Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation

What Is a Dissertation? | Guide, Examples, & Template
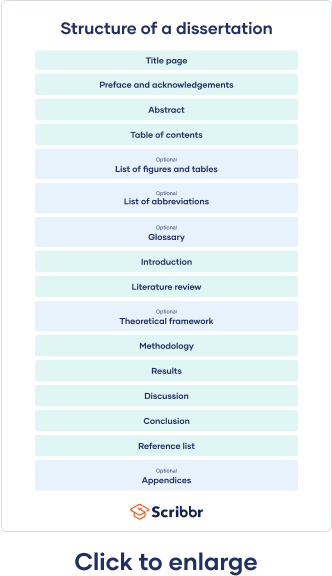
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program.
Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you’ve ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating to know where to begin.
Your department likely has guidelines related to how your dissertation should be structured. When in doubt, consult with your supervisor.
You can also download our full dissertation template in the format of your choice below. The template includes a ready-made table of contents with notes on what to include in each chapter, easily adaptable to your department’s requirements.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
- In the US, a dissertation generally refers to the collection of research you conducted to obtain a PhD.
- In other countries (such as the UK), a dissertation often refers to the research you conduct to obtain your bachelor’s or master’s degree.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Dissertation committee and prospectus process, how to write and structure a dissertation, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your dissertation, free checklist and lecture slides.
When you’ve finished your coursework, as well as any comprehensive exams or other requirements, you advance to “ABD” (All But Dissertation) status. This means you’ve completed everything except your dissertation.
Prior to starting to write, you must form your committee and write your prospectus or proposal . Your committee comprises your adviser and a few other faculty members. They can be from your own department, or, if your work is more interdisciplinary, from other departments. Your committee will guide you through the dissertation process, and ultimately decide whether you pass your dissertation defense and receive your PhD.
Your prospectus is a formal document presented to your committee, usually orally in a defense, outlining your research aims and objectives and showing why your topic is relevant . After passing your prospectus defense, you’re ready to start your research and writing.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The structure of your dissertation depends on a variety of factors, such as your discipline, topic, and approach. Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an overall argument to support a central thesis , with chapters organized around different themes or case studies.
However, hard science and social science dissertations typically include a review of existing works, a methodology section, an analysis of your original research, and a presentation of your results , presented in different chapters.
Dissertation examples
We’ve compiled a list of dissertation examples to help you get started.
- Example dissertation #1: Heat, Wildfire and Energy Demand: An Examination of Residential Buildings and Community Equity (a dissertation by C. A. Antonopoulos about the impact of extreme heat and wildfire on residential buildings and occupant exposure risks).
- Example dissertation #2: Exploring Income Volatility and Financial Health Among Middle-Income Households (a dissertation by M. Addo about income volatility and declining economic security among middle-income households).
- Example dissertation #3: The Use of Mindfulness Meditation to Increase the Efficacy of Mirror Visual Feedback for Reducing Phantom Limb Pain in Amputees (a dissertation by N. S. Mills about the effect of mindfulness-based interventions on the relationship between mirror visual feedback and the pain level in amputees with phantom limb pain).
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. In some cases, your acknowledgements are part of a preface.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150 to 300 words long. Though this may seem very short, it’s one of the most important parts of your dissertation, because it introduces your work to your audience.
Your abstract should:
- State your main topic and the aims of your research
- Describe your methods
- Summarize your main results
- State your conclusions
Read more about abstracts
The table of contents lists all of your chapters, along with corresponding subheadings and page numbers. This gives your reader an overview of your structure and helps them easily navigate your document.
Remember to include all main parts of your dissertation in your table of contents, even the appendices. It’s easy to generate a table automatically in Word if you used heading styles. Generally speaking, you only include level 2 and level 3 headings, not every subheading you included in your finished work.
Read more about tables of contents
While not usually mandatory, it’s nice to include a list of figures and tables to help guide your reader if you have used a lot of these in your dissertation. It’s easy to generate one of these in Word using the Insert Caption feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
Similarly, if you have used a lot of abbreviations (especially industry-specific ones) in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
In addition to the list of abbreviations, if you find yourself using a lot of highly specialized terms that you worry will not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary. Here, alphabetize the terms and include a brief description or definition.
Read more about glossaries
The introduction serves to set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance. It tells the reader what to expect in the rest of your dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving the background information needed to contextualize your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of your research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your research questions and objectives
- Outline the flow of the rest of your work
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant. By the end, the reader should understand the what, why, and how of your research.
Read more about introductions
A formative part of your research is your literature review . This helps you gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic.
Literature reviews encompass:
- Finding relevant sources (e.g., books and journal articles)
- Assessing the credibility of your sources
- Critically analyzing and evaluating each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g., themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps) to strengthen your overall point
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing sources. Your literature review should have a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear justification for your own research. It may aim to:
- Address a gap in the literature or build on existing knowledge
- Take a new theoretical or methodological approach to your topic
- Propose a solution to an unresolved problem or advance one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework. Here, you define and analyze the key theories, concepts, and models that frame your research.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to critically assess its credibility. Your methodology section should accurately report what you did, as well as convince your reader that this was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- The overall research approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative ) and research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment )
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Any tools and materials you used (e.g., computer programs, lab equipment)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses , or themes, but avoid including any subjective or speculative interpretation here.
Your results section should:
- Concisely state each relevant result together with relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Briefly state how the result relates to the question or whether the hypothesis was supported
- Report all results that are relevant to your research questions , including any that did not meet your expectations.
Additional data (including raw numbers, full questionnaires, or interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix. You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results. Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is your opportunity to explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research question. Here, interpret your results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. Refer back to relevant source material to show how your results fit within existing research in your field.
Some guiding questions include:
- What do your results mean?
- Why do your results matter?
- What limitations do the results have?
If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your dissertation’s conclusion should concisely answer your main research question, leaving your reader with a clear understanding of your central argument and emphasizing what your research has contributed to the field.
In some disciplines, the conclusion is just a short section preceding the discussion section, but in other contexts, it is the final chapter of your work. Here, you wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you found, with recommendations for future research and concluding remarks.
It’s important to leave the reader with a clear impression of why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known? Why is your research necessary for the future of your field?
Read more about conclusions
It is crucial to include a reference list or list of works cited with the full details of all the sources that you used, in order to avoid plagiarism. Be sure to choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your dissertation. Each style has strict and specific formatting requirements.
Common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA , but which style you use is often set by your department or your field.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
Your dissertation should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents such as interview transcripts or survey questions can be added as appendices, rather than adding them to the main body.
Read more about appendices
Making sure that all of your sections are in the right place is only the first step to a well-written dissertation. Don’t forget to leave plenty of time for editing and proofreading, as grammar mistakes and sloppy spelling errors can really negatively impact your work.
Dissertations can take up to five years to write, so you will definitely want to make sure that everything is perfect before submitting. You may want to consider using a professional dissertation editing service , AI proofreader or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect prior to submitting.
After your written dissertation is approved, your committee will schedule a defense. Similarly to defending your prospectus, dissertation defenses are oral presentations of your work. You’ll present your dissertation, and your committee will ask you questions. Many departments allow family members, friends, and other people who are interested to join as well.
After your defense, your committee will meet, and then inform you whether you have passed. Keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality; most committees will have resolved any serious issues with your work with you far prior to your defense, giving you ample time to fix any problems.
As you write your dissertation, you can use this simple checklist to make sure you’ve included all the essentials.
Checklist: Dissertation
My title page includes all information required by my university.
I have included acknowledgements thanking those who helped me.
My abstract provides a concise summary of the dissertation, giving the reader a clear idea of my key results or arguments.
I have created a table of contents to help the reader navigate my dissertation. It includes all chapter titles, but excludes the title page, acknowledgements, and abstract.
My introduction leads into my topic in an engaging way and shows the relevance of my research.
My introduction clearly defines the focus of my research, stating my research questions and research objectives .
My introduction includes an overview of the dissertation’s structure (reading guide).
I have conducted a literature review in which I (1) critically engage with sources, evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, (2) discuss patterns, themes, and debates in the literature, and (3) address a gap or show how my research contributes to existing research.
I have clearly outlined the theoretical framework of my research, explaining the theories and models that support my approach.
I have thoroughly described my methodology , explaining how I collected data and analyzed data.
I have concisely and objectively reported all relevant results .
I have (1) evaluated and interpreted the meaning of the results and (2) acknowledged any important limitations of the results in my discussion .
I have clearly stated the answer to my main research question in the conclusion .
I have clearly explained the implications of my conclusion, emphasizing what new insight my research has contributed.
I have provided relevant recommendations for further research or practice.
If relevant, I have included appendices with supplemental information.
I have included an in-text citation every time I use words, ideas, or information from a source.
I have listed every source in a reference list at the end of my dissertation.
I have consistently followed the rules of my chosen citation style .
I have followed all formatting guidelines provided by my university.
Congratulations!
The end is in sight—your dissertation is nearly ready to submit! Make sure it's perfectly polished with the help of a Scribbr editor.
If you’re an educator, feel free to download and adapt these slides to teach your students about structuring a dissertation.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation Binding and Printing | Options, Tips, & Comparison
- Example of a dissertation abstract
- Figure and Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Purpose and structure of an advisory report
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Shorten your abstract or summary
- Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Title Page | Free Templates & Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Get unlimited documents corrected
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- FindAMasters
- Researching and Writing a Masters Dissertation
Written by Mark Bennett
All Masters programmes include some form of extended individual project. Research-focussed programmes, such as an MRes , may include multiple independent research components. Taught courses usually culminate with a substantial research task, referred to as the Masters dissertation or thesis.
This article talks about how long a Masters dissertation is and the structure it follows.Before you get started on your dissertation, you'll usually need to write a proposal. Read our full guide to Masters dissertation proposals for more information on what this should include!
| Length | 15,000 - 20,000 words |
| Structure | Abstract (300 words) Introduction (1,000 words) Literature review (1,000 words) Research methodology (1,500 words) Results Discussion (12,000 words) Conclusion (1,500 words) References/Bibliography Appendices |
| Supervision | Yes, you’ll be paired with an academic from your own university |
| Assessment | External examiner along with additional members of faculty. There is not usually a viva at Masters level. |
On this page
What’s the difference between a masters dissertation and an undergraduate dissertation.
The Masters thesis is a bridge between undergraduate study and higher level postgraduate degrees such as the PhD .
A postgraduate dissertation may not look that different to its undergraduate equivalent. You’ll likely have to produce a longer piece of work but the foundations remain the same.
After all, one of the purposes of an undergraduate dissertation or final year project is to prepare you for more in-depth research work as a postgraduate. That said, there are some important differences between the two levels.
So, how long is a Masters dissertation? A Masters dissertation will be longer than the undergraduate equivalent – usually it’ll be somewhere between 15,000 and 20,000 words, but this can vary widely between courses, institutions and countries.
To answer your overall research question comprehensively, you’ll be expected to identify and examine specific areas of your topic. This can be like producing a series of shorter pieces of work, similar to those required by individual modules. However, there’s the additional requirement that they collectively support a broader set of conclusions.
This more involved Masters dissertation structure will:
- Give you the scope to investigate your subject in greater detail than is possible at undergraduate level
- Challenge you to be effective at organising your work so that its individual components function as stages in a coherent and persuasive overall argument
- Allow you to develop and hone a suitable research methodology (for example, choosing between qualitative and quantitative methods)
If the individual topics within your overall project require you to access separate sources or datasets, this may also have an impact on your research process.
As a postgraduate, you’ll be expected to establish and assert your own critical voice as a member of the academic community associated with your field .
During your Masters thesis you’ll need to show that you are not just capable of analysing and critiquing original data or primary source material. You should also demonstrate awareness of the existing body of scholarship relating to your topic .
So, if you’ll excuse the pun, a ‘Masters’ degree really is about achieving ‘mastery’ of your particular specialism and the dissertation is where you’ll demonstrate this: showing off the scholarly expertise and research skills that you’ve developed across your programme.
What’s the difference between a dissertation and a thesis?
A dissertation is a long piece of (usually) written work on the same topic. A thesis is a little more specific: it usually means something that presents an original argument based on the interpretation of data, statistics or content.
So, a thesis is almost always presented as a dissertation, but not all dissertations present a thesis.
Masters dissertation structure
As you can probably imagine, no two dissertations follow the exact same structure, especially given the differences found between Masters programmes from university to university and country to country .
That said, there are several key components that make up the structure of a typical Masters dissertation
How long is a Masters dissertation?
Most dissertations will typically be between 15,000 and 20,000 words long, although this can vary significantly depending on the nature of the programme.
You should also check with your university exactly which sections of the dissertation count towards the final word count (the abstract, bibliography and appendices won’t usually be included in the total).
Usually around 300 words long, the abstract is meant to be a concise summary of your dissertation. It should briefly cover the question(s) you aim to answer, your primary argument and your conclusion.
Introduction
The purpose of the introduction is to provide context for the rest of the dissertation, setting out your aims and the scope of what you want to achieve with your research. The introduction should give a clear overview of the dissertation’s chapters and will usually be around 1,000 words long.
Literature review
This part of the dissertation should examine the scholarship that has already been published in your field, presenting various arguments and counter-arguments while situating your own research within this wider body of work.
You should analyse and evaluate other publications and explain how your dissertation will contribute to the existing literature in your subject area. The literature review sometimes forms part of the introduction or follows immediately on from it. Most literature reviews are up to 1,000 words long.
Research methodology
Not all dissertations will require a section covering research methodology (Arts and Humanities dissertations won’t normally undertake the kind of research that involves a set methodology). However, if you are using a particular method to collect information for your dissertation, you should make sure to explain the rationale behind your choice of methodology. The word count for this part of the dissertation is usually around the 1,500 mark.
Those in the Arts and Humanities will usually outline their theoretical perspectives and approaches as part of the introduction, rather than requiring a detailed explanation of the methodology for their data collection and analysis.
Results / findings
If your research involves some form of survey or experiment, this is where you’ll present the results of your work. Depending on the nature of the study, this might be in the form of graphs, tables or charts – or even just a written description of what the research entailed and what the findings were.
This section forms the bulk of your dissertation and should be carefully structured using a series of related chapters (and sub-chapters). There should be a logical progression from one chapter to the next, with each part building on the arguments of its predecessor.
It can be helpful to think of your Masters dissertation as a series of closely interlinked essays, rather than one overwhelming paper. The size of this section will depend on the overall word count for your dissertation. However, to give you a rough idea for a 15,000-word dissertation, the discussion part will generally be about 12,000 words long.
Here you should draw together the threads of the previous discussion chapters and make your final concluding statements, drawing on evidence and arguments that you’ve already explored over the course of the dissertation. Explain the significance of your findings and point towards directions that future research could follow. This section of the Masters thesis will be around 1,500 words long.
References / bibliography
While planning and writing your dissertation, you should keep an extensive, organised record of any papers, sources or books you’ve quoted (or referred to). This will be a lot easier than leaving all of it until the end and struggling to work out where a particular quotation is from!
Appendices won’t be necessary in many dissertations, but you may need to include supplementary material to support your argument. This could be interview transcripts or questionnaires. If including such content within the body of the dissertation won’t be feasible – i.e. there wouldn’t be enough space or it would break the flow of your writing – you should consult with your supervisor and consider attaching it in an appendix.
It’s worth bearing in mind that these sections won’t always be discretely labelled in every dissertation. For example, everything up to ‘discussion’ might be covered in introductory chapter (rather than as distinct sections). If you’re unsure about the structure of your Masters dissertation, your supervisor will be able to help you map it out.
How does supervision work for a Masters dissertation?
As a Masters student at the dissertation stage you’ll usually be matched with an academic within your institution who will be tasked with guiding your work. This might be someone who has already taught you, or it may be another scholar whose research interests and expertise align well with what you want to do. You may be able to request a particular supervisor, but taught postgraduates are more likely to be assigned them by their department.
Specific arrangements with your supervisor will vary depending on your institution and subject area. They will usually meet with you at the beginning of the dissertation period to discuss your project and agree a suitable schedule for its undertaking. This timetable will probably set dates for:
- Subsequent discussions and progress checks
- The submission of draft chapters or sections
- Feedback appointments
Though your supervisor is there to help and advise you, it is important to remember that your dissertation is a personal research project with associated expectations of you as an independent scholar.
As a rule of thumb, you can expect your supervisor to read each part of your dissertation once at the draft stage and to offer feedback. Most will not have time to look at lots of subsequent revisions, but may respond favourably to polite requests for exceptions (provided their own workload permits it).
Inundating your supervisor with emails or multiple iterations of draft material is best avoided; they will have their own research to manage (as well as other supervision assignments) and will be able to offer better quality feedback if you stick to an agreed schedule.
How is a Masters dissertation assessed and examined?
On most courses your dissertation will be assessed by an external examiner (as well as additional members of faculty within your university who haven’t been responsible for supervising you), but these will read and critique the work you submit without personally questioning and testing you on it.
Though this examination process is not as challenging as the oral defence or ‘ viva voce ’ required for a PhD thesis, the grading of your Masters dissertation is still a fundamental component of your degree.
On some programmes the result awarded to a student’s dissertation may determine the upper grade-band that can be awarded to their degree.
Search for a Masters
Ready to start looking for your ideal postgraduate opportunity? Browse and compare Masters degrees on FindAMasters.com.
Our postgrad newsletter shares courses, funding news, stories and advice
You may also like....

Applying for a Masters can feel a bit daunting. Here is a checklist of all the things you need to do to make sure you have everything covered in your Masters application.

Postgraduate study is often very flexible, with the option to study a Masters degree or other qualification part-time, online or through blended learning.

How do Bachelors and Masters courses differ? We’ve covered the main differences you’ll encounter when making the transition from undergrad to postgrad study.

Our guide explains how online Masters degree work, what the benefits of online learning are and how to choose what to study online.

Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a Masters in Italy.
Our guide tells you everything about the application process for studying a Masters in the USA.
FindAMasters. Copyright 2005-2024 All rights reserved.
Unknown ( change )
Have you got time to answer some quick questions about Masters study?
Select your nearest city
- Aberystwyth
- Beaconsfield
- Bishop Burton
- Bournemouth
- Bridlington
- Chatham Maritime
- Cirencester
- East Malling
- Hemel Hempstead
- High Wycombe
- Huddersfield
- Isle of Man
- Jordanstown
- London Central
- London East
- London South
- London West
- Londonderry
- Loughborough
- Middlesbrough
- Milton Keynes
- Musselburgh
- Northampton
- Potters Bar
- Saffron Waldon
- Scarborough
- Southampton
- St Leonards on Sea
- Stoke on Trent
- Wolverhampton
You haven’t completed your profile yet. To get the most out of FindAMasters, finish your profile and receive these benefits:
- Monthly chance to win one of ten £10 Amazon vouchers ; winners will be notified every month.*
- Access to our £6,000 scholarship competition
- Weekly newsletter with funding opportunities, application tips and much more
- Early access to our physical and virtual postgraduate study fairs
Or begin browsing FindAMasters.com
or begin browsing FindAMasters.com
*Offer only available for the duration of your active subscription, and subject to change. You MUST claim your prize within 72 hours, if not we will redraw.

Do you want hassle-free information and advice?
Create your FindAMasters account and sign up to our newsletter:
- Find out about funding opportunities and application tips
- Receive weekly advice, student stories and the latest Masters news
- Hear about our upcoming study fairs
- Save your favourite programmes, track enquiries and get personalised subject updates

Create your account
Looking to list your Masters programmes? Log in here .

Let us help you find a Masters
Never miss a course
Enter our ambassador competition
Get funding news, tips and advice
Hear about upcoming events
Sign up to our newsletter today
We've been helping students find the right postgraduate course for over a decade.
Login to your account
Enter your username below to login to your account.
/images/cornell/logo35pt_cornell_white.svg" alt="post graduate dissertation"> Cornell University --> Graduate School
Guide to writing your thesis/dissertation, definition of dissertation and thesis.
The dissertation or thesis is a scholarly treatise that substantiates a specific point of view as a result of original research that is conducted by students during their graduate study. At Cornell, the thesis is a requirement for the receipt of the M.A. and M.S. degrees and some professional master’s degrees. The dissertation is a requirement of the Ph.D. degree.
Formatting Requirement and Standards
The Graduate School sets the minimum format for your thesis or dissertation, while you, your special committee, and your advisor/chair decide upon the content and length. Grammar, punctuation, spelling, and other mechanical issues are your sole responsibility. Generally, the thesis and dissertation should conform to the standards of leading academic journals in your field. The Graduate School does not monitor the thesis or dissertation for mechanics, content, or style.
“Papers Option” Dissertation or Thesis
A “papers option” is available only to students in certain fields, which are listed on the Fields Permitting the Use of Papers Option page , or by approved petition. If you choose the papers option, your dissertation or thesis is organized as a series of relatively independent chapters or papers that you have submitted or will be submitting to journals in the field. You must be the only author or the first author of the papers to be used in the dissertation. The papers-option dissertation or thesis must meet all format and submission requirements, and a singular referencing convention must be used throughout.
ProQuest Electronic Submissions
The dissertation and thesis become permanent records of your original research, and in the case of doctoral research, the Graduate School requires publication of the dissertation and abstract in its original form. All Cornell master’s theses and doctoral dissertations require an electronic submission through ProQuest, which fills orders for paper or digital copies of the thesis and dissertation and makes a digital version available online via their subscription database, ProQuest Dissertations & Theses . For master’s theses, only the abstract is available. ProQuest provides worldwide distribution of your work from the master copy. You retain control over your dissertation and are free to grant publishing rights as you see fit. The formatting requirements contained in this guide meet all ProQuest specifications.
Copies of Dissertation and Thesis
Copies of Ph.D. dissertations and master’s theses are also uploaded in PDF format to the Cornell Library Repository, eCommons . A print copy of each master’s thesis and doctoral dissertation is submitted to Cornell University Library by ProQuest.

Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings . In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
Published on 26 March 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 5 May 2022.
A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree.
The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the level and field of study. However, there are some key questions that can help you understand the requirements and get started on your dissertation project.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When and why do you have to write a dissertation, who will supervise your dissertation, what type of research will you do, how should your dissertation be structured, what formatting and referencing rules do you have to follow, frequently asked questions about dissertations.
A dissertation, sometimes called a thesis, comes at the end of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. It is a larger project than the other essays you’ve written, requiring a higher word count and a greater depth of research.
You’ll generally work on your dissertation during the final year of your degree, over a longer period than you would take for a standard essay . For example, the dissertation might be your main focus for the last six months of your degree.
Why is the dissertation important?
The dissertation is a test of your capacity for independent research. You are given a lot of autonomy in writing your dissertation: you come up with your own ideas, conduct your own research, and write and structure the text by yourself.
This means that it is an important preparation for your future, whether you continue in academia or not: it teaches you to manage your own time, generate original ideas, and work independently.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
During the planning and writing of your dissertation, you’ll work with a supervisor from your department. The supervisor’s job is to give you feedback and advice throughout the process.
The dissertation supervisor is often assigned by the department, but you might be allowed to indicate preferences or approach potential supervisors. If so, try to pick someone who is familiar with your chosen topic, whom you get along with on a personal level, and whose feedback you’ve found useful in the past.
How will your supervisor help you?
Your supervisor is there to guide you through the dissertation project, but you’re still working independently. They can give feedback on your ideas, but not come up with ideas for you.
You may need to take the initiative to request an initial meeting with your supervisor. Then you can plan out your future meetings and set reasonable deadlines for things like completion of data collection, a structure outline, a first chapter, a first draft, and so on.
Make sure to prepare in advance for your meetings. Formulate your ideas as fully as you can, and determine where exactly you’re having difficulties so you can ask your supervisor for specific advice.
Your approach to your dissertation will vary depending on your field of study. The first thing to consider is whether you will do empirical research , which involves collecting original data, or non-empirical research , which involves analysing sources.
Empirical dissertations (sciences)
An empirical dissertation focuses on collecting and analysing original data. You’ll usually write this type of dissertation if you are studying a subject in the sciences or social sciences.
- What are airline workers’ attitudes towards the challenges posed for their industry by climate change?
- How effective is cognitive behavioural therapy in treating depression in young adults?
- What are the short-term health effects of switching from smoking cigarettes to e-cigarettes?
There are many different empirical research methods you can use to answer these questions – for example, experiments , observations, surveys , and interviews.
When doing empirical research, you need to consider things like the variables you will investigate, the reliability and validity of your measurements, and your sampling method . The aim is to produce robust, reproducible scientific knowledge.
Non-empirical dissertations (arts and humanities)
A non-empirical dissertation works with existing research or other texts, presenting original analysis, critique and argumentation, but no original data. This approach is typical of arts and humanities subjects.
- What attitudes did commentators in the British press take towards the French Revolution in 1789–1792?
- How do the themes of gender and inheritance intersect in Shakespeare’s Macbeth ?
- How did Plato’s Republic and Thomas More’s Utopia influence nineteenth century utopian socialist thought?
The first steps in this type of dissertation are to decide on your topic and begin collecting your primary and secondary sources .
Primary sources are the direct objects of your research. They give you first-hand evidence about your subject. Examples of primary sources include novels, artworks and historical documents.
Secondary sources provide information that informs your analysis. They describe, interpret, or evaluate information from primary sources. For example, you might consider previous analyses of the novel or author you are working on, or theoretical texts that you plan to apply to your primary sources.
Dissertations are divided into chapters and sections. Empirical dissertations usually follow a standard structure, while non-empirical dissertations are more flexible.
Structure of an empirical dissertation
Empirical dissertations generally include these chapters:
- Introduction : An explanation of your topic and the research question(s) you want to answer.
- Literature review : A survey and evaluation of previous research on your topic.
- Methodology : An explanation of how you collected and analysed your data.
- Results : A brief description of what you found.
- Discussion : Interpretation of what these results reveal.
- Conclusion : Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your findings contribute to knowledge in your field.
Sometimes the order or naming of chapters might be slightly different, but all of the above information must be included in order to produce thorough, valid scientific research.
Other dissertation structures
If your dissertation doesn’t involve data collection, your structure is more flexible. You can think of it like an extended essay – the text should be logically organised in a way that serves your argument:
- Introduction: An explanation of your topic and the question(s) you want to answer.
- Main body: The development of your analysis, usually divided into 2–4 chapters.
- Conclusion: Answers to your research question(s) and summary of what your analysis contributes to knowledge in your field.
The chapters of the main body can be organised around different themes, time periods, or texts. Below you can see some example structures for dissertations in different subjects.
- Political philosophy
This example, on the topic of the British press’s coverage of the French Revolution, shows how you might structure each chapter around a specific theme.

This example, on the topic of Plato’s and More’s influences on utopian socialist thought, shows a different approach to dividing the chapters by theme.

This example, a master’s dissertation on the topic of how writers respond to persecution, shows how you can also use section headings within each chapter. Each of the three chapters deals with a specific text, while the sections are organised thematically.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Like other academic texts, it’s important that your dissertation follows the formatting guidelines set out by your university. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
Formatting guidelines concern things like:
- line spacing
- page numbers
- punctuation
- title pages
- presentation of tables and figures
If you’re unsure about the formatting requirements, check with your supervisor or department. You can lose marks unnecessarily over mistakes, so it’s worth taking the time to get all these elements right.
How will you reference your sources?
Referencing means properly listing the sources you cite and refer to in your dissertation, so that the reader can find them. This avoids plagiarism by acknowledging where you’ve used the work of others.
Keep track of everything you read as you prepare your dissertation. The key information to note down for a reference is:
- The publication date
- Page numbers for the parts you refer to (especially when using direct quotes)
Different referencing styles each have their own specific rules for how to reference. The most commonly used styles in UK universities are listed below.
| & | An author–date citation in brackets in the text… | …corresponding to an entry in the alphabetised reference list at the end. |
|---|---|---|
| A superscript or bracketed reference number in the text… | …corresponding to an entry in the numbered reference list at the end. | |
| A footnote in the text that gives full source information… | …and an alphabetised bibliography at the end listing all sources. |
You can use the free APA Reference Generator to automatically create and store your references.
APA Reference Generator
The words ‘ dissertation ’ and ‘thesis’ both refer to a large written research project undertaken to complete a degree, but they are used differently depending on the country:
- In the UK, you write a dissertation at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a thesis to complete a PhD.
- In the US, it’s the other way around: you may write a thesis at the end of a bachelor’s or master’s degree, and you write a dissertation to complete a PhD.
The main difference is in terms of scale – a dissertation is usually much longer than the other essays you complete during your degree.
Another key difference is that you are given much more independence when working on a dissertation. You choose your own dissertation topic , and you have to conduct the research and write the dissertation yourself (with some assistance from your supervisor).
Dissertation word counts vary widely across different fields, institutions, and levels of education:
- An undergraduate dissertation is typically 8,000–15,000 words
- A master’s dissertation is typically 12,000–50,000 words
- A PhD thesis is typically book-length: 70,000–100,000 words
However, none of these are strict guidelines – your word count may be lower or higher than the numbers stated here. Always check the guidelines provided by your university to determine how long your own dissertation should be.
At the bachelor’s and master’s levels, the dissertation is usually the main focus of your final year. You might work on it (alongside other classes) for the entirety of the final year, or for the last six months. This includes formulating an idea, doing the research, and writing up.
A PhD thesis takes a longer time, as the thesis is the main focus of the degree. A PhD thesis might be being formulated and worked on for the whole four years of the degree program. The writing process alone can take around 18 months.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, May 05). What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started. Scribbr. Retrieved 10 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/what-is-a-dissertation/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples.
Writing a Postgraduate or Doctoral Thesis: A Step-by-Step Approach
- First Online: 01 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Usha Y. Nayak 4 ,
- Praveen Hoogar 5 ,
- Srinivas Mutalik 4 &
- N. Udupa 6
967 Accesses
1 Citations
A key characteristic looked after by postgraduate or doctoral students is how they communicate and defend their knowledge. Many candidates believe that there is insufficient instruction on constructing strong arguments. The thesis writing procedure must be meticulously followed to achieve outstanding results. It should be well organized, simple to read, and provide detailed explanations of the core research concepts. Each section in a thesis should be carefully written to make sure that it transitions logically from one to the next in a smooth way and is free of any unclear, cluttered, or redundant elements that make it difficult for the reader to understand what is being tried to convey. In this regard, students must acquire the information and skills to successfully create a strong and effective thesis. A step-by-step description of the thesis/dissertation writing process is provided in this chapter.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or Ebook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

The Process of Scientific Writing: Developing a Research Question, Conducting a Literature Review, and Creating an Outline

Persistent Myths About Dissertation Writing and One Proven Way of Breaking Free of Their Spell

Research Writing: Tips and Common Errors
Carter S, Guerin C, Aitchison C (2020) Doctoral writing: practices, processes and pleasures. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-1808-9
Book Google Scholar
Odena O, Burgess H (2017) How doctoral students and graduates describe facilitating experiences and strategies for their thesis writing learning process: a qualitative approach. Stud High Educ 42:572–590. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2015.1063598
Article Google Scholar
Stefan R (2022) How to write a good PhD thesis and survive the viva, pp 1–33. http://people.kmi.open.ac.uk/stefan/thesis-writing.pdf
Google Scholar
Barrett D, Rodriguez A, Smith J (2021) Producing a successful PhD thesis. Evid Based Nurs 24:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1136/ebnurs-2020-103376
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Murray R, Newton M (2009) Writing retreat as structured intervention: margin or mainstream? High Educ Res Dev 28:541–553. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360903154126
Thompson P (2012) Thesis and dissertation writing. In: Paltridge B, Starfield S (eds) The handbook of english for specific purposes. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, Hoboken, NJ, pp 283–299. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118339855.ch15
Chapter Google Scholar
Faryadi Q (2018) PhD thesis writing process: a systematic approach—how to write your introduction. Creat Educ 09:2534–2545. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2018.915192
Faryadi Q (2019) PhD thesis writing process: a systematic approach—how to write your methodology, results and conclusion. Creat Educ 10:766–783. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2019.104057
Fisher CM, Colin M, Buglear J (2010) Researching and writing a dissertation: an essential guide for business students, 3rd edn. Financial Times/Prentice Hall, Harlow, pp 133–164
Ahmad HR (2016) How to write a doctoral thesis. Pak J Med Sci 32:270–273. https://doi.org/10.12669/pjms.322.10181
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Gosling P, Noordam LD (2011) Mastering your PhD, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 12–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15847-6
Cunningham SJ (2004) How to write a thesis. J Orthod 31:144–148. https://doi.org/10.1179/146531204225020445
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Azadeh F, Vaez R (2013) The accuracy of references in PhD theses: a case study. Health Info Libr J 30:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1111/hir.12026
Williams RB (2011) Citation systems in the biosciences: a history, classification and descriptive terminology. J Doc 67:995–1014. https://doi.org/10.1108/00220411111183564
Bahadoran Z, Mirmiran P, Kashfi K, Ghasemi A (2020) The principles of biomedical scientific writing: citation. Int J Endocrinol Metab 18:e102622. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijem.102622
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yaseen NY, Salman HD (2013) Writing scientific thesis/dissertation in biology field: knowledge in reference style writing. Iraqi J Cancer Med Genet 6:5–12
Gorraiz J, Melero-Fuentes D, Gumpenberger C, Valderrama-Zurián J-C (2016) Availability of digital object identifiers (DOIs) in web of science and scopus. J Informet 10:98–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2015.11.008
Khedmatgozar HR, Alipour-Hafezi M, Hanafizadeh P (2015) Digital identifier systems: comparative evaluation. Iran J Inf Process Manag 30:529–552
Kaur S, Dhindsa KS (2017) Comparative study of citation and reference management tools: mendeley, zotero and read cube. In: Sheikh R, Mishra DKJS (eds) Proceeding of 2016 International conference on ICT in business industry & government (ICTBIG). Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Piscataway, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICTBIG.2016.7892715
Kratochvíl J (2017) Comparison of the accuracy of bibliographical references generated for medical citation styles by endnote, mendeley, refworks and zotero. J Acad Librariansh 43:57–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2016.09.001
Zhang Y (2012) Comparison of select reference management tools. Med Ref Serv Q 31:45–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/02763869.2012.641841
Hupe M (2019) EndNote X9. J Electron Resour Med Libr 16:117–119. https://doi.org/10.1080/15424065.2019.1691963
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Pharmaceutics, Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Usha Y. Nayak & Srinivas Mutalik
Centre for Bio Cultural Studies, Directorate of Research, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India
Praveen Hoogar
Shri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara University, Dharwad, Karnataka, India
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to N. Udupa .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Retired Senior Expert Pharmacologist at the Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology, and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Gowraganahalli Jagadeesh
Professor & Director, Research Training and Publications, The Office of Research and Development, Periyar Maniammai Institute of Science & Technology (Deemed to be University), Vallam, Tamil Nadu, India
Pitchai Balakumar
Division Cardiology & Nephrology, Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Fortunato Senatore
Ethics declarations
No conflict of interest exists.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Nayak, U.Y., Hoogar, P., Mutalik, S., Udupa, N. (2023). Writing a Postgraduate or Doctoral Thesis: A Step-by-Step Approach. In: Jagadeesh, G., Balakumar, P., Senatore, F. (eds) The Quintessence of Basic and Clinical Research and Scientific Publishing. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_48
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_48
Published : 01 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-1283-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-1284-1
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Home »
find your perfect postgrad program Search our Database of 30,000 Courses
Dissertation methodology.

What Is The Methodology?
This is the section of your dissertation that explains how you carried out your research, where your data comes from, what sort of data gathering techniques you used, and so forth. Generally, someone reading your methodology should have enough information to be able to create methods very similar to the ones you used to obtain your data, but you do not have to include any questionnaires, reviews, interviews, etc that you used to conduct your research here. This section is primarily for explaining why you chose to use those particular techniques to gather your data. Read more about postgraduate research projects here .
Scientific Approach
The information included in the dissertation methodology is similar to the process of creating a science project: you need to present the subject that you aim to examine, and explain the way you chose to go about approaching your research. There are several different types of research , and research analysis, including primary and secondary research, and qualitative and quantitative analysis, and in your dissertation methodology, you will explain what types you have employed in assembling and analysing your data.
Explain Your methods
This aspect of the methodology section is important, not just for detailing how your research was conducted, but also how the methods you used served your purposes, and were more appropriate to your area of study than other methods. For example, if you create and use a series of ‘yes’ or ‘no’ survey questions, which you then processed into percentages per response, then the quantitative method of data analysis to determine the results of data gathered using a primary research method. You would then want to explain why this combination was more appropriate to your topic than say, a review of a book that included interviews with participants asking open-ended questions: a combination of secondary research and qualitative data analysis.

Writing A Dissertation Methodology
It's important to keep in mind that your dissertation methodology is about description: you need to include details that will help others understand exactly what you aimed to do, how you went about doing it, and why you chose to do it that way. Don’t get too bogged down in listing methods and sources, and forget to include why and how they were suitable for your particular research. Be sure you speak to your course advisor about what specific requirements there may be for your particular course. It is possible that you may need to include more or less information depending on your subject. The type of research you conducted will also determine how much detail you will need to include in the description of your methods. If you have created a series of primary research sources, such as interviews, surveys, and other first hand accounts taken by either yourself or another person active during the time period you are examining, then you will need to include more detail in specifically breaking down the steps you took to both create your sources and use them in conducting your research. If you are using secondary sources when writing your dissertation methodology, or books containing data collected by other researchers, then you won’t necessarily need to include quite as much detail in your description of your methods, although you may want to be more thorough in your description of your analysis.
Research Techniques
You may also want to do some research into research techniques – it sounds redundant, but it will help you identify what type of research you are doing, and what types will be best to achieve the most cohesive results from your project. It will also help you write your dissertation methodology section, as you won’t have to guess when it comes to whether documents written in one time period, re-printed in another, and serialised in book form in a third are primary, secondary, or tertiary sources. Read more on dissertation research here .
Whether or not you have conducted your research using primary sources, you will still want to be sure that you include relevant references to existing studies on your topic. It is important to show that you have carefully researched what data already exists, and are seeking to build on the knowledge that has already been collected. As with all of your dissertation, be sure that you’ve fully supported your research with a strong academic basis. Use research that has already been conducted to illustrate that you know your subject well.
Draft As You Go
Because your dissertation methodology is basically an explanation of your research, you may want to consider writing it – or at least drafting it – as you gather your data. If you are on a PhD course, or a longer masters course, then you may be able to finish researching before you begin writing but it doesn’t hurt to start working on it early that way you can keep on top of what you need to do. Analysing your own methods of research may help you spot any errors in data collection, interpretation or sources.
Dissertation Methodology Structure Example
There are several ways that you can structure your dissertation methodology, and the following headings are designed to further give you a better idea of what you may want to include, as well as how you might want to present your findings. By referring to this example you should be able to effectively structure your dissertation methodology.
Research Overview: where you reiterate the topic of your research.
Research Design: How you’ve set up your project, and what each piece of it aims to accomplish. Data Collection: What you used to collect the data (surveys, questionnaires, interviews, trials, etc.). Don’t forget to includes sample size and any attempts to defeat bias.
Data Analysis: Finally, what does your data mean in the context of your research? Were your results conclusive or not? Remember to include what type of data you were working with (qualitative or quantitative? Primary or secondary sources?) and how any variables, spurious or otherwise factor into your results.
Related articles
Planning A Good Research Project
PhD By Publication
Qualitative Research V Quantitative Research
Qualitative Research
Quantitative Research
Top Tips When Writing Your Dissertation
Everything You Need To Know About Your Research Project
Choosing A Dissertation Topic
How To Edit Your Own Postgraduate Writing
How To Effectively Conduct Postgraduate Research
Top Tips For Easy Postgraduate Research
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Sign up now!

Take 2 minutes to sign up to PGS student services and reap the benefits…
- The chance to apply for one of our 5 PGS Bursaries worth £2,000 each
- Fantastic scholarship updates
- Latest PG news sent directly to you.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Thesis & Dissertation Overview

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
When writing a long document such as a thesis or dissertation over a sustained time period, writers may find it difficult to stay motivated and make progress. Some institutions offer “dissertation retreats” or camps for helping writers make progress. An Intensive Writing Experience (IWE) is a similar event in which a writer makes a concerted effort both to make progress on a document and to become a better writer. The writer sets aside a predetermined amount of time in order to make progress on a particular writing project, such as a dissertation. The material here is meant to be used to conduct a Personal IWE that a writer can use when a group event such as a retreat or camp is not available.
This section contains detailed directions for setting up a Personal IWE. We've included vidcasts and handouts useful for a potential three-day event covering a variety of writing-related topics. Writers can view the vidcasts and read through the handouts and then apply what they have learned to their own writing. We suggest starting with the handout entitled “Conducting a Personal Intensive Writing Experience (IWE)”; this will provide details for structuring time and offers a schedule for the order of topics across a multi-day event.
- Dissertation
Requirements, deadlines, and other information on preparing and submitting a dissertation.
- Fellowships
- Maximizing Your Degree
- Before You Arrive
- First Weeks at Harvard
- Harvard Speak
- Pre-Arrival Resources for New International Students
- Alumni Council
- Student Engagement
- Applying to Degree Programs
- Applying to the Visiting Students Program
- Admissions Policies
- Cost of Attendance
- Express Interest
- Campus Safety
- Commencement
- Diversity & Inclusion Fellows
- Student Affinity Groups
- Recruitment and Outreach
- Budget Calculator
- Find Your Financial Aid Officer
- Funding and Aid
- Regulations Regarding Employment
- Financial Wellness
- Consumer Information
- Life Sciences
- Policies (Student Handbook)
- Student Center
- Title IX and Gender Equity
PhD candidates must successfully complete and submit a dissertation to qualify for degree conferral. It is perhaps the most important and far-reaching undertaking in the entire doctoral program, having an impact that extends well beyond graduate studies.
Requirements and Deadlines
Each graduate program maintains specific requirements for the content and evaluation of the dissertation. Be sure to review your program’s departmental requirements prior to beginning the process. You should also review Harvard Griffin GSAS’s dissertation policies for important information about formatting, submission, and publishing and distribution options, including embargoes.
Degrees are awarded in November, March, and May. Dissertation submission deadlines are noted in the Degree Calendar section of Policies .
Help with the Dissertation
Library research .
It’s never too early to start planning for your dissertation. The Harvard Library can help! The Library maintains a guide for graduate students engaged in scholarly writing titled the Writing Oasis . They also offer access to Overleaf , which is an online LaTeX and Rich Text collaborative writing and publishing tool that makes the process of academic writing, editing, and publishing quicker and easier. Overleaf has a section on Writing Your Dissertation that you may find useful.
Writing
Students can find support with planning and preparing to write the dissertation from their academic advisors and programs. The Fellowships & Writing Center also offers workshops on various aspects of dissertation writing, holds brainstorming office hours during which students may discuss their dissertations, and provides written feedback on dissertation chapters.
Dissertation Completion Fellowships
Harvard Griffin GSAS provides a dissertation completion fellowship (DCF) for one academic year to eligible PhD students in the humanities and social sciences who anticipate completing their dissertations within the year. Find out more in Policies .
Student Affairs
Share this page, explore events.
Ohio State nav bar
The Ohio State University
- BuckeyeLink
- Find People
- Search Ohio State
Dissertations and Theses
The dissertation is the hallmark of the research expertise demonstrated by a doctoral student. It is a scholarly contribution to knowledge in the student’s area of specialization. By researching and writing a dissertation, the student is expected to demonstrate a high level of knowledge and the capability to function as an independent scholar.
A thesis is a hallmark of some master’s programs. It is a piece of original research, generally less comprehensive than a dissertation, and is meant to show the student’s knowledge of an area of specialization.
Document Preparation
PhD and master’s students are responsible for meeting all requirements for preparing theses and dissertations. They are expected to confer with their advisors about disciplinary and program expectations and to follow Graduate School procedure requirements.
The Graduate School’s format review is in place to help the document submission process go smoothly for the student. Format reviews for PhD dissertations and master’s theses can be done remotely or in-person. The format review is required at or before the two-week notice of the final defense.
Access and Distribution
Ohio State has agreements with two organizations— OhioLINK and ProQuest/UMI Dissertation Publishing —that store and provide access to Ohio State theses and dissertations.
Examinations
Graduate degree examinations are a major milestone in all graduate students’ pursuit of their graduate degree. Much hinges on the successful completion of these examinations, including the ability to continue in a graduate program.
The rules and processes set by the Graduate School ensure the integrity of these examinations for graduate students, the graduate faculty, and for Ohio State.
Final Semester
During your final semester as a graduate student there are many activities that lead up to commencement and receiving your degree. Complete the final semester checklist and learn more about commencement activities.
Graduation Calendar
Select your expected graduation term below to see specific dates concerning when to apply for graduation, complete your examinations and reports, submit approved thesis and dissertation, commencement, and the end-of semester deadline.
Applications to Graduate Due 1 : January 26, 2024
Examinations and Reports completed by 2 : April 12, 2024
Approved thesis and dissertation submitted and accepted by 3 : April 19, 2024
Commencement 4 : May 5, 2024
End of Semester Deadline 5 : May 6, 2024
Applications to Graduate Due 1 : May 24, 2024
Examinations and Reports completed by 2 : July 12, 2024
Approved thesis and dissertation submitted and accepted by 3 : July 19, 2024
Commencement 4 : August 4, 2024
End of Semester Deadline 5 : August 19, 2024
Applications to Graduate Due 1 : September 6, 2024
Examinations and Reports completed by 2 : November 22, 2024
Approved thesis and dissertation submitted and accepted by 3 : November 27, 2024
Commencement 4 : December 15, 2024
End of Semester Deadline 5 : January 3, 2025
Applications to Graduate Due 1 : January 24, 2025
Examinations and Reports completed by 2 : April 11, 2025
Approved thesis and dissertation submitted and accepted by 3 : April 18, 2025
Commencement 4 : May 4, 2025
End of Semester Deadline 5 : May 5, 2025
1 Applications to graduate include current semester or End-of-Semester deadline. Applications must be received by close of business.
2 Format reviews may occur electronically or in person at the Graduate School during announced business hours. Both options require submitting a digital version of the dissertation or DMA document draft in a PDF format to [email protected] .
3 Approved documents must be submitted via OhioLINK and accepted by the Graduate School by the close of business before the Report on Final Document will be processed.
4 Students not attending commencement must complete the commencement section on the Application to Graduate to indicate how their diploma should be disbursed.
5 A degree applicant who does not meet published graduation deadlines but who does complete all degree requirements by the last business day prior to the first day of classes for the following semester or summer term will graduate the following semester or summer term without registering or paying fees
Still Have Questions?
Dissertations & Theses 614-292-6031 [email protected]
Doctoral Exams, Master's Examination, Graduation Requirements 614-292-6031 [email protected]

- Study and research support
- Academic skills
Dissertation examples
Listed below are some of the best examples of research projects and dissertations from undergraduate and taught postgraduate students at the University of Leeds We have not been able to gather examples from all schools. The module requirements for research projects may have changed since these examples were written. Refer to your module guidelines to make sure that you address all of the current assessment criteria. Some of the examples below are only available to access on campus.
- Undergraduate examples
- Taught Masters examples
| These dissertations achieved a mark of 80 or higher:
|
| The following two examples have been annotated with academic comments. This is to help you understand why they achieved a good 2:1 mark but also, more importantly, how the marks could have been improved. Please read to help you make the most of the two examples. (Mark 68) (Mark 66) These final year projects achieved a mark of a high first:
For students undertaking a New Venture Creation (NVC) approach, please see the following Masters level examples:
|
|
|
|
|
| Projects which attained grades of over 70 or between 60 and 69 are indicated on the lists (accessible only by students and staff registered with School of Computer Science, when on campus).
|
| These are good quality reports but they are not perfect. You may be able to identify areas for improvement (for example, structure, content, clarity, standard of written English, referencing or presentation quality).
|
|
|
| The following examples have their marks and feedback included at the end of of each document.
The following examples have their feedback provided in a separate document.
|
|
|
| School of Media and Communication . |
|
|
| The following outstanding dissertation example PDFs have their marks denoted in brackets. (Mark 78) (Mark 91) (Mark 85) |
| This dissertation achieved a mark of 84: . |
| LUBS5530 Enterprise
|
| MSc Sustainability
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
| The following outstanding dissertation example PDFs have their marks denoted in brackets. (Mark 70) (Mark 78) |

Postgraduate Thesis Statement
Ai generator.
Navigating the world of postgraduate research is a pivotal stage in one’s academic journey. As you advance into this realm, the emphasis on a well-structured thesis statement becomes even more crucial. A robust thesis statement not only anchors your research but also serves as a beacon, guiding your inquiries and arguments. Delve into these postgraduate thesis statement examples, along with an elucidative guide and valuable tips, to craft a statement that can stand the test of rigorous academic scrutiny.
What is a thesis statement for a Postgraduate? – Definition
A postgraduate thesis statement concise summary of the main point or claim of a research paper or essay at the postgraduate level. It serves as a roadmap for readers, outlining the central argument or purpose of the study. It’s typically more complex and in-depth than undergraduate thesis statements, reflecting the advanced nature of postgraduate research and the nuanced understanding required of the topic.
What is an example of a Postgraduate thesis statement?
Topic: The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Modern Healthcare Systems
Thesis Statement : “This research explores the transformative potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in modern healthcare, asserting that AI’s integration not only optimizes diagnostic accuracy and treatment efficacy but also presents challenges concerning patient data privacy and the role of human medical practitioners.”
100 Thesis Statement Examples for a Postgraduate

Size: 277 KB
Crafting an impactful postgraduate thesis statement requires precision, depth, and a thorough understanding of your research domain. These examples span various disciplines, offering a glimpse into the intricacy and focus expected at this advanced academic level.
- Climate Change and Agriculture : “This study posits that climate change’s adverse effects significantly decrease agricultural yield, necessitating innovative adaptive measures for global food security.”
- Neuroscience and Memory : “This research delves into the neurobiological mechanisms underpinning memory retention, suggesting a pivotal role of the hippocampus in long-term memory consolidation.”
- Cultural Impacts on Marketing : “Examining Eastern versus Western marketing strategies reveals that cultural nuances significantly influence consumer behavior and brand perception.”
- Quantum Computing : “This thesis explores the potential of quantum computing in revolutionizing the computational landscape, emphasizing its superiority in solving specific algorithms compared to classical computers.”
- Mental Health and Social Media : “The correlation between social media usage and mental health outcomes among millennials suggests a significant increase in anxiety and depression rates.”
- Sustainable Architecture : “Green architectural practices not only reduce environmental footprints but also offer cost-efficient solutions in urban developments.”
- Blockchain in Banking : “Blockchain technology, with its decentralized nature, presents transformative prospects for banking security, transparency, and operational efficiency.”
- Child Psychology and Learning : “Play-based learning strategies in early childhood education yield superior cognitive and social development outcomes.”
- AI in Autonomous Vehicles : “Autonomous vehicles utilizing AI algorithms demonstrate a substantial reduction in road accidents compared to human-driven cars.”
- Genetic Engineering and Ethics : “The ethical ramifications of CRISPR technology in human gene editing necessitate stringent regulatory frameworks.”
- Migration and Global Economy : “Mass migrations, driven by socio-political factors, have a dual impact on global economies – rejuvenating labor markets while straining social services.”
- Gender Studies in Workplace Dynamics : “Gender diversity in corporate leadership roles directly correlates with increased creativity and profitability.”
- Astrophysics and Dark Matter : “The quest for understanding dark matter’s nature is pivotal in decoding the universe’s evolutionary trajectory.”
- Augmented Reality in Education : “Augmented Reality (AR) tools in educational settings foster immersive learning experiences, enhancing retention and engagement.”
- Global Health and Pandemics : “The global response to pandemics like COVID-19 underscores the necessity for unified international health protocols and rapid information dissemination.”
- Renewable Energy Adoption : “The transition to renewable energy sources is imperative for sustainable development, yet geopolitical and economic factors often hinder its large-scale adoption.”
- Linguistics and Language Evolution : “The evolution of human language is intrinsically linked to socio-cultural shifts, with technology playing a significant role in modern linguistic transformations.”
- Digital Transformation in Businesses : “Digital transformation, while streamlining operations, introduces challenges related to data privacy and workforce adaptation.”
- Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services : “A decline in global biodiversity directly impacts ecosystem services, affecting human sustenance and well-being.”
- Post-Colonial Literature : “Post-colonial literary works provide a lens to understand the enduring socio-cultural impacts of colonialism on previously colonized societies.
- Forensic Science and Crime : “Incorporating advanced forensic methodologies can significantly increase the conviction rate in criminal justice systems.”
- Space Exploration and Humanity : “The pursuit of interstellar travel holds implications not just for technological advancement but for understanding human resilience and adaptability.”
- Digital Art and Society : “The rise of digital art mediums challenges traditional art conventions, emphasizing the dynamic nature of artistic expression.”
- Nanotechnology in Medicine : “The infusion of nanotechnology in medicine offers prospects for targeted drug delivery, reducing side-effects.”
- Urban Planning and Mental Health : “Urban planning that incorporates green spaces directly influences inhabitants’ mental well-being.”
- Virtual Reality and Rehabilitation : “Virtual reality tools hold transformative potential in physical and psychological rehabilitation strategies.”
- Philosophy and Artificial Intelligence : “The evolution of AI compels a reexamination of philosophical constructs related to consciousness and autonomy.”
- Economics of Climate Change : “The economic ramifications of climate change encompass more than tangible damages, including the revaluation of assets and shifts in global labor markets.”
- Robotics in Healthcare : “Incorporating robotics in healthcare optimizes patient care, especially in surgeries and rehabilitation, but also raises ethical dilemmas.”
- Musicology and Emotions : “The intricate relationship between music and human emotion has neurobiological underpinnings, affecting mood regulation.
- Epigenetics and Disease : “Epigenetic modifications, though reversible, have profound implications in disease onset, progression, and potential therapeutic interventions.”
- Political Science and Media Influence : “The role of media in shaping public political opinions has intensified with the rise of social media platforms, necessitating a reevaluation of election campaign strategies.”
- Marine Biology and Coral Reefs : “The deteriorating health of coral reefs globally serves as an indicator of broader marine ecosystem imbalance and stresses the importance of conservation efforts.”
- Data Science and Privacy : “The surge in big data analytics offers unparalleled insights for businesses but simultaneously poses significant challenges to individual privacy.”
- Anthropology and Ancient Civilizations : “A study of ancient civilizations through anthropological lenses can unearth patterns of human social evolution and provide insights into contemporary societal structures.”
- Astrobiology and Extraterrestrial Life : “The quest for extraterrestrial life in astrobiology reshapes our understanding of life’s potential existence beyond Earth and its implications for humanity.”
- Sports Science and Athlete Performance : “Cutting-edge sports science technologies, from biomechanics to nutrition, have revolutionized athlete training, contributing to record-breaking performances.”
- Cryptography and Cybersecurity : “As cyber threats evolve, so does the field of cryptography, playing a pivotal role in ensuring data integrity and confidentiality in an increasingly digital world.”
- Sociology and Urbanization : “The rapid urbanization of modern societies presents challenges in social cohesion, demanding innovative solutions for ensuring inclusive growth.”
- Quantum Physics and Reality : “Quantum physics, with its counterintuitive principles, challenges classical notions of reality, necessitating a paradigm shift in our understanding of the universe.”
- Mathematical Modelling and Pandemics : “Mathematical models, especially when adapted promptly, provide critical insights into pandemic trajectories, aiding governments in crafting timely interventions.”
- Archaeology and Human Migration : “Modern archaeological techniques reveal intricate patterns of ancient human migrations, challenging conventional narratives of human history.”
- Psychology and Virtual Reality : “The immersion in virtual reality can have profound psychological effects, ranging from therapeutic benefits to potential mental health challenges.”
- Environmental Law and Conservation : “Contemporary environmental laws must adapt to the accelerating climate crisis, emphasizing both conservation and sustainable development.”
- Bioinformatics and Genomic Medicine : “Harnessing bioinformatics in genomic medicine allows for personalized medical treatments, revolutionizing patient care in the 21st century.”
- Space Technology and Satellite Communication : “The advancements in space technology have paved the way for more efficient satellite communication systems, reshaping global connectivity.”
- Geopolitics and Energy Resources : “The geopolitics of energy resources, especially in the Middle East, play a pivotal role in global economic dynamics and international relations.”
- Organic Chemistry and Drug Design : “Innovations in organic chemistry have revolutionized drug design, enabling the creation of targeted therapies for complex diseases.”
- Differential Equations and Engineering : “Differential equations serve as the backbone for modeling in engineering, from fluid dynamics to electrical circuits.”
- Sustainable Finance and Global Economy : “The rise of sustainable finance is not merely an ethical imperative but has tangible impacts on global economic stability and growth prospects.
- Ethnomusicology and Globalization : “Globalization has significantly influenced traditional music forms, introducing a confluence of styles while risking the erasure of unique cultural sounds.”
- Astronomy and Exoplanets : “The discovery of exoplanets challenges our understanding of planetary systems, suggesting myriad possibilities for life beyond Earth.”
- International Law and Cyber Warfare : “The increasing prevalence of cyber warfare necessitates the reevaluation and adaptation of international law to address virtual, borderless conflicts.”
- Biophysics and Cellular Mechanisms : “Biophysical studies reveal the intricate mechanics at cellular levels, promising potential breakthroughs in disease treatment.”
- Comparative Literature and Cultural Identity : “Exploring literature across cultures offers insights into evolving cultural identities in a rapidly globalizing world.”
- Environmental Engineering and Waste Management : “Advancements in environmental engineering have ushered in sustainable waste management practices, pivotal in combating pollution.”
- Metaphysics and Modern Physics : “Contemporary physics, especially quantum mechanics, intersects with metaphysical questions about the nature of reality and consciousness.”
- Robotics and Human Interaction : “The integration of robotics into daily life reshapes human interaction, posing questions about societal adaptation and ethical considerations.”
- Public Health and Aging Population : “With global populations aging, public health initiatives must recalibrate to address the unique challenges and healthcare needs of older adults.”
- Econometrics and Policy Making : “Econometrics, with its empirical analytical tools, plays a vital role in informing and refining economic policy-making.”
- Paleontology and Earth’s History : “Paleontological findings provide a window into Earth’s history, influencing our understanding of evolution and environmental changes.”
- Behavioral Economics and Consumer Behavior : “Behavioral economics uncovers the irrational patterns in consumer behavior, challenging traditional economic theories.”
- Human Rights and Globalization : “The trajectory of human rights in the age of globalization presents a paradox: while rights awareness has spread, violations persist and even intensify in some regions.”
- Topology and Quantum Computing : “The field of topology, focusing on properties of space, holds keys to advancements in quantum computing.”
- Comparative Politics and Democratization : “Comparative studies in politics reveal varying paths to democratization, shaped by historical, economic, and societal factors.”
- Bioethics and Genetic Engineering : “Bioethics emerges as a crucial field as genetic engineering capabilities advance, especially concerning human genome editing.”
- Nanoengineering and Material Science : “Nanoengineering has revolutionized material science, leading to the development of materials with unprecedented properties.”
- Migration Studies and Urban Development : “Migration patterns profoundly influence urban development, with cities evolving in response to diverse influxes of populations.”
- Cognitive Science and Artificial Intelligence : “Exploring the intersections of cognitive science and AI provides insights into replicating human-like learning and thinking in machines.”
- Art History and Digital Media : “Digital media has transformed art history, enabling immersive experiences of art and innovative methods of analysis.
- Oceanography and Climate Change : “The in-depth study of oceans reveals their critical role in regulating global climate, emphasizing the urgent need for marine conservation efforts.”
- Philosophy and Cognitive Sciences : “The intersections of philosophy and cognitive sciences offer profound insights into human consciousness, thought processes, and decision-making.”
- Microbiology and Antibiotic Resistance : “The rise of antibiotic-resistant pathogens necessitates urgent microbiological research to pave the way for new therapeutic approaches.”
- Linguistics and Neural Networks : “The relationship between linguistics and neural networks can provide insights into the development of advanced natural language processing tools in AI.”
- Forensic Science and Legal Systems : “Advancements in forensic science provide pivotal evidence in the legal system, but they also introduce ethical dilemmas related to privacy and potential misuse.”
- Criminology and Urban Safety : “Research in criminology indicates that urban safety strategies must evolve to address the changing dynamics of crime in densely populated areas.”
- Architecture and Sustainable Design : “Sustainable architectural practices are reshaping the built environment, ensuring energy efficiency and ecological harmony.”
- Biomedical Science and Personalized Medicine : “Personalized medicine, backed by biomedical research, holds the promise of tailor-made treatments, optimizing therapeutic outcomes for individual patients.”
- Agriculture and Food Security : “In the face of climate change, innovative agricultural techniques are paramount to ensuring global food security.”
- Dermatology and Nanotechnology : “Nanotechnology’s application in dermatology introduces potent solutions for skin ailments, but it also presents potential risks that require thorough investigation.”
- Political Economy and Global Inequalities : “The political economy framework reveals how power dynamics on a global scale perpetuate economic inequalities.”
- Aerospace Engineering and Interstellar Travel : “While interstellar travel remains a concept of science fiction, advancements in aerospace engineering gradually bring us closer to the possibility of exploring distant star systems.”
- Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases : “Emerging research in endocrinology offers novel insights into metabolic diseases, opening avenues for innovative treatment protocols.”
- Theology and Interfaith Dialogue : “In an increasingly interconnected world, interfaith dialogues become essential to understanding and bridging theological differences.”
- Optometry and Digital Screen Usage : “Increased digital screen usage poses challenges to ocular health, necessitating innovations in optometry for prevention and management.”
- Veterinary Medicine and Zoonotic Diseases : “Understanding zoonotic diseases in veterinary medicine is crucial, given the increasing frequency of animal-human disease transmission events.”
- Urban Planning and Smart Cities : “The concept of smart cities, backed by technological innovations, promises to reshape urban planning to create more sustainable and efficient urban environments.”
- Quantum Mechanics and Classical Physics : “The divergence between quantum mechanics and classical physics continues to intrigue scientists, pushing the boundaries of our understanding of the universe.”
- Pedagogy and Digital Learning : “The rise of digital learning platforms challenges traditional pedagogy, calling for new educational strategies that cater to the digital generation.”
- Entomology and Ecosystem Balance : “Studying insects, especially their interactions within ecosystems, is essential to understand broader ecological balances and the impacts of environmental changes.”
- Neuroscience and Meditation : “Exploring the neural impacts of meditation uncovers its profound effects on cognitive function, stress reduction, and emotional regulation.”
- Maritime Studies and Global Trade : “The intricate world of maritime studies is pivotal in understanding the nuances of global trade, geopolitical tensions, and environmental challenges.”
- Sociology and Social Media : “The integration of social media into daily life has dramatically reshaped societal structures, influencing individual behavior, communal relationships, and even political movements.”
- Paleobotany and Climate Archives : “Studying ancient plant remains offers a unique window into Earth’s climatic history, assisting scientists in predicting future climatic shifts.”
- Film Studies and Cultural Representation : “Cinema serves as a mirror to society, and the study of films provides insights into cultural representation, societal norms, and evolving ideologies.”
- Epistemology and Artificial Intelligence : “The philosophical study of knowledge, or epistemology, prompts crucial questions about AI’s capacity for knowledge and understanding.”
- Chemical Engineering and Renewable Energy : “Innovations in chemical engineering hold the potential to revolutionize renewable energy sources, making them more efficient and widely accessible.”
- Ornithology and Biodiversity : “Studying birds, their habitats, and migratory patterns offers vital information on biodiversity, ecological health, and the impacts of climate change.”
- Pharmacology and Personalized Treatment : “Advanced pharmacological research paves the way for personalized treatments, optimizing drug efficacy based on individual genetic profiles.”
- Anthropology and Globalization : “Through the lens of anthropology, the impacts of globalization on indigenous cultures, traditions, and societal structures become evident, revealing both positive integrations and adverse assimilations.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Postgraduate Argumentative Essay
Postgraduate argumentative essays thesis statement challenge students to take a position on a contentious issue, supported by rigorous research and evidence. Here are thesis statements that showcase diverse angles on various subjects:
- Online Learning : “Despite its convenience, online learning can’t replicate the experiential richness of traditional classroom interactions.”
- Artificial Intelligence : “AI has the potential to outpace human intelligence, making its ethical implications a top priority.”
- Climate Change : “Global warming is the definitive challenge of our generation, and deniers are on the wrong side of science.”
- Mandatory Voting : “Compulsory voting infringes on personal freedoms and doesn’t guarantee a more engaged electorate.”
- Telemedicine : “The rise of telemedicine, accelerated by the pandemic, promises equitable healthcare access but also raises concerns about the quality of remote diagnoses.”
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) : “While CSR initiatives are often lauded, they can sometimes serve as mere PR strategies rather than genuine efforts for societal betterment.”
- Gene Editing : “CRISPR technology holds transformative medical potential, but unchecked edits might lead to unintended genetic consequences.”
- Work-from-Home : “Permanent work-from-home policies could revolutionize work-life balance, but might also blur boundaries leading to employee burnout.”
- Digital Privacy : “Given the increasing intrusiveness of tech giants, stringent data protection regulations are not just preferable but essential.”
- Nuclear Energy : “Nuclear energy, while a potent solution to energy crises, poses significant environmental and security risks.”
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Research paper
Postgraduate thesis statement for research papers delve deep into specialized areas of study, often contributing to existing academic literature. These thesis statements reflect some of these investigative pursuits:
- Microbiome and Health : “Gut microbiota plays a pivotal role in human health, influencing everything from digestion to mental well-being.”
- Quantum Computing : “Quantum computing promises computational power leaps but faces hurdles in practical, scalable applications.”
- Space Exploration : “The recent discovery of water on Mars rekindles debates about its potential habitability.”
- Renewable Energy Storage : “Efficient storage solutions are paramount to maximizing the benefits of renewable energy sources like solar and wind.”
- Mental Health in Adolescents : “The rise in adolescent mental health issues in the digital age hints at social media’s role in exacerbating anxiety and depression.”
- Sustainable Agriculture : “Permaculture practices present a sustainable solution to the global food crisis by promoting ecological balance and reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.”
- Virtual Reality (VR) : “VR technologies in medical training can revolutionize surgical techniques, offering risk-free practice environments.”
- Linguistics : “The rapid extinction of indigenous languages threatens cultural diversity, necessitating urgent preservation efforts.”
- Nanotechnology in Medicine : “Nanobots, while still in nascent stages, hold transformative potential in targeted drug delivery, potentially minimizing side-effects.”
- Blockchain : “Beyond cryptocurrency, blockchain technology offers potential solutions to issues of data transparency and authentication in various sectors.
Postgraduate 3 Point Thesis Statement Examples
Three-point thesis statements succinctly introduce the main points to be discussed in the paper, creating a roadmap for the reader. Here are some tailored to postgraduate topics:
- Augmented Reality : “Augmented Reality enhances user interaction, offers education opportunities, and revolutionizes business models.”
- Bioinformatics : “Bioinformatics streamlines drug discovery, aids in genome sequencing, and offers insights into evolutionary biology.”
- Cognitive Neuroscience : “Cognitive neuroscience sheds light on memory processes, decodes decision-making, and unravels the mysteries of perception.”
- Data Science and Business : “Through predicting consumer behavior, optimizing logistics, and enhancing product recommendations, data science drives business innovation.”
- Green Architecture : “Green architecture promotes energy efficiency, utilizes sustainable materials, and enhances residents’ overall well-being.”
- Healthcare Policies : “Effective healthcare policies reduce medical costs, improve patient outcomes, and ensure universal access.”
- International Relations in the Digital Age : “The digital age reshapes international diplomacy, alters state security dynamics, and fosters new global partnerships.”
- Machine Learning : “Machine learning optimizes automation, delivers personalized content, and aids scientific research.”
- Urban Planning and Sustainability : “Sustainable urban planning ensures efficient transportation, promotes green spaces, and prioritizes community welfare.”
- Zero-Waste Movement : “The zero-waste movement reduces environmental degradation, fosters sustainable consumer habits, and promotes circular economies.”
Thesis Statement Examples For Masters Degree
Masters’ theses delve into intricate research topics, combining comprehensive literature reviews with original research. Here are examples for various fields:
- Global Health : “Addressing global health disparities necessitates international cooperation, local stakeholder engagement, and technological innovations.”
- Marine Biology : “Coral reef bleaching, driven by climate change, jeopardizes marine biodiversity and the livelihoods of coastal communities.”
- Artificial Neural Networks : “Neural networks, mimicking human cognition, revolutionize sectors from finance to healthcare, but require careful calibration.”
- Pedagogical Strategies : “Innovative pedagogical strategies, blending traditional and digital learning, cater to diverse student needs and foster holistic development.”
- Financial Markets : “Algorithmic trading, while maximizing market efficiency, raises concerns about fairness and systemic risks.”
- Contemporary Literature : “Postcolonial narratives in contemporary literature unveil suppressed histories, challenge dominant discourses, and reimagine identity.”
- Green Chemistry : “Green chemistry practices, minimizing environmental footprints, are imperative in the modern industrial landscape.”
- Space Physics : “Explorations into heliophysics provide insights into solar phenomena and their implications for Earth’s space environment.”
- Clinical Psychology : “Mindfulness-based interventions offer promising results in treating anxiety disorders, promoting long-term well-being.”
- Cultural Anthropology : “The digital age reshapes cultural practices, offering a lens to examine evolving societal norms and values.
Thesis Statement Examples To Study Abroad
Studying abroad enriches educational experiences, broadens cultural horizons, and fosters personal growth. Here are thesis statements that explore various facets of international education:
- Language Acquisition : “Studying abroad accelerates language acquisition by immersing students in native-speaking environments, enhancing linguistic fluency.”
- Cultural Identity : “Navigating a new cultural context challenges students’ perceptions, prompting a deeper understanding of both self and others.”
- Global Networking : “Studying abroad fosters international networks, offering cross-cultural collaborations and global career opportunities.”
- Academic Excellence : “Experiencing diverse pedagogical approaches in foreign institutions enhances critical thinking and academic prowess.”
- Cultural Adaptation : “Navigating cultural differences and adapting to new norms sharpens students’ adaptability skills and global perspectives.”
- Career Advancement : “International education equips graduates with a global skillset, making them more attractive to multinational employers.”
- Cultural Exchange : “Cultural exchange programs promote cross-cultural understanding, challenging stereotypes and fostering mutual respect.”
- Personal Growth : “Navigating unfamiliar terrains encourages self-reliance, resilience, and personal development.”
- Global Perspectives : “A global education broadens perspectives, nurturing empathy and a more holistic understanding of global issues.”
- Interdisciplinary Learning : “Studying abroad encourages cross-disciplinary exploration, enriching students’ academic and personal journeys.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Grad School
Graduate school, whether master’s or doctoral, entails rigorous research and academic inquiry. Here are thesis statements that exemplify the depth of inquiry at the graduate level:
- Medicine and Ethics : “Bioethics in medical practice ensures patient autonomy, informed consent, and ethical decision-making, even in complex cases.”
- Literary Theory : “Poststructuralist literary theory deconstructs conventional narratives, revealing hidden power dynamics and challenging literary norms.”
- Economic Policy : “Monetary policies that prioritize financial stability must also consider their social and economic implications for vulnerable populations.”
- Medical Imaging Advances : “Emerging medical imaging technologies promise quicker diagnoses, reduced patient exposure, and enhanced medical insights.”
- Education and Technology : “Integrating technology into education offers opportunities for personalized learning, but also raises concerns about equity and privacy.”
- Sustainable Development : “Sustainable development policies must balance ecological preservation, social equity, and economic growth in a rapidly changing world.”
- Criminal Justice Reform : “Criminal justice reform requires interdisciplinary approaches, addressing systemic racism, rehabilitation, and restorative justice.”
- Artificial Intelligence and Ethics : “Ethical considerations in AI development ensure that AI algorithms align with human values and avoid perpetuating biases.”
- Medical Ethics : “Euthanasia debates revolve around autonomy, dignity, and the responsibilities of healthcare professionals in end-of-life decisions.”
- Social Work and Vulnerable Populations : “Social workers play a pivotal role in advocating for vulnerable populations, addressing systemic inequalities, and promoting social justice.”
Doctoral Thesis Statement Examples
Doctoral theses are pinnacle works of original research, often contributing significantly to their fields. Here are examples that reflect the rigor and innovation expected at the doctoral level:
- Neuroplasticity and Rehabilitation : “Investigating the brain’s adaptive capacities can revolutionize rehabilitation strategies for neurological injuries.”
- Quantum Mechanics and Gravity : “The unification of quantum mechanics and gravity remains elusive, demanding new theoretical paradigms to reconcile the two.”
- Sustainable Urban Design : “Creating eco-friendly, socially inclusive urban spaces requires holistic planning that incorporates environmental, economic, and societal factors.”
- Political Discourse Analysis : “Analyzing political discourse unveils power dynamics, linguistic strategies, and media’s role in shaping public opinion.”
- Cancer Immunotherapy : “Advancing cancer immunotherapy necessitates a deep understanding of the immune system’s complex interactions with tumor cells.”
- Modernist Literature and Identity : “Modernist literature’s fragmentation and ambivalence mirror the complexities of identity in the shifting modern world.”
- Nanomaterials for Clean Energy : “Designing nanomaterials with efficient energy conversion properties can revolutionize the clean energy landscape.”
- Historical Reconstruction through Archaeology : “Archaeological findings reconstruct historical narratives, offering insights into ancient societies, cultures, and practices.”
- Ethnobotany and Traditional Medicine : “Exploring ethnobotanical knowledge deepens our understanding of traditional medicines’ efficacy, informing modern healthcare practices.”
- Astrophysics and Dark Matter : “The elusive nature of dark matter challenges our fundamental understanding of the universe’s composition and gravitational forces.
Thesis Statement Examples for Postgraduate Nursing
Postgraduate nursing studies delve into advanced healthcare practices and research. Here are thesis statements encompassing diverse nursing topics:
- Telehealth in Nursing : “Integrating telehealth technologies enhances nursing care accessibility, especially in remote areas, while ensuring patient privacy and data security.”
- Mental Health Nursing : “Psychiatric-mental health nurses play a pivotal role in treating and destigmatizing mental health conditions, catering to holistic well-being.”
- Emergency Nursing Protocols : “Developing standardized emergency nursing protocols ensures timely, efficient care delivery in critical situations, optimizing patient outcomes.”
- Nursing Leadership : “Effective nursing leadership fosters a culture of collaboration, staff empowerment, and improved patient safety within healthcare institutions.”
- Pediatric Palliative Care : “Specialized pediatric palliative care addresses the unique needs of seriously ill children, offering comfort, pain relief, and emotional support.”
- Nurse Education Strategies : “Innovative nurse education approaches, from simulation-based learning to flipped classrooms, enhance critical thinking and clinical skills.”
- Nurse Advocacy in Policy : “Nurse advocacy in healthcare policy-making safeguards patient rights, promotes evidence-based care, and addresses healthcare disparities.”
- Nursing Research Impact : “Translating nursing research findings into clinical practice ensures evidence-based care, improving patient outcomes and healthcare quality.”
- Nursing Ethics : “Navigating ethical dilemmas in nursing involves balancing patient autonomy, beneficence, and non-maleficence while upholding professional integrity.”
- Global Health Nursing : “Global health nursing addresses disparities, infectious diseases, and healthcare access challenges across diverse cultures and settings.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Postgraduate Degree
Postgraduate degrees encompass a wide array of subjects. Here are thesis statements that highlight the advanced research and expertise required for various disciplines:
- Cultural Heritage Management : “Cultural heritage management requires interdisciplinary collaboration, legal frameworks, and community engagement to preserve diverse histories.”
- Digital Humanities : “Digital humanities marry technological advancements with humanistic inquiry, fostering new ways to analyze and understand cultural artifacts.”
- Environmental Economics : “Environmental economics evaluates the economic impacts of environmental policies, assessing trade-offs between growth and sustainability.”
- Organizational Psychology : “Organizational psychology studies human behavior in workplaces, aiding in employee motivation, team dynamics, and organizational performance.”
- Music Therapy : “Music therapy combines artistic expression and psychology, improving mental health outcomes and emotional well-being through musical interventions.”
- Fashion Sustainability : “Sustainable fashion integrates ethical practices, eco-friendly materials, and circular economies, reshaping the fashion industry’s ecological impact.”
- Robotics Engineering : “Robotics engineering advances automation, prosthetics, and AI, necessitating breakthroughs in mechanics, electronics, and artificial intelligence.”
- Comparative Literature : “Comparative literature transcends cultural and linguistic boundaries, analyzing narratives’ universal themes and cultural contexts.”
- Global Supply Chain Management : “Effective global supply chain management demands risk assessment, supplier collaboration, and dynamic logistical strategies.”
- Visual Communication Design : “Visual communication design merges aesthetics with functionality, influencing how information is conveyed and experienced in various media.”
Short Thesis Statement Examples for Postgraduate
Concise and impactful, short thesis statements convey the essence of postgraduate research topics. Here are succinct examples:
- Medical Ethics : “Balancing patient autonomy and medical beneficence raises pivotal ethical questions in healthcare.”
- Renewable Energy : “Advancing renewable energy technologies is vital for mitigating climate change and achieving energy security.”
- Diversity in Education : “Embracing diversity in education enriches learning environments, fostering global citizenship and empathy.”
- Cybersecurity : “Ensuring cybersecurity safeguards data integrity, privacy, and digital infrastructures from cyber threats.”
- Community Policing : “Community policing bridges gaps, enhancing police-public relations, and fostering safer neighborhoods.”
- Corporate Sustainability : “Corporate sustainability integrates profit with social responsibility, driving ethical business practices and ecological preservation.”
- Aging Population : “Adapting to an aging population requires comprehensive healthcare strategies and social support systems.”
- AI in Healthcare : “AI-driven diagnostics accelerate medical diagnoses, revolutionizing patient care and disease management.”
- Urban Resilience : “Building urban resilience addresses climate-related challenges, ensuring cities thrive despite environmental uncertainties.”
- Cancer Immunotherapy : “Immunotherapy’s personalized approach transforms cancer treatment, enhancing survival rates and patient quality of life.
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Biomedical Engineering
The field of biomedical engineering bridges the gap between medicine and engineering. It focuses on innovative solutions to medical problems, aiming to improve patient care and health outcomes. The following thesis statements reflect the intricate blend of engineering principles and biological sciences to address pressing health challenges.
- Prosthetics and AI : “The integration of AI into prosthetic limbs can significantly enhance functionality, mimicking natural movement more closely than ever before.”
- Tissue Engineering : “Advancements in tissue engineering promise revolutionary treatments for organ damage and loss, potentially reducing the need for donor transplants.”
- Neural Interfaces : “Creating efficient neural interfaces can transform treatments for neurological disorders, offering improved communication tools for patients with severe paralysis.”
- Medical Imaging : “Harnessing the power of quantum physics in medical imaging techniques can lead to earlier and more accurate disease diagnosis.”
- Wearable Health Monitors : “With the rise of wearable tech, biomedical engineering plays a crucial role in developing devices that offer real-time health monitoring outside of clinical settings.”
- Biomaterials for Drug Delivery : “Innovative biomaterials can revolutionize drug delivery systems, providing targeted treatment and reducing systemic side effects.”
- 3D Bioprinting : “3D bioprinting presents a promising future in regenerative medicine, potentially creating functional organs for transplantation.”
- Nanomedicine : “Harnessing nanotechnology in medicine offers targeted treatments at the molecular level, especially promising for cancer therapeutics.”
- Bioinformatics in Genomic Medicine : “Bioinformatics tools can decode complex genomic data, paving the way for personalized medicine and treatments tailored to individual genetic makeup.”
- Rehabilitation Robots : “Robot-assisted therapy, designed via biomedical engineering, can drastically improve recovery outcomes for patients post-stroke or traumatic injuries.”
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Environmental Law
Environmental law at the postgraduate level delves into the legal aspects of environmental protection and sustainable development. These thesis statements emphasize the regulatory, ethical, and global dimensions of laws formulated to protect our planet.
- International Treaties on Climate Change : “Analyzing international treaties reveals the challenges and successes in creating a global consensus on climate action.”
- Environmental Justice : “Environmental law must address the disproportionate environmental burdens faced by marginalized communities, ensuring justice and equity.”
- Marine Conservation Laws : “Stricter marine conservation laws are pivotal in preventing the ongoing degradation of marine ecosystems and ensuring sustainable fisheries.”
- Deforestation Regulations : “Strengthening deforestation regulations is imperative in preserving biodiversity, maintaining carbon sinks, and supporting indigenous communities.”
- Wildlife Trafficking : “Reinforced legal measures against wildlife trafficking can deter illicit activities, protecting endangered species from the brink of extinction.”
- Corporate Accountability in Pollution : “Enforcing stringent laws against corporate pollution can ensure companies prioritize sustainable practices over profit margins.”
- Land Use and Zoning Laws : “Refined land use and zoning regulations can guide sustainable urban development while preserving vital green spaces.”
- Freshwater Resource Laws : “Given escalating water crises, creating robust legal frameworks is essential in managing and preserving freshwater resources for future generations.”
- Genetic Resource Rights : “Legal measures concerning genetic resources can safeguard biodiversity and ensure fair benefit-sharing with indigenous communities.”
- Chemical Waste Disposal : “Enhanced legal frameworks governing chemical waste disposal can prevent environmental contamination and safeguard public health.
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Digital Marketing
Digital marketing harnesses the power of online platforms to connect businesses with their target audiences. It constantly evolves with technology and consumer behavior. The following thesis statements explore various facets of digital marketing in the modern era, from social media strategies to the implications of big data.
- Consumer Behavior in E-commerce : “Analyzing digital footprints offers a deeper understanding of consumer behavior, allowing e-commerce businesses to personalize shopping experiences.”
- SEO and Web Traffic : “Optimizing website content for search engines is a cornerstone of digital visibility, directly impacting web traffic and potential conversions.”
- Influencer Marketing : “Leveraging influencer partnerships can significantly boost brand awareness and credibility, especially among younger demographics.”
- Big Data in Marketing Strategy : “Harnessing big data analytics allows businesses to predict market trends and tailor marketing strategies for optimized engagement.”
- Video Content Engagement : “In the age of short attention spans, video content emerges as a leading tool for sustained audience engagement and brand retention.”
- Social Media Algorithms : “Understanding the intricacies of social media algorithms is pivotal for brands aiming to maintain visibility and engagement on platforms like Instagram and Facebook.”
- Digital Marketing Ethics : “As digital marketing tools become more invasive, ethical considerations must guide strategies to protect consumer privacy.”
- Augmented Reality Advertising : “Incorporating augmented reality (AR) into advertising campaigns offers immersive experiences, revolutionizing consumer-brand interactions.”
- Chatbots and Customer Service : “Integrating AI-powered chatbots on business platforms enhances customer service efficiency and accessibility.”
- Mobile-First Marketing : “With the ubiquity of smartphones, adopting a mobile-first approach in digital marketing strategies is no longer optional but essential.”
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Contemporary Literature
Contemporary literature offers a reflection of society, addressing its complexities, challenges, and transformations. The thesis statements below delve into various themes and narrative techniques that define modern literary works.
- Postcolonial Narratives : “Contemporary literature frequently revisits postcolonial themes, shedding light on the lasting impacts of colonialism and the complexities of identity.”
- Dystopian Literature in the Digital Age : “Modern dystopian narratives often address concerns related to digital technology, surveillance, and loss of individuality.”
- Gender and Sexuality : “Contemporary literary works play a pivotal role in challenging traditional gender norms and exploring diverse spectrums of sexuality.”
- Magical Realism and Cultural Identity : “Magical realism in literature serves as a bridge between cultural myths and contemporary realities, especially in postcolonial contexts.”
- Migration and Diaspora : “Modern literary works often tackle themes of migration and diaspora, reflecting global movements and the challenges of cultural integration.”
- Ecocriticism and Environmental Concerns : “Contemporary literature is increasingly colored by ecocritical perspectives, mirroring global concerns about environmental degradation.”
- Metafiction and Narrative Structure : “Metafictional techniques in modern literature challenge traditional narrative structures, prompting readers to question the nature of storytelling itself.”
- Posthumanism in Literature : “Recent literary works explore posthumanist themes, grappling with the implications of AI, biotechnology, and the blurring boundaries between human and machine.”
- Literature in the Age of Terrorism : “The post-9/11 world sees a surge in literary works addressing the socio-political implications of terrorism and its impact on global consciousness.”
- Digital Narratives and E-literature : “The rise of e-literature and digital narratives redefines the boundaries of literature, offering interactive and multimedia reading experiences.”
Postgraduate Thesis Statement Examples for Urban Planning
Urban planning shapes the physical layout of cities, aiming to improve the quality of life, sustainability, and functionality of urban spaces. The following thesis statements address various challenges and strategies in urban development and design.
- Sustainable Urban Design : “Incorporating sustainable practices in urban design is essential for creating eco-friendly, energy-efficient cities of the future.”
- Public Transportation Systems : “Developing efficient public transportation systems can drastically reduce urban congestion and environmental pollution.”
- Urban Green Spaces : “The integration of green spaces in urban layouts promotes biodiversity, enhances mental well-being, and mitigates the heat island effect.”
- Urban Regeneration : “Regenerating dilapidated urban areas not only revitalizes the physical space but also boosts socio-economic growth and community development.”
- Smart Cities and Technology : “Harnessing smart technologies in urban planning can lead to more efficient, adaptable, and user-friendly cities.”
- Housing and Affordability : “Addressing housing affordability in urban planning strategies ensures diverse, inclusive, and cohesive urban communities.”
- Historical Preservation : “Balancing modern urban development with historical preservation maintains a city’s cultural heritage while catering to contemporary needs.”
- Urban Agriculture : “Promoting urban agriculture can bolster local food systems, reduce transportation emissions, and offer green recreational spaces for residents.”
- Infrastructure and Climate Resilience : “Modern urban planning must prioritize climate-resilient infrastructure to mitigate risks posed by climate change-related events.”
- Pedestrian-Friendly Designs : “Designing pedestrian-friendly urban layouts promotes physical activity, reduces vehicular traffic, and fosters community interactions.
How to Write a Postgraduate Thesis Introduction
The introduction of your postgraduate thesis sets the stage for your research, capturing the reader’s interest while providing context for your study. Follow these steps to craft an engaging and informative introduction:
- Understand the Purpose : Clearly define the purpose of your thesis introduction. It should introduce your research topic, explain its significance, and outline the research questions you aim to address.
- Provide Background Information : Give the reader a solid foundation by providing relevant background information about the subject. Highlight key concepts, theories, and prior research that will help frame your study.
- State the Problem or Gap : Clearly articulate the problem, gap, or research question that your thesis addresses. Explain why this topic is worth investigating and how it contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
- Establish Relevance : Connect your research to broader contexts such as societal, academic, or practical implications. Show why your study matters and how it can address real-world challenges.
- State Your Hypothesis or Research Objectives : If applicable, state your thesis’s hypothesis or the objectives guiding your research. This provides a roadmap for what you’ll explore in the subsequent chapters.
- Outline the Methodology : Briefly describe the research methods and approaches you’ll employ. This helps the reader understand how you’ll gather data and analyze it to answer your research questions.
- Highlight Structure : Give a concise overview of the chapters that will follow in your thesis. This helps readers anticipate the organization of your work.
- Capture Attention : Craft a compelling opening paragraph that grabs the reader’s attention. This could be a relevant anecdote, a surprising fact, or a thought-provoking question.
- Maintain Clarity : Write in clear and concise language. Avoid jargon that might confuse readers who are not experts in your field.
- Revise and Polish : Your introduction is the first impression readers have of your thesis. Revise, edit, and proofread to ensure it’s well-structured, coherent, and free of grammatical errors.
How to Write a Postgraduate Thesis – Step by Step Guide
Writing a postgraduate thesis is a comprehensive endeavor that demands careful planning, research, and writing. Follow these steps to navigate the process effectively:
- Choose a Relevant Topic : Select a topic that aligns with your field of study, interests, and academic goals. Ensure it’s specific, researchable, and adds value to existing literature.
- Conduct Preliminary Research : Familiarize yourself with the existing literature on your chosen topic. Identify gaps, controversies, or unanswered questions that your research can address.
- Craft a Research Proposal : Outline your research objectives, research questions, methodology, and expected contributions. Seek feedback from mentors or advisors before proceeding.
- Formulate a Thesis Statement : Your thesis statement encapsulates the main argument of your thesis. It should be clear, concise, and specific, guiding your research and shaping your paper’s focus.
- Plan Your Research : Create a detailed research plan outlining the scope, methods, data sources, and timeline for each phase of your study.
- Gather and Analyze Data : Collect data through surveys, experiments, interviews, or archival research, depending on your field. Analyze the data using appropriate methods.
- Structure Your Thesis : Organize your thesis into sections such as introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion. Follow any specific formatting guidelines.
- Write Drafts of Each Section : Start writing early. Draft each section of your thesis, focusing on clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Revise and refine as you go.
- Cite Sources Properly : Adhere to the citation style required by your institution or field. Properly cite all sources to avoid plagiarism and give credit to prior research.
- Revise and Proofread : Once you have a complete draft, take time to revise for content, clarity, and coherence. Proofread meticulously for grammar and punctuation errors.
- Seek Feedback : Share your draft with mentors, advisors, or peers for constructive feedback. Address their suggestions and refine your thesis accordingly.
- Write the Introduction and Conclusion Last : Writing the introduction and conclusion becomes easier once you have a clear understanding of your entire thesis. These sections should succinctly summarize your work’s essence.
Tips for Writing a Thesis Statement for a Postgraduate
A strong thesis statement forms the foundation of your postgraduate thesis. Follow these tips to craft an effective and impactful thesis statement:
- Be Clear and Specific : Your thesis statement should convey a clear and specific argument or research question. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Reflect Your Focus : Your thesis statement should accurately reflect the main focus of your research. It sets the tone for your entire thesis.
- Make It Debatable : A good thesis statement is one that can be debated or challenged. Avoid statements that are universally accepted or obvious.
- Avoid Ambiguity : Ensure that your thesis statement is not open to multiple interpretations. Ambiguity can confuse readers.
- Use Concise Language : Keep your thesis statement concise, usually consisting of one or two sentences. Avoid unnecessary wordiness.
- Incorporate Key Terms : Include important keywords or concepts relevant to your field. This helps readers understand the context of your research.
- Highlight Significance : Your thesis statement should communicate why your research is significant and what contributions it will make to your field.
- Refine Through Revision : Your thesis statement may evolve as you progress in your research. Don’t hesitate to revise and refine it for accuracy and clarity.
- Align with Evidence : Ensure that your thesis statement aligns with the evidence you gather during your research. Avoid making claims that your data cannot support.
- Seek Feedback : Share your thesis statement with mentors or peers for feedback. Their input can help you refine and improve it before finalizing.
Writing a postgraduate thesis demands dedication, diligence, and a keen eye for detail. By following these guidelines, you can craft an engaging introduction, navigate the thesis writing process, and create a compelling thesis statement that captures the essence of your research. Remember that the journey of research and writing is as important as the final product, as it allows you to contribute to your field and showcase your expertise. You should also take a look at our thesis statement for review .
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- Open access
- Published: 12 July 2024
Evaluating the perceived impact and legacy of master’s degree level research in the allied health professions: a UK-wide cross-sectional survey
- Terry Cordrey 1 , 2 ,
- Amanda Thomas 3 ,
- Elizabeth King 1 , 2 &
- Owen Gustafson 1 , 2
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 750 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
44 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
Post graduate master’s degree qualifications are increasingly required to advance allied health profession careers in education, clinical practice, leadership, and research. Successful awards are dependent on completion of a research dissertation project. Despite the high volume of experience gained and research undertaken at this level, the benefits and impact are not well understood. Our study aimed to evaluate the perceived impact and legacy of master’s degree training and research on allied health profession practice and research activity.
A cross-sectional online survey design was used to collect data from allied health professionals working in the United Kingdom who had completed a postgraduate master’s degree. Participants were recruited voluntarily using social media and clinical interest group advertisement. Data was collected between October and December 2022 and was analysed using descriptive statistics and narrative content analysis. Informed consent was gained, and the study was approved by the university research ethics committee.
Eighty-four responses were received from nine allied health professions with paramedics and physiotherapists forming the majority (57%) of respondents. Primary motivation for completion of the master’s degree was for clinical career progression ( n = 44, 52.4%) and formation of the research dissertation question was predominantly sourced from individual ideas ( n = 58, 69%). Formal research output was low with 27.4% ( n = 23) of projects published in peer reviewed journal and a third of projects reporting no output or dissemination at all. Perceived impact was rated highest in individual learning outcomes, such as improving confidence and capability in clinical practice and research skills. Ongoing research engagement and activity was high with over two thirds ( n = 57, 67.9%) involved in formal research projects.
The focus of master's degree level research was largely self-generated with the highest perceived impact on individual outcomes rather than broader clinical service and organisation influence. Formal output from master’s research was low, but ongoing research engagement and activity was high suggesting master’s degree training is an under-recognised source for AHP research capacity building. Future research should investigate the potential benefits of better coordinated and prioritised research at master’s degree level on professional and organisational impact.
Peer Review reports
Higher levels of research engagement by healthcare organisations and clinicians are associated with improved organisational performance and clinical outcomes [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. The Allied Health Professions (AHPs) comprise one third of the health and social care workforce in the United Kingdom and when engaged in research, offer substantial benefit to population health and organisational performance [ 4 ]. The strategic focus on AHP research has grown substantially in recent years. This includes the first ever national research and innovation strategy for AHPs in England, as well as clear strategic intention through AHP clinical research networks hosted by the National Institute for Health Research [ 5 , 6 ]. These strategies reinforce the need for capacity building, engagement, and cultural improvements for advancing AHP research. Realising these ambitions has, to date, been limited by insufficient funding, career infrastructure, and organisational support [ 7 ].
Alongside the strategic ambitions for AHP research, is the increasing requirement for post-graduate master’s degree qualifications for career progression in academic, leadership and clinically advanced AHP roles. For example, 69% of Advanced Clinical Practitioners (ACP’s) state the requirement for master’s degree qualification for their current ACP role [ 8 ].
With few exceptions, a master’s degree award is dependent on the successful completion of a supervised research dissertation project. This is usually accompanied by taught research methodology to support the development of research knowledge and skills. Master’s degree research ideas are conceived in a variety of ways, either as stand-alone projects, supplied by a university academic as one part of a larger programme of work, or developed in collaboration with a health service [ 9 ]. AHP research projects developed collaboratively between health and academic centres are more likely to be widely disseminated, impactful on clinical practice, and lead to further research compared to projects undertaken exclusively within a university setting [ 10 ].
Despite the high cumulation of training and research at this level over the years, the broader impact on clinical services, employing organisations, and the wider research community is currently unknown [ 11 ]. Beyond the fulfilment of individual learning objectives, it is difficult to determine what real-world impact AHP master’s research offers in terms of original knowledge contribution. Similarly, the rate of conversion of AHP master’s degree research to peer reviewed publications or conference proceedings remains unexplored [ 12 ]. This situation risks a low return on investment in terms of the generation and translation of knowledge to address the challenges faced by AHPs in healthcare practice [ 13 ]. Responsible practice in AHP post graduate training and research should, in part, be concerned with reducing waste that arises from decisions about what research to prioritise, as well as educational benefit to the individuals [ 14 ]. Aligning and coordinating more AHP master's degree research activity through collaboration may prevent AHP dissertations entering the “relevance waste quadrant” [ 15 ]. Models of portfolio research, which are coordinated efforts to address the highest priority knowledge gaps through research collaborations, represent an alternative approach to the current system [ 16 ].
The primary aim of our study is to evaluate the perceived impact and sustained effect of master’s degree research dissertation projects on AHP research capacity, capability, and clinical practice. In doing this, we have set out five supporting objectives:
To understand how master’s degree research dissertation questions were determined.
To establish the rate of conversion of master’s degree research to traditional measures of research output and dissemination.
To establish whether successful completion of master’s degree research promotes the maturation of ongoing research active clinicians.
To determine the perceived impact of research skills developed through master’s degree completion on AHP research capacity building within individuals and organisations.
To determine the perceived impact of master’s degree research on clinical practice and services.
An online cross-sectional survey design was chosen as the method to conduct this study, and it is being reported according to the consensus-based checklist for reporting of survey studies [ 17 ]. A bespoke survey was constructed using Microsoft Forms software and was hosted online via Microsoft Office 365. The survey comprised 27 questions arranged into sections to collect data on participant demographics, and the experience, outcomes, and perceived impact of master’s degree training and completion of a research dissertation project (see additional file 2 in supplementary information). To develop the survey, a pilot survey was undertaken using four qualified AHP volunteers to appraise the structure, content, and readability of the questions. Feedback from the pilot was used to revise and finalise the survey.
The target population were AHPs, which is an umbrella term for fourteen different professions usually employed in a variety of roles across health, care, academic, and voluntary sectors ( https://www.england.nhs.uk/ahp/role/ ). Participants were eligible to take part if they were 1) qualified AHPs currently working in the United Kingdom (UK), 2) held a post graduate master’s degree award, and 3) were able to provide informed consent. Participants were ineligible if their master’s degree was obtained as a pre-registration qualification, and they did not meet the other inclusion criteria. A target sample size of 139 was calculated by estimating the proportion of all registered AHPs in the UK holding a master’s degree qualification. This estimation was determined by profiling the qualifications of AHP staff in two large National Health Service (NHS) teaching hospitals. To account for a sampling calculation error, a confidence interval (95%) and margin of error (5%) threshold were applied accordingly (see additional file 3 in supplementary information).
Participant recruitment was achieved through advertising on social media platforms, and via newsletters and bulletins circulated by AHP professional and clinical interest groups. Participant information was provided outlining the study details, anonymity of survey responses, and the requirement to provide informed consent and eligibility at the start of the online survey. Those taking part were asked to reflect on their experiences of completing a post graduate master’s degree and research dissertation project in relation to its impact and legacy. The ‘one response per participant’ feature was enabled to prevented multiple completion of the survey by the same participant. The survey was live for data collection for three months running from October to the end of December 2022. During data collection, several efforts were made to promote the survey through social media to increase participation.
The survey data was analysed in two ways. First, descriptive statistics were used to analyse numerical, multiple choice, and ordinal scale data. Second, free text responses providing reflective accounts and experiences underwent coding and content analysis using NVivo software (version 12).
This study was approved by the university research ethics committee (registration number: 221613) and was conducted in accordance with the principles of good clinical practice.
The survey received 84 responses from nine of the fourteen allied health professions, which represents 60% of the target sample of 139. The majority of responses were from physiotherapists ( n = 40, 47.6%) and respondents had been qualified for a median (IQR) of 18 years (12–23). Respondents worked in a variety of clinical specialties, with emergency/pre-hospital medicine ( n = 18, 21.4%), neurology ( n = 12, 14.3%) and critical care ( n = 11, 13.1%) the most common. Most respondents had completed their master’s degree after 2010 ( n = 68, 81%) and were employed at band 6 grade when starting ( n = 39, 46.4%). Most respondents worked in the NHS ( n = 78, 92.3%) and had undertaken a Master of Science (MSc) award ( n = 70, 83.3%). Most participants were employed in a higher paid position after completing their master's degree ( n = 62, 73.8%). The full characteristics of the respondents are detailed in Table 1 .
Respondents predominantly formed their dissertation research questions from their own area of interest (Table 2 ). Less than 10% of the dissertation questions were based on published research priorities or set by the Higher Education Institute (HEI), regional or local healthcare organisation/collaborative ( n = 7, 8.3%). A variety of methodologies were used to conduct the master’s research dissertation with evidence synthesis being the most common ( n = 30, 35.7%).
Formal research output from the dissertations was low (Table 2 ). Half the dissertations were presented at a local research symposium ( n = 44, 52.4%), 27.4% ( n = 23) were published in a peer reviewed journal, and over a third of dissertations had no output at all ( n = 30, 35.7%). Master’s degree programmes contributing to the peer reviewed publications as a proportion of students were Master by Research (MRes) ( n = 5, 45.5%), and MSc ( n = 18, 25.7%).
Of the dissertations formed through the individual's own ideas, 27.6% ( n = 16) were published in a peer reviewed journal, compared to 57.1% ( n = 4) of those set through research priorities, or the HEI/healthcare organisation. The most common methodologies published in a peer review journal were evidence synthesis ( n = 7, 30.4%), qualitative interviews/focus groups ( n = 6, 26.1%) and quantitative experimental studies ( n = 6, 26.1%). The methodology of dissertation projects with the highest proportion of peer reviewed journal publication was qualitative interviews/focus groups ( n = 7, 36.8%).
The respondents reported their master's degree dissertation as having a positive impact on their professional development (Fig. 1 ). Qualitative content analysis of the free text responses demonstrated that respondents felt the dissertation increased their research capability and confidence at multiple stages of the research process while providing opportunities for networking and collaborations.
Perceived impact of master’s degree research on professional and clinical service development
Most participants continued to engage in research activities after their dissertation ( n = 65, 77.4%) through supporting others ( n = 63, 75%), taking part in formal research projects ( n = 57, 67.9%) and publishing research papers ( n = 41, 48.8%) (Table 3 ). Less than ten percent (9.5%, n = 8) reported being deterred from undertaking further research (Fig. 1 ).
The wider perceived impact of the dissertation on services in which the respondents worked was more varied (Fig. 1 ). Improved service user outcome/experience and team practice was reported by 60.7% ( n = 51) and 53.6% ( n = 45) respectively. Analysis of free text responses demonstrated wide ranging perceived impact on services from no local impact to improved team education, service delivery and application of evidence-based practice.
Our study evaluated the perceived impact of master's degree level research on AHP professional development, research capacity, and clinical practice. Our findings indicate a relatively low level of dissemination and formal output arising from master’s degree research, but a high perception of impact on individual AHPs and the clinical services in which they work. The level of ongoing engagement in research activity following master’s degree completion was high indicating a positive legacy in this respect. The degree to which this meaningfully contributes to AHP research capacity building requires further investigation.
The majority (69%) of master’s degree research questions were developed from the respondent’s own ideas rather than drawing on published research priorities or collaborations between health and academic organisations. The limited use of research priorities may be explained by a potential lack of awareness. A qualitative study of 95 AHPs working in Australia found that in the absence of a recognised framework to guide research prioritisation, individual clinicians conducted research in areas important to them [ 18 ]. Pursuing individual preferences in this way stemmed from evaluations of their personal work, departmental policies or procedures, models of care innovation, and a clear preference for research which “tested solutions”. Similarly, Amalkumaran et al. (2016) explored critical care research priorities and found that research topics suggested by professional sub-groups tended to be related to their daily practice rather than broader research priorities [ 19 ].
It is also possible that the choice of research question is influenced by the career motivation of the individual AHP. A UK wide cross-sectional survey of AHPs working in health and social care reported primary motivators for research participation were to develop skills (80%) and increase job satisfaction (63%), rather than contribute to the prioritised evidential knowledge base [ 20 ]. Davis et al. (2019) also recognise this self-actualising motivation for research participation in their AHP cohort [ 18 ]. It is possible that the debut, non-commissioned research activity introduced by master’s level academic programmes emphasises process over content , decreasing the alignment of research activity with known research priorities.
We found a low conversion rate from master’s dissertation completion to formal research output. This is well illustrated in that just one in four (27.4%) master’s theses resulted in a peer-reviewed publication. Similar publication rates have been reported in master’s students of other healthcare disciplines; these are also considered low by way of expected research output [ 21 ]. Understanding this further is challenging due to the limited research in this subject area, which suggests a lack of interest and/or perceived importance. However, there are two key issues that arguably counter this view. First, master’s degree research projects are typically approved by a university research ethics committee, and thus are guided by the principle that the value in their conduct and knowledge contribution should outweigh the burden or risks to participants [ 22 ]. Fidelity to this principle can only be meaningfully appraised if the results are published for wider critical evaluation. Second, AHP skill and success level in research activities, such as writing for peer-reviewed publication is widely and consistently reported as low [ 23 , 24 , 25 ]. This clearly represents an area for improvement for AHPs and failing to challenge the development of this skill in those undertaking post graduate level research seems counter intuitive. Higher rates of master’s degree research publication could offer a meaningful contribution to AHP research capacity building, since our findings suggest there is continued engagement in research activity from this group beyond completion of their studies.
Respondents to our survey indicated a good level of research engagement after master’s degree training. Over three quarters reported continued involvement in research beyond the completion of their programme. This finding supports the idea that research education is a key lever and greatly needed to successfully build AHP research capacity [ 26 , 27 ]. However, the degree to which master’s degree training translates to growth in the research capacity of individuals has not been subject to causal investigation. Proxy indicators of individual research capacity from our cohort can be found in the self-reported high levels of research confidence and capability derived from master’s degree training (Fig. 1 ) and ongoing research activity. This activity included 60% taking part in formal research projects, around half had published research papers, and over a third had embarked on a higher research degree. The lack of previous research in this area makes it challenging to fully contextualise our findings, but in conducting our study, we have set out a benchmark for the perceived impact of masters degree training on individual AHP research capacity for future investigation.
We explored higher level outcomes of master’s degree training on research capacity building, such as those that might influence policy, career pathways, and organisational practice. Using the Kirkpatrick-Barr model of educational outcomes, we found the activity and outcomes from our cohort aligned best to an individual learner level [ 28 ]. This finding is typical of outcomes from education at this level, which centre largely on the individuals through self-reported satisfaction and perceptions of learning [ 29 ]. Understanding the impact of research education and training in relation to higher Kirkpatrick-Barr outcomes requires objective and longitudinal evaluation of research metrics and impact at organisational and system level [ 30 ]. This is likely to include contributions to larger programmes of work requiring large grant awards, significant publications, and translation of those research findings to health organisation and system level innovation [ 31 , 32 ]. Research capacity building at this level is known to be challenging due to the inherent complexities involving political, financial, structural, and cultural factors [ 33 ]. To overcome this, the use of theoretical frameworks has been suggested to help conceptualise and integrate a culture and proliferation of AHP research at various health system structural levels [ 34 ]. The positioning of AHP master’s degree training and research activity as part of this may foster greater academic-health system collaboration for professional, service user, and population benefit [ 35 ].
The perceived impact of master’s degree research included improvements to service user outcomes, clinical pathways, and organisational policies and/or guidelines. Research impact, defined as the demonstrable benefit of research to individuals and society, is complex and requires wide stakeholder engagement to determine whether research has addressed known priorities through effective translation of knowledge from its findings [ 36 ]. The self-generated research questions and low level of dissemination and output reported by our cohort suggests a degree of dissonance between the level of perceived impact versus what is measurably impactful to clinical services and end users. This difference may be explained by the challenges in defining and quantifying research impact for novice researchers, which is described as an ambiguous and subjective concept [ 37 ]. It is therefore not surprising to see the highest levels of reported impact from our cohort was on their own professional development in terms of improved confidence, leadership and research capability, and clinical practice development. Without a more objective assessment of the wider impact from the research undertaken at this level, it is difficult to reconcile its actual impact. The emergence of assessment frameworks, such as the visible impact of research tool, make it accessible for relatively inexperienced researchers to understand how their research has led to visible changes and impact on services and other research consumers [ 38 ].
Strengths and limitations
A key strength of our study lies in its novelty; we believe it to be the first to evaluate the perceived impact of research undertaken by AHPs at master’s degree level. This represents an important first step in highlighting the conduct and contribution of research undertaken at this level, as well providing opportunities to improve future practice and impact. There are several limitations to our study. We only managed to recruit 60% of our target sample via a non-probability sampling technique, which included a lack of representation from five of the 14 professions. This means our findings are vulnerable to sampling bias by potentially excluding AHPs who do not use social media or subscribe to clinical interest groups, which were the two main platforms for our recruitment. Our recruitment practice and the method of a self-reporting survey means our findings are not generalisable to the wider AHP population and they should be interpreted with these limitations in mind. A further limitation is the disproportionate representation of two of the fourteen allied health professions. Responses from paramedics and physiotherapists constituted 57% of our data with very few responses from seven other professions and no responses from five of the professions.
The perceived impact of AHP master’s degree training and research was highest on individual development rather than service and organisation outcomes. This is likely to derive from the individual motivation in undertaking post-graduate study and self-determined research dissertation focus. Whilst the formal research output arising from the master’s research was relatively low, the legacy in terms of ongoing research engagement and activity was positive indicating that master’s degree completion maybe an under-recognised source of AHP research capacity building. Our study provides novel insights into the perceived impact of AHP master’s degree level research. Future research should explore the feasibility and benefits of coordinating AHP master’s degree research with local or national priorities to understand the impact beyond that realised at an individual level.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Abbreviations
Allied Health Professions
Advanced Clinical Practitioner
United Kingdom
National Health Service
Qualitative data analysis software
Interquartile Range
Master of Science
Higher Education Institute
Masters by Research
Master of Art
Doctor of Philosophy
Boaz A, Hanney S, Jones T, et al. Does the engagement of clinicians and organisations in research improve healthcare performance: a three-stage review. BMJ Open. 2015;5:e009415. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009415 .
Article Google Scholar
Hanney S, Boaz A, Jones T, Soper B. Engagement in research: an innovative three-stage review of the benefits for health-care performance. Southampton: NIHR Journals Library; 2013.
Google Scholar
Harding K, Lynch L, Porter J, Taylor NF. Organisational benefits of a strong research culture in a health service: a systematic review. Aust Health Rev. 2017;41(1):45–53. https://doi.org/10.1071/AH15180 .
Harris J, Grafton K, Cooke J. Developing a consolidated research framework for clinical allied health professionals practising in the UK. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20:852. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05650-3 .
Health Education England. Allied health professions research and innovation strategy. NHS England; 2022. https://www.hee.nhs.uk/our-work/allied-health-professions/enable-workforce/allied-health-professions%E2%80%99-research-innovation-strategy-england . Accessed 21 Jan 2023.
National Institute of Health Research. NIHR Clinical Research Network (CRN) allied health professionals strategy 2018–2020. 2018. https://www.nihr.ac.uk/documents/nihr-crn-allied-health-professionals-strategy-2018-2020/11530 . Accessed 4 Jan 2023.
Pager S, Holden L, Golenko X. Motivators, enablers, and barriers to building allied health research capacity. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2012;5:53–9. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S27638 .
Stewart-Lord A, Beanlands C, Khine R, Shamah S, Sinclair N, Woods S, Woznitza N, Baillie L. The role and development of advanced clinical practice within allied health professions: a mixed method study. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2020;25(13):1705–15. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S267083 .
Angus RL, Hattingh HL, Weir KA. Experiences of hospital allied health professionals in collaborative student research projects: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22:729. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-08119-7 .
Whelan K, Thomas JE, Madden AM. Student research projects: the experiences of student dietitians, university faculty members, and collaborators. J Am Diet Assoc. 2007;107(9):1567–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jada.2007.06.009 .
Zwanikken PA, Dieleman M, Samaranayake D, et al. A systematic review of outcome and impact of Master’s in health and health care. BMC Med Educ. 2013;13:18. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6920-13-18 .
Murray C, Judd D, Snyder P. Evaluation of a post-professional master’s program in allied health. J Allied Health. 2001;30(4):223–8.
Salbach NM, O’Brien K, Evans C, Yoshida K. Dissemination of student research in a Canadian master of science in physical therapy programme. Physiother Can. 2013;65(2):154–7. https://doi.org/10.3138/ptc.2012-18 .
Choi T, Palermo C, Sarkar M, Whitton J, Rees C, Clemans A. Priority setting in higher education research using a mixed methods approach. Higher Ed Res Dev. 2022;42(4):816–30. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2022.2082389 .
Chalmers I, Bracken MB, Djulbegovic B, Garattini S, Grant J, Gülmezoglu AM, Howells DW, Ioannidis JP, Oliver S. How to increase value and reduce waste when research priorities are set. Lancet. 2014;383(9912):156–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62229-1 .
Nyström ME, Karltun J, Keller C, et al. Collaborative and partnership research for improvement of health and social services: researcher’s experiences from 20 projects. Health Res Policy Sys. 2018;16:46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-018-0322-0 .
Sharma A, Minh Duc N, Luu Lam Thang T, et al. A consensus-based checklist for reporting of survey studies (CROSS). J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36:3179–87. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-021-06737-1 .
Davis A, Lee D, Wenzel L, Haines T. Setting research priorities within allied health: what do clinicians think? Int J Allied Health Sci Pract. 2019;17(1):Article 6.
Arulkumaran N, Reay H, Brett SJ, JLA Intensive Care Research Priority Setting Partnership. Research priorities by professional background - a detailed analysis of the James Lind Alliance Priority Setting Partnership. J Intensive Care Soc. 2016;17(2):111–6. https://doi.org/10.1177/1751143715609954 .
Comer C, Collings R, McCracken A, Payne C, Moore A. Allied health professionals’ perceptions of research in the United Kingdom national health service: a survey of research capacity and culture. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22(1):1094. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-08465-6 .
Resta RG, McCarthy Veach P, Charles S, Vogel K, Blase T, Palmer CG. Publishing a master’s thesis: a guide for novice authors. J Genet Couns. 2010;19(3):217–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10897-009-9276-2 .
United Kingdom Research and Innovation. Framework for research ethics. 2021. https://www.ukri.org/councils/esrc/guidance-for-applicants/research-ethics-guidance/framework-for-research-ethics/our-core-principles/ . Accessed 23 Jan 2023.
Cordrey T, King E, Pilkington E, et al. Exploring research capacity and culture of allied health professionals: a mixed methods evaluation. BMC Health Serv Res. 2022;22:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-022-07480-x .
Frakking T, Craswell A, Clayton A, Waugh J. Evaluation of research capacity and culture of health professionals working with women, children and families at an Australian Public Hospital: a cross sectional observational study. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2021;14:2755–66. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S330647 . Published 2021 Oct 1.
Matus J, Wenke R, Hughes I, Mickan S. Evaluation of the research capacity and culture of allied health professionals in a large regional public health service. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2019;12(83):96. https://doi.org/10.2147/JMDH.S178696 .
King O, West E, Lee S, Glenister K, Quilliam C, Wong Shee A, Beks H. Research education and training for nurses and allied health professionals: a systematic scoping review. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):385. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-022-03406-7 .
King E, Cordrey T, Gustafson O. Exploring individual character traits and behaviours of clinical academic allied health professionals: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23:1025. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-023-10044-2 .
Barr H, Koppel I, Reeves S, Hammick M, Freeth DS. Effective interprofessional education: argument, assumption and evidence (promoting partnership for health). Chichester: John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated; 2005.
Book Google Scholar
Famure O, Batoy B, Minkovich M, Liyanage I, Kim SJ. Evaluation of a professional development course on research methods for healthcare professionals. Healthc Manage Forum. 2021;34(3):186–92.
Madi M, Hamzeh H, Griffiths M, et al. Exploring taught masters education for healthcare practitioners: a systematic review of literature. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19:340. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-019-1768-7 .
Duncanson K, Webster EL, Schmidt DD. Impact of a remotely delivered, writing for publication program on publication outcomes of novice researchers. Rural Remote Health. 2018;18(2):4468.
Schmidt D, Duncanson K, Webster E, Saurman E, Lyle D. Critical realist exploration of long-term outcomes, impacts and skill development from an Australian rural research capacity building programme: a qualitative study. BMJ Open. 2022;12(12):e065972.
Whitehouse CL, Copping J, Morris P, Guledew D, Chilson B, Gray R, et al. An organisational approach to building research capacity among nurses, midwives and allied health professionals (NMAHPs) in clinical practice. Int Pract Dev J. 2022;12(2):1.
Slade SC, Philip K, Morris ME. Frameworks for embedding a research culture in allied health practice: a rapid review. Health Res Policy Sys. 2018;16:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12961-018-0304-2 .
Matus J, Walker A, Mickan S. Research capacity building frameworks for allied health professionals - a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18(1):716. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-018-3518-7 .
Reed MS, Ferré M, Martin-Ortega J, Blanche R, Lawford-Rolfe R, Dallimer M, Holden J. Evaluating impact from research: a methodological framework. Res Policy. 2021;50(4):104147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2020.104147
Belcher B, Halliwell J. Conceptualizing the elements of research impact: towards semantic standards. Humanit Soc Sci Commun. 2021;8:183. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-021-00854-2 .
Jones NL, Cooke J, Holliday J. Making occupational therapy research visible: amplifying and elevating the contribution and impacts. Br J Occup Ther. 2021;84(4):197–9. https://doi.org/10.1177/0308022620988473 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the allied health professionals who gave their time to participate in this survey.
Dr Owen Gustafson, Clinical Doctoral Research Fellow (NIHR301569), is funded by Health Education England (HEE)/National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NIHR, NHS or the UK Department of Health and Social Care.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Oxford Allied Health Professions Research and Innovation Unit, Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Oxford, OX3 9DU, UK
Terry Cordrey, Elizabeth King & Owen Gustafson
Centre for Movement, Occupational, and Rehabilitation Sciences, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford, OX3 0BP, UK
Barts Health NHS Trust, Royal London Hospital, London, E1 1BB, UK
Amanda Thomas
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors conceived and designed the study. All authors designed the survey content and structure. TC prepared the online survey. All authors promoted recruitment to the survey. EK and OG undertook data analysis and interpretation. TC prepared Fig. 1 . OG prepared Tables 1 , 2 and 3 . AT wrote the background and part of the discussion. TC wrote the abstract, methods, part of the discussion, and conclusion. EK and OG wrote the results. All authors reviewed the manuscript and consented to publication.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Terry Cordrey .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was approved by Oxford Brookes University research ethics committee and assigned registration number: 221613. This study was conducted according to the relevant guidelines and regulations of the Declaration of Helsinki. Survey respondents were required to read the participant information sheet and provide informed consent prior to taking part.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., supplementary material 2., supplementary material 3., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Cordrey, T., Thomas, A., King, E. et al. Evaluating the perceived impact and legacy of master’s degree level research in the allied health professions: a UK-wide cross-sectional survey. BMC Med Educ 24 , 750 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05582-0
Download citation
Received : 20 March 2023
Accepted : 21 May 2024
Published : 12 July 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05582-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Master’s degree
- Research training
- Allied health professions
- Research capacity
- Research impact
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Teaching & Learning
- Education Excellence
- Professional development
- Case studies
- Teaching toolkits
- MicroCPD-UCL
- Assessment resources
- Student partnership
- Generative AI Hub
- Community Engaged Learning
- UCL Student Success

Supervising Masters Projects and Dissertations, 21 May 2025 [online]
21 May 2025, 10:00 am–11:30 am

This session will introduce staff who supervise masters (PGT) projects and dissertations on how to navigate common challenges, support students' academic growth, and ensure successful project completion. Whether you're an experienced supervisor or new to the role, this workshop will empower you with the essential tools to enhance your supervision and drive student success.
This event is free.
Event Information
Availability, wednesday 21 may 2025, 10:00 - 11:30 (online).
In this workshop we will:
- Explore how to establish a good relationship from the start and set expectations
- Identify and address common challenges in supervision
- Consider the practicalities such as managing boundaries and establishing ground rules
- Address the pastoral as well as academic role taken on by the supervisor
Participants who have completed this course/session will be able to:
- Confidently conduct a first meeting with a new masters (PGT) supervisee and ensure that ground rules are established, and expectations shared
- Identify strategies for monitoring progress, giving feedback and supporting student through the masters (PGT) project and/or dissertation
- Demonstrate an understanding of how the masters (PGT) supervisory experience can be used to evidence your teaching experience for an Advance HE Fellowship application
Participants should be mindful that our focus is masters (PGT) students and that many aspects of masters (PGT) supervision are unique to masters (PGT) contexts and are less relevant for research students. We offer a session called Developing as a Doctoral Supervisor where issues related to research students are discussed in greater depth.
Who should attend
Early career, mid career, masters (PGT) supervisors.
Related content
Research supervision training and development
Upcoming Events
Funnelback feed: https://search2.ucl.ac.uk/s/search.json?collection=drupal-teaching-learn... Double click the feed URL above to edit
Sign up to the monthly UCL education e-newsletter to get the latest teaching news, events & resources.
- Learning Mall
- Undergraduate
- Short, Summer Courses
- Executive Education & Professional Development
- International Mobility
- Why study at XJTLU
- Chinese Mainland
- Entry Requirements
- How to Apply
- Fees & Scholarship
- China's Hong Kong, Macao, & Taiwan
- International
- Programme Fees
- Postgraduate Research Scholarships
- Visa Information for International Students
- Pre-Arrival Information for International Students
- Key Research Areas
- Research Strategies
- Research Innovation Ecosystem
- Research Publications
- Research Projects
- Centres, Labs, Institutes and Schools
- Academy of Film and Creative Technology
- Academy of Future Education
- XJTLU-JITRI Academy of Industrial Technology
- XJTLU Wisdom Lake Academy of Pharmacy
- School of Advanced Technology
- Design School
- School of Film and TV Arts
- School of Humanities and Social Sciences
- International Business School Suzhou
- School of Languages
- School of Mathematics and Physics
- School of Science
- Chinese Cultural Teaching Centre
- Physical Education Centre
- School of AI and Advanced Computing
- School of CHIPS
- School of Cultural Technology
- Entrepreneurship and Enterprise Hub
- School of Intelligent Finance and Business
- School of Intelligent Manufacturing Ecosystem
- School of Internet of Things
- School of Robotics
- HeXie Academy
- Digital Transformation Research Centre
- Industrial Software Ecosystem Research Centre
- Strategic Issues of Industrial Innovation & Development Research Centre
- Test Centres
- Health & Wellbeing
- Sports and Club Activities
- Accommodation
- Life in Suzhou
- Vision and Mission
- Partnership
- Higher Education in China
- Associate Vice Presidents & Deans
- Previous Senior Staff
- Jobs & Careers
- Policies & Regulations
- Professional Services
- Meta Education
- Brand Resources
- Publications

XJTLU holds its First Three Minute Thesis Competition
12 Jul 2024

2024 Academic Excellence Award winners revealed
10 Jul 2024
Quick Links
- Undergraduate Programmes
Author Catherine Diamond
Editor Tamara Kaup and Patricia Pieterse
The finalists of XJTLU's first Three Minute Thesis competition, with the judges and Professor Adam Cross Credit: XJTLU
Could you describe 90,000 words of research in just three minutes? That’s just what nine PhD students did as XJTLU recently wrapped up its first Three Minute Thesis competition.
The annual worldwide contest, started by The University of Queensland in 2008, celebrates doctoral research by asking PhD students to explain their research within three minutes and with only one static presentation slide.
After preliminary selection, nine students from across the University’s schools and academies were chosen to present in XJTLU’s final.
They finalists were:
| Entrepreneurship and Enterprise Hub | Business | |
| International Business School Suzhou (IBSS) | Business | |
| School of Advanced Technology | Electronic and Electrical Engineering | |
| School of Advanced Technology | Electronic and Electrical Engineering | |
| Academy of Film and Creative Technology | English Culture and Communication | |
| School of Science | Environmental Science | |
| School of Science | Environmental Science | |
| School of Science | Chemistry | |
| School of Science | Public Health |
Dr Sophie Sturup, Senior Associate Professor in the Design School’s Department of Urban Planning and Design, was one of the five judges. She explains why academics being able to speak effectively to anyone about their research in three minutes is useful.
“It gives you a way of letting people in on the secret you have been working on all this time,” she says.
The judges named Peiyun Li the winner and Yuhua Duan the runner-up. Both students are in the Department of Health and Environmental Sciences in the School of Science. Professor Adam Cross, Associate Vice-President for Education, awarded the trophies.
Li explains why she joined the competition: “At first, I signed up just to practice my presentation skills. However, when I carefully read the competition requirements, I realised it would be an important opportunity for my future career.”

Peiyun Li, winner of XJTLU’s Three Minute Thesis final, is a PhD student in the Department of Health and Environmental Sciences. Credit: Peiyun Li
Reaching a wider audience
Li says that researchers in her field need to be able to clearly communicate their findings and suggestions to different audiences, including the public and policymakers, to advocate for the importance of conservation.
“Unlike other academic presentations, this competition required me to use familiar terms so everyone could grasp the gist of my research. It was excellent training and a challenge for me,” she says.
Li and Duan both encountered difficulties while creating their presentations, with Li highlighting the complexity of balancing the introduction, results, and discussion in only three minutes.
Duan agrees, saying: “Three minutes is a short time to present a complete research thesis. It is necessary not only to set up the experimental background so that the audience can understand the significance of the subject, but also to present our experimental design and results.”

Runner-up in XJTLU’s Three Minute Thesis final: Yuhua Duan, a PhD student in the Department of Health and Environmental Sciences. Credit: Yuhua Duan
Dr Sturup explains both Li’s and Duan’s abilities to distill all aspects of their research into three-minute presentations led to their being awarded the top prizes.
She says: “Both students talked about their research specifically. Their whole talk was about what they were doing and why.
“They both made a strong connection between what they were doing and how it was going to solve a problem or help some problem they felt passionately about in some way.”
Li and Duan found the experience valuable and recommended other PhD students take part next year.
Duan says: “I think it’s a good way for PhD students to practise presenting in English. And in the process of preparing for the competition, everyone needs to think about how to quickly capture the focus and significance of our scientific research.”
Li will go on to represent XJTLU at the 2024 Asia-Pacific Three Minute Thesis Competition in October.
The judges of the competition were:
Dr Sophie Sturup , Senior Associate Professor in the Department of Urban Planning and Design, Design School;
Dr Ye Bai , Senior Associate Professor in the Department of Economics, IBSS;
Dr Sekar Raju , Senior Associate Professor in the Department of Biological Sciences, School of Science;
Dr Hua Li, Senior Language Lecturer in the English Language Centre, School of Languages; and
Ran Zang , a PhD student in Civil Engineering, Design School and one of the awardees of Best Presentation in the 2023 XJTLU Postgraduate Research Symposium.

Professor Zhoulin Ruan, Vice President of Academic Affairs, gives an opening speech at XJTLU’s Three Minute Thesis Competition . Credit: XJTLU
By Catherine Diamond
Edited by Tamara Kaup and Patricia Pieterse
RELATED NEWS

Research outreach programme enhances impact
XJTLU’s University Marketing and Communications (UMC) office recently held the Research Outreach Ambassadors Programme, which aims to help academics increase...

On 2 July, Xi’an Jiaotong-Liverpool University announced the eight winners of this year’s Academic Excellence Awards. This is the second year of the Aca...

All eyes on future researchers at postgraduate symposium
Postgraduate research is pivotal to solving world problems and making advancements, said the keynote speaker last week at the First Wisdom Lake Postgraduate ...
- Skip to Content
- Catalog Home
- Institution Home
- Pay Tuition
- Online Toolkit
- Shuttle Tracker

- Undergraduate Degree Programs
- Graduate Degree Programs
- Undergraduate
Print Options
- College of Health Professions
- School of Health Administration
- M.H.A. Major in Healthcare Administration (Non-thesis Option)
- General Information
- Admission Information
- Admission Documents
- Registration and Course Credit
- Academic and Grading Policies
- Degree Information
- Graduate Degrees
- Graduate Majors
- Graduate Minors
- Graduate Certificates
- Tuition and Fees
- Additional Fees and Expenses
- Refund of Fees
- College of Applied Arts
- Emmett and Miriam McCoy College of Business
- College of Education
- College of Fine Arts and Communication
- Department of Communication Disorders
- M.H.A. Major in Healthcare Administration (Non-thesis Option)
- M.H.A. Major in Healthcare Administration (Thesis Option)
- M.H.A. Major in Healthcare Administration (Executive Concentration) -TXST Global
- M.H.A. Major in Healthcare Administration / M.B.A. Major in Business Administration (Dual Degree Option)
- M.L.T.C.A. Major in Long Term Care Administration
- Minor in Healthcare Administration
- Certificate in Long Term Care Administration
- Department of Health Informatics & Information Management
- St. David’s School of Nursing
- Department of Physical Therapy
- Department of Respiratory Care
- College of Liberal Arts
- College of Science and Engineering
- Graduate Faculty
Master of Healthcare Administration (M.H.A.) Major in Healthcare Administration (Non-thesis Option)
Program overview.
The Master of Healthcare Administration (M.H.A.) degree with a major in Healthcare Administration offers courses designed to enhance the career mobility of persons currently employed in health professions as well as to provide a solid base of academic and directed experiences for persons who may desire entry into the field of health administration. The primary focus of the curriculum is middle-to senior-level management.
Principal areas of study include health and disease; sociological, economic, legal, and political forces which affect health care; and management organizational behaviors including such specializations as financial management, human resource management, planning, marketing, and data generation and analysis.
Application Requirements
The items listed below are required for admission consideration for applicable semesters of entry during the current academic year. Submission instructions, additional details, and changes to admission requirements for semesters other than the current academic year can be found on The Graduate College's website . International students should review the International Admission Documents page for additional requirements.
- completed online application
- $55 nonrefundable application fee
or
- $90 nonrefundable application fee for applications with international credentials
- baccalaureate degree from a regionally accredited university (Non-U.S. degrees must be equivalent to a four-year U.S. Bachelor’s degree. In most cases, three-year degrees are not considered. Visit our International FAQs for more information.)
- official transcripts from each institution where course credit was granted
- a 2.75 overall GPA or a 2.75 GPA in your last 60 hours of undergraduate course work (plus any completed graduate courses)
- GRE is not required
- resume/CV including relevant experience (volunteer, research, employment and other)
- statement of purpose indicating the student’s ability and interest in completing the degree program in healthcare administration
- three letters of recommendation from professionals or academics competent to assess the student’s interest in pursuing a career in healthcare administration
Approved English Proficiency Exam Scores
Applicants are required to submit an approved English proficiency exam score that meets the minimum program requirements below unless they have earned a bachelor’s degree or higher from a regionally accredited U.S. institution or the equivalent from a country on our exempt countries list .
- official TOEFL iBT scores required with a 85 overall
- official PTE scores required with a 57
- official IELTS (academic) scores required with a 6.5 overall and minimum individual module scores of 6.0
- official Duolingo Scores required with a 110 overall
- official TOEFL Essentials scores required with an 8.5 overall
This program does not offer admission if the scores above are not met.
Degree Requirements
The Master of Healthcare Administration (M.H.A.) degree with a major in Healthcare Administration requires 42 semester credit hours.
Course Requirements
| Code | Title | Hours |
|---|---|---|
| Required Courses | ||
| Healthcare Organization and Delivery | 3 | |
| Analytics and Information Systems Management in Healthcare | 3 | |
| Healthcare Financial Management I | 3 | |
| Healthcare Financial Management II | 3 | |
| Healthcare Law and Policy | 3 | |
| Health Care Quality and Operations Improvement | 3 | |
| Data-Guided Healthcare Decision-Making | 3 | |
| Public Health for Healthcare Administrators | 3 | |
| Strategic Management and Marketing for Healthcare Organizations | 3 | |
| Emerging Trends in Healthcare Human Resources | 3 | |
| Healthcare Organizational Behavior, Theory, and Leadership | 3 | |
| Program Competencies Assessments and Integrative Experience Preparation | 1 | |
| Intership or Practicum | ||
| Administrative Field Placement | 8 | |
| Total Hours | 42 | |
Comprehensive Examination Requirement
All degree-seeking graduate students must pass a comprehensive examination at the end of the didactic portion of their program. The School of Health Administration administers comprehensive exams at the end of the fall and spring terms. Students with field placements on their degree audits must pass the comprehensive exam before they begin their field placement. Students who fail the comprehensive exam may take the exam again the next term it is offered. Two failures will result in dismissal from the program.
Master's level courses in Health Administration: HA
Courses Offered
Health administration (ha).
HA 5111. Topics in Health Administration.
An in-depth study of a singular topic or a related problem being faced by practicing managers in the rapidly changing healthcare industry. Special emphasis will be placed on the topic’s current relevance and its utilitarian value to the participant. May be repeated if topic differs.
HA 5191. Field Experience Orientation.
This course will assist the student to prepare for the field experience and to prepare for the comprehensive exam. An extensive orientation to the field experience will be provided to better enable students to move from the classroom setting to a workplace scenario.
HA 5199B. Thesis.
This course represents a student’s continuing thesis enrollments. The student continues to enroll in this course until the thesis is submitted for binding.
HA 5299B. Thesis.
HA 5300. Healthcare Organization and Delivery.
A survey of the organization and delivery of health services focusing on the history and development of health systems as they relate to the overall health and medical care systems. Major attention is given to governing bodies, patient care organizations, and executive management structures.
HA 5301. Healthcare Administration Research Methods.
A study of research methodology as it pertains to healthcare administration. Included are hypothesis forming, designing research, and the collection, manipulation and analysis of data. Knowledge of numeracy and statistics is essential.
HA 5303. Information Systems Management in Healthcare.
This course provides a comprehensive introduction to information systems management for healthcare organizations. It covers the determination of information required by whom, design of information flows, procurement of information systems technology resources, assurance of information security, and management of systems integration.
HA 5304. Healthcare Economics and Financial Theory.
A study of economic theories that have an impact on the healthcare industry. Special emphasis will be placed on emerging economic research and its impact on potential policy ramifications.
HA 5311. Trends in Health Administration.
An in-depth study of singular trend or a related problem being faced by practicing managers in the rapidly changing healthcare industry. Special emphasis will be placed on the topic’s current relevance and its utilitarian value to the participant. Examples of trends, which are typically offered, include trends in rural health, managed care ethical issues, and in total quality management. This course may be repeated for credit with a different subject area.
HA 5316. Healthcare Financial Management.
An introduction to healthcare financial management including the financial management in healthcare organizations, healthcare payment systems, financing and investment decisions, and financial planning, analysis, and control. Prerequisites: accounting, economics, and statistics.
HA 5321. Healthcare Law.
An in-depth analysis of healthcare law and its effect on the relationships between the patient, the patient’s family, the provider, and other interested third parties. Analysis of cases is the primary method of study.
HA 5325. Health Care Quality Improvement Concepts and Tools.
This course teaches the concepts of quality in health care and the use of quality improvement tools. Quality management will be explored using Lean Six Sigma continuous process improvement methodologies. This course is intended to help students learn and translate health care quality management theory, concepts, and knowledge into practice.
HA 5334. Operational Decision Making for Healthcare Managers.
An introduction to the fundamentals of selected operations research techniques essential to the analysis of healthcare managerial problem situations, the design of new and improved systems, and the implementation of systems to achieve desired systems performance.
HA 5335. Public Health for Healthcare Administrators.
This course introduces the healthcare manager to public health and its role in preventing illnesses and improving the health of the community. Students will learn of the role of the manager in disease prevention and how to participate and lead community efforts for the wellness of the community.
HA 5346. Healthcare Strategic Management.
This capstone course examines mission, vision, strategy, and operations from both the formulation and implementation perspectives. Emphasis will be on the role of the manager/leader in strategic management analysis, creativity, and action. This course is available to HA majors only.
HA 5355. Human Resource Management in Healthcare Facilities.
A study of personnel administration in the healthcare facility and the environment in which it functions. Emphasis will be on the role of the Personnel Office in forecasting, developing, and managing human resources, in addition to a review of current legislation affecting the personnel function.
HA 5356. Policy Development in Healthcare Arena.
Prospective healthcare administrators analyze changing healthcare paradigm to determine decision-points where policies can be affected. Course allows students to apply existing skills to real world policy issues at state and national levels and to analyze policy development from numerous stakeholders’ viewpoints.
HA 5362. Healthcare Organizational Behavior/Theory.
This course is a study of theory and concepts drawn from the behavioral and social sciences. These concepts are applied as a foundation and conceptual framework for the analysis, diagnosis, prediction and guidance of human behavior in healthcare organizations.
HA 5371. Marketing of Health Services.
A study of marketing functions and principles as they relate to the healthcare delivery system. Analysis of marketing concepts such as market segmentation, marketing planning, marketing audit, marketing positioning, and marketing mix will be discussed.
HA 5375. Healthcare Accounting.
An introduction to financial accounting in healthcare with an emphasis on the preparation of non-profit financial statements for healthcare service organizations, control procedures for healthcare entities, and accounting issues unique to the healthcare industry. This course does not earn graduate degree credit.
HA 5399A. Thesis.
This course represents a student’s initial thesis enrollment. No thesis credit is awarded until student has completed the thesis, HA 5399B .
HA 5399B. Thesis.
HA 5450. Administrative Field Placement.
A one-semester, full-time field experience which allows students to apply their foundational didactic education by means of rotations, experiences, and projects in a healthcare organization. This course is graded on a credit (CR), no-credit (F) basis. Prerequisite: Instructor approval.
HA 5599B. Thesis.
HA 5640. Administrative Practicum.
A one-semester, part-time field experience designed for the student already working full-time in healthcare. The practicum provides a broader orientation to the student’s organization and exposure to special projects.
HA 5840. Administrative Field Placement.
A one-semester, full-time field experience which allows students to apply their foundational didactic education by means of rotations, experiences, and projects in a healthcare organization.
HA 5999B. Thesis.
2024-2025 Catalogs
- About Texas State
- About This Site
- Emergency Info
- Job Opportunities
- Search Texas State
Print this page.
The PDF will include all information unique to this page.
A PDF of the entire 2022-2023 catalog.

- Games & Quizzes
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center

Elektrostal
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.

Elektrostal , city, Moscow oblast (province), western Russia . It lies 36 miles (58 km) east of Moscow city. The name, meaning “electric steel,” derives from the high-quality-steel industry established there soon after the October Revolution in 1917. During World War II , parts of the heavy-machine-building industry were relocated there from Ukraine, and Elektrostal is now a centre for the production of metallurgical equipment. Pop. (2006 est.) 146,189.
Post comment
or continue as guest
Structured data
Items portrayed in this file, 31 august 2007, source of file, original creation by uploader, image/svg+xml, a40fce78c48333073766c67e926dbd360cea4343, 38,005 byte.
- Coats of arms of cities and villages of Moscow Oblast
- Culture of Elektrostal
- Hephaestus in heraldry
- Hammers sable in heraldry
- 2 flashes Or in heraldry
- Atom symbols in heraldry
- SVG coats of arms of Russia
- PD-RU-exempt (coats of arms)
Navigation menu

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
Writing a masters dissertation or thesis is a sizable task. It takes a considerable amount of research, studying and writing. Usually, students need to write around 10,000 to 15,000 words. It is completely normal to find the idea of writing a masters thesis or dissertation slightly daunting, even for students who have written one before at ...
Most dissertations run a minimum of 100-200 pages, with some hitting 300 pages or more. When editing your dissertation, break it down chapter by chapter. Go beyond grammar and spelling to make sure you communicate clearly and efficiently. Identify repetitive areas and shore up weaknesses in your argument.
Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples. Published on September 9, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. It can be difficult to know where to start when writing your thesis or dissertation.One way to come up with some ideas or maybe even combat writer's block is to check out previous work done by other students on a similar thesis or dissertation topic to yours.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
A Masters dissertation will be longer than the undergraduate equivalent - usually it'll be somewhere between 15,000 and 20,000 words, but this can vary widely between courses, institutions and countries. To answer your overall research question comprehensively, you'll be expected to identify and examine specific areas of your topic.
Definition of Dissertation and Thesis. The dissertation or thesis is a scholarly treatise that substantiates a specific point of view as a result of original research that is conducted by students during their graduate study. At Cornell, the thesis is a requirement for the receipt of the M.A. and M.S. degrees and some professional master's ...
Time to recap…. And there you have it - the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows: Title page. Acknowledgments page. Abstract (or executive summary) Table of contents, list of figures and tables.
Thesis and Dissertation: Getting Started. The resources in this section are designed to provide guidance for the first steps of the thesis or dissertation writing process. They offer tools to support the planning and managing of your project, including writing out your weekly schedule, outlining your goals, and organzing the various working ...
A dissertation or thesis is a long piece of academic writing based on original research, submitted as part of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree. The structure of a dissertation depends on your field, but it is usually divided into at least four or five chapters (including an introduction and conclusion chapter).
Revised on 5 May 2022. A dissertation is a large research project undertaken at the end of a degree. It involves in-depth consideration of a problem or question chosen by the student. It is usually the largest (and final) piece of written work produced during a degree. The length and structure of a dissertation vary widely depending on the ...
The foundation of the entire postgraduate or doctoral research program is disciplinary knowledge. At most universities, one of the main requirements is that the research introduces or expands a novelty that contributes to the advancement of the subject [].Even though the writing is a clear component of higher-level coursework and is frequently acknowledged as a source of significant concern ...
Read more about postgraduate research projects here. Scientific Approach. The information included in the dissertation methodology is similar to the process of creating a science project: you need to present the subject that you aim to examine, and explain the way you chose to go about approaching your research.
Thesis & Dissertation Overview. When writing a long document such as a thesis or dissertation over a sustained time period, writers may find it difficult to stay motivated and make progress. Some institutions offer "dissertation retreats" or camps for helping writers make progress. An Intensive Writing Experience (IWE) is a similar event in ...
You should also review Harvard Griffin GSAS's dissertation policies for important information about formatting, submission, and publishing and distribution options, including embargoes. Degrees are awarded in November, March, and May. Dissertation submission deadlines are noted in the Degree Calendar section of Policies. Help with the ...
As stated above, a thesis is the final project required in the completion of many master's degrees. The thesis is a research paper, but it only involves using research from others and crafting your own analytical points. On the other hand, the dissertation is a more in-depth scholarly research paper completed mostly by doctoral students.
The dissertation is the hallmark of the research expertise demonstrated by a doctoral student. It is a scholarly contribution to knowledge in the student's area of specialization. By researching and writing a dissertation, the student is expected to demonstrate a high level of knowledge and the capability to function as an independent scholar.
Dissertation examples. Listed below are some of the best examples of research projects and dissertations from undergraduate and taught postgraduate students at the University of Leeds. We have not been able to gather examples from all schools. The module requirements for research projects may have changed since these examples were written.
The guide focuses on research for Postgraduate certificates, diplomas and Masters' programmes. These programmes shall normally be by coursework and thesis, dissertation or project, as determined in the curriculum documents of individual programmes. Differentiating between Thesis, Dissertation and Project
How to Write a Postgraduate Thesis - Step by Step Guide. Writing a postgraduate thesis is a comprehensive endeavor that demands careful planning, research, and writing. Follow these steps to navigate the process effectively: Choose a Relevant Topic: Select a topic that aligns with your field of study, interests, and academic goals. Ensure it ...
Post graduate master's degree qualifications are increasingly required to advance allied health profession careers in education, clinical practice, leadership, and research. Successful awards are dependent on completion of a research dissertation project. Despite the high volume of experience gained and research undertaken at this level, the benefits and impact are not well understood.
Eligibility: three-year dissertations and postgraduate theses, including a 5-page presentation, dealing with issues related to Europe, as well as the different relationships, in different disciplinary fields, between Europe itself and the territories on which the UNITA Universities are located.
This session will introduce staff who supervise masters (PGT) projects and dissertations on how to navigate common challenges, support students' academic growth, and ensure successful project completion. Whether you're an experienced supervisor or new to the role, this workshop will empower you with the essential tools to enhance your supervision and drive student success.
The finalists of XJTLU's first Three Minute Thesis competition, with the judges and Professor Adam Cross Credit: ... Design School and one of the awardees of Best Presentation in the 2023 XJTLU Postgraduate Research Symposium. Professor Zhoulin Ruan, Vice President of Academic Affairs, gives an opening speech at XJTLU's Three Minute Thesis ...
Program Overview. The Master of Healthcare Administration (M.H.A.) degree with a major in Healthcare Administration offers courses designed to enhance the career mobility of persons currently employed in health professions as well as to provide a solid base of academic and directed experiences for persons who may desire entry into the field of health administration.
Elektrostal, city, Moscow oblast (province), western Russia.It lies 36 miles (58 km) east of Moscow city. The name, meaning "electric steel," derives from the high-quality-steel industry established there soon after the October Revolution in 1917. During World War II, parts of the heavy-machine-building industry were relocated there from Ukraine, and Elektrostal is now a centre for the ...
A residential and industrial region in the south-east of Mocsow. It was founded on the spot of two villages: Chagino (what is now the Moscow Oil Refinery) and Ryazantsevo (demolished in 1979). in 1960 the town was incorporated into the City of Moscow as a district. Population - 45,000 people (2002). The district is one of the most polluted residential areas in Moscow, due to the Moscow Oil ...
↑ Official documents, state symbols and signs of 14 other Soviet Republics are the subject of law of their legal successors. See respective license tags.
Cities near Elektrostal. Places of interest. Pavlovskiy Posad Noginsk. Travel guide resource for your visit to Elektrostal. Discover the best of Elektrostal so you can plan your trip right.