- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

GroupsandTeams →
No results found in working knowledge.
- Were any results found in one of the other content buckets on the left?
- Try removing some search filters.
- Use different search filters.

- 1-800-565-8735
- [email protected]
16 Team Building Case Studies and Training Case Studies
From corporate groups to remote employees and everything in between, the key to a strong business is creating a close-knit team. in this comprehensive case study, we look at how real-world organizations benefited from team building, training, and coaching programs tailored to their exact needs. .
Updated: December 21, 2021
We’re big believers in the benefits of team building , training and development , and coaching and consulting programs. That’s why our passion for helping teams achieve their goals is at the core of everything we do.
At Outback Team Building & Training, our brand promis e is to be recommended , flexible, and fast. Because we understand that when it comes to building a stronger and more close-knit team, there’s no one-size-fits-all formula. Each of our customers have a unique set of challenges, goals, and definitions of success.
And they look to us to support them in three key ways: making their lives easy by taking on the complexities of organizing a team building or training event; acting fast so that they can get their event planned and refocus on all the other tasks they have on their plates, and giving them the confidence that they’ll get an event their team will benefit from – and enjoy.
In this definitive team building case study , we’ll do a deep dive into real-world solutions we provided for our customers.
4 Unique Team Building Events & Training Programs Custom-Tailored for Customer Needs
1. a custom charity event for the bill & melinda gates foundation , 2. how principia built a stronger company culture even with its remote employees working hundreds of miles apart , 3. custom change management program for the royal canadian mint, 4. greenfield global uses express team building to boost morale and camaraderie during a challenging project, 5 virtual team building activities to help remote teams reconnect, 1. how myzone used virtual team building to boost employee morale during covid-19, 2. americorps equips 90 temporary staff members for success with midyear virtual group training sessions, 3. how microsoft’s azure team used virtual team building to lift spirits during the covid-19 pandemic, 4. helping the indiana cpa society host a virtual team building activity that even the most “zoom fatigued” guests would love, 5. stemcell brightens up the holiday season for its cross-departmental team with a virtually-hosted team building activity, 3 momentum-driving events for legacy customers, 1. how a satellite employee “garnered the reputation” as her team’s pro event planner, 2. why plentyoffish continues to choose ‘the amazing race’ for their company retreat, 3. how team building helped microsoft employees donate a truckload of food, 4 successful activities executed on extremely tight timelines, 1. finding a last-minute activity over a holiday, 2. from inquiry to custom call in under 30 minutes, 3. a perfect group activity organized in one business day, 4. delivering team building for charity in under one week.

We know that every team has different needs and goals which is why we are adept at being flexible and have mastered the craft of creating custom events for any specifications.

When the Seattle, Washington -based head office of the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation – a world-renowned philanthropic organization – approached us in search of a unique charity event, we knew we needed to deliver something epic. Understanding that their team had effectively done it all when it comes to charity events, it was important for them to be able to get together as a team and give back in new ways .
Our team decided the best way to do this was to create a brand-new event for the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation which had never been executed before. We created an entirely new charitable event – Bookworm Builders – for them and their team loved it! It allowed them to give back to their community, collaborate, get creative, and work together for a common goal. Bookworm Builders has since gone on to become a staple activity for tons of other Outback Team Building & Training customers!
To learn more about how it all came together, read the case study: A Custom Charity Event for the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation .

Who said hosting an impactful training program means having your full team in the same place at the same time? Principia refused to let distance prevent them from having a great team, so they contacted us to help them find a solution. Their goals were to find better ways of working together and to create a closer-knit company culture among their 20 employees and contractors living in various parts of the country.
We worked with Principia to host an Emotional Intelligence skill development training event customized to work perfectly for their remote team. The result was a massive positive impact for the company. They found they experienced improved employee alignment with a focus on company culture, as well as more emotionally aware and positive day-to-day interactions. In fact, the team made a 100% unanimous decision to bring back Outback for additional training sessions.
To learn more about this unique situation, read the full case study: How Principia Built a Stronger Company Culture Even with its Remote Employees Working Hundreds of Miles Apart .
We know that employee training that is tailored to your organization can make the difference between an effective program and a waste of company time. That’s why our team jumped at the opportunity to facilitate a series of custom development sessions to help the Royal Canadian Mint discover the tools they needed to manage a large change within their organization.
We hosted three custom sessions to help the organization recognize the changes that needed to be made, gain the necessary skills to effectively manage the change, and define a strategy to implement the change:
- Session One: The first session was held in November and focused on preparing over 65 employees for change within the company.
- Session Two: In December, the Mint’s leadership team participated in a program that provided the skills and mindset required to lead employees through change.
- Session Three: The final session in February provided another group of 65 employees with guidance on how to implement the change.
To learn more, read the full case study: Custom Change Management Program for the Royal Canadian Mint .

When Greenfield Global gathered a team of its A-Players to undertake a massive, challenging project, they knew it was important to build rapports among colleagues, encourage collaboration, and have some fun together.
So, we helped them host an Express Clue Murder Mystery event where their team used their unique individual strengths and problem-solving approaches in order to collaboratively solve challenges.
To learn more, read the full case study: Greenfield Global Uses Express Team Building to Boost Morale and Camaraderie During a Challenging Project .
When the COVID-19 pandemic struck, we were proud to be able to continue supporting our customers’ goals with virtual team building activities and group training sessions.
With remote work being mandated as self-quarantine requirements are enforced on a global scale, companies began seeking ways to keep their newly-remote teams engaged and ensure morale remained as high as possible.
And MyZone was no exception. When the company found themselves feeling the effects of low employee morale and engagement, they noticed a decrease in productivity and motivation.
To make matters even more difficult, MyZone’s team works remotely with employees all over the world. This physical distancing makes it challenging for them to build a strong rapport, reinforce team dynamics, and boost morale and engagement.
The company was actively searching for an activity to help bring their employees closer together during this challenging time but kept running into a consistent issue: the majority of the team building activities they could find were meant to be done in person.
They reached out to Outback Team Building and Training and we were able to help them achieve their goals with a Virtual Clue Murder Mystery team building activity.
AmeriCorps members are dedicated to relieving the suffering of those who have been impacted by natural disasters. And to do so, they rely on the support of a team of temporary staff members who work one-year terms with the organization. These staff focus on disseminating emergency preparedness information and even providing immediate assistance to victims of a disaster.
During its annual midyear training period, AmeriCorps gathers its entire team of temporary staff for a week of professional development seminars aimed at both helping them during their term with the company as well as equipping them with skills they can use when they leave AmeriCorps.
But when the COVID-19 pandemic got underway, AmeriCorps was forced to quickly re-evaluate the feasibility of its midyear training sessions.
That’s when they reached out to Outback. Rather than having to cancel their midyear training entirely, we were able to help them achieve their desired results with four virtual group training sessions: Clear Communication , Performance Management Fundamentals , Emotional Intelligence , and Practical Time Management .
Find all the details in the full case study: AmeriCorps Equips 90 Temporary Staff Members for Success with Midyear Virtual Training Sessions.
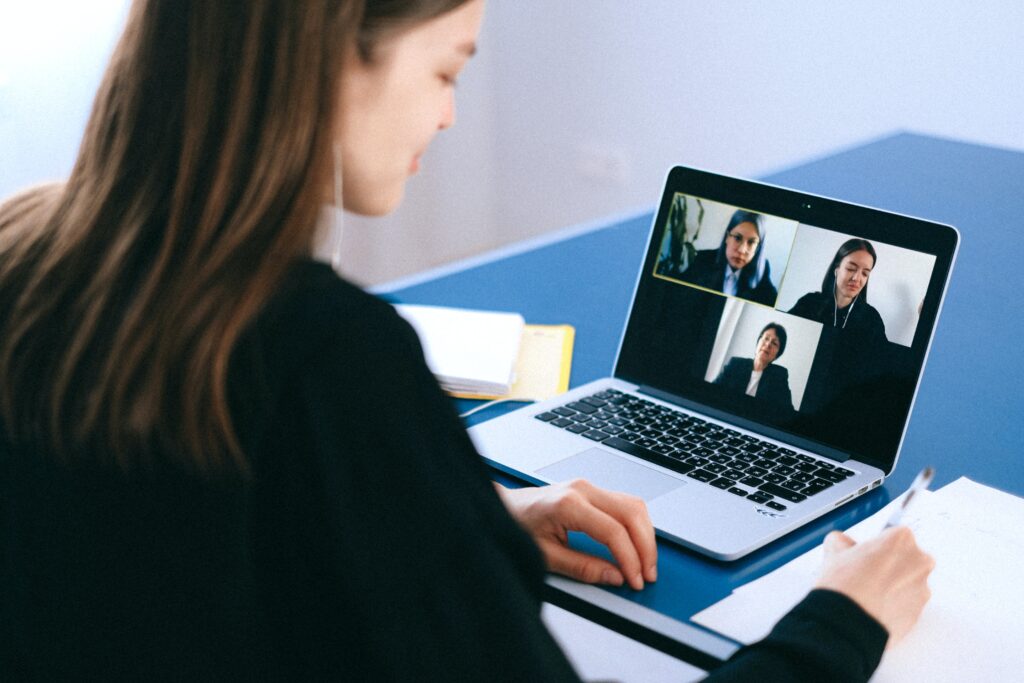

With the COVID-19 pandemic taking a significant toll on the morale of its employees, Microsoft’s Azure team knew they were overdue for an uplifting event.
It was critical for their team building event to help staff reconnect and reengage with one another. But since the team was working remotely, the activity needed to be hosted virtually and still be fun, engaging, and light-hearted.
When they reached out to Outback Team Building and Training, we discussed the team’s goals and quickly identified a Virtual Clue Murder Mystery as the perfect activity to help their team get together online and have some fun together.
For more information, check out the entire case study: How Microsoft’s Azure Team Used Virtual Team Building to Lift Spirits During the COVID-19 Pandemic.
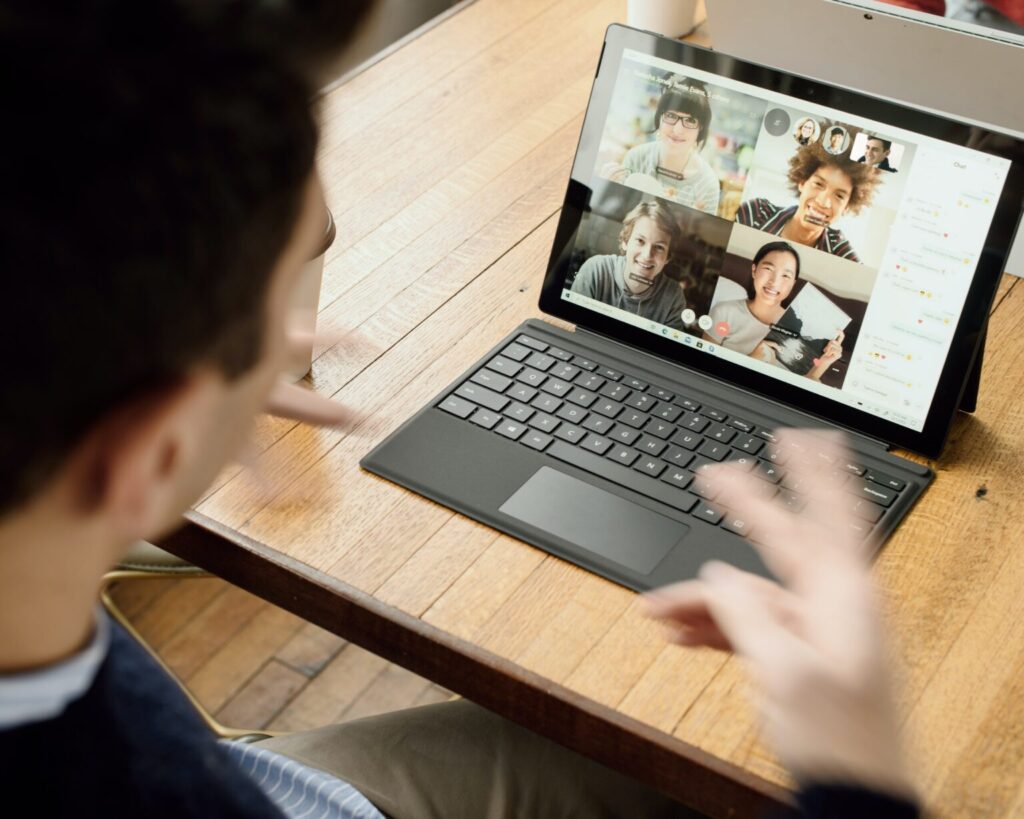

The Indiana CPA Society is the go-to resource for the state’s certified public accountants. The organization supports CPAs with everything from continuing education to networking events and even advocacy or potential legislation issues that could affect them.
But as the time approached for one of INCPAS’ annual Thanksgiving event, the Indiana CPA Society’s Social Committee needed to plan a modified, pandemic-friendly event for a group of people who were burnt out my online meetings and experiencing Zoom fatigue.
So, we helped the team with a Self-Hosted Virtual Code Break team building activity that INCPAS staff loved so much, the organization decided to host a second event for its Young Pros and volunteers.
For INCPAS’ Social Committee, the pressure to put on an event that everyone will enjoy is something that’s always on their mind when planning out activities. And their event lived up to their hopes.
For more information, check out the entire case study: Helping the Indiana CPA Society Host a Virtual Team Building Activity That Even the Most “Zoom Fatigued” Guests Would Love .
When Stemcell was looking for a way to celebrate the holidays, lift its team members’ spirits, and help connect cross-departmental teams during the pandemic, they contacted us to help host the perfect team building activity.
They tasked us with finding an event that would help team members connect, get in the holiday spirit, and learn more about the business from one another during the midst of a stressful and challenging time.
So, we helped them host a festive, virtually-hosted Holiday Hijinks team building activity for employees from across the company.
For more information, check out the entire case study: Stemcell Brightens Up the Holiday Season for its Cross-Departmental Team with a Virtually-Hosted Team Building Activity .
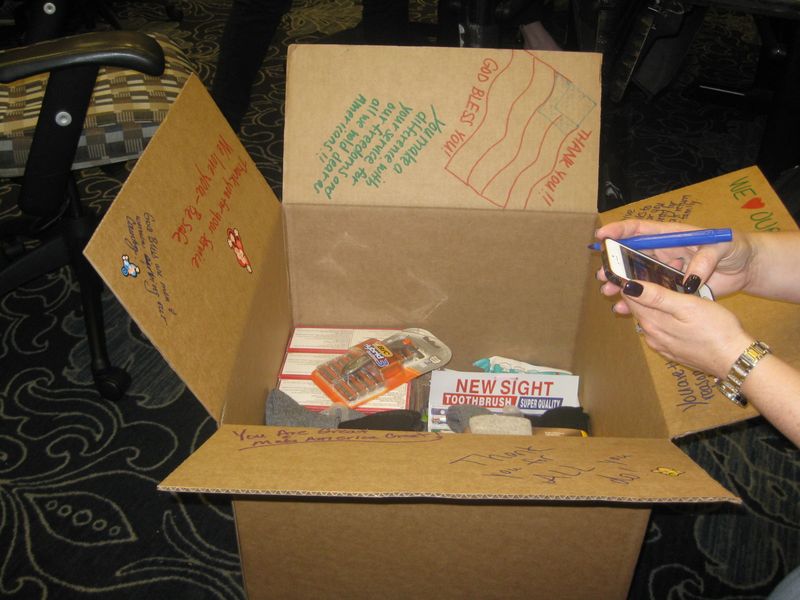

We take pride in being recommended by more than 14,000 corporate groups because it means that we’ve earned their trust through delivering impactful results.
We’ve been in this business for a long time, and we know that not everybody who’s planning a corporate event is a professional event planner. But no matter if it’s their first time planning an event or their tenth, we love to help make our customers look good in front of their team. And when an employee at Satellite Healthcare was tasked with planning a team building event for 15 of her colleagues, she reached out to us – and we set out to do just that!
Our customer needed a collaborative activity that would help a diverse group of participants get to know each other, take her little to no time to plan, and would resonate with the entire group.
With that in mind, we helped her facilitate a Military Support Mission . The event was a huge success and her colleagues loved it. In fact, she has now garnered a reputation as the team member who knows how to put together an awesome team building event.
To learn more, read the case study here: How a Satellite Employee “Garnered the Reputation” as Her Team’s Pro Event Planner .
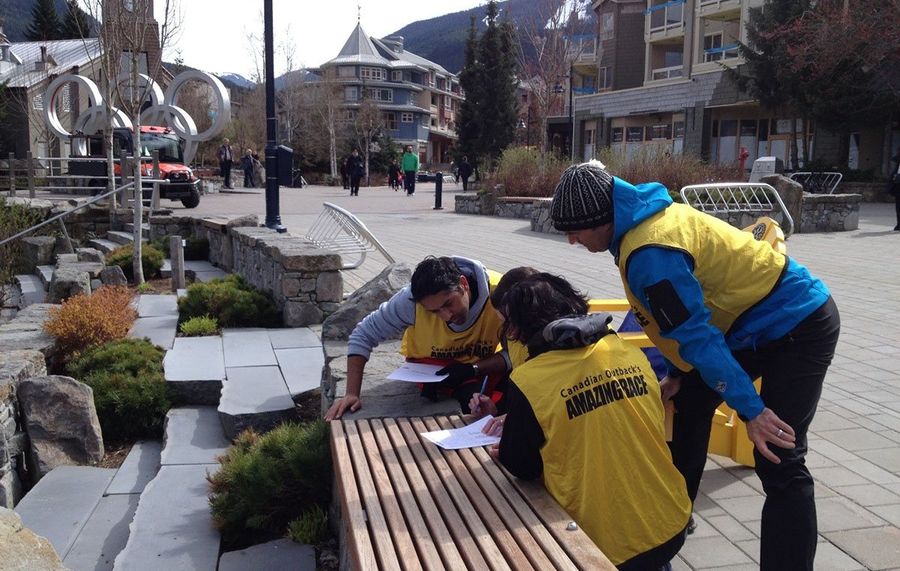

In 2013, international dating service POF (formerly known as PlentyOfFish) reached out to us in search of an exciting outdoor team building activity that they could easily put to work at their annual retreat in Whistler, B.C . An innovative and creative company, they were in search of an activity that could help their 60 staff get to know each other better. They also wanted the event to be hosted so that they could sit back and enjoy the fun.
The solution? We helped them host their first-ever Amazing Race team building event.
Our event was so successful that POF has now hosted The Amazing Race at their annual retreat for five consecutive years .
To learn more, check out our full case study: Why PlentyOfFish Continues to Choose ‘The Amazing Race’ for Their Company Retreat .

As one of our longest-standing and most frequent collaborators, we know that Microsoft is always in search of new and innovative ways to bring their teams closer together. With a well-known reputation for being avid advocates of corporate social responsibility, Microsoft challenged us with putting together a charitable team building activity that would help their team bond outside the office and would be equal parts fun, interactive, and philanthropic.
We analyzed which of our six charitable team building activities would be the best fit for their needs, and we landed on the perfect one: End-Hunger Games. In this event, the Microsoft team broke out into small groups, tackled challenges like relay races and target practice, and earned points in the form of non-perishable food items. Then, they used their cans and boxes of food to try and build the most impressive structure possible in a final, collaborative contest. As a result, they were able to donate a truckload of goods to the local food bank.
For more details, check out the comprehensive case study: How Team Building Helped Microsoft Employees Donate a Truckload of Food .
Time isn’t always a luxury that’s available to our customers when it comes to planning a great team activity which is why we make sure we are fast, agile, and can accommodate any timeline.
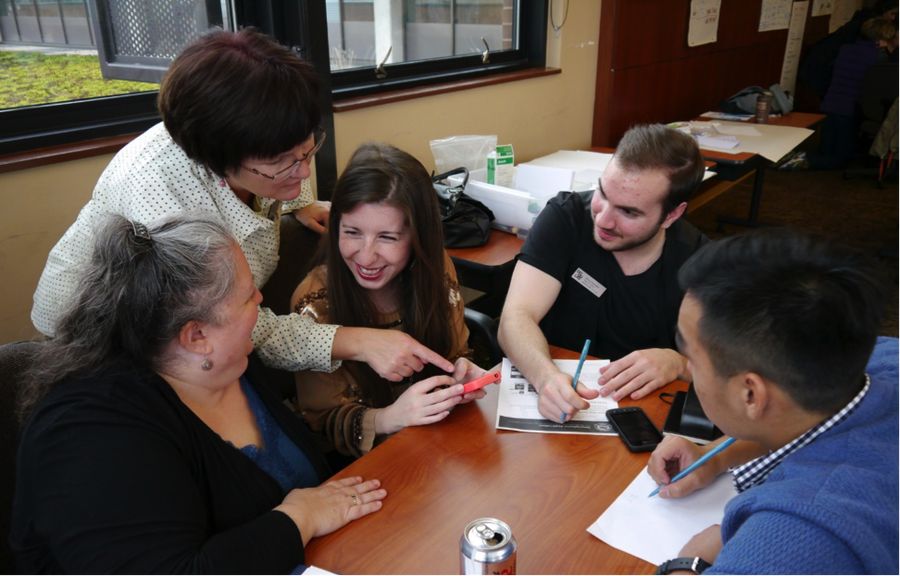

Nothing dampens your enjoyment of a holiday more than having to worry about work – even if it’s something fun like a team building event. But for one T-Mobile employee, this was shaping up to be the case. That’s because, on the day before the holiday weekend, she found out that she needed to organize a last-minute activity for the day after July Fourth.
So, she reached out to Outback Team Building & Training to see if there was anything we could do to help – in less than three business days. We were happy to be able to help offer her some peace of mind over her holiday weekend by recommending a quick and easy solution: a Code Break team building activity. It was ready to go in less than three days, the activity organized was stress-free during her Fourth of July weekend, and, most importantly, all employees had a great experience.
For more details, check out the full story here: Finding a Last-Minute Activity Over a Holiday .
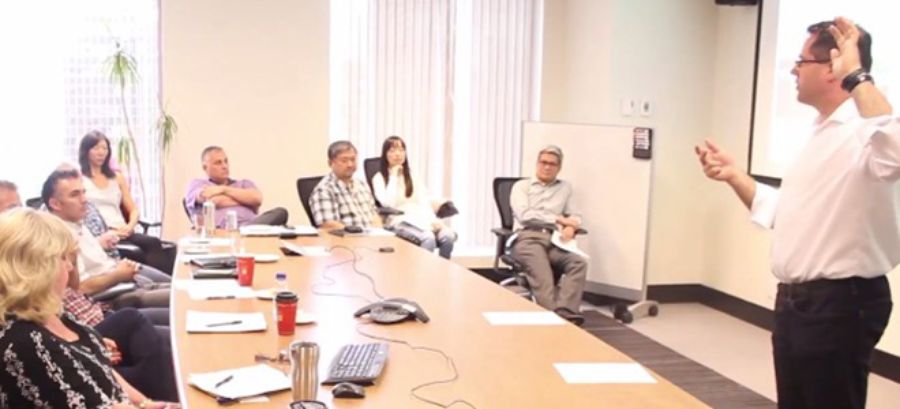

At Outback Team Building & Training, we know our customers don’t always have time on their side when it comes to planning and executing an event. Sometimes, they need answers right away so they can get to work on creating an unforgettable experience for their colleagues.
This was exactly the case when Black & McDonald approached us about a learning and development session that would meet the needs of their unique group, and not take too much time to plan. At 10:20 a.m., the organization reached out with an online inquiry. By 10:50 a.m., they had been connected with one of our training facilitators for a more in-depth conversation regarding their objectives.
Three weeks later, a group of 14 Toronto, Ontario -based Black & McDonald employees took part in a half-day tailor-made training program that was built around the objectives of the group, including topics such as emotional intelligence and influence, communication styles, and the value of vulnerability in a leader.
To learn more about how this event was able to come together so quickly, check out the full story: From Inquiry to Custom Call in Under 30 Minutes .

When Conexus Credit Union contacted us on a Friday afternoon asking if we could facilitate a team building event for six employees the following Monday morning, we said, “Absolutely!”
The team at Conexus Credit Union were looking for an activity that would get the group’s mind going and promote collaboration between colleagues. And we knew just what to recommend: Code Break Express – an activity filled with brainteasers, puzzles, and riddles designed to test the group’s mental strength.
The Express version of Code Break was ideal for Conexus Credit Union’s shorter time frame because our Express activities have fewer challenges and can be completed in an hour or less. They’re self-hosted, so the company’s group organizer was able to easily and efficiently run the activity on their own.
To learn more about how we were able to come together and make this awesome event happen, take a look at our case study: A Perfect Group Activity Organized in One Business Day .
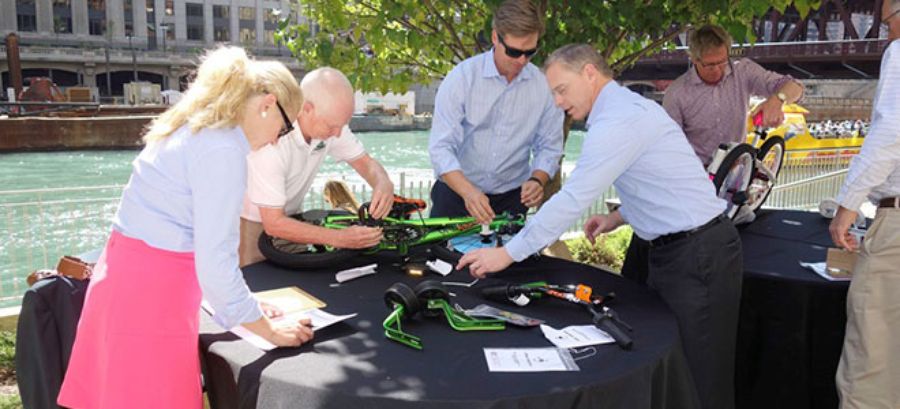

We’ve been lucky enough to work with Accenture – a company which has appeared on FORTUNE’s list of “World’s Most Admired Companies” for 14 years in a row – on a number of team building activities in the past.
The organization approached us with a request to facilitate a philanthropic team building activity for 15 employees. The hitch? They needed the event to be planned, organized, and executed within one week.
Staying true to our brand promise of being fast to act on behalf of our customers, our team got to work planning Accenture’s event. We immediately put to work the experience of our Employee Engagement Consultants, the flexibility of our solutions, and the organization of our event coordinators. And six days later, Accenture’s group was hard at work on a Charity Bike Buildathon , building bikes for kids in need.
To learn more about how we helped Accenture do some good in a short amount of time, read the full case study: Delivering Team Building for Charity in Under One Week .
Learn More About Team Building, Training and Development, and Coaching and Consulting Solutions
For more information about how Outback Team Building & Training can help you host unforgettable team activities to meet your specific goals and needs on virtually any time frame and budget, just reach out to our Employee Engagement Consultants.
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
And stay updated, related articles.

The 5 Best Remote Teamwork Tactics to Implement in 2024

How to Create an Engaging And Productive Virtual Internship Program

How to Develop an Employee Volunteer Training Program
From corporate groups to remote employees and everything in between, the key to a strong business is creating a close-knit team. That’s why you need to do team-building sessions as much as you can.
![case study on teamwork in organizations Real Life Examples of Successful Teamwork [9 Cases]](https://activecollab.com/upload/blog/143/cover.png)
- Real Life Examples of Successful Teamwork [9 Cases]
Instead of retelling the same old stories about best teamwork practices from companies such as Google, Chevron, or Southwest airlines (which don’t really help when you have a small-to-medium team), we decided to find real-life examples of successful teamwork.
We asked everyday entrepreneurs, CEOs, and HR managers one simple question:
How did you improve teamwork in your organization?
Here are the best 9 examples we came across.
3-step onboarding

Developing teamwork should start as soon as the new employee walks through the door. According to Lauren McAdams , career advisor and hiring manager at ResumeCompanion.com , the most successful method for creating excellent intra-team relations was instilling a sense of teamwork early on in the onboarding process.
”While we do experiment with different team-building measures, there are three that have become common practice:
First, during onboarding, we have new employees shadow an experienced “coach” who is tasked with helping their integration into the team. After the initial phase, we assign the new employees to shadow other people so they get to have more than one “coach”.
Next, when we begin a new project, I personally assign mini-teams to handle those projects. These smaller units are often comprised, in part, of employees who haven't had a chance to work together. This way, new hires get an opportunity to work and develop relationships with everyone they collaborate with.
And finally, leadership rotates on these projects so different people have a chance to test their leadership skills. Also, since project teams always have different people on them, everyone in the company gets to know each other at some point by working together. This level of exposure and collaboration resulted in very strong teamwork at our company.”
Role switching

Some organizations encourage their employees to walk a mile in someone else's shoes. Lee Fisher , an HR manager at Blinds Direct , says that successful teamwork should be based on solidarity, respect, communication, and mutual understanding. With that in mind, his company has been organizing a series of team-building events over the years.
“Our most unconventional event to date was the 'Role Switch'. It was launched across our web and marketing department . In the event, each team member switches roles with a colleague. Usually, team members work together closely but they don’t really understand the complexities of other person’s role.
Spending a day in your colleague’s shoes highlights their efforts, which brings more understanding and respect for one another. The 'Role Switch' was a huge success: it brought the team closer together and made people more considerate of other's workloads and requirements .”
Cross-training

Sharing experience with your peers is important, but recognizing where they can best help you improve is even more important. According to Steven Benson , founder, and CEO of Badger Maps , his company has benefited from one self-initiated cross-training session which resulted in an increase in both teamwork and productivity.
”An example of successful teamwork at our company was when the customer relation department put together an initiative of cross-training and specializing team members for different roles. After deciding who will focus on what, the group sat down and taught one another what they would need to become the expert in their respective area.
Because people were cross-trained, they had a broader set of skills they could use to handle customer interaction - which resulted in fewer hand-offs. This not only enhanced teamwork and productivity, but also improved customer satisfaction. Everyone worked as a team and covered for one another, which made everything move smoothly and quickly."

The Big Book of Team Culture
All Newsletter subscribers can download this (and other) ActiveCollab Project Management Guides.
*Enter your email address and subscribe to our newsletter to get your hands on this, as well as many other free project management guides.
Sorry, we could not subscribe you at this moment. please double check your email address. If issue still persist, please let us know by sending an email to [email protected]
Scheduled breaks and self-reflection

Publicly reflecting on achievements increases everyone’s morale. Bryan Koontz , CEO of Guidefitter , considers teamwork to be more than just brainstorming ideas or helping a colleague on a project - it’s about fostering a culture of trust and respect.
“A few ways we cultivate an environment of trust and respect is through meetings, or rather "breaks", that don't necessarily focus on work. By scheduling “break” times in our calendars, we allow our employees to talk, relax, and discuss the ins-and-outs of their days.
We also strengthen our teams through brief weekly meetings with the entire office: each Wednesday morning we huddle up to recap the past week, with each employee sharing one professional and one personal "win". This encourages everyone to pause for self-reflection on their achievements, often serving as motivation to their peers while forging a bond among our team members.”
Team traditions

Members of jelled teams have a strong sense of identity and often share traditions like getting together for a drink after work. According to Katerina Trajchevska co-founder and CEO of Adeva , establishing team traditions is the foundation upon which teamwork is built.
“Rather than using one particular method for strengthening our team, we focus on creating an environment that fosters team spirit and communication. We organize after hours drinks and hangouts, and develop a culture that encourages everyone to speak up and take part in the big decisions for the company.
Team traditions can do wonders, no matter how trivial they seem: we have a team lunch every Friday, celebrate birthdays and other important dates, and celebrate one of our national holidays together. All of this has contributed to a more cohesive and a close-knit team.”
Unconventional business meetings

Some companies use their business meetings to improve teamwork within the organization by making them fun and laid-back. James Lloyd-Townshend , CEO of Frank Recruitment Group believes that bringing teams together in an informal environment improves teamwork, strengthens bonds, and bolsters morale - which is why he decided to spice up the company’s monthly meetings.
”One unusual method we’ve introduced is “First Thursdays”: we start off our monthly business meetings with a business review, promotions, and awards - and then move on to an open bar event.
Apart from “First Thursdays,” we also have “Lunch Club”: another monthly event where employees enjoy an all-expense-paid afternoon to celebrate their success and enjoy fine dining and have fun with their colleagues.
However, the most popular team building method we employ is our incentivised weekends away. Our top-performing consultants get the chance to travel to major cities such as London, New York, and Miami as the rewards for their hard work.”
Peer recommendations

Some companies are building teamwork through peer recognition. Jacob Dayan , a partner, and co-founder of Community Tax said that encouraging employees to be active participants in recognizing their peers has proven to be quite a powerful motivational tool.
”I ask employees to share or report instances when someone on their or another team has been particularly helpful or has gone above and beyond their call of duty. After we thank the contributing employee for their input, we make sure the employee being acknowledged knows the source of information. Having employees “nominate” their peers for recognition has the additional bonus of bringing them closer together and building camaraderie with long-term productivity benefits.”
However, Mr. Dayan is well aware that peer reports and nominations can be driven by personal feelings (positive as well as negative), and can give an unrealistic representation of certain employee's contribution.
”Personal relationships, both close and less so, are an important consideration when pursuing this approach, which is why we do not hand out recognition without validating the worthiness of the employee's contribution. We ask the appropriate manager to review the submission and keep an eye on it over time, just to make sure there are no dubious activities.”
Conflict resolving

Successful teamwork happens when members of a group trust each other, are comfortable expressing themselves, and deal effectively with conflict, according to Laura MacLeod , a licensed social worker specialized in group work, an HR consultant, and a mastermind behind “From the inside out project” .
”Many companies think that team building is about company picnics, happy hours, and other fun events. These things are fine, but they don't address the real issues people face when they have to work together. Going out for a drink with someone you can't get along with will be just as uncomfortable and awkward as trying to finish a project with that person - the only difference is having alcohol as a buffer.”
According to Laura, certain team-building exercises can help individuals overcome both intragroup and personal conflicts .
“Choose simple activities that help build cohesion and trust amongst team members. For example, you can use “Pantomime in a circle” exercise: without using words, pass an imaginary object (a bucket of water or a ball) around the circle; the point of the exercise is for group members to rely on each other to complete the activity.
When it comes to personal misunderstandings, you might want to choose an activity where you are actually allowed to yell at a person. So, pair off people and have them repeat opposing sentences (such as it’s hot/it’s cold) back and forth - going from soft to very loud. This will allow people to get out strong emotions in a non-threatening way, and blow off some steam in the process.”
"Spotless" team-building exercise

Dmitri Kara , a tenancy expert at Fantastic Cleaners , shared with us a team-building exercise his team uses to increase cooperation and efficiency.
”Everybody in the office has to simultaneously perform a 2-to-5-minute cleaning routine (like wipe their desk, keyboard, monitor, shelves). But there’s a catch: the tools are limited. For example, make everybody wipe the dust off their desks at the same time but provide only 2 sprayers and 1 roll of paper towel (if your team has 10 members)-. Scarcity will encourage people to share and help each other.”
Besides providing obvious benefits (like a cleaner working environment), Dmitri says this team building activity boosts organization, improves long-term productivity, and develops a sense of morale, discipline, and shared responsibility. He even shares how the exercise came into being:
”At first it was not really a dedicated exercise. The first time we did it all together, it was because of a video shoot. But since it felt good, a few days later somebody said, "let's do that again". And that's where the whole thing came to be.”

ActiveCollab 2021 Calendar
Make real work happen.
Start your trial today, free for 14 days! Onboard your team, plan, collaborate, organize your work, and get paid.
By signing up you are agreeing to the ActiveCollab Terms of Service & Privacy Policy .
Great, just a few seconds and you're in.
We detected that you already have an ActiveCollab account
You can log in to existing account or you may start a new one
Great, your account has been created!
You will be redirected to your new account in a couple of seconds.
Sorry, we could not create an account for you at this moment.
Please double check your email address. If the issue still persists, please let us know by sending an email to [email protected]
Other posts in the series on The Big Book of Team Culture
- Tips To Take Better Meeting Notes
- How To Be a Good Team Leader
- Belbin Team Roles: Theory and Practice
- How To Deal With a Toxic Coworker
- Organizational Culture and Its Impact on Team Performance
What Is Teamwork Actually?
- High Performing Teams: What Are They and How Do I Build One?
Characteristics of a Productive Team
- All Leadership Theories in Under 15 Minutes
- How to Create Organizational Culture
- Group vs Team [Differences, Comparison, Transformation]
- Types of Teams [Advantages and Disadvantages]
Sign up for ActiveCollab newsletter!
Choose your favorite topics and we'll send our stories from the tech front lines straight to your inbox.
Unsubscribe at any time * Privacy Policy
Just a second
Thank you for subscribing to our newsletter.
Oops, something went wrong! Please try again later.
Related Articles
Start your free trial
Enter your email to get 14 days of ActiveCollab absolutely free, without any limitations.
Mark as disposable account.
ActiveCollab Is Using Cookies
By accepting all cookies you are giving us permission to use our tracking technologies to personalize your content and provide you the best possible experience on our website. Essential cookies are always on as we need them to make sure our website is working properly.
Read more about our cookie policy.
To read this content please select one of the options below:
Please note you do not have access to teaching notes, cohesiveness within teamwork: the relationship to performance effectiveness – case study.
Education, Business and Society: Contemporary Middle Eastern Issues
ISSN : 1753-7983
Article publication date: 30 May 2008
This paper aims to explore the nature and the function of teamwork cohesiveness in organizations in the UAE.
Design/methodology/approach
While many organizations are successful at managing the materials and machinery of the organization, they fall short in managing the human side of their business. This research addresses and assesses how teams can progress to be of maximum use through teamwork and to view teams as performing organizational units which is similar to other studies that focus on teamwork processes. Teamwork cohesiveness is defined as a small number of people with complimentary skills who are committed to common purposes, performance goals, and approaches for which they hold themselves mutually accountable. These include being a team player with participation propensity, cooperative behaviors, and leadership skills. A model was tested, relating teamwork cohesiveness with intelligence and skills; reduce conflict, and 2D of organizational commitment, i.e. value, and performance. Survey data from 76 teams ( n =294) were collected in three industrial institutions in the UAE.
The results are supportive of a multi‐component structure for cohesiveness and of its importance to the functioning of teams and organizations. Teamwork cohesiveness appeared strongly related with team member's attitudes towards the organization. Cohesiveness between team members was positively associated with value commitment and negatively with performance commitment. In addition, intelligence and skills appeared strongly related to team satisfaction.
Originality/value
The paper offers insights into cohesiveness within teamwork.
- Team working
- Performance levels
- United Arab Emirates
Al‐Rawi, K. (2008), "Cohesiveness within teamwork: the relationship to performance effectiveness – case study", Education, Business and Society: Contemporary Middle Eastern Issues , Vol. 1 No. 2, pp. 92-106. https://doi.org/10.1108/17537980810890284
Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2008, Emerald Group Publishing Limited
Related articles
We’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Teamwork: a case study on development and performance

The most popular model of team development in Dutch socio-technical literature is a linear approach, which states that teams develop in four successive phases. A method for defining the particular phase a team is in was developed a number of years ago and was recently used in a large-scale survey at Volvo’s cab manufacturing plant in Umea ̊ (northern Sweden). Thirty-seven semi-autonomous teams were studied at this plant during a seven-month period. This paper examines the development of the teams and addresses the effects of team development on overall team performance. The aspect of team development was correlated to both performance in terms of quality of working life (QWL) and business performance (BP), which is an empirically unexplored field within team literature. The linear phase approach of team development could not be proved. Nevertheless, teams were found to develop in four important areas, with each aspect significantly affecting team performance.
Related Papers
Ben Kuipers , M. Witte
n this paper, we will show that the debate between advocates of lean production and the socio-technical approach has concentrated too much on the design aspect of the production structure, while neglecting the development aspect of teamwork. This paper addresses the question whether it is production design or team development that explains business performance and the quality of working life. The data are taken from four departments of the Volvo truck plant in Umea ̊ (Sweden) that is redesigning from socio-technical based assembly to line-assembly. We conclude that good design of the production structure is necessary, but not sufficient for good performance; team development is just as important, although it requires a favorable context.
Ben Kuipers
Several theories have been developed that prescribe the team development of self- managing work teams (SMWTs). Some of these have led to models with successive linear developmental phases. However, both the theory and the empirical data show little support for these models. Based on an extensive review of team development literature, we propose, instead of linear phases, describing team development in three general team processes. These processes, internal relations, task management, and external relations and improvement, were empirically explored in a longitudinal field- study of more than 150 blue-collar and white-collar SMWTs in a Volvo plant in Sweden. The three processes were found to be consistent over time and appeared to relate to one-year-later objective SMWT performance measures for product quality, the incidence of sick-leave and long-term sick-leave. Based on these findings, a result- oriented team development approach is proposed, in which the achieved results determine the processes followed to develop SMWTs further. Also, managers and HR practitioners are encouraged to monitor the three ongoing team processes and to relate these to the desired team performance. Such an analysis should be the starting point of a dialogue between manager and team to improve the functioning and performance of SMWTs.
Anabela Alves , Pedro Arezes , Dinis Carvalho
Career Development International
Franz Gellert
Ben Kuipers , Natalia Tolkacheva , M. Witte
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is one of the most common personality assessments and a frequently used instrument for team development. However, in relation to team development processes, there is little research and literature on the role of personality in general and the usefulness of MBTI in particular. This article starts with a review of the MBTI and explores the relationship between MBTI profiles and team processes using a sample of 1,630 people working in 156 teams in a Swedish industrial organization. The results show that only a small number of MBTI personality profiles have a significant relationship with team processes. Overall, the composition of teams in terms of MBTI profiles does not seem to predict team development very well. Findings suggest that the MBTI may be used as an instrument for personal development and as a vehicle for group members to gain a better understanding of each other.
This article describes a diagnostic model for empowerment in team- based organizations that portrays four dimensions of the organization's control structure: the level of routine, the nature of expertise, the level of dependence and the line of command. The combined positions of the set of job regulation tasks distinguished for these dimensions express empowerment in terms of a functional balance and a balance of authority. The diagnostic model can be used to measure the control structure in practice and to provide input for a well-founded and managerial debate on empowerment and control. The model is illustrated with quantitative data from a pilot study of 16 semi-autonomous work teams within the manufacturing industry. Considerable differences in the local interpretation of the design of the control structure by team managers were observed. In general, the empowerment of teams is rather limited. The impression given is that there is a temporary `double control structure', meaning simultaneous bottom-up and top-down control of the teams.
New Technology, Work and Employment
Roel Schouteten , Jos Benders
International Journal of Operations & Production Management
Jos Benders
The Learning Organization
Employee Relations
René Schalk
RELATED PAPERS
Economic and Industrial Democracy
Roel Schouteten
Rune Todnem By
Journal of Management Studies
Computers & Industrial Engineering
Bryan Norman , Wipawee Tharmmaphornphilas
Bram Steijn
Revista Ingenieria Industrial
Jose Moyano-Fuentes
Production and Services Balancing Knowledge in Product and Service Life Cycle Ifip Tc5 Wg5 3 Fifth Ifip Ieee International Conference on Information Technology For Balanced Automation Systems in Manufacturing and Services
Anabela Alves
Solaja Mayowa
Texila International Journal
Small Group Research
Isabelle Reymen
Rob Macklin
Team Performance Management
Personnel Review
adrian wilkinson
European Scientific Journal
Jaime Eduardo Gonzalez-Díaz
Gerben van der Vegt , Ben Kuipers , S. Bunderson
Theoretical Issues in …
Neville Stanton
annie Hondeghem
Torbjørn Netland
Essamadi Chaimaa
alessia contu
Applied Ergonomics
Christian Korunka
lavanya ravi
Dinis Carvalho
Niels E Wergin-Cheek
European Journal …
Michelle Mcintyre
Hans Doorewaard , Rik Huys , Geert Van Hootegem , Van Geert Hootegem
Julia Connell
American Journal
Evaluation & the Health Professions
Massimiliano Panella
BMC Health Services Research
nassera touati , Danièle Roberge , Linda Cazale
Zhanna Vavilova
Felipe Silva-Riesco
The Oxford Handbook of Leadership and Organizations
Ruth Wageman , Colin Fisher
Peter Oeij , S. Dhondt , F. Pot
Tariq Abdelhamid
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
Complex Problem Solving in Teams: The Impact of Collective Orientation on Team Process Demands
Associated data.
Complex problem solving is challenging and a high-level cognitive process for individuals. When analyzing complex problem solving in teams, an additional, new dimension has to be considered, as teamwork processes increase the requirements already put on individual team members. After introducing an idealized teamwork process model, that complex problem solving teams pass through, and integrating the relevant teamwork skills for interdependently working teams into the model and combining it with the four kinds of team processes (transition, action, interpersonal, and learning processes), the paper demonstrates the importance of fulfilling team process demands for successful complex problem solving within teams. Therefore, results from a controlled team study within complex situations are presented. The study focused on factors that influence action processes, like coordination, such as emergent states like collective orientation, cohesion, and trust and that dynamically enable effective teamwork in complex situations. Before conducting the experiments, participants were divided by median split into two-person teams with either high ( n = 58) or low ( n = 58) collective orientation values. The study was conducted with the microworld C3Fire, simulating dynamic decision making, and acting in complex situations within a teamwork context. The microworld includes interdependent tasks such as extinguishing forest fires or protecting houses. Two firefighting scenarios had been developed, which takes a maximum of 15 min each. All teams worked on these two scenarios. Coordination within the team and the resulting team performance were calculated based on a log-file analysis. The results show that no relationships between trust and action processes and team performance exist. Likewise, no relationships were found for cohesion. Only collective orientation of team members positively influences team performance in complex environments mediated by action processes such as coordination within the team. The results are discussed in relation to previous empirical findings and to learning processes within the team with a focus on feedback strategies.
Introduction
Complex problems in organizational contexts are seldom solved by individuals. Generally, interdependently working teams of experts deal with complex problems (Fiore et al., 2010 ), which are characterized by element interactivity/ interconnectedness, dynamic developments, non-transparency and multiple, and/or conflicting goals (Dörner et al., 1983 ; Brehmer, 1992 ; Funke, 1995 ). Complex problem solving “takes place for reducing the barrier between a given start state and an intended goal state with the help of cognitive activities and behavior. Start state, intended goal state, and barriers prove complexity, change dynamically over time, and can be partially intransparent” (Funke, 2012 , p. 682). Teams dealing with complex problems in interdependent work contexts, for example in disaster, crisis or accident management, are called High Responsibility Teams. They are named High Responsibility Teams (HRTs; Hagemann, 2011 ; Hagemann et al., 2011 ) due to their dynamic and often unpredictable working conditions and demanding work contexts, in which technical faults and slips have severe consequences for human beings and the environment if they are not identified and resolved within the team immediately (Kluge et al., 2009 ). HRTs bear responsibility regarding lives of third parties and their own lives based on their actions and consequences.
The context of interdependently working HRTs, dealing with complex problems, is described as follows (Zsambok, 1997 ): Members of interdependently working teams have to reach ill-defined or competing goals in common in poor structured, non-transparent and dynamically changing situations under the consideration of rules of engagement and based on several cycles of joint action. Some or all goals are critical in terms of time and the consequences of actions result in decision-based outcomes with high importance for the culture (e.g., human life). In HRT contexts, added to the features of the complexity of the problem, is the complexity of relationships, which is called social complexity (Dörner, 1989/2003 ) or crew coordination complexity (Kluge, 2014 ), which results from the interconnectedness between multiple agents through coordination requirements. The dynamic control aspect of the continuous process is coupled with the need to coordinate multiple highly interactive processes imposing high coordination demands (Roth and Woods, 1988 ; Waller et al., 2004 ; Hagemann et al., 2012 ).
Within this article, it is important to us to describe the theoretical background of complex problem solving in teams in depth and to combine different but compatible theoretical approaches, in order to demonstrate their theoretical and practical use in the context of the analysis of complex problem solving in teams. In Industrial and Organizational Psychology, a detailed description of tasks and work contexts that are in the focus of the analysis is essential. The individual or team task is the point of intersection between organization and individual as a “psychologically most relevant part” of the working conditions (Ulich, 1995 ). Thus, the tasks and the teamwork context of teams that deal with complex problems is of high relevance in the present paper. We will comprehensively describe the context of complex problem solving in teams by introducing a model of an idealized teamwork process that complex problem solving teams pass through and extensively integrate the relevant teamwork skills for these interdependently working teams into the idealized teamwork process model.
Furthermore, we will highlight the episodic aspect concerning complex problem solving in teams and combine the agreed on transition, action, interpersonal and learning processes of teamwork with the idealized teamwork process model. Because we are interested in investigating teamwork competencies and action processes of complex problem solving teams, we will analyze the indirect effect of collective orientation on team performance through the teams' coordination behavior. The focusing of the study will be owed to its validity. Even though that we know that more aspects of the theoretical framework might be of interest and could be analyzed, we will focus on a detail within the laboratory experiment for getting reliable and valid results.
Goal, task, and outcome interdependence in teamwork
Concerning interdependence, teamwork research focuses on three designated features, which are in accordance with general process models of human action (Hertel et al., 2004 ). One type is goal interdependence, which refers to the degree to which teams have distinct goals as well as a linkage between individual members and team goals (Campion et al., 1993 ; Wageman, 1995 ). A second type is task interdependence, which refers to the interaction between team members. The team members depend on each other for work accomplishment, and the actions of one member have strong implications for the work process of all members (Shea and Guzzo, 1987 ; Campion et al., 1993 ; Hertel et al., 2004 ). The third type is outcome interdependence, which is defined as the extent to which one team member's outcomes depend on the performance of other members (Wageman, 1995 ). Accordingly, the rewards for each member are based on the total team performance (Hertel et al., 2004 ). This can occur, for instance, if a team receives a reward based on specific performance criteria. Although interdependence is often the reason why teams are formed in the first place, and it is stated as a defining attribute of teams (Salas et al., 2008 ), different levels of task interdependence exist (Van de Ven et al., 1976 ; Arthur et al., 2005 ).
The workflow pattern of teams can be
- Independent or pooled (activities are performed separately),
- Sequential (activities flow from one member to another in a unidirectional manner),
- Reciprocal (activities flow between team members in a back and forth manner) or
- Intensive (team members must simultaneously diagnose, problem-solve, and coordinate as a team to accomplish a task).
Teams that deal with complex problems work within intensive interdependence, which requires greater coordination patterns compared to lower levels of interdependence (Van de Ven et al., 1976 ; Wageman, 1995 ) and necessitates mutual adjustments as well as frequent interaction and information integration within the team (Gibson, 1999 ; Stajkovic et al., 2009 ).
Thus, in addition to the cognitive requirements related to information processing (e.g., encoding, storage and retrieval processes (Hinsz et al., 1997 ), simultaneously representing and anticipating the dynamic elements and predicting future states of the problem, balancing contradictory objectives and decide on the right timing for actions to execute) of individual team members, the interconnectedness between the experts in the team imposes high team process demands on the team members. These team process demands follow from the required interdependent actions of all team members for effectively using all resources, such as equipment, money, time, and expertise, to reach high team performance (Marks et al., 2001 ). Examples for team process demands are the communication for building a shared situation awareness, negotiating conflicting perspectives on how to proceed or coordinating and orchestrating actions of all team members.
A comprehensive model of the idealized teamwork process
The cognitive requirements, that complex problem solving teams face, and the team process demands are consolidated within our model of an idealized teamwork process in Figure Figure1 1 (Hagemann, 2011 ; Kluge et al., 2014 ). Individual and team processes converge sequential and in parallel and influencing factors as well as process demands concerning complex problem solving in teams can be extracted. The core elements of the model are situation awareness, information transfer, individual and shared mental models, coordination and leadership, and decision making.

Relevant teamwork skills (orange color) for interdependently working teams (see Wilson et al., 2010 ) integrated into the model of an idealized teamwork process.
Complex problem solving teams are responsible for finding solutions and reaching specified goals. Based on the overall goals various sub goals will be identified at the beginning of the teamwork process in the course of mission analysis, strategy formulation and planning, all aspects of the transition phase (Marks et al., 2001 ). The transition phase processes occur during periods of time when teams focus predominantly on evaluation and/or planning activities. The identified and communicated goals within the team represent relevant input variables for each team member in order to build up a Situation Awareness (SA). SA contains three steps and is the foundation for an ideal and goal directed collaboration within a team (Endsley, 1999 ; Flin et al., 2008 ). The individual SA is the start and end within the idealized teamwork process model. SA means the assessment of a situation which is important for complex problem solving teams, as they work based on the division of labor as well as interdependently and each team member needs to achieve a correct SA and to share it within the team. Each single team member needs to utilize all technical and interpersonal resources in order to collect and interpret up-to-date goal directed information and to share this information with other team members via “closed-loop communication.”
This information transfer focuses on sending and receiving single SA between team members in order to build up a Shared Situation Awareness (SSA). Overlapping cuts of individual SA are synchronized within the team and a bigger picture of the situation is developed. Creating a SSA means sharing a common perspective of the members concerning current events within their environment, their meaning and their future development. This shared perspective enables problem-solving teams to attain high performance standards through corresponding and goal directed actions (Cannon-Bowers et al., 1993 ).
Expectations of each team member based on briefings, individual mental models and interpositional knowledge influence the SA, the information transfer and the consolidation process. Mental models are internal and cognitive representations of relations and processes (e.g., execution of tactics) between various aspects or elements of a situation. They help team members to describe, explain and predict circumstances (Mathieu et al., 2000 ). Mental models possess knowledge elements required by team members in order to assess a current situation in terms of SA. Interpositional knowledge refers to an individual understanding concerning the tasks and duties of all team members, in order to develop an understanding about the impact of own actions on the actions of other team members and vice versa. It supports the team in identifying the information needs and the amount of required help of other members and in avoiding team conflicts (Smith-Jentsch et al., 2001 ). This knowledge is the foundation for anticipating the team members' needs for information and it is important for matching information within the team.
Based on the information matching process within the team, a common understanding of the problem, the goals and the current situation is developed in terms of a Shared Mental Model (SMM), which is important for the subsequent decisions. SMM are commonly shared mental models within a team and refer to the organized knowledge structures of all team members, that are shared with each other and which enable the team to interact goal-oriented (Mathieu et al., 2000 ). SMM help complex problem solving teams during high workload to adapt fast and efficiently to changing situations (Waller et al., 2004 ). They also enhance the teams' performance and communication processes (Cannon-Bowers et al., 1993 ; Mathieu et al., 2000 ). Especially under time pressure and in crucial situations when overt verbal communication and explicit coordination is not applicable, SMM are fundamental in order to coordinate implicitly. This information matching process fosters the building of a shared understanding of the current situation and the required actions. In order to do so teamwork skills (see Wilson et al., 2010 ) such as communication, coordination , and cooperation within the team are vitally important. Figure Figure1 1 incorporates the teamwork skills into the model of an idealized teamwork process.
Depending on the shared knowledge and SA within the team, the coordination can be based either on well-known procedures or shared expectations within the team or on explicit communication based on task specific phraseology or closed-loop communication. Cooperation needs mutual performance monitoring within the team, for example, in order to apply task strategies to accurately monitor teammate performance and prevent errors (Salas et al., 2005 ). Cooperation also needs backup behavior of each team member, for example, and continuous actions in reference to the collective events. The anticipation of other team members' needs under high workload maintains the teams' performance and the well-being of each team member (Badke-Schaub, 2008 ). A successful pass through the teamwork process model also depends e.g., on the trust and the cohesion within the team and the collective orientation of each team member.
Collective orientation (CO) is defined “as the propensity to work in a collective manner in team settings” (Driskell et al., 2010 , p. 317). Highly collectively oriented people work with others on a task-activity and team-activity track (Morgan et al., 1993 ) in a goal-oriented manner, seek others' input, contribute to team outcomes, enjoy team membership, and value cooperativeness more than power (Driskell et al., 2010 ). Thus, teams with collectively oriented members perform better than teams with non-collectively oriented members (Driskell and Salas, 1992 ). CO, trust and cohesion as well as other coordination and cooperation skills are so called emergent sates that represent cognitive, affective, and motivational states, and not traits, of teams and team members, and which are influenced, for example, by team experience, so that emergent states can be considered as team inputs but also as team outcomes (Marks et al., 2001 ).
Based on the information matching process the complex problem solving team or the team leader needs to make decisions in order to execute actions. The task prioritization and distribution is an integrated part of this step (Waller et al., 2004 ). Depending on the progress of the dynamic, non-transparent and heavily foreseeable situation tasks have to be re-prioritized during episodes of teamwork. Episodes are “temporal cycles of goal-directed activity” in which teams perform (Marks et al., 2001 , p. 359). Thus, the team acts adaptive and is able to react flexible to situation changes. The team coordinates implicitly when each team member knows what he/she has to do in his/her job, what the others expect from him/her and how he/she interacts with the others. In contrast, when abnormal events occur and they are recognized during SA processes, the team starts coordinating explicitly via communication, for example. Via closed-loop communication and based on interpositional knowledge new strategies are communicated within the team and tasks are re-prioritized.
The result of the decision making and action taking flows back into the individual SA and the as-is state will be compared with the original goals. This model of an idealized teamwork process (Figure (Figure1) 1 ) is a regulator circuit with feedback loops, which enables a team to adapt flexible to changing environments and goals. The foundation of this model is the classic Input-Process-Outcome (IPO) framework (Hackman, 1987 ) with a strong focus on the process part. IPO models view processes as mechanisms linking variables such as member, team, or organizational features with outcomes such as performance quality and quantity or members' reactions. This mediating mechanism, the team process , can be defined as “members' interdependent acts that convert inputs to outcomes through cognitive, verbal, and behavioral activities directed toward organizing taskwork to achieve collective goals” (Marks et al., 2001 , p. 357). That means team members interact interdependently with other members as well as with their environment. These cognitive, verbal, and behavioral activities directed toward taskwork and goal attainment are represented as gathering situation awareness, communication, coordination, cooperation, the consolidation of information, and task prioritization within our model of an idealized teamwork process. Within the context of complex problem solving, teams have to face team process demands in addition to cognitive challenges related to individual information processing. That means teamwork processes and taskwork to solve complex problems co-occur, the processes guide the execution of taskwork.
The dynamic nature of teamwork and temporal influences on complex problem solving teams are considered within adapted versions (Marks et al., 2001 ; Ilgen et al., 2005 ) of the original IPO framework. These adaptations propose that teams experience cycles of joint action, so called episodes, in which teams perform and also receive feedback for further actions. The IPO cycles occur sequentially and simultaneously and are nested in transition and action phases within episodes in which outcomes from initial episodes serve as inputs for the next cycle (see Figure Figure2). 2 ). These repetitive IPO cycles are a vital element of our idealized teamwork process model, as it incorporates feedback loops in such a way, that the outcomes, e.g., changes within the as-is state, are continuously compared with the original goals. Detected discrepancies within the step of updating SA motivate the team members to consider further actions for goal accomplishment.

Teamwork episodes with repetitive IPO cycles (Marks et al., 2001 ).
When applying this episodic framework to complex problem solving teams it becomes obvious that teams handle different types of taskwork at different phases of task accomplishment (Marks et al., 2001 ). That means episodes consist of two phases, so-called action and transition phases , in which teams are engaged in activities related to goal attainment and in other time in reflecting on past performance and planning for further common actions. The addition of the social complexity to the complexity of the problem within collaborative complex problem solving comes to the fore here. During transition phases teams evaluate their performance, compare the as-is state against goals, reflect on their strategies and plan future activities to guide their goal accomplishment. For example, team members discuss alternative courses of action, if their activities for simulated firefighting, such as splitting team members in order to cover more space of the map, are not successful. During action phases, teams focus directly on the taskwork and are engaged in activities such as exchanging information about the development of the dynamic situation or supporting each other. For example, a team member recognizes high workload of another team member and supports him/her in collecting information or in taking over the required communication with other involved parties.
Transition and action phases
The idealized teamwork process model covers these transition and action phases as well as the processes occurring during these two phases of team functioning, which can be clustered into transition, action, and interpersonal processes. That means during complex problem solving the relevant or activated teamwork processes in the transition and action phases change as teams move back and forth between these phases. As this taxonomy of team processes from Marks et al. ( 2001 ) states that a team process is multidimensional and teams use different processes simultaneously, some processes can occur either during transition periods or during action periods or during both periods. Transition processes especially occur during transition phases and enable the team to understand their tasks, guide their attention, specify goals and develop courses of action for task accomplishment. Thus, transition processes include (see Marks et al., 2001 ) mission analysis, formulation and planning (Prince and Salas, 1993 ), e.g., fighting a forest fire, goal specification (Prussia and Kinicki, 1996 ), e.g., saving as much houses and vegetation as possible, and strategy formulation (Prince and Salas, 1993 ; Cannon-Bowers et al., 1995 ), e.g., spreading team members into different geographic directions. Action processes predominantly occur during action phases and support the team in conducting activities directly related to goal accomplishment. Thus, action processes are monitoring progress toward goals (Cannon-Bowers et al., 1995 ), e.g., collecting information how many cells in a firefighting simulation are still burning, systems monitoring (Fleishman and Zaccaro, 1992 ), e.g., tracking team resources such as water for firefighting, team monitoring and backup behavior (Stevens and Campion, 1994 ; Salas et al., 2005 ), e.g., helping a team member and completing a task for him/her, and coordination (Fleishman and Zaccaro, 1992 ; Serfaty et al., 1998 ), e.g., orchestrating the interdependent actions of the team members such as exchanging information during firefighting about positions of team members for meeting at the right time at the right place in order to refill the firefighters water tanks. Especially the coordination process is influenced by the amount of task interdependence as coordination becomes more and more important for effective team functioning when interdependence increases (Marks et al., 2001 ). Interpersonal processes occur during transition and action phases equally and lay the foundation for the effectiveness of other processes and govern interpersonal activities (Marks et al., 2001 ). Thus, interpersonal processes include conflict management (Cannon-Bowers et al., 1995 ), like the development of team rules, motivation and confidence building (Fleishman and Zaccaro, 1992 ), like encourage team members to perform better, and affect management (Cannon-Bowers et al., 1995 ), e.g., regulating member emotions during complex problem solving.
Summing up, process demands such as transition processes that complex problem solving teams pass through, are mission analysis, planning, briefing and goal specification, visualized on the left side of the idealized teamwork process model (see Figure Figure3). 3 ). The results of these IPO cycles lay the foundation for gathering a good SA and initiating activities directed toward taskwork and goal accomplishment and therefore initiating action processes. The effective execution of action processes depends on the communication, coordination, cooperation, matching of information, and task prioritization as well as emergent team cognition variables (SSA and SMM) within the team. The results, like decisions, of these IPO cycles flow back into the next episode and may initiate further transition processes. In addition, interpersonal processes play a crucial role for complex problem solving teams. That means, conflict management, motivating and confidence building, and affect management are permanently important, no matter whether a team runs through transition or action phases and these interpersonal processes frame the whole idealized teamwork process model. Therefore, interpersonal processes are also able to impede successful teamwork at any point as breakdowns in conflict or affect management can lead to coordination breakdowns (Wilson et al., 2010 ) or problems with monitoring or backing up teammates (Marks et al., 2001 ). Thus, complex problem solving teams have to face these multidimensional team process demands in addition to cognitive challenges, e.g., information storage or retrieval (Hinsz et al., 1997 ), related to individual information processing.

The integration of transition, action, interpersonal, and learning processes into the model of an idealized teamwork process.
Team learning opportunities for handling complex problems
In order to support teams in handling complex situations or problems, learning opportunities seem to be very important for successful task accomplishment and for reducing possible negative effects of team process demands. Learning means any kind of relative outlasted changes in potential of human behavior that cannot be traced back to age-related changes (Bower and Hilgard, 1981 ; Bredenkamp, 1998 ). Therefore, Schmutz et al. ( 2016 ) amended the taxonomy of team processes developed by Marks et al. ( 2001 ) and added learning processes as a fourth category of processes, which occur during transition and action phases and contribute to overall team effectiveness. Learning processes (see also Edmondson, 1999 ) include observation, e.g., observing own and other team members' actions such as the teammate's positioning of firewalls in order to protect houses in case of firefighting, feedback, like giving a teammate information about the wind direction for effective positioning of firewalls, and reflection, e.g., talking about procedures for firefighting or refilling water tanks, for example, within the team. Learning from success and failure and identifying future problems is crucial for the effectiveness of complex problem solving teams and therefore possibilities for learning based on repetitive cycles of joint action or episodes and reflection of team members' activities during action and transition phases should be used effectively (Edmondson, 1999 ; Marks et al., 2001 ). The processes of the idealized teamwork model are embedded into these learning processes (see Figure Figure3 3 ).
The fulfillment of transition, action, interpersonal and learning processes contribute significantly to successful team performance in complex problem solving. For clustering these processes, transition and action processes could be seen as operational processes and interpersonal and learning process as support processes. When dealing with complex and dynamic situations teams have to face these team process demands more strongly than in non-complex situations. For example, goal specification and prioritization or strategy formulation, both aspects of transition processes, are strongly influenced by multiple goals, interconnectedness or dynamically and constantly changing conditions. The same is true for action processes, such as monitoring progress toward goals, team monitoring and backup behavior or coordination of interdependent actions. Interpersonal processes, such as conflict and affect management or confidence building enhance the demands put on team members compared to individuals working on complex problems. Interpersonal processes are essential for effective teamwork and need to be cultivated during episodes of team working, because breakdowns in confidence building or affect management can lead to coordination breakdowns or problems with monitoring or backing up teammates (Marks et al., 2001 ). Especially within complex situations aspects such as interdependence, delayed feedback, multiple goals and dynamic changes put high demands on interpersonal processes within teams. Learning processes, supporting interpersonal processes and the result of effective teamwork are e.g., observation of others' as well as own actions and receiving feedback by others or the system and are strongly influenced by situational characteristics such as non-transparency or delayed feedback concerning actions. It is assumed that amongst others team learning happens through repetitive cycles of joint action within the action phases and reflection of team members within the transition phases (Edmondson, 1999 ; Gabelica et al., 2014 ; Schmutz et al., 2016 ). The repetitive cycles help to generate SMM (Cannon-Bowers et al., 1993 ; Mathieu et al., 2000 ), SSA (Endsley and Robertson, 2000 ) or transactive memory systems (Hollingshead et al., 2012 ) within the team.
Emergent states in complex team work and the role of collective orientation
IPO models propose that input variables and emergent states are able to influence team processes and therefore outcomes such as team performance positively. Emergent states represent team members' attitudes or motivations and are “properties of the team that are typically dynamic in nature and vary as a function of team context, inputs, processes, and outcomes” (Marks et al., 2001 , p. 357). Both emergent states and interaction processes are relevant for team effectiveness (Kozlowski and Ilgen, 2006 ).
Emergent states refer to conditions that underlie and dynamically enable effective teamwork (DeChurch and Mesmer-Magnus, 2010 ) and can be differentiated from team process, which refers to interdependent actions of team members that transform inputs into outcomes based on activities directed toward task accomplishment (Marks et al., 2001 ). Emergent states mainly support the execution of behavioral processes (e.g., planning, coordination, backup behavior) during the action phase, meaning during episodes when members are engaged in acts that focus on task work and goal accomplishment. Emergent states like trust, cohesion and CO are “products of team experiences (including team processes) and become new inputs to subsequent processes and outcomes” (Marks et al., 2001 , p. 358). Trust between team members and cohesion within the team are emergent states that develop over time and only while experiencing teamwork in a specific team. CO is an emergent state that a team member brings along with him/her into the teamwork, is assumed to be more persistent than trust and cohesion, and can, but does not have to, be positively and negatively influenced by experiencing teamwork in a specific team for a while or by means of training (Eby and Dobbins, 1997 ; Driskell et al., 2010 ). Thus, viewing emergent states on a continuum, trust and cohesion are assumed more fluctuating than CO, but CO is much more sensitive to change and direct experience than a stable trait such as a personality trait.
CO of team members is one of the teamwork-relevant competencies that facilitates team processes, such as collecting and sharing information between team members, and positively affects the success of teams, as people who are high in CO work with others in a goal-oriented manner, seek others' input and contribute to team outcomes (Driskell et al., 2010 ). CO is an emergent state, as it can be an input variable as well as a teamwork outcome. CO is context-dependent, becomes visible in reactions to situations and people, and can be influenced by experience (e.g., individual learning experiences with various types of teamwork) or knowledge or training (Eby and Dobbins, 1997 ; Bell, 2007 ). CO enhances team performance through activating transition and action processes such as coordination, evaluation and consideration of task inputs from other team members while performing a team task (Driskell and Salas, 1992 ; Salas et al., 2005 ). Collectively oriented people effectively use available resources in due consideration of the team's goals, participate actively and adapt teamwork processes adequately to the situation.
Driskell et al. ( 2010 ) and Hagemann ( 2017 ) provide a sound overview of the evidence of discriminant and convergent validity of CO compared to other teamwork-relevant constructs, such as cohesion, also an emergent state, or cooperative interdependence or preference for solitude. Studies analyzing collectively and non-collectively oriented persons' decision-making in an interdependent task demonstrated that teams with non-collectively oriented members performed poorly in problem solving and that members with CO judged inputs from teammates as more valuable and considered these inputs more frequently (Driskell and Salas, 1992 ). Eby and Dobbins ( 1997 ) also showed that CO results in increased coordination among team members, which may enhance team performance through information sharing, goal setting and strategizing (Salas et al., 2005 ). Driskell et al. ( 2010 ) and Hagemann ( 2017 ) analyzed CO in relation to team performance and showed that the effect of CO on team performance depends on the task type (see McGrath, 1984 ). Significant positive relationships between team members' CO and performance were found in relation to the task types choosing/decision making and negotiating (Driskell et al., 2010 ) respectively choosing/decision making (Hagemann, 2017 ). These kinds of tasks are characterized by much more interdependence than task types such as executing or generating tasks. As research shows that the positive influence of CO on team performance unfolds especially in interdependent teamwork contexts (Driskell et al., 2010 ), which require more team processes such as coordination patterns (Van de Ven et al., 1976 ; Wageman, 1995 ) and necessitate mutual adjustments as well as frequent information integration within the team (Gibson, 1999 ; Stajkovic et al., 2009 ), CO might be vitally important for complex problem solving teams. Thus, CO as an emergent state of single team members might be a valuable resource for enhancing the team's performance when exposed to solving complex problems. Therefore, it will be of interest to analyze the influence of CO on team process demands such as coordination processes and performance within complex problem solving teams. We predict that the positive effect of CO on team performance is an indirect effect through coordination processes within the team, which are vitally important for teams working in intensive interdependent work contexts.
- Hypothesis 1: CO leads to a better coordination behavior, which in turn leads to a higher team performance.
As has been shown in team research that emergent states like trust and cohesion (see also Figure Figure1) 1 ) affect team performance, these two constructs are analyzed in conjunction with CO concerning action processes, such as coordination behavior and team performance. Trust between team members supports information sharing and the willingness to accept feedback, and therefore positively influences teamwork processes (McAllister, 1995 ; Salas et al., 2005 ). Cohesion within a team facilitates motivational factors and group processes like coordination and enhances team performance (Beal et al., 2003 ; Kozlowski and Ilgen, 2006 ).
- Hypothesis 2: Trust shows a positive relationship with (a) action processes (team coordination) and with (b) team performance.
- Hypothesis 3: Cohesion shows a positive relationship with (a) action processes (team coordination) and with (b) team performance.
Materials and methods
In order to demonstrate the importance of team process demands for complex problem solving in teams, we used a computer-based microworld in a laboratory study. We analyzed the effectiveness of complex problem solving teams while considering the influence of input variables, like collective orientation of team members and trust and cohesion within the team, on action processes within teams, like coordination.
The microworld for investigating teams process demands
We used the simulation-based team task C 3 Fire (Granlund et al., 2001 ; Granlund and Johansson, 2004 ), which is described as an intensive interdependence team task for complex problem solving (Arthur et al., 2005 ). C 3 Fire is a command, control and communications simulation environment that allows teams' coordination and communication in complex and dynamic environments to be analyzed. C 3 Fire is a microworld, as important characteristics of the real world are transferred to a small and well-controlled simulation system. The task environment in C 3 Fire is complex, dynamic and opaque (see Table Table1) 1 ) and therefore similar to the cognitive tasks people usually encounter in real-life settings, in and outside their work place (Brehmer and Dörner, 1993 ; Funke, 2001 ). Figure Figure4 4 demonstrates how the complexity characteristics mentioned in Table Table1 1 are realized in C 3 Fire. The screenshot represents the simulation manager's point of view, who is able to observe all units and actions and the scenario development. For more information about the units and scenarios, please (see the text below and the Supplementary Material). Complexity requires people to consider a number of facts. Because executed actions in C 3 Fire influence the ongoing process, the sequencing of actions is free and not stringent, such as a fixed (if X then Y) or parallel (if X then Y and Z) sequence (Ormerod et al., 1998 ). This can lead to stressful situations. Taking these characteristics of microworlds into consideration, team processes during complex problem solving can be analyzed within laboratories under controlled conditions. Simulated microworlds such as C 3 Fire allow the gap to be bridged between laboratory studies, which might show deficiencies regarding ecological validity, and field studies, which have been criticized due to their small amount of control (see Brehmer and Dörner, 1993 ).
Overview of complexity characteristics of microworlds in general and in C 3 Fire (cf. Funke, 2001 ).

Examples for the complexity characteristics in Table Table1 1 represented within a simulation scenario in C 3 Fire.
In C 3 Fire, the teams' task is to coordinate their actions to extinguish a forest fire whilst protecting houses and saving lives. The team members' actions are interdependent. The simulation includes, e.g., forest fires, houses, tents, gas tanks, different kinds of vegetation and computer-simulated agents such as firefighting units (Granlund, 2003 ). It is possible, for example, that the direction of wind will change during firefighting and the time until different kinds of vegetation are burned down varies between those. In the present study, two simulation scenarios were developed for two-person teams and consisted of two firefighting units, one mobile water tank unit (responsible for re-filling the firefighting units' water tanks that contain a predefined amount of water) and one fire-break unit (a field defended with a fire-break cannot be ignited; the fire spreads around its ends). The two developed scenarios lasted for 15 min maximum. Each team member was responsible for two units in each scenario; person one for firefighting and water tank unit and person two for firefighting and fire-break unit. The user interface was a map system (40 × 40 square grid) with all relevant geographic information and positions of all symbols representing houses, water tank units and so on. All parts of the map with houses and vegetation were visible for the subjects, but not the fire itself or the other units; instead, the subjects were close to them with their own units (restricted visibility field; 3 × 3 square grid). The simulation was run on computers networked in a client-server configuration. The subjects used a chat system for communication that was logged. For each scenario, C 3 Fire creates a detailed log file containing all events that occurred over the course of the simulation. Examples of the C 3 Fire scenarios are provided in the Figures S1 – 3 and a short introduction into the microworld is given in the video. Detailed information regarding the scenario characteristics are given in Table S1 . From scenario one to two, the complexity and interdependence increased.
Participants
The study was conducted from Mai 2014 until March 2015. Undergraduate and graduate students ( N = 116) studying applied cognitive sciences participated in the study (68.1% female). Their mean age was 21.17 years ( SD = 3.11). Participants were assigned to 58 two-person teams, with team assignments being based on the pre-measured CO values (see procedure). They received 2 hourly credits as a trial subject and giveaways such as pencils and non-alcoholic canned drinks. The study was approved by the university's ethics committee in February 2014.
The study was conducted within a laboratory setting at a university department for business psychology. Prior to the experiment, the participants filled in the CO instrument online and gave written informed consent (see Figure Figure5). 5 ). The median was calculated subsequently ( Md = 3.12; range: 1.69–4.06; scale range: 1–5) relating to the variable CO and two individuals with either high ( n = 58) or low ( n = 58) CO values were randomly matched as teammates. The matching process was random in part, as those two subjects were matched to form a team, whose preferred indicated time for participation in a specific week during data collection were identical. The participants were invited to the experimental study by e-mail 1–2 weeks after filling in the CO instrument. The study began with an introduction to the experimental procedure and the teams' task. The individuals received time to familiarize themselves with the simulation, received 20 min of training and completed two practice trials. After the training, participants answered a questionnaire collecting demographic data. Following this, a simulation scenario started and the participants had a maximum of 15 min to coordinate their actions to extinguish a forest fire whilst protecting houses and saving lives. After that, at measuring time T1, participants answered questionnaires assessing trust and cohesion within the team. Again, the teams worked on the following scenario 2 followed by a last round of questionnaires assessing trust and cohesion at T2.

Overview about the procedure and measures.
Demographic data such as age, sex, and study course were assessed after the training at the beginning of the experiment.
Collective Orientation was measured at an individual level with 16 items rated on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree ) developed by the authors (Hagemann, 2017 ) based on the work of Driskell et al. ( 2010 ). The factorial structure concerning the German-language CO scale was proven prior to this study (χ 2 = 162.25, df = 92, p = 0.000, χ 2 /df = 1.76, CFI = 0.97, TLI = 0.96, RMSEA = 0.040, CI = 0.030-0.051, SRMR = 0.043) and correlations for testing convergent and discriminant evidence of validity were satisfying. For example, CO correlated r = 0.09 ( p > 0.10) with cohesion, r = 0.34 ( p < 0.01) with cooperative interdependence and r = −0.28 ( p < 0.01) with preference for solitude (Hagemann, 2017 ). An example item is “ I find working on team projects to be very satisfying ”. Coefficient alpha for this scale was 0.81.
Trust in team members' integrity, trust in members' task abilities and trust in members' work-related attitudes (Geister et al., 2006 ) was measured with seven items rated on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree ). An example item is “ I can trust that I will have no additional demands due to lack of motivation of my team member .” Coefficient alpha for this scale was 0.83 (T1) and 0.87 (T2).
Cohesion was measured with a six-item scale from Riordan and Weatherly ( 1999 ) rated on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree to 5 = strongly agree ). An example item is “ In this team, there is a lot of team spirit among the members .” Coefficient alpha for this scale was 0.87 (T1) and 0.87 (T2).
Action process: coordination
Successful coordination requires mechanisms that serve to manage dependencies between the teams' activities and their resources. Coordination effectiveness was assessed based on the time the firefighting units spent without water in the field in relation to the total scenario time. This measure is an indicator of the effectiveness of resource-oriented coordination, as it reflects an efficient performance regarding the water refill process in C 3 Fire, which requires coordinated actions between the two firefighting units and one water tank unit (Lafond et al., 2011 ). The underlying assumption is that a more successful coordination process leads to fewer delays in conducting the refill process. Coordination was calculated by a formula and values ranged between 0 and 1, with lower values indicating better coordination in the team (see Jobidon et al., 2012 ).
Team performance
This measure related to the teams' goals (limiting the number of burned out cells and saving as many houses/buildings as possible) and was quantified as the number of protected houses and the number of protected fields and bushes/trees in relation to the number of houses, fields, and bushes/trees, respectively, which would burn in a worst case scenario. This formula takes into account that teams needing more time for firefighting also have more burning cells and show a less successful performance than teams that are quick in firefighting. To determine the worst case scenario, both 15-min scenarios were run with no firefighting action taken. Thus, the particularities (e.g., how many houses would burn down if no action was taken) of each scenario were considered. Furthermore, the houses, bushes/trees and fields were weighted according to their differing importance, mirroring the teams' goals. Houses should be protected and were most important. Bushes/trees (middle importance) burn faster than fields (lowest importance) and foster the expansion of the fire. Values regarding team performance ranged between 0 and 7.99, with higher values indicating a better overall performance. Team performance was calculated as follows (see Table Table2 2 ):
Explanation of formula for calculating team performance in both scenarios.
Means, standard deviations, internal consistencies, and correlations for all study variables are provided in Table Table3 3 .
Means, standard deviations, internal consistencies, and correlations for all study variables.
Performance range from 0 to 7.99; Time without Water range from 0 to 1 (lower values indicate a more effective handling of water); CO range from 1 to 5 .
Team complex problem solving in scenario 1 correlated significantly negative with time without water in scenario 1, indicating that a high team performance is attended by the coordination behavior (as a team process). The same was true for scenario 2. In addition, time without water as an indicator for team coordination correlated significantly negative with the team members' CO, indicating that team members with high CO values experience less time without water in the microworld than teams with members with low CO values.
In order to analyze the influence of CO on team process demands such as coordination processes and thereby performance within complex problem solving teams we tested whether CO would show an indirect effect on team performance through the teams' coordination processes. To analyze this assumption, indirect effects in simple mediation models were estimated for both scenarios (see Preacher and Hayes, 2004 ). The mean for CO was 3.44 ( SD = 0.32) for teams with high CO values and it was 2.79 ( SD = 0.35) for teams with low CO values. The mean concerning team performance in scenario 1 for teams with high CO values was 6.30 ( SD = 1.64) and with low CO values 5.35 ( SD = 2.30). The mean concerning time without water (coordination behavior) for teams with high CO values was 0.16 ( SD = 0.08) and with low CO values 0.20 ( SD = 0.09). In scenario 2 the mean for team performance was 6.26 ( SD = 2.51) for teams with high CO values and it was 4.36 ( SD = 2.24) for teams with low CO values. The mean concerning time without water for teams with high CO values was 0.18 ( SD = 0.08) and with low CO values 0.25 ( SD = 0.11).
For analyzing indirect effects, CO was the independent variable, time without water the mediator and team performance the dependent variable. The findings indicated that CO has an indirect effect on team performance mediated by time without water for scenario 1 (Table (Table4) 4 ) and scenario 2 (Table (Table5). 5 ). In scenario 1, CO had no direct effect on team performance ( b(YX) ), but CO significantly predicted time without water ( b(MX) ). A significant total effect ( b(YX) ) is not an assumption in the assessment of indirect effects, and therefore the non-significance of this relationship does not violate the analysis (see Preacher and Hayes, 2004 , p. 719). Furthermore, time without water significantly predicted team performance when controlling for CO ( b(YM.X) ), whereas the effect of CO on team performance was not significant when controlling for time without water ( b(YX.M) ). The indirect effect was 0.40 and significant when using normal distribution and estimated with the Sobel test ( z = 1.97, p < 0.05). The bootstrap procedure was applied to estimate the effect size not based on the assumption of normal distribution. As displayed in Table Table4, 4 , the bootstrapped estimate of the indirect effect was 0.41 and the true indirect effect was estimated to lie between 0.0084 and 0.9215 with a 95% confidence interval. As zero is not in the 95% confidence interval, it can be concluded that the indirect effect is indeed significantly different from zero at p < 0.05 (two-tailed).
Indirect Effect for Coordination and Team Performance in Scenario 1.
Y = Team Performance Scenario 1; X = Collective Orientation T0; M = Coordination (time without water in scenario 1); Number of Bootstrap Resamples 5000 .
Indirect Effect for Coordination and Team Performance in Scenario 2.
Y = Team Performance Scenario 2; X = Collective Orientation T0; M = Coordination (time without water in scenario 2); Number of Bootstrap Resamples 5000 .
Regarding scenario 2, CO had a direct effect on team performance ( b(YX) ) and on time without water ( b(MX) ). Again, time without water significantly predicted team performance when controlling for CO ( b(YM.X) ), whereas the effect of CO on team performance was not significant when controlling for time without water ( b(YX.M) ). This time, the indirect effect was 0.60 (Sobel test, z = 2.31, p < 0.05). As displayed in Table Table5, 5 , the bootstrapped estimate of the indirect effect was 0.61 and the true indirect effect was estimated to lie between 0.1876 and 1.1014 with a 95% confidence interval and between 0.0340 and 1.2578 with a 99% confidence interval. Because zero is not in the 99% confidence interval, it can be concluded that the indirect effect is indeed significantly different from zero at p < 0.01 (two-tailed).
The indirect effects for both scenarios are visualized in Figure Figure6. 6 . Summing up, the results support hypothesis 1 and indicate that CO has an indirect effect on team performance mediated by the teams' coordination behavior, an action process. That means, fulfilling team process demands affect the dynamic decision making quality of teams acting in complex situations and input variables such as CO influence the action processes within teams positively.

Indirect effect of collective orientation on team performance via coordination within the teams for scenario 1 and 2, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, numbers in italic represent results from scenario 2, non-italic numbers are from scenario 1.
Trust between team members assessed after scenario 1 (T1) and after scenario 2 (T2) did not show any significant correlation with the coordination behavior or with team complex problem solving in scenarios 1 and 2 (Table (Table3). 3 ). Thus, hypotheses 2a and 2b are not supported. Cohesion at T1 showed no significant relationship with team performance in both scenarios, one significant negative correlation ( r = −0.22, p < 0.05) with the coordination behavior in scenario 1 and no correlation with the coordination behavior in scenario 2. Cohesion at T2 did not show any significant correlation with the coordination behavior or with team performance in both scenarios. Thus, hypotheses 3a and 3b could also not be supported. Furthermore, the results showed no significant relations between CO and trust and cohesion. The correlations between trust and cohesion ranged between r = 0.39 and r = 0.51 ( p < 0.01).
The purpose of our paper was first to give a sound theoretical overview and to combine theoretical approaches about team competencies and team process demands in collaborative complex problem solving and second to demonstrate the importance of selected team competencies and processes on team performance in complex problem solving by means of results from a laboratory study. We introduced the model of an idealized teamwork process that complex problem solving team pass through and integrated the relevant teamwork skills for interdependently working teams into it. Moreover, we highlighted the episodic aspect concerning complex problem solving in teams and combined the well-known transition, action, interpersonal and learning processes of teamwork with the idealized teamwork process model. Finally, we investigated the influence of trust, cohesion, and CO on action processes, such as coordination behavior of complex problem solving teams and on team performance.
Regarding hypothesis 1, studies have indicated that teams whose members have high CO values are more successful in their coordination processes and task accomplishment (Eby and Dobbins, 1997 ; Driskell et al., 2010 ; Hagemann, 2017 ), which may enhance team performance through considering task inputs from other team members, information sharing and strategizing (Salas et al., 2005 ). Thus, we had a close look on CO as an emergent state in the present study, because emergent states support the execution of behavioral processes. In order to analyze this indirect effect of CO on team performance via coordination processes, we used the time, which firefighters spent without water in a scenario, as an indicator for high-quality coordination within the team. A small amount of time without water represents sharing information and resources between team members in a reciprocal manner, which are essential qualities of effective coordination (Ellington and Dierdorff, 2014 ). One of the two team members was in charge of the mobile water tank unit and therefore responsible for filling up the water tanks of his/her own firefighting unit and that of the other team member on time. In order to avoid running out of water for firefighting, the team members had to exchange information about, for example, their firefighting units' current and future positions in the field, their water levels, their strategies for extinguishing one or two fires, and the water tank unit's current and future position in the field. The simple mediation models showed that CO has an indirect effect on team performance mediated by time without water, supporting hypothesis 1. Thus, CO facilitates high-quality coordination within complex problem solving teams and this in turn influences decision-making and team performance positively (cf. Figure Figure1). 1 ). These results support previous findings concerning the relationships between emergent states, such as CO, and the team process, such as action processes like coordination (Cannon-Bowers et al., 1995 ; Driskell et al., 2010 ) and between the team process and the team performance (Stevens and Campion, 1994 ; Dierdorff et al., 2011 ).
Hypotheses 2 and 3 analyzed the relationships between trust and cohesion and coordination and team performance. Because no correlations between trust and cohesion and the coordination behavior and team complex problem solving existed, further analyses, like mediation analyses, were unnecessary. In contrast to other studies (McAllister, 1995 ; Beal et al., 2003 ; Salas et al., 2005 ; Kozlowski and Ilgen, 2006 ), the present study was not able to detect effects of trust and cohesion on team processes, like action processes, or on team performance. This can be attributed to the restricted sample composition or the rather small sample size. Nevertheless, effect sizes were small to medium, so that they would have become significant with an increased sample sizes. The prerequisite, mentioned by the authors, that interdependence of the teamwork is important for identifying those effects, was given in the present study. Therefore, this aspect could not have been the reason for finding no effects concerning trust and cohesion. Trust and cohesion within the teams developed during working on the simulation scenarios while fighting fires, showed significant correlations with each other, and were unrelated to CO, which showed an effect on the coordination behavior and the team performance indeed. The results seem to implicate, that the influence of CO on action processes and team performance might be much more stronger than those of trust and cohesion. If these results can be replicated should be analyzed in future studies.
As the interdependent complex problem-solving task was a computer-based simulation, the results might have been affected by the participants' attitudes to using a computer. For example, computer affinity seems to be able to minimize potential fear of working with a simulation environment and might therefore, be able to contribute to successful performance in a computer-based team task. Although computers and other electronic devices are pervasive in present-day life, computer aversion has to be considered in future studies within complex problem-solving research when applying computer-based simulation team tasks. As all of the participants were studying applied cognitive science, which is a mix of psychology and computer science, this problem might not have been influenced the present results. However, the specific composition of the sample reduces the external validity of the study and the generalizability of the results. A further limitation is the small sample size, so that moderate to small effects are difficult to detect.
Furthermore, laboratory research of teamwork might have certain limitations. Teamwork as demonstrated in this study fails to account for the fact that teams are not simple, static and isolated entities (McGrath et al., 2000 ). The validity of the results could be reduced insofar as the complex relationships in teams were not represented, the teamwork context was not considered, not all teammates and teams were comparable, and the characteristic as a dynamic system with a team history and future was not given in the present study. This could be a possible explanation why no effects of trust and cohesion were found in the present study. Maybe, the teams need more time working together on the simulation scenarios in order to show that trust and cohesion influence the coordination with the team and the team performance. Furthermore, Bell ( 2007 ) demonstrated in her meta-analysis that the relationship between team members' attitudes and the team's performance was proven more strongly in the field compared to the laboratory. In consideration of this fact, the findings of the present study concerning CO are remarkable and the simulation based microworld C3Fire (Granlund et al., 2001 ; Granlund, 2003 ) seems to be appropriate for analyzing complex problem solving in interdependently working teams.
An asset of the present study is, that the teams' action processes, the coordination performance, was assessed objectively based on logged data and was not a subjective measure, as is often the case in group and team research studies (cf. Van de Ven et al., 1976 ; Antoni and Hertel, 2009 ; Dierdorff et al., 2011 ; Ellington and Dierdorff, 2014 ). As coordination was the mediator in the analysis, this objective measurement supports the validity of the results.
As no transition processes such as mission analysis, formulation, and planning (Prince and Salas, 1993 ), goal specification (Prussia and Kinicki, 1996 ), and strategy formulation (Prince and Salas, 1993 ; Cannon-Bowers et al., 1995 ) as well as action processes such as monitoring progress toward goals (Cannon-Bowers et al., 1995 ) and systems monitoring (Fleishman and Zaccaro, 1992 ) were analyzed within the present study, future studies should collect data concerning these processes in order to show their importance on performance within complex problem solving teams. Because these processes are difficult to observe, subjective measurements are needed, for example asking the participants after each scenario how they have prioritized various tasks, if and when they have changed their strategy concerning protecting houses or fighting fires, and on which data within the scenarios they focused for collecting information for goal and systems monitoring. Another possibility could be using eye-tracking methods in order to collect data about collecting information for monitoring progress toward goals, e.g., collecting information how many cells are still burning, and systems monitoring, e.g., tracking team resources like water for firefighting.
CO is an emergent state and emergent states can be influenced by experience or learning, for example (Kozlowski and Ilgen, 2006 ). Learning processes (Edmondson, 1999 ), that Schmutz et al. ( 2016 ) added to the taxonomy of team processes developed by Marks et al. ( 2001 ) and which occur during transition and action phases and contribute to team effectiveness include e.g., feedback . Feedback can be useful for team learning when team learning is seen as a form of information processing (Hinsz et al., 1997 ). Because CO supports action processes, such as coordination and it can be influenced by learning, learning opportunities, such as feedback, seem to be important for successful task accomplishment and for supporting teams in handling complex situations or problems. If the team is temporarily and interpersonally unstable, as it is the case for most of the disaster or crisis management teams dealing with complex problems, there might be less opportunities for generating shared mental models by experiencing repetitive cycles of joint action (cf. Figure Figure2) 2 ) and strategies such as cross training (Salas et al., 2007 ) or feedback might become more and more important for successful complex problem solving in teams. Thus, for future research it would be of interest to analyze what kind of feedback is able to influence CO positively and therefore is able to enhance coordination and performance within complex problem-solving teams.
Depending on the type of feedback, different main points will be focused during the feedback (see Gabelica et al., 2012 ). Feedback can be differentiated into performance and process feedback. Process feedback can be further divided into task-related and interpersonal feedback. Besides these aspects, feedback can be given on a team-level or an individual-level. Combinations of the various kinds of feedback are possible and are analyzed in research concerning their influence on e.g., self- and team-regulatory processes and team performance (Prussia and Kinicki, 1996 ; Hinsz et al., 1997 ; Jung and Sosik, 2003 ; Gabelica et al., 2012 ). For future studies it would be relevant to analyze, whether it is possible to positively influence the CO of team members and therefore action processes such as coordination and team performance or not. A focus could be on the learning processes, especially on feedback, and its influence on CO in complex problem solving teams. So far, no studies exist that analyzed the relationship between feedback and a change in CO, even though researchers already discuss the possibility that team-level process feedback shifts attention processes on team actions and team learning (McLeod et al., 1992 ; Hinsz et al., 1997 ). These results would be very helpful for training programs for fire service or police or medical teams working in complex environments and solving problems collaboratively, in order to support their team working and their performance.
In summary, the idealized teamwork process model is in combination with the transition, action, interpersonal and learning processes a good framework for analyzing the impact of teamwork competencies and teamwork processes in detail on team performance in complex environments. Overall, the framework offers further possibilities for investigating the influence of teamwork competencies on diverse processes and teamwork outcomes in complex problem solving teams than demonstrated here. The results of our study provide evidence of how CO influences complex problem solving teams and their performance. Accordingly, future researchers and practitioners would be well advised to find interventions how to influence CO and support interdependently working teams.
Ethics statement
This study was carried out in accordance with the recommendations of Ethical guidelines of the German Association of Psychology, Ethics committee of the University of Duisburg-Essen, Department of Computer Science and Applied Cognitive Science with written informed consent from all subjects. All subjects gave written informed consent in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocol was approved by the Ethics committee of the University of Duisburg-Essen, Department of Computer Science and Applied Cognitive Science.
Author contributions
VH and AK were responsible for the conception of the work and the study design. VH analyzed and interpreted the collected data. VH and AK drafted the manuscript. They approved it for publication and act as guarantors for the overall content.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.

Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.01730/full#supplementary-material
- Antoni C., Hertel G. (2009). Team processes, their antecedents and consequences: implications for different types of teamwork . Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 18 , 253–266. 10.1080/13594320802095502 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Arthur W., Edwards B., Bell S., Villado A., Bennet W. (2005). Team task analysis: identifying tasks and jobs that are team based . Hum. Factors 47 , 654–669. 10.1518/001872005774860087 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Badke-Schaub P. (2008). Teamarbeit und Teamführung: Erfolgsfaktoren und sicheres Handeln. [Teamwork and Team leadership: Factors of success and reliable action] , in Führung und Teamarbeit in kritischen Situationen [Leadership and teamwork in critical situations] eds Buerschaper C., Starke S. (Frankfurt: Verlag für Polizeiwissenschaft; ), 3–19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Beal D. J., Cohen R. R., Burke M. J., McLendon C. L. (2003). Cohesion and performance in groups: a meta-analytic clarification of construct relations . J. Appl. Psychol. 88 , 989–1004. 10.1037/0021-9010.88.6.989 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bell S. T. (2007). Deep-level composition variables as predictors of team performance: a meta-analysis . J. Appl. Psychol. 92 , 595–615. 10.1037/0021-9010.92.3.595 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bower G. H., Hilgard E. R. (1981). Theories of Learning . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bredenkamp J. (1998). Lernen, Erinnern, Vergessen [Learning, Remembering, Forgetting]. München: C.H. Beck. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brehmer B. (1992). Dynamic decision-making: human control of complex systems . Acta Psychol. 81 , 211–241. 10.1016/0001-6918(92)90019-A [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brehmer B., Dörner D. (1993). Experiments with computer-simulated microworlds: escaping both the narrow straits of the laboratory and the deep blue sea of the field study . Comput. Hum. Behav. 9 , 171–184. 10.1016/0747-5632(93)90005-D [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Campion M. A., Medsker G. J., Higgs C. (1993). Relations between work group characteristics and effectiveness: implications for designing effective work groups . Pers. Psychol. 46 , 823–850. 10.1111/j.1744-6570.1993.tb01571.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Cannon-Bowers J. A., Salas E., Converse S. (1993). Shared mental models in expert team decision making , in Individual and Group Decision Making , ed Castellan N. J. (Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; ), 221–246. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cannon-Bowers J. A., Tannenbaum S. I., Salas E., Volpe C. E. (1995). Defining competencies and establishing team training requirements , in Team Effectiveness and Decision Making in Organizations , eds Guzzo R. A., E. Salas and Associates (San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass; ), 333–380. [ Google Scholar ]
- DeChurch L. A., Mesmer-Magnus J. R. (2010). The cognitive underpinnings of effective teamwork: a meta-analysis . J. Appl. Psychol. 95 , 32–53. 10.1037/a0017328 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dierdorff E. C., Bell S. T., Belohlav J. A. (2011). The “power of we”: effects of psychological collectivism on team performance over time . J. Appl. Psychol. 96 , 247–262. 10.1037/a0020929 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dörner D. (1989/2003). Die Logik des Misslingens. Strategisches Denken in komplexen Situationen [The logic of failure. Strategic thinking in complex situations] 11th Edn . Reinbeck: rororo. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dörner D., Kreuzig H. W., Reither F., Stäudel T. (1983). Lohhausen. Vom Umgang mit Unbestimmtheit und Komplexität. Bern; Stuttgart; Wien: Verlag Hans Huber. [ Google Scholar ]
- Driskell J. E., Salas E. (1992). Collective behavior and team performance . Hum. Factors 34 , 277–288. 10.1177/001872089203400303 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Driskell J., Salas E., Hughes S. (2010). Collective orientation and team performance: development of an individual differences measure . Hum. Factors 52 , 316–328. 10.1177/0018720809359522 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Eby L. T., Dobbins G. H. (1997). Collectivistic orientation in teams: an individual and group-level analysis . J. Organ. Behav. 18 , 275–295. 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1379(199705)18:3<275::AID-JOB796>3.0.CO;2-C [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edmondson A. (1999). Psychological safety and learning behavior in work teams . Adm. Sci. Q. 44 , 350–383. 10.2307/2666999 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellington J. K., Dierdorff E. C. (2014). Individual learning in team training: self-regulation and team context effects . Small Group Res. 45 , 37–67. 10.1177/1046496413511670 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Endsley M. R. (1999). Situation Awareness in Aviation Systems , in Handbook of Aviation Human Factors , eds Garland D. J., Wise J. A., Hopkin V. D. (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers; ), 257–276. [ Google Scholar ]
- Endsley M. R., Robertson M. M. (2000). Training for Situation Awareness in Individuals and Teams , in Situation awareness Analysis and Measurement , eds Endsley M. R., Garland D. J. (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers; ), 349–365. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fiore S. M., Rosen M. A., Smith-Jentsch K. A., Salas E., Letsky M., Warner N. (2010). Toward an understanding of macrocognition in teams: predicting processes in complex collaborative contexts . Hum. Factors 52 , 203–224. 10.1177/0018720810369807 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fleishman E. A., Zaccaro S. J. (1992). Toward a taxonomy of team performance funtions , in Teams: Their Training and Performance , eds Swezey R. W., Salas E. (Norwood, NJ: Ables; ), 31–56. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flin R., O'Connor P., Crichton M. (2008). Safety at the Sharp End. Aldershot: Ashgate. [ Google Scholar ]
- Funke J. (1995). Experimental research on complex problem solving , in Complex Problem Solving: The European Perspective eds Frensch P. A., Funke J. (Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; ), 243–268. [ Google Scholar ]
- Funke J. (2001). Daynamic systems as tools for analysing human judgement . Think. Reason. 7 , 69–89. 10.1080/13546780042000046 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Funke J. (2012). Complex Problem Solving , in Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning ed Seel N. M. (Heidelberg: Springer; ), 682–685. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gabelica C., van den Bossche P., de Maeyer S., Segers M., Gijselaers W. (2014). The effect of team feedback and guided reflexivity on team performance change . Learn. Instruct. 34 , 86–96. 10.1016/j.learninstruc.2014.09.001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gabelica C., Van den Bossche P., Segers M., Gijselaers W. (2012). Feedback, a powerful lever in teams: a review . Educ. Res. Rev. 7 , 123–144. 10.1016/j.edurev.2011.11.003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Geister S., Konradt U., Hertel G. (2006). Effects of process feedback on motivation, satisfaction, and performance in virtual teams . Small Group Res. 37 , 459–489. 10.1177/1046496406292337 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gibson C. B. (1999). Do they do what they believe they can? group efficacy and group effectiveness across tasks and cultures . Acad. Manag. J. 42 , 138–152. 10.2307/257089 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Granlund R. (2003). Monitoring experiences from command and control research with the C 3 Fire microworld . Cogn. Technol. Work 5 , 183–190. 10.1007/s10111-003-0129-8 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Granlund R., Johansson B. (2004). Monitoring distributed collaboration in the C 3 Fire Microworld , in Scaled Worlds: Development, Validation and Applications , eds Schiflett G., Elliot L. R., Salas E., Coovert M. D. (Aldershot: Ashgate; ), 37–48. [ Google Scholar ]
- Granlund R., Johansson B., Persson M. (2001). C3Fire a micro-world for collaboration training and investigations in the ROLF environment , in Proceedings of 42nd Conference on Simulation and Modeling: Simulation in Theory and Practice (Porsgrunn: ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Hackman J. R. (1987). The design of work teams , in Handbook of Organizational Behavior ed Lorsch J. W. (Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall; ), 315–342. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hagemann V. (2011). Trainingsentwicklung für High Responsibility Teams [Training development for High Responsibility Teams] . Lengerich: Pabst Verlag. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hagemann V. (2017). Development of a German-language questionnaire to measure collective orientation as an individual attitude . Swiss J. Psychol. 76 , 91–105. 10.1024/1421-0185/a000198 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hagemann V., Kluge A., Ritzmann S. (2011). High responsibility teams - Eine systematische Analyse von Teamarbeitskontexten für einen effektiven Kompetenzerwerb [A systematic analysis of teamwork contexts for effective competence acquisition] . Psychologie des Alltagshandelns 4 , 22–42. Available online at: http://www.allgemeine-psychologie.info/cms/images/stories/allgpsy_journal/Vol%204%20No%201/hagemann_kluge_ritzmann.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Hagemann V., Kluge A., Ritzmann S. (2012). Flexibility under complexity: work contexts, task profiles and team processes of high responsibility teams . Empl. Relat. 34 , 322–338. 10.1108/01425451211217734 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hertel G., Konradt U., Orlikowski B. (2004). Managing distance by interdependence: goal setting, task interdependence, and team-based rewards in virtual teams . Euro. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 13 , 1–28. 10.1080/13594320344000228 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hinsz V., Tindale R., Vollrath D. (1997). The emerging concept of groups as information processors . Psychol. Bull. 121 , 43–64. 10.1037/0033-2909.121.1.43 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hollingshead A. B., Gupta N., Yoon K., Brandon D. (2012). Transactive memory theory and teams: past, present, and future , in Theories of Team Cognition , eds Salas E., Fiore S. M., Letsky M. (New York, NY: Routledge Taylor & Francis Group; ), 421–455. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ilgen D. R., Hollenbeck J. R., Johnson M., Jundt D. (2005). Teams in organizations: from input-process-output models to IMOI models . Annu. Rev. Psychol. 56 , 517–543. 10.1146/annurev.psych.56.091103.070250 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jobidon M.-E., Muller-Gass A., Duncan M., Blais A.-R. (2012). The enhance of mental models and its impact on teamwork . Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet. 56 , 1703–1707. 10.1177/1071181312561341 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jung D. I., Sosik J. J. (2003). Group potency and collective efficacy . Group Organ. Manage. 28 , 366–391. 10.1177/1059601102250821 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kluge A. (2014). The Acquisition of Knowledge and Skills for Taskwork and Teamwork to Control Complex Technical Systems: A Cognitive and Macroergonomics Perspective . Dordrecht: Springer. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kluge A., Hagemann V., Ritzmann S. (2014). Military crew resource management – Das Streben nach der bestmöglichen Teamarbeit [Striving for the best of teamwork] , in Psychologie für Einsatz und Notfall [Psychology for mission and emergency] , eds Kreim G., Bruns S., Völker B. (Bonn: Bernard & Graefe in der Mönch Verlagsgesellschaft mbH; ), 141–152. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kluge A., Sauer J., Schüler K., Burkolter D. (2009). Designing training for process control simulators: a review of empirical findings and current practices, theoretical issues in ergonomics Science 10 , 489–509. 10.1080/14639220902982192 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kozlowski S. W. J., Ilgen D. R. (2006). Enhancing the effectiveness of work groups and teams . Psychol. Sci. Public Interest 7 , 77–124. 10.1111/j.1529-1006.2006.00030.x [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lafond D., Jobidon M.-E., Aubé C., Tremblay S. (2011). Evidence of structure- specific teamwork requirements and implications for team design . Small Group Res. 42 , 507–535. 10.1177/1046496410397617 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marks M. A., Mathieu J. E., Zaccaro S. J. (2001). A temporally based framework and taxonomy of team processes . Acad. Manag. Rev. 26 , 356–376. 10.2307/259182 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mathieu J. E., Heffner T. S., Goodwin G. F., Salas E., Cannon-Bowers J. A. (2000). The influence of shared mental models on team process and performance . J. Appl. Psychol. 85 , 273–283. 10.1037/0021-9010.85.2.273 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McAllister D. J. (1995). Affect- and cognition-based trust as foundations for interpersonal cooperation in organizations . Acad. Manag. J. 38 , 24–59. 10.2307/256727 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McGrath J. E. (1984). Groups: Interaction and Performance . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall. [ Google Scholar ]
- McGrath J. E., Arrow H., Berdahl J. L. (2000). The study of groups: past, present, and future . Pers. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 4 , 95–105. 10.1207/S15327957PSPR0401_8 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McLeod P. L., Liker J. K., Lobel S. A. (1992). Process feedback in task groups: an application of goal setting . J. Appl. Behav. Sci. 28 , 15–41. 10.1177/0021886392281003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan B. B., Salas E., Glickman A. S. (1993). An analysis of team evolution and maturation . J. Gen. Psychol. 120 , 277–291. 10.1080/00221309.1993.9711148 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ormerod T. C., Richardson J., Shepherd A. (1998). Enhancing the usability of a task analysis method: a notation and environment for requirements specification . Ergonomics 41 , 1642–1663. 10.1080/001401398186117 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Preacher K., Hayes A. (2004). SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models . Behav. Res. Methods Instrum. Comput. 36 , 717–731. 10.3758/BF03206553 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Prince C., Salas E. (1993). Training and research for teamwork in the military aircrew , in Cockpit Resource Management , eds Wiener E. L., Kanki B. G., Helmreich R. L. (San Diego, CA: Academic Press; ), 337–366. [ Google Scholar ]
- Prussia G. E., Kinicki A. J. (1996). A motivation investigation of group effectiveness using social-cognitive theory . J. Appl. Psychol. 81 , 187–198. 10.1037/0021-9010.81.2.187 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Riordan C. M., Weatherly E. W. (1999). Defining and measuring employees‘identification with their work groups . Educ. Psychol. Meas. 59 , 310–324. 10.1177/00131649921969866 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roth E. M., Woods D. D. (1988). Aiding human performance i: cognitive analysis . Trav. Hum. 51 , 39–64. [ Google Scholar ]
- Salas E., Cooke N. J., Rosen M. A. (2008). On teams, teamwork, and team performance: discoveries and developments . Hum. Factors 50 , 540–547. 10.1518/001872008X288457 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salas E., Nichols D. R., Driskell J. E. (2007). Testing three team training strategies in intact teams . Small Group Res. 38 , 471–488. 10.1177/1046496407304332 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Salas E., Sims D., Burke S. (2005). Is there a “big five” in teamwork? Small Group Res. 36 , 555–599. 10.1177/1046496405277134 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schmutz J., Welp A., Kolbe M. (2016). Teamwork in healtcare organizations , in Management Innovations for Health Care Organizations , eds Örtenblad A., Löfström C. A., Sheaff R. (New York, NY: Routledge Taylor & Francis; ), 359–377. [ Google Scholar ]
- Serfaty D., Entin E. E., Johnston J. H. (1998). Team coordination training , in Making Decisions Under Stress , eds Cannon-Bowers J. A., Salas E. (Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; ), 221–246. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shea G. P., Guzzo R. A. (1987). Group effectiveness: what really matters? Sloan Manage. Rev. 28 , 25–31. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith-Jentsch K. A., Baker D. P., Salas E., Cannon-Bowers J. A. (2001). Uncovering differences in team competency requirements: The case of air traffic control teams , in Improving Teamwork in Organizations. Applications of Resource Management Training , eds Salas E., Bowers C. A., Edens E. (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers; ), 31–54. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stajkovic A. D., Lee D., Nyberg A. J. (2009). Collective efficacy, group potency, and group performance: meta-analyses of their relationships, and test of a mediation model . J. Appl. Psychol. 94 , 814–828. 10.1037/a0015659 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stevens M. J., Campion M. A. (1994). The knowledge, skill, and ability requirements for teamwork: implications for human resource management . J. Manage. 20 , 503–530. 10.1177/014920639402000210 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ulich E. (1995). Gestaltung von Arbeitstätigkeiten [Designing job tasks] , in Lehrbuch Organisationspsychologie [Schoolbook Organizational Psychology] , ed Schuler H. (Bern: Huber; ), 189–208. [ Google Scholar ]
- Van de Ven A. H., Delbecq A. L., Koenig R. (1976). Determinants of coordination modes with organizations . Am. Sociol. Rev. 41 , 322–338. 10.2307/2094477 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wageman R. (1995). Interdependence and group effectiveness . Adm. Sci. Q. 40 , 145–180. 10.2307/2393703 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Waller M. J., Gupta N., Giambatista R. C. (2004). Effects of adaptive behaviors and shared mental models on control crew performance . Manage. Sci. 50 , 1534–1544. 10.1287/mnsc.1040.0210 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilson K. A., Salas E., Andrews D. H. (2010). Preventing errors in the heat of the battle: formal and informal learning strategies to prevent teamwork breakdowns , in Human Factors Issues in Combat Identification , eds Andrews D. H., Herz R. P., Wolf M. B. (Aldershot: Ashgate; ), 1–28. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zsambok C. E. (1997). Naturalistic decision making: where are we now? , in Naturalistic Decision Making , eds Zsambok C. E., Klein G. (New York, NY: Routledge; ), 3–16. [ Google Scholar ]

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Case Study #1
Erika pribanic-smith, department of communication, project description.
My goal was to determine if interventions to improve team cohesion through interpersonal communication would result in better team performance as measured by presentation cohesiveness on the final project. I conducted this assessment in a required course for all majors in the Department of Communication. Initial enrollment for the course was 123 students; four withdrew before the semester ended, and nine additional students stopped attending class but did not drop.
Each semester, students self-select into teams of 6-7 students on the first day of class. Students work in these teams throughout the semester on discussion exercises after lecture, team quizzes, and ultimately, a team presentation. In previous semesters, teams that communicated well with each other delivered excellent presentations, but most delivered the dreaded “patchwork project”; team members independently completed their tasks and then cobbled everything together at the last minute without knowing what others on the team were doing. Furthermore, Student Feedback Surveys indicated that a few students loved the team aspect of the course, but many hated it.
Employing team cohesion literature as well as Decision Emergence and Social Penetration theories, I hypothesized that developing stronger interpersonal ties among teammates via self-disclosure would assist in developing team cohesion, which in turn would motivate students to achieve team goals as a unit and keep each other accountable. I encouraged self-disclosure by developing discussion exercises that required students to come up with examples from their own lives for theoretical application. The disclosures grew more personal over the first half of the semester, starting with “Describe a situation in which you were misunderstood” (General Semantics Theory) and progressing to “Describe a situation in which someone shared your secret or you shared someone else’s” (Communication Privacy Management). A second intervention I employed to improve communication involved guided in-class team meetings, in which I assigned specific tasks related to the presentation assignment and provided instruction on the teamwork behaviors that should be exhibited at that stage of the project.
To measure team cohesion, students completed a team cohesion assessment survey (adapted from a Group Communication textbook’s team cohesion index) at four points during the semester: Week 2, Week 6, Week 10, and Week 14; the index consisted of 20 Likert-scale questions and one open-response question (“Is there anything you’d like to add?”). A Toastmasters list of criteria for group presentation cohesiveness was converted into a rubric for analyzing team performance on the final presentation.
Project Evaluation
Overall, the team cohesion assessment revealed a steady decline in team cohesion from the Week 2 survey to the Week 10 survey, then a spike between the Week 10 and Week 14 surveys. However, the literature recommends assessing team cohesion at both the individual level and the group level, and each level of analysis told a slightly different story in this project. The assessment survey included both individual-level and group-level questions, such that most individual-level questions (e.g., “I identify with the team and its members”) had a group-level counterpart (e.g., “Members of the team identify with the team”). The index of questions that gauged individual team members’ level of connection and commitment to the team demonstrated a relatively even measure of cohesion across the first three surveys with a slight bump in the second survey; the individual-level index rose sharply for the fourth survey. However, the index of questions that asked students to assess their fellow team members’ level of connection and commitment to the team sharply declined from Week 2 to Week 6, stayed nearly the same from Week 6 to Week 10, and then sharply rose by Week 14. In each survey, the individual-level index was higher than the group-level index, though the two indices were closer at Weeks 2 and 14 than in Weeks 6 and 10. (See figure below.)
Significantly, the Week 6 survey coincided with a presentation progress report deadline, and the Week 10 survey occurred around the deadline for teams’ presentation outlines. The open-ended responses at Week 10 in particular indicated that tensions were running high on teams in which students perceived their teammates were not doing their parts to complete the work. The Week 14 survey fell in the middle of presentations, and the overwhelming success of the presentations seems to have generated good will among most of the respondents.
Only one out of the 20 teams failed to score 100 percent on the presentation cohesiveness rubric, for an overall average of 96.4 percent (per Blackboard statistics). Nearly all of the presentations had good flow, consistent visuals (design of each PowerPoint slide), and consistent voice. In most cases, each teammate demonstrated knowledge of what each other teammate was doing. The presentations were tight and well-rehearsed. In short, most teams met the criteria for presentation cohesiveness. However, some went well beyond the Toastmasters criteria. Some teams coordinated their wardrobes; a few even coordinated the size and color of their notecards. Overall, with only one exception, the presentations were engaging and informative. Anecdotally speaking, they were the best presentations I have seen in my seven years teaching theory at UTA. A few even drew enthusiastic ovations from their peers.
Therefore, the class achieved the ultimate goal of cohesive team presentations, and despite dips in the middle, team cohesion was higher at the end of the semester than at the start. I do not believe the self-disclosure intervention affected team cohesion as anticipated, however. Reflections submitted the last week of the semester revealed that several students learned communication is a crucial part of effective teamwork, and some students even indicated that getting to know their teammates made a difference. I think much of that communication and bonding occurred outside of class, though. More significantly, because the team cohesion index increased amid successful presentations, team achievement affected team cohesion more than team cohesion affected team performance. I believe improved communication affected presentation cohesiveness directly rather than affecting team cohesion as a mediating factor .
Though a few students stubbornly insist that teamwork is terrible and they do better work on their own, the end-of-semester reflection responses were overwhelmingly positive, demonstrating that students found the teamwork experience this semester to be not only valuable but also enjoyable. Several students indicated they made close friends or at least expanded their campus network, and some said they loved the class because of their teams. (See responses to the teamwork reflection in Appendix A.)
In sum, I believe the project was successful, not only at improving the team presentations but also at improving most of my students’ ability to work in teams and their view of teamwork in an academic setting.
Despite the successes outlined above, some issues arose that limited the development of team cohesion in some teams and specifically hampered the self-disclosure intervention. These are issues I hope to address in future semesters:
- Several students were absent the first class, and a handful missed the whole first week. Therefore, some students were placed into groups that already had formed and were not able to self-select into teams, and a few of those students were vocal about disliking the teams to which I assigned them. Significantly, the one team that consisted entirely of people who first attended on the second day of class had a disastrous presentation, and direct communication with some of the students on that team revealed they never gelled.
- Attendance throughout the semester became an issue for multiple teams. Based on open-ended survey responses, some students who missed a lot of class did not bond with their teammates as much as students who did attend, and those students also missed a lot of the decision-making and task-planning for the presentation, so they were not as involved or invested in the project as other team members.
- Some teams did not fully and properly engage in the self-disclosure exercises. I eventually discovered that some teams skipped the discussion altogether and just had the person who was providing the real-life example write out the discussion report due at the end of class to save time. Therefore, the members of those teams weren’t learning about each other at all; they just treated the exercise as something they had to turn in for a participation grade. Furthermore, although a different person was supposed to provide an example each time so that everyone was disclosing about themselves, some groups had the same person sharing an example every time.
- Attrition occurred on a handful of teams as some students officially dropped the class or simply stopped coming. Two teams suffered severely; both began the semester with seven members, but one presented with three members at the semester’s end, and another ended the term with only two members. Those few teammates certainly bonded, but their view of the team experience was negative.
Future Direction
Given the general success of this project, I will continue emphasizing communication in future semesters. However, to overcome some of the issues I encountered this semester, I will make a few changes.
- I feel self-selection works great for the most part. However, I will shift team selection to the second day of class to reduce the number of students who are absent at the time of selection and do not get to select their own teams.
- I will monitor the self-disclosure exercises more closely to ensure that teams are a) actually discussing and b) distributing the self-disclosure across team members more evenly. Though it will make attendance record-keeping more difficult and eliminate a valuable check on students’ understanding of the concepts, I will consider doing away with the written report so that students are more focused on the discussion and not just submitting something for a grade.
- I will have more in-class team meetings. We only had three this semester, and they were in the last half-hour of quiz days because I knew most students would be present for the quizzes. Some students stated in their open-ended responses that coordinating schedules outside of class was difficult, though, and they wished we had some full class periods designated for team work. Therefore, I will work some full-class work days into the schedule next time. Deadline stress and failure of teammates to contribute seemed to hamper team cohesion more than anything else, but hopefully having more time to work together in person will increase participation in the project and decrease tension. Doing so in class also will give me more opportunity to guide their communication and teamwork behaviors.
- Some students still will skip class and fail to become a true part of the team or contribute meaningfully to the project. Therefore, I will do more to monitor and alleviate those situations earlier in the semester. Some teams exercised their ability to “fire” team members after the outline, but others didn’t realize or remember that was an option and complained that they presented with teammates who hadn’t contributed to the research and writing. Furthermore, teams only exercised the firing option after the outline was due; none did so earlier in the semester. I believe completing a large component of the project with dead weight increased tension and decreased team cohesion. I will make sure at every checkpoint that students remember they can remove teammates who are not participating in the project, and I will increase the number of peer evaluations students complete to facilitate this process. After they present, students complete a peer evaluation that evaluates each teammates’ cooperation, timeliness of contribution, preparation (research, writing, selecting/producing visuals), and presentation performance. I considered implementing a modified version of that evaluation at each checkpoint but decided against it because I didn’t want students to confuse the peer evaluations with the team cohesion assessments or become overwhelmed with paperwork. I will discontinue the team cohesion assessments, though, and have students complete peer evaluations more frequently instead. These will alert me to issues earlier while encouraging students to think critically about their teammates’ contributions throughout the process and take action as needed. Hopefully issues coming to light sooner will enable me to combine teams that may end up with few members well before the presentation.
Reflection: What is the most important thing you learned about teamwork this semester? (unedited responses)
Be flexible when working with everyone’s schedules
Being ahead of the curve.
being flexible and allowing others to contribute
Coming together in person can make a lot of things a lot simpler as opposed to doing it all online
Communication is the key for a successful team environment.
Communication so the team can adjust to fit everyones’ needs.
Don’t let negativity ruin a good presentation.
Everybody has to work together toward the team’s goals. One person can’t carry the team effectively and if one or more people don’t do their work it make the rest of the team’s jobs much harder and more frustrating. With that said, when people do actually participate it helps to bond those members together and make a better, cohesive, end project.
How to collaborate
How to communicate & get things done on time by planning as a team.
How without fail, working as a team is awful.
I didn’t learn it because I already knew it, but the most important thing I already know is that I work better alone and I still really don’t like group work with random people.
I know now to be here the first day of class, so I can pick my own group members considering I have to pay over a thousand dollars a class.
I learned how to better understand people’s opinions and what they had to say about the issues we were talking about.
I learned that a lot of the time someone on the team will not put in as much effort and will just float along in which the other members will have to carry the extra weight.
I learned that if everyone is on the same page and at least somewhat dedicated to the end goal, the group work will be successful and maybe even enjoyable, which contradicted my previous ideas of group work.
I learned that if you set up expectations for how you want your team to work, it will be more successful.
I learned that most people are not willing to work on teams no matter how old they are or the level of education they have.
I learned that working on big teams is difficult and its important to find meeting times.
I learned that you cannot expect the same amount of effort from each team member, but that oftentimes other members of the team will step up and fill the gaps made. The best strategy for success is to work well with those who demonstrate a willingness to give their time and effort to making the project the best it can be.
If you don’t get to know the people you are in a group with, it makes it hard to work with them.
It definitely takes a lot of work to make your team effective. You must always put in effort to try to restructure your schedule so everyone can meet. You also have to trust and depend on one another.
It is tough to have all team members focus on a task and be organized, especially when we each have much more going on in our lives, but as long as we all communicate well the job can definitely be done. Communication is key, for sure.
Leaders shape the future, and every team needs a strong leader to succeed.
Learning to speak up and state my own opinion even when I’m not entirely confident. Communication and openness is key in order to fully thrive in a group project. I enjoyed my group and the time we spent working together. I consider them my friends.
making new friends 🙂
Making sacrifices to achieve the big picture the team set out to attain.
Most people do things last minuet and you can’t make anyone do anything on your time frame.
Not everyone is going to do their part, but what counts is that the other members have the integrity to step up and cover the people who are slacking.
Organization is important
Planning and communication are key
Sometimes, you gotta pick it up and be leader.
Start the team project ahead of time and not wait until last minute because then you might get some team members that do not contribute.
Teams hold me down and block me from my shine I learned I don’t work well well with others. But the assignment was cool. Groups make my head hurt
that communication is very important
That everyone needs to do their part to make the team run smoothly. Also, communication is key.
That google docs saves lives. It is very easy for everyone to be working on the same slides at once and that automatically save once you stop typing so nothing gets lost.
That some people are disrespectful. I also learned that others are extremely respectful. Projects definitely can’t be pushed back to the last minute. I also learned that understanding concepts after a lesson were much easier to understand working in a group because we were able to apply them to things we knew in real life.
That time is a key concept in getting things done in the time allotted, giving us the opportunity to finish our work thoroughly to where we have time to go over it a second time.
That time managing is essential to being prepared.
That we all have busy lives and we all work differently but we all trusted each other and that we would get all of our parts done, not micro manage each other and it would all workout.
The important thing I learn is that communication is one of the most important things to make a team successful. We kicked a few people out of our team because they did not execute their role as agreed. Once they were notified they were kicked out they were offended because the rest of the team did not understand their personal life situations, nonetheless, they never spoke about the problems they had at all to maybe find an alternate way as a team to complete each task as we had agreed to. We could not help them at the end nor feel empathic because they were not communicating with us how they said they were. Everyone was open about their situations they had going on outside of class, either school related, work or even personal but those people never did. They would agree to everything and say they would do it but at the end they did not and we did not feel compassionate about it because they never once did communicate anything about the possible encounters they could have or had been facing.
The longer we worked together the more stuff we had in common and accomplished our goals.
The most important thing I learned about being on a team is that unplanned circumstances happen and you have to be ready for them.
The most important thing I learned about working in a team is that sometimes, you can’t count on everyone to keep their word.
The most important thing I learned about working with a team this semester was planning and working around difficult schedules, improvising to get the job done.
The most important thing I learned from working in a team, was mostly time management and working together to achieve the same goal. Our theory had a lot to do with how our team functioned so it was nice to incorporate the two together.
The most important thing I learned on this team is that its best to not be last minute about things but to be ahead of things.
The most important thing I learned this semester about working in a team is how busy schedules can impact your plans. This led to working even harder in finding the best solution, where sometimes it meant dividing up who meets up on one day and who the other, with some meeting both days. Figuring out schedules can be the most daunting task but it can easily have a solution if you begin making a plan.
The work gets done when everyone is involved!
Things move better when you work together
This has been one of my favorite classes yet and I am thrilled to have gotten to meet every member in my group. I personally believe we will all never forget each other.
This semester i learned that even in a college setting where everyone is here to learn and get a good grade you may still encounter other that don’t play well. Sometimes it takes someone to be the bigger person and groom the team to just understand that we are all here just to get the job done.
To be more assertive in all aspects of my life.
To listen more than anything because there are so many things to learn and value about one another. We all come different places but somehow we all ended up in the same group! I love my team!!
To make sure that I am available to the team and to organize my time around the team’s schedule so as to make sure we get everything done.
to properly plan and create timetables for the group assignment.
We’re all different and unique, but yet we all think as one, all have the same mindset in order to reach our goal for this semester.
When everyone puts out and carries their own responsibilities like they should, the team can take ideas and form them into what we need, be it for an assignment or anything else.
Working in a big team is difficult but if at least most of the members coordinate to work towards the same goal then the team can create a fantastic piece of work.
Working in a team requires a lot of organization and patience. Now that we are in college, we all have different schedules and sometimes is hard to contact each member of the group however it’s not impossible. I have seen many people with busy schedules and still made the effort to contribute to the team. I have learn that we must be willing to work hard, have patience, and organization in order to have a strong contributing team. I am glad this class requires to grade our members because in that way I can show the great or minimal effort that each member did on the project.
You have to be willingly to sacrifice your schedule in order to work effectively with a team.
You need to be patient with people, but you can’t be a pushover.
Teamwork: An Open Access Practical Guide - Instructor Companion Copyright © 2020 by Andrew M. Clark and Justin T. Dellinger is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Innovations in Teamwork for Health Care
Don’t leave teaming up to chance. Create better teamwork through science.
In this course, experts from Harvard Business School and the T.H. Chan School of Public Health teach learners to implement a strategy for organizational teamwork in health care.

What You'll Learn
Health care is a team effort. From the front desk administrators to the nurses, doctors, insurers, and even the patients and their families, there are many people involved in an individual’s care. To deliver quality care in today’s fast-paced environment, practitioners and caregivers must go beyond medical problem-solving and rely on effective collaboration and communication skills.
While other businesses may organize around a functional area or project, allowing team members to learn each other's working styles and strengths over time, health care workers often find themselves in ad hoc scenarios, coordinating with near-strangers on life and death situations. As a leader, how do you encourage trust and meet shared goals when teams are formed quickly? How do you strengthen flexibility and collaboration even as team membership and structures fluctuate across departments?
In Innovations in Teamwork for Health Care, leaders in the field of organizational behavior and teamwork, Amy Edmondson, Professor at Harvard Business School, and Michaela Kerrissey, Assistant Professor at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, share their latest research and present their concept of "teaming" as it relates to the health care and life science industries.
In this course, you will explore the complexities of collaboration in dynamic cross-functional teams and its impact on quality of care. You will examine the theory of teaming – where individuals join together to lend their expertise – to appreciate what enables effective teamwork and why teamwork fails; articulate the importance of psychological safety and a joint problem-solving orientation; understand the particular needs of time-limited teams; and rethink the role of hierarchy and leadership in the context of teaming.
You’ll hear firsthand from experts with experience inside and outside the health care industry, from CEO and President of the Cleveland Clinic, Tomislav Mihaljevic, to Andres Sougarret, the engineer who led the miraculous rescue of 33 Chilean miners in 2011.
Ultimately, this course provides you with the tools needed to implement effective teaming strategies for patient-centered care and provides your organization with a framework to empower robust communication, improve efficiency, and elevate patient safety.
The course will be delivered via HBS Online’s course platform and immerse learners in real-world examples from experts at industry-leading organizations. By the end of the course, participants will be able to:
- Explore the science of teamwork, focusing on the psychological and sociological aspects of teaming, collaboration, and defining effective outcomes.
- Understand the complexity of building trust in ad hoc teams, including how to define purpose, build trust, and navigate interpersonal risks to reach common goals.
- Apply communication strategies that encourage psychological safety and create a safe space for all to contribute.
- Understand the value in adopting a model of joint problem-solving for patient care.
- Identify the distinct needs of time-limited project teams and how to incorporate effective and transparent feedback loops.
- Ensure accountability and identify leaders, breaking down hierarchy and encouraging the right person to step up at the right time.
- Implement a PDSA (Plan, Do, Study, and Act) framework for your organization.
Continuing Education Credits
In support of improving patient care, Harvard Medical School is jointly accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME), the Accreditation Council for Pharmacy Education (ACPE), and the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC), to provide continuing education.
The Harvard Medical School designates this enduring material for a maximum of 20 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity. Harvard Medical School is accredited as a provider of nursing continuing professional development by the American Nurses Credentialing Center’s Commission on Accreditation.
This activity is approved for 20.00 contact hours. Contact hours are awarded commensurate with participation and completion of the online evaluation and attendance attestation. We suggest claiming your hours within 30 days of the activity date, after this time, the attendance attestation will still be required to claim your hours.
Groups of 10 or more receive Amy Edmondson's latest book!
A free, hard copy of right kind of wrong: the science of failing well for each participant. .

Your Instructors
Amy C. Edmondson is the Novartis Professor of Leadership and Management at Harvard Business School, a chair established to support the study of human interactions that lead to the creation of successful enterprises that contribute to the betterment of society. She has pioneered the concept of psychological safety for over 20 years and was recognized in 2021 as #1 on the Thinkers50 global ranking of management thinkers.
She is the author of Teaming: How Organizations Learn, Innovate, and Compete in the Knowledge Economy (2012), The Fearless Organization: Creating Psychological Safety in the Workplace for Learning, Innovation, and Growth (2018), and Right Kind of Wrong: The Science of Failing Well (2023).
Michaela Kerrissey is an Assistant Professor of Management at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. She conducts research on how teams and organizations innovate, integrate, and perform, with a focus on health care. Dr. Kerrissey has authored over 30 publications on these topics and has won numerous best-paper awards, such as from the Academy of Management. She designed the Management Science for a New Era course at Harvard’s School of Public Health. In 2023, she was listed on Thinkers50 Radar, a global listing of top management thinkers.
Real World Case Studies
Affiliations are listed for identification purposes only.

Tomislav Mihaljevic, MD
Learn from the President and CEO of the Cleveland Clinic about how to implement joint problem solving in complex care organizations.

Maya Rupert
Hear from a top political strategist and campaign manager about how she leads within a teaming structure.

Trishan Panch, MD, MPH
Learn from Harvard faculty and founder of Wellframe about the importance of team learning.
Available Discounts and Benefits for Groups and Individuals
Experience Harvard Online by utilizing our wide variety of discount programs for individuals and groups.
Past participant discounts.
Learners who have enrolled in at least one qualifying Harvard Online program hosted on the HBS Online platform are eligible to receive a 30% discount on this course, regardless of completion or certificate status in the first purchased program. Past Participant Discounts are automatically applied to the Program Fee upon time of payment. Learn more here .
Learners who have earned a verified certificate for a HarvardX course hosted on the edX platform are eligible to receive a 30% discount on this course using a discount code. Discounts are not available after you've submitted payment, so if you think you are eligible for a discount on a registration, please check your email for a code or contact us .
Nonprofit, Government, Military, and Education Discounts
For this course we offer a 30% discount for learners who work in the nonprofit, government, military, or education fields.
Eligibility is determined by a prospective learner’s email address, ending in .org, .gov, .mil, or .edu. Interested learners can apply below for the discount and, if eligible, will receive a promo code to enter when completing payment information to enroll in a Harvard Online program. Click here to apply for these discounts.
Gather your team to experience Innovations in Teamwork for Health Care and other Harvard Online courses to enjoy the benefits of learning together:
- Single invoicing for groups of 10 or more
- Tiered discounts and pricing available with up to 50% off
- Growth reports on your team's progress
- Flexible course and partnership plans
Learn more and enroll your team !
Course Syllabus
Learning requirements: There are no prerequisites required to enroll in this course. In order to earn a Certificate of Completion from Harvard Online and Harvard Business School Online, participants must thoughtfully complete all 5 modules, including satisfactory completion of the associated assignments, by stated deadlines.
Download Full Syllabus
- Study the Mining Accident Rescue and Cleveland Clinic cases.
- Understand the concept of teaming and how it can be applied to the health care industry.
- Brainstorm how to organize with a team to rescue 33 trapped miners.
- Analyze the problems solved and new challenges created by organizational structures that were implemented to facilitate teamwork at the Cleveland Clinic.
- Outline and analyze an individualized teaming breakdown for your organization.
- Study the NASA and Google cases on psychological safety.
- Collaborate with team members and leadership to create a space of psychological safety.
- Identify the indicators of psychological safety in a group. Analyze data from Project Aristotle’s study of teams at Google.
- Consider how past experiences can affect current feelings of psychological safety.
- Study the Cleveland Clinic , Boehringer Ingelheim , and Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center cases.
- Implement a joint problem-solving orientation in which team members view problems as shared and solutions as requiring collaboration.
- Match different types of diversity in the workplace with the interpersonal boundaries that they imply.
- Articulate what you bring to a team and what you might need from others.
- Walk down the ladder of inference to get to the root of a problem.
- Study the Virginia Mason Medical Center and Institute for Healthcare Improvement cases.
- Cultivate an organization where team learning is valued and mobilized for improved performance.
- Identify different kinds of work on the process knowledge spectrum.
- Brainstorm how a nursing team could learn from an accidental morphine overdose.
- Study the cases of Julio Castro's Presidential Campaign and Wellframe .
- Practice leadership skills that include coaching, enabling, and ensuring that the right voices are present or represented within the team structure.
- Build a leadership workshop for your team using the concepts addressed in this course.
- Practice asking meaningful questions as a way to encourage input and express authentic humility.
- Learn the difference between confirmatory and exploratory responses.
Earn Your Certificate
Enroll today in this course.
Still Have Questions?
What are the learning requirements? How do I list my certificate on my resume? Learn the answers to these and more in our FAQs.

Related Courses
Health care economics.
Taught by Harvard Medical School faculty, this course provides insights into the interactions between industries in the US health care sector and teaches what economic forces are shaping health care.
Digital Health
Digital technologies and big data offer tremendous opportunities to improve health care.
Reducing Racial Disparities in Health Care
In partnership with the Disparities Solutions Center at MGH, this course will help you deliver high-quality health care to all through organizational change.
More From Forbes
How to organize your employees into teams to maximize productivity.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
UNSPLASH.COM
Teamwork can have a multiplier effect, cross-pollinating team members’ skills and knowledge. But before you begin corralling employees into distinct units, remember that collaboration can come at a cost. Teams don’t always work out, according to J. Richard Hackman , the late Harvard organizational psychology professor and leading expert on teams. Hackman’s research demonstrated the surprising ways that teamwork can hurt productivity.
That said, certain strategies have been shown to improve the efficacy of teams. Here are some tips for strategically creating teams that boost organizational productivity and innovation—rather than chip away at it.
Build small, cross-functional teams
Speaking of cross-pollination, bees understand the value of teamwork. In a recent study , Finnish researchers taught bumblebees to push a small brick to clear the way or navigate a tunnel to get a treat. Researchers taught the bees to go it alone or to execute the task with a partner. In both cases, the partnered bees waited for their teammates. The takeaway: teamwork is nature’s way to get things done.
A growing body of research shows that when humans pool their skills, knowledge, and motivation, the whole is greater than the sum of its parts. Science teams are more productive and make a greater impact when collaborating across organizational and geographic boundaries. In academia, interdisciplinary teams publish more and in more diverse outlets. In controlled studies from the American Psychological Association , groups of three, four, and five people delivered better performance on coding challenges than individuals or groups of two.
The caveat: it’s critical to maintain small team sizes. Hackman told Harvard Business Review that as teams get bigger, the number of links to manage among members increases exponentially, creating extra administrative, people-managing tasks. Adding another wrinkle: many teams don’t have clear boundaries. Hackman’s data on 120 top teams around the world showed that fewer than 10% agreed about who was on their team. Leaders should clearly articulate team members and limit them to single digits.
Matt Damon Movie Dud Falls Off Netflix Top 10 Global Chart After 1 Week
Ios 17.5.1: apple fixes frustrating iphone photos glitch, bezos reclaims world s 2nd richest title from musk as net worth tops 200 billion.
At my company, Jotform, I realized we needed to create teams when we expanded from five employees to 15. Suddenly, productivity suffered. We were no longer working towards a unified mission. The company vision became hazy. When we broke into cross-disciplinary teams of five to six employees, with self-determined goals and deadlines, we regained momentum. Each team lived and breathed its unique mission. Teams had dedicated designers, who reviewed every design decision, and our products improved. As the numbers showed, users (aka the most important stakeholders) were happier, too.
In short, leaders must deliberately create diverse teams with clear members and roles, and keep a cap on members or run the risk of diluting the team’s efficacy.
Designate a team leader
When each team has a leader, teams can avoid some of the pitfalls of collaboration and capitalize on their strengths. Studies have shown successful teams have a clear purpose, established roles, and a formal communication system. A leader can step in to ensure that these higher-level administrative tasks are taken care of, for example, to make sure communication is working effectively before issues snowball.
Team structures have the unintended positive outcome of creating leadership pipelines throughout the company. Since every team has a lead, employees acquire management skills while working full-time, putting them on a path to advancement. At Jotform, our current VP of Product, Enterprise began 11 years ago as an introverted developer. She became one of our first team leads, then went on to product management before her most recent promotion to VP. She’s progressed on an individual career level while championing teams toward their collective goals.
Create shared workspaces
A 2023 study found that collaboration hurts efficiency when team members can’t observe each other and communication is less efficient than face-to-face interactions. To avoid this pitfall, teams need shared workspaces. Physically shared workspaces are ideal.
At Jotform, we hired an architect to design team rooms for six people maximum. Every room had whiteboards and closed glass doors, giving teams privacy. With three people sitting next to each other on one side and three on the other, even the computers were organized to promote collaboration. Any team member could easily see their colleague’s monitor and observe what they were working on. We opted for team productivity over individual privacy, propelling us toward our larger organizational goals.
Remote teams must take extra measures to build shared workspaces so collaboration feels near-seamless and doesn’t dampen efficiency. Luckily, today there are numerous applications to choose from, like Notion and Google Google Workspace. ( G2 is a great resource for researching the latest tools and reviews.)
Teamwork can make the dream work if managed and organized strategically. Hopefully, the above tips can help your team members build off each other’s strengths and make the most of your organization’s talent pool.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
Ready. Set. Scale. Shaping leaders for hypergrowth
Imagine two talented entrepreneurs developing a groundbreaking, solar-powered flying car to revolutionize sustainable mobility. Propelled mainly by entrepreneurial spirit, charisma, and business savvy, their start-up builds a following as quickly as their electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) prototype grabs headlines and dazzles consumers. Orders pour in from across the globe.
Now comes a critical inflection point. Can our hypothetical company scale from building a handful of bespoke eVTOL prototypes to establishing a global assembly line without losing the innovative edge at the heart of its appeal? The founders cannot afford to wait, but start-ups (companies whose funding stage is pre-Series B) face obvious challenges, including securing capital, maintaining differentiation in an emerging market, and contending with competition from more prominent players. A less obvious challenge—but no less essential to success—is bringing new leaders into the ranks (potentially including professional managers from larger companies) and undertaking rapid, effective leadership development to avoid the pitfalls that keep 80 percent of start-ups from succeeding. 1 Based on a sample of 3,164 companies with Series A funding in 2011 to 2013, assuming six to eight years to scale or exit, PitchBook data, April 2021.
Intentionally investing in leadership development can help hypergrowth companies 2 Based on McKinsey analysis, hypergrowth refers to a period of rapid expansion with a CAGR of 20 to 40 percent and three phases: build and launch (annualized return on revenue [ARR] of $0 to $10 million); grow (ARR between $10 million and $100 million); and scale (ARR greater than $100 million). counter the forces that may otherwise stand in their way, such as limited management skill sets, less experienced talent, and relative inexperience leading larger teams. Once start-ups manage to emerge from the early stages in which many fail, they need sustainable leadership capabilities to give the organization the flex and muscle required to adapt as growth continues.
To be sure, this leadership transition will present challenges, especially because leadership development should be what we call “at pace, on purpose”—that is, enabling rapid transformation while preserving the entrepreneurial spirit and the core tenets of the organization’s culture. That’s a tricky balance, whether the CEO founded the company or stepped in during the growth phase. But it’s worth the effort. By recognizing the importance of leadership in the hypergrowth process and investing intentionally in its development, startups can not only make the transition to “scale-ups” (companies whose funding stage is from Series B to IPO) but widen their competitive advantage.
Leadership development is not optional
There are some things in business which, if done suboptimally, will not necessarily impose significant liabilities. Leadership is not one of these things. Well-developed, high-quality leadership has a profound positive impact on an organization and its operating model. 3 Claudy Jules, Alok Kshirsagar, and Kate Lloyd George, “ Scaling up: How founder CEOs and teams can go beyond aspiration to ascent ,” McKinsey, November 9, 2022. McKinsey research shows that the EBITDA of organizations performing in the top quartile of leadership is almost double that of others, while organizations are 1.9 times more likely to have above-median financial performance when the leadership team has a shared, meaningful, and engaging vision.
Case study: Investing early in leadership development
When consumers expressed distrust in providers of housing finance in an Asian market, one multinational conglomerate decided to act. Leveraging its brand reputation, it set out to show the market how housing finance should be done: with honesty, integrity, and care.
The company had successfully built many businesses before, but this was its first financial institution. Its executive committee didn’t want to acquire an existing company that was part of the problem, so it chose to create a start-up and attract the best external real estate and financial talent. Looking at the market potential, the start-up CEO and his new team felt confident and planned for hypergrowth.
But the CEO was also concerned. He noticed that his new team had significant differences in leadership styles and cultural backgrounds that were already leading to friction. And looking at the steep curve in talent attraction plans, he feared inconsistent ways of working and a fuzzy culture would, over time, slow the company’s growth. He wanted to get it right before launch.
The CEO chose to take his 30-person leadership team beyond the technical plans for growth. In multiple workshops with external facilitators, he and the team jointly defined the identity of the company by including its higher purpose, desired culture, and aspirational leadership style. The process provided not only a point of reference for the existing team but also a clear set of criteria for hiring future talent. With significantly increased cohesion, clarity, and confidence, the company entered the market.
In the eyes of investors, leadership quality can affect a company’s market value by up to 30 percent. 4 Derek Matthews, “Why founders should focus more on people development to increase startup value,” Forbes, January 31, 2019. In addition, savvy general partners in private equity know that founders and their top teams have an outsize effect on the culture and operations of a start-up—and they have a keen interest in evaluating leadership potential as they make investment decisions. This is because effective founder-led companies have the potential to outperform peers. For instance, S&P 500 companies in which the founder is still the CEO generate 31 percent more patents than the rest. 5 Chris Zook, “Founder-led companies outperform the rest—here’s why,” Harvard Business Review, March 24, 2016.
Yet investors also know that leadership is not a static characteristic and that leaders must evolve for a company to grow. This is especially true for start-ups, in which the skill sets and approaches crucial to early success are often quite different from those required as an organization rapidly grows. Why? Because start-ups typically have less infrastructure and fewer processes, rapidly changing environments, a strong sense of culture, founder CEOs who are often also direct managers, and senior leaders who take on multiple roles. Start-ups can’t wait until the dust settles to acquire and develop the leadership capabilities they need. For hypergrowth companies and typical market disruptors, the dust does not settle, and founders may not want it to: the excitement of the start-up mentality is arguably part of the ride that appeals to visionary founders (see sidebar “Case study: Investing early in leadership development”).
Priorities in tension: Moving at pace while retaining purpose
Two vital elements are essential for building leadership capabilities in a growing, founder-led organization: pace and purpose. Understanding each in the context of leadership development and capability building is crucial, as is understanding their interplay.
Pace is important because rapid growth often leads to instability, along with sizable gaps in leaders’ experience, skills, and capabilities. When it comes to purpose, the challenge lies in transforming leadership mindsets and skills targeted to the scaling ambitions of the organization, together with its vision. This is difficult, because the target is inherently a moving one: leaders need the stability to function with the size and scope of their existing teams but must also embrace the dynamism and ongoing growth that will match the organization’s evolution. 6 Chris Zook, “Founder-led companies outperform the rest—here’s why,” Harvard Business Review, March 24, 2016. Moreover, CEOs must manage any tension created between leaders who have been there from the beginning and those who arrive during the growth stage—coming from different company cultures and with potentially different ideas for how to scale.
The trick is determining how to keep the ongoing transformation occurring at a tempo that maximizes performance and aligns disparate units of the fast-growing organization while staying true to the company’s purpose. This means leadership development has to be “at pace, on purpose” to enable rapid transformation while preserving the entrepreneurial spirit and the core tenets of the organization’s culture.
Four essential questions to guide leadership development
As the founders of our imaginary eVTOL start-up grapple with the challenges of growing their successful enterprise, they often ponder big questions that get to the heart of the company’s present and future:
- Who leads? Expand focus beyond the early few leaders to the top 40 to 50 critical roles and build capabilities early.
- How do we empower leaders? Give leaders authority as a way to expand their strengths and confidence.
- How do we keep the entrepreneurial spirit alive? Create a “founder mentality” throughout the organization and infuse the energy of the early days throughout all layers.
- What’s needed from us? Founders and top leaders need to shift priorities from building to managing relationships with shareholders and investors and preparing for a potential IPO or challenging times ahead.
1. Who leads?
As an organization expands beyond the start-up phase, it’s vital to understand what its leadership entails and demands. This requires a fundamental shift in how leadership is conceptualized: for example, from focusing on founders and a handful of senior leaders to a broader scope, shaping a few dozen critical top roles into one connected leadership team.
As leadership grows in structure and scope, the vital task becomes clarifying and articulating the company’s culture—the values and behaviors essential to the next generation of leaders. This is a delicate task involving some tension: founding teams must simultaneously embrace adaptation while doubling down on core values (see sidebar “Case study: The top-team leadership journey at an e-commerce platform”).
Case study: The top-team leadership journey at an e-commerce platform
A European e-commerce company experienced high growth during the COVID-19 pandemic, followed by a hard correction. To boost competitiveness and move faster, they sharpened their strategy, updated their operating model, and evolved their culture. The executive team realized that the key to improvement was changing the leadership behavior of the executive team and the surrounding top 50 roles. These leaders needed to work in different ways with each other and with the company. A project team was convened to create a nine-month leadership development journey comprising diagnostics, multiday workshops, and one-on-one coaching. The executive team aligned on priorities in the new strategy, drove decision making according to new roles, and mutually supported each other’s growth and development. The top-50 team shifted from a strict functional focus to a shared understanding of full company context, developed new behaviors around decision making and empowerment to speed up processes, and integrated new communication mechanisms to stay more connected.
Specific roles may change even as the founders and top team are charged with stewardship of the company and its culture. While leaders may wear multiple hats in the early stages, organizational growth will likely call for more structure and clearer roles. Moreover, the small circle of early leaders must acknowledge that the expanding enterprise will demand leadership and people skills that may be outside of their current knowledge and experience. As the company expands, it becomes crucial to enhance the matching of roles and profiles within the organization. This requires a thoughtful evaluation to “match the A players to the A jobs.” It may require hiring new people with different skills or investing in upskilling current employees to ensure the right individuals are in the right roles.
2. How do we empower leaders?
As start-ups grow exponentially, new hires are rapidly brought on, mostly for expertise. This often results in a wide range of leadership experience and leaders facing an ever-changing and expanding scope.
Case study: How tailoring leadership development built capabilities at a new joint venture
Leadership development should support both the business and cultural growth. A Philippines-based telecom company created a leadership development program that began with these objectives in mind, tying business skills and capabilities to the company’s vision and values. After carefully examining where things stood, it envisioned and built solutions, implemented them, and then—crucially—sought to ensure the changes and benefits could be maintained. Ultimately, leaders were able to draw clearer links between business objectives and their individual and collective roles. They were also equipped to cascade core skills and capabilities to the rest of the enterprise.
Maximizing leadership growth across a growing company hinges on creating highly customized programs that focus on the development of specific leadership skills and enabling leaders to understand their roles within the company’s big picture. Leaders at every level need to see how they contribute to the strategic evolution of the organization and have a shared understanding of the full company context in order to act as enterprise leaders beyond their functional scope. To do so, they need the opportunity and support to rise above daily firefighting. This is particularly relevant for younger talent with less experience leading others. A fast-growing consumer tech and media company implemented this by sharing internal data, such as subscription evolutions, with all employees to ensure organizational focus went in the right direction.
In addition, it’s common for leaders to feel overwhelmed or even burned out due to the execution pace. Companies can get ahead of this by building resilience through nuanced exposure to high-stress situations with the opportunity for reflection and debriefs (see sidebar “Case study: How tailoring leadership development built capabilities at a new joint venture”).
3. How do we keep the entrepreneurial spirit alive?
To ensure the continuity of a start-up’s original energy and spirit throughout its growth, it is vital to infuse the core “founder mentality” across all layers of the organization. This can be especially crucial at the stage when the company has grown such that core leaders feel more removed from employees. That’s when it can be particularly powerful to ensure all individuals—regardless of level or function—feel empowered to take ownership of the company’s culture, while also embracing the dynamism and agility that fuel growth (see sidebar “Case study: How a hypergrowth tech company cascaded its culture”).
Case study: How a hypergrowth tech company cascaded its culture
A rapidly growing Singapore-based tech company needed to ensure that its core business culture evolved from tacit to intentional as it entered its next phase of growth and prepared for an upcoming IPO.
The company invited about 100 functional and business leaders to participate in an 18-month program to build leadership skills that reinforced its values and future direction. This approach enabled participating leaders to test and pass along what they learned, generating an amplifying effect that allowed more than 2,000 colleagues to benefit from the program.
As companies expand, senior leaders can recognize their essential roles as coaches, mentors, and champions of the company empowering the next cohort of leaders. From a leadership development standpoint, it is valuable to work with individuals who excel at handling challenges and help shape them into purposeful leaders who grasp the bigger picture. In our experience, founders who adhere to proper delegation also tend to see empowered employees in response.
As organizations become more complex, there is merit to functions implementing their own objectives and key results (OKRs) to imbue structure and accountability in a more scaled environment. However, there is a risk of functions becoming overly focused on those OKRs, which is where leaders can benefit from fostering a “one organization” mindset and identifying early on what sets the company apart. 7 Blair Epstein, Caitlin Hewes, and Scott Keller, “ Capturing the value of ‘one firm,’ ” McKinsey Quarterly , May 9, 2023.
Embracing creative disruption is critical in maintaining the entrepreneurial spirit. But the founding company culture itself must change so that the company may scale. Gone are the days when growth was the only metric that mattered; investors want returns, which can incite companies to take actions that go against the founding culture, such as eliminating perks and cutting the workforce. A healthy culture can keep company spirit alive while also adapting to new realities.
4. What is needed from us?
All CEOs overseeing a growing organization—regardless of whether they founded it—are not leading the same organization in the scaling-growth stage as they were at the start-up stage. This may sound obvious, but, in practice, it is no small feat for founders and early-stage CEOs to acknowledge they need to grow and adapt to the same extent as their organizations—let alone take action to do so.
Complexity multiplies as companies grow. This necessitates, of course, increased delegation so leaders and top teams can prioritize what will become their most important role: the management of relationships with key stakeholders, including shareholders and investors (especially in turbulent times or in preparation for an IPO). If this results in a compounding number of granular daily tasks and decisions flowing to top leadership for vetting, it spells trouble: the speed of decisions will no longer match the organization’s speed.
Case study: Scaling a food pioneer in North America
A fast-growing food company found its broad ambitions challenged by the limits of its operating model. The CEO was the sole owner of enterprise finances, making accountability unclear across functions and geographies. Resources weren’t allocated for strategic effectiveness and efficiency, and SG&A expenses were spiraling as a result. Talent shortages in critical roles were hampering growth, and the enterprise lacked a performance culture. The company acted, starting with a comprehensive diagnostic followed by the design of a blueprint for how it should evolve. A talent “win room” accelerated hiring for key roles and helped build out the performance management ecosystem. Early results indicate that the company’s operating model is now more intentional, with appropriate profit and loss accountability and resource allocation as well as tighter control over SG&A spending. And the right people are in the right positions, with employees across the enterprise understanding their roles and being held accountable for their performance.
CEOs of growing firms must discern what is needed from them as the company evolves. How do they want to show up? Instead of trying to do everything—as they may have during the early days—leaders need to ascertain what they can and should do, delegating the rest to a top-quality team. But they also need to marry this distance from everyday tasks with keeping the needs of customers at the forefront of their minds. Managing this simultaneous awareness and delegation is at the core of how founders can drive business value as the company grows (see sidebar “Case study: Scaling a food pioneer in North America”).
Engage the questions to drive growth
While every company is unique, all must adapt as they grow. We recommend leaders take these four questions to heart, reflect on them, and discuss them in depth within the organization. It’s worth investing time and space to dig in because leaders who discern and articulate meaningful answers to all four may derive tremendous value for their organizations. This simple checklist provides founders with an effective way to assess their own leadership health, as well as that of their top teams:
- What have we done to focus closely on our top 15–20 critical roles that drive strategic value, understanding what they are and what they do?
- Beyond existing leadership skills, which additional skills are needed to scale to the next level?
- Which efforts help us define the values and behavioral characteristics of a shaper-leader?
- What crucial learning experiences have we developed with ongoing development pushes and apprenticeship opportunities?
- What highly customized programs, including comprehensive class options for different topics, do we have for learners?
- What pilot projects are creating resilience to prepare leaders in advance?
- How are we developing purposeful leaders with a strong understanding of why they are leaders?
- How have we developed a unified organization with a culture of “whatever it takes” for customer impact?
- How do we continually ask how we can make it better, disrupt, and create “business insurgency”?
4. What is needed from founders?
- How effectively am I delegating, spending less time with day-to-day operations and more time on big moves to drive enterprise strategy, such as M&A or product expansion?
- What can we let go of so we can stop trying to do everything and work on things we care about instead?
- How are we staying in touch with customers to ensure we maintain a deep “frontline obsession”?
Like our imaginary sustainable-mobility founders who hit on something revolutionary, today’s hyperscalers often have the potential to disrupt life as we know it with new ideas and the energy, discipline, teamwork, and persistence it takes to turn those ideas into reality. That opportunity is a compelling call to leadership. But achieving it requires a steadfast growth mindset, a tremendous dose of self-awareness, a commitment to ongoing adaptation, and a clear understanding that in the ranks of the world’s best organizations, leadership development is never finished.
Arne Gast is a senior partner in McKinsey’s Amsterdam office, where Fleur Tonies is an associate partner; Claudy Jules is a partner in the Washington, DC, office; and Alok Kshirsagar is a senior partner in the Mumbai office.
The authors wish to thank Cornelius Chang, Kate Lloyd George, Michael Park, Karolina Rosa, and Joachim Talloen for their contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

New leadership for a new era of thriving organizations

The State of Organizations 2023: Ten shifts transforming organizations

Scaling up: How founder CEOs and teams can go beyond aspiration to ascent
A Process for Using LLMs in a National Security Research Organization
This article originally appeared in Forbes Technology Council .
Every company must forge a path to balance the disruptive risks and opportunities posed by large language models (LLMs). But for an organization like ours, working in national security, the stakes and complexity are considerably higher. CNA is an independent nonprofit that produces analysis for the military and for homeland security agencies. Our success over more than 80 years has depended upon government confidence in our research quality and in our ability to manage risk to our networks and privileged information. To balance the heightened risks posed by using LLMs with the need to get the latest tools in the hands of our researchers quickly, we engaged in a collaborative and flexible four-step process:
- Understand requirements and risks
Establish policy and guidance
Enter into a contract with employees, collect feedback and adjust, understand requirements and risk.
Our scientific and professional staff consistently demand the latest tools and technology, and they pressed us to incorporate LLMs into CNA’s infrastructure. Researchers wanted to use LLMs to summarize long reports, speed up programming, and quickly generate outlines. Professional staff wanted to rapidly produce draft position descriptions, policies, and company-wide communications. The trick was to address these demands while maintaining a secure, safe, and compliant infrastructure.
We tasked a team in our Global Information Security group at CNA to develop processes to assess risk. The public servers that LLMs run on concerned us most. As a partner in U.S. national security, CNA operates under many rules that govern our information technology infrastructure and security—especially what we can put into the public space. LLMs potentially create risks, especially to proprietary and sensitive data.
LLMs also introduce risks that could affect the analytical quality that sustains our reputation. One risk is that they can “hallucinate” or make things up. For example, LLMs claimed CNA had published a specific piece of work, returning a title and author, when an exhaustive search of our document repository showed that such a report doesn’t exist. Another is that LLMs are trained on internet data, which introduces bias and false information. A third research risk is that many LLMs do not provide complete citations for generated text, raising concerns about plagiarism.
We needed a collaborative approach bridging research and technology to address these risks. We formed a four-person executive team—the chief information officer, chief research officer, and two executive vice presidents. The team settled on four technical governing policies compliant with current government information technology regulations and security requirements:
- LLM governance policy, a new framework to harness the benefits of AI while managing risks
- Acceptable use policy, updated to describe acceptable and unacceptable employee behavior on CNA's network
- Bring your own device policy, updated to allow greater flexibility while ensuring safeguards to manage security risks
- Software/custom code development policy, updated to standardize secure software development for all CNA-developed code
In addition to these policies, we developed guidance that provides general direction to users and lays out validation and accountability requirements for LLM-generated content. Key principles include:
- LLMs are tools that can help with some aspects of the research process and corporate tasks.
- LLMs do not replace critical thinking by a human.
- LLM users may not enter into an LLM any classified or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI), nor any proprietary, privileged, protected health information, personally identifiable information, or business sensitive information.
- LLM users are responsible for any LLM-generated content, which must be validated by a human. This includes checking for biases and factual or statistical errors.
- LLM use must be transparent, described in the methodology section of reports and briefings and acknowledged in footnotes—including the name of the analyst who verified the results.
- LLMs cannot be authors.
Together, our technical governing policies and research guidance mitigate both technical and research risks, reducing the likelihood of an information spill and helping users apply LLMs in a responsible manner.
Establishing sound technical policies and research guidance is necessary for success, but it isn’t enough. We needed employees to acknowledge their responsibility for reducing risk through a formal LLM access request process.
To access LLMs, employees first read the technical governing policies and guidance. They then complete and sign an LLM Request and User Agreement Form. On the form, an employee specifies all LLM tools they plan to use for CNA work, whether on a company computer or personal device. The employee’s manager signs and approves the form, and the CIO’s information security team reviews it for technical risks before sending the approved tools list to the information technology team to allow user access. The process creates a record of requests and insight into which tools are most requested.
To encourage cross-organizational collaboration, we provide authorized LLM users with a collaboration space inside a Microsoft Teams channel, where they learn from each other, sharing what works and what doesn’t. We also collect feedback on the LLM user experience through regular surveys and small group discussions. So far, 94 percent of users find LLMs to be useful, and 80 percent will continue to use them. Still, 75 percent identified drawbacks, including wrong code, incorrect content, opinionated language, and nonsense answers. Many felt limited by the inability to upload proprietary documents or PDFs. In focus groups, staff asked for guidance on prompt development—to get the most effective answers to the questions they ask of LLMs. And they told us they wanted LLMs that could operate inside CNA’s firewalls. We are incorporating this feedback into program improvements underway now.
Developed in just under six weeks, our approach to access has enabled employees to stay curious, explore further, and witness firsthand the incredible power of language models within deliberate bounds. Since the regulations that organizations like ours work under cannot keep pace with the disruptive changes created by LLMs, leaders must learn to prudently manage risk. Cross-discipline collaboration at the leadership level has allowed us to find this critical balance between opportunity and risk in harnessing LLMs to further our mission.
Rizwan Jan is Vice President and Chief Information Officer and Kim Deal is Chief Research Officer at CNA.
Related Articles

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
4 Common Types of Team Conflict — and How to Resolve Them
- Randall S. Peterson,
- Priti Pradhan Shah,
- Amanda J. Ferguson,
- Stephen L. Jones

Advice backed by three decades of research into thousands of team conflicts around the world.
Managers spend 20% of their time on average managing team conflict. Over the past three decades, the authors have studied thousands of team conflicts around the world and have identified four common patterns of team conflict. The first occurs when conflict revolves around a single member of a team (20-25% of team conflicts). The second is when two members of a team disagree (the most common team conflict at 35%). The third is when two subgroups in a team are at odds (20-25%). The fourth is when all members of a team are disagreeing in a whole-team conflict (less than 15%). The authors suggest strategies to tailor a conflict resolution approach for each type, so that managers can address conflict as close to its origin as possible.
If you have ever managed a team or worked on one, you know that conflict within a team is as inevitable as it is distracting. Many managers avoid dealing with conflict in their team where possible, hoping reasonable people can work it out. Despite this, research shows that managers spend upwards of 20% of their time on average managing conflict.
- Randall S. Peterson is the academic director of the Leadership Institute and a professor of organizational behavior at London Business School. He teaches leadership on the School’s Senior Executive and Accelerated Development Program.
- PS Priti Pradhan Shah is a professor in the Department of Work and Organization at the Carlson School of Management at the University of Minnesota. She teaches negotiation in the School’s Executive Education and MBA Programs.
- AF Amanda J. Ferguson is an associate professor of Management at Northern Illinois University. She teaches Organizational Behavior and Leading Teams in the School’s MBA programs.
- SJ Stephen L. Jones is an associate professor of Management at the University of Washington Bothell. He teaches Organizational and Strategic Management at the MBA level.
Partner Center

- Liberty University
- Jerry Falwell Library
- Special Collections
- < Previous
Home > ETD > Doctoral > 5648
Doctoral Dissertations and Projects
A study of followership in an organizational-wide change of the ministry of child evangelism fellowship.
Michelle M. Russell , Liberty University Follow
Rawlings School of Divinity
Doctor of Philosophy
Alvin Dockett
leadership, followership, Child Evangelism Fellowship, Good News Clubs, organizational change, strategic change
Disciplines
Leadership Studies | Religion
Recommended Citation
Russell, Michelle M., "A Study of Followership in an Organizational-Wide Change of the Ministry of Child Evangelism Fellowship" (2024). Doctoral Dissertations and Projects . 5648. https://digitalcommons.liberty.edu/doctoral/5648
The influence of Child Evangelism Fellowship saw a significant increase across the United States of America after an organizational change following a 2001 Supreme Court case ruling. The purpose of this phenomenological study was to describe the role of followership on the change and followership principles that emerged during the change that was implemented following the ruling Good News Club v. Milford Central School on the Good News Club ministry of Child Evangelism Fellowship. Organizational change was defined as intentional actions promoted by leadership and intentional actions taken by followers who took advantage of the rights guaranteed by the ruling. The theories guiding this study were Followership Theory as popularized by Kelley, and Lewin’s Organizational Change Theory. The methodology for this study was open-ended, qualitative interviews of CEF directors to determine what they perceived to be the leadership and followership qualities displayed in this organizational change. The researcher coded the results of these interviews using NVivo software. This coding identified guiding principles for leaders of both Child Evangelism Fellowship and similarly structured ministries and organizations in the case of future strategic changes. These principles were that followership is a role, it can be described in positive teams, and there are many expectations for followers in a workplace or ministry.
Since May 22, 2024
Included in
Leadership Studies Commons , Religion Commons
- Collections
- Faculty Expert Gallery
- Theses and Dissertations
- Conferences and Events
- Open Educational Resources (OER)
- Explore Disciplines
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS .
Faculty Authors
- Submit Research
- Expert Gallery Login
Student Authors
- Undergraduate Submissions
- Graduate Submissions
- Honors Submissions
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The science of teamwork has been extensively studied, 1 and with good reason. Successful teams improve business outcomes, including revenue and performance. 2 Many organizations are intentionally fostering a collaborative team-based culture, 2 and feeling like a part of a team is a primary driver of employee engagement. 3 Prior to the pandemic, organizational shifts had resulted in teams that ...
Martine Haas. and. Mark Mortensen. From the Magazine (June 2016) RW13 (Fair Game), oil on canvas, Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, 2010 Jeff Perrott. Summary. Over the years, as teams have grown more ...
This paper focuses on the critical role of work teams, arguing that managers must leverage the knowledge generated by teams to support innovation and strategic change. It matches types of team learning to innovation activities. 28 Feb 2018. Sharpening Your Skills.
A case study is used to investigate two teams of final year multimedia students completing a project-based unit, in which teamwork was an essential ingredient and immersed in an authentic context ...
Summary. In this fictional case, the CEO of a sports apparel manufacturer is faced with an ongoing conflict between two of his top executives. Specifically, the head of sales and the CFO are at ...
Industrial and organizational psychology (IOP), which studies people at work, primarily studied factors at the individual level that influenced work behaviors and reactions. In the 1980s, however, organizations world-wide began an ongoing restructuring of work around small groups and teams in an effort to enable more rapid, agile, and adaptive ...
When team members are high in conscientiousness, they are better at self-regulating their teamwork. And groups composed of high-ability members who are able to learn, reason, adapt and solve problems are more likely to work well together. Researchers are working to design algorithms that help organizations create effective teams for specific goals.
High-Performing Teams Start with a Culture of Shared Values. by. Greg Satell. and. Cathy Windschitl. May 11, 2021. Tim Robberts/Getty Images. Summary. In today's disruptive marketplace, every ...
Team composition and the ABCs of teamwork. American Psychologist, 73: 349-362. ... Harvard Business School Case No. 619-013. Google Scholar; Edmondson, A. C., & McManus, S. E. 2007. Methodological fit in management field research. ... A systems psychodynamic approach to organization studies. Academy of Management Annals, 14: 411-449. Google ...
Abstract. This 3-year research project assessed the effectiveness of a teambuilding intervention among a group of department leaders who supervised a fire management unit working in the forests of the western United States. The intervention began with a 3-day retreat that covered three basic areas: communication skills, consensus building, and ...
From corporate groups to remote employees and everything in between, the key to a strong business is creating a close-knit team. In this comprehensive case study, we look at how real-world organizations benefited from team building, training, and coaching programs tailored to their exact needs. Updated: December 21, 2021
Contextual factors of teamwork effectiveness. Based on a large body of team research from various domains, we hypothesise that several contextual and methodological factors might moderate the effectiveness of teamwork, indicating that teamwork is more important under certain conditions. 31 32 Therefore, we investigate several factors: (a) team characteristics (ie, professional composition ...
Lee Fisher, an HR manager at Blinds Direct, says that successful teamwork should be based on solidarity, respect, communication, and mutual understanding. With that in mind, his company has been organizing a series of team-building events over the years. "Our most unconventional event to date was the 'Role Switch'.
In this article, we study the impact of teamwork on an organization's performance, considering a cooperative game's framework. To promote teamwork culture, performance indexes were considered both ...
Cohesiveness within teamwork: the relationship to performance effectiveness - case study - Author: Khalid Al‐Rawi - This paper aims to explore the nature and the function of teamwork cohesiveness in organizations in the UAE., - While many organizations are successful at managing the materials and machinery of the organization, they fall ...
This study shows the impact of teamwork over organizational behavior and Organization performance. Moreover it is covered the communication between employees of the organization. Also, highlight the main positive effect points by present a model to show the difference between the top and Middle managements and their impact on the organization ...
This study compared the organization of two different postal sorting facilities on the effects on QWL and productivity. The study compared the teamwork approach to traditional working methods. ... Teamwork: a case study 197 followed by co-operation ðR 2 D ¼ 0:171 with sign: ¼ 0:006Þ: The level of productivity at t1 is mainly dependent on ...
Teamwork is defined by Scarnati (2001, p. 5) "as a cooperative process that allows ordinary people to achieve extraordinary results". Harris & Harris (1996) also explain that a team has a common goal or purpose where team members can develop effective, mutual relationships to achieve team goals. Teamwork replies upon individuals working ...
Develop processes and procedures for how the team will: share work, meet the objectives of the project, solve problems and resolve conflicts and make decisions. When the team members get to know each other, they will begin to support each other and will be more concerned about their team mates. Bottom line, they will function as a team.
Teamwork as demonstrated in this study fails to account for the fact that teams are not simple, static and ... as is often the case in group and team research studies (cf. Van de Ven et al., 1976; Antoni and Hertel, 2009; Dierdorff et ... in Improving Teamwork in Organizations. Applications of Resource Management Training, eds Salas E ...
Keywords: Teamwork, Incentives, Operating Performance, and Organization Performance. DOI: 10.7176/RJFA/11-14-05. Publication date:July 31st 2020. 1. Introduction. Teamwork is a means of working together towards a set goal providing the necessary synergy where people get empowered in the working relationship to achieve continuous performance ...
Collaboration and teams Digital Article. Eric Quintane. Sunny Lee. Jung Won Lee. Camila Umaña Ruiz. Martin Kilduff. And how companies can better support these important cross-functional workers ...
being flexible and allowing others to contribute. Coming together in person can make a lot of things a lot simpler as opposed to doing it all online. Communication is the key for a successful team environment. Communication so the team can adjust to fit everyones' needs. Don't let negativity ruin a good presentation.
The course will be delivered via HBS Online's course platform and immerse learners in real-world examples from experts at industry-leading organizations. By the end of the course, participants will be able to: Explore the science of teamwork, focusing on the psychological and sociological aspects of teaming, collaboration, and defining effective outcomes.
A 2023 study found that collaboration hurts efficiency when team members can't observe each other and communication is less efficient than face-to-face interactions. To avoid this pitfall, teams ...
Two vital elements are essential for building leadership capabilities in a growing, founder-led organization: pace and purpose. Understanding each in the context of leadership development and capability building is crucial, as is understanding their interplay. Pace is important because rapid growth often leads to instability, along with sizable ...
To balance the heightened risks posed by using LLMs with the need to get the latest tools in the hands of our researchers quickly, we engaged in a collaborative and flexible four-step process: Understand requirements and risks. Establish policy and guidance. Enter into a contract with employees. Collect feedback and adjust.
The first occurs when conflict revolves around a single member of a team (20-25% of team conflicts). The second is when two members of a team disagree (the most common team conflict at 35%). The ...
The influence of Child Evangelism Fellowship saw a significant increase across the United States of America after an organizational change following a 2001 Supreme Court case ruling. The purpose of this phenomenological study was to describe the role of followership on the change and followership principles that emerged during the change that was implemented following the ruling Good News Club v.
The urban texture is the physical manifestation of the urban form's evolution. In the rapid process of urbanization, protecting and reshaping the urban texture has become an essential means to sustain the overall form and vitality of cities. Previous studies in this field have primarily relied on image analysis or typological methods, lacking a quantitative approach to identify and analyze ...