- Interesting MedStuff
- International News
- Medical Devices
- Social Media
- Life Experiences
- Student Articles
- Student Tips
- Clinical Medicine
- Clinical Procedures
- Clinical Surgery
- Guidelines & Protocols
- Publisher Square
- Smartphone Apps
- Aesthetic Medicine
- Beauty & Cosmetics
- Elderly Health
- Kid’s Health
- Medical Tips for Daily Life
- Men’s Health
- Mental Health
- Women’s Health
- Subscription Options
- Partners & Supporters
- Publishing Guidelines
- Medicalopedia Citations
- DMCA Notice
- Privacy Policy


Technology Meets Health: 7 Core Benefits of Telehealth

Virginia Beach Chiropractor Offers Free Consultation Coupon on Website

How To Use Synthetic Urine For A Drug Test

Ease Your Pain With Regenerative Medicine

How to Minimize the Risk of an Injury During a Car…

- Medical News
Why Is Medical Research Important?
Medical research has become an important part of the health care industry, and advances in technology have made it possible for much of it to be done on an outpatient basis, meaning that investigators sometimes don’t need to do extensive studies in a research facility. The field of medical research is one of the most interesting fields in all of science because of its focus on science and medicine in conjunction with a great deal of research.
Medical research covers a wide variety of studies, stretching from ‘baseline’ investigation, through systematic reviews and to the cutting-edge of medical science. It involves the study of all human diseases or may have only disease-specific research. For example, AIDS research includes both studying patients who have AIDS and those who do not, as well as studying children with AIDS and children without AIDS. Similarly, researchers may be investigating the causes of Parkinson’s disease in old age and Parkinson’s disease in young adulthood.
4 Phases of Medical Research Studies
The four phases of Medical Research Studies are experimental, comparative/expository, understudy, and last, analysis and validation/regression.
- Comparative/expository medical research compares experimental and comparative samples from which the study population is developed; compare post hoc comparisons with the initial data; evaluates associations among variables measured.
- Understudy studies consist of data from observational studies and random chance sampling.
- Experimental refers to clinical trials that are done specifically to test a new medical product, device, or technique.
- Finally, validation/ regression Research studies compare new designs or drugs to earlier designs and evaluate their effect on any association found.
There are many reasons why medical research is so valuable. Whether you aim to start a career in this field or to gain more knowledge about health conditions and their treatments, it’s important to understand the benefits that medical research provides. You can learn about medical research at http://hrmdresearch.com/ .
The Importance Of Medical Research
The breakthroughs that people enjoy today are virtually unimaginable without the knowledge gained through medical research. Here are some of the most important reasons medical research is important:
- Generate Valuable Insights
Medical research helps people learn more about themselves and their health. The knowledge gained by medical research is constantly improving.
- With new scientific information coming from medical studies, people will be able to take care of their health and well-being more effectively.
- It also seeks to understand the reasons for diseases, to discover new methods of preventing or controlling diseases, and to develop treatments for these diseases and their effects.
2. Development Of New Drugs
Medical research must be done to find a cure for diseases and illnesses. Without medical research, medicine and other medical innovations as we know it could not exist. Sometimes called pharmaceutical research, medical research encompasses a broad spectrum of scientific studies. It starts with the research and development of drugs, followed by treatments and procedures used in clinical practice.
The process of new drug development may involve the following steps:
- It can be done in several different ways, including doing laboratory experiments in bioresources such as blood and cells, or cell culture, to studying the effects of chronic exposure to toxins, drugs, hormones, and other compounds in the environment.
- Other research is directed toward understanding disease mechanisms, to find better ways of treating or preventing disease, and how disease progression is influenced by environmental factors.
3. Improve The Quality Of Life
Medical researchers don’t just look for ways to manage the symptoms of diseases, they try their best to find a cure for a specific illness or a group of diseases. There are several ways drug research and testing improve the quality of life:
- Medical studies that aid in the development and administration of vaccines allow people to live without worrying about deadly diseases. An example will be the ongoing development and clinical trials for the COVID-19 vaccine which may help the world go back to normal.
- Some people can live with their conditions for years by understanding how to manage them properly. As time goes by, everyone is also learning how to prevent certain illnesses from occurring and even eliminate them.
Why is medical research so important? Medical research saves lives every day. Scientists and researchers work day and night to develop new treatments, drugs, and procedures. Without the help of dedicated scientists, doctors, and other medical professionals, the advances made would be slow and limited.
When a patient participates in a trial, they must undergo several physical tests and provide some information about their lifestyle and diet. The findings and insights derived from these studies and trials are invaluable in coming up with treatments and cures for various health conditions.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR

The Impact of Consolidation: Healthcare Mergers and Acquisitions Explained

Importance of Peptides In Therapeutics

The Impact of Employee Health on Productivity

Omaha Orthopedic Clinic Knee Damage Types and What They Mean

6 Factors that affect successful change in healthcare organizations

WFH Neck Pain- Effective Measures For Lasting Relief
Read our research on: Abortion | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
Most americans say science has brought benefits to society and expect more to come.
About seven-in-ten U.S. adults (73%) say science has had a positive effect on society, just 3% say it has had a negative effect and 23% say it has yielded an equal mix of positive and negative effects, according to a Pew Research Center survey .
White adults are more likely than black and Hispanic adults to see the effects of science in positive terms. And people who have higher levels of factual knowledge about science, based on an 11-item index , are especially likely to think science has had a positive effect overall.
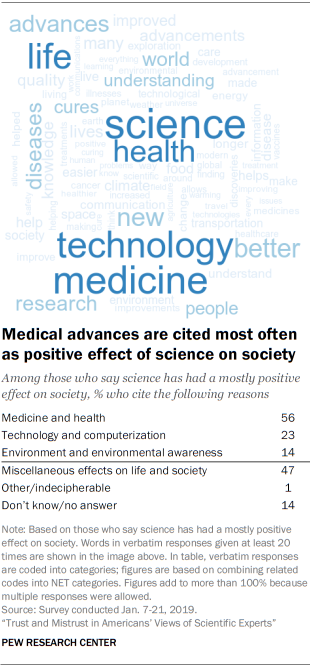
Some mentioned benefits from an aspect of technology and computerization (23% of those asked), offering general references to new or helpful technology and changes to communication. One respondent put it this way: “Science has advanced our communication avenues which opens the world to all.” Others highlighted benefits for the environment (14% of those asked), with one respondent saying that science has “kept us abreast of what to expect from climate change.” Still others (47% of those asked) cited a miscellany of effects, ranging from improvements in food production to developing a better understanding of our world.
Those who saw negative or mixed effects of science on society were also asked their reasons why, and they cited a range of reasons. About one-in-ten (11%) in this group mentioned concerns about scientists and scientific theories. One said, “Scientific research has been contaminated by big business paying to have findings skewed in their favor to deceive the public.” Another replied, “Conflicting results reported on breakthroughs, don’t know what is true. What is true today will change over time.”
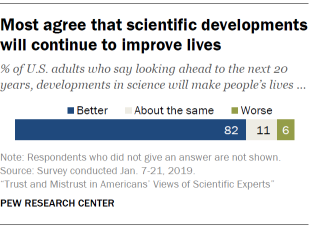
Here, too, medical advances prevail in the public mind as a likely source for improvements ahead, with six-in-ten U.S. adults (60%) referencing this topic when asked to think about developments in science that will make people’s lives better.
Note: The quoted responses above are lightly edited for spelling and punctuation. See topline for full question wording and the Methodology section of the main report for more information on the index of science knowledge.

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
Americans’ Trust in Scientists, Other Groups Declines
Trust in america: in the age of covid-19, do americans trust science, science and scientists held in high esteem across global publics, black americans have less confidence in scientists to act in the public interest, public confidence in scientists has remained stable for decades, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- News Feature
- Published: 05 December 2019
Looking forward 25 years: the future of medicine
Nature Medicine volume 25 , pages 1804–1807 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
62k Accesses
6 Citations
320 Altmetric
Metrics details
A Publisher Correction to this article was published on 27 January 2020
This article has been updated
To celebrate the end of our 25th anniversary year, we asked thought leaders and experts in the field to answer one question: What will shape the next 25 years of medical research?

Core member and chair of the faculty, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard; director, Klarman Cell Observatory, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard; professor of biology, MIT; investigator, Howard Hughes Medical Institute; founding co-chair, Human Cell Atlas.
For many years, biology and disease appeared ‘too big’ to tackle on a broad level: with millions of genome variants, tens of thousands of disease-associated genes, thousands of cell types and an almost unimaginable number of ways they can combine, we had to approximate a best starting point—choose one target, guess the cell, simplify the experiment.
But we are now on the cusp of an inflection point, where the ‘bigness’ of biomedicine turns into an advantage. We are beginning to see advances towards these goals already, in polygenic risk scores, in understanding the cell and modules of action of genes through genome-wide association studies (GWAS), and in predicting the impact of combinations of interventions. Going forward, our success in harnessing bigness will rely on our ability to leverage structure, prediction and expanded data scale. Disease is highly structured at the molecular, genetic, gene program, cell and tissue levels; acknowledging and understanding this structure can help us reduce the overwhelming lists of genes and variants to a manageable number of meaningful gene modules . We cannot test every possible combination, so we need algorithms to make better computational predictions of experiments we have never performed in the lab or in clinical trials. But only when data are truly big, scaled massively and rich in content, will we have the most effective structuring and prediction power towards building a much-needed Roadmap of Disease for patients.
To achieve this, we need to invest in building the right initiatives—like the Human Cell Atlas and the International Common Disease Alliance—and in new experimental platforms: data platforms and algorithms. But we also need a broader ecosystem of partnerships in medicine that engages interaction between clinical experts and mathematicians, computer scientists and engineers who together will bring new approaches to drive experiments and algorithms to build this Roadmap.

PhD investigator, Howard Hughes Medical Institute; core member, Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard; James and Patricia Poitras Professor of Neuroscience, McGovern Institute for Brain Research, MIT.
Although it is difficult to pinpoint an exact value, it is safe to estimate that more than 250 patients have been treated with gene therapies for monogenic diseases for which there previously were no treatment options. Add in the patients who have received CAR-T therapy, and that number rises into the thousands. This is an enormous success, and it represents the beginning of a fundamental shift in medicine away from treating symptoms of disease and toward treating disease at its genetic roots.
Gene therapy has been under development for more than 30 years, but several recent major advances have tipped the scales toward clinical feasibility, including improved delivery methods and the development of robust molecular technologies for gene editing in human cells. In parallel, affordable genome sequencing has accelerated our ability to identify the genetic causes of disease. With these advances, the stage is set for the widespread use of gene therapy. Already, nearly 1,000 clinical trials testing gene therapies are ongoing, and the pace of clinical development is likely to accelerate.
To fulfil the potential of gene therapy and ensure that all patients have access to this revolutionary treatment, we will need to continue developing delivery approaches that are practical and widely usable, to refine molecular technologies for gene editing, to push our understanding of gene function in health and disease forward, and to engage with all members of society to openly discuss the risks and benefits of gene therapy.
Elizabeth Jaffee

Dana and Albert “Cubby” Broccoli Professor of Oncology, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine; deputy director, Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins.
“An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” Benjamin Franklin said this in reference to fire safety, but it can easily be applied to health too. The twentieth century saw amazing advances aimed at preventing the onset of disease—including vaccines and risk-factor interventions—nearly doubling life expectancy worldwide. Only two decades into the twenty-first century, healthcare has already entered its next phase of rapid advancements. By using precision medicine technologies, genetic vulnerabilities to chronic and deadly diseases at the individual level can now be identified, potentially pre-empting disease decades later.
My hope for the next 25 years is that someday a single blood test could inform individuals of the diseases they are at risk of (diabetes, cancer, heart disease, etc.) and that safe interventions will be available. I am particularly excited about the possibility of developing cancer vaccines. Vaccines targeting the causative agents of cervical and hepatocellular cancers have already proven to be effective. With these technologies and the wealth of data that will become available as precision medicine becomes more routine, new discoveries identifying the earliest genetic and inflammatory changes occurring within a cell as it transitions into a pre-cancer can be expected. With these discoveries, the opportunities to develop vaccine approaches preventing cancers development will grow.
But, as is the case today, prevention technologies can only be fully successful if they are widely available, to reduce unnecessary morbidity and mortality and healthcare costs and further raise life expectancy. Global accessibility is key to reduce global disparities. For these strategies to work, funding agencies should consider prioritizing prevention strategies.
Jeremy Farrar

Director, Wellcome Trust.
Politics, demographics, economics, climate—how the world changes and interacts fundamentally affects all of us. Research is part of that and can help provide solutions to the great challenges we face, but only if the three pillars of science, innovation and society come together in an environment where people and teams can thrive. We must therefore take the opportunity today to shape how the culture of research will develop over the next 25 years.
Building a career in research can be incredibly rewarding, yet it often comes at a cost. The drive for research excellence—to which Wellcome has certainly contributed—has created a culture that cares more about what is achieved than how it is achieved. We can do better, and building a creative, inclusive and open research culture will unleash greater discoveries with greater impact.
Changing culture requires us to acknowledge the issue and then make a long-term commitment. As an independent foundation, Wellcome is able to acknowledge the issue and make that commitment. This is a permanent shift in our thinking. Working openly with, and as part of, the wider research community, we aim to make research inclusive, more inspiring, more fun, more rewarding. As a result, it will contribute even more to making the world a healthier place to live.
John Nkengasong

Director, Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention.
Population wise, Africa is the continent of the future. By 2050, it is estimated that its population will be 2.5 billion people. This means that one in every four persons in the world might be an African, with rapidly growing economies and a rising middle class. These demographic changes have important implications for both communicable and noncommunicable disease patterns, including emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases; resistance to antibiotics; and rising rates of cancers, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and maternal and child deaths. To meet its health challenges by 2050, the continent will have to be innovative in order to leapfrog toward solutions in public health.
Precision medicine will need to take center stage in a new public health order—whereby a more precise and targeted approach to screening, diagnosis, treatment and, potentially, cure is based on each patient’s unique genetic and biologic make-up. For example, universal newborn screening and a more accurate analysis of causes of death in this age group could be established to curb under-five mortality; genetic screening programs could help avoid progression towards aggressive cancers; and medicine side effects could be reduced if tests could predict negative reactions and enable caregivers to proactively prescribe alternative treatments.
In Africa, precision medicine should not be seen from the lens of sequencing whole genomes, diagnosing DNA abnormalities and developing medications targeted to very small populations. Rather, African countries should begin pursuing policy approaches and partnerships to advance precision medicine to meet the African Union’s Agenda 2063 goals. This includes the integration of precision medicine approaches into national strategies to improve healthcare—including genomic data policy—and increase diagnostic capacity, and the creation of biobanks, such as H3Africa, that encompass both physical and bioinformatics facilities.

Executive vice-president, Scripps Research Institute; founder and director, Scripps Research Translational Institute.
Twenty-five years ago, the World Wide Web was just getting off the ground. Therefore, when thinking of the medical research landscape in 25 years, it is reasonable to think big and without limits.
In 2045, I hope we will have developed a planetary health infrastructure based on deep, longitudinal, multimodal human data, ideally collected from and accessible to as many as possible of the 9+ billion people projected to then inhabit the Earth.
This infrastructure, by using hybrid artificial intelligence (AI) models—including various deep neural networks, federated AI, nearest-neighbor analysis and systems yet to be developed—could provide individualized guidance for the prevention and optimal management of medical conditions, acting as a virtual medical coach for patients and a platform for clinicians to review a patient’s real-time, real-world, extensive and cumulative dataset.
Some have projected that, by this juncture, artificial general intelligence (AGI) will have been developed, giving machines enhanced capabilities to perform functions that are not feasible now. Notwithstanding that uncertainty, it is likely that machines’ ability to ingest and process biomedical text at scale—such as the corpus of the up-to-date medical literature—will be used routinely by physicians and patients. Accordingly, the concept of a learning health system will be redefined.
Linda Partridge

Professor, Max Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing.
Human life expectancy has increased over the past 170 years in many parts of the world. Unfortunately, the healthy lifespan has not, and the period of life when a person lives with disability and illness at the end of life is growing, especially in women.
But ageing is malleable, and mounting evidence suggests that late-life ill health can be combated. In laboratory animals, including mice and rhesus monkeys, genetic, lifestyle and pharmacological interventions can increase not only the lifespan, but also the healthspan. In humans, improvements in diet and the implementation of physical exercise regimes can effect major health improvements, but better lifestyle is not enough to prevent age-related diseases.
The big hope is that 25 years from now, medical sciences will have progressed enough to enable people to have healthier and more active lives almost up until their eventual death. Going forward, the direct targeting of mechanisms of ageing, including with existing drugs, presents an opportunity to reduce disability and illness in late life. Sirolimus, an mTORC1 inhibitor, extends the lifespan of laboratory animals and in clinical trials has proved to boost the immune response of older people to vaccination against influenza. Other drugs, such as the combination of desatinib and the BCL-2 inhibitor quercetin, which kill senescent cells, are farther from the clinic but show promise. Plasma from younger mice has been shown to have a beneficial effect on the stem cell function of several tissues in older mice; work to identify the natural metabolites responsible for this effect could open up avenues for translation to the clinic. Geroprotective drugs, which target the underlying molecular mechanisms of ageing, are coming over the scientific and clinical horizons, and may help to prevent the most intractable age-related disease, dementia.
Trevor Mundel

President of Global Health, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
The most essential innovations in medical research over the next 25 years won’t just come from the explorations of bench scientists or the emergence of new technologies. They will come from what we do—as partners across the public and private sectors—to forge a new applied research ecosystem dedicated to the rapid discovery, development and delivery of life-changing tools that have been designed with the end user in mind.
This will mean finding new ways to share clinical data that are as open as possible and as closed as necessary. It will mean moving beyond drug donations toward a new era of corporate social responsibility that encourages biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies to offer their best minds and their most promising platforms. And it will mean working with governments and multilateral organizations much earlier in the product life cycle to finance the introduction of new interventions and to ensure the sustainable development of the health systems that will deliver them. If we focus on these goals, we can deliver on the promise of global health equity.
Josep Tabernero

Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO); president, European Society for Medical Oncology (2018–2019).
Let’s briefly skip back 25 years. In oncology, who could have predicted that the stunning advances in genome sequencing would come to shape clinical decision-making? Who could have foreseen the increasing availability of genetic patient screenings or the promise of liquid biopsy policing of disease? Very few, which is why it is a fool’s errand to make sweeping predictions. But let’s try.
Over the next 25 years, genomic-driven analysis will continue to broaden the impact of personalized medicine in healthcare globally. Precision medicine will continue to deliver its new paradigm in cancer care and reach more patients. Immunotherapy will deliver on its promise to dismantle cancer’s armory across tumor types.
I also anticipate that AI will help guide the development of individually matched therapies, the harnessing and exchange of big data, and advances in telemedicine to bring crucial medical expertise to more patients everywhere. But the prospect is not all rosy. I worry about the exacerbating burden of comorbidities in cancer patients. We must collectively seek to strengthen and unify medical fields, with particular emphasis on oncology and cardiology. This is an emerging area for collaboration. Implementation research in the prevention and control of cancer will also be critical, as will be the shaping and strengthening of cancer policy-making at the global, national and regional levels.
With continued belief that scientific endeavors should be prioritized to respond to society’s and citizens’ needs, the scientific community must grasp future opportunities to uphold the very ethos of medicine as we continue to push boundaries in discovering new ways to extend and improve patients’ lives.
Pardis Sabeti

Professor, Harvard University & Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health and Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard; investigator, Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
A cataclysmic global pandemic is one of the greatest risks to humanity. Over the last 25 years, we have seen SARS, Ebola, Zika and other viruses spread undetected for months, leading to international emergencies and often devastating consequences. Even in the best US hospitals, most infectious diseases are not properly diagnosed or tracked.
But advances in two fields, genomics and information science, can transform our fight against viral threats. Ultrasensitive genome sequencing technologies are enabling the detection and characterization of viruses circulating under the radar. The advent of novel CRISPR, synthetic biology and microfluidic tools have allowed the development of rapid, ultrasensitive point-of-care diagnostics that can be deployed anywhere in the world. The resulting diagnostic and surveillance data can be integrated across healthcare nodes, from rural clinics to city hospitals, thanks to powerful new information systems. Together with advances from AI and other fields, these information systems can aid the rapid detection of infectious threats, to track their spread, and guide public health decision-making.
Over the next 25 years, the development and integration of these tools into an early-warning system embedded into healthcare systems around the world could revolutionize infectious disease detection and response. But this will only happen with a commitment from the global community.
Els Torreele

Executive director, Médecins Sans Frontières Access Campaign.
Of the many biomedical advances made by the scientific community, only those that can generate large financial profits are taken up for development by for-profit companies. This leaves many gaps—but also opportunities—in regard to developing new treatments to meet public health needs.
My hope is that the scientific community will step up and target efforts to develop innovative therapeutics and other health tools for populations across the world. This includes people affected by tuberculosis, hepatitis, Ebola, advanced HIV, neglected tropical diseases, vaccine-preventable diseases, antimicrobial resistance, snakebite—the list goes on. The creativity and brainpower of the global research community are required to find solutions addressing these grave human needs.
But to do this, we need a paradigm shift such that medicines are no longer lucrative market commodities but are global public health goods—available to all those who need them. This will require members of the scientific community to go beyond their role as researchers and actively engage in R&D policy reform mandating health research in the public interest and ensuring that the results of their work benefit many more people. The global research community can lead the way toward public-interest-driven health innovation, by undertaking collaborative open science and piloting not-for-profit R&D strategies that positively impact people’s lives globally.
Change history
27 january 2020.
An amendment to this paper has been published and can be accessed via a link at the top of the paper.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Looking forward 25 years: the future of medicine. Nat Med 25 , 1804–1807 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0693-y
Download citation
Published : 05 December 2019
Issue Date : December 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-019-0693-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- Why all doctors should...
Why all doctors should be involved in research
- Related content
- Peer review
- Hannah Jacob , academic clinical fellow
- 1 UCL Institute of Child Health, London WC1N 1EH
- hcjacob{at}gmail.com
Neena Modi tells Hannah Jacob about her career in research and why this is a fundamental part of every doctor’s job
Neena Modi is president of the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health and professor of neonatal medicine at Imperial College, London. She is a practising clinician and academic lead of a neonatal research programme focusing on nutritional and other perinatal determinants of lifelong metabolic health. After a period as vice president for science and research at the college, she was elected president in April 2015.
How did you become interested in research?
I realised that what I was being taught during my training was wrong, and my very enlightened consultant challenged me to design a trial to back my contention. There were no training posts in neonatal medicine when I started my paediatric training, but there were lots of opportunities to learn and undertake research because the rate of change was so great. That was really exciting.
Which research projects are you most proud of? Which do you think has had the biggest impact?
We did a series of studies to develop methods for measuring body water compartments in extremely preterm babies and to describe the postnatal alterations in fluid balance. We also tested the hypothesis that immediate sodium supplementation in babies with respiratory distress syndrome was harmful. That was a big achievement.
Most recently we have identified possible biological mechanisms that underpin the epidemiological associations between early onset of features of the metabolic syndrome and being born extremely preterm. That is of real interest as we learn more about the long term effects of extremely preterm birth.
How have you coped with the inevitable setbacks of a career in clinical research?
Real life is about being refused things and carrying on anyway, so I have developed resilience. There was no academic training route when I started out, so I have had to forge my own way. People will always tell you that it cannot be done. You have to pursue the things you are passionate about.
Do you have any advice for junior doctors interested in doing research?
Work out what interests you, and then find the person who is going to help you do it. Being approached by an enthusiastic junior doctor is always well received, and once you have found the right senior person they can support you in achieving your goals. Do not lose heart if you don’t get an academic training post as they are not the only way into research. Some of the best research students I have worked with have not come through the standard path.
What would you say to doctors who have no interest in doing research?
I would argue that they may not be thinking broadly enough about what research actually is. Every clinician is responsible for evaluating their own practice, and to do that in a robust and meaningful way you need to use the tools of research. We all need to be able to critically review research done by others. For example, the guidelines used in everyday clinical practice are based on meta-analyses and systematic reviews. So I think all doctors need to be involved in research in some way, and that may be different for different people.
How can undertaking research help doctors in their careers?
It’s not just a help, it’s essential. There are few absolutes in science, and without inquiring minds medicine will stand still. Participation in research enables doctors to evaluate their practice objectively and to be involved in advancing their discipline. You can learn so many skills that make you a better clinician around appraising the evidence and thinking critically about a situation.
What are the benefits and downsides of doing research—both on a personal and professional level?
The benefits come from knowing you are contributing to the science of medicine as well as the art, and are able to question, evaluate, and test different approaches objectively. Everyone has a role in supporting research—many will contribute, and some will be research leaders.
As for downsides, life has ups and downs, and research is no different. You have to not be too disheartened when a grant application gets rejected. When you want to achieve something, you have to keep speaking to the powers that be until you find someone who can be an advocate.
How do you juggle the research, clinical, and leadership aspects of your working life?
It is a balance that is evolving all the time and that provides me with a huge stimulus. Every time I have been presented with an opportunity I have had to evaluate its potential effect on the other components of my work. I always say yes to the things that interest me and follow my muse. We are very privileged as doctors to have such a range of tremendous opportunities available to us.
Do you have a particular philosophy that has guided you in your career?
When life offers you an opportunity, do not turn it down. I believe you must do what grabs your interest, and if you are still doing it years later you know you made the right decision. When you lose the excitement, it is time for a change. The future lies with junior doctors, and you can be a part of shaping it in the way you think is right.
Is there anything you would do differently if you had your career again?
I would have much greater confidence to fight for something I believed in.
Competing interests: I have read and understood BMJ policy on declaration of interests and declare that I am the academic officer for the Paediatric Educators Special Interest Group of the Royal College of Paediatrics and Child Health.
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 17 January 2018
What motivates medical students to select medical studies: a systematic literature review
- Sonu Goel 1 ,
- Federica Angeli 2 , 3 ,
- Nonita Dhirar 1 ,
- Neetu Singla 1 &
- Dirk Ruwaard 4
BMC Medical Education volume 18 , Article number: 16 ( 2018 ) Cite this article
17k Accesses
60 Citations
23 Altmetric
Metrics details
There is a significant shortage of health workers across and within countries. It is of utmost importance to determine the factors that motivate students to opt for medical studies. The objective of this study is to group and review all the studies that investigated the motivational factors that underpin students’ selection of medical study in recent years.
The literature search was carried out by two researchers independently in PubMed, Google Scholar, Wiley and IndMED databases for articles published from year 2006 till 2016. A total of 38 combinations of MeSH words were used for search purpose. Studies related to medical students and interns have been included. The application of inclusion and exclusion criteria and PRISMA guidelines for reporting systematic review led to the final selection of 24 articles.
The majority of the studies ( n = 16; 66.6%) were from high-income countries followed by an equal number from upper-middle and lower-middle income countries ( n = 4,16.7%). None of the studies were from low-income countries. All of the studies were cross-sectional in nature. The main motivating factors that emerged were scientific (interest in science / medicine, social interest and academia, flexible work hours and work independence), societal (prestige, job security, financial security) and humanitarian (serving the poor and under priviledged) in high-, upper-middle and lower-middle income countries, respectively. The findings were comparable to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory of motivation.
This systematic review identifies the motivational factors influencing students to join medical studies in different parts of the globe. These factors vary per country depending on the level of income. This study offers cues to policy makers and educators to formulate policy in order to tackle the shortage of health workers, i.e. medical doctors. However, more research is needed to translate health policy into concrete and effective measures.
Peer Review reports
The world is currently facing a dual problem of shortage and inequitable distribution of health workers, especially in middle- and low-income countries [ 1 ]. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated a need for an additional 4.3 million health workers in 57 countries to fulfill the Millennium Development Goals [ 2 ]. In addition, 83 countries (44.6%) do not currently meet the 2006 World Health Report threshold of 22.8 skilled health professionals per 10,000 population [ 3 ]. Among many, the main reasons cited for shortage of health workers in rural areas include poor working conditions, lack of accommodation, lack of transport, poor pay structure, overburden with additional administrative responsibility and political interference [ 4 ]. In middle- and low-income countries, the situation is more critical because of migration of doctors to high-income (developed) countries whereas inequitable distribution of health workers between urban and rural areas is primarily due to poor motivation of health workers to work in rural areas [ 5 ].
The choice of medical study depends upon various factors such as interest in the medical field, good job opportunities, a desire to serve others, medical background of the parents and many more [ 6 , 7 ]. In literature, no review has been conducted in the last ten years about motivation factors of students to select medical studies. The existing reviews have either been conducted before ten years or with different objectives [ 8 , 9 ]. One review by Puertas et al. [ 8 ] published in 2013 was conducted to review the factors influencing medical student’s choice in primary care while another one by Brissette and Howes [ 9 ] published in 2010 was conducted on the articles available till 2008. Brisstte and Howes identified that motivation to take up medical studies lies in addressing learner’s needs for competence, autonomy, and relatedness. Providing optimal challenge and positive performance feedback, choice and opportunity for self-direction, and a sense of belongingness and connection to the medical profession can all be focused on to address the above mentioned motivators [ 9 ]. The review has given points for educators to act upon.The lacunae left by the previous review studies need to be addressed in a finer manner in context with the current challenge of the global workforce.
In last few years, human resources for health has attracted substantial scholarly attention. Over the last decade, there have been advancement in different fields of medical sciences, from prevention, patient care to laboratory workup and management of severe diseases and palliation. With the growing population and improving health care owing to better technologies, it is gravely important to improve the medical workforce, mostly doctors.
Globally, several health-related goals and programs are giving priority to human resource development in the health sector. The major health related initiatives like Sustainable Development Goals [ 10 ] and WHO’s six building blocks [ 11 ] focus on human resource development for achieving universal health coverage. The National health programs, like the National Health Mission in India, focuses on increasing human resources to upbring the health care services in the country.
The prospective medical students form a significant pool of health care workers that can help overcome the shortage globally. Therefore, understanding the current common motivational factors is essential and a summary of the factors through a review of these studies would derive a clearer picture. A strong predictor for any student to take up a career in any field is the motivation or drive from within. Motivation is defined as the process that initiates, guides, and maintains goal-oriented behaviors. It involves the biological, emotional, social, and cognitive forces that activate behavior. Fulfillment of needs results in some type of behavior, which can be either intrinsic or extrinsic [ 7 ]. Understanding motivation is very important in the medical sector because a motivated individual is willing to exert and maintain an effort to provide good-quality health services.
The objective of this study is to group and review all the studies that investigated the motivational factors that underpin students’ selection of medical study in recent years.
Search strategy
The literature search was carried out with the purpose to identify the perceptions of medical students to enter medical studies. The search was carried out by two researchers (NS and ND) independently in PubMed, Google Scholar, Wiley and IndMED databases for original studies conducted from 2006 to 2016. This time frame was chosen as many studies were done during this period to identify the motivational factors. MeSH and free-text terms “(Motivat*) AND (select* OR choice OR choose) AND (medical student* OR medical school* OR interns) have been used. Internship in the period of practical application of theoretical (mostly) knowledge of the previous medical school years, hence interns were also made a part of the search strategy. Search terms and keywords were altered as per specification of individual databases. A total of 38 combinations were used for search purpose.
An initial search identified thousands of related records from the Google scholar, PubMed, Ind Med and Wiley online library databases. The articles which were not related to motivation were excluded at the first step. Then search results were imported to Microsoft Excel and duplications were removed by sorting the titles of articles. The selected studies were then screened by reading the title and abstract resulting in shortlisting 91 articles. Of these, 62 articles were excluded based on eligibility criteria. The remaining 29 full-text articles were further assessed, and five were excluded because the articles were in Korean, Spanish and Chinese. A total of 24 studies were selected. Any differences of opinion were debated and consensus was reached. Further differences were resolved by the third researcher (SG). PRISMA guidelines were strictly followed during the study. Figure 1 represents the flow chart leading to sample selection.
Flow chart of selection and exclusion of studies for the systematic review
Selection criteria and sample
All studies carried out and published from year 2006 till 2016 were included in the review. Inclusion criteria were studies describing motivation to study medicine, conducted among medical students and interns and available in English language. Exclusion criteria were those studies done before 2006, published in languages other than English, and those not related to motivation or medical students and interns.
Data analysis
A thematic analysis of selected papers was performed, wherein two research assistants coded the papers independently and reached consensus on relevant themes [ 12 ]. They also extracted details of the final articles using a standardized abstraction form that collected information on: the author, the journal, the year of publication, location, study objectives, study design, major findings, limitations, and observations. In this paper, we systematically review the literature related to medical education with the goal of identifying the motivating factors influencing the medical students to join medical studies.
The results of the studies’ review were categorized under different heads viz. scientific factors, social factors and humanitarian factors based upon criteria devised by Goel S et al. in their study on development and validation of the motivations for selection of medical study in India [ 13 ]. In this study a ‘Motivation of Selection of Medical Study (MSMS)’ tool was developed using extensive literature review followed by Delphi technique. The three domains and the issues that emerged are shown in Table 1 .
Ethical considerations
The study was granted ethical approval from the Institute’s Ethical Committee, PGIMER, Chandigarh (PGI/IEC/2012/810–1 P-154). Since the study is a systematic review of studies and individual level data is neither obtained nor presented, the consent.
The characteristics of the studies included in the systematic review are shown in Table 2 . The assessment of factors of motivations for medical students to select medical studies was based on the World Bank categorization of low-, middle- and high-income countries [ 14 ].The low-income, lower middle-income, upper middle-income and high-income economies are defined as those with a Gross National Income (GNI) per capita of $1005 or less, between $1006 and $3955, between $3956 and $12,235 and $12,236 or more, respectively in the year 2016. The majority of the studies ( n = 16, 66.6%) were from high-income countries followed by an equal number from upper middle and lower middle income countries ( n = 4,16.7%). None of the studies were from low-income countries. All of the studies were cross sectional in nature ( n = 24). Figure 2 shows the geographic distribution of the different studies.
Geographical distribution of the different studies across the globe (used a web page https://mapchart.net which is free of cost and specifically designed for making customised maps)
Predominance of motivating factors according to income group
Results reported for motivation to select medicine by medical students changes in the context of place (see Fig. 3 and Table 3 ). The choice of medical study among students differs between students in high-income countries, and those in upper-middle and lower–middle-income countries. The individual motivation factors that emerged are presented in Table 4 .
Categorization of motivation factors across different income country groups
High-income countries
In most of the high-income counties, scientific and humanitarian factors were described as the main motivators to select medicine by medical students [ 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 ]. Most of the high income countries including Spain, Croatia, Poland, UK, Hungary, Germany and South Korea reported similar type of motivators to motivate the medical students for choosing medicine: interest in science/medicine, social interest, flexible work hours and work independence. Results reported by Kim et al.(2016) [ 16 ], Becker et al. (2015) [ 29 ], Wouters (2014) [ 19 ] emphasized on the scientific factors. Societal factors were also reported in most of these studies but fell lower in hierarchy.
Uppermiddle income countries
The main motivators to select medicine by medical students of upper-middle income countries include the societal and scientific factors [ 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 ]. A study by Kavousipour et al. (2015) [ 30 ] conducted in Iran explains that the factors which were most significant to motivate the students were family attitudes, getting good jobs in future, respect for themselves, the ability to learn, believing their role in victory and defeat and the tendency toward optimism about themselves. Pagnin et al. (2013) [ 32 ] also concluded similar findings. Social and professional status of the job, healthcare-people factor, others’ recommendation and advices, personal interest and nature of occupation, occupational experience and personal life had been identified as main factors of motivation. The findings reported by Korkmaz et al. (2013) [ 31 ] also found societal and scientific factors to be more significant motivators.
Lower-middle -income
In low-middle income countries, students have mixed responses for the choice of medical studies. [ 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 ]. Humanitarian and societal factors had been reported as main influences to join medicine.
Few studies conducted in various parts of India had reported almost similar results. A study conducted in Madhya Pradesh, India by Diwan et al. (2013) [ 35 ] concluded that reasons for entering medical education included personal ambition, parental desire, prestigious profession, altruistic reasons and pecuniary incentives. Similar to these findings were those reported by Kuriakose (2015) [ 34 ], Seetharaman et al. (2012) [ 36 ] and Lal et al. in 2007 [ 37 ]. The main reasons that motivate the medical students were to serve the sick and society and having a high status in society.
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review of motivational factors for choosing medical studies by medical students globally. Earlier reviews were related to factors influencing student rating in undergraduate medical education course evaluations and factors that influence a career choice in primary care among medical students from high-, middle- and low-income countries [ 8 ]. The present systematic review, which has analyzed 24 studies in detail, is important as it identifies the motivational factors influencing the medical students to join medical studies in different parts of the globe along with the variations among the factors in lower-middle, upper-middle and high-income countries. As such, it provides essential insights into how students could be motivated, and how this varies across countries. No study was found from low-income countries. The limited research on this topic in low-income countries could be related to the lack of interest in this particular area, or to an overall deficit in research in developing nations, or both. These countries could identify the issues and intervene according to the research done in lower-middle and upper-middle income countries.
Several theories of motivation have been described in relation to career choice among student including intrinsic and extrinsic factors as described by Brissette and Howe [ 9 ] and by Maslow [ 38 ],. Taylor, McClelland and Herzberg [ 39 ]. However, Maslow’s theory remains to be the most detailed and frequently used theory [ 38 ]. The Maslow’s hierarchy of needs describes motivational factors under five broad segments: the physiological needs, the needs for safety and security, the needs for love and belonging, the needs for esteem, and the need to actualize the self, in that order [ 38 ]. Physiological needs are the basic needs required by an individual, such as food, water, sleep, etc. Once these needs are met, the second segment of needs comes into picture making safety, stability, protection the prime concerns. Following these factors the third segment consists of desires to marry, have a family, become a part of their community etc. The fourth segment of esteem has two versions as described by Maslow. The need for respect, prestige, prominence, magnificence, appreciation, attention, status, self-esteem, and dominance forms the lower version while the higher form involves the need for self-respect which includes feelings as self-confidence, capability, accomplishment, mastery, and freedom. The last segment is the phase of self-actualization which is a desire for self-fulfillment [ 38 ].
In low-middle income countries, students are still striving to fulfill primary basic needs and safety and security of employment, family, health. They fall under the first two segments of the pyramid comprising of basic needs, safety stability and protection and hence the predominant motivational factors are humanitarian in this group. In some areas where these needs are fulfilled, the higher segment of self-esteem also come into picture, hence societal factors are also seen in lower-middle income countries. The prime reasons for selecting medical studies among students in low-income countries were parental desire, respected profession and economic incentives, respect in society, high societal status and to serve the sick. The desire to serve the poor is deeply ingrained in this society. Most of the students belong to lower or middle socio-economic groups and understand the miseries of poor well and these factors lead them to serve the humanity and poor people. Here medical students are more sensitive to the social needs of population. The very reasons identified to take up medical career in these countries can be used to encourage students to take up medical studies. Mainly, the respect and feeling of altruism, followed by the monetary and social benefits are a driving force that can be used to attract the students into medical profession, hence improving the workforce. As the motivational factors are mostly innate, their further interest in medical studies and serving the nation will remain significant.
In the upper-middle income countries the factors as described by the middle zone in the Maslow’s hierarchy of needs pyramid were identified. The majority of studies identified societal factors as better predictors as compared to humanitarian and scientific factors. The main motivators to select medicine by medical students of upper-middle income countries are job security, social status, and parental wish. The reason behind this is that, to become a doctor is one of the highest ambition of many school-going students and their parents in middle- and low-income countries, along with the fact that the medical profession is preferred by the students due to its high prospect of financial security and high social status. Being a respected profession with high social status and higher salaries has been found to be motivating factor for students. The students in these countries have mostly met their basic needs and are more attracted towards a better lifestyle and income. Security in all fronts is a strong predictor for picking medical studies, and this can help enroll more students into this career. Excelling in their medical education may act as a strong target as their competition decides their future prospects.
The motivational factors commonly reported by most of the studies in high-income countries were the third and fourth segments of the Maslow’s hierarchy of needs pyramid. The scientific factors were the main motivators to select medicine by students. This may be due to the fact that the students in high-income countries chose medicine or science, who have prime interest in these subjects. The interest in science is usually developed during their school times to become medical school academics in a well-developed education system and with advanced technologies (modern laboratory facilities). The availability of good technologies and advanced education helps in developing specialized skills through the medical school years and beyond. In addition, the ability to earn well, pay their debts and live comfortably are strong motivators as well.
There are various strengths of the study. Firstly, the review was done on a sizeable number of 24 studies across the globe, hence generating stronger evidence. Secondly, the study relates the motivational factors across different countries with the Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory [ 38 ]. This helps to understand the motivational factors of medical students to work in rural areas with respect to the innate motivational factors of a human being.
This review has a few limitations. Despite our efforts to identify all relevant studies by searching four different databases and using a fairly large number of search terms, we might have missed relevant studies. Additionally, unpublished studies from low- and middle-income countries were not represented (publication bias). The exclusion of articles published before 2006 may have omitted literature that could have provided valuable information. However, our review supplement two existing reviews published earlier [ 8 , 9 ].
In conclusion, this systematic review investigated the reasons that affect students’ decisions to join medical profession. The motivational factors are being classified in scientific factors (e.g. ‘interest in medicine’), societal factors (e.g. ‘respect/prestige’) and humanitarian factors (e.g.‘desire to help others’). The predominance of factors varied among students in high-, upper-middle and lower-middle income countries. Hence, this study offers cues to policy makers and educators in different countries to understand the motivational factors as a first step to formulate policy in order to tackle the shortage of health workers to improve the status of human resources across nations. However, more research on the subject would assist in promoting as well as translating health policy into concrete and effective measures at the local, national, regional and global levels in low- and middle- income countries.
Abbreviations
Motivation of selection of Medical Study
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
World Health Organization
World Health Organization. The world health report 2006: working together for health. Geneva: WHO; 2006 [Internet]. 2015. Available from: http://www.who.int/whr/2006/en/ . Accessed 12 Oct 2015.
Smith MK, Henderson Andrade N. Facing the health worker crisis in developing countries: a call for global solidarity. Bull World Heal Organ. 84(6):425–504.
Campbell J, Dussault G, Buchan J, Pozo-Martin F, Guerra Arias M, Leone C, Siyam A, Cometto G. A universal truth: no health without a workforce. Forum Report, Third Global Forum on Human Resources for Health, Recife, Brazil. Geneva: Global Health Workforce Alliance and World Health Organization; 2013.
Rao K, Bhatnagar A, Berman P. India’s health workforce: size, composition and distribution. In: La Forgia KR J, editor. India health beat. New Delhi: World Bank; New Delhi and Public Health Foundation of India; 2009.
Google Scholar
Hurst SA. Eroding students’ rural motivation: first do no harm? Swiss Med Wkly. 2014;144
Lambrou P, Kontodimopoulos ND. Motivation and job satisfaction among medical ; and nursing staff in a Cyprus public general hospital. Hum Res Health. 2010;8:26.
Article Google Scholar
Kusurkar RA, Ten Cate TJ, Van Asperen M, Croiset G. Motivation as an independent and a dependent variable in medical education: a review of the literature. Med Teach. 2011;33(5):e242–62.
Puertas EB, Arósquipa C. Factors that influence a career choice in primary care among medical students from high-, middle-, and low-income countries: a systematic review. Rev PanamSalud Publica. 2013;34(5):351–8.
Brissette A, Howes D. Motivation in medical education: a systematic review. Web Med Central Med Educ. 2010;1(12):WMC001261.
The Sustainable Development Goals Report. Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA). New York: United Nations Publications; 2017.
Monitoring the building blocks of health systems: a handbook of indicators and their measurement strategies. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010.
Egger M, Smith DG, Altman DG, ediors. Systematic reviews in health care: meta-analysis in context. 2nd ed. UK: BMJ Publishing Group; 2008.
Goel S, Angeli F, Singla N, Ruwaard D. Development and validation of the motivations for selection of medical study (MSMS) questionnaire in India. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0164581.
Bank TW. The World bank. World bank country and lending groups [internet]. [cited 16 Jan 2017]. Available from: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups .
Győrffy Z, Birkás E, Sándor I. Career motivation and burnout among medical students in Hungary-could altruism be a protection factor? BMC Med Educ. 2016;16(1):182.
Kim KJ, Hwang JY, Kwon BS. Differences in medical students’ academic interest and performance across career choice motivations. Int J Med Educ. 2016;7:52.
Gąsiorowski J, Rudowicz E, Safranow K. Motivation towards medical career choice and future career plans of polish medical students. Adv Heal Sci Educ. 2015;20(3):709–25.
Sulong S, McGrath D, Finucane P, Horgan M, O’Flynn S, O’Tuathaigh C. Studying medicine–a cross-sectional questionnaire-based analysis of the motivational factors which influence graduate and undergraduate entrants in Ireland. JRSM open. 2014;5(4):2042533313510157.
Wouters A, Bakker AH, van Wijk IJ, Croiset G, Kusurkar RA. A qualitative analysis of statements on motivation of applicants for medical school. BMC Med Educ. 2014;14(1):200.
Laurence CM, Zajac IT, Turnbull DA, Sumner KE, Fleming J. Applicants to the University of Adelaide medical school: influences, motivation and alternative career choices. Focus Heal Prof Educ A Multi-disciplinary J. 2013;14(2):81.
Toso A, Ayala MJ, Brunner V, Rodriguez J, Hernández MI, Urquidi C, et al. Interests and perspectives of first and last year medical students. Rev Med Chil. 2012;140(5):609–15.
Girasek E, Molnár R, Eke E, Szócska M. The medical career choice motivations—results from a Hungarian study. Open Med. 2011;6(4):502–9.
Kusurkar R, Kruitwagen C, ten Cate O, Croiset G. Effects of age, gender and educational background on strength of motivation for medical school. Adv Heal Sci Educ. 2010;15(3):303–13.
Amin Z, Tani M, Hoon Eng K, Samarasekara DD, Huak CY. Motivation, study habits, and expectations of medical students in Singapore. Med Teach. 2009;31(12):e560–9.
Wilson JI. A two factor model of performance approach goals in student motivation for starting medical school. Issues Educ Res. 2009;19(3):271–81.
Kim MK, Kang JO. Comparison of career choice motivation and moral reasoning ability between students in baccalaureate and graduate-entry programs. Korean J Med Educ. 2007;19(2):91–9.
Puljak L, Kraljevic JB, Latas VB, Sapunar D. Demographics and motives of medical school applicants in Croatia. Med Teach. 2007;29(8):e227–34.
McManus IC, Livingston G, Katona C. The attractions of medicine: the generic motivations of medical school applicants in relation to demography, personality and achievement. BMC Med Educ. 2006;6(1):11.
Becker JC, Burghaus D, Kappe K, Heue M, Liebelt A, Kindler Röhrborn BP A. No title. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2015;140(21):e207–16.
Kavousipour S, Noorafshan A, Pourahmad S, Dehghani-Nazhvani A. Achievement motivation level in students of Shiraz University of Medical Sciences and its influential factors. J Adv Med Educ Prof. 2015;3(1):26.
Korkmaz H, Şenol YY. The characteristics of medical students and motivation towards career choice: implications for curriculum. Hacettepe Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Derg. 2013;28:28–1.
Pagnin D, De Queiroz V, De Oliveira Filho MA, Gonzalez NVA, Salgado AET, Oliveira BCE, et al. Burnout and career choice motivation in medical students. Med Teach. 2013;35(5):388–94.
Fevzi Dikici M, Yaris F, Topsever P, Muge Filiz T, Serdar Gurel F, Cubukcu M, et al. Factors affecting choice of specialty among first-year medical students of four universities in different regions of Turkey. Croat Med J. 2008;49(3):415–20.
Kuriakose S, Revankar SKB, Viveka S, Shetty B, Rao CP. Why become a doctor? Evaluation of motivational factors for selecting medical profession as career. Engineer. 2015;16(14):30.
Diwan V, Minj C, Chhari N, De Costa A. Indian medical students in public and private sector medical schools: are motivations and career aspirations different?–studies from Madhya Pradesh, India. BMC Med Educ. 2013;13(1):127.
Seetharaman N, Logaraj M. Why become a doctor? Exploring the career aspirations and apprehensions among interns in South India. Natl J Res Community Med. 2012;1(4):188–95.
Lal P, Malhotra C, Nath A, Malhotra R, Ingle GK. Career aspirations and apprehensions regarding medical education among first year medical students in Delhi. Indian J Community Med. 2007;32(3):217.
Maslow AH. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. Psychol Rev. 1943;50:370–96.
Asperoni G. Motivation, teamwork and agile development. Agile Times. 2004. Available at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229037802_Motivation_teamwork_and_agile_development . Accessed 12 Jan 2018.
Download references
Acknowledgements
This study did not receive any funding.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Public Health, PGIMER, Sector-12, Chandigarh, 160012, India
Sonu Goel, Nonita Dhirar & Neetu Singla
Department of Health Services Research, Care and Public Health Research Institute, Faculty of Health, Medicine and Life Sciences, Maastricht University, Maastricht, The Netherlands
Federica Angeli
Department of Organization Studies, School of Social and Behavioural Sciences, Tilburg University, Tilburg, the Netherlands
Dirk Ruwaard
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization: SG FA. Data curation: SG ND NS. Formal analysis: SG ND NS. Funding acquisition: SG. Investigation: SG. Methodology: SG FA DR. Project administration: SG. Resources: SG. Software: NS, ND. Supervision: SG. Validation: SG ND. Writing original draft: ND NS. Writing review & editing: SG FA DR. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sonu Goel .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was granted ethical approval from the Institute’s Ethical Committee, PGIMER, Chandigarh (PGI/IEC/2012/810–1 P-154). The anonymity and confidentiality of participants in the studies were ensured. Since the study is a systematic review of studies and individual level data is not obtained, the consent was not required.
Consent for publication
Since individual level data is not presented, the consent for publication of data was not required.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Goel, S., Angeli, F., Dhirar, N. et al. What motivates medical students to select medical studies: a systematic literature review. BMC Med Educ 18 , 16 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-018-1123-4
Download citation
Received : 12 May 2017
Accepted : 09 January 2018
Published : 17 January 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-018-1123-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Medical students
- Rural areas
- Systematic review
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
What are the benefits of studying health sciences?

Checked : Alexandra L. , Vallary O.
Latest Update 18 Jan, 2024
Table of content
Health is among the rapidly developing markets in the world. Since individuals are living longer, there is an expanding necessity for treatment and help. So the health science graduates can have confidence that their aptitudes and mastery will consistently be in high demand after graduation. The foundation of health education is so far-reaching to record the historical backdrop of health treatment. This subject is so exhaustive, you can even graduate from health science instruction, or you can acquire a degree in this interdisciplinary region. The study of prosperity has developed with the advancement of society, business, and designing.
With the headway of society and its stratification, medicinal services need to grow and its methodologies created. Over the thousands of year’s history of human health services, preparing has been utilized as an instrument to separate itself and to pick up the abilities and experience to exceed expectations in the field.
In each country, therapeutic consideration is required with the goal that your callings are not restricted uniquely to a specific nation. In actuality, the health educational plan accessible in the vast majority of the countries is exceptionally complicated, with the goal that you could be qualified and ready to tail it when you are searching for circumstances and skills globally. A few health graduates have visited nations around the globe, in particular, India, Sri Lanka, Australia, Taiwan, South Korean, and Vietnam.
Health science brings science and human services together to an assortment of professional zones that look to improve the health insurance industry and give patients top-notch care, independent of the populace. You can work in a broad scope of approaches to enhance human prosperity. However, you will utilize science, innovation, designing, and math to achieve your objective in your field of core interest. In contrast to various other occupation areas, your job in the health sciences gives an alternative of working expertly or inside the school, and the investigation field. You can likewise serve to improve the framework.
How you will function relies upon your inclinations. The health callings pursue five courses.
Diagnostic services cover the aversion and appraisal of a medical issue by watching present and new conditions and by chronicle manifestations through tests like the direction of a mammogram on bosom oddities.
In Curative services, the patients look for sufficient consideration, potential medicines, treatment, and data concerning their issues or troubles in a shorter or longer period.
Support Services incorporates the broad and significant group of colleagues and partners, crossing from medicinal guide staff and veterinarian workers, helping essential consideration suppliers and customers in all fields of health, including specialists, therapeutic supplies, and home health.
Health data designing is the health science field for you if you are gifted in programming improvement and need to serve in the health part.
The utilization of data frameworks is in planning, obtainment, and organization of health administrations is restorative data building — innovative work of biotechnological designing. Moving into increasingly relevant fields of health sciences, researchers in biotechnology are examining maladies and concocting prescription and cures by natural procedures to deliver items to improve the general health.
While preparing for a particular therapeutic position, it is anything but difficult to build up the extra skill to improve work prospects in an assortment of regions. All Healthcare representatives have self-improvement designs that enable them to secure new abilities, accept additional obligations, and gain ground in fields you appreciate.
Although grants never cover all costs for studying health science, there is a great deal of subsidizing accessible for you if you are engaged with a therapeutic degree. You can meet all requirements for assets from undergraduate financing in the event that you have a degree previously yet plan to seek after a second degree in instruction.
Medicinal services research could never be a low paying assignment; it can bring you unlimited positions and undertakings. When you practice, you have numerous conceivable outcomes to improve new abilities or move into new fields of wellness so that you can get to a scope of jobs and obligations after some time.
Healthcare research would never be a low paying task, and it can bring you endless positions and functions. When you practice, you have many possibilities to improve new skills or move into new fields of fitness, so that you can access a range of roles and duties over time.
The requirement to use innovation in the field of health science as a primary means of treating and mitigating diseases and as a regular instrument of standard safety and interaction is becoming a normal part of life.
Health Science Students enjoy the Heal Accreditation, which is the certification certificate issued to colleagues in the academic and business who frequently review the college and its programs to guarantee that its values and currencies are of the utmost reliability within the sector.

We Will Write an Essay for You Quickly
Employers choose to employ students of accredited universities, and accreditation makes sure that your debts are passed if you want to research more. Science courses and learns to train themselves for various functions in the health sector. A health science student has much strength. Persons who graduate quickly transfer to insurance, health, and academic jobs. They often undergo training that contributes to the recognition and better compensation to fulfill a master's and Ph.D.
Here are a couple of advantages that you get when you seek a degree in health science.
- The individuals who wish to have some expertise in health science frequently have high pay rates. They get high income while those with a health science qualification can have a wide range of positions.
- A degree gives you by and large high open doors for business. Employments are relied upon to increment by 26% in clinical consideration. Health labs are relied upon to develop by as much as 23%. The requirement for the board of work in health offices would ascend by 12%.
There are a few advantages to the investigation of health sciences. The individuals who have examined here ought to consider they are prepared to work in social insurance, logical labs, and different zones of medication. We have incredible prospects for work as opposed to different graduates. In the end, the people who graduate from a master's level college make great applicants. Some of them even talk at the college level.
Looking for a Skilled Essay Writer?

- Montana Tech University Master of Science (MS),
No reviews yet, be the first to write your comment
Write your review
Thanks for review.
It will be published after moderation
Latest News

What happens in the brain when learning?
10 min read
20 Jan, 2024

How Relativism Promotes Pluralism and Tolerance

Everything you need to know about short-term memory
The Importance of Medical Research
Dr. Peace Chikezie
Published 01 Jun 2022 - Updated 17 Mar 2023

Introduction
Every treatment, intervention, medication, way of care, and aftercare in the medical field or health care system came from discoveries. This high quality of care we can experience today was not discovered overnight, but rather through years of effort by medical professionals who investigated the risk factors, causes, preventions, and treatments of diseases. This type of investigation is known as medical/health research.
The general definition of research is, 'an investigation that is intentionally designed to help develop or contribute to knowledge'. When you add a medical purpose to 'research', the general definition stays the same, but the goal becomes more specific. Ultimately, the goal shifts to a focus on increasing medical knowledge, improving patient care, developing new medicines or procedures, and enhancing the already existing medicines and procedures.
Forms of Medical Research
There are several forms of medical research being conducted today. Here are 3 common forms:
- Basic or Laboratory-based research: This is usually conducted in a laboratory where chemical interactions of biological materials are observed in a controlled environment. For most researchers, this is the first step toward developing methods or products that can be used in other forms of research studies.
- Clinical Trials: This is perhaps the most familiar form of healthcare research. Often, patients volunteer to participate in these studies to test the efficacy and safety of new medical interventions. Alternatively, medical interventions on participants may not be used, but only observation instead.
- Epidemiological Research: An increasingly large portion of health research is now information based. A great deal of research entails the analysis of data and biological samples that were initially collected for diagnostic, treatment, or billing purposes, or that were collected as part of other research projects, and are now being used for new research purposes. This secondary use of data is a common research approach in fields such as epidemiology, health services research, and public health research, and includes analysis of patterns of occurrences, determinants, and natural history of the disease; evaluation of health care interventions and services; drug safety surveillance; and some genetic and social studies
The Importance of Research in Medicine
Why is research important in medicine? The simple answer is that medical research has led to many medical breakthroughs and developments. It would also strongly contribute to shaping the future of medicine.
Here's how:
A. Medical research importance in disease diagnosis:
Medical research has led to the development of diagnostic tools and technologies that allow for earlier and more accurate diagnoses of diseases.
For instance, breast cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide. Medical research led to the development of an effective screening method known as mammography which has resulted in earlier detection and a 20% fall in mortality rates.
Another example is the development of pap smears for the early diagnosis of cervical cancer. This as well as caused a significant decrease in late presentation and mortality rates due to cervical cancer.
A host of other effective screening methods have been developed as a result of medical research such as genetic testing, imaging techniques, and so on.
B. The importance of medical research in innovative treatments
Medical research has led to the development of new treatments for a wide range of diseases, such as cancer, allergies, HIV/AIDS, heart disease, and so on.
Research is essential to find out what treatments work best, and more specifically what treatments work best for what patient. It can provide important information about how effective a medical intervention is and its possible adverse effects. These interventions include drugs, vaccines, medical devices, and others.
By being specific with participant requirements, medical professionals can study how certain groups of people react to certain treatments . An example of this can be seen here at Infiuss Health. As a CRO in Africa, we at Infiuss Health focus on the demographics of the continent to ensure people of African ancestry receive effective care.
Medical research would lead to newer developments in medicine such as personalized medicine and targeted therapies, that would ensure that each individual would have treatment options unique to them. Increasing research in this area is the only way to make this a reality in the future of medicine.
C. The role of medical research in disease prevention
Medical research has contributed to the prevention of diseases such as polio, smallpox, and measles which caused the deaths of millions of people in the past.
Recently, following the Covid-19 pandemic, medical research led to the development of vaccines that gradually slowed down the progress of the disease.
D. The importance of medical research in public health
Medical research has contributed to our understanding of public health issues and how to address them.
A typical example was in 1854 when there was an outbreak of cholera in the Golden Square Area in London. An Anaesthesiologist known as John Snow conducted an epidemiological study and found that the source of contamination was a public pump. When the contaminated pump was closed from public access, the outbreak of cholera ended.
Research provides important information about disease trends and risk factors, outcomes of treatment or public health interventions, functional abilities, patterns of care, and health care costs and use.
E. Medical research's importance in improving the economy:
Economists have found that medical research can have an enormous impact on the quality of healthcare which in turn affects human health and longevity.
Healthy individuals tend to be more productive and that contributes greatly to the national economy. If the research enterprise is impeded, or if it is less robust, important societal interests are affected.
Covid-19 vaccine development, for example, contributed to the lifting of the lockdown in many countries and allowed individuals to resume work.
Compared to treatment, current research on disease prevention shows that preventive services are able to significantly reduce deaths and illnesses at reasonable costs. All of these findings have informed and influenced national budget planning and policy decisions.
The simple fact is that clinical research improves our lives. It leads to significant discoveries, improves health care, and ensures that patients receive the best care possible. It is what makes the development of new medicines and treatments possible, without it we would not be able to move forward in the development of medicine.
Infiuss Health, as a CRO in Africa, aims to make it easier to do more clinical trials/ medical research in Africa by use of technology and other means.
When you support, participate in, or conduct medical research, you are helping to continue to build the future of medicine.
Find new health insights
Infiuss Health insights contains inspiring thought leadership on health issues and the future of health data management and new research.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Understanding Science
How science REALLY works...
- Understanding Science 101
- Scientific findings frequently benefit society through technological and other innovations.
- Technological innovations may lead to new scientific breakthroughs.
- Some scientists are motivated by potential applications of their research.
Benefits of science
The process of science is a way of building knowledge about the universe — constructing new ideas that illuminate the world around us. Those ideas are inherently tentative, but as they cycle through the process of science again and again and are tested and retested in different ways, we become increasingly confident in them. Furthermore, through this same iterative process, ideas are modified, expanded, and combined into more powerful explanations. For example, a few observations about inheritance patterns in garden peas can — over many years and through the work of many different scientists — be built into the broad understanding of genetics offered by science today. So although the process of science is iterative, ideas do not churn through it repetitively. Instead, the cycle actively serves to construct and integrate scientific knowledge.
And that knowledge is useful for all sorts of things: designing bridges, slowing climate change, and prompting frequent hand washing during flu season. Scientific knowledge allows us to develop new technologies , solve practical problems, and make informed decisions — both individually and collectively. Because its products are so useful, the process of science is intertwined with those applications:
- New scientific knowledge may lead to new applications. For example, the discovery of the structure of DNA was a fundamental breakthrough in biology. It formed the underpinnings of research that would ultimately lead to a wide variety of practical applications, including DNA fingerprinting, genetically engineered crops, and tests for genetic diseases.
- New technological advances may lead to new scientific discoveries. For example, developing DNA copying and sequencing technologies has led to important breakthroughs in many areas of biology, especially in the reconstruction of the evolutionary relationships among organisms.
- Potential applications may motivate scientific investigations. For example, the possibility of engineering microorganisms to cheaply produce drugs for diseases like malaria motivates many researchers in the field to continue their studies of microbe genetics.
The process of science and you
This flowchart represents the process of formal science, but in fact, many aspects of this process are relevant to everyone and can be used in your everyday life. Sure, some elements of the process really only apply to formal science (e.g., publication, feedback from the scientific community), but others are widely applicable to everyday situations (e.g., asking questions, gathering evidence, solving practical problems). Understanding the process of science can help anyone develop a scientific outlook on life.
- Take a sidetrip
To find out how to develop a scientific outlook, visit A scientific approach to life: A science toolkit .
- Science in action
- Teaching resources
Scientific results regularly make their way into our everyday lives. Follow scientific ideas from lab bench to application:
- The structure of DNA: Cooperation and competition
- Ozone depletion: Uncovering the hidden hazard of hairspray
Want to learn even more about the relationship between science and its applications? Jump ahead to these units:
- Science and society
- What has science done for you lately?
- Use our web interactive to help students document and reflect on the process of science.
- Learn strategies for building lessons and activities around the Science Flowchart: Grades 3-5 Grades 6-8 Grades 9-12 Grades 13-16
- Find lesson plans for introducing the Science Flowchart to your students in: Grades 3-5 Grades 6-8 Grades 9-16
- Get graphics and pdfs of the Science Flowchart to use in your classroom. Translations are available in Spanish, French, Japanese, and Swahili.
Copycats in science: The role of replication
Science at multiple levels
Subscribe to our newsletter
- The science flowchart
- Science stories
- Grade-level teaching guides
- Teaching resource database
- Journaling tool
- Misconceptions
Bookings Open for Online Summer Courses

Studying medicine empowers you to have an immediate, positive impact on people’s lives and society. We’ve put together 10 reasons why you should study medicine, and pursue a career in the medical field.
Table of Contents
10 Reasons to Study Medicine
1) studying medicine means making a real difference.
If you are in the process of writing your personal statement for UCAS , make sure you’ve got a focus on people, because that’s what medicine is really all about. Doctors have the enormous power and privilege to impact the course of many people’s lives for the better. Remember that a career in medicine won’t look like a TV show, and caring for the sick and ill can be far from charming at times.
2) Doctors offer important support in the community
Doctors are some of the most important individuals in a community. They are reference figures and trusted professionals. Doctors, and general practitioners (GPs) in particular, get to know their regular patients closely, and become confidants and figures of support.
As a doctor, you will be an important part of your community, and you’ll have the opportunity to give back to society more than you can imagine. There are lots of resources out there to learn more and begin to really appreciate how much a physician impacts patients’ lives and networks .
3) Medicine enables lifelong learning
‘Constancy’ is another keyword in medicine.
Studying medicine will entail constant learning. Doctors need to be up to date, renew their licences, and continue to pass exams in order to progress in their career. Clinicians also face constant challenges. Challenges assume all sorts of shapes in medicine: emotional challenges, skillset challenges, legal challenges. It is extremely likely that you will encounter lots of challenges in a clinical work environment, and being able to deal with them professionally and ethically is a challenge itself. The constant nature of medicine is therefore stressful in essence, but will surely give you great satisfaction once you will learn to master it (and you will).
4) Being a doctor is not a 9 to 5 job
Medicine doesn’t obey schedules. Some people may find this appealing, others may find it horrifying. I personally find the unexpected nature of medicine and the ever-changing working field fascinating; it keeps me interested in the job and ready for the next challenge.
It is, of course, a life choice. You may well be woken up in the middle of the night and summoned to the hospital for an emergency aortic dissection. This can sometimes seem to get in the way of other aspects of your life, but a medical career is all about balance; you’ll find your equilibrium eventually.
5) You’ll have a wide range of career options
However, a medicine degree also offers a wide range of other options. A good proportion of doctors will go into academia and complete research alongside their clinical practice. Being a clinician in research offers advantages, such as being able to collect samples from patients for use in experiments and clinical trials.
Find Out More
Sign up to join the OxBright newsletter, cram-packed with helpful content designed to inspire you to improve your chances of getting into your dream university.
Thanks! We'll look forward to sending you our newsletter.
6) medicine is constantly evolving, 7) it’s an art and a science, 8) it’s an adventure, 9) practical benefits, 10) is there a doctor onboard.
It’s important to note that admissions officers will be looking for an awareness of the realities of the field in your medical school applications – studying medicine and working as a doctor are incredibly rewarding, but it’s also an emotionally and physically challenging job. It’s important to appreciate the positives, while also making sure you’re not viewing it through rose tinted glasses.

By Diego Balassini Diego is a final year medical student at Cambridge University. He graduated in Biomedical Sciences from Barts and The London School of Medicine, with a research thesis on cancer biology and therapeutics.
- Health Sciences and Medicine
Health and Medicine Essay Examples
- Biology and Life Sciences
- Engineering and Construction
- Environmental Science
- Environmental protection
- Healthcare and Nursing
- Microbiology
Why We're Not Able To Live Forever
Cloud computing technology in the healthcare industry, adaptive behavior in youth with autism.
Hire an expert to write you a 100% unique paper aligned to your needs.
Malaria: A Global Public Health Issue
Reasons why smoking remains to be a contentious issue in many workplaces, gastroesophageal reflux disease: causes, symptoms, treatment, should pregnant women eat for two, narrow-angle glaucoma treatment, are e-cigarettes safe, pneumonia diagnosis and management.
- Essay of any type
- Scholarship essay
- Admission essay
- College essay
- High School
Fine collection of free essay examples, paper samples and topics
Access a vast arsenal of free writing examples covering any subject or topic. Use these academic essay examples to draw inspiration or deepen your knowledge in various areas. Start exploring now!
- Persuasive essays
- Argumentative essays
- Analytical essays
- Expository essays
- Classification essays
- Cause-and-effect
- Problem-and-solution
- Compare-and-contrast
- Descriptive essays
- Narrative essays
- Definition essays
- Informative essays
- Critical analysis
- Rhetorical analysis
- Admission essays
- Human Resources
- Political Science
- Government Studies
- Linguistics
- Gun control
- Capital punishment
- Domestic violence
- Police brutality
- Marijuana legalization
- Climate change
- Globalization
- Illegal immigration
- Overpopulation
- Gender roles
- American Revolution
- World War 1
- The Great Depression
- World War 2
- Vietnam War
- American Dream
- The Great Gatsby
- Romeo and Juliet
- To Kill a Mockingbird
- Catcher in the Rye
- Miscellaneous
Health Sciences Essay That Will Blow Your Mind
Such type of work as a health sciences essay is written when analyzing relevant topics in classroom for consolidation. Also, free essays are often used to highlight dissertation paper sections at a deeper level and to explore certain issues of scientific interest.
The author includes several theses in an essay – usually, no more than three – and further reveals them, expressing their personal opinion supported by reasoned arguments. Thus, this task is both scientific and creative. It demonstrates writer’s creativity and field-specific knowledge of a particular topic.
Health Essay Topics
Choosing health essay topics is the most important part in your work since text format and selection of theses for it depends on them. You can also visit our nursing essay examples in case you need more. Even experienced authors often have problems when choosing their topic, so we have selected several options:
- How important proper sleep regime is for a young body.
- Bipolar disorder: psychological and medical treatment.
- Paid vs free medical systems: advantages and disadvantages of the forms.
- Is free medicine possible without compulsory insurance?
- Euthanasia over the globe: the approaches overview.
- Methods of inducing vaccination: from democracy to constraint. (Read our vaccination essay .)
- Bulimia and anorexia nervosa: the plague of the 21st century.
Above-listed topics are universally applicable and quite general ones. When writing them, you can express your ideas and highlight a broad view of a certain issue.
Argumentative Essay Topics About Mental Health
The used health argumentative essay topics are a popular research field, especially in the mental health area. We have selected promising topics from this category:
- Homeless people – a special risk group for mental disorders. (Take as an example our homeless essay .)
- Soldiers’ post-traumatic syndrome – an insurmountable problem.
- A person’s eagerness to cause pain is genetically inherent.
- OCD patients need a special approach from a psychologist.
- Mental disorders are getting younger: statistics of mental diagnoses.
- Inefficiency of an existing care system for patients with mental disorders.
- It is impossible to self-diagnose mental disorders: the main arguments.
Such essays should convince readers of an author’s point of view. Therefore, it is important to build a strong evidence base and write high-quality conclusions, without which your paper will be incomplete.
Significant Health Care Legislation: Essay Topic Examples
Statistics show that related to significant health care legislation essay topic examples are becoming increasingly popular. Laws are constantly being updated and adapted, new precedents appear, so we have compiled a list of interesting topics:
- Problems of assessing health risks by physicians in attendance.
- Protecting people with diagnosed HIV/AIDS and guaranteed state support.
- Legitimacy of medical experiments on humans.
- Current liability of doctors for negligence.
- Opportunities for medical institutions' autonomy in the USA.
- Legislative healthcare reforms of the 21st century.
- Legal obstacles to cloning creatures.
An author of an essay is to analyze legislation and check out additional sources, as well as provide some personal interpretation of regulatory acts.
Mental Health Essay Topics
Above, we have suggested topics for argumentative essays on mental health issues; however, those related to mental health persuasive essay topics are no less common. If you feel like writing about it, you should pay attention to these topics:
- Problems of poor quality of school psychological care.
- Injuries and drug use as mental disorder causes.
- Strengthening mental endurance – every person’s duty.
- Women’s high susceptibility to depressive conditions.
- Peculiarities of education in specialized schools for children with mental disorders.
- Art as an effective method of psychiatric treatment.
- Prerequisites for growing number of mental disorders in society.
To demonstrate your expert knowledge on this topic, immerse into it and find weighty arguments. To broaden your mind, browse our art and humanities essay examples . Should the need arise, consult practitioners to get their professional opinion for your essay.
Health Essay Examples
To find the right way to compile your text, you will need health essay examples, which clearly demonstrate good quality content. On our site, you will find many samples that are always available for free and regularly updated.
Essay examples are used to get acquainted with paper structure and its contents. From introductory texts, beginners can learn sources and approaches to revealing their topic, as well as adapt theses to suit their opinion and research directions. More experienced authors often use samples to find inspiration and new vectors of progress in works they are writing.
Convenient topics and essay types sorting make it possible to find a necessary sample in a few minutes. This means that you will start working on your text without unnecessary delay and perform it as efficiently as possible.
Health Sciences Scholarship Essay: Undergraduate Example
A separate work type is health sciences scholarship essay undergraduate, which is subject to high requirements. In a written paper, it is required to develop a high-quality structure, completely reveal your topic according to your thesis and draw decent conclusions by convincing a scholarship provider of your talent.
Thanks to our scholarship essays examples , you will understand how to write a scholarship essay and find promising topics. It is important to support your theses and make your paper convincing by adhering to reliable information. In this case, your text will be successful, and you will get a scholarship for further research, as well as find useful acquaintances in scientific circles.
Free Essay About Medicine
Unlike a health topic, an essay about medicine is written by medical students or practitioners in the field since a research subject requires field-specific knowledge. They are written for consolidation of some certain educational topic or to reveal an issue detected during practical activities.
If you are working on a dissertation paper or a course project, such an essay can be used to publish intermediate research results on a certain section, for example. Anyway, an essay on medicine is serious and creative content that should be written by an expert in this field – only in this case, you can ensure high quality.
Medicine Essay Topics
One of the main sticking points is choosing the right direction since there is a wide range of medicine essay topics available. We will suggest a few basic options that give every author the utmost freedom:
- Medical consequences of caffeine addiction.
- Treating insomnia with homeopathic medicines.
- Poverty and poor health: the related phenomena.
- How uncontrolled antibiotics use affects mass immunity.
- Risks of alternative medicine.
- Palliative medicine: the current state of the industry.
- Abortion bans: arguments and decision risks. (Consult: abortion essay examples .)
Medical essays should be defensible and contain reliable information. At the same time, a personal opinion, which proves or refutes the specified theses, is allowed. You can create a creative and interesting topic considering different issues connected with medicine. For instance, take euthanasia essay examples .
Technology and Medicine: Essay Topic
A written technology and medicine essay is an interesting experience for the author since it is in the healthcare field that the latest innovations are used and secret technologies are tested. We have come up with a few promising topics for writing the paper:
- Special requirements for medical equipment manufacturers.
- Problems of mastering new technologies by the “old school” doctors.
- Medical technologies save lives: summary statistics on the industry.
- How does bionics give a second chance for a full-quality life?
- Telemedicine as an opportunity for high-quality medical care in Third World countries.
- Complementary technologies for diagnosing the patients’ condition.
- Incurable diagnoses transformation under technology development.
You can also find a topic yourself – you just need to scroll through the latest news from the high-tech world. Many innovations are experimentally used in medicine, so there are more than enough topics.
Essay Topic on Traditional or Holistic Medicine
An essay topic on traditional or holistic medicine will be a niche trend since this direction is often denied by scientific medicine but has a lot of supporters at the same time. And if you are one of them, further topics will be perfectly suitable:
- Holistic medicine – perfect prevention of health disorders.
- Capabilities of traditional medicine in the context of overcoming incurable diseases.
- Evidence base of traditional medicine: skeptical points of view.
- Comparison of scientific and traditional medicine by efficiency indicator.
- Traditional medicine as a counterweight to the pharmaceutical companies’ monopoly.
- Efficiency of Asian traditional medical directions in the modern world.
- Elements of traditional practices in modern scientific medicine.
When working on such topics, you should keep a balance of opinions and prepare weighty arguments. Prepare for criticism – this direction is known to be quite controversial.
Research Essay Topic: Chinese Medicine
If you choose a research essay topic Chinese medicine , study this area to the full. Ancient knowledge is a trend and is widely used around the globe; further, we will suggest a few interesting topics:
- Chinese healthcare evolution: from traditional medicine to the status of the world’s best system.
- Traditional Chinese medicine in the context of modern practices.
- Treatment with herbs and natural medications in Chinese medicine.
- Features of teaching Chinese traditional medicine.
- Role of massage and physiotherapy in Chinese medicine.
- Yin-Yang rules and their relation to the treatment principles.
- Problems of attitude to traditional Chinese medicine.
Worthy works on these topics are extremely rare, so your essay can become a successful page in your scientific career. But prepare weighty arguments, because there will be a lot of disputes.
Examples for Essay About Medicine
To help with compiling an essay about medicine, we have prepared a lot of examples from other students for you. The examples have been tested in the real scientific community and got positive reviews, so you can feel free to use them as a basis.
A correctly organized structure makes it possible to present the topic gradually and fully, with high-quality argumentation being a perfect example for independent use. The ready paper samples help you to achieve a positive result and compile an essay that will be in demand in scientific circles. To get new and interesting ideas browse articles about different diseases. For instance, look at a cancer essay example in our database.
FAQ About Health and Medicine Essay
Of course, any medicine essay that you find on our platform is absolutely free. You will get inspiration and a solid basis for future research without spending your personal funds.
We don’t recommend doing this since all of our essay on medicine have already been published by students and are posted on our website for reference purposes only. An internal check performed by your teacher or research department will show plagiarism, which can result in certain problems. Therefore, use the samples as a basis for your personal research only.
The essay type that explains why are you interested in the medical field essay is quite simple. Here, express your personal opinion and tell the readers why you have decided on the medical field and what plans to achieve. The essay is especially important for future doctors since it is an opportunity to become additionally inspired for training and systematize all the advantages and disadvantages of the profession.
Yes, since we are a professional service for writing student papers, including essays. Our writers are highly qualified and possess experience in preparing such texts. The facts originate from authoritative sources only. Therefore, you will get high-quality work on time, without delays and controversial points.
Running out of time ?
Entrust your assignment to proficient writers and receive TOP-quality paper before the deadline is over.

Transforming the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses.
Información en español
Celebrating 75 Years! Learn More >>
- About the Director
- Advisory Boards and Groups
- Strategic Plan
- Offices and Divisions
- Careers at NIMH
- Staff Directories
- Getting to NIMH

Decoding the Mind: Basic Science Revolutionizes Treatment of Mental Illnesses
By Linda Brady, Margaret Grabb, Susan Koester, Yael Mandelblat-Cerf, David Panchision, Jonathan Pevsner, Ashlee Van’t-Veer, and Aleksandra Vicentic on behalf of the NIMH Division of Neuroscience and Basic Behavioral Science
March 21, 2024 • 75th Anniversary
Follow the NIMH Director on
For 75 years, NIMH has transformed the understanding and treatment of mental illnesses through basic and clinical research—bringing hope to millions of people. This Director’s Message, guest written by NIMH’s Division of Neuroscience and Basic Behavioral Science , is part of an anniversary series celebrating this momentous milestone.
The Division of Neuroscience and Basic Behavioral Science (DNBBS) at the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) supports research on basic neuroscience, genetics, and basic behavioral science. These are foundational pillars in the quest to decode the human mind and unravel the complexities of mental illnesses.
At NIMH, we are committed to supporting and conducting genomics research as a priority research area . As the institute celebrates its 75th Anniversary , we are spotlighting DNBBS-supported efforts connecting genes to cells to circuits to behavior that have led to a wealth of discoveries and knowledge that can improve the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of mental illnesses.
Making gene discoveries
Medical conditions often run in families. For instance, if someone in your immediate family has high blood pressure, you are more likely to have it too. It is the same with mental disorders—often they run in families. NIMH is supporting research into human genetics to better understand why this occurs. This research has already led to the discovery of hundreds of gene variants that make us more or less likely to develop a mental disorder.
There are two types of genetic variation: common and rare. Common variation refers to DNA changes often seen in the general population, whereas rare variation is DNA changes found in only a small proportion of the population. Individually, most common gene variants have only a minor impact on the risk for a mental disorder. Instead, most disorders result from many common gene variants that, together, contribute to the risk for and severity of that disorder.
NIMH is committed to uncovering the role of genes in mental disorders with the aim of improving the lives of people who experience them. One of the many ways NIMH contributes to the discovery of common gene variants is by supporting the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium (PGC) . The consortium of almost 1,000 scientists across the globe, including ones in the NIMH Intramural Research Program and others conducting NIMH-supported research, is one of the largest and most innovative biological investigations in psychiatry.
Global collaborations such as the PGC are critical to amassing the immense sample sizes needed to identify common gene variants. Data from the consortium’s almost one million participants have already led to transformative insights about genetic contributors to mental illnesses and the genetic relationships of these illnesses to each other. To date, studies conducted as part of the consortium have uncovered common variation in over a dozen mental illnesses.
In contrast to common gene variants, rare gene variants are very uncommon in the general population. When they do occur, they often have a major impact on the occurrence of an illness, particularly when they disrupt gene function or regulation. Rare variants involving mutations in a single gene have been linked to several mental disorders, often through NIMH-supported research. For instance, a recent NIMH-funded study found that rare variation in 10 genes substantially increased the risk for schizophrenia. However, it is important to note that genetics is not destiny; even rare variants only raise the risk for mental disorders, but many other factors, including your environment and experiences, play important roles as well.
Because of the strong interest among researchers and the public in understanding how genes translate to changes in the brain and behavior, NIMH has developed a list of human genes associated with mental illnesses. These genes were identified through rare variation studies and are meant to serve as a resource for the research community. The list currently focuses on rare variants, but NIMH plans to continue expanding it as evidence accumulates for additional gene variants (rare or common).
Moreover, mental illnesses are a significant public health burden worldwide . For this reason, NIMH investments in genomics research extend across the globe. NIMH has established the Ancestral Populations Network (APN) to make genomics studies more diverse and shed light on how genetic variation contributes to mental disorders across populations. APN currently includes seven projects with more than 100 researchers across 25 sites worldwide.
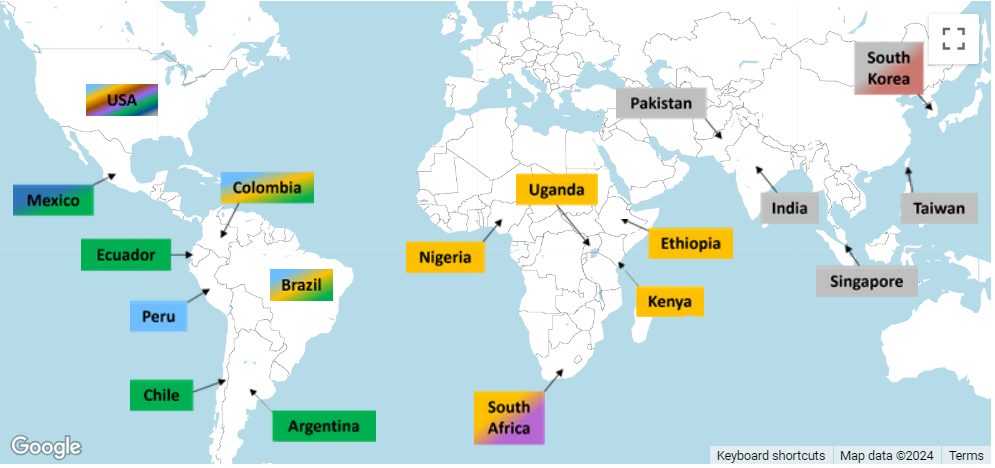
Connecting biology to behavior
While hundreds of individual genes have been linked to mental illnesses, the function of most of these genes in the brain remains poorly understood. But high-tech advances and the increased availability of computational tools are enabling researchers to begin unraveling the intricate roles played by genes.
In addition to identifying genetic variation that raises the risk for mental illnesses, NIMH supports research that will help us understand how genes contribute to human behavior. This information is critical to discovering approaches to diagnose, treat, and ultimately prevent or cure mental illnesses.
An NIMH-funded project called the PsychENCODE consortium focuses on understanding how genes impact brain function. PsychENCODE is furthering knowledge of how gene risk maps onto brain function and dysfunction by cataloging genomic elements in the human brain and studying the actions of different cell types. The PsychENCODE dataset currently includes multidimensional genetic data from the postmortem brains of thousands of people with and without mental disorders.
Findings from the first phase of PsychENCODE were published as a series of 11 papers examining functional genomics in the developing and adult brains and in mental disorders. A second batch of PsychENCODE papers will be published later this year. These findings help clarify the complex relationships between gene variants and the biological processes they influence.
PsychENCODE and other NIMH-supported projects are committed to sharing biospecimens quickly and openly to help speed research and discovery.

Facilitating these efforts is the NIMH Repository and Genomics Resource (NRGR) , where samples are stored and shared. NRGR includes hundreds of thousands of samples, such as DNA, RNA, and cell lines, from people with and without mental disorders, along with demographic and diagnostic information.

Another NIMH initiative to connect risk genes to brain function is Scalable and Systematic Neurobiology of Psychiatric and Neurodevelopmental Disorder Risk Genes (SSPsyGene) . This initiative uses cutting-edge techniques to characterize the biological functions of 250 mental health risk genes—within the cells where they are expressed—to better understand how those genes contribute to mental illnesses. By systematically characterizing the biological functions of risk genes in cells, SSPsyGene will empower researchers to learn about biological pathways that may serve as new targets for treatment.
Genes also affect behavior by providing the blueprint for neurons, the basic units of the nervous system. Neurons communicate with each other via circuits in the brain, which enables us to process, integrate, and convey information. NIMH supports many initiatives to study the foundational role of neural networks and brain circuits in shaping diverse mental health-related behaviors like mood, learning, memory, and motivation.
For instance, studies supported through a basic-to-translational science initiative at NIMH focus on modifying neural activity to improve cognitive, emotional, and social processing . Similarly, another new funding opportunity encourages studies in humans and animals examining how emotional and social cues are represented across brain circuits to help address a core deficit in many mental disorders. These studies will increase understanding of the biological mechanisms that support behavior throughout life and offer interventions to improve these functions in healthy and clinical populations.
Developing treatments and therapeutics
The gene discovery and biology-to-behavior programs described here will lay the foundation for delivering novel therapeutics. To be prepared to rapidly implement findings from this research, NIMH supports several initiatives to identify behavioral and biological markers for use in clinical studies and increase our ability to translate research into practice.
Through its therapeutics discovery research programs , NIMH advances early stage discovery and development studies in humans and early efficacy trials for mental disorders. Taking these efforts a step further, NIMH supports the National Cooperative Drug Discovery/Development Groups for the Treatment of Mental Disorders , which encourage public–private partnerships to accelerate the discovery and development of novel therapeutics and new biomarkers for use in human trials. Moreover, NIMH is one of several institutes and centers in the NIH Blueprint Neurotherapeutics Network , launched to enable neuroscientists in academia and biotechnology companies to develop new drugs for nervous system disorders.
For the treatments of tomorrow, NIMH is building a new research program called Pre-Clinical Research on Gene Therapies for Rare Genetic Neurodevelopmental Disorders , which encourages early stage research to optimize gene therapies to treat disorders with prominent cognitive, social, or affective impairment. In parallel, NIMH’s Planning Grants for Natural History Studies of Rare Genetic Neurodevelopmental Disorders encourage the analysis of pre-existing data from people with rare disorders to learn about disease progression and enable future clinical trials with these populations.
NIMH's Division of Neuroscience and Basic Behavioral Science supports many different research projects that help us learn about genes and gene functions, how the brain develops and works, and impacts on behavior. By investing in basic neuroscience, genetics, and behavioral research, we're trying to find new targets for treatment and develop better therapies for mental disorders. We're hopeful these efforts will lead to new ways to treat and prevent mental illnesses in the near future and, ultimately, improve the lives of people in this country and across the globe.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

The role of data science in healthcare advancements: applications, benefits, and future prospects
Sri venkat gunturi subrahmanya.
1 Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka India
Dasharathraj K. Shetty
2 Department of Humanities and Management, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka India
Vathsala Patil
3 Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Manipal College of Dental Sciences, Manipal, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal Karnataka, India
B. M. Zeeshan Hameed
4 Department of Urology, Father Muller Medical College, Mangalore, Karnataka India
5 Department of Radiation Oncology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA USA
Komal Smriti
Nithesh naik.
6 Department of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, Manipal Institute of Technology, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka India
Bhaskar K. Somani
7 Department of Urology, University Hospital Southampton NHS Trust, Southampton, UK
Data science is an interdisciplinary field that extracts knowledge and insights from many structural and unstructured data, using scientific methods, data mining techniques, machine-learning algorithms, and big data. The healthcare industry generates large datasets of useful information on patient demography, treatment plans, results of medical examinations, insurance, etc. The data collected from the Internet of Things (IoT) devices attract the attention of data scientists. Data science provides aid to process, manage, analyze, and assimilate the large quantities of fragmented, structured, and unstructured data created by healthcare systems. This data requires effective management and analysis to acquire factual results. The process of data cleansing, data mining, data preparation, and data analysis used in healthcare applications is reviewed and discussed in the article. The article provides an insight into the status and prospects of big data analytics in healthcare, highlights the advantages, describes the frameworks and techniques used, briefs about the challenges faced currently, and discusses viable solutions. Data science and big data analytics can provide practical insights and aid in the decision-making of strategic decisions concerning the health system. It helps build a comprehensive view of patients, consumers, and clinicians. Data-driven decision-making opens up new possibilities to boost healthcare quality.
Introduction
The evolution in the digital era has led to the confluence of healthcare and technology resulting in the emergence of newer data-related applications [ 1 ]. Due to the voluminous amounts of clinical data generated from the health care sector like the Electronic Health Records (EHR) of patients, prescriptions, clinical reports, information about the purchase of medicines, medical insurance-related data, investigations, and laboratory reports, there lies an immense opportunity to analyze and study these using recent technologies [ 2 ]. The huge volume of data can be pooled together and analyzed effectively using machine-learning algorithms. Analyzing the details and understanding the patterns in the data can help in better decision-making resulting in a better quality of patient care. It can aid to understand the trends to improvise the outcome of medical care, life expectancy, early detection, and identification of disease at an initial stage and required treatment at an affordable cost [ 3 ]. Health Information Exchange (HIE) can be implemented which will help in extracting clinical information across various distinct repositories and merge it into a single person’s health record allowing all care providers to access it securely. Hence, the organizations associated with healthcare must attempt to procure all the available tools and infrastructure to make use of the big data, which can augment the revenue and profits and can establish better healthcare networks, and stand apart to reap significant benefits [ 4 , 5 ]. Data mining techniques can create a shift from conventional medical databases to a knowledge-rich, evidence-based healthcare environment in the coming decade.
Big data and its utility in healthcare and medical sciences have become more critical with the dawn of the social media era (platforms such as Facebook and Twitter) and smartphone apps that can monitor personal health parameters using sensors and analyzers [ 6 , 7 ]. The role of data mining is to improvise the stored user information to provide superior treatment and care. This review article provides an insight into the advantages and methodologies of big data usage in health care systems. It highlights the voluminous data generated in these systems, their qualities, possible security-related problems, data handling, and how this analytics support gaining significant insight into these data set.
Search strategy
A non-systematic review of all data science, big data in healthcare-related English language literature published in the last decade (2010–2020) was conducted in November 2020 using MEDLINE, Scopus, EMBASE, and Google Scholar. Our search strategy involved creating a search string based on a combination of keywords. They were: “Big Data,” “Big Data Analytics,” “Healthcare,” “Artificial Intelligence,” “AI,” “Machine learning,” “ML,” “ANN,” “Convolutional Networks,” “Electronic Health Records,” “EHR,” “EMR,” “Bioinformatics,” and “Data Science.” We included original articles published in English.
Inclusion criteria
- Articles on big data analytics, data science, and AI.
- Full-text original articles on all aspects of application of data science in medical sciences.
Exclusion criteria
- Commentaries, reviews, and articles with no full-text context and book chapters.
- Animal, laboratory, or cadaveric studies.
The literature review was performed as per the above-mentioned strategy. The evaluation of titles and abstracts, screening, and the full article text was conducted for the chosen articles that satisfied the inclusion criteria. Furthermore, the authors manually reviewed the selected article’s references list to screen for any additional work of interest. The authors resolved the disagreements about eligibility for a consensus decision after discussion.
Knowing more about “big data”
Big data consists of vast volumes of data, which cannot be managed using conventional technologies. Although there are many ways to define big data, we can consider the one defined by Douglas Laney [ 8 ] that represents three dimensions, namely, volume, velocity, and variety (3 Vs). The “big” in big data implies its large volume. Velocity demonstrates the speed or rate at which data is processed. Variety focuses on the various forms of structured and raw data obtained by any method or device, such as transaction-level data, videos, audios, texts, emails, and logs. The 3 Vs became the default description of big data, while many other Vs are added to the definition [ 9 ]. “Veracity” remains the most agreed 4th “V.” Data veracity focuses on the accuracy and reliability of a dataset. It helps to filter through what is important and what is not. The data with high veracity has many records that are valuable to analyze and that contribute in a meaningful way to the overall results. This aspect poses the biggest challenge when it comes to big data. With so much data available, ensuring that it is relevant and of high quality is important. Over recent years, big data has become increasingly popular across all parts of the globe.
Big data needs technologically sophisticated applications that use high-end computing resources and Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based algorithms to understand such huge volumes of data. Machine learning (ML) approaches for automatic decision-making by applying fuzzy logic and neural networks will be added advantage. Innovative and efficient strategies for dealing with data, smart cloud-based applications, effective storage, and user-friendly visualization are required for big data to gain practical insights [ 10 ].
Medical care as a repository for big data
Healthcare is a multilayered system developed specifically for preventing, diagnosing, and treating diseases. The key elements of medical care are health practitioners (physicians and nurses), healthcare facilities (which include clinics, drug delivery centers, and other testing or treatment technologies), and a funding agency that funds the former. Health care practitioners belong to different fields of health such as dentistry, pharmacy, medicine, nursing, psychology, allied health sciences, and many more. Depending on the severity of the cases, health care is provided at many levels. In all these stages, health practitioners need different forms of information such as the medical history of the patient (data related to medication and prescriptions), clinical data (such as data from laboratory assessments), and other personal or private medical data. The usual practice for a clinic, hospital, or patient to retain these medical documents would be maintaining either written notes or in the form of printed reports [ 11 ].
The clinical case records preserve the incidence and outcome of disease in a person’s body as a tale in the family, and the doctor plays an integral role in this tale [ 12 ]. With the emergence of electronic systems and their capacity, digitizing medical exams, health records, and investigations is a common procedure today. In 2003, the Institute of Medicine, a division in the National Academies of Sciences and Engineering coined the term “Electronic Health Records” for representing an electronic portal that saves the records of the patients. Electronic health records (EHRs) are automated medical records of patients related to an individual’s physical/mental health or significant reports that are saved in an electronic system and used to record, send, receive, store, retrieve, and connect the medical personnel and patient with medical services [ 13 ].
Open-source big data platforms
It is an inefficient idea to work with big data or vast volumes of data into storage considering even the most powerful computers. Hence, the only logical approach to process large quantities of big data available in a complex form is by spreading and processing it on several parallel connected nodes. Nevertheless, the volume of the data is typically so high that a large number of computing machines are needed in a reasonable period to distribute and finish processing. Working with thousands of nodes involves coping with issues related to paralleling the computation, spreading of data, and manage failures. Table Table1 1 shows the few open sources of big data platforms and their utilities for data scientists.
source big data platforms and their utilities
Data mining
Data types can be classified based on their nature, source, and data collection methods [ 14 ]. Data mining techniques include data grouping, data clustering, data correlation, and mining of sequential patterns, regression, and data storage. There are several sources to obtain healthcare-related data (Fig. 1 ). The most commonly used type (77%) is the data generated by humans (HG data) which includes Electronic Medical Records (EMR), Electronic Health Records (EHR), and Electronic Patient Records (EPR). Online data through Web Service (WS) is considered as the second largest form of data (11%) due to the increase in the number of people using social media day by day and current digital development in the medical sector [ 15 ]. Recent advances in the Natural Language Processing (NLP)-based methodologies are also making WS simpler to use [ 16 ]. The other data forms such as Sensor Data (SD), Big Transactional Data (BTD), and Biometric Data (BM) make around 12% of overall data use, but wearable personal health monitoring devices’ prominence and market growth [ 17 ] may need SD and BM data.

Sources of big data in healthcare
Applications of analytics in healthcare
There are six areas of applications of analytics in healthcare (Fig. 2 ) including disease surveillance, health care management and administration, privacy protection and fraud detection, mental health, public health, and pharmacovigilance. Researchers have implemented data extraction for data deposition and cloud-based computing, optimizing quality, lowering costs, leveraging resources, handling patients, and other fields.

Various applications of data science in healthcare
Disease surveillance
It involves the perception of the disease, understanding its condition, etiology (the manner of causation of a disease), and prevention (Fig. 3 ).

The disease analysis system
Information obtained with the help of EHRs, and the Internet has a huge prospect for disease analysis. The various surveillance methods would aid the planning of services, evaluation of treatments, priority setting, and the development of health policy and practice.
Image processing of healthcare data from the big data point of view
Image processing on healthcare data offers valuable knowledge about anatomy and organ functioning and identifies the disease and patient health conditions. The technique currently has been used for organ delineation, identification of lung tumors, diagnosis of spinal deformity, detection of arterial stenosis, detection of an aneurysm, etc. [ 18 ]. The wavelets technique is commonly used for image processing techniques such as segmentation, enhancement, and noise reduction. The use of artificial intelligence in image processing will enhance aspects of health care including screening, diagnosis, and prognosis, and integrating medical images with other types of data and genomic data will increase accuracy and facilitate early diagnosis of diseases [ 18 , 19 ]. The exponential increase in the count of medical facilities and patients has led to better use of clinical settings of computer-based healthcare diagnostics and decision-making systems.
Data from wearable technology
Multi-National Companies like Apple and Google are working on health-based apps and wearable technology as part of a broader range of electronic sensors, the so-called IoT, and toolkits for healthcare-related apps. The possibility of collecting accurate medical data on real-time (e.g., mood, diet followed, exercise, and sleep cycles patterns), linked to physiological indicators (e.g., heart rate, calories burned, level of blood glucose, cortisol levels), is perhaps discrete and omnipresent at minimum cost, unrelated to traditional health care. “True Colors” is a wearable designed to collect continuous patient-centric data with the accessibility and acceptability needed to allow for accurate longitudinal follow-up. More importantly, this system is presently being piloted as a daily health-monitoring substitute.
Medical signal analytics
Telemetry and the devices for the monitoring of physiological parameters generate large amounts of data. The data generated generally are retained for a shorter duration, and thus, extensive research into produced data is neglected. However, advancements in data science in the field of healthcare attempt to ensure better management of data and provide enhanced patient care [ 20 – 23 ].
The use of continuous waveform in health records containing information generated through the application of statistical disciplines (e.g., statistical, quantitative, contextual, cognitive, predictive, etc.) can drive comprehensive care decision-making. Data acquisition apart from an ingestion-streaming platform is needed that can control a set of waveforms at various fidelity rates. The integration of this waveform data with the EHR’s static data results in an important component for giving analytics engine situational as well as contextual awareness. Enhancing the data collected by analytics will not just make the method more reliable, but will also help in balancing predictive analytics’ sensitivity and specificity. The signal processing species must mainly rely on the kind of disease population under observation.
Various signal-processing techniques can be used to derive a large number of target properties that are later consumed to provide actionable insight by a pre-trained machine-learning model. Such observations may be analytical, prescriptive, or predictive. Such insights can be furthermore built to activate other techniques such as alarms and physician notifications. Maintaining these continuous waveforms–based data along with specific data obtained from the remaining sources in perfect harmony to find the appropriate patient information to improve diagnosis and treatments of the next generation can be a daunting task [ 24 ]. Several technological criteria and specifications at the framework, analytical, and clinical levels need to be planned and implemented for the bedside implementation of these systems into medical setups.
Healthcare administration
Knowledge obtained from big data analysis gives healthcare providers insights not available otherwise (Fig. 4 ). Researchers have implemented data mining techniques to data warehousing as well as cloud computing, increasing quality, minimizing costs, handling patients, and several other fields of healthcare.

Role of big data in accelerating the treatment process
Data storage and cloud computing
Data warehousing and cloud storage are primarily used for storing the increasing amount of electronic patient-centric data [ 25 , 26 ] safely and cost-effectively to enhance medical outcomes. Besides medical purposes, data storage is utilized for purposes of research, training, education, and quality control. Users can also extract files from a repository containing the radiology results by using keywords following the predefined patient privacy policy.
Cost and quality of healthcare and utilization of resources
The migration of imaging reports to electronic medical recording systems offers tremendous potential for advancing research and practice on radiology through the continuous updating, incorporation, and exchange of a large volume of data. However, the heterogeneity in how these data can be formatted still poses major challenges. The overall objective of NLP is that the natural human language is translated into structured with a standardized set of value choices that are easily manipulated into subsections or searches for the presence or absence of a finding through software, among other things [ 27 ].
Greaves et al. [ 28 ] analyzed sentiment (computationally dividing them into categories such as optimistic, pessimistic, and neutral) based on the online response of patients stating their overall experience to predict healthcare quality. They found an agreement above 80% between online platform sentiment analysis and conventional paper-based quality prediction surveys (e.g., cleanliness, positive conduct, recommendation). The newer solution can be a cost-effective alternative to conventional healthcare surveys and studies. The physician’s overuse of screening and testing often leads to surplus data and excess costs [ 29 ]. The present practice in pathology is restricted by the emphasis on illness. Zhuang et al. [ 29 ] compared the disease-based approach in conjunction with database reasoning and used the data mining technique to build a decision support system based on evidence to minimize the unnecessary testing to reduce the total expense of patient care.
Patient data management
Patient data management involves effective scheduling and the delivery of patient care during the period of a patient’s stay in a hospital. The framework of patient-centric healthcare is shown in Fig. 5 . Daggy et al. [ 30 ] conducted a study on “no shows” or missing appointments that lead to the clinical capability that has been underused. A logistical regression model is developed using electronic medical records to estimate the probabilities of patients to no-show and show the use of estimates for creating clinical schedules that optimize clinical capacity use while retaining limited waiting times and clinical extra-time. The 400-day clinical call-in process was simulated, and two timetables were developed per day: the conventional method, which assigns one patient per appointment slot, and the proposed method, which schedules patients to balance patient waiting time, additional time, and income according to no-show likelihood.

Elemental structure of patient-centric healthcare and ecosystem
If patient no-show models are mixed with advanced programming approaches, more patients can be seen a day thus enhancing clinical performance. The advantages of implementation of planning software, including certain methodologies, should be considered by clinics as regards no-show costs [ 30 ].
A study conducted by Cubillas et al. [ 31 ] pointed out that it takes less time for patients who came for administrative purposes than for patients for health reasons. They also developed a statistical design for estimating the number of administrative visits. With a time saving of 21.73% (660,538 min), their model enhanced the scheduling system. Unlike administrative data/target finding patients, a few come very regularly for their medical treatment and cover a significant amount of medical workload. Koskela et al. [ 32 ] used both supervised and unsupervised learning strategies to identify and cluster records; the supervised strategy performed well in one cluster with 86% accuracy in distinguishing fare documents from the incorrect ones, whereas the unsupervised technique failed. This approach can be applied to the semi-automate EMR entry system [ 32 ].
Privacy of medical data and fraudulency detection
The anonymization of patient data, maintaining the privacy of the medical data and fraudulency detection in healthcare, is crucial. This demands efforts from data scientists to protect the big data from hackers. Mohammed et al. [ 33 ] introduced a unique anonymization algorithm that works for both distributed and centralized anonymization and discussed the problems of privacy security. For maintaining data usefulness without the loss of any data privacy, the researchers further proposed a model that performed far better than the traditional K-anonymization model. In addition to this, their algorithm could also deal with voluminous, multi-dimensional datasets.
A mobile-based cloud-computing framework [ 34 ] of big data has been introduced to overcome the shortcomings of today’s medical records systems. EHR data systems are constrained due to a lack of interoperability, size of data, and privacy. This unique cloud-based system proposed to store EHR data from multiple healthcare providers within the facility of an internet provider to provide authorized restricted access to healthcare providers and patients. They used algorithms for encryption, One Time Password (OTP), or a 2-factor authentication to ensure data security.
The analytics of the big data can be performed using Google’s efficient tools such as big query tools and MapReduce. This approach will reduce costs, improve efficiency, and provide data protection compared to conventional techniques that are used for anonymization. The conventional approach generally leaves data open to re-identification. Li et al. in a case study showed that hacking can make a connection between tiny chunks of information as well as recognize patients [ 35 ]. Fraud detection and abuse (i.e., suspicious care behavior, deliberate act of falsely representing facts, and unwanted repeated visits) make excellent use of big data analytics [ 36 ].
By using data from gynecology-based reports, Yang et al. framed a system that manually distinguishes characteristics of suspicious specimens from a set of medical care plans that any doctor would mostly adopt [ 37 ]. The technique was implemented on the data from Taiwan’s Bureau of National Health Insurance (BNHI), where the proposed technique managed to detect 69% of the total cases as fraudulent, enhancing the current model, which detected only 63% of fraudulent cases. To sum up, the protection of patient data and the detection of fraud are of significant concern due to the growing usage of social media technology and the propensity of people to place personal information on these platforms. The already existing strategies for anonymizing the data may become less successful if they are not implemented because a significant section of the personal details of everyone is now accessible through these platforms.
Mental health
According to National Survey conducted on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH), 52.2% of the total population in the United States (U.S.) was affected by either mental problems or drug addiction/abuse [ 38 ]. In addition, approximately 30 million suffer from panic attacks and anxiety disorders [ 39 ].
Panagiotakopoulos et al. [ 40 ] developed a data analysis–focused treatment technique to help doctors in managing patients with anxiety disorders. The authors used static information that includes personal information such as the age of the individual, sex, body and skin types, and family details and dynamic information like the context of stress, climate, and symptoms to construct static and dynamic information based on user models. For the first three services, relationships between different complex parameters were established, and the remaining one was mainly used to predict stress rates under various scenarios. This model was verified with the help of data collected from twenty-seven volunteers who are selected via the anxiety assessment survey. The applications of data analytics in the disease diagnosis, examination, or treatment of patients with mental wellbeing are very different from using analytics to anticipate cancer or diabetes. In this case, the data context (static, dynamic, or non-observable environment) seems to be more important compared to data volume [ 39 ].
The leading cause of perinatal morbidity and death is premature birth, but an exact mechanism is still unclear. The research carried by Chen et al. [ 41 ] intended to investigate the risk factors of preterm use of neural networks and decision tree C5.0 data mining. The original medical data was obtained by a specialist study group at the National University of Taiwan from a prospective pregnancy cohort. A total of 910 mother–child dyads from 14,551 in the original data have been recruited using the nest case–control design. In this data, thousands of variables are studied, including basic features, medical background, the climate and parents’ occupational factors, and the variables related to children. The findings suggest that the main risk factors for pre-born birth are multiple births, blood pressure during pregnancy, age, disease, prior preterm history, body weight and height of pregnant women, and paternal life risks associated with drinking and smoking. The results of the study are therefore helpful in the attempt to diagnose high-risk pregnant women and to provide intervention early to minimize and avoid early births in parents, healthcare workers, and public health workers [ 41 , 42 ].
Public health
Data analytics have also been applied to the detection of disease during outbreaks. Kostkova et al. [ 43 ] analyzed online records based on behavior patterns and media reporting the factors that affect the public as well as professional patterns of search-related disease outbreaks. They found distinct factors affecting the public health agencies’ skilled and layperson search patterns with indications for targeted communications during emergencies and outbreaks. Rathore et al. [ 44 ] have suggested an emergency tackling response unit using IoT-based wireless network of wearable devices called body area networks (BANs). The device consists of “intelligent construction,” a model that helps in processing and decision making from the data obtained from the sensors. The system was able to process millions of users’ wireless BAN data to provide an emergency response in real-time.
Consultation online is becoming increasingly common and a possible solution to the scarcity of healthcare resources and inefficient delivery of resources. Numerous online consultation sites do however struggle to attract customers who are prepared to pay and maintain them, and health care providers on the site have the additional challenge to stand out from a large number of doctors who can provide similar services [ 45 ]. In this research, Jiang et al. [ 45 ] used ML approaches to mine massive service data, in order (1) to define the important characteristics related to patient payment rather than free trial appointments, (2) explore the relative importance of those features, and (3) understand how these attributes work concerning payment, whether linearly or not. The dataset refers to the largest online medical consultation platform in China, covering 1,582,564 consultation documents among patient pairs between 2009 and 2018. The results showed that compared with features relating to reputation as a physician, service-related features such as quality of service (e.g., intensity of consultation dialogue and response rate), the source of patients (e.g., online vs offline patients), and the involvement of patients (e.g., social returns and previous treatments revealed). To facilitate payment, it is important to promote multiple timely responses in patient-provider interactions.
Pharmacovigilance
Pharmacovigilance requires tracking and identification of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) after launch, to guarantee patient safety. ADR events’ approximate social cost per year reaches a billion dollars, showing it as a significant aspect of the medical care system [ 46 ]. Data mining findings from adverse event reports (AERs) revealed that mild to lethal reactions might be caused in paclitaxel among which docetaxel is linked with the lethal reaction while the remaining 4 drugs were not associated with hypersensitivity [ 47 ] while testing ADR’s “hypersensitivity” to six anticancer agents [ 47 ]. Harpaz et al. [ 46 ] disagreed with the theory that adverse events might be caused not just due to a single medication but also due to a mixture of synthetic drugs. It is found that there is a correlation between a minimum of one drug and two AEs or two drugs and one AE in 84% of AERs studies. Harpaz R et al. [ 47 ] improved precision in the identification of ADRs by jointly considering several data sources. When using EHRs that are available publicly in conjunction with the AER studies of the FDA, they achieved a 31% (on average) increase in detection [ 45 ]. The authors identified dose-dependent ADRs with the help of models built from structured as well as unstructured EHR data [ 48 ]. Of the top 5 ADR-related drugs, 4 were observed to be dose-related [ 49 ]. The use of text data that is unstructured in EHRs [ 50 ]; pharmacovigilance operation was also given priority.
ADRs are uncommon in conventional pharmacovigilance, though it is possible to get false signals while finding a connection between a drug and any potential ADRs. These false alarms can be avoided because there is already a list of potential ADRs that can be of great help in potential pharmacovigilance activities [ 18 ].
Overcoming the language barrier
Having electronic health records shared worldwide can be beneficial in analyzing and comparing disease incidence and treatments in different countries. However, every country would use their language for data recording. This language barrier can be dealt with the help of multilingual language models, which would allow diversified opportunities for Data Science proliferation and to develop a model for personalization of services. These models will be able to understand the semantics — the grammatical structure and rules of the language along with the context — the general understanding of words in different contexts.
For example: “I’ll meet you at the river bank.”
“I have to deposit some money in my bank account.”
The word bank means different things in the two contexts, and a well-trained language model should be able to differentiate between these two. Cross-lingual language model trains on multiple languages simultaneously. Some of the cross lingual language models include:
mBERT — the multilingual BERT which was developed by Google Research team.
XLM — cross lingual model developed by Facebook AI, which is an improvisation over mBERT.
Multifit — a QRNN-based model developed by Fast.Ai that addresses challenges faced by low resource language models.
Millions of data points are accessible for EHR-based phenotyping involving a large number of clinical elements inside the EHRs. Like sequence data, handling and controlling the complete data of millions of individuals would also become a major challenge [ 51 ]. The key challenges faced include:
- The data collected was mostly either unorganized or inaccurate, thus posing a problem to gain insights into it.
- The correct balance between preserving patient-centric information and ensuring the quality and accessibility of this data is difficult to decide.
- Data standardization, maintaining privacy, efficient storage, and transfers require a lot of manpower to constantly monitor and make sure that the needs are met.
- Integrating genomic data into medical studies is critical due to the absence of standards for producing next-generation sequencing (NGS) data, handling bioinformatics, data deposition, and supporting medical decision-making [ 52 ].
- Language barrier when dealing data
Future directions
Healthcare services are constantly on the lookout for better options for improving the quality of treatment. It has embraced technological innovations intending to develop for a better future. Big data is a revolution in the world of health care. The attitude of patients, doctors, and healthcare providers to care delivery has only just begun to transform. The discussed use of big data is just the iceberg edge. With the proliferation of data science and the advent of various data-driven applications, the health sector remains a leading provider of data-driven solutions to a better life and tailored services to its customers. Data scientists can gain meaningful insights into improving the productivity of pharmaceutical and medical services through their broad range of data on the healthcare sector including financial, clinical, R&D, administration, and operational details.
Larger patient datasets can be obtained from medical care organizations that include data from surveillance, laboratory, genomics, imaging, and electronic healthcare records. This data requires proper management and analysis to derive meaningful information. Long-term visions for self-management, improved patient care, and treatment can be realized by utilizing big data. Data Science can bring in instant predictive analytics that can be used to obtain insights into a variety of disease processes and deliver patient-centric treatment. It will help to improvise the ability of researchers in the field of science, epidemiological studies, personalized medicine, etc. Predictive accuracy, however, is highly dependent on efficient data integration obtained from different sources to enable it to be generalized. Modern health organizations can revolutionize medical therapy and personalized medicine by integrating biomedical and health data. Data science can effectively handle, evaluate, and interpret big data by creating new paths in comprehensive medical care.
OOpen access funding provided by Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal.
Declarations
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
4 Health Benefits of Inositol, According to Science
Bonus: Research indicates this supplement is unlikely to produce severe side effects.

Food sources
Dosage information, inositol side effects.
Since inositol is present in nature, it may come as no surprise that some foods contain it as well. That said, some research suggests that certain people may benefit from higher amounts of inositol that are difficult to get from food alone. That’s where supplements come in. To figure out if inositol might be a good addition to your daily regimen, we’ve highlighted the research-backed health benefits of inositol below along with safety tips to keep in mind.
Take note: Our registered dietitians in the Good Housekeeping Institute Nutrition Lab review and evaluate every single supplement we recommend in accordance with our dietary supplement methodology . We then have a registered dietitian on our Medical Review Board review each article for scientific accuracy. A supplement should do just that: supplement the diet, not replace high-quality, nutritious food and important healthy lifestyle practices. Check with your healthcare provider before starting any dietary supplement regimen.
Inositol health benefits
These are the four most-studied health issues that inositol supplements may help with.
.css-zjsofe{-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;background-color:#ffffff;border:0;border-bottom:none;border-top:thin solid #CDCDCD;color:#000;cursor:pointer;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;font-style:inherit;font-weight:inherit;-webkit-box-pack:start;-ms-flex-pack:start;-webkit-justify-content:flex-start;justify-content:flex-start;padding-bottom:0.3125rem;padding-top:0.3125rem;scroll-margin-top:0rem;text-align:left;width:100%;}@media(min-width: 64rem){.css-zjsofe{scroll-margin-top:3.375rem;}} .css-jtmji2{border-radius:50%;width:1.875rem;border:thin solid #6F6F6F;height:1.875rem;padding:0.4rem;margin-right:0.625rem;} .css-jlx6sx{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;width:0.9375rem;height:0.9375rem;margin-right:0.625rem;-webkit-transform:rotate(90deg);-moz-transform:rotate(90deg);-ms-transform:rotate(90deg);transform:rotate(90deg);-webkit-transition:-webkit-transform 250ms ease-in-out;transition:transform 250ms ease-in-out;} Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
People with PCOS may experience irregular periods, acne, weight gain, skin tags, darkening of the skin, thinning hair on the head and an overgrowth of hair in other areas of the body, according to the Office on Women’s Health . Interestingly, research has shown inositol supplements may be effective in treating PCOS.
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance occurs when “cells in your muscles, fat and liver don’t respond well to insulin and can’t easily take up glucose from your blood,” according to the National Institutes of Health . If your pancreas can’t keep up its production of insulin, too much glucose remains in your blood and you end up with diabetes. What’s interesting about inositol is that studies have found taking it as a supplement may help a person improve their insulin resistance, particularly patients with gestational diabetes or PCOS .
High cholesterol
“Cholesterol is one of the risk factors of coronary artery disease, which can lead to heart attacks, strokes and sudden death,” says Dr. Monka. “This is why doing everything you can to lower your cholesterol is essential.” In research studies , inositol helped people lower their LDL (“bad”) cholesterol as well as their total cholesterol levels, but it didn’t increase their HDL (“good”) cholesterol. To improve HDL levels, Dr. Monka recommends aerobic exercises such as running, rowing, walking , biking, swimming, hiking and yoga.
Mood disorders
Some research suggests that inositol supplements may lower symptoms of depression and anxiety, but study results are mixed. “As an osteopathic physician, we see that increased inositol levels decrease mood disorders due to hormonal changes,” says Dr. Monka.
Dr. Monka notes the following inositol can be found in:
- Grapefruits
- Fresh vegetables
Currently, there is no official recommended daily allowance for inositol, so it’s a good idea to ask your physician what they think is best for your body. “Most studies recommend 1,000 to 2,000 milligrams of inositol twice daily, especially if you have polycystic ovary syndrome or insulin resistance,” says Dr. Monka. “But that still means that we need more research in the area before simply recommending increased supplements to your daily routine.”
Inositol seems safe and unlikely to produce severe side effects, but one research analysis found that the highest doses studied (12 grams per day) could lead to “mild gastrointestinal side effects such as nausea, flatus and diarrhea.”
“There is much research that needs to be done on inositol levels and its side effects,” says Dr. Monka. “We need to understand more to fully comprehend what take an additional inositol supplement can do to a person’s body.”
The bottom line: An inositol supplement may be beneficial for some people, but a lot is still unknown so it’s smart to talk to your doctor before you take any. “The medical community should invest in more trials and opportunities where inositol can be studied,” says Dr. Monka. “Anything that can potentially help your body process insulin better or relieve issues of mood disorders or depression must be analyzed and examined to see if it produces better health outcomes.”
Kaitlyn Phoenix is a deputy editor in the Hearst Health Newsroom, where she reports, writes and edits research-backed health content for Good Housekeeping , Prevention and Woman's Day . She has more than 10 years of experience talking to top medical professionals and poring over studies to figure out the science of how our bodies work. Beyond that, Kaitlyn turns what she learns into engaging and easy-to-read stories about medical conditions, nutrition, exercise, sleep and mental health. She also holds a B.S. in magazine journalism from Syracuse University.
Dr. Deena Adimoolam, known by many of her patients as "Dr. Deena", received her medical degree and training at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. She then completed her residency training in primary care/internal medicine and subsequent fellowship in endocrinology, diabetes and metabolism at Yale University.
After her many years at Yale, she returned back to Mount Sinai as an Assistant Professor of Medicine and Associate Program Director of the endocrinology fellowship program.
Dr. Adimoolam has published research and written chapters for major textbooks in the areas of diabetes and obesity.
She is passionate for educating the public on disease prevention and hormone health, and uses various media outlets to do so. She serves as a media expert and has worked with most major news organizations in print, online, and television.
She works closely as a spokeswoman for the Endocrine Society - the largest medical organization in the field of endocrinology and metabolism and is very active with other local and national health organizations.
@media(max-width: 64rem){.css-o9j0dn:before{margin-bottom:0.5rem;margin-right:0.625rem;color:#ffffff;width:1.25rem;bottom:-0.2rem;height:1.25rem;content:'_';display:inline-block;position:relative;line-height:1;background-repeat:no-repeat;}.loaded .css-o9j0dn:before{background-image:url(/_assets/design-tokens/goodhousekeeping/static/images/Clover.5c7a1a0.svg);}}@media(min-width: 48rem){.loaded .css-o9j0dn:before{background-image:url(/_assets/design-tokens/goodhousekeeping/static/images/Clover.5c7a1a0.svg);}} Diet & Nutrition

Our Guide to the Healthiest Starbucks Drinks

Is Oat Milk Really a Scam? Not Exactly

13 Foods That'll Help You Sleep Through the Night

4 Health-Focused Smoothies To Brighten Your Day

What to Eat for Healthy Hair

The Best Multivitamins for Women
Good Housekeeping Dietary Supplements Methodology

Top Health Benefits of Coconut Water

Get Cooking With Celebrity Chef Jason Roberts

The Surprising Health Benefits of Black Rice

Popeye: Our Newest GH Nutritionist Approved Member
Do turmeric supplements really treat pain, boost mood, and improve allergies? Experts say they work best for 2 conditions

Americans spend around $50 billion a year on vitamins and supplements. One of the most popular is turmeric, a bright orange root that has its roots in both traditional Eastern medicine and cuisine. Proponents are willing to pay $20 or more for a bottle, hoping to relieve arthritis pain and inflammation , lower cholesterol and blood sugar levels , and treat whatever else happens to ail them. But is it worth the money?
While a lot of research has highlighted turmeric’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, the wide range of supplement potencies and doses used in studies has made it hard to confirm any health claims.
Dr. Keith Singletary , professor emeritus of nutrition at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, has reviewed the evidence on turmeric. His take? “I think it’s promising,” he says, but he stresses that it isn’t “the cure-all that marketing would make it appear.”
Health benefits of turmeric
The health properties attributed to turmeric come from natural compounds called curcuminoids. “Curcumin, which is the major one, is believed to be largely responsible for the health benefits of turmeric,” says Singletary.
What might curcumin do? The best evidence centers on two conditions: arthritis and metabolic syndrome.
Considering turmeric’s anti-inflammatory properties, it’s not surprising that researchers have investigated its use for arthritis . The supplement does appear to reduce pain and stiffness from osteoarthritis, the most common form of this achy joint disease.
“It’s not a miracle drug, but it probably works as well as ibuprofen or acetaminophen,” says Dr. Janet L. Funk , professor of medicine and vice chair of research for the Department of Medicine at the University of Arizona College of Medicine-Tucson. Her lab studies plant-derived dietary supplements for inflammatory diseases.
Metabolic syndrome
This isn’t a disease, but rather a cluster of conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and high triglycerides that collectively increase the risk for diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. About 1 in 3 American adults have metabolic syndrome, according to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) .
Studies have looked at the effects of turmeric on blood sugar, triglycerides, and insulin levels, as well as on inflammation (which also plays a role in metabolic syndrome). “In general, there was a strong preponderance of evidence that it might help reduce all those things. So it might have some benefit in people who are overweight and concerned about inflammation and diabetes,” Funk says.
But—there’s a very big caveat. “There’s a lot of inconsistency between studies,” Singletary says. And therein lies the problem in evaluating turmeric.
An imperfect science
Though plenty of research is being done on turmeric, the studies aren’t consistent. Researchers have tested different amounts of the supplement in different groups of people for different amounts of time. Some studies added a compound like piperine, found in black pepper, to make turmeric more active in the body (researchers call this increased “bioavailability”).
For example, one study on knee osteoarthritis had participants take 180 milligrams (mg) of curcumin for eight weeks. Another one used doses of 500 mg plus 5 mg of BioPerine (black pepper) extract three times a day for six weeks.
Because most of the studies have lasted four months or less, researchers don’t know what might happen with long-term use. “The bottom line is, there’s no definitive, well-designed studies at this point,” Funk says. She’s skeptical that there ever will be, given that the nutraceutical industry and the National Institutes of Health aren’t funding them.
The risks of turmeric
Turmeric is probably safe if you get it from the spice or you take only the recommended amount in supplements, says the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health . In larger quantities, it could cause GI side effects like nausea or diarrhea.
Piperine poses its own set of issues, because it increases the bioavailability of curcumin by inactivating an enzyme in the liver that would otherwise break it down. “That enzyme is really important for [breaking down] most drugs people take,” says Funk. Theoretically, piperine might cause a buildup of medications in the body, thus increasing the risk for side effects. “Generally speaking, if you’re taking other medications, I would shy away from any product that has piperine in it, just in case it could interfere with the metabolism of your other drugs,” she adds.
An even bigger concern is a rare but serious risk of liver damage from turmeric supplements, as well as high levels of lead in these products. Several studies, including one that Funk co-authored, found excessive amounts of lead in some turmeric supplements—especially those that contained turmeric root. Exposure to lead in large quantities can have toxic effects on the body, including heart and kidney problems.
Should you take turmeric?
Is it worth taking turmeric? “That’s the million- dollar question,” says Singletary. Given the lack of clear evidence on its benefits and the potential risks, he says you’re safest getting turmeric through your diet. You can add the spice to soups, stews, sauces, and smoothies. Top them with a pinch of black pepper or cook turmeric in oil to enhance its bioavailability.
If you do use turmeric supplements, it can be difficult to know which form is best, or how much to take. The best advice is to ask your health care provider, says Singletary. Start out with a low dose to see how your body responds to it. And don’t expect turmeric to be a “cure-all for all your ailments, which is unlikely to be the case,” he adds.
Read more on supplements:
- Multivitamins are the most commonly taken supplement. Here’s what they can (and can’t) do for your health
- Does apple cider vinegar really help with weight loss and lower cholesterol? Experts explain the science-backed benefits and how much to take
- The dark side of daily vitamin D supplements: After a man died from an ‘overdose’ in the UK, experts explain how much is healthy
- Is colostrum a new superfood? Experts explain its immune-boosting benefits
Most Popular

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Biden Administration Finalizes Rule Curbing Use of Short-Term Health Plans
The new regulation reverses a Trump-era policy that expanded access to health plans with fewer benefits than those sold on the Affordable Care Act’s marketplaces.

By Noah Weiland
Reporting from Washington
The Biden administration announced on Thursday that it had finalized a new regulation that curbs the use of short-term health insurance plans that do not comply with the Affordable Care Act, reversing a move by the Trump administration to give consumers more access to cheaper but skimpier plans.
Under the new rule , the short-term plans will be able to last for only 90 days, with an option for a one-month extension.
In 2018, the Trump administration issued a rule allowing the plans to last for just under a year , with the option of renewing them for a total duration of up to three years. Previously, under an Obama-era policy, the plans were required to last for less than three months.
The plans, often with lower premiums than those found on the Affordable Care Act’s marketplaces, do not have to cover people with pre-existing conditions. They are also free from the health law’s requirement that plans offer a minimum set of benefits, like prescription drug coverage and maternity care.
Democrats deride the so-called short-term, limited-duration plans as “junk” insurance, and the Obama-era policy was meant to ensure that healthy consumers could not use that option to sidestep the Affordable Care Act’s marketplaces, leaving a sicker pool of customers enrolling in the comprehensive plans offered under the health law.
The White House cast the new rule as a way to fortify the marketplaces. In a briefing with reporters on Wednesday, Neera Tanden, President Biden’s domestic policy adviser, said that 45 million Americans were now covered through the marketplaces or the expansion of Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act. More than 20 million people signed up for plans on the marketplaces during the most recent open enrollment period.
“President Biden is not taking his foot off the gas,” Ms. Tanden said.
Supporters of the short-term plans have said that the less expensive options are well suited for people who are unable to afford a marketplace plan. Brian Blase, who worked on the 2018 rule as a White House official under President Donald J. Trump, said the plans were also ideal for contract and self-employed workers, including those with incomes too high to qualify for more generous subsidies on the Affordable Care Act’s marketplaces.
Mr. Blase said the new rule could cause insurers offering marketplace plans to face less competition. Sick consumers buying a three-month plan could also lose coverage without a better immediate option, he added.
“Nobody benefits,” he said.
But critics of the short-term plans have warned that insurers can mislead consumers who enroll in them, including people who might be eligible for free coverage through the marketplaces. The new regulation requires insurers to provide a disclaimer explaining what the short-term plans cover.
In its announcement on Thursday, the White House cited a man in Montana who accumulated over $40,000 in health costs because his cancer was considered a pre-existing condition, and a woman in Pennsylvania who underwent an amputation and received roughly $20,000 in bills that her plan would not cover.
Sabrina Corlette, a research professor at Georgetown University’s Center on Health Insurance Reforms, said the plans often showed up prominently when consumers searched online for health insurance, with deceptive advertising.
“Often the marketing materials say they cover hospitalizations and prescription drugs,” she said. “To the average consumer it looks like a real health insurance plan.”
Georgetown researchers last year conducted a so-called secret shopper study , calling 20 sales representatives to ask about health plans for people who had lost Medicaid coverage and were eligible for free marketplace plans. They found that none of the representatives mentioned the availability of the free plans. The brokers often used aggressive and misleading tactics to sell short-term plans without providing written plan information, the researchers found.
Ms. Corlette said that brokers typically received higher commissions for selling short-term plans than they did for more comprehensive options.
As a consumer, she said, “you have to be so savvy and careful.”
After the Trump administration issued its rule in 2018, some states moved on their own to limit the sale of short-term plans. Democratic lawmakers urged the Biden administration to reverse the regulation, and the administration issued a proposed rule to do so last summer.
Noah Weiland writes about health care for The Times. More about Noah Weiland

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In fact, medical science has made life healthier, happier and longer than before. Man always wishes to remain healthy. The saying, 'Health is wealth' is absolutely true. Medical science has been of great help to man against various diseases. Medical science has helped in the proper working of the human machine.
Here are some of the most important reasons medical research is important: Generate Valuable Insights. Medical research helps people learn more about themselves and their health. The knowledge gained by medical research is constantly improving. With new scientific information coming from medical studies, people will be able to take care of ...
As such, to navigate the ever-evolving advances in medical practice and technology, literacy in research remains crucial for the effective application of evidence-based medicine. In particular, medical research equips clinicians with skills to critically analyze the clinical relevance of papers to provide invaluable insights into novel treatments.
About seven-in-ten U.S. adults (73%) say science has had a positive effect on society, just 3% say it has had a negative effect and 23% say it has yielded an equal mix of positive and negative effects, according to a Pew Research Center survey. White adults are more likely than black and Hispanic adults to see the effects of science in positive ...
The authors describe the important role of medical schools and graduate medical education programs (residencies) in relationship to the advances in Medicine witnessed during the twentieth century; diagnosis, prognosis and treatment were revolutionized. This historical essay details the evolution of the education system and the successful ...
But let's try. Over the next 25 years, genomic-driven analysis will continue to broaden the impact of personalized medicine in healthcare globally. Precision medicine will continue to deliver ...
Every clinician is responsible for evaluating their own practice, and to do that in a robust and meaningful way you need to use the tools of research. We all need to be able to critically review research done by others. For example, the guidelines used in everyday clinical practice are based on meta-analyses and systematic reviews.
In many of your Health Sciences classes, you will be asked to write an essay on a variety of topics. For help with writing these essays, you can refer to our OWL page on Rhetorical Styles, which outlines all the parts of the essay-writing process piece by piece. "Rhetorical styles" refers to the different kinds of essays you may be asked to write, such as argumentative, descriptive, or ...
When asked about the purpose of medical research most people would hopefully reply: to advance knowledge for the good of society; to improve the health of people worldwide; or to find better ways to treat and prevent disease. The reality is different. The research environment, with its different players, is now much less conducive to thinking ...
Need Help with Essay Topics on health it data governance. WORDS 839. 1. The importance of data governance in healthcare IT systems. 2. The role of data governance in ensuring patient privacy and confidentiality in health IT. 3. Challenges and solutions in implementing effective data governance strategies in healthcare organizations. 4.
Full text. Full text is available as a scanned copy of the original print version. Get a printable copy (PDF file) of the complete article (201K), or click on a page image below to browse page by page.
Therefore, our findings provide empirical evidence for writing to be adopted in medical classroom settings for greater benefits, in light of the transfer of knowledge. Overall, students who learned through writing showed a similar level of memorization with those who engaged in self-studying but higher performance in transfer type items.
Background There is a significant shortage of health workers across and within countries. It is of utmost importance to determine the factors that motivate students to opt for medical studies. The objective of this study is to group and review all the studies that investigated the motivational factors that underpin students' selection of medical study in recent years. Methods The literature ...
A few health graduates have visited nations around the globe, in particular, India, Sri Lanka, Australia, Taiwan, South Korean, and Vietnam. Health science brings science and human services together to an assortment of professional zones that look to improve the health insurance industry and give patients top-notch care, independent of the ...
Health Science Essay Topics. Heather has a bachelor's degree in elementary education and a master's degree in special education. She was a public school teacher and administrator for 11 years. The ...
A. Medical research importance in disease diagnosis: Medical research has led to the development of diagnostic tools and technologies that allow for earlier and more accurate diagnoses of diseases. For instance, breast cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide. Medical research led to the development of an effective screening method ...
Benefits of science. The process of science is a way of building knowledge about the universe — constructing new ideas that illuminate the world around us. Those ideas are inherently tentative, but as they cycle through the process of science again and again and are tested and retested in different ways, we become increasingly confident in them.
Table of Contents. 10 Reasons to Study Medicine. 1) Studying medicine means making a real difference. 2) Doctors offer important support in the community. 3) Medicine enables lifelong learning. 4) Being a doctor is not a 9 to 5 job. 5) You'll have a wide range of career options. 6) Medicine is constantly evolving.
The purpose of this research will be to show the benefits or demerits of using e-cigarettes... Words: 503. Pages: 2. Views: 393. 17 Sep 2023. Health Sciences and Medicine. ... Such type of work as a health sciences essay is written when analyzing relevant topics in classroom for consolidation. Also, free essays are often used to highlight ...
860 Words4 Pages. Medical sciences have had a great impact on our lives. Medical labs as a main part in the medical field are the backbone of medicine since medical sciences wholly depend on the reports issued by them. A small fault will lead to a catastrophe, for example a woman underwent a mastectomy because of a misdiagnosis by a medical lab.
The Division of Neuroscience and Basic Behavioral Science (DNBBS) at the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) supports research on basic neuroscience, genetics, and basic behavioral science. These are foundational pillars in the quest to decode the human mind and unravel the complexities of mental illnesses. At NIMH, we are committed to supporting and conducting genomics research as a ...
Abstract. This essay examines the state of Artificial Intelligence (AI) based technology applications in healthcare and the impact they have on the industry. This study comprised a detailed review ...
By Elizabeth Pennisi. Science. 29 Oct 2021. One of the many functions performed by our brains during sleep is the consolidation of memories. Recent episodes in our daily lives are processed for long-term storage. ILLUSTRATION: DION MBD. Open in viewer. Every night we lie down, close our eyes, and lose consciousness for several hours.
Introduction. The evolution in the digital era has led to the confluence of healthcare and technology resulting in the emergence of newer data-related applications [].Due to the voluminous amounts of clinical data generated from the health care sector like the Electronic Health Records (EHR) of patients, prescriptions, clinical reports, information about the purchase of medicines, medical ...
Inositol health benefits. ... She has more than 10 years of experience talking to top medical professionals and poring over studies to figure out the science of how our bodies work. Beyond that ...
The health properties attributed to turmeric come from natural compounds called curcuminoids. "Curcumin, which is the major one, is believed to be largely responsible for the health benefits of ...
The Biden administration announced on Thursday that it had finalized a new regulation that curbs the use of short-term health insurance plans that do not comply with the Affordable Care Act ...