Reading & Writing Purposes
Introduction: critical thinking, reading, & writing, critical thinking.
The phrase “critical thinking” is often misunderstood. “Critical” in this case does not mean finding fault with an action or idea. Instead, it refers to the ability to understand an action or idea through reasoning. According to the website SkillsYouNeed [1]:
Critical thinking might be described as the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking.
In essence, critical thinking requires you to use your ability to reason. It is about being an active learner rather than a passive recipient of information.
Critical thinkers rigorously question ideas and assumptions rather than accepting them at face value. They will always seek to determine whether the ideas, arguments, and findings represent the entire picture and are open to finding that they do not.
Critical thinkers will identify, analyze, and solve problems systematically rather than by intuition or instinct.
Someone with critical thinking skills can:
- Understand the links between ideas.
- Determine the importance and relevance of arguments and ideas.
- Recognize, build, and appraise arguments.
- Identify inconsistencies and errors in reasoning.
- Approach problems in a consistent and systematic way.
- Reflect on the justification of their own assumptions, beliefs and values.
Read more at: https://www.skillsyouneed.com/learn/critical-thinking.html

Critical thinking—the ability to develop your own insights and meaning—is a basic college learning goal. Critical reading and writing strategies foster critical thinking, and critical thinking underlies critical reading and writing.

Critical Reading
Critical reading builds on the basic reading skills expected for college.
College Readers’ Characteristics
- College readers are willing to spend time reflecting on the ideas presented in their reading assignments. They know the time is well-spent to enhance their understanding.
- College readers are able to raise questions while reading. They evaluate and solve problems rather than merely compile a set of facts to be memorized.
- College readers can think logically. They are fact-oriented and can review the facts dispassionately. They base their judgments on ideas and evidence.
- College readers can recognize error in thought and persuasion as well as recognize good arguments.
- College readers are skeptical. They understand that not everything in print is correct. They are diligent in seeking out the truth.
Critical Readers’ Characteristics
- Critical readers are open-minded. They seek alternative views and are open to new ideas that may not necessarily agree with their previous thoughts on a topic. They are willing to reassess their views when new or discordant evidence is introduced and evaluated.
- Critical readers are in touch with their own personal thoughts and ideas about a topic. Excited about learning, they are eager to express their thoughts and opinions.
- Critical readers are able to identify arguments and issues. They are able to ask penetrating and thought-provoking questions to evaluate ideas.
- Critical readers are creative. They see connections between topics and use knowledge from other disciplines to enhance their reading and learning experiences.
- Critical readers develop their own ideas on issues, based on careful analysis and response to others’ ideas.
The video below, although geared toward students studying for the SAT exam (Scholastic Aptitude Test used for many colleges’ admissions), offers a good, quick overview of the concept and practice of critical reading.
Critical Reading & Writing
College reading and writing assignments often ask you to react to, apply, analyze, and synthesize information. In other words, your own informed and reasoned ideas about a subject take on more importance than someone else’s ideas, since the purpose of college reading and writing is to think critically about information.
Critical thinking involves questioning. You ask and answer questions to pursue the “careful and exact evaluation and judgment” that the word “critical” invokes (definition from The American Heritage Dictionary ). The questions simply change depending on your critical purpose. Different critical purposes are detailed in the next pages of this text.
However, here’s a brief preview of the different types of questions you’ll ask and answer in relation to different critical reading and writing purposes.
When you react to a text you ask:
- “What do I think?” and
- “Why do I think this way?”
e.g., If I asked and answered these “reaction” questions about the topic assimilation of immigrants to the U.S. , I might create the following main idea statement, which I could then develop in an essay: I think that assimilation has both positive and negative effects because, while it makes life easier within the dominant culture, it also implies that the original culture is of lesser value.
When you apply text information you ask:
- “How does this information relate to the real world?”
e.g., If I asked and answered this “application” question about the topic assimilation , I might create the following main idea statement, which I could then develop in an essay: During the past ten years, a group of recent emigrants has assimilated into the local culture; the process of their assimilation followed certain specific stages.
When you analyze text information you ask:
- “What is the main idea?”
- “What do I want to ‘test’ in the text to see if the main idea is justified?” (supporting ideas, type of information, language), and
- “What pieces of the text relate to my ‘test?'”
e.g., If I asked and answered these “analysis” questions about the topic immigrants to the United States , I might create the following main idea statement, which I could then develop in an essay: Although Lee (2009) states that “segmented assimilation theory asserts that immigrant groups may assimilate into one of many social sectors available in American society, instead of restricting all immigrant groups to adapting into one uniform host society,” other theorists have shown this not to be the case with recent immigrants in certain geographic areas.
When you synthesize information from many texts you ask:
- “What information is similar and different in these texts?,” and
- “What pieces of information fit together to create or support a main idea?”
e.g., If I asked and answered these “synthesis” questions about the topic immigrants to the U.S. , I might create the following main idea statement, which I could then develop by using examples and information from many text articles as evidence to support my idea: Immigrants who came to the United States during the immigration waves in the early to mid 20th century traditionally learned English as the first step toward assimilation, a process that was supported by educators. Now, both immigrant groups and educators are more focused on cultural pluralism than assimilation, as can be seen in educators’ support of bilingual education. However, although bilingual education heightens the child’s reasoning and ability to learn, it may ultimately hinder the child’s sense of security within the dominant culture if that culture does not value cultural pluralism as a whole.

Critical reading involves asking and answering these types of questions in order to find out how the information “works” as opposed to just accepting and presenting the information that you read in a text. Critical writing involves recording your insights into these questions and offering your own interpretation of a concept or issue, based on the meaning you create from those insights.
- Crtical Thinking, Reading, & Writing. Authored by : Susan Oaks, includes material adapted from TheSkillsYouNeed and Reading 100; attributions below. Project : Introduction to College Reading & Writing. License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Critical Thinking. Provided by : TheSkillsYouNeed. Located at : https://www.skillsyouneed.com/ . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright . License Terms : Quoted from website: The use of material found at skillsyouneed.com is free provided that copyright is acknowledged and a reference or link is included to the page/s where the information was found. Read more at: https://www.skillsyouneed.com/
- The Reading Process. Authored by : Scottsdale Community College Reading Faculty. Provided by : Maricopa Community College. Located at : https://learn.maricopa.edu/courses/904536/files/32966438?module_item_id=7198326 . Project : Reading 100. License : CC BY: Attribution
- image of person thinking with light bulbs saying -idea- around her head. Authored by : Gerd Altmann. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/light-bulb-idea-think-education-3704027/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- video What is Critical Reading? SAT Critical Reading Bootcamp #4. Provided by : Reason Prep. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5Hc3hmwnymw . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- image of man smiling and holding a lightbulb. Authored by : africaniscool. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/man-african-laughing-idea-319282/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved

Privacy Policy

Writing to Think: Critical Thinking and the Writing Process
“Writing is thinking on paper.” (Zinsser, 1976, p. vii)
Google the term “critical thinking.” How many hits are there? On the day this tutorial was completed, Google found about 65,100,000 results in 0.56 seconds. That’s an impressive number, and it grows more impressively large every day. That’s because the nation’s educators, business leaders, and political representatives worry about the level of critical thinking skills among today’s students and workers.
What is Critical Thinking?
Simply put, critical thinking is sound thinking. Critical thinkers work to delve beneath the surface of sweeping generalizations, biases, clichés, and other quick observations that characterize ineffective thinking. They are willing to consider points of view different from their own, seek and study evidence and examples, root out sloppy and illogical argument, discern fact from opinion, embrace reason over emotion or preference, and change their minds when confronted with compelling reasons to do so. In sum, critical thinkers are flexible thinkers equipped to become active and effective spouses, parents, friends, consumers, employees, citizens, and leaders. Every area of life, in other words, can be positively affected by strong critical thinking.
Released in January 2011, an important study of college students over four years concluded that by graduation “large numbers [of American undergraduates] didn’t learn the critical thinking, complex reasoning and written communication skills that are widely assumed to be at the core of a college education” (Rimer, 2011, para. 1). The University designs curriculum, creates support programs, and hires faculty to help ensure you won’t be one of the students “[showing]no significant gains in . . . ‘higher order’ thinking skills” (Rimer, 2011, para. 4). One way the University works to help you build those skills is through writing projects.
Writing and Critical Thinking
Say the word “writing” and most people think of a completed publication. But say the word “writing” to writers, and they will likely think of the process of composing. Most writers would agree with novelist E. M. Forster, who wrote, “How can I know what I think until I see what I say?” (Forster, 1927, p. 99). Experienced writers know that the act of writing stimulates thinking.
Inexperienced and experienced writers have very different understandings of composition. Novice writers often make the mistake of believing they have to know what they’re going to write before they can begin writing. They often compose a thesis statement before asking questions or conducting research. In the course of their reading, they might even disregard material that counters their pre-formed ideas. This is not writing; it is recording.
In contrast, experienced writers begin with questions and work to discover many different answers before settling on those that are most convincing. They know that the act of putting words on paper or a computer screen helps them invent thought and content. Rather than trying to express what they already think, they express what the act of writing leads them to think as they put down words. More often than not, in other words, experienced writers write their way into ideas, which they then develop, revise, and refine as they go.
What has this notion of writing to do with critical thinking? Everything.
Consider the steps of the writing process: prewriting, outlining, drafting, revising, editing, seeking feedback, and publishing. These steps are not followed in a determined or strict order; instead, the effective writer knows that as they write, it may be necessary to return to an earlier step. In other words, in the process of revision, a writer may realize that the order of ideas is unclear. A new outline may help that writer re-order details. As they write, the writer considers and reconsiders the effectiveness of the work.
The writing process, then, is not just a mirror image of the thinking process: it is the thinking process. Confronted with a topic, an effective critical thinker/writer
- asks questions
- seeks answers
- evaluates evidence
- questions assumptions
- tests hypotheses
- makes inferences
- employs logic
- draws conclusions
- predicts readers’ responses
- creates order
- drafts content
- seeks others’ responses
- weighs feedback
- criticizes their own work
- revises content and structure
- seeks clarity and coherence
Example of Composition as Critical Thinking
“Good writing is fueled by unanswerable questions” (Lane, 1993, p. 15).
Imagine that you have been asked to write about a hero or heroine from history. You must explain what challenges that individual faced and how they conquered them. Now imagine that you decide to write about Rosa Parks and her role in the modern Civil Rights movement. Take a moment and survey what you already know. She refused to get up out of her seat on a bus so a White man could sit in it. She was arrested. As a result, Blacks in Montgomery protested, influencing the Montgomery Bus Boycott. Martin Luther King, Jr. took up leadership of the cause, and ultimately a movement was born.
Is that really all there is to Rosa Parks’s story? What questions might a thoughtful writer ask? Here a few:
- Why did Rosa Parks refuse to get up on that particular day?
- Was hers a spontaneous or planned act of defiance?
- Did she work? Where? Doing what?
- Had any other Black person refused to get up for a White person?
- What happened to that individual or those individuals?
- Why hadn’t that person or those persons received the publicity Parks did?
- Was Parks active in Civil Rights before that day?
- How did she learn about civil disobedience?
Even just these few questions could lead to potentially rich information.
Factual information would not be enough, however, to satisfy an assignment that asks for an interpretation of that information. The writer’s job for the assignment is to convince the reader that Parks was a heroine; in this way the writer must make an argument and support it. The writer must establish standards of heroic behavior. More questions arise:
- What is heroic action?
- What are the characteristics of someone who is heroic?
- What do heroes value and believe?
- What are the consequences of a hero’s actions?
- Why do they matter?
Now the writer has even more research and more thinking to do.
By the time they have raised questions and answered them, raised more questions and answered them, and so on, they are ready to begin writing. But even then, new ideas will arise in the course of planning and drafting, inevitably leading the writer to more research and thought, to more composition and refinement.
Ultimately, every step of the way over the course of composing a project, the writer is engaged in critical thinking because the effective writer examines the work as they develop it.
Why Writing to Think Matters
Writing practice builds critical thinking, which empowers people to “take charge of [their] own minds” so they “can take charge of [their] own lives . . . and improve them, bringing them under [their] self command and direction” (Foundation for Critical Thinking, 2020, para. 12). Writing is a way of coming to know and understand the self and the changing world, enabling individuals to make decisions that benefit themselves, others, and society at large. Your knowledge alone – of law, medicine, business, or education, for example – will not be enough to meet future challenges. You will be tested by new unexpected circumstances, and when they arise, the open-mindedness, flexibility, reasoning, discipline, and discernment you have learned through writing practice will help you meet those challenges successfully.
Forster, E.M. (1927). Aspects of the novel . Harcourt, Brace & Company.
The Foundation for Critical Thinking. (2020, June 17). Our concept and definition of critical thinking . https://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/our-concept-of-critical-thinking/411
Lane, B. (1993). After the end: Teaching and learning creative revision . Heinemann.
Rimer, S. (2011, January 18). Study: Many college students not learning to think critically . The Hechinger Report. https://www.mcclatchydc.com/news/nation-world/national/article24608056.html
Zinsser, W. (1976). On writing well: The classic guide to writing nonfiction . HarperCollins.
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed

- Houston Community College
- Eagle Online

- Desmond Lewis
- Integrated Reading and Writing (INRW 0420)
- Course Materials
- Week 12/ Summer Week 4/ F8 Week 6
Critical Thinking Skills.ppt
To print or download this file, click the link below:
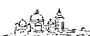
- News, tips, inspiration you can trust to thrive in today’s digital age.
Search form
The importance of critical thinking in writing (and how to apply it).

Developing unique ideas for writing and writing a story worth reading can be challenging. Even when the ideas for writing are already in your head, writing requires research, organization, and a great deal of creativity. But, you already knew that, right?
What many people don’t know or don't realize, however, is that all those processes for effective writing depend on how well you’ve developed your critical thinking skills.
According to the Texas A&M University Writing Center, critical thinking is "the ability to view any object of study from multiple perspectives, to recognize the cultural, ideological, and cognitive frames (or schemata) we bring to understanding."
You can learn everything about story structure and all the rules that come with it such as formatting, language and grammar rules , but applying your ideas effectively in an actual piece of writing requires critical thinking.
Critical thinking is what glues all of the writing processes together and defines your writing style .
Critical Thinking Informs All Good Writing

The best writers are those who think critically and may have even undergone some form of critical thinking training . The value of critical thinking is clear thought-processing, which results in well-developed plots and writings. When you need to write a story that reads well and avoids plot holes and inconsistencies , honing your critical thinking is necessary.
You can perform the research necessary for a story and plan to finish with a strong conclusion. But, when you don’t apply critical thinking in your story, your ideas risk coming across as ambiguous or not well thought out. This is because you can’t really plan out your arguments or provide the story’s premises effectively without critical thinking.
Critical thinking in writing is related to research in the way you deliberately search, analyze and evaluate ideas that you'll put on paper. However, critical thinking discriminates information and ideas to ensure you pick and use only the most appropriate, concise words and paragraphs that deliver messages powerfully and with great impact on readers.
Reserchers have also come to understand that critical thinking is in itself a habit and a skill, something which you can practice, polish, and develop.
Hone Your Critical Thinking Skills
To consciously direct and hone your critical thinking skills, you’ll need to answer some basic questions before writing your story:
- How good is my argument or story idea?
- Is my argument or idea defensible and valid?
- Am I using a rational, reasonable position on the idea or issue?
- What should I use to best present this idea and deal with its complexity?
- Should I go deep into the topic or only touch upon the key issues lightly?
- Should I address any other points of view, and which ones?
- What are my goals with the story?
- What sources of information should I consult?
- What's the best way to present the information?
When asking (and answering) these questions, your analytical skills and quality of answers will depend greatly on the clarity of your thoughts, sources, and intentions. Once that's done sufficiently, you can apply it all to your writing.
8 Ways to Apply Critical Thinking in Your Writing

To make sure you write your story based on sound critical thinking, use these handy tips:
1. Research by questioning everything
Not all of the sources you will be using for your story, research, and critical analysis will be accurate or even relevant. Thinking critically means that you should question all your sources and be careful about the acquisition of data you’ll use in your story.
To write critically, you must examine every little piece of information before using it; validate and parse as part of your research . Basically, you need a rather active, critical and detailed approach throughout the accumulation of information.
2. Scrutinize your method of gathering information
Before you use any of the evidence or information you have found during the research for your story , look at the method for its gathering.
Think of sources you plan to use and places where you can find them. But, most importantly, think of the sources’ credibility and whether or not you can ascertain this.
Only use information that is reliable in your stories.
3. Stay true to the evidence
Before you jump into any conclusions, examine the evidence and the unbiased direction it is pointing towards.
Carefully examining the evidence for your ideas will help you find information that is valid, and any other information you might have missed out on an argument of big importance.
To avoid turning your story into a poorly written one, stay true to the evidence you’ve collected. Also consider the evidence itself in detail.
Is the evidence too broad? Does it have too many details? Are there any other explanations you can provide for it? Do you have enough evidence to support your arguments? Use only the most appropriate and accurate evidence.
4. Eliminate truisms and tautologies
Truism is a truth that is self-evident, while tautology is a statement that repeats the same thing. Both create redundancy that in most cases, doesn’t add directly to your story.
Even though truism and tautology used masterfully could give a story a certain artistic quality, you should generally try to avoid them in your writing.
Critically look for statements in your writing that repeat themselves or are self-evident. These are unnecessary features of your writing that should be removed to improve precision and clarity in your story.
5. Avoid oversimplification
There is a fine line between improving clarity and oversimplification. Try to achieve the former, while eradicating the latter as much as possible.
We are talking about using short, concise, easy to understand and simple explanations, and avoiding dumbed down explanations that insult the intelligence of the reader and demonstrate a lack of breadth and depth.
That certainly calls for high critical thinking and judgment when writing or crafting a story.
6. Plan ahead
When selecting a topic for your story, brainstorm ideas for it beforehand. Make sure the topic you chose is right for the specific purpose. Think of your objectives and goals, and also what you represent.
By brainstorming and planning ahead, you’ll be better equipped to write a story that is concise, relevant, and properly organized.
One grand factor of planning is organization. To plan ahead and do it well, you need to prioritize and reorganize your concepts, ideas, and arguments well.
In other words, you need a chronology of ideas and arguments. Use careful discretion and judgment to create a plan that makes sense and demonstrates your critical thinking abilities.
7. Define your approaches
In writing, you need arguments and ideas. But, you cannot just toss them around anyhow and expect them to make sense.
Instead, you’ll not only need good organization and planning skills, but also a strategy or an approach for presenting them in the most effective way possible.
As soon as you have all the evidence and material ready for use in your story, analyze the strengths and weaknesses of your sources and the arguments they raise. This will help you define the best possible approach for using the evidence and material in your story.
While you take care of this part, remember that each and every argument and evidence used in your story should be as reasonable as it is valid.
8. Break down your arguments
To better present the relationships between arguments in your story, and to find the best writing approach, break down arguments into smaller, easy to understand parts. For this purpose, you can use priority ranking, comparison and contrast, cause and effect, making inferences, and drawing conclusions.
Cons of Not Using Critical Thinking in Your Writing
If you are thinking applying critical thinking in writing is too much of a hassle, then understand that not incorporating critical thinking leads to poor writing.
And it’s easy to detect the effects of not using critical thinking in writing. Some of the obvious signs of not applying critical thinking is a piece of writing include:
- Relationships between concepts aren’t clearly described, but only summarized or alluded to.
- The arguments or thesis are repetitive and don’t relate to the rest of the story.
- Poor or no order whatsoever in the presentation of arguments, summaries, and evidence.
- No chronology or sequel in sentences, arguments, and or paragraphs.
- Weak summaries or summaries with no order.
- Relationships between arguments aren’t fully developed.
- Heavy use of truisms, tautologies, and or abstractions.
If you want to write powerfully and ensure your stories (be they blogs, essays, or reports) yield results and impact readers , you have to improve clarity and add informational value. The only way to do this is by employing critical thinking in your writing.
Critical thinking is an essential skill and practice not just for good writing, but also for effective storytelling within your writings.
Alexandra Reay is a journalist, writer, and editor. She is also a professional content writer who enjoys researching and writing on the topics of self-improvement, technology innovations, and global education development. Follow her on Twitter .
Related stories
Things Successful Writers Do Differently to Write More Fluidly
Quirky Things Top Creative Minds Did to Generate Brilliant Ideas
Types of Music for Inspiration While Writing
Practical Tips for Beating Writers' Block
Why Writing Longhand Is Still So Important
View the discussion thread.
Share this article

SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
Get our best content, news, tips, and inspiration in your inbox free.
Join Over 20,000 Subscribers!
Get our best content, tips, and inspiration free in your inbox. Subscribe ››
Most read this week

Got a story or tip for us?

Here's how to submit it →
Latest posts
How product differentiation can help your business unlock its full potential.

Each brand, product, or service has a unique story behind it. It is a company's responsibility to communicate what differentiates them from competitors to win. Here's how...
App Store Optimization (ASO): What It Is and Why You Need It
App Store optimization is essential to boost your app's rankings on app stores and marketplaces like Google Play Store.
3 Strategies Brits Are Using to Achieve Financial Freedom

6 Content Creation Ideas for Aspiring Student Influencers
![6 Content Creation Ideas for Aspiring Student Influencers [node:title]](https://webwriterspotlight.com/sites/default/files/styles/front_featured__front_/public/smiley%20woman%20with%20ring%20light%20content%20creator%20influencing%20ideas.jpeg?itok=xZW21mJh)
The Jobs Artificial Intelligence Will Take Over First
![The Jobs Artificial Intelligence Will Take Over First [node:title]](https://webwriterspotlight.com/sites/default/files/styles/front_featured__front_/public/adult-person-interacting-with-futuristic-delivery-robot-jobs-ai-will-take-over.jpeg?itok=EeXB8aVo)
A robotic revolution is underway, with AI technology impacting many industries and rendering jobs redundant. Some jobs are more at risk than others.
- Load 5 More Stories ▽
Contributors blogs
Blog here »

Cable TV vs. Streaming Services: Which One Is Better?

The US Has Lots to Lose and Little to Gain by Banning TikTok and WeChat

How to Reboot Your Life & Build Confidence Even in Tough Times

The Impact of the Gambling Industry On US Economy

Necessities Restaurants Should Have to Serve Customers Safely During COVID

How to Make Blogging a Successful Business Opportunity

Delicious Family Meals You Can Prepare at Home in No Time
Like this content subscribe for updates.
EXPLORE MORE ...
News & Features ›

New Research Shows Over a Third of Brits Still Find Running a Business Attractive Despite COVID

New Internet Safeguards Could Put Web Users at Risk
VPN Usage Shoots by 65% as Working from Home Grows Amid Covid-19 Crisis

Tech & Trends ›

Is Canada a Good Place to Move to As a Tech Worker?

Best Practices for Reporting & Documenting Software Bugs

5 Tips to Design a Logo That Makes Your Brand Stand Out
Arts & culture ›.

How New Innovations in Book Publishing Industry Are Democratizing Creativity

Print Books Still More Popular than eBooks or Audio Books, Study Finds

Journaling for Mental Health: Quick Tips for Writers

Business & Economy ›

To Accelerate Your Business Growth, Stay in Touch with Your Customers

How to Manage Remote Workers & Boost Their Productivity

7 Best Ways to Raise Money to Launch or Expand a Business

Health & Style ›
The Benefits (& Science) of Doodling for a Healthy Brain

8 Landscaping Improvements That'll Boost Your Home's Value

How Do You Limit the Spread of Germs in Your Home? Quick Tips
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

18 templates

26 templates

16 templates

17 templates

pediatrician
27 templates

41 templates
Critical Thinking Lesson
Critical thinking lesson presentation, free google slides theme and powerpoint template.
Critical thinking appears to be a difficult matter to understand. Well, we can help you with the design of a presentation about that topic! You'll notice the colorful nature of the elements used in the slides, which may encourage viewers (or students!) to think about this concept. Try this template and use it in class!

Features of this template
- 100% editable and easy to modify
- 32 different slides to impress your audience
- Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups
- Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon’s extension for customizing your slides
- Designed to be used in Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint
- 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens
- Includes information about fonts, colors, and credits of the free resources used
How can I use the template?
Am I free to use the templates?
How to attribute?
Attribution required If you are a free user, you must attribute Slidesgo by keeping the slide where the credits appear. How to attribute?
Related posts on our blog.

How to Add, Duplicate, Move, Delete or Hide Slides in Google Slides

How to Change Layouts in PowerPoint

How to Change the Slide Size in Google Slides
Related presentations.

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access


How Essay Writing Can Enhance Your Critical Thinking Skills
Josh carlyle.
- November 13, 2018

Learning how to develop ideas in writing is a major challenge for many students. Developing critical thinking means learning to think clearly and form judgments. Writing can be used as a tool to evaluate a student’s ability to develop coherent arguments.
75 percent of American 12 th and 8 th graders have insufficient writing skills , as estimated by the National Assessment of Educational Progress.
Poor writing skills among students isn’t a new phenomenon, however. Students have always struggled with critical thinking that is both difficult to teach and difficult to learn. Students who cannot think critically have a hard time developing their ideas in writing. Teaching students to develop an original idea and support it is more complicated than teaching them how to avoid spelling errors. Critical thinking involves evaluation, problem solving, and decision making which are all necessary ingredients in a good essay. Here are 8 ways how essay writing can enhance your students’ critical thinking skills:
- Evaluating the reliability of information
When writing essays, students have to evaluate the reliability of the information that they have. Where did it come from, and how it was acquired? Does it serve someone’s interests, and is there a reason to assume that it could biased?
Differentiating between facts and opinions
Evaluating different sources of information is important when presenting arguments. There is a difference between backing up your arguments with facts and opinions. Students will learn that facts are truths that can be proven, whereas opinions are only based on personal experiences, feelings, and beliefs that have not been tested.
Reflecting on information
Writing an essay allows students to understand how they react to information. Do they agree or disagree with it? Does it make them surprised, excited, or confused? And most importantly, why they react that way?
- Making decisions
Decision-making is a crucial part of critical thinking. It concerns how we make the most optimal choice between different alternatives. Students need to make decisions when they’re writing an essay and they have to choose the best way to argue their position.
Solving problems
Every writer encounters problems, and the key to being successful is to have techniques to overcome those problems. A useful technique for students is to break down their problem into smaller parts. Writing an essay becomes easier to manage when they break it down to parts such as title, introduction, body, and ending paragraph.
Using information in different forms
Understanding how information is presented is essential for formulating arguments. Is the information in the form of a graph, table, paragraph, or chart? Why is it presented in this way? Students will learn to utilize information in many different forms.
Evaluating arguments
Before students can draw their own conclusions, they must evaluate arguments from other people. Does the argument make sense in light of all evidence? When formulating their own thoughts in their essays, students will have to evaluate existing arguments. Can they find flaws in them, and is there a way to improve them?
Presenting arguments
After students have weighed up the evidence and evaluated other arguments, it’s time to present their own arguments. Writing an essay is a good practice for students to learn to present their arguments after forming judgments and making their decisions. Teaching your students to develop their critical thinking through writing essays is one thing but making sure that their language is polished and free of errors is something another. Lucky for your students, there are tools and services that can help them with this stage. The following can be useful for students who need editing for their essays:
- Grammar Girl – a writing blog and podcast offering helpful tips for people who want to improve their writing skills.
- Purdue OWL – an online writing lab that provides guidelines and useful tips for writing and editing your content.
- Readable – a text analysis tool that gives you statistics about the readability of your text.
If you want to read more about how to help your students improve their essay writing skills, you can check our earlier post about tools that can make essay writing easier .
Author Bio: Josh Carlyle is an experienced writer, who covers different topics relating to educational innovations, college life and new technologies in teaching, such as 4 Top eLearning Development Trends To Look Out For and 5 Myths About Business Writing You Probably Still Believe . He has been sharing his knowledge with communities and blogs for more than four years.
- Categories: American Board Tips , Career Tips , Writing Tips
- Tags: Testing
About The Author
Josh Carlyle is an experienced writer, who covers different topics relating to educational innovations, college life and new technologies in teaching, such as 4 Top eLearning Development Trends To Look Out For and 5 Myths About Business Writing You Probably Still Believe. He is sharing his knowledge with communities and blogs for more than four years.
Related Posts

Top Education Trends of 2023
- December 23, 2023

Consider Earning Your Mississippi Teacher Certification
- July 16, 2021

National Good Teen Day
- January 16, 2024

The Truth about the Teacher Shortage (Part 1)
- February 15, 2021
- About the American Board Blog
- American Board

Currently Empty: $ 0.00
Continue shopping
- Development
Enhancing Creativity and Critical Thinking Skills: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction.
In today’s rapidly evolving world, creativity and critical thinking have become invaluable skills for navigating the complexities of life. Whether you’re a student, professional, or simply someone seeking personal growth, developing these skills can greatly enhance your problem-solving abilities, decision-making processes, and overall mental agility. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various strategies and techniques to foster creativity and critical thinking, empowering you to approach challenges with a fresh perspective and uncover innovative solutions.
Table of Contents
Understanding Creativity and Critical Thinking
Creativity refers to the ability to generate original ideas, approaches, and solutions. It involves thinking beyond conventional boundaries, connecting seemingly unrelated concepts, and exploring new perspectives. On the other hand, critical thinking is the process of analyzing and evaluating information, arguments, and situations in a logical and systematic manner. It involves questioning assumptions, considering multiple viewpoints, and making informed judgments based on evidence and reasoning.
The Importance of Creativity and Critical Thinking
Creativity and critical thinking are vital skills that have a profound impact on various aspects of our lives. In academic settings, they promote deeper understanding, encourage independent thinking, and foster innovative problem-solving abilities. In professional environments, they enable individuals to adapt to changing circumstances, identify opportunities, and make sound decisions. Moreover, in everyday life, these skills empower us to navigate complex challenges, effectively communicate our ideas, and lead fulfilling lives.
Strategies for Enhancing Creativity and Critical Thinking
Embracing curiosity and open-mindedness.
Curiosity is the driving force behind creativity and critical thinking. Cultivating a sense of wonder and actively seeking knowledge about diverse subjects expands our mental horizons and stimulates new ideas. By maintaining an open mind, we become receptive to different perspectives and are more likely to challenge assumptions, explore alternatives, and arrive at novel solutions.
Engaging in Diverse Perspectives
Exposing ourselves to a range of viewpoints and experiences broadens our understanding and nurtures creativity and critical thinking. Actively seeking out diverse sources of information, engaging in discussions with people from different backgrounds, and embracing multicultural experiences can significantly enhance our ability to think critically and generate innovative ideas.
Practicing Reflective Thinking
Reflective thinking involves examining our thoughts, actions, and experiences with a critical lens. By intentionally reflecting on our successes, failures, and the lessons learned, we gain valuable insights that shape our future endeavors. Journaling, meditation, and engaging in meaningful conversations with mentors or peers are effective ways to cultivate reflective thinking.
Encouraging Brainstorming and Idea Generation
Brainstorming is a powerful technique for stimulating creativity and critical thinking. By creating a supportive environment that encourages free-flowing idea generation, we can unlock our imaginative potential. This process involves suspending judgment, allowing for unconventional ideas, and building upon the contributions of others. Collaboration and team-based brainstorming sessions can yield remarkable results by harnessing collective intelligence.
Seeking Feedback and Constructive Criticism
Seeking feedback from trusted sources can provide valuable insights and help refine our creative and critical thinking skills. Constructive criticism enables us to identify blind spots, overcome biases, and enhance the quality of our ideas and arguments. By actively seeking diverse feedback, we open ourselves to continuous improvement and personal growth.
Applying Creativity and Critical Thinking in Different Domains
Education and learning.
Creativity and critical thinking are essential for effective learning. Students who actively engage in these skills are better equipped to analyze information, develop logical arguments, and apply knowledge in real-world scenarios. Educators can facilitate creativity and critical thinking by designing interactive lessons, encouraging active participation, and providing opportunities for independent exploration.
Problem Solving in the Workplace
In today’s competitive job market, creativity and critical thinking are highly sought-after skills. Employers value individuals who can approach problems from different angles, propose innovative solutions, and adapt to rapidly changing circumstances. By leveraging creativity and critical thinking, employees can navigate complex challenges, improve efficiency, and contribute to the overall growth of their organizations.
Everyday Life Challenges
Creativity and critical thinking extend beyond academic and professional contexts. They empower us to approach everyday life challenges with resilience and resourcefulness. Whether it’s finding alternative routes during a traffic jam, coming up with unique gift ideas, or making informed decisions about personal finances, these skills enhance our ability to navigate various situations and seize opportunities.
Overcoming Barriers to Creativity and Critical Thinking
Fear of failure.
Fear of failure often hinders creative and critical thinking processes. To overcome this barrier, it’s important to reframe failure as a valuable learning experience. Embracing a growth mindset allows us to view setbacks as opportunities for growth and improvement. By acknowledging that failures are stepping stones to success, we become more open to taking risks and exploring new ideas.
Narrow-Mindedness and Biases
Narrow-mindedness and biases limit our ability to think critically and inhibit creativity. Recognizing our own biases and actively seeking diverse perspectives can help overcome this barrier. Engaging in empathy-building exercises, exploring opposing viewpoints, and fostering inclusive environments enable us to challenge our assumptions and broaden our perspectives.
Lack of Exposure to Diverse Ideas
Exposure to diverse ideas is crucial for stimulating creativity and critical thinking. Actively seeking out new experiences, exploring different cultures, and engaging with a variety of disciplines can break the monotony and expand our knowledge base. By embracing diversity in all its forms, we foster a rich environment for creative and critical exploration.
External Pressures and Time Constraints
External pressures and time constraints can stifle creativity and critical thinking. Prioritizing self-care, setting aside dedicated time for reflection, and establishing a supportive network can alleviate these challenges. Creating a conducive environment that allows for uninterrupted focus and creative expression is essential for nurturing these skills.
Cultivating a Creative and Critical Mindset
Embracing a growth mindset.
A growth mindset is the belief that intelligence and abilities can be developed through dedication and hard work. By adopting a growth mindset, we embrace challenges, persist in the face of obstacles, and see failures as opportunities for growth. This mindset fosters a sense of curiosity, resilience, and a willingness to experiment, ultimately enhancing creativity and critical thinking.
Developing a Habit of Continuous Learning
Continuous learning is the cornerstone of creativity and critical thinking. Cultivating a habit of seeking knowledge, exploring new fields, and staying updated with emerging trends nurtures our intellectual curiosity and broadens our perspectives. Embracing lifelong learning not only enhances our skills but also keeps us adaptable and open to new ideas and possibilities.
Engaging in Creative and Intellectual Pursuits
Engaging in creative and intellectual pursuits is an excellent way to exercise and enhance our creativity and critical thinking skills. Activities such as writing, painting, playing musical instruments, solving puzzles, or participating in debates and discussions provide avenues for self-expression, problem-solving, and exploring new ideas. By actively engaging in these pursuits, we unlock our creative potential and sharpen our critical thinking abilities.
Tools and Resources for Enhancing Creativity and Critical Thinking
Online courses and workshops.
Online platforms offer a wealth of courses and workshops designed to enhance creativity and critical thinking. Websites like Coursera, Udemy, and FutureLearn provide a wide range of options, from introductory courses to advanced programs. These resources offer structured learning experiences and opportunities to engage with instructors and fellow learners, facilitating the development of these skills.
Books and Reading Materials
Books and reading materials are invaluable sources for enhancing creativity and critical thinking. Authors such as Sir Ken Robinson, Daniel Kahneman, and Steven Johnson provide insights into the creative process, cognitive biases, and innovative thinking. Reading works from different genres, including fiction and non-fiction, exposes us to diverse perspectives and nurtures our intellectual curiosity.
Collaborative Platforms and Idea-sharing Communities
Collaborative platforms and idea-sharing communities foster a supportive environment for creativity and critical thinking. Platforms like GitHub, Stack Overflow, and TED Talks enable individuals to connect with like-minded individuals, share ideas, and collaborate on projects. Engaging with these communities not only provides exposure to diverse perspectives but also allows for valuable feedback and collaborative problem-solving.
Enhancing creativity and critical thinking is a continuous journey that opens doors to innovation, personal growth, and a deeper understanding of the world around us. By embracing curiosity, seeking diverse perspectives, practicing reflective thinking, and engaging in creative pursuits, we can cultivate these skills and apply them in various domains of our lives. Overcoming barriers, adopting a growth mindset, and utilizing available tools and resources further strengthen our creative and critical thinking abilities. Let us embark on this empowering journey of self-discovery, armed with the power of creativity and critical thinking.
Read More: For further insights into creativity and critical thinking, consider exploring the following resources:
- The Harvard Business Review provides a wealth of articles and research papers on critical thinking, its applications, and its impact on decision-making processes.
- TED Talks features engaging talks by experts from various fields, sharing their insights and experiences related to critical thinking and its significance in today’s world.
Q: How can creativity and critical thinking benefit me in my professional life? A: Creativity and critical thinking are highly valued in the professional sphere. They enable individuals to adapt to changing circumstances, identify innovative solutions, and make informed decisions. These skills can contribute to professional growth, open up new opportunities, and enhance problem-solving abilities.
Q: Can creativity and critical thinking be developed, or are they innate abilities? A: While some individuals may have a natural inclination towards creativity and critical thinking, these skills can be developed and nurtured through practice, exposure to diverse perspectives, and continuous learning. Adopting a growth mindset and actively engaging in activities that stimulate these skills can significantly enhance them over time.
Q: How can I overcome the fear of failure and embrace creative thinking? A: Overcoming the fear of failure requires a shift in mindset. Viewing failures as learning opportunities and reframing them as stepping stones to success can help mitigate the fear. Embracing a growth mindset and surrounding yourself with a supportive environment that encourages experimentation and risk-taking can also foster creative thinking.
Top Courses

EMDR therapy training
Product Management Training Course

Six Sigma Course Online

Agile & Scrum Course Online

Supply Chain Management Course

Finance Management Course in Hospitality

Creating Smart Future For Next Generation. We’re simplifying the process to find and select the industry’s top 1% Courses.
- All Courses
- Digital Skill
- Digital Marketing
- IT and Software
- Personal Development
- Help Center
- Privacy Policy
© SmartCourses – All Right Reserved.
- Term Conditions
- Returns Policy
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content

Critical Thinking Through Reading
Aug 08, 2014
100 likes | 219 Views
Critical Thinking Through Reading. Adapted from The College Writer’s Handbook. What is Critical Thinking?. The process of examining ideas and drawing conclusions based on evidence and observation. Read Systematically: Read Actively: Read Critically:.
Share Presentation
- www thecollegewriter
- good practice
- read systematically
- larger context
- central ideas

Presentation Transcript
Critical Thinking Through Reading Adapted from The College Writer’s Handbook
What is Critical Thinking? • The process of examining ideas and drawing conclusions based on evidence and observation
Read Systematically: Read Actively: Read Critically: Know why you’re reading and what you’re looking for by setting up a plan Annotate while you read so that you can make assertions about the ideas Examine, Reflect, Evaluate, Respond to what you read Three Ways Reading Improves Writing:
Read Actively using Arthur Costa’s Levels of Questioning • Summarize, Question, Clarify, Predict, Evaluate • WRITE after you read. Try to “talk to yourself” after you read • Mark up the text, if you can, and immediately follow that with notetaking. Don’t simply mark the book--take it a step further
What does it mean to annotate a text? To ‘mark’ a text by circling important (or confusing) words, underlining key ideas (or things that strike you), writing questions in the margin, and reflecting in the margins
Check out the website for samples! www.thecollegewriter.com
Other ways to react to text • Map the text--write central ideas and then connect ideas • Outline the text--write out all of the major parts, points, and subpoints of the reading or ‘text’ by focusing on the introduction, the ideas, the thesis, and the conclusion
EVALUATING: this means to thoughtfully inspect and then react to the reading and the ideas in the reading, as well as HOW the writer presented the ideas Judge the credibility of the text--who wrote it and why? Put the text in a larger context--how do the ideas connect to other ideas Analyze the evidence and how the writer comes to particular conclusions How were you challenged by the reading? Purposes for annotating and note-taking
Responding to the text • Sometimes you’ll be required to write a ‘formal’ response to a text, but it’s always good to write an informal journal entry response to a text, whether you’re required to write something formal later or not. This type of responding will help cement ideas from the text, and will help you build your foundation of information on a given topic
And don’t forget! No matter if you think you’ll NEVER reference it again, make an MLA citation and a 25-word annotation. It’s good practice, and you never know!
- More by User

Teaching Critical Thinking through Dance-Making
Teaching Critical Thinking through Dance-Making. The Thinking Tools. Based on the book Sparks of Genius: The 13 Thinking Tools of the World’s Most Creative People By Robert & Michele Root-Bernstein Published by Houghton Mifflin in 1999. Observing Recognizing patterns Empathizing
450 views • 27 slides

Promoting Critical Thinking through ICTs
Teaching the Net Generation: Curriculum, Pedagogy and the Challenge of 21 st Century Learning 10 to 11 September Cebu City, Philippines. Promoting Critical Thinking through ICTs. Monalisa M. Te-Sasing. 10 September 2008. The Pitcher is Half-full.
363 views • 11 slides

Critical thinking, reading and taking notes
Critical thinking, reading and taking notes . Developing Business Practice – 302LON. Unit: 4 Knowledgecast : 2. Module Learning Outcomes. In this Knowledgecast, we will: Analyse a range of learning styles and the factors that influence successful study
341 views • 19 slides
Critical Thinking and Reading Science
Critical Thinking and Reading Science . Logical Fallacies . Hasty Generalization. This is a conclusion based on insufficient or biased evidence. In other words, you are rushing to a conclusion before you have all the relevant facts. . Shifting the burden of truth . Argument from ignorance .
431 views • 33 slides

GENERATING ORAL PROJECTS THROUGH CRITICAL THINKING
GENERATING ORAL PROJECTS THROUGH CRITICAL THINKING . REFLECTING. Have you worked with a project in your classroom ? Share your experience . What was your role as a teacher ?. 1.ORAL PROJECTS . Experiences gear to a specific goal or objective.
307 views • 24 slides

Critical Thinking: Close Reading of Texts
Critical Thinking: Close Reading of Texts. Presented by Dr. Cheryl Torok Fleming November, 2013 Based on Paul, R. & Elder, L. (2006). Critical Thinking: Learn the Tools the Best Thinkers Use. Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ. Chapter 7, pages 133-187. Be sure your speakers are turned on!.
367 views • 15 slides

Critical thinking, reading and taking notes . Developing Business Practice – 302LON. Unit: 4 Knowledgecast : 1. Module Learning Outcomes. In this Knowledgecast, we will: Analyse a range of learning styles and the factors that influence successful study
249 views • 17 slides

Academic Research, Critical Thinking & Critical Reading
Academic Research, Critical Thinking & Critical Reading. December 2, 2010. Academic Research. How to Use the Subject Guides Using Google’s Wonderwheel Navigating Around Refworks Avoiding Plagarism www.procon.org. Critical Thinking. Understanding Bloom’s Taxonomy
418 views • 11 slides

Critical Thinking Critical Reading Critical Writing
Critical Thinking Critical Reading Critical Writing. Don’t think about it, just sign it!. Uncritical Thinkers. Pretend to know more than they do. Get annoyed by problems. Are impatient. Judge on first impressions and intuition. Focus on their own opinions.
1.09k views • 37 slides

BBI 3420 CRITICAL READING AND THINKING
BBI 3420 CRITICAL READING AND THINKING. Think critically with data - Graphic Organizers. A graphic organizer is a visual representation of knowledge. Graphic organisers are ideal tools to support critical thinking.
334 views • 12 slides

Critical Reading Critical Thinking
Critical Reading Critical Thinking. Agenda. What is critical reading/ thinking? Why is it important? Techniques. New thing?. Not really. Easy ? Not really. Why not? Because you need to engage a part of your brain that is not normally used. Our brains.
763 views • 23 slides

Critical Thinking, Problem Solving, and Critical Reading
Critical Thinking, Problem Solving, and Critical Reading. JCTC-DT READING/ACADEMIC SUCCSS GOAL 2001-2002 Use Critical Thinking and Problem Solving skills to learn and use with the content in the Study Skills/Academic Success Courses and
427 views • 7 slides

Critical Thinking through Simulations
Critical Thinking through Simulations. Mario Polisena –Merivale High School, Ottawa-Carleton D.S.B. (Paul) + (Sena.) -14 years of teaching; History, Civics, Economics, etc. -Department Head of CWS, Social Science & Humanities, Business. Why create simulations?. Simulations:
342 views • 23 slides

BBI 3420 Critical Reading and Thinking
BBI 3420 Critical Reading and Thinking. FACE TO FACE MEETING PART II. Critical thinking is primarily about the evaluation of arguments. Definition of an argument:
645 views • 55 slides

Improving Student Engagement Through Critical Thinking
Improving Student Engagement Through Critical Thinking. 16 th International Conference on the First-Year Experience July 7-10, 2003 Vancouver, British Columbia Dr. Joseph Burke, Director of Residence Life Jenny Hall-Jones, Assistant Director Residence Life Ohio University.
348 views • 25 slides

Teaching Critical Thinking in Academic Reading
Teaching Critical Thinking in Academic Reading. 张颖 外文学院. Academic English for Social Sciences in Fudan University Teaching Critical Thinking in Academic Reading Two 45-minute Classes as an Example. OUTLINE. Two 45-minute classes a week Maximum 30 students in one class
619 views • 45 slides

Developing Critical Reading, Writing, and Thinking Skills Through Stasis Interrogation
Developing Critical Reading, Writing, and Thinking Skills Through Stasis Interrogation. Lorraine Wallace Utah Valley University UCTE Fall Conference November 9, 2018. What is Stasis Interrogation?. Literally means “slowing down.” (Greek) “Struggle,” “stopping point” (Cicero)
239 views • 21 slides

BBI 3215 CRITICAL THINKING AND READING
BBI 3215 CRITICAL THINKING AND READING. Facts vs. opinion. Introduction. Much of what you read in newspapers or magazines is a mix of factual information and the opinions of the author. Often the opinions are disguised as fact, to make the author's argument seem more believable.
113 views • 11 slides

553 views • 55 slides

Chapter 10: Critical Thinking and Reading
Chapter 10: Critical Thinking and Reading. College Reading and Study Skills, Ninth Edition by Kathleen T. McWhorter. Objectives:. This chapter will show you how to improve your critical reading skills by reacting to and analyzing what you read.
194 views • 15 slides

BBI 3420 CRITICAL READING AND THINKING. SOCRATIC QUESTIONING DR. ZALINA MOHD. KASIM. SOCRATES. “The unexamined life is not worth living...” -- Socrates (469-399 B.C.E.). A Classical Greek philosopher. Considered one of the founders of Western philosophy.
385 views • 38 slides

BBI 3420 CRITICAL READING AND THINKING. INFERENCES. What can you infer from these photos?. The people were celebrating some kind of festival. They were happy. The event was very “messy”. People threw tomatoes at random directions (that was why some wore goggles to protect their eyes).
133 views • 12 slides
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

DEVELOPING CRITICAL THINKING SKILLS:EXPLORATION OF THEORY AND PRACTICE

Related Papers
Sugih Pamungkas
Anales de Psicologia
Ana Mª Nieto
Sabina Saldanha
Khánh Linh Nguyễn
Assessment Update
Peter A Facione
Abdiya Al-Askari
Critical Thinking Across the Disciplines
Jorge Valenzuela
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
European Journal of Service Management
Robert Sobiech
Richard Fransko Halim
Barbara Sa Carvalho
Journal of Theoretical Biology
scott clearwater
CIENCIA-UANL
Karla Rodríguez Burgos
Joselyn Rodriguez
Ì'UlÅ«m va muhandisÄ«-i Ä?byÄ?rÄ«
mehri saeedinia
Modern Physics Letters A
Branislav Sazdovic
Revista de Estudios e Investigación en Psicología y Educación
Suzana Nunes Caldeira
Anthropologiai Közlemények
Sarolta Darvay
HOME WIFI VIETTEL
Viettel Home Wifi
Ecología Austral
fernando zurita
Arif Basuki
Journal of animal science
Blake Wilson
Selim SAYGIN
Godspower Ekuobase
Damian Deamici
Lebensmittel-Wissenschaft & Technologie
Elfadil Babiker
Frontiers in Veterinary Science
Bambang Purwantara
Petra Gretsch
Macromolecules
psicoanálisis transferencia
Josselyn Rosero
Experimental Mathematics
Francesco Moauro
hjhjgfg freghrf
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Critical thinking is general term given to a wide range of cognitive and intellectual skills needed to: Effectively identify, analyze and evaluate arguments. Discover and overcome personal prejudices and biases. Formulate and present convincing reasons in support of conclusions. Make reasonable, intelligent decisions about what to believe and ...
The role of critical thinking • "Skills in critical thinking bring precision to the way you think and work" (Cottrell, 2005, p.4) • Provides you with a basis to evaluate the different types of information • Helps turn an opinion into an informed opinion Form an opinion Gather information Ask a question Identify an informed
The process of thinking is informed by the reading and enacted by writing and vice versa. Deploying critical reading and writing tasks related to course content allows content learning and skill building to occur in unison. Paul (2004) summarises this relationship well: Learning how to read closely and write substantively are complex critical ...
The Foundation for Critical Thinking explains how the "Role of critical thinking in enhancing writing skills" is connected to improving critical reading and thinking skills. Here's the breakdown: 1. Understanding Goals: Whether understanding what an author is saying or expressing our ideas in writing, knowing our goals is crucial. A clear ...
Critical thinkers will identify, analyze, and solve problems systematically rather than by intuition or instinct. Someone with critical thinking skills can: Understand the links between ideas. Determine the importance and relevance of arguments and ideas. Recognize, build, and appraise arguments. Identify inconsistencies and errors in reasoning.
The University designs curriculum, creates support programs, and hires faculty to help ensure you won't be one of the students "[showing]no significant gains in . . . 'higher order' thinking skills" (Rimer, 2011, para. 4). One way the University works to help you build those skills is through writing projects. Writing and Critical ...
The results reveal that EFL MA students are aware of the important role that critical thinking skills play in developing academic writing courses and in producing quality content texts. Discover ...
We particularly focus on writing assignments for two reasons: First, writing, as "thought on paper,"2 can provide a unique oppor- tunity to develop critical thinking skil s, and second, our experi- ence with writing assignments is commonly shared among faculty from across the disciplines.
Critical Thinking Skills.ppt — HCC Learning Web. Home. Faculty. Desmond Lewis. Integrated Reading and Writing (INRW 0420) Course Materials. Week 12/ Summer Week 4/ F8 Week 6. Critical Thinking Skills.ppt.
Here are a few strategies to help you harness the power of critical thinking and improve your writing: Read Widely: Expose yourself to a variety of genres, styles, and subjects.
Cultivating Critical Thinking in Classroom. Critical thinking skills are necessary to succeed in education or in the workplace. Therefore, this ppt aims to foster independent thinking, personal autonomy and reasoned judgment in thought and action by elucidating in-depth understanding of the concept and its importance.
If you are thinking applying critical thinking in writing is too much of a hassle, then understand that not incorporating critical thinking leads to poor writing. And it's easy to detect the effects of not using critical thinking in writing. Some of the obvious signs of not applying critical thinking is a piece of writing include:
Free Google Slides theme and PowerPoint template. Critical thinking appears to be a difficult matter to understand. Well, we can help you with the design of a presentation about that topic! You'll notice the colorful nature of the elements used in the slides, which may encourage viewers (or students!) to think about this concept.
Critical thinking involves evaluation, problem solving, and decision making which are all necessary ingredients in a good essay. Here are 8 ways how essay writing can enhance your students' critical thinking skills: Evaluating the reliability of information. When writing essays, students have to evaluate the reliability of the information ...
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various strategies and techniques to foster creativity and critical thinking, empowering you to approach challenges with a fresh perspective and uncover innovative solutions. Education and Learning. Narrow-Mindedness and Biases. Lack of Exposure to Diverse Ideas. External Pressures and Time Constraints.
Critical Thinking Critical Reading Critical Writing. Critical Thinking Critical Reading Critical Writing. Don't think about it, just sign it!. Uncritical Thinkers. Pretend to know more than they do. Get annoyed by problems. Are impatient. Judge on first impressions and intuition. Focus on their own opinions. 1.07k views • 37 slides
This document is a summary of key readings in critical thinking and creativity, prepared for school teachers. It focuses on four topics: (a) critical thinking and its relationship to creativity; (b)an education-related concept of creativity (i.e., understanding what you are trying to promote); (c) recognizing classroom creativity when you see ...
The instruments used were writing prompts and rubrics for assessing the observed skills namely critical thinking, writing performance and topic familiarity. Path analysis was used to figure out ...
Critical Thinking Skills Developing Effective Analysis and Argument osl chl rave. Khánh Linh Nguyễn. Download Free PDF View PDF. ... Psychodidae): transtadial passage and the role of female diet. 2002 • Alexandr Nemec. Download Free PDF View PDF. Anuario Filosófico. MARTÍNEZ CARRASCO, ALEJANDRO, D'Ors y Ortega frente a frente, Dykinson ...
Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) proven because it plays a significant role in education. Students with HOTS (Higher Order Thinking Skills) are regarded more capable than those with Low Order Thinking Skills (LOTS). HOTS is also claimed to be related to student work readiness (Hasan & Pardjono, 2019, cited in Purnama & Nurdianingsih, 2019).
Developing students' critical thinking and reading comprehension is crucial, particularly for those in colleges, because. they need to read numerous scientific journals and textbooks written in ...
speaking, reading and writing. These skills are equally. related to and supportive of each other. Writing is. considered as a very important skill among all the skills. Most people believe that ...