
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths Sets Free PDF

Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Sets in order to fully complete your preparation . They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams!
I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams. To download the latest CBSE Case Study Questions , just click ‘ Download PDF ’.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths Sets PDF
Checkout our case study questions for other chapters.
- Chapter 2 Relations and Functions Case Study Questions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Case Study Questions
- Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction Case Study Questions
- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Case Study Questions
How should I study for my upcoming exams?
First, learn to sit for at least 2 hours at a stretch
Solve every question of NCERT by hand, without looking at the solution.
Solve NCERT Exemplar (if available)
Sit through chapter wise FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS
Practice MCQ Questions (Very Important)
Practice Assertion Reason & Case Study Based Questions
Sit through FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS involving MCQs. Assertion reason & Case Study Based Questions
After Completing everything mentioned above, Sit for atleast 6 full syllabus TESTS.
Contact Form
Privacy Policy

(Education-Your Door To The Future)
CBSE Class 11 Term-1 Maths 2021-22: Topic-Wise MCQs, Case-Based & Assertion/Reason
CBSE Class 11 Term-1 Maths 2021-22: Topic-Wise MCQs, Case-Based & Assertion/Reason

In this Post I Have Provided Mathematics Class 11 Chapter-Wise MCQs, Case-Based Question And Assertion/Reason For Term-1 Session 2021-22 With Solutions. CBSE has Recently Included These Types Of MCQs And Assertion/Reason For Term-1 Exam 2020. Every Student Knows these types of Questions Are Very Important For Their Term-1 Examination.
Any student who want to download these MCQs, then they have to click on given respective download links and it will be automatically download in your Google Drive.
CBSE Class 11th Physics Term-1 2021-22: Topic-Wise MCQs, Case-Based & Assertion/Reason
For Downlod Click Here
Given Below Are The Class 11 Mathematics Chapter Name with Respective Download Links Containing Study Material:
| 1. Sets | |
| 2. Relations and Functions | |
| 3. Complex Numbers | |
| 4. Sequence and Series | |
| 5. Straight Lines | |
| 6. Limits | |
| 7. Statistics |
CBSE Sample Papers For Class 11 Mathematics
CBSE sample paper for class 11th Maths is an important tools to analyse itself. Before going to final examinations every student try to solve different types of sample question paper. It will enhance your knowledge and also provide to increase mental ability. Sample question paper are the best resources for the student to prepare for their Board examinations.
These sample question papers are very helpful to the student to get an entire experience before attempting the Board examinations papers. If students solve different types of sample question papers then they get the good confidence about the appropriate answer and they make good score in their Board examinations.
As every student know CBSE always change their exam pattern and also the model paper for their Board examinations that is why it is very important to all the student to understand the Model paper pattern before going to the final examinations.
In this articles I have provided different types of question papers on the basis of CBSE latest exam pattern which will definitely help to the student for the good preparation for their examinations.
In every year before the Board examination, CBSE provide model test paper to the student, on the basis of these model test papers I have prepared sample question papers for class 11th Maths which will help to the student to understand the concept of model test paper and also it will help to the student for good preparation for their board examination.
CBSE Sample Paper:
Maths And Physics With Pandey Sir is a website which provide free study material and notes to every students who are preparing for their Board examinations. By going in Level Section you can select CBSE sample papers. In this section, I have provided CBSE sample paper for class 9th to 12th.
Also if you are preparing for any competitive exams, they can find out study material and important notes in Level Section. In this website I have also provided most important MCQs questions, Assertion/Reason based questions and case study based questions for Board examinations or any other competitive examinations.
Benefits Of Solving CBSE Sample Papers for Examination:
Time Management:-
With the help of CBSE sample question papers you can make a proper strategy for their examinations also by practicing sample question papers you can manage your time during the Board examinations.
Examination Strategy:-
After practicing different types of sample question papers you can understand on which section you have spend more time and which section is easy and which section is hard. In this way you can make a proper examination strategy.
Self Evaluation:-
Self evaluation is very important to every student because with the help of self evaluation, student can understand their weak and strong point, which is very important for any Board examinations. After practicing more and more simple paper you can evaluate himself.
To Identify Silly Mistakes:-
As every student know there are many questions in their question paper which are very easy but student make mistakes in this types of question. By solving different types of sample question papers you can reduce their silly mistakes.
Advantages Of CBSE Sample Question Papers:
* To get a good exam ideas about your examination paper patterns
* Student can easily access to the question papers
* It is very helpful to know about the mark distribution system.
* Helpful in self evaluation
* To know about the pattern of CBSE
* Help to adjust a proper time management
* Available in PDF format
* Chapter wise CBSE sample papers
* CBSE sample papers for class 10
* CBSE sample paper class 12
* CBSE sample paper 2021-22 class 12 Solutions
* CBSE sample paper class 11
* CBSE Sample paper class 9
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets
June 18, 2022 by Sastry CBSE
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets.
Short Answer Type Questions Q1. Write the following sets in the roaster from
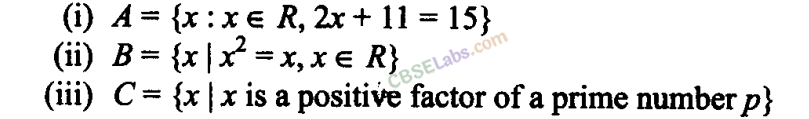
Q3. If Y = {x\x is a positive factor of the number 2 P (2 P – 1), where 2 P – 1 is a prime number}. Write Y in the roaster form.
Sol: Y- {x | x is a positive factor of the number 2 P-1 (2 P – 1), where 2 P – 1 is a prime number}. So, the factors of 2 P-1 are 1,2,2 2 ,2 3 ,…, 2 P- 1 . Y= {1,2,2 2 ,2 3 , …,2 p-1 ,2 p -1}
Q4. State which of the following statements are true and which are false. Justify your answer. (i) 35 ∈ {x | x has exactly four positive factors}. (ii) 128 e {y | the sum of all the positive factorsofy is 2y} (iii) 3∉{x|x 4 -5x 3 + 2jc 2 -112x + 6 = 0} (iv) 496 ∉{y | the sum of all the positive factors of y is 2y}. Sol: (i) The factors of 35 are 1, 5, 7 and 35. So, 35 is an element of the set. Hence, statement is true.
(ii) The factors of 128 hre 1,2,4, 8, 16, 32, 64 and 128. Sum of factors = 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + 16 + 32 + 64 + 128 = 255 * 2 x 128 Hence, statement is false.
(iii) We have, x 4 – 5x 3 + 2x 2 – 1 12jc + 6 = 0 Forx = 3, we have (3) 4 – 5(3) 3 + 2(3) 2 – 112(3) + 6 = 0 => 81 – 135 + 18-336 + 6 = 0 => -346 = 0, which is not true. So 3 is not an element of the set Hence, statement is true.
(iv) 496 = 2 4 x 31 So, the factors of 496 are 1,2,4, 8, 16,31,62, 124,248 and 496. Sum of factors = 1 +2 + 4 + 8+ 16 + 31+62+124 + 248 + 496 = 992 = 2(496) So, 496 is the element of the set Hence, statement is false
Q5. Given L, = {1,2, 3,4},M= {3,4, 5, 6} and N= {1,3,5} Verify that L-(M⋃N) = (L-M)⋂(L-N) Sol: Given L,= {1,2, 3,4}, M= {3,4,5,6} and N= {1,3,5} M⋃N= {1,3,4, 5,6} L – (M⋃N) = {2} Now, L-M= {1, 2} and L-N= {2,4} {L-M) ⋂{L-N)= {2} Hence, L-{M⋃N) = {L-M) ⋂ (L-N).
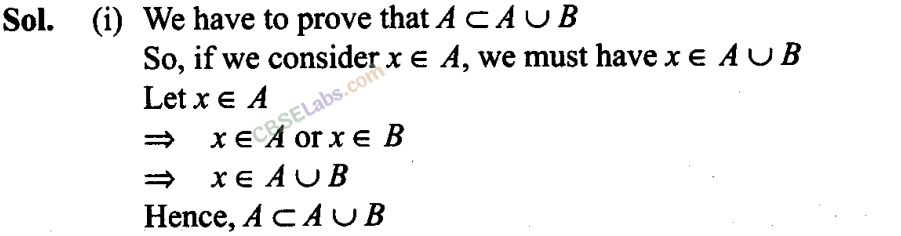
Q8. If X= {1, 2, 3}, if n represents any member of X, write the following sets containing all numbers represented by (i) 4n (ii) n + 6 (iii) n/2 (iv) n-1
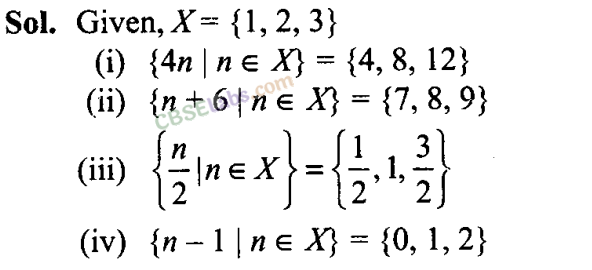
Q11. Let U be the set of all boys and girls in a school, G be the set of all girls in the school, B be the set of all boys in the school, and S be the set of all students in the school who take swimming. Some, but not all, students in the school take swimming. Draw a Venn diagram showing one of the possible interrelationship among sets U, G, B and S.
Instruction for Exercises 13-17: Determine whether each of the statements in these exercises is true or false. Justify your answer.
Q13. For all sets A and B, (A – B)∪ (A∩ B) = A Sol: True L.H.S. = (A-B) ∪ (A∩B) = [(A-B) ∪A] ∩ [(A – B) ∪B] = A∩ (A-B) = A= R.H.S. Hence, given statement is true.
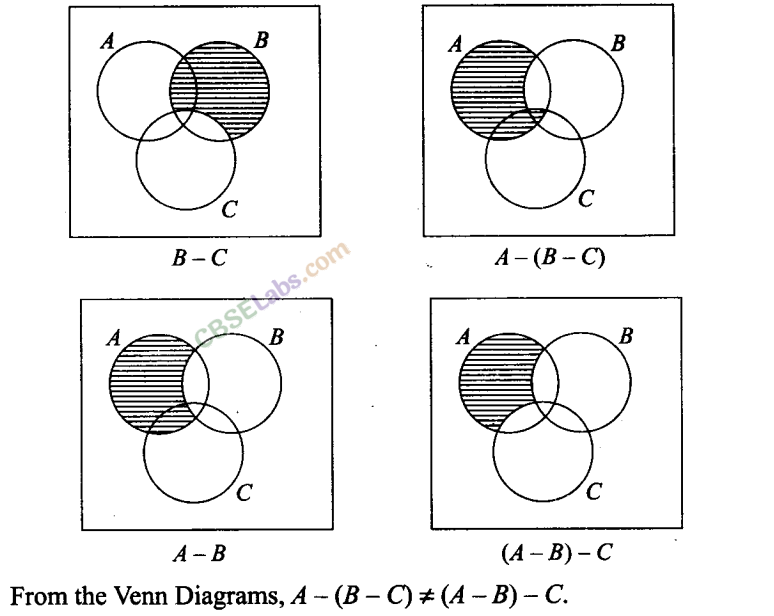
Q14. For all sets A, B and C, A – (B-C) = (A- B)-C Sol: False
Q15. For all sets A, B and C, if A ⊂ B, then A ∩C<⊂B ∩C
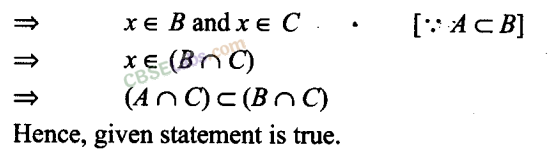
Q16. For all sets A, B and C, if A⊂ B, then A ∪ C⊂ B ∪ C Sol: True

Q17. For all sets A, B and C, if A⊂ C and B ⊂ C,then A∪ B ⊂ C
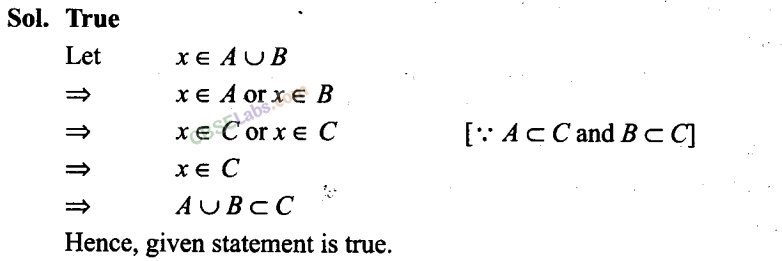
Instruction for Exercises 18-22: Using properties of sets prove the statements given in these exercises.
Q18. For all sets A and B, A ∪ (B -A) = A ∪ B
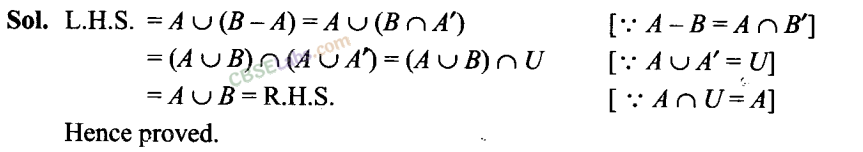
Q20. For all sets A and B, A – (A ∩ B) = A – B

Q21. For all sets A and B,(A ∪ B)- B = A-B
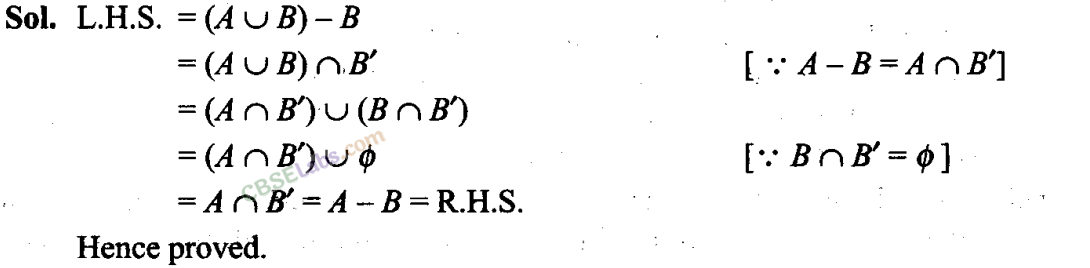
Long Answer Type Questions
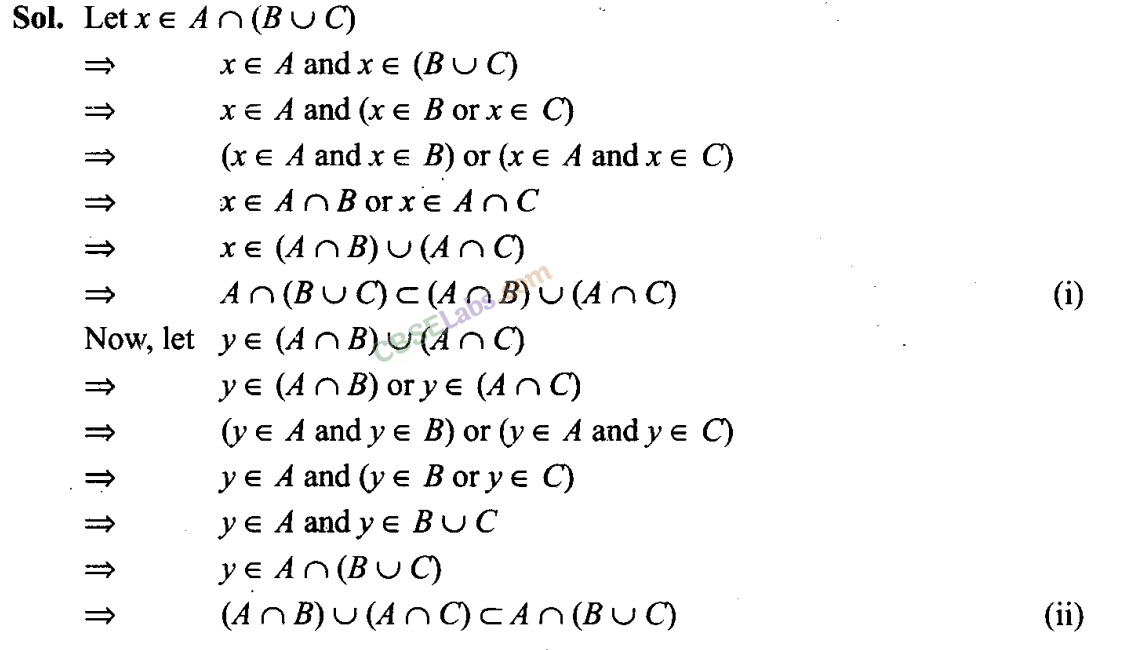
From (i) and (ii), we get . . A ∩ (B ∪ C) = (A ∩ B) ∪ (A ∩ C)
Q24. Out of 100 students; 15 passed in English, 12 passed in Mathematics, 8 in Science,6 in English and Mathematics, 7 in Mathematics and Science; 4 in English and Science; 4 in all the three. Find how many passed (i) in English and Mathematics but not in Science (ii) in Mathematics and Science but not in English (iii) in Mathematics only (iv) in more than one subject only Sol. Let M be the set of students who passed in Mathematics, E be the set of students who passed in English and S be the set of students who passed in Science.
Given n (U) = 100, n(E) = 15, n(M) = 12, n(S) = 8, n(E ∩ M) = 6, n(M ∩S) = 7, n(E ∩ S) — 4, and n(E ∩M ∩ S) = 4,
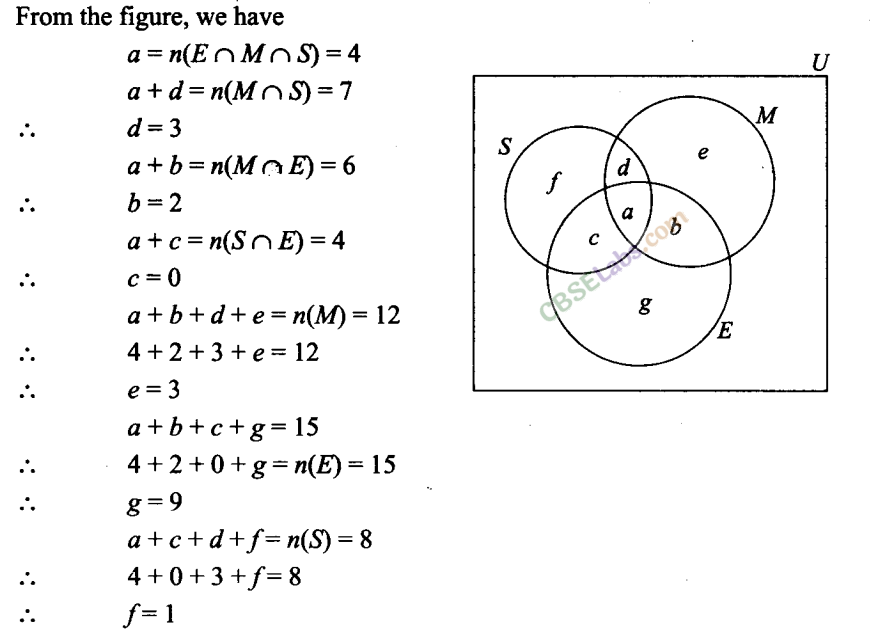
Number of students passed in English and Mathematics but not in Science = b = 2 (ii) Number of students passed in Mathematics and Science but not in English = d = 3 (iii) Number of students passed in Mathematics only = e = 3 (iv) Number of students passed in more than one subject = a + b + c + d =4+2+0+3=9
Q25. In a class of 60 students, 25 students play cricket and 20 students play tennis, and 10 students play both the games. Find the number of students who play neither. Sol: Let C be the set of students who play cricket and T be the set of students who play tennis. n(U) = 60, n(C) = 25, n(T) = 20, and n(C ∩ T) = 10 n(C ∪ T) = n(C) + n(T) – n(C n T) = 25 + 20 – 10 = 35
Q26. In a survey of 200 students of a school, it was found that 120 study Mathematics, 90 study Physics and 70 study Chemistry, 40 study Mathematics and Physics, 30 study Physics and Chemistry, 50 study Chemistry and Mathematics and 20 none of these subjects. Find the number of students who study all the three subjects. Sol: Let M be the set of students who study Mathematics, P be the set of students who study E Physics and C be the set of students who study Chemistry
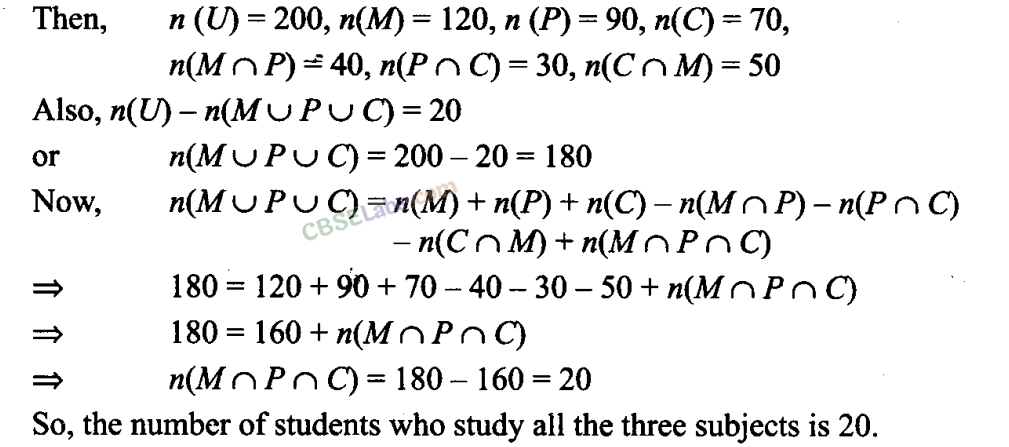
Q27. In a town of 10,000 families it was found that 40% families buy newspaper A, 20% families buy newspaper B, 10% families buy newspaper C, 5% families buy A and B, 3% buy B and C and 4% buy A and C. If 2% families buy all the three newspapers. Find (a) The number of families which buy newspaper A only. (b) The number of families which buy none of A, B and C. Sol: Let A be the set of families which buy newspaper A, B be the set of families which buy newspaper B and C be the set of families which buy newspaper C. The
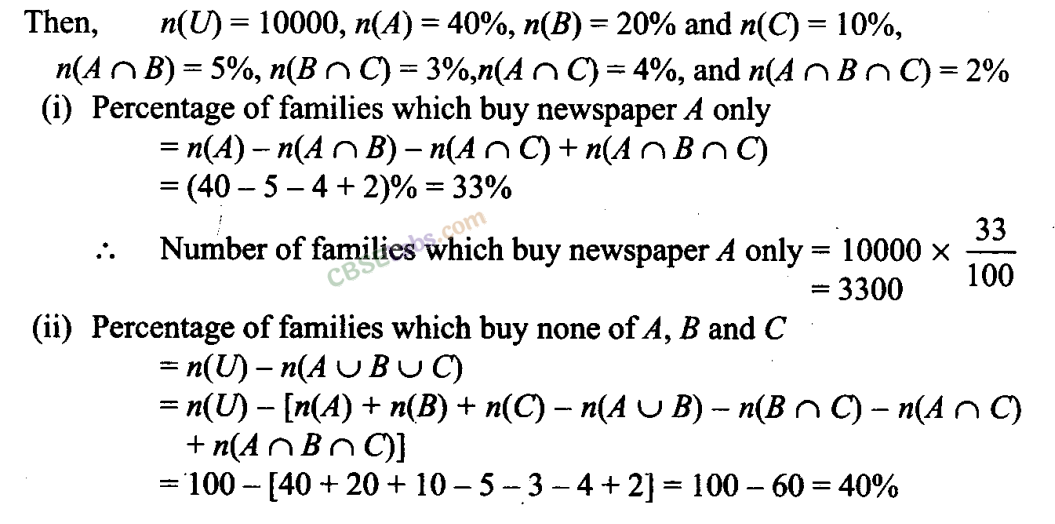
Number of families which buy none of A, B and C = 10000 x (40/100)
Q28. In a group of 50 students, the number of students studying French, English, Sanskrit were found to be as follows: French = 17, English = 13, Sanskrit = 15, French and English = 09, English and Sanskrit = 4,French and Sanskrit = 5, English, French and Sanskrit = 3. Find the number of students who study (i) French only (ii) English only (iii) Sanskrit only (iv) English and Sanskrit (v) French and Sanskrit but not English (vi) French and English but not Sanskrit (vii) at least one of the three languages (viii) none of the three languages but not French
Sol: Let F be the set of students who study French, E be the set of students who study English and S be the set of students who study Sanskrit. Then, n{U) = 50, n(F) =17, n{E) = 13, and n{S) = 15, n(F ∩ E) = 9, n(E ∩ S) = 4, n(F ∩ S) = 5, n(F ∩ E ∩ S) = 3
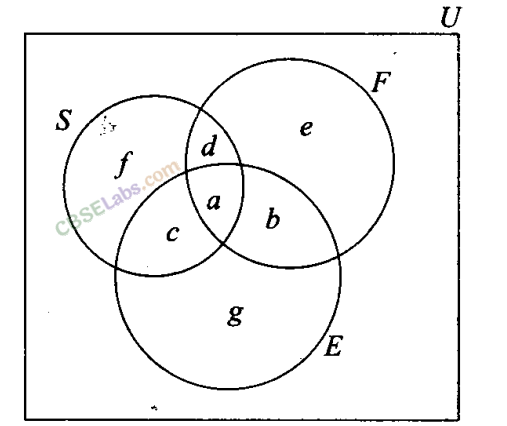
(i) Number of students studying French only = e = 6 (ii) Number of students studying English only = g = 3 (iii) Number of students studying Sanskrit only =f= 9 (iv) Number of students studying English and Sanskrit but not French = c = 1 (v) Number of students studying French and Sanskrit but not English = d = 2 (vi) Number of students studying French and English but not Sanskrit = b = 6 (vii) Number of students studying at least one of the three languages = a + b + c + d + e+f+g = 30 (viii) Number of students studying none of the three languages but not French = 50-30 = 20
Q30. Two finite sets have m and n elements. The number of subsets of the first set is 112 more than that of the second set. The values of m and n are, respectively, (a) 4,7 (b) 7,4 (c) 4,4 (d) 7, 7
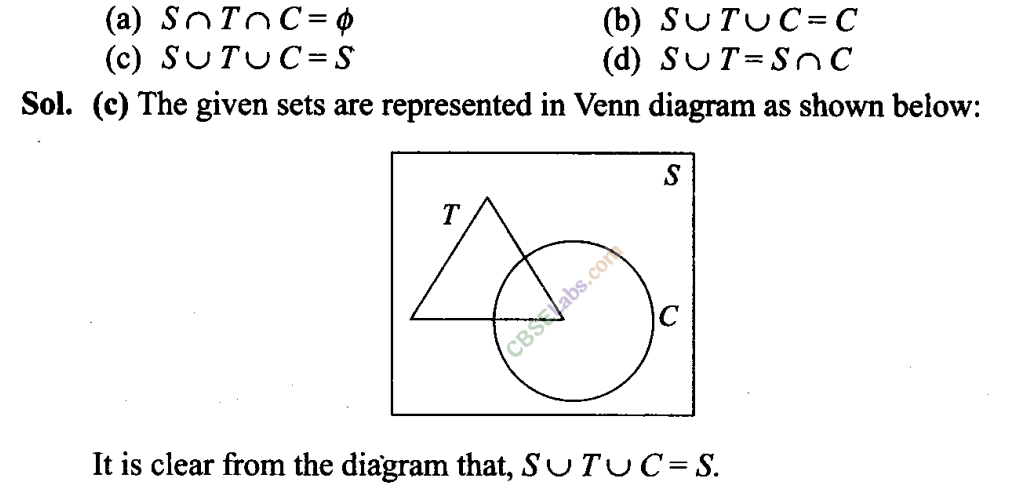
Q32. Let F 1 be the set of parallelograms, F 2 the set of rectangles, F 3 the set of rhombuses, F 4 the set of squares and F 5 the set of trapeziums in a plane. Then F 1 may be equal to (a) F 2 ∩F 3 (b) F 3 ∩F 4 (c) F 2 u F s (d) F 2 ∪ F 3 ∪ F 4 ∪ F 1 Sol: (d) Every rectangle, rhombus, square in a plane is a parallelogram but every trapezium is not a parallelogram. F 1 = F 2 ∪ F 3 ∪ F 4 ∪ F 1
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Solutions
- Chapter 1 Sets
- Chapter 2 Relations and Functions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction
- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities
- Chapter 7 Permutations and Combinations
- Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem
- Chapter 9 Sequence and Series
- Chapter 10 Straight Lines
- Chapter 11 Conic Sections
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Three-Dimensional Geometry
- Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives
- Chapter 14 Mathematical Reasoning
- Chapter 15 Statistics
- Chapter 16 Probability
NCERT Exemplar Problems Maths Physics Chemistry Biology
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chapter 1 Class 11 Sets
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Learn Chapter 1 Sets of Class 11 free with solutions of all NCERT Questions for CBSE Maths. All examples, formulas and exercise questions explained in an easy way. Important questions are also marked for your reference
Topics in the chapter include
- Definition - What is set and how is it used
- Depiction of set - How to represent it, Roster form, Set-builder form
- Intervals - Interval notation and how it is related to sets.
- Types of sets - Null set, Finite set, Infinite Set, Equal Set, Subset, Power set, Universal set
- Union, Intersection and Difference of Sets - Explanation and its questions
- Venn diagram - What is Venn diagram and representing union, intersection, difference of sets in the Venn Diagram
- Complement of set - How to find complement and its representation in venn diagram
- Number of elements formula - Using number of elements formula for 2 and 3 sets and solving questions
- Proof questions - Solving proof questions using properties of sets and its application of properties of sets
Explanation of individual topics with questions to practice are given in Concept wise. Check out Concept wise, or the NCERT Exercise wise.
Serial order wise
Concept wise.
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 - Sets 2024-25
- Class 11 Important Question
- Chapter 1: Sets

Crucial Practice Problems for CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 1: Sets
Class 11th is quite important in making students understand the complex concepts of mathematics and preparing them for the JEE Main exams . Class 11th needs a significant amount of hard work from a student's point of view, and the same goes for the teachers as well. Vedantu is pushing the limits of education by helping students in their journey of making a strong foundation for the exams which they are going to give at the end of the year along with the entrance exams. Let's provide you with the briefing of the important questions for class 11 maths chapter 1 .
In this chapter, students will be learning about the different types of sets and how to represent them. They will also get to know about empty sets, finite and infinite sets, equal sets, subsets, power sets, Universal sets, union and intersection of the given sets. Moreover, as the student studies the chapter and reaches its end, they will be able to solve the problems that use the formulas from the above topic and the difference of sets, a complement of sets, and properties of Complement. A lot of questions you are going to see in the competitive exams like JEE Main will use the concepts you have learned in class 11th as the competitive exams test you on your learning ability and come up with the answer constraint environment.
Download CBSE Class 11 Maths Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 11 Maths Important Questions for other chapters:
CBSE Class 11 Maths Important Questions | ||
Sl.No | Chapter No | Chapter Name |
1 | Chapter 1 | Sets |
2 | Chapter 2 |
|
3 | Chapter 3 |
|
4 | Chapter 4 |
|
5 | Chapter 5 |
|
6 | Chapter 6 |
|
7 | Chapter 7 |
|
8 | Chapter 8 |
|
9 | Chapter 9 |
|
10 | Chapter 10 |
|
11 | Chapter 11 |
|
12 | Chapter 12 |
|
13 | Chapter 13 |
|
14 | Chapter 14 |
|
15 | Chapter 15 |
|
16 | Chapter 16 |
|
Boost Your Performance in CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Exam Chapter 1 with Important Questions
Very short questions and answers (1 marks questions).
Which of the following are sets? Justify your answer.
1. The collection of all the months of a year beginning with letter M
Ans: Set, because collection of certain and unique type of data is called a set.
2. The collection of difficult topics in Mathematics.
Ans: Not a set, because difficult topics differ person to person.
Let \[A=\{1,3,5,7,9\}\]. Insert the appropriate symbol in blank spaces:-(Question3,4)
Ans: \[\in \]
4. 5-A
5. Write the set $A=\left\{ x:x\text{ is an integer},-1\le x \le 4 \right\}$ in roster form.
Ans: The elements in roster form is as shown
\[A=\{-1,0,1,2,3\}\]
6. List all the elements of the set, $A=\left\{ x:x \in Z,\dfrac{-1}{2}\le x\le \dfrac{11}{2} \right\}$
Ans: All the elements are as shown
\[A=\{0,1,2,3,4,5\}\]
7. Write the set $B=\left\{ 3,9,27,81 \right\}$ in set-builder form.
Ans: The above set in set builder form is as shown
\[B=\{x:x={{3}^{n}},n\in N\text{ and }1\le n\le 4\}\]
Which of the following are empty sets? Justify.
8. $A=\left\{ x:x\in N,3\le x \le 4 \right\}$
Ans: Empty set, because there is no natural number that lies between \[3\] and \[4\]
9. $B=\left\{ x:x\in N,{{x}^{2}}=x \right\}$
Ans: Non-empty set, because there exist natural number which equals to square of itself. For example ${{1}^{2}}=1$ and so on.
Which of the sets are finite or infinite? Justify.
10. The set of all points on the circumference of a circle.
Ans: Infinite set, because there are many points in the circumference of circle
11. $B=\left\{ x:x\in N\text{ and x is an even prime number} \right\}$
Ans: Finite set, because the only even prime number is two.
12. Are sets $A=\left\{ -2,2 \right\},B=\left\{ x:x\in R,{{x}^{2}}-4=0 \right\}$ equal? Why?
Ans: Yes because the number of elements in A is equal to that of B
13. Write $\left( -5,\left. 9 \right] \right.$in set-builder form
Ans: \[\left\{ x:x\in ,-5 \le x\le 9 \right\}\]
14. Write $A=\left\{ x:-3\le x \le 7 \right\}$ as interval
Ans: Clearly in interval the above set is written as
\[\left[ -3,\left. 7 \right) \right.\]
15. If $A=\left\{ 1,3,5 \right\}$ how many elements has P(A)?
Ans: Clearly the number of elements in \[P\left( A \right)={{2}^{3}}=8\]
16. Write all the possible subsets of $A=\left\{ 5,6 \right\}$.
Ans: Clearly the possible values of \[A=\left\{ 5,6, \right\}\]is given by
\[\left\{ \varphi ,\left\{ 5 \right\},\left\{ 6 \right\},\left\{ 5,6 \right\} \right\}\]
17. If $A=\left\{ 2,3,4,5 \right\},B=\left\{ 3,5,6,7 \right\}$. Find $A\bigcup B$
Ans: Clearly \[A\bigcup B=\left\{ 2,3,4,5,6,7 \right\}\]
18.In above question find $A\bigcap B$
Ans: Clearly \[A\bigcap B=\left\{ 3,5 \right\}\]
19. If $A=\left\{ 1,2,3,6 \right\},B=\left\{ 1,2,4,8 \right\}$ find $B-A$
Ans: We are given with sets as shown
\[A=\left\{ 1,2,3,6 \right\}\]
\[B=\left\{ 1,2,4,8 \right\}\]
Hence \[B-A=\left\{ 4,8 \right\}\]
20. If $A=\left\{ p,q \right\},B=\left\{ p,q,r \right\}$, is B a superset of \[A\]? Why?
Ans: Yes, because A is a subset of B.
21. Are sets $A=\left\{ 1,2,3,4 \right\},B=\left\{ x:x\in N\text{ and 5}\le \text{x}\le \text{7} \right\}$ disjoint? Why?
Ans: The above mentioned sets are disjoint because \[\left( A\bigcup B \right)=\varphi \].
22. If X and Y are two sets such that $n\left( X \right)=19,n\left( Y \right)=37,n\left( X\bigcap Y \right)=12$ find $n\left( X\bigcup Y \right)$.
Ans: We know that \[n\left( X\bigcup Y \right)\] is given by
\[n\left( X\bigcup Y \right)=n\left( X \right)+n\left( Y \right)-n\left( X\bigcap Y \right)\]
Hence we get \[n\left( X\bigcup Y \right)=44\]
23. Describe the set in Roster form.
$\left\{ x:\text{x is a two digit number such that the sum of its digits is 8 } \right\}$
Ans: The set in Roster form of above mentioned set is
\[\left\{ 17,26,35,44,53,62,71,80 \right\}\]
24. Are the following pair of sets equal? Give reasons.
$A=\left\{ x:\text{x is a letter in the word FOLLOW } \right\}$
$B=\left\{ x:\text{x is a letter in the word WOLF } \right\}$
Ans: We can write above mentioned sets as shown
\[A=\left\{ F,O,L,W \right\}\]
\[n\left( A \right)=4\]
\[B=\left\{ W,O,L,F \right\}\]
\[n\left( B \right)=4\]
Hence \[A=B\]
25. Write down all the subsets of the set $\left\{ 1,2,3 \right\}$
Ans: All the subsets of the set \[\{1,2,3\}\] is given below
\[\left\{ \varnothing ,\{1\},\{2\},\{3\},\{1,2\},\{1,3\},\{2,3\},\{1,2,3\} \right\}\]
26. Let $A=\left\{ 1,2,\left\{ 3,4 \right\},5 \right\}$ is $\left\{ \left\{ 3,4 \right\} \right\}\in A$ is incorrect. Give a reason.
Ans: Clearly \[\left\{ 3,4 \right\}\] is an element of set A, therefore \[\left\{ \left\{ 3,4 \right\} \right\}\] is a set containing element \[\left\{ 3,4 \right\}\] which belongs to A.
Hence, \[\left\{ \left\{ 3,4 \right\} \right\}\in A\] is correct.
27. Draw Venn diagram for $\left( A\bigcap B \right)'$
Ans: We know that
\[\left( A\bigcap B \right)'=U-A\bigcap B\]
Hence the region is shown in the venn diagram below
Fig: \[(A\cap B)'\]
28. Write the set in roster form A the set of letters in TRIGNOMETRY
Ans: The set of letters in TRIGNOMETRY in roster form is written as
\[A=\left\{ T,R,I,G,N,O,M,E,T,R,Y \right\}\]
29. Are the following pair of sets are equal? Give reasons
A, the set of letters in “ALLOY” and B, the set of letters in “LOYAL”.
Ans: The set of letters in ALLOY is written as
\[A=\left\{ A,,L,O,Y \right\}\]
Similarly, the set of letters in LOYAL is written as
\[B=\left\{ L,O,Y,A \right\}\]
Hence \[A=B\]
30. Write down the power set of A, $A=\left\{ 1,2,3 \right\}$
Ans: We know that power set is written as shown
\[P(A)=\left\{ \varnothing ,\{1\},\{2\},\{3\},\{1,2\},\{1,3\},\{2,3\},\{1,2,3\} \right\}\]
31. $A=\left\{ 1,2,\left\{ 3,4 \right\},5 \right\}$ which is incorrect and why.
(i) \[\{3,4\}\subset A\]
Ans: Clearly we can see that \[\left\{ 3,4 \right\}\in A\]
Hence \[\left\{ 3,4 \right\}\subset A\] is incorrect
(ii) \[\{3,4\}\in A\]
Hence \[\left\{ 3,4 \right\}\in A\] is correct
32. Fill in the blanks:
(i) $A\bigcup A'$
Ans: We know that \[A\bigcup A'=U\] where U is the universal set
(ii) $\left( A' \right)'$
Ans: We know that \[\left( A' \right)'=A\]
(iii) $A\bigcap A'$
Ans: We know that \[A\bigcap A'=\varphi \]where \[\varphi \] is the universal set.
33. Write the set $\left\{\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{2}{3},\dfrac{3}{4},\dfrac{4}{5},\dfrac{5}{6},\dfrac{6}{7} \right\}$ in the set builder form.
Ans: The set builder form of above set is given by
\[\left\{ \dfrac{n}{n+1}:n\text{ is a natural number less than or equal to 6} \right\}\]
34. Is set $C=\left\{ x:x-5=0 \right\}$ and
$E=\left\{ x:\text{x is an integral positive root of the equation }{{x}^{2}}-2x-15=0 \right\}$ are equal?
Ans: From set C we get
Hence \[C=\left\{ 5 \right\}\]
Also on solving the equation
\[{{x}^{2}}-2x-15=0\]
We get the positive root as shown
Hence both the sets are equal
35. Write down all possible proper subsets of the set $\left\{ 1,\left\{ 2 \right\} \right\}$.
Ans: All possible proper subsets of the given set are
\[\varphi ,\left\{ 1 \right\},\left\{ 2 \right\},\left\{ 1,\left\{ 2 \right\} \right\}\]
36. State whether each of the following statements is true or false.
(i) $A=\left( 2,3,4,5 \right),B=\left\{ 3,6 \right\}$are disjoint sets.
Ans: Clearly we have
\[\left\{ 2,3,4,5 \right\}\bigcap \left\{ 3,6 \right\}=\left\{ 3 \right\}\ne \varphi \]
Hence the above statement is false
(ii) $A=\left( 2,6,10 \right),B=\left\{ 3,7,11 \right\}$are disjoint sets.
\[\left\{ 2,6,10 \right\}\bigcap \left\{ 3,7,11 \right\}=\varphi \]
Hence the above statement is true
37. Solve the followings:
(i) $\left( A\bigcup B \right)'$
Ans: By the properties we write
\[\left( A\bigcup B \right)'=A'\bigcap B'\]
(ii) $\left( A\bigcap B \right)'$
\[\left( A\bigcap B \right)'=A'\bigcup B'\]
38. Write the set of all vowels in the English alphabet which precede k in roster form.
Ans: The set of all vowels in the English alphabet which precede k in roster form is as shown
\[N=\left\{ a,e,i \right\}\]
39. Is pair of sets equal? Give reasons.
$A=\left( 2,3 \right),B=\left\{ x:\text{x is the solution of }{{x}^{2}}+5x+6=0 \right\}$
Ans: Given we have
\[A=\left\{ 2,3 \right\}\]
\[B=\left\{ x:x\text{ is the solution of }{{\text{x}}^{2}}+5x+6 \right\}\]
Now we can easily find the solution of \[{{\text{x}}^{2}}+5x+6\] to be the set \[B=\left\{ -2,-3 \right\}\]
Hence \[A\ne B\]
So the given pair of sets are not equal
40. Write the following intervals in set builder form: $\left( -3,0 \right)$ and $\left[ \left( 6,12 \right) \right]$
Ans: The set builder form of above intervals is given by
\[\left\{ -3,0 \right\}\to \left\{ x:x\in R,-3\le x \le 0 \right\}\]
\[\left\{ 6,12 \right\}\to \left\{ x:x\in R,6\le x\le 12 \right\}\]
41. If $X=\left\{ a,b,c,d \right\}$
$Y=\left\{ f,b,d,g \right\}$
Find $X-Y$ and $Y-X$
Ans: We are given with the following sets
\[X=\left\{ a,b,c,d \right\}\]
\[Y=\left\{ f,b,d,g \right\}\]
Hence \[X-Y=\left\{ a,c \right\}\]
Similarly, \[Y-X=\left\{ f,g \right\}\]
42. If A and B are two given sets, then represent the set $\left( A-B \right)'$, using the Venn diagram.
\[\left( A-B \right)'=U-\left( A-B \right)\] and hence the venn diagram is as shown
Fig-\[(A-B)'\]
43. List all the element of the set $A=\left\{ x:x\text{ is an integer},{{x}^{2}}\le 4 \right\}$
Ans: The elements which we will get is as shown
\[\left\{ -2,-1,0,1,2 \right\}\]
44. From the sets given below pair the equivalent sets.
$A=\left\{ 1,2,3 \right\},B=\left\{ x,y,z,t \right\},C=\left\{ a,b,c \right\},D=\left\{ 0,a \right\}$
Ans: From the data given A and C are equivalent sets because the number of elements in each is same.
45. Write the following as interval
(i) $\left\{ x:x\in R,-4 \le x\le 6 \right\}$
Ans : The interval form of above is given as shown
\[\left( -4,6 \right]\]
(ii) $\left\{ x:x\in R,3\le x\le 4 \right\}$
Ans: The interval form of above is given as shown
\[\left[ 3,4 \right]\]
46. If $A=\left\{ 3,5,7,9,11 \right\},B=\left\{ 7,9,11,13 \right\},C=\left\{ 11,13,15 \right\}$ Find $\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcap \left( B\bigcup C \right)$
Ans: From the data given we have
\[A=\left\{ 3,5,7,9,11 \right\}\]
\[B=\left\{ 7,9,11,13 \right\}\]
\[C=\left\{ 11,13,15 \right\}\]
Now \[A\bigcap B=\left\{ 7,9,11 \right\}\]
\[B\bigcup C=\left\{ 7,9,11,13,15 \right\}\]
Therefore \[\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcap \left( B\bigcup C \right)=\left\{ 7,9,11 \right\}\]
47. Write the set $\left\{ \dfrac{1}{3},\dfrac{3}{5},\dfrac{5}{7},\dfrac{7}{9},\dfrac{9}{11},\dfrac{11}{13} \right\}$in set builder form.
Ans: \[\left\{ \dfrac{2n-1}{2n+1}:n\text{ is a natural number less than 7} \right\}\]
Long Questions and Answers (4 Marks Questions)
1. In a group of $800$ people, $500$ can speak Hindi and $320$ can speak English. Find
(i) How many can speak both Hindi and English?
Ans: We will use following notation
H-People who can speak Hindi
E-People who can speak English
It is given in the question that
\[n\left( E\bigcup H \right)=800\]
\[n\left( E \right)=320\]
\[n\left( H \right)=500\]
Also we know that
\[n\left( E\bigcup H \right)=n\left( E \right)+n\left( H \right)-n\left( E\bigcap H \right)\]
800=320+500\[-n\left( E\bigcap H \right)\]
Hence on solving above we get \[20\] people can speak both Hindi and English
(ii) How many can speak Hindi only?
Also we find that
\[n\left( E\bigcap H \right)=20\]
\[n\left( E'\bigcap H \right)=n\left( H \right)-n\left( E\bigcap H \right)\]
Hence on solving above we get \[480\] people can speak both Hindi and English
2. A survey shows that $84$ percent of Indians like grapes, whereas $45$ percent like pineapple. What percentage of Indians like both grapes and pineapple?
A-set of Indians who like grapes
O-set of Indians who like pineapple
\[n\left( A\bigcup O \right)=100\]
\[n\left( A \right)=84\]
\[n\left( O \right)=45\]
Now we know that
\[n\left( A\bigcup O \right)=n\left( A \right)+n\left( O \right)-n\left( A\bigcap O \right)\]
Hence on solving the above we get
\[n\left( A\bigcap O \right)=29\]
Therefore \[29\] percent of Indians like both apples and oranges
3. In a survey of $450$ people, it was found that $110$ play cricket, $160$ play tennis and $70$ play both cricket as well as tennis. How many plays neither cricket nor tennis?
S-set of surveyed people
A-set of people who play cricket
O- set of people who play tennis
\[n\left( A\bigcap O \right)=70\]
\[n\left( A \right)=110\]
\[n\left( O \right)=160\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( A\bigcup O \right)=110+160-70=200\]
Therefore students who like neither cricket nor tennis is given by
\[n\left( A'\bigcap O' \right)=450-200=250\]
4. In a group of students, $225$ students know French, $100$ know Spanish and $45$ know both. Each student knows either French or Spanish. How many students are there in the group?
A-set of students who know French
O- set of students who know Spanish
\[n\left( A\bigcap O \right)=45\]
\[n\left( O \right)=100\]
\[n\left( A \right)=225\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( A\bigcup O \right)=225+100-45=280\]
Hence there are 280 students in the group.
5. If $A=\left[ \left( -3,5 \right),B=\left( 0,6 \right) \right]$ then find
(i) $A-B$,
Ans: Given we have
\[A=\left( -3,5 \right)\]
\[B=\left( 0,6 \right)\]
We know that \[A-B=A\bigcap B'\]
Hence \[A-B=\left[ -3,0 \right]\]
(ii) $A\bigcup B$
We know that \[A\bigcup B\] means occurrence of at least one
Hence \[A\bigcup B=\left[ -3,6 \right]\]
6. In a survey of $400$ students in a school, $100$ were listed as taking apple juice, $150$ as taking orange juice and $75$ were listed as taking both apple as well as orange juice. Find how many students were taking neither apple juice nor orange juice.
A-set of students who like apple juice
O- set of students who like orange juice
\[n\left( A\bigcap O \right)=75\]
\[n\left( A \right)=100\]
\[n\left( O \right)=150\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( A\bigcup O \right)=100+150-75=175\]
Therefore students who take neither apple nor orange juice is given by
\[n\left( A'\bigcap O' \right)=400-175=225\]
7. A survey shows that $73$ percent of Indians like apples, whereas $65$ percent like oranges. What percent of Indians like both apples and oranges?
A-set of Indians who like apples
O-set of Indians who like oranges
\[n\left( A \right)=73\]
\[n\left( O \right)=65\]
\[n\left( A\bigcap O \right)=38\]
Therefore \[38\] percent of Indians like both apples and oranges
8. In a school there are $20$ teachers who teach mathematics or physics. Of these $12$ teach mathematics and $4$ teach both physics and mathematics. How many teach physics?
Ans: We will use following notation
P-Number of physics teachers
M- Number of mathematics teachers
We are given
\[n\left( P\bigcup M \right)=20\]
\[n\left( M \right)=12\]
\[n\left( P\bigcap M \right)=4\]
\[n\left( P\bigcup M \right)=n\left( P \right)+n\left( M \right)-n\left( M\bigcap P \right)\]
On putting the respected values and solving we get
\[n\left( P \right)=12\]
9. Let $U=\left\{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 \right\},A=\left\{ 2,3 \right\},B=\left\{ 3,4,5 \right\}$. Find $A'\bigcap B',A\bigcup B$and hence show that $A\bigcup B=A'\bigcap B'$.
Ans : We know that
$=\left\{ 1,4,5,6 \right\}$
$=\left\{ 1,2,6 \right\}$
$A\bigcup B=\left\{ 2,3,4,5 \right\}$
$\left( A'\bigcap B' \right)=\left\{ 1,6 \right\}$
Hence proved.
10. For any two sets A and B prove by using properties of sets that:
$\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)=A$
Ans: We write LHS and RHS as shown
$LHS=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A-B \right)$
$=\left( A\bigcap B \right)\bigcup \left( A\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)$ (since $\left( A-B \right)=\left( A\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)$)
$=A\bigcap \left( B\bigcup {{B}^{'}} \right)$
$=A\bigcap \left( U \right)$
11. If A and B are two sets and $U$ is the universal set such that
$n\left( U \right)=1000,n\left( A \right)=300,n\left( B \right)=300,n\left( A\bigcap B \right)=200$ find $n\left( {{A}^{'}}\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)$.
$n\left( {{A}^{'}}\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)=n{{\left( A\bigcup B \right)}^{'}}$
$\Rightarrow n\left( {{A}^{'}}\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)=n\left( U \right)-n\left( A\bigcup B \right)$
$\Rightarrow n\left( {{A}^{'}}\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)=n\left( U \right)-\left[ n\left( A \right)+n\left( B \right)-n\left( A\bigcap B \right) \right]$
$\Rightarrow n\left( {{A}^{'}}\bigcap {{B}^{'}} \right)=1000-\left[ 300+300-200 \right]=600$
12. There are $210$ members in a club. $100$ of them drink tea and $65$ drink tea but not coffee, each member drinks tea or coffee. Find how many drinks coffee. How many drink coffee, but not tea.
Ans: Let us have following notation
S-total members in the club
T-members who drink tea
C- members who drink coffee
$n\left( T \right)=100$
$n\left( T-C \right)=65$
$n\left( T\bigcup C \right)=210=n\left( S \right)$(since $n\left( T\bigcap C \right)=0$
We know that
\[n\left( T-C \right)=n\left( T \right)-n\left( T\bigcap C \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( T\bigcap C \right)=35\]
$n\left( T\bigcup C \right)=n\left( T \right)+n\left( C \right)-n\left( T\bigcap C \right)$
$\Rightarrow n\left( C \right)=145$
Therefore $n\left( C-T \right)=110$
13. If $P\left( A \right)=P\left( B \right)$, Show that $A=B$
Ans: For every $a\in A$
$\left\{ a \right\}\subset A$
$\Rightarrow \left\{ a \right\}\in P\left( A \right)$
$\Rightarrow \left\{ a \right\}\in P\left( B \right)$ (since $P\left( A \right)=P\left( B \right)$)
$\Rightarrow \left\{ a \right\}\in B$
$\left\{ a \right\}\subset B$
$\Rightarrow A\subset B$
Similarly we can easily say $B\subset A$
Therefore $B=A$
14. In a class of $25$ students, $12$ have taken mathematics, $8$ have taken mathematics but not biology. Find the no. of students who have taken both mathematics and biology and the no. of those who have taken biology but not mathematics each student has taken either mathematics or biology or both.
T-total number of students
M- number of students who have taken mathematics
B- number of students who have taken biology
$n\left( M \right)=12$
$n\left( M-B \right)=8$
$n\left( M\bigcup B \right)=25$
$n\left( M\bigcup B \right)=n\left( M \right)+n\left( B-M \right)$
$\Rightarrow 25=12+n\left( B-M \right)$
$\Rightarrow n\left( B-M \right)=13$
\[n\left( M\bigcup B \right)=n\left( M-B \right)+n\left( B-M \right)+n\left( M\bigcap B \right)\]
Hence we get \[n\left( M\bigcap B \right)=4\]
15. A and B are two sets such that $n\left( A-B \right)=14+x,n\left( B-A \right)=3x,n\left( A\bigcap B \right)=x$. Draw a Venn diagram to illustrate this information. If $n\left( A \right)=n\left( B \right)$, Find
(i) the value of $x$
Ans: It is given in the question
$n\left( A-B \right)=14+x$
$n\left( B-A \right)=3x$
$n\left( A\bigcap B \right)=x$
The venn diagram is as shown
$n\left( A \right)=n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( A\bigcap B \right)$
$\Rightarrow n\left( A \right)=14+2x$
$n\left( A \right)=n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\bigcap B \right)$
$\Rightarrow n\left( B \right)=4x$
Also it is given that $n\left( B \right)=n\left( A \right)$
Hence $14+2x=4x$
$\Rightarrow x=7$
(ii) $n\left( A\bigcup B \right)$
Ans: From the above data we have
$n\left( A\bigcup B \right)=n\left( A-B \right)+n\left( B-A \right)+n\left( A\bigcap B \right)$
$\Rightarrow n\left( A\bigcup B \right)=14+x+3x+x=14+5x$
Hence $n\left( A\bigcup B \right)=49$ (since $x=7$)
16. If A and B are two sets such that $A\bigcup B=A\bigcap B$ , then prove that $A=B$.
Ans: Let us have $a\in A\Rightarrow a\in A\bigcap B$
It is given that $A\bigcup B=A\bigcap B$
Since we have $a\in A\bigcap B$
Therefore $A\subset B$
And similarly $B\subset A$
Therefore $A=B$ proved
17. Prove that if $A\bigcup B=C$ and $A\bigcap B=\varphi $ then $A=C-B$
Ans: Given $\left( A\bigcup B \right)=C$and $\left( A\bigcap B \right)=\varphi $
$\left( A\bigcup B \right)-B=\left( A\bigcup B \right)\bigcap {{B}^{'}}$
$=\left( {{B}^{'}}\bigcap A \right)\bigcup \left( {{B}^{'}}\bigcap B \right)$
$=\left( {{B}^{'}}\bigcap A \right)$
$=A$(since $\left( A\bigcap B \right)=\varphi $)
Hence proved
18. In a group of $65$ people, $40$ like cricket, $10$ like both cricket and tennis. How many like tennis only and not cricket? How many like tennis?
Ans: Let us have following denotion
C-the set of people who like cricket
T-the set of people who like tennis
$n\left( C\bigcup T \right)=65$
$n\left( C \right)=40$
$n\left( C\bigcap T \right)=10$
We know that
$n\left( C\bigcup T \right)=n\left( C \right)+n\left( T \right)-n\left( C\bigcap T \right)$
$\Rightarrow 65=40+n\left( T \right)-10$
Hence we get people who like tennis as $n\left( T \right)=35$
Now people who like tennis only not cricket is given by
$n\left( T-C \right)=n\left( T \right)-n\left( C\bigcap T \right)$
$\Rightarrow n\left( T-C \right)=35-10=25$
19. Let A,B and C be three sets $A\bigcup B=A\bigcup C$ and $A\bigcap B=A\bigcap C$ show that $B=C$
Ans: Let us have $b\in B\Rightarrow b\in A\bigcup B$
Also it is given $A\bigcup B=A\bigcup C$
Therefore $b\in A\bigcup C$
Hence we get $b\in A\text{ or }b\in C$
In both cases B is subset of C
Similarly in both cases C is subset of B
Therefore $B=C$
20. If $U=\left\{ a,e,i,o,u \right\}$
$A=\left\{ a,e,i \right\}$ and $B=\left\{ e,o,u \right\}$, $C=\left\{ a,e,i \right\}$
Then verify that \[A\bigcap \left( B-C \right)=A\bigcap B-A\bigcap C\]\[A\cap (B-C)=(A\cap B)-(A\cap C)\]
$B-C=\left\{ e,o \right\}$
$A\bigcap \left( B-C \right)=\left\{ e \right\}$
$A\bigcap B=\left\{ e,o \right\}$and
$A\bigcap C=\left\{ a \right\}$
Hence proved
$A\bigcap \left( B-C \right)=\left( A\bigcap B \right)-\left( A\bigcap C \right)$
Very Long Questions and Answers (6 Marks Questions)
1. In a survey it is found that $21$ people like product A, $26$ people like product B and $29$ like product C. If $14$ people like product A and B, $15$ people like product and C, $12$ people like product C and A, and $8$ people like all the three products. Find
(i) How many people are surveyed in all?
Ans : Let us have A, B, C denote respectively the set of people who like the products A, B, C.
Then we can have a venn diagram as shown
From the above diagram
Total number of surveyed people is given by
$a+b+c+d+e+f+g$
$a=21,e=26,g=29,d=12,b=14,f=15,c=8$
Therefore total number of surveyed people is given by
$21+14+8+12+26+15+29=125$
(ii) How many like product C only?
Ans: The number of people who like product C only is $29$
2. A college awarded $38$ medals in football, $15$ in basketball and $20$ in cricket. If these medals went to a total of $50$ men and only five men got medals in all the three sports, how many received medals in exactly two of the three sports?
Ans : Let us have a notation F, B, and C for medals in football, basketball, and cricket respectively
C is intersection of all A,B,C and a,e,g are intersections of A and not B, B and not C, A and not C respectively.
From the above venn diagram
\[f=5\] ……(a)
\[a+b+e+f=38\]……(b)
\[b+c+d+f=15\]……(c)
\[e+d+f+g=20\]……(d)
$a+b+c+d+e+f+g=50$ ……(e)
From equations (d), (e) we get as shown
$a+b+c=30$……(f)
Now from equation (b) and (f) we get as shown
$e-3=c$ …….(g)
put value of c in the equation € as shown
$a+e+g+b+e+d=50-5+3$
Also from equation (d) and (e) we get
Therefore the medals received in exactly 2 of three sports is given by solving above equations as shown
\[b+e+d=13\]
3. There are 200 individuals with a skin disorder, $120$ had been exposed to the chemical ${{C}_{1}}$, 50 to chemical ${{C}_{2}}$, and 30 to both the chemicals ${{C}_{1}}$ and ${{C}_{2}}$. Find the number of individuals exposed to
(i). Chemical ${{C}_{1}}$ but not chemical ${{C}_{2}}$
Ans: Let us have a following notation
A- Denote the set of individuals exposed to the chemical \[{{C}_{1}}\]
B- Denote the set of individuals exposed to the chemical \[{{C}_{2}}\]
Given
\[n\left( S \right)=200\]
\[n\left( A \right)=120\]
\[n\left( B \right)=50\]
\[n\left( A\bigcap B \right)=30\]
\[\therefore n\left( A\bigcap \overline{B} \right)=n\left( A \right)-n\left( A\bigcap B \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( A\bigcap \overline{B} \right)=120-30=90\]
Hence the number of individuals exposed to chemical \[{{C}_{1}}\] but not to \[{{C}_{2}}\] is \[90\]
(ii). Chemical ${{C}_{2}}$ but not chemical ${{C}_{1}}$
\[\therefore n\left( \overline{A}\bigcap B \right)=n\left( B \right)-n\left( A\bigcap B \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( \overline{A}\bigcap B \right)=50-30=20\]
Hence the number of individuals exposed to chemical \[{{C}_{2}}\] but not to \[{{C}_{1}}\] is \[20\]
(iii). Chemical ${{C}_{1}}$ or chemical ${{C}_{2}}$
Ans : Let us have a following notation
\[\therefore n\left( A\bigcup B \right)=n\left( A \right)+n\left( B \right)-n\left( A\bigcap B \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( A\bigcup B \right)=120+50-30=140\]
Hence the number of individuals exposed to chemical \[{{C}_{2}}\]or \[{{C}_{1}}\] is \[140\]
4. In a survey it was found that $21$ people liked product A, $26$ liked product B and $29$ liked product C. If $14$ people liked products A and B, $12$ people like C and A, $15$ people like B and C and $8$ liked all the three products. Find now many liked product C only.
Ans: Let us have a venn diagram of above information as shown
The followings are given in the question
$a+b+c+d=21$
$b+c+e+f=26$
$c+d+f+g=29$
Also it is given in the question
$\therefore d=4$
$\therefore f=7$
Hence the number of people who like product C only is $g=10$
5. A college awarded $38$ medals in football, $15$ in basketball and $20$ in cricket. If these medals went to a total of $58$ men and only three men got medals in all the three sports, how many received medals in exactly two of the three sports?
Ans: Let us denote A, B and C as the sets of men who received medals in football, basketball and cricket respectively.
\[n\left( A \right)=38\]
\[n\left( B \right)=15\]
\[n\left( C \right)=20\]
\[n\left( A\bigcup B\bigcup C \right)=58\]
\[n\left( A\bigcap B\bigcap C \right)=3\]
\[\left( A\bigcup B\bigcup C \right)=n\left( A \right)+n\left( B \right)+n\left( C \right)-\left[ n\left( A\bigcap B \right)+n\left( B\bigcap C \right)+n\left( C\bigcap A \right) \right]+n\left( A\bigcap B\bigcap C \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 58=38+15+20-\left( a+d \right)-\left( d+c \right)-\left( b+d \right)+3\]
\[\Rightarrow 18=a+b+c+3d\]
Hence we get \[a+b+c=9\]
6. In a survey of $60$ people, it was found that $25$ people read newspaper H, $26$ read newspaper T, $26$ read newspaper I, $9$ read both H and I, $11$ read both H and T, $8$ read both T and I, $3$ read all three newspapers. Find
i) The no. of people who read at least one of the newspapers.
Ans: Let us have a venn diagram as shown
We are given with the following data
\[a+b+c+d=25\]
\[b+c+e+f=26\]
\[d+c+g+f=26\]
And also it is given
\[\therefore f=5\]
\[\therefore b=8\]
\[\therefore d=6\]
\[\therefore g=12\]
\[\therefore e=10\]
\[\therefore a=8\]
The no. of people who read at least one of the newspapers is \[a+b+c+d+e+f+g=52\]
ii) The no. of people who read exactly one newspaper
The no. of people who read exactly one newspaper is \[a+e+g=30\]
7. These are $20$ students in a chemistry class and $30$ students in a physics class. Find the number of students which are either in physics class or chemistry class in the following cases.
(i) Two classes meet at the same hour.
Ans: Let \[C\] be the set of students in chemistry class and \[P\] be the set of students in physics class.
\[n\left( P \right)=30\]
Now it is given that two classes meet at the same hour and hence
\[n\left( C\bigcap P \right)=0\]
\[\therefore n\left( C\bigcup P \right)=n\left( C \right)+n\left( P \right)-0\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( C\bigcup P \right)=20+30=50\]
Hence the number of students which are either in physics class or chemistry class when classes are at the same time is \[50\].
(ii) The two classes met at different hours and ten students are enrolled in both the courses.
\[n\left( C\bigcap P \right)=10\]
\[\therefore n\left( C\bigcup P \right)=n\left( C \right)+n\left( P \right)-10\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( C\bigcup P \right)=20+30-10=40\]
The number of students which are either in physics class or chemistry class when the two classes met at different hours and ten students are enrolled in both the courses is.
8. In a survey of $25$ students, it was found that $15$ had taken mathematics, $12$ had taken physics and $11$ had taken chemistry, $5$ had taken mathematics and chemistry, $9$ had taken mathematics and physics, $4$ had taken physics and chemistry and $3$ had taken all three subjects.
Find the no. of students that had taken
(i). only chemistry
\[n\left( M \right)=a+b+d+e=15\]
\[n\left( P \right)=b+c+f+e=12\]
\[n\left( C \right)=d+e+f+g=11\]
\[n\left( M\bigcap P \right)=b+e=9\]
\[n\left( M\bigcap C \right)=d+e=5\]
\[n\left( P\bigcap C \right)=f+e=4\]
Also it is given that \[e=3\]
\[\therefore b=6,\therefore d=2,\therefore f=1\]
Also \[\therefore a=4,\therefore g=5,\therefore c=2\]
Therefore the number of students who had taken only chemistry is \[g=5\]
(ii). only mathematics
Therefore the number of students who had taken only mathematics is \[a=4\]
(iii). only physics
Therefore the number of students who had taken only physics is \[c=2\]
(iv). physics and chemistry but not mathematics
Therefore the number of students who had taken physics and chemistry but not mathematics is \[f=1\]
(v). mathematics and physics but not chemistry
Therefore the number of students who had taken physics and mathematics but not chemistry is \[b=6\]
(vi). only one of the subjects
Ans : Let us have a venn diagram of above information as shown
Therefore the number of students who had taken only one of the subjects is \[\therefore a+g+c=11\]
(vii). at least one of three subjects
Therefore the number of students who had taken atleast one of the subjects is \[a+b+c+d+e+f+g=23\]
(viii). None of three subjects.
Therefore the number of students who had taken none of the subjects is \[25-\left( a+b+c+d+e+f+g \right)=2\]
9. In a survey of $100$ students, the no. of students studying the various languages were found to be English only $18$, English but not Hindi $23$, English and Sanskrit $8$, English $26$, Sanskrit $48$, Sanskrit and Hindi $8$, no language $24$. Find
(i) How many students were studying Hindi?
Ans: Let the total number of students be
Let us have the venn diagram as shown
\[a+e+g+d=26\]
\[g+e+f+c=48\]
So we get
\[e=5,g=3,d=0,f=5,c=35\]
Therefore the number of students studying Hindi is \[f+b+g+d=18\]
(ii) How many students were studying English and Hindi?
Therefore the number of students studying Hindi and English is \[g+d=3\]
10. In a class of $50$ students, $30$ students like Hindi, $25$ like science and $16$ like both. Find the no. of students who like
(i) Either Hindi or Science
Ans: Let the total number of students be
Let us denote number of students who like Hindi with H and who like science with S
\[n\left( H\bigcup S \right)=n\left( H \right)+n\left( S \right)-n\left( H\bigcap S \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( H\bigcup S \right)=30+25-16=39\]
Therefore the number of students who like either Hindi or Science is \[39\]
(ii) Neither Hindi nor Science.
\[n\left( {{H}^{'}}\bigcap {{S}^{'}} \right)=T-n\left( H\bigcup S \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow n\left( {{H}^{'}}\bigcap {{S}^{'}} \right)=50-39=11\]
Therefore the number of students who like either Hindi or Science is \[39\]
11. In a town of 10,000 families, it was found that 40% of families buy newspaper A, 20% families buy newspaper B, and 10% of families buy newspaper C. 5% of families buy A and B, 3% buy B and C and 4% buy A and C. If 2% families buy all the three papers. Find the no. of families which buy
(i) A only
Ans: Let the total number of families be
\[T=10,000\]
Let us have the venn diagram of above information as shown
It is given in the question that
\[x+a+c+d=4000\]
\[y+a+b+d=2000\]
\[z+b+c+d=1000\]
\[a+d=500\]
\[b+d=300\]
\[c+d=400\]
Hence on solving we get
\[a=300,b=100,c=200\]
Therefore the number of families who buy newspaper A only is \[x=4000-300-200-20=3380\]
(ii) B only
Ans : Let the total number of families be
Let us have the venn diagram of above informations as shown
Therefore the number of families who buy newspaper B only is \[y=2000-300-200-100=1400\]
(iii) none of A, B, and C.
From the above we get
\[z=1000-100-200-200=500\]
Therefore the number of families who buy newspaper none of A, B or C is
\[10000-\left[ 3300+1400+500+300+100+200+200 \right]=5000\]
12. Two finite sets have m and n elements. The total no. of subsets of the first set is 56 more than the total no. of subsets of the second set. Find the value of m and n.
Ans: Assume A and B be two sets having m and n elements respectively
Hence we know that number of subsets will be given as shown
Number of subsets of A is \[{{2}^{m}}\]
Number of subsets of B is \[{{2}^{n}}\]
According to the question
\[{{2}^{m}}=56+{{2}^{n}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{2}^{m}}-{{2}^{n}}=56\]
\[\Rightarrow {{2}^{n}}\left( {{2}^{m-n}}-1 \right)=56\]
On comparing we get
\[n=3,m-n=3\] \[\Rightarrow m=6\]
Sets Important Question PDF For Download
There is no doubt that we need help when we are solving something for the first time. The same goes for the important questions for class 11 maths chapter 1. Vedantu has provided its students with some tips in the pdf which can make their learning of sets in class 11 extra questions a bit less complicated and fun.
The chapter first of the 11th notebook is easy and has all the essential questions which make students test their formula-solving skills for sets. You can quickly check out the step-by-step solutions of this chapter's important questions in the pdf format and download it offline, so it can be viewed anytime even when the person is offline.
Important Concepts Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Related to Sets
Given below, we have breakdown of important concepts you will study in class 11 maths chapter 1. These will help you get a better grip of the formulas and the theorems which you need to use to solve the questions.
Equal Sets
For sets in class 11 important questions, one needs to know about sets as they are defined as a collection of well-defined, distinct objects. On the other hand, items which come together to form a set are called elements. The condition of two sets to become equal can happen when each set's element is also a part of the other set. Likewise, if both the sets are subsets of each other, you can even say these two sets are equal.
Venn Diagram
It is a diagram which is used by students and mathematicians to represent sets and their relation from each other. By seeing a Venn diagram, you can determine which operation has been done on the given two sets such as the intersection of the sets and their difference. Likewise, one can easily show the subsets of a given set using these diagrams.
Union & Intersection of Sets
In class 11 sets important questions students will learn about the concept of a cardinal number of a set which is several distinct elements or members in a finite set. With the cardinality's help, we can define the size of a set if you want to denote the cardinal number of a set A you need to write it down like this n(A).
There are three properties of which you need to remember for the cardinal numbers and these are:
If A ∩ B = ∅, then, n(A ∪ B) = n(A) + n(B) this is a Union of disjoint sets.
If A and B are two finite sets, then n(A ∪ B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A ∩ B) which is said to be a union of two sets.
If A, B and C are three finite sets, then; n(A ∪ B ∪ C) = n(A) + n(B) + n(C) – n(A ∩ B) – n(B ∩ C) – n(A ∩ C) + n(A ∩ B ∩ C) this shows the union of three sets.
Sets Class 11 Extra Questions
Well, if you are preparing to give the exams this year or next year, one thing is sure you need to prepare for the additional questions which are a bit tricky, and you can't find them in your textbook as well. Students studying in 11th can prepare their academic and competitive exams by solving these additional questions from Sets class 11.
Q.1 Which of the following sets. Explain your answer.
(a). A collection of all days which are present in a single week and starts with an alphabet S.
(b). The collection of the ten most famous singers of India.
(c). A group of best football strikers in the world.
(d). The collection of all boys in your school.
(e). The collection of all the possible odd numbers below 100.
(f). A collection of poems which are penned down by the famous poet Shakespeare.
(g). The collection of all prime numbers.
(h). The collection of questions in a science book.
(i). A collection of most dangerous reptiles in India.
Q.2: Let P = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}. Insert the correct symbol inside the given blank spaces below:
(a). 2 . . . . . . . . . . P
(b). 9 . . . . . . . . . P
(c). 11 . . . . . . . . P
(d). 4 . . . . . . . . P
(e). 0 . . . . . . . . P
(f). 7 . . . . . . . . P
Q.3: List all the elements from the given set P = {y: y is even natural number}
Q.4: If A = {(x,y) : x² + y²= 25 where x, y ∈ W } write a set of all possible ordered pairs.
Q.5: If P(X) = P(Y) show that A = B.
Q.6: Let N and M be sets ; if N∩M = M∩X = ∅ and N∪X = M∪X for some set X.Show that N=M.
Q.7: If X ={1,2,3,4,5}, then solve the question to find out the proper subsets of A.
Q.8: For this question Write a Roster form of the given set A={x: x ∈ R, 2x+10 =12}
Q.9 Let X and Y are the two sets which have 3 and 6 elements present in them respectively. Find the maximum and the minimum number of elements in X ∪ Y.
Q.10: If X = {(a,b) : a² + b²= 25 where a, b ∈ W } write a set of all possible ordered pairs.
Practice Questions
Write the set {-2,7} in the set builder form.
If the set N = { 1,3,7), then how many elements have set P(N).
If the universal set (U) = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7}, A = {2,4,6} , B= { 3,5} and C = { 1,2,4,7}, Find: A′ ∪ (B ∩ C′), and (B – A) ∪ (A – C)
If X, Y, and Z are three sets, then X – (Y ∪ Z) is equal to.
If A = {x, y} and B = { x, y, z). Is Z a superset of Y? Why?
Chapterwise Links for CBSE Class 11 Maths
Chapter 2 - Relations and Functions
Chapter 3 - Trigonometric Functions
Chapter 4 - Principle of Mathematical Induction
Chapter 5 - Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Chapter 6 - Linear Inequalities
Chapter 7 - Permutations and Combinations
Chapter 8 - Binomial Theorem
Chapter 9 - Sequences and Series
Chapter 10 - Straight Lines
Chapter 11 - Conic Sections
Chapter 12 - Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry
Chapter 13 - Limits and Derivatives
Chapter 14 - Mathematical Reasoning
Chapter 15 - Statistics
Chapter 16 - Probability
Benefits of Solving Important Questions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 1
Let's try to find out why solving the important questions for class 11th maths chapters are pretty essential and need to be done as much as possible.
Understanding the Formulae: many times, students might skip the derivation and keep on mugging the formula all along. Knowing your formulas is a good thing, but when you don't know which one to use to solve a question is when the problem comes. With our PDF of solved sets examples, you will be able to understand which formula will be suitable for solving the problem.
Makes Your Problem Solving Efficient: Once you get a good grip on how to solve the problem, you can easily find out which problem will take more time and start writing it before anything else.
Covers Important Topics: With this Pdf designed by Vedantu students get to know about all the main concepts of Venn Diagrams and how to use them along with Complement's properties. As a result, students will understand every topic they need to learn for their upcoming exams.
Confidence Booster: When you start solving a question, and it comes out that you managed to get the right answer, you feel uplifted as it boosts your morale. If you have an issue with the answer, you can find out the step by step solving of the union and intersection sets answers.
Gives More Questions for Practise: A student needs to be solving different types of problems to sharpen their mind and test their knowledge of the subject, and these important questions do the same thing.
There you have it, these are some of the basic concepts you are going to study in the class 11th maths chapter 1 based on Sets . The important questions are solved and were written down so that it will be easier for you to understand their language. You need to keep on practising even if you think you are done with the chapter and have enough understanding. Always revise the chapter by doing some questions before you finally appear in exams. For the important questions of class 11th maths chapter 1 , you need to put both your mind and heart to study its concepts and get them memorized.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 11
CBSE Class 11 Study Materials |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Important Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 - Sets offered by Vedantu is an excellent resource for students who want to excel in their mathematical studies. The questions cover all the important topics in the chapter, including the definition of sets, types of sets, operations on sets, and Venn diagrams, making it easier for students to understand and improve their mathematical skills. The questions are designed by subject matter experts according to the CBSE syllabus for Class 11 students and provide a comprehensive and detailed explanation of the concepts. Additionally, the questions offer practice exercises that help students test their understanding of the chapter and prepare for their exams. Vedantu also provides interactive live classes and doubt-solving sessions to help students clarify their doubts and improve their understanding of the chapter. Overall, the Important Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 - Sets offered by Vedantu are an essential resource for students who want to improve their mathematical skills and score well in their exams.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 - Sets 2024-25
1. How to utilize Important Questions for CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets to score well in exams?
Students can solve important questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets available online to score well in school exams as well as competitive exams. The extra questions provided by e-learning sites on the first chapter of Class 11 Maths can be utilized to understand what types of questions can be expected from exams. These questions are really helpful for practice and clearing the concepts related to the chapter. On platforms like Vedantu, these questions are solved by expert teachers. By referring to the PDF file of important questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets, students will be able to practice the chapter effectively. These questions will also help in revision.
2. Where can I find Important Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets?
Vedantu caters to a well-prepared set of Important Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets as well as other chapters. Vedantu is a well-known online learning site known for its top quality study materials. It selects questions for a chapter based on the exam pattern and most frequently asked questions. Vedantu provides a free PDF of Important Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets. These solutions are also solved by subject matter experts to provide a clear cut understanding of the chapter. These are proven to be helpful in exam preparation and provide effective revision during exams.
3. What is the importance of Vedantu’s extra questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets?
Vedantu’s extra questions for CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets is crucial during the exam preparation. The important questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets allow students to practice the chapter thoroughly. Working on these questions will make students familiar with all types of questions that can be asked in the exam. The important questions PDF file at Vedantu is designed to cover all the important topics of the chapters. These questions are based on the exam pattern and are added after referring to previous year question papers. The free PDF of CBSE Maths Class 11 Chapter 1 can be utilized at the time of revision. These are really helpful in scoring well in the paper and are a confidence booster during the exam time.
4. What are the important learning outcomes from Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets?
From Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets, students will learn what are sets and how to represent sets. Students will also learn about types of sets such as Empty Sets, Equal Sets and what are Subsets and how to identify them. Also, one will learn how to design Venn diagrams. The chapter also includes the knowledge of different operations on sets such as Union of sets, Intersection of sets, Difference of sets, Complement of a set, etc. Students are also taught about practical problems on Union and Intersection of Two Sets .
5. What are the important topics of the Chapter-Sets of Class 11 Maths?
Chapter 1 'Sets' of Class 11 Maths is an entirely new concept that is quite significant for the Class 11 exams. The chapter 'Sets' consists of the following important topics that students must pay attention to:
What are sets?
Sets and their representations
Finite sets and infinite sets
Universal sets
Venn diagrams
Operation on sets: Union and intersection of sets
Complement of the sets and their properties
Practical problems of union and intersection of two sets
6. How many chapters are there in Class 11 Maths apart from Chapter 1-Sets?
Class 11 Maths has a total of 16 chapters. The following are the chapters prescribed in the NCERT textbook:
Ch. 1: Sets
Ch. 2: Relations and Functions
Ch. 3: Trigonometric Functions
Ch. 4: Principle of Mathematical Induction
Ch. 5: Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
Ch. 6: Linear Inequalities
Ch. 7: Permutations and Combinations
Ch. 8: Binomial Theorem
Ch. 9: Sequence and Series
Ch. 10: Straight Lines
Ch. 11: Conic Sections
Ch. 12: Introduction to Three–dimensional Geometry
Ch. 13: Limits and Derivatives
Ch. 14: Mathematical Reasoning
Ch. 15: Statistics
Ch. 16: Probability
7. What should I keep in mind while solving Chapter 1 of Class 11 Maths?
It makes a lot of difference how you present your answers in your answer sheet. Especially when it's a subject like Maths, students should make sure that their answers look neat and tidy. There are marks allocated to the steps of any solution, therefore one should ensure that his answers are written step-wise. Don't forget to mention and highlight the formula or theorem you are using in the solution. Avoid making silly mistakes with operation signs and numbers. A single mistake can make your entire solution wrong.
8. Is Chapter Sets of Class 11 Maths an important chapter?
Sets is definitely an important chapter in Class 11 Maths. It holds a major part in the exam holding a pretty good enough weightage of marks. This chapter is a whole new chapter for any student who enters Class 11 and since it is a significant chapter, students must be very keen in comprehending this chapter thoroughly. This chapter explains various types of sets in detail and questions related to them. To study more about sets students can download the Important Questions free of cost from the Vedantu website or mobile app.
9. How can I complete my Maths class test paper of Chapter 1 of Class 11 Maths on time?
Most of the students face the difficulty of not being able to finish their papers on time. The chief reason behind this is the lack of time management. If you waste too much time solving trivial questions, you may end up skipping some really important questions. Therefore, divide your time evenly on each question before you start the exam. Regular practice using NCERT solutions and Mock tests from Vedantu can help students learn to manage their time better.
CBSE Class 11 Maths Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
CBSE Class 11 Maths – Chapter 1 Sets- Study Materials
NCERT Solutions Class 11 All Subjects Sample Papers Past Years Papers
Sets : Notes and Study Materials -pdf
- Concepts of Sets
- Sets Master File
- Sets Revision Notes
- R D Sharma Solution : Sets
- NCERT Solution Sets
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Sets
- Sets : Solved Example 1
CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 1 Sets
Set A set is a well-defined collection of objects.
Representation of Sets There are two methods of representing a set
- Roster or Tabular form In the roster form, we list all the members of the set within braces { } and separate by commas.
- Set-builder form In the set-builder form, we list the property or properties satisfied by all the elements of the sets.
Types of Sets – Class 11 Maths Notes
- Empty Sets: A set which does not contain any element is called an empty set or the void set or null set and it is denoted by {} or Φ.
- Singleton Set: A set consists of a single element, is called a singleton set.
- Finite and infinite Set: A set which consists of a finite number of elements, is called a finite set, otherwise the set is called an infinite set.
- Equal Sets: Two sets A and 6 are said to be equal, if every element of A is also an element of B or vice-versa, i.e. two equal sets will have exactly the same element.
- Equivalent Sets: Two finite sets A and 6 are said to be equal if the number of elements are equal, i.e. n(A) = n(B)
Subset – Class 11 Maths Notes
A set A is said to be a subset of set B if every element of set A belongs to set B. In symbols, we write A ⊆ B, if x ∈ A ⇒ x ∈ B
- Every set is o subset of itself.
- The empty set is a subset of every set.
- The total number of subsets of a finite set containing n elements is 2 n .
Intervals as Subsets of R Let a and b be two given real numbers such that a < b, then
- an open interval denoted by (a, b) is the set of real numbers {x : a < x < b}.
- a closed interval denoted by [a, b] is the set of real numbers {x : a ≤ x ≤ b}.
- intervals closed at one end and open at the others are known as semi-open or semi-closed interval and denoted by (a, b] is the set of real numbers {x : a < x ≤ b} or [a, b) is the set of real numbers {x : a ≤ x < b}.
Power Set The collection of all subsets of a set A is called the power set of A. It is denoted by P(A). If the number of elements in A i.e. n(A) = n, then the number of elements in P(A) = 2 n .
Universal Set A set that contains all sets in a given context is called the universal set.
Venn-Diagrams Venn diagrams are the diagrams, which represent the relationship between sets. In Venn-diagrams the universal set U is represented by point within a rectangle and its subsets are represented by points in closed curves (usually circles) within the rectangle.
Operations of Sets Union of sets: The union of two sets A and B, denoted by A ∪ B is the set of all those elements which are either in A or in B or in both A and B. Thus, A ∪ B = {x : x ∈ A or x ∈ B}.
Intersection of sets: The intersection of two sets A and B, denoted by A ∩ B, is the set of all elements which are common to both A and B. Thus, A ∩ B = {x : x ∈ A and x ∈ B}
Disjoint sets: Two sets Aand Bare said to be disjoint, if A ∩ B = Φ.
Intersecting or Overlapping sets: Two sets A and B are said to be intersecting or overlapping if A ∩ B ≠ Φ
Difference of sets: For any sets A and B, their difference (A – B) is defined as a set of elements, which belong to A but not to B. Thus, A – B = {x : x ∈ A and x ∉ B} also, B – A = {x : x ∈ B and x ∉ A}
Complement of a set: Let U be the universal set and A is a subset of U. Then, the complement of A is the set of all elements of U which are not the element of A. Thus, A’ = U – A = {x : x ∈ U and x ∉ A}
Some Properties of Complement of Sets
Symmetric difference of two sets: For any set A and B, their symmetric difference (A – B) ∪ (B – A) (A – B) ∪ (B – A) defined as set of elements which do not belong to both A and B. It is denoted by A ∆ B. Thus, A ∆ B = (A – B) ∪ (B – A) = {x : x ∉ A ∩ B}.
Laws of Algebra of Sets – Class 11 Maths Notes
Idempotent Laws: For any set A, we have
Identity Laws: For any set A, we have
Commutative Laws: For any two sets A and B, we have
- A ∪ B = B ∪ A
- A ∩ B = B ∩ A
Associative Laws: For any three sets A, B and C, we have
- A ∪ (B ∪ C) = (A ∪ B) ∪ C
- A ∩ (B ∩ C) = (A ∩ B) ∩ C
Distributive Laws: If A, B and Care three sets, then
- A ∪ (B ∩ C) = (A ∪ B) ∩ (A ∪ C)
- A ∩ (B ∪ C) = (A ∩ B) ∪ (A ∩ C)
De-Morgan’s Laws: If A and B are two sets, then
- (A ∪ B)’ = A’ ∩ B’
- (A ∩ B)’ = A’ ∪ B’
Formulae to Solve Practical Problems on Union and Intersection of Two Sets Let A, B and C be any three finite sets, then
- n(A ∪ B) = n(A) + n (B) – n(A ∩ B)
- If (A ∩ B) = Φ, then n (A ∪ B) = n(A) + n(B)
- n(A – B) = n(A) – n(A ∩ B)
- n(A ∪ B ∪ C) = n(A) + n(B) + n(C) – n(A ∩ B) – n(B ∩ C) – n(A ∩ C) + n(A ∩ B ∩ C)
Sets Class 11 MCQs Questions with Answers
Question 1. If A, B and C are any three sets, then A – (B ∪ C) is equal to (a) (A – B) ∪ (A – C) (b) (A – B) ∪ C (c) (A – B) ∩ C (d) (A – B) ∩ (A – C)
Answer: (d) (A – B) ∩ (A – C) Hint: Given A, B and C are any three sets. Now, A – (B ∪ C) = (A – B) ∩ (A – C)
Question 2. (A’)’ = ? (a) ∪ – A (b) A’ (c) ∪ (d) A
Answer: (d) A Hint: (A’)’ = A
Question 3. A – B is read as? (a) Difference of A and B of B and A (b) None of the above (c) Difference of B and A (d) Both a and b
Answer: (a) Difference of A and B of B and A Hint: A – B will read as difference of A and B of B and A Ex: Let A = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} and B = {1, 3, 5, 7} Now, A – B = {2, 4}
Question 4. If A, B and C are any three sets, then A × (B ∪ C) is equal to (a) (A × B) ∪ (A × C) (b) (A ∪ B) × (A ∪ C) (c) None of these (d) (A × B) ∩ (A × C)
Answer: (a) (A × B) ∪ (A × C) Hint: Given A, B and C are any three sets. Now, A × (B ∪ C) = (A × B) ∪ (A × C)
Question 5. IF A = [5, 6, 7] and B = [7, 8, 9] then A ∪ B is equal to (a) [5, 6, 7, 8, 9] (b) [5, 6, 7] (c) [7, 8, 9] (d) None of these
Answer: (a) [5, 6, 7, 8, 9] Hint: Given A = [5, 6, 7] and B = [7, 8, 9] then A ∪ B = [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
Question 6. Which of the following sets are null sets (a) {x: |x |< -4, x ?N} (b) 2 and 3 (c) Set of all prime numbers between 15 and 19 (d) {x: x < 5, x > 6}
Answer: (b) 2 and 3 Hint: 2 and 3 is the null set.
Question 7. IF R = {(2, 1),(4, 3),(4, 5)}, then range of the function is? (a) Range R = {2, 4} (b) Range R = {1, 3, 5} (c) Range R = {2, 3, 4, 5} (d) Range R {1, 1, 4, 5}
Answer: (b) Range R = {1, 3, 5} Hint: Given R = {(2, 1),(4, 3),(4, 5)} then Range(R) = {1, 3, 5}
Question 8. The members of the set S = {x | x is the square of an integer and x < 100} is (a) {0, 2, 4, 5, 9, 58, 49, 56, 99, 12} (b) {0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81} (c) {1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 64, 81, 85, 99} (d) {0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 121}
Answer: (b) {0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81} Hint: The set S consists of the square of an integer less than 100 So, S = {0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81}
Question 9. In a class of 120 students numbered 1 to 120, all even numbered students opt for Physics, whose numbers are divisible by 5 opt for Chemistry and those whose numbers are divisible by 7 opt for Math. How many opt for none of the three subjects? (a) 19 (b) 41 (c) 21 (d) 57
Answer: (b) 41 Hint: The number of students who took at least one of the three subjects can be found by finding out A ∪ B ∪ C, where A is the set of those who took Physics, B the set of those who took Chemistry and C the set of those who opted for Math. Now, A ∪ B ∪ C = A + B + C – (A ∩ B + B ∩ C + C ∩ A) + (A ∩ B ∩ C) A is the set of those who opted for Physics = 120/2 = 60 students B is the set of those who opted for Chemistry = 120/5 = 24 C is the set of those who opted for Math = 120/7 = 17 The 10th, 20th, 30th….. numbered students would have opted for both Physics and Chemistry. Therefore, A ∩ B = 120/10 = 12 The 14th, 28th, 42nd….. Numbered students would have opted for Physics and Math. Therefore, C ∩ A = 120/14 = 8 The 35th, 70th…. numbered students would have opted for Chemistry and Math. Therefore, B ∩ C = 120/35 = 3 And the 70th numbered student would have opted for all three subjects. Therefore, A ∪ B ∪ C = 60 + 24 + 17 – (12 + 8 + 3) + 1 = 79 Number of students who opted for none of the three subjects = 120 – 79 = 41
Question 10. { (A, B) : A² +B² = 1} on the sets has the following relation (a) reflexive (b) symmetric (c) none (d) reflexive and transitive
Answer: (b) symmetric Hint: Given {(a, b) : a² + b² = 1} on the set S. Now a² +b² = b² + a² = 1 So, the given relation is symmetric.
Question 11. Two finite sets have N and M elements. The number of elements in the power set of first set is 48 more than the total number of elements in power set of the second test. Then the value of M and N are (a) 7, 6 (b) 6, 4 (c) 7, 4 (d) 6, 3
Answer: (b) 6, 4 Hint: Let A and B be two sets having m and n numbers of elements respectively Number of subsets of A = 2m Number of subsets of B = 2n Now, according to question 2m – 2n = 48 ⇒ 2n(2m – n – 1) = 24(22 – 1) So, n = 4 and m – n = 2 ⇒ m – 4 = 2 ⇒ m = 2 + 4 ⇒ m = 6
Question 12. The range of the function f(x) = 3x – 2‚ is (a) (- ∞, ∞) (b) R – {3} (c) (- ∞, 0) (d) (0, – ∞)
Answer: (a) (- ∞, ∞) Hint: Let the given function is y = 3x – 2 ⇒ y + 2 = 3x ⇒ x = (y + 2)/3 Now x is saisfied by all values. So, Range{f(x)} = R = (-∞, ∞)
Question 13. If A, B, C be three sets such that A ∪ B = A ∪ C and A ∩ B = A ∩ C, then, (a) B = C (b) A = C (c) A = B = C (d) A = B
Answer: (a) B = C Hint: Given A, B, C be three sets such that A ∪ B = A ∪ C and A ∩ B = A ∩ C then B = C
Question 14. In 2nd quadrant? (a) X < 0, Y < 0 (b) X < 0, Y > 0 (c) X > 0, Y > 0 (d) X > 0, Y < 0
Question 15. How many rational and irrational numbers are possible between 0 and 1? (a) 0 (b) Finite (c) Infinite (d) 1
Answer: (c) Infinite Hint: There are infinite many rational and irrational numbers are possible between 0 and 1 This is because between any two numbers, there are infinite numbers.
Question 16. Empty set is a? (a) Finite Set (b) Invalid Set (c) None of the above (d) Infinite Set
Answer: (a) Finite Set Hint: In mathematics, and more specifically set theory, the empty set is the unique set having no elements and its size or cardinality (count of elements in a set) is zero. So, an empty set is a finite set.
Question 17. If A = [5, 6, 7] and B = [7, 8, 9] then A U B is equal to (a) [5, 6, 7, 8, 9] (b) [5, 6, 7] (c) [7, 8, 9] (d) None of these
Answer: (a) [5, 6, 7, 8, 9] Hint: Given A = [5, 6, 7] and B = [7, 8, 9] then A U B = [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
Question 18. Which of the following two sets are equal? (a) A = {1, 2} and B = {1} (b) A = {1, 2} and B = {1, 2, 3} (c) A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {2, 1, 3} (d) A = {1, 2, 4} and B = {1, 2, 3}
Answer: (c) A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {2, 1, 3} Hint: Two sets are equal if and only if they have the same elements. So, A = {1, 2, 3} and B = {2, 1, 3} are equal sets.
Question 19. In a class of 50 students, 10 did not opt for math, 15 did not opt for science and 2 did not opt for either. How many students of the class opted for both math and science. (a) 24 (b) 25 (c) 26 (d) 27
Answer: (d) 27 Hint: Total students = 50 Students who did not opt for math = 10 Students who did not opt for Science = 15 Students who did not opt for either maths or science = 2 Total of 40 students in math and 13 did not opt for science but did for math = 40 – 13 = 27 So, students of the class opted for both math and science is 27
Question 20. In last quadrant? (a) X < 0, Y > 0 (b) X < 0, Y < 0 (c) X > 0, Y < 0 (d) X > 0, Y > 0
myCBSEguide
- Entrance Exam
- Competitive Exams
- ICSE & ISC
- Teacher Exams
- UP Board
- Uttarakhand Board
- Bihar Board
- Chhattisgarh Board
- Haryana Board
- Jharkhand Board
- MP Board
- Rajasthan Board
- Courses
- Test Generator
- Homework Help
- News & Updates

- Dashboard
- Mobile App (Android)
- Browse Courses
- New & Updates
- Join Us
- Login
- Register
No products in the cart.
- Mathematics
Class 11 Maths Sample Papers, NCERT Solutions | Mock Tests
Designed for the toppers, the course content of CBSE Class 11 Maths like Sample Papers, NCERT Solutions, Notes, and Important Questions can be availed as PDF on myCBSEguide.
- CBSE Syllabus
CBSE Sample Papers
Cbse last year papers, user submitted papers, case study questions, mock tests, relations and functions, trigonometric functions, complex numbers and quadratic equations, linear inequalities, permutations and combinations, binomial theorem, sequences and series, straight lines, conic sections, introduction to 3d geometry, limits and derivatives, probability.
- CBSE Test Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
CBSE Important Questions
Other useful resourses, online tests, learning videos.
Regarded as a scoring subject, Mathematics is equally important, especially when it comes to the senior secondary level. One can master this subject with little effort. All they need to do is to apply the flow of reasons while proving a result or solving a problem. To attain this level of competence you need good practice. For having the good practice you need to have quality course material. You can get the best resources for CBSE class 11 Mathematics on myCBSEguide as we gave a huge question bank with a variety of questions. Download the latest Sample Papers for CBSE Class 11 Mathematics, chapter-related Revision Notes, NCERT solution, and test papers all in PDF files.
CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Resources
Trusted by millions of teachers and students alike, myCBSEguide is a one-stop solution for quality course content for CBSE subjects. Students must put some extra effort to excel in Mathematics at the senior secondary level, as it will be working as the foundation of their future careers and profession. We provide a wide range of products with the help of which you can prepare for senior secondary Mathematics on myCBSEguide beginning from the syllabus to the model test papers. There are online tests, mock tests, learning videos, revision notes, NCERT solutions, and some important questions for class 11 Mathematics.
Class 11 Mathematics Syllabus
The syllabus is regularly updated based on the latest development. Students of senior secondary level, i.e., Class 11 Mathematics are on the threshold of higher academics. The marks they score here will play a decisive role in choosing their career options. Therefore, the syllabus of class 11 Maths includes every such topic that helps the students to develop a positive attitude to think, analyze and articulate logically. Given below are the name and the weightage of chapters of Class 11 Mathematics.
| 23 25 12 08 12 | |
The prescribed books for class 11 Mathematics are:
- Mathematics Textbook for Class XI, NCERT Publications
- Mathematics Lab Manual class XI, published by NCERT
To know the chapter and topic-related details check out our detailed blog on the Class 11 Mathematics syllabus .
Class 11 Mathematics Notes and NCERT Solutions
All CBSE students should practice NCERT textbook solutions because most of the time the questions asked in the final board examination are based on them. As we know that the CBSE encourages following NCERT textbooks because they cover almost all possible topics of any central examination. Some of the topics of class 11 Mathematics are:
- Binomial Theorem Miscellaneous
- Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations Miscellaneous
- Conic Sections Miscellaneous
- Limits and Derivatives Miscellaneous
To get the complete notes based on the exercise check out Class 11 Mathematics NCERT Solutions .
Although Mathematics is not a theory subject, an explanation of each chapter is needed. One cannot understand the chapter if they are not aware of the subject-specific terms and jargon along with the explanation of theorems. You can find a step-by-step explanation of each example sum of a particular topic of class 11 Mathematics. Do check our Revision Notes for Class 11 Mathematics and download them in PDF.
CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
Case study questions are the latest type of questions included in the CBSE question paper. This change is to promote competency-based learning and motivate topics from real-life and other subject areas, greater emphasis has been laid on the application of various concepts. The class 11 Mathematics case study questions look forward to acquainting students with different aspects of Mathematics used in daily life. Being the newest question format, it is difficult to get an assured quality of CBQs in the market or over the internet. Check our Class 11 Maths case study questions to know the actual standard of the questions. These case-based questions have sub-questions which can be objective or subjective type depending on the CBSE sample question paper. To get these questions get a subscription to our student dashboard.
CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Sample Papers
A student who aims to get good grades must solve sample papers religiously. Based on the official sample papers of the CBSE, myCBSEguide prepares around ten sample papers in each subject. Knowing the blueprint and MS can help the students to write their papers confidently. Even the school-level examinations follow the CBSE pattern, therefore it is advised to solve full-length class 11 Mathematic model test papers. Get the app to download the latest Class 11 Maths Sample Papers 2023 .
Sample papers are also helpful for periodic assessment too. This is because a sample paper has an assortment of questions. A standard sample paper has all types of questions such as very short answer (VSA), short answer (SA) and, long answer (LA) to effectively assess the knowledge, understanding, application, skills, analysis, evaluation and, synthesis. We can say that ideally, a sample paper matches the modalities of a proper pen-paper test.

CBSE Class 11 Maths Test Papers & Important Questions
Memorizing the rules and formulas is one thing and applying them is another. Good coordination between the two can make wonders. This can be achieved by enthusiastic practice. You can get the Test paper set for Class 11 Mathematics, which you can practice according to the level of your preparation. This helps in segmented learning. Test papers are good ways to learn and test simultaneously. The class 11 mathematics test papers have all types of questions. Besides, we make efforts to chalk out the most important questions from every chapter so that our students do not miss out on crucial information. Class 11 Mathematics important questions are available on myCBSEguide.
You can find such valuable study material for other CBSE subjects in our CBSE module .
Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
If you’re seeking a comprehensive and dependable study resource with Class 11 mathematics case study questions for CBSE, myCBSEguide is the place to be. It has a wide range of study notes, case study questions, previous year question papers, and practice questions to help you ace your examinations. Furthermore, it …
CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Syllabus 2022-23
CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Syllabus 2022-23 includes Sets and Functions, Coordinate Geometry, Statistics and Probability, Calculus etc for the session 2022 – 2023. Here is the detailed syllabus. To download class 11 Mathematics CBSE latest sample question papers for the 2023 exams, please install the myCBSEguide App which is the …
CBSE Term-1 MCQ Sample Papers 2021-22
CBSE will ask only MCQs in Term-1 Examination this year. The board will hold this first term exam in Nov-Dec 2021. As CBSE has already cleared that 1st term exam will carry 90 minutes, now it’s time to start preparation. Students can download CBSE Term-1 MCQ Sample Papers from myCBSEguide …
CBSE to Conduct Two Term Exams in 2021-22
CBSE has issued a circular on 5th July 2021 regarding the Special Scheme of Assessment for Board Examination Classes X and XII for the Session 2021-22. Here is the complete text of the circular. COVID 19 pandemic caused almost all CBSE schools to function in a virtual mode for the …
CBSE Class-11 New Stream Selection Rules
The New Education Policy-2020 has suggested eliminating rigid stream selection rules. We know that there are three streams in class 11 and the choices to select subjects are limited. Students have to select subjects within the stream only. Thus, if you are taking Science Stream, you have no option to …
CBSE Reduced Syllabus by 30% for Session 2020-21
CBSE, New Delhi has reduced the syllabus for classes 9 to 12 by 30%. The CBSE Revised Syllabus 2020-21 is available in CBSE official website and myCBSEguide mobile app. Here is the complete circular regarding CBSE Revised Syllabus 2020-21: CBSE Reduced the Syllabus The prevailing health emergency in the country …
Multiple Choice Questions for CBSE Class 10 and 12
The new curriculum issued by CBSE, New Delhi includes objective type questions along with Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ). Now CBSE will ask around 20% questions based on objective type questions. myCBSEguide App has more than one lakh MCQ from class 3 to 12 in almost all major subjects. MCQ questions …
CBSE Online MCQ Quiz Maker
The ultimate quiz builder helps CBSE schools and teachers, create MCQ quiz online and share the same with their students. Now schools and coaching institutes can create and share MCQ quiz online with their own Name and Logo. The students will attempt the quiz and teachers will get the result …
Create CBSE Question Papers Online
Creating question papers online is easy. You can create question papers online with your name and logo in minutes. So, why to waste time consulting many books and finding suitable questions. Just log in to myCBSEguide Test Generator here and create question papers online. Follow 3 simple steps: Select your …
CBSE Syllabus for Class 11 Mathematics 2019-20
CBSE Syllabus for Class 11 Mathematics 2019-20 contains all the topics of this session. myCBSEguide provides you latest Syllabus for Class 11 Mathematics. Mathematics is the study of numbers, shape, and patterns. Mathematics is not only important for success in life, but it is all around us. Mathematics is the …

Student Subscription
Unlock the exclusive content designed for the toppers, more courses.

Accountancy

Download myCBSEguide App
All courses.
- Entrance Exams
- Competative Exams
- Teachers Exams
- Uttrakand Board
- Bihar Board
- Chhattisgarh Board
- Haryana Board
- Jharkhand Board
- Rajasthan Board
Other Websites
- Examin8.com
CBSE Courses
- CBSE Class 12
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Class 09
- CBSE Class 08
- CBSE Class 07
- CBSE Class 06
- CBSE Class 05
- CBSE Class 04
- CBSE Class 03
- CBSE Class 02
- CBSE Class 01
- CBSE MCQ Tests
- CBSE 10 Year Papers
NCERT Solutions
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 09
- NCERT Solutions for Class 08
- NCERT Solutions for Class 07
- NCERT Solutions for Class 06
- NCERT Solutions for Class 05
- NCERT Solutions for Class 04
- NCERT Solutions for Class 03
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 11 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 09 Sample Papers
- CBSE Results | CBSE Datesheet
Please Wait..
Sets- Case Based Type Questions | Mathematics (Maths) Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Correct Answer is Option (c) From the table, it is observed that there are 5 colleges whose fees for 4 year course is less than or equal to 8 lakhs. So, the required set is {Manipal, LPU, Thapar, Jaypee, Chandigarh, Kalinga}.
Question 2: If Sri and Ram wants to take admission in the same college. Find the set of college in which both Sri and Ram can take their admission. If Ram and Sri have a Budget of 8 lakhs and 4 lakhs respectively ? (a) {Chandigarh, Kalinga} (b) {Jaypee} (c) {SRM, LPU} (d) Ø
Correct Answer is Option (a) The common colleges in which Sri and Ram both of them can take admission are Chandigarh and Kalinga. So, the required set is {Chandigarh, Kalinga}.
Question 3: Sri has taken an education loan of 3 lakhs to increase his overall budget. Find the set of college in which Ram can take admission but Sri cannot. (a) {Birla, Thapar} (b) {Thapar} (c) {SRM} (d) {Manipal, Thapar}
Correct Answer is Option (b) On increasing the budget of Sri by 3 lakh, the total budget will be 7 lakhs. So, the set of college in which she can take admission are {Manipal, LPU, Jaypee, Chandigarh, Kalinga}. But the set of colleges in which Ram can take admission are {Manipal, LPU, Thapar, Jaypee, Chandigarh, Kalinga}. Since there is one element that is not common in both the sets, the required set is {Thapar}.
Question 4: Sri has a total budget of 4 lakhs and she wanted admission in the famous college. Will she able to take admission in the colleges given in table. Find the set of college in which she can take admission. (a) Yes, {SRM, Birla, LPU} (b) No, {Jaypee, LPU, Kalinga} (c) Yes, {Chandigarh, Kalinga} (d) None of the above
Correct Answer is Option (c) Yes, there are two colleges whose fees are either equal to or less than 4 lakhs. So, the required set is {Chandigarh, Kalinga}.
Question 5: Ram has taken an education loan of 2 lakhs to increase his overall budget. Find the number of college in which he can take admission after raising his budget. (a) 4 (b) 9 (c) 7 (d) 6
Correct Answer is Option (b) Earlier when the budget was 8 lakh, the set of colleges are {Manipal, LPU, Thapar, Jaypee, Chandigarh, Kalinga}. On increasing the budget by 2 lakhs, the total budget of Ram becomes 10 lakhs. So, the set of college in which he can take admission are {Manipal, LPU, Thapar, Jaypee, Chandigarh, Kalinga, Amity, SRM, VIT}.
Direction: A survey is conducted by a career counsellor in a college to find career choice of students after the Intermediate. There are 100 students that goes for Engineering Courses, 50 wants to make their career in Medical, 100 students continue their further study in Arts. There are 10 students that go for both Engineering and Medical, and 3 goes for Medical and Arts. There are 3 students that do not go for any further studies. Question 6: Find the total number of students on which the survey is conducted. (a) 250 (b) 230 (c) 240 (d) 238
Correct Answer is Option (c) Let A set denotes Engineering, B set denotes Medical and C set denotes Art. Draw the Venn’s diagram for the given situation. Total number of students is the sum of elements in all the regions. So, the total number of students are 240.
Question 7: Find the number of students that goes for both Medical and Art. (a) 5 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4
Correct Answer is Option (c) Let A set denotes Engineering, B set Medical and C set Art. Draw the Venn’s diagram for the given situation. The region VI shows the student that goes for both Medical and Arts. So, n(B ∩ C) = 3.
Question 8: Find the number of students that goes for only engineering course. (a) 90 (b) 95 (c) 100 (d) 93
Correct Answer is Option (a) Let A set denotes Engineering, B set denotes Medical and C set denotes Art. Draw the Venn’s diagram for the given situation. So, the number of students that goes for only engineering course are 90.
Question 9: Find the number of students that goes for medical or engineering. (a) 150 (b) 140 (c) 160 (d) No of the above
Correct Answer is Option (b) Let A set denotes Engineering, B set denotes Medical and C set denotes Art. Draw the Venn’s diagram for the given situation. The region I, II, III, IV, V, and VI shows the student that goes for Engineering or Medical. So, the required number of students is 140.
Question 10: Find the number of students that goes for Engineering or Art. (a) 150 (b) 200 (c) 190 (d) 197
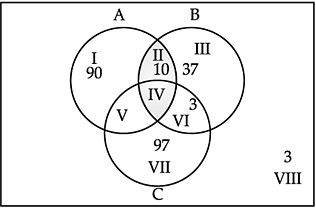
| |238 docs|91 tests |
Top Courses for Commerce
FAQs on Sets- Case Based Type Questions - Mathematics (Maths) Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. ¿Cuál es la importancia de los conjuntos en matemáticas? |
| 2. ¿Cómo se representan los conjuntos en notación de conjuntos? |
| 3. ¿Qué es un subconjunto y cómo se identifica? |
| 4. ¿Qué es la unión de conjuntos y cómo se representa? |
| 5. ¿Qué es la intersección de conjuntos y cómo se representa? |
| Views | |
| Rating | |
| Last updated |
Sets- Case Based Type Questions | Mathematics (Maths) Class 11 - Commerce
Sample paper, viva questions, past year papers, study material, shortcuts and tricks, previous year questions with solutions, objective type questions, practice quizzes, video lectures, important questions, mock tests for examination, extra questions, semester notes.

Sets- Case Based Type Questions Free PDF Download
Importance of sets- case based type questions, sets- case based type questions notes, sets- case based type questions commerce, study sets- case based type questions on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.
- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships
CBSE 11th Standard CBSE all question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 11th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and Scholorships in one place.
Latest 11th Standard CBSE Case study Questions Update
Cbse 11th physics motion in a straight line chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 11th physics units and measurements chapter case study questions with answers, cbse 11th chemistry structure of atom chapter case study question with answers, cbse 11th chemistry some basic concept of chemistry chapter case study questions with answers, 11th biology biological classification chapter case study question with answers cbse, 11th biology the living world chapter case study question with answers cbse, 11th standard cbse study materials.

11th Standard CBSE Subjects

Study Materials for Other CBSE Board Standards

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

Latest CBSE 11th Standard CBSE Study Material Updates
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1
Ncert solutions for class 11 maths chapter 1 sets.
Are you searching for the best NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets? Here in this article, Study Path has provided what you need exactly. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets includes all the questions of the NCERT textbook that are solved and explained beautifully using Vann diagrams, images etc. Here you can get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets in one place.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Set solved by expert teachers at Study Path. The Solutions to the questions of Chapter 1 Sets Maths Class 11 have been solved in a very logical, step-by-step manner. It is as prepared per the latest Syllabus and NCERT Guidelines.
Download PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets
In this section, we have provided the links of different exercises of the chapter. Click on the appropriate links to access the solutions we want.
- Exercise 1.1
- Exercise 1.2
- Exercise 1.3
- Exercise 1.4
- Exercise 1.5
- Exercise 1.6
- Miscellaneous Exercise
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets – A Brief Discussion
Chapter Overview: In the above section, we have listed the major concepts of Maths covered in Chapter 1- Sets of NCERT Solutions for Class 11. In this section, we will explain some important terms that you must know to understand the concepts of sets easily.
Set: A set is a well-defined collection of objects.
Null set: A set which does not contain any element is called the empty set or the null set or the void set.
Finite and Infinite Set: A set which is empty or consists of a definite number of elements is called finite otherwise, the set is called infinite set.
Equal and Unequal Sets: Two sets A and B are said to be equal if they have exactly the same elements and we write A = B. Otherwise, the sets are said to be unequal and we write A ≠ B.
Subset: A set A is said to be a subset of a set B if every element of A is also an element of B. In other words, A ⊂ B if whenever a ∈ A, then a ∈ B. It is often convenient to use the symbol “⇒” which means implies. Using this symbol, we can write the definiton of subset as : A ⊂ B if a ∈ A ⇒ a ∈ B
Power Set: The collection of all subsets of a set A is called the power set of A. It is denoted by P(A).
Venn Diagrams: Most of the relationships between sets can be represented by means of diagrams which are known as Venn diagrams.
Union of Sets: Let A and B be any two sets. The union of A and B is the set which consists of all the elements of A and all the elements of B, the common elements being taken only once. The symbol ‘∪’ is used to denote the union. Symbolically, we write A ∪ B and usually read as ‘A union B’
Intersection of sets: The intersection of sets A and B is the set of all elements which are common to both A and B. The symbol ‘∩’is used to denote the intersection. The intersection of two sets A and B is the set of all those elements which belong to both A and B. Symbolically, we write A ∩ B = {x : x ∈ A and x ∈ B}
Difference of sets: The difference of the sets A and B in this order is the set of elements which belong to A but not to B. Symbolically, we write A – B and read as “ A minus B”.
De Morgan,s Law: The complement of the union of two sets is the intersection of their complements and the complement of the intersection of two sets is the union of their complements. These are called De Morgan’s laws.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
My Study materials – Kumar
Ltsm (learning and teaching study materials).
👉CLASS XI MATHS PRACTICE PAPER SERIES Maths Class XI Chapter 01 Sets Practice Paper 01 Maths Class XI Chapter 01 Sets Practice Paper 01 Answers Maths Class XI Chapter 02 Relations and Functions Practice Paper 02 Maths Class XI Chapter 02 Relations and Functions Practice Paper 02 Answers Maths Class XI Chapter 03 Trigonometric Functions Practice Paper 03 Maths Class XI Chapter 03 Trigonometric Functions Practice Paper 03 Answers Maths Class XI Chapter 04 Complex Numbers Practice Paper 04 Maths Class XI Chapter 04 Complex Numbers Practice Paper 04 Answers Maths Class XI Chapter 05 & 06 Permutation, Combinations and Binomial Theorem Practice Paper 05 Maths Class XI Chapter 05 & 06 Permutation, Combinations and Binomial Theorem Practice Paper 05 Answers Maths Class XI Chapter 09 Sequence and Series Practice Paper 06 Maths Class XI Chapter 09 Sequence and Series Practice Paper 06 Answers Maths Class XI Chapter 10 Straight Lines Practice Paper 07 Maths Class XI Chapter 10 Straight Lines Practice Paper 07 Answers Maths Class XI Chapter 11 Conic Sections Practice Paper 08 Maths Class XI Chapter 11 Conic Sections Practice Paper 08 Answers Maths Class XI Straight Lines and Conic Sections Practice Paper 09 Maths Class XI Straight Lines and Conic Sections Practice Paper 09 Answers Maths Class XI Straight Lines and Conic Sections Practice Paper 10 Maths Class XI Straight Lines and Conic Sections Practice Paper 10 Answers Maths Class XI Introduction to 3-Dimensional Geometry Practice Paper 11 Maths Class XI Introduction to 3-Dimensional Geometry Practice Paper 11 Answers Maths Class XI Introduction to 3-Dimensional Geometry Practice Paper 12 Maths Class XI Introduction to 3-Dimensional Geometry Practice Paper 12 Answers
👉 Blue Print and Sample Papers(3 different sets) for Class XI SEE 2023 Maths Class XI Sample Paper Test 01 Blue Print for Annual Exam 2022-23 Maths Class XI Sample Paper Test 01 for Annual Exam 2022-23
Maths Class XI Sample Paper Test 02 Blue Print for Annual Exam 2022-23 Maths Class XI Sample Paper Test 02 for Annual Exam 2022-23
Maths Class XI Sample Paper Test 03 Blue Print for Annual Exam 2022-23 Maths Class XI Sample Paper Test 03 for Annual Exam 2022-23
Maths Class XI – Limits & Derivatives Practice papers
Maths Class XI – Limits & Derivatives Practice paper 01
Maths Class XI – Limits & Derivatives Practice paper 02
Maths Class XI – Limits & Derivatives Practice paper 03
Maths Class XI – Limits & Derivatives Practice paper 04
Maths Class XI – Limits & Derivatives Practice paper 05
Maths Class XI – Coordinate Geometry Unit & Probability Practice Papers
Maths Class XI – Coordinate Geometry Unit & Probability Practice Paper 01
Maths Class XI – Coordinate Geometry Unit & Probability Practice Paper 02
Maths Class XI – Coordinate Geometry Unit & Probability Practice Paper 03
Maths Class XI – Coordinate Geometry Unit & Probability Practice Paper 04
Maths Class XI – Coordinate Geometry Unit & Probability Practice Paper 05
Maths Class XI – Conic Section Unit Practice papers
Maths Class XI – Practice paper 01 – Straight Lines
Maths Class XI – Practice paper 02 – Straight Lines
Maths Class XI – Practice paper 03 – Straight Lines and Conic Section
Maths Class XI – Practice paper 04 – Conic Section Unit
Maths Class XI – Practice paper 05 – Conic Section Unit
Maths Class XI – Sequence & Series Practice papers
Maths Class XI – Sequence & Series Practice paper 01
Maths Class XI – Sequence & Series Practice paper 02
Maths Class XI – Sequence & Series Practice paper 03
Maths Class XI – Sequence & Series Practice paper 04
SAMPLE PAPERS FOR SEE 2021
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01 for 2020-21
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02 for 2020-21
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03 for 2020-21
SAMPLE PAPERS FOR SEE 2020
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01 for 2019-20
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 02 for 2019-20
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 03 for 2019-20
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 04 for 2019-20
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 05 for 2019-20
Maths Class XI Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 01 2019
Maths Class XI Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 02 2019
Maths Class XI Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 03 2019
Maths Class XI Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 04 2019
Maths Class XI Half Yearly Exam Sample Paper 05 2019
CLASS – XI
Maths XI Blue Print of Periodic Test-1 2019
Maths XI Periodic Test-1 Sample Paper 01 2019
Maths XI Periodic Test-1 Sample Paper 02 2019
Maths XI Periodic Test-1 Sample Paper 03 2019
Maths Class XI Trigonometry Practice Questions 2015-16
Maths Class XI Permutations & Combinations Practice Questions 2015-16
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Question Paper 01 for 2017-18
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Question Paper 02 for 2017-18
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Question Paper 03 for 2017-18
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Question Paper 04 for 2017-18
Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Question Paper 05 for 2017-18
Share this:

- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- Manage subscriptions
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Ganita Prakash Chapter 1 Patterns in Mathematics
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Maths Ganita Prakash Chapter 1 Patterns in Mathematics in Hindi and English Medium updated for academic session 2024-25. Get here simplified solutions of Class 6 Maths textbook Ganita Prakash chapter 1 with complete explanation.
Class 6 Maths Ganita Prakash Chapter 1 Patterns in Mathematics Question Answers
- Class 6 Maths Ganita Prakash Chapter 1 Solutions
- Class 6 Maths Ganita Prakash Chapter 1 NCERT
- Class 6 Maths Ganita Prakash NCERT Solutions
- Class 6 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
In class 6 mathematics textbook GANITA PRAKASH chapter 1, we explore the beauty of patterns in mathematics. Patterns are everywhere around us—in nature, our homes, schools and even the stars. Mathematics helps us identify these patterns and understand why they exist. Imagine how exciting it is to see a pattern in something as simple as counting numbers or as complex as the structure of DNA! This chapter will help you discover different patterns, making you feel like a detective, searching for clues in the world of numbers and shapes. Remember, math is both art and science and discovering patterns can be fun and creative!
Number Patterns – Recognising Sequences One of the most common patterns we encounter in mathematics is number sequences. For example, counting numbers like 1, 2, 3, 4 or even numbers like 2, 4, 6, 8, follow specific rules. These rules are easy to identify, making math feel predictable and structured. In this chapter, you will learn about various number sequences such as triangular numbers (1, 3, 6, 10…), squares (1, 4, 9, 16…) and cubes (1, 8, 27, 64…). Each sequence has a unique rule that generates the next number and you will be challenged to figure out these rules for yourself!
Patterns can also be seen through pictures. For instance, when we talk about square numbers, we can arrange dots in a square grid, helping us visualise how the numbers grow. Triangular numbers can be seen as dots forming triangles. This visualisation helps us understand the pattern even better. In this chapter, you will practice drawing these visual patterns, which will make it easier to grasp the concepts behind number sequences.
Exploring Shape Patterns Mathematics isn’t just about numbers; patterns also exist in shapes. Regular polygons, like triangles , squares, pentagons, and hexagons, all follow predictable patterns. For instance, the number of sides in a polygon can be described using counting numbers. These shape sequences can be just as fascinating as number sequences and they show how connected different areas of mathematics are. By observing shapes, you will discover new ways to see the world of math.
Sometimes, number sequences and shape sequences are connected. For example, the number of sides in a shape sequence of polygons follows a number sequence, starting from 3 for a triangle, 4 for a square and so on. This relationship between numbers and shapes is what makes mathematics so beautiful and interconnected. Understanding these connections will give you a deeper insight into both number and shape patterns.
One interesting activity in this chapter is adding odd numbers. For example, when you add 1 + 3 + 5, you get 9, which is a square number. This pattern continues forever! The chapter explains that visualizing this through pictures can help us understand why this happens. By drawing squares and counting dots, you can see how adding odd numbers gives us square numbers. This concept shows how patterns can be hidden in simple things like adding numbers.
Throughout this chapter, we’ve explored patterns in numbers and shapes, learning how they are connected and how we can visualize them. Now, to fully master the concepts and solve more exciting problems, I encourage you to visit Tiwari Academy for the complete NCERT Solutions for all chapter. Tiwari Academy offers step-by-step explanations and answers that will help you practice and deepen your understanding of patterns in mathematics. Keep discovering and exploring, because math is full of exciting patterns waiting to be uncovered!

Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

- Visualizing Solid Shapes Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 13

Last Updated on September 7, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 7 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 7 maths. In this article, you will find case study questions for CBSE Class 7 Maths Chapter 13 Visualizing Solid Shapes. It is a part of Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 7 Maths Series.
| Visualizing Solid Shapes | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 7 | |
| Maths | |
| Class 7 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Visualizing Solid Shapes
An ice-cream cart has an ice-candy drawn on all sides, except the top and the bottom
Q. 1. Which geometric shape does the ice-cream container resemble? (a) Cuboid (b) Cylinder (c) Cone (d) Pyramid
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: Cuboid
Q. 2. How many ice-candies are drawn on the cart? (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 4 (d) 6
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: There are 4 ice-candies drawn on the cart.
- Symmetry Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 12
- Exponents and Powers Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 11
- Algebraic Expressions Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 10
- Perimeter and Area Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 9
- Rational Numbers Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 8
- Comparing Quantities Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 7
- Triangle and its Properties Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 6
- Lines and Angles Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 5
- Simple Equations Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 4
- Data Handling Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 3
Fractions and Decimals Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 2
Integers class 7 case study questions maths chapter 1, topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Plane figures and solid shapes
- Faces, edges and vertices of solid shapes
- Nets for building 3-D shapes
- Drawing solids on a flat surface
- Visualising different section of a solid
Plane figures are of two-dimensions and solid figures are of three-dimensions. In a solid figure, the corners are the vertices, the line segments are its edges and its flat surface are its faces.
A net is an arrangement of plane figures connected at their edges, lying in the same plane, that can be folded to make a three-dimensional solid.
Figures drawn on paper are called plane figure. Solid figures are those figures which occupy space.
Case study questions from the above given topic may be asked.
Plane figures are 2-dimensional, while solids are 3-dimensional. Visualising solid shapes is a very useful skill. You should be able to see ‘hidden’ parts of the solid shape.
Download Customised White Label Study Materials in MS Word Format
We are providing teaching resources to teachers and coaching institute looking for customised study materials in MS word format. Our High-quality editable study material which is prepared by the expert faculties are Highly useful for Teachers, Mentors, Tutors, Faculties, Coaching Institutes, Coaching Experts, Tuition Centers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Visualizing Solid Shapes Case Study
Q1: what are solid shapes.
A1: Solid shapes are three-dimensional figures that have length, breadth, and height. Common examples of solid shapes include cubes, cuboids, cones, and cylinders. Unlike two-dimensional shapes, these objects occupy space and can be viewed from different perspectives.
Q2: What is the difference between 2D and 3D shapes?
A2: 2D shapes have only two dimensions—length and breadth—and can be drawn on flat surfaces, like squares or circles. In contrast, 3D shapes have three dimensions—length, breadth, and height—like cubes or spheres. While 2D shapes can be represented easily on paper, 3D shapes are visualized as solid objects that occupy space.
Q3: What are oblique and isometric sketches?
A3: An oblique sketch is a simple way to represent a 3D object on a 2D plane. It gives a distorted view because one side is drawn at an angle. An isometric sketch , on the other hand, provides a more accurate representation of a solid object, with all dimensions to scale, giving a clearer idea of how the object looks from different angles
Q4: How can we visualize cross-sections of solids?
A4: Cross-sections are the shapes you get when you slice a solid object along a plane. For example, cutting a cylinder horizontally would give a circular cross-section, while cutting a cube horizontally or vertically would give a square cross-section.
Q5: How are shadows of 3D objects formed?
A5: Shadows of 3D objects depend on the shape of the object and the angle of light. For example, a cube can cast a square or rectangular shadow, while a cylinder can cast a circular or rectangular shadow based on how light falls on it. Visualizing shadows helps in understanding how 3D objects interact with light.
Q6: What are polyhedrons?
A6: Polyhedrons are three-dimensional shapes with flat faces. Each face is a polygon, and the edges of the polygons meet at vertices. Common examples of polyhedrons include cubes (with square faces) and pyramids (with triangular faces). A polyhedron is named based on the shape and number of its faces.
Q7: How do you calculate the number of faces, edges, and vertices of a solid shape?
A7: For polyhedrons, the relationship between the number of faces (F), edges (E), and vertices (V) is given by Euler’s formula: V − E + F = 2 This formula helps in identifying the structure of a polyhedron. For example, a cube has 8 vertices, 12 edges, and 6 faces, satisfying Euler’s formula.
Q10: Are there any online resources or tools available for practicing Visualizing Solid Shapes case study questions?
A10: We provide case study questions for CBSE Class 7 Maths on our website . Students can visit the website and practice sufficient case study questions and prepare for their exams. If you need more case study questions, then you can visit Physics Gurukul website. they are having a large collection of case study questions for all classes.

Related Posts


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Class 11 Mathematics case study question 1. Read the Case study given below and attempt any 4 sub parts: In drilling world's deepest hole, the Kola Superdeep Borehole, the deepest manmade hole on Earth and deepest artificial point on Earth, as a result of a scientific drilling project, it was found that the temperature T in degree Celsius, x ...
Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions Class 11 Maths Sets in order to fully complete your preparation.They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams!. I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams.
In this article, we are sharing Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets case study questions. All case study questions of class 11 maths are solved so that students can check their solutions after attempting questions. What is meant by Case Study Question? In the context of CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education), a case study question is a type of ...
elation and FunctionCASE STUDY 1:A general election o. Lok Sabha is a gigantic exercise. About 911 million people were eligible to vote and voter turn. EMOCRACY GENERAL ELECTION - 2019Let I be the set of all citizens of India who were eligible to exercise their voting righ. in general election held in 2019. A relation. R = {( 1, 2)∶. 1, 2 ∈.
In this Post I Have Provided Mathematics Class 11 Chapter-Wise MCQs, Case-Based Question And Assertion/Reason For Term-1 Session 2021-22 With Solutions. CBSE has Recently Included These Types Of MCQs And Assertion/Reason For Term-1 Exam 2020.
Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Maths with Solutions Set 1 are designed as per the ... of marks 1, 1, and 2 respectively. The third case study question has two sub-parts of 2 marks each. Question 36. Read the following passage and answer the questions given below: ... NCERT Solutions for Class ...
Important Questions & Answers For Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets. Q. 1: Write the following sets in the roster form. (i) A = {x | x is a positive integer less than 10 and 2x - 1 is an odd number} (ii) C = {x : x2 + 7x - 8 = 0, x ∈ R} Solution: (i) 2 x - 1 is always an odd number for all positive integral values of x since 2 x is an even ...
☑ For early access to our Tests & Assignments, plz join Telegram Group MATHEMATICIA By O.P. GUPTA -- https://t.me/MathematiciaByOPGuptaThanks for Watching th...
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets. Short Answer Type Questions. Q1. Write the following sets in the roaster from. Q2. Write the following sets in the roaster form: Q3. If Y = {x\x is a positive factor of the number 2P(2P - 1), where 2P - 1 is a prime number}. Write Y in the roaster form.
Learn Chapter 1 Sets of Class 11 free with solutions of all NCERT Questions for CBSE Maths. All examples, formulas and exercise questions explained in an easy way. Important questions are also marked for your reference. Topics in the chapter include. Intervals - Interval notation and how it is related to sets.
Regular practice using NCERT solutions and Mock tests from Vedantu can help students learn to manage their time better. Get chapter-wise important questions for CBSE Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 - Sets with answers on Vedantu. Download the PDF for free and revise these important questions for CBSE exam 2024-25.
CBSE Class 11 Maths Notes Chapter 1 Sets. Set A set is a well-defined collection of objects. Representation of Sets There are two methods of representing a set. Roster or Tabular form In the roster form, we list all the members of the set within braces { } and separate by commas. Set-builder form In the set-builder form, we list the property or ...
REAL NUMBERS- CASE STUDYCASE STUDY 1.To enhance the reading skills of grade X students, the school nominates you and two of. our friends to set up a class library. There are two sectio. s- section A and section B of grade X. There are 32 students. ection A and 36 students in sectionB.What is the minimum number of books you will acquire for the ...
The Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 of NCERT, categorised under the CBSE syllabus, also has some basic definitions and operations involving the sets. It is necessary to get fundamental knowledge on Sets since the study of sequences, geometry, and probability requires it.
CLASSS 11 MATHS - CASE STUDY QUESTIONS - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets MCQs (Multiple-choice questions) are available here with answers. All the MCQs are prepared as per the latest exam pattern and CBSE Syllabus (2022-2023). The objective questions are prepared by our subject experts, with proper explanations. MCQs of Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 will include all the concepts of the NCERT ...
Case Study Questions for Class 11 Maths. Chapter 1 Sets. Chapter 2 Relations and Functions. Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions. Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction. Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations. Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities. Chapter 7 Permutations and Combinations.
The class 11 Mathematics case study questions look forward to acquainting students with different aspects of Mathematics used in daily life. Being the newest question format, it is difficult to get an assured quality of CBQs in the market or over the internet. Check our Class 11 Maths case study questions to know the actual standard of the ...
Document Description: Sets- Case Based Type Questions for Commerce 2024 is part of Mathematics (Maths) Class 11 preparation. The notes and questions for Sets- Case Based Type Questions have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about Sets- Case Based Type Questions covers topics like and Sets- Case Based Type Questions Example, for Commerce 2024 Exam.
CBSE 11th Standard CBSE all question papers, important notes , study materials , Previuous Year questions, Syllabus and exam patterns. Free 11th Standard CBSE all books and syllabus online. Practice Online test for free in QB365 Study Material. Important keywords, Case Study Questions and Solutions. Updates about latest education news and ...
Here in this article, Study Path has provided what you need exactly. NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets includes all the questions of the NCERT textbook that are solved and explained beautifully using Vann diagrams, images etc. Here you can get complete NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 1 Sets in one place.
Maths Class XI - Sequence & Series Practice paper 01. Maths Class XI - Sequence & Series Practice paper 02. Maths Class XI - Sequence & Series Practice paper 03. Maths Class XI - Sequence & Series Practice paper 04. SAMPLE PAPERS FOR SEE 2021. Maths Class XI Session Ending Exam Sample Paper 01 for 2020-21.
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 7 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. ... Exponents and Powers Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 11 . Related Posts . Integers Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 1.
Case Study Questions on Rational Numbers. Questions. Passage 1: Class VII students were asked to compare numbers. The numbers were $\frac{-14}{9}$ and -1.05.
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 7 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. ... Exponents and Powers Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 11; Algebraic Expressions Class 7 Case Study Questions Maths Chapter 10;
Case Study Questions on Exponents and Powers. Questions. Passage 1: In a class science teacher give some information to all students about Solar system in following manner.
Case study questions are an important aspect of mathematics education at the Class 11 level. These questions require students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world scenarios, helping them develop critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills. Here are some reasons why case study questions are important in Class 11 maths ...
In class 6 mathematics textbook GANITA PRAKASH chapter 1, we explore the beauty of patterns in mathematics. Patterns are everywhere around us—in nature, our homes, schools and even the stars. Mathematics helps us identify these patterns and understand why they exist.
Reading Time: 6 minutes Last Updated on September 7, 2024 by XAM CONTENT. Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 7 maths. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board.