula, and contains 0.57 tons of Platinum group of metals. The Chernogorskoye nickel-copper-platinum deposit also contains a significant amount of platinum and is located on the Taymyr Peninsula, and to the south of the Norilsk-1 deposit. The government has in recent years increased spending to enhance the extraction of the platinum group of metals. The increased investment is supported by favorable global prices for both metals.
Russia holds the second highest coal deposits in the world only beaten to the top position by the US. The country has a total of 173 billion tons of coal deposits which represents 17.6% of global coal reserves. Coal is extracted across 129 separate deposits and 22 basins. About 85% of the nation's coal is produced across three jurisdictions namely the Zabaikal'skiy, Kemerovskaya Oblast, and the Krasnoyarskiy Kray. On the other hand, 66% of explored coal is extracted from two basins, Kuznetskiy basin, and the Kansko-Achinskiy basin. The Kansko-Achinskiy basin has 40.7% of the nation’s resource deposits. The Kuznetskiy basin contains 27.4% of the nation's resources, and it also produces the highest amount of coal in the nation. The Kuznetskiy basin produced an estimated 59% of the nation's output. Russia produced an estimated 393.4 million tons of coal in the year 2013. Total Anthracite coal production was 14 million tons while bituminous coal and lignite coal was 302.5 million tons and 75.9 million tons respectively. Open cast mining is the most popular method of coal extraction accounting for an estimated 70.6% of total production. Coal is mainly exported to China, the UK, Japan, and South Korea.
Natural Gas
Russia is among the largest producers of natural gas in the world. The country produced an estimated 22,707 billion cubic feet in gas in 2014. The country produces about 19% of global output. The market share has however been gradually decreasing due to increased production by countries such as Qatar, the US, and Iran. Russia's natural gas reserves are estimated to be 1,748 trillion cubic feet. The Urengoyskoye is Russia's largest natural gas deposit with about 187.17 trillion cubic feet. The Bovanenkovskoye deposit has an estimated 151.85 trillion cubic feet. Other significant deposits include the Yamburgskoye with 113 trillion cubic feet, Shtokmanovskoye deposit with 137.7 trillion cubic feet, the Zapolyarnoye and Astrakhanskoye each with about 88.3 trillion cubic feet in gas. About 80% of the country’s production comes from the Nadym-Pur-Taz region.The Urengoyskoye, Zapolyarnoye, and Yamburgskoye accounted for 40% of the total gas production. Natural gas is mainly exported to the European market. The main importers of Russian gas are Germany, Belarus, Turkey, Ukraine, Japan, Kazakhstan, and France.
Russia produced an estimated 579.8 million tons of oil in 2014. The country sits among the top three largest global producers of petroleum alongside Saudi Arabia and the US. The country refined an estimated 325.2 million tons of oil in the same year. A significant amount of oil deposits are located in Western Siberia. The Western Siberia deposits account for an estimated 66.6% of total production in the country. Eastern Siberia is also known to hold large amounts of oil reserves.
The country produced an estimated 47,000 tons of titanium sponge in the year 2014 which represented a 2.2% increase in production compared to the previous year.
Other Metals
Russia is thought to have an estimated 25-40% of global un-mined gold reserves. The Russian Federation is the sixth largest gold producer in the world with an estimated 249 tons produced in 2017 alone. Russia has 10% of the world’s Uranium reserves. The country produced 8% of the world’s total Uranium output. The country also contributes 17% of the world total nickel production, and 22% of the world’s total magnesium output.
Challenges In Natural Resource Extraction
In recent years the country has witnessed mounting challenges in the extraction of its natural resources. Some of the challenges include inadequate capital investment owing to sanctions on the country from major global powers including the United States and Europe due to its involvement in the Ukraine conflict among other issues. Other challenges include difficulty accessing mineral resources in remote areas in the vast territory. The country is continuously developing mechanisms to overcome the challenges it faces. The country is keen on developing new automated technologies to replace aging equipment which severely limits production. The efforts to develop new indigenous technologies are also driven by restrictions on the importation of new mineral extraction technology from other countries imposed by some members of the international community. The nation’s declining population has also made it necessary to invest in technology.
More in Economics
The Richest Countries In Europe

The 10 Largest Iron Ore Mines in the World
The 10 Largest Iron Mines In The World

The Richest Landlocked Countries In The World

The 10 Largest Potash Producing Countries in the World

The 10 Largest Coal Mines in the World
10 Richest US States

The 10 Largest Copper Mines in the World
Create an account
Create a free IEA account to download our reports or subcribe to a paid service.

Global Energy Crisis
How the energy crisis started, how global energy markets are impacting our daily life, and what governments are doing about it
- English English
What is the energy crisis?
Record prices, fuel shortages, rising poverty, slowing economies: the first energy crisis that's truly global.
Energy markets began to tighten in 2021 because of a variety of factors, including the extraordinarily rapid economic rebound following the pandemic. But the situation escalated dramatically into a full-blown global energy crisis following Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in February 2022. The price of natural gas reached record highs, and as a result so did electricity in some markets. Oil prices hit their highest level since 2008.
Higher energy prices have contributed to painfully high inflation, pushed families into poverty, forced some factories to curtail output or even shut down, and slowed economic growth to the point that some countries are heading towards severe recession. Europe, whose gas supply is uniquely vulnerable because of its historic reliance on Russia, could face gas rationing this winter, while many emerging economies are seeing sharply higher energy import bills and fuel shortages. While today’s energy crisis shares some parallels with the oil shocks of the 1970s, there are important differences. Today’s crisis involves all fossil fuels, while the 1970s price shocks were largely limited to oil at a time when the global economy was much more dependent on oil, and less dependent on gas. The entire word economy is much more interlinked than it was 50 years ago, magnifying the impact. That’s why we can refer to this as the first truly global energy crisis.
Some gas-intensive manufacturing plants in Europe have curtailed output because they can’t afford to keep operating, while in China some have simply had their power supply cut. In emerging and developing economies, where the share of household budgets spent on energy and food is already large, higher energy bills have increased extreme poverty and set back progress towards achieving universal and affordable energy access. Even in advanced economies, rising prices have impacted vulnerable households and caused significant economic, social and political strains.
Climate policies have been blamed in some quarters for contributing to the recent run-up in energy prices, but there is no evidence. In fact, a greater supply of clean energy sources and technologies would have protected consumers and mitigated some of the upward pressure on fuel prices.
Russia's invasion of Ukraine drove European and Asian gas prices to record highs
Evolution of key regional natural gas prices, june 2021-october 2022, what is causing it, disrupted supply chains, bad weather, low investment, and then came russia's invasion of ukraine.
Energy prices have been rising since 2021 because of the rapid economic recovery, weather conditions in various parts of the world, maintenance work that had been delayed by the pandemic, and earlier decisions by oil and gas companies and exporting countries to reduce investments. Russia began withholding gas supplies to Europe in 2021, months ahead of its invasion of Ukraine. All that led to already tight supplies. Russia’s attack on Ukraine greatly exacerbated the situation . The United States and the EU imposed a series of sanctions on Russia and many European countries declared their intention to phase out Russian gas imports completely. Meanwhile, Russia has increasingly curtailed or even turned off its export pipelines. Russia is by far the world’s largest exporter of fossil fuels, and a particularly important supplier to Europe. In 2021, a quarter of all energy consumed in the EU came from Russia. As Europe sought to replace Russian gas, it bid up prices of US, Australian and Qatari ship-borne liquefied natural gas (LNG), raising prices and diverting supply away from traditional LNG customers in Asia. Because gas frequently sets the price at which electricity is sold, power prices soared as well. Both LNG producers and importers are rushing to build new infrastructure to increase how much LNG can be traded internationally, but these costly projects take years to come online. Oil prices also initially soared as international trade routes were reconfigured after the United States, many European countries and some of their Asian allies said they would no longer buy Russian oil. Some shippers have declined to carry Russian oil because of sanctions and insurance risk. Many large oil producers were unable to boost supply to meet rising demand – even with the incentive of sky-high prices – because of a lack of investment in recent years. While prices have come down from their peaks, the outlook is uncertain with new rounds of European sanctions on Russia kicking in later this year.
What is being done?
Pandemic hangovers and rising interest rates limit public responses, while some countries turn to coal.
Some governments are looking to cushion the blow for customers and businesses, either through direct assistance, or by limiting prices for consumers and then paying energy providers the difference. But with inflation in many countries well above target and budget deficits already large because of emergency spending during the Covid-19 pandemic, the scope for cushioning the impact is more limited than in early 2020. Rising inflation has triggered increases in short-term interest rates in many countries, slowing down economic growth. Europeans have rushed to increase gas imports from alternative producers such as Algeria, Norway and Azerbaijan. Several countries have resumed or expanded the use of coal for power generation, and some are extending the lives of nuclear plants slated for de-commissioning. EU members have also introduced gas storage obligations, and agreed on voluntary targets to cut gas and electricity demand by 15% this winter through efficiency measures, greater use of renewables, and support for efficiency improvements. To ensure adequate oil supplies, the IEA and its members responded with the two largest ever releases of emergency oil stocks. With two decisions – on 1 March 2022 and 1 April – the IEA coordinated the release of some 182 million barrels of emergency oil from public stocks or obligated stocks held by industry. Some IEA member countries independently released additional public stocks, resulting in a total of over 240 million barrels being released between March and November 2022.
The IEA has also published action plans to cut oil use with immediate impact, as well as plans for how Europe can reduce its reliance on Russian gas and how common citizens can reduce their energy consumption . The invasion has sparked a reappraisal of energy policies and priorities, calling into question the viability of decades of infrastructure and investment decisions, and profoundly reorientating international energy trade. Gas had been expected to play a key role in many countries as a lower-emitting "bridge" between dirtier fossil fuels and renewable energies. But today’s crisis has called into question natural gas’ reliability.
The current crisis could accelerate the rollout of cleaner, sustainable renewable energy such as wind and solar, just as the 1970s oil shocks spurred major advances in energy efficiency, as well as in nuclear, solar and wind power. The crisis has also underscored the importance of investing in robust gas and power network infrastructure to better integrate regional markets. The EU’s RePowerEU, presented in May 2022 and the United States’ Inflation Reduction Act , passed in August 2022, both contain major initiatives to develop energy efficiency and promote renewable energies.
The global energy crisis can be a historic turning point
Energy saving tips

1. Heating: turn it down
Lower your thermostat by just 1°C to save around 7% of your heating energy and cut an average bill by EUR 50-70 a year. Always set your thermostat as low as feels comfortable, and wear warm clothes indoors. Use a programmable thermostat to set the temperature to 15°C while you sleep and 10°C when the house is unoccupied. This cuts up to 10% a year off heating bills. Try to only heat the room you’re in or the rooms you use regularly.
The same idea applies in hot weather. Turn off air-conditioning when you’re out. Set the overall temperature 1 °C warmer to cut bills by up to 10%. And only cool the room you’re in.
2. Boiler: adjust the settings
Default boiler settings are often higher than you need. Lower the hot water temperature to save 8% of your heating energy and cut EUR 100 off an average bill. You may have to have the plumber come once if you have a complex modern combi boiler and can’t figure out the manual. Make sure you follow local recommendations or consult your boiler manual. Swap a bath for a shower to spend less energy heating water. And if you already use a shower, take a shorter one. Hot water tanks and pipes should be insulated to stop heat escaping. Clean wood- and pellet-burning heaters regularly with a wire brush to keep them working efficiently.
3. Warm air: seal it in
Close windows and doors, insulate pipes and draught-proof around windows, chimneys and other gaps to keep the warm air inside. Unless your home is very new, you will lose heat through draughty doors and windows, gaps in the floor, or up the chimney. Draught-proof these gaps with sealant or weather stripping to save up to EUR 100 a year. Install tight-fitting curtains or shades on windows to retain even more heat. Close fireplace and chimney openings (unless a fire is burning) to stop warm air escaping straight up the chimney. And if you never use your fireplace, seal the chimney to stop heat escaping.
4. Lightbulbs: swap them out
Replace old lightbulbs with new LED ones, and only keep on the lights you need. LED bulbs are more efficient than incandescent and halogen lights, they burn out less frequently, and save around EUR 10 a year per bulb. Check the energy label when buying bulbs, and aim for A (the most efficient) rather than G (the least efficient). The simplest and easiest way to save energy is to turn lights off when you leave a room.
5. Grab a bike
Walking or cycling are great alternatives to driving for short journeys, and they help save money, cut emissions and reduce congestion. If you can, leave your car at home for shorter journeys; especially if it’s a larger car. Share your ride with neighbours, friends and colleagues to save energy and money. You’ll also see big savings and health benefits if you travel by bike. Many governments also offer incentives for electric bikes.
6. Use public transport
For longer distances where walking or cycling is impractical, public transport still reduces energy use, congestion and air pollution. If you’re going on a longer trip, consider leaving your car at home and taking the train. Buy a season ticket to save money over time. Your workplace or local government might also offer incentives for travel passes. Plan your trip in advance to save on tickets and find the best route.
7. Drive smarter
Optimise your driving style to reduce fuel consumption: drive smoothly and at lower speeds on motorways, close windows at high speeds and make sure your tires are properly inflated. Try to take routes that avoid heavy traffic and turn off the engine when you’re not moving. Drive 10 km/h slower on motorways to cut your fuel bill by around EUR 60 per year. Driving steadily between 50-90 km/h can also save fuel. When driving faster than 80 km/h, it’s more efficient to use A/C, rather than opening your windows. And service your engine regularly to maintain energy efficiency.
Analysis and forecast to 2026
Fuel report — December 2023

Europe’s energy crisis: Understanding the drivers of the fall in electricity demand
Commentary — 09 May 2023
Where things stand in the global energy crisis one year on
Commentary — 23 February 2023
The global energy crisis pushed fossil fuel consumption subsidies to an all-time high in 2022
Commentary — 16 February 2023
Fossil Fuels Consumption Subsidies 2022
Policy report — February 2023

Background note on the natural gas supply-demand balance of the European Union in 2023
Report — February 2023
Analysis and forecast to 2025
Fuel report — December 2022

How to Avoid Gas Shortages in the European Union in 2023
A practical set of actions to close a potential supply-demand gap
Flagship report — December 2022
Subscription successful
Thank you for subscribing. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the link at the bottom of any IEA newsletter.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Natural Resources Essay. The above material contained an essay on Natural Resources which had a lot of information about the topic. It outlined the ways to write an essay, both, long and short. But, writing is all about creative ideas and is considered to be the most loved form of expression.
Learn what natural resources are, how they are classified, and why they are important for human survival. Find sample essays on natural resources in different word limits with examples and tips to write your own essay.
Natural Resources Essay: Our survival has always wholly depended on the natural resources of the Earth. The natural resources are the blessing of Mother Nature that has provided us with abundant elements to make our life comfortable and prosperous. Natural resources are all those things that are readily present in the environment like air ...
Learn about the meaning, types, and distribution of natural resources with examples and FAQs. This essay is suitable for students and children who want to know more about the gifts of nature and how to use them sustainably.
Learn about natural resources, their classification, examples and distribution in this essay. Find out how natural resources are essential for life on earth and how they are exploited and conserved.
Earth 's natural resources include air, water, soil, minerals, fuels, plants, and animals. Conservation is the practice of caring for these resources so all living things can benefit from them now and in the future. All the things we need to survive, such as food, water, air, and shelter, come from natural resources.Some of these resources, like small plants, can be replaced quickly after ...
Essay on Natural Resources. Natural resources are the treasures that Mother Earth has bestowed upon us. They include water, air, soil, minerals, and all living things. In this essay, we will delve into the importance of these resources, their sustainable use, and the vital role they play in our lives and the health of our planet.
Learn about the classification, significance, and global distribution of natural resources, such as renewable and non-renewable energy sources, minerals, and metals. Explore the challenges and opportunities of conserving and sustainably managing these vital assets for economic, environmental, and social well-being.
Accessed 26 August 2024. Natural resource, any biological, mineral, or aesthetic asset afforded by nature without human intervention that can be used for some form of benefit, whether material (economic) or immaterial. What is considered a "resource" (or, for that matter, "natural") has varied over time and from one.
Essay on Depletion of Natural Resources (Essay 5 - 500 Words) Introduction: In ancient times, people used energy only for daily activities, such as lighting, guarding, and cooking. But as the development took place, in terms of industrial revolution and urbanization, animals were domesticated for household and farming activities and later as ...
Essay On Conservation of Natural Resource. Natural resources are the resources that occur naturally on Earth. It is an indispensable part of our lives. Natural resources consist of air, water, sunlight, coal, petroleum, natural gas, fossil fuels, oil, etc. However, humans have exploited these resources for their economic gains.
Learn about the importance, categories and examples of natural resources for human life on earth. Read short and long essays on natural resources with detailed information and tips for students.
Natural Resources Essay. Introduction Natural resources are the elements that are found naturally and useful. Natural resources include fuels, oil, natural gas, materials and timber. Natural resources could be renewable or non-renewable. Renewable are those resources that are substituted in nature e. animals plants and forests.
Minerals such as silver and gold are used to make jewellery. Natural gases: These natural gases are used to generate electricity and in kitchens for cooking. Coal: This is another natural resource used to generate electricity. Plants: Plants offer a range of natural resources such as wood, fruit, and vegetables.
Natural resources are gifts from nature. These are things that we find on Earth that help us live our lives. We did not make them. Instead, they come from the environment. Examples include water, air, land, trees, coal, and oil. Some of these resources, like sunlight and wind, are always there and don't run out.
Conservation of nature means the preservation of forests, land, water bodies, and minerals, fuels, natural gases, etc. And to make sure that all these continue to be available in abundance. Thus all these natural resources make life worth living on Earth. Life would not be imaginable without air, water, sunlight as well as other natural ...
500+ Words Essay on Conservation of Natural Resources. Natural resources are something that is occurring naturally on Earth. It forms an indispensable part of our lives. It comprises of air, water, sunlight, coal, petroleum, natural gas, fossil fuels, oil, etc. However, they are exploited by humans for economic gain.
Russia's mineral resources are vast and diverse, making it one of the world leaders in terms of both discovered reserves and the production and export of natural gas, oil, coal, iron ore, copper, nickel, zinc, gold, palladium, and diamonds, among others. Its discovered mineral deposits are found throughout Russia's territory and continental ...
Master of Natural Resources Online (M.N.R.) The Master of Natural Resources (MNR) is an interdisciplinary course-based graduate program designed for current and aspiring professionals who wish to enhance their educational credentials for a career in natural resources. The fundamental objective of the MNR graduate program is to integrate and ...
500+ Words Nature Essay. Nature is an important and integral part of mankind. It is one of the greatest blessings for human life; however, nowadays humans fail to recognize it as one. Nature has been an inspiration for numerous poets, writers, artists and more of yesteryears. This remarkable creation inspired them to write poems and stories in ...
College of Natural Resources: Graduate Studies Office Phone: 208-885-1505. Academic Program Information. Other Requirements. Master Natural Resources Specific Deadlines. ... Wrote a detailed statement/essay describing your professional experience and potential to succeed academically;
The country produces about 19% of global output. The market share has however been gradually decreasing due to increased production by countries such as Qatar, the US, and Iran. Russia's natural gas reserves are estimated to be 1,748 trillion cubic feet. The Urengoyskoye is Russia's largest natural gas deposit with about 187.17 trillion cubic feet.
Background note on the natural gas supply-demand balance of the European Union in 2023. Report — February 2023 Ministers from around 40 countries meet to discuss the current gas crisis and collaborative actions on global energy security and the clean energy transition. News — 15 February 2023 ...