ON YOUR 1ST ORDER

How to Conclude a Literature Review
By Laura Brown on 6th March 2019
The conclusion of the dissertation literature review focuses on a few critical points,
- Highlight the essential parts of the existing body of literature in a concise way.
- Next, you should analyse the current state of the reviewed literature .
- Explain the research gap for your chosen topic/existing knowledge.
- Now, outline the areas for future study by mentioning main agreements and disagreements in the literature.
- Finally, link the research to existing knowledge .
Now, any of you who have been into research would agree that literature review is a very exhausting process and may stress you during your academic career. It is tougher because it requires you to be organised. We have seen many students asking does a literature review need a conclusion.
Well, the answer is simple, a good literature review will always have a proper ending. But there is nothing to worry about how to write a conclusion for a literature review. Here is a complete guide for you in “four” simple yet convenient steps. These steps can really be valuable in providing an excellent presentation to your literature review help . Furthermore, you can ask us for literature review conclusion examples anytime using our live chat or email option.
Now, without further ado, let’s move towards the steps.
How To Write A Literature Review Conclusion

Get Expert Assistance For Literature Review
Here are four major steps which can help you with how to conclude a literature review with ease.
1. Enlist Key Points
The conclusion can also be said as judgement because it gives a clear view of your work, whether you achieved your targeted objectives or not. Typically, it is not too difficult to conclude a review, but it can be challenging as well if not carried out properly.
It is crucial to find key features which should be engaging and useful as well for a reader. So at first, draft or enlist key factors before moving forward towards initialising your summary.
2. Summarise The Key Features Briefly
This is a most sensitive and important step of a dissertation literature review conclusion, where you should stick to the following things to get the job done efficiently.
- Once you are done drafting the important points , here you should mention them briefly.
- You can also take the liberty to agree or disagree with whatever literature you have gone through.
- Make sure you don’t drag your arguments while counter-arguing. Keeping your points specific is key.
- Describe, in one to two lines, how you addressed the previously identified gap .
- It is also important to point out the lapses you have noticed in previous authors’ work. Those lapses could be a misquotation of figures, a wrong pattern of research and so on.
- Alongside this, discuss existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research.
3. Educational Implications Of The Reviewed Literature
After mentioning the key factors, it is suggested to put implications to the already reviewed research. Like, as identifying problems in the already done research and giving recommendations on how these problems can be resolved.
Need Help in Writing Your Literature Review?
4. Indicating Room For Future Research
After completing the whole analysis of the particular research, you will be capable of identifying the work which can be done in future. You can also leave some gaps for future researchers so others can extend your work. This will be the final step, and this is how to end a literature review.
Tips That Can Enlighten Your Conclusion

We hope that things are very clear to you on how to write a conclusion for a literature review. If you want it to be even better and more meaningful, then you should keep the below points in mind.
- It should not be burdened with an unnecessary chain of details.
- It should be as precise and easy to understand as possible.
- You should mention important key points and findings .
- Make sure to put all points in a flow so the reader can understand your research in one go.
- Do not add anything from your own.
“Simply put, touch the prominent factors and leave them unexplained here”.
Get Help to Conclude Your Literature Review
If you are able to keep your focus around these steps and mentioned points, believe us, you will never ask anyone how to conclude literature review.
Looking At Literature Review Conclusion Example
Below are three examples which will help you understand how to conclude a literature review.
1. Firstly, you should summarise the important aspects and evaluate the current state of the existing literature.
Overall, the findings from this literature review highlight the need for further research to address the gaps in knowledge on the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression in college students.
2. Now, along with mentioning the gaps, come up with your approach to future study.
Therefore, to address this gap in the literature, we incorporated larger and more diverse samples, used standardised measures of mindfulness and mental health outcomes, and included longer follow-up periods to assess the long-term effects of mindfulness-based interventions on anxiety and depression.
3. Now summarise on how your findings will contribute to the particular field by linking it to the existing knowledge.
The findings from the study will provide important insights for researchers, clinicians, and educators interested in developing and implementing effective interventions to promote mental health and well-being among college students, and highlight the need for further research to establish the effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in this population.
We hope that these examples will bring in more clarification and you can have a better idea about the literature review conclusion.
What basically is a literature review?
What are the 3 primary parts of a literature review, what are the goals of writing a literature review.
There are four primary objectives of writing a literature review:
1. Determining the background from the previous scholarly literature related to the topic.
2. Identifying the gaps between literature to boost further research.
3. Analysing if the theory is applicable and associating a suitable methodology.
Why is a literature review conclusion necessary?
- https://azhin.org/cummings/basiclitreview/conclusions
- https://www.citewrite.qut.edu.au/write/writing-well/litreview.html
- https://psychology.ucsd.edu/undergraduate-program/undergraduate-resources/academic-writing-resources/writing-research-papers/writing-lit-review.html
- https://students.unimelb.edu.au/academic-skills/resources/report-writing/reviewing-the-literature

Laura Brown, a senior content writer who writes actionable blogs at Crowd Writer.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved August 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

The Guide to Literature Reviews

- What is a Literature Review?
- The Purpose of Literature Reviews
- Guidelines for Writing a Literature Review
- How to Organize a Literature Review?
- Software for Literature Reviews
- Using Artificial Intelligence for Literature Reviews
- How to Conduct a Literature Review?
- Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in a Literature Review
- Methods for Literature Reviews
- What is a Systematic Literature Review?
- What is a Narrative Literature Review?
- What is a Descriptive Literature Review?
- What is a Scoping Literature Review?
- What is a Realist Literature Review?
- What is a Critical Literature Review?
- Meta Analysis vs. Literature Review
- What is an Umbrella Literature Review?
- Differences Between Annotated Bibliographies and Literature Reviews
- Literature Review vs. Theoretical Framework
- How to Write a Literature Review?
- How to Structure a Literature Review?
- How to Make a Cover Page for a Literature Review?
- How to Write an Abstract for a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Introduction?
- How to Write the Body of a Literature Review?
How to Write the Conclusion of a Literature Review?
How to write a literature review conclusion, important reminders when writing a conclusion.
- How to Make a Literature Review Bibliography?
- How to Format a Literature Review?
- How Long Should a Literature Review Be?
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- How to Present a Literature Review?
- How to Publish a Literature Review?
Writing an effective conclusion for a literature review is a vital aspect of academic writing. It summarizes the key points and insights gained from analyzing literature review articles. An effective conclusion synthesizes existing knowledge and highlights the critical analysis of key concepts and theories. A good literature review conclusion ties together the findings from the research journey. It identifies gaps in the literature and suggests how further research can address important unanswered questions. This section demonstrates how the reviewed literature contributes to the broader context of the research area. In the social sciences, a strong conclusion emphasizes the importance of the research. It provides new insights and situates the findings within existing theories. This approach shows the relevance of the study and its implications for further research.

An effective conclusion also evaluates the current state of research. It reflects on the source material, offering a summary that connects key terms and ideas. This part of the literature review, found in the literature review section, not only reviews existing studies but also advances academic knowledge by proposing new areas for inquiry and exploration.
For example, in a few sentences, a literature review conclusion might summarize key points, highlight new ideas, and identify gaps in existing research. An introductory paragraph and a strong conclusion provide a comprehensive overview and set the stage for future directions in the field. Writing a good literature review involves crafting a conclusion that encapsulates the critical analysis and key concepts discussed, bringing the review to a thoughtful and informative close.
There are important aspects that conclusions need to have to be useful and close a literature review successfully. Use clear and concise language to convey key messages. Avoid ambiguity and vagueness in your conclusion. Focus on the significance and impact of the research, and highlight the key findings and implications of the literature review. Here are some important steps you can take when writing a literature review conclusion:
Summarize key findings . Briefly summarize the most important findings from your literature review. Highlight the major themes, patterns, and trends that emerged from the literature. This summary should encapsulate the core ideas without introducing new information.
Highlight research gaps . Identifying gaps in the existing literature is a crucial aspect of the conclusion. Point out areas that have not been thoroughly explored and clearly explain why it is important to address these unanswered questions. This helps establish the relevance and necessity of further investigation in your field of study.
Review your research question and objectives . Restate your research question and objectives in a concise and clear way, using different words than in the introduction. Briefly summarize the main themes or categories that you have discussed in the body of your literature review, and how they relate to your research question and objectives.

Discuss the implications. Discuss the broader implications of the findings. Explain how the insights gained from the literature review can impact your specific field or topic. This discussion should connect the reviewed literature to the larger academic or practical context, demonstrating the significance of your work. Synthesize your main findings to identify patterns and gaps. Integrate and compare the results and arguments of the different sources that you have reviewed, and show how they support or contradict each other. Highlight the most important or relevant points that you have made in the body of your literature review, and explain how they inform your research question or meet your objectives.
Reflect on the research process . Reflect on the methodology and approach used in your literature review, especially when you are writing a review as a full research paper. Consider any limitations encountered during the review process and how they might have influenced your findings. This reflection adds a layer of transparency and critical evaluation to your work.
Provide a final thought . End the conclusion with a final thought that encapsulates the overall importance of your literature review. This could be a call to action, a statement on the importance of ongoing research, or a prediction about future developments in your area of study. Focus on the significance and impact of the research. Explain how your literature review contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field, and how it informs or guides your own research project. Identify any gaps or limitations that still exist in the literature, and propose some possible directions or questions for further investigation.
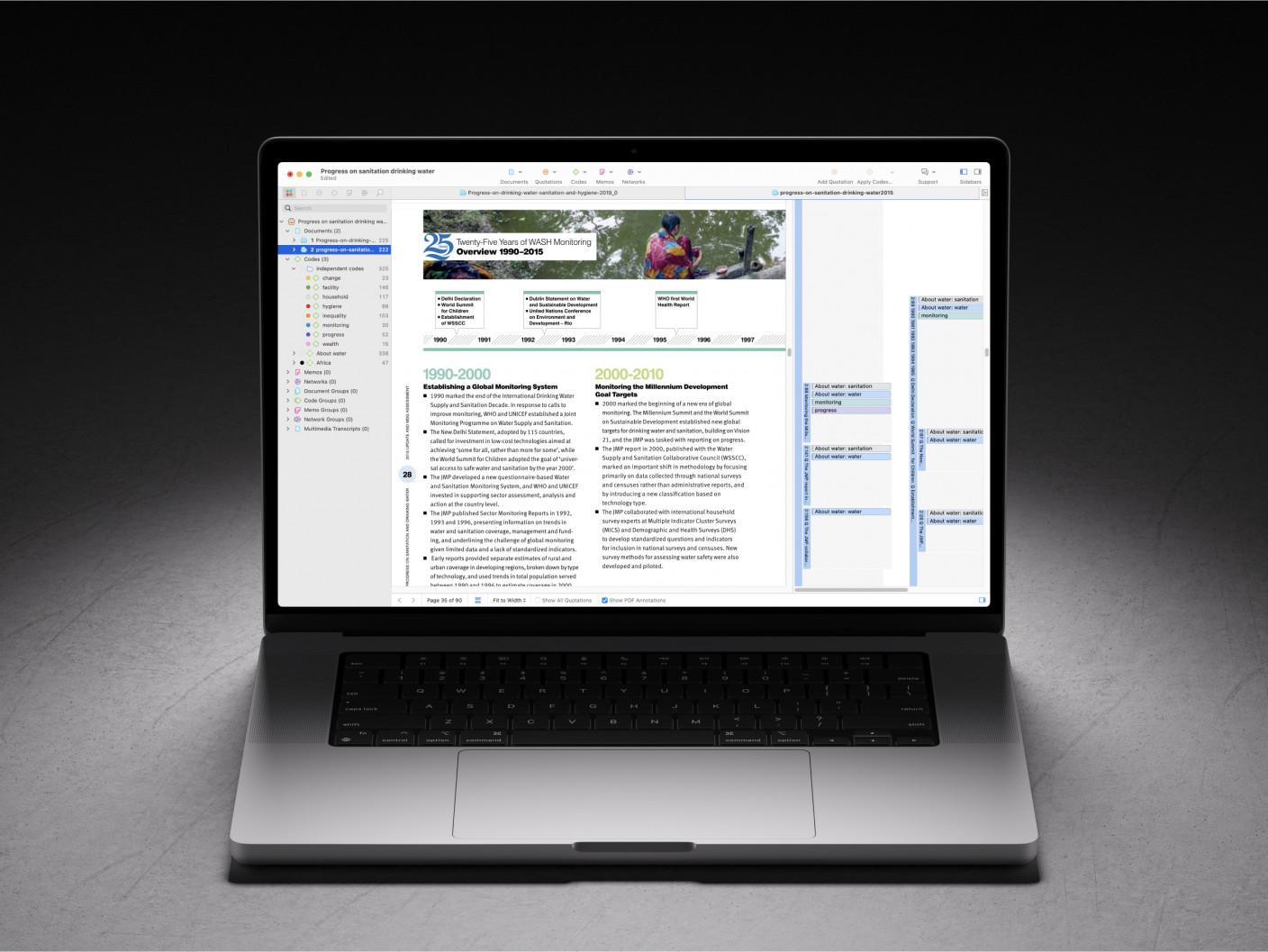
Quality literature reviews start with ATLAS.ti
From research objective to conclusion, ATLAS.ti is there for you at every step. See how with a free trial.
Use a logical structure to present your findings . Use a logical structure to present your findings , and organize your conclusion in a way that flows smoothly from the introduction and body of your literature review.
Use transitions to connect your ideas and paragraphs . Use transitions to connect your ideas and paragraphs, and make sure your conclusion is well-organized and easy to follow.
Avoid ambiguity and vagueness in your conclusion . Use clear and concise language to convey key messages, and avoid ambiguity and vagueness in your conclusion.
Steer clear of overly broad or general statements . Steer clear of overly broad or general statements, and focus on the specific key findings and implications of your literature review. Avoid introducing new information in your conclusion, and stick to summarizing the main points and findings of your literature review.
Discuss the limitations and gaps in the existing research . Discuss the limitations and gaps in the existing research, and identify areas for future research in your literature review. Explain how your literature review contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field, and how it informs or guides your own research project.
Identify areas for future research in your literature review . Propose some possible directions or questions for further investigation and discuss the limitations and gaps in the existing research. Explain how your research addresses these gaps and limitations.
Edit and revise your conclusion carefully . Make sure it is well-organized and easy to follow. Ensure consistency with the rest of your research paper, and check for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors.
Review your conclusion in the context of your entire literature review . Make sure it accurately reflects the content and significance of your research. Ensure your conclusion effectively summarizes your research findings, and provides a clear direction for future research.

The literature review conclusion is important because it synthesizes findings, highlights research gaps, establishes the review's significance, provides a coherent end, reflects on the research process , informs future research, and enhances academic rigor . These functions collectively ensure that the literature review is a valuable and impactful academic contribution. In a literature review conclusion, you should briefly summarize the most important findings from your literature review. Highlight the major themes, patterns, and trends that emerged from the literature. This summary should encapsulate the core ideas without introducing new information. Identifying gaps in the existing literature is a crucial aspect of the conclusion. Point out areas that have not been thoroughly explored and suggest potential directions for future research. This helps establish the relevance and necessity of further investigation in your field of study.

Develop powerful literature reviews with ATLAS.ti
Use our intuitive data analysis platform to make the most of your literature review.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

CREATE ACCOUNT LOG IN

Writing: Literature Review Basics
- What is Synthesis?
- Organizing Your Research
- Paraphrasing, Summary, or Direct Quotation?
- Introductions
- Conclusions
- All Writing Guides: Home
- CORE Library Home
The Job of the Conclusion
The job of the conclusion is, quite literally, to conclude ... or to wrap things up so the reader feels a sense of closure. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main argument.
Whereas an introduction started out generally and moved towards discussion of a specific focus, the conclusion takes the opposite approach. It starts by reminding the reader of the contents and importance of your findings and then moves out gradually to more general topics.
For most written assignments, the conclusion is a single paragraph. It does not introduce any new information; rather, it succinctly restates your chief conclusions and places the importance of your findings within your field. Depending upon the purpose of the literature review, you may also include a brief statement of future directions or self-reflection.
Here is an easy checklist for writing a conclusion:
Is the main argument of the paper accurately restated as the first sentence (but is not copied verbatim?
In a literature review, you basicaly want to answer the question, "What did I find out? What conclusions did I come to?" Giving the reader a one-sentence answer to this question that provides a summary of your findings is a solid way to begin a conclusion.
What recommendations do you have?
Here you may offer the reader your suggestions on what you think should happen next. You can make recommendations that are specific to the evidence you have uncovered, or you can make recommendations for future research. When this area is well done, it links to previous conclusions you have already made and gives the conclusion a finished feeling.
Did you remind the reader of the importance of the topic and how it can contribute to the knowledge in the field?
Make sure that the paper places its findings in the context of some kind of needed change, relevance, or solution. If you addressed why the topic was interesting, important, or relevant in your introduction, you can loop back to that here. Other ways that can be done are to remind the reader of other research you have discussed and how your work builds upon theirs, or what gaps there may yet be to explore.
Keep these items in mind as "what not to do":
Is there a sense of closure without using words such as "In conclusion?"
If you have to use the words "In conclusion" or similar ones to launch your conclusion so the reader knows the end is near, you've got a problem. Make sure the reader has a distinct sense that the paper has come to an end without telling them it is ending. It is important to not leave the reader hanging.
Did you avoid presenting any new information?
No new ideas should be introduced in the conclusion. It is simply a review of the material that is already present in the paper. The only new idea would be the suggesting of a direction for future research.
Stigmatization of the mentally ill is caused by the public’s belief in myths about the dangerousness of the mentally ill and exposing those myths can reduce stigmatization. At least one-third of the people sampled in one study said that they would both reject socially and fear violence from someone displaying behaviors associated with different mentally illnesses. Other research discovered that this rejection is associated to lack of contact with the mentally ill and that as contact increased, fear of the mentally ill decreased. The direction of the relationship between fear and rejection seems to be that fear (possibly based upon myths about mental illness) causes rejection. Taken as a whole, it appears that exposing these myths as myths increases the acceptance of the mentally ill and that staged contact with a mentally person to expose myths has an even more powerful effect. Caution must be advised, though; Martin et al.’s (2002) and Alexander and Link’s (2003) studies and the first study of Corrigan et al. (2002) were based upon paper and pencil methodologies. And while Corrigan et al.’s (2002) second study involved staged Myths of violence 6 presentations, it was conducted in a college setting with a college sample. Future research should replicate these findings in more natural settings with different populations.
Now let's break that down.
| Stigmatization of the mentally ill is caused by the public’s belief in myths about the dangerousness of the mentally ill and exposing those myths can reduce stigmatization. | This opening sentence reminds the reader of "what was I trying to figure out here?" |
| At least one-third of the people sampled in one study said that they would both reject socially and fear violence from someone displaying behaviors associated with different mentally illnesses. Other research discovered that this rejection is associated to lack of contact with the mentally ill and that as contact increased, fear of the mentally ill decreased. The direction of the relationship between fear and rejection seems to be that fear (possibly based upon myths about mental illness) causes rejection. Taken as a whole, it appears that exposing these myths as myths increases the acceptance of the mentally ill and that staged contact with a mentally person to expose myths has an even more powerful effect. | Summarizes the key points, or answers the question of "what conclusions did I come to?" |
| Taken as a whole, it appears that exposing these myths as myths increases the acceptance of the mentally ill and that staged contact with a mentally person to expose myths has an even more powerful effect. | This is why we should care! |
| Caution must be advised, though; Martin et al.’s (2002) and Alexander and Link’s (2003) studies and the first study of Corrigan et al. (2002) were based upon paper and pencil methodologies. And while Corrigan et al.’s (2002) second study involved staged Myths of violence 6 presentations, it was conducted in a college setting with a college sample. Future research should replicate these findings in more natural settings with different populations. | Recommendations for what happens next |
- << Previous: Introductions
- Next: All Writing Guides: Home >>
- Last Updated: Feb 12, 2024 9:02 AM
- URL: https://azhin.org/cummings/basiclitreview
© 2015 - 2024

What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
1. Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
2. Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
Find academic papers related to your research topic faster. Try Research on Paperpal
3. Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
4. Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
5. Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
6. Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

Strengthen your literature review with factual insights. Try Research on Paperpal for free!
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Write and Cite as you go with Paperpal Research. Start now for free.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
Whether you’re exploring a new research field or finding new angles to develop an existing topic, sifting through hundreds of papers can take more time than you have to spare. But what if you could find science-backed insights with verified citations in seconds? That’s the power of Paperpal’s new Research feature!
How to write a literature review faster with Paperpal?
Paperpal, an AI writing assistant, integrates powerful academic search capabilities within its writing platform. With the Research feature, you get 100% factual insights, with citations backed by 250M+ verified research articles, directly within your writing interface with the option to save relevant references in your Citation Library. By eliminating the need to switch tabs to find answers to all your research questions, Paperpal saves time and helps you stay focused on your writing.
Here’s how to use the Research feature:
- Ask a question: Get started with a new document on paperpal.com. Click on the “Research” feature and type your question in plain English. Paperpal will scour over 250 million research articles, including conference papers and preprints, to provide you with accurate insights and citations.
- Review and Save: Paperpal summarizes the information, while citing sources and listing relevant reads. You can quickly scan the results to identify relevant references and save these directly to your built-in citations library for later access.
- Cite with Confidence: Paperpal makes it easy to incorporate relevant citations and references into your writing, ensuring your arguments are well-supported by credible sources. This translates to a polished, well-researched literature review.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a good literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses. By combining effortless research with an easy citation process, Paperpal Research streamlines the literature review process and empowers you to write faster and with more confidence. Try Paperpal Research now and see for yourself.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
| Annotated Bibliography | Literature Review | |
| Purpose | List of citations of books, articles, and other sources with a brief description (annotation) of each source. | Comprehensive and critical analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. |
| Focus | Summary and evaluation of each source, including its relevance, methodology, and key findings. | Provides an overview of the current state of knowledge on a particular subject and identifies gaps, trends, and patterns in existing literature. |
| Structure | Each citation is followed by a concise paragraph (annotation) that describes the source’s content, methodology, and its contribution to the topic. | The literature review is organized thematically or chronologically and involves a synthesis of the findings from different sources to build a narrative or argument. |
| Length | Typically 100-200 words | Length of literature review ranges from a few pages to several chapters |
| Independence | Each source is treated separately, with less emphasis on synthesizing the information across sources. | The writer synthesizes information from multiple sources to present a cohesive overview of the topic. |
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- How Long Should a Chapter Be?
- How to Use Paperpal to Generate Emails & Cover Letters?
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, the ai revolution: authors’ role in upholding academic..., the future of academia: how ai tools are..., how to write a research proposal: (with examples..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), five things authors need to know when using..., 7 best referencing tools and citation management software..., maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing....
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 5 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- Literature Review Help
- Systematic Review Help
- Annotated Bibliographies Help
- Literature Review Editing & Proofreading
- Literature Review Topic Selection
- Literature Review Writing
- Literature Review Dissertation
- Literature Review Structure & Formatting
- UK Student Blog: Assignment Help, Lit Reviews, Insights
How to Write a Literature Review Conclusion

A literature review conclusion is the culminating chapter of a literature review . It draws together the key elements of your research and wraps up the story of how you came to your conclusions.
The conclusion should be concise and clear, summarising your argument and findings in a few sentences. It should also emphasise any implications for future research or practice that might result from your findings, and any connections between the different sources you have consulted during the writing process.
This blog provides some tips on how to write a literature review conclusion effectively. We will look at what this important final chapter should include and provide writing tips on how to write strong conclusions in general.
Table of Contents
Summarise the Main Findings of the Review
A literature review is an organised summary of scholarly sources that provide a comprehensive overview of research on a specific topic. Drawing upon previously established research and scholarship, the conclusion of your literature review should summarise the main finding of the review.
To do this, you will need to discuss the findings into several succinct points that convey the overall message of the literature review . Start by summarising each section—the introduction , body, and any additional sections—into key takeaways. Highlight specific quotes that stood out to you or caught your attention as you read through each source. Picking out certain phrases or concepts from each source can help you make connections between different authors and topics in the literature.
Synthesise and Evaluate the Studies
The conclusion should also synthesise and evaluate the studies you have discussed, showing how they support or contradict each other. It is also important to explain any relationships between the studies, including similarities and differences.
It’s important to remember that a literature review conclusion isn’t a stand-alone piece of writing—it should be integrated with your overall argument.
Addressing Research Gaps and Limitations
A literature review conclusion should be an opportunity to draw together the key themes, insights and conclusions from your research into the topic. It should provide answers to the questions you set out to answer, address any research gaps and limitations , and expand upon existing knowledge on the subject.
To achieve this, there are a few steps you can take:
Discuss Research Gaps and Limitations
When highlighting research gaps in a literature review , it is important to also provide potential solutions or recommendations for further study. Think critically about what could be done in future studies to address any limitations you encountered with your own research.
Expand on Existing Knowledge
Finally, use your conclusion as an opportunity to open up the discussion around existing knowledge on the subject. Consider how what you’ve learned could be applied in other contexts, or if more research is needed in order to deepen our understanding of the topic.
Implications and Practical Applications
When writing a literature review conclusion, it is important to consider the implications and practical applications of the research. Did the research lead to any new methods or processes that could be used for future studies? Did it provide any insights into how the topic can be applied in a practical setting?
When discussing implications and practical applications, it is important to consider:
- Potential implications of the research findings
- How the results can be used in practice
- The relevance and importance of the research
- Unanswered questions and areas for further exploration
Suggestions for Future Research
Now that you have successfully written and summarised the literature review , it is important to provide readers with some directions for future research. Suggestions for future research can come in many forms and may depend on the focus of the literature review . Some general suggestions include:
- Identifying gaps in current research and providing new areas to explore
- Developing further research questions or hypotheses
- Recommending further methodological approaches
- Exploring new ways of interpreting data or results
- Introducing innovative ideas or solutions to existing problems
When providing these suggestions, it is important to be specific and give concrete examples of what needs to be done. By doing so, you will have provided a valuable service to your readers and colleagues who are interested in the subject.
All in all, writing a literature review conclusion is a tough task that requires a lot of thought and research. The conclusions you draw should be supported by the evidence you have gathered in your literature review process. Make sure to be clear-cut and succinct, and remember to revisit your conclusion periodically to ensure that it is still valid. Be sure to back up your conclusions with reliable sources, and leave the readers with something to think about.
About Harry G.
What you can read next.

AI Resources Every Uni Student Should Bookmark

How a Custom Literature Review Template Can Boost Your Research

The Pros and Cons of Secondary Data Analysis in Literature Review
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Get Affordable Expert Help Today!

Welcome to our dedicated literature review services, designed to support UK students in their academic journey. We provide expert assistance in conducting comprehensive literature reviews, ensuring high-quality research and academic success.
- Systematic Review
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Editing & Proofreading
- Literature Review Structure & Formatting
- Literature Review Plan
- Psychology Literature Review
- Do My Assignment
- PhD Literature Review
- Conclusion on Literature Review
- Literature Review Outline
- Literature Review Table
- Tabular Literature Review
- Thematic Lit Review
- EPQ Literature Review
- Narrative Literature Review
- Thematic Literature Review
- Do My Homework
Email: [email protected]
Phone: +44 7308 518706
Address: 27 Market Place, Penzance, TR18 2JD, United Kingdom
Disclaimer: Documents provided by Literature Review serve as model papers and are not meant to be submitted directly to the university or reuse/resell in any way. They are written for individual research and reference purpose only.
Copyright © Literature Review All rights reserved.
About Us | Contact Us | Terms of Service | Privacy Policy | Sitemap
Limited Time Offer! - 40% OFF on all Services Get Expert Assistance Today!
Get Literature Review Help at Low Price!
How to Write a Literature Review
- What Is a Literature Review
- What Is the Literature
Writing the Review
Why Are You Writing This?
There are two primary points to remember as you are writing your literature review:
- Stand-alone review: provide an overview and analysis of the current state of research on a topic or question
- Research proposal: explicate the current issues and questions concerning a topic to demonstrate how your proposed research will contribute to the field
- Research report: provide the context to which your work is a contribution.
- Write as you read, and revise as you read more. Rather than wait until you have read everything you are planning to review, start writing as soon as you start reading. You will need to reorganize and revise it all later, but writing a summary of an article when you read it helps you to think more carefully about the article. Having drafts and annotations to work with will also make writing the full review easier since you will not have to rely completely on your memory or have to keep thumbing back through all the articles. Your draft does not need to be in finished, or even presentable, form. The first draft is for you, so you can tell yourself what you are thinking. Later you can rewrite it for others to tell them what you think.
General Steps for Writing a Literature Review
Here is a general outline of steps to write a thematically organized literature review. Remember, though, that there are many ways to approach a literature review, depending on its purpose.
- Stage one: annotated bibliography. As you read articles, books, etc, on your topic, write a brief critical synopsis of each. After going through your reading list, you will have an abstract or annotation of each source you read. Later annotations are likely to include more references to other works since you will have your previous readings to compare, but at this point the important goal is to get accurate critical summaries of each individual work.
- Stage two: thematic organization. Find common themes in the works you read, and organize the works into categories. Typically, each work you include in your review can fit into one category or sub-theme of your main theme, but sometimes a work can fit in more than one. (If each work you read can fit into all the categories you list, you probably need to rethink your organization.) Write some brief paragraphs outlining your categories, how in general the works in each category relate to each other, and how the categories relate to each other and to your overall theme.
- Stage three: more reading. Based on the knowledge you have gained in your reading, you should have a better understanding of the topic and of the literature related to it. Perhaps you have discovered specific researchers who are important to the field, or research methodologies you were not aware of. Look for more literature by those authors, on those methodologies, etc. Also, you may be able to set aside some less relevant areas or articles which you pursued initially. Integrate the new readings into your literature review draft. Reorganize themes and read more as appropriate.
- Stage four: write individual sections. For each thematic section, use your draft annotations (it is a good idea to reread the articles and revise annotations, especially the ones you read initially) to write a section which discusses the articles relevant to that theme. Focus your writing on the theme of that section, showing how the articles relate to each other and to the theme, rather than focusing your writing on each individual article. Use the articles as evidence to support your critique of the theme rather than using the theme as an angle to discuss each article individually.
- Stage five: integrate sections. Now that you have the thematic sections, tie them together with an introduction, conclusion, and some additions and revisions in the sections to show how they relate to each other and to your overall theme.
Specific Points to Include
More specifically, here are some points to address when writing about specific works you are reviewing. In dealing with a paper or an argument or theory, you need to assess it (clearly understand and state the claim) and analyze it (evaluate its reliability, usefulness, validity). Look for the following points as you assess and analyze papers, arguments, etc. You do not need to state them all explicitly, but keep them in mind as you write your review:
- Be specific and be succinct. Briefly state specific findings listed in an article, specific methodologies used in a study, or other important points. Literature reviews are not the place for long quotes or in-depth analysis of each point.
- Be selective. You are trying to boil down a lot of information into a small space. Mention just the most important points (i.e. those most relevant to the review's focus) in each work you review.
- Is it a current article? How old is it? Have its claims, evidence, or arguments been superceded by more recent work? If it is not current, is it important for historical background?
- What specific claims are made? Are they stated clearly?
- What evidence, and what type (experimental, statistical, anecdotal, etc) is offered? Is the evidence relevant? sufficient?
- What arguments are given? What assumptions are made, and are they warranted?
- What is the source of the evidence or other information? The author's own experiments, surveys, etc? Historical records? Government documents? How reliable are the sources?
- Does the author take into account contrary or conflicting evidence and arguments? How does the author address disagreements with other researchers?
- What specific conclusions are drawn? Are they warranted by the evidence?
- How does this article, argument, theory, etc, relate to other work?
These, however, are just the points that should be addressed when writing about a specific work. It is not an outline of how to organize your writing. Your overall theme and categories within that theme should organize your writing, and the above points should be integrated into that organization. That is, rather than write something like:
Smith (2019) claims that blah, and provides evidence x to support it, and says it is probably because of blip. But Smith seems to have neglected factor b. Jones (2021) showed that blah by doing y, which, Jones claims, means it is likely because of blot. But that methodology does not exclude other possibilities. Johnson (2022) hypothesizes blah might be because of some other cause.
list the themes and then say how each article relates to that theme. For example:
Researchers agree that blah (Smith 2019, Jones 2021, Johnson 2022), but they do not agree on why. Smith claims it is probably due to blip, but Jones, by doing y, tries to show it is likely because of blot. Jones' methodology, however, does not exclude other possibilities. Johnson hypothesizes ...
- << Previous: What Is the Literature
- Last Updated: Jan 11, 2024 9:48 AM
- URL: https://libguides.wesleyan.edu/litreview
15 Literature Review Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
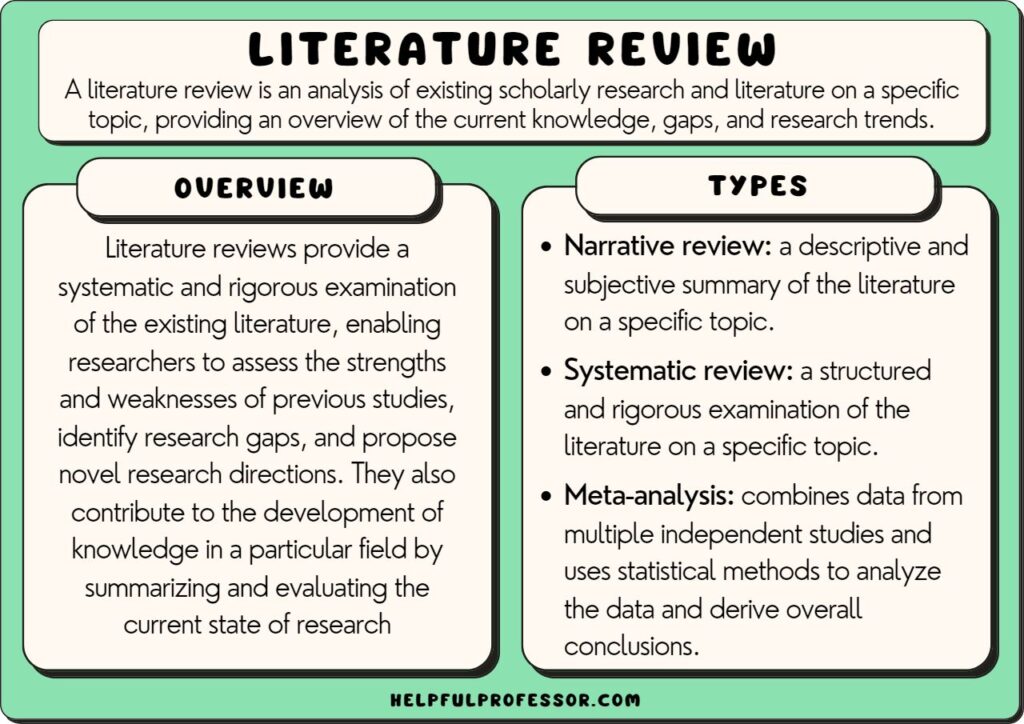
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here
3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Number Games for Kids (Free and Easy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Word Games for Kids (Free and Easy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Outdoor Games for Kids
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 50 Incentives to Give to Students
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Aug 8, 2024 11:00 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview


Literature Reviews
- What is a Literature Review?
- Steps for Creating a Literature Review
- Providing Evidence / Critical Analysis
- Challenges when writing a Literature Review
- Systematic Literature Reviews
Structuring Literature Reviews
Structuring/writing a literature review.
There are several common approaches when structuring a literature review:
- Chronological: This approach traces the development of the topic over time, analyzing patterns and key debates that have shaped the field.
- Thematic: Organizing the review around recurring central themes or aspects of the topic. For example, a review on migrant health outcomes might be divided into subsections on healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, etc..
- Methodological: This structure compares results and conclusions from different research approaches, such as qualitative vs. quantitative studies or empirical vs. theoretical scholarship.
- Theoretical : This approach discusses various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts related to the topic.
- Funnel approach: Moving from broad to specific, this structure starts with the wider context and gradually narrows down to the specific focus of your research.
Regardless of the chosen structure, a literature review typically includes:
- An introduction that outlines the purpose and scope of the review.
- A main body that presents, analyzes, and synthesizes the existing research.
- A conclusion that summarizes key findings and identifies gaps or areas for future research.
When grouping literature into subsections or themes, it's important to:
- Identify patterns and connections between different sources.
- Critically evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of existing research.
- Highlight controversies or debates within the field.
- Show how your research relates to or addresses gaps in the existing literature.
The best structure depends on your specific topic and goals. Generally, you want to group related studies together and present information in a logical flow, moving from broad to narrow focus. Use clear topic sentences and transitions between sections to guide the reader. It's important to synthesize findings across studies rather than just summarizing each one. Critically analyze the literature to identify key themes, debates, and gaps. Your own voice and analysis should come through as you evaluate the existing research. Remember to keep the focus on how the literature relates to your research questions or objectives. The structure should help tell the "story" of the current state of knowledge and how your work fits in.
Academics often use an "hour-glass structure" to describe the relationship between a literature review and a discussion section, with the review beginning broad, then focusing on the influence of previous research.
In your literature review, focus on relevant research that helps you understand your own investigation. Avoid referencing everything in the same depth, and prioritize recent studies. Older, dated studies should be highlighted briefly before discussing more accurate methods. This helps refine your understanding of wider issues and identify relevant research for your investigation.
Brown University Library (2024) Organizing and creating information . Available at: https://libguides.brown.edu/organize/litreview (Accessed: 31 July 2024).
Newcastle University (2024) Structuring the literature review . Available at: https://www.ncl.ac.uk/mediav8/academic-skills-kit/file-downloads/Structuring%20a%20literature%20review.pdf (Accessed: 31 July 2024).
Royal Literary Fund (2024) The structure of a literature review. Available at: https://www.rlf.org.uk/resources/the-structure-of-a-literature-review/ (Accessed 23 July 2024).
University of Westminster (2024) Literature reviews: structure . Available at: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/literature-reviews/structure (Accessed: 31 July 2024).
Further Reading:
Writing a literature review
- << Previous: Providing Evidence / Critical Analysis
- Next: Challenges when writing a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Aug 6, 2024 4:42 PM
- URL: https://library.lsbu.ac.uk/litreviews

How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
28 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Asking questions are actually fastidious thing if you are not understanding anything fully, but this article presents good understanding yet.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Writing well
How to write a literature review
- Starting well
- How to write an annotated bibliography
- How to write a case study response
- How to write a critique
- How to write an empirical article
- How to write an essay
- How to write a reflective task
- How to write a report
- Finishing well
Structure of a literature review
Determine your purpose.
Work out what you need to address in the literature review. What are you being asked to do in your literature review? What are you searching the literature to discover? Check your assignment question and your criteria sheet to know what to focus on.
Do an extensive search of the literature
Find out what has been written on the topic.
What kind of literature?
Select appropriate source material: Use a variety of academic or scholarly sources that are relevant, current and authoritative. An extensive review of relevant material will include — books, journal articles, reports, government documents, conference proceedings and web resources. The Library would be the best place to search for your sources.
How many resources?
The number of sources that you will be required to review will depend on what the literature review is for and how advanced you are in your studies. It could be from five sources at first year undergraduate level to more than fifty for a thesis. Your lecturer will advise you on these details.
Note the bibliographical details of your sources
Keep a note of the publication title, date, authors’ names, page numbers and publishers. These details will save you time later.
Read the literature
- Critically read each source, look for the arguments presented rather than for facts.
- Take notes as you read and start to organise your review around themes and ideas.
- Consider using a table, matrix or concept map to identify how the different sources relate to each other.
Analyse the literature you have found
In order for your writing to reflect strong critical analysis, you need to evaluate the sources. For each source you are reviewing ask yourself these questions:
- What are the key terms and concepts?
- How relevant is this article to my specific topic?
- What are the major relationships, trends and patterns?
- How has the author structured the arguments?
- How authoritative and credible is this source?
- What are the differences and similarities between the sources?
- Are there any gaps in the literature that require further study?
Write the review
- Start by writing your thesis statement. This is an important introductory sentence that will tell your reader what the topic is and the overall perspective or argument you will be presenting.
- Like essays, a literature review must have an introduction, a body and a conclusion.
Introduction
Your introduction should give an outline of:
- why you are writing a review, and why the topic is important
- the scope of the review — what aspects of the topic will be discussed
- the criteria used for your literature selection (e.g. type of sources used, date range)
- the organisational pattern of the review.
Body paragraphs
Each body paragraph should deal with a different theme that is relevant to your topic. You will need to synthesise several of your reviewed readings into each paragraph, so that there is a clear connection between the various sources. You will need to critically analyse each source for how they contribute to the themes you are researching.
The body could include paragraphs on:
- historical background
- methodologies
- previous studies on the topic
- mainstream versus alternative viewpoints
- principal questions being asked
- general conclusions that are being drawn.
Your conclusion should give a summary of:
- the main agreements and disagreements in the literature
- any gaps or areas for further research
- your overall perspective on the topic.
- outlined the purpose and scope?
- identified appropriate and credible (academic/scholarly) literature?
- recorded the bibliographical details of the sources?
- analysed and critiqued your readings?
- identified gaps in the literature and research?
- explored methodologies / theories / hypotheses / models?
- discussed the varying viewpoints?
- written an introduction, body and conclusion?
- checked punctuation and spelling?
Further information
- HiQ: Managing weekly readings
- HiQ: Notetaking
- HiQ: Structuring your assignment
- RMIT University: Literature review - Overview
Global links and information
- Referencing and using sources
- Background and development
- Changes to QUT cite|write
- Need more help?
- Current students
- Current staff
- TEQSA Provider ID: PRV12079 (Australian University)
- CRICOS No. 00213J
- ABN 83 791 724 622
- Last modified: 28-May-2024
- Accessibility
- Right to Information
- Feedback and suggestions

Acknowledgement of Traditional Owners
QUT acknowledges the Traditional Owners of the lands where QUT now stands.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
How to write a literature review introduction (+ examples)

The introduction to a literature review serves as your reader’s guide through your academic work and thought process. Explore the significance of literature review introductions in review papers, academic papers, essays, theses, and dissertations. We delve into the purpose and necessity of these introductions, explore the essential components of literature review introductions, and provide step-by-step guidance on how to craft your own, along with examples.
Why you need an introduction for a literature review
In academic writing , the introduction for a literature review is an indispensable component. Effective academic writing requires proper paragraph structuring to guide your reader through your argumentation. This includes providing an introduction to your literature review.
It is imperative to remember that you should never start sharing your findings abruptly. Even if there isn’t a dedicated introduction section .
When you need an introduction for a literature review
There are three main scenarios in which you need an introduction for a literature review:
What to include in a literature review introduction
It is crucial to customize the content and depth of your literature review introduction according to the specific format of your academic work.
In practical terms, this implies, for instance, that the introduction in an academic literature review paper, especially one derived from a systematic literature review , is quite comprehensive. Particularly compared to the rather brief one or two introductory sentences that are often found at the beginning of a literature review section in a standard academic paper. The introduction to the literature review chapter in a thesis or dissertation again adheres to different standards.
Academic literature review paper
The introduction of an academic literature review paper, which does not rely on empirical data, often necessitates a more extensive introduction than the brief literature review introductions typically found in empirical papers. It should encompass:
Regular literature review section in an academic article or essay
In a standard 8000-word journal article, the literature review section typically spans between 750 and 1250 words. The first few sentences or the first paragraph within this section often serve as an introduction. It should encompass:
In some cases, you might include:
Introduction to a literature review chapter in thesis or dissertation
Some students choose to incorporate a brief introductory section at the beginning of each chapter, including the literature review chapter. Alternatively, others opt to seamlessly integrate the introduction into the initial sentences of the literature review itself. Both approaches are acceptable, provided that you incorporate the following elements:
Examples of literature review introductions
Example 1: an effective introduction for an academic literature review paper.
To begin, let’s delve into the introduction of an academic literature review paper. We will examine the paper “How does culture influence innovation? A systematic literature review”, which was published in 2018 in the journal Management Decision.
Example 2: An effective introduction to a literature review section in an academic paper
The second example represents a typical academic paper, encompassing not only a literature review section but also empirical data, a case study, and other elements. We will closely examine the introduction to the literature review section in the paper “The environmentalism of the subalterns: a case study of environmental activism in Eastern Kurdistan/Rojhelat”, which was published in 2021 in the journal Local Environment.
Thus, the author successfully introduces the literature review, from which point onward it dives into the main concept (‘subalternity’) of the research, and reviews the literature on socio-economic justice and environmental degradation.
Examples 3-5: Effective introductions to literature review chapters
Numerous universities offer online repositories where you can access theses and dissertations from previous years, serving as valuable sources of reference. Many of these repositories, however, may require you to log in through your university account. Nevertheless, a few open-access repositories are accessible to anyone, such as the one by the University of Manchester . It’s important to note though that copyright restrictions apply to these resources, just as they would with published papers.
Master’s thesis literature review introduction
Phd thesis literature review chapter introduction, phd thesis literature review introduction.
The last example is the doctoral thesis Metacognitive strategies and beliefs: Child correlates and early experiences Chan, K. Y. M. (Author). 31 Dec 2020 . The author clearly conducted a systematic literature review, commencing the review section with a discussion of the methodology and approach employed in locating and analyzing the selected records.
Steps to write your own literature review introduction
Master academia, get new content delivered directly to your inbox, the best answers to "what are your plans for the future", 10 tips for engaging your audience in academic writing, related articles, minor revisions: sample peer review comments and examples, sample emails to your thesis supervisor, co-authorship guidelines to successfully co-author a scientific paper, how to select a journal for publication as a phd student.

Essay Conclusion
Essay conclusion generator.

Captivating your readers until the very end is a crucial goal in essay writing. The conclusion holds the power to leave a lasting impression, reinforcing your arguments and providing a sense of closure. In this article, we will delve into the art of crafting essay conclusions that resonate with your audience. Whether you’re a student seeking guidance or a seasoned writer in search of inspiration, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the tools to master the art of concluding your essays effectively.
1. Argumentative Essay Conclusion

Size: 110 KB
2. University Essay Conclusion

Size: 857 KB
3. Essay Conclusion Structure

Size: 529 KB
4. English Essay Conclusion

Size: 507 KB
5. Essay Paragraph Conclusion

Size: 66 KB
6. Essay on Mental Health Conclusion
7. Essay on Research Conclusion

Size: 668 KB
8. Social Media Essay Conclusion

Size: 220 KB
9. Education Essay Conclusion

Size: 42 KB
10. Essay Conclusion Sentence

Size: 58 KB
11. Call to Action Essay Conclusion

Size: 257 KB
12. Family Essay Conclusion

Size: 728 KB
13. Thesis Essay Conclusion

Size: 158 KB
14. Romeo and Juliet Essay Conclusion

Size: 103 KB
15. Air Pollution Essay Conclusion

16. Essay Conclusion Template

Size: 148 KB
17. Essay Conclusion Example

Size: 120 KB
18. Academic Essay Conclusion
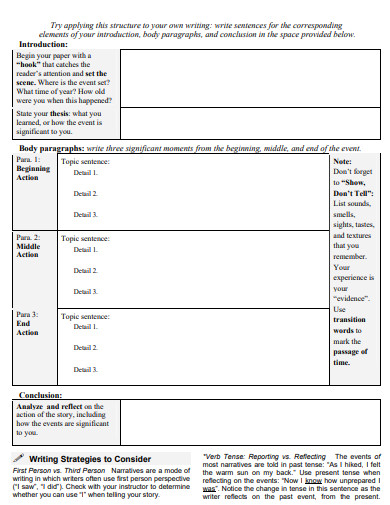
Size: 72 KB
19. Informative Essay Conclusion
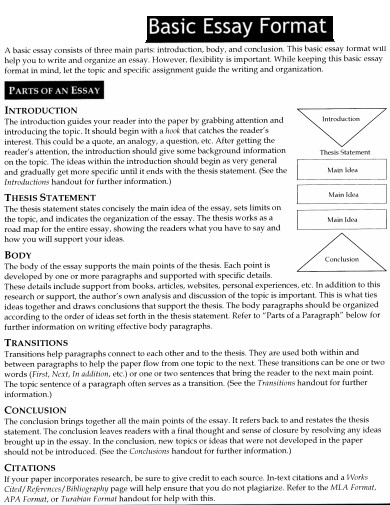
Size: 151 KB
20. Music Essay Conclusion

Size: 566 KB
21. 4th Grade Essay Conclusion

Size: 584 KB
22. 6th Grade Essay Conclusion
Size: 22 KB
23. Essay on Technology Conclusion

Size: 46 KB
24. Communication Essay Conclusion

Size: 494 KB
25. Deforestation Essay Conclusion

Size: 188 KB
26. Business Essay Conclusion

Size: 283 KB
27. Planning Guide Essay Conclusion

Size: 182 KB
28. Basic Essay Conclusion
Size: 123 KB
29. Leadership Essay Conclusion

Size: 194 KB
30. Standard Essay Conclusion

Size: 276 KB
What is an Essay Conclusion?
An essay conclusion serves as the final segment of your written composition. It brings together all the ideas, arguments, and evidence presented throughout the essay and synthesizes them into a concise and coherent final statement. Think of it as the grand finale that encapsulates your main points and leaves a lasting impression on your readers.
How to Write an Essay Conclusion
To create a compelling essay conclusion, follow these step-by-step guidelines
Step 1: Restate your thesis:
Begin by restating your thesis statement, reminding readers of the central argument you have been supporting throughout your essay. However, avoid repeating it verbatim. Instead, rephrase it to maintain reader engagement.
Step 2: Summarize your main points:
Provide a succinct summary of the key points and arguments discussed in the body paragraphs. Focus on the most significant aspects while maintaining a logical flow. Avoid introducing new information or ideas at this stage.
Step 3: Emphasize the significance:
Highlight the broader implications of your essay’s topic and the relevance of your arguments in a wider context. Convey the importance of your findings and their potential impact on the subject matter or the reader’s perspective.
Step 4: Evoke emotions:
Create an emotional connection with your readers by emphasizing the significance of your topic or appealing to their values and beliefs. Stirring emotions can leave a lasting impact and make your conclusion more memorable.
Step 5: Offer a call to action or recommendation:
Depending on the nature of your essay, conclude with a call to action or a thoughtful recommendation that encourages readers to consider further action or reflection on the topic. This can inspire them to continue exploring or take specific steps related to the subject matter.
What is the ideal length for an essay conclusion?
The length of an essay conclusion varies depending on the overall length of your essay. As a general guideline, aim for a conclusion that is concise yet comprehensive, spanning approximately 10-15% of your total essay length.
Can I introduce new information in my essay conclusion?
Avoid introducing new information or arguments in your conclusion. Instead, focus on summarizing and reinforcing the ideas already presented, providing a sense of closure to your essay.
How can I make my essay conclusion more impactful?
To make your essay conclusion more impactful, strive for clarity, emotional resonance, and a sense of closure. Utilize strong language, vivid imagery, and rhetorical devices to leave a lasting impression on your readers.
Just as every book needs a captivating ending to satisfy its readers, your essay deserves a conclusion that lingers in the minds of your audience. By employing the strategies discussed here, you can transform your essay conclusions into thought-provoking reflections, leaving your readers with a sense of fulfillment and a desire to explore your ideas further.
If you’re hungry for more examples and guidance, here are some related articles to inspire you:
- Dive into the world of narratives with 26+ Narrative Essay Examples in PDF .
- Explore the diverse realm of collage essays with 20+ College Essay Examples .
- Enhance your analytical skills with 4+ Interview Analysis Essay Examples in PDF .
- Master concise reporting with 11+ Short Report Essay Examples .
- Uncover the secrets of academic writing with 4+ Short Academic Essay Examples .
- Understand the essay text structure to elevate your writing.
- Delve into self-reflection with 7+ Self Evaluation Essay Examples in PDF .
- Craft persuasive arguments with an Argument Essay .
- For a comprehensive understanding of essay writing, refer to 21+ Essay Writing Examples in PD F.
Remember, the conclusion is your final chance to leave a lasting impact on your readers. Mastering the art of essay conclusions will undoubtedly elevate your writing and captivate your audience. So, go forth and craft memorable endings that resonate with the hearts and minds of your readers.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write an essay conclusion on the future of space exploration.
Develop an essay conclusion on the long-term effects of the internet on human cognition.
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with giant retinal tear: case series and literature review.

1. Introduction
2. materials and methods, 4. discussion, 5. conclusions, author contributions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
- Schepens, C.L.; Dobble, J.G.; Mcmeel, J.W. Retinal detachments with giant breaks: Preliminary report. Trans. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. 1962 , 66 , 471–479. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ang, G.S.; Townend, J.; Lois, N. Epidemiology of giant retinal tears in the United Kingdom: The British giant retinal tear epidemiology eye study (BGEES). Retina 2010 , 51 , 4781–4787. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Ghosh, Y.K.; Banerjee, S.; Savant, V.; Kotamarthi, V.; Benson, M.T.; Scott, R.A.; Tyagi, A.K. Surgical treatment and outcome of patients with giant retinal tears. Eye 2004 , 18 , 996–1000. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Shunmugam, M.; Ang, G.S.; Lois, N. Giant retinal tears. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2014 , 59 , 192–216. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Berrocal, M.H.; Chenworth, M.L.; Acaba, L.A. Management of Giant Retinal Tear Detachments. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2017 , 12 , 93–97. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Kohmoto, R.; Fukumoto, M.; Sato, T.; Oosuka, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Kida, T.; Suzuki, H.; Ikeda, T. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with a giant tear located in the intermediate periphery: Two case reports. Medicine 2019 , 98 , e14271. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Samanta, R.; Sood, G.; Waghamare, S.R.; Mareguddi, R.R.; Mittal, S.K.; Agrawal, A. Management of a unique case of post-traumatic posterior giant retinal tear and macular hole-associated rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020 , 68 , 2577–2580. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Sehgal, P.; Narang, S.; Chandra, D. Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with giant retinal tear in a child with Marfan’s syndrome: A rare ocular emergency. BMJ Case Rep. 2021 , 14 , e241354. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Goezinne, F.; LA Heij, E.C.; Berendschot, T.T.; Gast, S.T.; Liem, A.T.; Lundqvist, I.L.; Hendrikse, F. Low redetachment rate due to encircling scleral buckle in giant retinal tears treated with vitrectomy and silicone oil. Retina 2008 , 28 , 485–492. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Leaver, P.K.; Cooling, R.J.; Feretis, E.B.; Lean, J.S.; McLeod, D. Vitrectomy and fluid/ silicone-oil exchange for giant retinal tears: Results at six months. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1984 , 68 , 432–438. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fan, J.; Lin, J.; Fan, K.C.; Sridhar, J. The Perioperative Management of Giant Retinal Tears. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2020 , 60 , 103–113. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Bottoni, F.; Sborgia, M.; Arpa, P.; De Casa, N.; Bertazzi, E.; Monticelli, M.; De Molfetta, V. Perfluorocarbon liquids as postoperative short-term vitreous substitutes in complicated retinal detachment. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1993 , 231 , 619–628. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Sirimaharaj, M.; Balachandran, C.; Chan, W.C.; Hunyor, A.P.; Chang, A.A.; Gregory-Roberts, J.; Hunyor, A.B.; Playfair, T.J. Vitrectomy with short term postoperative tamponade using perfluorocarbon liquid for giant retinal tears. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2005 , 89 , 1176–1179. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Ambresin, A.; Wolfensberger, T.J.; Bovey, E.H. Management of giant retinal tears with vitrectomy, internal tamponade, and peripheral 360 degrees retinal photocoagulation. Retina 2003 , 23 , 622–628. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Batman, C.; Cekic, O. Vitrectomy with silicone oil or long-acting gas in eyes with giant retinal tears: Long-term follow-up of a randomized clinical trial. Retina 1999 , 19 , 188–192. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Er, H. Using perfluoro-n-octane as a postoperative tamponade in the management of giant retinal tears. Retina 2006 , 26 , 713. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chang, S.; Lincoff, H.; Zimmerman, N.J.; Fuchs, W. Giant retinal tears. Surgical techniques and results using perfluorocarbon liquids. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1989 , 107 , 761–766. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Nangia, V.; Jonas, J.B.; Sinha, A.; Matin, A.; Kulkarni, M.; Panda-Jonas, S. Ocular Axial Length and Its Associations in an Adult Population of Central Rural India: The Central India Eye and Medical Study. Ophthalmology 2010 , 117 , 1360–1366. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Tideman, J.W.; Snabel, M.C.; Tedja, M.S.; van Rijn, G.A.; Wong, K.T.; Kuijpers, R.W.; Vingerling, J.R.; Hofman, A.; Buitendijk, G.H.; Keunen, J.E.; et al. Association of Axial Length with Risk of Uncorrectable Visual Impairment for Europeans With Myopia. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016 , 134 , 1355–1363. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kertes, P.J.; Wafapoor, H.; Peyman, G.A.; Calixto, N., Jr.; Thompson, H. The management of giant retinal tears using perfluoroperhydrophenanthrene. A multicenter case series. Vitreon Collaborative Study Group. Ophthalmology 1997 , 104 , 1159–1165. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lee, S.Y.; Ong, S.G.; Wong, D.W.; Ang, C.L. Giant retinal tear management: An Asian experience. Eye 2009 , 23 , 601–605. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Fu, Y.; Xie, T.H.; Gu, Z.H.; Yang, N.; Geng, R.F.; Zhang, Y.L. Recurrent retinal detachment after pars plana vitrectomy with silicone oil tamponade for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Int. Ophthalmol. 2022 , 42 , 3813–3820. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Bopp, S.; Böhm, K. Reamotio mehr als 1 Jahr nach primär erfolgreicher Ablatiochirurgie: Ursachen und Häufigkeit [Late recurrences more than 1 year after primary successful surgery for rhegmatogenous retinal detachment]. Klin. Monatsblatter Fur Augenheilkd. 2008 , 225 , 227–235. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Quiroz-Reyes, M.A.; Quiroz-Gonzalez, E.A.; Kim-Lee, J.H.; Esparza-Correa, F.; Morales-Navarro, J.G.; Quiroz-Gonzalez, M.A.; Alsaber, A.R.; Moreno-Andrade, B.; Montano, M.; Lima-Gomez, V.; et al. A Critical Analysis of Postoperative Outcomes in Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment Associated with Giant Tears: A Consecutive, Multicenter Study. Res. Sq. 2021 , 1 , 1–42. [ Google Scholar ]
- Guner, M.E.; Guner, M.K.; Cebeci, Z.; Kır, N. Preoperative and Postoperative Factors Affecting Functional Success in Anatomically Successful Retinal Detachment Surgery. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2022 , 36 , 477–485. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Angermann, R.; Bechrakis, N.E.; Rauchegger, T.; Casazza, M.; Nowosielski, Y.; Zehetner, C. Effect of Timing on Visual Outcomes in Fovea-Involving Retinal Detachments Verified by SD-OCT. J. Ophthalmol. 2020 , 2020 , 2307935. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Frings, A.; Markau, N.; Katz, T.; Stemplewitz, B.; Skevas, C.; Druchkiv, V.; Wagenfeld, L. Visual recovery after retinal detachment with macula-off: Is surgery within the first 72 h better than after? Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016 , 100 , 1466–1469. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Van Bussel, E.M.; van der Valk, R.; Bijlsma, W.R.; La Heij, E.C. Impact of duration of macula-off retinal detachment on visual outcome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of literature. Retina 2014 , 34 , 1917–1925. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Greven, M.A.; Leng, T.; Silva, R.A.; Leung, L.B.; Karth, P.A.; Moshfeghi, D.M.; Sanislo, S.R.; Schachar, I.H. Reductions in final visual acuity occur even within the first 3 days after a macula-off retinal detachment. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019 , 103 , 1503–1506. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Scott, I.U.; Murray, T.G.; Flynn, H.W., Jr.; Feuer, W.J.; Schiffman, J.C.; Perfluoron Study Group. Outcomes and complications associated with giant retinal tear management using perfluoro-n-octane. Ophthalmology 2002 , 109 , 1828–1833. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Aptel, F.; Colin, C.; Kaderli, S.; Deloche, C.; Bron, A.M.; Stewart, M.W.; Chiquet, C.; OSIRIS Group. Management of postoperative inflammation after cataract and complex ocular surgeries: A systematic review and Delphi survey. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2017 , 101 , 1451–1460. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kim, S.J.; Lo, W.R.; Hubbard, G.B., 3rd; Srivastava, S.K.; Denny, J.P.; Martin, D.F.; Yan, J.; Bergstrom, C.S.; Cribbs, B.E.; Schwent, B.J.; et al. Topical ketorolac in vitreoretinal surgery: A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-masked trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2008 , 126 , 1203–1208. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Koerner, F.; Koener-Stiefbold, U.; Garweg, J.G. Systemic corticosteroids reduce the risk of cellophane membranes after retinal detachment surgery: A prospective randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012 , 250 , 981–987. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bonfiglio, V.; Reibaldi, M.; Macchi, I.; Fallico, M.; Pizzo, C.; Patane, C.; Russo, A.; Longo, A.; Pizzo, A.; Cillino, G.; et al. Preoperative, Intraoperative and Postoperative Corticosteroid Use as an Adjunctive Treatment for Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment. J. Clin. Med. 2020 , 9 , 1556. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Luo, L.J.; Yang, C.J.; Lai, J.Y. Highly Retina-Permeating and Long-Acting Resveratrol/Metformin Nanotherapeutics for Enhanced Treatment of Macular Degeneration. ACS Nano 2023 , 17 , 168–183. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ting, D.S.W.; Foo, V.H.X.; Tan, T.E.; Sie, N.M.; Wong, C.W.; Tsai, A.S.H.; Tan, G.S.W.; Lim, L.S.; Yeo, I.Y.S.; Wong, D.W.K.; et al. 25-years Trends and Risk factors related to Surgical Outcomes of Giant Retinal Tear-Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachments. Sci. Rep. 2020 , 10 , 5474. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Author (Year) | Eyes (n) | Mean Age (Years) | Sex (%) | Etiology | Retinal Reattachment | BCVA 20/40 or Better after OP | Recurrent RD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | F | Idiopathic | Trauma | High Myopia | Primary | Final | |||||
| Kertes et al. [ ] (1997) | 162 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 41 (23.5%) | 20 (12.3%) | 78 (48.1%) | 147 (90.7%) | 24 (14.8%) | 80 (49.4%) |
| Ambresin et al. [ ] (2003) | 18 | 44 | 72 | 28 | N/A | 2 (11.1%) | 7 (38.9%) | 16 (88.9%) | 17 (94.4%) | 9 (50.0%) | 2 (11.1%) |
| Gosh et al. [ ] (2004) | 29 | 35 | 86 | 14 | 10 (34.5%) | 9 (31.0%) | 10 (34.5%) | 19 (65.5%) | 25 (86.2%) | N/A | 6 (20.7%) |
| Sirimaharaj et al. [ ] (2005) | 62 | 44 | 84 | 16 | N/A | 19 (30.6%) | 10 (16.1%) | 49 (79.0%) | 58 (93.5%) | 27 (43.5%) | 13 (21.0%) |
| Goezinne et al. [ ] (2008) | 30 | 53 | N/A | N/A | N/A | 4 (13.3%) | N/A | 21 (70.0%) | 29 (96.7%) | N/A | 9 (30.0%) |
| Lee et al. [ ] (2008) | 128 | 40 | 91 | 9 | N/A | 17 (13.3%) | 52 (40.6%) | 71 (71.7%) | 84 (84.8%) | N/A | 15 (15.2%) |
| Ang et al. [ ] (2010) | 62 | 42 | 72 | 28 | 34 (54.8%) | 10 (16.1%) | 11 (17.7%) | 50 (87.7%) | 54 (94.7%) | 24 (42.1%) | 12 (21.1%) |
| Age | Sex | AXL (mm) | Days to OP | Follow-Up (Months) | BCVA before OP | BCVA after OP | Additional Barrier PC | Complication | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | 57 | M | 27.52 | 4 | 6 | 20/100 | 20/20 | 3 | - |
| Case 2 | 66 | M | 23.91 | 0 | 6 | 20/63 | 20/20 | 5 | - |
| Case 3 | 60 | M | 25.98 | 0 | 6 | 20/100 | 20/20 | 0 | Secondary ERM |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Lee, S.; Kim, J. Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Giant Retinal Tear: Case Series and Literature Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024 , 13 , 4690. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164690
Lee S, Kim J. Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Giant Retinal Tear: Case Series and Literature Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine . 2024; 13(16):4690. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164690
Lee, Siyun, and Joonhyung Kim. 2024. "Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Giant Retinal Tear: Case Series and Literature Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 16: 4690. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164690
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals

IMAGES
COMMENTS
By Laura Brown on 6th March 2019. The conclusion of the dissertation literature review focuses on a few critical points, Highlight the essential parts of the existing body of literature in a concise way. Next, you should analyse the current state of the reviewed literature. Explain the research gap for your chosen topic/existing knowledge.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
For example, in a few sentences, a literature review conclusion might summarize key points, highlight new ideas, and identify gaps in existing research. An introductory paragraph and a strong conclusion provide a comprehensive overview and set the stage for future directions in the field.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
For most written assignments, the conclusion is a single paragraph. It does not introduce any new information; rather, it succinctly restates your chief conclusions and places the importance of your findings within your field. Depending upon the purpose of the literature review, you may also include a brief statement of future directions or ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
he simplest thing of all—structure. Everything you write has three components: a beginning, a middle and an e. d and each serves a different purpose. In practice, this means your review will have an introduction, a main body where you review the literature an. a conclusion where you tie things up.
Your introduction should give an outline of why you are writing the review, and why the topic is important. ü "the scope of the review — what aspects of the topic will be discussed. ü the criteria used for your literature selection (e.g. type of sources used, date range) ü the organisational pattern of the review" (Citewrite, 2016 ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
If you're working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter, you've come to the right place.. In this video, we walk you through an A-grade literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction.We start off by discussing the five core sections of a literature review chapter by unpacking our free literature review template.
1. Restate your research question and objectives. 2. Synthesize your main findings. 3. Evaluate the quality and relevance of the sources. 4. Suggest implications and recommendations for future ...
A literature review conclusion is the culminating chapter of a literature review. It draws together the key elements of your research and wraps up the story of how you came to your conclusions. The conclusion should be concise and clear, summarising your argument and findings in a few sentences. It should also emphasise any implications for ...
Here is a general outline of steps to write a thematically organized literature review. Remember, though, that there are many ways to approach a literature review, depending on its purpose. Stage one: annotated bibliography. As you read articles, books, etc, on your topic, write a brief critical synopsis of each.
Literature Review Examples. For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics. 1. Narrative Review Examples ... Conclusion. Literature reviews don't have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong ...
1. Format of a literature review 2. Steps for writing a literature review . 1. Format of a literature review . A literature review follows an essay format (Introduction, Body, Conclusion) if you are asked to write it as a stand-alone essay. • Introduction . Topic sentences that contextualise your review (purpose, significance and scope)
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
The conclusion of the literature review should summarize the main findings, identify any gaps in the literature, and suggest areas for future research. It should also reiterate the importance of the research question or hypothesis and the contribution of the literature review to the overall research project. ... For example, after conducting a ...
Structuring/Writing a Literature Review. There are several common approaches when structuring a literature review: Chronological: This approach traces the development of the topic over time, analyzing patterns and key debates that have shaped the field. Thematic: Organizing the review around recurring central themes or aspects of the topic. For example, a review on migrant health outcomes ...
How To Structure Your Literature Review. Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components - an introduction, a body and a conclusion. Let's take a closer look at each of these. 1: The Introduction Section
Sample Literature Review Conclusion #2 Conclusion This research review's purpose is to help the reader understand different aspects posed by the research on the Deaf community's rejection to cochlear implants. This is significant because many hearing people have a different approach to cochlear implants than the Deaf do, often
Write the review. Start by writing your thesis statement. This is an important introductory sentence that will tell your reader what the topic is and the overall perspective or argument you will be presenting. Like essays, a literature review must have an introduction, a body and a conclusion.
Firstly, the amount of literature on second homes is very limited; widely neglected as a focus by a number of academics. The varied and dispersed nature of second-home literature means that it has not been able to ... LITeRaTuRe RevIew: COnCLuSIOn exaMPLe Title: "Second homes: Investigating local perceptions and ...
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
These sections serve to establish a scholarly basis for the research or discussion within the paper. In a standard 8000-word journal article, the literature review section typically spans between 750 and 1250 words. The first few sentences or the first paragraph within this section often serve as an introduction.
Objectives: This systematic literature review investigated the inter‐rater and test-retest reliability of case formulations. We considered the reliability of case formulations across a range of theoretical modalities and the general quality of the primary research studies. Methods: A systematic search of five electronic databases was conducted in addition to reference list trawling to find ...
Discover the art of crafting captivating essay conclusions that leave a lasting impact. Learn how to restate your thesis, summarize key points, evoke emotions, and offer recommendations. Explore examples and gain valuable insights in this comprehensive guide. Elevate your writing skills with 29+ Essay Conclusion Examples in PDF.
Conclusions: While limited by the small sample size, this report underscores the potential benefits of prompt surgical intervention, meticulous postoperative care, and proactive management of complications in RRD with GRT. Insights from these cases, supported by multiple literature reviews, may inform treatment strategies and highlight areas ...