Research Paper Examples

Research paper examples are of great value for students who want to complete their assignments timely and efficiently. If you are a student in the university, your first stop in the quest for research paper examples will be the campus library where you can get to view the research sample papers of lecturers and other professionals in diverse fields plus those of fellow students who preceded you in the campus. Many college departments maintain libraries of previous student work, including large research papers, which current students can examine.
Embark on a journey of academic excellence with iResearchNet, your premier destination for research paper examples that illuminate the path to scholarly success. In the realm of academia, where the pursuit of knowledge is both a challenge and a privilege, the significance of having access to high-quality research paper examples cannot be overstated. These exemplars are not merely papers; they are beacons of insight, guiding students and scholars through the complex maze of academic writing and research methodologies.
At iResearchNet, we understand that the foundation of academic achievement lies in the quality of resources at one’s disposal. This is why we are dedicated to offering a comprehensive collection of research paper examples across a multitude of disciplines. Each example stands as a testament to rigorous research, clear writing, and the deep understanding necessary to advance in one’s academic and professional journey.
Access to superior research paper examples equips learners with the tools to develop their own ideas, arguments, and hypotheses, fostering a cycle of learning and discovery that transcends traditional boundaries. It is with this vision that iResearchNet commits to empowering students and researchers, providing them with the resources to not only meet but exceed the highest standards of academic excellence. Join us on this journey, and let iResearchNet be your guide to unlocking the full potential of your academic endeavors.

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, what is a research paper.
- Anthropology
- Communication
- Criminal Justice
- Criminal Law
- Criminology
- Mental Health
- Political Science
Importance of Research Paper Examples
- Research Paper Writing Services
A Sample Research Paper on Child Abuse
A research paper represents the pinnacle of academic investigation, a scholarly manuscript that encapsulates a detailed study, analysis, or argument based on extensive independent research. It is an embodiment of the researcher’s ability to synthesize a wealth of information, draw insightful conclusions, and contribute novel perspectives to the existing body of knowledge within a specific field. At its core, a research paper strives to push the boundaries of what is known, challenging existing theories and proposing new insights that could potentially reshape the understanding of a particular subject area.
The objective of writing a research paper is manifold, serving both educational and intellectual pursuits. Primarily, it aims to educate the author, providing a rigorous framework through which they engage deeply with a topic, hone their research and analytical skills, and learn the art of academic writing. Beyond personal growth, the research paper serves the broader academic community by contributing to the collective pool of knowledge, offering fresh perspectives, and stimulating further research. It is a medium through which scholars communicate ideas, findings, and theories, thereby fostering an ongoing dialogue that propels the advancement of science, humanities, and other fields of study.
Research papers can be categorized into various types, each with distinct objectives and methodologies. The most common types include:
- Analytical Research Paper: This type focuses on analyzing different viewpoints represented in the scholarly literature or data. The author critically evaluates and interprets the information, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Argumentative or Persuasive Research Paper: Here, the author adopts a stance on a contentious issue and argues in favor of their position. The objective is to persuade the reader through evidence and logic that the author’s viewpoint is valid or preferable.
- Experimental Research Paper: Often used in the sciences, this type documents the process, results, and implications of an experiment conducted by the author. It provides a detailed account of the methodology, data collected, analysis performed, and conclusions drawn.
- Survey Research Paper: This involves collecting data from a set of respondents about their opinions, behaviors, or characteristics. The paper analyzes this data to draw conclusions about the population from which the sample was drawn.
- Comparative Research Paper: This type involves comparing and contrasting different theories, policies, or phenomena. The aim is to highlight similarities and differences, thereby gaining a deeper understanding of the subjects under review.
- Cause and Effect Research Paper: It explores the reasons behind specific actions, events, or conditions and the consequences that follow. The goal is to establish a causal relationship between variables.
- Review Research Paper: This paper synthesizes existing research on a particular topic, offering a comprehensive analysis of the literature to identify trends, gaps, and consensus in the field.
Understanding the nuances and objectives of these various types of research papers is crucial for scholars and students alike, as it guides their approach to conducting and writing up their research. Each type demands a unique set of skills and perspectives, pushing the author to think critically and creatively about their subject matter. As the academic landscape continues to evolve, the research paper remains a fundamental tool for disseminating knowledge, encouraging innovation, and fostering a culture of inquiry and exploration.
Browse Sample Research Papers
iResearchNet prides itself on offering a wide array of research paper examples across various disciplines, meticulously curated to support students, educators, and researchers in their academic endeavors. Each example embodies the hallmarks of scholarly excellence—rigorous research, analytical depth, and clear, precise writing. Below, we explore the diverse range of research paper examples available through iResearchNet, designed to inspire and guide users in their quest for academic achievement.
Anthropology Research Paper Examples
Our anthropology research paper examples delve into the study of humanity, exploring cultural, social, biological, and linguistic variations among human populations. These papers offer insights into human behavior, traditions, and evolution, providing a comprehensive overview of anthropological research methods and theories.
- Archaeology Research Paper
- Forensic Anthropology Research Paper
- Linguistics Research Paper
- Medical Anthropology Research Paper
- Social Problems Research Paper
Art Research Paper Examples
The art research paper examples feature analyses of artistic expressions across different cultures and historical periods. These papers cover a variety of topics, including art history, criticism, and theory, as well as the examination of specific artworks or movements.
- Performing Arts Research Paper
- Music Research Paper
- Architecture Research Paper
- Theater Research Paper
- Visual Arts Research Paper
Cancer Research Paper Examples
Our cancer research paper examples focus on the latest findings in the field of oncology, discussing the biological mechanisms of cancer, advancements in diagnostic techniques, and innovative treatment strategies. These papers aim to contribute to the ongoing battle against cancer by sharing cutting-edge research.
- Breast Cancer Research Paper
- Leukemia Research Paper
- Lung Cancer Research Paper
- Ovarian Cancer Research Paper
- Prostate Cancer Research Paper
Communication Research Paper Examples
These examples explore the complexities of human communication, covering topics such as media studies, interpersonal communication, and public relations. The papers examine how communication processes affect individuals, societies, and cultures.
- Advertising Research Paper
- Journalism Research Paper
- Media Research Paper
- Public Relations Research Paper
- Public Speaking Research Paper
Crime Research Paper Examples
The crime research paper examples provided by iResearchNet investigate various aspects of criminal behavior and the factors contributing to crime. These papers cover a range of topics, from theoretical analyses of criminality to empirical studies on crime prevention strategies.
- Computer Crime Research Paper
- Domestic Violence Research Paper
- Hate Crimes Research Paper
- Organized Crime Research Paper
- White-Collar Crime Research Paper
Criminal Justice Research Paper Examples
Our criminal justice research paper examples delve into the functioning of the criminal justice system, exploring issues related to law enforcement, the judiciary, and corrections. These papers critically examine policies, practices, and reforms within the criminal justice system.
- Capital Punishment Research Paper
- Community Policing Research Paper
- Corporal Punishment Research Paper
- Criminal Investigation Research Paper
- Criminal Justice System Research Paper
- Plea Bargaining Research Paper
- Restorative Justice Research Paper
Criminal Law Research Paper Examples
These examples focus on the legal aspects of criminal behavior, discussing laws, regulations, and case law that govern criminal proceedings. The papers provide an in-depth analysis of criminal law principles, legal defenses, and the implications of legal decisions.
- Actus Reus Research Paper
- Gun Control Research Paper
- Insanity Defense Research Paper
- International Criminal Law Research Paper
- Self-Defense Research Paper
Criminology Research Paper Examples
iResearchNet’s criminology research paper examples study the causes, prevention, and societal impacts of crime. These papers employ various theoretical frameworks to analyze crime trends and propose effective crime reduction strategies.
- Cultural Criminology Research Paper
- Education and Crime Research Paper
- Marxist Criminology Research Paper
- School Crime Research Paper
- Urban Crime Research Paper
Culture Research Paper Examples
The culture research paper examples examine the beliefs, practices, and artifacts that define different societies. These papers explore how culture shapes identities, influences behaviors, and impacts social interactions.
- Advertising and Culture Research Paper
- Material Culture Research Paper
- Popular Culture Research Paper
- Cross-Cultural Studies Research Paper
- Culture Change Research Paper
Economics Research Paper Examples
Our economics research paper examples offer insights into the functioning of economies at both the micro and macro levels. Topics include economic theory, policy analysis, and the examination of economic indicators and trends.
- Budget Research Paper
- Cost-Benefit Analysis Research Paper
- Fiscal Policy Research Paper
- Labor Market Research Paper
Education Research Paper Examples
These examples address a wide range of issues in education, from teaching methods and curriculum design to educational policy and reform. The papers aim to enhance understanding and improve outcomes in educational settings.
- Early Childhood Education Research Paper
- Information Processing Research Paper
- Multicultural Education Research Paper
- Special Education Research Paper
- Standardized Tests Research Paper
Health Research Paper Examples
The health research paper examples focus on public health issues, healthcare systems, and medical interventions. These papers contribute to the discourse on health promotion, disease prevention, and healthcare management.
- AIDS Research Paper
- Alcoholism Research Paper
- Disease Research Paper
- Health Economics Research Paper
- Health Insurance Research Paper
- Nursing Research Paper
History Research Paper Examples
Our history research paper examples cover significant events, figures, and periods, offering critical analyses of historical narratives and their impact on present-day society.
- Adolf Hitler Research Paper
- American Revolution Research Paper
- Ancient Greece Research Paper
- Apartheid Research Paper
- Christopher Columbus Research Paper
- Climate Change Research Paper
- Cold War Research Paper
- Columbian Exchange Research Paper
- Deforestation Research Paper
- Diseases Research Paper
- Earthquakes Research Paper
- Egypt Research Paper
Leadership Research Paper Examples
These examples explore the theories and practices of effective leadership, examining the qualities, behaviors, and strategies that distinguish successful leaders in various contexts.
- Implicit Leadership Theories Research Paper
- Judicial Leadership Research Paper
- Leadership Styles Research Paper
- Police Leadership Research Paper
- Political Leadership Research Paper
- Remote Leadership Research Paper
Mental Health Research Paper Examples
The mental health research paper examples provided by iResearchNet discuss psychological disorders, therapeutic interventions, and mental health advocacy. These papers aim to raise awareness and improve mental health care practices.
- ADHD Research Paper
- Anxiety Research Paper
- Autism Research Paper
- Depression Research Paper
- Eating Disorders Research Paper
- PTSD Research Paper
- Schizophrenia Research Paper
- Stress Research Paper
Political Science Research Paper Examples
Our political science research paper examples analyze political systems, behaviors, and ideologies. Topics include governance, policy analysis, and the study of political movements and institutions.
- American Government Research Paper
- Civil War Research Paper
- Communism Research Paper
- Democracy Research Paper
- Game Theory Research Paper
- Human Rights Research Paper
- International Relations Research Paper
- Terrorism Research Paper
Psychology Research Paper Examples
These examples delve into the study of the mind and behavior, covering a broad range of topics in clinical, cognitive, developmental, and social psychology.
- Artificial Intelligence Research Paper
- Assessment Psychology Research Paper
- Biological Psychology Research Paper
- Clinical Psychology Research Paper
- Cognitive Psychology Research Paper
- Developmental Psychology Research Paper
- Discrimination Research Paper
- Educational Psychology Research Paper
- Environmental Psychology Research Paper
- Experimental Psychology Research Paper
- Intelligence Research Paper
- Learning Disabilities Research Paper
- Personality Psychology Research Paper
- Psychiatry Research Paper
- Psychotherapy Research Paper
- Social Cognition Research Paper
- Social Psychology Research Paper
Sociology Research Paper Examples
The sociology research paper examples examine societal structures, relationships, and processes. These papers provide insights into social phenomena, inequality, and change.
- Family Research Paper
- Demography Research Paper
- Group Dynamics Research Paper
- Quality of Life Research Paper
- Social Change Research Paper
- Social Movements Research Paper
- Social Networks Research Paper
Technology Research Paper Examples
Our technology research paper examples address the impact of technological advancements on society, exploring issues related to digital communication, cybersecurity, and innovation.
- Computer Forensics Research Paper
- Genetic Engineering Research Paper
- History of Technology Research Paper
- Internet Research Paper
- Nanotechnology Research Paper

Other Research Paper Examples
- Abortion Research Paper
- Adoption Research Paper
- Animal Testing Research Paper
- Bullying Research Paper
- Diversity Research Paper
- Divorce Research Paper
- Drugs Research Paper
- Environmental Issues Research Paper
- Ethics Research Paper
- Evolution Research Paper
- Feminism Research Paper
- Food Research Paper
- Gender Research Paper
- Globalization Research Paper
- Juvenile Justice Research Paper
- Law Research Paper
- Management Research Paper
- Philosophy Research Paper
- Public Health Research Paper
- Religion Research Paper
- Science Research Paper
- Social Sciences Research Paper
- Statistics Research Paper
- Other Sample Research Papers
Each category of research paper examples provided by iResearchNet serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers seeking to deepen their understanding of a specific field. By offering a comprehensive collection of well-researched and thoughtfully written papers, iResearchNet aims to support academic growth and encourage scholarly inquiry across diverse disciplines.
Sample Research Papers: To Read or Not to Read?
When you get an assignment to write a research paper, the first question you ask yourself is ‘Should I look for research paper examples?’ Maybe, I can deal with this task on my own without any help. Is it that difficult?
Thousands of students turn to our service every day for help. It does not mean that they cannot do their assignments on their own. They can, but the reason is different. Writing a research paper demands so much time and energy that asking for assistance seems to be a perfect solution. As the matter of fact, it is a perfect solution, especially, when you need to work to pay for your studying as well.
Firstly, if you search for research paper examples before you start writing, you can save your time significantly. You look at the example and you understand the gist of your assignment within several minutes. Secondly, when you examine some sample paper, you get to know all the requirements. You analyze the structure, the language, and the formatting details. Finally, reading examples helps students to overcome writer’s block, as other people’s ideas can motivate you to discover your own ideas.
The significance of research paper examples in the academic journey of students cannot be overstated. These examples serve not only as a blueprint for structuring and formatting academic papers but also as a beacon guiding students through the complex landscape of academic writing standards. iResearchNet recognizes the pivotal role that high-quality research paper examples play in fostering academic success and intellectual growth among students.
Blueprint for Academic Success
Research paper examples provided by iResearchNet are meticulously crafted to demonstrate the essential elements of effective academic writing. These examples offer clear insights into how to organize a paper, from the introductory paragraph, through the development of arguments and analysis, to the concluding remarks. They showcase the appropriate use of headings, subheadings, and the integration of tables, figures, and appendices, which collectively contribute to a well-organized and coherent piece of scholarly work. By studying these examples, students can gain a comprehensive understanding of the structure and formatting required in academic papers, which is crucial for meeting the rigorous standards of academic institutions.
Sparking Ideas and Providing Evidence
Beyond serving as a structural guide, research paper examples act as a source of inspiration for students embarking on their research projects. These examples illuminate a wide array of topics, methodologies, and analytical frameworks, thereby sparking ideas for students’ own research inquiries. They demonstrate how to effectively engage with existing literature, frame research questions, and develop a compelling thesis statement. Moreover, by presenting evidence and arguments in a logical and persuasive manner, these examples illustrate the art of substantiating claims with solid research, encouraging students to adopt a similar level of rigor and depth in their work.
Enhancing Research Skills
Engagement with high-quality research paper examples is instrumental in improving research skills among students. These examples expose students to various research methodologies, from qualitative case studies to quantitative analyses, enabling them to appreciate the breadth of research approaches applicable to their fields of study. By analyzing these examples, students learn how to critically evaluate sources, differentiate between primary and secondary data, and apply ethical considerations in research. Furthermore, these papers serve as a model for effectively citing sources, thereby teaching students the importance of academic integrity and the avoidance of plagiarism.

In essence, research paper examples are a fundamental resource that can significantly enhance the academic writing and research capabilities of students. iResearchNet’s commitment to providing access to a diverse collection of exemplary papers reflects its dedication to supporting academic excellence. Through these examples, students are equipped with the tools necessary to navigate the challenges of academic writing, foster innovative thinking, and contribute meaningfully to the scholarly community. By leveraging these resources, students can elevate their academic pursuits, ensuring their research is not only rigorous but also impactful.
Custom Research Paper Writing Services
In the academic journey, the ability to craft a compelling and meticulously researched paper is invaluable. Recognizing the challenges and pressures that students face, iResearchNet has developed a suite of research paper writing services designed to alleviate the burden of academic writing and research. Our services are tailored to meet the diverse needs of students across all academic disciplines, ensuring that every research paper not only meets but exceeds the rigorous standards of scholarly excellence. Below, we detail the multifaceted aspects of our research paper writing services, illustrating how iResearchNet stands as a beacon of support in the academic landscape.
At iResearchNet, we understand the pivotal role that research papers play in the academic and professional development of students. With this understanding at our core, we offer comprehensive writing services that cater to the intricate process of research paper creation. Our services are designed to guide students through every stage of the writing process, from initial research to final submission, ensuring clarity, coherence, and scholarly rigor.
The Need for Research Paper Writing Services
Navigating the complexities of academic writing and research can be a daunting task for many students. The challenges of identifying credible sources, synthesizing information, adhering to academic standards, and articulating arguments cohesively are significant. Furthermore, the pressures of tight deadlines and the high stakes of academic success can exacerbate the difficulties faced by students. iResearchNet’s research paper writing services are crafted to address these challenges head-on, providing expert assistance that empowers students to achieve their academic goals with confidence.
Why Choose iResearchNet
Selecting the right partner for research paper writing is a pivotal decision for students and researchers aiming for academic excellence. iResearchNet stands out as the premier choice for several compelling reasons, each designed to meet the diverse needs of our clientele and ensure their success.
- Expert Writers : At iResearchNet, we pride ourselves on our team of expert writers who are not only masters in their respective fields but also possess a profound understanding of academic writing standards. With advanced degrees and extensive experience, our writers bring depth, insight, and precision to each paper, ensuring that your work is informed by the latest research and methodologies.
- Top Quality : Quality is the cornerstone of our services. We adhere to rigorous quality control processes to ensure that every paper we deliver meets the highest standards of academic excellence. Our commitment to quality means thorough research, impeccable writing, and meticulous proofreading, resulting in work that not only meets but exceeds expectations.
- Customized Solutions : Understanding that each research project has its unique challenges and requirements, iResearchNet offers customized solutions tailored to your specific needs. Whether you’re grappling with a complex research topic, a tight deadline, or specific formatting guidelines, our team is equipped to provide personalized support that aligns with your objectives.
- Affordable Prices : We believe that access to high-quality research paper writing services should not be prohibitive. iResearchNet offers competitive pricing structures designed to provide value without compromising on quality. Our transparent pricing model ensures that you know exactly what you are paying for, with no hidden costs or surprises.
- Timely Delivery : Meeting deadlines is critical in academic writing, and at iResearchNet, we take this seriously. Our efficient processes and dedicated team ensure that your paper is delivered on time, every time, allowing you to meet your academic deadlines with confidence.
- 24/7 Support : Our commitment to your success is reflected in our round-the-clock support. Whether you have a question about your order, need to communicate with your writer, or require assistance with any aspect of our service, our friendly and knowledgeable support team is available 24/7 to assist you.
- Money-Back Guarantee : Your satisfaction is our top priority. iResearchNet offers a money-back guarantee, ensuring that if for any reason you are not satisfied with the work delivered, you are entitled to a refund. This policy underscores our confidence in the quality of our services and our dedication to your success.
Choosing iResearchNet for your research paper writing needs means partnering with a trusted provider committed to excellence, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Our unparalleled blend of expert writers, top-quality work, customized solutions, affordability, timely delivery, 24/7 support, and a money-back guarantee makes us the ideal choice for students and researchers seeking to elevate their academic performance.
How It Works: iResearchNet’s Streamlined Process
Navigating the process of obtaining a top-notch research paper has never been more straightforward, thanks to iResearchNet’s streamlined approach. Our user-friendly system ensures that from the moment you decide to place your order to the final receipt of your custom-written paper, every step is seamless, transparent, and tailored to your needs. Here’s how our comprehensive process works:
- Place Your Order : Begin your journey to academic success by visiting our website and filling out the order form. Here, you’ll provide details about your research paper, including the topic, academic level, number of pages, formatting style, and any specific instructions or requirements. This initial step is crucial for us to understand your needs fully and match you with the most suitable writer.
- Make Payment : Once your order details are confirmed, you’ll proceed to the payment section. Our platform offers a variety of secure payment options, ensuring that your transaction is safe and hassle-free. Our transparent pricing policy means you’ll know exactly what you’re paying for upfront, with no hidden fees.
- Choose Your Writer : After payment, you’ll have the opportunity to choose a writer from our team of experts. Our writers are categorized based on their fields of expertise, academic qualifications, and customer feedback ratings. This step empowers you to select the writer who best matches your research paper’s requirements, ensuring a personalized and targeted approach to your project.
- Receive Your Work : Our writer will commence work on your research paper, adhering to the specified guidelines and timelines. Throughout this process, you’ll have the ability to communicate directly with your writer, allowing for updates, revisions, and clarifications to ensure the final product meets your expectations. Once completed, your research paper will undergo a thorough quality check before being delivered to you via your chosen method.
- Free Revisions : Your satisfaction is our priority. Upon receiving your research paper, you’ll have the opportunity to review the work and request any necessary revisions. iResearchNet offers free revisions within a specified period, ensuring that your final paper perfectly aligns with your academic requirements and expectations.
Our process is designed to provide you with a stress-free experience and a research paper that reflects your academic goals. From placing your order to enjoying the success of a well-written paper, iResearchNet is here to support you every step of the way.
Our Extras: Enhancing Your iResearchNet Experience
At iResearchNet, we are committed to offering more than just standard research paper writing services. We understand the importance of providing a comprehensive and personalized experience for each of our clients. That’s why we offer a range of additional services designed to enhance your experience and ensure your academic success. Here are the exclusive extras you can benefit from:
- VIP Service : Elevate your iResearchNet experience with our VIP service, offering you priority treatment from the moment you place your order. This service ensures your projects are given first priority, with immediate attention from our team, and direct access to our top-tier writers and editors. VIP clients also benefit from our highest level of customer support, available to address any inquiries or needs with utmost urgency and personalized care.
- Plagiarism Report : Integrity and originality are paramount in academic writing. To provide you with peace of mind, we offer a detailed plagiarism report with every research paper. This report is generated using advanced plagiarism detection software, ensuring that your work is unique and adheres to the highest standards of academic honesty.
- Text Messages : Stay informed about your order’s progress with real-time updates sent directly to your phone. This service ensures you’re always in the loop, providing immediate notifications about key milestones, writer assignments, and any changes to your order status. With this added layer of communication, you can relax knowing that you’ll never miss an important update about your research paper.
- Table of Contents : A well-organized research paper is key to guiding readers through your work. Our service includes the creation of a detailed table of contents, meticulously structured to reflect the main sections and subsections of your paper. This not only enhances the navigability of your document but also presents your research in a professional and academically appropriate format.
- Abstract Page : The abstract page is your research paper’s first impression, summarizing the essential points of your study and its conclusions. Crafting a compelling abstract is an art, and our experts are skilled in highlighting the significance, methodology, results, and implications of your research succinctly and effectively. This service ensures that your paper makes a strong impact from the very beginning.
- Editor’s Check : Before your research paper reaches you, it undergoes a final review by our team of experienced editors. This editor’s check is a comprehensive process that includes proofreading for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors, as well as ensuring that the paper meets all your specifications and academic standards. This meticulous attention to detail guarantees that your paper is polished, professional, and ready for submission.
To ensure your research paper is of the highest quality and ready for submission, it undergoes a rigorous editor’s check. This final review process includes a thorough examination for any grammatical, punctuation, or spelling errors, as well as a verification that the paper meets all your specified requirements and academic standards. Our editors’ meticulous approach guarantees that your paper is polished, accurate, and exemplary.
By choosing iResearchNet and leveraging our extras, you can elevate the quality of your research paper and enjoy a customized, worry-free academic support experience.
A research paper is an academic piece of writing, so you need to follow all the requirements and standards. Otherwise, it will be impossible to get the high results. To make it easier for you, we have analyzed the structure and peculiarities of a sample research paper on the topic ‘Child Abuse’.
The paper includes 7300+ words, a detailed outline, citations are in APA formatting style, and bibliography with 28 sources.
To write any paper you need to write a great outline. This is the key to a perfect paper. When you organize your paper, it is easier for you to present the ideas logically, without jumping from one thought to another.
In the outline, you need to name all the parts of your paper. That is to say, an introduction, main body, conclusion, bibliography, some papers require abstract and proposal as well.
A good outline will serve as a guide through your paper making it easier for the reader to follow your ideas.
I. Introduction
Ii. estimates of child abuse: methodological limitations, iii. child abuse and neglect: the legalities, iv. corporal punishment versus child abuse, v. child abuse victims: the patterns, vi. child abuse perpetrators: the patterns, vii. explanations for child abuse, viii. consequences of child abuse and neglect, ix. determining abuse: how to tell whether a child is abused or neglected, x. determining abuse: interviewing children, xi. how can society help abused children and abusive families, introduction.
An introduction should include a thesis statement and the main points that you will discuss in the paper.
A thesis statement is one sentence in which you need to show your point of view. You will then develop this point of view through the whole piece of work:
‘The impact of child abuse affects more than one’s childhood, as the psychological and physical injuries often extend well into adulthood.’
Child abuse is a very real and prominent social problem today. The impact of child abuse affects more than one’s childhood, as the psychological and physical injuries often extend well into adulthood. Most children are defenseless against abuse, are dependent on their caretakers, and are unable to protect themselves from these acts.
Childhood serves as the basis for growth, development, and socialization. Throughout adolescence, children are taught how to become productive and positive, functioning members of society. Much of the socializing of children, particularly in their very earliest years, comes at the hands of family members. Unfortunately, the messages conveyed to and the actions against children by their families are not always the positive building blocks for which one would hope.
In 2008, the Children’s Defense Fund reported that each day in America, 2,421 children are confirmed as abused or neglected, 4 children are killed by abuse or neglect, and 78 babies die before their first birthday. These daily estimates translate into tremendous national figures. In 2006, caseworkers substantiated an estimated 905,000 reports of child abuse or neglect. Of these, 64% suffered neglect, 16% were physically abused, 9% were sexually abused, 7% were emotionally or psychologically maltreated, and 2% were medically neglected. In addition, 15% of the victims experienced “other” types of maltreatment such as abandonment, threats of harm to the child, and congenital drug addiction (National Child Abuse and Neglect Data System, 2006). Obviously, this problem is a substantial one.
In the main body, you dwell upon the topic of your paper. You provide your ideas and support them with evidence. The evidence include all the data and material you have found, analyzed and systematized. You can support your point of view with different statistical data, with surveys, and the results of different experiments. Your task is to show that your idea is right, and make the reader interested in the topic.
In this example, a writer analyzes the issue of child abuse: different statistical data, controversies regarding the topic, examples of the problem and the consequences.
Several issues arise when considering the amount of child abuse that occurs annually in the United States. Child abuse is very hard to estimate because much (or most) of it is not reported. Children who are abused are unlikely to report their victimization because they may not know any better, they still love their abusers and do not want to see them taken away (or do not themselves want to be taken away from their abusers), they have been threatened into not reporting, or they do not know to whom they should report their victimizations. Still further, children may report their abuse only to find the person to whom they report does not believe them or take any action on their behalf. Continuing to muddy the waters, child abuse can be disguised as legitimate injury, particularly because young children are often somewhat uncoordinated and are still learning to accomplish physical tasks, may not know their physical limitations, and are often legitimately injured during regular play. In the end, children rarely report child abuse; most often it is an adult who makes a report based on suspicion (e.g., teacher, counselor, doctor, etc.).
Even when child abuse is reported, social service agents and investigators may not follow up or substantiate reports for a variety of reasons. Parents can pretend, lie, or cover up injuries or stories of how injuries occurred when social service agents come to investigate. Further, there is not always agreement about what should be counted as abuse by service providers and researchers. In addition, social service agencies/agents have huge caseloads and may only be able to deal with the most serious forms of child abuse, leaving the more “minor” forms of abuse unsupervised and unmanaged (and uncounted in the statistical totals).
While most laws about child abuse and neglect fall at the state levels, federal legislation provides a foundation for states by identifying a minimum set of acts and behaviors that define child abuse and neglect. The Federal Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act (CAPTA), which stems from the Keeping Children and Families Safe Act of 2003, defines child abuse and neglect as, at minimum, “(1) any recent act or failure to act on the part of a parent or caretaker which results in death, serious physical or emotional harm, sexual abuse, or exploitation; or (2) an act or failure to act which presents an imminent risk or serious harm.”
Using these minimum standards, each state is responsible for providing its own definition of maltreatment within civil and criminal statutes. When defining types of child abuse, many states incorporate similar elements and definitions into their legal statutes. For example, neglect is often defined as failure to provide for a child’s basic needs. Neglect can encompass physical elements (e.g., failure to provide necessary food or shelter, or lack of appropriate supervision), medical elements (e.g., failure to provide necessary medical or mental health treatment), educational elements (e.g., failure to educate a child or attend to special educational needs), and emotional elements (e.g., inattention to a child’s emotional needs, failure to provide psychological care, or permitting the child to use alcohol or other drugs). Failure to meet needs does not always mean a child is neglected, as situations such as poverty, cultural values, and community standards can influence the application of legal statutes. In addition, several states distinguish between failure to provide based on financial inability and failure to provide for no apparent financial reason.
Statutes on physical abuse typically include elements of physical injury (ranging from minor bruises to severe fractures or death) as a result of punching, beating, kicking, biting, shaking, throwing, stabbing, choking, hitting (with a hand, stick, strap, or other object), burning, or otherwise harming a child. Such injury is considered abuse regardless of the intention of the caretaker. In addition, many state statutes include allowing or encouraging another person to physically harm a child (such as noted above) as another form of physical abuse in and of itself. Sexual abuse usually includes activities by a parent or caretaker such as fondling a child’s genitals, penetration, incest, rape, sodomy, indecent exposure, and exploitation through prostitution or the production of pornographic materials.
Finally, emotional or psychological abuse typically is defined as a pattern of behavior that impairs a child’s emotional development or sense of self-worth. This may include constant criticism, threats, or rejection, as well as withholding love, support, or guidance. Emotional abuse is often the most difficult to prove and, therefore, child protective services may not be able to intervene without evidence of harm to the child. Some states suggest that harm may be evidenced by an observable or substantial change in behavior, emotional response, or cognition, or by anxiety, depression, withdrawal, or aggressive behavior. At a practical level, emotional abuse is almost always present when other types of abuse are identified.
Some states include an element of substance abuse in their statutes on child abuse. Circumstances that can be considered substance abuse include (a) the manufacture of a controlled substance in the presence of a child or on the premises occupied by a child (Colorado, Indiana, Iowa, Montana, South Dakota, Tennessee, and Virginia); (b) allowing a child to be present where the chemicals or equipment for the manufacture of controlled substances are used (Arizona, New Mexico); (c) selling, distributing, or giving drugs or alcohol to a child (Florida, Hawaii, Illinois, Minnesota, and Texas); (d) use of a controlled substance by a caregiver that impairs the caregiver’s ability to adequately care for the child (Kentucky, New York, Rhode Island, and Texas); and (e) exposure of the child to drug paraphernalia (North Dakota), the criminal sale or distribution of drugs (Montana, Virginia), or drug-related activity (District of Columbia).
One of the most difficult issues with which the U.S. legal system must contend is that of allowing parents the right to use corporal punishment when disciplining a child, while not letting them cross over the line into the realm of child abuse. Some parents may abuse their children under the guise of discipline, and many instances of child abuse arise from angry parents who go too far when disciplining their children with physical punishment. Generally, state statutes use terms such as “reasonable discipline of a minor,” “causes only temporary, short-term pain,” and may cause “the potential for bruising” but not “permanent damage, disability, disfigurement or injury” to the child as ways of indicating the types of discipline behaviors that are legal. However, corporal punishment that is “excessive,” “malicious,” “endangers the bodily safety of,” or is “an intentional infliction of injury” is not allowed under most state statutes (e.g., state of Florida child abuse statute).
Most research finds that the use of physical punishment (most often spanking) is not an effective method of discipline. The literature on this issue tends to find that spanking stops misbehavior, but no more effectively than other firm measures. Further, it seems to hinder rather than improve general compliance/obedience (particularly when the child is not in the presence of the punisher). Researchers have also explained why physical punishment is not any more effective at gaining child compliance than nonviolent forms of discipline. Some of the problems that arise when parents use spanking or other forms of physical punishment include the fact that spanking does not teach what children should do, nor does it provide them with alternative behavior options should the circumstance arise again. Spanking also undermines reasoning, explanation, or other forms of parental instruction because children cannot learn, reason, or problem solve well while experiencing threat, pain, fear, or anger. Further, the use of physical punishment is inconsistent with nonviolent principles, or parental modeling. In addition, the use of spanking chips away at the bonds of affection between parents and children, and tends to induce resentment and fear. Finally, it hinders the development of empathy and compassion in children, and they do not learn to take responsibility for their own behavior (Pitzer, 1997).
One of the biggest problems with the use of corporal punishment is that it can escalate into much more severe forms of violence. Usually, parents spank because they are angry (and somewhat out of control) and they can’t think of other ways to discipline. When parents are acting as a result of emotional triggers, the notion of discipline is lost while punishment and pain become the foci.
In 2006, of the children who were found to be victims of child abuse, nearly 75% of them were first-time victims (or had not come to the attention of authorities prior). A slight majority of child abuse victims were girls—51.5%, compared to 48% of abuse victims being boys. The younger the child, the more at risk he or she is for child abuse and neglect victimization. Specifically, the rate for infants (birth to 1 year old) was approximately 24 per 1,000 children of the same age group. The victimization rate for children 1–3 years old was 14 per 1,000 children of the same age group. The abuse rate for children aged 4– 7 years old declined further to 13 per 1,000 children of the same age group. African American, American Indian, and Alaska Native children, as well as children of multiple races, had the highest rates of victimization. White and Latino children had lower rates, and Asian children had the lowest rates of child abuse and neglect victimization. Regarding living arrangements, nearly 27% of victims were living with a single mother, 20% were living with married parents, while 22% were living with both parents but the marital status was unknown. (This reporting element had nearly 40% missing data, however.) Regarding disability, nearly 8% of child abuse victims had some degree of mental retardation, emotional disturbance, visual or hearing impairment, learning disability, physical disability, behavioral problems, or other medical problems. Unfortunately, data indicate that for many victims, the efforts of the child protection services system were not successful in preventing subsequent victimization. Children who had been prior victims of maltreatment were 96% more likely to experience another occurrence than those who were not prior victims. Further, child victims who were reported to have a disability were 52% more likely to experience recurrence than children without a disability. Finally, the oldest victims (16–21 years of age) were the least likely to experience a recurrence, and were 51% less likely to be victimized again than were infants (younger than age 1) (National Child Abuse and Neglect Data System, 2006).
Child fatalities are the most tragic consequence of maltreatment. Yet, each year, children die from abuse and neglect. In 2006, an estimated 1,530 children in the United States died due to abuse or neglect. The overall rate of child fatalities was 2 deaths per 100,000 children. More than 40% of child fatalities were attributed to neglect, but physical abuse also was a major contributor. Approximately 78% of the children who died due to child abuse and neglect were younger than 4 years old, and infant boys (younger than 1) had the highest rate of fatalities at 18.5 deaths per 100,000 boys of the same age in the national population. Infant girls had a rate of 14.7 deaths per 100,000 girls of the same age (National Child Abuse and Neglect Data System, 2006).
One question to be addressed regarding child fatalities is why infants have such a high rate of death when compared to toddlers and adolescents. Children under 1 year old pose an immense amount of responsibility for their caretakers: they are completely dependent and need constant attention. Children this age are needy, impulsive, and not amenable to verbal control or effective communication. This can easily overwhelm vulnerable parents. Another difficulty associated with infants is that they are physically weak and small. Injuries to infants can be fatal, while similar injuries to older children might not be. The most common cause of death in children less than 1 year is cerebral trauma (often the result of shaken-baby syndrome). Exasperated parents can deliver shakes or blows without realizing how little it takes to cause irreparable or fatal damage to an infant. Research informs us that two of the most common triggers for fatal child abuse are crying that will not cease and toileting accidents. Both of these circumstances are common in infants and toddlers whose only means of communication often is crying, and who are limited in mobility and cannot use the toilet. Finally, very young children cannot assist in injury diagnoses. Children who have been injured due to abuse or neglect often cannot communicate to medical professionals about where it hurts, how it hurts, and so forth. Also, nonfatal injuries can turn fatal in the absence of care by neglectful parents or parents who do not want medical professionals to possibly identify an injury as being the result of abuse.
Estimates reveal that nearly 80% of perpetrators of child abuse were parents of the victim. Other relatives accounted for nearly 7%, and unmarried partners of parents made up 4% of perpetrators. Of those perpetrators that were parents, over 90% were biological parents, 4% were stepparents, and 0.7% were adoptive parents. Of this group, approximately 58% of perpetrators were women and 42% were men. Women perpetrators are typically younger than men. The average age for women abusers was 31 years old, while for men the average was 34 years old. Forty percent of women who abused were younger than 30 years of age, compared with 33% of men being under 30. The racial distribution of perpetrators is similar to that of victims. Fifty-four percent were white, 21% were African American, and 20% were Hispanic/Latino (National Child Abuse and Neglect Data System, 2006).
There are many factors that are associated with child abuse. Some of the more common/well-accepted explanations are individual pathology, parent–child interaction, past abuse in the family (or social learning), situational factors, and cultural support for physical punishment along with a lack of cultural support for helping parents here in the United States.
The first explanation centers on the individual pathology of a parent or caretaker who is abusive. This theory focuses on the idea that people who abuse their children have something wrong with their individual personality or biological makeup. Such psychological pathologies may include having anger control problems; being depressed or having post-partum depression; having a low tolerance for frustration (e.g., children can be extremely frustrating: they don’t always listen; they constantly push the line of how far they can go; and once the line has been established, they are constantly treading on it to make sure it hasn’t moved. They are dependent and self-centered, so caretakers have very little privacy or time to themselves); being rigid (e.g., having no tolerance for differences—for example, what if your son wanted to play with dolls? A rigid father would not let him, laugh at him for wanting to, punish him when he does, etc.); having deficits in empathy (parents who cannot put themselves in the shoes of their children cannot fully understand what their children need emotionally); or being disorganized, inefficient, and ineffectual. (Parents who are unable to manage their own lives are unlikely to be successful at managing the lives of their children, and since many children want and need limits, these parents are unable to set them or adhere to them.)
Biological pathologies that may increase the likelihood of someone becoming a child abuser include having substance abuse or dependence problems, or having persistent or reoccurring physical health problems (especially health problems that can be extremely painful and can cause a person to become more self-absorbed, both qualities that can give rise to a lack of patience, lower frustration tolerance, and increased stress).
The second explanation for child abuse centers on the interaction between the parent and the child, noting that certain types of parents are more likely to abuse, and certain types of children are more likely to be abused, and when these less-skilled parents are coupled with these more difficult children, child abuse is the most likely to occur. Discussion here focuses on what makes a parent less skilled, and what makes a child more difficult. Characteristics of unskilled parents are likely to include such traits as only pointing out what children do wrong and never giving any encouragement for good behavior, and failing to be sensitive to the emotional needs of children. Less skilled parents tend to have unrealistic expectations of children. They may engage in role reversal— where the parents make the child take care of them—and view the parent’s happiness and well-being as the responsibility of the child. Some parents view the parental role as extremely stressful and experience little enjoyment from being a parent. Finally, less-skilled parents tend to have more negative perceptions regarding their child(ren). For example, perhaps the child has a different shade of skin than they expected and this may disappoint or anger them, they may feel the child is being manipulative (long before children have this capability), or they may view the child as the scapegoat for all the parents’ or family’s problems. Theoretically, parents with these characteristics would be more likely to abuse their children, but if they are coupled with having a difficult child, they would be especially likely to be abusive. So, what makes a child more difficult? Certainly, through no fault of their own, children may have characteristics that are associated with child care that is more demanding and difficult than in the “normal” or “average” situation. Such characteristics can include having physical and mental disabilities (autism, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder [ADHD], hyperactivity, etc.); the child may be colicky, frequently sick, be particularly needy, or cry more often. In addition, some babies are simply unhappier than other babies for reasons that cannot be known. Further, infants are difficult even in the best of circumstances. They are unable to communicate effectively, and they are completely dependent on their caretakers for everything, including eating, diaper changing, moving around, entertainment, and emotional bonding. Again, these types of children, being more difficult, are more likely to be victims of child abuse.
Nonetheless, each of these types of parents and children alone cannot explain the abuse of children, but it is the interaction between them that becomes the key. Unskilled parents may produce children that are happy and not as needy, and even though they are unskilled, they do not abuse because the child takes less effort. At the same time, children who are more difficult may have parents who are skilled and are able to handle and manage the extra effort these children take with aplomb. However, risks for child abuse increase when unskilled parents must contend with difficult children.
Social learning or past abuse in the family is a third common explanation for child abuse. Here, the theory concentrates not only on what children learn when they see or experience violence in their homes, but additionally on what they do not learn as a result of these experiences. Social learning theory in the context of family violence stresses that if children are abused or see abuse (toward siblings or a parent), those interactions and violent family members become the representations and role models for their future familial interactions. In this way, what children learn is just as important as what they do not learn. Children who witness or experience violence may learn that this is the way parents deal with children, or that violence is an acceptable method of child rearing and discipline. They may think when they become parents that “violence worked on me when I was a child, and I turned out fine.” They may learn unhealthy relationship interaction patterns; children may witness the negative interactions of parents and they may learn the maladaptive or violent methods of expressing anger, reacting to stress, or coping with conflict.
What is equally as important, though, is that they are unlikely to learn more acceptable and nonviolent ways of rearing children, interacting with family members, and working out conflict. Here it may happen that an adult who was abused as a child would like to be nonviolent toward his or her own children, but when the chips are down and the child is misbehaving, this abused-child-turned-adult does not have a repertoire of nonviolent strategies to try. This parent is more likely to fall back on what he or she knows as methods of discipline.
Something important to note here is that not all abused children grow up to become abusive adults. Children who break the cycle were often able to establish and maintain one healthy emotional relationship with someone during their childhoods (or period of young adulthood). For instance, they may have received emotional support from a nonabusing parent, or they received social support and had a positive relationship with another adult during their childhood (e.g., teacher, coach, minister, neighbor, etc.). Abused children who participate in therapy during some period of their lives can often break the cycle of violence. In addition, adults who were abused but are able to form an emotionally supportive and satisfying relationship with a mate can make the transition to being nonviolent in their family interactions.
Moving on to a fourth familiar explanation for child abuse, there are some common situational factors that influence families and parents and increase the risks for child abuse. Typically, these are factors that increase family stress or social isolation. Specifically, such factors may include receiving public assistance or having low socioeconomic status (a combination of low income and low education). Other factors include having family members who are unemployed, underemployed (working in a job that requires lower qualifications than an individual possesses), or employed only part time. These financial difficulties cause great stress for families in meeting the needs of the individual members. Other stress-inducing familial characteristics are single-parent households and larger family size. Finally, social isolation can be devastating for families and family members. Having friends to talk to, who can be relied upon, and with whom kids can be dropped off occasionally is tremendously important for personal growth and satisfaction in life. In addition, social isolation and stress can cause individuals to be quick to lose their tempers, as well as cause people to be less rational in their decision making and to make mountains out of mole hills. These situations can lead families to be at greater risk for child abuse.
Finally, cultural views and supports (or lack thereof) can lead to greater amounts of child abuse in a society such as the United States. One such cultural view is that of societal support for physical punishment. This is problematic because there are similarities between the way criminals are dealt with and the way errant children are handled. The use of capital punishment is advocated for seriously violent criminals, and people are quick to use such idioms as “spare the rod and spoil the child” when it comes to the discipline or punishment of children. In fact, it was not until quite recently that parenting books began to encourage parents to use other strategies than spanking or other forms of corporal punishment in the discipline of their children. Only recently, the American Academy of Pediatrics has come out and recommended that parents do not spank or use other forms of violence on their children because of the deleterious effects such methods have on youngsters and their bonds with their parents. Nevertheless, regardless of recommendations, the culture of corporal punishment persists.
Another cultural view in the United States that can give rise to greater incidents of child abuse is the belief that after getting married, couples of course should want and have children. Culturally, Americans consider that children are a blessing, raising kids is the most wonderful thing a person can do, and everyone should have children. Along with this notion is the idea that motherhood is always wonderful; it is the most fulfilling thing a woman can do; and the bond between a mother and her child is strong, glorious, and automatic—all women love being mothers. Thus, culturally (and theoretically), society nearly insists that married couples have children and that they will love having children. But, after children are born, there is not much support for couples who have trouble adjusting to parenthood, or who do not absolutely love their new roles as parents. People look askance at parents who need help, and cannot believe parents who say anything negative about parenthood. As such, theoretically, society has set up a situation where couples are strongly encouraged to have kids, are told they will love kids, but then society turns a blind or disdainful eye when these same parents need emotional, financial, or other forms of help or support. It is these types of cultural viewpoints that increase the risks for child abuse in society.
The consequences of child abuse are tremendous and long lasting. Research has shown that the traumatic experience of childhood abuse is life changing. These costs may surface during adolescence, or they may not become evident until abused children have grown up and become abusing parents or abused spouses. Early identification and treatment is important to minimize these potential long-term effects. Whenever children say they have been abused, it is imperative that they be taken seriously and their abuse be reported. Suspicions of child abuse must be reported as well. If there is a possibility that a child is or has been abused, an investigation must be conducted.
Children who have been abused may exhibit traits such as the inability to love or have faith in others. This often translates into adults who are unable to establish lasting and stable personal relationships. These individuals have trouble with physical closeness and touching as well as emotional intimacy and trust. Further, these qualities tend to cause a fear of entering into new relationships, as well as the sabotaging of any current ones.
Psychologically, children who have been abused tend to have poor self-images or are passive, withdrawn, or clingy. They may be angry individuals who are filled with rage, anxiety, and a variety of fears. They are often aggressive, disruptive, and depressed. Many abused children have flashbacks and nightmares about the abuse they have experienced, and this may cause sleep problems as well as drug and alcohol problems. Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and antisocial personality disorder are both typical among maltreated children. Research has also shown that most abused children fail to reach “successful psychosocial functioning,” and are thus not resilient and do not resume a “normal life” after the abuse has ended.
Socially (and likely because of these psychological injuries), abused children have trouble in school, will have difficulty getting and remaining employed, and may commit a variety of illegal or socially inappropriate behaviors. Many studies have shown that victims of child abuse are likely to participate in high-risk behaviors such as alcohol or drug abuse, the use of tobacco, and high-risk sexual behaviors (e.g., unprotected sex, large numbers of sexual partners). Later in life, abused children are more likely to have been arrested and homeless. They are also less able to defend themselves in conflict situations and guard themselves against repeated victimizations.
Medically, abused children likely will experience health problems due to the high frequency of physical injuries they receive. In addition, abused children experience a great deal of emotional turmoil and stress, which can also have a significant impact on their physical condition. These health problems are likely to continue occurring into adulthood. Some of these longer-lasting health problems include headaches; eating problems; problems with toileting; and chronic pain in the back, stomach, chest, and genital areas. Some researchers have noted that abused children may experience neurological impairment and problems with intellectual functioning, while others have found a correlation between abuse and heart, lung, and liver disease, as well as cancer (Thomas, 2004).
Victims of sexual abuse show an alarming number of disturbances as adults. Some dislike and avoid sex, or experience sexual problems or disorders, while other victims appear to enjoy sexual activities that are self-defeating or maladaptive—normally called “dysfunctional sexual behavior”—and have many sexual partners.
Abused children also experience a wide variety of developmental delays. Many do not reach physical, cognitive, or emotional developmental milestones at the typical time, and some never accomplish what they are supposed to during childhood socialization. In the next section, these developmental delays are discussed as a means of identifying children who may be abused.
There are two primary ways of identifying children who are abused: spotting and evaluating physical injuries, and detecting and appraising developmental delays. Distinguishing physical injuries due to abuse can be difficult, particularly among younger children who are likely to get hurt or receive injuries while they are playing and learning to become ambulatory. Nonetheless, there are several types of wounds that children are unlikely to give themselves during their normal course of play and exploration. These less likely injuries may signal instances of child abuse.
While it is true that children are likely to get bruises, particularly when they are learning to walk or crawl, bruises on infants are not normal. Also, the back of the legs, upper arms, or on the chest, neck, head, or genitals are also locations where bruises are unlikely to occur during normal childhood activity. Further, bruises with clean patterns, like hand prints, buckle prints, or hangers (to name a few), are good examples of the types of bruises children do not give themselves.
Another area of physical injury where the source of the injury can be difficult to detect is fractures. Again, children fall out of trees, or crash their bikes, and can break limbs. These can be normal parts of growing up. However, fractures in infants less than 12 months old are particularly suspect, as infants are unlikely to be able to accomplish the types of movement necessary to actually break a leg or an arm. Further, multiple fractures, particularly more than one on a bone, should be examined more closely. Spiral or torsion fractures (when the bone is broken by twisting) are suspect because when children break their bones due to play injuries, the fractures are usually some other type (e.g., linear, oblique, compacted). In addition, when parents don’t know about the fracture(s) or how it occurred, abuse should be considered, because when children get these types of injuries, they need comfort and attention.
Head and internal injuries are also those that may signal abuse. Serious blows to the head cause internal head injuries, and this is very different from the injuries that result from bumping into things. Abused children are also likely to experience internal injuries like those to the abdomen, liver, kidney, and bladder. They may suffer a ruptured spleen, or intestinal perforation. These types of damages rarely happen by accident.
Burns are another type of physical injury that can happen by accident or by abuse. Nevertheless, there are ways to tell these types of burn injuries apart. The types of burns that should be examined and investigated are those where the burns are in particular locations. Burns to the bottom of the feet, genitals, abdomen, or other inaccessible spots should be closely considered. Burns of the whole hand or those to the buttocks are also unlikely to happen as a result of an accident.
Turning to the detection and appraisal of developmental delays, one can more readily assess possible abuse by considering what children of various ages should be able to accomplish, than by noting when children are delayed and how many milestones on which they are behind schedule. Importantly, a few delays in reaching milestones can be expected, since children develop individually and not always according to the norm. Nonetheless, when children are abused, their development is likely to be delayed in numerous areas and across many milestones.
As children develop and grow, they should be able to crawl, walk, run, talk, control going to the bathroom, write, set priorities, plan ahead, trust others, make friends, develop a good self-image, differentiate between feeling and behavior, and get their needs met in appropriate ways. As such, when children do not accomplish these feats, their circumstances should be examined.
Infants who are abused or neglected typically develop what is termed failure to thrive syndrome. This syndrome is characterized by slow, inadequate growth, or not “filling out” physically. They have a pale, colorless complexion and dull eyes. They are not likely to spend much time looking around, and nothing catches their eyes. They may show other signs of lack of nutrition such as cuts, bruises that do not heal in a timely way, and discolored fingernails. They are also not trusting and may not cry much, as they are not expecting to have their needs met. Older infants may not have developed any language skills, or these developments are quite slow. This includes both verbal and nonverbal means of communication.
Toddlers who are abused often become hypervigilant about their environments and others’ moods. They are more outwardly focused than a typical toddler (who is quite self-centered) and may be unable to separate themselves as individuals, or consider themselves as distinct beings. In this way, abused toddlers cannot focus on tasks at hand because they are too concerned about others’ reactions. They don’t play with toys, have no interest in exploration, and seem unable to enjoy life. They are likely to accept losses with little reaction, and may have age-inappropriate knowledge of sex and sexual relations. Finally, toddlers, whether they are abused or not, begin to mirror their parents’ behaviors. Thus, toddlers who are abused may mimic the abuse when they are playing with dolls or “playing house.”
Developmental delays can also be detected among abused young adolescents. Some signs include the failure to learn cause and effect, since their parents are so inconsistent. They have no energy for learning and have not developed beyond one- or two-word commands. They probably cannot follow complicated directions (such as two to three tasks per instruction), and they are unlikely to be able to think for themselves. Typically, they have learned that failure is totally unacceptable, but they are more concerned with the teacher’s mood than with learning and listening to instruction. Finally, they are apt to have been inadequately toilet trained and thus may be unable to control their bladders.
Older adolescents, because they are likely to have been abused for a longer period of time, continue to get further and further behind in their developmental achievements. Abused children this age become family nurturers. They take care of their parents and cater to their parents’ needs, rather than the other way around. In addition, they probably take care of any younger siblings and do the household chores. Because of these default responsibilities, they usually do not participate in school activities; they frequently miss days at school; and they have few, if any, friends. Because they have become so hypervigilant and have increasingly delayed development, they lose interest in and become disillusioned with education. They develop low self-esteem and little confidence, but seem old for their years. Children this age who are abused are still likely to be unable to control their bladders and may have frequent toileting accidents.
Other developmental delays can occur and be observed in abused and neglected children of any age. For example, malnutrition and withdrawal can be noticed in infants through teenagers. Maltreated children frequently have persistent or untreated illnesses, and these can become permanent disabilities if medical conditions go untreated for a long enough time. Another example can be the consequences of neurological damage. Beyond being a medical issue, this type of damage can cause problems with social behavior and impulse control, which, again, can be discerned in various ages of children.
Once child abuse is suspected, law enforcement officers, child protection workers, or various other practitioners may need to interview the child about the abuse or neglect he or she may have suffered. Interviewing children can be extremely difficult because children at various stages of development can remember only certain parts or aspects of the events in their lives. Also, interviewers must be careful that they do not put ideas or answers into the heads of the children they are interviewing. There are several general recommendations when interviewing children about the abuse they may have experienced. First, interviewers must acknowledge that even when children are abused, they likely still love their parents. They do not want to be taken away from their parents, nor do they want to see their parents get into trouble. Interviewers must not blame the parents or be judgmental about them or the child’s family. Beyond that, interviews should take place in a safe, neutral location. Interviewers can use dolls and role-play to help children express the types of abuse of which they may be victims.
Finally, interviewers must ask age-appropriate questions. For example, 3-year-olds can probably only answer questions about what happened and who was involved. Four- to five-year-olds can also discuss where the incidents occurred. Along with what, who, and where, 6- to 8-year-olds can talk about the element of time, or when the abuse occurred. Nine- to 10-year-olds are able to add commentary about the number of times the abuse occurred. Finally, 11-year-olds and older children can additionally inform interviewers about the circumstances of abusive instances.
A conclusion is not a summary of what a writer has already mentioned. On the contrary, it is the last point made. Taking every detail of the investigation, the researcher makes the concluding point. In this part of a paper, you need to put a full stop in your research. You need to persuade the reader in your opinion.
Never add any new information in the conclusion. You can present solutions to the problem and you dwell upon the results, but only if this information has been already mentioned in the main body.
Child advocates recommend a variety of strategies to aid families and children experiencing abuse. These recommendations tend to focus on societal efforts as well as more individual efforts. One common strategy advocated is the use of public service announcements that encourage individuals to report any suspected child abuse. Currently, many mandatory reporters (those required by law to report abuse such as teachers, doctors, and social service agency employees) and members of communities feel that child abuse should not be reported unless there is substantial evidence that abuse is indeed occurring. Child advocates stress that this notion should be changed, and that people should report child abuse even if it is only suspected. Public service announcements should stress that if people report suspected child abuse, the worst that can happen is that they might be wrong, but in the grander scheme of things that is really not so bad.
Child advocates also stress that greater interagency cooperation is needed. This cooperation should be evident between women’s shelters, child protection agencies, programs for at-risk children, medical agencies, and law enforcement officers. These agencies typically do not share information, and if they did, more instances of child abuse would come to the attention of various authorities and could be investigated and managed. Along these lines, child protection agencies and programs should receive more funding. When budgets are cut, social services are often the first things to go or to get less financial support. Child advocates insist that with more resources, child protection agencies could hire more workers, handle more cases, conduct more investigations, and follow up with more children and families.
Continuing, more educational efforts must be initiated about issues such as punishment and discipline styles and strategies; having greater respect for children; as well as informing the community about what child abuse is, and how to recognize it. In addition, Americans must alter the cultural orientation about child bearing and child rearing. Couples who wish to remain child-free must be allowed to do so without disdain. And, it must be acknowledged that raising children is very difficult, is not always gloriously wonderful, and that parents who seek help should be lauded and not criticized. These kinds of efforts can help more children to be raised in nonviolent, emotionally satisfying families, and thus become better adults.
Bibliography
When you write a paper, make sure you are aware of all the formatting requirements. Incorrect formatting can lower your mark, so do not underestimate the importance of this part.
Organizing your bibliography is quite a tedious and time-consuming task. Still, you need to do it flawlessly. For this reason, analyze all the standards you need to meet or ask professionals to help you with it. All the comas, colons, brackets etc. matter. They truly do.
Bibliography:
- American Academy of Pediatrics: https://www.aap.org/
- Bancroft, L., & Silverman, J. G. (2002). The batterer as parent. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
- Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act, 42 U.S.C.A. § 5106g (1998).
- Childhelp: Child Abuse Statistics: https://www.childhelp.org/child-abuse-statistics/
- Children’s Defense Fund: https://www.childrensdefense.org/
- Child Stats.gov: https://www.childstats.gov/
- Child Welfare League of America: https://www.cwla.org/
- Crosson-Tower, C. (2008). Understanding child abuse and neglect (7th ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
- DeBecker, G. (1999). Protecting the gift: Keeping children and teenagers safe (and parents sane). New York: Bantam Dell.
- Family Research Laboratory at the University of New Hampshire: https://cola.unh.edu/family-research-laboratory
- Guterman, N. B. (2001). Stopping child maltreatment before it starts: Emerging horizons in early home visitation services. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
- Herman, J. L. (2000). Father-daughter incest. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Medline Plus, Child Abuse: https://medlineplus.gov/childabuse.html
- Myers, J. E. B. (Ed.). (1994). The backlash: Child protection under fire. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
- National Center for Missing and Exploited Children: https://www.missingkids.org/home
- National Child Abuse and Neglect Data System. (2006). Child maltreatment 2006: Reports from the states to the National Child Abuse and Neglect Data System. Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families.
- New York University Silver School of Social Work: https://socialwork.nyu.edu/
- Pitzer, R. L. (1997). Corporal punishment in the discipline of children in the home: Research update for practitioners. Paper presented at the National Council on Family Relations Annual Conference, Washington, DC.
- RAND, Child Abuse and Neglect: https://www.rand.org/topics/child-abuse-and-neglect.html
- Richards, C. E. (2001). The loss of innocents: Child killers and their victims. Wilmington, DE: Scholarly Resources.
- Straus, M. A. (2001). Beating the devil out of them: Corporal punishment in American families and its effects on children. Edison, NJ: Transaction.
- Thomas, P. M. (2004). Protection, dissociation, and internal roles: Modeling and treating the effects of child abuse. Review of General Psychology, 7(15).
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Administration for Children and Families: https://www.acf.hhs.gov/
Your Pathway to Academic Excellence with iResearchNet
Embarking on your academic journey with iResearchNet not only sets the foundation for your success but also ensures you navigate the complexities of research paper writing with ease and confidence. Our comprehensive suite of services, from expertly crafted research papers to an array of exclusive extras, is designed with your academic needs and aspirations in mind. By choosing iResearchNet, you’re not just securing a service; you’re investing in your future, in a partnership that values excellence, integrity, and your personal academic goals.
We invite you to take the first step towards transforming your academic challenges into opportunities for growth and learning. Starting is simple, and the benefits are immense. With iResearchNet, you gain access to a world of expertise, personalized support, and resources tailored to elevate your research and writing to the highest standard. Our commitment to quality, alongside our promise of customization, affordability, and timely delivery, ensures that every paper we deliver meets and exceeds your expectations.
Whether you’re seeking to inspire your academic journey with our diverse research paper examples, require the specialized assistance of our expert writers, or wish to enhance your experience with our additional services, iResearchNet is here to support you every step of the way. Our process is streamlined for your convenience, ensuring that from the moment you place your order to the final receipt of your paper, your journey is smooth, transparent, and fully aligned with your academic objectives.
Embrace the opportunity to excel, to stand out, and to make your academic work truly remarkable. Choose iResearchNet today, and let us be your partner in achieving academic excellence. Begin your journey by placing your order, and experience firsthand the impact of professional support and exceptional writing on your academic endeavors. Your success is our priority, and with iResearchNet, it’s within reach.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

How To Write A Research Paper
Research Paper Example

Research Paper Example - Examples for Different Formats
Published on: Jun 12, 2021
Last updated on: Jul 19, 2024

People also read
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Proposal For a Research Paper in 10 Steps
A Comprehensive Guide to Creating a Research Paper Outline
Types of Research - Methodologies and Characteristics
300+ Engaging Research Paper Topics to Get You Started
Interesting Psychology Research Topics & Ideas
Qualitative Research - Types, Methods & Examples
Understanding Quantitative Research - Definition, Types, Examples, And More
How To Start A Research Paper - Steps With Examples
How To Write a Literature Review for a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Types of Qualitative Research Methods - An Overview
Understanding Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research - A Complete Guide
How to Cite a Research Paper in Different Citation Styles
Easy Sociology Research Topics for Your Next Project
200+ Outstanding History Research Paper Topics With Expert Tips
How To Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Write a Good Research Paper Title
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper in 3 Simple Steps
How to Write an Abstract For a Research Paper with Examples
How To Write a Thesis For a Research Paper Step by Step
How to Write a Discussion For a Research Paper | Objectives, Steps & Examples
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper - Structure and Tips
How to Write a Problem Statement for a Research Paper in 6 Steps
How To Write The Methods Section of a Research Paper Step-by-Step
How to Find Sources For a Research Paper | A Guide
Share this article
Writing a research paper is the most challenging task in a student's academic life. researchers face similar writing process hardships, whether the research paper is to be written for graduate or masters.
A research paper is a writing type in which a detailed analysis, interpretation, and evaluation are made on the topic. It requires not only time but also effort and skills to be drafted correctly.
If you are working on your research paper for the first time, here is a collection of examples that you will need to understand the paper’s format and how its different parts are drafted. Continue reading the article to get free research paper examples.
On This Page On This Page -->
Research Paper Example for Different Formats
A research paper typically consists of several key parts, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and annotated bibliography .
When writing a research paper (whether quantitative research or qualitative research ), it is essential to know which format to use to structure your content. Depending on the requirements of the institution, there are mainly four format styles in which a writer drafts a research paper:
Letâs look into each format in detail to understand the fundamental differences and similarities.
Research Paper Example APA
If your instructor asks you to provide a research paper in an APA format, go through the example given below and understand the basic structure. Make sure to follow the format throughout the paper.
APA Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example MLA
Another widespread research paper format is MLA. A few institutes require this format style as well for your research paper. Look at the example provided of this format style to learn the basics.
MLA Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example Chicago
Unlike MLA and APA styles, Chicago is not very common. Very few institutions require this formatting style research paper, but it is essential to learn it. Look at the example given below to understand the formatting of the content and citations in the research paper.
Chicago Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example Harvard
Learn how a research paper through Harvard formatting style is written through this example. Carefully examine how the cover page and other pages are structured.
Harvard Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
A research paper is based on different parts. Each part plays a significant role in the overall success of the paper. So each chapter of the paper must be drafted correctly according to a format and structure.
Below are examples of how different sections of the research paper are drafted.
Research Proposal Example
A research proposal is a plan that describes what you will investigate, its significance, and how you will conduct the study.
Research Proposal Sample (PDF)
Abstract Research Paper Example
An abstract is an executive summary of the research paper that includes the purpose of the research, the design of the study, and significant research findings.
It is a small section that is based on a few paragraphs. Following is an example of the abstract to help you draft yours professionally.
Abstract Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Literature Review Research Paper Example
A literature review in a research paper is a comprehensive summary of the previous research on your topic. It studies sources like books, articles, journals, and papers on the relevant research problem to form the basis of the new research.
Writing this section of the research paper perfectly is as important as any part of it.
Literature Review in Research Sample (PDF)
Methods Section of Research Paper Example
The method section comes after the introduction of the research paper that presents the process of collecting data. Basically, in this section, a researcher presents the details of how your research was conducted.
Methods Section in Research Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Conclusion Example
The conclusion is the last part of your research paper that sums up the writerâs discussion for the audience and leaves an impression. This is how it should be drafted:
Research Paper Conclusion Sample
Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
The research papers are not limited to a particular field. They can be written for any discipline or subject that needs a detailed study.
In the following section, various research paper examples are given to show how they are drafted for different subjects.
Science Research Paper Example
Are you a science student that has to conduct research? Here is an example for you to draft a compelling research paper for the field of science.
Science Research Paper Sample (PDF)
History Research Paper Example
Conducting research and drafting a paper is not only bound to science subjects. Other subjects like history and arts require a research paper to be written as well. Observe how research papers related to history are drafted.
History Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Psychology Research Paper Example
If you are a psychology student, look into the example provided in the research paper to help you draft yours professionally.
Psychology Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example for Different Levels
Writing a research paper is based on a list of elements. If the writer is not aware of the basic elements, the process of writing the paper will become daunting. Start writing your research paper taking the following steps:
- Choose a topic
- Form a strong thesis statement
- Conduct research
- Develop a research paper outline
Once you have a plan in your hand, the actual writing procedure will become a piece of cake for you.
No matter which level you are writing a research paper for, it has to be well structured and written to guarantee you better grades.
If you are a college or a high school student, the examples in the following section will be of great help.
Research Paper Outline (PDF)
Research Paper Example for College
Pay attention to the research paper example provided below. If you are a college student, this sample will help you understand how a winning paper is written.
College Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Research Paper Example for High School
Expert writers of CollegeEssay.org have provided an excellent example of a research paper for high school students. If you are struggling to draft an exceptional paper, go through the example provided.
High School Research Paper Sample (PDF)
Examples are essential when it comes to academic assignments. If you are a student and aim to achieve good grades in your assignments, it is suggested to get help from CollegeEssay.org .
We are the best writing company that delivers essay help for students by providing free samples and writing assistance.
Professional writers have your back, whether you are looking for guidance in writing a lab report, college essay, or research paper.
Simply hire a writer by placing your order at the most reasonable price. You can also take advantage of our essay writer to enhance your writing skills.
Nova A. (Literature, Marketing)
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.

APA Formatting and Style (7th ed.)
- What's New in the 7th ed.?
- Principles of Plagiarism: An Overview
- Basic Paper Formatting
- Basic Paper Elements
- Punctuation, Capitalization, Abbreviations, Apostrophes, Numbers, Plurals
- Tables and Figures
- Powerpoint Presentations
- Reference Page Format
- Periodicals (Journals, Magazines, Newspapers)
- Books and Reference Works
- Webpage on a Website
- Discussion Post
- Company Information & SWOT Analyses
- Dissertations or Theses
- ChatGPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Online Images
- Online Video
- Computer Software and Mobile Apps
- Missing Information
- Two Authors
- Three or More Authors
- Group Authors
- Missing Author
- Chat GPT and other AI Large Language Models
- Secondary Sources
- Block Quotations
- Fillable Template and Sample Paper
- Government Documents and Legal Materials
- APA Style 7th ed. Tutorials
- Additional APA 7th Resources
- Grammarly - your writing assistant
- Writing Center - Writing Skills This link opens in a new window
- Brainfuse Online Tutoring
APA 7th ed. Fillable Word Template and Sample Paper
- APA 7th ed. Template Download this Word document, fill out the title page and get writing!
- Sample Paper APA 7th ed. Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper.
- APA 7th Sample Papers from Purdue Owl
- << Previous: Block Quotations
- Next: Government Documents and Legal Materials >>
- Last Updated: Aug 9, 2024 11:50 AM
- URL: https://national.libguides.com/apa_7th

How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications . If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
Can you help me with a full paper template for this Abstract:
Background: Energy and sports drinks have gained popularity among diverse demographic groups, including adolescents, athletes, workers, and college students. While often used interchangeably, these beverages serve distinct purposes, with energy drinks aiming to boost energy and cognitive performance, and sports drinks designed to prevent dehydration and replenish electrolytes and carbohydrates lost during physical exertion.
Objective: To assess the nutritional quality of energy and sports drinks in Egypt.
Material and Methods: A cross-sectional study assessed the nutrient contents, including energy, sugar, electrolytes, vitamins, and caffeine, of sports and energy drinks available in major supermarkets in Cairo, Alexandria, and Giza, Egypt. Data collection involved photographing all relevant product labels and recording nutritional information. Descriptive statistics and appropriate statistical tests were employed to analyze and compare the nutritional values of energy and sports drinks.
Results: The study analyzed 38 sports drinks and 42 energy drinks. Sports drinks were significantly more expensive than energy drinks, with higher net content and elevated magnesium, potassium, and vitamin C. Energy drinks contained higher concentrations of caffeine, sugars, and vitamins B2, B3, and B6.
Conclusion: Significant nutritional differences exist between sports and energy drinks, reflecting their intended uses. However, these beverages’ high sugar content and calorie loads raise health concerns. Proper labeling, public awareness, and responsible marketing are essential to guide safe consumption practices in Egypt.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Research Paper
Few things strike more fear in academics than the accursed research paper , a term synonymous with long hours and hard work. Luckily there’s a secret to help you get through them. As long as you know how to write a research paper properly, you’ll find they’re not so bad . . . or at least less painful.
In this guide we concisely explain how to write an academic research paper step by step. We’ll cover areas like how to start a research paper, how to write a research paper outline, how to use citations and evidence, and how to write a conclusion for a research paper.
But before we get into the details, let’s take a look at what a research paper is and how it’s different from other writing .
Write papers with confidence Grammarly helps you make the grade Write with Grammarly
What is a research paper?
A research paper is a type of academic writing that provides an in-depth analysis, evaluation, or interpretation of a single topic, based on empirical evidence. Research papers are similar to analytical essays, except that research papers emphasize the use of statistical data and preexisting research, along with a strict code for citations.
Research papers are a bedrock of modern science and the most effective way to share information across a wide network. However, most people are familiar with research papers from school; college courses often use them to test a student’s knowledge of a particular area or their research skills in general.
Considering their gravity, research papers favor formal, even bland language that strips the writing of any bias. Researchers state their findings plainly and with corresponding evidence so that other researchers can consequently use the paper in their own research.
Keep in mind that writing a research paper is different from writing a research proposal . Essentially, research proposals are to acquire the funding needed to get the data to write a research paper.
How long should a research paper be?
The length of a research paper depends on the topic or assignment. Typically, research papers run around 4,000–6,000 words, but it’s common to see short papers around 2,000 words or long papers over 10,000 words.
If you’re writing a paper for school, the recommended length should be provided in the assignment. Otherwise, let your topic dictate the length: Complicated topics or extensive research will require more explanation.
How to write a research paper in 9 steps
Below is a step-by-step guide to writing a research paper, catered specifically for students rather than professional researchers. While some steps may not apply to your particular assignment, think of this as more of a general guideline to keep you on track.
1 Understand the assignment
For some of you this goes without saying, but you might be surprised at how many students start a research paper without even reading the assignment guidelines.
So your first step should be to review the assignment and carefully read the writing prompt. Specifically, look for technical requirements such as length , formatting requirements (single- vs. double-spacing, indentations, etc.) and citation style . Also pay attention to the particulars, such as whether or not you need to write an abstract or include a cover page.
Once you understand the assignment, the next steps in how to write a research paper follow the usual writing process , more or less. There are some extra steps involved because research papers have extra rules, but the gist of the writing process is the same.
2 Choose your topic
In open-ended assignments, the student must choose their own topic. While it may seem simple enough, choosing a topic is actually the most important decision you’ll make in writing a research paper, since it determines everything that follows.
Your top priority in how to choose a research paper topic is whether it will provide enough content and substance for an entire research paper. You’ll want to choose a topic with enough data and complexity to enable a rich discussion. However, you also want to avoid general topics and instead stick with topics specific enough that you can cover all the relevant information without cutting too much.
3 Gather preliminary research
The sooner you start researching, the better—after all, it’s called a research paper for a reason.
To refine your topic and prepare your thesis statement, find out what research is available for your topic as soon as possible. Early research can help dispel any misconceptions you have about the topic and reveal the best paths and approaches to find more material.
Typically, you can find sources either online or in a library. If you’re searching online, make sure you use credible sources like science journals or academic papers. Some search engines—mentioned below in the Tools and resources section—allow you to browse only accredited sources and academic databases.
Keep in mind the difference between primary and secondary sources as you search. Primary sources are firsthand accounts, like published articles or autobiographies; secondary sources are more removed, like critical reviews or secondhand biographies.
When gathering your research, it’s better to skim sources instead of reading each potential source fully. If a source seems useful, set it aside to give it a full read later. Otherwise, you’ll be stuck poring over sources that you ultimately won’t use, and that time could be better spent finding a worthwhile source.
Sometimes you’re required to submit a literature review , which explains your sources and presents them to an authority for confirmation. Even if no literature review is required, it’s still helpful to compile an early list of potential sources—you’ll be glad you did later.
4 Write a thesis statement
Using what you found in your preliminary research, write a thesis statement that succinctly summarizes what your research paper will be about. This is usually the first sentence in your paper, making it your reader’s introduction to the topic.
A thesis statement is the best answer for how to start a research paper. Aside from preparing your reader, the thesis statement also makes it easier for other researchers to assess whether or not your paper is useful to them for their own research. Likewise, you should read the thesis statements of other research papers to decide how useful they are to you.
A good thesis statement mentions all the important parts of the discussion without disclosing too many of the details. If you’re having trouble putting it into words, try to phrase your topic as a question and then answer it .
For example, if your research paper topic is about separating students with ADHD from other students, you’d first ask yourself, “Does separating students with ADHD improve their learning?” The answer—based on your preliminary research—is a good basis for your thesis statement.
5 Determine supporting evidence
At this stage of how to write an academic research paper, it’s time to knuckle down and do the actual research. Here’s when you go through all the sources you collected earlier and find the specific information you’d like to use in your paper.
Normally, you find your supporting evidence by reading each source and taking notes. Isolate only the information that’s directly relevant to your topic; don’t bog down your paper with tangents or unnecessary context, however interesting they may be. And always write down page numbers , not only for you to find the information later, but also because you’ll need them for your citations.
Aside from highlighting text and writing notes, another common tactic is to use bibliography cards . These are simple index cards with a fact or direct quotation on one side and the bibliographical information (source citation, page numbers, subtopic category) on the other. While bibliography cards are not necessary, some students find them useful for staying organized, especially when it’s time to write an outline.
6 Write a research paper outline
A lot of students want to know how to write a research paper outline. More than informal essays, research papers require a methodical and systematic structure to make sure all issues are addressed, and that makes outlines especially important.
First make a list of all the important categories and subtopics you need to cover—an outline for your outline! Consider all the information you gathered when compiling your supporting evidence and ask yourself what the best way to separate and categorize everything is.
Once you have a list of what you want to talk about, consider the best order to present the information. Which subtopics are related and should go next to each other? Are there any subtopics that don’t make sense if they’re presented out of sequence? If your information is fairly straightforward, feel free to take a chronological approach and present the information in the order it happened.
Because research papers can get complicated, consider breaking your outline into paragraphs. For starters, this helps you stay organized if you have a lot of information to cover. Moreover, it gives you greater control over the flow and direction of the research paper. It’s always better to fix structural problems in the outline phase than later after everything’s already been written.
Don’t forget to include your supporting evidence in the outline as well. Chances are you’ll have a lot you want to include, so putting it in your outline helps prevent some things from falling through the cracks.
7 Write the first draft
Once your outline is finished, it’s time to start actually writing your research paper. This is by far the longest and most involved step, but if you’ve properly prepared your sources and written a thorough outline, everything should run smoothly.
If you don’t know how to write an introduction for a research paper, the beginning can be difficult. That’s why writing your thesis statement beforehand is crucial. Open with your thesis statement and then fill out the rest of your introduction with the secondary information—save the details for the body of your research paper, which comes next.
The body contains the bulk of your research paper. Unlike essays , research papers usually divide the body into sections with separate headers to facilitate browsing and scanning. Use the divisions in your outline as a guide.
Follow along your outline and go paragraph by paragraph. Because this is just the first draft, don’t worry about getting each word perfect . Later you’ll be able to revise and fine-tune your writing, but for now focus simply on saying everything that needs to be said. In other words, it’s OK to make mistakes since you’ll go back later to correct them.
One of the most common problems with writing long works like research papers is connecting paragraphs to each other. The longer your writing is, the harder it is to tie everything together smoothly. Use transition sentences to improve the flow of your paper, especially for the first and last sentences in a paragraph.
Even after the body is written, you still need to know how to write a conclusion for a research paper. Just like an essay conclusion , your research paper conclusion should restate your thesis , reiterate your main evidence , and summarize your findings in a way that’s easy to understand.
Don’t add any new information in your conclusion, but feel free to say your own personal perspective or interpretation if it helps the reader understand the big picture.
8 Cite your sources correctly
Citations are part of what sets research papers apart from more casual nonfiction like personal essays . Citing your sources both validates your data and also links your research paper to the greater scientific community. Because of their importance, citations must follow precise formatting rules . . . problem is, there’s more than one set of rules!
You need to check with the assignment to see which formatting style is required. Typically, academic research papers follow one of two formatting styles for citing sources:
- MLA (Modern Language Association)
- APA (American Psychological Association)
The links above explain the specific formatting guidelines for each style, along with an automatic citation generator to help you get started.
In addition to MLA and APA styles, you occasionally see requirements for CMOS (The Chicago Manual of Style), AMA (American Medical Association) and IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers).
Citations may seem confusing at first with all their rules and specific information. However, once you get the hang of them, you’ll be able to properly cite your sources without even thinking about it. Keep in mind that each formatting style has specific guidelines for citing just about any kind of source, including photos , websites , speeches , and YouTube videos .
9 Edit and proofread
Last but not least, you want to go through your research paper to correct all the mistakes by proofreading . We recommend going over it twice: once for structural issues such as adding/deleting parts or rearranging paragraphs and once for word choice, grammatical, and spelling mistakes. Doing two different editing sessions helps you focus on one area at a time instead of doing them both at once.
To help you catch everything, here’s a quick checklist to keep in mind while you edit:
Structural edit:
- Is your thesis statement clear and concise?
- Is your paper well-organized, and does it flow from beginning to end with logical transitions?
- Do your ideas follow a logical sequence in each paragraph?
- Have you used concrete details and facts and avoided generalizations?
- Do your arguments support and prove your thesis?
- Have you avoided repetition?
- Are your sources properly cited?
- Have you checked for accidental plagiarism?
Word choice, grammar, and spelling edit:
- Is your language clear and specific?
- Do your sentences flow smoothly and clearly?
- Have you avoided filler words and phrases ?
- Have you checked for proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation?
Some people find it useful to read their paper out loud to catch problems they might miss when reading in their head. Another solution is to have someone else read your paper and point out areas for improvement and/or technical mistakes.
Revising is a separate skill from writing, and being good at one doesn’t necessarily make you good at the other. If you want to improve your revision skills, read our guide on self-editing , which includes a more complete checklist and advanced tips on improving your revisions.
Technical issues like grammatical mistakes and misspelled words can be handled effortlessly if you use a spellchecker with your word processor, or even better, a digital writing assistant that also suggests improvements for word choice and tone, like Grammarly (we explain more in the Tools and resources section below).
Tools and resources
If you want to know more about how to write a research paper, or if you want some help with each step, take a look at the tools and resources below.
Google Scholar
This is Google’s own search engine, which is dedicated exclusively to academic papers. It’s a great way to find new research and sources. Plus, it’s free to use.
Zotero is a freemium, open-source research manager, a cross between an organizational CMS and a search engine for academic research. With it, you can browse the internet for research sources relevant to your topic and share them easily with colleagues. Also, it automatically generates citations.

FocusWriter
Writing long research papers is always a strain on your attention span. If you have trouble avoiding distractions during those long stretches, FocusWriter might be able to help. FocusWriter is a minimalist word processor that removes all the distracting icons and sticks only to what you type. You’re also free to choose your own customized backgrounds, with other special features like timed alarms, daily goals, and optional typewriter sound effects.
Google Charts
This useful and free tool from Google lets you create simple charts and graphs based on whatever data you input. Charts and graphs are excellent visual aids for expressing numeric data, a perfect complement if you need to explain complicated evidential research.
Grammarly goes way beyond grammar, helping you hone word choice, checking your text for plagiarism, detecting your tone, and more. For foreign-language learners, it can make your English sound more fluent, and even those who speak English as their primary language benefit from Grammarly’s suggestions.
Research paper FAQs
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that analyzes, evaluates, or interprets a single topic with empirical evidence and statistical data.
When will I need to write a research paper in college?
Many college courses use research papers to test a student’s knowledge of a particular topic or their research skills in general. While research papers depend on the course or professor, you can expect to write at least a few before graduation.
How do I determine a topic for my research paper?
If the topic is not assigned, try to find a topic that’s general enough to provide ample evidence but specific enough that you’re able to cover all the basics. If possible, choose a topic you’re personally interested in—it makes the work easier.
Where can I conduct research for my paper?
Today most research is conducted either online or in libraries. Some topics might benefit from old periodicals like newspapers or magazines, as well as visual media like documentaries. Museums, parks, and historical monuments can also be useful.
How do I cite sources for a research paper?
The correct formatting for citations depends on which style you’re using, so check the assignment guidelines. Most school research reports use either MLA or APA styles, although there are others.
This article was originally written by Karen Hertzberg in 2017. It’s been updated to include new information.

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Research Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Research Paper
There will come a time in most students' careers when they are assigned a research paper. Such an assignment often creates a great deal of unneeded anxiety in the student, which may result in procrastination and a feeling of confusion and inadequacy. This anxiety frequently stems from the fact that many students are unfamiliar and inexperienced with this genre of writing. Never fear—inexperience and unfamiliarity are situations you can change through practice! Writing a research paper is an essential aspect of academics and should not be avoided on account of one's anxiety. In fact, the process of writing a research paper can be one of the more rewarding experiences one may encounter in academics. What is more, many students will continue to do research throughout their careers, which is one of the reasons this topic is so important.
Becoming an experienced researcher and writer in any field or discipline takes a great deal of practice. There are few individuals for whom this process comes naturally. Remember, even the most seasoned academic veterans have had to learn how to write a research paper at some point in their career. Therefore, with diligence, organization, practice, a willingness to learn (and to make mistakes!), and, perhaps most important of all, patience, students will find that they can achieve great things through their research and writing.
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper:
- Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper.
- Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics, whether the topic be one that is assigned or one that the student chooses themselves.
- Identifying an Audience - This section will help the student understand the often times confusing topic of audience by offering some basic guidelines for the process.
- Where Do I Begin - This section concludes the handout by offering several links to resources at Purdue, and also provides an overview of the final stages of writing a research paper.
- How to Order
Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
14 min read
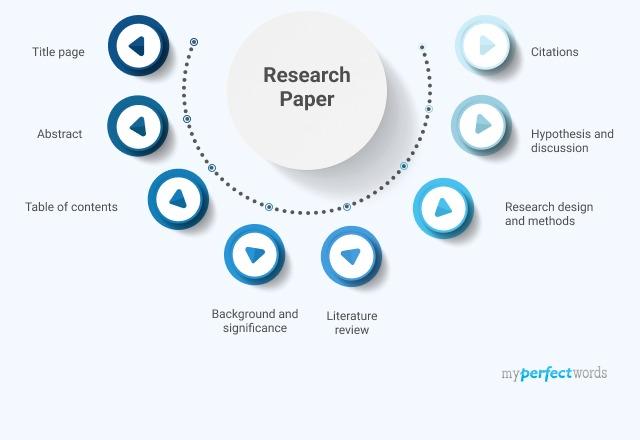
People also read
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Have you ever felt overwhelmed by the prospect of writing a research paper? Do complex guidelines and the sheer volume of work leave you feeling stuck?
The pressure to produce a well-researched paper can be daunting, often overshadowing the excitement of exploring new ideas.
But fret not!
In this blog, we'll guide you through the research paper writing process with simplicity and clarity. We'll also provide you with step-by-step instructions and valuable insights on how to write an effective research paper.
Let’s get started.
- 1. What is a Research Paper?
- 2. How to Write a Research Paper?
- 3. Research Paper Examples
- 4. Research Paper Writing Checklist
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is a scholarly document that presents a systematic and structured exploration of a specific topic, issue, or question.
It is a formal academic piece of writing that synthesizes existing knowledge, incorporates original research or analysis, and offers well-supported conclusions or insights.
Research papers are typically written by students, academics, or researchers and serve to contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field of study.
How Long Should A Research Paper be?
Generically, a research paper typically falls within the range of 6,000 to 8,000 words, which is equivalent to approximately 15-20 pages double-spaced with standard formatting.
However, for different academic levels, here is a general idea:
- Undergraduate Research Paper : Around 10-15 pages (double-spaced).
- Master's Thesis : 50-100 pages or more, depending on the institution and discipline.
- Doctoral Dissertation : 150-300 pages or more, depending on the field and research depth.
How to Write a Research Paper?
Writing a research paper is a structured and methodical process that involves several essential steps.
Following these guidelines will help you produce a well-organized and academically sound research paper.
How to Start a Research Paper?
A good research paper must follow a proper structure and format. The first important step in the writing process is to start your paper perfectly.
1. Understand the Research Paper Requirements
To succeed in your research paper assignment, it's crucial to comprehend the topic and the paper's structure requirements fully. Here are key steps to enhance your understanding:
- Read Instructions : Thoroughly read assignment instructions. Seek clarification from your professor if any parts are unclear.
- Identify Purpose : Understand the main purpose of your research paper, whether it's informing or persuading readers.
- Note Key Details: Take note of essential details, including the deadline, word count, submission method, and required formatting style.
- List Key Points : Create a list of key points you need to cover in your paper.
- Set a Timeline : Plan a schedule for starting, writing, and editing your research paper.
2. Consider the Target Audience
Consider your audience's knowledge and expertise level as it influences writing style, word choice, and the depth of information required:
- For master's level research, expect an expert audience.
- Undergraduate papers can cater to both general and expert readers.
3. Choose the Right Research Paper Topic
Selecting the right topic is crucial. If you have the option to choose, follow these steps:
- Brainstorm Ideas : Generate ideas for your topic. Seek input from professors or specialists for a unique approach.
- Freewrite : Use freewriting to narrow down a broad topic.
- Review Research Work : Find inspiration in other research papers, especially in their discussion and recommendation sections.
- Challenge and Interest : Choose a challenging research paper topic that piques your interest and can engage your audience.
- Specificity : Avoid overly technical or general topics. Opt for an original, specific idea aligned with your research paper's criteria.
4. Conduct Thorough Research
Thorough research is vital for finding relevant ideas, focus, and direction. Ask these questions:
- Gap in Research : Is there a gap in previous research on your topic?
- Recent Developments : Are there recent developments in your subject?
- Debates : Are there ongoing debates related to your topic?
- Unique Perspective : Do you possess a unique perspective on the topic?
5. Developing a Strong Thesis Statement
After research, create a strong, concise thesis statement. It should serve as the central argument, stating the purpose and position of your paper.
Support it with solid evidence and reasoning. Ensure your thesis is clear concise, and guides your writing throughout the research paper process.
If you’re struggling in starting your paper, check out this guide on how to start a research paper!
Preparing a Research Paper Proposal
A research proposal is vital for framing your research project. To create an effective research proposal, address these key questions:
- What is your research objective?
- Why is this research necessary?
- How will you approach it?
A well-structured research proposal includes these sections:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Background and significance
- Literature review
- Research design and methods
- Hypothesis and discussion

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Writing the First Draft
In the first draft, your focus is on:
- Translating ideas into arguments
- Adding detail and structureUnderstanding the paper's overall flow
- Adhering to the research paper format
- Maintaining clear organization
- Properly explaining ideas and findings
- Ensuring flexibility for future adjustments
- Providing proper citations
1. Create a Research Paper Outline
An organized research paper outline is crucial for planning your structure and content. It serves as a roadmap for your writing process. Here are some components of an effective outline:
- Table of Contents
- Literature Review
- Bibliography
2. Writing an Abstract
The abstract is a concise summary of your paper. Keep it between 150 and 250 words, highlighting key points from each section.
3. Writing a Research Paper Introduction
The introduction should answer 'What,' 'Why,' and 'How' questions:
- What : Clearly specify the topic, historical context, and key terms.
- Why : Discuss the significance of your research.
- How : Outline the main elements to be covered.
4. Crafting a Literature Review
In the literature review , discuss existing research on your topic. Locate and analyze scholarly articles, highlighting their relevance to your study. Present the past, present, and expected future of the issue.
5. Methodology
Methodology outlines how you conducted your research and collected data. It should be detailed enough that another researcher could replicate your study. In this section, you should include:
- Study Design : Describe the type of study (e.g., experimental, observational, survey) and its rationale.
- Participants : Provide information about the number, characteristics, and selection criteria of the participants.
- Data Collection: Explain the instruments, tools, or techniques used to gather data. Include details such as questionnaires, surveys, interviews, or experiments.
- Procedure : Describe the step-by-step process of your research, including how data was collected and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis: Specify the statistical or analytical methods used to process and interpret the data.
The Results section presents the findings of your study. It should be factual and data-driven, without interpretation. Include:
- Data Presentation: Use tables, figures, and charts to present your data clearly.
- Descriptive Statistics : Report essential statistical measures like means, standard deviations, or percentages.
- Inferential Statistics: Use appropriate statistical tests to analyze your data.
- Textual Description : Summarize the key findings and refer to tables or figures where necessary.
7. Discussion
This is where you interpret your results, discuss their implications, and relate them to your research question. Include:
- Interpretation : Explain the meaning and significance of your findings.
- Comparison to Existing Research : Compare your results to previous studies and explain how they align or differ.
- Limitations : Address the limitations of your study and potential sources of bias.
- Future Research : Suggest areas for future research or improvements to your methodology.
8. Writing a Research Paper Conclusion
In the conclusion:
- Summarize your paper
- Reiterate how you addressed the main idea and research questions
- Avoid introducing new information
- Suggest potential future research
9. Bibliography
The Bibliography (or References) section lists all the sources you cited in your paper. It should follow a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Arrange your sources alphabetically and format them according to the style guidelines.
10. Appendix
The Appendix is an optional section where you can include supplementary material that supports your research but is too detailed or extensive to include in the main body of the paper.
Examples of content for the appendix might include raw data, additional charts, questionnaires, or extended descriptions of methods.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Writing the Second Draft
Once you've roughly organized your thoughts in the first draft, proceed to craft the second draft of your paper.
Consider the following aspects to perfect your second draft:
- Effectively Address the Main Argument : Review your paper to ensure you've effectively addressed the main argument or research problem statement.
- Identify Assumptions : Identify any assumptions that may need inclusion or clarification in your paper.
- Logical Structure : Rearrange and structure your ideas logically to enhance the paper's flow.
- Trim Irrelevant Ideas : Remove any outdated or irrelevant ideas from the first draft and introduce fresh, unique approaches.
- Create a Work Cited List : Start compiling a list of works cited according to your chosen citation style guide.
Revising and Proofreading
The final step in the writing process involves revising and proofreading to ensure your paper is well-developed and error-free.
Confirm the following aspects:
- Meeting Requirements : Verify if your paper meets all the specified requirements.
- Logical Paragraph Order : Check for a logical order of paragraphs and ideas.
- Eliminate Irrelevant Details : Remove any irrelevant or extra details.
- Grammar and Punctuation : Look for grammatical, punctuation, and spelling errors.
- Sentence Structure : Identify and rectify any issues with sentence structures.
- Consistency : Ensure consistency in font, headings, page numbers, and formatting throughout the paper.
- Proper Referencing : Confirm that all sources are correctly referenced following the guidelines of your chosen citation style.
Research Paper Examples
Examples serve as valuable templates and guides, showcasing various formatting styles, organization, and approaches to research paper writing.
Research Paper Example
Research Paper Sample
APA Style Research Paper
MLA Style Research Paper
How to Write a Research Paper pdf
How to Write a Research Paper sample
How to Write a Research Paper for journal publication
How to Write a Research Paper format
If you want more examples for research papers, check out our blog about research paper examples !
Research Paper Writing Checklist
This stage often refers to the phase of conducting research for your paper. This checklist will help you ensure that you cover all the necessary steps during this phase:
|
In summary, this guide will assist you in writing a perfect research paper. However, we understand that it may be quite challenging for students who lack strong writing and research skills.
At MyPerfectWords.com, we will assist you with any type of writing, whether it be research paper or thesis writing.
You can hire an expert writer for your research papers from our essay writer service .
So why wait? Contact us with “ write my research paper ” requests, and let us handle the rest!
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write a research paper using chatgpt.
While ChatGPT can assist in the writing process, it should not replace scholarly research, or critical analysis. Avoid relying solely on ChatGPT for factual information, and always verify data through authoritative sources. Use it as a complementary tool rather than the primary source for your research paper.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading


APA 7: Sample Paper
- Paper Sections
- Quote & Paraphrase
- Format in Word
- In-Text Citations
- Reference List
- Sample Paper
Examples of the Different Paper Sections
- Title Page - APA 7 Example
- References Page
- Student Paper - Example in APA Format Includes title page, body, and references.
- Sample Annotated Student Paper in APA Style
- APA 7 Quick Reference Guide
Optional Paper Sections
- Headings - APA 7 Style Guide
- Accessible Use of Colors in APA 7
- Figures - APA 7 The basics of figure setup, including figure components, principles of figure construction, and placement of figures in a paper.
- Tables - APA 7 The basics of table setup, including table components, principles of table construction, and placement of tables in the paper.
- << Previous: Reference List
- Next: FAQs >>
Home / MLA Sample Paper
MLA Sample Paper
Mla sample paper #1.
If you’ve been wondering how to produce a research paper that is strong in both formatting and writing, you’ve come to the right place.
Check out our first sample paper below. It is a helpful and clearly labeled visual aid to refer to. Note that while these sample papers do not include MLA abstracts , you should check with your instructor to see if an abstract should be included.
Visual Sample Paper
The example research paper below is one that was written in college for a course on the Inklings. The Inklings were a group of writers in England before WWII, including C.S. Lewis and J.R.R. Tolkien.
The abbreviated MLA paper below (linked here without annotations) is about J.R.R. Tolkien’s Lord of the Rings and how the author used myth, story, and song to link all of his works together. Tolkien is famous for creating a fantasy universe called Middle-earth, which readers can’t truly understand until they read all of the books about Middle-earth ( The Silmarillian, The Hobbit, and The Lord of the Rings ).
Since we’re here to learn how to format an essay, we’ve pointed out some important things about the paper to help you write a correctly formatted essay.
For starters, the essay is in MLA format. That means it follows the style manual of the Modern Language Association, which tells you how to format the paper itself and every source you cite. You’ll also see notes like how long a paragraph should be, how to use commas properly, and how to correctly punctuate a title. Some of these guidelines are different from those in APA format , so be sure to confirm you are using the correct style in your paper.
Pay special attention to the MLA format works cited. We only used one type of source (books), but both citations are correct according to the 9th edition of MLA, published in 2021. When you’re writing your own paper, you need to make sure you always use the most recent edition of the style manual. You’ll also want to check with your instructor to see if you need to include an MLA annotated bibliography with your paper, which contains additional information summarizing and evaluating each source after the regular citation.
Whether you need MLA, APA citations , or Chicago style notes, look up the latest edition before turning in a paper.

MLA Sample Paper #2
See below for an example paper or click below to download it as a Word Document.
The MLA header should be one inch from the top and left margins. The heading and the entire paper should be double spaced.
Eli YaffarabeProfessor Rapheor
28 August 2018
Privatization of Prisons in Texas
The privatization of governmental services has increased dramatically in the past decade as local, state, and federal agencies have searched for ways to cut costs while still meeting their mandated responsibility to provide various public services. This privatizing trend has particularly affected the criminal justice system. Since the early 1990s, privatized correctional facilities have increased significantly, nationally and statewide. This policy has far-ranging consequences not only within the criminal justice system, but as an instructive example for government officials when considering the costs and benefits of privatization as a public policy option. By 2001, thirty states, the District of Columbia, and Puerto Rico had privately-operated correctional facilities (Austin and Coventry 4). This movement has incited considerable debate and controversy, mainly because prison privatization calls for giving the private sector direct control over the lives of a captive human population.
Surprisingly, there has been little objective and concrete analysis of the privatization of prisons in the United States. This is probably for two reasons: first, ideological arguments on the matter have pushed out substantive research, and second, because this trend has only recently accelerated in the U.S. and mainly on a state level. However, case studies and statistics at the state level are more accessible. With capacity for over 30,000 prisoners in 43 facilities, the state of Texas has privatized more of its prison system than any state in the nation (McDonald and Patten Jr. iv).
Yaffarabe 2
Public policy concerning the criminal justice system has become more daunting and important in the last decade. The problems in the system are twofold: an overcrowding prison population, mainly due to “three strikes” legislation and reducing early parole; and the costs of operating prisons with this growing population (Austin and Coventry). According to the most recent U.S. Department of Justice survey, slightly over 2.2 million people were incarcerated in correctional facilities in this country in 2003. In comparison, in 1993, 1.37 million people were imprisoned in this country (Beck and Harrison 1).
At the same time, the growth of privately operated correctional facilities has increased significantly in this country. Private prisons now hold 95,522 inmates in this country, which is 6.5 percent of total prisoners (Beck and Harrison 5). In Texas, 16,570 inmates (10 percent of its prison population) are held in private facilities, about 10,000 more than the next highest state. Furthermore, six states had at least 25 percent of their prison population housed in private prisons, led by New Mexico (44%), Alaska (31%), and Montana (29%). These current statistics show that while state governments have been forced to manage and operate overcrowded and over-capacity prisons at considerable costs, many have turned to the private sector to operate prisons (McDonald and Patten Jr.). According to the General Accounting Office, prison operating costs have grown steadily since 1980, increasing almost 550 percent since 1980 based on inflation-adjusted dollars (Austin and Coventry 1).
Prison privatization started in the early 1980s, ostensibly to ease the burden on taxpayers by offering financial relief to private companies to run state prisons. Thomas Beasley founded Corrections Corporation of America in 1983, “the nation’s leader in the construction and management of private prisons” (Darling). That year, Corrections Corporation of America set up the first privately-operated prison in Tennessee. Since then, the number of private
Yaffarabe 3
correctional facility firms has grown to 14 (Austin and Coventry 3). The privatization of prisons occurs in two ways. First, state government can contract out (or outsource) specific services in a correctional facility to a private company after a bidding process. Second, and more radically, private companies build their own privately-managed prisons and contract with state governments to house their inmates. This latter approach, giving private correctional facility firms wide latitude over inmates, is taken in the Texas criminal justice system. In fact, many of these privately operated facilities “have no relationship at all with the state governments in these states, other than an obligation to pay corporate income taxes” (McDonald and Patten Jr. v).
(Due to its length, the remainder of this sample paper is omitted).
Yaffarabe 4
Works Cited Page
Austin, James, and Garry Coventry. Emerging Issues on Privatized Prisons . Bureau of Justice Assistance, Feb. 2001, www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/bja/181249.pdf.
Beck, Allen J., and Paige Harrison. Prisoners in 2003 . Bureau of Justice Statistics, Nov. 2004, www.bjs.gov/content/pub/pdf/p03.pdf.
McDonald, Douglas, and Carl Patten Jr. Governments’ Management of Private Prisons . Abt Associates, 15 Sept. 2003, www.ncjrs.gov/pdffiles1/nij/grants/203968.pdf.
Darling, Michael. “Pitt News: University of Pittsburgh Shouldn’t Lend Its Name to Prison Privatization.” CorpWatch , 15 Nov. 2004, corpwatch.org/article/pitt-news-univeristy-pittsburgh-shouldnt-lend-its-name-prison-privatization.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed next to the text being cited. The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s name . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when text is quoted from the source being cited. In-text citations are mentioned in the text in two ways: as a citation in prose or a parenthetical citation.
Citation in prose
Citations in prose are incorporated into the text and act as a part of the sentence. Usually, citations in prose use the author’s full name when cited the first time in the text. Thereafter, only the surname is used. Avoid including the middle initial even if it is present in the works-cited-list entry. An example of the first citation in prose for a source with one author is given below:
Doug Barry explains the status of the UK.
Parenthetical
Parenthetical citations add only the author’s surname at the end of the sentence in parentheses. An example of a parenthetical citation is given below:
The status of the UK is explained (Barry).
Examples of in-text citations
Here are a few examples of in-text citations for works with various numbers and types of authors:
Use both the first name and surname of the author if you are mentioning the author for the first time in the prose. In subsequent occurrences, use only the author’s surname. Always use only the author’s surname in parenthetical citations.
Citation in prose:
First mention: Stephen George asserts …. (17).
Subsequent occurrences: George argues …. (17).
Parenthetical:
…. (George 17).
Two authors
Use the first name and surname of both authors if you are mentioning the work for the first time in the prose. In subsequent occurrences, use only the surnames of the two authors. Always use only the authors’ surnames in parenthetical citations. Use “and” to separate the two authors in parenthetical citations.
First mention: Kane Williams and Clark Ronald ….
Subsequent occurrences: Williams and Ronald ….
…. (Williams and Ronald).
Three or more authors
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues.” For parenthetical citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “et al.”
Krishnan Sethu and colleagues…. or Krishnan Sethu and others ….
…. (Sethu et al.).
Corporate author
For citations in prose, treat the corporate author like you would treat the author’s name. For parenthetical citations, shorten the organization name to the shortest noun phrase. For example, shorten the Modern Language Association of America to Modern Language Association.
The Language Literary Association of Canada….
…. (Language Literary Association).
If there is no author for the source, use the source’s title in place of the author’s name for both citations in prose and parenthetical citations.
When you add such in-text citations, italicize the text of the title. If the source title is longer than a noun phrase, use a shortened version of the title. For example, shorten the title Fantastic Beasts and Where to Find Them to Fantastic Beasts .
Endgame explains …. (121).
…. ( Endgame 121).
In MLA style, two types of citations are used to cite a source: a short citation used within the text (called the in-text citation) and a full citation (called the works cited list entry) within the works cited list, which appears at the end of a paper.
The works cited list entry provides the complete details of a source. An in-text citation is a short citation that is placed next to the text being cited. The in-text citation lets the reader know that the information is derived from the cited source, and helps the reader find the full citation within the works cited list.
In order to properly cite a source in MLA style, you must have both citation types in your paper. Every in-text citation has a works cited list entry. Every works cited list entry has at least one (maybe more) corresponding in-text citation.
In-text citations
The basic element needed for an in-text citation is the author’s surname . The publication year is not required in in-text citations. Sometimes, page numbers or line numbers are also included, especially when text is quoted from the source being cited.
First mention: Sian Anderson studies ….
Subsequent occurrences: Anderson analyzes ….
….(Anderson)
or if quoting directly:
…(Anderson 9)
First mention: Paul Fin and Anna Gabriel ….
Subsequent occurrences: Fin and Gabriel ….
….(Fin and Gabriel)
…(Fin and Gabriel 27)
Paul Hill and colleagues…. or Paul Hill and others ….
….(Hill et al.)
…(Hill et al. 138)
Examples of works cited list entries
Below are a few examples of different types of works cited list entries. The examples given are for one author.
Steinman, Louise. The Knowing Body: Elements of Contemporary Performance and Dance . Shambhala Publications, 1986.
Journal article
Barad, K. “Nature’s Queer Performativity.” Qui Parle , vol. 19, no. 2, 2011, pp. 121–58.
Webpage of a website
Midgelow, Vida L. “Experiences and Perceptions of the Artistic Doctorate: A Survey Report.” Artistic Doctorates in Europe, 5 Feb. 2018, www.artisticdoctorates.com/2017/12/28/experiences-and-perceptions-of-the-artistic-doctorate-survey-report/ .
YouTube video
“Behind the Scenes Chili’s Baby Back Ribs Spot.” YouTube , uploaded by Alvin Chea, 11 Sept. 2017, www.youtube.com/watch?v=gTDLh7gNRYA .
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Example
Last updated on: Nov 20, 2023
Research Paper Example: Samples to Write a Research Paper
By: Nathan D.
Reviewed By: Jacklyn H.
Published on: Jun 11, 2019

Working on your research paper?
Want to learn the dos and don’ts of writing a research paper? Learn from examples!
We have compiled some examples to help you get started. If you are in need of a research paper example, take a look at these samples and choose one that is best suited for your research paper writing needs.
You can also use these as templates to create your own research papers. There are many different samples available here so please feel free to browse around and find the perfect one for yourself.
Stay with us to learn more.

On this Page
What is a Research Paper?
A research paper is different from a usual kind of essay and assignment. It requires more research and explanation than any other assignment and has a set structure for it. It is a complex type of academic paper. Usually, students studying science write them for their coursework and as a degree requirement.
It is generally simpler than high school term papers and a dissertation that students write in humanities and other academic groups. Research papers are common in the academic world, and students, regardless of the field of study, get them as part of their degree requirements.
The research writing skills are invaluable for everyone and not just for the students only. Young professionals and entrepreneurs benefit a lot from these skills. Writing a research paper properly means that you have to study, observe, and choose a topic. The step-by-step guide for writing a research paper will help you find answers to your research questions.

Get Quick AI Research Help!
College Research Paper Example
Examples work great when you are looking to learn something in less time and with more efficiency. Below, we have added some good research paper examples. With them, you could learn about a research paper format and structure.
Moreover, we will also be able to add relevant and credible sources in each section.
APA Style Research Paper
Below is an APA-style sample research paper guide. Each section is explained separately. By going through it, you will know how to format and write each section of your APA research paper successfully.
APA STYLE RESEARCH PAPER
MLA Style Research Paper
This MLA-style research paper explains all the sections and formatting of the paper in detail. This will help you in writing an MLA-style paper successfully.
MLA STYLE RESEARCH PAPER
Subject-Related Research Paper Example
Research papers are not limited to a specific field area. Instead, students need to write research papers for almost every subject. Check out the following research paper examples for several subjects.
Computer Science Research Paper
The research paper is about computer science and how science is a part of it. Scientific research papers are different from what the students do in other disciplines. They are more statistical in nature and often have graphs and visual representations of the data.
COMPUTER SCIENCE RESEARCH PAPER
Chemical Engineering Research Paper
Chemical engineering studies the engineering of different chemicals and how they work together. The following chemical engineering research paper is about the calcium looping cycle for carbon dioxide obtained from different manufacturing processes.
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING RESEARCH PAPER
Nursing Research Paper
The research paper explores the benefits of participating in research. Medical sciences heavily rely on real-life research and results, and therefore, it uses medical professionals as subjects. The paper discusses how the experience contributes to their professional life and helps them work better.
NURSING RESEARCH PAPER
Psychology Research Paper
Psychology is the study of the mind. The paper examines the positive effects of psychology at school. It discusses how it will help in controlling the mental illnesses in adolescents and help in enhancing their health.
PSYCHOLOGY RESEARCH PAPER

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
Research Paper Outline Example
A research paper’s outline may consist of different formats and sections based on the research topic. Therefore, you must ask your instructor to go through the research content and guide you.
Before starting to write a research paper, you will need to write and submit a research proposal. A research proposal includes the details of your proposed research, the significance of the research, the impact your research will have on the area of research, and the methodology that you will use. For writing a research proposal , you need to discuss all of these factors.
A research paper follows a set pattern and structure. Just like an essay or any other assignment, it also has some sections that you have to include in it. However, before formatting, make sure that you follow the referencing style that your teacher has provided.
The main research paper outline is given below. Pay attention to the document to get a detailed idea of the writing process.
RESEARCH PAPER OUTLINE EXAMPLE
This outline includes the following sections:
An abstract is usually written after the entire paper. It explains the research question and the expected outcome of the research.
Here, we have added an abstract example to help you see how to write an engaging abstract in no time.
RESEARCH PAPER ABSTRACT EXAMPLE
Introduction
It is the first section of the research. It gives a background of the research, explains the main research topic briefly, and presents the hypothesis.
A strong introduction is essential for a strong research paper because no one will read the paper if the introduction is lousy and weak. Go through the attached example to learn how to write a good research paper example.
RESEARCH PAPER INTRODUCTION EXAMPLE
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement presents the main topic and aim of the research. It is brief and based on a few lines only.
The following downloadable PDF has some great thesis statement examples that are engaging and help to convey the message powerfully.
RESEARCH PAPER THESIS EXAMPLE
This is the meatiest part of the research paper. It includes all the chapters and sections of the research.
The main body of the paper discusses the entire paper in detail. All the main points and arguments of the paper are added in this section. Learn how to add and discuss everything by going through the following downloadable PDF.
EXAMPLE OF DISCUSSION IN RESEARCH PAPER
Literature Review
It is added in the main body section. It includes the study of previous relevant studies and research and discusses their outcome. You will discuss your main topic and draw parallels and contrasts with these existing studies.
EXAMPLE OF A LITERATURE REVIEW IN A RESEARCH PAPER
Research Methodology
Discuss the type of research that you are going to use for the research. Usually, scientific research is based on quantitative research and includes statistical analysis. Theoretical research uses qualitative method and includes studying of theory and other research.
EXAMPLE OF METHODOLOGY IN RESEARCH PAPER
Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
This is the closing part of your research paper as you will conclude your research here. Mention your thesis statement and main research findings here and close it.
The conclusion does not mean that you have a chance to add some new ideas or points here; it would be a disaster. To know better, go through the following PDF.
RESEARCH PAPER CONCLUSION EXAMPLE
An appendix is an optional section in the research paper. It contains terms and topics that are too detailed to be added to the main text. It also states the topics and page number, which makes it easier to find relevant topics.
APPENDICES EXAMPLE IN RESEARCH PAPER
Now you must have explored different examples of a research paper. You can generate more examples according to your field of study by using our FREE AI powered paper typer .
However, if you are still wondering how to write it perfectly, consult the best write essay for me? service now.
5StarEssays.com offers high-quality and affordable research paper writing help. Place your order now to get your scientific research paper, or any other type of paper, written by experts.

Education, Literature
Nathan completed his Ph.D. in journalism and has been writing articles for well-respected publications for many years now. His work is carefully researched and insightful, showing a true passion for the written word. Nathan's clients appreciate his expertise, deep understanding of the process, and ability to communicate difficult concepts clearly.
Was This Blog Helpful?
Keep reading.
- How to Write a Research Paper - Writing Guide & Examples

- 20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Research Papers

- Learn How to Write an Abstract - Steps & Examples

- How to Write a Literature Review: Steps and Outline

- How to Start a Research Paper - 9 Simple Steps

- Psychology Research Topics - 170+ Ideas for Your Paper

- How to Write a Hypothesis - A Step-by-Step Guide

- Writing a Research Proposal - Outline, Format, and Examples

- Good Research Paper Topics & Ideas for Students

- Good History Research Paper Topics For Your Help

- How to Cite a Research Paper with the Help of Examples

- How to Write a Research Methodology in 10 Simple Steps

- Research Paper Outline - Basic Format & Sample

- Great Sociology Research Topics & Ideas (2024)

People Also Read
- literary analysis essay writing
- debate topics
- how to write a press release
- personal essay
- how to write a rhetorical analysis essay
Burdened With Assignments?

Advertisement
- Homework Services: Essay Topics Generator
© 2024 - All rights reserved
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example
Published on August 7, 2022 by Courtney Gahan . Revised on August 15, 2023.

A research paper outline is a useful tool to aid in the writing process , providing a structure to follow with all information to be included in the paper clearly organized.
A quality outline can make writing your research paper more efficient by helping to:
- Organize your thoughts
- Understand the flow of information and how ideas are related
- Ensure nothing is forgotten
A research paper outline can also give your teacher an early idea of the final product.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Research paper outline example, how to write a research paper outline, formatting your research paper outline, language in research paper outlines.
- Definition of measles
- Rise in cases in recent years in places the disease was previously eliminated or had very low rates of infection
- Figures: Number of cases per year on average, number in recent years. Relate to immunization
- Symptoms and timeframes of disease
- Risk of fatality, including statistics
- How measles is spread
- Immunization procedures in different regions
- Different regions, focusing on the arguments from those against immunization
- Immunization figures in affected regions
- High number of cases in non-immunizing regions
- Illnesses that can result from measles virus
- Fatal cases of other illnesses after patient contracted measles
- Summary of arguments of different groups
- Summary of figures and relationship with recent immunization debate
- Which side of the argument appears to be correct?
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Follow these steps to start your research paper outline:
- Decide on the subject of the paper
- Write down all the ideas you want to include or discuss
- Organize related ideas into sub-groups
- Arrange your ideas into a hierarchy: What should the reader learn first? What is most important? Which idea will help end your paper most effectively?
- Create headings and subheadings that are effective
- Format the outline in either alphanumeric, full-sentence or decimal format
There are three different kinds of research paper outline: alphanumeric, full-sentence and decimal outlines. The differences relate to formatting and style of writing.
- Alphanumeric
- Full-sentence
An alphanumeric outline is most commonly used. It uses Roman numerals, capitalized letters, arabic numerals, lowercase letters to organize the flow of information. Text is written with short notes rather than full sentences.
- Sub-point of sub-point 1
Essentially the same as the alphanumeric outline, but with the text written in full sentences rather than short points.
- Additional sub-point to conclude discussion of point of evidence introduced in point A
A decimal outline is similar in format to the alphanumeric outline, but with a different numbering system: 1, 1.1, 1.2, etc. Text is written as short notes rather than full sentences.
- 1.1.1 Sub-point of first point
- 1.1.2 Sub-point of first point
- 1.2 Second point
To write an effective research paper outline, it is important to pay attention to language. This is especially important if it is one you will show to your teacher or be assessed on.
There are four main considerations: parallelism, coordination, subordination and division.
Parallelism: Be consistent with grammatical form
Parallel structure or parallelism is the repetition of a particular grammatical form within a sentence, or in this case, between points and sub-points. This simply means that if the first point is a verb , the sub-point should also be a verb.
Example of parallelism:
- Include different regions, focusing on the different arguments from those against immunization
Coordination: Be aware of each point’s weight
Your chosen subheadings should hold the same significance as each other, as should all first sub-points, secondary sub-points, and so on.
Example of coordination:
- Include immunization figures in affected regions
- Illnesses that can result from the measles virus
Subordination: Work from general to specific
Subordination refers to the separation of general points from specific. Your main headings should be quite general, and each level of sub-point should become more specific.
Example of subordination:
Division: break information into sub-points.
Your headings should be divided into two or more subsections. There is no limit to how many subsections you can include under each heading, but keep in mind that the information will be structured into a paragraph during the writing stage, so you should not go overboard with the number of sub-points.
Ready to start writing or looking for guidance on a different step in the process? Read our step-by-step guide on how to write a research paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Gahan, C. (2023, August 15). How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/outline/
Is this article helpful?
Courtney Gahan
Other students also liked, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, writing a research paper introduction | step-by-step guide, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

How to Write a Research Proposal: (with Examples & Templates)

Table of Contents
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers’ plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed research that you intend to undertake. It provides readers with a snapshot of your project by describing what you will investigate, why it is needed, and how you will conduct the research.
Your research proposal should aim to explain to the readers why your research is relevant and original, that you understand the context and current scenario in the field, have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, and that the research is feasible given the usual constraints.
This article will describe in detail the purpose and typical structure of a research proposal , along with examples and templates to help you ace this step in your research journey.
What is a Research Proposal ?
A research proposal¹ ,² can be defined as a formal report that describes your proposed research, its objectives, methodology, implications, and other important details. Research proposals are the framework of your research and are used to obtain approvals or grants to conduct the study from various committees or organizations. Consequently, research proposals should convince readers of your study’s credibility, accuracy, achievability, practicality, and reproducibility.
With research proposals , researchers usually aim to persuade the readers, funding agencies, educational institutions, and supervisors to approve the proposal. To achieve this, the report should be well structured with the objectives written in clear, understandable language devoid of jargon. A well-organized research proposal conveys to the readers or evaluators that the writer has thought out the research plan meticulously and has the resources to ensure timely completion.
Purpose of Research Proposals
A research proposal is a sales pitch and therefore should be detailed enough to convince your readers, who could be supervisors, ethics committees, universities, etc., that what you’re proposing has merit and is feasible . Research proposals can help students discuss their dissertation with their faculty or fulfill course requirements and also help researchers obtain funding. A well-structured proposal instills confidence among readers about your ability to conduct and complete the study as proposed.
Research proposals can be written for several reasons:³
- To describe the importance of research in the specific topic
- Address any potential challenges you may encounter
- Showcase knowledge in the field and your ability to conduct a study
- Apply for a role at a research institute
- Convince a research supervisor or university that your research can satisfy the requirements of a degree program
- Highlight the importance of your research to organizations that may sponsor your project
- Identify implications of your project and how it can benefit the audience
What Goes in a Research Proposal?
Research proposals should aim to answer the three basic questions—what, why, and how.
The What question should be answered by describing the specific subject being researched. It should typically include the objectives, the cohort details, and the location or setting.
The Why question should be answered by describing the existing scenario of the subject, listing unanswered questions, identifying gaps in the existing research, and describing how your study can address these gaps, along with the implications and significance.
The How question should be answered by describing the proposed research methodology, data analysis tools expected to be used, and other details to describe your proposed methodology.
Research Proposal Example
Here is a research proposal sample template (with examples) from the University of Rochester Medical Center. 4 The sections in all research proposals are essentially the same although different terminology and other specific sections may be used depending on the subject.

Structure of a Research Proposal
If you want to know how to make a research proposal impactful, include the following components:¹
1. Introduction
This section provides a background of the study, including the research topic, what is already known about it and the gaps, and the significance of the proposed research.
2. Literature review
This section contains descriptions of all the previous relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. Every study cited should be described in a few sentences, starting with the general studies to the more specific ones. This section builds on the understanding gained by readers in the Introduction section and supports it by citing relevant prior literature, indicating to readers that you have thoroughly researched your subject.
3. Objectives
Once the background and gaps in the research topic have been established, authors must now state the aims of the research clearly. Hypotheses should be mentioned here. This section further helps readers understand what your study’s specific goals are.
4. Research design and methodology
Here, authors should clearly describe the methods they intend to use to achieve their proposed objectives. Important components of this section include the population and sample size, data collection and analysis methods and duration, statistical analysis software, measures to avoid bias (randomization, blinding), etc.
5. Ethical considerations
This refers to the protection of participants’ rights, such as the right to privacy, right to confidentiality, etc. Researchers need to obtain informed consent and institutional review approval by the required authorities and mention this clearly for transparency.
6. Budget/funding
Researchers should prepare their budget and include all expected expenditures. An additional allowance for contingencies such as delays should also be factored in.
7. Appendices
This section typically includes information that supports the research proposal and may include informed consent forms, questionnaires, participant information, measurement tools, etc.
8. Citations

Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing. Planning the research proposal structure and content is an important stage, which if done efficiently, can help you seamlessly transition into the writing stage. 3,5
The Planning Stage
- Manage your time efficiently. Plan to have the draft version ready at least two weeks before your deadline and the final version at least two to three days before the deadline.
- What is the primary objective of your research?
- Will your research address any existing gap?
- What is the impact of your proposed research?
- Do people outside your field find your research applicable in other areas?
- If your research is unsuccessful, would there still be other useful research outcomes?
The Writing Stage
- Create an outline with main section headings that are typically used.
- Focus only on writing and getting your points across without worrying about the format of the research proposal , grammar, punctuation, etc. These can be fixed during the subsequent passes. Add details to each section heading you created in the beginning.
- Ensure your sentences are concise and use plain language. A research proposal usually contains about 2,000 to 4,000 words or four to seven pages.
- Don’t use too many technical terms and abbreviations assuming that the readers would know them. Define the abbreviations and technical terms.
- Ensure that the entire content is readable. Avoid using long paragraphs because they affect the continuity in reading. Break them into shorter paragraphs and introduce some white space for readability.
- Focus on only the major research issues and cite sources accordingly. Don’t include generic information or their sources in the literature review.
- Proofread your final document to ensure there are no grammatical errors so readers can enjoy a seamless, uninterrupted read.
- Use academic, scholarly language because it brings formality into a document.
- Ensure that your title is created using the keywords in the document and is neither too long and specific nor too short and general.
- Cite all sources appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
- Make sure that you follow guidelines, if provided. This includes rules as simple as using a specific font or a hyphen or en dash between numerical ranges.
- Ensure that you’ve answered all questions requested by the evaluating authority.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a summary of the main points about research proposals discussed in the previous sections:
- A research proposal is a document that outlines the details of a proposed study and is created by researchers to submit to evaluators who could be research institutions, universities, faculty, etc.
- Research proposals are usually about 2,000-4,000 words long, but this depends on the evaluating authority’s guidelines.
- A good research proposal ensures that you’ve done your background research and assessed the feasibility of the research.
- Research proposals have the following main sections—introduction, literature review, objectives, methodology, ethical considerations, and budget.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is a research proposal evaluated?
A1. In general, most evaluators, including universities, broadly use the following criteria to evaluate research proposals . 6
- Significance —Does the research address any important subject or issue, which may or may not be specific to the evaluator or university?
- Content and design —Is the proposed methodology appropriate to answer the research question? Are the objectives clear and well aligned with the proposed methodology?
- Sample size and selection —Is the target population or cohort size clearly mentioned? Is the sampling process used to select participants randomized, appropriate, and free of bias?
- Timing —Are the proposed data collection dates mentioned clearly? Is the project feasible given the specified resources and timeline?
- Data management and dissemination —Who will have access to the data? What is the plan for data analysis?
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal ?
A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Q3. How long should a research proposal be?
A3. Research proposal lengths vary with the evaluating authority like universities or committees and also the subject. Here’s a table that lists the typical research proposal lengths for a few universities.
| Arts programs | 1,000-1,500 | |
| University of Birmingham | Law School programs | 2,500 |
| PhD | 2,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Research degrees | 2,000-3,500 |
Q4. What are the common mistakes to avoid in a research proposal ?
A4. Here are a few common mistakes that you must avoid while writing a research proposal . 7
- No clear objectives: Objectives should be clear, specific, and measurable for the easy understanding among readers.
- Incomplete or unconvincing background research: Background research usually includes a review of the current scenario of the particular industry and also a review of the previous literature on the subject. This helps readers understand your reasons for undertaking this research because you identified gaps in the existing research.
- Overlooking project feasibility: The project scope and estimates should be realistic considering the resources and time available.
- Neglecting the impact and significance of the study: In a research proposal , readers and evaluators look for the implications or significance of your research and how it contributes to the existing research. This information should always be included.
- Unstructured format of a research proposal : A well-structured document gives confidence to evaluators that you have read the guidelines carefully and are well organized in your approach, consequently affirming that you will be able to undertake the research as mentioned in your proposal.
- Ineffective writing style: The language used should be formal and grammatically correct. If required, editors could be consulted, including AI-based tools such as Paperpal , to refine the research proposal structure and language.
Thus, a research proposal is an essential document that can help you promote your research and secure funds and grants for conducting your research. Consequently, it should be well written in clear language and include all essential details to convince the evaluators of your ability to conduct the research as proposed.
This article has described all the important components of a research proposal and has also provided tips to improve your writing style. We hope all these tips will help you write a well-structured research proposal to ensure receipt of grants or any other purpose.
References
- Sudheesh K, Duggappa DR, Nethra SS. How to write a research proposal? Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):631-634. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- Writing research proposals. Harvard College Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships. Harvard University. Accessed July 14, 2024. https://uraf.harvard.edu/apply-opportunities/app-components/essays/research-proposals
- What is a research proposal? Plus how to write one. Indeed website. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-proposal
- Research proposal template. University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed July 16, 2024. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/pediatrics/research/documents/Research-proposal-Template.pdf
- Tips for successful proposal writing. Johns Hopkins University. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://research.jhu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Tips-for-Successful-Proposal-Writing.pdf
- Formal review of research proposals. Cornell University. Accessed July 18, 2024. https://irp.dpb.cornell.edu/surveys/survey-assessment-review-group/research-proposals
- 7 Mistakes you must avoid in your research proposal. Aveksana (via LinkedIn). Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-mistakes-you-must-avoid-your-research-proposal-aveksana-cmtwf/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a phd research proposal.
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Avoid Plagiarism When Using Generative AI Tools
- What is Hedging in Academic Writing?
How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
The future of academia: how ai tools are changing the way we do research, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.

Title Page Setup
A title page is required for all APA Style papers. There are both student and professional versions of the title page. Students should use the student version of the title page unless their instructor or institution has requested they use the professional version. APA provides a student title page guide (PDF, 199KB) to assist students in creating their title pages.
Student title page
The student title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation, course number and name for which the paper is being submitted, instructor name, assignment due date, and page number, as shown in this example.
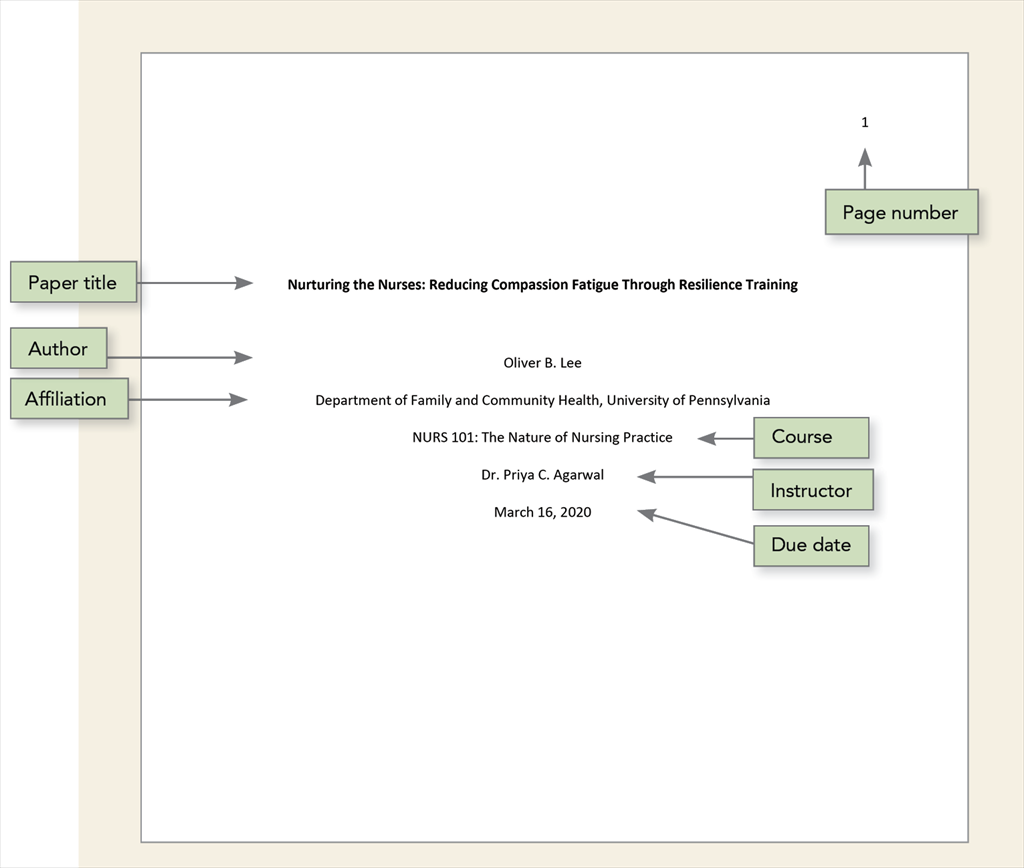
Title page setup is covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 2.3 and the Concise Guide Section 1.6
Related handouts
- Student Title Page Guide (PDF, 263KB)
- Student Paper Setup Guide (PDF, 3MB)
Student papers do not include a running head unless requested by the instructor or institution.
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the student title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names | Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Cecily J. Sinclair and Adam Gonzaga |
| Author affiliation | For a student paper, the affiliation is the institution where the student attends school. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author name(s). | Department of Psychology, University of Georgia |
| Course number and name | Provide the course number as shown on instructional materials, followed by a colon and the course name. Center the course number and name on the next double-spaced line after the author affiliation. | PSY 201: Introduction to Psychology |
| Instructor name | Provide the name of the instructor for the course using the format shown on instructional materials. Center the instructor name on the next double-spaced line after the course number and name. | Dr. Rowan J. Estes |
| Assignment due date | Provide the due date for the assignment. Center the due date on the next double-spaced line after the instructor name. Use the date format commonly used in your country. | October 18, 2020 |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
Professional title page
The professional title page includes the paper title, author names (the byline), author affiliation(s), author note, running head, and page number, as shown in the following example.
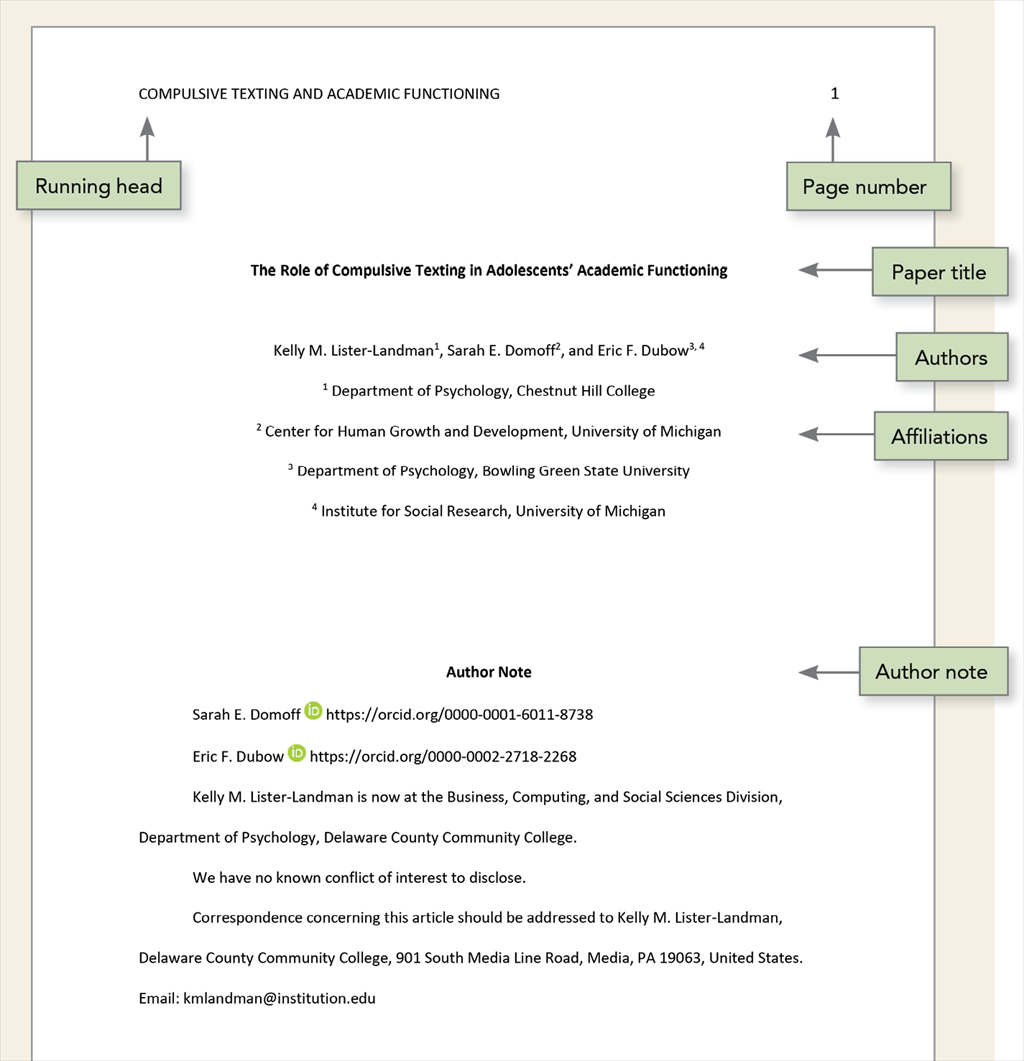
Follow the guidelines described next to format each element of the professional title page.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Paper title | Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. Capitalize of the title. Place the main title and any subtitle on separate double-spaced lines if desired. There is no maximum length for titles; however, keep titles focused and include key terms. |
|
| Author names
| Place one double-spaced blank line between the paper title and the author names. Center author names on their own line. If there are two authors, use the word “and” between authors; if there are three or more authors, place a comma between author names and use the word “and” before the final author name. | Francesca Humboldt |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals after author names to connect the names to the appropriate affiliation(s). If all authors have the same affiliation, superscript numerals are not used (see Section 2.3 of the for more on how to set up bylines and affiliations). | Tracy Reuter , Arielle Borovsky , and Casey Lew-Williams | |
| Author affiliation
| For a professional paper, the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated by a comma. Center the affiliation on the next double-spaced line after the author names; when there are multiple affiliations, center each affiliation on its own line.
| Department of Nursing, Morrigan University |
| When different authors have different affiliations, use superscript numerals before affiliations to connect the affiliations to the appropriate author(s). Do not use superscript numerals if all authors share the same affiliations (see Section 2.3 of the for more). | Department of Psychology, Princeton University | |
| Author note | Place the author note in the bottom half of the title page. Center and bold the label “Author Note.” Align the paragraphs of the author note to the left. For further information on the contents of the author note, see Section 2.7 of the . | n/a |
|
| The running head appears in all-capital letters in the page header of all pages, including the title page. Align the running head to the left margin. Do not use the label “Running head:” before the running head. | Prediction errors support children’s word learning |
|
| Use the page number 1 on the title page. Use the automatic page-numbering function of your word processing program to insert page numbers in the top right corner of the page header. | 1 |
Macro-Financial Implications of the Surging Global Demand (and Supply) of International Reserves
Research has shown that the unilateral accumulation of international reserves by a country can improve its own macro-financial stability. However, we show that when many countries accumulate reserves, the induced general equilibrium effects weaken financial and macroeconomic stability, especially for countries that do not accumulate reserves. The issuance of public debt by advanced economies has the opposite effect. We derive these results from a two-region model where private defaultable debt has a productive use. Quantitative counterfactuals show that the surge in reserves (public debt) contributed to reduce (increase) world interest rates but also to increase (reduce) private leverage. This in turn increased (decreased) volatility in both emerging and advanced economies.
We thank participants at the Impulse and Propagation Mechanisms Workshop of the 2024 NBER Summer Institute, the 2024 China International Conference in Macroeconomics at ChineseUniversity of Hong Kong, the Eighth CCER Summer Institute at Peking University, the Macroeconomics in Emerging Markets Conference at Columbia University, the conference on Emerging Markets: Capital Flows, Debt Overhang, Inflation, and Growth organized by the NBER, FLAR, and Banco Central de Reserva del Peru, and presentations at the IMF and the Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. We also thank our discussants, Mark Aguiar and Luis Gonzalo Llosa Velásquez, as well as Cristina Arellano, Javier Bianchi, and Illenin Kondo for helpful comments and suggestions. The views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Bureau of Economic Research.
MARC RIS BibTeΧ
Download Citation Data
More from NBER
In addition to working papers , the NBER disseminates affiliates’ latest findings through a range of free periodicals — the NBER Reporter , the NBER Digest , the Bulletin on Retirement and Disability , the Bulletin on Health , and the Bulletin on Entrepreneurship — as well as online conference reports , video lectures , and interviews .

- Library of Congress
- Research Guides
- Science & Technology
Technical Reports & Standards Collection Guide
Introduction.
- Technical Reports Collections
- Standards Collection
- American Documentation Institute (ADI)
- Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD) Collection
- Synthetic Rubber Project
- Technical Translations (TT) Series
- Locating Technical Reports and Standards
- Research Assistance and Reproductions
- Online Resources and Databases
- Using the Library of Congress
- Jennifer Harbster, Head, Science Section, Researcher Engagement & General Collections Division
- Sean Bryant, Reference Librarian, Researcher Engagement & General Collections Division
- Ashley Fielder, Librarian for Medicine and Life Science. Science Section, Researcher Engagement & General Collections
- Created: September 22, 2023
Last Updated: May 7, 2024
Science & Technical Reports : Ask a Librarian
Have a question? Need assistance? Use our online form to ask a librarian for help.

Get connected to the Library’s large and diverse collections related to science, technology, and business through our Inside Adams Blog. This blog also features upcoming events and collection displays, classes and orientations, new research guides, and more.
The Library of Congress is completing a project to update and modernize Library reading room websites. As a part of the process, “The Technical Reports and Standards Collection” is in the process of being updated and migrated to this new platform. The process has not yet been completed and the guide remains subject to change.
Researchers with questions about the collection are encouraged to contact a science or business librarian using the Ask-a-Librarian: Science and Technical Reports or Ask a Librarian: Business online form, by phone, at (202) 707-5639, or in person, at the reference desk, in the Science and Business Reading Room, on the fifth floor of the Library's John Adams Building.
Technical Reports

Technical reports are designed to quickly alert researchers to recent findings and developments in scientific and technical research. These reports are issued for a variety of purposes:
- to communicate results or describe progress of a research project
- to convey background information on an emerging or critical research topic
- to provide lists of instructions or procedures for current practices
- to determine the feasibility of a technology and recommend if research should be continued (and how to evaluate any further progress made)
- to detail technical specifications (materials, functions, features, operation, market potential, etc.)
Technical reports first appeared in the early part of the 20th century. The U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) published a series of professional papers beginning in 1902, and the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) issued its first report in 1915. But, the format gained importance during World War II, emerged in the postwar era, and remains, to this day, a major tool for reporting progress in science and technology, as well as in education, business, and social sciences research. The names given to series of these publications vary, but are often such generic terms as "technical reports," "working papers," "research memoranda," "internal notes," "occasional papers," "discussion papers" or "gray (or grey) literature." In the physical and natural sciences, "technical report" seems to be the preferred designation. For reports dealing with business, education, and the social sciences, on the other hand, the terms "working paper," "occasional paper," and "memorandum" are often the designations of choice. Other, more specific types of technical reports include "preprints" and "reprints." Preprints generally are versions of papers issued by researchers before their final papers are published by commercial publishers. Preprints allow researchers to communicate their findings quickly, but usually have not been peer reviewed. Reprints are typically released to heighten awareness of the research being conducted in a particular field or at a single institution. The term, "technical report" encompasses all of these designations.
Since many of these publications are intended to provide just a temporary snapshot of current research in a particular field or topic, they may contain the some of following distinctions:
- Rapid communication of new research results
- Dissemination to a targeted audience.
- Detailed methodologies, in order to facilitate review of research results by others
- No peer review, though there is often another selection process for publication (grant, contract, or institutional affiliation)
- Not published by typical commercial publishers (instead reports are issued or sponsored by government agencies, professional associations, societies, councils, foundations, laboratories, universities, etc.)
- Corporate authorship, where present, is typically emphasized
Unfortunately, uncertain availability, limited print runs, and decentralized distribution patterns with little bibliographic information are also often characteristics of this literature.
The Federal Government issues many different types of technical reports. An overview of some of these can be found in a May 2001 GAO report, " Information Management: Dissemination of Technical Reports ." Government issued or sponsored reports contain an additional characteristic - they may be subject to distribution restrictions linked to their classification status. Although references to classified reports may be found in technical reports literature, the security status or limited distribution of reports may make them unavailable to the general public and to the Library as well, as the Library holds only titles in the public domain. Those interested in locating such materials can consult the U.S. Department of Justice's Freedom of Information Act site for guidance in obtaining these reports.
To enable them to be identified and located, technical reports are assigned report codes by agencies or organizations involved in their production or distribution. These codes may be referred to as "accession numbers," "agency report series numbers," "contract numbers," "grant numbers" or by other names, and include dates and individual report numbers. Typically, reports are assigned multiple codes and these codes help to identify the sponsoring agency, the organization performing the research or the organization disseminating the report. Most technical reports held by the Library of Congress are not cataloged, and, for these reports, one or more report codes is required for Library staff to check the collections for a report or to locate and retrieve it. For more information about the current Standard Technical Report Number format (STRN) see ANSI/NISO Z39.23- 1997 (S2015) Standard Technical Reports Number Format and Creation .
Standards are specifications which define products, methods, processes or practices, and are known to have existed as early as 7000 B.C., when cylindrical stones were used as units of weight in Egypt. According to Office of Management and Budget (OMB) Circular A-119 , as revised in 2016, the term "standard" or "technical standard" refers to:
- common and repeated use of rules, conditions, guidelines or characteristics for products or related processes and production methods, and related management systems practices;
- the definition of terms; classification of components; delineation of procedures; specification of dimensions, materials, performance, designs, or operations; measurement of quality and quantity in describing materials, processes, products, systems, services, or practices; test methods and sampling procedures; or descriptions of fit and measurements of size or strength; and
- terminology, symbols, packaging, marking or labeling requirements as they apply to a product, process, or production method.
Technical standards are not "professional standards of personal conduct; or institutional codes of ethics." (p. 15).
Standards are typically generated by governments or by professional associations and organizations interested in or affected by the subject matter of particular standards. For example, U.S. government standards mandated by the Fair Packaging & Labeling Act (FPLA) have standardized the labeling required for packaging in which consumer commodities is sold. Standards set the basis for determining consistent and acceptable minimum levels of reliability and safety, and are adhered to either voluntarily or as mandated by law. For a more complete overview, see the NIST report " The ABC's of Standards Activities " by Maureen A. Breitenberg (2009).
The Library of Congress standards collection includes military and other federal standards, industry standards, and a few older international standards from Russia, China, and South Africa. Material from the collection is available in various formats, including digital, print, and microform materials. The majority of the Library's standards collection held in the Science Section's Technical Reports and Standards Collection. The collection remains largely uncatalogued, and as a result, most items from this collection are not discoverable in the Library's online catalog. Inquires on Library holdings can be sent to the Science Section using the Science and Technical Reports Ask-a-Librarian form . Some standards, however, are housed in the Library's general collections and discoverable by searching the online catalog -- the ASTM standards are one example. Other standards are in custody of appropriate specialized research centers, such as the Law Library , which maintains OSHA standards and some building codes.
About the Science Section
Part of the Science & Business Reading Room at the Library of Congress, the Science Section is the starting point for conducting research at the Library of Congress in the subject areas of science, medicine and engineering. Here, reference specialists in specific subject areas of science and engineering assist patrons in formulating search strategies and gaining access to the information and materials contained in the Library's rich collections of science, medicine, and engineering materials.
- Next: Technical Reports Collections >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 11:51 AM
- URL: https://guides.loc.gov/technical-reports

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Find sample papers formatted in seventh edition APA Style for different types of professional and student papers. Download Word files to use as templates and edit them as needed for your own papers.
A Sample Research Paper on Child Abuse. A research paper is an academic piece of writing, so you need to follow all the requirements and standards. Otherwise, it will be impossible to get the high results. To make it easier for you, we have analyzed the structure and peculiarities of a sample research paper on the topic 'Child Abuse'. ...
Abstract Research Paper Example. An abstract is an executive summary of the research paper that includes the purpose of the research, the design of the study, and significant research findings. It is a small section that is based on a few paragraphs. Following is an example of the abstract to help you draft yours professionally.
Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist.
Research Paper Example. Note: The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. ...
APA 7th ed. Fillable Word Template and Sample Paper. APA 7th ed. Template. ... Sample Paper APA 7th ed. Our APA sample paper shows you how to format the main parts of a basic research paper. APA 7th Sample Papers from Purdue Owl << Previous: Block Quotations; Next: Government Documents and Legal Materials >> Last Updated: Aug 9, 2024 11:50 AM;
Research Paper Example Outline. Before you plan on writing a well-researched paper, make a rough draft. An outline can be a great help when it comes to organizing vast amounts of research material for your paper. Here is an outline of a research paper example: I. Title Page. A. Title of the Research Paper.
Learn how to format a research paper in APA, MLA, or Chicago style with free templates and examples. See the main guidelines for font, margins, spacing, headings, citations, and more.
Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature. As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question.More specifically, that's called a research question, and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What's important to understand though is that you'll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources - for ...
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader. Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication).
Place your paper title 3 or 4 lines down from your paper's top margin. The title's typeface should appear in boldface and title case. This title should also be placed at the top of your paper's first page of text. Each of the following items appear centered, double spaced, in title case and regular typeface: 2.
Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings.The format of a research paper depends on various factors such as the discipline, style guide, and purpose of the research. It includes guidelines for the structure, citation style, referencing, and other elements of the paper that contribute to its overall ...
What is a research paper? A research paper is a type of academic writing that provides an in-depth analysis, evaluation, or interpretation of a single topic, based on empirical evidence. Research papers are similar to analytical essays, except that research papers emphasize the use of statistical data and preexisting research, along with a strict code for citations.
The pages in this section cover the following topic areas related to the process of writing a research paper: Genre - This section will provide an overview for understanding the difference between an analytical and argumentative research paper. Choosing a Topic - This section will guide the student through the process of choosing topics ...
Set a Timeline: Plan a schedule for starting, writing, and editing your research paper. 2. Consider the Target Audience. Consider your audience's knowledge and expertise level as it influences writing style, word choice, and the depth of information required: For master's level research, expect an expert audience.
The basics of figure setup, including figure components, principles of figure construction, and placement of figures in a paper. Tables - APA 7. The basics of table setup, including table components, principles of table construction, and placement of tables in the paper. Last Updated: May 14, 2024 3:23 PM. URL: https://libguides.sullivan.edu/apa7.
Liberty University requires. undergraduate students to follow APA-7's guidelines for "student papers" (graduate/doctoral. students must follow APA-7's guidelines for "professional papers ...
The featured example is a research paper on the uses of biometrics to inform design decisions in the tech industry, authored by our UX Research Intern Peace Iyiewuare. Like most APA style papers, it includes an APA title page, tables, and several references and APA in-text citations to scholarly journals relevant to its topic. References are an ...
How do you format a research paper? Learn more about the basic outline for any research paper, complete with example text and formatting tips.
MLA Sample Paper #1. If you've been wondering how to produce a research paper that is strong in both formatting and writing, you've come to the right place. Check out our first sample paper below. It is a helpful and clearly labeled visual aid to refer to. Note that while these sample papers do not include MLA abstracts, you should check ...
A research proposal includes the details of your proposed research, the significance of the research, the impact your research will have on the area of research, and the methodology that you will use. For writing a research proposal, you need to discuss all of these factors. A research paper follows a set pattern and structure.
How to write a research paper outline. Follow these steps to start your research paper outline: Decide on the subject of the paper. Write down all the ideas you want to include or discuss. Organize related ideas into sub-groups.
The authority on APA Style and the 7th edition of the APA Publication Manual. Find tutorials, the APA Style Blog, how to format papers in APA Style, and other resources to help you improve your writing, master APA Style, and learn the conventions of scholarly publishing.
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers' plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed ...
research paper is an iterative and self-editing process, where each component informs the other in an evolving narrative. The title of your paper is an abbreviated summary of your work's essence, a snapshot of your findings, and a nod to your unique contribution to the field. To craft such a title effectively, it is vital
Example. Paper title. Place the title three to four lines down from the top of the title page. Center it and type it in bold font. ... For a professional paper, the affiliation is the institution at which the research was conducted. Include both the name of any department and the name of the college, university, or other institution, separated ...
Of course, you'll need to come up with an effective title. Though a title is less substantial than a section, it makes the first impression on the research committee. It's also the most concise representation of what you hope to accomplish with your research paper. A good title conveys your research goal in enough detail to show uniqueness.
Research has shown that the unilateral accumulation of international reserves by a country can improve its own macro-financial stability. However, we show that when many countries accumulate reserves, the induced general equilibrium effects weaken financial and macroeconomic stability, especially for countries that do not accumulate reserves.
The names given to series of these publications vary, but are often such generic terms as "technical reports," "working papers," "research memoranda," "internal notes," "occasional papers," "discussion papers" or "gray (or grey) literature." In the physical and natural sciences, "technical report" seems to be the preferred designation.