Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


What Are Research Objectives and How to Write Them (with Examples)

Table of Contents
Introduction
Research is at the center of everything researchers do, and setting clear, well-defined research objectives plays a pivotal role in guiding scholars toward their desired outcomes. Research papers are essential instruments for researchers to effectively communicate their work. Among the many sections that constitute a research paper, the introduction plays a key role in providing a background and setting the context. 1 Research objectives, which define the aims of the study, are usually stated in the introduction. Every study has a research question that the authors are trying to answer, and the objective is an active statement about how the study will answer this research question. These objectives help guide the development and design of the study and steer the research in the appropriate direction; if this is not clearly defined, a project can fail!
Research studies have a research question, research hypothesis, and one or more research objectives. A research question is what a study aims to answer, and a research hypothesis is a predictive statement about the relationship between two or more variables, which the study sets out to prove or disprove. Objectives are specific, measurable goals that the study aims to achieve. The difference between these three is illustrated by the following example:
- Research question : How does low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) compare with a placebo device in managing the symptoms of skeletally mature patients with patellar tendinopathy?
- Research hypothesis : Pain levels are reduced in patients who receive daily active-LIPUS (treatment) for 12 weeks compared with individuals who receive inactive-LIPUS (placebo).
- Research objective : To investigate the clinical efficacy of LIPUS in the management of patellar tendinopathy symptoms.
This article discusses the importance of clear, well-thought out objectives and suggests methods to write them clearly.
What is the introduction in research papers?
Research objectives are usually included in the introduction section. This section is the first that the readers will read so it is essential that it conveys the subject matter appropriately and is well written to create a good first impression. A good introduction sets the tone of the paper and clearly outlines the contents so that the readers get a quick snapshot of what to expect.
A good introduction should aim to: 2,3
- Indicate the main subject area, its importance, and cite previous literature on the subject
- Define the gap(s) in existing research, ask a research question, and state the objectives
- Announce the present research and outline its novelty and significance
- Avoid repeating the Abstract, providing unnecessary information, and claiming novelty without accurate supporting information.
Why are research objectives important?
Objectives can help you stay focused and steer your research in the required direction. They help define and limit the scope of your research, which is important to efficiently manage your resources and time. The objectives help to create and maintain the overall structure, and specify two main things—the variables and the methods of quantifying the variables.
A good research objective:
- defines the scope of the study
- gives direction to the research
- helps maintain focus and avoid diversions from the topic
- minimizes wastage of resources like time, money, and energy
Types of research objectives
Research objectives can be broadly classified into general and specific objectives . 4 General objectives state what the research expects to achieve overall while specific objectives break this down into smaller, logically connected parts, each of which addresses various parts of the research problem. General objectives are the main goals of the study and are usually fewer in number while specific objectives are more in number because they address several aspects of the research problem.
Example (general objective): To investigate the factors influencing the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
Example (specific objective): To assess the influence of firm size on the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
In addition to this broad classification, research objectives can be grouped into several categories depending on the research problem, as given in Table 1.
Table 1: Types of research objectives
Characteristics of research objectives
Research objectives must start with the word “To” because this helps readers identify the objective in the absence of headings and appropriate sectioning in research papers. 5,6
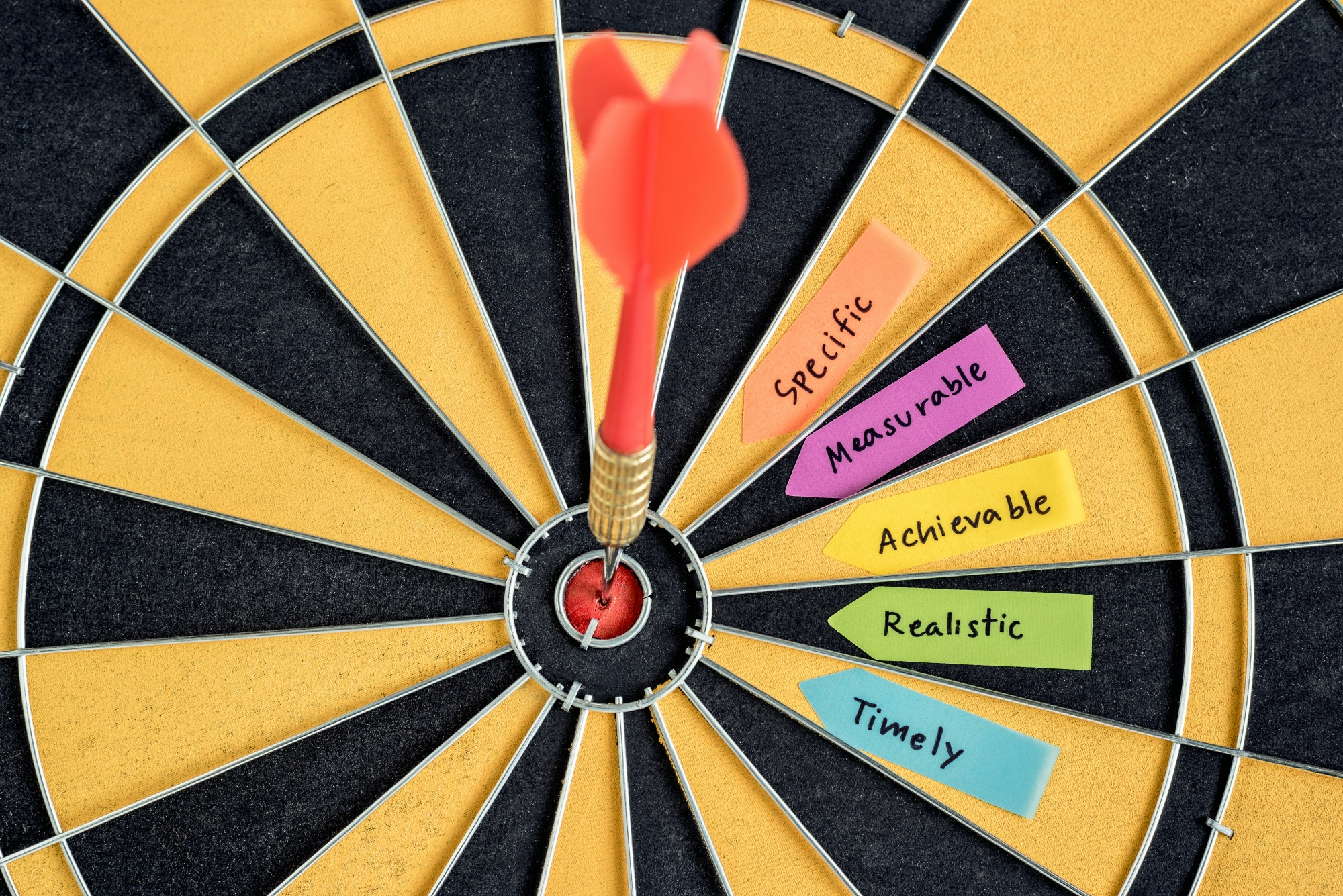
- A good objective is SMART (mostly applicable to specific objectives):
- Specific—clear about the what, why, when, and how
- Measurable—identifies the main variables of the study and quantifies the targets
- Achievable—attainable using the available time and resources
- Realistic—accurately addresses the scope of the problem
- Time-bound—identifies the time in which each step will be completed
- Research objectives clarify the purpose of research.
- They help understand the relationship and dissimilarities between variables.
- They provide a direction that helps the research to reach a definite conclusion.
How to write research objectives?
Research objectives can be written using the following steps: 7
- State your main research question clearly and concisely.
- Describe the ultimate goal of your study, which is similar to the research question but states the intended outcomes more definitively.
- Divide this main goal into subcategories to develop your objectives.
- Limit the number of objectives (1-2 general; 3-4 specific)
- Assess each objective using the SMART
- Start each objective with an action verb like assess, compare, determine, evaluate, etc., which makes the research appear more actionable.
- Use specific language without making the sentence data heavy.
- The most common section to add the objectives is the introduction and after the problem statement.
- Add the objectives to the abstract (if there is one).
- State the general objective first, followed by the specific objectives.
Formulating research objectives
Formulating research objectives has the following five steps, which could help researchers develop a clear objective: 8
- Identify the research problem.
- Review past studies on subjects similar to your problem statement, that is, studies that use similar methods, variables, etc.
- Identify the research gaps the current study should cover based on your literature review. These gaps could be theoretical, methodological, or conceptual.
- Define the research question(s) based on the gaps identified.
- Revise/relate the research problem based on the defined research question and the gaps identified. This is to confirm that there is an actual need for a study on the subject based on the gaps in literature.
- Identify and write the general and specific objectives.
- Incorporate the objectives into the study.
Advantages of research objectives
Adding clear research objectives has the following advantages: 4,8
- Maintains the focus and direction of the research
- Optimizes allocation of resources with minimal wastage
- Acts as a foundation for defining appropriate research questions and hypotheses
- Provides measurable outcomes that can help evaluate the success of the research
- Determines the feasibility of the research by helping to assess the availability of required resources
- Ensures relevance of the study to the subject and its contribution to existing literature
Disadvantages of research objectives
Research objectives also have few disadvantages, as listed below: 8
- Absence of clearly defined objectives can lead to ambiguity in the research process
- Unintentional bias could affect the validity and accuracy of the research findings
Key takeaways
- Research objectives are concise statements that describe what the research is aiming to achieve.
- They define the scope and direction of the research and maintain focus.
- The objectives should be SMART—specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.
- Clear research objectives help avoid collection of data or resources not required for the study.
- Well-formulated specific objectives help develop the overall research methodology, including data collection, analysis, interpretation, and utilization.
- Research objectives should cover all aspects of the problem statement in a coherent way.
- They should be clearly stated using action verbs.
Frequently asked questions on research objectives
Q: what’s the difference between research objectives and aims 9.
A: Research aims are statements that reflect the broad goal(s) of the study and outline the general direction of the research. They are not specific but clearly define the focus of the study.
Example: This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.
Research objectives focus on the action to be taken to achieve the aims. They make the aims more practical and should be specific and actionable.
Example: To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation.
Q: What are the examples of research objectives, both general and specific?
A: Here are a few examples of research objectives:
- To identify the antiviral chemical constituents in Mumbukura gitoniensis (general)
- To carry out solvent extraction of dried flowers of Mumbukura gitoniensis and isolate the constituents. (specific)
- To determine the antiviral activity of each of the isolated compounds. (specific)
- To examine the extent, range, and method of coral reef rehabilitation projects in five shallow reef areas adjacent to popular tourist destinations in the Philippines.
- To investigate species richness of mammal communities in five protected areas over the past 20 years.
- To evaluate the potential application of AI techniques for estimating best-corrected visual acuity from fundus photographs with and without ancillary information.
- To investigate whether sport influences psychological parameters in the personality of asthmatic children.
Q: How do I develop research objectives?
A: Developing research objectives begins with defining the problem statement clearly, as illustrated by Figure 1. Objectives specify how the research question will be answered and they determine what is to be measured to test the hypothesis.
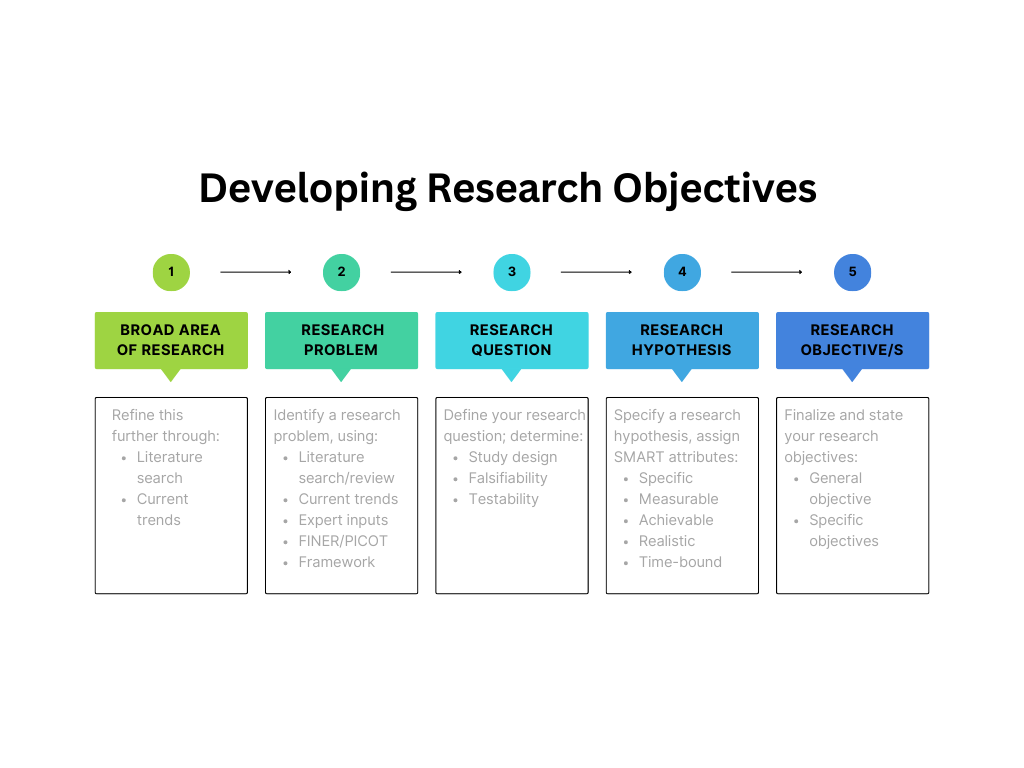
Q: Are research objectives measurable?
A: The word “measurable” implies that something is quantifiable. In terms of research objectives, this means that the source and method of collecting data are identified and that all these aspects are feasible for the research. Some metrics can be created to measure your progress toward achieving your objectives.
Q: Can research objectives change during the study?
A: Revising research objectives during the study is acceptable in situations when the selected methodology is not progressing toward achieving the objective, or if there are challenges pertaining to resources, etc. One thing to keep in mind is the time and resources you would have to complete your research after revising the objectives. Thus, as long as your problem statement and hypotheses are unchanged, minor revisions to the research objectives are acceptable.
Q: What is the difference between research questions and research objectives? 10
Q: are research objectives the same as hypotheses.
A: No, hypotheses are predictive theories that are expressed in general terms. Research objectives, which are more specific, are developed from hypotheses and aim to test them. A hypothesis can be tested using several methods and each method will have different objectives because the methodology to be used could be different. A hypothesis is developed based on observation and reasoning; it is a calculated prediction about why a particular phenomenon is occurring. To test this prediction, different research objectives are formulated. Here’s a simple example of both a research hypothesis and research objective.
Research hypothesis : Employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
Research objective : To assess whether employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
To summarize, research objectives are an important part of research studies and should be written clearly to effectively communicate your research. We hope this article has given you a brief insight into the importance of using clearly defined research objectives and how to formulate them.
- Farrugia P, Petrisor BA, Farrokhyar F, Bhandari M. Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Can J Surg. 2010 Aug;53(4):278-81.
- Abbadia J. How to write an introduction for a research paper. Mind the Graph website. Accessed June 14, 2023. https://mindthegraph.com/blog/how-to-write-an-introduction-for-a-research-paper/
- Writing a scientific paper: Introduction. UCI libraries website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://guides.lib.uci.edu/c.php?g=334338&p=2249903
- Research objectives—Types, examples and writing guide. Researchmethod.net website. Accessed June 17, 2023. https://researchmethod.net/research-objectives/#:~:text=They%20provide%20a%20clear%20direction,track%20and%20achieve%20their%20goals .
- Bartle P. SMART Characteristics of good objectives. Community empowerment collective website. Accessed June 16, 2023. https://cec.vcn.bc.ca/cmp/modules/pd-smar.htm
- Research objectives. Studyprobe website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.studyprobe.in/2022/08/research-objectives.html
- Corredor F. How to write objectives in a research paper. wikiHow website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.wikihow.com/Write-Objectives-in-a-Research-Proposal
- Research objectives: Definition, types, characteristics, advantages. AccountingNest website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://www.accountingnest.com/articles/research/research-objectives
- Phair D., Shaeffer A. Research aims, objectives & questions. GradCoach website. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://gradcoach.com/research-aims-objectives-questions/
- Understanding the difference between research questions and objectives. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://board.researchersjob.com/blog/research-questions-and-objectives
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

Academic Writing vs Non-Academic Writing

How to Define a Research Problem?
General objectives and specific objectives
The general and specific objectives are fundamental elements for the accomplishment of academic works, like for example, a thesis of degree.
The general objective is a statement that summarizes the central idea and purpose of a work.
The specific objectives detail the processes necessary for the complete accomplishment of the work.
General objective
The general objective should present the central idea of an academic work, succinctly and objectively stating the purpose of the study and the goal to be achieved.
In other words, the general objective synthesizes the hypothesis or problem to be investigated, specifies the purpose of the study and defines the topic.
General objective example
“Verify if there is a relationship between the increase in Internet access and the decrease in the use of television in the southwestern region of Mexico.”
The purpose of the work is expressed in “verifying if there is a relationship between the increase in Internet access and the decrease in the use of television.” The delimitation is expressed in “in the southwestern region of Mexico.”
Specific objectives
The specific objectives are directly related to the general objectives, detailing the processes necessary for their realization. In this way, the specific objectives serve as a guide for how the work will be approached.
The specific objectives should present in detail the goals of the project. This is how the object studied is related to its particularities and the steps to be followed to meet the general objective are identified.
Example of specific objectives
Continuing with the previous example, the specific objectives could be:
- Analyze the increase in Internet access in the last year;
- Analyze the number of televisions in homes in the southwestern region of Mexico;
- Verify the use of television in homes in the southwestern region of Mexico;
- Compare the standard of increasing Internet access with a decrease in the use of televisions.
See also Goal and objective .
Related Posts

Reference and bibliography

Types of hypotheses

Accident and accident
About author.
JessicaTempest
Bachelor in Technological and Industrial Chemistry from the Federal University of Alagoas in 2018 and a Technical in Chemistry from the Federal Institute of Education, Science, and Technology of Pernambuco in 2011. Completed complementary courses involving information management, intellectual property, laboratory techniques, and operation of chemical processes. I have been working since 2016 with online content production. I also held positions in the administrative, educational, laboratory, and industrial areas.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Email Address: *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- How it works

How to Write the Dissertation Aims and Objectives – Guide & Examples
Published by Grace Graffin at January 27th, 2023 , Revised On October 9, 2023
Aims and objectives are among the essential aspects of a dissertation. If you write aims and objectives effectively, they can act as a foundation to give your research clarity and focus.
This article will provide you with all the necessary information regarding aims and objectives, their differences, writing tips , and the common mistakes you should avoid while writing them.
The aim is often a single sentence or a short paragraph that describes your dissertation’s main goal and intent. It tells what you hope to achieve at the end. You should write the aim so that it becomes identifiable when it is achieved with the completion of your dissertation .
The aim is written in a subsection of the introduction to clarify the overall purpose of the dissertation .
Example: It is often observed that employees in culturally diverse workplaces struggle to work effectively in a team. A probable cause of this issue is bullying at the workplace. This research investigates the impact of bullying on employee job satisfaction at culturally diverse workplaces and the resulting loss of employee productivity. This research will use surveys and case study analysis to analyze the impact of bullying on employees.
The objectives in a dissertation describe the ways through which you intend to achieve the research aim. They are specific statements that break down the aim into several smaller key sections of the overall research. Suitable objectives can help you stay focused and conduct research in the direction of your aim.
The number of objectives should be realistic; usually, between three to six, and each one should be possible to achieve. The following example shows the objectives for the previously-mentioned dissertation aim.
1. identification of the behaviors that are considered as bullying 2. exploring the factors that cause bullying at a culturally diverse workplace 3. analyzing the relationship between bullying and job satisfaction of employees 4. providing suitable recommendations on minimizing the bullying at the workplace
The objectives of a dissertation should be SMART.
- Specific: should be precise, focused, and well-defined
- Measurable: the progress should be measurable, and you should be able to determine when you have achieved an objective.
- Achievable: you should be able to carry out the required action within your available resources
- Relevant: should be related to the dissertation aim
- Time-bound: should be possible within the available time
Differences between aims and objectives
Aims and objectives are often mixed, but there are clear differences between them.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

How to write aims and objectives?
There is no particular way or standard to write the aims and objectives. Different researchers have different writing styles, and often it can be influenced by your research supervisor. However, you should follow certain basic principles while writing aims and objectives in a dissertation.
Writing the aim statement
The aim statement should cover the following essential elements.
- Why is the research necessary? (covers the underlying problem on which the study is to be conducted)
- What is the research about? (description of the research title)
- How are you going to conduct it? (a brief statement of intended research methods)
An appropriate aim clearly defines the research purpose without confusing the reader. If you struggle to explain your research and its importance in simpler terms, you should consider refining your research to clarify it further.
Writing objectives
The objectives describe how you would achieve your research aim. You can do this through the following steps,
- The first one to two objectives can be applied to the literature review . (Verbs to be used: investigate, examine, study)
- One objective can be applied to the methodology portion. (Verbs to be used: collect, select, demonstrate, estimate)
- Two to three objectives can cover the critical evaluation or discussion chapters (Verbs to be used: analyze, compare, evaluate)
- The final objective will cover the conclusion or recommendation portion. (Verbs to be used: conclude, recommend)
Instead of writing like a paragraph, the objectives should be written as a numbered list to give them more clarity.
How many aims and objectives should be there?
It depends upon the topic of your research and mainly upon your supervisor’s requirements. Generally, a dissertation has a single broad statement as the research aim. However, it is acceptable to include a main aim along with two to three subsidiary aims.
Similarly, the number of objectives should be realistic and sufficient to measure the progress regarding the achievement of the research aim. Their number can generally vary from three to six depending upon the aim.
Common mistakes to avoid while writing research aims and objectives
- Writing a broad research aim
Writing a broad research aim is a common mistake, and it often becomes difficult to achieve. It may create a problem when you are asked to prove how you have achieved your aims during your viva defense . It would be best to narrow your study to a specific area in the early stages of the dissertation.
- Formulating overlapping research objectives
The objectives should be written such that they are measurable and distinct from each other. If they overlap, it makes it difficult to structure your dissertation properly in specific chapters.
- Setting unrealistic aims
Students often get over-ambitious while describing the research aim and face problems afterward in achieving those aims. You should avoid this mistake and be realistic about what you can achieve in the available time and resources.
Aims and objectives are the sections that require significant time and attention to avoid future hassles while conducting research and writing your dissertation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to set dissertation aims and objectives.
To set dissertation aims and objectives, define your research goals clearly. Aims state what you want to achieve, while objectives outline specific, measurable steps to reach those goals. Ensure they align with your research question and contribute to your study’s significance.
You May Also Like
Explore the top 4 AI essay writer tools of 2024 – Writeressay.ai, Aiessaybot.org, Essayrewriter.io, and Aiarticlespinner.com.
Learn about What a dissertation generator is and how reliable they are compared to a professional writing service.
Elevate your professional profile with the CapCut Creative Suite! Craft compelling video resumes that captivate employers in the job market.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

- Aims and Objectives – A Guide for Academic Writing
- Doing a PhD
One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and your reader clarity, with your aims indicating what is to be achieved, and your objectives indicating how it will be achieved.
Introduction
There is no getting away from the importance of the aims and objectives in determining the success of your research project. Unfortunately, however, it is an aspect that many students struggle with, and ultimately end up doing poorly. Given their importance, if you suspect that there is even the smallest possibility that you belong to this group of students, we strongly recommend you read this page in full.
This page describes what research aims and objectives are, how they differ from each other, how to write them correctly, and the common mistakes students make and how to avoid them. An example of a good aim and objectives from a past thesis has also been deconstructed to help your understanding.
What Are Aims and Objectives?
Research aims.
A research aim describes the main goal or the overarching purpose of your research project.
In doing so, it acts as a focal point for your research and provides your readers with clarity as to what your study is all about. Because of this, research aims are almost always located within its own subsection under the introduction section of a research document, regardless of whether it’s a thesis , a dissertation, or a research paper .
A research aim is usually formulated as a broad statement of the main goal of the research and can range in length from a single sentence to a short paragraph. Although the exact format may vary according to preference, they should all describe why your research is needed (i.e. the context), what it sets out to accomplish (the actual aim) and, briefly, how it intends to accomplish it (overview of your objectives).
To give an example, we have extracted the following research aim from a real PhD thesis:
Example of a Research Aim
The role of diametrical cup deformation as a factor to unsatisfactory implant performance has not been widely reported. The aim of this thesis was to gain an understanding of the diametrical deformation behaviour of acetabular cups and shells following impaction into the reamed acetabulum. The influence of a range of factors on deformation was investigated to ascertain if cup and shell deformation may be high enough to potentially contribute to early failure and high wear rates in metal-on-metal implants.
Note: Extracted with permission from thesis titled “T he Impact And Deformation Of Press-Fit Metal Acetabular Components ” produced by Dr H Hothi of previously Queen Mary University of London.
Research Objectives
Where a research aim specifies what your study will answer, research objectives specify how your study will answer it.
They divide your research aim into several smaller parts, each of which represents a key section of your research project. As a result, almost all research objectives take the form of a numbered list, with each item usually receiving its own chapter in a dissertation or thesis.
Following the example of the research aim shared above, here are it’s real research objectives as an example:
Example of a Research Objective
- Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
- Investigate the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup.
- Determine the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types.
- Investigate the influence of non-uniform cup support and varying the orientation of the component in the cavity on deformation.
- Examine the influence of errors during reaming of the acetabulum which introduce ovality to the cavity.
- Determine the relationship between changes in the geometry of the component and deformation for different cup designs.
- Develop three dimensional pelvis models with non-uniform bone material properties from a range of patients with varying bone quality.
- Use the key parameters that influence deformation, as identified in the foam models to determine the range of deformations that may occur clinically using the anatomic models and if these deformations are clinically significant.
It’s worth noting that researchers sometimes use research questions instead of research objectives, or in other cases both. From a high-level perspective, research questions and research objectives make the same statements, but just in different formats.
Taking the first three research objectives as an example, they can be restructured into research questions as follows:
Restructuring Research Objectives as Research Questions
- Can finite element models using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum together with explicit dynamics be used to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion?
- What is the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup?
- What is the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types?
Difference Between Aims and Objectives
Hopefully the above explanations make clear the differences between aims and objectives, but to clarify:
- The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved.
- Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific.
- Research aims focus on a project’s long-term outcomes; research objectives focus on its immediate, short-term outcomes.
- A research aim can be written in a single sentence or short paragraph; research objectives should be written as a numbered list.
How to Write Aims and Objectives
Before we discuss how to write a clear set of research aims and objectives, we should make it clear that there is no single way they must be written. Each researcher will approach their aims and objectives slightly differently, and often your supervisor will influence the formulation of yours on the basis of their own preferences.
Regardless, there are some basic principles that you should observe for good practice; these principles are described below.
Your aim should be made up of three parts that answer the below questions:
- Why is this research required?
- What is this research about?
- How are you going to do it?
The easiest way to achieve this would be to address each question in its own sentence, although it does not matter whether you combine them or write multiple sentences for each, the key is to address each one.
The first question, why , provides context to your research project, the second question, what , describes the aim of your research, and the last question, how , acts as an introduction to your objectives which will immediately follow.
Scroll through the image set below to see the ‘why, what and how’ associated with our research aim example.

Note: Your research aims need not be limited to one. Some individuals per to define one broad ‘overarching aim’ of a project and then adopt two or three specific research aims for their thesis or dissertation. Remember, however, that in order for your assessors to consider your research project complete, you will need to prove you have fulfilled all of the aims you set out to achieve. Therefore, while having more than one research aim is not necessarily disadvantageous, consider whether a single overarching one will do.
Research Objectives
Each of your research objectives should be SMART :
- Specific – is there any ambiguity in the action you are going to undertake, or is it focused and well-defined?
- Measurable – how will you measure progress and determine when you have achieved the action?
- Achievable – do you have the support, resources and facilities required to carry out the action?
- Relevant – is the action essential to the achievement of your research aim?
- Timebound – can you realistically complete the action in the available time alongside your other research tasks?
In addition to being SMART, your research objectives should start with a verb that helps communicate your intent. Common research verbs include:
Table of Research Verbs to Use in Aims and Objectives
Last, format your objectives into a numbered list. This is because when you write your thesis or dissertation, you will at times need to make reference to a specific research objective; structuring your research objectives in a numbered list will provide a clear way of doing this.
To bring all this together, let’s compare the first research objective in the previous example with the above guidance:
Checking Research Objective Example Against Recommended Approach
Research Objective:
1. Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
Checking Against Recommended Approach:
Q: Is it specific? A: Yes, it is clear what the student intends to do (produce a finite element model), why they intend to do it (mimic cup/shell blows) and their parameters have been well-defined ( using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum ).
Q: Is it measurable? A: Yes, it is clear that the research objective will be achieved once the finite element model is complete.
Q: Is it achievable? A: Yes, provided the student has access to a computer lab, modelling software and laboratory data.
Q: Is it relevant? A: Yes, mimicking impacts to a cup/shell is fundamental to the overall aim of understanding how they deform when impacted upon.
Q: Is it timebound? A: Yes, it is possible to create a limited-scope finite element model in a relatively short time, especially if you already have experience in modelling.
Q: Does it start with a verb? A: Yes, it starts with ‘develop’, which makes the intent of the objective immediately clear.
Q: Is it a numbered list? A: Yes, it is the first research objective in a list of eight.
Mistakes in Writing Research Aims and Objectives
1. making your research aim too broad.
Having a research aim too broad becomes very difficult to achieve. Normally, this occurs when a student develops their research aim before they have a good understanding of what they want to research. Remember that at the end of your project and during your viva defence , you will have to prove that you have achieved your research aims; if they are too broad, this will be an almost impossible task. In the early stages of your research project, your priority should be to narrow your study to a specific area. A good way to do this is to take the time to study existing literature, question their current approaches, findings and limitations, and consider whether there are any recurring gaps that could be investigated .
Note: Achieving a set of aims does not necessarily mean proving or disproving a theory or hypothesis, even if your research aim was to, but having done enough work to provide a useful and original insight into the principles that underlie your research aim.
2. Making Your Research Objectives Too Ambitious
Be realistic about what you can achieve in the time you have available. It is natural to want to set ambitious research objectives that require sophisticated data collection and analysis, but only completing this with six months before the end of your PhD registration period is not a worthwhile trade-off.
3. Formulating Repetitive Research Objectives
Each research objective should have its own purpose and distinct measurable outcome. To this effect, a common mistake is to form research objectives which have large amounts of overlap. This makes it difficult to determine when an objective is truly complete, and also presents challenges in estimating the duration of objectives when creating your project timeline. It also makes it difficult to structure your thesis into unique chapters, making it more challenging for you to write and for your audience to read.
Fortunately, this oversight can be easily avoided by using SMART objectives.
Hopefully, you now have a good idea of how to create an effective set of aims and objectives for your research project, whether it be a thesis, dissertation or research paper. While it may be tempting to dive directly into your research, spending time on getting your aims and objectives right will give your research clear direction. This won’t only reduce the likelihood of problems arising later down the line, but will also lead to a more thorough and coherent research project.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
Research Objective Generator for Theses & Papers
Here's how to start using our objective generator for research:
- Choose an action verb from the drop-down list.
- Enter your aim.
- Move the toggle if needed.
- Click “Generate now” and enjoy a properly formulated objective.
In this article, you will find the definition of the research objective, its importance to the scientific paper, and practical tips that’ll help you to create a great one for your research.
- ️✅ The Tool’s Benefits
- ️🎯 Research Objective Basics
- ️✍️ How to Write
- ️✨ Research Objective Tips
- ️🔍 Free Examples
- ️🔗 References
✅ Research Objective Generator: the Benefits
A research objective is a crucial part of your paper that points to purpose of the study. Creating an effective research objective is a challenging task, even for experienced researchers.
Not sure how to do it?
No worries!
Our research objective generator can help you out.
Here are its main advantages:
🎯 Research Objective: the Basics
What is a research objective.
The research objective specifies how you are going to achieve your goal . It’s like a roadmap of your study that summarizes its aims, describes the results you expect to accomplish at the end, and helps you to keep track of your research.
The objective should always appear in the introduction of your paper or scientific article, right after the problem or thesis statement .
Importance of a Research Objective
Find below the list of reasons why a research objective is important.

A good research objective is important because it:
- Describes the scope of your study. It allows you to keep an eye on your findings.
- Establishes the design of your research. It helps to choose the appropriate methods and procedures for data collection and measurement .
- Defines data and factors you need to evaluate. It narrows down your research to several measurable components you have to assess or compare.
- Specifies the contribution of your project to existing research. That’s a great way to show you know the studies conducted in your field and have something valuable to add to them.
✍️ How to Write a Research Objective
To write a strong and clear research objective, follow our three-step guide.
Step 1 - Define the Central Point of Your Research
It’s the first and the most crucial step. Begin with looking through the literature and studies in your area to determine the gaps in existing research . Then, consider how your project can fill these gaps and formulate the primary aim and objective.
Step 2 - Break Down Your Point into Several Objectives
So, you have the primary objective that states what you intend to achieve through your research. Now, it’s time to break it down. Think about what smaller steps you can take to attain your goal. These will be your specific, narrow objectives.
Step 3 - Write Down Your Objectives Using the SMART Format
The SMART format will help you to achieve your goals by keeping them clear and easy to understand.
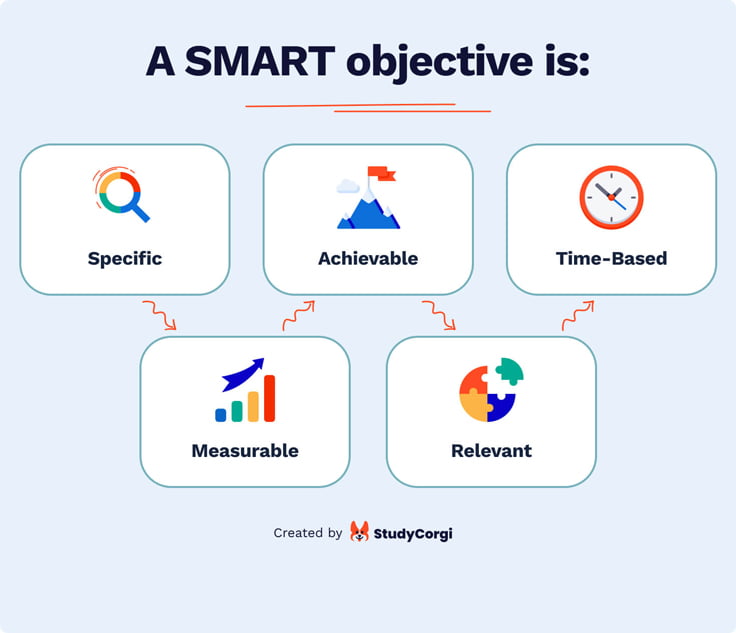
A SMART objective is:
✨ Research Objective Writing Tips
To formulate effective research objectives, follow these actionable tips:
- Keep them realistic. Ensure you can actually achieve your goals. Make them simple enough to avoid getting overwhelmed.
- Define your goals. You must distinctly understand what issue you are going to solve with your research. For example, you can start by making a list of questions and then using them to formulate your research aims. After you have your goals, think about how you will achieve them—these will be your objectives.
- Use action verbs. Strong action verbs make your objectives measurable and more actionable.
- Proofread your objectives. To make your research competent and reliable, ensure your writing is free of typos and grammar mistakes.
- Ask for feedback. Make a draft of your objectives and ask a peer to review them. That’s a perfect way to ensure your research goals are clear to others.
🔍 Research Objectives Examples
Finally, let’s take a look at some practical examples and review them:
This research aims to analyze the reasons for teenage smoking, identify the change in the smoking rates among teenagers for the last year, and map out actionable solutions to address the issue.
This research aims to assess the influence of flipped classroom learning method on student scores and compare the scores of students exposed to flipped classroom learning method versus the direct instruction method.
This research aims to study the influence of deforestation on the animal species in the sample region in the past 5 years, evaluate the species extinction risk in the area, and propose practical solutions to the problem.
These objectives include strong action verbs (identify, analyze, assess, compare, map out, etc.), time limits, and measurable outcomes. Based on them, the researcher can decide on the methods to use and the variables to measure.
Now, you know everything to create a perfect objective for your research. Go for it! Or you can save your time and use our objective maker for research. It’ll generate a well-formulated research objective just in a few seconds!
If you need to write a thesis statement, try our thesis maker .
❓ Research Objective Generator FAQ
❓ how do you write a smart objective in research.
The first step to writing a SMART objective for your research is to determine your principal aim and consider how you will achieve it. Next, write down your objective and ensure it fits the following criteria: specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-based.
❓ What is a SMART research objective?
A SMART research objective is specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-based. It means that the objective must include a precise, realistic task that is concise with the rest of the research, suppose some definite results, and be finished by a specific time.
❓ What are research objectives examples?
Research objectives show how you will address the aim of your research, for example: "This research aims to indicate the connection between a sedentary lifestyle and muscular atrophy, evaluate the health risks of a sedentary lifestyle, and map out practical solutions to the issue."
❓ What are the 5 SMART goals examples?
To check whether your goals are SMART, ask the following questions:
- What’ll you achieve? (Specific)
- How do you know it’s done? (Measurable)
- Can you do it? (Achievable)
- Is it concise with the study in general? (Relevant)
- When will you accomplish it? (Time-based)
🔗 References
- Research Objectives: Definition and How To Write Them: Indeed
- Research Objectives: OpenLearn
- Formulating Research Aims and Objectives: Oxford University Press
- Defining Goals, Objectives, and Hypotheses: GitLab
- Log in / Register

- Getting started
- Criteria for a problem formulation
- Find who and what you are looking for
- Too broad, too narrow, or o.k.?
- Test your knowledge
- Lesson 5: Meeting your supervisor
- Getting started: summary
- Literature search
- Searching for articles
- Searching for Data
- Databases provided by your library
- Other useful search tools
- Free text, truncating and exact phrase
- Combining search terms – Boolean operators
- Keep track of your search strategies
- Problems finding your search terms?
- Different sources, different evaluations
- Extract by relevance
- Lesson 4: Obtaining literature
- Literature search: summary
- Research methods
- Combining qualitative and quantitative methods
- Collecting data
- Analysing data
- Strengths and limitations
- Explanatory, analytical and experimental studies
- The Nature of Secondary Data
- How to Conduct a Systematic Review
- Directional Policy Research
- Strategic Policy Research
- Operational Policy Research
- Conducting Research Evaluation
- Research Methods: Summary
- Project management
- Project budgeting
- Data management plan
- Quality Control
- Project control
- Project management: Summary
- Writing process
- Title page, abstract, foreword, abbreviations, table of contents
- Introduction, methods, results
- Discussion, conclusions, recomendations, references, appendices, layout
- Use citations correctly
- Use references correctly
- Bibliographic software
- Writing process – summary
- Getting started /
Lesson 3: Research objectives
While your problem formulation serves to describe the aim of your thesis, the objectives provide an accurate description of the specific actions you will take in order to reach this aim. As with the problem formulation, the overall objective should be framed in a single sentence.
Once again, take a look at the problem formulation from the previous lesson: “Is the level of knowledge on recommended nutritional practices related to the nutritional status of pregnant women attending antenatal care in Northern Uganda?”
The correspondent overall objective should be written as an infinitive sentence e.g.: “To analyse the association between nutritional knowledge and the nutritional status of pregnant women attending antenatal care (ANC) in Northern Uganda.
Here you see that the overall objective states exactly how you intend to address your problem: “I want to find the answer to problem A, by completing action B”. You then have to explain or detail action B through a set of specific objectives (usually between two and four), e.g.:
- To assess the knowledge level among ANC attendees on the recommended nutritional practices during pregnancy
- To assess the nutritional status of pregnant women attending ANC
- To analyse the statistical association between nutritional knowledge level and nutritional status in pregnant women attending ANC
Each specific objective consists of one infinitive sentence and should be phrased in a way that makes it possible to draw a conclusion from within the scope of the thesis.
The more precisely you formulate your specific objectives, the simpler it will be to define the type of study and which method(s) you will use in your further research. You can refine your specific objective by clearly stating if your given action is to understand, analyse or create – in tune with the hierarchy of learning objectives and the key to the assessment of knowledge content as found in for example Bloom’s taxonomy. In this way, your specific objectives will signal your level of ambition as well as where you will place the greatest effort in your thesis.
TIP! Your well-defined research objectives will help you identify the type of study you will do. Practical limitations and/or advice from your supervisor may require that you reformulate all or some of your objectives. Don’t worry; this is all part of the research process.
Do you now know how to formulate objectives? Test your knowledge in the following.
Your friend's e-mail
Message (Note: The link to the page is attached automtisk in the message to your friend)

Did you know...
How To Write A Research Proposal
A Straightforward How-To Guide (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2019 (Updated April 2023)
Writing up a strong research proposal for a dissertation or thesis is much like a marriage proposal. It’s a task that calls on you to win somebody over and persuade them that what you’re planning is a great idea. An idea they’re happy to say ‘yes’ to. This means that your dissertation proposal needs to be persuasive , attractive and well-planned. In this post, I’ll show you how to write a winning dissertation proposal, from scratch.
Before you start:
– Understand exactly what a research proposal is – Ask yourself these 4 questions
The 5 essential ingredients:
- The title/topic
- The introduction chapter
- The scope/delimitations
- Preliminary literature review
- Design/ methodology
- Practical considerations and risks
What Is A Research Proposal?
The research proposal is literally that: a written document that communicates what you propose to research, in a concise format. It’s where you put all that stuff that’s spinning around in your head down on to paper, in a logical, convincing fashion.
Convincing is the keyword here, as your research proposal needs to convince the assessor that your research is clearly articulated (i.e., a clear research question) , worth doing (i.e., is unique and valuable enough to justify the effort), and doable within the restrictions you’ll face (time limits, budget, skill limits, etc.). If your proposal does not address these three criteria, your research won’t be approved, no matter how “exciting” the research idea might be.
PS – if you’re completely new to proposal writing, we’ve got a detailed walkthrough video covering two successful research proposals here .

How do I know I’m ready?
Before starting the writing process, you need to ask yourself 4 important questions . If you can’t answer them succinctly and confidently, you’re not ready – you need to go back and think more deeply about your dissertation topic .
You should be able to answer the following 4 questions before starting your dissertation or thesis research proposal:
- WHAT is my main research question? (the topic)
- WHO cares and why is this important? (the justification)
- WHAT data would I need to answer this question, and how will I analyse it? (the research design)
- HOW will I manage the completion of this research, within the given timelines? (project and risk management)
If you can’t answer these questions clearly and concisely, you’re not yet ready to write your research proposal – revisit our post on choosing a topic .
If you can, that’s great – it’s time to start writing up your dissertation proposal. Next, I’ll discuss what needs to go into your research proposal, and how to structure it all into an intuitive, convincing document with a linear narrative.
The 5 Essential Ingredients
Research proposals can vary in style between institutions and disciplines, but here I’ll share with you a handy 5-section structure you can use. These 5 sections directly address the core questions we spoke about earlier, ensuring that you present a convincing proposal. If your institution already provides a proposal template, there will likely be substantial overlap with this, so you’ll still get value from reading on.
For each section discussed below, make sure you use headers and sub-headers (ideally, numbered headers) to help the reader navigate through your document, and to support them when they need to revisit a previous section. Don’t just present an endless wall of text, paragraph after paragraph after paragraph…
Top Tip: Use MS Word Styles to format headings. This will allow you to be clear about whether a sub-heading is level 2, 3, or 4. Additionally, you can view your document in ‘outline view’ which will show you only your headings. This makes it much easier to check your structure, shift things around and make decisions about where a section needs to sit. You can also generate a 100% accurate table of contents using Word’s automatic functionality.

Ingredient #1 – Topic/Title Header
Your research proposal’s title should be your main research question in its simplest form, possibly with a sub-heading providing basic details on the specifics of the study. For example:
“Compliance with equality legislation in the charity sector: a study of the ‘reasonable adjustments’ made in three London care homes”
As you can see, this title provides a clear indication of what the research is about, in broad terms. It paints a high-level picture for the first-time reader, which gives them a taste of what to expect. Always aim for a clear, concise title . Don’t feel the need to capture every detail of your research in your title – your proposal will fill in the gaps.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #2 – Introduction
In this section of your research proposal, you’ll expand on what you’ve communicated in the title, by providing a few paragraphs which offer more detail about your research topic. Importantly, the focus here is the topic – what will you research and why is that worth researching? This is not the place to discuss methodology, practicalities, etc. – you’ll do that later.
You should cover the following:
- An overview of the broad area you’ll be researching – introduce the reader to key concepts and language
- An explanation of the specific (narrower) area you’ll be focusing, and why you’ll be focusing there
- Your research aims and objectives
- Your research question (s) and sub-questions (if applicable)
Importantly, you should aim to use short sentences and plain language – don’t babble on with extensive jargon, acronyms and complex language. Assume that the reader is an intelligent layman – not a subject area specialist (even if they are). Remember that the best writing is writing that can be easily understood and digested. Keep it simple.

Note that some universities may want some extra bits and pieces in your introduction section. For example, personal development objectives, a structural outline, etc. Check your brief to see if there are any other details they expect in your proposal, and make sure you find a place for these.
Ingredient #3 – Scope
Next, you’ll need to specify what the scope of your research will be – this is also known as the delimitations . In other words, you need to make it clear what you will be covering and, more importantly, what you won’t be covering in your research. Simply put, this is about ring fencing your research topic so that you have a laser-sharp focus.
All too often, students feel the need to go broad and try to address as many issues as possible, in the interest of producing comprehensive research. Whilst this is admirable, it’s a mistake. By tightly refining your scope, you’ll enable yourself to go deep with your research, which is what you need to earn good marks. If your scope is too broad, you’re likely going to land up with superficial research (which won’t earn marks), so don’t be afraid to narrow things down.
Ingredient #4 – Literature Review
In this section of your research proposal, you need to provide a (relatively) brief discussion of the existing literature. Naturally, this will not be as comprehensive as the literature review in your actual dissertation, but it will lay the foundation for that. In fact, if you put in the effort at this stage, you’ll make your life a lot easier when it’s time to write your actual literature review chapter.
There are a few things you need to achieve in this section:
- Demonstrate that you’ve done your reading and are familiar with the current state of the research in your topic area.
- Show that there’s a clear gap for your specific research – i.e., show that your topic is sufficiently unique and will add value to the existing research.
- Show how the existing research has shaped your thinking regarding research design . For example, you might use scales or questionnaires from previous studies.
When you write up your literature review, keep these three objectives front of mind, especially number two (revealing the gap in the literature), so that your literature review has a clear purpose and direction . Everything you write should be contributing towards one (or more) of these objectives in some way. If it doesn’t, you need to ask yourself whether it’s truly needed.
Top Tip: Don’t fall into the trap of just describing the main pieces of literature, for example, “A says this, B says that, C also says that…” and so on. Merely describing the literature provides no value. Instead, you need to synthesise it, and use it to address the three objectives above.

Ingredient #5 – Research Methodology
Now that you’ve clearly explained both your intended research topic (in the introduction) and the existing research it will draw on (in the literature review section), it’s time to get practical and explain exactly how you’ll be carrying out your own research. In other words, your research methodology.
In this section, you’ll need to answer two critical questions :
- How will you design your research? I.e., what research methodology will you adopt, what will your sample be, how will you collect data, etc.
- Why have you chosen this design? I.e., why does this approach suit your specific research aims, objectives and questions?
In other words, this is not just about explaining WHAT you’ll be doing, it’s also about explaining WHY. In fact, the justification is the most important part , because that justification is how you demonstrate a good understanding of research design (which is what assessors want to see).
Some essential design choices you need to cover in your research proposal include:
- Your intended research philosophy (e.g., positivism, interpretivism or pragmatism )
- What methodological approach you’ll be taking (e.g., qualitative , quantitative or mixed )
- The details of your sample (e.g., sample size, who they are, who they represent, etc.)
- What data you plan to collect (i.e. data about what, in what form?)
- How you plan to collect it (e.g., surveys , interviews , focus groups, etc.)
- How you plan to analyse it (e.g., regression analysis, thematic analysis , etc.)
- Ethical adherence (i.e., does this research satisfy all ethical requirements of your institution, or does it need further approval?)
This list is not exhaustive – these are just some core attributes of research design. Check with your institution what level of detail they expect. The “ research onion ” by Saunders et al (2009) provides a good summary of the various design choices you ultimately need to make – you can read more about that here .
Don’t forget the practicalities…
In addition to the technical aspects, you will need to address the practical side of the project. In other words, you need to explain what resources you’ll need (e.g., time, money, access to equipment or software, etc.) and how you intend to secure these resources. You need to show that your project is feasible, so any “make or break” type resources need to already be secured. The success or failure of your project cannot depend on some resource which you’re not yet sure you have access to.
Another part of the practicalities discussion is project and risk management . In other words, you need to show that you have a clear project plan to tackle your research with. Some key questions to address:
- What are the timelines for each phase of your project?
- Are the time allocations reasonable?
- What happens if something takes longer than anticipated (risk management)?
- What happens if you don’t get the response rate you expect?
A good way to demonstrate that you’ve thought this through is to include a Gantt chart and a risk register (in the appendix if word count is a problem). With these two tools, you can show that you’ve got a clear, feasible plan, and you’ve thought about and accounted for the potential risks.
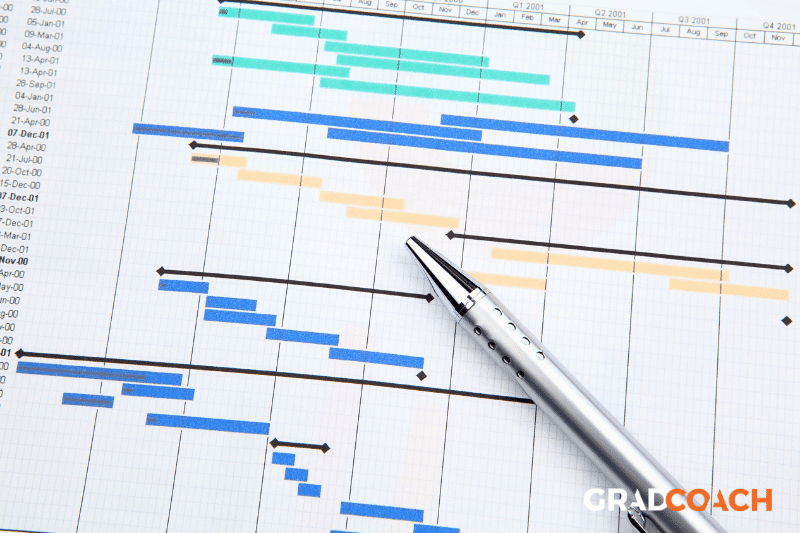
Tip – Be honest about the potential difficulties – but show that you are anticipating solutions and workarounds. This is much more impressive to an assessor than an unrealistically optimistic proposal which does not anticipate any challenges whatsoever.
Final Touches: Read And Simplify
The final step is to edit and proofread your proposal – very carefully. It sounds obvious, but all too often poor editing and proofreading ruin a good proposal. Nothing is more off-putting for an assessor than a poorly edited, typo-strewn document. It sends the message that you either do not pay attention to detail, or just don’t care. Neither of these are good messages. Put the effort into editing and proofreading your proposal (or pay someone to do it for you) – it will pay dividends.
When you’re editing, watch out for ‘academese’. Many students can speak simply, passionately and clearly about their dissertation topic – but become incomprehensible the moment they turn the laptop on. You are not required to write in any kind of special, formal, complex language when you write academic work. Sure, there may be technical terms, jargon specific to your discipline, shorthand terms and so on. But, apart from those, keep your written language very close to natural spoken language – just as you would speak in the classroom. Imagine that you are explaining your project plans to your classmates or a family member. Remember, write for the intelligent layman, not the subject matter experts. Plain-language, concise writing is what wins hearts and minds – and marks!
Let’s Recap: Research Proposal 101
And there you have it – how to write your dissertation or thesis research proposal, from the title page to the final proof. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- The purpose of the research proposal is to convince – therefore, you need to make a clear, concise argument of why your research is both worth doing and doable.
- Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper.
- Title – provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms
- Introduction – explains what you’ll be researching in more detail
- Scope – explains the boundaries of your research
- Literature review – explains how your research fits into the existing research and why it’s unique and valuable
- Research methodology – explains and justifies how you will carry out your own research
Hopefully, this post has helped you better understand how to write up a winning research proposal. If you enjoyed it, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . If your university doesn’t provide any template for your proposal, you might want to try out our free research proposal template .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:


30 Comments
Thank you so much for the valuable insight that you have given, especially on the research proposal. That is what I have managed to cover. I still need to go back to the other parts as I got disturbed while still listening to Derek’s audio on you-tube. I am inspired. I will definitely continue with Grad-coach guidance on You-tube.
Thanks for the kind words :). All the best with your proposal.
First of all, thanks a lot for making such a wonderful presentation. The video was really useful and gave me a very clear insight of how a research proposal has to be written. I shall try implementing these ideas in my RP.
Once again, I thank you for this content.
I found reading your outline on writing research proposal very beneficial. I wish there was a way of submitting my draft proposal to you guys for critiquing before I submit to the institution.
Hi Bonginkosi
Thank you for the kind words. Yes, we do provide a review service. The best starting point is to have a chat with one of our coaches here: https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Hello team GRADCOACH, may God bless you so much. I was totally green in research. Am so happy for your free superb tutorials and resources. Once again thank you so much Derek and his team.
You’re welcome, Erick. Good luck with your research proposal 🙂
thank you for the information. its precise and on point.
Really a remarkable piece of writing and great source of guidance for the researchers. GOD BLESS YOU for your guidance. Regards
Thanks so much for your guidance. It is easy and comprehensive the way you explain the steps for a winning research proposal.
Thank you guys so much for the rich post. I enjoyed and learn from every word in it. My problem now is how to get into your platform wherein I can always seek help on things related to my research work ? Secondly, I wish to find out if there is a way I can send my tentative proposal to you guys for examination before I take to my supervisor Once again thanks very much for the insights
Thanks for your kind words, Desire.
If you are based in a country where Grad Coach’s paid services are available, you can book a consultation by clicking the “Book” button in the top right.
Best of luck with your studies.
May God bless you team for the wonderful work you are doing,
If I have a topic, Can I submit it to you so that you can draft a proposal for me?? As I am expecting to go for masters degree in the near future.
Thanks for your comment. We definitely cannot draft a proposal for you, as that would constitute academic misconduct. The proposal needs to be your own work. We can coach you through the process, but it needs to be your own work and your own writing.
Best of luck with your research!
I found a lot of many essential concepts from your material. it is real a road map to write a research proposal. so thanks a lot. If there is any update material on your hand on MBA please forward to me.
GradCoach is a professional website that presents support and helps for MBA student like me through the useful online information on the page and with my 1-on-1 online coaching with the amazing and professional PhD Kerryen.
Thank you Kerryen so much for the support and help 🙂
I really recommend dealing with such a reliable services provider like Gradcoah and a coach like Kerryen.
Hi, Am happy for your service and effort to help students and researchers, Please, i have been given an assignment on research for strategic development, the task one is to formulate a research proposal to support the strategic development of a business area, my issue here is how to go about it, especially the topic or title and introduction. Please, i would like to know if you could help me and how much is the charge.
This content is practical, valuable, and just great!
Thank you very much!
Hi Derek, Thank you for the valuable presentation. It is very helpful especially for beginners like me. I am just starting my PhD.
This is quite instructive and research proposal made simple. Can I have a research proposal template?
Great! Thanks for rescuing me, because I had no former knowledge in this topic. But with this piece of information, I am now secured. Thank you once more.
I enjoyed listening to your video on how to write a proposal. I think I will be able to write a winning proposal with your advice. I wish you were to be my supervisor.
Dear Derek Jansen,
Thank you for your great content. I couldn’t learn these topics in MBA, but now I learned from GradCoach. Really appreciate your efforts….
From Afghanistan!
I have got very essential inputs for startup of my dissertation proposal. Well organized properly communicated with video presentation. Thank you for the presentation.
Wow, this is absolutely amazing guys. Thank you so much for the fruitful presentation, you’ve made my research much easier.
this helps me a lot. thank you all so much for impacting in us. may god richly bless you all
How I wish I’d learn about Grad Coach earlier. I’ve been stumbling around writing and rewriting! Now I have concise clear directions on how to put this thing together. Thank you!
Fantastic!! Thank You for this very concise yet comprehensive guidance.
Even if I am poor in English I would like to thank you very much.
Thank you very much, this is very insightful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write Research Objectives

3-minute read
- 22nd November 2021
Writing a research paper, thesis, or dissertation ? If so, you’ll want to state your research objectives in the introduction of your paper to make it clear to your readers what you’re trying to accomplish. But how do you write effective research objectives? In this post, we’ll look at two key topics to help you do this:
- How to use your research aims as a basis for developing objectives.
- How to use SMART criteria to refine your research objectives.
For more advice on how to write strong research objectives, see below.
Research Aims and Objectives
There is an important difference between research aims and research objectives:
- A research aim defines the main purpose of your research. As such, you can think of your research aim as answering the question “What are you doing?”
- Research objectives (as most studies will have more than one) are the steps you will take to fulfil your aims. As such, your objectives should answer the question “How are you conducting your research?”
For instance, an example research aim could be:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia.
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
- Replicat ing a small Singaporean study into the role of dehydration in UTIs in hospital patients (Sepe, 2018) in a larger Australian cohort.
- Trialing the use of intravenous fluids for intensive care patients to prevent dehydration.
- Assessing the relationship between the age of patients and quantities of intravenous fluids needed to counter dehydration.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Note that the objectives don’t go into any great detail here. The key is to briefly summarize each component of your study. You can save details for how you will conduct the research for the methodology section of your paper.
Make Your Research Objectives SMART
A great way to refine your research objectives is to use SMART criteria . Borrowed from the world of project management, there are many versions of this system. However, we’re going to focus on developing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and timebound objectives.
In other words, a good research objective should be all of the following:
- S pecific – Is the objective clear and well-defined?
- M easurable – How will you know when the objective has been achieved? Is there a way to measure the thing you’re seeking to do?
- A chievable – Do you have the support and resources necessary to undertake this action? Are you being overly ambitious with this objective?
- R elevant – Is this objective vital for fulfilling your research aim?
- T imebound – Can this action be realistically undertaken in the time you have?
If you follow this system, your research objectives will be much stronger.
Expert Research Proofreading
Whatever your research aims and objectives, make sure to have your academic writing proofread by the experts!
Our academic editors can help you with research papers and proposals , as well as any other scholarly document you need checking. And this will help to ensure that your academic writing is always clear, concise, and precise.
Submit a free sample document today to trial our services and find out more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
- Research Papers
How to Write Objectives in a Research Proposal
Last Updated: April 30, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Felipe Corredor . Felipe is a Senior College Admissions Consultant at American College Counselors with over seven years of experience. He specializes in helping clients from all around the world gain admission into America's top universities through private, one-on-one consulting. He helps guide clients through the entire college admissions process and perfect every aspect of their college applications. Felipe earned a Bachelor's Degree from the University of Chicago and recently received his MBA. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 126,394 times.
A research proposal is a detailed outline for a significant research project. They’re common for class assignments, capstone papers, grant applications, and even job applications in some fields, so it's possible you'll have to prepare one at some point. The objectives are a very important part of a research proposal because they outline where the project is headed and what it will accomplish. Developing objectives can be a little tricky, so take some time to consider them. Then work on wording them carefully so your readers understand your goals. With clear objectives, your research proposal will be much stronger.
Brainstorming Your Objectives

- For example, your research question might be “What is the effect of prolonged TV-watching on children?” You can then use that question to build your study around.
- Narrow down your research topic if it’s too broad. A broad research topic makes breaking the objectives down much more difficult. A research question like “How can we save the environment?” is a huge question. Something like “What safety measures would prevent ocean pollution?” is more specific and attainable. [2] X Research source

- Remember that in most cases, you shouldn’t state that your study will prove or disprove something exactly since you haven’t done the work yet. Don’t say “This study proves that honey is not an effective treatment for acne.” Instead, make it something like “This study will demonstrate whether or not honey is an effective treatment for acne.”

- If your research question was “What is the effect of prolonged TV-watching on children?” then there are a few categories you could look at. Objectives wrapped up within that question might be: 1) the incidence of eyestrain among children who watch a lot of TV, 2) their muscular development, 3) their level of socialization with other children. Design your objectives around answering these questions.

- You could always state in your research proposal that you plan to design future experiments or studies to answer additional questions. Most experiments leave unanswered questions and subsequent studies try to tackle them.

- A general objective might be "Establish the effect of diet on mental health." Some specific goals in that project could be 1) Determine if processed foods make depression worse, 2) Identify foods that improve mood, 3) Measure if portion sizes have an impact on mood.
- Not all research proposals want you to divide between general and specific goals. Remember to follow the instructions for the proposal you're writing.

- The best goals align with each letter in the SMART acronym. The weaker ones are missing some letters. For example, you might come up with a topic that’s specific, measurable, and time-bound, but not realistic or attainable. This is a weak objective because you probably can’t achieve it.
- Think about the resources at your disposal. Some objectives might be doable with the right equipment, but if you don’t have that equipment, then you can’t achieve that goal. For example, you might want to map DNA structures, but you can’t view DNA without an electron microscope.
- Ask the same question for your entire project. Is it attainable overall? You don’t want to try to achieve too much and overwhelm yourself.
- The specific words in this acronym sometimes change, but the sentiment is the same. Your objectives should overall be clear and specific, measurable, feasible, and limited by time.
Using the Right Language

- Verbs like use, understand, or study is vague and weak. Instead, choose words like calculate, compare, and assess.
- Your objective list might read like this: 1) Compare the muscle development of children who play video games to children who don’t, 2) Assess whether or not video games cause eyestrain, 3) Determine if videogames inhibit a child’s socialization skills.
- Some proposals use the infinitive form of verbs, like “to measure” or “to determine.” This is also fine but refer to the proposal instructions to see if this is correct.

- You can further explain your objectives further in the research proposal. No need to elaborate a lot when you’re just listing them.
- If you’re having trouble shortening an objective to 1 sentence, then you probably need to split it into 2 objectives. It might also be too complicated for this project.

- For example, “Determine if sunlight is harmful” is too vague. Instead, state the objective as “Determine if prolonged sun exposure increases subjects’ risk of skin cancer.”
- It’s helpful to let someone else read your proposal and see if they understand the objectives. If they’re confused, then you need to be more specific.

- For example, don’t say “Measure the effect of radiation on living tissue.” Instead, say “Determine what level of radiation is dangerous to living tissue.”
- Remember, don’t state the objectives as you’ve already done the experiments. They’re still not answered.
Writing the Objectives

- This is a common format for research proposals, but not universal. Always follow the format that the instructions provided.
- Depending on how long your introduction has to be, you might also list the objectives there. This depends on whether or not you have room.

- At the very least, the abstract should list the general objective. This tells the readers what your study is working towards.

- In some research projects, the general objective is called a long-term goal instead. Adjust your language to the proposal requirements.
- Some proposals directions may just want the specific objectives rather than a division between the general and specific ones. Don’t divide them if the instructions tell you not to.

- Your introduction may be as follows: "My long-term objective with this project is determining whether or not prolonged video-game playing is harmful to children under 5. I will accomplish this aim by meeting the following objectives: 1) Compare the muscle development of children who play videogames to children who don’t 2) Assess whether or not videogames cause eyestrain 3) Determine if videogames inhibit a child’s socialization skills"
- The specific objectives are usually listed as a bullet or numbered points. However, follow the instructions given.
Research Proposal Templates

Expert Q&A
- It’s always a good idea to let someone else read your research proposals and make sure they’re clear. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Proofread! A great proposal could be ruined by typos and errors. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Some proposal instructions are very specific, and applicants that don’t follow the format are eliminated. Always follow the instructions given to stay within the requirements. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://uk.sagepub.com/sites/default/files/upm-assets/15490_book_item_15490.pdf
- ↑ https://research-methodology.net/research-methodology/research-aims-and-objectives/
- ↑ https://www.uh.edu/~lsong5/documents/A%20sample%20proposal%20with%20comment.pdf
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3282423/
- ↑ https://www.cdc.gov/healthyyouth/evaluation/pdf/brief3b.pdf
- ↑ https://www.open.edu/openlearncreate/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=231§ion=8.6.2
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6398294/
- ↑ https://arxiv.org/pdf/physics/0601009.pdf
- ↑ https://www.bpcc.edu/institutional-advancement-grants/how-to-write-goals-and-objectives-for-grant-proposals
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Aug 9, 2022
Did this article help you?
Mar 20, 2023
Relyn Jungco
May 15, 2022

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Table of contents.

Definition:
Thesis is a scholarly document that presents a student’s original research and findings on a particular topic or question. It is usually written as a requirement for a graduate degree program and is intended to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research.
History of Thesis
The concept of a thesis can be traced back to ancient Greece, where it was used as a way for students to demonstrate their knowledge of a particular subject. However, the modern form of the thesis as a scholarly document used to earn a degree is a relatively recent development.
The origin of the modern thesis can be traced back to medieval universities in Europe. During this time, students were required to present a “disputation” in which they would defend a particular thesis in front of their peers and faculty members. These disputations served as a way to demonstrate the student’s mastery of the subject matter and were often the final requirement for earning a degree.
In the 17th century, the concept of the thesis was formalized further with the creation of the modern research university. Students were now required to complete a research project and present their findings in a written document, which would serve as the basis for their degree.
The modern thesis as we know it today has evolved over time, with different disciplines and institutions adopting their own standards and formats. However, the basic elements of a thesis – original research, a clear research question, a thorough review of the literature, and a well-argued conclusion – remain the same.
Structure of Thesis
The structure of a thesis may vary slightly depending on the specific requirements of the institution, department, or field of study, but generally, it follows a specific format.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure of a thesis:
This is the first page of the thesis that includes the title of the thesis, the name of the author, the name of the institution, the department, the date, and any other relevant information required by the institution.
This is a brief summary of the thesis that provides an overview of the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
This page provides a list of all the chapters and sections in the thesis and their page numbers.
Introduction
This chapter provides an overview of the research question, the context of the research, and the purpose of the study. The introduction should also outline the methodology and the scope of the research.
Literature Review
This chapter provides a critical analysis of the relevant literature on the research topic. It should demonstrate the gap in the existing knowledge and justify the need for the research.
Methodology
This chapter provides a detailed description of the research methods used to gather and analyze data. It should explain the research design, the sampling method, data collection techniques, and data analysis procedures.
This chapter presents the findings of the research. It should include tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate the results.
This chapter interprets the results and relates them to the research question. It should explain the significance of the findings and their implications for the research topic.
This chapter summarizes the key findings and the main conclusions of the research. It should also provide recommendations for future research.
This section provides a list of all the sources cited in the thesis. The citation style may vary depending on the requirements of the institution or the field of study.
This section includes any additional material that supports the research, such as raw data, survey questionnaires, or other relevant documents.
How to write Thesis
Here are some steps to help you write a thesis:
- Choose a Topic: The first step in writing a thesis is to choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. You should also consider the scope of the topic and the availability of resources for research.
- Develop a Research Question: Once you have chosen a topic, you need to develop a research question that you will answer in your thesis. The research question should be specific, clear, and feasible.
- Conduct a Literature Review: Before you start your research, you need to conduct a literature review to identify the existing knowledge and gaps in the field. This will help you refine your research question and develop a research methodology.
- Develop a Research Methodology: Once you have refined your research question, you need to develop a research methodology that includes the research design, data collection methods, and data analysis procedures.
- Collect and Analyze Data: After developing your research methodology, you need to collect and analyze data. This may involve conducting surveys, interviews, experiments, or analyzing existing data.
- Write the Thesis: Once you have analyzed the data, you need to write the thesis. The thesis should follow a specific structure that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, and references.
- Edit and Proofread: After completing the thesis, you need to edit and proofread it carefully. You should also have someone else review it to ensure that it is clear, concise, and free of errors.
- Submit the Thesis: Finally, you need to submit the thesis to your academic advisor or committee for review and evaluation.
Example of Thesis
Example of Thesis template for Students:
Title of Thesis
Table of Contents:
Chapter 1: Introduction
Chapter 2: Literature Review
Chapter 3: Research Methodology
Chapter 4: Results
Chapter 5: Discussion
Chapter 6: Conclusion
References:
Appendices:
Note: That’s just a basic template, but it should give you an idea of the structure and content that a typical thesis might include. Be sure to consult with your department or supervisor for any specific formatting requirements they may have. Good luck with your thesis!
Application of Thesis
Thesis is an important academic document that serves several purposes. Here are some of the applications of thesis:
- Academic Requirement: A thesis is a requirement for many academic programs, especially at the graduate level. It is an essential component of the evaluation process and demonstrates the student’s ability to conduct original research and contribute to the knowledge in their field.
- Career Advancement: A thesis can also help in career advancement. Employers often value candidates who have completed a thesis as it demonstrates their research skills, critical thinking abilities, and their dedication to their field of study.
- Publication : A thesis can serve as a basis for future publications in academic journals, books, or conference proceedings. It provides the researcher with an opportunity to present their research to a wider audience and contribute to the body of knowledge in their field.
- Personal Development: Writing a thesis is a challenging task that requires time, dedication, and perseverance. It provides the student with an opportunity to develop critical thinking, research, and writing skills that are essential for their personal and professional development.
- Impact on Society: The findings of a thesis can have an impact on society by addressing important issues, providing insights into complex problems, and contributing to the development of policies and practices.
Purpose of Thesis
The purpose of a thesis is to present original research findings in a clear and organized manner. It is a formal document that demonstrates a student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. The primary purposes of a thesis are:
- To Contribute to Knowledge: The main purpose of a thesis is to contribute to the knowledge in a particular field of study. By conducting original research and presenting their findings, the student adds new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- To Demonstrate Research Skills: A thesis is an opportunity for the student to demonstrate their research skills. This includes the ability to formulate a research question, design a research methodology, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- To Develop Critical Thinking: Writing a thesis requires critical thinking and analysis. The student must evaluate existing literature and identify gaps in the field, as well as develop and defend their own ideas.
- To Provide Evidence of Competence : A thesis provides evidence of the student’s competence in their field of study. It demonstrates their ability to apply theoretical concepts to real-world problems, and their ability to communicate their ideas effectively.
- To Facilitate Career Advancement : Completing a thesis can help the student advance their career by demonstrating their research skills and dedication to their field of study. It can also provide a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
When to Write Thesis
The timing for writing a thesis depends on the specific requirements of the academic program or institution. In most cases, the opportunity to write a thesis is typically offered at the graduate level, but there may be exceptions.
Generally, students should plan to write their thesis during the final year of their graduate program. This allows sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis. It is important to start planning the thesis early and to identify a research topic and research advisor as soon as possible.
In some cases, students may be able to write a thesis as part of an undergraduate program or as an independent research project outside of an academic program. In such cases, it is important to consult with faculty advisors or mentors to ensure that the research is appropriately designed and executed.
It is important to note that the process of writing a thesis can be time-consuming and requires a significant amount of effort and dedication. It is important to plan accordingly and to allocate sufficient time for conducting research, analyzing data, and writing the thesis.
Characteristics of Thesis
The characteristics of a thesis vary depending on the specific academic program or institution. However, some general characteristics of a thesis include:
- Originality : A thesis should present original research findings or insights. It should demonstrate the student’s ability to conduct independent research and contribute to the knowledge in their field of study.
- Clarity : A thesis should be clear and concise. It should present the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions in a logical and organized manner. It should also be well-written, with proper grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
- Research-Based: A thesis should be based on rigorous research, which involves collecting and analyzing data from various sources. The research should be well-designed, with appropriate research methods and techniques.
- Evidence-Based : A thesis should be based on evidence, which means that all claims made in the thesis should be supported by data or literature. The evidence should be properly cited using appropriate citation styles.
- Critical Thinking: A thesis should demonstrate the student’s ability to critically analyze and evaluate information. It should present the student’s own ideas and arguments, and engage with existing literature in the field.
- Academic Style : A thesis should adhere to the conventions of academic writing. It should be well-structured, with clear headings and subheadings, and should use appropriate academic language.
Advantages of Thesis
There are several advantages to writing a thesis, including:
- Development of Research Skills: Writing a thesis requires extensive research and analytical skills. It helps to develop the student’s research skills, including the ability to formulate research questions, design and execute research methodologies, collect and analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Contribution to Knowledge: Writing a thesis provides an opportunity for the student to contribute to the knowledge in their field of study. By conducting original research, they can add new insights and perspectives to the existing body of knowledge.
- Preparation for Future Research: Completing a thesis prepares the student for future research projects. It provides them with the necessary skills to design and execute research methodologies, analyze data, and draw conclusions based on their findings.
- Career Advancement: Writing a thesis can help to advance the student’s career. It demonstrates their research skills and dedication to their field of study, and provides a basis for future publications, presentations, or research projects.
- Personal Growth: Completing a thesis can be a challenging and rewarding experience. It requires dedication, hard work, and perseverance. It can help the student to develop self-confidence, independence, and a sense of accomplishment.
Limitations of Thesis
There are also some limitations to writing a thesis, including:
- Time and Resources: Writing a thesis requires a significant amount of time and resources. It can be a time-consuming and expensive process, as it may involve conducting original research, analyzing data, and producing a lengthy document.
- Narrow Focus: A thesis is typically focused on a specific research question or topic, which may limit the student’s exposure to other areas within their field of study.
- Limited Audience: A thesis is usually only read by a small number of people, such as the student’s thesis advisor and committee members. This limits the potential impact of the research findings.
- Lack of Real-World Application : Some thesis topics may be highly theoretical or academic in nature, which may limit their practical application in the real world.
- Pressure and Stress : Writing a thesis can be a stressful and pressure-filled experience, as it may involve meeting strict deadlines, conducting original research, and producing a high-quality document.
- Potential for Isolation: Writing a thesis can be a solitary experience, as the student may spend a significant amount of time working independently on their research and writing.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .

25 Thesis Statement Examples
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
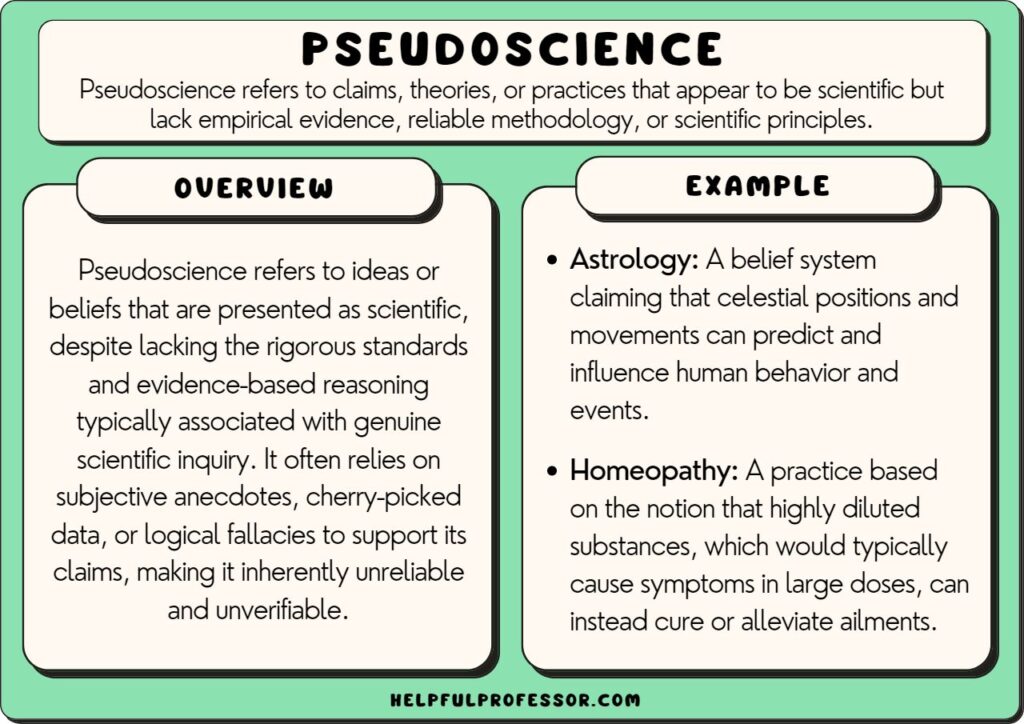
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
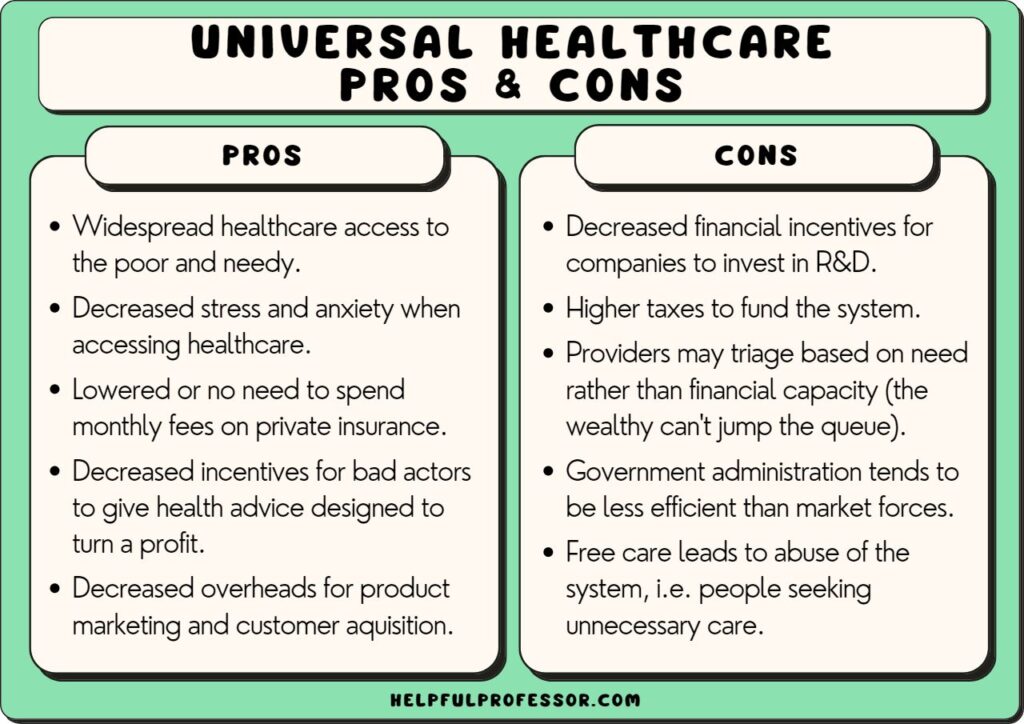
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is IQ? (Intelligence Quotient)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
General objectives are the main goals of the study and are usually fewer in number while specific objectives are more in number because they address several aspects of the research problem. Example (general objective): To investigate the factors influencing the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
Examples of Specific Research Objectives: 1. "To examine the effects of rising temperatures on the yield of rice crops during the upcoming growth season.". 2. "To assess changes in rainfall patterns in major agricultural regions over the first decade of the twenty-first century (2000-2010).". 3.
The general and specific objectives are fundamental elements for the accomplishment of academic works, like for example, a thesis of degree. The general objective is a statement that summarizes the central idea and purpose of a work. The specific objectives detail the processes necessary for the complete accomplishment of the work. Summarize ...
1. identification of the behaviors that are considered as bullying. 2. exploring the factors that cause bullying at a culturally diverse workplace. 3. analyzing the relationship between bullying and job satisfaction of employees. 4. providing suitable recommendations on minimizing the bullying at the workplace.
Summary. One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and ...
Research objectives describe what your research project intends to accomplish. They should guide every step of the research process, including how you collect data, build your argument, and develop your conclusions. Your research objectives may evolve slightly as your research progresses, but they should always line up with the research carried ...
The research aims, objectives and research questions (collectively called the "golden thread") are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you're crafting a research proposal, dissertation or thesis.We receive questions almost every day about this "holy trinity" of research and there's certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we've crafted this post to help ...
Research Objectives. Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research.The objectives are typically based on the research questions and hypotheses formulated at the beginning of the study and are used to guide the research process.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough. Note.
Get your 100% customized paper done in as little as 1 hour. Let's start. Show example. Here's how to start using our objective generator for research: Choose an action verb from the drop-down list. Enter your aim. Move the toggle if needed. Click "Generate now" and enjoy a properly formulated objective.
Lesson 3: Research objectives. While your problem formulation serves to describe the aim of your thesis, the objectives provide an accurate description of the specific actions you will take in order to reach this aim. As with the problem formulation, the overall objective should be framed in a single sentence.
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example: This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
Divide your objectives into 1 general and 3-4 specific ones. In many research proposals, the proper format is a general or long-term objective followed by a few specific ones. The general objective is essentially what you hope to achieve with the project. The specific objectives are the building blocks of that general goal.
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic. A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire ...
Example of Thesis template for Students: Title of Thesis. A Thesis Presented to the Faculty of [Name of University] ... and outlining the scope and objectives of your research. It should also include a brief overview of the structure of your thesis, indicating what will be covered in each chapter.] ... some general characteristics of a thesis ...
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is ...
A good thesis statement needs to do the following: Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences. Answer your project's main research question. Clearly state your position in relation to the topic. Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
Step 2: Summarize and reflect on your research. Step 3: Make future recommendations. Step 4: Emphasize your contributions to your field. Step 5: Wrap up your thesis or dissertation. Full conclusion example. Conclusion checklist. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about conclusion sections.
Example 1: Passive construction. The passive voice is a common choice for outlines and overviews because the context makes it clear who is carrying out the action (e.g., you are conducting the research ). However, overuse of the passive voice can make your text vague and imprecise. Example: Passive construction.