Student Academic Success Center
Related work / literature review / research review, download pdf handout: literature reviews, watch video: literature reviews.
A literature review, research review, or related work section compares, contrasts, synthesizes, and provides introspection about the available knowledge for a given topic or field. The two terms are sometimes used interchangeably (as they are here), but while both can refer to a section of a longer work, “literature review” can also describe a stand-alone paper.
When you start writing a literature review, the most straightforward course may be to compile all relevant sources and compare them, perhaps evaluating their strengths and weaknesses. While this is a good place to start, your literature review is incomplete unless it creates something new through these comparisons. Luckily, our resources can help you do this!
With these resources, you’ll learn:
- How to write a literature review that contributes rather than summarizes
- Common mistakes to avoid
- Useful phrases to show agreement and disagreement between sources
Need one-on-one help with your literature review or research article? Schedule an appointment with one of our consultants now!
Schedule an Appointment

Quick Links
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Integrity
- Bias Reporting and Response
- Statement of Assurance
- Documents, Forms, and News [Internal Staff Only]
Other Helpful Departments
- Disability Resources
- Center for Student Diversity & Inclusion
- Graduate Education
- Office of International Education
- University Health Services
Francesco Lelli
Related work/literature review/survey paper: a collection of resources.
A scientific literature review (sometimes also called related work or survey paper) is an integral part of:
- Writing scientific papers
- Writing position reports in a non-academic job
- Writing your Bachelor/Master/PhD thesis
Here, you will find a collection of resources that should help you in addressing your scholarly needs.

Not All Publications Are Equal
Yes, quality matters. I am talking about both (i) the quality of a venue/journal and (ii) the quality of a paper published in the particular venue/journal.
In talking about a venue you want to consider impact factor , self-citation ratio and indexing of the venue as some key heuristics for understanding the “prestige” of the venue. If you have trouble in understanding the meaning of these terms, I described these aspects extensively in one of my recent articles that talks about understanding scientific venues . I also presented what white papers are and how you should consider them in your research.
You have to be aware of the quality of a publication per se and independently from where it has been published. It is particularly important for saving time as well as for being able to read works that can actually help you in solving your problem instead of making it more complicated. Over time, every scientist develops his/her heuristics and in this article I described mine . In a nutshell, it is about looking at the citations of the article, its abstract, the venue, and the authors.
Much more can be said about the topic. This is an extensive lecture series from the University of Washington. If you are curious, you can learn some of the dynamics of scientific publishing. The title “Calling Bullshit in the Age of Big Data” gives you a good idea of the content.
Related Work/Literature Review and Active Reading
Do not limit yourself to only passive reading of scientific papers: instead, follow an active reading approach. In particular, you should take into account that scientific articles follow an IMRaD structure. It stands for I ntroduction, M ethods, Re sults and D iscussion . In a recent article, I discussed how to take advantage of that structure for reading scientific papers quickly and effectively .
It is also important to always keep in mind the reason why you are doing a related work/literature review and act accordingly. Maybe you are trying to understand a problem or are trying to find the proper methodology for solving a clear problem. Your reading approach should be finetuned for the particular goal, and in this article you can find suggestions for taking advantage of a literature review for your research. Starting from asking yourself “why should I read this paper?” .
Leverage Proper Tools for Organizing Your Work
The more you will read, in particular if you will practice active reading, the more you will need to effectively organize your work. You should start organizing your work early on, when you have not yet accumulated an unmanageable amount of scientific resources. Otherwise, the inertia will cost you an unbearable amount of time.
There are dedicated tools for this task. In this article, I describe how you could organize your references using specific features of Microsoft words . There are several other tools like Mendeley and Citeulike that could help you in reducing the complexity of managing a large amount of resources.
Other Practical Aspects for a Literature Review:
In this video, Javed Vasillis presents a practical approach for conducting a literature review with a focus on the HCI domain.
However, many of the suggestions are valid for every domain of research. In particular, how to use the keywords of scientific papers as well as scientific research engines.
In this video, Shady Attia presents his view on how to conduct a literature review.
In addition, in case you are doing a literature review for non-scientific purposes or for the purpose of conducting an assignment, you may want to watch this video. You will find a quick and effective approach for this task.
However, in case you are not writing a company report or a white paper I would encourage you to take a more formal approach as described in this article and in the other videos. If your goal is to produce a (relatively) quick deliverable for an assignment you may want to consider it.
Reading a good literature review (or related work or survey paper, call it in the way you prefer) can help you in understanding a problem and in providing you with clear ideas on how to solve a particular challenge. Writing an outstanding literature review can help you in positioning yourself as an expert in a field. They key is leveraging the structure of scientific papers, using an active reading approach, as well as using tools that can help you manage the increasing complexity.
This article (Related Work/Literature Review/Survey Paper: a collection of resources) is part of the miniseries on how to do a good thesis , you can see the full list of posts at the following links:
How to Do a Good Thesis: the Miniseries
Share this:

- Share on Tumblr
- ← European Factory Platform (EFPF): €2.5 million for Industry 4.0 Initiatives
- Can You Use the Internet of Things to Fight Addiction? →
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Privacy Overview
Terms and Conditions - Privacy Policy
Instantly share code, notes, and snippets.
ikbelkirasan / writing-a-state-of-the-art-section.md
- Download ZIP
- Star ( 9 ) 9 You must be signed in to star a gist
- Fork ( 1 ) 1 You must be signed in to fork a gist
- Embed Embed this gist in your website.
- Share Copy sharable link for this gist.
- Clone via HTTPS Clone using the web URL.
- Learn more about clone URLs
- Save ikbelkirasan/848f97c4a1aee1fa6277ced7b5be80af to your computer and use it in GitHub Desktop.
Writing the "Related Work" Section of a Paper/thesis
By: Chamin Morikawa ( https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/writing-related-work-section-paperthesis-chamin-morikawa/ )
For most students, writing about what they did on their own is not hard. But writing about others' work - which is what you have to do in the "State of the Art" or "Related Work" section - is quite hard for them. Here are a few guidelines to make this task a bit easier.
Let's lay down our assumptions before continuing. I assume that you want to write a "Related Work" section for a research paper or a thesis that describes your approach to solve some problem. Let's also assume that there are other publications that attempt to solve the same problem, but the solutions in them are not perfect. Finally, let's assume that your approach has some difference when compared to those by others, and some improvement (faster, more accurate, easier to afford, etc.).
The question is, how do you come up with a good Related Work section for this publication?
The Reasons
Let's start by looking at the reasons for having this section in a paper or a thesis. While most of you already know them, a reminder can help us to compose it properly.
The primary reason for detailing the state of the art is to highlight that somebody else had not already tried what you did, when you started your research. In order to do this convincingly, you will have to have done a good survey of related research, make a good summary of them if there is a lot of work, and identify the need for improvement. Doing this allows you to demonstrate the motivation for your approach to solve the given problem, and also point out the difference between your approach and the others.
There are a few secondary reasons for writing this section. If you are writing a Master's or PhD thesis, this section serves as evidence of your research skills. Including a good description of the state of the art in a research paper will allow readers who are not very familiar with your topic to learn more about it (if you want your paper to be recommended by professors to their students, this will definitely help). A third reason, one that many researchers won't mention directly, is to have a place for "citations". Citations in other publications is the most important metric for assessing the value of a research publication. A description on others' research can help sustain this metric, and also give an opportunity to make favors (not that I recommend it, but many researchers are guilty of mutual citations and citation loops that boost their records).
One thing to keep in mind when writing the "Related work" section is that it should be shaped "like a funnel". To be more specific, the content should be broad at the start, and focused at the end.
Start with a very brief introduction of the basic research area that your work belongs to. For example, if your paper is about automatic age estimation using digital photos of faces, you can start by mentioning Automated Face Image Analysis as the basic area. You don't have to get down to Computer Vision; Automated Face Image Analysis is already a large research area. Selecting a couple of survey papers to show the advances of this area should be sufficient.
Now it is time to mention other papers that try to solve the same problem as the one that your paper does. You can organize them by idea, into paragraphs, so that the reader won't feel lost among a mix of research works. It is fine to mention the accuracies, and it is essential to mention the state-of-the art if there is a clear evaluation metric to identify it.
Now you are coming to the end of this section. If you are writing a thesis, or a survey paper, this is a good place to summarize the approaches with their performances, advantages and disadvantages, on a table.Otherwise, you can write a paragraph that summarize same content. In either case, the ending paragraph should be a pointer to you work; you point out the limitations in the existing approaches and then state that you are going to try approach X that is different from what has been tried before.
If you are writing a short paper or a demo, you can actually avoid having a specific section detailing related research. The primary reason for this is that the page count for such papers is smaller. In such a case, you can extend the introduction of the paper mentioning work that is closest to your approach. If your solution to the given research problem is very different from others, you can keep the related work section short; but some reviewers might be unhappy with this.
Concluding remarks
I gave you some guidelines on writing a "Related Work" section, based on my experience as a student, researcher, reviewer, and a teacher. I hope you find them useful. Finally, an unofficial guideline; know the snakes in your jungle! I know of a few reviewers who used to reject papers that did not cite their work, even though their work was so old that they could be cited only in the first couple of paragraphs of the related work section. Your advisor usually knows the culprits for your field.
A Small Guide to Writing Your Thesis
Kevin Elphinstone
This is not intended to be a definitive guide to scientific authorship. There are many other guides available that are more comprehensive, both on the internet and in print. I suggest you refer to one or more of them before beginning to author a thesis.
This guide was motivated by reading many draft theses and the observation that most first-time thesis writers make very similar mistakes. One goal of this guide is mostly self-serving, it 's to avoid me spending my entire life repeating the same advice to every student whose draft thesis I receive. However, following this guide has advantages for both me and the thesis writer. It will allow me to spend my time concentrating on providing clear technical feedback, and not sounding like a tedious tape recording that is played independently of the submitted document. Heeding the advice contained herein is likely to produce a better thesis than simply taking a hit and miss approach.
Prerequisites
Before submitting a draft to me, I expect the following work to be done.
- The thesis has a title and an author. You have seen my office, your thesis will be placed in it at some point. You increase the odds dramatically of your thesis being found again if it is not an anonymous, untitled, pile of paper amongst all the other paper.
- The thesis has page numbers. Have you ever tried to piece together a 50+ page document without page numbers? I don't plan to!
- There are section headings and a table of contents. Like a long journey, a large document needs navigation aids to help steer the intrepid reader along the way. Don't risk me getting lost trying to find something.
- There is a bibliography with citations that are correct where cited . Have you ever tried checking the reference [?] ?
And most importantly
- The thesis has been spell checked, and proofread for clarity and grammatical correctness.
If you are too lazy to go to the trouble to provide me with a coherent document mostly free of inconsequential distractions (simple typos, etc.), then I will not read it.
The Thesis Itself
Simplistically, a thesis is a proposition advanced or position taken, that is then substantiated by argument or experiment. A dissertation, the document that embodies the proposed thesis and substantiation, is also termed thesis. However, thesis is not a fancy name for a report, or pile of paper. A thesis is expected to contain exactly that described above, a proposed position or solution, and a methodical substantiation. Avoid the common mistake of writing a chronological report of all the work you did. This is a good way to waste my time, and miss your chance to get feedback on the real thesis.
You should also note that a thesis is not a collection of ideas. A thesis has a single theme that is obvious from the start to the end of the document . If there is no obvious theme, you should seriously ask yourself why? Potential answers include a simple lack of coherent structure (the thesis is in there, but your hiding it), attempting more than one thesis (avoid tackling too many problems in too little detail), and having no clear thesis at all. Avoid the "build and experiment without clear reason" approach to research, you should identify the thesis prior to starting, not after supposedly finishing.
Contents
Theses usually have an expected format. You should not stick rigidly to a standard format (show initiative and creativity), however you also should not deviate significantly from it. The more you deviate, the more you will have to lead the reader through your thesis. Don't risk losing the reader by trying to be "clever".
The standard thesis looks something like
Introduction
- Background & Related Work
Proposed Solution
Experimental results.
Now looking at each section in detail
A reader of the introduction should be able to answer the following questions, although not in any depth.
- What is the thesis about?
- Why is it relevant or important?
- What are the issues or problems?
- What is the proposed solution or approach?
- What can one expect in the rest of the thesis?
State what the thesis is about early. Don't keep the reader guessing until the end of the introduction, or worse, the end of the thesis (don't laugh, I have read draft theses that left me wondering after reading the entire document). You should provide a brief and gentle overview of the thesis topic (or problem) to give the reader enough context to understand the rest of the introduction. Don't overwhelm the reader with detail at the start. You will provide the details later elsewhere in the thesis. Target the level of writing at one of your peers, but not necessarily somebody working in the same area.
State why the topic is important. Address the "so what?" criteria. Why are you working on the topic? Why should somebody else be interested? Your motivation should be obvious after the introduction, but not necessarily provably so at this point.
State what the major issues are in solving your problem. Coherently overview the issues in enough detail to be able to understand they exist, but don't go into details yet or attempt to prove they exist. The overview should be in just enough depth to understand why you might propose the your particular solution or approach you are taking.
Describe your proposed solution or position your taking. Again, you should not go into minute details, nor should you attempt to prove your solution at this point; the remainder of the thesis will describe and substantiate your solution in detail, that what a thesis is :-)
At this point the reader will know what your working on, why, what are the major issues, and what your proposed solution is, but usually only if he takes your word for it. You should outline what the reader should expect in the rest of the thesis. This is not just the table of contents in sentence form, it is an overview of the remainder of the thesis so the reader knows what to expect.
Related Work and Background
The related work section (sometimes called literature review ) is just that, a review of work related to the problem you are attempting to solve. It should identify and evaluate past approaches to the problem. It should also identify similar solutions to yours that have been applied to other problems not necessarily directly related to the one your solving. Reviewing the successes or limitations of your proposed solution in other contexts provides important understanding that should result in avoiding past mistakes, taking advantage of previous successes, and most importantly, potentially improving your solution or the technique in general when applied in your context and others. In addition to the obvious purpose indicated, the related work section also can serve to:
- justify that the problem exists by example and argument,
- motivate interest in your work by demonstrating relevance and importance,
- identify the important issues,
- and provide background to your solution.
Any remaining doubts over the existence, justification, motivation, or relevance of your thesis topic or problem at the end of the introduction should be gone by the end of related work section.
Note that a literature review is just that, a review. It is not a list of papers and a description of their contents! A literature review should critique, categorize, evaluate, and summarize work related to your thesis. Related work is also not a brain dump of everything you know in the field. You are not writing a textbook; only include information directly related to your topic, problem, or solution.
At this point the reader will have enough background (from the related work and introduction) to begin a detailed problem analysis and solution proposal. You should clearly identify in detail what the problem is, what you believe are the important issues, describe your proposed solution to the problem, and demonstrate why you believe your particular proposal is worth exploring. Note you might have one or more variants that are worth exploring. This is okay assuming you have time to explore them as they can be compared experimentally if you cannot clearly justify the preference for a particular varient.
You must also clearly identify what the outstanding issues are with your solution. These are the issues that must be resolved by experiment. If you don't need to experiment, you must have proved your solution correct. This situation occurs in mathematics, but it is rare in operating systems.
The reader now knows your proposed solution(s), understands the problem in detail, and knows what are the outstanding issues. You can now introduce the experiments you used to resolve the outstanding issues in your solution. You must describe how these experiments resolve the outstanding issues. Experiments without clear motivation why they were conducted are a waste of paper, give me an interesting novel to read if you really feel compelled to give me dead trees.
Describe the experimental set up in such a way that somebody could reproduce your results. This should be aimed at the level of somebody externally tackling the same problem, using your solution, and wanting to verify your results. This should not be targeted at the level of somebody within the local group, using your code, on our machines. Details such as "do blah on machine X to get machine Y to perform monitor" should not be in a thesis. Such information is useful, but make it available outside your thesis.
Present the results in a comprehendible manner. Describe them in words. Don't simply include ten pages of tables and graphs. Again, buy me a book instead. Make sure that the tables and graphs have clear labels, scales, keys, and captions.
This section takes the outstanding issues you previously identified, the experimental results, and analyzes them. Did the experimental results substantiate your solution, and how do they substantiate your solution. Where the results what you expected? Did the experiments create new issues? If so, identify them.
By the end of this section the reader should know how your proposed solution worked out. The reader should know what issues were resolve, what the resolution was, and what issues remain.
Recap on your thesis. It has been a long journey if the reader has made it this far. Remind the reader what the big picture was. Briefly outline your thesis, motivation, problem, and proposed solution.
Now the most important part, draw conclusions based on your analysis. Did your proposed solution work? What are the strong points? What are the limitations?
Significant issues identified in the thesis, or still outstanding after the thesis, should be describe as future work.
After Completing the Draft
It is normal for most thesis authors to get lost in the details while writing such a large and detailed work. I highly recommend forgetting your thesis for at least a day or so (a week is recommended). Take a break, play sport, learn to parachute, read a book, just do something that distracts you completely from the job at hand. After taking a break, read the thesis from front to back in one attempt. Use a pen and critically review your own work, but don't distract yourself from reading by immediately fixing the thesis when you find problems. Ask yourself does the thesis convey the big picture, are the details comprehensible, are there holes in your arguments, is there irrelevant stuff in there, is there relevant stuff missing? You will be surprised what you find the first time you read from front to back after taking a break from the thesis.
At this point you should have a coherent document that you can be proud of, and I am now quite happy to proofread your thesis :-)
Second Opinions
I recommend getting a second opinion when dealing with any doctors :-)
Here are some links you may find useful in no particular order.
While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
Generating a related work section for scientific papers: an optimized approach with adopting problem and method information
- Published: 21 July 2022
- Volume 127 , pages 4397–4417, ( 2022 )
Cite this article

- Pengcheng Li 1 ,
- Wei Lu 2 &
- Qikai Cheng ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3904-8901 2
996 Accesses
2 Citations
Explore all metrics
The rapid explosion of scientific publications has made related work writing increasingly laborious. In this paper, we propose a fully automated approach to generate related work sections by leveraging a seq2seq neural network. In particular, the main goal of our work is to improve the abstractive generation of related work by introducing problem and method information, which serve as a pivot to connect the previous works in the related work section and has been ignored by the existing studies. More specifically, we employ a title-generation strategy to automatically obtain problem and method information from given references and add the problem and method information as an additional feature to enhance the generation of related work. To verify the effectiveness and feasibility of our approach, we conduct a comparative experiment on publicly available datasets using several common neural summarizers. The experimental results indicate that the introduction of problem and method information contributes to the better generation of related work and our approach substantially outperforms the informed baseline on ROUGE-1 and ROUGE-L. The case study shows that the problem and method information enables considerable topic coherence between the generated related work section and the original paper.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions

Similar content being viewed by others

Automatic related work section generation: experiments in scientific document abstracting

An Analytical Study on a Benchmark Corpus Constructed for Related Work Generation

The Concept of System for Automated Scientific Literature Reviews Generation
https://github.com/smalot/pdfparser .
https://github.com/dwadden/dygiepp .
https://huggingface.co/models .
https://github.com/nlpyang/PreSumm .
https://github.com/abisee/pointer-generator .
https://github.com/zhongxiangboy/Improving-related-work-generation-by-introducing-problem-and-method-information .
Chen, J., & Zhuge, H. (2019). Automatic generation of related work through summarizing citations. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 31 (3), e4261.
Article Google Scholar
Chen, Y. C., & Bansal, M. (2018). Fast abstractive summarization with reinforce-selected sentence rewriting. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) (pp. 675–686).
Cheng, S. W., Kuo, C. W., & Kuo, C. H. (2012). Research article titles in applied linguistics. Journal of Academic Language and Learning, 6 (1), A1–A14.
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Das, S., & Paik, J. H. (2021). Context-sensitive gender inference of named entities in text. Information Processing & Management, 58 (1), 102423.
Day, R. A. (1996). How to write and publish a scientific paper. General Pharmacology, 6 (27), 1077.
Google Scholar
Devlin, J., Chang, M. W., Lee, K., & Toutanova, K. (2019). BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies , Vol. 1 (Long and Short Papers) (pp. 4171–4186).
Flowerdew, L. (2008). Corpus-based analyses of the problem-solution pattern: A phraseological approach (Vol. 29). John Benjamins Publishing.
Book Google Scholar
Gehrmann, S., Deng, Y., & Rush, A. M. (2018). Bottom-up abstractive summarization. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) (pp. 4098–4109).
Heffernan, K., & Teufel, S. (2018). Identifying problems and solutions in scientific text. Scientometrics, 116 (2), 1367–1382.
Hoang, C. D. V., & Kan, M. Y. (2010). Towards automated related work summarization. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Computational Linguistics: Posters (pp. 427–435).
Hsu, W. T., Lin, C. K., Lee, M. Y., Min, K., Tang, J., & Sun, M. (2018). A unified model for extractive and abstractive summarization using inconsistency loss. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) (pp. 132–141).
Hu, Y., & Wan, X. (2014, October). Automatic generation of related work sections in scientific papers: An optimization approach. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) (pp. 1624–1633).
Jaidka, K., Khoo, C., & Na, J. C. (2013). Deconstructing human literature reviews–a framework for multi-document summarization. In Proceedings of the 14th European Workshop on Natural Language Generation (pp. 125–135).
Jamali, H. R., & Nikzad, M. (2011). Article title type and its relation with the number of downloads and citations. Scientometrics, 88 (2), 653–661.
Ji, D., Tao, P., Fei, H., & Ren, Y. (2020). An end-to-end joint model for evidence information extraction from court record document. Information Processing & Management, 57 (6), 102305.
Khoo, C. S., Na, J. C., & Jaidka, K. (2011). Analysis of the macro-level discourse structure of literature. Online Information Review, 35 (2), 255–271.
Lewis, M., Liu, Y., Goyal, N., Ghazvininejad, M., Mohamed, A., Levy, O., & Zettlemoyer, L. (2020). BART: Denoising sequence-to-sequence pre-training for natural language generation, translation, and comprehension. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 7871–7880).
Lin, C. Y., & Hovy, E. (2003). Automatic evaluation of summaries using n-gram co-occurrence statistics. In Proceedings of the 2003 Human Language Technology Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 150–157).
Liu, Y., & Lapata, M. (2019). Text summarization with pretrained encoders. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and the 9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP) (pp. 3721–3731).
Lu, Y., Dong, Y., & Charlin, L. (2020). Multi-XScience: A large-scale dataset for extreme multi-document summarization of scientific articles. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) (pp. 8068–8074).
Luan, Y., Wadden, D., He, L., Shah, A., Ostendorf, M., & Hajishirzi, H. (2019). A general framework for information extraction using dynamic span graphs. In Proceedings of NAACL-HLT (pp. 3036–3046).
Ma, S., Zhang, C., & Liu, X. (2020). A review of citation recommendation: From textual content to enriched context. Scientometrics, 122 (3), 1445–1472.
Miao, L., Cao, D., Li, J., & Guan, W. (2020). Multi-modal product title compression. Information Processing & Management, 57 (1), 102123.
Mohammad, S., Dorr, B., Egan, M., Hassan, A., Muthukrishnan, P., Qazvinian, V., & Zajic, D. (2009). Using citations to generate surveys of scientific paradigms. In Proceedings of Human Language Technologies: The 2009 Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 584–592).
Mutlu, B., Sezer, E. A., & Akcayol, M. A. (2020). Candidate sentence selection for extractive text summarization. Information Processing & Management, 57 (6), 102359.
Nasar, Z., Jaffry, S. W., & Malik, M. K. (2018). Information extraction from scientific articles: A survey. Scientometrics, 117 (3), 1931–1990.
Paiva, C. E., Lima, J. P. D. S. N., & Paiva, B. S. R. (2012). Articles with short titles describing the results are cited more often. Clinics, 67 (5), 509–513.
Papineni, K., Roukos, S., Ward, T., & Zhu, W. J. (2002, July). Bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (pp. 311–318).
Putra, J. W. G., & Khodra, M. L. (2017). Automatic title generation in scientific articles for authorship assistance: A summarization approach. Journal of ICT Research and Applications, 11 (3), 253–267.
Radford, A., Narasimhan, K., Salimans, T., & Sutskever, I. (2018). Improving language understanding by generative pre-training . University of British Colombia.
Saggion, H., Shvets, A., & Bravo, À. (2020). Automatic related work section generation: Experiments in scientific document abstracting. Scientometrics, 125 (3), 3159–3185.
Scott, M. (2001). Mapping key words to problem and solution. In M. Scott & G. Thompson (Eds.), Patterns of Text: In Honour of Michael Hoey (pp. 109–127). Benjamins.
Chapter Google Scholar
See, A., Liu, P. J., & Manning, C. D. (2017). Get to the point: Summarization with pointer-generator networks. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers) (pp. 1073–1083).
Swales, J. M., & Feak, C. B. (2004). Academic writing for graduate students: Essential tasks and skills (Vol. 1). University of Michigan Press.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., & Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (pp. 6000–6010).
Wang, P., Li, S., Zhou, H., Tang, J., & Wang, T. (2019). ToC-RWG: Explore the combination of topic model and citation information for automatic related work generation. IEEE Access, 8 , 13043–13055.
Wang, Y., Liu, X., & Gao, Z. (2018). Neural related work summarization with a joint context-driven attention mechanism. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP) (pp. 1776–1786).
Widyantoro, D. H., & Amin, I. (2014). Citation sentence identification and classification for related work summarization. In 2014 International Conference on Advanced Computer Science and Information System (pp. 291–296). IEEE.
Yasunaga, M., Kasai, J., Zhang, R., Fabbri, A. R., Li, I., Friedman, D., & Radev, D. R. (2019). ScisummNet: A large annotated corpus and content-impact models for scientific paper summarization with citation networks. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 33, pp. 7386–7393).
Zaman, F., Shardlow, M., Hassan, S. U., Aljohani, N. R., & Nawaz, R. (2020). HTSS: A novel hybrid text summarisation and simplification architecture. Information Processing & Management, 57 (6), 102351.
Zhang, M., Zhou, G., Yu, W., & Liu, W. (2021). FAR-ASS: Fact-aware reinforced abstractive sentence summarization. Information Processing & Management, 58 (3), 102478.
Download references
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by Major Projects of National Social Science Foundation of China (No. 17ZDA292).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Economics and Management, Hubei University of Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Pengcheng Li
School of Information Management, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Wei Lu & Qikai Cheng
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
PL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—Original Draft. WL: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Supervision. QC: Data Curation, Writing—Review & Editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Qikai Cheng .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Li, P., Lu, W. & Cheng, Q. Generating a related work section for scientific papers: an optimized approach with adopting problem and method information. Scientometrics 127 , 4397–4417 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-022-04458-8
Download citation
Received : 10 May 2021
Accepted : 23 June 2022
Published : 21 July 2022
Issue Date : August 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-022-04458-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Automatic related work generation
- Scientific summarization
- seq2seq neural network
- Problem and method extraction
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Make a Literature Review in Research (RRL Example)
What is an RRL in a research paper?
A relevant review of the literature (RRL) is an objective, concise, critical summary of published research literature relevant to a topic being researched in an article. In an RRL, you discuss knowledge and findings from existing literature relevant to your study topic. If there are conflicts or gaps in existing literature, you can also discuss these in your review, as well as how you will confront these missing elements or resolve these issues in your study.
To complete an RRL, you first need to collect relevant literature; this can include online and offline sources. Save all of your applicable resources as you will need to include them in your paper. When looking through these sources, take notes and identify concepts of each source to describe in the review of the literature.
A good RRL does NOT:
A literature review does not simply reference and list all of the material you have cited in your paper.
- Presenting material that is not directly relevant to your study will distract and frustrate the reader and make them lose sight of the purpose of your study.
- Starting a literature review with “A number of scholars have studied the relationship between X and Y” and simply listing who has studied the topic and what each scholar concluded is not going to strengthen your paper.
A good RRL DOES:
- Present a brief typology that orders articles and books into groups to help readers focus on unresolved debates, inconsistencies, tensions, and new questions about a research topic.
- Summarize the most relevant and important aspects of the scientific literature related to your area of research
- Synthesize what has been done in this area of research and by whom, highlight what previous research indicates about a topic, and identify potential gaps and areas of disagreement in the field
- Give the reader an understanding of the background of the field and show which studies are important—and highlight errors in previous studies
How long is a review of the literature for a research paper?
The length of a review of the literature depends on its purpose and target readership and can vary significantly in scope and depth. In a dissertation, thesis, or standalone review of literature, it is usually a full chapter of the text (at least 20 pages). Whereas, a standard research article or school assignment literature review section could only be a few paragraphs in the Introduction section .
Building Your Literature Review Bookshelf
One way to conceive of a literature review is to think about writing it as you would build a bookshelf. You don’t need to cut each piece by yourself from scratch. Rather, you can take the pieces that other researchers have cut out and put them together to build a framework on which to hang your own “books”—that is, your own study methods, results, and conclusions.
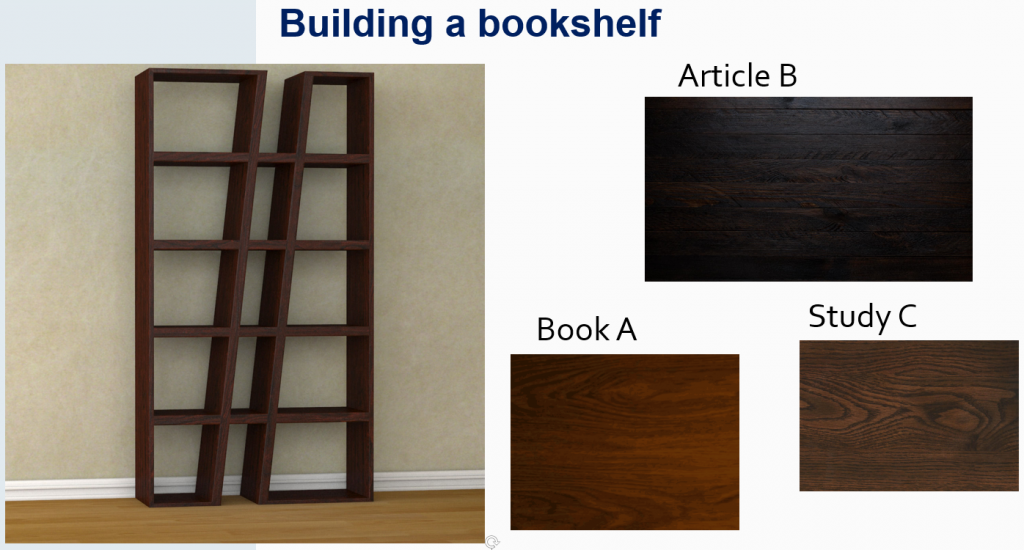
What Makes a Good Literature Review?
The contents of a literature review (RRL) are determined by many factors, including its precise purpose in the article, the degree of consensus with a given theory or tension between competing theories, the length of the article, the number of previous studies existing in the given field, etc. The following are some of the most important elements that a literature review provides.
Historical background for your research
Analyze what has been written about your field of research to highlight what is new and significant in your study—or how the analysis itself contributes to the understanding of this field, even in a small way. Providing a historical background also demonstrates to other researchers and journal editors your competency in discussing theoretical concepts. You should also make sure to understand how to paraphrase scientific literature to avoid plagiarism in your work.
The current context of your research
Discuss central (or peripheral) questions, issues, and debates in the field. Because a field is constantly being updated by new work, you can show where your research fits into this context and explain developments and trends in research.
A discussion of relevant theories and concepts
Theories and concepts should provide the foundation for your research. For example, if you are researching the relationship between ecological environments and human populations, provide models and theories that focus on specific aspects of this connection to contextualize your study. If your study asks a question concerning sustainability, mention a theory or model that underpins this concept. If it concerns invasive species, choose material that is focused in this direction.
Definitions of relevant terminology
In the natural sciences, the meaning of terms is relatively straightforward and consistent. But if you present a term that is obscure or context-specific, you should define the meaning of the term in the Introduction section (if you are introducing a study) or in the summary of the literature being reviewed.
Description of related relevant research
Include a description of related research that shows how your work expands or challenges earlier studies or fills in gaps in previous work. You can use your literature review as evidence of what works, what doesn’t, and what is missing in the field.
Supporting evidence for a practical problem or issue your research is addressing that demonstrates its importance: Referencing related research establishes your area of research as reputable and shows you are building upon previous work that other researchers have deemed significant.
Types of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews can differ in structure, length, amount, and breadth of content included. They can range from selective (a very narrow area of research or only a single work) to comprehensive (a larger amount or range of works). They can also be part of a larger work or stand on their own.
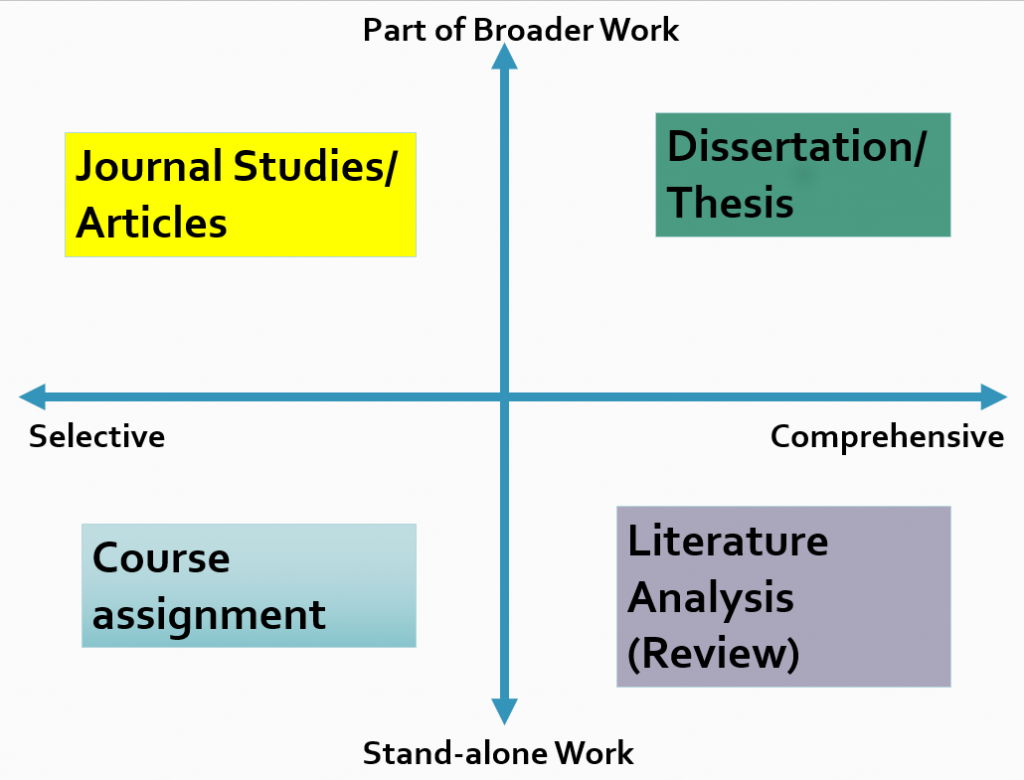
- A course assignment is an example of a selective, stand-alone work. It focuses on a small segment of the literature on a topic and makes up an entire work on its own.
- The literature review in a dissertation or thesis is both comprehensive and helps make up a larger work.
- A majority of journal articles start with a selective literature review to provide context for the research reported in the study; such a literature review is usually included in the Introduction section (but it can also follow the presentation of the results in the Discussion section ).
- Some literature reviews are both comprehensive and stand as a separate work—in this case, the entire article analyzes the literature on a given topic.
Literature Reviews Found in Academic Journals
The two types of literature reviews commonly found in journals are those introducing research articles (studies and surveys) and stand-alone literature analyses. They can differ in their scope, length, and specific purpose.
Literature reviews introducing research articles
The literature review found at the beginning of a journal article is used to introduce research related to the specific study and is found in the Introduction section, usually near the end. It is shorter than a stand-alone review because it must be limited to very specific studies and theories that are directly relevant to the current study. Its purpose is to set research precedence and provide support for the study’s theory, methods, results, and/or conclusions. Not all research articles contain an explicit review of the literature, but most do, whether it is a discrete section or indistinguishable from the rest of the Introduction.
How to structure a literature review for an article
When writing a literature review as part of an introduction to a study, simply follow the structure of the Introduction and move from the general to the specific—presenting the broadest background information about a topic first and then moving to specific studies that support your rationale , finally leading to your hypothesis statement. Such a literature review is often indistinguishable from the Introduction itself—the literature is INTRODUCING the background and defining the gaps your study aims to fill.
The stand-alone literature review
The literature review published as a stand-alone article presents and analyzes as many of the important publications in an area of study as possible to provide background information and context for a current area of research or a study. Stand-alone reviews are an excellent resource for researchers when they are first searching for the most relevant information on an area of study.
Such literature reviews are generally a bit broader in scope and can extend further back in time. This means that sometimes a scientific literature review can be highly theoretical, in addition to focusing on specific methods and outcomes of previous studies. In addition, all sections of such a “review article” refer to existing literature rather than describing the results of the authors’ own study.
In addition, this type of literature review is usually much longer than the literature review introducing a study. At the end of the review follows a conclusion that once again explicitly ties all of the cited works together to show how this analysis is itself a contribution to the literature. While not absolutely necessary, such articles often include the terms “Literature Review” or “Review of the Literature” in the title. Whether or not that is necessary or appropriate can also depend on the specific author instructions of the target journal. Have a look at this article for more input on how to compile a stand-alone review article that is insightful and helpful for other researchers in your field.

How to Write a Literature Review in 6 Steps
So how do authors turn a network of articles into a coherent review of relevant literature?
Writing a literature review is not usually a linear process—authors often go back and check the literature while reformulating their ideas or making adjustments to their study. Sometimes new findings are published before a study is completed and need to be incorporated into the current work. This also means you will not be writing the literature review at any one time, but constantly working on it before, during, and after your study is complete.
Here are some steps that will help you begin and follow through on your literature review.
Step 1: Choose a topic to write about—focus on and explore this topic.
Choose a topic that you are familiar with and highly interested in analyzing; a topic your intended readers and researchers will find interesting and useful; and a topic that is current, well-established in the field, and about which there has been sufficient research conducted for a review. This will help you find the “sweet spot” for what to focus on.
Step 2: Research and collect all the scholarly information on the topic that might be pertinent to your study.
This includes scholarly articles, books, conventions, conferences, dissertations, and theses—these and any other academic work related to your area of study is called “the literature.”
Step 3: Analyze the network of information that extends or responds to the major works in your area; select the material that is most useful.
Use thought maps and charts to identify intersections in the research and to outline important categories; select the material that will be most useful to your review.
Step 4: Describe and summarize each article—provide the essential information of the article that pertains to your study.
Determine 2-3 important concepts (depending on the length of your article) that are discussed in the literature; take notes about all of the important aspects of this study relevant to the topic being reviewed.
For example, in a given study, perhaps some of the main concepts are X, Y, and Z. Note these concepts and then write a brief summary about how the article incorporates them. In reviews that introduce a study, these can be relatively short. In stand-alone reviews, there may be significantly more texts and more concepts.
Step 5: Demonstrate how these concepts in the literature relate to what you discovered in your study or how the literature connects the concepts or topics being discussed.
In a literature review intro for an article, this information might include a summary of the results or methods of previous studies that correspond to and/or confirm those sections in your own study. For a stand-alone literature review, this may mean highlighting the concepts in each article and showing how they strengthen a hypothesis or show a pattern.
Discuss unaddressed issues in previous studies. These studies that are missing something you address are important to include in your literature review. In addition, those works whose theories and conclusions directly support your findings will be valuable to review here.
Step 6: Identify relationships in the literature and develop and connect your own ideas to them.
This is essentially the same as step 5 but focused on the connections between the literature and the current study or guiding concepts or arguments of the paper, not only on the connections between the works themselves.
Your hypothesis, argument, or guiding concept is the “golden thread” that will ultimately tie the works together and provide readers with specific insights they didn’t have before reading your literature review. Make sure you know where to put the research question , hypothesis, or statement of the problem in your research paper so that you guide your readers logically and naturally from your introduction of earlier work and evidence to the conclusions you want them to draw from the bigger picture.
Your literature review will not only cover publications on your topics but will include your own ideas and contributions. By following these steps you will be telling the specific story that sets the background and shows the significance of your research and you can turn a network of related works into a focused review of the literature.
Literature Review (RRL) Examples
Because creating sample literature reviews would take too long and not properly capture the nuances and detailed information needed for a good review, we have included some links to different types of literature reviews below. You can find links to more literature reviews in these categories by visiting the TUS Library’s website . Sample literature reviews as part of an article, dissertation, or thesis:
- Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
- Building Customer Loyalty: A Customer Experience Based Approach in a Tourism Context (Martina Donnelly)
Sample stand-alone literature reviews
- Literature Review on Attitudes towards Disability (National Disability Authority)
- The Effects of Communication Styles on Marital Satisfaction (Hannah Yager)
Additional Literature Review Format Guidelines
In addition to the content guidelines above, authors also need to check which style guidelines to use ( APA , Chicago, MLA, etc.) and what specific rules the target journal might have for how to structure such articles or how many studies to include—such information can usually be found on the journals’ “Guide for Authors” pages. Additionally, use one of the four Wordvice citation generators below, choosing the citation style needed for your paper:
Wordvice Writing and Academic Editing Resources
Finally, after you have finished drafting your literature review, be sure to receive professional proofreading services , including paper editing for your academic work. A competent proofreader who understands academic writing conventions and the specific style guides used by academic journals will ensure that your paper is ready for publication in your target journal.
See our academic resources for further advice on references in your paper , how to write an abstract , how to write a research paper title, how to impress the editor of your target journal with a perfect cover letter , and dozens of other research writing and publication topics.

Craft a Compelling Thesis: 9 pro tools for research and writing success
The journey from a captivating research topic to a compelling thesis can be long and winding. Between navigating mountains of information, organizing your thoughts, and crafting a well-structured argument, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. But fear not, intrepid researcher! This article introduces you to the categories of powerful tools that will streamline your research process, empower your writing, and ultimately help you craft a thesis that shines.
Part 1: Laying the Foundation – Research Powerhouses
Your research is the backbone of your thesis. To build a strong foundation, you need access to credible and diverse sources. Here are two essential online tools to kickstart your search:
Google Scholar and JSTOR: Unearthing scholarly gems
These academic search engines are goldmines for researchers. Google Scholar scours the web for scholarly articles, theses, books, and abstracts across a wide range of disciplines. JSTOR delivers a curated collection of high-quality, peer-reviewed journals and primary sources.
Power Up Your Research with Google Scholar and JSTOR:
1. Advanced Search Techniques: Both platforms offer advanced search functions. You can filter by publication date, author, title keywords, or specific journals.
2. Citation Tracking: Both Google Scholar and JSTOR allow you to track citations, helping you identify seminal works and build upon existing research.
3. Saved Searches and Alerts: Set up alerts to receive notifications when new articles relevant to your topic appear. This keeps you at the forefront of your field.
Choosing Between Them: Google Scholar offers a broader search across the web, while JSTOR provides a more focused collection of academically vetted sources. Use both in tandem for a comprehensive research strategy.
Part 2: Organizing the Chaos – From Drafts to Masterpieces
With research underway, the next hurdle is organizing your findings. Thankfully, digital note-taking apps like Evernote can be your savior.
Evernote: Your digital research vault
Evernote functions as a multi-functional information hub.
Evernote’s Powerhouse Features:
1. Text, Audio, and Image Capture: Capture ideas in various formats, including typed notes, voice recordings, and images of handwritten notes or scanned documents.
2. Organization and Tagging: Organize your notes using notebooks and tags, making it easy to find specific information later.
3. Web Clipper Integration: Save relevant web pages directly into Evernote, including text snippets, images, and links.
4. Collaboration: Share notes and collaborate with your peers on research projects.

Mastering Evernote for Thesis Success:
1. Create Subject-Specific Notebooks: Dedicate notebooks to different aspects of your thesis topic.
2. Maintain a Master Bibliography: Use a dedicated notebook to compile references you encounter during research.
3. Organize Quotes and Excerpts: Tag key quotes and excerpts with relevant keywords for easy retrieval.
4. Record Brainstorming Sessions: Use Evernote’s audio recording feature to capture fleeting ideas for future exploration.
Part 3: Roadmap to Success – Project Management Magic
With Evernote keeping your research organized, it’s time for project management tools to keep you on track. Trello, a popular visual project management platform, can be your guiding light.
Trello: Your thesis roadmap
Trello uses boards with lists and cards to visually represent your project progress.
Trello’s Advantages for Thesis Writers:
1. Visualizing Your Thesis Journey: Break down your thesis into manageable tasks within lists, and visualize your progress as you move cards across stages.
2. Setting Deadlines and Reminders: Assign deadlines to each task card and receive timely reminders to stay on schedule.
3. Collaboration Made Easy: Share your Trello board with your advisor or fellow researchers for collaborative brainstorming and task management.
Optimizing Trello for Your Thesis:
1. Create Lists for Different Stages: Set up lists like “Research,” “Outline,” “Writing,” “Revision,” and “Final Draft.”
2. Break Down Research Objectives: Within the “Research” list, create cards for specific sources you need to explore.
3. Track Writing Progress: Divide your writing into chapters or sections and create cards for each one, tracking progress as you write drafts.
4. Add Resources and Deadlines: Attach relevant research articles or outline notes to each card and set realistic deadlines to stay focused.
Part 4: Unveiling the Data – Statistical Power
If your research involves quantitative data analysis, statistics software like SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) becomes your secret weapon.
SPSS: Unveiling insights from data
SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Sciences) is a robust tool for quantitative data analysis, allowing you to explore relationships between variables, test hypotheses, and create data visualizations.
Unlocking the Power of SPSS:
1. Data Input and Cleaning: Enter your data into SPSS and utilize its cleaning tools to identify and address inconsistencies or missing values.
2. Statistical Analysis: Conduct various statistical tests depending on your research question. Explore correlations, conduct t-tests or ANOVAs, and analyze complex relationships.
3. Data Visualization: Create informative charts and graphs to visually represent your findings, making them easier to understand for yourself and your audience.
Part 5: Crafting Your Thesis – Writing and Polishing
With research organized, the project managed, and data analyzed, it’s time to translate your knowledge into a compelling thesis. Here, two writing powerhouses come into play:
Scrivener and MS Word: From drafts to polished prose
Scrivener : This software is designed specifically for writers, offering unique features to help you structure and organize your thesis.
Scrivener’s Strengths:
1. Corkboard Feature: Visually arrange your research notes, chapter outlines, and drafts on a digital corkboard for easy reorganization.
2. Focus Mode: Minimize distractions by hiding everything on the screen except the current section you’re working on.
3. Goal Setting and Tracking: Set daily writing goals and track your progress to maintain momentum.
MS Word : This ubiquitous word processor offers essential writing and editing tools.
MS Word’s Advantages:
1. Collaboration Tools : Share your thesis document with your advisor or peers for real-time feedback and collaborative editing.
2. Formatting and Styles: Utilize built-in styles and formatting options to ensure consistent formatting throughout your thesis.
3. Reference Management Tools: Integrate reference management software like Mendeley (mentioned later) for seamless in-text citations and bibliography creation.
Optimizing Your Writing Process:
1. Choose Your Weapon: Use Scrivener for initial brainstorming and organization, then switch to MS Word for fine-tuning formatting and referencing.
2. Utilize Templates: Both programs offer thesis templates to jumpstart your formatting process.
3. Embrace Collaboration: Share your drafts with others for constructive feedback and fresh perspectives.
Part 6: Extracting Text from Images – A Hidden Gem
Sometimes, your research may involve extracting text from images, such as scanned documents or screenshots. This is where Cardscanner.co comes in handy.
Cardscanner.co: Turning images into text
Cardscanner.co is an online OCR based Image to text converter which allows you to upload images, scanned documents, hand written notes and convert the text within them into editable digital format.
Cardscanner’s Benefits:
1. Effortless Text Extraction: Save time by quickly extracting text from images instead of manual retyping.
2. Supports Various Formats: Handle documents, scanned and printed images, hand written notes and more.
3. Batch Conversion: Allows you to process multiple files simultaneously and perform the text extracting conversion with complete accuracy.
4. Directly Export in Spreadsheet: Cardscanner also allows you to directly extract text from images containing any tabular data and export them directly into spreadsheets (XLSX, XLS, CSV).
5. Text Translation: With the translation feature, even if the image contains text in another language, the tool allows you to extract and translate the text without the need to translate it separately after extraction.
Part 7: Visual Storytelling – Infographics for Impact
Visuals can significantly enhance your thesis by making complex information more understandable and engaging. Here, two online infographic creation tools offer a helping hand:
Canva and Venngage: Simplifying visual communication
Canva and Venngage both are user-friendly platforms that provide a wide range of templates, icons, and design elements to create stunning infographics.
Canva and Venngage’s Advantages:
1. Drag-and-Drop Functionality: Easily design infographics without needing graphic design expertise.
2. Pre-designed Templates: Choose from a vast library of templates tailored to various topics and styles.
3. Collaboration Features: Work with your peers or advisor to create infographics collaboratively.
Tips for Creating Effective Infographics for Your Thesis:
1. Focus on Clarity: Keep your infographic focused on a single key message and avoid information overload.
2. Choose Data Wisely: Select the most impactful data points from your research to visually represent in your infographic.
3. Maintain Brand Consistency: Ensure your infographic aligns with the overall style and tone of your thesis.
Part 8: Citation Management Made Easy – Reference Powerhouse
Proper citation management is crucial for academic writing. Mendeley is a software specifically designed to streamline this process.
Mendeley: Your citation management ally
Mendeley helps you organize your research references, automatically generate in-text citations and bibliographies in various citation styles, and seamlessly integrate with writing software like MS Word.
Mendeley’s Benefits:
1. Reference Organization: Import references from various sources, including online databases and research papers.
2. Automatic Citation Generation: Generate in-text citations and bibliographies in the required format with a few clicks.
3. PDF Annotation and Highlighting: Annotate and highlight key passages within your research PDFs directly.
Part 9: Polishing Your Prose – Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Even the most meticulous researcher can benefit from a final polish. Here, two tools can empower you to deliver a grammatically sound and plagiarism-free thesis:
Trinka AI and Enago Plagiarism Checker : Ensuring Accuracy and Originality
Trinka AI : This online grammar checker utilizes AI technology to identify and correct grammatical errors, typos, and sentence structure issues.
Trinka AI’s Benefits:
1. Advanced Error Detection: Identifies a wider range of errors beyond basic grammar mistakes.
2. Contextual Analysis: Provides suggestions based on the context of your writing, ensuring appropriate phrasing.
3. Free Basic Plan: Offers a free plan with limited checks, with paid options for extended features.
Enago Plagiarism Checker : This online tool scans your thesis against a vast database of academic sources to identify unintentional plagiarism.
Enago Plagiarism Checker’s Advantages:
1. Peace of Mind: Ensures your work is original and avoids plagiarism accusations.
2. Detailed Report: Provides a report highlighting potential plagiarism instances with suggestions for correction.
3. Free Basic Version: Offers a free basic version with limited checks, with paid options for more comprehensive reports.
Final Words: A thesis triumph awaits!
With this arsenal of powerful tools at your disposal, you are well-equipped to navigate the research and writing journey with confidence. Remember, research and writing are iterative processes. Utilize these tools to organize your information, analyze data, craft compelling arguments, and present your findings in a clear and concise manner.
The path to a successful thesis may have its challenges, but with dedication and these tools as your allies, you can transform your research into a compelling and impactful document. Best of luck on your thesis journey!
Disclaimer: The opinions/views expressed in this article exclusively represent the individual perspectives of the author. While we affirm the value of diverse viewpoints and advocate for the freedom of individual expression, we do not endorse derogatory or offensive comments against any caste, creed, race, or similar distinctions. For any concerns or further information, we invite you to contact us at [email protected].
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.
Recommended from Academy

- Reporting Research
Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…
![how to write related work in thesis What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Industry News
- Publishing News
Unified AI Guidelines Crucial as Academic Writing Embraces Generative Tools
As generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools like ChatGPT are advancing at an accelerating pace, their…

- Promoting Research
- Thought Leadership
- Trending Now
How Enago Academy Contributes to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Through Empowering Researchers
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a universal call to action to end…

How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)
The pressure to “publish or perish” is a well-known reality for academics, striking fear into…

I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
How to Craft Your Ideal Thesis Research Topic
.webp)
Table of contents

Catherine Miller
Writing your undergraduate thesis is probably one of the most interesting parts of studying, especially because you get to choose your area of study. But as both a student and a teacher who’s helped countless students develop their research topics, I know this freedom can be just as intimidating as it is liberating.
Fortunately, there’a a step-by-step process you can follow that will help make the whole process a lot easier. In this article, I’ll show you how to choose a unique, specific thesis topic that’s true to your passions and interests, while making a contribution to your field.
.webp)
Choose a topic that you’re interested in
First things first: double-check with your teachers or supervisor if there are any constraints on your research topic. Once your parameters are clear, it’s time to identify what lights you up — after all, you’re going to be spending a lot of time thinking about it.
Within your field of study, you probably already have some topics that have grabbed your attention more than others. This can be a great place to start. Additionally, consider using the rest of your academic and extra-curricular interests as a source of ideas. At this stage, you only need a broad topic before you narrow it down to a specific question.
If you’re feeling stuck, here are some things to try:
- Look back through old course notes to remind yourself of topics you previously covered. Do any of these inspire you?
- Talk to potential supervisors about your ideas, as they can point you toward areas you might not have considered.
- Think about the things you enjoy in everyday life — whether that’s cycling, cinema, cooking, or fashion — then consider if there are any overlaps with your field of study.
- Imagine you have been asked to give a presentation or record a podcast in the next three days. What topics would you feel confident discussing?
- Watch a selection of existing lectures or explainer videos, or listen to podcasts by experts in your field. Note which topics you feel curious to explore further.
- Discuss your field of study with teachers friends and family, some with existing knowledge and some without. Which aspects do you enjoy talking about?
By doing all this, you might uncover some unusual and exciting avenues for research. For example, when writing my Master’s dissertation, I decided to combine my field of study (English teaching methodology) with one of my passions outside work (creative writing). In my undergraduate course, a friend drew on her lived experience of disability to look into the literary portrayal of disability in the ancient world.
Do your research
Once you’ve chosen your topic of interest, it’s time to dive into research. This is a really important part of this early process because it allows you to:
- See what other people have written about the topic — you don’t want to cover the same old ground as everyone else.
- Gain perspective on the big questions surrounding the topic.
- Go deeper into the parts that interest you to help you decide where to focus.
- Start building your bibliography and a bank of interesting quotations.
A great way to start is to visit your library for an introductory book. For example, the “A Very Short Introduction” series from the Oxford University Press provides overviews of a range of themes. Similar types of overviews may have the title “ A Companion to [Subject]” or “[Subject] A Student Companion”. Ask your librarian or teacher if you’re not sure where to begin.
Your introductory volume can spark ideas for further research, and the bibliography can give you some pointers about where to go next. You can also use keywords to research online via academic sites like JStor or Google Scholar. Check which subscriptions are available via your institution.
At this stage, you may not wish to read every single paper you come across in full — this could take a very long time and not everything will be relevant. Summarizing software like Wordtune could be very useful here.
Just upload a PDF or link to an online article using Wordtune, and it will produce a summary of the whole paper with a list of key points. This helps you to quickly sift through papers to grasp their central ideas and identify which ones to read in full.

Get Wordtune for free > Get Wordtune for free >
You can also use Wordtune for semantic search. In this case, the tool focuses its summary around your chosen search term, making it even easier to get what you need from the paper.

As you go, make sure you keep organized notes of what you’ve read, including the author and publication information and the page number of any citations you want to use.
Some people are happy to do this process with pen and paper, but if you prefer a digital method, there are several software options, including Zotero , EndNote , and Mendeley . Your institution may have an existing subscription so check before you sign up.
Narrowing down your thesis research topic
Now you’ve read around the topic, it’s time to narrow down your ideas so you can craft your final question. For example, when it came to my undergraduate thesis, I knew I wanted to write about Ancient Greek religion and I was interested in the topic of goddesses. So, I:
- Did some wide reading around the topic of goddesses
- Learned that the goddess Hera was not as well researched as others and that there were some fascinating aspects I wanted to explore
- Decided (with my supervisor’s support) to focus on her temples in the Argive region of Greece

As part of this process, it can be helpful to consider the “5 Ws”: why, what, who, when, and where, as you move from the bigger picture to something more precise.
Why did you choose this research topic?
Come back to the reasons you originally chose your theme. What grabbed you? Why is this topic important to you — or to the wider world? In my example, I knew I wanted to write about goddesses because, as a woman, I was interested in how a society in which female lives were often highly controlled dealt with having powerful female deities. My research highlighted Hera as one of the most powerful goddesses, tying into my key interest.
What are some of the big questions about your topic?
During your research, you’ll probably run into the same themes time and time again. Some of the questions that arise may not have been answered yet or might benefit from a fresh look.
Equally, there may be questions that haven’t yet been asked, especially if you are approaching the topic from a modern perspective or combining research that hasn’t been considered before. This might include taking a post-colonial, feminist, or queer approach to older texts or bringing in research using new scientific methods.
In my example, I knew there were still controversies about why so many temples to the goddess Hera were built in a certain region, and was keen to explore these further.
Who is the research topic relevant to?
Considering the “who” might help you open up new avenues. Is there a particular audience you want to reach? What might they be interested in? Is this a new audience for this field? Are there people out there who might be affected by the outcome of this research — for example, people with a particular medical condition — who might be able to use your conclusions?
Which period will you focus on?
Depending on the nature of your field, you might be able to choose a timeframe, which can help narrow the topic down. For example, you might focus on historical events that took place over a handful of years, look at the impact of a work of literature at a certain point after its publication, or review scientific progress over the last five years.
With my thesis, I decided to focus on the time when the temples were built rather than considering the hundreds of years for which they have existed, which would have taken me far too long.
Where does your topic relate to?
Place can be another means of narrowing down the topic. For example, consider the impact of your topic on a particular neighborhood, city, or country, rather than trying to process a global question.
In my example, I chose to focus my research on one area of Greece, where there were lots of temples to Hera. This meant skipping other important locations, but including these would have made the thesis too wide-ranging.
Create an outline and get feedback
Once you have an idea of what you are going to write about, create an outline or summary and get feedback from your teacher(s). It’s okay if you don’t know exactly how you’re going to answer your thesis question yet, but based on your research you should have a rough plan of the key points you want to cover. So, for me, the outline was as follows:
- Context: who was the goddess Hera?
- Overview of her sanctuaries in the Argive region
- Their initial development
- Political and cultural influences
- The importance of the mythical past
In the final thesis, I took a strong view on why the goddess was so important in this region, but it took more research, writing, and discussion with my supervisor to pin down my argument.
To choose a thesis research topic, find something you’re passionate about, research widely to get the big picture, and then move to a more focused view. Bringing a fresh perspective to a popular theme, finding an underserved audience who could benefit from your research, or answering a controversial question can make your thesis stand out from the crowd.
For tips on how to start writing your thesis, don’t miss our advice on writing a great research abstract and a stellar literature review . And don’t forget that Wordtune can also support you with proofreading, making it even easier to submit a polished thesis.
How do you come up with a research topic for a thesis?
To help you find a thesis topic, speak to your professor, look through your old course notes, think about what you already enjoy in everyday life, talk about your field of study with friends and family, and research podcasts and videos to find a topic that is interesting for you. It’s a good idea to refine your topic so that it’s not too general or broad.
Do you choose your own thesis topic?
Yes, you usually choose your own thesis topic. You can get help from your professor(s), friends, and family to figure out which research topic is interesting to you.
Share This Article:

How to Craft an Engaging Elevator Pitch that Gets Results
.webp)
Eight Steps to Craft an Irresistible LinkedIn Profile
.webp)
7 Common Errors in Writing + How to Fix Them (With Examples)
Looking for fresh content, thank you your submission has been received.
What Is a Capstone Project vs. Thesis

As students near the end of their academic journey, they encounter a crucial project called the capstone – a culmination of all they've learned. But what exactly is a capstone project?
This article aims to demystify capstone projects, explaining what they are, why they matter, and what you can expect when you embark on this final academic endeavor.
Capstone Project Meaning
A capstone project is a comprehensive, culminating academic endeavor undertaken by students typically in their final year of study.
It synthesizes their learning experiences, requiring students to apply the knowledge, skills, and competencies gained throughout their academic journey. A capstone project aims to address a real-world problem or explore a topic of interest in depth.
As interdisciplinary papers, capstone projects encourage critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. They allow students to showcase their mastery of their field of study and demonstrate their readiness for future academic or professional pursuits.
Now that we’ve defined what is a capstone project, let’s discuss its importance in the academic landscape. In case you have short-form compositions to handle, simply say, ‘ do my essay for me ,’ and our writers will take care of your workload.
Why Is a Capstone Project Important
A capstone project is crucial because it allows students to combine everything they've learned in school and apply it to real-life situations or big problems.
It's like the ultimate test of what they know and can do. By working on these projects, students get hands-on experience, learn to think critically and figure out how to solve tough problems.
Plus, it's a chance to show off their skills and prove they're ready for whatever comes next, whether that's starting a career or going on to more schooling.
Never Written Capstones Before?
Professional writers across dozens of subjects can help you right now.
What Is the Purpose of a Capstone Project
Here are three key purposes of a capstone project:
%20(1).webp)
Integration of Knowledge and Skills
Capstones often require students to draw upon the knowledge and skills they have acquired throughout their academic program. The importance of capstone project lies in helping students synthesize what they have learned and apply it to a real-world problem or project.
This integration helps students demonstrate their proficiency and readiness for graduation or entry into their chosen profession.
Culmination of Learning
Capstone projects culminate a student's academic journey, allowing them to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios.
tackling a significant project or problem, students demonstrate their understanding of concepts and their ability to translate them into practical solutions, reinforcing their learning journey.
Professional Development
Capstone projects allow students to develop skills relevant to their future careers. These projects can also be tangible examples of their capabilities to potential employers or graduate programs.
Whether it's conducting research, presenting findings, or collaborating with peers, students gain valuable experience that enhances their professional readiness.
Types of Capstone Projects
Capstones vary widely depending on the academic discipline, institution, and specific program requirements. Here are some common types:
What Is the Difference Between a Thesis and a Capstone Project
Here's a breakdown of the key differences between a thesis and a capstone project:
How to Write a Capstone Project
Let's dive into the specifics with actionable and meaningful steps for writing a capstone project:
1. Select a Pertinent Topic
Identify a topic that aligns with your academic interests, program requirements, and real-world relevance. Consider issues or challenges within your field that merit further exploration or solution.
Conduct thorough research to ensure the topic is both feasible and significant. Here are some brilliant capstone ideas for your inspiration.
2. Define Clear Objectives
Clearly articulate the objectives of your capstone project. What specific outcomes do you aim to achieve?
Whether it's solving a problem, answering a research question, or developing a product, ensure your objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
3. Conduct Comprehensive Research
Dive deep into existing literature, theories, and empirical evidence related to your chosen topic. Identify gaps, controversies, or areas for further investigation.
Synthesize relevant findings and insights to inform the development of your project and provide a solid foundation for your analysis or implementation.
4. Develop a Structured Plan
What is a capstone project in college without a rigid structure? Outline a comprehensive plan for your capstone project, including key milestones, tasks, and deadlines.
Break down the project into manageable phases, such as literature review, data collection, analysis, and presentation. Establish clear criteria for success and regularly monitor progress to stay on track.
5. Implement Methodological Rigor
If your project involves research, ensure methodological rigor by selecting appropriate research methods, tools, and techniques.
Develop a detailed research design or project plan that addresses key methodological considerations, such as sampling, data collection, analysis, and validity. Adhere to ethical guidelines and best practices throughout the research process.
6. Analyze and Interpret Findings
Analyze your data or findings using appropriate analytical techniques and tools. Interpret the results in relation to your research questions or objectives, highlighting key patterns, trends, or insights.
Critically evaluate the significance and implications of your findings within the broader context of your field or industry.
7. Communicate Effectively
Present your capstone project clearly, concisely, and compellingly. Whether it's a written report, presentation, or multimedia deliverable, tailor your communication style to your target audience. Clearly articulate your research questions, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
Use visuals, examples, and real-world applications to enhance understanding and engagement. Be prepared to defend your project and answer questions from peers, faculty, or stakeholders.
In wrapping up, what is a capstone project? It’s like the grand finale of your academic journey, where all the knowledge and skills you've acquired come together in one big project.
It's not just about passing a test or getting a grade – it's about proving you've got what it takes to make a real difference in the world. So, if you ever need capstone project help , our writers will gladly lend you a hand in no time.
Due Date Is Just Around the Corner?
Streamline the writing progress with our expert service!
What Is a Capstone Project in College?
How to do a capstone project, how long does a capstone project take to complete.

Annie Lambert
specializes in creating authoritative content on marketing, business, and finance, with a versatile ability to handle any essay type and dissertations. With a Master’s degree in Business Administration and a passion for social issues, her writing not only educates but also inspires action. On EssayPro blog, Annie delivers detailed guides and thought-provoking discussions on pressing economic and social topics. When not writing, she’s a guest speaker at various business seminars.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- T. (2023, June 16). What Is a Capstone Project? National University. https://www.nu.edu/blog/what-is-a-capstone-project/
- Lukins, S. (2024, May 12). What is a capstone project? And why is it important? Top Universities. https://www.topuniversities.com/student-info/careers-advice-articles/what-capstone-project-why-it-important
- Capstone Project vs. Thesis: What’s the Difference? (2021, December 9). UAGC. https://www.uagc.edu/blog/capstone-project-vs-thesis-whats-difference
Related Articles
.webp)
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
CS&E Announces 2024-25 Doctoral Dissertation Fellowship (DDF) Award Winners

Seven Ph.D. students working with CS&E professors have been named Doctoral Dissertation Fellows for the 2024-25 school year. The Doctoral Dissertation Fellowship is a highly competitive fellowship that gives the University’s most accomplished Ph.D. candidates an opportunity to devote full-time effort to an outstanding research project by providing time to finalize and write a dissertation during the fellowship year. The award includes a stipend of $25,000, tuition for up to 14 thesis credits each semester, and subsidized health insurance through the Graduate Assistant Health Plan.
CS&E congratulates the following students on this outstanding accomplishment:
- Athanasios Bacharis (Advisor: Nikolaos Papanikolopoulos )
- Karin de Langis (Advisor: Dongyeop Kang )
- Arshia Zernab Hassan (Advisors: Chad Myers )
- Xinyue Hu (Advisors: Zhi-Li Zhang )
- Lucas Kramer (Advisors: Eric Van Wyk )
- Yijun Lin (Advisors: Yao-Yi Chiang )
- Mingzhou Yang (Advisors: Shashi Shekhar )
Athanasios Bacharis

Bacharis’ work centers around the robot-vision area, focusing on making autonomous robots act on visual information. His research includes active vision approaches, namely, view planning and next-best-view, to tackle the problem of 3D reconstruction via different optimization frameworks. The acquisition of 3D information is crucial for automating tasks, and active vision methods obtain it via optimal inference. Areas of impact include agriculture and healthcare, where 3D models can lead to reduced use of fertilizers via phenotype analysis of crops and effective management of cancer treatments. Bacharis has a strong publication record, with two peer-reviewed conference papers and one journal paper already published. He also has one conference paper under review and two journal papers in the submission process. His publications are featured in prestigious robotic and automation venues, further demonstrating his expertise and the relevance of his research in the field.
Karin de Langis

Karin's thesis works at the intersection of Natural Language Processing (NLP) and cognitive science. Her work uses eye-tracking and other cognitive signals to improve NLP systems in their performance and cognitive interpretability, and to create NLP systems that process language more similarly to humans. Her human-centric approach to NLP is motivated by the possibility of addressing the shortcomings of current statistics-based NLP systems, which often become stuck on explainability and interpretability, resulting in potential biases. This work has most recently been accepted and presented at SIGNLL Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL) conference which has a special focus on theoretically, cognitively and scientifically motivated approaches to computational linguistics.
Arshia Zernab Hassan

Hassan's thesis work delves into developing computational methods for interpreting data from genome wide CRISPR/Cas9 screens. CRISPR/Cas9 is a new approach for genome editing that enables precise, large-scale editing of genomes and construction of mutants in human cells. These are powerful data for inferring functional relationships among genes essential for cancer growth. Moreover, chemical-genetic CRISPR screens, where population of mutant cells are grown in the presence of chemical compounds, help us understand the effect the chemicals have on cancer cells and formulate precise drug solutions. Given the novelty of these experimental technologies, computational methods to process and interpret the resulting data and accurately quantify the various genetic interactions are still quite limited, and this is where Hassan’s dissertation is focused on. Her research extends to developing deep-learning based methods that leverage CRISPR chemical-genetic and other genomic datasets to predict cancer sensitivity to candidate drugs. Her methods on improving information content in CRISPR screens was published in the Molecular Systems Biology journal, a highly visible journal in the computational biology field.

Hu's Ph.D. dissertation is concentrated on how to effectively leverage the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) – especially deep learning – to tackle challenging and important problems in the design and development of reliable, effective and secure (independent) physical infrastructure networks. More specifically, her research focuses on two critical infrastructures: power grids and communication networks, in particular, emerging 5G networks, both of which not only play a critical role in our daily life but are also vital to the nation’s economic well-being and security. Due to the enormous complexity, diversity, and scale of these two infrastructures, traditional approaches based on (simplified) theoretical models and heuristics-based optimization are no longer sufficient in overcoming many technical challenges in the design and operations of these infrastructures: data-driven machine learning approaches have become increasingly essential. The key question now is: how does one leverage the power of AI/ML without abandoning the rich theory and practical expertise that have accumulated over the years? Hu’s research has pioneered a new paradigm – (domain) knowledge-guided machine learning (KGML) – in tackling challenging and important problems in power grid and communications (e.g., 5G) network infrastructures.
Lucas Kramer

Kramer is now the driving force in designing tools and techniques for building extensible programming languages, with the Minnesota Extensible Language Tools (MELT) group. These are languages that start with a host language such as C or Java, but can then be extended with new syntax (notations) and new semantics (e.g. error-checking analyses or optimizations) over that new syntax and the original host language syntax. One extension that Kramer created was to embed the domain-specific language Halide in MELT's extensible specification of C, called ableC. This extension allows programmers to specify how code working on multi-dimensional matrices is transformed and optimized to make efficient use of hardware. Another embeds the logic-programming language Prolog into ableC; yet another provides a form of nondeterministic parallelism useful in some algorithms that search for a solution in a structured, but very large, search space. The goal of his research is to make building language extensions such as these more practical for non-expert developers. To this end he has made many significant contributions to the MELT group's Silver meta-language, making it easier for extension developers to correctly specify complex language features with minimal boilerplate. Kramer is the lead author of one journal and four conference papers on his work at the University of Minnesota, winning the distinguished paper award for his 2020 paper at the Software Language Engineering conference, "Strategic Tree Rewriting in Attribute Grammars".

Lin’s doctoral dissertation focuses on a timely, important topic of spatiotemporal prediction and forecasting using multimodal and multiscale data. Spatiotemporal prediction and forecasting are important scientific problems applicable to diverse phenomena, such as air quality, ambient noise, traffic conditions, and meteorology. Her work also couples the resulting prediction and forecasting with multimodal (e.g., satellite imagery, street-view photos, census records, and human mobility data) and multiscale geographic information (e.g., census records focusing on small tracts vs. neighborhood surveys) to characterize the natural and built environment, facilitating our understanding of the interactions between and within human social systems and the ecosystem. Her work has a wide-reaching impact across multiple domains such as smart cities, urban planning, policymaking, and public health.
Mingzhou Yang

Yang is developing a thesis in the broad area of spatial data mining for problems in transportation. His thesis has both societal and theoretical significance. Societally, climate change is a grand challenge due to the increasing severity and frequency of climate-related disasters such as wildfires, floods, droughts, etc. Thus, many nations are aiming at carbon neutrality (also called net zero) by mid-century to avert the worst impacts of global warming. Improving energy efficiency and reducing toxic emissions in transportation is important because transportation accounts for the vast majority of U.S. petroleum consumption as well as over a third of GHG emissions and over a hundred thousand U.S. deaths annually via air pollution. To accurately quantify the expected environmental cost of vehicles during real-world driving, Yang's thesis explores ways to incorporate physics in the neural network architecture complementing other methods of integration: feature incorporation, and regularization. This approach imposes stringent physical constraints on the neural network model, guaranteeing that its outputs are consistently in accordance with established physical laws for vehicles. Extensive experiments including ablation studies demonstrated the efficacy of incorporating physics into the model.
Related news releases
- Brock Shamblin Wins 2024 Riedl TA Award
- Ph.D. Student Angel Sylvester Mentor’s High School Student
- 2024 John T. Riedl Memorial Graduate Teaching Assistant Award
- CS&E Earns Five Awards at 2023 SIAM SDM
- CS&E Announces 2023-24 Doctoral Dissertation Fellowship (DDF) Award Winners
- Future undergraduate students
- Future transfer students
- Future graduate students
- Future international students
- Diversity and Inclusion Opportunities
- Learn abroad
- Living Learning Communities
- Mentor programs
- Programs for women
- Student groups
- Visit, Apply & Next Steps
- Information for current students
- Departments and majors overview
- Departments
- Undergraduate majors
- Graduate programs
- Integrated Degree Programs
- Additional degree-granting programs
- Online learning
- Academic Advising overview
- Academic Advising FAQ
- Academic Advising Blog
- Appointments and drop-ins
- Academic support
- Commencement
- Four-year plans
- Honors advising
- Policies, procedures, and forms
- Career Services overview
- Resumes and cover letters
- Jobs and internships
- Interviews and job offers
- CSE Career Fair
- Major and career exploration
- Graduate school
- Collegiate Life overview
- Scholarships
- Diversity & Inclusivity Alliance
- Anderson Student Innovation Labs
- Information for alumni
- Get engaged with CSE
- Upcoming events
- CSE Alumni Society Board
- Alumni volunteer interest form
- Golden Medallion Society Reunion
- 50-Year Reunion
- Alumni honors and awards
- Outstanding Achievement
- Alumni Service
- Distinguished Leadership
- Honorary Doctorate Degrees
- Nobel Laureates
- Alumni resources
- Alumni career resources
- Alumni news outlets
- CSE branded clothing
- International alumni resources
- Inventing Tomorrow magazine
- Update your info
- CSE giving overview
- Why give to CSE?
- College priorities
- Give online now
- External relations
- Giving priorities
- CSE Dean's Club
- Donor stories
- Impact of giving
- Ways to give to CSE
- Matching gifts
- CSE directories
- Invest in your company and the future
- Recruit our students
- Connect with researchers
- K-12 initiatives
- Diversity initiatives
- Research news
- Give to CSE
- CSE priorities
- Corporate relations
- Information for faculty and staff
- Administrative offices overview
- Office of the Dean
- Academic affairs
- Finance and Operations
- Communications
- Human resources
- Undergraduate programs and student services
- CSE Committees
- CSE policies overview
- Academic policies
- Faculty hiring and tenure policies
- Finance policies and information
- Graduate education policies
- Human resources policies
- Research policies
- Research overview
- Research centers and facilities
- Research proposal submission process
- Research safety
- Award-winning CSE faculty
- National academies
- University awards
- Honorary professorships
- Collegiate awards
- Other CSE honors and awards
- Staff awards
- Performance Management Process
- Work. With Flexibility in CSE
- K-12 outreach overview
- Summer camps
- Outreach events
- Enrichment programs
- Field trips and tours
- CSE K-12 Virtual Classroom Resources
- Educator development
- Sponsor an event
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Scientists use generative AI to answer complex questions in physics
Press contact :, media download.
*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."
Previous image Next image
When water freezes, it transitions from a liquid phase to a solid phase, resulting in a drastic change in properties like density and volume. Phase transitions in water are so common most of us probably don’t even think about them, but phase transitions in novel materials or complex physical systems are an important area of study.
To fully understand these systems, scientists must be able to recognize phases and detect the transitions between. But how to quantify phase changes in an unknown system is often unclear, especially when data are scarce.
Researchers from MIT and the University of Basel in Switzerland applied generative artificial intelligence models to this problem, developing a new machine-learning framework that can automatically map out phase diagrams for novel physical systems.
Their physics-informed machine-learning approach is more efficient than laborious, manual techniques which rely on theoretical expertise. Importantly, because their approach leverages generative models, it does not require huge, labeled training datasets used in other machine-learning techniques.
Such a framework could help scientists investigate the thermodynamic properties of novel materials or detect entanglement in quantum systems, for instance. Ultimately, this technique could make it possible for scientists to discover unknown phases of matter autonomously.
“If you have a new system with fully unknown properties, how would you choose which observable quantity to study? The hope, at least with data-driven tools, is that you could scan large new systems in an automated way, and it will point you to important changes in the system. This might be a tool in the pipeline of automated scientific discovery of new, exotic properties of phases,” says Frank Schäfer, a postdoc in the Julia Lab in the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) and co-author of a paper on this approach.
Joining Schäfer on the paper are first author Julian Arnold, a graduate student at the University of Basel; Alan Edelman, applied mathematics professor in the Department of Mathematics and leader of the Julia Lab; and senior author Christoph Bruder, professor in the Department of Physics at the University of Basel. The research is published today in Physical Review Letters.
Detecting phase transitions using AI
While water transitioning to ice might be among the most obvious examples of a phase change, more exotic phase changes, like when a material transitions from being a normal conductor to a superconductor, are of keen interest to scientists.
These transitions can be detected by identifying an “order parameter,” a quantity that is important and expected to change. For instance, water freezes and transitions to a solid phase (ice) when its temperature drops below 0 degrees Celsius. In this case, an appropriate order parameter could be defined in terms of the proportion of water molecules that are part of the crystalline lattice versus those that remain in a disordered state.
In the past, researchers have relied on physics expertise to build phase diagrams manually, drawing on theoretical understanding to know which order parameters are important. Not only is this tedious for complex systems, and perhaps impossible for unknown systems with new behaviors, but it also introduces human bias into the solution.
More recently, researchers have begun using machine learning to build discriminative classifiers that can solve this task by learning to classify a measurement statistic as coming from a particular phase of the physical system, the same way such models classify an image as a cat or dog.
The MIT researchers demonstrated how generative models can be used to solve this classification task much more efficiently, and in a physics-informed manner.
The Julia Programming Language , a popular language for scientific computing that is also used in MIT’s introductory linear algebra classes, offers many tools that make it invaluable for constructing such generative models, Schäfer adds.
Generative models, like those that underlie ChatGPT and Dall-E, typically work by estimating the probability distribution of some data, which they use to generate new data points that fit the distribution (such as new cat images that are similar to existing cat images).
However, when simulations of a physical system using tried-and-true scientific techniques are available, researchers get a model of its probability distribution for free. This distribution describes the measurement statistics of the physical system.
A more knowledgeable model
The MIT team’s insight is that this probability distribution also defines a generative model upon which a classifier can be constructed. They plug the generative model into standard statistical formulas to directly construct a classifier instead of learning it from samples, as was done with discriminative approaches.
“This is a really nice way of incorporating something you know about your physical system deep inside your machine-learning scheme. It goes far beyond just performing feature engineering on your data samples or simple inductive biases,” Schäfer says.
This generative classifier can determine what phase the system is in given some parameter, like temperature or pressure. And because the researchers directly approximate the probability distributions underlying measurements from the physical system, the classifier has system knowledge.
This enables their method to perform better than other machine-learning techniques. And because it can work automatically without the need for extensive training, their approach significantly enhances the computational efficiency of identifying phase transitions.
At the end of the day, similar to how one might ask ChatGPT to solve a math problem, the researchers can ask the generative classifier questions like “does this sample belong to phase I or phase II?” or “was this sample generated at high temperature or low temperature?”
Scientists could also use this approach to solve different binary classification tasks in physical systems, possibly to detect entanglement in quantum systems (Is the state entangled or not?) or determine whether theory A or B is best suited to solve a particular problem. They could also use this approach to better understand and improve large language models like ChatGPT by identifying how certain parameters should be tuned so the chatbot gives the best outputs.
In the future, the researchers also want to study theoretical guarantees regarding how many measurements they would need to effectively detect phase transitions and estimate the amount of computation that would require.
This work was funded, in part, by the Swiss National Science Foundation, the MIT-Switzerland Lockheed Martin Seed Fund, and MIT International Science and Technology Initiatives.
Share this news article on:
Press mentions.
Researchers at MIT and elsewhere have developed a new machine-learning model capable of “predicting a physical system’s phase or state,” report Kyle Wiggers and Devin Coldewey for TechCrunch .
Previous item Next item
Related Links
- Frank Schäfer
- Alan Edelman
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory
- Department of Mathematics
- Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
Related Topics
- Mathematics
- Computer science and technology
- Artificial intelligence
- Computer modeling
- Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL)
- Electrical Engineering & Computer Science (eecs)
Related Articles

Technique could efficiently solve partial differential equations for numerous applications
Computational model captures the elusive transition states of chemical reactions

Explained: Generative AI

From physics to generative AI: An AI model for advanced pattern generation
More mit news.
Turning up the heat on next-generation semiconductors
Read full story →

Sarah Millholland receives 2024 Vera Rubin Early Career Award

A community collaboration for progress

MIT scholars will take commercial break with entrepreneurial scholarship

MIT scientists learn how to control muscles with light
Using wobbling stellar material, astronomers measure the spin of a supermassive black hole for the first time
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
Looking back at former Trump fixer on the stand in hush money trial: Who is Michael Cohen?

Michael Cohen , Donald Trump 's former lawyer and fixer, took the witness stand Monday in Trump's criminal hush money trial .
Cohen's testimony could be a central link prosecutors use to show Trump authorized the $130,000 paid to porn star Stormy Daniels in an attempt to stop her story about an alleged affair from becoming public ahead of the 2016 election. Trump has been charged with 34 counts of falsifying business records to allegedly disguise reimbursing Cohen.
But Cohen's journey to the witness stand has been complicated. Once an adamant Trump loyalist, Cohen has repeatedly attacked Trump in recent years. He has also been convicted of several felonies, including lying to Congress:
Here is what to know about Cohen, a key witness in Trump's criminal trial:
Trump trial live updates: Latest updates as Michael Cohen returns as hush money witness
Prep for the polls: See who is running for president and compare where they stand on key issues in our Voter Guide
How long did Michael Cohen work for Trump?
Cohen was Trump's personal attorney and fixer from 2006 until 2018.
How long was Michael Cohen's prison sentence?
Michael Cohen was sentenced to three years in prison . He started his sentence in May 2019, but was sent home early for house arrest due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Where did Michael Cohen go to law school?
Michael Cohen went to Thomas M. Cooley Law School in Lansing, Michigan. Politico reported that "Cooley may be, by some measurements, the worst law school in America."
What did Michael Cohen lie about?
In November 2018, Michael Cohen pleaded guilty to one count of making false statements to Congress. In an effort to protect Trump, had told Congress his boss stopped trying to pursue a real-estate deal in Moscow in January 2016 when they actually continued efforts through June 2016.
That guilty plea came months after Cohen pleaded guilty to tax evasion, making false statements to a bank, and violating campaign finance laws by causing or issuing two hush money payments: $130,000 to Stormy Daniels and $150,00 to Karen McDougal, the latter of which was paid by American Media Inc. Those amounts greatly exceed the personal contribution limits to a political candidate.
Cohen was sentenced to three years in prison, according to a Department of Justice release .
Why did Michael Cohen turn on Trump?
Cohen's falling out with Trump was partly due to his conviction. In February 2019, he told a congressional committee he made a clean break with Trump.
"I have done bad things, but I am not a bad man. I have fixed things, but I am no longer your fixer, Mr. Trump," Cohen said in a dramatic testimony.
The two have continuously lobbed attacks at one another since then.
Contributing: Aysha Bagchi, Erin Kelly, Josh Meyer

COMMENTS
36. In the Related Works section, you should discuss briefly about published matter that technically relates to your proposed work. A short summary of what you can include (but not limited to) in the Related Works section: Work that proposes a different method to solve the same problem.
Related Work / Literature Review / Research Review Download PDF Handout: Literature Reviews Watch Video: Literature Reviews A literature review, research review, or related work section compares, contrasts, synthesizes, and provides introspection about the available knowledge for a given topic or field. The two terms are sometimes used interchangeably (as they are here), but while both can ...
The Shape. One thing to keep in mind when writing the "Related work" section is that it should be shaped "like a funnel". To be more specific, the content should be broad at the start, and focused ...
A good thesis has two parts. It should tell what you plan to argue, and it should "telegraph" how you plan to argue—that is, what particular support for your claim is going where in your essay. Steps in Constructing a Thesis. First, analyze your primary sources. Look for tension, interest, ambiguity, controversy, and/or complication.
Look at more recent work citing these works (e.g., Web of Science). ! In writing the review, chronology is often important. ! Capture the essence of the works you draw on. ! See Turco's "Token Theory" section. ! Provide supporting quotes when necessary. ! Avoid citing aspects of the works that aren't central (common mistake!).
Join our Facebook Page: https://www.facebook.com/people/CSMentor-Dr-Silvestri/61558667032153/In this video we discuss how write a related work section, commo...
A scientific literature review (sometimes also called related work or survey paper) is an integral part of: Writing scientific papers. Writing position reports in a non-academic job. Writing your Bachelor/Master/PhD thesis. Here, you will find a collection of resources that should help you in addressing your scholarly needs.
The Shape. One thing to keep in mind when writing the "Related work" section is that it should be shaped "like a funnel". To be more specific, the content should be broad at the start, and focused at the end. Start with a very brief introduction of the basic research area that your work belongs to. For example, if your paper is about automatic ...
Related Work This chapter surveys previous work in structured text processing. A common theme in much of this work is a choice between two approaches: the syntactic approach and the lexical approach. In general terms, the syntactic approach uses a formal, hierarchical definition of text struc-ture, invariably some form of grammar.
Significant issues identified in the thesis, or still outstanding after the thesis, should be describe as future work. After Completing the Draft. It is normal for most thesis authors to get lost in the details while writing such a large and detailed work. I highly recommend forgetting your thesis for at least a day or so (a week is recommended).
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
The rapid explosion of scientific publications has made related work writing increasingly laborious. In this paper, we propose a fully automated approach to generate related work sections by leveraging a seq2seq neural network. In particular, the main goal of our work is to improve the abstractive generation of related work by introducing problem and method information, which serve as a pivot ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Third, our work has made contributions to several learning issues, such as multi-strategy learning, learning with structured data, and relaxation labeling. Hence, we also review works related to such learning scenarios. Finally, we discuss works in other knowledge-intensive domains (e.g., information extrac-
How to outline your thesis or dissertation. While there are some inter-institutional differences, many outlines proceed in a fairly similar fashion. Working Title; Abstract "Elevator pitch" of your work (often written last). Introduction. Introduce your area of study, sharing details about your research question, problem statement, and ...
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
Studying abroad junior spring can be a great addition to your thesis work, particularly if you plan to write your thesis on some question related to the country where you'll be. Spring study abroad gives you the opportunity of getting a jump start on research you
A course assignment is an example of a selective, stand-alone work.It focuses on a small segment of the literature on a topic and makes up an entire work on its own. The literature review in a dissertation or thesis is both comprehensive and helps make up a larger work.; A majority of journal articles start with a selective literature review to provide context for the research reported in the ...
Create Subject-Specific Notebooks: Dedicate notebooks to different aspects of your thesis topic. 2. Maintain a Master Bibliography: Use a dedicated notebook to compile references you encounter during research. 3. Organize Quotes and Excerpts: Tag key quotes and excerpts with relevant keywords for easy retrieval. 4.
1. Define your research scope. Your literature review should help to define the specific research question of your thesis. It should give you a precise idea of what you want to research and what you're going to find. The literature review also helps to define the working parameters of your research.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
In the final thesis, I took a strong view on why the goddess was so important in this region, but it took more research, writing, and discussion with my supervisor to pin down my argument. Conclusion To choose a thesis research topic, find something you're passionate about, research widely to get the big picture, and then move to a more ...
Now, using this essay writing guide, let's explore how to create a well-structured introduction in ten steps. Each step is crucial in writing an essay introduction that captures attention and presents the thesis. Start with a hook: Begin with something that is engaging. Use a startling fact, a quote from a well-known figure, or a riveting ...
A capstone project is a comprehensive, culminating academic endeavor undertaken by students typically in their final year of study. It synthesizes their learning experiences, requiring students to apply the knowledge, skills, and competencies gained throughout their academic journey. A capstone project aims to address a real-world problem or ...
Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about conclusion sections.
Seven Ph.D. students working with CS&E professors have been named Doctoral Dissertation Fellows for the 2024-25 school year. The Doctoral Dissertation Fellowship is a highly competitive fellowship that gives the University's most accomplished Ph.D. candidates an opportunity to devote full-time effort to an outstanding research project by providing time to finalize and write a dissertation ...
When water freezes, it transitions from a liquid phase to a solid phase, resulting in a drastic change in properties like density and volume. Phase transitions in water are so common most of us probably don't even think about them, but phase transitions in novel materials or complex physical systems are an important area of study.
Cohen's testimony could be a central link prosecutors use to show Trump authorized the $130,000 paid to porn star Stormy Daniels in an attempt to stop her story about an alleged affair from ...