Rubrics for Oral Presentations
Introduction.
Many instructors require students to give oral presentations, which they evaluate and count in students’ grades. It is important that instructors clarify their goals for these presentations as well as the student learning objectives to which they are related. Embedding the assignment in course goals and learning objectives allows instructors to be clear with students about their expectations and to develop a rubric for evaluating the presentations.
A rubric is a scoring guide that articulates and assesses specific components and expectations for an assignment. Rubrics identify the various criteria relevant to an assignment and then explicitly state the possible levels of achievement along a continuum, so that an effective rubric accurately reflects the expectations of an assignment. Using a rubric to evaluate student performance has advantages for both instructors and students. Creating Rubrics
Rubrics can be either analytic or holistic. An analytic rubric comprises a set of specific criteria, with each one evaluated separately and receiving a separate score. The template resembles a grid with the criteria listed in the left column and levels of performance listed across the top row, using numbers and/or descriptors. The cells within the center of the rubric contain descriptions of what expected performance looks like for each level of performance.
A holistic rubric consists of a set of descriptors that generate a single, global score for the entire work. The single score is based on raters’ overall perception of the quality of the performance. Often, sentence- or paragraph-length descriptions of different levels of competencies are provided.
When applied to an oral presentation, rubrics should reflect the elements of the presentation that will be evaluated as well as their relative importance. Thus, the instructor must decide whether to include dimensions relevant to both form and content and, if so, which one. Additionally, the instructor must decide how to weight each of the dimensions – are they all equally important, or are some more important than others? Additionally, if the presentation represents a group project, the instructor must decide how to balance grading individual and group contributions. Evaluating Group Projects
Creating Rubrics
The steps for creating an analytic rubric include the following:
1. Clarify the purpose of the assignment. What learning objectives are associated with the assignment?
2. Look for existing rubrics that can be adopted or adapted for the specific assignment
3. Define the criteria to be evaluated
4. Choose the rating scale to measure levels of performance
5. Write descriptions for each criterion for each performance level of the rating scale
6. Test and revise the rubric
Examples of criteria that have been included in rubrics for evaluation oral presentations include:
- Knowledge of content
- Organization of content
- Presentation of ideas
- Research/sources
- Visual aids/handouts
- Language clarity
- Grammatical correctness
- Time management
- Volume of speech
- Rate/pacing of Speech
- Mannerisms/gestures
- Eye contact/audience engagement
Examples of scales/ratings that have been used to rate student performance include:
- Strong, Satisfactory, Weak
- Beginning, Intermediate, High
- Exemplary, Competent, Developing
- Excellent, Competent, Needs Work
- Exceeds Standard, Meets Standard, Approaching Standard, Below Standard
- Exemplary, Proficient, Developing, Novice
- Excellent, Good, Marginal, Unacceptable
- Advanced, Intermediate High, Intermediate, Developing
- Exceptional, Above Average, Sufficient, Minimal, Poor
- Master, Distinguished, Proficient, Intermediate, Novice
- Excellent, Good, Satisfactory, Poor, Unacceptable
- Always, Often, Sometimes, Rarely, Never
- Exemplary, Accomplished, Acceptable, Minimally Acceptable, Emerging, Unacceptable
Grading and Performance Rubrics Carnegie Mellon University Eberly Center for Teaching Excellence & Educational Innovation
Creating and Using Rubrics Carnegie Mellon University Eberly Center for Teaching Excellence & Educational Innovation
Using Rubrics Cornell University Center for Teaching Innovation
Rubrics DePaul University Teaching Commons
Building a Rubric University of Texas/Austin Faculty Innovation Center
Building a Rubric Columbia University Center for Teaching and Learning
Rubric Development University of West Florida Center for University Teaching, Learning, and Assessment
Creating and Using Rubrics Yale University Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning
Designing Grading Rubrics Brown University Sheridan Center for Teaching and Learning

Examples of Oral Presentation Rubrics
Oral Presentation Rubric Pomona College Teaching and Learning Center
Oral Presentation Evaluation Rubric University of Michigan
Oral Presentation Rubric Roanoke College
Oral Presentation: Scoring Guide Fresno State University Office of Institutional Effectiveness
Presentation Skills Rubric State University of New York/New Paltz School of Business
Oral Presentation Rubric Oregon State University Center for Teaching and Learning
Oral Presentation Rubric Purdue University College of Science
Group Class Presentation Sample Rubric Pepperdine University Graziadio Business School
© 2005: Christine Bauer-Ramazani ; last updated: October 24, 2017
Search form
- About Faculty Development and Support
- Programs and Funding Opportunities
Consultations, Observations, and Services
- Strategic Resources & Digital Publications
- Canvas @ Yale Support
- Learning Environments @ Yale
- Teaching Workshops
- Teaching Consultations and Classroom Observations
- Teaching Programs
- Spring Teaching Forum
- Written and Oral Communication Workshops and Panels
- Writing Resources & Tutorials
- About the Graduate Writing Laboratory
- Writing and Public Speaking Consultations
- Writing Workshops and Panels
- Writing Peer-Review Groups
- Writing Retreats and All Writes
- Online Writing Resources for Graduate Students
- About Teaching Development for Graduate and Professional School Students
- Teaching Programs and Grants
- Teaching Forums
- Resources for Graduate Student Teachers
- About Undergraduate Writing and Tutoring
- Academic Strategies Program
- The Writing Center
- STEM Tutoring & Programs
- Humanities & Social Sciences
- Center for Language Study
- Online Course Catalog
- Antiracist Pedagogy
- NECQL 2019: NorthEast Consortium for Quantitative Literacy XXII Meeting
- STEMinar Series
- Teaching in Context: Troubling Times
- Helmsley Postdoctoral Teaching Scholars
- Pedagogical Partners
- Instructional Materials
- Evaluation & Research
- STEM Education Job Opportunities
- Yale Connect
- Online Education Legal Statements
You are here
Creating and using rubrics.
A rubric describes the criteria that will be used to evaluate a specific task, such as a student writing assignment, poster, oral presentation, or other project. Rubrics allow instructors to communicate expectations to students, allow students to check in on their progress mid-assignment, and can increase the reliability of scores. Research suggests that when rubrics are used on an instructional basis (for instance, included with an assignment prompt for reference), students tend to utilize and appreciate them (Reddy and Andrade, 2010).
Rubrics generally exist in tabular form and are composed of:
- A description of the task that is being evaluated,
- The criteria that is being evaluated (row headings),
- A rating scale that demonstrates different levels of performance (column headings), and
- A description of each level of performance for each criterion (within each box of the table).
When multiple individuals are grading, rubrics also help improve the consistency of scoring across all graders. Instructors should insure that the structure, presentation, consistency, and use of their rubrics pass rigorous standards of validity , reliability , and fairness (Andrade, 2005).
Major Types of Rubrics
There are two major categories of rubrics:
- Holistic : In this type of rubric, a single score is provided based on raters’ overall perception of the quality of the performance. Holistic rubrics are useful when only one attribute is being evaluated, as they detail different levels of performance within a single attribute. This category of rubric is designed for quick scoring but does not provide detailed feedback. For these rubrics, the criteria may be the same as the description of the task.
- Analytic : In this type of rubric, scores are provided for several different criteria that are being evaluated. Analytic rubrics provide more detailed feedback to students and instructors about their performance. Scoring is usually more consistent across students and graders with analytic rubrics.
Rubrics utilize a scale that denotes level of success with a particular assignment, usually a 3-, 4-, or 5- category grid:

Figure 1: Grading Rubrics: Sample Scales (Brown Sheridan Center)
Sample Rubrics
Instructors can consider a sample holistic rubric developed for an English Writing Seminar course at Yale.
The Association of American Colleges and Universities also has a number of free (non-invasive free account required) analytic rubrics that can be downloaded and modified by instructors. These 16 VALUE rubrics enable instructors to measure items such as inquiry and analysis, critical thinking, written communication, oral communication, quantitative literacy, teamwork, problem-solving, and more.
Recommendations
The following provides a procedure for developing a rubric, adapted from Brown’s Sheridan Center for Teaching and Learning :
- Define the goal and purpose of the task that is being evaluated - Before constructing a rubric, instructors should review their learning outcomes associated with a given assignment. Are skills, content, and deeper conceptual knowledge clearly defined in the syllabus , and do class activities and assignments work towards intended outcomes? The rubric can only function effectively if goals are clear and student work progresses towards them.
- Decide what kind of rubric to use - The kind of rubric used may depend on the nature of the assignment, intended learning outcomes (for instance, does the task require the demonstration of several different skills?), and the amount and kind of feedback students will receive (for instance, is the task a formative or a summative assessment ?). Instructors can read the above, or consider “Additional Resources” for kinds of rubrics.
- Define the criteria - Instructors can review their learning outcomes and assessment parameters to determine specific criteria for the rubric to cover. Instructors should consider what knowledge and skills are required for successful completion, and create a list of criteria that assess outcomes across different vectors (comprehensiveness, maturity of thought, revisions, presentation, timeliness, etc). Criteria should be distinct and clearly described, and ideally, not surpass seven in number.
- Define the rating scale to measure levels of performance - Whatever rating scale instructors choose, they should insure that it is clear, and review it in-class to field student question and concerns. Instructors can consider if the scale will include descriptors or only be numerical, and might include prompts on the rubric for achieving higher achievement levels. Rubrics typically include 3-5 levels in their rating scales (see Figure 1 above).
- Write descriptions for each performance level of the rating scale - Each level should be accompanied by a descriptive paragraph that outlines ideals for each level, lists or names all performance expectations within the level, and if possible, provides a detail or example of ideal performance within each level. Across the rubric, descriptions should be parallel, observable, and measurable.
- Test and revise the rubric - The rubric can be tested before implementation, by arranging for writing or testing conditions with several graders or TFs who can use the rubric together. After grading with the rubric, graders might grade a similar set of materials without the rubric to assure consistency. Instructors can consider discrepancies, share the rubric and results with faculty colleagues for further opinions, and revise the rubric for use in class. Instructors might also seek out colleagues’ rubrics as well, for comparison. Regarding course implementation, instructors might consider passing rubrics out during the first class, in order to make grading expectations clear as early as possible. Rubrics should fit on one page, so that descriptions and criteria are viewable quickly and simultaneously. During and after a class or course, instructors can collect feedback on the rubric’s clarity and effectiveness from TFs and even students through anonymous surveys. Comparing scores and quality of assignments with parallel or previous assignments that did not include a rubric can reveal effectiveness as well. Instructors should feel free to revise a rubric following a course too, based on student performance and areas of confusion.
Additional Resources
Cox, G. C., Brathwaite, B. H., & Morrison, J. (2015). The Rubric: An assessment tool to guide students and markers. Advances in Higher Education, 149-163.
Creating and Using Rubrics - Carnegie Mellon Eberly Center for Teaching Excellence and & Educational Innovation
Creating a Rubric - UC Denver Center for Faculty Development
Grading Rubric Design - Brown University Sheridan Center for Teaching and Learning
Moskal, B. M. (2000). Scoring rubrics: What, when and how? Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation 7(3).
Quinlan A. M., (2011) A Complete Guide to Rubrics: Assessment Made Easy for Teachers of K-college 2nd edition, Rowman & Littlefield Education.
Andrade, H. (2005). Teaching with Rubrics: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. College Teaching 53(1):27-30.
Reddy, Y. M., & Andrade, H. (2010). A review of rubric use in higher education. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 35(4), 435-448.
Sheridan Center for Teaching and Learning , Brown University
Downloads
YOU MAY BE INTERESTED IN

The Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning routinely supports members of the Yale community with individual instructional consultations and classroom observations.

Instructional Enhancement Fund
The Instructional Enhancement Fund (IEF) awards grants of up to $500 to support the timely integration of new learning activities into an existing undergraduate or graduate course. All Yale instructors of record, including tenured and tenure-track faculty, clinical instructional faculty, lecturers, lectors, and part-time acting instructors (PTAIs), are eligible to apply. Award decisions are typically provided within two weeks to help instructors implement ideas for the current semester.

Reserve a Room
The Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning partners with departments and groups on-campus throughout the year to share its space. Please review the reservation form and submit a request.
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, grading and performance rubrics, what are rubrics.
A rubric is a scoring tool that explicitly represents the performance expectations for an assignment or piece of work. A rubric divides the assigned work into component parts and provides clear descriptions of the characteristics of the work associated with each component, at varying levels of mastery. Rubrics can be used for a wide array of assignments: papers, projects, oral presentations, artistic performances, group projects, etc. Rubrics can be used as scoring or grading guides, to provide formative feedback to support and guide ongoing learning efforts, or both.
Advantages of Using Rubrics
Using a rubric provides several advantages to both instructors and students. Grading according to an explicit and descriptive set of criteria that is designed to reflect the weighted importance of the objectives of the assignment helps ensure that the instructor’s grading standards don’t change over time. Grading consistency is difficult to maintain over time because of fatigue, shifting standards based on prior experience, or intrusion of other criteria. Furthermore, rubrics can reduce the time spent grading by reducing uncertainty and by allowing instructors to refer to the rubric description associated with a score rather than having to write long comments. Finally, grading rubrics are invaluable in large courses that have multiple graders (other instructors, teaching assistants, etc.) because they can help ensure consistency across graders and reduce the systematic bias that can be introduced between graders.
Used more formatively, rubrics can help instructors get a clearer picture of the strengths and weaknesses of their class. By recording the component scores and tallying up the number of students scoring below an acceptable level on each component, instructors can identify those skills or concepts that need more instructional time and student effort.
Grading rubrics are also valuable to students. A rubric can help instructors communicate to students the specific requirements and acceptable performance standards of an assignment. When rubrics are given to students with the assignment description, they can help students monitor and assess their progress as they work toward clearly indicated goals. When assignments are scored and returned with the rubric, students can more easily recognize the strengths and weaknesses of their work and direct their efforts accordingly.
Examples of Rubrics
Here are links to a diverse set of rubrics designed by Carnegie Mellon faculty and faculty at other institutions. Although your particular field of study and type of assessment activity may not be represented currently, viewing a rubric that is designed for a similar activity may provide you with ideas on how to divide your task into components and how to describe the varying levels of mastery.
Paper Assignments
- Example 1: Philosophy Paper This rubric was designed for student papers in a range of philosophy courses, CMU.
- Example 2: Psychology Assignment Short, concept application homework assignment in cognitive psychology, CMU.
- Example 3: Anthropology Writing Assignments This rubric was designed for a series of short writing assignments in anthropology, CMU.
- Example 4: History Research Paper . This rubric was designed for essays and research papers in history, CMU.
- Example 1: Capstone Project in Design This rubric describes the components and standard of performance from the research phase to the final presentation for a senior capstone project in the School of Design, CMU.
- Example 2: Engineering Design Project This rubric describes performance standards on three aspects of a team project: Research and Design, Communication, and Team Work.
Oral Presentations
- Example 1: Oral Exam This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing performance on an oral exam in an upper-division history course, CMU.
- Example 2: Oral Communication
- Example 3: Group Presentations This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing group presentations in a history course, CMU.
Class Participation/Contributions
- Example 1: Discussion Class This rubric assesses the quality of student contributions to class discussions. This is appropriate for an undergraduate-level course, CMU.
- Example 2: Advanced Seminar This rubric is designed for assessing discussion performance in an advanced undergraduate or graduate seminar.
Center for Excellence in Teaching
Home > Resources > Group presentation rubric
Group presentation rubric
This is a grading rubric an instructor uses to assess students’ work on this type of assignment. It is a sample rubric that needs to be edited to reflect the specifics of a particular assignment. Students can self-assess using the rubric as a checklist before submitting their assignment.
Download this file
Download this file [63.74 KB]
Back to Resources Page
Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.
How to Get Started
Best practices, moodle how-to guides.
- Workshop Recording (Fall 2022)
- Workshop Registration
Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Types of rubrics: holistic, analytic/descriptive, single-point
Holistic Rubric. A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubric . An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubric . A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.
Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper, single-point rubric, more examples:.
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
RUBRIC FOR A PERSUASIVE PRESENTATION
Dr. elise gold (engineering).
Below you will find the various criteria used to evaluate your presentation along with categories describing your performance in these areas. The boxes highlighted indicate your overall performance in the broader areas as described. Items specifically needing work may be underlined. Along with a grade, an overall evaluation follows, with a few major suggestions for improvement.
GRADE: _________
(Points lost for not showing up for presentation, not submitting copy of presentation outline, notes, and handout copy of slides on day of presentation for not being present to serve as a peer=s assigned questioner? __________)
OVERALL EVALUATION:
ESL Presentation Rubric
- Resources for Teachers
- Pronunciation & Conversation
- Writing Skills
- Reading Comprehension
- Business English
- TESOL Diploma, Trinity College London
- M.A., Music Performance, Cologne University of Music
- B.A., Vocal Performance, Eastman School of Music
In-class presentations are a great way to encourage a number of English communicative skills in a realistic task that provides students not only help with their English skills but prepares them in a broader way for future education and work situations. Grading these presentations can be tricky, as there are many elements such as key presentation phrases beyond simple grammar and structure, pronunciation and so on that make a good presentation. This ESL presentation rubric can help you provide valuable feedback to your students and has been created with English learners in mind. Skills included in this rubric include stress and intonation , appropriate linking language, body language , fluency, as well as standard grammar structures.
- ESL Essay Writing Rubric
- How to Teach Pronunciation
- Dear Abby Lesson Plan
- Writing English Drama Scripts in ESL Class
- Learn How to Use YouTube in the ESL Classroom
- Standard Lesson Plan Format for ESL Teachers
- Top Lesson Plans for ESL and EFL
- How to Successfully Teach English One-to-One
- CALL Use in the ESL/EFL Classroom
- Process Writing
- How to Build an ESL Class Curriculum
- Finding a Job for ESL Learners: Interview Basics
- Methods for Teaching Grammar in an ESL/EFL Setting
- Speaking Strategies for English Learners
- Top Essential Advanced Level English Learner Resources
- English Only?
Bestiality references allegedly made during presentation at Renmark High School
Warning for readers: This article contains graphic language.
The South Australian Department for Education is investigating a presentation delivered to year 9 girls in a regional high school that allegedly referenced bestiality as being accepted by the LGBTQIA+ community.
Female students said teachers at Renmark High School told them to leave their lessons and attend a presentation in a separate classroom.
Students who attended the presentation on March 22 say two staff from the Headspace centre in the neighbouring town of Berri introduced a "third-party" presenter who facilitated an hour-long presentation focused on relationships.
Parents said they were not notified about the presentation, nor was it consented to.
Students said they were left unsupervised for the duration of the presentation.
Student Courtney White, 14, said she felt confused and blindsided by the presentation.
"We had a teacher that told us to grab a chair and sit in front of the board, and then the Headspace people came in and then [the teacher] left, so then we're sitting in front of a board alone with no teachers, just the Headspace people," she said.
"The first slide of the PowerPoint on the board was 'You can see queerly now' and 'No point hiding.'"
Girls felt 'really uncomfortable'
Fourteen-year-old Emelia Wundenberg said the presenter was graphic when referencing their own sexual preferences and spoke in sexually explicit terms about growing up and being confused about whether they idolised people of the same gender or wanted to be intimate with them.
Students say they were then given an explanation of the initialism LGBTQIA+, with each word and its meaning displayed on the screen.
"There was a slide for what the 'plus' means, and they just started randomly saying words that no-one knew, like bestiality," Emelia said.
"It was on the board when they were showing what the 'plus' meant."
The students said bestiality was then explained in detail and the presenter seemed to imply it was something practised by people who identified as LGBTQIA+.
"They said [the queer community] just accepts all of it, even though … isn't it illegal?" Emelia said.
As the talk went on multiple girls, including Courtney, began to feel uncomfortable and asked to leave the classroom to "go to the bathroom".
"We're all just sitting there like, 'What the hell? What are we doing here? Why are we learning about animals having sex with humans?'" she said.
"It was really disgusting, it was really uncomfortable."
Emelia said many of those who asked to leave the classroom did not return.
When the ABC sought comment from the presenter a response was sent on the person's behalf asking that reporters refrained from reaching out or naming them in its coverage.
'Normal procedure' not followed
Letters seen by the ABC that were sent to parents on behalf of Renmark High School principal Mat Evans stated that the presentation was meant to discuss "respectful relationships".
The letter acknowledged that the school's "normal procedure for notifying parents ahead of specific presentations was not followed".
Mr Evans said the third-party presenter had "been suspended from department schools while the department undertakes an investigation".
"We are undertaking an internal review to ensure that processes around such notifications and procedures with regard to third parties attending at our school are always met," he said.
The ABC contacted the Department for Education, which provided a similar statement and said the presentation was being investigated.
SA education department chief executive Martin Westwell said the presentation was "unacceptable" and "shouldn't have happened".
Speaking with ABC Radio Adelaide on Thursday, Professor Westwell said conversations about sexual health, societal norms, stereotypes and sexuality were normal parts of the Australian curriculum, but the presentation at Renmark High School was not.
"The core idea that students should understand sexuality and other sexualities is, I think, really important — but the way [the presenter] went about it was unacceptable," he said.
"The school has clearly made some mistakes.
"There should have been a teacher in the room when that occurred, but there wasn't and the principal has apologised for that.
"They hadn't reviewed the content.
"There was a few things that went wrong and it ended up with this inappropriate language and a few things being discussed in that session that were just not appropriate."

Support being provided to students
Headspace's national head of clinical leadership Nicola Palfrey said the organisation was aware of concerns raised by members of the Renmark community.
"We take all feedback very seriously and are reviewing how we can support and guide Headspace centres … to ensure presentations they facilitate or deliver are aligned with evidence and best practice and are safe and appropriate for young people," she said.
FocusOne Health Board chair Ian Gartley said the "focus at Headspace Berri, operated under licence by FocusOne Health, is on the mental health and wellbeing of young people".
"We are aware of concerns raised by local members of the Renmark community following a presentation delivered by a lived experience speaker that Headspace Berri facilitated at Renmark High School," he said.
"Our priority right now is ensuring that any young people and their families who may be experiencing distress receive the support they need."
All parties involved in the alleged incident declined to provide the presentation to the ABC.
Following the presentation, a follow-up letter seen by the ABC was sent to parents offering counselling services from the education department, which had arranged a social worker to attend the school to help support affected students.
Parents express shock and outrage
Parents of students who attended the presentation said it was a poor representation of the queer community and had raised many concerns about the school's protocols for third-party presentations.
"Who vetted this material? Who made sure it was safe for 14- and 15-year-old girls? Some of them are still 13," Emelia's mother Kristy Fyfe said.
"It has done a huge disservice to the [queer] community."
Following the presentation, Courtney's mother Nicki Gaylard removed her three children from Renmark High School.
"My kids are in limbo," she said.
"They're not in an education department at this point.
"I'm not putting them anywhere until I know this won't happen again.
"Under no circumstances should a child in that school ever feel trapped and unsafe without someone with their certificate, meaning a teacher."
The ABC has spoken to five other parents whose children attended the presentation.
They substantiated the two girls' claims.
LGBTQIA+ educators condemn 'slur'
Sexuality educators and LGBTQIA+ inclusion advocates Mel Brush and Eleonora Bertsa-Fuchs conduct consent and queer inclusion training for schools, parents and workplaces via their social enterprise Let's Talk About X.
Both are secondary teachers and Mx Bertsa-Fuchs said queer education was important but should be delivered in a safe and appropriate setting.
"The teachers are the people that these young people have a relationship with, that they are familiar with, that they're comfortable with," Mx Bertsa-Fuchs said.
"When you're in a vulnerable situation, like a respectful relationships workshop or seminar, there should be someone in the room that you are familiar with."
Mx Brush said the alleged use of the word bestiality in the presentation was damaging to the queer community.
"It's pretty shocking to think about that term being thrown around like that, especially given how loaded it is, and for a historical context of the way that it's been used as a slur and to discriminate against LGBT+ people," Mx Brush said.
ABC Riverland — local news in your inbox
- X (formerly Twitter)
- Relationships
- Renmark South
- Safety Education
- Secondary Schools
Smart. Open. Grounded. Inventive. Read our Ideas Made to Matter.
Which program is right for you?

Through intellectual rigor and experiential learning, this full-time, two-year MBA program develops leaders who make a difference in the world.
A rigorous, hands-on program that prepares adaptive problem solvers for premier finance careers.
A 12-month program focused on applying the tools of modern data science, optimization and machine learning to solve real-world business problems.
Earn your MBA and SM in engineering with this transformative two-year program.
Combine an international MBA with a deep dive into management science. A special opportunity for partner and affiliate schools only.
A doctoral program that produces outstanding scholars who are leading in their fields of research.
Bring a business perspective to your technical and quantitative expertise with a bachelor’s degree in management, business analytics, or finance.
A joint program for mid-career professionals that integrates engineering and systems thinking. Earn your master’s degree in engineering and management.
An interdisciplinary program that combines engineering, management, and design, leading to a master’s degree in engineering and management.
Executive Programs
A full-time MBA program for mid-career leaders eager to dedicate one year of discovery for a lifetime of impact.
This 20-month MBA program equips experienced executives to enhance their impact on their organizations and the world.
Non-degree programs for senior executives and high-potential managers.
A non-degree, customizable program for mid-career professionals.
Presentation and Fireside Chat with Bundesbank President Joachim Nagel
- Google Calendar
- iCal Calendar
- Outlook Calendar
On April 16 at 10:30 am, Dr. Joachim Nagel, President of the Deutsche Bundesbank , the central bank of Germany, will visit the MIT Media Lab and share insights on proposals to issue a digital currency for the euro area of the European Union entitled “Digital Euro: Vision, Advancements, and Challenges.”
See details on the MIT Golub Center for Finance and Policy event page .
Upcoming Events
Mba class visit program, africa innovate conference 2024, mit emba: business analytics panel, thursday, april 18, 2024 - hsi lunch seminar series with don rucker, md, ms chief strategy officer, 1uphealth & former national coordinator for health information technology (onc).
Google Cloud Next 2024: Everything announced so far
Google’s Cloud Next 2024 event takes place in Las Vegas through Thursday, and that means lots of new cloud-focused news on everything from Gemini, Google’s AI-powered chatbot , to AI to devops and security. Last year’s event was the first in-person Cloud Next since 2019, and Google took to the stage to show off its ongoing dedication to AI with its Duet AI for Gmail and many other debuts , including expansion of generative AI to its security product line and other enterprise-focused updates and debuts .
Don’t have time to watch the full archive of Google’s keynote event ? That’s OK; we’ve summed up the most important parts of the event below, with additional details from the TechCrunch team on the ground at the event. And Tuesday’s updates weren’t the only things Google made available to non-attendees — Wednesday’s developer-focused stream started at 10:30 a.m. PT .
Google Vids
Leveraging AI to help customers develop creative content is something Big Tech is looking for, and Tuesday, Google introduced its version. Google Vids, a new AI-fueled video creation tool , is the latest feature added to the Google Workspace.
Here’s how it works: Google claims users can make videos alongside other Workspace tools like Docs and Sheets. The editing, writing and production is all there. You also can collaborate with colleagues in real time within Google Vids. Read more
Gemini Code Assist
After reading about Google’s new Gemini Code Assist , an enterprise-focused AI code completion and assistance tool, you may be asking yourself if that sounds familiar. And you would be correct. TechCrunch Senior Editor Frederic Lardinois writes that “Google previously offered a similar service under the now-defunct Duet AI branding.” Then Gemini came along. Code Assist is a direct competitor to GitHub’s Copilot Enterprise. Here’s why
And to put Gemini Code Assist into context, Alex Wilhelm breaks down its competition with Copilot, and its potential risks and benefits to developers, in the latest TechCrunch Minute episode.
Google Workspace
Image Credits: Google
Among the new features are voice prompts to kick off the AI-based “Help me write” feature in Gmail while on the go . Another one for Gmail includes a way to instantly turn rough email drafts into a more polished email. Over on Sheets, you can send out a customizable alert when a certain field changes. Meanwhile, a new set of templates make starting a new spreadsheet easier. For the Doc lovers, there is support for tabs now. This is good because, according to the company, you can “organize information in a single document instead of linking to multiple documents or searching through Drive.” Of course, subscribers get the goodies first. Read more
Google also seems to have plans to monetize two of its new AI features for the Google Workspace productivity suite. This will look like $10/month/user add-on packages. One will be for the new AI meetings and messaging add-on that takes notes for you, provides meeting summaries and translates content into 69 languages. The other is for the introduced AI security package, which helps admins keep Google Workspace content more secure. Read more
In February, Google announced an image generator built into Gemini, Google’s AI-powered chatbot. The company pulled it shortly after it was found to be randomly injecting gender and racial diversity into prompts about people. This resulted in some offensive inaccuracies. While we waited for an eventual re-release, Google came out with the enhanced image-generating tool, Imagen 2 . This is inside its Vertex AI developer platform and has more of a focus on enterprise. Imagen 2 is now generally available and comes with some fun new capabilities, including inpainting and outpainting. There’s also what Google’s calling “text-to-live images” where you can now create short, four-second videos from text prompts, along the lines of AI-powered clip generation tools like Runway , Pika and Irreverent Labs . Read more
Vertex AI Agent Builder
We can all use a little bit of help, right? Meet Google’s Vertex AI Agent Builder, a new tool to help companies build AI agents.
“Vertex AI Agent Builder allows people to very easily and quickly build conversational agents,” Google Cloud CEO Thomas Kurian said. “You can build and deploy production-ready, generative AI-powered conversational agents and instruct and guide them the same way that you do humans to improve the quality and correctness of answers from models.”
To do this, the company uses a process called “grounding,” where the answers are tied to something considered to be a reliable source. In this case, it’s relying on Google Search (which in reality could or could not be accurate). Read more
Gemini comes to databases
Google calls Gemini in Databases a collection of features that “simplify all aspects of the database journey.” In less jargony language, it’s a bundle of AI-powered, developer-focused tools for Google Cloud customers who are creating, monitoring and migrating app databases. Read more
Google renews its focus on data sovereignty

Image Credits: MirageC / Getty Images
Google has offered cloud sovereignties before, but now it is focused more on partnerships rather than building them out on their own. Read more
Security tools get some AI love

Image Credits: Getty Images
Google jumps on board the productizing generative AI-powered security tool train with a number of new products and features aimed at large companies. Those include Threat Intelligence, which can analyze large portions of potentially malicious code. It also lets users perform natural language searches for ongoing threats or indicators of compromise. Another is Chronicle, Google’s cybersecurity telemetry offering for cloud customers to assist with cybersecurity investigations. The third is the enterprise cybersecurity and risk management suite Security Command Center. Read more
Nvidia’s Blackwell platform
One of the anticipated announcements is Nvidia’s next-generation Blackwell platform coming to Google Cloud in early 2025. Yes, that seems so far away. However, here is what to look forward to: support for the high-performance Nvidia HGX B200 for AI and HPC workloads and GB200 NBL72 for large language model (LLM) training. Oh, and we can reveal that the GB200 servers will be liquid-cooled. Read more
Chrome Enterprise Premium
Meanwhile, Google is expanding its Chrome Enterprise product suite with the launch of Chrome Enterprise Premium . What’s new here is that it mainly pertains mostly to security capabilities of the existing service, based on the insight that browsers are now the endpoints where most of the high-value work inside a company is done. Read more
Gemini 1.5 Pro
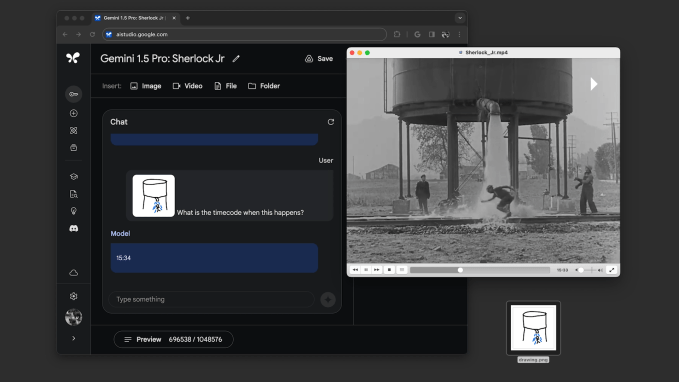
Everyone can use a “half” every now and again, and Google obliges with Gemini 1.5 Pro. This, Kyle Wiggers writes, is “Google’s most capable generative AI model,” and is now available in public preview on Vertex AI, Google’s enterprise-focused AI development platform. Here’s what you get for that half: T he amount of context that it can process, which is from 128,000 tokens up to 1 million tokens, where “tokens” refers to subdivided bits of raw data (like the syllables “fan,” “tas” and “tic” in the word “fantastic”). Read more
Open source tools

At Google Cloud Next 2024, the company debuted a number of open source tools primarily aimed at supporting generative AI projects and infrastructure. One is Max Diffusion, which is a collection of reference implementations of various diffusion models that run on XLA, or Accelerated Linear Algebra, devices. Then there is JetStream, a new engine to run generative AI models. The third is MaxTest, a collection of text-generating AI models targeting TPUs and Nvidia GPUs in the cloud. Read more
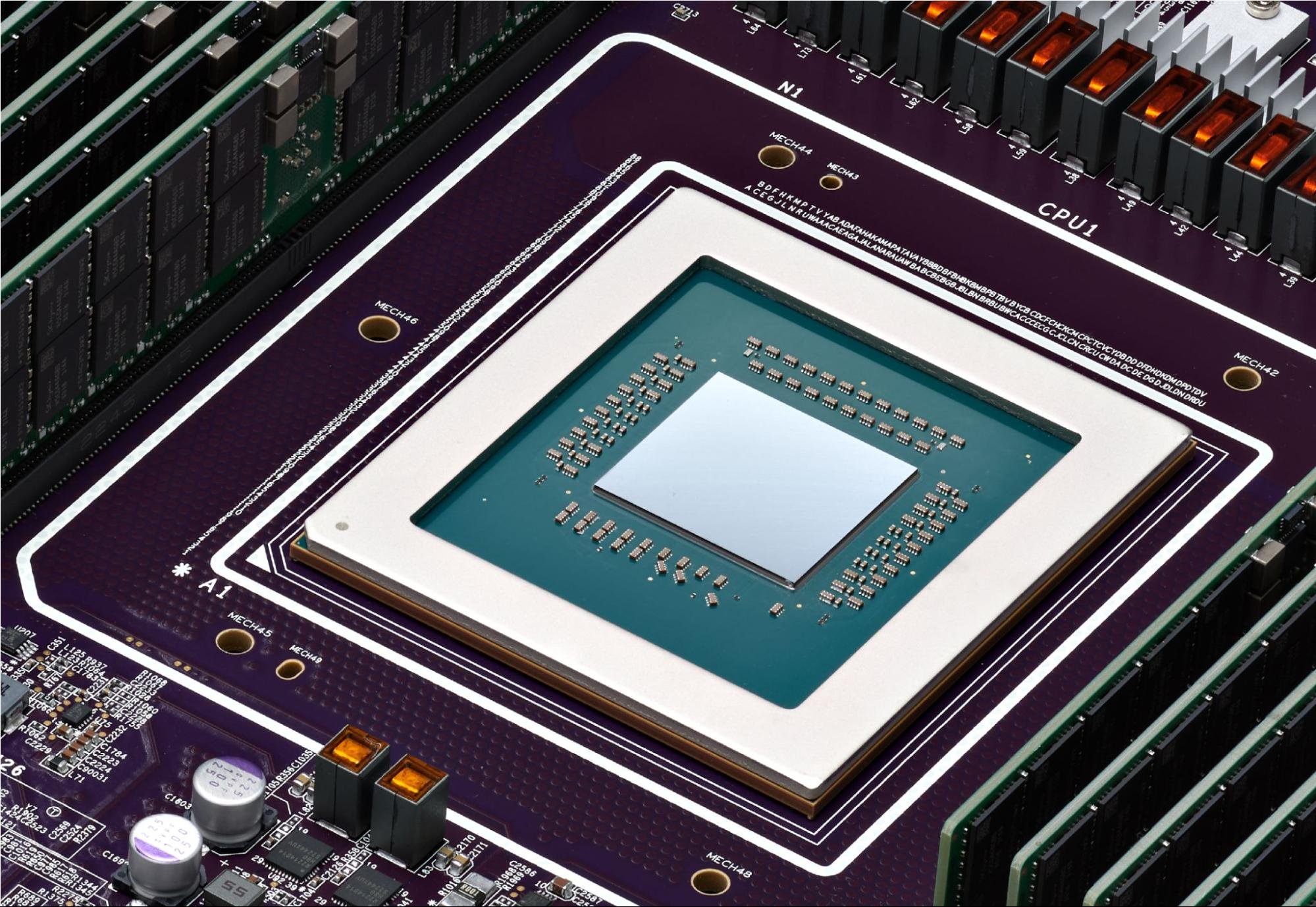
We don’t know a lot about this one, however, here is what we do know : Google Cloud joins AWS and Azure in announcing its first custom-built Arm processor, dubbed Axion. Frederic Lardinois writes that “based on Arm’s Neoverse 2 designs, Google says its Axion instances offer 30% better performance than other Arm-based instances from competitors like AWS and Microsoft and up to 50% better performance and 60% better energy efficiency than comparable X86-based instances.” Read more
The entire Google Cloud Next keynote
If all of that isn’t enough of an AI and cloud update deluge, you can watch the entire event keynote via the embed below.
Google Cloud Next’s developer keynote
On Wednesday, Google held a separate keynote for developers . They offered a deeper dive into the ins and outs of a number of tools outlined during the Tuesday keynote, including Gemini Cloud Assist, using AI for product recommendations and chat agents, ending with a showcase from Hugging Face. You can check out the full keynote below.
Follow Polygon online:
- Follow Polygon on Facebook
- Follow Polygon on Youtube
- Follow Polygon on Instagram
Site search
- Dragon’s Dogma 2
- FF7 Rebirth
- Zelda: Tears of the Kingdom
- Baldur’s Gate 3
- PlayStation
- Dungeons & Dragons
- Magic: The Gathering
- Board Games
- All Tabletop
- All Entertainment
- What to Watch
- What to Play
- Buyer’s Guides
- Really Bad Chess
- All Puzzles
Filed under:
- Entertainment
Five Nights at Freddy 2 hitting the big screen next year
Universal announced the sequel along with M3GAN 2
Share this story
- Share this on Facebook
- Share this on Reddit
- Share All sharing options
Share All sharing options for: Five Nights at Freddy 2 hitting the big screen next year
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73270635/StageTrio.0.jpg)
Five Nights at Freddy’s , the mostly reviled 2023 horror game adaptation that was also a colossal financial hit, is coming back to movie theaters. Universal Pictures announced a Five Nights at Freddy’s 2 during its CinemaCon 2024 presentation on Wednesday.
The presentation didn’t include any details on which cast members would be back for Five Nights at Freddy’s 2 or Emma Tammi would return to direct. While details on the new Blumhouse movie were thin, Universal did announce that it would be done time for a fall release next year. The sequel announcement shouldn’t come as much of a surprise considering the original movie made nearly $300 million dollars at the worldwide box office.
Universal’s presentation included quite a few other horror announcements for 2025, including Wolfman , directed by The Invisible Man ’s Leigh Whannell in January. Perhaps even more importantly, Universal announced that its other horror breakout of 2023, M3GAN , would get a sequel in 2025 as well.
Next Up In Horror
The next level of puzzles.
Take a break from your day by playing a puzzle or two! We’ve got SpellTower, Typeshift, crosswords, and more.
Sign up for the newsletter Patch Notes
A weekly roundup of the best things from Polygon
Just one more thing!
Please check your email to find a confirmation email, and follow the steps to confirm your humanity.
Oops. Something went wrong. Please enter a valid email and try again.
Loading comments...

Deadpool & Wolverine extended look is a swear-filled explanation of a multiversal mission

- Your guide to Fallout’s vaults and wastelands
Every Easter egg in the Fallout show, in which Easter eggs are very cheeky

- Dragon’s Dogma 2 guides, walkthroughs, and explainers
How to change your vocation in Dragon’s Dogma 2
Avatar: The Last Airbender creators’ first movie finds its Aang

Fallout’s glimpse of the Enclave is just the beginning

After Barbie tackled the patriarchy, Margot Robbie’s Monopoly movie could take a shot at capitalism next

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
the presentation. are effective; pacing, eye contact, and volume all help the presentation. Title slide with Title slide meets name, class, and title Title slide missing required elements. requirements. Timing (7-8 minutes) Timing is more than 30 seconds below stated minimum or more than 30 seconds more than stated maximum. Time limit is
This rubric is designed to help you evaluate the organization, design, and delivery of standard research talks and other oral presentations. Here are some ways to use it: Distribute the rubric to colleagues before a dress rehearsal of your talk. Use the rubric to collect feedback and improve your presentation and delivery.
The goal of this rubric is to identify and assess elements of research presentations, including delivery strategies and slide design. • Self-assessment: Record yourself presenting your talk using your computer's pre-downloaded recording software or by using the coach in Microsoft PowerPoint. Then review your recording, fill in the rubric ...
The rubric allows teachers to assess students in several key areas of oral presentation. Students are scored on a scale of 1-4 in three major areas. The first area is Delivery, which includes eye contact, and voice inflection. The second area, Content/Organization, scores students based on their knowledge and understanding of the topic being ...
Oral Presentation Rubric 4—Excellent 3—Good 2—Fair 1—Needs Improvement Delivery • Holds attention of entire audience with the use of direct eye contact, seldom looking at notes • Speaks with fluctuation in volume and inflection to maintain audience interest and emphasize key points • Consistent use of direct eye contact with ...
Examples of criteria that have been included in rubrics for evaluation oral presentations include: Knowledge of content. Organization of content. Presentation of ideas. Research/sources. Visual aids/handouts. Language clarity. Grammatical correctness. Time management.
presentation. Presenter mumbles, talks very fast, and speaks too quietly for a majority of students to hear & understand. Timing 4 - Exceptional 3 - Admirable 2 - Acceptable 1 - Poor Length of Presentation Within two minutes of allotted time +/-. Within four minutes of allotted time +/-. Within six minutes of allotted time +/-
Presentation appropriately cites requisite number of references. ... Length of presentation is within the assigned time limits. ... Title: Scoring Rubric for Oral Presentations: Example #1 Author: Testing and Evaluation Services Created Date: 8/10/2017 9:45:03 AM ...
Time used efficiently. Within 20 seconds of allotted time. Within 40 seconds of allotted time. Within 1 minute of allotted time. Substantially longer or shorter than indicated by assignment. Visual Aids (where Slides, posters, and/or handouts are professional and easy to read. Slides contain appropriate material but too much text or
Problematic Speaker is fluent and poised; uses language comfortably and appropriately; speaks at an effective rate and volume; few fillers Some degree of nervousness apparent; minor problems with language usage; speaker may speak too slowly or quickly, too loudly or softly; fillers are noticeable Speaker seems uncomfortable; several problems ...
presentation. Focus by audience is interrupted by speaker's mannerisms less than 20% of the time. • 2 points - Clothing is business-like or neat in appearance. Speaker lacks confidence and/or relies on note cards . more than 50% of the time but not more than 80% of the time. A moderate number of distracting mannerisms during presentation.
Whole group presentation is 5 or more minutes above or below the allotted time. Collaboration. Presenters worked as part of a team, providing effective transitions to next/previous speaker or making references to previous/next topics. Evidence of team work; transitions made to next/previous speaker or topics.
Oral Presentation Evaluation Rubric, Formal Setting. PRESENTER: Non-verbal skills (Poise) 5 4 3 2 1. Comfort Relaxed, easy presentation with minimal hesitation Generally comfortable appearance, occasional hesitation Somewhat comfortable appearance, some hesitation Generally uncomfortable, difficulty with flow of presentation Completely ...
Rubrics can be used to provide feedback to students on diverse types of assignments, from papers, projects, and oral presentations to artistic performances and group projects. ... Rubrics help instructors to: reduce the time spent grading by allowing instructors to refer to a substantive description without writing long comments;
Creating and Using Rubrics. A rubric describes the criteria that will be used to evaluate a specific task, such as a student writing assignment, poster, oral presentation, or other project. Rubrics allow instructors to communicate expectations to students, allow students to check in on their progress mid-assignment, and can increase the ...
Example 1: Oral Exam This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing performance on an oral exam in an upper-division history course, CMU. Example 2: Oral Communication. Example 3: Group Presentations This rubric describes a set of components and standards for assessing group presentations in a history course, CMU.
Group presentation rubric. This is a grading rubric an instructor uses to assess students' work on this type of assignment. It is a sample rubric that needs to be edited to reflect the specifics of a particular assignment. Students can self-assess using the rubric as a checklist before submitting their assignment. Download this file. Page.
Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations. Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. ... Disadvantages of analytic rubrics: More time-consuming to create and use than a ...
Along with a grade, an overall evaluation follows, with a few major suggestions for improvement. EXCEPTIONAL: A. STRONG: AB. EFFECTIVE: B. DEVELOPING: BC/C. INADEQUATE: D/F. MAJOR CRITERIA FOR EVALUATION. Presentation was excellent overall, shows outstanding control and skill, exceeds expectations in meeting the assignment's requirements.
This ESL presentation rubric can help you provide valuable feedback to your students and has been created with English learners in mind. Skills included in this rubric include stress and intonation, appropriate linking language, body language, fluency, as well as standard grammar structures. Read More.
AP® Research — Presentation and Oral Defense 2021 Scoring Guidelines. NOTE: To receive the highest performance level presumes that the student also achieved the preceding performance levels in that row. ADDITIONAL SCORES: In addition to the scores represented on the rubric, teachers can also assign scores of 0 (zero). A score of. A score of.
Presenters: Distribute this rubric to audience members in your practice runs to gather their feedback about the key aspects of your message, design, and delivery. Audience members: Circle the option in each row that best matches the presenter's performance and sum at the end. Presentation Assessment Rubric Presenter:
In addition to the scores represented on the rubrics, readers can also assign scores of 0 (zero) and NR (No Response). A score of 0 is assigned to a single row of the rubric when the response displays a below-minimum level of quality as identified in that row of the rubric. Does not meet the criteria for two points.
The Ukrainian community in Lisbon held a protest during the presentation of the pro-Russian book "A Guerra a Leste" ("War in the East") by the communist journalist Bruno Amaral de Carvalho at the Buchholz bookstore. Pavlo Sadokha, head of the Union of Ukrainians in Portugal, announced this on Facebook, Ukrinform reports.
The rubric for evaluating student presentations is included as a download in this article. In addition, the criteria on the rubric is explained in detail. The criteria included on this rubric is as follows: content, eye contact, volume and clarity, flow, confidence and attitude, visual aids, and time.
An investigation is underway into a presentation delivered to year 9 girls at Renmark High School.(ABC Riverland: Sophie Landau) In short: Year 9 girls at Renmark High School say they were given a ...
Presentation and Fireside Chat with Bundesbank President Joachim Nagel. MIT Media Lab, 6th floor 75 Amherst St E14-633 Cambridge, USA. Apr 16, 2024. Add to Calendar. Google Calendar. iCal Calendar. Outlook Calendar. 10:30AM - 11:30AM ET. On April 16 at 10:30 am, Dr. Joachim Nagel, President of the Deutsche Bundesbank, the central bank of ...
Google's Cloud Next 2024 event takes place in Las Vegas through Thursday, and that means lots of new cloud-focused news on everything from , to AI to devops and security. Last year's event was ...
Time to go back to Freeddy's. Five Nights at Freddy's 2 was announced during Universal's CinemaCon 2024 presentation and is set for theaters in fall 2025. Blumhouse is also back with M3GAN 2.0.