- Cookies & Privacy
- GETTING STARTED
- Introduction
- FUNDAMENTALS
Getting to the main article
Choosing your route
Setting research questions/ hypotheses
Assessment point
Building the theoretical case
Setting your research strategy
Data collection
Data analysis

Data analysis techniques
In STAGE NINE: Data analysis , we discuss the data you will have collected during STAGE EIGHT: Data collection . However, before you collect your data, having followed the research strategy you set out in this STAGE SIX , it is useful to think about the data analysis techniques you may apply to your data when it is collected.
The statistical tests that are appropriate for your dissertation will depend on (a) the research questions/hypotheses you have set, (b) the research design you are using, and (c) the nature of your data. You should already been clear about your research questions/hypotheses from STAGE THREE: Setting research questions and/or hypotheses , as well as knowing the goal of your research design from STEP TWO: Research design in this STAGE SIX: Setting your research strategy . These two pieces of information - your research questions/hypotheses and research design - will let you know, in principle , the statistical tests that may be appropriate to run on your data in order to answer your research questions.
We highlight the words in principle and may because the most appropriate statistical test to run on your data not only depend on your research questions/hypotheses and research design, but also the nature of your data . As you should have identified in STEP THREE: Research methods , and in the article, Types of variables , in the Fundamentals part of Lærd Dissertation, (a) not all data is the same, and (b) not all variables are measured in the same way (i.e., variables can be dichotomous, ordinal or continuous). In addition, not all data is normal , nor is the data when comparing groups necessarily equal , terms we explain in the Data Analysis section in the Fundamentals part of Lærd Dissertation. As a result, you might think that running a particular statistical test is correct at this point of setting your research strategy (e.g., a statistical test called a dependent t-test ), based on the research questions/hypotheses you have set, but when you collect your data (i.e., during STAGE EIGHT: Data collection ), the data may fail certain assumptions that are important to such a statistical test (i.e., normality and homogeneity of variance ). As a result, you have to run another statistical test (e.g., a Wilcoxon signed-rank test instead of a dependent t-test ).
At this stage in the dissertation process, it is important, or at the very least, useful to think about the data analysis techniques you may apply to your data when it is collected. We suggest that you do this for two reasons:
REASON A Supervisors sometimes expect you to know what statistical analysis you will perform at this stage of the dissertation process
This is not always the case, but if you have had to write a Dissertation Proposal or Ethics Proposal , there is sometimes an expectation that you explain the type of data analysis that you plan to carry out. An understanding of the data analysis that you will carry out on your data can also be an expected component of the Research Strategy chapter of your dissertation write-up (i.e., usually Chapter Three: Research Strategy ). Therefore, it is a good time to think about the data analysis process if you plan to start writing up this chapter at this stage.
REASON B It takes time to get your head around data analysis
When you come to analyse your data in STAGE NINE: Data analysis , you will need to think about (a) selecting the correct statistical tests to perform on your data, (b) running these tests on your data using a statistics package such as SPSS, and (c) learning how to interpret the output from such statistical tests so that you can answer your research questions or hypotheses. Whilst we show you how to do this for a wide range of scenarios in the in the Data Analysis section in the Fundamentals part of Lærd Dissertation, it can be a time consuming process. Unless you took an advanced statistics module/option as part of your degree (i.e., not just an introductory course to statistics, which are often taught in undergraduate and master?s degrees), it can take time to get your head around data analysis. Starting this process at this stage (i.e., STAGE SIX: Research strategy ), rather than waiting until you finish collecting your data (i.e., STAGE EIGHT: Data collection ) is a sensible approach.
Final thoughts...
Setting the research strategy for your dissertation required you to describe, explain and justify the research paradigm, quantitative research design, research method(s), sampling strategy, and approach towards research ethics and data analysis that you plan to follow, as well as determine how you will ensure the research quality of your findings so that you can effectively answer your research questions/hypotheses. However, from a practical perspective, just remember that the main goal of STAGE SIX: Research strategy is to have a clear research strategy that you can implement (i.e., operationalize ). After all, if you are unable to clearly follow your plan and carry out your research in the field, you will struggle to answer your research questions/hypotheses. Once you are sure that you have a clear plan, it is a good idea to take a step back, speak with your supervisor, and assess where you are before moving on to collect data. Therefore, when you are ready, proceed to STAGE SEVEN: Assessment point .
- How it works
How to Write the Dissertation Findings or Results – Steps & Tips
Published by Grace Graffin at August 11th, 2021 , Revised On October 9, 2023
Each part of the dissertation is unique, and some general and specific rules must be followed. The dissertation’s findings section presents the key results of your research without interpreting their meaning .
Theoretically, this is an exciting section of a dissertation because it involves writing what you have observed and found. However, it can be a little tricky if there is too much information to confuse the readers.
The goal is to include only the essential and relevant findings in this section. The results must be presented in an orderly sequence to provide clarity to the readers.
This section of the dissertation should be easy for the readers to follow, so you should avoid going into a lengthy debate over the interpretation of the results.
It is vitally important to focus only on clear and precise observations. The findings chapter of the dissertation is theoretically the easiest to write.
It includes statistical analysis and a brief write-up about whether or not the results emerging from the analysis are significant. This segment should be written in the past sentence as you describe what you have done in the past.
This article will provide detailed information about how to write the findings of a dissertation .
When to Write Dissertation Findings Chapter
As soon as you have gathered and analysed your data, you can start to write up the findings chapter of your dissertation paper. Remember that it is your chance to report the most notable findings of your research work and relate them to the research hypothesis or research questions set out in the introduction chapter of the dissertation .
You will be required to separately report your study’s findings before moving on to the discussion chapter if your dissertation is based on the collection of primary data or experimental work.
However, you may not be required to have an independent findings chapter if your dissertation is purely descriptive and focuses on the analysis of case studies or interpretation of texts.
- Always report the findings of your research in the past tense.
- The dissertation findings chapter varies from one project to another, depending on the data collected and analyzed.
- Avoid reporting results that are not relevant to your research questions or research hypothesis.
Does your Dissertation Have the Following?
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of the Dissertation strong.

1. Reporting Quantitative Findings
The best way to present your quantitative findings is to structure them around the research hypothesis or questions you intend to address as part of your dissertation project.
Report the relevant findings for each research question or hypothesis, focusing on how you analyzed them.
Analysis of your findings will help you determine how they relate to the different research questions and whether they support the hypothesis you formulated.
While you must highlight meaningful relationships, variances, and tendencies, it is important not to guess their interpretations and implications because this is something to save for the discussion and conclusion chapters.
Any findings not directly relevant to your research questions or explanations concerning the data collection process should be added to the dissertation paper’s appendix section.
Use of Figures and Tables in Dissertation Findings
Suppose your dissertation is based on quantitative research. In that case, it is important to include charts, graphs, tables, and other visual elements to help your readers understand the emerging trends and relationships in your findings.
Repeating information will give the impression that you are short on ideas. Refer to all charts, illustrations, and tables in your writing but avoid recurrence.
The text should be used only to elaborate and summarize certain parts of your results. On the other hand, illustrations and tables are used to present multifaceted data.
It is recommended to give descriptive labels and captions to all illustrations used so the readers can figure out what each refers to.
How to Report Quantitative Findings
Here is an example of how to report quantitative results in your dissertation findings chapter;
Two hundred seventeen participants completed both the pretest and post-test and a Pairwise T-test was used for the analysis. The quantitative data analysis reveals a statistically significant difference between the mean scores of the pretest and posttest scales from the Teachers Discovering Computers course. The pretest mean was 29.00 with a standard deviation of 7.65, while the posttest mean was 26.50 with a standard deviation of 9.74 (Table 1). These results yield a significance level of .000, indicating a strong treatment effect (see Table 3). With the correlation between the scores being .448, the little relationship is seen between the pretest and posttest scores (Table 2). This leads the researcher to conclude that the impact of the course on the educators’ perception and integration of technology into the curriculum is dramatic.
Paired Samples
Paired samples correlation, paired samples test.
Also Read: How to Write the Abstract for the Dissertation.
2. Reporting Qualitative Findings
A notable issue with reporting qualitative findings is that not all results directly relate to your research questions or hypothesis.
The best way to present the results of qualitative research is to frame your findings around the most critical areas or themes you obtained after you examined the data.
In-depth data analysis will help you observe what the data shows for each theme. Any developments, relationships, patterns, and independent responses directly relevant to your research question or hypothesis should be mentioned to the readers.
Additional information not directly relevant to your research can be included in the appendix .
How to Report Qualitative Findings
Here is an example of how to report qualitative results in your dissertation findings chapter;
How do I report quantitative findings?
The best way to present your quantitative findings is to structure them around the research hypothesis or research questions you intended to address as part of your dissertation project. Report the relevant findings for each of the research questions or hypotheses, focusing on how you analyzed them.
How do I report qualitative findings?
The best way to present the qualitative research results is to frame your findings around the most important areas or themes that you obtained after examining the data.
An in-depth analysis of the data will help you observe what the data is showing for each theme. Any developments, relationships, patterns, and independent responses that are directly relevant to your research question or hypothesis should be clearly mentioned for the readers.
Can I use interpretive phrases like ‘it confirms’ in the finding chapter?
No, It is highly advisable to avoid using interpretive and subjective phrases in the finding chapter. These terms are more suitable for the discussion chapter , where you will be expected to provide your interpretation of the results in detail.
Can I report the results from other research papers in my findings chapter?
NO, you must not be presenting results from other research studies in your findings.
You May Also Like
Dissertation discussion is where you explore the relevance and significance of results. Here are guidelines to help you write the perfect discussion chapter.
Dissertation Methodology is the crux of dissertation project. In this article, we will provide tips for you to write an amazing dissertation methodology.
Writing a dissertation can be tough if this is the first time you are doing it. You need to look into relevant literature, analyze past researches, conduct surveys, interviews etc.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- +44 7897 053596
- [email protected]

Get an experienced writer start working
Review our examples before placing an order, learn how to draft academic papers, a step-by-step guide to dissertation data analysis.

How to Write a Dissertation Conclusion? | Tips & Examples

What is PhD Thesis Writing? | Beginner’s Guide

A data analysis dissertation is a complex and challenging project requiring significant time, effort, and expertise. Fortunately, it is possible to successfully complete a data analysis dissertation with careful planning and execution.
As a student, you must know how important it is to have a strong and well-written dissertation, especially regarding data analysis. Proper data analysis is crucial to the success of your research and can often make or break your dissertation.
To get a better understanding, you may review the data analysis dissertation examples listed below;
- Impact of Leadership Style on the Job Satisfaction of Nurses
- Effect of Brand Love on Consumer Buying Behaviour in Dietary Supplement Sector
- An Insight Into Alternative Dispute Resolution
- An Investigation of Cyberbullying and its Impact on Adolescent Mental Health in UK
3-Step Dissertation Process!

Get 3+ Topics

Dissertation Proposal

Get Final Dissertation
Types of data analysis for dissertation.
The various types of data Analysis in a Dissertation are as follows;
1. Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis is a type of data analysis that involves analyzing data that cannot be measured numerically. This data type includes interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys. Qualitative data analysis can be used to identify patterns and themes in the data.
2. Quantitative Data Analysis
Quantitative data analysis is a type of data analysis that involves analyzing data that can be measured numerically. This data type includes test scores, income levels, and crime rates. Quantitative data analysis can be used to test hypotheses and to look for relationships between variables.
3. Descriptive Data Analysis
Descriptive data analysis is a type of data analysis that involves describing the characteristics of a dataset. This type of data analysis summarizes the main features of a dataset.
4. Inferential Data Analysis
Inferential data analysis is a type of data analysis that involves making predictions based on a dataset. This type of data analysis can be used to test hypotheses and make predictions about future events.
5. Exploratory Data Analysis
Exploratory data analysis is a type of data analysis that involves exploring a data set to understand it better. This type of data analysis can identify patterns and relationships in the data.
Time Period to Plan and Complete a Data Analysis Dissertation?
When planning dissertation data analysis, it is important to consider the dissertation methodology structure and time series analysis as they will give you an understanding of how long each stage will take. For example, using a qualitative research method, your data analysis will involve coding and categorizing your data.
This can be time-consuming, so allowing enough time in your schedule is important. Once you have coded and categorized your data, you will need to write up your findings. Again, this can take some time, so factor this into your schedule.
Finally, you will need to proofread and edit your dissertation before submitting it. All told, a data analysis dissertation can take anywhere from several weeks to several months to complete, depending on the project’s complexity. Therefore, starting planning early and allowing enough time in your schedule to complete the task is important.
Essential Strategies for Data Analysis Dissertation
A. Planning
The first step in any dissertation is planning. You must decide what you want to write about and how you want to structure your argument. This planning will involve deciding what data you want to analyze and what methods you will use for a data analysis dissertation.
B. Prototyping
Once you have a plan for your dissertation, it’s time to start writing. However, creating a prototype is important before diving head-first into writing your dissertation. A prototype is a rough draft of your argument that allows you to get feedback from your advisor and committee members. This feedback will help you fine-tune your argument before you start writing the final version of your dissertation.
C. Executing
After you have created a plan and prototype for your data analysis dissertation, it’s time to start writing the final version. This process will involve collecting and analyzing data and writing up your results. You will also need to create a conclusion section that ties everything together.
D. Presenting
The final step in acing your data analysis dissertation is presenting it to your committee. This presentation should be well-organized and professionally presented. During the presentation, you’ll also need to be ready to respond to questions concerning your dissertation.
Data Analysis Tools
Numerous suggestive tools are employed to assess the data and deduce pertinent findings for the discussion section. The tools used to analyze data and get a scientific conclusion are as follows:
a. Excel
Excel is a spreadsheet program part of the Microsoft Office productivity software suite. Excel is a powerful tool that can be used for various data analysis tasks, such as creating charts and graphs, performing mathematical calculations, and sorting and filtering data.
b. Google Sheets
Google Sheets is a free online spreadsheet application that is part of the Google Drive suite of productivity software. Google Sheets is similar to Excel in terms of functionality, but it also has some unique features, such as the ability to collaborate with other users in real-time.
c. SPSS
SPSS is a statistical analysis software program commonly used in the social sciences. SPSS can be used for various data analysis tasks, such as hypothesis testing, factor analysis, and regression analysis.
d. STATA
STATA is a statistical analysis software program commonly used in the sciences and economics. STATA can be used for data management, statistical modelling, descriptive statistics analysis, and data visualization tasks.
SAS is a commercial statistical analysis software program used by businesses and organizations worldwide. SAS can be used for predictive modelling, market research, and fraud detection.
R is a free, open-source statistical programming language popular among statisticians and data scientists. R can be used for tasks such as data wrangling, machine learning, and creating complex visualizations.
g. Python
A variety of applications may be used using the distinctive programming language Python, including web development, scientific computing, and artificial intelligence. Python also has a number of modules and libraries that can be used for data analysis tasks, such as numerical computing, statistical modelling, and data visualization.
Testimonials
Very satisfied students
This is our reason for working. We want to make all students happy, every day. Review us on Sitejabber
Tips to Compose a Successful Data Analysis Dissertation
a. Choose a Topic You’re Passionate About
The first step to writing a successful data analysis dissertation is to choose a topic you’re passionate about. Not only will this make the research and writing process more enjoyable, but it will also ensure that you produce a high-quality paper.
Choose a topic that is particular enough to be covered in your paper’s scope but not so specific that it will be challenging to obtain enough evidence to substantiate your arguments.
b. Do Your Research
data analysis in research is an important part of academic writing. Once you’ve selected a topic, it’s time to begin your research. Be sure to consult with your advisor or supervisor frequently during this stage to ensure that you are on the right track. In addition to secondary sources such as books, journal articles, and reports, you should also consider conducting primary research through surveys or interviews. This will give you first-hand insights into your topic that can be invaluable when writing your paper.
c. Develop a Strong Thesis Statement
After you’ve done your research, it’s time to start developing your thesis statement. It is arguably the most crucial part of your entire paper, so take care to craft a clear and concise statement that encapsulates the main argument of your paper.
Remember that your thesis statement should be arguable—that is, it should be capable of being disputed by someone who disagrees with your point of view. If your thesis statement is not arguable, it will be difficult to write a convincing paper.
d. Write a Detailed Outline
Once you have developed a strong thesis statement, the next step is to write a detailed outline of your paper. This will offer you a direction to write in and guarantee that your paper makes sense from beginning to end.
Your outline should include an introduction, in which you state your thesis statement; several body paragraphs, each devoted to a different aspect of your argument; and a conclusion, in which you restate your thesis and summarize the main points of your paper.
e. Write Your First Draft
With your outline in hand, it’s finally time to start writing your first draft. At this stage, don’t worry about perfecting your grammar or making sure every sentence is exactly right—focus on getting all of your ideas down on paper (or onto the screen). Once you have completed your first draft, you can revise it for style and clarity.
And there you have it! Following these simple tips can increase your chances of success when writing your data analysis dissertation. Just remember to start early, give yourself plenty of time to research and revise, and consult with your supervisor frequently throughout the process.
How Does It Work ?

Fill the Form

Writer Starts Working

3+ Topics Emailed!
Studying the above examples gives you valuable insight into the structure and content that should be included in your own data analysis dissertation. You can also learn how to effectively analyze and present your data and make a lasting impact on your readers.
In addition to being a useful resource for completing your dissertation, these examples can also serve as a valuable reference for future academic writing projects. By following these examples and understanding their principles, you can improve your data analysis skills and increase your chances of success in your academic career.
You may also contact Premier Dissertations to develop your data analysis dissertation.
For further assistance, some other resources in the dissertation writing section are shared below;
How Do You Select the Right Data Analysis
How to Write Data Analysis For A Dissertation?
How to Develop a Conceptual Framework in Dissertation?
What is a Hypothesis in a Dissertation?
Get an Immediate Response
Discuss your requirments with our writers
WhatsApp Us Email Us Chat with Us
Get 3+ Free Dissertation Topics within 24 hours?
Your Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Masters PhD
Area of Research
admin farhan
Related posts.

What is Conventions in Writing | Definition, Importance & Examples

Understanding TOK Concepts: A Beginner’s Guide

Research Hypotheses: Directional vs. Non-Directional Hypotheses
Comments are closed.

11 Tips For Writing a Dissertation Data Analysis
Since the evolution of the fourth industrial revolution – the Digital World; lots of data have surrounded us. There are terabytes of data around us or in data centers that need to be processed and used. The data needs to be appropriately analyzed to process it, and Dissertation data analysis forms its basis. If data analysis is valid and free from errors, the research outcomes will be reliable and lead to a successful dissertation.
Considering the complexity of many data analysis projects, it becomes challenging to get precise results if analysts are not familiar with data analysis tools and tests properly. The analysis is a time-taking process that starts with collecting valid and relevant data and ends with the demonstration of error-free results.
So, in today’s topic, we will cover the need to analyze data, dissertation data analysis, and mainly the tips for writing an outstanding data analysis dissertation. If you are a doctoral student and plan to perform dissertation data analysis on your data, make sure that you give this article a thorough read for the best tips!
What is Data Analysis in Dissertation?
Dissertation Data Analysis is the process of understanding, gathering, compiling, and processing a large amount of data. Then identifying common patterns in responses and critically examining facts and figures to find the rationale behind those outcomes.
Even f you have the data collected and compiled in the form of facts and figures, it is not enough for proving your research outcomes. There is still a need to apply dissertation data analysis on your data; to use it in the dissertation. It provides scientific support to the thesis and conclusion of the research.
Data Analysis Tools
There are plenty of indicative tests used to analyze data and infer relevant results for the discussion part. Following are some tests used to perform analysis of data leading to a scientific conclusion:
11 Most Useful Tips for Dissertation Data Analysis
Doctoral students need to perform dissertation data analysis and then dissertation to receive their degree. Many Ph.D. students find it hard to do dissertation data analysis because they are not trained in it.
1. Dissertation Data Analysis Services
The first tip applies to those students who can afford to look for help with their dissertation data analysis work. It’s a viable option, and it can help with time management and with building the other elements of the dissertation with much detail.
Dissertation Analysis services are professional services that help doctoral students with all the basics of their dissertation work, from planning, research and clarification, methodology, dissertation data analysis and review, literature review, and final powerpoint presentation.
One great reference for dissertation data analysis professional services is Statistics Solutions , they’ve been around for over 22 years helping students succeed in their dissertation work. You can find the link to their website here .
For a proper dissertation data analysis, the student should have a clear understanding and statistical knowledge. Through this knowledge and experience, a student can perform dissertation analysis on their own.
Following are some helpful tips for writing a splendid dissertation data analysis:
2. Relevance of Collected Data
If the data is irrelevant and not appropriate, you might get distracted from the point of focus. To show the reader that you can critically solve the problem, make sure that you write a theoretical proposition regarding the selection and analysis of data.
3. Data Analysis
For analysis, it is crucial to use such methods that fit best with the types of data collected and the research objectives. Elaborate on these methods and the ones that justify your data collection methods thoroughly. Make sure to make the reader believe that you did not choose your method randomly. Instead, you arrived at it after critical analysis and prolonged research.
On the other hand, quantitative analysis refers to the analysis and interpretation of facts and figures – to build reasoning behind the advent of primary findings. An assessment of the main results and the literature review plays a pivotal role in qualitative and quantitative analysis.
The overall objective of data analysis is to detect patterns and inclinations in data and then present the outcomes implicitly. It helps in providing a solid foundation for critical conclusions and assisting the researcher to complete the dissertation proposal.
4. Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data refers to data that does not involve numbers. You are required to carry out an analysis of the data collected through experiments, focus groups, and interviews. This can be a time-taking process because it requires iterative examination and sometimes demanding the application of hermeneutics. Note that using qualitative technique doesn’t only mean generating good outcomes but to unveil more profound knowledge that can be transferrable.
Presenting qualitative data analysis in a dissertation can also be a challenging task. It contains longer and more detailed responses. Placing such comprehensive data coherently in one chapter of the dissertation can be difficult due to two reasons. Firstly, we cannot figure out clearly which data to include and which one to exclude. Secondly, unlike quantitative data, it becomes problematic to present data in figures and tables. Making information condensed into a visual representation is not possible. As a writer, it is of essence to address both of these challenges.
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods
Following are the methods used to perform quantitative data analysis.
- Deductive Method
This method involves analyzing qualitative data based on an argument that a researcher already defines. It’s a comparatively easy approach to analyze data. It is suitable for the researcher with a fair idea about the responses they are likely to receive from the questionnaires.
- Inductive Method
In this method, the researcher analyzes the data not based on any predefined rules. It is a time-taking process used by students who have very little knowledge of the research phenomenon.
5. Quantitative Data Analysis
Quantitative data contains facts and figures obtained from scientific research and requires extensive statistical analysis. After collection and analysis, you will be able to conclude. Generic outcomes can be accepted beyond the sample by assuming that it is representative – one of the preliminary checkpoints to carry out in your analysis to a larger group. This method is also referred to as the “scientific method”, gaining its roots from natural sciences.
The Presentation of quantitative data depends on the domain to which it is being presented. It is beneficial to consider your audience while writing your findings. Quantitative data for hard sciences might require numeric inputs and statistics. As for natural sciences , such comprehensive analysis is not required.
Quantitative Analysis Methods
Following are some of the methods used to perform quantitative data analysis.
- Trend analysis: This corresponds to a statistical analysis approach to look at the trend of quantitative data collected over a considerable period.
- Cross-tabulation: This method uses a tabula way to draw readings among data sets in research.
- Conjoint analysis : Quantitative data analysis method that can collect and analyze advanced measures. These measures provide a thorough vision about purchasing decisions and the most importantly, marked parameters.
- TURF analysis: This approach assesses the total market reach of a service or product or a mix of both.
- Gap analysis: It utilizes the side-by-side matrix to portray quantitative data, which captures the difference between the actual and expected performance.
- Text analysis: In this method, innovative tools enumerate open-ended data into easily understandable data.
6. Data Presentation Tools
Since large volumes of data need to be represented, it becomes a difficult task to present such an amount of data in coherent ways. To resolve this issue, consider all the available choices you have, such as tables, charts, diagrams, and graphs.
Tables help in presenting both qualitative and quantitative data concisely. While presenting data, always keep your reader in mind. Anything clear to you may not be apparent to your reader. So, constantly rethink whether your data presentation method is understandable to someone less conversant with your research and findings. If the answer is “No”, you may need to rethink your Presentation.
7. Include Appendix or Addendum
After presenting a large amount of data, your dissertation analysis part might get messy and look disorganized. Also, you would not be cutting down or excluding the data you spent days and months collecting. To avoid this, you should include an appendix part.
The data you find hard to arrange within the text, include that in the appendix part of a dissertation . And place questionnaires, copies of focus groups and interviews, and data sheets in the appendix. On the other hand, one must put the statistical analysis and sayings quoted by interviewees within the dissertation.
8. Thoroughness of Data
It is a common misconception that the data presented is self-explanatory. Most of the students provide the data and quotes and think that it is enough and explaining everything. It is not sufficient. Rather than just quoting everything, you should analyze and identify which data you will use to approve or disapprove your standpoints.
Thoroughly demonstrate the ideas and critically analyze each perspective taking care of the points where errors can occur. Always make sure to discuss the anomalies and strengths of your data to add credibility to your research.
9. Discussing Data
Discussion of data involves elaborating the dimensions to classify patterns, themes, and trends in presented data. In addition, to balancing, also take theoretical interpretations into account. Discuss the reliability of your data by assessing their effect and significance. Do not hide the anomalies. While using interviews to discuss the data, make sure you use relevant quotes to develop a strong rationale.
It also involves answering what you are trying to do with the data and how you have structured your findings. Once you have presented the results, the reader will be looking for interpretation. Hence, it is essential to deliver the understanding as soon as you have submitted your data.
10. Findings and Results
Findings refer to the facts derived after the analysis of collected data. These outcomes should be stated; clearly, their statements should tightly support your objective and provide logical reasoning and scientific backing to your point. This part comprises of majority part of the dissertation.
In the finding part, you should tell the reader what they are looking for. There should be no suspense for the reader as it would divert their attention. State your findings clearly and concisely so that they can get the idea of what is more to come in your dissertation.
11. Connection with Literature Review
At the ending of your data analysis in the dissertation, make sure to compare your data with other published research. In this way, you can identify the points of differences and agreements. Check the consistency of your findings if they meet your expectations—lookup for bottleneck position. Analyze and discuss the reasons behind it. Identify the key themes, gaps, and the relation of your findings with the literature review. In short, you should link your data with your research question, and the questions should form a basis for literature.
The Role of Data Analytics at The Senior Management Level

From small and medium-sized businesses to Fortune 500 conglomerates, the success of a modern business is now increasingly tied to how the company implements its data infrastructure and data-based decision-making. According
The Decision-Making Model Explained (In Plain Terms)

Any form of the systematic decision-making process is better enhanced with data. But making sense of big data or even small data analysis when venturing into a decision-making process might
13 Reasons Why Data Is Important in Decision Making

Wrapping Up
Writing data analysis in the dissertation involves dedication, and its implementations demand sound knowledge and proper planning. Choosing your topic, gathering relevant data, analyzing it, presenting your data and findings correctly, discussing the results, connecting with the literature and conclusions are milestones in it. Among these checkpoints, the Data analysis stage is most important and requires a lot of keenness.
In this article, we thoroughly looked at the tips that prove valuable for writing a data analysis in a dissertation. Make sure to give this article a thorough read before you write data analysis in the dissertation leading to the successful future of your research.
Oxbridge Essays. Top 10 Tips for Writing a Dissertation Data Analysis.
Emidio Amadebai
As an IT Engineer, who is passionate about learning and sharing. I have worked and learned quite a bit from Data Engineers, Data Analysts, Business Analysts, and Key Decision Makers almost for the past 5 years. Interested in learning more about Data Science and How to leverage it for better decision-making in my business and hopefully help you do the same in yours.
Recent Posts
Causal vs Evidential Decision-making (How to Make Businesses More Effective)
In today’s fast-paced business landscape, it is crucial to make informed decisions to stay in the competition which makes it important to understand the concept of the different characteristics and...
Bootstrapping vs. Boosting
Over the past decade, the field of machine learning has witnessed remarkable advancements in predictive techniques and ensemble learning methods. Ensemble techniques are very popular in machine...

- Privacy Policy

Home » Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
- Table of Contents

Dissertation Methodology
In any research, the methodology chapter is one of the key components of your dissertation. It provides a detailed description of the methods you used to conduct your research and helps readers understand how you obtained your data and how you plan to analyze it. This section is crucial for replicating the study and validating its results.
Here are the basic elements that are typically included in a dissertation methodology:
- Introduction : This section should explain the importance and goals of your research .
- Research Design : Outline your research approach and why it’s appropriate for your study. You might be conducting an experimental research, a qualitative research, a quantitative research, or a mixed-methods research.
- Data Collection : This section should detail the methods you used to collect your data. Did you use surveys, interviews, observations, etc.? Why did you choose these methods? You should also include who your participants were, how you recruited them, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis : Explain how you intend to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, thematic analysis, content analysis, etc., depending on the nature of your study.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your study. For instance, you could discuss measures taken to reduce bias, how you ensured that your measures accurately capture what they were intended to, or how you will handle any limitations in your study.
- Ethical Considerations : This is where you state how you have considered ethical issues related to your research, how you have protected the participants’ rights, and how you have complied with the relevant ethical guidelines.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations of your methodology, including any biases and constraints that might have affected your study.
- Summary : Recap the key points of your methodology chapter, highlighting the overall approach and rationalization of your research.
Types of Dissertation Methodology
The type of methodology you choose for your dissertation will depend on the nature of your research question and the field you’re working in. Here are some of the most common types of methodologies used in dissertations:
Experimental Research
This involves creating an experiment that will test your hypothesis. You’ll need to design an experiment, manipulate variables, collect data, and analyze that data to draw conclusions. This is commonly used in fields like psychology, biology, and physics.
Survey Research
This type of research involves gathering data from a large number of participants using tools like questionnaires or surveys. It can be used to collect a large amount of data and is often used in fields like sociology, marketing, and public health.
Qualitative Research
This type of research is used to explore complex phenomena that can’t be easily quantified. Methods include interviews, focus groups, and observations. This methodology is common in fields like anthropology, sociology, and education.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research uses numerical data to answer research questions. This can include statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It’s common in fields like economics, psychology, and health sciences.
Case Study Research
This type of research involves in-depth investigation of a particular case, such as an individual, group, or event. This methodology is often used in psychology, social sciences, and business.
Mixed Methods Research
This combines qualitative and quantitative research methods in a single study. It’s used to answer more complex research questions and is becoming more popular in fields like social sciences, health sciences, and education.
Action Research
This type of research involves taking action and then reflecting upon the results. This cycle of action-reflection-action continues throughout the study. It’s often used in fields like education and organizational development.
Longitudinal Research
This type of research involves studying the same group of individuals over an extended period of time. This could involve surveys, observations, or experiments. It’s common in fields like psychology, sociology, and medicine.
Ethnographic Research
This type of research involves the in-depth study of people and cultures. Researchers immerse themselves in the culture they’re studying to collect data. This is often used in fields like anthropology and social sciences.
Structure of Dissertation Methodology
The structure of a dissertation methodology can vary depending on your field of study, the nature of your research, and the guidelines of your institution. However, a standard structure typically includes the following elements:
- Introduction : Briefly introduce your overall approach to the research. Explain what you plan to explore and why it’s important.
- Research Design/Approach : Describe your overall research design. This can be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain the rationale behind your chosen design and why it is suitable for your research questions or hypotheses.
- Data Collection Methods : Detail the methods you used to collect your data. You should include what type of data you collected, how you collected it, and why you chose this method. If relevant, you can also include information about your sample population, such as how many people participated, how they were chosen, and any relevant demographic information.
- Data Analysis Methods : Explain how you plan to analyze your collected data. This will depend on the nature of your data. For example, if you collected quantitative data, you might discuss statistical analysis techniques. If you collected qualitative data, you might discuss coding strategies, thematic analysis, or narrative analysis.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your research. This might include steps you took to reduce bias or increase the accuracy of your measurements.
- Ethical Considerations : If relevant, discuss any ethical issues associated with your research. This might include how you obtained informed consent from participants, how you ensured participants’ privacy and confidentiality, or any potential conflicts of interest.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations in your research methodology. This could include potential sources of bias, difficulties with data collection, or limitations in your analysis methods.
- Summary/Conclusion : Briefly summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps answer your research questions or hypotheses.
How to Write Dissertation Methodology
Writing a dissertation methodology requires you to be clear and precise about the way you’ve carried out your research. It’s an opportunity to convince your readers of the appropriateness and reliability of your approach to your research question. Here is a basic guideline on how to write your methodology section:
1. Introduction
Start your methodology section by restating your research question(s) or objective(s). This ensures your methodology directly ties into the aim of your research.
2. Approach
Identify your overall approach: qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain why you have chosen this approach.
- Qualitative methods are typically used for exploratory research and involve collecting non-numerical data. This might involve interviews, observations, or analysis of texts.
- Quantitative methods are used for research that relies on numerical data. This might involve surveys, experiments, or statistical analysis.
- Mixed methods use a combination of both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
3. Research Design
Describe the overall design of your research. This could involve explaining the type of study (e.g., case study, ethnography, experimental research, etc.), how you’ve defined and measured your variables, and any control measures you’ve implemented.
4. Data Collection
Explain in detail how you collected your data.
- If you’ve used qualitative methods, you might detail how you selected participants for interviews or focus groups, how you conducted observations, or how you analyzed existing texts.
- If you’ve used quantitative methods, you might detail how you designed your survey or experiment, how you collected responses, and how you ensured your data is reliable and valid.
5. Data Analysis
Describe how you analyzed your data.
- If you’re doing qualitative research, this might involve thematic analysis, discourse analysis, or grounded theory.
- If you’re doing quantitative research, you might be conducting statistical tests, regression analysis, or factor analysis.
Discuss any ethical issues related to your research. This might involve explaining how you obtained informed consent, how you’re protecting participants’ privacy, or how you’re managing any potential harms to participants.
7. Reliability and Validity
Discuss the steps you’ve taken to ensure the reliability and validity of your data.
- Reliability refers to the consistency of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve piloted your instruments or used standardized measures.
- Validity refers to the accuracy of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve ensured your measures reflect the concepts they’re supposed to measure.
8. Limitations
Every study has its limitations. Discuss the potential weaknesses of your chosen methods and explain any obstacles you faced in your research.
9. Conclusion
Summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps to address your research question or objective.
Example of Dissertation Methodology
An Example of Dissertation Methodology is as follows:
Chapter 3: Methodology
- Introduction
This chapter details the methodology adopted in this research. The study aimed to explore the relationship between stress and productivity in the workplace. A mixed-methods research design was used to collect and analyze data.
Research Design
This study adopted a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys with qualitative interviews to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research problem. The rationale for this approach is that while quantitative data can provide a broad overview of the relationships between variables, qualitative data can provide deeper insights into the nuances of these relationships.
Data Collection Methods
Quantitative Data Collection : An online self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from participants. The questionnaire consisted of two standardized scales: the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) to measure stress levels and the Individual Work Productivity Questionnaire (IWPQ) to measure productivity. The sample consisted of 200 office workers randomly selected from various companies in the city.
Qualitative Data Collection : Semi-structured interviews were conducted with 20 participants chosen from the initial sample. The interview guide included questions about participants’ experiences with stress and how they perceived its impact on their productivity.
Data Analysis Methods
Quantitative Data Analysis : Descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze the survey data. Pearson’s correlation was used to examine the relationship between stress and productivity.
Qualitative Data Analysis : Interviews were transcribed and subjected to thematic analysis using NVivo software. This process allowed for identifying and analyzing patterns and themes regarding the impact of stress on productivity.
Reliability and Validity
To ensure reliability and validity, standardized measures with good psychometric properties were used. In qualitative data analysis, triangulation was employed by having two researchers independently analyze the data and then compare findings.
Ethical Considerations
All participants provided informed consent prior to their involvement in the study. They were informed about the purpose of the study, their rights as participants, and the confidentiality of their responses.
Limitations
The main limitation of this study is its reliance on self-report measures, which can be subject to biases such as social desirability bias. Moreover, the sample was drawn from a single city, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Where to Write Dissertation Methodology
In a dissertation or thesis, the Methodology section usually follows the Literature Review. This placement allows the Methodology to build upon the theoretical framework and existing research outlined in the Literature Review, and precedes the Results or Findings section. Here’s a basic outline of how most dissertations are structured:
- Acknowledgements
- Literature Review (or it may be interspersed throughout the dissertation)
- Methodology
- Results/Findings
- References/Bibliography
In the Methodology chapter, you will discuss the research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and any ethical considerations pertaining to your study. This allows your readers to understand how your research was conducted and how you arrived at your results.
Advantages of Dissertation Methodology
The dissertation methodology section plays an important role in a dissertation for several reasons. Here are some of the advantages of having a well-crafted methodology section in your dissertation:
- Clarifies Your Research Approach : The methodology section explains how you plan to tackle your research question, providing a clear plan for data collection and analysis.
- Enables Replication : A detailed methodology allows other researchers to replicate your study. Replication is an important aspect of scientific research because it provides validation of the study’s results.
- Demonstrates Rigor : A well-written methodology shows that you’ve thought critically about your research methods and have chosen the most appropriate ones for your research question. This adds credibility to your study.
- Enhances Transparency : Detailing your methods allows readers to understand the steps you took in your research. This increases the transparency of your study and allows readers to evaluate potential biases or limitations.
- Helps in Addressing Research Limitations : In your methodology section, you can acknowledge and explain the limitations of your research. This is important as it shows you understand that no research method is perfect and there are always potential weaknesses.
- Facilitates Peer Review : A detailed methodology helps peer reviewers assess the soundness of your research design. This is an important part of the publication process if you aim to publish your dissertation in a peer-reviewed journal.
- Establishes the Validity and Reliability : Your methodology section should also include a discussion of the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your measurements, which is crucial for establishing the overall quality of your research.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples


What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on 27 October 2016 by Bas Swaen . Revised on 25 October 2022 by Tegan George.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean – any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs discussion vs conclusion, checklist: research results, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analysed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like ‘appears’ or ‘implies’.
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe shop: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the trainers, boots, sandals, etc.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualise trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarise or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.
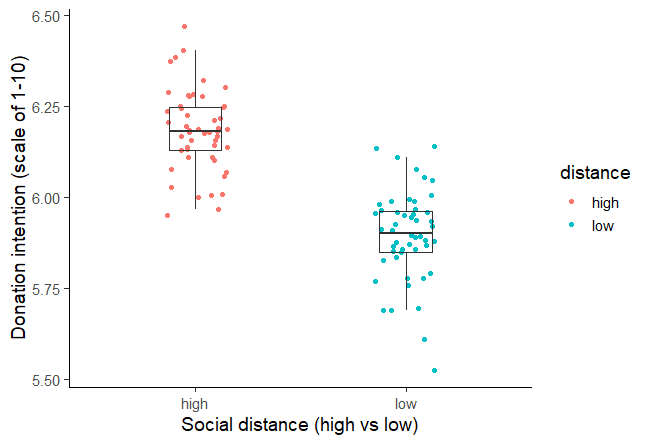
Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organisations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
‘I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.’
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Swaen, B. (2022, October 25). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/results-section/
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked
What is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion.
How to Analyse Secondary Data for a Dissertation
Secondary data refers to data that has already been collected by another researcher. For researchers (and students!) with limited time and resources, secondary data, whether qualitative or quantitative can be a highly viable source of data. In addition, with the advances in technology and access to peer reviewed journals and studies provided by the internet, it is increasingly popular as a form of data collection. The question that frequently arises amongst students however, is: how is secondary data best analysed?
The process of data analysis in secondary research
Secondary analysis (i.e., the use of existing data) is a systematic methodological approach that has some clear steps that need to be followed for the process to be effective. In simple terms there are three steps:
- Step One: Development of Research Questions
- Step Two: Identification of dataset
- Step Three: Evaluation of the dataset.
Let’s look at each of these in more detail:
Step One: Development of research questions
Using secondary data means you need to apply theoretical knowledge and conceptual skills to be able to use the dataset to answer research questions. Clearly therefore, the first step is thus to clearly define and develop your research questions so that you know the areas of interest that you need to explore for location of the most appropriate secondary data.
Step Two: Identification of Dataset
This stage should start with identification, through investigation, of what is currently known in the subject area and where there are gaps, and thus what data is available to address these gaps. Sources can be academic from prior studies that have used quantitative or qualitative data, and which can then be gathered together and collated to produce a new secondary dataset. In addition, other more informal or “grey” literature can also be incorporated, including consumer report, commercial studies or similar. One of the values of using secondary research is that original survey works often do not use all the data collected which means this unused information can be applied to different settings or perspectives.
Key point: Effective use of secondary data means identifying how the data can be used to deliver meaningful and relevant answers to the research questions. In other words that the data used is a good fit for the study and research questions.
Step Three: Evaluation of the dataset for effectiveness/fit
A good tip is to use a reflective approach for data evaluation. In other words, for each piece of secondary data to be utilised, it is sensible to identify the purpose of the work, the credentials of the authors (i.e., credibility, what data is provided in the original work and how long ago it was collected). In addition, the methods used and the level of consistency that exists compared to other works. This is important because understanding the primary method of data collection will impact on the overall evaluation and analysis when it is used as secondary source. In essence, if there is no understanding of the coding used in qualitative data analysis to identify key themes then there will be a mismatch with interpretations when the data is used for secondary purposes. Furthermore, having multiple sources which draw similar conclusions ensures a higher level of validity than relying on only one or two secondary sources.
A useful framework provides a flow chart of decision making, as shown in the figure below.
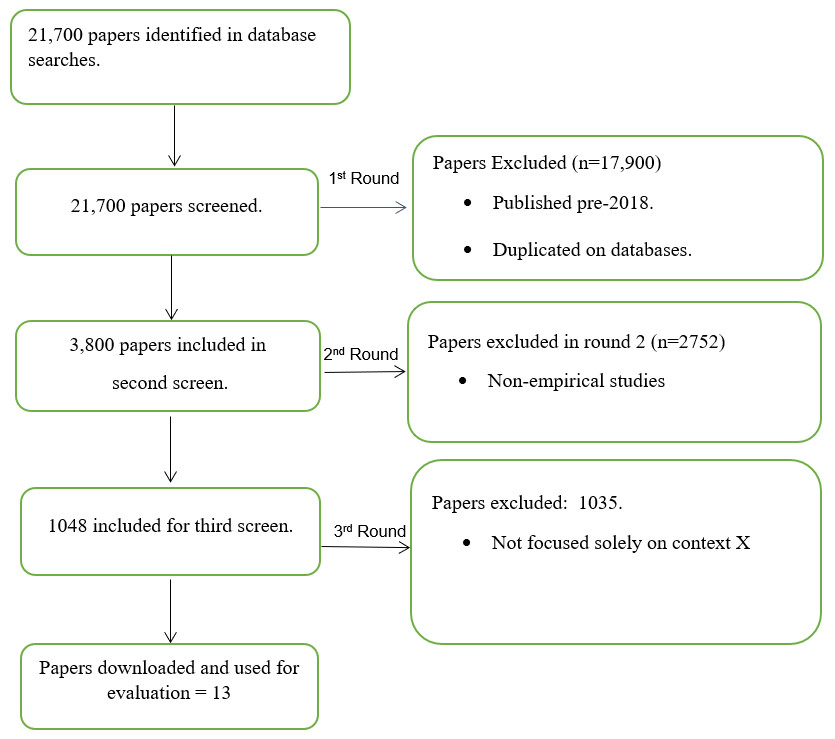
Following this process ensures that only those that are most appropriate for your research questions are included in the final dataset, but also demonstrates to your readers that you have been thorough in identifying the right works to use.
Writing up the Analysis
Once you have your dataset, writing up the analysis will depend on the process used. If the data is qualitative in nature, then you should follow the following process.
Pre-Planning
- Read and re-read all sources, identifying initial observations, correlations, and relationships between themes and how they apply to your research questions.
- Once initial themes are identified, it is sensible to explore further and identify sub-themes which lead on from the core themes and correlations in the dataset, which encourages identification of new insights and contributes to the originality of your own work.
Structure of the Analysis Presentation
Introduction.
The introduction should commence with an overview of all your sources. It is good practice to present these in a table, listed chronologically so that your work has an orderly and consistent flow. The introduction should also incorporate a brief (2-3 sentences) overview of the key outcomes and results identified.
The body text for secondary data, irrespective of whether quantitative or qualitative data is used, should be broken up into sub-sections for each argument or theme presented. In the case of qualitative data, depending on whether content, narrative or discourse analysis is used, this means presenting the key papers in the area, their conclusions and how these answer, or not, your research questions. Each source should be clearly cited and referenced at the end of the work. In the case of qualitative data, any figures or tables should be reproduced with the correct citations to their original source. In both cases, it is good practice to give a main heading of a key theme, with sub-headings for each of the sub themes identified in the analysis.
Do not use direct quotes from secondary data unless they are:
- properly referenced, and
- are key to underlining a point or conclusion that you have drawn from the data.
All results sections, regardless of whether primary or secondary data has been used should refer back to the research questions and prior works. This is because, regardless of whether the results back up or contradict previous research, including previous works shows a wider level of reading and understanding of the topic being researched and gives a greater depth to your own work.
Summary of results
The summary of the results section of a secondary data dissertation should deliver a summing up of key findings, and if appropriate a conceptual framework that clearly illustrates the findings of the work. This shows that you have understood your secondary data, how it has answered your research questions, and furthermore that your interpretation has led to some firm outcomes.
You may also like


Library Guides
Dissertations 2: structure: thematic.
In the humanities, a thematic dissertation is often structured like a long essay. It can contain:
Title page
Abstract
Table of contents
Introduction
Literature review (which can be included in the introduction rather than as a separate chapter. Check with your supervisor if you are unsure).
Theme 1
Theme 2
Theme 3
Conclusion
Bibliography
Appendices
Abstracts are used by other researchers to establish the relevance of the study to their own work. Therefore, they should contain the what, why, who, where and how of your project.
They are typically between 250 – 300 words long, offer a summary of the main findings and present the conclusions, so you should attempt to write an abstract (if requested), after you have finished writing the dissertation.
A typical abstract summarises:
What the study aimed to achieve
The methodology used
Why the research was conducted
Why the research is important
Who/what was researched
Table of Contents
The table of contents should list all the items included in your dissertation.
It is a good idea to use the electronic table of contents feature in Word to automatically link it to your chapter headings and page numbers. Attempting to manually create a table of contents means that you will have to adjust your page numbers every time you edit your work before submission, which may waste valuable time!
This useful video will walk you through the formatting of longer documents using the electronic table of contents feature.
Introduction
The introduction explains the how, what, where, when, why and who of the research. It introduces the reader to your dissertation and should act as a clear guide as to what it will cover.
The introduction may include the following content:
Introduce the topic of the dissertation
- State why the topic is of interest
- Give background information on the subject.
- Refer to the main debates in the field
Identify the scope of your research
- Highlight what hasn't already been said by the literature
- Demonstrate what you seek to investigate, and why
- Present the aim of the dissertation.
- Mention your research question or hypothesis
Indicate your approach
- Introduce your main argument (especially if you have a research question, rather than hypothesis).
- Mention your methods/research design.
- Outline the dissertation structure (introduce the main points that you will discuss in the order they will be presented).
Normally, the introduction is roughly 10% of a dissertation word count.
Literature Review
The term “literature” in “literature review” comprises scholarly articles, books, and other sources (e.g. reports) relevant to a particular issue, area of research or theory. In a dissertation, the literature review illustrates what the literature already says on your research subject, providing summary and synthesis of such literature.
It is generally structured by topic, starting from general background and concepts, and then addressing what can be found - and cannot be found - on the specific focus of your dissertation. Indeed, the literature review should identify gaps in the literature, that your research aims to fill. This requires you to engage critically with the literature, not merely reproduce the critical understanding of others.
In sum, literature reviews should demonstrate how your research question can be located in a wider field of inquiry. Therefore, a literature review needs to address the connections between your work and the work of others by highlighting links between them. In doing so, you will demonstrate the foundations of your project and show how you are taking the line of inquiry forwards.
By the end of your literature review, your reader should be able to see:
The gap in knowledge and understanding which you say exists in the field.
How your research question will work within that gap.
The work other researchers have carried out and the issues debated in the field.
That you have a good understanding of the field and that you are critically engaged with the debates (Burnett, 2009).
For more detailed guidance on how to write literature reviews, check out the Literature Review Guide.
Theme Chapters
In a thematic structure, the core chapters present analysis and discussion of different themes relevant to answer the research question and support the overall argument of the dissertation. The chapters will include analysis of texts/ research material. They can explore and connect academic theories/research to develop an argument. Stella Cottrell offers some good guidance on how to structure your theme chapters. Each chapter should have the following elements (Cottrell, 2014, p183):
Theme: What is the theme of this chapter? Sequence your themes logically (e.g. from general to specific).
Argument: What argument does this chapter present?
Material: What material you will be using for this chapter?
Clustering: What are the main points you want to make? Deal with one point at a time, and don't jum around? Dedicate your points to sub-headings and paragraphs.
Sequence: In what order are you going to present the points you want to make in this chapter? Draw an outline of the chapter before starting writing it.
Introduction and Conclusion: Each chapter should have a short introduction and conclusion.
The conclusion is the final chapter of your dissertation. It should flow logically from the previously presented text; therefore, you should avoid introducing new ideas, new data, or a new direction.
Ideally, the conclusion should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the discovery or argument you have advanced.
This can be done by:
Summarising and synthesising your main findings and how they relate to your research question or hypotheses
Demonstrating the relevance and importance of your work in the wider context of your field. For example, what recommendations would you make for future research? What do we know now that we didn’t know before?
Link your conclusion to your introduction as both frame your dissertation.
A conclusion is roughly five to ten percent of the word count of the dissertation.
Avoid excessive detail. Decide what your reader needs to know.
Don’t introduce any new information such as theories, data or ideas.
Sum up the main points of your research.
Bibliography
While writing your dissertation, you would have referred to the works and research of many different authors and editors in your field of study. These works should be acknowledged in the bibliography where you will list writers alphabetically by surname.
For example:
Poloian, L.R. (2013). Retailing principles: global, multichannel, and managerial viewpoints. New York: Fairchild. Biggs, J. and Tang, C. (2011). Teaching for quality learning at university . Maidenhead: Open University Press. Ramsay, P., Maier, P. and Price, G. (2010). Study skills for business and management students . Harlow: Longman.
Unless otherwise specified by your module leader, the University uses the Harvard (author-date) style of citing and referencing. For more guidance and support on how to reference effectively check out the Referencing Guide . You can also book an appointment with an Academic Engagement Librarian for extra help with referencing.
While the main results of your study should be placed in the body of your dissertation, any extra information can be placed in the appendices chapter. This supplementary information, for instance, can consist of graphs, charts, or tables that demonstrate less significant results or interview transcripts that would disrupt the flow of the main text if they were included within it.
You can create one long appendix section or divide it into smaller sections to make it easier to navigate. For example, you might want to have an appendix for images, an appendix for transcripts, and an appendix for graphs. Each appendix (each graph or chart, etc.) should have its own number and title. Further, the sources for all appendices should be acknowledged through referencing and listed in the bibliography.
Don’t forget to mention each appendix at least once during your dissertation! This can be done using brackets in the following way: (see appendix 1).
- << Previous: Standard
- Last Updated: Nov 23, 2021 3:47 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/c.php?g=692395
CONNECT WITH US
ON YOUR 1ST ORDER
Mastering Dissertation Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide
By Laura Brown on 29th December 2023
To craft an effective dissertation data analysis chapter, you need to follow some simple steps:
- Start by planning the structure and objectives of the chapter.
- Clearly set the stage by providing a concise overview of your research design and methodology.
- Proceed to thorough data preparation, ensuring accuracy and organisation.
- Justify your methods and present the results using visual aids for clarity.
- Discuss the findings within the context of your research questions.
- Finally, review and edit your chapter to ensure coherence.
This approach will ensure a well-crafted and impactful analysis section.
Before delving into details on how you can come up with an engaging data analysis show in your dissertation, we first need to understand what it is and why it is required.
What Is Data Analysis In A Dissertation?
The data analysis chapter is a crucial section of a research dissertation that involves the examination, interpretation, and synthesis of collected data. In this chapter, researchers employ statistical techniques, qualitative methods, or a combination of both to make sense of the data gathered during the research process.
Why Is The Data Analysis Chapter So Important?
The primary objectives of the data analysis chapter are to identify patterns, trends, relationships, and insights within the data set. Researchers use various tools and software to conduct a thorough analysis, ensuring that the results are both accurate and relevant to the research questions or hypotheses. Ultimately, the findings derived from this chapter contribute to the overall conclusions of the dissertation, providing a basis for drawing meaningful and well-supported insights.
Steps Required To Craft Data Analysis Chapter To Perfection
Now that we have an idea of what a dissertation analysis chapter is and why it is necessary to put it in the dissertation, let’s move towards how we can create one that has a significant impact. Our guide will move around the bulleted points that have been discussed initially in the beginning. So, it’s time to begin.

Step 1: Planning Your Data Analysis Chapter
Planning your data analysis chapter is a critical precursor to its successful execution.
- Begin by outlining the chapter structure to provide a roadmap for your analysis.
- Start with an introduction that succinctly introduces the purpose and significance of the data analysis in the context of your research.
- Following this, delineate the chapter into sections such as Data Preparation, where you detail the steps taken to organise and clean your data.
- Plan on to clearly define the Data Analysis Techniques employed, justifying their relevance to your research objectives.
- As you progress, plan for the Results Presentation, incorporating visual aids for clarity. Lastly, earmark a section for the Discussion of Findings, where you will interpret results within the broader context of your research questions.
This structured approach ensures a comprehensive and cohesive data analysis chapter, setting the stage for a compelling narrative that contributes significantly to your dissertation. You can always seek our dissertation data analysis help to plan your chapter.
Step 2: Setting The Stage – Introduction to Data Analysis
Your primary objective is to establish a solid foundation for the analytical journey. You need to skillfully link your data analysis to your research questions, elucidating the direct relevance and purpose of the upcoming analysis.
Simultaneously, define key concepts to provide clarity and ensure a shared understanding of the terms integral to your study. Following this, offer a concise overview of your data set characteristics, outlining its source, nature, and any noteworthy features.
This meticulous groundwork alongside our help with dissertation data analysis lays the base for a coherent and purposeful chapter, guiding readers seamlessly into the subsequent stages of your dissertation.
Step 3: Data Preparation
Now this is another pivotal phase in the data analysis process, ensuring the integrity and reliability of your findings. You should start with an insightful overview of the data cleaning and preprocessing procedures, highlighting the steps taken to refine and organise your dataset. Then, discuss any challenges encountered during the process and the strategies employed to address them.
Moving forward, delve into the specifics of data transformation procedures, elucidating any alterations made to the raw data for analysis. Clearly describe the methods employed for normalisation, scaling, or any other transformations deemed necessary. It will not only enhance the quality of your analysis but also foster transparency in your research methodology, reinforcing the robustness of your data-driven insights.
Step 4: Data Analysis Techniques
The data analysis section of a dissertation is akin to choosing the right tools for an artistic masterpiece. Carefully weigh the quantitative and qualitative approaches, ensuring a tailored fit for the nature of your data.
Quantitative Analysis
- Descriptive Statistics: Paint a vivid picture of your data through measures like mean, median, and mode. It’s like capturing the essence of your data’s personality.
- Inferential Statistics:Take a leap into the unknown, making educated guesses and inferences about your larger population based on a sample. It’s statistical magic in action.
Qualitative Analysis
- Thematic Analysis: Imagine your data as a novel, and thematic analysis as the tool to uncover its hidden chapters. Dissect the narrative, revealing recurring themes and patterns.
- Content Analysis: Scrutinise your data’s content like detectives, identifying key elements and meanings. It’s a deep dive into the substance of your qualitative data.
Providing Rationale for Chosen Methods
You should also articulate the why behind the chosen methods. It’s not just about numbers or themes; it’s about the story you want your data to tell. Through transparent rationale, you should ensure that your chosen techniques align seamlessly with your research goals, adding depth and credibility to the analysis.
Step 5: Presentation Of Your Results
You can simply break this process into two parts.
a. Creating Clear and Concise Visualisations
Effectively communicate your findings through meticulously crafted visualisations. Use tables that offer a structured presentation, summarising key data points for quick comprehension. Graphs, on the other hand, visually depict trends and patterns, enhancing overall clarity. Thoughtfully design these visual aids to align with the nature of your data, ensuring they serve as impactful tools for conveying information.
b. Interpreting and Explaining Results
Go beyond mere presentation by providing insightful interpretation by taking data analysis services for dissertation. Show the significance of your findings within the broader research context. Moreover, articulates the implications of observed patterns or relationships. By weaving a narrative around your results, you guide readers through the relevance and impact of your data analysis, enriching the overall understanding of your dissertation’s key contributions.
Step 6: Discussion of Findings
While discussing your findings and dissertation discussion chapter , it’s like putting together puzzle pieces to understand what your data is saying. You can always take dissertation data analysis help to explain what it all means, connecting back to why you started in the first place.
Be honest about any limitations or possible biases in your study; it’s like showing your cards to make your research more trustworthy. Comparing your results to what other smart people have found before you adds to the conversation, showing where your work fits in.
Looking ahead, you suggest ideas for what future researchers could explore, keeping the conversation going. So, it’s not just about what you found, but also about what comes next and how it all fits into the big picture of what we know.
Step 7: Writing Style and Tone
In order to perfectly come up with this chapter, follow the below points in your writing and adjust the tone accordingly,
- Use clear and concise language to ensure your audience easily understands complex concepts.
- Avoid unnecessary jargon in data analysis for thesis, and if specialised terms are necessary, provide brief explanations.
- Keep your writing style formal and objective, maintaining an academic tone throughout.
- Avoid overly casual language or slang, as the data analysis chapter is a serious academic document.
- Clearly define terms and concepts, providing specific details about your data preparation and analysis procedures.
- Use precise language to convey your ideas, minimising ambiguity.
- Follow a consistent formatting style for headings, subheadings, and citations to enhance readability.
- Ensure that tables, graphs, and visual aids are labelled and formatted uniformly for a polished presentation.
- Connect your analysis to the broader context of your research by explaining the relevance of your chosen methods and the importance of your findings.
- Offer a balance between detail and context, helping readers understand the significance of your data analysis within the larger study.
- Present enough detail to support your findings but avoid overwhelming readers with excessive information.
- Use a balance of text and visual aids to convey information efficiently.
- Maintain reader engagement by incorporating transitions between sections and effectively linking concepts.
- Use a mix of sentence structures to add variety and keep the writing engaging.
- Eliminate grammatical errors, typos, and inconsistencies through thorough proofreading.
- Consider seeking feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the clarity and coherence of your writing.
You can seek a data analysis dissertation example or sample from CrowdWriter to better understand how we write it while following the above-mentioned points.
Step 8: Reviewing and Editing
Reviewing and editing your data analysis chapter is crucial for ensuring its effectiveness and impact. By revising your work, you refine the clarity and coherence of your analysis, enhancing its overall quality.
Seeking feedback from peers, advisors or dissertation data analysis services provides valuable perspectives, helping identify blind spots and areas for improvement. Addressing common writing pitfalls, such as grammatical errors or unclear expressions, ensures your chapter is polished and professional.
Taking the time to review and edit not only strengthens the academic integrity of your work but also contributes to a final product that is clear, compelling, and ready for scholarly scrutiny.
Concluding On This Data Analysis Help
Be it master thesis data analysis, an undergraduate one or for PhD scholars, the steps remain almost the same as we have discussed in this guide. The primary focus is to be connected with your research questions and objectives while writing your data analysis chapter.
Do not lose your focus and choose the right analysis methods and design. Make sure to present your data through various visuals to better explain your data and engage the reader as well. At last, give it a detailed read and seek assistance from experts and your supervisor for further improvement.

Laura Brown, a senior content writer who writes actionable blogs at Crowd Writer.

- Engaging With Sources Effectively
by acburton | Apr 30, 2024 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources
We’ve talked about the three ways to integrate sources effectively that allow writers to provide evidence and support for their argument, enter the scholarly conversation, and give credit to the original authors of the work that has helped and informed them. Sources also encourage writers to share their own knowledge and authority with others, help readers find additional sources related to the topic they are interested in, and protect you by giving credit where credit is due (thus avoiding plagiarism). In other words, sources are much more than just something we add on at the end of our writing!
When writing about a source or simply referencing it, we are positioning ourselves in response to, or in conversation with that source, with the goal of focusing our writing on our own argument/thesis. Sources do not stand on their own within a piece of writing and that is why, alongside finding strong and reputable sources worth responding to and making sure that we fully understand sources (even before writing about them), it is critical to engage with our sources in meaningful ways. But how exactly do we effectively engage with our sources in our writing?
Joseph Harris, in How To Do Things with Texts , presents four different ways of “rewriting the work of others”, three of which provide insight into the how of engaging sources. When a writer forwards the work of another writer, they are applying the concepts, topics, or terms from one reading, text, or situation to a different reading, text or situation. By countering the ideas found in source material, a writer argues “against the grain of a text” by underlining and countering ideas that a writer may be in disagreement with. Taking an approach is the adaptation of a theory or method from one writer to a new set of issues or texts. Harris’ book provides a thorough classification of methods to engage with a source. For something a little simpler, here are three basic ways you can get started effectively engaging with sources (Harris 5-7).
3 Basic Ways to Engage with Sources Effectively
- Disagree and Explain Why. Persuade your reader that the argument or information in a source should be questioned or challenged.
- Agree, But With Your Own Take. Add something new to the conversation. Expand a source’s insights or argument to a new situation or your own example. Provide new evidence and discuss new implications.
- Agree and Disagree Simultaneously. This is a nuanced approach to complex sources or complex topics. You can, for example, agree with a source’s overall thesis, but disagree with some of its reasoning or evidence.
Remember that this is not an exhaustive list. When engaging with others’ sources as a way to support our own ideas and argument, it is crucial that we engage with critical thinking, nuance, and objectivity to ensure that we are constructing unbiased, thoughtful, and compelling arguments.
Some of the different areas throughout your essay that will benefit from effective engagement with source material include: your thesis statement, analysis, and conclusion.
- Thesis Statement. The argument that you make in your thesis statement can challenge, weaken, support, or strengthen what is being argued by your source or sources.
Analysis. Thorough analysis in your body paragraphs emphasize the role of your argument in comparison to that found in your source material. Bring your analysis back to your thesis statement to reinforce the connection between the two.
- Conclusion. Consider the “big picture” or “takeaways” to leave your reader with.
There are many other, sometimes optional, essay sections or writing styles that benefit from critical engagement with a source. These can include literature reviews, reflections, critiques, and so on.
Strategies for Engaging Critically From Start to Finish
- Aim to dig deeper than surface level. Ask the ‘how’ and ‘why’ of a source, as well as ‘how’ and ‘why’ it is relevant to the topic at hand and the argument you are making.
- Ask yourself if you’ve addressed every possible question, concern, critique, or “what if” that comes to mind; put yourself in the place of your readers.
- Use TEAL body paragraph development as a template and guide for developing thorough analysis in your body paragraphs. Effectively engaging with your sources is essential to the analysis portion of the TEAL formula and to creating meaningful engagement with your sources.
- Visit the Writing Center for additional support on crafting engaging analyses and for other ways to engage with your source material from thesis to conclusion.
Our Newest Resources!
- Revision vs. Proofreading
- The Dos and Don’ts of Using Tables and Figures in Your Writing
- Synthesis and Making Connections for Strong Analysis
- Writing Strong Titles
Additional Resources
- Graduate Writing Consultants
- Instructor Resources
- Student Resources
- Quick Guides and Handouts
- Self-Guided and Directed Learning Activities
Dissertation Structure & Layout 101: How to structure your dissertation, thesis or research project.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | July 2019
So, you’ve got a decent understanding of what a dissertation is , you’ve chosen your topic and hopefully you’ve received approval for your research proposal . Awesome! Now its time to start the actual dissertation or thesis writing journey.
To craft a high-quality document, the very first thing you need to understand is dissertation structure . In this post, we’ll walk you through the generic dissertation structure and layout, step by step. We’ll start with the big picture, and then zoom into each chapter to briefly discuss the core contents. If you’re just starting out on your research journey, you should start with this post, which covers the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis .

*The Caveat *
In this post, we’ll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
So, always check with your university if they have a prescribed structure or layout that they expect you to work with. If not, it’s safe to assume the structure we’ll discuss here is suitable. And even if they do have a prescribed structure, you’ll still get value from this post as we’ll explain the core contents of each section.
Overview: S tructuring a dissertation or thesis
- Acknowledgements page
- Abstract (or executive summary)
- Table of contents , list of figures and tables
- Chapter 1: Introduction
- Chapter 2: Literature review
- Chapter 3: Methodology
- Chapter 4: Results
- Chapter 5: Discussion
- Chapter 6: Conclusion
- Reference list
As I mentioned, some universities will have slight variations on this structure. For example, they want an additional “personal reflection chapter”, or they might prefer the results and discussion chapter to be merged into one. Regardless, the overarching flow will always be the same, as this flow reflects the research process , which we discussed here – i.e.:
- The introduction chapter presents the core research question and aims .
- The literature review chapter assesses what the current research says about this question.
- The methodology, results and discussion chapters go about undertaking new research about this question.
- The conclusion chapter (attempts to) answer the core research question .
In other words, the dissertation structure and layout reflect the research process of asking a well-defined question(s), investigating, and then answering the question – see below.

To restate that – the structure and layout of a dissertation reflect the flow of the overall research process . This is essential to understand, as each chapter will make a lot more sense if you “get” this concept. If you’re not familiar with the research process, read this post before going further.
Right. Now that we’ve covered the big picture, let’s dive a little deeper into the details of each section and chapter. Oh and by the way, you can also grab our free dissertation/thesis template here to help speed things up.
The title page of your dissertation is the very first impression the marker will get of your work, so it pays to invest some time thinking about your title. But what makes for a good title? A strong title needs to be 3 things:
- Succinct (not overly lengthy or verbose)
- Specific (not vague or ambiguous)
- Representative of the research you’re undertaking (clearly linked to your research questions)
Typically, a good title includes mention of the following:
- The broader area of the research (i.e. the overarching topic)
- The specific focus of your research (i.e. your specific context)
- Indication of research design (e.g. quantitative , qualitative , or mixed methods ).
For example:
A quantitative investigation [research design] into the antecedents of organisational trust [broader area] in the UK retail forex trading market [specific context/area of focus].
Again, some universities may have specific requirements regarding the format and structure of the title, so it’s worth double-checking expectations with your institution (if there’s no mention in the brief or study material).

Acknowledgements
This page provides you with an opportunity to say thank you to those who helped you along your research journey. Generally, it’s optional (and won’t count towards your marks), but it is academic best practice to include this.
So, who do you say thanks to? Well, there’s no prescribed requirements, but it’s common to mention the following people:
- Your dissertation supervisor or committee.
- Any professors, lecturers or academics that helped you understand the topic or methodologies.
- Any tutors, mentors or advisors.
- Your family and friends, especially spouse (for adult learners studying part-time).
There’s no need for lengthy rambling. Just state who you’re thankful to and for what (e.g. thank you to my supervisor, John Doe, for his endless patience and attentiveness) – be sincere. In terms of length, you should keep this to a page or less.
Abstract or executive summary
The dissertation abstract (or executive summary for some degrees) serves to provide the first-time reader (and marker or moderator) with a big-picture view of your research project. It should give them an understanding of the key insights and findings from the research, without them needing to read the rest of the report – in other words, it should be able to stand alone .
For it to stand alone, your abstract should cover the following key points (at a minimum):
- Your research questions and aims – what key question(s) did your research aim to answer?
- Your methodology – how did you go about investigating the topic and finding answers to your research question(s)?
- Your findings – following your own research, what did do you discover?
- Your conclusions – based on your findings, what conclusions did you draw? What answers did you find to your research question(s)?
So, in much the same way the dissertation structure mimics the research process, your abstract or executive summary should reflect the research process, from the initial stage of asking the original question to the final stage of answering that question.
In practical terms, it’s a good idea to write this section up last , once all your core chapters are complete. Otherwise, you’ll end up writing and rewriting this section multiple times (just wasting time). For a step by step guide on how to write a strong executive summary, check out this post .
Need a helping hand?
Table of contents
This section is straightforward. You’ll typically present your table of contents (TOC) first, followed by the two lists – figures and tables. I recommend that you use Microsoft Word’s automatic table of contents generator to generate your TOC. If you’re not familiar with this functionality, the video below explains it simply:
If you find that your table of contents is overly lengthy, consider removing one level of depth. Oftentimes, this can be done without detracting from the usefulness of the TOC.
Right, now that the “admin” sections are out of the way, its time to move on to your core chapters. These chapters are the heart of your dissertation and are where you’ll earn the marks. The first chapter is the introduction chapter – as you would expect, this is the time to introduce your research…
It’s important to understand that even though you’ve provided an overview of your research in your abstract, your introduction needs to be written as if the reader has not read that (remember, the abstract is essentially a standalone document). So, your introduction chapter needs to start from the very beginning, and should address the following questions:
- What will you be investigating (in plain-language, big picture-level)?
- Why is that worth investigating? How is it important to academia or business? How is it sufficiently original?
- What are your research aims and research question(s)? Note that the research questions can sometimes be presented at the end of the literature review (next chapter).
- What is the scope of your study? In other words, what will and won’t you cover ?
- How will you approach your research? In other words, what methodology will you adopt?
- How will you structure your dissertation? What are the core chapters and what will you do in each of them?
These are just the bare basic requirements for your intro chapter. Some universities will want additional bells and whistles in the intro chapter, so be sure to carefully read your brief or consult your research supervisor.
If done right, your introduction chapter will set a clear direction for the rest of your dissertation. Specifically, it will make it clear to the reader (and marker) exactly what you’ll be investigating, why that’s important, and how you’ll be going about the investigation. Conversely, if your introduction chapter leaves a first-time reader wondering what exactly you’ll be researching, you’ve still got some work to do.
Now that you’ve set a clear direction with your introduction chapter, the next step is the literature review . In this section, you will analyse the existing research (typically academic journal articles and high-quality industry publications), with a view to understanding the following questions:
- What does the literature currently say about the topic you’re investigating?
- Is the literature lacking or well established? Is it divided or in disagreement?
- How does your research fit into the bigger picture?
- How does your research contribute something original?
- How does the methodology of previous studies help you develop your own?
Depending on the nature of your study, you may also present a conceptual framework towards the end of your literature review, which you will then test in your actual research.
Again, some universities will want you to focus on some of these areas more than others, some will have additional or fewer requirements, and so on. Therefore, as always, its important to review your brief and/or discuss with your supervisor, so that you know exactly what’s expected of your literature review chapter.

Now that you’ve investigated the current state of knowledge in your literature review chapter and are familiar with the existing key theories, models and frameworks, its time to design your own research. Enter the methodology chapter – the most “science-ey” of the chapters…
In this chapter, you need to address two critical questions:
- Exactly HOW will you carry out your research (i.e. what is your intended research design)?
- Exactly WHY have you chosen to do things this way (i.e. how do you justify your design)?
Remember, the dissertation part of your degree is first and foremost about developing and demonstrating research skills . Therefore, the markers want to see that you know which methods to use, can clearly articulate why you’ve chosen then, and know how to deploy them effectively.
Importantly, this chapter requires detail – don’t hold back on the specifics. State exactly what you’ll be doing, with who, when, for how long, etc. Moreover, for every design choice you make, make sure you justify it.
In practice, you will likely end up coming back to this chapter once you’ve undertaken all your data collection and analysis, and revise it based on changes you made during the analysis phase. This is perfectly fine. Its natural for you to add an additional analysis technique, scrap an old one, etc based on where your data lead you. Of course, I’m talking about small changes here – not a fundamental switch from qualitative to quantitative, which will likely send your supervisor in a spin!
You’ve now collected your data and undertaken your analysis, whether qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods. In this chapter, you’ll present the raw results of your analysis . For example, in the case of a quant study, you’ll present the demographic data, descriptive statistics, inferential statistics , etc.
Typically, Chapter 4 is simply a presentation and description of the data, not a discussion of the meaning of the data. In other words, it’s descriptive, rather than analytical – the meaning is discussed in Chapter 5. However, some universities will want you to combine chapters 4 and 5, so that you both present and interpret the meaning of the data at the same time. Check with your institution what their preference is.
Now that you’ve presented the data analysis results, its time to interpret and analyse them. In other words, its time to discuss what they mean, especially in relation to your research question(s).
What you discuss here will depend largely on your chosen methodology. For example, if you’ve gone the quantitative route, you might discuss the relationships between variables . If you’ve gone the qualitative route, you might discuss key themes and the meanings thereof. It all depends on what your research design choices were.
Most importantly, you need to discuss your results in relation to your research questions and aims, as well as the existing literature. What do the results tell you about your research questions? Are they aligned with the existing research or at odds? If so, why might this be? Dig deep into your findings and explain what the findings suggest, in plain English.
The final chapter – you’ve made it! Now that you’ve discussed your interpretation of the results, its time to bring it back to the beginning with the conclusion chapter . In other words, its time to (attempt to) answer your original research question s (from way back in chapter 1). Clearly state what your conclusions are in terms of your research questions. This might feel a bit repetitive, as you would have touched on this in the previous chapter, but its important to bring the discussion full circle and explicitly state your answer(s) to the research question(s).

Next, you’ll typically discuss the implications of your findings? In other words, you’ve answered your research questions – but what does this mean for the real world (or even for academia)? What should now be done differently, given the new insight you’ve generated?
Lastly, you should discuss the limitations of your research, as well as what this means for future research in the area. No study is perfect, especially not a Masters-level. Discuss the shortcomings of your research. Perhaps your methodology was limited, perhaps your sample size was small or not representative, etc, etc. Don’t be afraid to critique your work – the markers want to see that you can identify the limitations of your work. This is a strength, not a weakness. Be brutal!
This marks the end of your core chapters – woohoo! From here on out, it’s pretty smooth sailing.
The reference list is straightforward. It should contain a list of all resources cited in your dissertation, in the required format, e.g. APA , Harvard, etc.
It’s essential that you use reference management software for your dissertation. Do NOT try handle your referencing manually – its far too error prone. On a reference list of multiple pages, you’re going to make mistake. To this end, I suggest considering either Mendeley or Zotero. Both are free and provide a very straightforward interface to ensure that your referencing is 100% on point. I’ve included a simple how-to video for the Mendeley software (my personal favourite) below:
Some universities may ask you to include a bibliography, as opposed to a reference list. These two things are not the same . A bibliography is similar to a reference list, except that it also includes resources which informed your thinking but were not directly cited in your dissertation. So, double-check your brief and make sure you use the right one.
The very last piece of the puzzle is the appendix or set of appendices. This is where you’ll include any supporting data and evidence. Importantly, supporting is the keyword here.
Your appendices should provide additional “nice to know”, depth-adding information, which is not critical to the core analysis. Appendices should not be used as a way to cut down word count (see this post which covers how to reduce word count ). In other words, don’t place content that is critical to the core analysis here, just to save word count. You will not earn marks on any content in the appendices, so don’t try to play the system!
Time to recap…
And there you have it – the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows:
- Acknowledgments page
Most importantly, the core chapters should reflect the research process (asking, investigating and answering your research question). Moreover, the research question(s) should form the golden thread throughout your dissertation structure. Everything should revolve around the research questions, and as you’ve seen, they should form both the start point (i.e. introduction chapter) and the endpoint (i.e. conclusion chapter).
I hope this post has provided you with clarity about the traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout. If you have any questions or comments, please leave a comment below, or feel free to get in touch with us. Also, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog .

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

36 Comments
many thanks i found it very useful
Glad to hear that, Arun. Good luck writing your dissertation.
Such clear practical logical advice. I very much needed to read this to keep me focused in stead of fretting.. Perfect now ready to start my research!
what about scientific fields like computer or engineering thesis what is the difference in the structure? thank you very much
Thanks so much this helped me a lot!
Very helpful and accessible. What I like most is how practical the advice is along with helpful tools/ links.
Thanks Ade!
Thank you so much sir.. It was really helpful..
You’re welcome!
Hi! How many words maximum should contain the abstract?
Thank you so much 😊 Find this at the right moment
You’re most welcome. Good luck with your dissertation.
best ever benefit i got on right time thank you
Many times Clarity and vision of destination of dissertation is what makes the difference between good ,average and great researchers the same way a great automobile driver is fast with clarity of address and Clear weather conditions .
I guess Great researcher = great ideas + knowledge + great and fast data collection and modeling + great writing + high clarity on all these
You have given immense clarity from start to end.
Morning. Where will I write the definitions of what I’m referring to in my report?
Thank you so much Derek, I was almost lost! Thanks a tonnnn! Have a great day!
Thanks ! so concise and valuable
This was very helpful. Clear and concise. I know exactly what to do now.
Thank you for allowing me to go through briefly. I hope to find time to continue.
Really useful to me. Thanks a thousand times
Very interesting! It will definitely set me and many more for success. highly recommended.
Thank you soo much sir, for the opportunity to express my skills
Usefull, thanks a lot. Really clear
Very nice and easy to understand. Thank you .
That was incredibly useful. Thanks Grad Coach Crew!
My stress level just dropped at least 15 points after watching this. Just starting my thesis for my grad program and I feel a lot more capable now! Thanks for such a clear and helpful video, Emma and the GradCoach team!
Do we need to mention the number of words the dissertation contains in the main document?
It depends on your university’s requirements, so it would be best to check with them 🙂
Such a helpful post to help me get started with structuring my masters dissertation, thank you!
Great video; I appreciate that helpful information
It is so necessary or avital course
This blog is very informative for my research. Thank you
Doctoral students are required to fill out the National Research Council’s Survey of Earned Doctorates
wow this is an amazing gain in my life
This is so good
How can i arrange my specific objectives in my dissertation?
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- What Is A Literature Review (In A Dissertation Or Thesis) - Grad Coach - […] is to write the actual literature review chapter (this is usually the second chapter in a typical dissertation or…
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

File(s) under embargo
until file(s) become available
Applications of Combinatorial Graph Theory to the Classical and Post-Quantum Security Analysis of Memory-Hard Functions and Proofs of Sequential Work
Combinatorial graph theory is an essential tool in the design and analysis of cryptographic primitives such as Memory-Hard Functions (MHFs) and Proofs of Sequential Work (PoSWs). MHFs are used to design egalitarian Proofs of Work and to help protect low-entropy secrets such as user passwords against brute-force attacks in password hashing. A PoSW is a protocol for proving that one spent significant sequential computation work to validate some statement. PoSWs have many applications, including time-stamping, blockchain design, and universally verifiable CPU benchmarks. Prior work has used combinatorial properties of graphs to construct provably secure MHFs and PoSWs. However, some open problems still exist, such as improving security bounds for MHFs, finding approximation algorithms for measuring their memory hardness, and analyzing the post-quantum security of MHFs and PoSWs. This dissertation addresses these challenges in the security analysis of MHFs and PoSWs using combinatorial graph theory.
We first improve the understanding of the classical security of MHFs in the following ways. (1) We present improved security bounds for MHF candidates such as Argon2i and DRSample under plausible graph-theoretic conjectures. (2) We prove that it is Unique Games-hard to approximate the cumulative pebbling complexity of a directed acyclic graph, which is an important metric to understand the memory-hardness of data-independent MHFs. (3) We provide the first explicit construction of extremely depth-robust graphs with small indegree. Here, (extreme) depth-robustness is a crucial combinatorial tool to construct secure MHFs and PoSWs. (4) We build a new family of graphs that achieves better provable parameters for concrete depth-robustness.
Second, as we progress toward developing quantum computers, we initiate the post-quantum security analysis of MHFs and PoSWs. Specifically, we make the following contributions. (1) We introduce the parallel reversible pebbling game, which captures additional restrictions in quantum computing. We use combinatorial graph theory as a tool to analyze the space-time complexity and the cumulative pebbling complexity of MHF candidates such as Argon2i and DRSample in a reversible setting, which we call reversible space-time/cumulative pebbling cost, respectively. (2) We prove that the reversible cumulative pebbling cost is never too much larger than the classical cumulative pebbling cost, along with the separation result that, in some instances, the reversible cumulative pebbling cost is asymptotically larger than the classical one. (3) We prove that it is also Unique Games-hard to approximate the reversible cumulative pebbling cost of a directed acyclic graph. (4) Finally, we establish the post-quantum security of a PoSW from Cohen and Pietrzak (EUROCRYPT 2018) in the parallel quantum random oracle model by extending Zhandry's compressed oracle technique (CRYPTO 2019) and utilizing underlying combinatorial techniques of PoSWs.
CRII: SaTC: Towards the Development of Stronger Memory-Hard Functions for Secure Password Hashing
Directorate for Computer & Information Science & Engineering
Emerging Frontiers of Science of Information
Career: cryptographic tools for usable human authentication, purdue bilsland dissertation fellowship, degree type.
- Doctor of Philosophy
- Computer Science
Campus location
- West Lafayette
Advisor/Supervisor/Committee Chair
Additional committee member 2, additional committee member 3, additional committee member 4, additional committee member 5, usage metrics.
- Cryptography


COMMENTS
The results chapter (also referred to as the findings or analysis chapter) is one of the most important chapters of your dissertation or thesis because it shows the reader what you've found in terms of the quantitative data you've collected. It presents the data using a clear text narrative, supported by tables, graphs and charts.
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively. In quantitative research, for each question or hypothesis, state: The type of analysis used; Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics; Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
DISSERTATION CHAPTERS Order and format of dissertation chapters may vary by institution and department. 1. Introduction 2. Literature review 3. Methodology 4. Findings 5. Analysis and synthesis 6. Conclusions and recommendations Chapter 1: Introduction This chapter makes a case for the signifi-cance of the problem, contextualizes the
Step 1: Explain your methodological approach. Step 2: Describe your data collection methods. Step 3: Describe your analysis method. Step 4: Evaluate and justify the methodological choices you made. Tips for writing a strong methodology chapter. Other interesting articles.
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations of your study. The fourth step in writing up your discussion chapter is to acknowledge the limitations of the study. These limitations can cover any part of your study, from the scope or theoretical basis to the analysis method (s) or sample.
A dissertation is a long-form piece of academic writing based on original research conducted by you. It is usually submitted as the final step in order to finish a PhD program. Your dissertation is probably the longest piece of writing you've ever completed. It requires solid research, writing, and analysis skills, and it can be intimidating ...
An understanding of the data analysis that you will carry out on your data can also be an expected component of the Research Strategy chapter of your dissertation write-up (i.e., usually Chapter Three: Research Strategy). Therefore, it is a good time to think about the data analysis process if you plan to start writing up this chapter at this ...
Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of the Dissertation strong. 1. Reporting Quantitative Findings. The best way to present your quantitative findings is to structure them around the research hypothesis or questions you intend to address as part of your dissertation project. Report the relevant findings for each research ...
if you write a scientific dissertation, or anyway using quantitative methods, you will have some objective results that you will present in the Results chapter. You will then interpret the results in the Discussion chapter. B) More common for qualitative methods. - Analysis chapter. This can have more descriptive/thematic subheadings.
The structure of a dissertation depends on your field, but it is usually divided into at least four or five chapters (including an introduction and conclusion chapter). The most common dissertation structure in the sciences and social sciences includes: An introduction to your topic. A literature review that surveys relevant sources.
Types of Data Analysis for Dissertation. The various types of data Analysis in a Dissertation are as follows; 1. Qualitative Data Analysis. Qualitative data analysis is a type of data analysis that involves analyzing data that cannot be measured numerically. This data type includes interviews, focus groups, and open-ended surveys.
And place questionnaires, copies of focus groups and interviews, and data sheets in the appendix. On the other hand, one must put the statistical analysis and sayings quoted by interviewees within the dissertation. 8. Thoroughness of Data. It is a common misconception that the data presented is self-explanatory.
Data Analysis: Explain how you intend to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, thematic analysis, content analysis, etc., depending on the nature of your study. ... The dissertation methodology section plays an important role in a dissertation for several reasons. Here are some of the advantages of having a ...
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively. In quantitative research, for each question or hypothesis, state: The type of analysis used; Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics; Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
The process of data analysis in secondary research. Secondary analysis (i.e., the use of existing data) is a systematic methodological approach that has some clear steps that need to be followed for the process to be effective. In simple terms there are three steps: Step One: Development of Research Questions. Step Two: Identification of dataset.
In a thematic structure, the core chapters present analysis and discussion of different themes relevant to answer the research question and support the overall argument of the dissertation. The chapters will include analysis of texts/ research material. They can explore and connect academic theories/research to develop an argument.
The results chapter in a dissertation or thesis (or any formal academic research piece) is where you objectively and neutrally present the findings of your qualitative analysis (or analyses if you used multiple qualitative analysis methods ). This chapter can sometimes be combined with the discussion chapter (where you interpret the data and ...
How to analyse your dissertation. *Your dissertation analysis section is the single most important part of your dissertation. It will decide whether you get a First, Second, or Third class degree. Without analysis your work is likely to fail. Some universities expect there to be separate chapters that deal specifically with the presentation of ...
This article is a practical guide to conducting data analysis in general literature reviews. The general literature review is a synthesis and analysis of published research on a relevant clinical issue, and is a common format for academic theses at the bachelor's and master's levels in nursing, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, public health and other related fields.
Mastering Dissertation Data Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide. By Laura Brown on 29th December 2023. To craft an effective dissertation data analysis chapter, you need to follow some simple steps: Start by planning the structure and objectives of the chapter. Clearly set the stage by providing a concise overview of your research design and ...
Thematic analysis is a research method used to identify and interpret patterns or themes in a data set; it often leads to new insights and understanding (Boyatzis, 1998; Elliott, 2018; Thomas, 2006).However, it is critical that researchers avoid letting their own preconceptions interfere with the identification of key themes (Morse & Mitcham, 2002; Patton, 2015).
Some of the different areas throughout your essay that will benefit from effective engagement with source material include: your thesis statement, analysis, and conclusion. Thesis Statement. The argument that you make in your thesis statement can challenge, weaken, support, or strengthen what is being argued by your source or sources. Analysis.
Time to recap…. And there you have it - the traditional dissertation structure and layout, from A-Z. To recap, the core structure for a dissertation or thesis is (typically) as follows: Title page. Acknowledgments page. Abstract (or executive summary) Table of contents, list of figures and tables.
Through scaling analysis, we explore the fundamental limit of various ultrafast mechanisms. In the second part, we explore the phenomenon of "topological damping", where entanglement in a soft-material causes mechanical jamming when they experience external stress. ... In this thesis, I present three major works. We first examine the ...
How to Do Thematic Analysis | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples. Published on September 6, 2019 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on June 22, 2023. Thematic analysis is a method of analyzing qualitative data.It is usually applied to a set of texts, such as an interview or transcripts.The researcher closely examines the data to identify common themes - topics, ideas and patterns of meaning that come up ...
Combinatorial graph theory is an essential tool in the design and analysis of cryptographic primitives such as Memory-Hard Functions (MHFs) and Proofs of Sequential Work (PoSWs). MHFs are used to design egalitarian Proofs of Work and to help protect low-entropy secrets such as user passwords against brute-force attacks in password hashing. A PoSW is a protocol for proving that one spent ...