
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

Chapter 12 Answers: Muscular System
12.2 introduction to the muscular system: review questions and answers.
- What is the muscular system? The muscular system is the organ system that consists of all the muscles in the body.
- Describe muscle cells and their function. Muscle cells (or fibres) are long, thin cells that are specialized for the function of contracting. They contain protein filaments that slide over one another using energy in ATP. The sliding filaments increase the tension in, or shorten the length of, the muscle fibres and cause contractions. Muscle contractions are responsible for virtually all the movements of the body, both inside and out.
- Identify three types of muscle tissue and where each type is found. Three types of muscles are skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones, cardiac muscle makes up the walls of the heart, and smooth muscle is found in the walls of internal organs and other internal structures.
- Define muscle hypertrophy and muscle atrophy. Muscle hypertrophy is an increase in the size of muscle. Muscle atrophy is a decrease in the size of muscle.
- What are possible causes of muscle hypertrophy? Possible causes of muscle hypertrophy include increased use (physical exercise) and hormones such as testosterone.
- Give three reasons that muscle atrophy may occur. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Three reasons that muscle atrophy may occur include lack of physical activity, such as might occur with immobility due to a broken bone or surgery; starvation; and certain diseases, such as AIDS or cancer.
- How do muscles change when they increase or decrease in size? When muscles increase or decrease in size, the individual muscle fibres grow wider or narrower, respectively.
- How do changes in muscle size affect strength? Muscle size is the main determinant of muscle strength. Therefore, an increase in muscle size generally causes an increase in strength, and a decrease in muscle size generally causes a decrease in strength.
- Explain why astronauts can easily lose muscle mass in space. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Astronauts can easily loss muscle mass in space because they are in a weightless environment. On Earth, muscle cells are continually challenged by gravity, and moving and lifting objects against gravity is a form of physical activity that helps maintain the size of muscle fibres. Without this constant challenge to the muscles, astronauts will lose muscle mass unless they proactively exercise.
- Describe how the terms muscle cells, muscle fibres, and myocytes relate to each other. Both muscle fibres and myocytes are muscle cells. The term muscle fibre is mainly used to describe muscle cells in skeletal and cardiac muscles. The term myocyte is mainly used to describe muscle cells in smooth muscles.
- Self-marking
- Name two systems in the body that work together with the muscular system to carry out movements. Answers will vary. Sample answer: The skeletal system and the nervous system.
- Describe one way in which the muscular system is involved in regulating body temperature. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Smooth muscles in the blood vessels can contract to cause vasoconstriction, or relax to cause vasodilation. This conserves body heat or dissipates it, respectively.
12.3 Types of Muscle Tissue: Review Questions and Answers
- What is muscle tissue? Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that makes up most of the tissues in the muscles of the human muscular system. It is the only type of tissue that has cells with the ability to contract.
- Where is skeletal muscle found, and what is its general function? Skeletal muscle is attached to bones by tendons. Its general function is to power voluntary body movements.
- Why do many skeletal muscles work in pairs? Many skeletal muscles work in opposing pairs to move bones back and forth at joints.
- Describe the structure of a skeletal muscle. A skeletal muscle consists of bundles of muscle fascicles, each of which in turn consists of bundles of muscle fibres. Skeletal muscles also have connective tissue supporting and protecting the muscle tissue.
- Relate muscle fibre structure to the functional units of muscles. Each muscle fibre consists of a bundle of myofibrils, which are bundles of protein filaments. The filaments are arranged in repeating units called sarcomeres, which are the basic functional units of skeletal muscles.
- Why is skeletal muscle tissue striated? Skeletal muscle tissue is striated because of the pattern of sarcomeres in its fibres.
- Where is smooth muscle found? What controls the contraction of smooth muscle? Smooth muscle is found in the walls of internal organs and vessels. Contractions of smooth muscles are not under conscious control. Instead, they are controlled by the autonomic nervous system, hormones, and other substances.
- Where is cardiac muscle found? What controls its contractions? Cardiac muscle is found only in the wall of the heart. Contractions of cardiac muscle are involuntary like those of smooth muscle. They are controlled by electrical impulses from specialized cardiac cells and may be influenced by hormones and other factors.
- The heart muscle is smaller and less powerful than some other muscles in the body. Why is the heart the muscle that performs the greatest amount of physical work in the course of a lifetime? How does the heart resist fatigue? The heart is the muscle that performs the greatest amount of physical work in the course of a lifetime because it beats continuously throughout life without rest. Its cells contains a great many mitochondria to produce ATP for energy and help the heart resist fatigue.
- Give one example of connective tissue that is found in muscles. Describe one of its functions. Answers will vary. Sample answer: The connective tissue called epimysium surrounds skeletal muscles and anchors the muscles to tendons.
12.4 Muscle Contraction: Review Questions and Answers
- What is a skeletal muscle contraction? A skeletal muscle contraction is an increase in the tension or a decrease in the length of a skeletal muscle.
- Explain sliding filament theory and describe crossbridge cycling. The sliding filament theory is the most widely accepted explanation for how a muscle contraction occurs. According to this theory, thick myosin filaments repeatedly attach to and pull on thin myosin filaments. This shortens sarcomeres and thus causes contractions.
- If the acetylcholine receptors on muscle fibres were blocked by a drug, what do you think this would do to muscle contraction? Explain your answer. Answers may vary. Sample answer: If the acetylcholine receptors were blocked, muscle contraction would be prevented or at least inhibited. This is because the neurotransmitter acetylcholine is necessary to trigger muscle contractions at the neuromuscular junction by binding to its receptors on the muscle fibres.
- Explain how crossbridge cycling and sliding filament theory are related to each other. Sliding filament theory describes how actin and myosin filaments slide past each other during muscle contraction. Crossbridge cycling is the specific mechanism by which the filaments slide past each other, which involves the use of ATP.
- When does anaerobic respiration typically occur in human muscle cells? Anaerobic respiration typically only occurs in human muscle cells during strenuous exercise when sufficient oxygen cannot be delivered to the muscle to keep up with the demand for ATP.
- If there were no ATP available in a muscle, how would this affect crossbridge cycling? What would this do to muscle contraction? Answers may vary. Sample answer: ATP is required to move the myosin head into the cocked position. If this does not occur, the myosin head cannot attach to the actin filament and the “power stroke” cannot occur. The filaments would not slide past each other and therefore muscle contraction would not occur.
12.5 Physical Exercise: Review Questions and Answers
- How do we define physical exercise? Physical exercise is defined as any bodily activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health even if it is not done for its health benefits.
- What are current recommendations for physical exercise for adults? Current recommendations for physical exercise for adults are 30 minutes a day of moderate exercise.
- Define flexibility exercise, and state its benefits. What are two examples of flexibility exercises? Flexibility exercise is any physical activity that stretches and lengthens muscles. Benefits of flexibility exercise include improving range of motion and reducing risk of injury. Examples may vary. Sample answer: Two examples of flexibility exercises include stretching and yoga.
- In general, how does physical exercise affect health, quality of life, and longevity? In general, physical exercise improves physical, mental, and emotional health. It also increases quality of life and longevity.
- What mechanism may underlie many of the general health benefits of physical exercise? The mechanism that may underlie many of the general health benefits of physical exercise is the release of hormones called myokines from contracting muscles. Myokines are endocrine hormones that promote tissue repair and growth and have anti-inflammatory effects.
- Relate physical exercise to cardiovascular disease risk. Physical exercise can reduce risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including hypertension, high levels of “bad” and total cholesterol, and excess body weight. Physical exercise can also increase factors associated with good cardiovascular health, such as “good” cholesterol level and the mechanical efficiency of the heart.
- What may explain the positive benefits of physical exercise on cognition? Positive benefits of physical exercise on cognition may be explained by an increase in blood flow to the brain, which brings more oxygen to brain cells; an increase in growth factors that promote growth of brain cells and neuronal pathways in the brain; and an increase in neurotransmitters in the brain.
- How does physical exercise compare with antidepressant drugs in the treatment of depression? Numerous studies suggest that regular aerobic exercise works as well as pharmaceutical antidepressants in treating mild-to-moderate depression, possibly because it increases synthesis of natural euphoriants in the brain.
- Identify several other health benefits of physical exercise. Other health benefits of physical exercise include improved sleep, better immune system function, and reduced risk of type 2 diabetes and obesity.
- Explain how genetics may influence the way individuals respond to physical exercise. Genetic differences in proportions of slow-twitch and fast-twitch skeletal muscle fibres may influence how people respond to physical exercise. People with more slow-twitch fibres may be able to develop greater endurance from aerobic exercise, whereas people with more fast-twitch fibres may be able to develop greater muscle size and strength from anaerobic exercise.
- Can too much physical exercise be harmful? Some adverse effects may occur if exercise is extremely intense and the body is not given proper rest between exercise sessions. Many people who overwork their muscles develop delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), which may be caused by tiny tears in muscle fibres.
12.6 Disorders of the Muscular System: Review Questions and Answers
- What are musculoskeletal disorders? What causes them? Musculoskeletal disorders are injuries that occur in muscles or associated tissues such as tendons because of biomechanical stresses. The disorders may be caused by sudden exertion, over-exertion, repetitive motions, and similar stresses.
- How does a muscle strain occur? A muscle strain occurs when muscle fibres tear as a result of overstretching.
- Define tendinitis. Why does it occur? Tendinitis is inflammation of a tendon. It occurs when a tendon is over-extended or worked too hard without rest.
- Identify first-aid steps for treating musculoskeletal disorders, such as muscle strains and tendinitis. First-aid steps for treating musculoskeletal disorders such as muscle strains and tendinitis include protection, rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
- Describe carpal tunnel syndrome and how it may be treated. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a biomechanical problem that occurs in the wrist when the median nerve becomes compressed between carpal bones, often due to repetitive use of the wrist and typically causing pain, numbness, and eventually muscle wasting in the thumb and first two fingers of the hand if untreated. Carpal tunnel syndrome may be treated by wearing a wrist splint, receiving corticosteroid injections, or undergoing surgery to cut the carpal ligament and reduce pressure on the median nerve.
- Define neuromuscular disorders. Neuromuscular disorders are systemic disorders that occur because of problems with the nervous control of muscle contractions or with the muscle cells themselves.
- Identify the cause and symptoms of muscular dystrophy. Muscular dystrophy is a genetic disorder caused by defective proteins in muscle cells. Its symptoms include progressive skeletal muscle weakness due to the death of muscle cells and tissues.
- Outline the cause and progression of myasthenia gravis. Myasthenia gravis is a genetic neuromuscular disorder most often caused by immune system antibodies blocking acetylcholine receptors on muscle cells and the actual loss of acetylcholine receptors. It is characterized by fluctuating muscle weakness and fatigue, with more muscles becoming affected and muscles becoming increasingly weakened as the disorder progresses.
- What is Parkinson’s disease? List four characteristic signs of the disorder. Parkinson’s disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the muscular system and movement. Four characteristic signs of the disorder are muscle tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and postural instability.
- What are the main differences between musculoskeletal disorders and neuromuscular disorders? Answers may vary. Sample answer: Musculoskeletal disorders are due to biomechanical stresses; typically only affect just one or a few muscles; and are often fully treatable. Neuromuscular disorders are not due to biomechanical stresses (they often have a genetic cause); they usually affect most or all of the muscles in the body; and they are often progressive and incurable.
- Why is padding of a strained muscle part of the typical treatment? A strained muscle is caused by the tearing of muscle fibres. Padding of a strained muscle protects it from further impact.
- What are two tissues — other than muscle tissue — that can experience problems that result in muscular system disorders? Answers may vary. Sample answer: Tendons and nervous system tissue.
12.7 Case Study Conclusion and Chapter Summary: Review Questions and Answers
- What are tendons? Name a muscular system disorder involving tendons. Tendons are bundles of collagen fibres that attach skeletal muscles to bone. Answers may vary. Sample answer. Tendonitis.
- When the biceps contract and become shorter (as in the picture above), what kind of motion does this produce in the arm? The arm bends at the elbow and the forearm will move up.
- Is the situation described in part (a) more likely to be an isometric or isotonic contraction? Explain your answer. It is more likely to be an isotonic contraction because the muscle is shortening and isotonic contractions involve a change in muscle length. Isometric contractions do not involve a change in muscle length.
- If the triceps were to then contract, which way would the arm move? The arm would straighten out.
- What are Z discs? What happens to them during muscle contraction? Z discs are structures that mark the end of a sarcomere in a muscle fibre. They are attached to actin filaments. During muscle contraction, the sliding of the actin and myosin filaments pulls the Z discs closer together, shortening the sarcomere.
- What is the function of mitochondria in muscle cells? Which type of muscle fibre has more mitochondria — slow-twitch or fast-twitch? The function of mitochondria in muscle cells is to provide energy for the muscles in the form of ATP, through aerobic respiration. Slow-twitch.
- What is the difference between primary and secondary Parkinson’s disease? Primary Parkinson’s disease occurs mostly in older people, for no known reason. Secondary Parkinson’s disease occurs due to some kind of known or suspected cause, such as repeated head trauma or exposure to toxins.
- Why can carpal tunnel syndrome cause muscle weakness in the hands? Answers may vary. Sample answer: Carpal tunnel syndrome is due to the compression of the median nerve in the wrist. This nerve is then unable to adequately stimulate the muscles that it innervates, causing muscle weakness.
Human Biology Copyright © 2020 by Christine Miller is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Science Notes Posts
- Contact Science Notes
- Todd Helmenstine Biography
- Anne Helmenstine Biography
- Free Printable Periodic Tables (PDF and PNG)
- Periodic Table Wallpapers
- Interactive Periodic Table
- Periodic Table Posters
- Science Experiments for Kids
- How to Grow Crystals
- Chemistry Projects
- Fire and Flames Projects
- Holiday Science
- Chemistry Problems With Answers
- Physics Problems
- Unit Conversion Example Problems
- Chemistry Worksheets
- Biology Worksheets
- Periodic Table Worksheets
- Physical Science Worksheets
- Science Lab Worksheets
- My Amazon Books
Human Anatomy Worksheets and Study Guides

This is a collection of free human anatomy worksheets. The completed worksheets make great study guides for learning bones, muscles, organ systems, etc. The worksheets come in a variety of formats for downloading and printing. In most cases, the PDF worksheets print the best. But, you may prefer to work online with Google Slides or print the PNG images.
Do you need a particular worksheet, but don’t see it? Ideas for worksheet topics you want covered are welcome!
Human Anatomy Worksheets
These worksheets cover major organs and organ systems.

Label the Heart
Label the parts of the human heart.
[ Google Apps worksheet ][ worksheet PDF ][ worksheet PNG ][ answers PNG ]

Label the Eye
Label the parts of the eye.
[ Google Apps worksheet ][ worksheet PDF ][ answers PDF ][ worksheet PNG ]

Types of Blood Cells
Identify the types of blood cells.
[ worksheet Google Apps ][ worksheet PDF ][ worksheet PNG ][ answers PNG ]

Label the Muscles
Label the major anterior muscles.
[ worksheet PDF ][ worksheet PNG ][ answers PNG ]

Label the Ear
Label the human ear.
[ Google Apps worksheet ][ Worksheet PDF ][ Worksheet PNG ][ Answers PNG ]

Label the Lungs
Identify the parts of the lungs.

Label the Kidney
Label the parts of the kidney.

Label the Liver
Identify the anatomy of the liver.

Label the Large Intestine
Label the parts of the large intestine.

Label the Stomach
Label the human stomach.
[ Google Apps worksheet ] [Worksheet PDF ][ Worksheet PNG ][ Answers PNG ]

External Nose Anatomy
Identify the parts of the nose.
[ Worksheet PDF ][ Worksheet Google Apps ][ Worksheet PNG ][ Answers PNG ]

Parts of the Nose
Here’s another way of identifying nose anatomy.

Label Bones of the Skeleton
Identify major bones of the skeleton.
[ Google Apps worksheet ][ worksheet PDF ][ answers PDF ][ worksheet PNG ][ answers PNG ]

Label the Lymph Node
Label the lymph node.

Label the Human Skull
[ worksheet PDF ][ worksheet Google Apps ][ worksheet PNG ][ answers PNG ]

Label the Skull (Advanced)

Label the Parts of the Brain
Identify parts of a human brain.

Label the Lobes of the Brain
Identify the different lobes of the brain.

Brain Anatomical Sections
Explore anatomical sections using a human brain as a reference.

Arteries of the Brain
Identify major brain arteries.

Label the Pancreas
Label the parts of the human pancreas.

Label the Spleen
Label spleen anatomy.

Label the Digestive System
Identify parts of the human digestive system.

Label the Respiratory System
Label the respiratory system.

Parts of a Neuron
Identify parts of a neuron.

Label the Lips
Label human lips.

Label the Skin
Label layers and structures in skin.

Label the Circulatory System
Label the circulatory system.

The Urinary Tract
[ Worksheet PDF ][ Worksheet Google Apps ][ Worksheet PNG ][ Answer Key PNG ]

The Bladder

The Female Reproductive System

Label Human Teeth

Identify Organs #1

Identify Organ Systems #1

Identify Organs #2

Identify Organ Systems #2
- Diagram of the Human Eye [ JPG ]
Human Anatomy Worksheets Terms of Use
You are welcome to print these resources for personal or classroom use. They may be used as handouts or posters. They may not be posted elsewhere online, sold, or used on products for sale.
This page doesn’t include all of the assets on the Science Notes site. If there’s a table or worksheet you need but don’t see, just let us know. The same goes if you need a different file format.
Related Posts

Human Muscular System (Functions, Types of Muscles, Worksheets and More)
Grade 6 science worksheets.
The human muscular system is the complex network of muscles throughout the body that allows movement, stability, and force generation. It comprises more than 600 muscles, ranging from large muscles in the arms and legs to smaller ones in the face and internal organs.
Put your knowledge to the test with this challenging 6th Grade Science Worksheet !
The primary purpose of the muscular system is to enable our body movements. They make up the bulk of the body and form almost 1/3 rd of the body weight. Blood vessels and nerves run to every muscle and control and regulate every muscle function.

Schedule a Free session to clear worksheet doubts
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase. Just schedule a FREE Sessions to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Functions of the Muscular System
- It helps us maintain posture and body position.
- It supports soft tissues and internal organs.
- It helps us maintain our body temperature.
- It enables all our voluntary movements like moving skeletal bones for body movements, like walking, running, chewing, playing the piano; and involuntary movements like breathing, beating of heart, moving food through the digestive system, blood through the circulatory system, and fluids through the excretory system. Doubts? A 6th-grade science tutor can help.
Properties of muscles
- Excitability – Muscles are capable of receiving and responding to nervous stimulation.
- Contractibility – After receiving stimulation, muscles are capable of contracting or shortening.
- Extensibility – A muscle can be stretched to about three times their contracted length without rupturing.
- Elasticity – It is the ability of a muscle to recoil or bounce back to the muscle’s original length and shape after contraction and extension.
- Adaptability – The response of a muscle depends upon the kind of stimulus received. In simple words, a muscle will enlarge (hypertrophy) with increased work, as in bodybuilders or they may waste away (atrophy) due to immobility, malnutrition, or aging.
Composition of Muscle Tissues
Muscle tissues are soft tissues that comprise of elongated cells, also known as muscle fibers tightly bundled together. A bundle of skeletal muscle fibers is called a fascicle . A basic rod-like unit of a muscle fiber or cell is called myofibril that is composed of proteins like actin, myosin , titin etc. Each time the bundles receive signals from the nervous system, they contract causing a force and motion. The muscular system includes the soft tissues of muscles, whereas the human skeletal system consists of the bones.

eTutorWorld Understands Math Tutoring | Online Math Worksheets are Important Tools
Understanding graphs, charts, and opinion polls in a newspaper, for calculating house and car payments, and for choosing a long-distance telephone service are impossible without strong math skills …and the only way to develop strong math skills is by constant practice.
‘Practice makes a man perfect’ holds true for no other field better than for math. A middle or high school student must set aside a minimum of an hour for math every day. Other than textbooks, worksheets help you revise and understand concepts better.
Our expert tutors prepare online maths worksheets that are age and grade-appropriate. Grade-wise math worksheets for Elementary Math , Arithmetic, Pre-Algebra, Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, Statistics, Pre-Calculus and Calculus can be solved to improve math skills, to get ahead or to even catch up.
You may download these FREE online math worksheets in the PDF format, and then print and email us their solutions for a free evaluation and analysis by eTutorworld’smath expert tutors.
You may solve these worksheets by yourself or with your peers while studying together.
The Answer Key at the end of each worksheet allows for a self-evaluation.
Personalized Online Tutoring
eTutorWorld offers affordable one-on-one live tutoring over the web for Grades K-12, Test Prep help for Standardized tests like SCAT, CogAT, MAP, SSAT, SAT, ACT, ISEE and AP. You may schedule online tutoring lessons at your personal scheduled times, all with a Money-Back Guarantee. The first one-on-one online tutoring lesson is always FREE, no purchase obligation, no credit card required.
For answers/solutions to any question or to learn concepts, take a FREE CLASS.
No credit card required, no obligation to purchase. Just book a free class to meet a tutor and get help on any topic you want!
Three types of muscle tissues
- Smooth muscles – Smooth muscles are involuntary muscles and constitute much of the musculature of internal organs and the digestive system. They contract slowly and automatically. They consist of narrow spindle-shaped cells with a single centrally located nucleus. They are found within the walls of organs and structures like the alimentary canal, bronchi, urinary tract and blood vessels.
- Cardiac muscles – Cardiac muscle tissue is only found in the heart. They are not subject to voluntary control . The contractions of cardiac muscles are highly coordinated to pump blood into the circulatory system. The heart and the circulatory system make up the cardiovascular system . Cardiac muscle fibers are shorter than skeletal muscle fibers and usually contain one centrally located nucleus.
- Skeletal muscles – Skeletal muscles attach to bones and move them voluntarily in response to signals from the nervous system. Attached to the skeletal system, they provide the skeleton with the ability to move. They help us maintain posture. Each skeletal muscle is made up of hundreds of muscle fibers bundled together. Each skeletal muscle fiber is a single cylindrical muscle cell. Skeletal muscles have an abundant supply of blood vessels and nerves.

Notice the striations on cardiac and skeletal muscles. They are thus known as striated muscles as they are packed into highly regular arrangement of bundles.
Five types of muscle movements
Adduction – Adduction involves moving a body part toward the mid-line of the body.
Abduction – abduction means moving a body part away from the body.
Flexion – Flexion means bending a joint to decrease the angle between two bones.
Extension – Extension means to extend or straighten a joint to increase the angle between two bones.
Rotation – Rotation involves moving a body part around an axis.
Other structures essential to the muscular system
Tendons – Tendon are tissues that attach muscles to bones. They are remarkably strong with high tensile strength that can be attributed to its constituent collagen (an important protein building block of our body systems ) fibers.
Fascia – Fascia is a soft fibrous tissue that envelopes, separates or binds together muscles, group of muscles, organs and other tissues of the body. Fascia also permits some other muscles to slide smoothly over each other. In simple words, they connect muscles to other muscles.
Coordination with the Nervous System and the Skeletal System –
As discussed earlier the skeletal muscles are controlled by the nervous system. The muscular system uses muscles to move the bones of the skeletal system. However, if the communication between the nervous system and the muscular system gets damaged, then the muscular system will not be able to bring about any movement in the body parts! This causes paralysis.
How do muscles move a bone?
Let’s say you want to pick up a book. In order to lift it, your biceps will have to contract and the triceps will have to lengthen or stretch to make your arm bend at the elbow.
When the muscle relationship is reversed, that is when the biceps relax and the triceps contract, the arm will come back to its original position and you can put the book down.

Thus muscles always work in pairs. When one muscle in a pair contracts to bend a joint, its counterpart then contracts and pulls in the opposite direction to straighten the joint out again. The two proteins actin and myosin present in muscle cells help in contraction of muscles by changing the length and shape of the cells.
So now you know why people take protein supplements to build their muscles! Aside from proteins, we also need carbohydrates, healthy fats, plenty of water, Magnesium (it helps in muscle contraction) and regular exercise to aid a healthy and strong Muscular System.
Check point
- The property of a muscle to recoil or bounce back to the muscle’s original length and shape after contraction is called _______.
- The enlargement of muscles due to extra work out is called muscular ________.
- Bending a joint to decrease the angle between two bones is called ______.
- The mineral that is required in our diet for healthy muscles is _______.
- Muscles always work in pairs, when one muscle contracts, the other ________.
- hypertrophy

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the human muscular system.
The human muscular system refers to the network of muscles in the body that enables movement, stability, and the generation of force. It includes over 600 muscles that work together to perform various functions.
How many types of muscles are there in the human body?
There are three main types of muscles in the human body: skeletal muscles, smooth muscles, and cardiac muscles. Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary movements, while smooth muscles control involuntary movements, and cardiac muscles are unique to the heart.
What is the function of the muscular system?
The muscular system serves multiple functions. It enables movement and locomotion, maintains posture and stability, generates heat to regulate body temperature, protects organs, and facilitates various bodily functions such as digestion and circulation.
How do muscles contract and relax?
Muscles contract and relax through a process called muscle contraction. When stimulated by nerve impulses, muscle fibers shorten and generate force, causing movement. Relaxation occurs when the impulses cease, allowing the muscle fibers to return to their original length.
Pricing for Online Tutoring
| Tutoring Package | Validity | Grade (1-12), College |
|---|---|---|
| 5 sessions | 1 Month | $139 |
| 1 session | 1 Month | $28 |
| 10 sessions | 3 months | $269 |
| 15 sessions | 3 months | $399 |
| 20 sessions | 4 months | $499 |
| 50 sessions | 6 months | $1189 |
| 100 sessions | 12 months | $2249 |
6th Grade Free Worksheets
- Inquiry process
- Nature of Science
- Scientific Inquiry
- Inquiry, Analysis and Problem Solving
- Ethical Practices
- Science and Society
- Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Impact of Organisms
- Spheres of Earth
- Natural Resources
- Environmental Issues
- Conservation of Earth
- Understanding Technology
- Abilities To Do Technological Design
- Structure of Earth
- Solar System
- Rocks and Fossils
- Earth Systems
- Plate Tectonics
- Magnetic Field of Earth
- Geologic Time
- Materials and Processes That Shape a Planet
- Kinetic and Potential Energy
- Energy Transfer
- Matter and its Structure
- States of Matter
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Force and Motion
- Electricity and Magnetism
- Wave Interactions
- Introduction to Life Science
- The Origin & History of Life On Earth
- Plant and Animal Cells
- Parts of a Cell
- The Cell Cycle
- How Living Organisms Get Energy
- Classification of Organisms
- How Plants Grow & Reproduce
- The Human Respiratory System
- The Human Cardiovascular System
- The Human Digestive System
- The Human Endocrine Systems
- The Human Nervous System
- The Human Muscular System
- The Human Skeletal System
Picture credits :
https://www.uc.edu/content/dam/uc/ce/images/OLLI/Page%20Content/Muscular%20System%20s.pdf
https://healthclubfinder.org/gym-workout-schedule-for-men/
http://www.healthfine.org/articles/192245
https://ftiinc.org/why-you-need-to-shred-protein-hot/
https://www.mutantworkout.org/muscles/function-of-smooth-muscle/
https://sequencewiz.org/2016/03/16/loosen-up-your-shoulders/
http://myscienceschool.org/index.php?/archives/1597-How-do-muscles-work.html
IN THE NEWS

Our mission is to provide high quality online tutoring services, using state of the art Internet technology, to school students worldwide.

Home Tutoring Test Prep Worksheets Pricing About Us Blog Free Class Login Terms of service Privacy Policy Money Back Guarantee Technical requirements FAQs Job Opportunities Sitemap
Connect with us (628)-272-0788
Online test prep and practice SCAT SSAT ISEE PSAT SAT ACT AP Exam
Science Tutoring Physics Tutoring Chemistry Tutoring Biology Tutoring
Math Tutoring Pre-Algebra Tutoring Algebra Tutoring Pre Calculus Tutoring Calculus Tutoring Geometry Tutoring Trigonometry Tutoring Statistics Tutoring
English Tutoring Reading Writing Grammar
Quick links Free Worksheets Fact sheet Sales Partner Opportunities Parents Passive Fundraising Virtual Fundraising Our Expert Tutors Safe and Secure Tutoring Interactive Online Tutoring After School Tutoring Elementary School Tutoring Middle School Tutoring High School Tutoring Home Work Help Math Tutors New York City Press
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird
©2022 eTutorWorld Terms of use Privacy Policy Site by Little Red Bird

Anatomy & Physiology
One organ at a time..., chapter 8: muscular system.
Part 1: Muscle Basics
Notes: Muscular System | Presentation Slides
Sarcomere Anatomy: Coloring | Sliding Filament Coloring
Muscle Anatomy Vocabulary
Study Guide: Muscle Structure | Crossword Puzzle: Muscle Anatomy
Case Study: The Tired Swimmer
Basic Muscles | Muscles - Cellular Structure Muscle Fiber Structure | Muscle - Sarcomere
Magic School Bus Works Out - Season 3/ Episode 9 (See Netflix)
Part 2: Naming of the Muscles

Muscle Lab Guide : Muscles you need to know
How Muscles are Named - descriptions / vocab
Muscles Coloring : Major groups represented, color and learn! Muscle Naming Crossword : practice spelling and identifying main groups
How Muscles Are Named
Naming the Muscles - Guided Learning Activity
Printout of ALL Muscles we labeled and colored in class
Google Slides of Muscle Groups: Head | Torso | Legs
Interactive Diagrams : Head | Back | Chest | Legs (anterior) | Legs (posterior) | Arm (flexors) | Arm (Extensors
.... Practice Test with Key
Additional Practice and Other Resources
GetBodySmart - tutorials on major muscle groups
Body Part Muscle Flashcards and use them to practice naming muscles.
More Labeling - Head | Full Body | Full Body Side
Part 3: Cat Muscles and Dissection
Cat Muscles Lab Guide - checklist of the muscles you need to identify on the cat
Presentation Slides - Muscles of the Arms and Chest
Presentation Slides - Muscles of the Legs and Abdomen
Coloring the Cat Muscles: Dorsal Side | Ventral Side

Cat Muscles - Photos of Muscles You Need to Know
Quizlet: Cat Muscles | Cat (Ventral Side) | Cat (Dorsal Side)
AnatomyCorner Resources - Virtual Cat Dissection | Cat Muscle Gallery

- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search
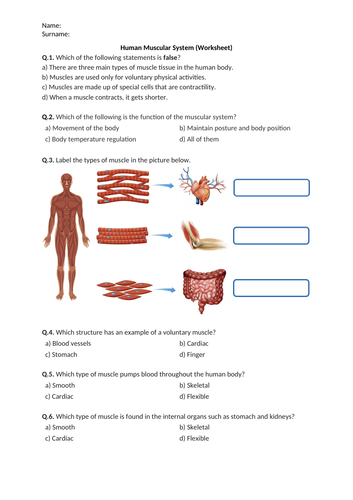
Human Muscular System - Worksheet | Printable and Distance Learning
Subject: Biology
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
6 December 2021
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This worksheet is the perfect way for helping your students learn and review Human Muscular System.
What is included in this resource?
- Printable and editable Student Worksheet (PDF and Word document)
- Paperless digital version for use in Google Drive (Prepared with Google Slides)
- Complete Answer Key
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Hunter's Woods PH

Montessori Biology
The muscular system: free educational worksheets for k-12 students, quick lesson and free printable/live worksheets on the muscular system for learners from kindergarten up. includes the types of muscles, how muscles work, and possible muscle injuries., muscular system: quick facts.
- Introduction to The Muscular System: Live Worksheet for Kindergarten to Grade 2
- Types of Muscles: Muscular System Live Worksheet for Grade 3
- How the Muscular System Works: Live Fill in the Blanks Worksheet for Grade 4
- How the Muscular System Works: Live Multiple Choice Worksheet for Grade 5
- Muscle Types and Injuries: Live Muscular System Worksheet for Grade 6
Muscles work closely with our bones and connective tissues in order to make our body move.
There are three types of muscles in the body:
Skeletal muscles
- These are the muscles attached to bones (thus the name “skeletal”) and are responsible for voluntary movement.
- You can use conscious thought to control them, that’s why they are also called voluntary muscles.
- When you look at them under a microscope, skeletal muscles are striated ; that is, they have regular stripes or lines.
Smooth muscles
- These are the muscles in places like the walls of your arteries and veins (which make your blood vessels wider or narrower as needed) and the walls of your intestines (which push food along the length of your gut).
- They work automatically without you being aware of them. You can’t control them — you can’t make your intestines stop squeezing the food along their length, for example — and so smooth muscles are also known as involuntary muscles.
- When you look at them under a microscope, smooth muscles are not striated .
Cardiac muscle
- Your heart is made up of a muscle that’s strong enough to pump out blood to your entire body.
- It’s a special kind of muscle: it’s striated (like skeletal muscles) but it’s involuntary (like smooth muscles) — you can’t tell it to stop working.
- The muscle part of your heart is called the myocardium from myo (muscle) + kardia (heart).
Muscles are attached to bones by tough cords of connective tissue called tendons .
There are around 650 muscles in the human body. This number only refers to the muscles that have been named — mostly skeletal muscles — and do not include countless nameless smooth muscles.
How Muscles Work
Muscles work by becoming shorter or contracting . When muscles contract, they pull on the tendons that connect them to bones. When the tendons are pulled, they also pull on the bones to which they are attached. This creates movement.
Muscles can only pull. They cannot push. For this reason, muscles need to work in pairs, so that bones can move in opposite directions.
The biceps and triceps muscles in the upper arm are an example of a pair of muscles that work to create movement in opposite directions. They work on the elbow joint to move the forearm.
- When the biceps contracts, the elbow is bent. The triceps relaxes.
- To straighten the elbow, the triceps contracts and the biceps relaxes.
- This coordinated movement is a result of instructions from the brain. When you decide to bend or straighten your elbow, your brain sends signals along the appropriate nerves, telling which muscle to contract and which to relax.
Muscle Health and Injuries
Protein is the building block of muscle tissue, so you need to have enough protein in your diet to keep your muscles healthy. You can do this by eating food rich in protein, such as (but not limited to) meat, fish, beans, eggs, and milk.
Exercising your muscles make them stronger.
There are several types of injuries that can happen to your muscles.
- This is the overstretching or partial tearing of a muscle or tendon .
- It is often called a “pulled muscle.”
- This is different from a sprain, which is an injury to a ligament (the connective tissue that connects bones to other bones).
- These are also called “muscle spasms.”
- They are sudden, involuntary, and often painful contractions of one or more muscles.
- They can be caused by overuse of a muscle or by holding a position for a very long period. Sometimes, however, the cause of a cramp is not known.
- This is what happens when something hits a part of your body and it doesn’t tear open the skin in that part BUT it causes damage to the muscles and connective tissue underneath.
- The medical term for a muscle bruise is a “muscle contusion.”
First aid for soft tissue injuries like muscle injuries is known by the acronym R.I.C.E .
- Rest – Stop whatever you’re doing. Continuing to use the part that is injured may just make the damage worse. Rest that part for a few days.
- Ice – Cold will reduce the pain and swelling. It doesn’t have to be ice, necessarily; you could also use other things from your freezer, like a bag of frozen peas. Make sure you wrap whatever cold thing you use in a light towel so you won’t get frostbite. This should only be done for the first 2-3 days, until the swelling is gone.
- Compression – Wrapping the injured area will help prevent or reduce swelling. Don’t wrap it too tight, though! An elastic bandage is the best thing to use for this.
- Elevation – Keep the injured part of your body at or above the level of your heart — or at least above hip level — to keep the pain, throbbing, and swelling down. You can prop it on a chair when you’re sitting down or on a pillow when you’re in bed.
The worksheets below are interactive “live worksheets” — they can be answered and corrected/submitted right on this page.
Printable (PDF) versions of these worksheets are also available for free download — just click on links provided before each worksheet.
Note on the Worksheets
You can reduce the size of the worksheet by zooming out your browser screen. For Windows users, scroll down the mouse wheel while pressing the Ctrl key in your keyboard. If there are any errors/glitches, just refresh and try again.
Introduction to The Muscular System: Worksheet for Kindergarten to Grade 2
A printable version of this worksheet can be downloaded here: Introduction to The Muscular System: Worksheet for Kindergarten to Grade 2 PDF
Types of Muscles: Muscular System Worksheet for Grade 3
A printable version of this worksheet can be downloaded here: Types of Muscles: Muscular System Worksheet for Grade 3 PDF
How the Muscular System Works: Fill in the Blanks Worksheet for Grade 4
A printable version of this worksheet can be downloaded here: How the Muscular System Works: Fill in the Blanks Worksheet for Grade 4 PDF
How the Muscular System Works: Multiple Choice Worksheet for Grade 5
A printable version of this worksheet can be downloaded here: How the Muscular System Works: Multiple Choice Worksheet for Grade 5 PDF
Muscle Types and Injuries: Muscular System Worksheet for Grade 6
A printable version of this worksheet can be downloaded here: Muscle Types and Injuries: Muscular System Worksheet for Grade 6 PDF
Did you enjoy these muscular system worksheets? See all our free printable and interactive worksheets here:
LEARNING AND GROWING
Learning / Education Financial Education for Kids Inspiration for Kids
MONTESSORI EDUCATION Montessori Homeschooling Montessori for Toddlers and Preschoolers Montessori for Elementary School Kids Montessori-Inspired Worksheets Montessori-Inspired Interactive Online Quizzes Why Choose Montessori
LEARNING ABOUT THE WORLD Books Environmental Issues Philippine Heritage and Culture World History, Arts and Culture
LEARNING TO ADULT Career Budgeting and Financial Education
How To [Do Stuff]
Family Adventures

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Lab Workbook # 9. MUSCULAR SYSTEM. Introduction. The muscular system consists of skeletal muscles, which through their connectionto bones via. tendons help to produce movementof the body. Inaddition to movement, skeletal muscleassists in. heat production, posture, and glycemic control. Smooth and skeletalmuscles work to control body.
extensor digitorum longus. slender shin muscle. tibialis anterior. thick shin muscle. orbicularis oculi. nasalis. triangularis. extensor retinaculum. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like frontalis, orbicularis oris, zygomaticus major and more.
2 Muscular System Worksheet Student Name: Time Estimate: 35 minutes Examine Part 1: Follow these steps to complete the table. 1. Locate the four muscles in the table on the muscle and skeleton diagrams. 2. Using the diagrams, identify the origin and insertion for each muscle. Record them in the chart.
Actin is thin. Myosin heads pull actin to shorten muscle. Origin v insertion. Immovable v movable. Sarcomere. Contractile unit of muscle fiber (actin and myosin) Sarcolemma. Muscle fiber membrane. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Functions of muscular system., Smooth muscle, Cardiac muscle and more.
Answers will vary. Sample answer: The skeletal system and the nervous system. Describe one way in which the muscular system is involved in regulating body temperature. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Smooth muscles in the blood vessels can contract to cause vasoconstriction, or relax to cause vasodilation.
Matching Muscle Directions and Positions. 4.11. transverse. 4.12. sphincter. 4.13. oblique. See more. Medical Terminology for Health Professions: 8th Edition / Chapter 4 The Muscular System Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free.
worksheet for chapter 9 outline chapters muscles fill in the following table to describe, compare and contrast the three types of muscle: voluntary cell shape ... Chapter 9 Worksheet - muscle answers. worksheet for chapter 9. Course. Human Anatomy and Physiology I (BIOL 227 ) ... Lab 12 KD Central Nervous System FA22 Shelley; Thompson son5 ch01 ...
Muscular System Worksheet . 1. Write a definition for each of the following terms. (a) tendon connective tissue that attaches muscles to bones (b) ligament . connective tissue that connects bones to each other (c) skeletal muscle . voluntary muscles attached to bones capable of providing motion (d) cardiac muscle
Chapter 6 The Muscular System General Body Muscle Review 23. Complete the following statements describing muscles. Insert the correct 107 answers in the answer blanks. 1. 5. 10. Three muscles— (1) (2) and (3) —are commonly used for intramuscular injections in adults. The insertion tendon of the (4) group contains a large sesamoid bone, the ...
This is a collection of free human anatomy worksheets. The completed worksheets make great study guides for learning bones, muscles, organ systems, etc. The worksheets come in a variety of formats for downloading and printing. In most cases, the PDF worksheets print the best. But, you may prefer to work online with Google Slides or print the ...
The human muscular system is the complex network of muscles throughout the body that allows movement, stability, and force generation. It comprises more than 600 muscles, ranging from large muscles in the arms and legs to smaller ones in the face and internal organs. Put your knowledge to the test with this challenging 6th Grade Science Worksheet!
Chapter 8: Muscular System. This chapter is divided into three main sections: muscle basics and cellular components, naming of the muscles, and cat muscles with dissection. Be prepared to spend a fair amount of time on this unit. Part 1: Muscle Basics. Notes: Muscular System | Presentation Slides. Sarcomere Anatomy: Coloring | Sliding Filament ...
Age range: 7-11. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. docx, 1.59 MB. pdf, 1.51 MB. docx, 1.6 MB. txt, 88 Bytes. This worksheet is the perfect way for helping your students learn and review Human Muscular System. What is included in this resource?
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Two muscles named for the muscle location:, Two muscles named for the muscle shape:, Two muscles named for the muscle size: and more.
Montessori Biology. The Muscular System: Free Educational Worksheets for K-12 Students. Quick lesson and free printable/live worksheets on the muscular system for learners from kindergarten up. Includes the types of muscles, how muscles work, and possible muscle injuries. Contents:
MUSCULAR SYSTEM HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT. The homework assignment provides students with a diagram of the muscles in the body. Students will use the terms in the word bank to label the muscles in the correct places. Afterward, they will write a short story correctly using a specific list of words. The lesson plan provides an answer key for this ...
Under the direction of the nervous system, all the muscles provide for motion of some type for your body. The body has three major types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. We begin with a general description and comparison of these three muscle types and then get more specific about each type. Pro•nun•ci•.
Muscular System Reading Worksheet Instructions: Read the following passage all about the muscular system and answer the questions on the information. The muscular system is a complex network of tissues, organs, and cells that work together to facilitate movement and maintain body posture. It plays a vital role in human anatomy and
Health Chapter 6:5 Muscular System. 40 terms. Golf1121. Chapter 7:5 Muscular System ... Skeleton Test. 68 terms. baylee_smith89 PLUS. 7.9 Lymphatic System assignment sheet. 22 terms. Stephanie_Custodia. Other sets by this creator. ... Verified questions. ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. Which part of the renal tubule begins at the glomerular capsule ...
The main function of the muscular system is movement. This includes walking, breathing, pumping the heart, and moving food through your digestive tract, just name a few important examples. Muscles also create heat as they contract, helping to maintain a constant body temperature. Muscle tissue makes up nearly half of an individual's total ...
Exercise 13 Review Sheet Physiology of the Muscular System Name Lab Section Date 1. From a functional standpoint, discuss the difference between isotonic and isometric muscle contractions. 2. The graph on the right compares speed of muscle contraction with load. Which object will you be able to lift most quickly, and which will you lift most ...
Here are some extra muscle resources we have found helpful so far in our Apologia Anatomy and Physiology study: *Links may be affiliate. Experimenting With Flexibility - The Homeschool Scientist. KidsHealth.org - interactive lesson on muscles and bones. University of Minnesota - Web Anatomy muscle name self-test.
Biology questions and answers; The Muscular System Worksheet Answer each of the following questions and submit this assignment through the "Muscular System Worksheet" link on Blackboard 1. During skeletal muscle contraction, there is an increased amount of calcium released into the sarcoplasm of skeletal muscle cells. a.