- Open access
- Published: 26 August 2024

Evaluating panel discussions in ESP classes: an exploration of international medical students’ and ESP instructors’ perspectives through qualitative research
- Elham Nasiri ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0644-1646 1 &
- Laleh Khojasteh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6393-2759 1
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 925 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
65 Accesses
Metrics details
This study investigates the effectiveness of panel discussions, a specific interactive teaching technique where a group of students leads a pre-planned, topic-focused discussion with audience participation, in English for Specific Purposes (ESP) courses for international medical students. This approach aims to simulate professional conference discussions, preparing students for future academic and clinical environments where such skills are crucial. While traditional group presentations foster critical thinking and communication, a gap exists in understanding how medical students perceive the complexities of preparing for and participating in panel discussions within an ESP setting. This qualitative study investigates the perceived advantages and disadvantages of these discussions from the perspectives of both panelists (medical students) and the audience (peers). Additionally, the study explores potential improvements based on insights from ESP instructors. Utilizing a two-phase design involving reflection papers and focus group discussions, data were collected from 46 medical students and three ESP instructors. Thematic analysis revealed that panel discussions offer unique benefits compared to traditional presentations, including enhanced engagement and more dynamic skill development for both panelists and the audience. Panelists reported gains in personal and professional development, including honing critical thinking, communication, and presentation skills. The audience perceived these discussions as engaging learning experiences that fostered critical analysis and information synthesis. However, challenges such as academic workload and concerns about discussion quality were also identified. The study concludes that panel discussions, when implemented effectively, can be a valuable tool for enhancing critical thinking, communication skills, and subject matter knowledge in ESP courses for medical students. These skills are transferable and can benefit students in various academic and professional settings, including future participation in medical conferences. This research provides valuable insights for ESP instructors seeking to integrate panel discussions into their curriculum, ultimately improving student learning outcomes and preparing them for future success in professional communication.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
In the field of medical education, the acquisition and application of effective communication skills are crucial for medical students in today’s global healthcare environment [ 1 ]. This necessitates not only strong English language proficiency but also the ability to present complex medical information clearly and concisely to diverse audiences.
Language courses, especially English for Specific Purposes (ESP) courses for medical students, are highly relevant in today’s globalized healthcare environment [ 2 ]. In non-English speaking countries like Iran, these courses are particularly important as they go beyond mere language instruction to include the development of critical thinking, cultural competence, and professional communication skills [ 3 ]. Proficiency in English is crucial for accessing up-to-date research, participating in international conferences, and communicating with patients and colleagues from diverse backgrounds [ 4 ]. Additionally, ESP courses help medical students understand and use medical terminologies accurately, which is essential for reading technical articles, listening to audio presentations, and giving spoken presentations [ 5 ]. In countries where English is not the primary language, ESP courses ensure that medical professionals can stay current with global advancements and collaborate effectively on an international scale [ 6 ]. Furthermore, these courses support students who may seek to practice medicine abroad, enhancing their career opportunities and professional growth [ 7 ].
Moreover, ESP courses enable medical professionals to communicate effectively with international patients, which is crucial in multicultural societies and for medical tourism, ensuring that patient care is not compromised due to language barriers [ 8 ]. Many medical textbooks, journals, and online resources are available primarily in English, and ESP courses equip medical students with the necessary language skills to access and comprehend these resources, ensuring they are well-informed about the latest medical research and practices [ 9 ].
Additionally, many medical professionals from non-English speaking countries aim to take international certification exams, such as the USMLE or PLAB, which are conducted in English, and ESP courses prepare students for these exams by familiarizing them with the medical terminology and language used in these assessments [ 10 ]. ESP courses also contribute to the professional development of medical students by improving their ability to write research papers, case reports, and other academic documents in English, which is essential for publishing in international journals and contributing to global medical knowledge [ 11 ]. In the increasingly interdisciplinary field of healthcare, collaboration with professionals from other countries is common, and ESP courses facilitate effective communication and collaboration with international colleagues, fostering innovation and the exchange of ideas [ 12 ].
With the rise of telemedicine and online medical consultations, proficiency in English is essential for non-English speaking medical professionals to provide remote healthcare services to international patients, and ESP courses prepare students for these modern medical practices [ 13 ].
Finally, ESP courses often include training on cultural competence, which is crucial for understanding and respecting the cultural backgrounds of patients and colleagues, leading to more empathetic and effective patient care and professional interactions [ 14 ]. Many ESP programs for medical students incorporate group presentations as a vital component of their curriculum, recognizing the positive impact on developing these essential skills [ 15 ].
Group projects in language courses, particularly in ESP for medical students, are highly relevant for several reasons. They provide a collaborative environment that mimics real-world professional settings, where healthcare professionals often work in multidisciplinary teams [ 16 ]. These group activities foster not only language skills but also crucial soft skills such as teamwork, leadership, and interpersonal communication, which are essential in medical practice [ 17 ].
The benefits of group projects over individual projects in language learning are significant. Hartono, Mujiyanto [ 18 ] found that group presentation tasks in ESP courses led to higher self-efficacy development compared to individual tasks. Group projects encourage peer learning, where students can learn from each other’s strengths and compensate for individual weaknesses [ 19 ]. They also provide a supportive environment that can reduce anxiety and increase willingness to communicate in the target language [ 20 ]. However, it is important to note that group projects also come with challenges, such as social loafing and unequal contribution, which need to be managed effectively [ 21 ].
Traditional lecture-based teaching methods, while valuable for knowledge acquisition, may not effectively prepare medical students for the interactive and collaborative nature of real-world healthcare settings [ 22 ]. Panel discussions (hereafter PDs), an interactive teaching technique where a group of students leads a pre-planned, topic-focused discussion with audience participation, are particularly relevant in this context. They simulate professional conference discussions and interdisciplinary team meetings, preparing students for future academic and clinical environments where such skills are crucial [ 23 ].
PDs, also known as moderated discussions or moderated panels, are a specific type of interactive format where a group of experts or stakeholders engage in a facilitated conversation on a particular topic or issue [ 22 ]. In this format, a moderator guides the discussion, encourages active participation from all panelists, and fosters a collaborative environment that promotes constructive dialogue and critical thinking [ 24 ]. The goal is to encourage audience engagement and participation, which can be achieved through various strategies such as asking open-ended questions, encouraging counterpoints and counterarguments, and providing opportunities for audience members to pose questions or share their own experiences [ 25 ]. These discussions can take place in-person or online, and can be designed to accommodate diverse audiences and settings [ 26 ].
In this study, PD is considered a speaking activity where medical students are assigned specific roles to play during the simulation, such as a physician, quality improvement specialist, policymaker, or patient advocate. By taking on these roles, students can gain a better understanding of the diverse perspectives and considerations that come into play in real-world healthcare discussions [ 23 ]. Simulating PDs within ESP courses can be a powerful tool for enhancing medical students’ learning outcomes in multiple areas. This approach improves language proficiency, academic skills, and critical thinking abilities, while also enabling students to communicate effectively with diverse stakeholders in the medical field [ 27 , 28 ].
Theoretical framework
The panel discussions in our study are grounded in the concept of authentic assessment (outlined by Villarroel, Bloxham [ 29 ]), which involves designing tasks that mirror real-life situations and problems. In the context of medical education, this approach is particularly relevant as it prepares students for the complex, multidisciplinary nature of healthcare communication. Realism can be achieved through two means: providing a realistic context that describes and delivers a frame for the problem to be solved and creating tasks that are similar to those faced in real and/or professional life [ 30 ]. In our study, the PDs provide a realistic context by simulating scenarios where medical students are required to discuss and present complex medical topics in a professional setting, mirroring the types of interactions they will encounter in their future careers.
The task of participating in PDs also involves cognitive challenge, as students are required to think critically about complex medical topics, analyze information, and communicate their findings effectively. This type of task aims to generate processes of problem-solving, application of knowledge, and decision-making that correspond to the development of cognitive and metacognitive skills [ 23 ]. For medical students, these skills are crucial in developing clinical reasoning and effective patient communication. The PDs encourage students to go beyond the textual reproduction of fragmented and low-order content and move towards understanding, establishing relationships between new ideas and previous knowledge, linking theoretical concepts with everyday experience, deriving conclusions from the analysis of data, and examining both the logic of the arguments present in the theory and its practical scope [ 24 , 25 , 27 ].
Furthermore, the evaluative judgment aspect of our study is critical in helping students develop criteria and standards about what a good performance means in medical communication. This involves students judging their own performance and regulating their own learning [ 31 ]. In the context of panel discussions, students reflect on their own work, compare it with desired standards, and seek feedback from peers and instructors. By doing so, students can develop a sense of what constitutes good performance in medical communication and what areas need improvement [ 32 ]. Boud, Lawson and Thompson [ 33 ] argue that students need to build a precise judgment about the quality of their work and calibrate these judgments in the light of evidence. This skill is particularly important for future medical professionals who will need to continually assess and improve their communication skills throughout their careers.
The theoretical framework presented above highlights the importance of authentic learning experiences in medical education. By drawing on the benefits of group work and panel discussions, university instructor-researchers aimed to provide medical students with a unique opportunity to engage with complex cases and develop their communication and collaboration skills. As noted by Suryanarayana [ 34 ], authentic learning experiences can lead to deeper learning and improved retention. Considering the advantages of group work in promoting collaborative problem-solving and language development, the instructor-researchers designed a panel discussion task that simulates real-world scenarios, where students can work together to analyze complex cases, share knowledge, and present their findings to a simulated audience.
While previous studies have highlighted the benefits of interactive learning experiences and critical thinking skills in medical education, a research gap remains in understanding how medical students perceive the relevance of PDs in ESP courses. This study aims to address this gap by investigating medical students’ perceptions of PD tasks in ESP courses and how these perceptions relate to their language proficiency, critical thinking skills, and ability to communicate effectively with diverse stakeholders in the medical field. This understanding can inform best practices in medical education, contributing to the development of more effective communication skills for future healthcare professionals worldwide [ 23 ]. The research questions guiding this study are:
What are the perceived advantages of PDs from the perspectives of panelists and the audience?
What are the perceived disadvantages of PDs from the perspectives of panelists and the audience?
How can PDs be improved for panelists and the audience based on the insights of ESP instructors?
Methodology
Aim and design.
For this study, a two-phase qualitative design was employed to gain an understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of PDs from the perspectives of both student panelists and the audience (Phase 1) and to acquire an in-depth understanding of the suggested strategies provided by experts to enhance PPs for future students (Phase 2).
Participants and context of the study
This study was conducted in two phases (Fig. 1 ) at Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (SUMS), Shiraz, Iran.
Participants of the study in two phases
In the first phase, the student participants were 46 non-native speakers of English and international students who studied medicine at SUMS. Their demographic characteristics can be seen in Table 1 .
These students were purposefully selected because they were the only SUMS international students who had taken the ESP (English for Specific Purposes) course. The number of international students attending SUMS is indeed limited. Each year, a different batch of international students joins the university. They progress through a sequence of English courses, starting with General English 1 and 2, followed by the ESP course, and concluding with academic writing. At the time of data collection, the students included in the study were the only international students enrolled in the ESP course. This mandatory 3-unit course is designed to enhance their language and communication skills specifically tailored to their profession. As a part of the Medicine major curriculum, this course aims to improve their English language proficiency in areas relevant to medicine, such as understanding medical terminology, comprehending original medicine texts, discussing clinical cases, and communicating with patients, colleagues, and other healthcare professionals.
Throughout the course, students engage in various interactive activities, such as group discussions, role-playing exercises, and case studies, to develop their practical communication skills. In this course, medical students receive four marks out of 20 for their oral presentations, while the remaining marks are allocated to their written midterm and final exams. From the beginning of the course, they are briefed about PDs, and they are shown two YouTube-downloaded videos about PDs at medical conferences, a popular format for discussing and sharing knowledge, research findings, and expert opinions on various medical topics.
For the second phase of the study, a specific group of participants was purposefully selected. This group consisted of three faculty members from SUMS English department who had extensive experience attending numerous conferences at national and international levels, particularly in the medical field, as well as working as translators and interpreters in medical congresses. Over the course of ten years, they also gained considerable experience in PDs. They were invited to discuss strategies helpful for medical students with PDs.
Panel discussion activity design and implementation
When preparing for a PD session, medical students received comprehensive guidance on understanding the roles and responsibilities of each panel member. This guidance was aimed at ensuring that each participant was well-prepared and understood their specific role in the discussion.
Moderators should play a crucial role in steering the conversation. They are responsible for ensuring that all panelists have an opportunity to contribute and that the audience is engaged effectively. Specific tasks include preparing opening remarks, introducing panelists, and crafting transition questions to facilitate smooth topic transitions. The moderators should also manage the time to ensure balanced participation and encourage active audience involvement.
Panelists are expected to be subject matter experts who bring valuable insights and opinions to the discussion. They are advised to conduct thorough research on the topic and prepare concise talking points. Panelists are encouraged to draw from their medical knowledge and relevant experiences, share evidence-based information, and engage with other panelists’ points through active listening and thoughtful responses.
The audience plays an active role in the PDs. They are encouraged to participate by asking questions, sharing relevant experiences, and contributing to the dialogue. To facilitate this, students are advised to take notes during the discussion and think of questions or comments they can contribute during the Q&A segment.
For this special course, medical students were advised to choose topics either from their ESP textbook or consider current medical trends, emerging research, and pressing issues in their field. Examples included breast cancer, COVID-19, and controversies in gene therapy. The selection process involved brainstorming sessions and consultation with the course instructor to ensure relevance and appropriateness.
To accommodate the PD sessions within the course structure, students were allowed to start their PD sessions voluntarily from the second week. However, to maintain a balance between peer-led discussions and regular course content, only one PD was held weekly. This approach enabled the ESP lecturer to deliver comprehensive content while also allowing students to engage in these interactive sessions.
A basic time structure was suggested for each PD (Fig. 2 ):
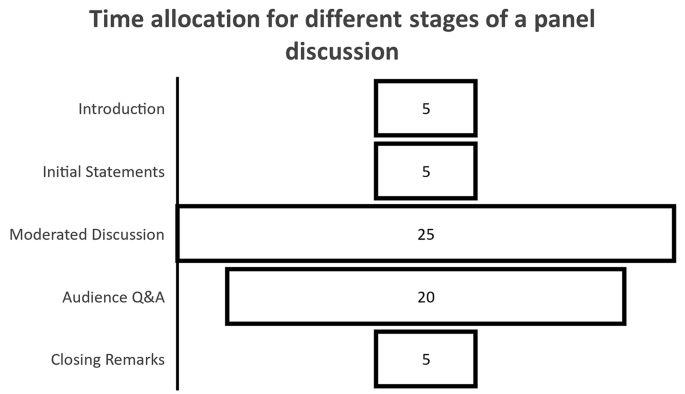
Time allocation for panel discussion stages in minutes
To ensure the smooth running of the course and maintain momentum, students were informed that they could cancel their PD session only once. In such cases, they were required to notify the lecturer and other students via the class Telegram channel to facilitate rescheduling and minimize disruptions. This provision was essential in promoting a sense of community among students and maintaining the course’s continuity.
Research tools and data collection
The study utilized various tools to gather and analyze data from participants and experts, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the research topic.
Reflection papers
In Phase 1 of the study, 46 medical students detailed their perceptions of the advantages and disadvantages of panel discussions from dual perspectives: as panelists (presenters) and as audience members (peers).
Participants were given clear instructions and a 45-minute time frame to complete the reflection task. With approximately 80% of the international language students being native English speakers and the rest fluent in English, the researchers deemed this time allocation reasonable. The questions and instructions were straightforward, facilitating quick comprehension. It was estimated that native English speakers would need about 30 min to complete the task, while non-native speakers might require an extra 15 min for clarity and expression. This time frame aimed to allow students to respond thoughtfully without feeling rushed. Additionally, students could request more time if needed.
Focus group discussion
In phase 2 of the study, a focus group discussion was conducted with three expert participants. The purpose of the focus group was to gather insights from expert participants, specifically ESP (English for Specific Purposes) instructors, on how presentation dynamics can be improved for both panelists and the audience.
According to Colton and Covert [ 35 ], focus groups are useful for obtaining detailed input from experts. The appropriate size of a focus group is determined by the study’s scope and available resources [ 36 ]. Morgan [ 37 ] suggests that small focus groups are suitable for complex topics where specialist participants might feel frustrated if not allowed to express themselves fully.
The choice of a focus group over individual interviews was based on several factors. First, the exploratory nature of the study made focus groups ideal for interactive discussions, generating new ideas and in-depth insights [ 36 ]. Second, while focus groups usually involve larger groups, they can effectively accommodate a limited number of experts with extensive knowledge [ 37 ]. Third, the focus group format fostered a more open environment for idea exchange, allowing participants to engage dynamically [ 36 ]. Lastly, conducting a focus group was more time- and resource-efficient than scheduling three separate interviews [ 36 ].
Data analysis
The first phase of the study involved a thorough examination of the data related to the research inquiries using thematic analysis. This method was chosen for its effectiveness in uncovering latent patterns from a bottom-up perspective, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of complex educational phenomena [ 38 ]. The researchers first familiarized themselves with the data by repeatedly reviewing the reflection papers written by the medical students. Next, an initial round of coding was independently conducted to identify significant data segments and generate preliminary codes that reflected the students’ perceptions of the advantages and disadvantages of presentation dynamics PDs from both the presenter and audience viewpoints [ 38 ].
The analysis of the reflection papers began with the two researchers coding a subset of five papers independently, adhering to a structured qualitative coding protocol [ 39 ]. They convened afterward to compare their initial codes and address any discrepancies. Through discussion, they reached an agreement on the codes, which were then analyzed, organized into categories and themes, and the frequency of each code was recorded [ 38 ].
After coding the initial five papers, the researchers continued to code the remaining 41 reflection paper transcripts in batches of ten, meeting after each batch to review their coding, resolve any inconsistencies, and refine the coding framework as needed. This iterative process, characterized by independent coding, joint reviews, and consensus-building, helped the researchers establish a robust and reliable coding approach consistently applied to the complete dataset [ 40 ]. Once all 46 reflection paper transcripts were coded, the researchers conducted a final review and discussion to ensure accurate analysis. They extracted relevant excerpts corresponding to the identified themes and sub-themes from the transcripts to provide detailed explanations and support for their findings [ 38 ]. This multi-step approach of separate initial coding, collaborative review, and frequency analysis enhanced the credibility and transparency of the qualitative data analysis.
To ensure the trustworthiness of the data collected in this study, the researchers adhered to the Guba and Lincoln standards of scientific accuracy in qualitative research, which encompass credibility, confirmability, dependability, and transferability [ 41 ] (Table 2 ).
The analysis of the focus group data obtained from experts followed the same rigorous procedure applied to the student participants’ data. Thematic analysis was employed to examine the experts’ perspectives, maintaining consistency in the analytical approach across both phases of the study. The researchers familiarized themselves with the focus group transcript, conducted independent preliminary coding, and then collaboratively refined the codes. These codes were subsequently organized into categories and themes, with the frequency of each code recorded. The researchers engaged in thorough discussions to ensure agreement on the final themes and sub-themes. Relevant excerpts from the focus group transcript were extracted to provide rich, detailed explanations of each theme, thereby ensuring a comprehensive and accurate analysis of the experts’ insights.
1. What are the advantages of PDs from the perspective of panelists and the audience?
The analysis of the advantages of PDs from the perspectives of both panelists and audience members revealed several key themes and categories. Tables 2 and 3 present the frequency and percentage of responses for each code within these categories.
From the panelists’ perspective (Table 3 ), the overarching theme was “Personal and Professional Development.” The most frequently reported advantage was knowledge sharing (93.5%), followed closely by increased confidence (91.3%) and the importance of interaction in presentations (91.3%).
Notably, all categories within this theme had at least one code mentioned by over 80% of participants, indicating a broad range of perceived benefits. The category of “Effective teamwork and communication” was particularly prominent, with collaboration (89.1%) and knowledge sharing (93.5%) being among the most frequently cited advantages. This suggests that PDs are perceived as valuable tools for fostering interpersonal skills and collective learning. In the “Language mastery” category, increased confidence (91.3%) and better retention of key concepts (87.0%) were highlighted, indicating that PDs are seen as effective for both language and content learning.
The audience perspective (Table 4 ), encapsulated under the theme “Enriching Learning Experience,” showed similarly high frequencies across all categories.
The most frequently mentioned advantage was exposure to diverse speakers (93.5%), closely followed by the range of topics covered (91.3%) and increased audience interest (91.3%). The “Broadening perspectives” category was particularly rich, with all codes mentioned by over 70% of participants. This suggests that audience members perceive PDs as valuable opportunities for expanding their knowledge and viewpoints. In the “Language practice” category, the opportunity to practice language skills (89.1%) was the most frequently cited advantage, indicating that even as audience members, students perceive significant language learning benefits.
Comparing the two perspectives reveals several interesting patterns:
High overall engagement: Both panelists and audience members reported high frequencies across all categories, suggesting that PDs are perceived as beneficial regardless of the role played.
Language benefits: While panelists emphasized increased confidence (91.3%) and better retention of concepts (87.0%), audience members highlighted opportunities for language practice (89.1%). This indicates that PDs offer complementary language learning benefits for both roles.
Interactive learning: The importance of interaction was highly rated by panelists (91.3%), while increased audience interest was similarly valued by the audience (91.3%). This suggests that PDs are perceived as an engaging, interactive learning method from both perspectives.
Professional development: Panelists uniquely emphasized professional growth aspects such as experiential learning (84.8%) and real-world application (80.4%). These were not directly mirrored in the audience perspective, suggesting that active participation in PDs may offer additional professional development benefits.
Broadening horizons: Both groups highly valued the diversity aspect of PDs. Panelists appreciated diversity and open-mindedness (80.4%), while audience members valued diverse speakers (93.5%) and a range of topics (91.3%).
2. What are the disadvantages of PDs from the perspective of panelists and the audience?
The analysis of the disadvantages of panel discussions (PDs) from the perspectives of both panelists and audience members revealed several key themes and categories. Tables 4 and 5 present the frequency and percentage of responses for each code within these categories.
From the panelists’ perspective (Table 5 ), the theme “Drawbacks of PDs” was divided into two main categories: “Academic Workload Challenges” and “Coordination Challenges.” The most frequently reported disadvantage was long preparation (87.0%), followed by significant practice needed (82.6%) and the time-consuming nature of PDs (80.4%). These findings suggest that the primary concern for panelists is the additional workload that PDs impose on their already demanding academic schedules. The “Coordination Challenges” category, while less prominent than workload issues, still presented significant concerns. Diverse panel skills (78.3%) and finding suitable panelists (73.9%) were the most frequently cited issues in this category, indicating that team dynamics and composition are notable challenges for panelists.
The audience perspective (Table 6 ), encapsulated under the theme “Drawbacks of PDs,” was divided into two main categories: “Time-related Issues” and “Interaction and Engagement Issues.” In the “Time-related Issues” category, the most frequently mentioned disadvantage was the inefficient use of time (65.2%), followed by the perception of PDs as too long and boring (60.9%). Notably, 56.5% of respondents found PDs stressful due to overwhelming workload from other studies, and 52.2% considered them not very useful during exam time. The “Interaction and Engagement Issues” category revealed more diverse concerns. The most frequently mentioned disadvantage was the repetitive format (82.6%), followed by limited engagement with the audience (78.3%) and the perception of PDs as boring (73.9%). The audience also noted issues related to the panelists’ preparation and coordination, such as “Not practiced and natural” (67.4%) and “Coordination and Interaction Issues” (71.7%), suggesting that the challenges faced by panelists directly impact the audience’s experience.
Workload concerns: Both panelists and audience members highlighted time-related issues. For panelists, this manifested as long preparation times (87.0%) and difficulty balancing with other studies (76.1%). For the audience, it appeared as perceptions of inefficient use of time (65.2%) and stress due to overwhelming workload from other studies (56.5%).
Engagement issues: While panelists focused on preparation and coordination challenges, the audience emphasized the quality of the discussion and engagement. This suggests a potential mismatch between the efforts of panelists and the expectations of the audience.
Boredom and repetition: The audience frequently mentioned boredom (73.9%) and repetitive format (82.6%) as issues, which weren’t directly mirrored in the panelists’ responses. This indicates that while panelists may be focused on content preparation, the audience is more concerned with the delivery and variety of the presentation format.
Coordination challenges: Both groups noted coordination issues, but from different perspectives. Panelists struggled with team dynamics and finding suitable co-presenters, while the audience observed these challenges manifesting as unnatural or unpracticed presentations.
Academic pressure: Both groups acknowledged the strain PDs put on their academic lives, with panelists viewing it as a burden (65.2%) and the audience finding it less useful during exam times (52.2%).
3. How can PDs be improved for panelists and the audience from the experts’ point of view?
The presentation of data for this research question differs from the previous two due to the unique nature of the information gathered. Unlike the quantifiable student responses in earlier questions, this data stems from expert opinions and a reflection discussion session, focusing on qualitative recommendations for improvement rather than frequency of responses (Braun & Clarke, 2006). The complexity and interconnectedness of expert suggestions, coupled with the integration of supporting literature, necessitate a more narrative approach (Creswell & Poth, 2018). This format allows for a richer exploration of the context behind each recommendation and its potential implications (Patton, 2015). Furthermore, the exploratory nature of this question, aimed at generating ideas for improvement rather than measuring prevalence of opinions, is better served by a detailed, descriptive presentation (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016). This approach enables a more nuanced understanding of how PDs can be enhanced, aligning closely with the “how” nature of the research question and providing valuable insights for potential implementation (Yin, 2018).
The experts provided several suggestions to address the challenges faced by students in panel discussions (PDs) and improve the experience for both panelists and the audience. Their recommendations focused on six key areas: time management and workload, preparation and skill development, engagement and interactivity, technological integration, collaboration and communication, and institutional support.
To address the issue of time management and heavy workload, one expert suggested teaching students to “ break down the task to tackle the time-consuming nature of panel discussions and balance it with other studies .” This approach aims to help students manage the extensive preparation time required for PDs without compromising their other academic responsibilities. Another expert emphasized “ enhancing medical students’ abilities to prioritize tasks , allocate resources efficiently , and optimize their workflow to achieve their goals effectively .” These skills were seen as crucial not only for PD preparation but also for overall academic success and future professional practice.
Recognizing the challenges of long preparation times and the perception of PDs being burdensome, an expert proposed “ the implementation of interactive training sessions for panelists .” These sessions were suggested to enhance coordination skills and improve the ability of group presenters to engage with the audience effectively. The expert emphasized that such training could help students view PDs as valuable learning experiences rather than additional burdens, potentially increasing their motivation and engagement in the process.
To combat issues of limited engagement and perceived boredom, experts recommended increasing engagement opportunities for the audience through interactive elements like audience participation and group discussions. They suggested that this could transform PDs from passive listening experiences to active learning opportunities. One expert suggested “ optimizing time management and restructuring the format of panel discussions ” to address inefficiency during sessions. This restructuring could involve shorter presentation segments interspersed with interactive elements to maintain audience attention and engagement.
An innovative solution proposed by one expert was “ using ChatGPT to prepare for PDs by streamlining scenario presentation preparation and role allocation. ” The experts collectively discussed the potential of AI to assist medical students in reducing their workload and saving time in preparing scenario presentations and allocating roles in panel discussions. They noted that AI could help generate initial content drafts, suggest role distributions based on individual strengths, and even provide practice questions for panelists, significantly reducing preparation time while maintaining quality.
Two experts emphasized the importance of enhancing collaboration and communication among panelists to address issues related to diverse panel skills and coordination challenges. They suggested establishing clear communication channels and guidelines to improve coordination and ensure a cohesive presentation. This could involve creating structured team roles, setting clear expectations for each panelist, and implementing regular check-ins during the preparation process to ensure all team members are aligned and progressing.
All experts were in agreement that improving PDs would not be possible “ if nothing is done by the university administration to reduce the ESP class size for international students .” They believed that large class sizes in ESP or EFL classes could negatively influence group oral presentations, hindering language development and leading to uneven participation. The experts suggested that smaller class sizes would allow for more individualized attention, increased speaking opportunities for each student, and more effective feedback mechanisms, all of which are crucial for developing strong presentation skills in a second language.
Research question 1: what are the advantages of PDs from the perspective of panelists and the audience?
The results of this study reveal significant advantages of PDs for both panelists and audience members in the context of medical education. These findings align with and expand upon previous research in the field of educational presentations and language learning.
Personal and professional development for panelists
The high frequency of reported benefits in the “Personal and Professional Development” theme for panelists aligns with several previous studies. The emphasis on language mastery, particularly increased confidence (91.3%) and better retention of key concepts (87.0%), supports the findings of Hartono, Mujiyanto [ 42 ], Gedamu and Gezahegn [ 15 ], Li [ 43 ], who all highlighted the importance of language practice in English oral presentations. However, our results show a more comprehensive range of benefits, including professional growth aspects like experiential learning (84.8%) and real-world application (80.4%), which were not as prominently featured in these earlier studies.
Interestingly, our findings partially contrast with Chou [ 44 ] study, which found that while group oral presentations had the greatest influence on improving students’ speaking ability, individual presentations led to more frequent use of metacognitive, retrieval, and rehearsal strategies. Our results suggest that PDs, despite being group activities, still provide significant benefits in these areas, possibly due to the collaborative nature of preparation and the individual responsibility each panelist bears. The high frequency of knowledge sharing (93.5%) and collaboration (89.1%) in our study supports Harris, Jones and Huffman [ 45 ] emphasis on the importance of group dynamics and varied perspectives in educational settings. However, our study provides more quantitative evidence for these benefits in the specific context of PDs.
Enriching learning experience for the audience
The audience perspective in our study reveals a rich learning experience, with high frequencies across all categories. This aligns with Agustina [ 46 ] findings in business English classes, where presentations led to improvements in all four language skills. However, our study extends these findings by demonstrating that even passive participation as an audience member can lead to significant perceived benefits in language practice (89.1%) and broadening perspectives (93.5% for diverse speakers). The high value placed on diverse speakers (93.5%) and range of topics (91.3%) by the audience supports the notion of PDs as a tool for expanding knowledge and viewpoints. This aligns with the concept of situated learning experiences leading to deeper understanding in EFL classes, as suggested by Li [ 43 ] and others [ 18 , 31 ]. However, our study provides more specific evidence for how this occurs in the context of PDs.
Interactive learning and engagement
Both panelists and audience members in our study highly valued the interactive aspects of PDs, with the importance of interaction rated at 91.3% by panelists and increased audience interest at 91.3% by the audience. This strong emphasis on interactivity aligns with Azizi and Farid Khafaga [ 19 ] study on the benefits of dynamic assessment and dialogic learning contexts. However, our study provides more detailed insights into how this interactivity is perceived and valued by both presenters and audience members in PDs.
Professional growth and real-world application
The emphasis on professional growth through PDs, particularly for panelists, supports Li’s [ 43 ] assertion about the power of oral presentations as situated learning experiences. Our findings provide more specific evidence for how PDs contribute to professional development, with high frequencies reported for experiential learning (84.8%) and real-world application (80.4%). This suggests that PDs may be particularly effective in bridging the gap between academic learning and professional practice in medical education.
Research question 2: what are the disadvantages of pds from the perspective of panelists and the audience?
Academic workload challenges for panelists.
The high frequency of reported challenges in the “Academic Workload Challenges” category for panelists aligns with several previous studies in medical education [ 47 , 48 , 49 ]. The emphasis on long preparation (87.0%), significant practice needed (82.6%), and the time-consuming nature of PDs (80.4%) supports the findings of Johnson et al. [ 24 ], who noted that while learners appreciate debate-style journal clubs in health professional education, they require additional time commitment. This is further corroborated by Nowak, Speed and Vuk [ 50 ], who found that intensive learning activities in medical education, while beneficial, can be time-consuming for students.
Perceived value of pds relative to time investment
While a significant portion of the audience (65.2%) perceived PDs as an inefficient use of time, the high frequency of engagement-related concerns (82.6% for repetitive format, 78.3% for limited engagement) suggests that the perceived lack of value may be more closely tied to the quality of the experience rather than just the time investment. This aligns with Dyhrberg O’Neill [ 27 ] findings on debate-based oral exams, where students perceived value despite the time-intensive nature of the activity. However, our results indicate a more pronounced concern about the return on time investment in PDs. This discrepancy might be addressed through innovative approaches to PD design and implementation, such as those proposed by Almazyad et al. [ 22 ], who suggested using AI tools to enhance expert panel discussions and potentially improve efficiency.
Coordination challenges for panelists
The challenges related to coordination in medical education, such as diverse panel skills (78.3%) and finding suitable panelists (73.9%), align with previous research on teamwork in higher education [ 21 ]. Our findings support the concept of the free-rider effect discussed by Hall and Buzwell [ 21 ], who explored reasons for non-contribution in group projects beyond social loafing. This is further elaborated by Mehmood, Memon and Ali [ 51 ], who proposed that individuals may not contribute their fair share due to various factors including poor communication skills or language barriers, which is particularly relevant in medical education where clear communication is crucial [ 52 ]. Comparing our results to other collaborative learning contexts in medical education, Rodríguez-Sedano, Conde and Fernández-Llamas [ 53 ] measured teamwork competence development in a multidisciplinary project-based learning environment. They found that while teamwork skills improved over time, initial coordination challenges were significant. This aligns with our findings on the difficulties of coordinating diverse panel skills and opinions in medical education settings.
Our results also resonate with Chou’s [ 44 ] study comparing group and individual oral presentations, which found that group presenters often had a limited understanding of the overall content. This is supported by Wilson, Ho and Brookes [ 54 ], who examined student perceptions of teamwork in undergraduate science degrees, highlighting the challenges and benefits of collaborative work, which are equally applicable in medical education [ 52 ].
Quality of discussions and perception for the audience
The audience perspective in our study reveals significant concerns about the quality and engagement of PDs in medical education. The high frequency of issues such as repetitive format (82.6%) and limited engagement with the audience (78.3%) aligns with Parmar and Bickmore [ 55 ] findings on the importance of addressing individual audience members and gathering feedback. This is further supported by Nurakhir et al. [ 25 ], who explored students’ views on classroom debates as a strategy to enhance critical thinking and oral communication skills in nursing education, which shares similarities with medical education. Comparing our results to other interactive learning methods in medical education, Jones et al. [ 26 ] reviewed the use of journal clubs and book clubs in pharmacy education. They found that while these methods enhanced engagement, they also faced challenges in maintaining student interest over time, similar to the boredom issues reported in our study of PDs in medical education. The perception of PDs as boring (73.9%) and not very useful during exam time (52.2%) supports previous research on the stress and pressure experienced by medical students [ 48 , 49 ]. Grieve et al. [ 20 ] specifically examined student fears of oral presentations and public speaking in higher education, which provides context for the anxiety and disengagement observed in our study of medical education. Interestingly, Bhuvaneshwari et al. [ 23 ] found positive impacts of panel discussions in educating medical students on specific modules. This contrasts with our findings and suggests that the effectiveness of PDs in medical education may vary depending on the specific context and implementation.
Comparative analysis and future directions
Our study provides a unique comparative analysis of the challenges faced by both panelists and audience members in medical education. The alignment of concerns around workload and time management between the two groups suggests that these are overarching issues in the implementation of PDs in medical curricula. This is consistent with the findings of Pasandín et al. [ 56 ], who examined cooperative oral presentations in higher education and their impact on both technical and soft skills, which are crucial in medical education [ 52 ]. The mismatch between panelist efforts and audience expectations revealed in our study is a novel finding that warrants further investigation in medical education. This disparity could be related to the self-efficacy beliefs of presenters, as explored by Gedamu and Gezahegn [ 15 ] in their study of TEFL trainees’ attitudes towards academic oral presentations, which may have parallels in medical education. Looking forward, innovative approaches could address some of the challenges identified in medical education. Almazyad et al. [ 22 ] proposed using AI tools like ChatGPT to enhance expert panel discussions in pediatric palliative care, which could potentially address some of the preparation and engagement issues identified in our study of medical education. Additionally, Ragupathi and Lee [ 57 ] discussed the role of rubrics in higher education, which could provide clearer expectations and feedback for both panelists and audience members in PDs within medical education.
Research question 3: how can PDs be improved for panelists and the audience from the experts’ point of view?
The expert suggestions for improving PDs address several key challenges identified in previous research on academic presentations and student workload management. These recommendations align with current trends in educational technology and pedagogical approaches, while also considering the unique needs of medical students.
The emphasis on time management and workload reduction strategies echoes findings from previous studies on medical student stress and academic performance. Nowak, Speed and Vuk [ 50 ] found that medical students often struggle with the fast-paced nature of their courses, which can lead to reduced motivation and superficial learning approaches. The experts’ suggestions for task breakdown and prioritization align with Rabbi and Islam [ 58 ] recommendations for reducing workload stress through effective assignment prioritization. Additionally, Popa et al. [ 59 ] highlight the importance of acceptance and planning in stress management for medical students, supporting the experts’ focus on these areas.
The proposed implementation of interactive training sessions for panelists addresses the need for enhanced presentation skills in professional contexts, a concern highlighted by several researchers [ 17 , 60 ]. This aligns with Grieve et al. [ 20 ] findings on student fears of oral presentations and public speaking in higher education, emphasizing the need for targeted training. The focus on interactive elements and audience engagement also reflects current trends in active learning pedagogies, as demonstrated by Pasandín et al. [ 56 ] in their study on cooperative oral presentations in engineering education.
The innovative suggestion to use AI tools like ChatGPT for PD preparation represents a novel approach to leveraging technology in education. This aligns with recent research on the potential of AI in scientific research, such as the study by Almazyad et al. [ 22 ], which highlighted the benefits of AI in supporting various educational tasks. However, it is important to consider potential ethical implications and ensure that AI use complements rather than replaces critical thinking and creativity.
The experts’ emphasis on enhancing collaboration and communication among panelists addresses issues identified in previous research on teamwork in higher education. Rodríguez-Sedano, Conde and Fernández-Llamas [ 53 ] noted the importance of measuring teamwork competence development in project-based learning environments. The suggested strategies for improving coordination align with best practices in collaborative learning, as demonstrated by Romero-Yesa et al. [ 61 ] in their qualitative assessment of challenge-based learning and teamwork in electronics programs.
The unanimous agreement on the need to reduce ESP class sizes for international students reflects ongoing concerns about the impact of large classes on language learning and student engagement. This aligns with research by Li [ 3 ] on issues in developing EFL learners’ oral English communication skills. Bosco et al. [ 62 ] further highlight the challenges of teaching and learning ESP in mixed classes, supporting the experts’ recommendation for smaller class sizes. Qiao, Xu and bin Ahmad [ 63 ] also emphasize the implementation challenges for ESP formative assessment in large classes, further justifying the need for reduced class sizes.
These expert recommendations provide a comprehensive approach to improving PDs, addressing not only the immediate challenges of preparation and delivery but also broader issues of student engagement, workload management, and institutional support. By implementing these suggestions, universities could potentially transform PDs from perceived burdens into valuable learning experiences that enhance both academic and professional skills. This aligns with Kho and Ting [ 64 ] systematic review on overcoming oral presentation anxiety among tertiary ESL/EFL students, which emphasizes the importance of addressing both challenges and strategies in improving presentation skills.
This study has shed light on the complex challenges associated with PDs in medical education, revealing a nuanced interplay between the experiences of panelists and audience members. The findings underscore the need for a holistic approach to implementing PDs that addresses both the academic workload concerns and the quality of engagement.
Our findings both support and extend previous research on the challenges of oral presentations and group work in medical education settings. The high frequencies of perceived challenges across multiple categories for both panelists and audience members suggest that while PDs may offer benefits, they also present significant obstacles that need to be addressed in medical education. These results highlight the need for careful consideration in the implementation of PDs in medical education, with particular attention to workload management, coordination strategies, and audience engagement techniques. Future research could focus on developing and testing interventions to mitigate these challenges while preserving the potential benefits of PDs in medical education.
Moving forward, medical educators should consider innovative approaches to mitigate these challenges. This may include:
Integrating time management and stress coping strategies into the PD preparation process [ 59 ].
Exploring the use of AI tools to streamline preparation and enhance engagement [ 22 ].
Developing clear rubrics and expectations for both panelists and audience members [ 57 ].
Incorporating interactive elements to maintain audience interest and participation [ 25 ].
Limitations and future research
One limitation of this study is that it focused on a specific population of medical students, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other student populations. Additionally, the study relied on self-report data from panelists and audience members, which may introduce bias and affect the validity of the results. Future research could explore the effectiveness of PDs in different educational contexts and student populations to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the benefits and challenges of panel discussions.
Future research should focus on evaluating the effectiveness of these interventions and exploring how PDs can be tailored to the unique demands of medical education. By addressing the identified challenges, PDs have the potential to become a more valuable and engaging component of medical curricula, fostering both academic and professional development. Ultimately, the goal should be to transform PDs from perceived burdens into opportunities for meaningful learning and skill development, aligning with the evolving needs of medical education in the 21st century.
Future research could also examine the long-term impact of PDs on panelists’ language skills, teamwork, and communication abilities. Additionally, exploring the effectiveness of different training methods and tools, such as AI technology, in improving coordination skills and reducing workload stress for panelists could provide valuable insights for educators and administrators. Further research could also investigate the role of class size and audience engagement in enhancing the overall effectiveness of PDs in higher education settings. By addressing these gaps in the literature, future research can contribute to the ongoing development and improvement of PDs as a valuable learning tool for students in higher education.
However, it is important to note that implementing these changes may require significant institutional resources and a shift in pedagogical approaches. Future research could focus on piloting these recommendations and evaluating their effectiveness in improving student outcomes and experiences with PDs.
Data availability
We confirm that the data supporting the findings are available within this article. Raw data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author, upon request.
Abbreviations
Artificial Intelligence
English as a Foreign Language
English for Specific Purposes
Panel Discussion
Shiraz University of Medical Sciences
Harden RM, Laidlaw JM. Essential skills for a medical teacher: an introduction to teaching and learning in medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences; 2020.
Ibrahim Mohamed O, Al Jadaan DO. English for Specific purposes (Esp) Needs Analysis for Health Sciences students: a cross-sectional study at a University in the UAE. English for Specific purposes (Esp) Needs Analysis for Health Sciences Students: A Cross-Sectional Study at a University in the UAE.
Li Y, Heron M. English for general academic purposes or English for specific purposes? Language learning needs of medical students at a Chinese university. Theory Pract Lang Stud. 2021;11(6):621–31.
Article Google Scholar
Chan SMH, Mamat NH, Nadarajah VD. Mind your language: the importance of English language skills in an International Medical Programme (IMP). BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):405.
Cortez Faustino BS, Ticas de Córdova CK, de la Hernández DI. Teaching English for specific purposes: contents and methodologies that could be implemented in the English for Medical purposes (EMP) course for the doctor of Medicine Major at the University of El Salvador. Universidad de El Salvador; 2022.
BENYAMINA E-Z BOUKAHLAH. Enhancing Specialty Language learning through content-based instruction: students of Paramedical Institute of Tiaret as a case study. Université IBN KHALDOUN-Tiaret; 2023.
Prikazchikov M. Medical English course for russian-speaking dentists: a needs analysis study. Iowa State University; 2024.
Kim C, Lee SY, Park S-H. Is Korea Ready to be a key player in the Medical Tourism Industry? An English Education Perspective. Iran J Public Health. 2020;49(2):267–73.
Google Scholar
Syakur A, Zainuddin H, Hasan MA. Needs analysis English for specific purposes (esp) for vocational pharmacy students. Budapest International Research and Critics in Linguistics and Education (BirLE). Journal. 2020;3(2):724–33.
Chan S, Taylor L. Comparing writing proficiency assessments used in professional medical registration: a methodology to inform policy and practice. Assess Writ. 2020;46:100493.
Hyland K, Jiang FK. Delivering relevance: the emergence of ESP as a discipline. Engl Specif Purp. 2021;64:13–25.
Maftuna B. The role of English in ESP. Am J Adv Sci Res. 2024;1(2):1–5.
LEON LI, HUMANIZING THE FOREIGN LANGUAGE. COURSE: NEW TEACHING METHODS FOR MEDICAL STUDENTS. Language, Culture and Change. 2022:243.
Dahm MR, Yates L. Rapport, empathy and professional identity: Some challenges for international medical graduates speaking English as a second or foreign language. Multilingual Healthcare: A Global View on Communicative Challenges. 2020:209 – 34.
Gedamu AD, Gezahegn TH. TEFL trainees’ attitude to and self-efficacy beliefs of academic oral presentation. Cogent Educ. 2023;10(1):2163087.
Saliu B, Hajrullai H. Best practices in the English for specific purpose classes at the language center. Procedia-Social Behav Sci. 2016;232:745–9.
Clokie TL, Fourie E. Graduate employability and communication competence: are undergraduates taught relevant skills? Bus Prof Communication Q. 2016;79(4):442–63.
Hartono H, Mujiyanto J, Fitriati SW, Sakhiyya Z, Lotfie MM, Maharani MM. English Presentation Self-Efficacy Development of Indonesian ESP students: the effects of Individual versus Group Presentation tasks. Int J Lang Educ. 2023;7(3):361–76.
Azizi Z, Farid Khafaga A. Scaffolding via Group-dynamic Assessment to positively affect motivation, learning anxiety, and willingness to Communicate: a Case Study of High School Students. J Psycholinguist Res. 2023;52(3):831–51.
Grieve R, Woodley J, Hunt SE, McKay A. Student fears of oral presentations and public speaking in higher education: a qualitative survey. J Furth High Educ. 2021;45(9):1281–93.
Hall D, Buzwell S. The problem of free-riding in group projects: looking beyond social loafing as reason for non-contribution. Act Learn High Educ. 2013;14(1):37–49.
Almazyad M, Aljofan F, Abouammoh NA, Muaygil R, Malki KH, Aljamaan F, et al. Enhancing Expert Panel discussions in Pediatric Palliative Care: innovative scenario development and summarization with ChatGPT-4. Cureus. 2023;15(4):e38249.
Bhuvaneshwari S, Rashmi R, Deepika K, Anirudh VM, Vijayamathy A, Rekha S, Kathiravan R. Impact of panel discussion in educating AETCOM First Module among Undergraduate Medical Students. Latin Am J Pharmacy: Life Sci J. 2023;42(6):407–12.
Johnson BR, Logan LD, Darley A, Stone RH, Smith SE, Osae SP, et al. A scoping review for Debate-Style Journal Clubs in Health Professional Education. Am J Pharm Educ. 2023;87(6):100064.
Nurakhir A, Palupi FN, Langeveld C, Nurmalia D. Students’ views of classroom debates as a strategy to enhance critical thinking and oral communication skills. 2020.
Jones EP, Nelson NR, Thorpe CT, Rodgers PT, Carlson RB. Use of journal clubs and book clubs in pharmacy education: a scoping review. Currents Pharm Teach Learn. 2022;14(1):110–9.
Dyhrberg O’Neill L. Assessment of student debates in support of active learning? Students’ perceptions of a debate-based oral final exam. Act Learn High Educ. 2024.
Dyment JE, O’Connell TS. Assessing the quality of reflection in student journals: a review of the research. Teach High Educ. 2011;16(1):81–97.
Villarroel V, Bloxham S, Bruna D, Bruna C, Herrera-Seda C. Authentic assessment: creating a blueprint for course design. Assess Evaluation High Educ. 2018;43(5):840–54.
Schultz M, Young K, Gunning K, Harvey T. Defining and measuring authentic assessment: a case study in the context of tertiary science. Assess Evaluation High Educ. 2022;47(1):77–94.
Sundrarajun C, Kiely R. The oral presentation as a context for learning and assessment. Innov Lang Learn Teach. 2010;4(2):101–17.
Wyatt-Smith C, Adie L. The development of students’ evaluative expertise: enabling conditions for integrating criteria into pedagogic practice. J Curriculum Stud. 2021;53(4):399–419.
Boud D, Lawson R, Thompson DG. The calibration of student judgement through self-assessment: disruptive effects of assessment patterns. High Educ Res Dev. 2015;34(1):45–59.
A. S. Enhancing Meaningful Learning experiences through Comprehension and Retention by students. Twentyfirst Century Publications Patiala. 2023;49.
Colton D, Covert RW. Designing and constructing instruments for social research and evaluation. Wiley; 2007.
Krueger RA, Casey MA. Focus group interviewing. Handbook of practical program evaluation. 2015:506 – 34.
Morgan DL. Handbook of interview research: Context and method. Oaks, CA, USA: Sage Publications Thousand; 2002.
Braun V, Clarke V. Conceptual and design thinking for thematic analysis. Qualitative Psychol. 2022;9(1):3.
Elliott V. Thinking about the coding process in qualitative data analysis. Qualitative Rep. 2018;23(11).
Syed M, Nelson SC. Guidelines for establishing reliability when coding narrative data. Emerg Adulthood. 2015;3(6):375–87.
Lincoln Y. Naturalistic inquiry: Sage; 1985.
Hartono H, Mujiyanto J, Fitriati SW, Sakhiyya Z, Lotfie MM, Maharani MM. English presentation self-efficacy development of Indonesian ESP students: the effects of Individual versus Group Presentation tasks. Int J Lang Educ. 2023;7(3).
Li X. Teaching English oral presentations as a situated task in an EFL classroom: a quasi-experimental study of the effect of video-assisted self-reflection. Revista Signos. 2018;51(98):359–81.
Chou M-h. The influence of learner strategies on oral presentations: a comparison between group and individual performance. Engl Specif Purp. 2011;30(4):272–85.
Harris A, Jones M, Huffman J. Teachers leading educational reform. The power of. 2017.
Agustina L. Stimulating students to speak up through presentation in business English class. J Appl Stud Lang. 2019;3(1):21–8.
Babal JC, Abraham O, Webber S, Watterson T, Moua P, Chen J. Student pharmacist perspectives on factors that influence wellbeing during pharmacy school. Am J Pharm Educ. 2020;84(9):ajpe7831.
Moir F, Yielder J, Sanson J, Chen Y. Depression in medical students: current insights. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2018;323:33.
Pavlinac Dodig I, Lusic Kalcina L, Demirovic S, Pecotic R, Valic M, Dogas Z. Sleep and lifestyle habits of medical and non-medical students during the COVID-19 lockdown. Behav Sci. 2023;13(5):407.
Nowak G, Speed O, Vuk J. Microlearning activities improve student comprehension of difficult concepts and performance in a biochemistry course. Currents Pharm Teach Learn. 2023;15(1):69–78.
Mehmood K, Memon S, Ali F. Language barriers to Effective Communication in speaking English: a phenomenological study of Pakistan International cricketers. Pakistan Lang Humanit Rev. 2024;8(1):107–14.
Buelow JR, Downs D, Jorgensen K, Karges JR, Nelson D. Building interdisciplinary teamwork among allied health students through live clinical case simulations. J Allied Health. 2008;37(2):e109–23.
Rodríguez-Sedano FJ, Conde M, Fernández-Llamas C, editors. Measuring teamwork competence development in a multidisciplinary project based learning environment. Learning and Collaboration Technologies Design, Development and Technological Innovation: 5th International Conference, LCT 2018, Held as Part of HCI International 2018, Las Vegas, NV, USA, July 15–20, 2018, Proceedings, Part I 5; 2018: Springer.
Wilson L, Ho S, Brookes RH. Student perceptions of teamwork within assessment tasks in undergraduate science degrees. Assess Evaluation High Educ. 2018;43(5):786–99.
Parmar D, Bickmore T. Making it personal: addressing individual audience members in oral presentations using augmented reality. Proc ACM Interact Mob Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2020;4(2):1–22.
Pasandín AMR, Pérez IP, Iglesias PO, Díaz JJG. Cooperative oral presentations in higher education to enhance technical and soft skills in engineering students. Int J Continuing Eng Educ Life Long Learn. 2023;33(6):592–607.
Ragupathi K, Lee A. Beyond fairness and consistency in grading: The role of rubrics in higher education. Diversity and inclusion in global higher education: Lessons from across Asia. 2020:73–95.
Rabbi MF, Islam MS. The effect of academic stress and Mental anxiety among the students of Khulna University. Edukasiana: Jurnal Inovasi Pendidikan. 2024;3(3):280–99.
Popa CO, Schenk A, Rus A, Szasz S, Suciu N, Szabo DA, Cojocaru C. The role of acceptance and planning in stress management for medical students. Acta Marisiensis-Seria Med. 2020;66(3):101–5.
Christianson M, Payne S. Helping students develop skills for better presentations: Using the 20x20 format for presentation training. 語学研究. 2012;26:1–15.
Romero-Yesa S, Fonseca D, Aláez M, Amo-Filva D. Qualitative assessment of a challenge-based learning and teamwork applied in electronics program. Heliyon. 2023;9(12).
Bosco TJ, Gabriel B, Florence M, Gilbert N. Towards effective teaching and learning ESP in mixed classes: students’ interest, challenges and remedies. Int J Engl Literature Social Sci. 2020;5(2):506–16.
Qiao L, Xu Y, bin Ahmad N, An Analysis Of Implementation Challenges For English, For Specific Purposes (Esp) Formative Assessment Via Blended Learning Mode At Chinese Vocational Polytechnics. Journal Of Digital Education, Communication, And Arts (DECA). 2023;6(02):64–76.
Kho MG-W, Ting S-H. Overcoming oral presentation anxiety: a systematic review of Tertiary ESL/EFL Students’ challenges and strategies. Qeios. 2023.
Download references
We confirm that no funding was received for this work.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of English Language, School of Paramedical Sciences, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran
Elham Nasiri & Laleh Khojasteh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
L.KH was involved in writing the proposal, reviewing the text, analyzing the data, and writing the manuscript. E. N was involvedin designing the research and collecting and analyzing the data. Both authors have reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Laleh Khojasteh .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Our study, entitled “Evaluating Panel Discussions in ESP Classes: An Exploration of International Medical Students’ and ESP Instructors’ Perspectives through Qualitative Research,” was reviewed by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the School of Paramedical Sciences, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences (SUMS). The IRB reviewed the study on August 14th, 2024, and determined that formal ethics approval or a reference number was not required. This decision was based on the fact that the research posed minimal risk to participants and focused solely on their educational experiences without involving any intervention or the collection of sensitive personal data.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
We confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and that this work did not receive any financial support.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Nasiri, E., Khojasteh, L. Evaluating panel discussions in ESP classes: an exploration of international medical students’ and ESP instructors’ perspectives through qualitative research. BMC Med Educ 24 , 925 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05911-3
Download citation
Received : 08 May 2024
Accepted : 14 August 2024
Published : 26 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05911-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Group oral presentations
- Medical students
- Panel discussions
- ESP courses
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption
- Start Monitoring for Free
What is a product designer? Skills, duties, and career path

Have you ever used an app so intuitive it felt like it could read your mind and knew exactly how to help you achieve your goal? Or have you visited a website that was so visually appealing you couldn’t look away? Behind these seamless experiences lies the work of a product designer.

Product designers are creatives who bridge the gap between user needs, business goals, and technological possibilities. Their job is to translate complex ideas into user-friendly interfaces so that products are not just functional, but also enjoyable and easy to use.
Let’s take a deeper look at the role of a product designer, discussing everything from the essential skills you need to the diverse career paths you can take. If you’re an aspiring designer or simply curious, this article will equip you with the knowledge you need to navigate this field.
What is a product designer?
Think of a product designer as the architect of a user’s experience with a digital product. They typically work hand-in-hand with product managers and engineers to decide what a product will look like, how it will behave, and the steps a user will take to achieve their goals.
What do product designers do?
The scope of a product designer can be quite broad, but there are four main responsibilities of a product designer: user research, UI/UX design, prototyping, and collaborating on or facilitating design thinking. Let’s get into these responsibilities in more detail.
User research
Product designers need to understand user needs and pain points to design effective, enjoyable products. You can do user research through methods like interviews, surveys, and usability testing. The goal is to scope out:
- The needs of their target user needs
- How their target users behave
- How their target users are currently solving their problems
- Issues or limitations in existing solutions
User research allows product designers to see from the user’s perspective and figure out how to address user needs in a way that aligns with their behaviors and improves on what’s already out there.
UI/UX design
When thinking about product design, it’s important to consider how to make user interactions with the product smooth, intuitive, and enjoyable. That’s where UI and UX design come into play.
Part of a product designer’s responsibilities are to design the user interface (UI), i.e. the visual elements users interact with, as well as the user experience (UX), which refers to the overall flow and feel of using the product.
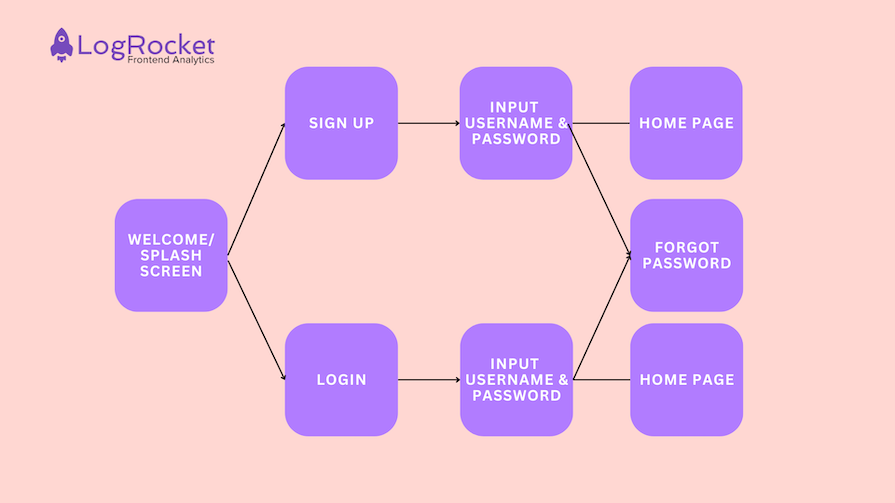
Here’s an example of how you might think about a product’s UX design using a user flow diagram :
Prototyping
Prototyping involves creating interactive mockups and using them to test and refine design ideas before full development. This allows businesses to validate a product designer’s ideas and rapidly iterate on solution concepts before committing to expensive development efforts.
Collaborating on and facilitating design thinking
Product designers work closely with developers, engineers, product managers, user researchers, data analysts, and other stakeholders to bring their designs to life. They act as facilitators during design thinking sessions, guiding their cross-functional teammates through brainstorming exercises, user research analysis, and solution development.
Taking this collaborative approach helps you consider all perspectives during the product design process , leading to well-rounded product solutions that meet both user needs and business goals within technical possibilities and constraints.
How product designers can specialize
Product design is a broad field. However, you can choose to specialize in a number of ways, including:
- UX designer — Makes sure the product is easy and enjoyable to use. In an ideal user experience, the user should be able to achieve their goal in the fastest way possible, and there should be provisions in place to solve issues that may arise in edge cases
- UI designer — Focuses on the visual design of the product, creating aesthetically pleasing and user-friendly interfaces
- Interaction designer — Creates the interactive elements of a product, focusing on how users navigate and interact with the interface
- Visual designer — Specializes in the overall visual style and branding of a product, ensuring consistency and user recognition
- Design researcher — Conducts in-depth user research to inform design decisions, focusing on understanding user needs, behaviors, and pain points
- Product design accessibility specialist — Ensures digital products are usable by everyone, regardless of ability, by following accessibility guidelines and best practices
It’s also important to keep product management concepts in mind throughout the product design process. For example, UX, UI, interaction, and visual designers need to make design decisions that are in line with business goals, while design researchers and accessibility specialists should deeply understand market needs.
Essential skills for product designers
What skills do you need to be a product designer? Through practice and experience, you’ll need to develop a combination of hard skills and soft skills.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
Hard skills could include:
- Proficiency with UX research methods
- Proficiency with UI/UX design tools such as Figma or Sketch
- Prototyping tools like Framer, InVision
- Knowledge of design principles (usability, accessibility, heuristics).
While soft skills encompass:
- Clear communication when presenting design ideas to stakeholders, explaining design decisions to developers, or reviewing writing UI copy with copywriters
- Collaborating with engineers, user researchers, product managers, and other designers to bring a product to life
- Empathy when conducting user interviews, understanding user pain points, advocating for the user and designing solutions that address user needs
- Problem-solving when encountering usability issues during prototyping, identifying the root cause of a design challenge, and developing creative solutions
- Critical thinking to better evaluate design solutions, analyze user research data, and make informed decisions based on evidence
Is product design right for you?
Product design can be a highly rewarding field, but it’s not for everyone. Before you take the leap, you should consider if your personality and interests align with the role. Let’s look at some of the traits that help a great product designer thrive:
- Curiosity — Are you constantly asking “why” and eager to understand how things work? A good product designer is driven by a desire to learn and explore user behavior
- Empathy — Can you put yourself in someone else’s shoes? User empathy is crucial for understanding user needs and designing solutions that resonate with them
- Passion for solving problems — Do you thrive on tackling confusing or outright difficult challenges and finding creative solutions? Product designers are constantly working to improve experiences and overcome design hurdles
- Detail-oriented — Do you have a keen eye for detail, ensuring that everything is pixel perfect? This is essential for creating seamless user experiences
Take this self-assessment exercise to see if product design aligns with your interests:
- Do you enjoy using digital products and analyzing their design?
- Are you someone who likes to sketch, brainstorm, and come up with creative ways to tackle challenges?
- Do you find working collaboratively with others to be stimulating and rewarding?
- Would you describe yourself as detail-oriented and organized?
- Are you constantly seeking ways to improve things around you?
If you answered yes to most of these questions, then product design might be a perfect fit for your personality! The good news is, even if you don’t have a design background, there are plenty of learning resources and alternative paths to becoming a product designer.
What qualifications do you need to be a product designer?
There are two main paths to break into product design:
- The traditional path involves studying for a formal design degree and building a design portfolio. John Ive , former Chief Design Officer at Apple has a bachelor’s degree in Art and Design. Well-known designer Femke van Schoonhoven has a bachelor’s degree in Commerce, majoring in Marketing & Media, and obtained a post-graduate diploma in Design
- Alternative paths involve taking bootcamps, online courses and self-directed learning. You can become a product designer without a design degree — just focus on improving your skills and building a strong portfolio
Here are some programs you can explore if you’re taking an alternative path to a career in product design:
- Udacity product design course
- Co.Lab product design bootcamp
- Google UX design course on Coursera
Why become a product designer?
Product design is a special role that offers a unique blend of creativity, problem-solving, and impact. It’s a career path that allows you to:
- Make a positive impact — The products you design have the power to improve people’s lives. For example, if you were working on streamlining a complex workflow or creating an engaging learning platform, your work can make a real difference
- Solve complex problems — Product design is a constant intellectual challenge. You’ll get to tackle intricate user needs, make tradeoffs while navigating technical constraints, and develop innovative solutions, allowing you to exercise both the creative and analytical parts of your brain
- Shape the future of technology — The technological possibilities are endless, as evidenced by the rapid boom in AI tools and use cases. Product designers are at the forefront of this change. You’ll have the opportunity to contribute to creating and adopting cutting-edge technologies that influence how we interact with the digital world
- Earn a lucrative salary — Product design can be professionally, intellectually, and socially rewarding, but it’s also a financially rewarding career choice. The increasing demand for skilled designers has led to competitive salaries, and as you gain experience and expertise, you can grow into leadership positions and further elevate your earning potential
Product designer career path
Product design offers a variety of career paths to explore. You may even have the chance to encounter related or “diagonal” careers throughout your journey, allowing you to develop your specific interests and skills:
Let’s go over what your traditional professional career path may look like in more detail.
Early career
At the start of your career, you’ll focus on gaining experience through assisting senior designers, contributing to various projects, and honing your design skills. You might start out as a Product Design Intern; otherwise, you’ll likely be a Junior or Associate Product Designer.
Then, as a Product Designer with a strong design portfolio and refined skills, you’ll take ownership of projects, leading user research, designing interfaces, and collaborating with cross-functional teams.
As you progress in your career to the role of a Senior Product Designer, you’ll mentor junior designers, provide design direction, and ensure design consistency across projects.
This is a good place in your career to hone your understanding of how product design fits into the larger picture. Think about product strategy and business goals to set yourself up to become a leader in the field.
Senior leadership
As a design leader, you could be a Product Design Lead or Head of Design. In these senior leadership roles you’ll set the design vision, manage resources, and ensure alignment with business goals.
At the executive level, your title will likely be Director of Product Design or VP of Design. You’ll oversee the entire design strategy, fostering innovation and advocating for user-centric design across the organization.
Diagonal careers
Your product design expertise can also open doors to other fulfilling career specializations, such as:
- Product management — Transitioning to product management leverages your user empathy and design thinking skills to focus on the broader product strategy and roadmap
- UX writing — Your understanding of user experience can be valuable in crafting clear, concise, and user-friendly content within digital products
Consider what you’re best at as well as what you most enjoy doing to further refine your career path.
Product designer vs. product manager
You may have noticed that product design overlaps with both UX/UI design as well as product management. Given their similar names, the roles of product designer and product manager are often confused. While both roles are crucial for product success, there are key differences in:
- Areas of focus — Product designers focus on the user experience, crafting intuitive interfaces and interactions. Product managers focus on the overall product strategy, considering market needs, business goals, and technical feasibility.
- Required skills — Product designers excel in visual design, user research, and prototyping. Product managers will also do user research and discovery, but will require strong analytical skills, business acumen, some data analysis skills, and both technical proficiency and project management expertise
Can you transition from product designer to product manager?
Yes, definitely. The skills developed in product design can provide a strong foundation for transitioning to product management.
However, you will take on additional responsibilities that bridge the gap, like market analysis or competitive analysis, and this can demonstrate your well-roundedness. As you gain more experience, you can also earn certifications in product management to further strengthen your expertise.
So, you want to be a product designer?
If you’re passionate about creating intuitive solutions, tackling challenges head-on, and leaving your mark on the digital world, then product design might be the perfect career path for you. However, we’ve seen that becoming a product designer isn’t just about mastering the design tools.
You’ll need to cultivate a curious mind that constantly asks “why” and a relentless drive to understand user needs. You’ll learn to embrace challenges as opportunities to innovate and solve complex problems. You’ll constantly advocate for your users, putting yourself in their shoes to design experiences that feel effortless and intuitive.
The good news is that there are resources and opportunities galore. You can start by exploring online courses, attending design workshops, or even building a personal design portfolio to showcase your skills.
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #career development

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
An overview of feature-driven development (FDD)
FDD is an agile framework for software development that emphasizes incremental and iterative progress on product features development.

Leader Spotlight: Making the customer feel like a regular, with Judy Yao
Judy Yao talks about creating a digital experience that makes customers feel as if they were repeat, familiar customers in a physical store.

How can PMs benefit from generative AI
AI amplifies your potential when you use it as a co-pilot. However, don’t forget you’re the driver, not the passenger.

Leader Spotlight: Creating ‘magical’ customer experiences, with Karapet Gyumjibashyan
Karapet Gyumjibashyan talks about how going above and beyond to exceed customer expectations can make their experience “magical.”
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- DOI: 10.1145/3631802.3631852
- Corpus ID: 267523741
Deep Talk: Ascertain Soft Skills in Graduates to Improve Computing Education
- M. Ntinda , E. Sutinen , +1 author Juli‐Anna Aerila
- Published in European Conference on… 13 November 2023
- Computer Science, Education
Figures from this paper

10 References
Gaps between industry expectations and the abilities of graduates, play and productivity: enhancing the creative climate at workplace meetings with play cues, using storytelling to maintain employee loyalty during change, the story cookbook: practical recipes for change, a sense of community, the catalan immersion program: a european point of view, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

Student Learning Development
View the contact page for more contact and location information
/prod01/channel_3/media/tcd/student-learning/images/student-learning.jpg)
Reach your potential
Student Learning Development supports Trinity students reach their academic potential.
/prod01/channel_3/media/tcd/student-learning/images/student-learning-2.jpg)
New to College? We offer a range of helpful services!
We offer a range of services including individual appointments, workshops and skills events.
Welcome to Student Learning Development
These services are designed to develop your skills in areas such as academic writing, self and time management, exam & assessment skills for PG & UG students.
READ MORE ABOUT US

Postgraduate Writing Retreat - Mon 15th July 9.30-15.00
Over a dedicated 5.5 hour online session, we will use the pomodoro method along with writing tasks to help you generate writing...

Academic Writing Centre - Run by SLD TCD
30 minute online individual sessions where students gain advice with writing strategies, structuring, critical thinking & writing and referencing...

What's at SLD for STEM Students?
See the highlights some of the main services tailored to students studying in the Faculty of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics and also those studying in the Faculty of Health Science.

Shut Up and Write Café for PG Students
The Shut Up and Write Café runs all year. Sessions are hosted using Blackboard Collaborate. No video or audio is necessary to join...

Individual Support
If you need support with any area of Academic/Learning Skills e.g. assessment, self management, procrastination, organisation, study skills, PG theses/viva or any general queries you have...

Academic Skills Webinars
We run a wide range of FREE workshops for undergraduates and postgraduates. These are based on proven strategies to help students improve their performance in their studies.
Further Services
Services for staff, student counselling, student to student s2s, other college services.
- Critical Thinking
Critical Thinking: Components, Skills, and Strategies
- February 2021
- Revista Argentina de Clinica Psicologica 30(2):1-6

- Qassim University
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Ahmed Almaghrabi

- Ahmad Jusoha

- Abelhalim Al-Harbis
- Feras Al-Saleeti
- Aziza Al-Sayed
- Tarkhan Mohamed
- Robert Eniss
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

The Importance of Critical Thinking Skills in Research
Why is Critical Thinking Important: A Disruptive Force
Research anxiety seems to be taking an increasingly dominant role in the world of academic research. The pressure to publish or perish can warp your focus into thinking that the only good research is publishable research!
Today, your role as the researcher appears to take a back seat to the perceived value of the topic and the extent to which the results of the study will be cited around the world. Due to financial pressures and a growing tendency of risk aversion, studies are increasingly going down the path of applied research rather than basic or pure research . The potential for breakthroughs is being deliberately limited to incremental contributions from researchers who are forced to worry more about job security and pleasing their paymasters than about making a significant contribution to their field.
A Slow Decline
So what lead the researchers to their love of science and scientific research in the first place? The answer is critical thinking skills. The more that academic research becomes governed by policies outside of the research process, the less opportunity there will be for researchers to exercise such skills.
True research demands new ideas , perspectives, and arguments based on willingness and confidence to revisit and directly challenge existing schools of thought and established positions on theories and accepted codes of practice. Success comes from a recursive approach to the research question with an iterative refinement based on constant reflection and revision.
The importance of critical thinking skills in research is therefore huge, without which researchers may even lack the confidence to challenge their own assumptions.
A Misunderstood Skill
Critical thinking is widely recognized as a core competency and as a precursor to research. Employers value it as a requirement for every position they post, and every survey of potential employers for graduates in local markets rate the skill as their number one concern.
Related: Do you have questions on research idea or manuscript drafting? Get personalized answers on the FREE Q&A Forum!
When asked to clarify what critical thinking means to them, employers will use such phrases as “the ability to think independently,” or “the ability to think on their feet,” or “to show some initiative and resolve a problem without direct supervision.” These are all valuable skills, but how do you teach them?
For higher education institutions in particular, when you are being assessed against dropout, graduation, and job placement rates, where does a course in critical thinking skills fit into the mix? Student Success courses as a precursor to your first undergraduate course will help students to navigate the campus and whatever online resources are available to them (including the tutoring center), but that doesn’t equate to raising critical thinking competencies.
The Dependent Generation
As education becomes increasingly commoditized and broken-down into components that can be delivered online for maximum productivity and profitability, we run the risk of devaluing academic discourse and independent thought. Larger class sizes preclude substantive debate, and the more that content is broken into sound bites that can be tested in multiple-choice questions, the less requirement there will be for original thought.
Academic journals value citation above all else, and so content is steered towards the type of articles that will achieve high citation volume. As such, students and researchers will perpetuate such misuse by ensuring that their papers include only highly cited works. And the objective of high citation volume is achieved.
We expand the body of knowledge in any field by challenging the status quo. Denying the veracity of commonly accepted “facts” or playing devil’s advocate with established rules supports a necessary insurgency that drives future research. If we do not continue to emphasize the need for critical thinking skills to preserve such rebellion, academic research may begin to slowly fade away.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Avoiding the AI Trap: Pitfalls of relying on ChatGPT for PhD applications
10 Ways to Help Students Restore Focus on Learning
Switching Your Major As a Researcher: Things to Consider Before Making the Decision

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- Promoting Research
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?

How to Improve Your Critical Thinking Skills
Traditional tools and new technologies..
Posted September 29, 2023 | Reviewed by Lybi Ma

Technology provides access to vast information and makes daily life easier. Yet, too much reliance on technology potentially interferes with the acquisition and maintenance of critical thinking skills in several ways:
1. Information Overload : The constant influx of data can discourage deep critical thinking as we may come to rely on quick, surface-level information rather than delving deeply into a subject.
2. Shortened Attention Span: Frequent digital distractions can disrupt our ability for the sustained focus and concentration required for critical thinking.
3. Confirmatory Bias and Echo Chambers: Technology, including social media and personalized content algorithms, can reinforce confirmation bias . People are often exposed to information that aligns with their beliefs and opinions, making them less likely to encounter diverse perspectives and engage in critical thinking about opposing views.
4. Reduced Problem-Solving Opportunities: Technology often provides quick solutions to problems. While this benefits efficiency, it may discourage individuals from engaging in complex problem-solving, a fundamental aspect of critical thinking.
5. Loss of Research Skills: The ease of accessing information online can diminish traditional research skills, such as library research or in-depth reading. These skills are essential for critical thinking, as they involve evaluating sources, synthesizing information, and analyzing complex texts.
While technology can pose challenges to developing critical thinking skills, it's important to note that technology can also be a valuable tool for learning and skill development. It can provide access to educational resources, facilitate collaboration , and support critical thinking when used thoughtfully and intentionally. Balancing technology use with activities that encourage deep thinking and analysis is vital to lessening its potential adverse effects on critical thinking.
Writing is a traditional and powerful tool to exercise and improve your critical thinking skills. Consider these ways writing can help enhance critical thinking:
1. Clarity of Thought: Writing requires that you articulate your thoughts clearly and coherently. When you need to put your ideas on paper, you must organize them logically, which requires a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
2. Analysis and Evaluation: Critical thinking involves analyzing and evaluating information. When you write, you often need to assess the validity and relevance of different sources, arguments, or pieces of evidence, which hone your critical thinking skills.
3. Problem-Solving: Writing can be a problem-solving exercise in itself. Whether crafting an argument, developing a thesis, or finding the right words to express your ideas, writing requires thinking critically about approaching these challenges effectively.
4. Research Skills: Good writing often involves research, and research requires critical thinking. You need to assess the credibility of sources, synthesize information, and draw conclusions based on the evidence you gather.
5. Argumentation: Constructing a persuasive argument in writing is a complex process requiring critical thinking. You must anticipate counterarguments, provide evidence to support your claims, and address potential weaknesses in your reasoning.
6. Revision and Editing: To be an influential writer, you must learn to read your work critically. Editing and revising requires evaluating your writing objectively, identifying areas that need improvement, and refining your ideas and arguments.
7. Problem Identification: In some cases, writing can help you identify problems or gaps in your thinking. As you write, you might realize that your arguments are not as strong as you initially thought or that you need more information to support your claims. This recognition of limitations is a crucial aspect of critical thinking.
Writing is a dynamic process that engages multiple facets of critical thinking. It has been a valuable tool used in education , business, and personal development for centuries.
Yet, this traditional approach of self-generated written thoughts is rapidly being supplanted by AI -generated writing tools like Chat GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer. With over 100 million users of Chat GPT alone, we cannot ignore its potential impact. How might the increasing reliance on AI-generated writing tools influence our critical thinking skills? The impact can vary depending on how the tools are used and the context in which they are employed.

Critical thinking involves evaluating information sources for credibility, relevance, and bias. If individuals consistently trust the information provided by chatbots without critically assessing its quality, it can hinder their development of critical thinking skills. This is especially true if they depend on the chatbot to provide answers without questioning or verifying the information. Relying solely on chatbots for answers may also reduce people's effort in problem-solving. Critical thinking often requires wrestling with complex problems, considering multiple perspectives, and generating creative solutions. If we default to chatbots for quick answers, we may miss opportunities to develop these skills.
However, it's essential to note that the impact of chatbots on critical thinking skills may not be entirely negative. These tools can also have positive effects:
1. Chatbots provide quick access to vast information, which can benefit research and problem-solving. When used as a supplement to critical thinking, they can enhance the efficiency of information retrieval.
2. Chatbots can sometimes assist in complex tasks by providing relevant data or suggestions. When individuals critically evaluate and integrate this information into their decision-making process, it can enhance their critical thinking.
3. Chatbots can be used as learning aids. They can provide explanations, examples, and guidance, which can support skill development and, when used effectively, encourage critical thinking.
In summary, the impact of chatbots on critical thinking skills depends on how we use them. The effect will be harmful if they become a crutch to avoid independent thought or analysis. However, they can be valuable resources when used as tools to facilitate and augment critical thinking and writing processes. Individuals must balance leveraging the convenience of chatbots and actively engaging in independent critical thinking and problem-solving to maintain and enhance their cognitive abilities. You can do that effectively through writing regularly.
Copyright 2023 Tara Well, PhD

Tara Well, Ph.D. , is a professor in the department of psychology at Barnard College of Columbia University.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.
Find your coach
-1.png)
Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
Critical thinking is the one skillset you can't afford not to master

Jump to section
What is critical thinking?
5 characteristics of critical thinking, what are critical thinking skills, and why are they important, 6 key critical thinking skills, critical thinking example in real-life, 13 ways to start thinking critically.
Whether you’re aiming to improve your performance at work or simply trying to live a more fulfilling life , you’ll need a variety of hard and soft skills to move the needle. Some skills come naturally to some people, while others need to develop them actively.
One of these skills is critical thinking. But critical thinking itself is made up of several types of skills that contribute to solving problems more effectively.
Let’s explore the different types of critical thinking skills and how you can start improving them to level up your career.
Critical thinking is the ability to analyze facts objectively and form a judgment. It is a form of emotional intelligence .
Someone with critical thinking skills can think clearly and rationally when the situation demands it. It allows them to perform problem-solving and decision-making more effectively.
As a result, you can look further than what you see at face value. You’re able to analyze what you see from a situation and gain some insight that goes further than what’s obvious to anyone from the outside.
Critical thinking also requires being able to understand the logical connection between two or more ideas or concepts. For example, a team working on a company’s pricing strategy needs to think critically about several concepts.
Both the marketing and sales teams must work together. They need to analyze how to maximize sales. But they need to do so while also meeting profit goals. It’s important to understand the logical connection between sales strategy and marketing logistics. It’s the only way to get a good outcome.
Critical thinking is different from creative thinking . Creative thinking is the ability to generate brand new, innovative ideas. On the other hand, critical thinking requires you to carefully and logically analyze what information is given to you. Both are important to maximize results in any given situation.

What defines critical thinking? How does it affect the decision-making process? Here are five characteristics that make up the ability to think critically.
1. Dispositions
Critical thinkers have specific traits that allow them to think the way they do. Some people are predisposed to these traits, while others need to develop them actively.
Some of these dispositions include:
- Open-mindedness
- Respecting evidence and reasoning
- Being able to consider different perspectives and points of view: in other words, having cognitive flexibility
- Not being stuck in one position
- Clarity and precision
2. Argument
Good critical thinkers need to make solid arguments.
An argument is making a statement aided by supporting evidence. It’s important to use well thought-out arguments when you’re in a constructive conflict . When analyzing a situation critically, you’ll need to make several arguments in your own mind to come to a judgment.
3. Reasoning
In addition to arguments, critical thinking also requires inferring conclusions. From the facts and arguments presented to you, you need to use reasoning skills to come to a logical conclusion.
This conclusion will determine the best course of action to take.

4. Criteria
Critical thinking is sometimes a matter of discerning truth from fiction. Not all facts presented to you may have the same level of truth. Certain conditions need to be met for something to be considered believable, and a critical thinker needs to be able to understand that.
5. Metacognition
Metacognition is the ability to think about your own thinking. Critical thinkers should be able to analyze their thoughts so that they can judge whether or not they’ve thought everything through. This helps them come up with better hypotheses.
The critical thinking skills definition is: soft skills that help you in the critical thinking process. Developing these skills can improve your ability to think critically.
Critical thinking skills are considered one of many durable skills in the workplace . Many of these are soft skills that are also useful in other situations.
According to research by America Succeeds, critical thinking is in the top five most requested durable skills in job postings. Those top five durable skills get requested 2.6x more often than the top five hard skills. This goes to show that soft skills like critical thinking skills are in demand in the workplace.
Critical thinking skills are important for several reasons. These include helping you work independently and solve problems . Not all positions require ongoing critical thinking. But, those skills definitely matter to anyone who wants to uplevel their career. And even the most easygoing positions require at least some level of critical thinking skills.
For example, working as an accountant can be straightforward in most cases. But it may require critical thinking skills. For instance, what if certain expenses aren’t easily distributed in simple categories? Without critical thinking skills, an accountant will struggle to work independently and solve problems on their own.
Critical thinking abilities also matter in everyday life. Having a foundation for critical thinking can help you analyze several possible solutions for problems that pop up in the home. It can also help you:
- Analyze different viewpoints
- Come up with the best solution for complex problems
- Become a better learner
The key critical thinking skills are identifying biases, inference, research, identification, curiosity, and judging relevance.
Let’s explore these six critical thinking skills you should learn and why they’re so important to the critical thinking process.
1. Identifying biases
This critical thinking skill is necessary for metacognition, which is the fifth characteristic of critical thinking. It involves knowing when others have a cognitive bias and when you have one yourself.
Biases can influence how someone understands the facts presented to them. But when you’re aware of those biases, you can question yourself on those biases and consider other points of view.
Identifying biases is especially important for people who make hiring decisions. That’s because biases against groups of minorities can lead to inequalities in the workplace when not identified.
For example, imagine a hiring manager comparing two resumes. Their gut feeling could guide them to discount one of the resumes due to a bias against the opposite gender. But let’s say this hiring manager realizes they have this bias. They can then question themselves on whether or not this bias is influencing their judgment.
2. Inference
Inference is the ability to draw conclusions based on the information you have. Without inference, it can be difficult to take action once you’ve analyzed the facts presented to you. Processing information is key to coming up with a reasoned judgment.
For example, let’s go back to the accountant struggling to assign the correct category to a business expense. They can analyze other similar situations and infer the most logical category based on that information.
3. Research
Before you analyze facts and infer a conclusion, you need to find out what those facts are. Researching skills allow you to discover facts and figures to make an argument.
Not all situations will have the required information available to you. Researching skills are necessary to dig into a situation and gather the information you need to think critically.
Some situations don’t require further research. For example, a first responder who arrives on the scene of an automobile accident won’t perform further research. They’ll have to analyze what they see in front of them and decide which injuries are the most urgent to care for.
On the other hand, someone performing a market analysis will need to research competitors and gather information before coming up with an opinion.
4. Identification
Identification is different from inference and research. It involves being able to identify a problem but also what’s influencing that problem.
In short, identification is necessary for someone to realize that they need to think critically about something. Without proper identification skills, it will be difficult for someone to know when it’s time to analyze a situation.
For example, let’s say you’re entering numbers in a spreadsheet. The numbers aren’t coming out as they usually do. Without identification skills, you could easily keep going without realizing there’s an issue. But when you identify what’s going on, you can see that something is broken in the spreadsheet’s formula.
Only once you identify the fact that the formula is broken can you start analyzing what’s going on to solve the issue.
5. Curiosity
Don’t be afraid to question everything and explore what you’re curious about. That’s because intellectual curiosity is a valuable skill, especially when it comes to critical thinking.
One way to practice curiosity is to adopt a beginner’s mindset . When you come into every situation with the mindset of a beginner, you’re able to keep an open mind. You’ll be able to perceive things you may not have noticed when keeping your mind closed.
6. Judging relevance
Not all information is equally pertinent. In order to make a critical judgment, it’s important to be able to judge the relevance of the information you have.
Take, for instance, basic online researching skills. You have access to a plethora of information on virtually every topic imaginable. But performing online research requires you to constantly judge the relevance of what you see.
Without judging relevance, you’d spend too much time on details that don’t matter as much for the final desired outcome. But when you’re able to discern what’s most pertinent, you can give that information more weight as you’re thinking critically.

So what would critical thinking skills look like in a real-life situation?
Let’s imagine you’re working in software quality assurance (QA) as a team lead. But every time your team needs to enter bug regression, everyone gets bottlenecked because you must manually populate the spreadsheet used for the regression. While you do this task, your team cannot be productive without you.
This process happens once a week and easily wastes half an hour for each team member.
First, you must identify what’s going on. The team gets bottlenecked because only you, as the team lead, can access the information required to fill in the regression spreadsheet.
Next, you can research information. You can inquire to higher-ups about the reason why only you have access to this information. You can also speak to other teams about what potential solutions they’ve come up with to solve this problem.
Once you’ve done your research, it’s time to analyze the information and judge relevance. Some teams have solutions that don’t apply to you, so that information isn’t relevant anymore.
Figure out if there are any personal biases before you analyze your information.
For example, it’s possible that you don’t get along with one of the other team leads. As a result, you could discount the information they’ve given you. But by identifying this bias, you can look past your personal opinion of this person and see how valuable their solution is.
Based on what you’ve analyzed, it’s time to brainstorm and come up with a solution. You realize that creating a simple, automated script will save your team’s time. And it will do so without consuming too many resources from the engineering department.
Next, present your solution to your manager. Explain how you came to this conclusion.
Now, let’s say your spreadsheet automation solution is approved. It’s important to go back and analyze what happens after implementing the solution. But only do this once the spreadsheet has been in place for long enough to gather plenty of information.
Here’s an example. You could realize that the solution did solve the bottleneck. But, the script also slows down the spreadsheet and makes it difficult to work with. This would require you to go back to the drawing board and start the process all over again.
Want to start improving your own critical thinking skill sets? Here’s how you can improve critical thinking skills using 13 techniques:
- Play games that require critical thinking skills
- Ask more questions, even basic ones
- Question your assumptions
- Develop your technical skills so that you can identify problems more easily
- Find ways to solve more problems (at work and at home)
- Become aware of your mental processes, like the availability heuristic
- Think for yourself: don’t adopt other people’s opinions without questioning them first
- Seek out diversity of thought
- Start developing foresight
- Try active listening
- Weigh the consequences of different actions before you act
- Seek a mentor who can help you develop these skills
- Get professional coaching

How to improve your critical thinking skills
Critical thinking skills aren’t always easy to develop. But it’s much easier to start thinking critically when you have someone to work with. Try a custom BetterUp demo to see how a coach can help you develop your critical thinking skills today.
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Maggie Wooll, MBA
Maggie Wooll is a researcher, author, and speaker focused on the evolving future of work. Formerly the lead researcher at the Deloitte Center for the Edge, she holds a Bachelor of Science in Education from Princeton University and an MBA from the University of Virginia Darden School of Business. Maggie is passionate about creating better work and greater opportunities for all.
How to develop critical thinking skills
What’s convergent thinking how to be a better problem-solver, why self-management is key to success and how to improve yours, how intrapersonal skills shape teams, plus 5 ways to build them, how to be optimistic, the most critical skills for leaders are fundamentally human, the new skill set needed to succeed in the hybrid workplace, building strength for tomorrow: new president of betterup care™ on extending proactive mental health across the enterprise, the 5 business communication skills worth perfecting, what is lateral thinking 7 techniques to encourage creative ideas, 9 cognitive skill examples and how to improve them, 8 brainstorming techniques to harness the power of teamwork, how to pitch ideas: 8 tips to captivate any audience, what are analytical skills examples and how to level up, how divergent thinking can drive your creativity, how the minto pyramid principle can enhance your communication skills, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- Archives & Special Collections home
- Art Library home
- Ekstrom Library home
- Kornhauser Health Sciences Library home
- Law Library home
- Music Library home
- University of Louisville Hospital home
- Interlibrary Loan
- Off-Campus Login
- Renew Books
- Cardinal Card
- My Print Center
- Business Ops
- Cards Career Connection
Search Site
Search catalog, critical thinking and academic research: intro.
- Information
- Point of View
- Assumptions
- Implications
Critical Thinking and Academic Research
Academic research focuses on the creation of new ideas, perspectives, and arguments. The researcher seeks relevant information in articles, books, and other sources, then develops an informed point of view within this ongoing "conversation" among researchers.
The research process is not simply collecting data, evidence, or "facts," then piecing together this preexisting information into a paper. Instead, the research process is about inquiry—asking questions and developing answers through serious critical thinking and thoughtful reflection.
As a result, the research process is recursive, meaning that the researcher regularly revisits ideas, seeks new information when necessary, and reconsiders and refines the research question, topic, or approach. In other words, research almost always involves constant reflection and revision.
This guide is designed to help you think through various aspects of the research process. The steps are not sequential, nor are they prescriptive about what steps you should take at particular points in the research process. Instead, the guide should help you consider the larger, interrelated elements of thinking involved in research.
Research Anxiety?
Research is not often easy or straightforward, so it's completely normal to feel anxious, frustrated, or confused. In fact, if you feel anxious, it can be a good sign that you're engaging in the type of critical thinking necessary to research and write a high-quality paper.
Think of the research process not as one giant, impossibly complicated task, but as a series of smaller, interconnected steps. These steps can be messy, and there is not one correct sequence of steps that will work for every researcher. However, thinking about research in small steps can help you be more productive and alleviate anxiety.
Paul-Elder Framework
This guide is based on the "Elements of Reasoning" from the Paul-Elder framework for critical thinking. For more information about the Paul-Elder framework, click the link below.
Some of the content in this guide has been adapted from The Aspiring Thinker's Guide to Critical Thinking (2009) by Linda Elder and Richard Paul.
- Next: Purpose >>
- Last Updated: Jul 10, 2023 11:50 AM
- Librarian Login
Developing Scientific Thinking and Research Skills Through the Research Thesis or Dissertation
- First Online: 22 September 2019
Cite this chapter

- Gina Wisker 3 , 4
1369 Accesses
3 Citations
This chapter explores higher level scientific thinking skills that research students need to develop during their research learning journeys towards their dissertation/thesis at postgraduate levels, and also final year undergraduate (Australian honours year) dissertation. A model of four quadrants is introduced. Practice and experience-informed examples are presented to show how higher order skills can be realised and embedded so that they become established ways of thinking, researching, creating, and expressing knowledge and understanding.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions

Similar content being viewed by others

Building Confidence About the Academic Journey

How Do Teachers Meet the Academic Needs of High-Ability Students in Science?
Transforming from naïve research student to confident critical thinker.
Aitchison, C., & Guerin, C. (Eds.). (2014). Writing groups for doctoral education and beyond: Innovations in practice and theory . Abingdon: Routledge.
Google Scholar
Archer, L. (2008). Younger academics’ constructions of ‘authenticity’, ‘success’ and professional identity. Studies in Higher Education, 33 (4), 385–403. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070802211729 .
Article Google Scholar
Baker, V. L., & Lattuca, L. R. (2010). Developmental networks and learning: Toward an interdisciplinary perspective on identity development during doctoral study. Studies in Higher Education, 35 (7), 807–827. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070903501887 .
Bell, J. (2010). Doing your research project: A guide for first-time researchers in education, health and social science . Maidenhead: McGraw-Hill Open University Press.
Boud, D. (Ed.). (1988). Developing student autonomy in learning (2nd ed.). New York: Nichols Publishing Company.
Boud, D., & Walker, D. (1998). Promoting reflection in professional courses: The challenge of context. Studies in Higher Education, 23 (2), 191–206. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079812331380384 .
Brew, A. (2001). Conceptions of research: A phenomenographic study. Studies in Higher Education, 26 (3), 271–285. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070120076255 .
Bruce, N. (1995). Practising what we preach: Creating the conditions for student autonomy. Hong Kong Papers in Linguistics & Language Teaching , 18 , 73–88. Retrieved from http://hkjo.lib.hku.hk/archive/files/30cc63ad3122e0ad29590de2006ba6d0.pdf .
Butler, S. (1999). Catalysing student autonomy through action research in a problem centered learning environment. Research in Science Education, 29 (1), 127–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02461184 .
Carver, C., & Scheier, M. (2005). Optimism. In C. R. Snyder & S. J. Lopez (Eds.), Handbook of positive psychology (pp. 231–256). New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Castello, M., Kobayashi, S., McGinn, M. K., Pechar, H., Vekkaila, J., & Wisker, G. (2017). Researcher identity in transition: Signals to identify and manage spheres of activity in a risk-career. Frontline Learning Research , 3 (3), 19–33. https://doi.org/10.14786/flr.v3i3.149 .
Davies, A., & Danaher, P. A. (2014). Capacity-building for western expatriate nurses and Australian early career researchers. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences, 112, 373–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.1177 .
Elbow, P. (1973). Writing without teachers . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Fazey, D. M. A., & Fazey, J. A. (2001). The potential for autonomy in learning: Perceptions of competence, motivation and locus of control in first-year undergraduate students. Studies in Higher Education, 26 (3), 345–361. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075070120076309 .
Flanagan, M. (2018). Michael Thomas Flanagan, University College London, London . Retrieved April 4, 2019, from https://www.ee.ucl.ac.uk/~mflanaga .
Grant, B. M. (2008). Agonistic struggle: Master-slave dialogues in humanities supervision. Arts and Humanities in Higher Education, 7 (1), 9–27. https://doi.org/10.1177/1474022207084880 .
Haksever, A. M., & Manisali, E. (2000). Assessing supervision requirements of PhD students: The case of construction management and engineering in the UK. European Journal of Engineering Education, 25 (1), 19–32. https://doi.org/10.1080/030437900308616 .
Healey, M., Bovill, C., & Jenkins, A. (2015). Students as partners in learning. In J. Lea (Ed.), Enhancing learning and teaching in higher education: Engaging with the dimensions of practice (pp. 141–172). Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Healey, M., Flint, A., & Harrington, K. (2014). Engagement through partnership: Students as partners in learning and teaching in higher education . York: HE Academy. Retrieved from https://www.heacademy.ac.uk/knowledge-hub/engagement-through-partnership-students-partners-learning-and-teaching-higher .
Healey, M., Flint, A., & Harrington, K. (2016). Students as partners: Reflections on a conceptual model. Teaching and Learning Inquiry , 4 (2), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.20343/teachlearninqu.4.2.3 .
Holbrook, A., Shaw, K., Scevak, J., Bourke, S., Cantwell, R., & Budd, J. (2014). PhD candidate expectations: Exploring mismatch with experience. International Journal of Doctoral Studies , 9 , 329–346. https://doi.org/10.28945/2078 .
Ivanic, R. (1998). Writing and identity: The discoursal construction of identity in academic writing . Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Book Google Scholar
Jenkins, E. W. (2001). Research in science education in Europe: Retrospect and prospect. In H. Behrendt (Ed.), Research in science education: Past, present and future (pp. 17–26). Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-47639-8_2 .
Johansson, T., Wisker, G., Claesson, S., Strandler, O., & Saalman, E. (2013). PhD supervision as an emotional process—Critical situations and emotional boundary work. Pertanika: Journal of Social Science and Humanities , 22 , 605–622.
Kiley, M., & Wisker, G. (2009). Threshold concepts in research education and evidence of threshold crossing. Higher Education Research and Development, 28 (4), 431–441. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360903067930 .
Kobayashi, S., Grout, B., & Rump, C. Ø. (2013). Interaction and learning in PhD supervision—A qualitative study of supervision with multiple supervisors. Dansk Universitetspaedagogisk Tidsskrift , 8 (14), 13–25. Retrieved from https://tidsskrift.dk/dut/article/download/7174/6653 .
Kobayashi, S., Grout, B. W., & Rump, C. Ø. (2015). Opportunities to learn scientific thinking in joint doctoral supervision. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 52 (1), 41–51. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2014.981837 .
Li, S., & Seale, C. (2007). Learning to do qualitative data analysis: An observational study of doctoral work. Qualitative Health Research, 17 (10), 1442–1452. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732307306924 .
Land, R., Meyer, J., & Smith, J. (Eds.). (2008). Threshold concepts within the disciplines . Rotterdam: Sense.
Leibowitz, B., Wisker, G., & Lamberti, P. (2018). ‘Crossing over’ into research on teaching and learning. In E. Bitzer (Ed.), Spaces, journeys and new horizons for postgraduate supervision (pp. 149–162). Stellenbosch, South Africa: SUN Press.
Lombardo, T. (2006). The evolution of future consciousness: The nature and historical development of the human capacity to think about the future . Bloomington, IN: AuthorHouse.
Lombardo, T. (2007). Developing constructive and creative attitudes and behaviors about the future: Part III—The self‐narrative, optimism and self‐efficacy, and the evolving future self. World Futures Study Federation : Futures Bulletin , 32 (2). Retrieved from https://www.centerforfutureconsciousness.com/pdf_files/WFSFArticles/Bulletins/FutConsArticle3.pdf .
Lombardo, T., & Richter, J. (2004). Evolving future consciousness through the pursuit of virtue. In H. Didsbury (Ed.), Thinking creatively in turbulent times . Bethesda, MD: World Future Society.
Meyer, J. H. F., & Land, R. (2003). Threshold concepts and troublesome knowledge: Linkages to ways of thinking and practising within the disciplines. In C. Rust (Ed.), Improving student learning: Improving student learning theory and practice—Ten years on . Oxford: Oxford Centre for Staff and Learning Development.
McAlpine, L. (2012). Shining a light on doctoral reading: Implications for doctoral identities and pedagogies. Innovations in Education and Teaching International, 49 (4), 351–361. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2012.728875 .
McAlpine, L., Amundsen, C., & Turner, G. (2013). Identity-trajectory: Reframing early career academic experience. British Educational Research Journey, 40 (6), 952–969. https://doi.org/10.1002/berj.3123 .
Morris, C., & Wisker, G. (2011). Troublesome encounters: Strategies for managing the wellbeing of master’s and doctoral education students during their learning processes (HEA ESCalate Subject Centre Report). Retrieved from http://escalate.ac.uk/6828 .
Muurlink, O., & Poyatos Matas, C. (2010). A higher degree of stress: Academic wellbeing. In L. Marshall & C. Morris (Eds.), Taking wellbeing forward in higher education: Reflections on theory and practice (pp. 60–71). Falmer: University of Brighton Press.
Murray, R. (2016). How to write a thesis (4th ed.). Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Murtonen, M. (2005). University students’ research orientations: Do negative attitudes exist toward quantitative methods? Scandinavian Journal of Educational Research, 49 (3), 263–280. https://doi.org/10.1080/00313830500109568 .
Murtonen, M. (2015). University students’ understanding of the concepts empirical, theoretical, qualitative, and quantitative research. Teaching in Higher Education, 20 (7), 684–698. https://doi.org/10.1080/13562517.2015.1072152 .
Murtonen, M., Olkinuora, E., Tynjälä, P., & Lehtinen, E. (2008). “Do I need research skills in working life?”: University students’ motivation and difficulties in quantitative methods courses. Higher Education, 56 (5), 599–612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-008-9113-9 .
Phillips, E., & Pugh, D. S. (2010). How to get a PhD: A handbook for students and their supervisors . Maidenhead: McGraw-Hill Open University Press.
Poyatos Matas, C. (2008, July). An innovative approach to research supervision . Paper presented at the University of Brighton Learning and Teaching Conference, Brighton, UK.
Poyatos Matas, C. (2009). A new approach to research supervision. In J. Barlow, G. Louw, & M. Rice (Eds.), Social purpose and creativity—Integrating learning in the real world (pp. 28–32). Falmer: University of Brighton Press.
Pyhältö, K., Nummenmaa, A. R., Soini, T., Stubb, J., & Lonka, K. (2012). Research on scholarly communities and development of scholarly identity in Finnish doctoral education. In T. S. Ahola & D. M. Hoffman (Eds.), Higher education research in Finland: Emerging structures and contemporary issues (pp. 337–357). Jyväskylä, Finland: Jyväskylä University Press.
Schulze, S. (2012). Empowering and disempowering students in student-supervisor relationships. Koers-Bulletin for Christian Scholarship, 77 (2), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.4102/koers.v77i2.47 .
Strandler, O., Johansson, T., Wisker, G., & Claesson, S. (2014). Supervisor or counsellor? Emotional boundary work in supervision. International Journal for Researcher Development, 5 (2), 70–82. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJRD-03-2014-0002 .
Trafford, V., & Leshem, S. (2009). Doctorateness as a threshold concept. Innovations in Education and Teaching International , 46 (3), 305–316. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703290903069027 .
Vekkaila, J., Pyhältö, K., & Lonka, K. (2013). Focusing on doctoral students’ experiences of engagement in thesis work. Frontline Learning Research, 1 (2), 10–32. https://doi.org/10.14786/flr.v1i2.43 .
Walliman, N. S. R. (2011). Your research project: Designing and planning your work . London: Sage.
Willison, J. (2009). Multiple contexts, multiple outcomes, one conceptual framework for research skill development in the undergraduate curriculum. CUR Quarterly , 29 (3), 10–14. Retrieved from https://www.adelaide.edu.au/rsd/evidence/related-articles/willison_2009_CURQ_29_3_.pdf .
Willison, J. (2012). When academics integrate research skill development in the curriculum. Higher Education Research & Development, 31 (6), 905–919. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2012.658760 .
Willison, J., & O’Regan, K. (2005). 2020 Vision: An information literacy continuum for students primary school to post graduation. In A. Brew & C. Asmar (Eds.), Higher education in a changing world: Proceedings of the 28th HERDSA annual conference (pp. 633–641). Sydney, NSW, Australia: Higher Education Research and Development Society of Australasia.
Willison, J., & O’Regan, K. (2006). Research skill development framework . Retrieved April 4, 2019, from www.adelaide.edu.au/rsd .
Willison, J., Sabir, F., & Thomas, J. (2017). Shifting dimensions of autonomy in students’ research and employment. Higher Education Research and Development, 36 (2), 430–443. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2016.1178216 .
Wisker, G. (2001). The postgraduate research handbook . Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Wisker, G. (2009/2018). The undergraduate research handbook. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Wisker, G. (2012). The good supervisor: Supervising postgraduate and undergraduate research for doctoral theses and dissertations . Basingstoke: Palgrave Research Skills.
Wisker, G. (2014). Voice, vision and articulation: Conceptual threshold crossing in academic writing. In C. O’Mahony, A. Buchanan, M. O’Rourke, & B. Higgs (Eds.), Proceedings of the National Academy’s sixth annual conference and the fourth biennial threshold concepts conference (pp. 159–164). Cork, Ireland: NAIRTL. Retrieved from https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ED558533 .
Wisker, G. (2015). Getting published . London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Wisker, G. (2016). Toil and trouble: Professional and personal expectations and identities in academic writing for publication. In J. Smith (Ed.), Identity work in the contemporary university: Exploring an uneasy profession (pp. 143–154). Rotterdam: Sense.
Wisker, G. (2018). Frameworks and freedoms: Supervising research learning and the undergraduate dissertation. Journal of University Teaching and Learning Practice , 15 (4), 1–14. Retrieved from https://ro.uow.edu.au/jutlp/vol15/iss4/2 .
Wisker, G., & Kiley, M. (2017). Helping students demonstrate mastery of doctoral threshold concepts. In S. Carter & D. Laurs (Eds.), Developing research writing: A handbook for supervisors and advisers (pp. 173–178). Abingdon: Routledge.
Chapter Google Scholar
Wisker, G., Kiley, M., & Aiston, S. (2006, March). Making the learning leap: Research students crossing conceptual thresholds . Paper presented at the quality in postgraduate research conference, Adelaide, Australia.
Wisker, G., Morris, C., Cheng, M., Masika, R., Warnes, M., Lilly, J. …, Robinson, G. (2010). Doctoral learning journeys—Final report of the NTFS-funded project . Retrieved from http://www.heacademy.ac.uk/resources/detail/ntfs/Projects/Doctoral_Learning_Journeys .
Wisker, G., & Robinson, G. (2013). Doctoral ‘orphans’: Nurturing and supporting the success of postgraduates who have lost their supervisors. Higher Education Research & Development, 32 (2), 300–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2012.657160 .
Wisker, G., Robinson, G., & Kiley, M. (2008, March). Crossing liminal spaces: Encouraging postgraduate students to cross conceptual thresholds and achieve threshold concepts in their research . Paper presented at the quality in postgraduate research: Research education in the new global environment—Part 2. Canberra, Australia.
Wisker, G., Robinson, G., Trafford, V., Warnes, M., & Creighton, E. (2003). From supervisory dialogues to successful PhDs: Strategies supporting and enabling the learning conversations of staff and students at postgraduate level. Teaching in Higher Education, 8 (3), 383–397. https://doi.org/10.1080/13562510309400 .
Wisker, G., & Savin-Baden, M. (2009). Priceless conceptual thresholds: Beyond the ‘stuck place’ in writing. London Review of Education, 7 (3), 235–247. https://doi.org/10.1080/14748460903290207 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Brighton, Brighton, UK
Gina Wisker
University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gina Wisker .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Education and Culture, Tampere University, Tampere, Finland
Mari Murtonen
Department of Higher Education, University of Surrey, Guildford, UK
Kieran Balloo
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Wisker, G. (2019). Developing Scientific Thinking and Research Skills Through the Research Thesis or Dissertation. In: Murtonen, M., Balloo, K. (eds) Redefining Scientific Thinking for Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24215-2_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-24215-2_9
Published : 22 September 2019
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-24214-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-24215-2
eBook Packages : Education Education (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
- What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
The Most Important Research Skills (With Examples)
- What Are Hard Skills?
- What Are Technical Skills?
- What Are What Are Life Skills?
- What Are Social Media Skills Resume?
- What Are Administrative Skills?
- What Are Analytical Skills?
- What Are Research Skills?
- What Are Transferable Skills?
- What Are Microsoft Office Skills?
- What Are Clerical Skills?
- What Are Computer Skills?
- What Are Core Competencies?
- What Are Collaboration Skills?
- What Are Conflict Resolution Skills?
- What Are Mathematical Skills?
- How To Delegate
Find a Job You Really Want In
Research skills are the ability to find out accurate information on a topic. They include being able to determine the data you need, find and interpret those findings, and then explain that to others. Being able to do effective research is a beneficial skill in any profession, as data and research inform how businesses operate. Whether you’re unsure of your research skills or are looking for ways to further improve them, then this article will cover important research skills and how to become even better at research. Key Takeaways Having strong research skills can help you understand your competitors, develop new processes, and build your professional skills in addition to aiding you in finding new customers and saving your company money. Some of the most valuable research skills you can have include goal setting, data collection, and analyzing information from multiple sources. You can and should put your research skills on your resume and highlight them in your job interviews. In This Article Skip to section What are research skills? Why are research skills important? 12 of the most important research skills How to improve your research skills Highlighting your research skills in a job interview How to include research skills on your resume Resume examples showcasing research skills Research skills FAQs References Sign Up For More Advice and Jobs Show More What are research skills?
Research skills are the necessary tools to be able to find, compile, and interpret information in order to answer a question. Of course, there are several aspects to this. Researchers typically have to decide how to go about researching a problem — which for most people is internet research.
In addition, you need to be able to interpret the reliability of a source, put the information you find together in an organized and logical way, and be able to present your findings to others. That means that they’re comprised of both hard skills — knowing your subject and what’s true and what isn’t — and soft skills. You need to be able to interpret sources and communicate clearly.
Why are research skills important?
Research skills are useful in any industry, and have applications in innovation, product development, competitor research, and many other areas. In addition, the skills used in researching aren’t only useful for research. Being able to interpret information is a necessary skill, as is being able to clearly explain your reasoning.
Research skills are used to:
Do competitor research. Knowing what your biggest competitors are up to is an essential part of any business. Researching what works for your competitors, what they’re doing better than you, and where you can improve your standing with the lowest resource expenditure are all essential if a company wants to remain functional.
Develop new processes and products. You don’t have to be involved in research and development to make improvements in how your team gets things done. Researching new processes that make your job (and those of your team) more efficient will be valued by any sensible employer.
Foster self-improvement. Folks who have a knack and passion for research are never content with doing things the same way they’ve always been done. Organizations need independent thinkers who will seek out their own answers and improve their skills as a matter of course. These employees will also pick up new technologies more easily.
Manage customer relationships. Being able to conduct research on your customer base is positively vital in virtually every industry. It’s hard to move products or sell services if you don’t know what people are interested in. Researching your customer base’s interests, needs, and pain points is a valuable responsibility.
Save money. Whether your company is launching a new product or just looking for ways to scale back its current spending, research is crucial for finding wasted resources and redirecting them to more deserving ends. Anyone who proactively researches ways that the company can save money will be highly appreciated by their employer.
Solve problems. Problem solving is a major part of a lot of careers, and research skills are instrumental in making sure your solution is effective. Finding out the cause of the problem and determining an effective solution both require accurate information, and research is the best way to obtain that — be it via the internet or by observation.
Determine reliable information. Being able to tell whether or not the information you receive seems accurate is a very valuable skill. While research skills won’t always guarantee that you’ll be able to tell the reliability of the information at first glance, it’ll prevent you from being too trusting. And it’ll give the tools to double-check .
12 of the most important research skills
Experienced researchers know that worthwhile investigation involves a variety of skills. Consider which research skills come naturally to you, and which you could work on more.
Data collection . When thinking about the research process, data collection is often the first thing that comes to mind. It is the nuts and bolts of research. How data is collected can be flexible.
For some purposes, simply gathering facts and information on the internet can fulfill your need. Others may require more direct and crowd-sourced research. Having experience in various methods of data collection can make your resume more impressive to recruiters.
Data collection methods include: Observation Interviews Questionnaires Experimentation Conducting focus groups
Analysis of information from different sources. Putting all your eggs in one source basket usually results in error and disappointment. One of the skills that good researchers always incorporate into their process is an abundance of sources. It’s also best practice to consider the reliability of these sources.
Are you reading about U.S. history on a conspiracy theorist’s blog post? Taking facts for a presentation from an anonymous Twitter account?
If you can’t determine the validity of the sources you’re using, it can compromise all of your research. That doesn’t mean just disregard anything on the internet but double-check your findings. In fact, quadruple-check. You can make your research even stronger by turning to references outside of the internet.
Examples of reliable information sources include: Published books Encyclopedias Magazines Databases Scholarly journals Newspapers Library catalogs
Finding information on the internet. While it can be beneficial to consulate alternative sources, strong internet research skills drive modern-day research.
One of the great things about the internet is how much information it contains, however, this comes with digging through a lot of garbage to get to the facts you need. The ability to efficiently use the vast database of knowledge that is on the internet without getting lost in the junk is very valuable to employers.
Internet research skills include: Source checking Searching relevant questions Exploring deeper than the first options Avoiding distraction Giving credit Organizing findings
Interviewing. Some research endeavors may require a more hands-on approach than just consulting internet sources. Being prepared with strong interviewing skills can be very helpful in the research process.
Interviews can be a useful research tactic to gain first-hand information and being able to manage a successful interview can greatly improve your research skills.
Interviewing skills involves: A plan of action Specific, pointed questions Respectfulness Considering the interview setting Actively Listening Taking notes Gratitude for participation
Report writing. Possessing skills in report writing can assist you in job and scholarly research. The overall purpose of a report in any context is to convey particular information to its audience.
Effective report writing is largely dependent on communication. Your boss, professor , or general reader should walk away completely understanding your findings and conclusions.
Report writing skills involve: Proper format Including a summary Focusing on your initial goal Creating an outline Proofreading Directness
Critical thinking. Critical thinking skills can aid you greatly throughout the research process, and as an employee in general. Critical thinking refers to your data analysis skills. When you’re in the throes of research, you need to be able to analyze your results and make logical decisions about your findings.
Critical thinking skills involve: Observation Analysis Assessing issues Problem-solving Creativity Communication
Planning and scheduling. Research is a work project like any other, and that means it requires a little forethought before starting. Creating a detailed outline map for the points you want to touch on in your research produces more organized results.
It also makes it much easier to manage your time. Planning and scheduling skills are important to employers because they indicate a prepared employee.
Planning and scheduling skills include: Setting objectives Identifying tasks Prioritizing Delegating if needed Vision Communication Clarity Time-management
Note-taking. Research involves sifting through and taking in lots of information. Taking exhaustive notes ensures that you will not neglect any findings later and allows you to communicate these results to your co-workers. Being able to take good notes helps summarize research.
Examples of note-taking skills include: Focus Organization Using short-hand Keeping your objective in mind Neatness Highlighting important points Reviewing notes afterward
Communication skills. Effective research requires being able to understand and process the information you receive, either written or spoken. That means that you need strong reading comprehension and writing skills — two major aspects of communication — as well as excellent listening skills.
Most research also involves showcasing your findings. This can be via a presentation. , report, chart, or Q&A. Whatever the case, you need to be able to communicate your findings in a way that educates your audience.
Communication skills include: Reading comprehension Writing Listening skills Presenting to an audience Creating graphs or charts Explaining in layman’s terms
Time management. We’re, unfortunately, only given 24 measly hours in a day. The ability to effectively manage this time is extremely powerful in a professional context. Hiring managers seek candidates who can accomplish goals in a given timeframe.
Strong time management skills mean that you can organize a plan for how to break down larger tasks in a project and complete them by a deadline. Developing your time management skills can greatly improve the productivity of your research.
Time management skills include: Scheduling Creating task outlines Strategic thinking Stress-management Delegation Communication Utilizing resources Setting realistic expectations Meeting deadlines
Using your network. While this doesn’t seem immediately relevant to research skills, remember that there are a lot of experts out there. Knowing what people’s areas of expertise and asking for help can be tremendously beneficial — especially if it’s a subject you’re unfamiliar with.
Your coworkers are going to have different areas of expertise than you do, and your network of people will as well. You may even know someone who knows someone who’s knowledgeable in the area you’re researching. Most people are happy to share their expertise, as it’s usually also an area of interest to them.
Networking involves: Remembering people’s areas of expertise Being willing to ask for help Communication Returning favors Making use of advice Asking for specific assistance
Attention to detail. Research is inherently precise. That means that you need to be attentive to the details, both in terms of the information you’re gathering, but also in where you got it from. Making errors in statistics can have a major impact on the interpretation of the data, not to mention that it’ll reflect poorly on you.
There are proper procedures for citing sources that you should follow. That means that your sources will be properly credited, preventing accusations of plagiarism. In addition, it means that others can make use of your research by returning to the original sources.
Attention to detail includes: Double checking statistics Taking notes Keeping track of your sources Staying organized Making sure graphs are accurate and representative Properly citing sources
How to improve your research skills
As with many professional skills, research skills serve us in our day to day life. Any time you search for information on the internet, you’re doing research. That means that you’re practicing it outside of work as well. If you want to continue improving your research skills, both for professional and personal use, here are some tips to try.
Differentiate between source quality. A researcher is only as good as their worst source. Start paying attention to the quality of the sources you use, and be suspicious of everything your read until you check out the attributions and works cited.
Be critical and ask yourself about the author’s bias, where the author’s research aligns with the larger body of verified research in the field, and what publication sponsored or published the research.
Use multiple resources. When you can verify information from a multitude of sources, it becomes more and more credible. To bolster your faith in one source, see if you can find another source that agrees with it.
Don’t fall victim to confirmation bias. Confirmation bias is when a researcher expects a certain outcome and then goes to find data that supports this hypothesis. It can even go so far as disregarding anything that challenges the researcher’s initial hunch. Be prepared for surprising answers and keep an open mind.
Be open to the idea that you might not find a definitive answer. It’s best to be honest and say that you found no definitive answer instead of just confirming what you think your boss or coworkers expect or want to hear. Experts and good researchers are willing to say that they don’t know.
Stay organized. Being able to cite sources accurately and present all your findings is just as important as conducting the research itself. Start practicing good organizational skills , both on your devices and for any physical products you’re using.
Get specific as you go. There’s nothing wrong with starting your research in a general way. After all, it’s important to become familiar with the terminology and basic gist of the researcher’s findings before you dig down into all the minutia.
Highlighting your research skills in a job interview
A job interview is itself a test of your research skills. You can expect questions on what you know about the company, the role, and your field or industry more generally. In order to give expert answers on all these topics, research is crucial.
Start by researching the company . Look into how they communicate with the public through social media, what their mission statement is, and how they describe their culture.
Pay close attention to the tone of their website. Is it hyper professional or more casual and fun-loving? All of these elements will help decide how best to sell yourself at the interview.
Next, research the role. Go beyond the job description and reach out to current employees working at your desired company and in your potential department. If you can find out what specific problems your future team is or will be facing, you’re sure to impress hiring managers and recruiters with your ability to research all the facts.
Finally, take time to research the job responsibilities you’re not as comfortable with. If you’re applying for a job that represents increased difficulty or entirely new tasks, it helps to come into the interview with at least a basic knowledge of what you’ll need to learn.
How to include research skills on your resume
Research projects require dedication. Being committed is a valuable skill for hiring managers. Whether you’ve had research experience throughout education or a former job, including it properly can boost the success of your resume .
Consider how extensive your research background is. If you’ve worked on multiple, in-depth research projects, it might be best to include it as its own section. If you have less research experience, include it in the skills section .
Focus on your specific role in the research, as opposed to just the research itself. Try to quantify accomplishments to the best of your abilities. If you were put in charge of competitor research, for example, list that as one of the tasks you had in your career.
If it was a particular project, such as tracking the sale of women’s clothing at a tee-shirt company, you can say that you “directed analysis into women’s clothing sales statistics for a market research project.”
Ascertain how directly research skills relate to the job you’re applying for. How strongly you highlight your research skills should depend on the nature of the job the resume is for. If research looks to be a strong component of it, then showcase all of your experience.
If research looks to be tangential, then be sure to mention it — it’s a valuable skill — but don’t put it front and center.
Resume examples showcasing research skills
Example #1: Academic Research
Simon Marks 767 Brighton Blvd. | Brooklyn, NY, 27368 | (683)-262-8883 | [email protected] Diligent and hardworking recent graduate seeking a position to develop professional experience and utilize research skills. B.A. in Biological Sciences from New York University. PROFESSIONAL EXPERIENCE Lixus Publishing , Brooklyn, NY Office Assistant- September 2018-present Scheduling and updating meetings Managing emails and phone calls Reading entries Worked on a science fiction campaign by researching target demographic Organizing calendars Promoted to office assistant after one year internship Mitch’s Burgers and Fries , Brooklyn, NY Restaurant Manager , June 2014-June 2018 Managed a team of five employees Responsible for coordinating the weekly schedule Hired and trained two employees Kept track of inventory Dealt with vendors Provided customer service Promoted to restaurant manager after two years as a waiter Awarded a $2.00/hr wage increase SKILLS Writing Scientific Research Data analysis Critical thinking Planning Communication RESEARCH Worked on an ecosystem biology project with responsibilities for algae collection and research (2019) Lead a group of freshmen in a research project looking into cell biology (2018) EDUCATION New York University Bachelors in Biological Sciences, September 2016-May 2020
Example #2: Professional Research
Angela Nichols 1111 Keller Dr. | San Francisco, CA | (663)-124-8827 |[email protected] Experienced and enthusiastic marketer with 7 years of professional experience. Seeking a position to apply my marketing and research knowledge. Skills in working on a team and flexibility. EXPERIENCE Apples amp; Oranges Marketing, San Francisco, CA Associate Marketer – April 2017-May 2020 Discuss marketing goals with clients Provide customer service Lead campaigns associated with women’s health Coordinating with a marketing team Quickly solving issues in service and managing conflict Awarded with two raises totaling $10,000 over three years Prestigious Marketing Company, San Francisco, CA Marketer – May 2014-April 2017 Working directly with clients Conducting market research into television streaming preferences Developing marketing campaigns related to television streaming services Report writing Analyzing campaign success statistics Promoted to Marketer from Junior Marketer after the first year Timberlake Public Relations, San Francisco, CA Public Relations Intern – September 2013–May 2014 Working cohesively with a large group of co-workers and supervisors Note-taking during meetings Running errands Managing email accounts Assisting in brainstorming Meeting work deadlines EDUCATION Golden Gate University, San Francisco, CA Bachelor of Arts in Marketing with a minor in Communications – September 2009 – May 2013 SKILLS Marketing Market research Record-keeping Teamwork Presentation. Flexibility
Research skills FAQs
What research skills are important?
Goal-setting and data collection are important research skills. Additional important research skills include:
Using different sources to analyze information.
Finding information on the internet.
Interviewing sources.
Writing reports.
Critical thinking.
Planning and scheduling.
Note-taking.
Managing time.
How do you develop good research skills?
You develop good research skills by learning how to find information from multiple high-quality sources, by being wary of confirmation bias, and by starting broad and getting more specific as you go.
When you learn how to tell a reliable source from an unreliable one and get in the habit of finding multiple sources that back up a claim, you’ll have better quality research.
In addition, when you learn how to keep an open mind about what you’ll find, you’ll avoid falling into the trap of confirmation bias, and by staying organized and narrowing your focus as you go (rather than before you start), you’ll be able to gather quality information more efficiently.
What is the importance of research?
The importance of research is that it informs most decisions and strategies in a business. Whether it’s deciding which products to offer or creating a marketing strategy, research should be used in every part of a company.
Because of this, employers want employees who have strong research skills. They know that you’ll be able to put them to work bettering yourself and the organization as a whole.
Should you put research skills on your resume?
Yes, you should include research skills on your resume as they are an important professional skill. Where you include your research skills on your resume will depend on whether you have a lot of experience in research from a previous job or as part of getting your degree, or if you’ve just cultivated them on your own.
If your research skills are based on experience, you could put them down under the tasks you were expected to perform at the job in question. If not, then you should likely list it in your skills section.
University of the People – The Best Research Skills for Success
Association of Internet Research Specialists — What are Research Skills and Why Are They Important?
MasterClass — How to Improve Your Research Skills: 6 Research Tips
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Sky Ariella is a professional freelance writer, originally from New York. She has been featured on websites and online magazines covering topics in career, travel, and lifestyle. She received her BA in psychology from Hunter College.

Related posts

10 Important Interpersonal Skills (With Examples)

The Most Important Clerical Skills (With Examples)

Master’s In Psychology Jobs [10 Best-Paying + 10 Entry-Level Jobs You Can Do With A Psychology Degree]

What Is Emotional Intelligence (EQ)? (With Examples)
- Career Advice >
- Hard Skills >
- Research Skills
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
The Art and Science of Critical Thinking in Research: A Guide to Academic Excellence
Critical thinking is a fundamental skill in research and academia that involves analyzing, evaluating, and interpreting information in a systematic and logical manner. It is the process of objectively evaluating evidence, arguments, and ideas to arrive at well-reasoned conclusions or make informed decisions.
The art and science of critical thinking in research is a multifaceted and dynamic process that requires intellectual rigor, creativity, and an open mind.
In research, critical thinking is essential for developing research questions, designing research studies, collecting and analyzing data, and interpreting research findings. It allows researchers to evaluate the quality and validity of research studies, identify gaps in the literature, and make evidence-based decisions.
Critical thinking in research also involves being open to alternative viewpoints and being willing to revise one’s own conclusions based on new evidence. It requires intellectual humility and a willingness to challenge one’s own assumptions and biases.
Why Critical Thinking is Important in Research?
Critical thinking is important in research for the following reasons:
Rigor and accuracy
It helps researchers to approach their work with rigor and accuracy, ensuring that the research methods and findings are reliable and valid.
Evaluation of evidence
Critical thinking helps researchers to evaluate the evidence they encounter and determine its relevance and reliability to the research question or hypothesis.
Identification of biases and assumptions
Critical thinking helps research ers to identify their own biases and assumptions and those of others, which can influence the research process and findings.
Problem-solving
It helps researchers to identify and solve problems that may arise during the research process, such as inconsistencies in data or unexpected results.
Development of new ideas
Critical thinking can help researchers develop new ideas and theories based on their analysis of the evidence.
Communication
Critical thinking helps researchers to communicate their findings and ideas in a clear and logical manner, making it easier for others to understand and build on their work.
Therefore, critical thinking is essential for conducting rigorous and impactful research that can advance our understanding of the world around us.
It helps researchers to approach their work with a critical and objective perspective, evaluating evidence and developing insights that can contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their field.
How to develop critical thinking skills in research?
Developing critical thinking skills in research requires a specific set of strategies. Here are some ways to develop critical thinking skills in research:
Evaluate the credibility of sources
In research, it is important to evaluate the credibility of sources to determine if the information is reliable and valid. To develop your critical thinking skills, practice evaluating the sources you encounter and assessing their credibility.
Assess the quality of evidence
Critical thinking in research involves assessing the quality of evidence and determining if it supports the research question or hypothesis. Practice evaluating the quality of evidence and understanding how it impacts the research findings.
Consider alternative explanations
To develop critical thinking skills in research, practice considering alternative explanations for the findings. Evaluate the evidence and consider if there are other explanations that could account for the results.
Challenge assumptions
Critical thinking in research involves challenging assumptions and exploring alternative perspectives. Practice questioning assumptions and considering different viewpoints to develop your critical thinking skills.
Seek out feedback
Seek out feedback from colleagues, advisors, or peers on your research methods and findings. This can help you identify areas where you need to improve your critical thinking skills and provide valuable insights for your research.
Practice analyzing data
Critical thinking in research involves analyzing and interpreting data. Practice analyzing different types of data to develop your critical thinking skills.
Attend conferences and seminars
Attend conferences and seminars in your field to learn about the latest research and to engage in critical discussions with other researchers. This can help you develop your critical thinking skills and keep up-to-date with the latest research in your field.
By consistently practicing these strategies, you can develop your critical thinking skills in research and become a more effective and insightful researcher.
The Art and Science of Critical Thinking in Research
The art and science of critical thinking in research is a vital skill for academic excellence. Here’s a guide to academic excellence through the art and science of critical thinking in research:
Define the research problem
The first step in critical thinking is to define the research problem or question. This involves identifying the key concepts, understanding the context, and formulating a clear and concise research question or hypothesis. Clearly define the research question or problem you are trying to address. This will help you focus your thinking and avoid unnecessary distractions.
Conduct a comprehensive literature review
A thorough review of relevant literature is essential in critical thinking. It helps you understand the existing knowledge and research in the field, identify research gaps, and evaluate the quality and reliability of the evidence. It also allows you to identify different perspectives and theories related to the research problem.
Evaluate evidence and sources
Critical thinking requires careful evaluation of evidence and sources. This includes assessing the credibility, reliability, and validity of research studies, data sources, and information. It also involves identifying potential biases, limitations, and assumptions in the evidence and sources. Use reputable, peer-reviewed sources and critically analyze the evidence and arguments presented in those sources.
Analyze and synthesize information
Critical thinking involves analyzing and synthesizing information from various sources. This includes identifying patterns, trends, and relationships among different pieces of information. It also requires organizing and integrating information to develop a coherent and logical argument.
Question assumptions
Challenge your assumptions and biases. Be aware of your own biases and preconceived notions, and critically examine them to avoid potential bias in your research.
Evaluate arguments and reasoning
Critical thinking involves evaluating the strength and validity of arguments and reasoning. This includes identifying logical fallacies, evaluating the coherence and consistency of arguments, and assessing the evidence and support for arguments. It also involves considering alternative viewpoints and perspectives.
Apply critical thinking tools
Use critical thinking tools such as SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats), mind maps, concept maps, and flowcharts to organize and analyze information in a structured and systematic manner.
Apply critical thinking skills in research design and methodology: Critical thinking is essential in research design and methodology. This includes making informed decisions about research approaches, sampling methods, data collection, and data analysis techniques. It also involves anticipating potential limitations and biases in the research design and methodology.
Consider multiple perspectives
Avoid tunnel vision by considering multiple perspectives and viewpoints on the issue at hand. This will help you gain a more comprehensive understanding of the topic and make informed decisions based on a broader range of information.
Ask critical questions
Critical questions in research.
Some of the sample critical questions in the research are listed below.
1. What is the research question, and is it clearly defined?
2. What are the assumptions underlying the research question?
3. What is the methodology being used, and is it appropriate for the research organized
4. What are the limitations of the study, and how might they affect the results?
5. How representative is the sample being studied, and are there any biases in the selection process?
6. What are the potential sources of error or bias in the data collection process?
7. Are the statistical analyses used appropriate, and do they support the conclusions drawn from the data?
8. What are the implications of the research findings, and do they have practical significance?
9. Are there any ethical considerations that arise from the research, and have they been adequately addressed?
10. Are there any alternative explanations for the results, and have they been considered and ruled out?
Communicate effectively
Critical thinking requires effective communication skills to articulate and present research findings and arguments clearly and convincingly.
This includes writing clearly and concisely, using appropriate evidence and examples, and presenting information in a logical and organized manner. It also involves listening and responding critically to feedback and engaging in constructive discussions and debates.
Practice self-reflection
Critical thinking involves self-reflection and self-awareness. Reflect on your own thinking and decision-making process throughout the research. It requires regularly evaluating your own biases, assumptions, and limitations in your thinking process. It also involves being mindful of your emotions and personal beliefs that may influence your critical thinking and decision-making.
Embrace creativity and open-mindedness
Critical thinking involves being open to new ideas, perspectives, and approaches. It requires creativity in generating and evaluating alternative solutions or interpretations.
It also involves being willing to revise your conclusions or change your research direction based on new information. Avoid confirmation bias and strive for objectivity in your research.
Seek feedback and engage in peer review
Critical thinking benefits from feedback and peer review. Seeking feedback from mentors, colleagues, or peer reviewers can help identify potential flaws or weaknesses in your research or arguments. Engaging in peer review also provides an opportunity to critically evaluate the work of others and learn from their perspectives.
By following these best practices and techniques, you can cultivate critical thinking skills that will enhance the quality and rigor of your research, leading to more successful outcomes.
Critical thinking is an essential component of research that enables researchers to evaluate information, identify biases, and draw valid conclusions.
It involves defining research problems, conducting literature reviews, evaluating evidence and sources, analyzing and synthesizing information, evaluating arguments and reasoning, applying critical thinking in research design and methodology, communicating effectively, embracing creativity and open-mindedness, practicing self-reflection, seeking feedback, and engaging in peer review.
By cultivating and applying critical thinking skills in research, you can enhance the quality and rigor of your work and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in your field.
Remember to continuously practice and refine your critical thinking skills as they are valuable not only in research but also in various aspects of life. Happy researching!
- academic excellence
- Academic Research
- academic success
- critical thinking
- practical tips
- research skills
What is a PhD? A Comprehensive Guide for Indian Scientists and Aspiring Researchers
Fellowships in india 2024 -comprehensive guide, agi in research: unraveling the future of artificial intelligence, most popular, the nippon foundation fellowship programme 2025, working sci-hub proxy links 2024: access research papers easily, abstract template for research paper, 10 types of plagiarism – every academic writer should know – updated, the harsh reality: why revoked graduate degrees aren’t easily reclaimed, top 50 research institutions in india: nirf rankings 2024, top 35 scopus indexed journals in english literature, best for you, 24 best online plagiarism checker free – 2024, popular posts, newly accepted scopus indexed journals june 2024, top 10 scopus indexed agronomy and crop science journals, popular category.
- POSTDOC 317
- Interesting 257
- Journals 235
- Fellowship 134
- Research Methodology 102
- All Scopus Indexed Journals 93
Mail Subscription

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
Contact us: [email protected]
Google News
Copyright © 2024 iLovePhD. All rights reserved
- Artificial intelligence
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples
What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples
Published on May 30, 2022 by Eoghan Ryan . Revised on May 31, 2023.
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment .
To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources .
Critical thinking skills help you to:
- Identify credible sources
- Evaluate and respond to arguments
- Assess alternative viewpoints
- Test hypotheses against relevant criteria
Table of contents
Why is critical thinking important, critical thinking examples, how to think critically, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about critical thinking.
Critical thinking is important for making judgments about sources of information and forming your own arguments. It emphasizes a rational, objective, and self-aware approach that can help you to identify credible sources and strengthen your conclusions.
Critical thinking is important in all disciplines and throughout all stages of the research process . The types of evidence used in the sciences and in the humanities may differ, but critical thinking skills are relevant to both.
In academic writing , critical thinking can help you to determine whether a source:
- Is free from research bias
- Provides evidence to support its research findings
- Considers alternative viewpoints
Outside of academia, critical thinking goes hand in hand with information literacy to help you form opinions rationally and engage independently and critically with popular media.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Critical thinking can help you to identify reliable sources of information that you can cite in your research paper . It can also guide your own research methods and inform your own arguments.
Outside of academia, critical thinking can help you to be aware of both your own and others’ biases and assumptions.
Academic examples
However, when you compare the findings of the study with other current research, you determine that the results seem improbable. You analyze the paper again, consulting the sources it cites.
You notice that the research was funded by the pharmaceutical company that created the treatment. Because of this, you view its results skeptically and determine that more independent research is necessary to confirm or refute them. Example: Poor critical thinking in an academic context You’re researching a paper on the impact wireless technology has had on developing countries that previously did not have large-scale communications infrastructure. You read an article that seems to confirm your hypothesis: the impact is mainly positive. Rather than evaluating the research methodology, you accept the findings uncritically.
Nonacademic examples
However, you decide to compare this review article with consumer reviews on a different site. You find that these reviews are not as positive. Some customers have had problems installing the alarm, and some have noted that it activates for no apparent reason.
You revisit the original review article. You notice that the words “sponsored content” appear in small print under the article title. Based on this, you conclude that the review is advertising and is therefore not an unbiased source. Example: Poor critical thinking in a nonacademic context You support a candidate in an upcoming election. You visit an online news site affiliated with their political party and read an article that criticizes their opponent. The article claims that the opponent is inexperienced in politics. You accept this without evidence, because it fits your preconceptions about the opponent.
There is no single way to think critically. How you engage with information will depend on the type of source you’re using and the information you need.
However, you can engage with sources in a systematic and critical way by asking certain questions when you encounter information. Like the CRAAP test , these questions focus on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
When encountering information, ask:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert in their field?
- What do they say? Is their argument clear? Can you summarize it?
- When did they say this? Is the source current?
- Where is the information published? Is it an academic article? Is it peer-reviewed ?
- Why did the author publish it? What is their motivation?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence? Does it rely on opinion, speculation, or appeals to emotion ? Do they address alternative arguments?
Critical thinking also involves being aware of your own biases, not only those of others. When you make an argument or draw your own conclusions, you can ask similar questions about your own writing:
- Am I only considering evidence that supports my preconceptions?
- Is my argument expressed clearly and backed up with credible sources?
- Would I be convinced by this argument coming from someone else?
If you want to know more about ChatGPT, AI tools , citation , and plagiarism , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- ChatGPT vs human editor
- ChatGPT citations
- Is ChatGPT trustworthy?
- Using ChatGPT for your studies
- What is ChatGPT?
- Chicago style
- Paraphrasing
Plagiarism
- Types of plagiarism
- Self-plagiarism
- Avoiding plagiarism
- Academic integrity
- Consequences of plagiarism
- Common knowledge
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Critical thinking skills include the ability to:
You can assess information and arguments critically by asking certain questions about the source. You can use the CRAAP test , focusing on the currency , relevance , authority , accuracy , and purpose of a source of information.
Ask questions such as:
- Who is the author? Are they an expert?
- How do they make their argument? Is it backed up by evidence?
A credible source should pass the CRAAP test and follow these guidelines:
- The information should be up to date and current.
- The author and publication should be a trusted authority on the subject you are researching.
- The sources the author cited should be easy to find, clear, and unbiased.
- For a web source, the URL and layout should signify that it is trustworthy.
Information literacy refers to a broad range of skills, including the ability to find, evaluate, and use sources of information effectively.
Being information literate means that you:
- Know how to find credible sources
- Use relevant sources to inform your research
- Understand what constitutes plagiarism
- Know how to cite your sources correctly
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search, interpret, and recall information in a way that aligns with our pre-existing values, opinions, or beliefs. It refers to the ability to recollect information best when it amplifies what we already believe. Relatedly, we tend to forget information that contradicts our opinions.
Although selective recall is a component of confirmation bias, it should not be confused with recall bias.
On the other hand, recall bias refers to the differences in the ability between study participants to recall past events when self-reporting is used. This difference in accuracy or completeness of recollection is not related to beliefs or opinions. Rather, recall bias relates to other factors, such as the length of the recall period, age, and the characteristics of the disease under investigation.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Ryan, E. (2023, May 31). What Is Critical Thinking? | Definition & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 29, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/working-with-sources/critical-thinking/
Is this article helpful?

Eoghan Ryan
Other students also liked, student guide: information literacy | meaning & examples, what are credible sources & how to spot them | examples, applying the craap test & evaluating sources, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Articles Hub | Return to Main page

Student Success
How to improve your critical thinking and research skills.
Critical thinking doesn’t always come naturally to us. It requires analyzing the facts, gathering as much information as possible, thinking open-mindedly, and then forming a judgment.
Rest assured, you can teach yourself to think critically. Here are tips to help you get started.
Be aware of authors’ motivations
You can evaluate an author’s work if you’re aware of what drove that person to undertake the research and writing in the first place. Here are things to be aware of:
- Avoid personal feelings
- Be wary of phrases like always , a lot , or never unless you can attach a number to confirm the characterization
- Steer clear of first-person (using “I”) and second-person (using “you”) pronouns unless you’re asked to reflect or give advice
- Find credible sources ( more on this below!)
- Read multiple articles from different perspectives
Find credible evidence
A rule of thumb for most writing is to make a claim, provide evidence to support the claim, and then use reasoning to tie it all together. How do you analyze your sources? Use critical thinking skills. Ask questions such as:
- Did the researchers only study 10 people?
- Is the writer representing a particular company or industry?
- What other articles and studies has the writer published?
- Is this article published in a scholarly journal, or on a website selling something?
Research well
It’s easier to find credible evidence when you’re looking in the right places. Here are key tips for researching well:
- Use your school’s online library to find scholarly articles. Peer-reviewed articles have been reviewed by other professionals or scholars in the field and are generally the most accurate.
- When you read something compelling, check out the reference page at the end of that article, and look up some of those sources.
- When an author cites another source, try to find that original source, and read it for yourself.
- Beware of bias, and consider the credibility of the authors you read.
- Pay close attention to dates. If the research was completed more than five to ten years ago, it’s probably outdated.
Make the most of your findings
The key to using evidence in your paper is not just to sprinkle quotes throughout, but rather to integrate the research into your argument. Explain the significance and implications of that research. It’s one thing to write, “Carrots are good for you,” but it’s much more compelling to explain how and why carrots are good for you based on statistics and research. To demonstrate real critical thinking skills, synthesize what you read (citing it accurately), and incorporate it into your argument, paying special attention to the flow and structure. Read how other authors use information to gain your trust, and utilize their strategies to do the same for your reader.
Critical thinking leads to better research skills, which in turn lead to better writing. When you find credible evidence, it will support your claims more effectively, and you’ll learn to read and listen to information with a critical eye for bias and persuasion. As an added bonus, you’ll also learn to be a better conversationalist outside of school.
To get more insights into sharpening your critical thinking and research skills, watch our webinar:
Proudly Serving
Data Protection Statement | Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Terms of Use
©2024 Tutor.com / The Princeton Review. Not Affiliated with Princeton University
Tutor.com is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
Home › Study Tips › Research Skills: What They Are and How They Benefit You
Research Skills: What They Are and How They Benefit You
- Published May 23, 2024

Research skills give you the ability to gather relevant information from different sources and analyse it critically in order to develop a comprehensive understanding of a subject. Thus, research skills are fundamental to academic success.
Developing these skills will improve your studies, helping you understand subjects better and positioning you for academic success.
That said, how can you develop important research skills? This will explore what research skills are, identify the core ones, and explain how you can develop them.
What Are Research Skills?
Research skills are a set of abilities that allow individuals to find and gather reliable information and then evaluate the information to find answers to questions.
Good research skills are important in academic settings, as finding and critically evaluating relevant information can help you gain a deeper understanding of a subject.
These skills are also important in professional and personal settings. When you graduate and are working in a professional capacity, you’ll often need to analyse sets of data to identify issues and determine how to solve them.
In personal contexts, you’ll always need to assess relevant information to make an informed decision. Whether you’re deciding on a major purchase, choosing a healthcare provider, or planning to make an investment, you’ll need to evaluate options to ensure better decision outcomes.
Different Types of Research Skills
Research skills are categorised into different sub-skills. The most common types are:
Quantitative Skills
Quantitative skills refer to the ability to work with numerical data and perform mathematical and statistical analyses to extract meaningful insights and draw conclusions.
When you have quantitative skills, you’ll be able to apply mathematical concepts and operations in research design and data analysis.
You’ll also be proficient in using statistical methods to analyse data and interpreting numerical data to draw meaningful conclusions.
Analytical Skills
Analytical skills refer to the ability to gather data, evaluate it, and draw sound conclusions. When you have analytical skills, you’ll be able to systematically analyse information to reach a reasonable conclusion.
Analytical skills are important in problem-solving. They help you to break down complex problems into more manageable components, think critically about the information at hand, analyse root causes, and develop effective solutions.
Qualitative Skills
Qualitative skills refer to the ability to collect, analyse, and interpret non-numerical data. When you have qualitative skills, you’ll be proficient in observation, interviewing, and other methods for collecting qualitative research data.
You’ll also be able to analyse non-numerical data, such as documents and images, to identify themes, patterns, and meanings.
Research Skills Examples
The core research skills you need for success in academic, professional, and personal contexts include:
Data Collection
Data is at the centre of every research, as data is what you assess to find the answers you seek. Thus, research starts with collecting relevant data.
Depending on the research, there are two broad categories of data you can collect: primary and secondary.
Primary data is generated by the researcher, like data from interviews, observations, or experiments. Secondary data is pre-existing data obtained from different existing databases, like published literature, government reports, etc.
Thus, data collection is more than gathering information from the Internet. Depending on the research, it can require more advanced skills for conducting experiments to generate your own data.
Source Evaluation
When doing research on any subject (especially when using the Internet), you’ll be amazed at the volume of information you’ll find. And a lot is pure garbage that can compromise your research work.
Thus, an important research skill is being able to dig through the garbage to get to the real facts. This is where source evaluation comes in!
Good research skills call for being able to identify biases, assess the authority of the author, and determine the accuracy of information before using it.
Time Management Skills

Have you ever felt that there is not enough time in a day for all that you need to do? When you already have so much to do, adding research can be overwhelming.
Good time management skills can help you find the time to do all you need to do, including relevant research work, making it an essential research skill.
Time management allows you to plan and manage your research project effectively. It includes breaking down research tasks into more manageable parts, setting priorities, and allocating time to the different stages of the research.
Communication Skills

Communication is an important aspect of every research, as it aids in data collection and sharing research findings.
Important communication skills needed in research include active listening, active speaking, interviewing, report writing, data visualisation, and presentation, etc.
For example, when research involves collecting primary data via interviews, you must have sound speaking and listening skills.
When you conclude the research and need to share findings, you’ll need to write a research report and present key findings in easy-to-understand formats like charts.
Attention to Detail
Attention to detail is the ability to achieve thoroughness and accuracy when doing something. It requires focusing on every aspect of the tasks, even small ones.
Anything you miss during your research will affect the quality of your research findings. Thus, the ability to pay close attention to details is an important research skill.
You need attention to detail at every stage of the research process. During data collection, it helps you ensure reliable data.
During analysis, it reduces the risk of error to ensure your results are trustworthy. It also helps you express findings precisely to minimise ambiguity and facilitate understanding.
Note-Taking

Note-taking is exactly what it sounds like—writing down key information during the research process.
Remember that research involves sifting through and taking in a lot of information. It’s impossible to take in all the information and recall it from memory. This is where note-taking comes in!
Note-taking helps you capture key information, making it easier to remember and utilise for the research later. It also involves writing down where to look for important information.
Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is the ability to think rationally and synthesise information in a thoughtful way. It is an important skill needed in virtually all stages of the research process.
For example, when collecting data, you need critical thinking to assess the quality and relevance of data. It can help you identify gaps in data to formulate your research question and hypothesis.
It can also help you to identify patterns and make reasonable connections when interpreting research findings.
Data Analysis
Data may not mean anything until you analyse it qualitatively or quantitatively (using techniques like Excel or SPSS). For this reason, data analysis analysis is an important research skill.
Researchers need to be able to build hypotheses and test these using appropriate research techniques. This helps to draw meaningful conclusions and gain a comprehensive understanding of research data.
Problem-Solving Skills
Research often involves addressing specific questions and solving problems. For this reason, problem-solving skills are important skills when conducting research.
Problem-solving skills refer to the ability to identify, analyse, and solve problems effectively.
With problem-solving skills, you’ll be able to assess a situation, consider various solutions, and choose the most appropriate course of action toward finding a solution.
Benefits of Research Skills
Research skills have many benefits, including:
Enhances Critical Thinking
Research skills and critical thinking are intertwined such that developing one enhances the other.
Research requires people to question assumptions, evaluate evidence, analyse information, and draw conclusions. These activities require you to think critically about the information at hand. Hence, engaging in research enhances critical thinking.
Develops Problem-Solving Skills
Research helps you acquire a set of critical skills that are directly transferable to problem-solving.
For example, research fosters creative thinking, as it often requires synthesising data from different sources and connecting different concepts. After developing creative thinking via research, you can apply the skill to generate innovative solutions in problem-solving situations.
Helps in Knowledge Acquisition
Engaging in research is a powerful way to acquire knowledge. Research involves exploring new ideas, and this helps you expand your breadth of knowledge.
It also involves applying research methods and methodologies. So, you’ll acquire knowledge about research methods, enhancing your ability to design and conduct studies in your higher education or professional life.
Why Are Research Skills Important?
Strong research skills offer numerous benefits, especially for students’ academic learning and development.
When you develop good research skills, you’ll reap great academic rewards that include:
In-Depth Understanding
Conducting research allows you to delve deep into specific topics, helping you gain a thorough understanding of the subject matter beyond what is covered in standard coursework.
Critical Thinking Development
Research involves critical evaluation of information and making informed decisions. This builds your ability to think critically.
This skill will not only help you solve academic problems better, but it’s also crucial to your personal and professional growth.
Encouragement of Independent Learning
Research encourages independent learning. When you engage in research, you seek answers independently. You take the initiative to find, retrieve, and evaluate information relevant to your research.
That helps you develop self-directed study habits. You’ll be able to take ownership of your education and actively seek out information for a better understanding of the subject matter.
Intellectual Curiosity Development
Research skills encourage intellectual curiosity and a love of learning, as they’ll make you explore topics you find intriguing or important. Thus, you’ll be more motivated to explore topics beyond the scope of your coursework.
Enhanced Communication Skills
Research helps you build better interpersonal skills as well as report-writing skills.
Research helps you sharpen your communication skills when you interact with research subjects during data collection. Communicating research findings to an audience also helps sharpen your presentation skills or report writing skills.
Assistance in Career Preparation
Many professions find people with good research skills. Whether you’ll pursue a career in academia, business, healthcare, or IT, being able to conduct research will make you a valuable asset.
So, researching skills for students prepares you for a successful career when you graduate.
Contribution to Personal Growth
Research also contributes to your personal growth. Know that research projects often come with setbacks, unexpected challenges, and moments of uncertainty. Navigating these difficulties helps you build resilience and confidence.
Acquisition of Time Management Skills
Research projects often come with deadlines. Such research projects force you to set goals, prioritise tasks, and manage your time effectively.
That helps you acquire important time management skills that you can use in other areas of academic life and your professional life when you graduate.
Ways to Improve Research Skills
The ways to improve your research skills involve a combination of learning and practice.
You should consider enrolling in research-related programmes, learning to use data analysis tools, practising summarising and synthesising information from multiple sources, collaborating with more experienced researchers, and more.
Looking to improve your research skills? Read our 11 ways to improve research skills article.
How Can I Learn Research Skills?
You can learn research skills using these simple three-point framework:
Clarifying the Objective
Start by articulating the purpose of your research. Identify the specific question you are trying to answer or the problem you are aiming to solve.
Then, determine the scope of your research to help you stay focused and avoid going after irrelevant information.
Cross-Referencing Sources
The next step is to search for existing research on the topic. Use academic databases, journals, books, and reputable online sources.
It’s important to compare information from multiple sources, taking note of consensus among studies and any conflicting findings.
Also, check the credibility of each source by looking at the author’s expertise, information recency, and reputation of the publication’s outlet.
Organise the Research
Develop a note-taking system to document key findings as you search for existing research. Create a research outline, then arrange your ideas logically, ensuring that each section aligns with your research objective.
As you progress, be adaptable. Be open to refining your research plan as new understanding evolves.
Enrolling in online research programmes can also help you build strong research skills. These programmes combine subject study with academic research project development to help you hone the skills you need to succeed in higher education.
Immerse Education is a foremost provider of online research programmes.
Acquire Research Skills with Immerse Education
Research skills are essential to academic success. They help you gain an in-depth understanding of subjects, enhance your critical thinking and problem-solving skills, improve your time management skills, and more.
In addition to boosting you academically, they contribute to your personal growth and prepare you for a successful professional career.
Thankfully, you can learn research skills and reap these benefits. There are different ways to improve research skills, including enrolling in research-based programmes. This is why you need Immerse Education!
Immerse Education provides participants aged 13-18 with unparalleled educational experience. All our programmes are designed by tutors from top global universities and help prepare participants for future success.
Our online research programme expertly combines subject study with academic research projects to help you gain subject matter knowledge and the important research skills you need to succeed in higher education. With one-on-one tutoring or group sessions from an expert academic from Oxford or Cambridge University and a flexible delivery mode, the programme is designed for you to succeed. Subsequently, enrolling in our accredited Online Research Programme will award students with 8 UCAS points upon completion.
- I'm a Parent
- I'm a Student
- First Name *
- Last Name *
- Which subjects interest you? (Optional) Architecture Artificial Intelligence Banking and Finance Biology Biotechnology Business Management Chemistry Coding Computer Science Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Creative Writing Creative Writing and Film Criminology Data Science and Analytics Earth Science Economics Encryption and Cybersecurity Engineering English Literature Entrepreneurship Fashion and Design Female Future Leaders Film Studies Fine Arts Global Society and Sustainability Health and Biotechnology History International Relations Law Marketing and Entertainment Mathematics Medicine Medicine and Health Sciences Nanotechnology Natural Sciences Philosophy Philosophy Politics and Economics Physics Psychology Software Development and AI Software Development and Gaming Veterinary Studies Online Research Programme
Secure priority enrolment for our new summer school location with a small refundable deposit.
" * " indicates required fields
Receive priority enrolment for new summer school locations by registering your interest below.
Our programme consultant will contact you to talk about your options.
- Family Name *
- Phone Number
- Yes. See Privacy Policy.
Subject is unavailable at location
You have selected a subject that is not available at the location that you have previously chosen.
The location filter has been reset, and you are now able to search for all the courses where we offer the subject.

Critical Thinking in Academic Research - Second Edition
(5 reviews)
Cindy Gruwell, University of West Florida
Robin Ewing, St. Cloud State University
Copyright Year: 2022
Last Update: 2023
Publisher: Minnesota State Colleges and Universities
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Erin Weldon, Director of Instructional Design and Development, Trine University on 8/28/24
The textbook offers a comprehensive overview of academic research with a focus on essential tools and strategies for researchers. It includes a valuable section on barriers of critical thinking. To enhance its utility, consider adding a section... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
The textbook offers a comprehensive overview of academic research with a focus on essential tools and strategies for researchers. It includes a valuable section on barriers of critical thinking. To enhance its utility, consider adding a section highlighting the advantages or benefits of critical thinking, which can help mitigate these barriers. While discussing challenges is crucial, perhaps positioning this section later in the textbook would allow readers to build a stronger foundation before addressing potential obstacles. A suggestion for the readers is to read the barriers chapter toward the end after you have a strong foundation of critical thinking in academic research.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The textbook presents unbiased information and offers descriptive evidence to support its arguments on critical thinking topics. Examples illustrate the application of critical thinking in research. Throughout the text, valuable tips encourage readers to cultivate critical thinking skills and provide practical suggestions that they can put into action. For instance, in Chapter 5, learners are provided with tips on how to keep track of information. I appreciate the citation management software options. This is a great resource to get readers started on their research journey.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
The textbook effectively aligns with current research methods and strategies. The text includes the most recent academic trends. Its strategies provide learners with practical guidance on conducting thorough research, ensuring proper attribution and compliance with copyright regulations, which are increasingly important in today's world.
Clarity rating: 4
The textbook provides clear chapters that coincide with the purpose. I appreciate the examples to clarify the strategies for critical thinking in research. A few interactive quizzes could benefit from clearer instructions to enhance their effectiveness. For instance, in Chapter 8, providing specific guidance within the Main Concepts section would clarify the quiz's purpose. While the questions may appear factual, they actually require learners to identify the main concept or topic. This added clarity would improve the overall learning experience.
Consistency rating: 5
The textbook's topics are interconnected and progressively build upon one another, forming a comprehensive and reliable resource. The text begins by introducing key concepts of critical thinking, then progresses into effective research strategies, skills, and methodologies, concluding with a discussion of ethical considerations and standards for responsible research practices.
Modularity rating: 5
The text displays excellent readability. I appreciate the awareness of accessibility with the use of alt-text on the images. There should be little to no barriers for readers. To further enhance inclusivity, adding audio narration to the text would provide an alternative format that is easily accessible within the book.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 4
The overall organization of the textbook is clear and concise. See comment above about rearranging the barriers chapter later in the book such as after a section on the benefits as mentioned above.
Interface rating: 5
There does not appear to be any navigational issues throughout the book. From an accessibility standpoint, everything appears to be accessible in a way that would not distract or cause barriers to the reader.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
No grammatical errors present or noticeable that I could see.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
This comprehensive textbook fosters an inclusive learning environment by presenting a diverse range of examples that illustrate various perspectives. Readers are encouraged to develop a deep understanding of different cultures and experiences and appreciate the value of diverse viewpoints.
This text is an excellent resource for anyone who needs a textbook for a research class,. his comprehensive text serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, providing a solid foundation for coursework in research methods.
Reviewed by Julie Jaszkowiak, Community Faculty, Metropolitan State University on 12/22/23
Organized in 11 parts, this his textbook includes introductory information about critical thinking and details about the academic research process. The basics of critical thinking related to doing academic research in Parts I and II. Parts III –... read more
Organized in 11 parts, this his textbook includes introductory information about critical thinking and details about the academic research process. The basics of critical thinking related to doing academic research in Parts I and II. Parts III – XI provide specifics on various steps in doing academic research including details on finding and citing source material. There is a linked table of contents so the reader is able to jump to a specific section as needed. There is also a works cited page with information and links to works used for this textbook.
The content of this textbook is accurate and error free. It contains examples that demonstrate concepts from a variety of disciplines such as “hard science” or “popular culture” that assist in eliminating bias. The authors are librarians so it is clear that their experience as such leads to clear and unbiased content.
General concepts about critical thinking and academic research methodology is well defined and should not become obsolete. Specific content regarding use of citation tools and attribution structure may change but the links to various research sites allow for simple updates.
Clarity rating: 5
This textbook is written in a conversational manner that allows for a more personal interaction with the textbook. It is like the reader is having a conversation with a librarian. Each part has an introduction section that fully defines concepts and terms used for that part.
In addition to the written content, this textbook contains links to short quizzes at the end of each section. This is consistent throughout each part. Embedded links to additional information are included as necessary.
Modularity rating: 4
This textbook is arranged in 11 modular parts with each part having multiple sections. All of these are linked so a reader can go to a distinct part or section to find specific information. There are some links that refer back to previous sections in the document. It can be challenging to return to where you were once you have jumped to a different section.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
There is clear definition as to what information is contained within each of the parts and subsequent sections. The textbook follows the logical flow of the process of researching and writing a research paper.
Interface rating: 4
The pictures have alternative text that appears when you hover over the text. There is one picture on page 102 that is a link to where the downloaded picture is from. The pictures are clear and supportive of the text for a visual learner. All the links work and go to either the correct area of the textbook or to a valid website. If you are going to use the embedded links to go to other sections of the textbook you need to keep track of where you are as it can sometimes get confusing as to where you went based on clicking links.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
This is not really a grammatical error but I did notice on some of the quizzes if you misspelled a work for fill in the blank it was incorrect. It was also sometimes challenging to come up with the correct word for the fill in the blanks.
There are no examples or text that are culturally insensitive or offensive. The examples are general and would be applicable to a variety of students study many different academic subjects. There are references and information to many research tools from traditional such as checking out books and articles from the library to more current such as blogs and other electronic sources. This information appeals to a wide expanse of student populations.
I really enjoyed the quizzes at the end of each section. It is very beneficial to test your knowledge and comprehension of what you just read. Often I had to return and reread the content more critically based on my quiz results! They are just the right length to not disrupt the overall reading of the textbook and cover the important content and learning objectives.
Reviewed by Sara Stigberg, Adjunct Reference Librarian, Truman College, City Colleges of Chicago on 3/15/23
Critical Thinking in Academic Research thoroughly covers the basics of academic research for undergraduates, including well-guided deeper dives into relevant areas. The authors root their introduction to academic research principles and practices... read more
Critical Thinking in Academic Research thoroughly covers the basics of academic research for undergraduates, including well-guided deeper dives into relevant areas. The authors root their introduction to academic research principles and practices in the Western philosophical tradition, focused on developing students' critical thinking skills and habits around inquiry, rationales, and frameworks for research.
This text conforms to the principles and frames of the Framework for Information Literacy for Higher Education, published by the Association of College and Research Libraries. It includes excellent, clear, step-by-step guides to help students understand rationales and techniques for academic research.
Essential for our current information climate, the authors present relevant information for students who may be new to academic research, in ways and with content that is not too broad or too narrow, or likely to change drastically in the near future.
The authors use clear and well-considered language and explanations of ideas and terms, contextualizing the scholarly research process and tools in a relatable manner. As mentioned earlier, this text includes excellent step-by-step guides, as well as illustrations, visualizations, and videos to instruct students in conducting academic research.
(4.75) The terminology and framework of this text are consistent. Early discussions of critical thinking skills are tied in to content in later chapters, with regard to selecting different types of sources and search tools, as well as rationales for choosing various formats of source references. Consciously making the theme of critical thinking as applied to the stages of academic research more explicit and frequent within the text would further strengthen it, however.
Chapters are divided in a logical, progressive manner throughout the text. The use of embedded links to further readings and some other relevant sections of the text are an excellent way of providing references and further online information, without overwhelming or side-tracking the reader.
Topics in the text are organized in logical, progressive order, transitioning cleanly from one focus to the next. Each chapter begins with a helpful outline of topics that will be covered within it.
There are no technical issues with the interface for this text. Interactive learning tools such as the many self-checks and short quizzes that are included throughout the text are a great bonus for reinforcing student learning, and the easily-accessible table of contents was very helpful. There are some slight inconsistencies across chapters, however, relative to formatting images and text and spacing, and an image was missing in the section on Narrowing a Topic. Justifying copy rather than aligning-left would prevent hyphenation, making the text more streamlined.
(4.75) A few minor punctuation errors are present.
The authors of this text use culturally-relevant examples and inclusive language. The chapter on Barriers to Critical Thinking works directly to break down bias and preconceived notions.
Overall, Critical Thinking in Academic Research is an excellent general textbook for teaching the whys and hows of academic research to undergraduates. A discussion of annotated bibliographies would be a great addition for future editions of the text. ---- (As an aside for the authors, I am curious if the anonymous data from the self-checks and quizzes is being collected and analyzed for assessment purposes. I'm sure it would be interesting!)
Reviewed by Ann Bell-Pfeifer, Program Director/ Instructor, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 2/15/23
The book has in depth coverage of academic research. A formal glossary and index were not included. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The book has in depth coverage of academic research. A formal glossary and index were not included.
The book appears error free and factual.
The content is current and would support students who are pursuing writing academic research papers.
Excellent explanations for specific terms were included throughout the text.
The text is easy to follow with a standardized format and structure.
The text contains headings and topics in each section.
It is easy to follow the format and review each section.
The associated links were useful and not distracting.
No evidence of grammatical errors were found in the book.
The book is inclusive.
The book was informative, easy to follow, and sequential allowing the reader to digest each section before moving into another.
Reviewed by Jenny Inker, Assistant Professor, Virginia Commonwealth University on 8/23/22
This book provides a comprehensive yet easily comprehensible introduction to critical thinking in academic research. The author lays a foundation with an introduction to the concepts of critical thinking and analyzing and making arguments, and... read more
This book provides a comprehensive yet easily comprehensible introduction to critical thinking in academic research. The author lays a foundation with an introduction to the concepts of critical thinking and analyzing and making arguments, and then moves into the details of developing research questions and identifying and appropriately using research sources. There are many wonderful links to other open access publications for those who wish to read more or go deeper.
The content of the book appears to be accurate and free of bias.
The examples used throughout the book are relevant and up-to-date, making it easy to see how to apply the concepts in real life.
The text is very accessibly written and the content is presented in a simple, yet powerful way that helps the reader grasp the concepts easily. There are many short, interactive exercises scattered throughout each chapter of the book so that the reader can test their own knowledge as they go along. It would be even better if the author had provided some simple feedback explaining why quiz answers are correct or incorrect in order to bolster learning, but this is a very minor point and the interactive exercises still work well without this.
The book appears consistent throughout with regard to use of terminology and tone of writing. The basic concepts introduced in the early chapters are used consistently throughout the later chapters.
This book has been wonderfully designed into bite sized chunks that do not overwhelm the reader. This is perhaps its best feature, as this encourages the reader to take in a bit of information, digest it, check their understanding of it, and then move on to the next concept. I loved this!
The book is organized in a manner that introduces the basic architecture of critical thinking first, and then moves on to apply it to the subject of academic research. While the entire book would be helpful for college students (undergraduates particularly), the earlier chapters on critical thinking and argumentation also stand well on their own and would be of great utility to students in general.
This book was extremely easy to navigate with a clear, drop down list of chapters and subheadings on the left side of the screen. When the reader clicks on links to additional material, these open up in a new tab which keeps things clear and organized. Images and charts were clear and the overall organization is very easy to follow.
I came across no grammatical errors in the text.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
This is perhaps an area where the book could do a little more. I did not come across anything that seemed culturally insensitive or offensive but on the other hand, the book might have taken more opportunities to represent a greater diversity of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This book seems tailor made for undergraduate college students and I would highly recommend it. I think it has some use for graduate students as well, although some of the examples are perhaps little basic for this purpose. As well as using this book to guide students on doing academic research, I think it could also be used as a very helpful introduction to the concept of critical thinking by focusing solely on chapters 1-4.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Part I. What is Critical Thinking?
- Part II. Barriers to Critical Thinking
- Part III. Analyzing Arguments
- Part IV. Making an Argument
- Part V. Research Questions
- Part VI. Sources and Information Needs
- Part VII. Types of Sources
- Part VIII. Precision Searching
- Part IX. Evaluating Sources
- Part X. Ethical Use and Citing Sources
- Part XI. Copyright Basics
- Works Cited
- About the Authors
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Critical Thinking in Academic Research - 2nd Edition provides examples and easy-to-understand explanations to equip students with the skills to develop research questions, evaluate and choose the right sources, search for information, and understand arguments. This 2nd Edition includes new content based on student feedback as well as additional interactive elements throughout the text.
About the Contributors
Cindy Gruwell is an Assistant Librarian/Coordinator of Scholarly Communication at the University of West Florida. She is the library liaison to the department of biology and the College of Health which has extensive nursing programs, public health, health administration, movement, and medical laboratory sciences. In addition to supporting health sciences faculty, she oversees the Argo IRCommons (Institutional Repository) and provides scholarly communication services to faculty across campus. Cindy graduated with her BA (history) and MLS from the University of California, Los Angeles and has a Masters in Education from Bemidji State University. Cindy’s research interests include academic research support, publishing, and teaching.
Robin Ewing is a Professor/Collections Librarian at St. Cloud State University. Robin is the liaison to the College of Education and Learning Design. She oversees content selection for the Library’s collections. Robin graduated with her BBA (Management) and MLIS from the University of Oklahoma. She also has a Masters of Arts in Teaching from Bemidji State University. Robin’s research interests include collection analysis, assessment, and online teaching.
Contribute to this Page

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This research demonstrates that faculty focusing on enhancing critical thinking development in their courses can effectively improve students' critical thinking skills. This collaborative effort can synergize with other courses in which students are enrolled, collectively contributing to the necessary practice hours for developing critical ...
The study concludes that panel discussions, when implemented effectively, can be a valuable tool for enhancing critical thinking, communication skills, and subject matter knowledge in ESP courses for medical students. ... This research provides valuable insights for ESP instructors seeking to integrate panel discussions into their curriculum ...
Critical thinking to better evaluate design solutions, analyze user research data, and make informed decisions based on evidence; Is product design right for you? Product design can be a highly rewarding field, but it's not for everyone. Before you take the leap, you should consider if your personality and interests align with the role.
Preliminary results show that graduates possess soft skills: communication, decision-making, critical thinking, critical thinking, and empathy, Hence, the curriculum can be re-evaluated to address competencies lacking in graduates. Universities face challenges to keep abreast with the ever-evolving industry demands. One strategy involves identifying the lacking competencies of previous ...
Critical thinking and problem-solving: AI is all about solving complex problems. Strong analytical and problem-solving skills are key. Strong analytical and problem-solving skills are key. Domain knowledge: While not always required, having deep knowledge of a specific industry (e.g., healthcare, finance) can make you a highly sought-after AI ...
Student Learning Development supports Trinity students reach their academic potential. We offer a range of services including individual appointments, workshops and skills events. These services are designed to develop your skills in areas such as academic writing, self and time management, exam ...
Critical thinking skills are used every day in a myriad of ways and can be applied to situations such as a CEO approaching a group project or a nurse deciding in which order to treat their patients. ... Research: Researching details and facts allows you to be prepared when presenting your information to people. You'll know exactly what you ...
The research paper aimed at uncovering the components of critical thinking and identifying critical thinking skills and strategies by analyzing the relevant sources and inferring the components ...
Submissions to the journal are judged on the engagement of research and scholarship designed to advance creativity and thinking skills research. The major criteria for acceptance of a research article will be its relevance, its importance and its contribution to the field of teaching for thinking and creativity, and its persuasive, analytical ...
The answer is critical thinking skills. The more that academic research becomes governed by policies outside of the research process, the less opportunity there will be for researchers to exercise such skills. True research demands new ideas, perspectives, and arguments based on willingness and confidence to revisit and directly challenge ...
Critical thinking. Critical thinking refers to a person's ability to think rationally and analyze and interpret information and make connections. This skill is important in research because it allows individuals to better gather and evaluate data and establish significance. Common critical thinking skills include: Open-mindedness.
4. Research Skills: Good writing often involves research, and research requires critical thinking. You need to assess the credibility of sources, synthesize information, and draw conclusions based ...
The key critical thinking skills are identifying biases, inference, research, identification, curiosity, and judging relevance. Let's explore these six critical thinking skills you should learn and why they're so important to the critical thinking process. 1. Identifying biases.
Critical Thinking and Academic Research. Academic research focuses on the creation of new ideas, perspectives, and arguments. The researcher seeks relevant information in articles, books, and other sources, then develops an informed point of view within this ongoing "conversation" among researchers. The research process is not simply collecting ...
They concern conceptual, scientific thinking skills, practical skills, research writing, and academic identity development. Each need attention in any development process. For researchers, there is an international, ever-changing community to join.
Research skills are the ability to find out accurate information on a topic. They include being able to determine the data you need, find and interpret those findings, and then explain that to others. ... When thinking about the research process, data collection is often the first thing that comes to mind. It is the nuts and bolts of research.
The instructors ranked ten critical thinking skills drawn from the research literature and they identified the approaches and learning activities that they used to teach critical thinking. The key findings showed that there was broad consensus in the critical thinking skills that instructors considered most important (analysis, evaluation, and ...
Phenomenography is suggested as a way to handle problems in critical thinking research. ... Developing students' critical thinking skills is regarded as a highly important educational goal in many societies around the world, as it is seen as promoting such disparate qualities as democracy and personal development (Behar-Horenstein and Niu ...
Apply critical thinking skills in research design and methodology: Critical thinking is essential in research design and methodology. This includes making informed decisions about research approaches, sampling methods, data collection, and data analysis techniques. It also involves anticipating potential limitations and biases in the research ...
Critical thinking is the ability to effectively analyze information and form a judgment. To think critically, you must be aware of your own biases and assumptions when encountering information, and apply consistent standards when evaluating sources. Critical thinking skills help you to: Identify credible sources. Evaluate and respond to arguments.
Critical thinking is inherent to the research process. Critical thinking starts with a curious and open mind, and a willingness to look deeper and wider than those who explored this topic before. We look deeply at sources, and the questions at the heart of those sources. We look widely to cross established boundaries of field, discipline, and ...
Critical thinking is one of the most frequently discussed higher order skills, believed to play a central role in logical thinking, decision making, and problem solving (Butler, 2012; Halpern, 2003).It is also a highly contentious skill in that researchers debate about its definition; its amenability to assessment; its degree of generality or specificity; and the evidence of its practical ...
Critical thinking leads to better research skills, which in turn lead to better writing. When you find credible evidence, it will support your claims more effectively, and you'll learn to read and listen to information with a critical eye for bias and persuasion.
Critical thinking (CT) ability, which involves both a set of analytical skills and dispositional qualities (Facione, 1990), is an important component that students can acquire from research and apply in their present and future academic and work context.
Here are some steps you can take when using critical thinking for problem-solving at work: Identify a problem or issue. Create inferences on why the problem exists and how it can be solved. Collect information or data on the issue through research. Organize and sort data and findings. Develop and execute solutions.
Sep 5, 2018. by Janet Salmons, PhD Research Community Manager for Sage Research Methods Community. Critical thinking and creative thinking are distinctly different, but highly interconnected. Nowhere is the symbiotic relationship of creative and critical thinking more apparent than in the practices inherent to research design, conduct, and ...
People with excellent critical thinking skills are commonly thought to be purposeful, reasoning and goal-directed when solving problems ... According to the Web of Science database (hereafter, WOS), critical thinking research has been conducted in 101 research areas from 2000 to 2021. Of all these areas, research on education accounted for the ...
Research skills and critical thinking are intertwined such that developing one enhances the other. Research requires people to question assumptions, evaluate evidence, analyse information, and draw conclusions. These activities require you to think critically about the information at hand. Hence, engaging in research enhances critical thinking.
Critical Thinking in Academic Research - 2nd Edition provides examples and easy-to-understand explanations to equip students with the skills to develop research questions, evaluate and choose the right sources, search for information, and understand arguments. This 2nd Edition includes new content based on student feedback as well as additional interactive elements throughout the text.