- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence

How to Write a Business Plan: Beginner’s Guide (& Templates)

Written by: Chloe West

Thinking about starting a business? One of the first steps you’ll need to take is to write a business plan. A business plan can help guide you through your financial planning, marketing strategy, unique selling point and more.
Making sure you start your new business off on the right foot is key, and we’re here to help. We’ve put together this guide to help you write your first business plan. Or, you can skip the guide and dive right into a business plan template .
Ready to get started?
Here’s a short selection of 8 easy-to-edit business plan templates you can edit, share and download with Visme. View more templates below:

8-Step Process for Writing a Business Plan
What is a business plan, why is a business plan important, step #1: write your executive summary, step #2: put together your company description, step #3: conduct your market analysis, step #4: research your competition, step #5: outline your products or services, step #6: summarize your financial plan, step #7: determine your marketing strategy, step #8: showcase your organizational chart, 14 business plan templates to help you get started.
A business plan is a document that helps potential new business owners flesh out their business idea and put together a bird’s eye view of their business. Writing a business plan is an essential step in any startup’s ideation process.
Business plans help determine demographics, market analysis, competitive analysis, financial projections, new products or services, and so much more.
Each of these bits of information are important to have on hand when you’re trying to start a business or pitching investors for funds.
Here’s an example of a business plan that you can customize to incorporate your own business information.

We’re going to walk you through some of the most important parts of your business plan as well as how to write your own business plan in 8 easy steps.
If you’re in the beginning stages of starting a business , you might be wondering if it’s really worth your time to write out your business plan.
We’re here to tell you that it is.
A business plan is important for a number of reasons, but mostly because it helps to set you up for success right from the start.
Here are four reasons to prove to you why you need to start your business off on the right foot with a plan.
Reason #1: Set Realistic Goals and Milestones
Putting together a business plan helps you to set your objectives for growth and make realistic goals while you begin your business.
By laying out each of the steps you need to take in order to build a successful business, you’re able to be more reasonable about what your timeline is for achieving everything as well as what your financial projections are.
The best way to set goals is using the SMART goals guidelines, outlined below.

Reason #2: Grow Your Business Faster
Having a business plan helps you be more organized and strategic, improving the overall performance of your business as you start out. In fact, one study found that businesses with a plan grow 30% faster than businesses that don’t.
Doesn’t that sound reason enough alone to start out your business venture with a solidified plan? We thought so too, but we’ve still got two more reasons.
Reason #3: Minimize Risk
Starting a new business is uncharted territory. However, when you start with a roadmap for your journey, it makes it easier to see success and minimize the risks that come with startups.
Minimize risk and maximize profitability by documenting the most important parts of your business planning.
Reason #4: Secure Funding
And finally, our last reason that business plans are so important is that if you plan to pitch investors for funding for your new venture, they’re almost always going to want to see a detailed business plan before deciding whether or not to invest.
You can easily create your business plan and investor pitch deck right here with Visme. Just sign up for a free account below to get started.
Hey executives! Looking to cut design costs?
- Spend less time on presentations and more time strategizing
- Ensure your brand looks and feels visually consistent across all your organization's documents
- Impress clients and stakeholders with boardroom ready presentations
Sign up. It’s free.

The executive summary is a brief overview of your entire business plan, giving anyone who reads through your document a quick understanding of what they’re going to learn about your business idea.
However, you need to remember that some of the people who are going to read your business plan don’t want to or have time to read the entire thing. So your executive summary needs to incorporate all of the most important aspects of your plan.
Here’s an example of an executive summary from a business plan template you can customize and turn into your own.

Your executive summary should include:
- Key objective(s)
- Market research
- Competitor information
- Products/services
- Value proposition
- Overview of your financial plan
- How you’re going to actually start your business
One thing to note is that you should actually write your executive summary after the rest of your business plan so that you can properly summarize everything you’ve already created.
So at this point, simply leave a page blank for your executive summary so you can come back to it at the end of your business plan.

The next step is to write out a full description of your business and its core offerings. This section of your business plan should include your mission statement and objectives, along with your company history or overview.
In this section, you may also briefly describe your business formation details from a legal perspective.
Mission Statement
Don’t spend too much time trying to craft this. Your mission statement is a simple “why” you started this business. What are you trying to achieve? Or what does your business solve?
This can be anything from one single quote or a paragraph, but it doesn’t need to be much longer than that. In fact, this could be very similar to your value proposition.

What are your goals? What do you plan to achieve in the first 90 days or one year of your business? What kind of impact do you hope to make on the market?
These are all good points to include in your objectives section so anyone reading your business plan knows upfront what you hope to achieve.
History or Overview
If you’re not launching a brand new business or if you’ve previously worked on another iteration of this business, let potential investors know the history of your company.
If not, simply provide an overview of your business, sharing what it does or what it will do.

Your third step is to conduct a market analysis so you know how your business will fit into its target market. This page in your business plan is simply meant to summarize your findings. Most of your time should be spent actually doing the research.
Your market analysis needs to look at things like:
- Market size, and if it’s grown in recent years or shrinking
- The segment of the market you plan to target
- Demographics and behavior of your target audience
- The demand for your product or service
- Your competitive advantage or differentiation strategy
- The average price of your product or service
Put together a summary of your market analysis and industry research in a 1-2 page format, like we see below.

Your next step is to conduct a competitive analysis. While you likely touched on this briefly during your market analysis, now is the time to do a deep dive so that you have a good grasp on what your competitors are doing and how they are generating customers.
Start by creating a profile of all your existing competitors, or at the very least, your closest competitors – the ones who are offering very similar products or services to you, or are in a similar vicinity (if you’re opening a brick and mortar store).
Focus on their strengths and what they’re doing really well so that you can emulate their best qualities in your own way. Then, look at their weaknesses and what your business can do better.
Take note of their current marketing strategy, including the outlets you see a presence, whether it’s on social media, you hear a radio ad, you see a TV ad, etc. You won’t always find all of their marketing channels, but see what you can find online and on their website.

After this, take a minute to identify potential competitors based on markets you might try out in the future, products or services you plan to add to your offerings, and more.
Then put together a page or two in your business plan that highlights your competitive advantage and how you’ll be successful breaking into the market.
Step five is to dedicate a page to the products or services that your business plans to offer.
Put together a quick list and explanation of what each of the initial product or service offerings will be, but steer clear of industry jargon or buzzwords. This should be written in plain language so anyone reading has a full understanding of what your business will do.

You can have a simple list like we see in the sample page above, or you can dive a little deeper. Depending on your type of business, it might be a good idea to provide additional information about what each product or service entails.
The next step is to work on the financial data of your new business. What will your overhead be? How will your business make money? What are your estimated expenses and profits over the first few months to a year? The expenses should cover all the spending whether they are recurring costs or just one-time LLC filing fees .
There is so much that goes into your financial plan for a new business, so this is going to take some time to compile. Especially because this section of your business plan helps potential cofounders or investors understand if the idea is even viable.

Your financial plan should include at least five major sections:
- Sales Forecast: The first thing you want to include is a forecast or financial projection of how much you think your business can sell over the next year or so. Break this down into the different products, services or facets of your business.
- Balance Sheet: This section is essentially a statement of your company’s financial position. It includes existing assets, liabilities and equity to demonstrate the company’s overall financial health.
- Income Statement: Also known as a profit and loss statement (P&L), this covers your projected expenses and revenue, showcasing whether your business will be profitable or not.
- Operating Budget: A detailed outline of your business’s income and expenses. This should showcase that your business is bringing in more than it’s spending.
- Cash Flow Statements: This tracks how much cash your business has at any given point, regardless of whether customers or clients have paid their bills or have 30-60+ days to do so.
While these are the most common financial statements, you may discover that there are other sections that you want to include or that lenders may want to see from you.
You can automate the process of looking through your documents with an OCR API , which will collect the data from all your financial statements and invoices.
The next step is coming up with a successful marketing plan so that you can actually get the word out about your business.
Throughout your business plan, you’ve already researched your competitors and your target market, both of which are major components of a good marketing strategy. You need to know who you’re marketing to, and you want to do it better than your competition.

On this page or throughout this section of your business plan, you need to focus on your chosen marketing channels and the types of marketing content you plan to create.
Start by taking a look at the channels that your competitors are on and make sure you have a good understanding of the demographics of each channel as well. You don’t want to waste time on a marketing channel that your target audience doesn’t use.
Then, create a list of each of your planned marketing avenues. It might look something like:
- Social media ( Facebook, Instagram, Pinterest)
- Email newsletter
- Digital ads
Depending on the type of business you’re starting, this list could change quite a bit — and that’s okay. There is no one-size-fits-all marketing strategy, and you need to find the one that brings in the highest number of potential customers.
Your last section will be all about your leadership and management team members. Showcasing that you have a solid team right from the start can make potential investors feel better about funding your venture.
You can easily put together an organizational chart like the one below, with the founder/CEO at the top and each of your team leaders underneath alongside the department they’re in charge of.

Simply add an organizational chart like this as a page into your overall business plan and make sure it matches the rest of your design to create a cohesive document.
If you want to create a good business plan that sets your new business up for success and attracts new investors, it’s a good idea to start with a template.
We’ve got 14 options below from a variety of different industries for you to choose from. You can customize every aspect of each template to fit your business branding and design preferences.
If you're pressed for time, Visme's AI business plan generator can churn out compelling business plans in minutes. Just input a detailed prompt, choose the design, and watch the tool generate your plan in a few seconds.
Template #1: Photography Business Plan Template

This feminine and minimalistic business plan template is perfect for getting started with any kind of creative business. Utilize this template to help outline the step-by-step process of getting your new business idea up and running.
Template #2: Real Estate Business Plan Template

Looking for a more modern business plan design? This template is perfect for plainly laying out each of your business plans in an easy-to-understand format. Adjust the red accents with your business’s colors to personalize this template.
Template #3: Nonprofit Business Plan Template

Creating a business and marketing plan for your nonprofit is still an essential step when you’re just starting out. You need to get the word out to increase donations and awareness for your cause.
Template #4: Restaurant Business Plan Template

If your business plan needs to rely heavily on showcasing photos of your products (like food), this template is perfect for you. Get potential investors salivating at the sight of your business plan, and they’re sure to provide the capital you need.
Template #5: Fashion Business Plan Template

Serifs are in. Utilize this template with stunning serif as all the headers to create a contemporary and trendy business plan design that fits your business. Adjust the colors to match your brand and easily input your own content.
Template #6: Daycare Business Plan Template

Creating a more kid-friendly or playful business? This business plan template has bold colors and design elements that will perfectly represent your business and its mission.
Use the pages you need, and remove any that you don’t. You can also duplicate pages and move the elements around to add even more content to your business plan.
Template #7: Consulting Business Plan Template

This classic business plan template is perfect for a consulting business that wants to use a stunning visual design to talk about its services.
Template #8: Coffee Shop Business Plan Template

Customize this coffee shop business plan template to match your own business idea. Adjust the colors to fit your brand or industry, replace photos with your own photography or stock photos that represent your business, and insert your own logo, fonts and colors throughout.
Template #9: SaaS Business Plan Template

A SaaS or service-based company also needs a solid business plan that lays out its financials, list of services, target market and more. This template is the perfect starting point.
Template #10: Small Business Plan Template

Every startup or small business needs to start out with a strong business plan in order to start off on the right foot and set yourself up for success. This template is an excellent starting point for any small business.
Template #11: Ecommerce Business Plan Template

An ecommerce business plan is ideal for planning out your pricing strategy of all of your online products, as well as the site you plan to use for setting up your store, whether WordPress, Shopify, Wix or something else.
Template #12: Startup Business Plan Template

Customize this template and make it your own! Edit and Download
This is another generic business plan template for any type of startup to customize. Switch out the content, fonts and colors to match your startup branding and increase brand equity.
Template #13: One-Page Business Plan Template

Want just a quick business plan to get your idea going before you bite the bullet and map out your entire plan? This one-page template is perfect for those just starting to flesh out a new business idea.
Template #14: Salon Business Plan Template

This salon business plan template is easy on the design and utilizes a light color scheme to put more focus on the actual content. You can use the design as is or keep it as a basis for your own design elements.
Create Your Own Business Plan Today
Ready to write your business plan? Once you’ve created all of the most important sections, get started with a business plan template to really wow your investors and organize your startup plan.
Design beautiful visual content you can be proud of.

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Chloe West is the content marketing manager at Visme. Her experience in digital marketing includes everything from social media, blogging, email marketing to graphic design, strategy creation and implementation, and more. During her spare time, she enjoys exploring her home city of Charleston with her son.
14 Reasons Why You Need a Business Plan

10 min. read
Updated May 10, 2024

There’s no question that starting and running a business is hard work. But it’s also incredibly rewarding. And, one of the most important things you can do to increase your chances of success is to have a business plan.
A business plan is a foundational document that is essential for any company, no matter the size or age. From attracting potential investors to keeping your business on track—a business plan helps you achieve important milestones and grow in the right direction.

A business plan isn’t just a document you put together once when starting your business. It’s a living, breathing guide for existing businesses – one that business owners should revisit and update regularly.
Unfortunately, writing a business plan is often a daunting task for potential entrepreneurs. So, do you really need a business plan? Is it really worth the investment of time and resources? Can’t you just wing it and skip the whole planning process?
Good questions. Here’s every reason why you need a business plan.
- 1. Business planning is proven to help you grow 30 percent faster
Writing a business plan isn’t about producing a document that accurately predicts the future of your company. The process of writing your plan is what’s important. Writing your plan and reviewing it regularly gives you a better window into what you need to do to achieve your goals and succeed.
You don’t have to just take our word for it. Studies have proven that companies that plan and review their results regularly grow 30 percent faster. Beyond faster growth, research also shows that companies that plan actually perform better. They’re less likely to become one of those woeful failure statistics, or experience cash flow crises that threaten to close them down.
- 2. Planning is a necessary part of the fundraising process
One of the top reasons to have a business plan is to make it easier to raise money for your business. Without a business plan, it’s difficult to know how much money you need to raise, how you will spend the money once you raise it, and what your budget should be.
Investors want to know that you have a solid plan in place – that your business is headed in the right direction and that there is long-term potential in your venture.
A business plan shows that your business is serious and that there are clearly defined steps on how it aims to become successful. It also demonstrates that you have the necessary competence to make that vision a reality.
Investors, partners, and creditors will want to see detailed financial forecasts for your business that shows how you plan to grow and how you plan on spending their money.
- 3. Having a business plan minimizes your risk
When you’re just starting out, there’s so much you don’t know—about your customers, your competition, and even about operations.
As a business owner, you signed up for some of that uncertainty when you started your business, but there’s a lot you can do to reduce your risk . Creating and reviewing your business plan regularly is a great way to uncover your weak spots—the flaws, gaps, and assumptions you’ve made—and develop contingency plans.
Your business plan will also help you define budgets and revenue goals. And, if you’re not meeting your goals, you can quickly adjust spending plans and create more realistic budgets to keep your business healthy.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- 4. Crafts a roadmap to achieve important milestones
A business plan is like a roadmap for your business. It helps you set, track and reach business milestones.
For your plan to function in this way, your business plan should first outline your company’s short- and long-term goals. You can then fill in the specific steps necessary to reach those goals. This ensures that you measure your progress (or lack thereof) and make necessary adjustments along the way to stay on track while avoiding costly detours.
In fact, one of the top reasons why new businesses fail is due to bad business planning. Combine this with inflexibility and you have a recipe for disaster.
And planning is not just for startups. Established businesses benefit greatly from revisiting their business plan. It keeps them on track, even when the global market rapidly shifts as we’ve seen in recent years.
- 5. A plan helps you figure out if your idea can become a business
To turn your idea into reality, you need to accurately assess the feasibility of your business idea.
You need to verify:
- If there is a market for your product or service
- Who your target audience is
- How you will gain an edge over the current competition
- If your business can run profitably
A business plan forces you to take a step back and look at your business objectively, which makes it far easier to make tough decisions down the road. Additionally, a business plan helps you to identify risks and opportunities early on, providing you with the necessary time to come up with strategies to address them properly.
Finally, a business plan helps you work through the nuts and bolts of how your business will work financially and if it can become sustainable over time.
6. You’ll make big spending decisions with confidence
As your business grows, you’ll have to figure out when to hire new employees, when to expand to a new location, or whether you can afford a major purchase.
These are always major spending decisions, and if you’re regularly reviewing the forecasts you mapped out in your business plan, you’re going to have better information to use to make your decisions.
7. You’re more likely to catch critical cash flow challenges early
The other side of those major spending decisions is understanding and monitoring your business’s cash flow. Your cash flow statement is one of the three key financial statements you’ll put together for your business plan. (The other two are your balance sheet and your income statement (P&L).
Reviewing your cash flow statement regularly as part of your regular business plan review will help you see potential cash flow challenges earlier so you can take action to avoid a cash crisis where you can’t pay your bills.
- 8. Position your brand against the competition
Competitors are one of the factors that you need to take into account when starting a business. Luckily, competitive research is an integral part of writing a business plan. It encourages you to ask questions like:
- What is your competition doing well? What are they doing poorly?
- What can you do to set yourself apart?
- What can you learn from them?
- How can you make your business stand out?
- What key business areas can you outcompete?
- How can you identify your target market?
Finding answers to these questions helps you solidify a strategic market position and identify ways to differentiate yourself. It also proves to potential investors that you’ve done your homework and understand how to compete.
- 9. Determines financial needs and revenue models
A vital part of starting a business is understanding what your expenses will be and how you will generate revenue to cover those expenses. Creating a business plan helps you do just that while also defining ongoing financial needs to keep in mind.
Without a business model, it’s difficult to know whether your business idea will generate revenue. By detailing how you plan to make money, you can effectively assess the viability and scalability of your business.
Understanding this early on can help you avoid unnecessary risks and start with the confidence that your business is set up to succeed.
- 10. Helps you think through your marketing strategy
A business plan is a great way to document your marketing plan. This will ensure that all of your marketing activities are aligned with your overall goals. After all, a business can’t grow without customers and you’ll need a strategy for acquiring those customers.
Your business plan should include information about your target market, your marketing strategy, and your marketing budget. Detail things like how you plan to attract and retain customers, acquire new leads, how the digital marketing funnel will work, etc.
Having a documented marketing plan will help you to automate business operations, stay on track and ensure that you’re making the most of your marketing dollars.
- 11. Clarifies your vision and ensures everyone is on the same page
In order to create a successful business, you need a clear vision and a plan for how you’re going to achieve it. This is all detailed with your mission statement, which defines the purpose of your business, and your personnel plan, which outlines the roles and responsibilities of current and future employees. Together, they establish the long-term vision you have in mind and who will need to be involved to get there.
Additionally, your business plan is a great tool for getting your team in sync. Through consistent plan reviews, you can easily get everyone in your company on the same page and direct your workforce toward tasks that truly move the needle.
- 12. Future-proof your business
A business plan helps you to evaluate your current situation and make realistic projections for the future.
This is an essential step in growing your business, and it’s one that’s often overlooked. When you have a business plan in place, it’s easier to identify opportunities and make informed decisions based on data.
Therefore, it requires you to outline goals, strategies, and tactics to help the organization stay focused on what’s important.
By regularly revisiting your business plan, especially when the global market changes, you’ll be better equipped to handle whatever challenges come your way, and pivot faster.
You’ll also be in a better position to seize opportunities as they arise.
Further Reading: 5 fundamental principles of business planning
- 13. Tracks your progress and measures success
An often overlooked purpose of a business plan is as a tool to define success metrics. A key part of writing your plan involves pulling together a viable financial plan. This includes financial statements such as your profit and loss, cash flow, balance sheet, and sales forecast.
By housing these financial metrics within your business plan, you suddenly have an easy way to relate your strategy to actual performance. You can track progress, measure results, and follow up on how the company is progressing. Without a plan, it’s almost impossible to gauge whether you’re on track or not.
Additionally, by evaluating your successes and failures, you learn what works and what doesn’t and you can make necessary changes to your plan. In short, having a business plan gives you a framework for measuring your success. It also helps with building up a “lessons learned” knowledge database to avoid costly mistakes in the future.
- 14. Your business plan is an asset if you ever want to sell
Down the road, you might decide that you want to sell your business or position yourself for acquisition. Having a solid business plan is going to help you make the case for a higher valuation. Your business is likely to be worth more to a buyer if it’s easy for them to understand your business model, your target market, and your overall potential to grow and scale.

Free business plan template
Join over 1-million businesses and make planning easy with our simple, modern, investor-approved business plan template.
Download Template
- Writing your business plan
By taking the time to create a business plan, you ensure that your business is heading in the right direction and that you have a roadmap to get there. We hope that this post has shown you just how important and valuable a business plan can be. While it may still seem daunting, the benefits far outweigh the time investment and learning curve for writing one.
Luckily, you can write a plan in as little as 30 minutes. And there are plenty of excellent planning tools and business plan templates out there if you’re looking for more step-by-step guidance. Whatever it takes, write your plan and you’ll quickly see how useful it can be.
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- 6. You’ll make big spending decisions with confidence
- 7. You’re more likely to catch critical cash flow challenges early
Related Articles

7 Min. Read
8 Business Plan Templates You Can Get for Free

5 Min. Read
How to Run a Productive Monthly Business Plan Review Meeting

11 Min. Read
Use This Simple Business Plan Outline Example to Organize Your Plan

5 Consequences of Skipping a Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 28, 2024
Years ago, I had an idea to launch a line of region-specific board games. I knew there was a market for games that celebrated local culture and heritage. I was so excited about the concept and couldn't wait to get started.

But my idea never took off. Why? Because I didn‘t have a plan. I lacked direction, missed opportunities, and ultimately, the venture never got off the ground.

And that’s exactly why a business plan is important. It cements your vision, gives you clarity, and outlines your next step.
In this post, I‘ll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you’d need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
Table of Contents
What is a business plan?
What is a business plan used for.
- Business Plan Template [Download Now]
Purposes of a Business Plan
What does a business plan need to include, types of business plans.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections. It provides a detailed description of the business, including its products or services, target market, competitive landscape, and marketing and sales strategies. The plan also includes a financial section that forecasts revenue, expenses, and cash flow, as well as a funding request if the business is seeking investment.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

23 of My Favorite Free Marketing Newsletters
![most important business planning The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/free-flowchart-template-1-20240716-6679104-1.webp)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

18 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![most important business planning 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-1-20240625-3861486-1.webp)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![most important business planning How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]
20 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2024

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
How to Write a Business Plan in 9 Steps (+ Template and Examples)
Every successful business has one thing in common, a good and well-executed business plan. A business plan is more than a document, it is a complete guide that outlines the goals your business wants to achieve, including its financial goals . It helps you analyze results, make strategic decisions, show your business operations and growth.
If you want to start a business or already have one and need to pitch it to investors for funding, writing a good business plan improves your chances of attracting financiers. As a startup, if you want to secure loans from financial institutions, part of the requirements involve submitting your business plan.
Writing a business plan does not have to be a complicated or time-consuming process. In this article, you will learn the step-by-step process for writing a successful business plan.
You will also learn what you need a business plan for, tips and strategies for writing a convincing business plan, business plan examples and templates that will save you tons of time, and the alternatives to the traditional business plan.
Let’s get started.
What Do You Need A Business Plan For?
Businesses create business plans for different purposes such as to secure funds, monitor business growth, measure your marketing strategies, and measure your business success.
1. Secure Funds
One of the primary reasons for writing a business plan is to secure funds, either from financial institutions/agencies or investors.
For you to effectively acquire funds, your business plan must contain the key elements of your business plan . For example, your business plan should include your growth plans, goals you want to achieve, and milestones you have recorded.
A business plan can also attract new business partners that are willing to contribute financially and intellectually. If you are writing a business plan to a bank, your project must show your traction , that is, the proof that you can pay back any loan borrowed.
Also, if you are writing to an investor, your plan must contain evidence that you can effectively utilize the funds you want them to invest in your business. Here, you are using your business plan to persuade a group or an individual that your business is a source of a good investment.
2. Monitor Business Growth
A business plan can help you track cash flows in your business. It steers your business to greater heights. A business plan capable of tracking business growth should contain:
- The business goals
- Methods to achieve the goals
- Time-frame for attaining those goals
A good business plan should guide you through every step in achieving your goals. It can also track the allocation of assets to every aspect of the business. You can tell when you are spending more than you should on a project.
You can compare a business plan to a written GPS. It helps you manage your business and hints at the right time to expand your business.
3. Measure Business Success
A business plan can help you measure your business success rate. Some small-scale businesses are thriving better than more prominent companies because of their track record of success.
Right from the onset of your business operation, set goals and work towards them. Write a plan to guide you through your procedures. Use your plan to measure how much you have achieved and how much is left to attain.
You can also weigh your success by monitoring the position of your brand relative to competitors. On the other hand, a business plan can also show you why you have not achieved a goal. It can tell if you have elapsed the time frame you set to attain a goal.
4. Document Your Marketing Strategies
You can use a business plan to document your marketing plans. Every business should have an effective marketing plan.
Competition mandates every business owner to go the extraordinary mile to remain relevant in the market. Your business plan should contain your marketing strategies that work. You can measure the success rate of your marketing plans.
In your business plan, your marketing strategy must answer the questions:
- How do you want to reach your target audience?
- How do you plan to retain your customers?
- What is/are your pricing plans?
- What is your budget for marketing?

How to Write a Business Plan Step-by-Step
1. create your executive summary.
The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans . Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.

Generally, there are nine sections in a business plan, the executive summary should condense essential ideas from the other eight sections.
A good executive summary should do the following:
- A Snapshot of Growth Potential. Briefly inform the reader about your company and why it will be successful)
- Contain your Mission Statement which explains what the main objective or focus of your business is.
- Product Description and Differentiation. Brief description of your products or services and why it is different from other solutions in the market.
- The Team. Basic information about your company’s leadership team and employees
- Business Concept. A solid description of what your business does.
- Target Market. The customers you plan to sell to.
- Marketing Strategy. Your plans on reaching and selling to your customers
- Current Financial State. Brief information about what revenue your business currently generates.
- Projected Financial State. Brief information about what you foresee your business revenue to be in the future.
The executive summary is the make-or-break section of your business plan. If your summary cannot in less than two pages cannot clearly describe how your business will solve a particular problem of your target audience and make a profit, your business plan is set on a faulty foundation.
Avoid using the executive summary to hype your business, instead, focus on helping the reader understand the what and how of your plan.
View the executive summary as an opportunity to introduce your vision for your company. You know your executive summary is powerful when it can answer these key questions:
- Who is your target audience?
- What sector or industry are you in?
- What are your products and services?
- What is the future of your industry?
- Is your company scaleable?
- Who are the owners and leaders of your company? What are their backgrounds and experience levels?
- What is the motivation for starting your company?
- What are the next steps?
Writing the executive summary last although it is the most important section of your business plan is an excellent idea. The reason why is because it is a high-level overview of your business plan. It is the section that determines whether potential investors and lenders will read further or not.
The executive summary can be a stand-alone document that covers everything in your business plan. It is not uncommon for investors to request only the executive summary when evaluating your business. If the information in the executive summary impresses them, they will ask for the complete business plan.
If you are writing your business plan for your planning purposes, you do not need to write the executive summary.
2. Add Your Company Overview
The company overview or description is the next section in your business plan after the executive summary. It describes what your business does.
Adding your company overview can be tricky especially when your business is still in the planning stages. Existing businesses can easily summarize their current operations but may encounter difficulties trying to explain what they plan to become.
Your company overview should contain the following:
- What products and services you will provide
- Geographical markets and locations your company have a presence
- What you need to run your business
- Who your target audience or customers are
- Who will service your customers
- Your company’s purpose, mission, and vision
- Information about your company’s founders
- Who the founders are
- Notable achievements of your company so far
When creating a company overview, you have to focus on three basics: identifying your industry, identifying your customer, and explaining the problem you solve.
If you are stuck when creating your company overview, try to answer some of these questions that pertain to you.
- Who are you targeting? (The answer is not everyone)
- What pain point does your product or service solve for your customers that they will be willing to spend money on resolving?
- How does your product or service overcome that pain point?
- Where is the location of your business?
- What products, equipment, and services do you need to run your business?
- How is your company’s product or service different from your competition in the eyes of your customers?
- How many employees do you need and what skills do you require them to have?
After answering some or all of these questions, you will get more than enough information you need to write your company overview or description section. When writing this section, describe what your company does for your customers.

The company description or overview section contains three elements: mission statement, history, and objectives.
- Mission Statement
The mission statement refers to the reason why your business or company is existing. It goes beyond what you do or sell, it is about the ‘why’. A good mission statement should be emotional and inspirational.
Your mission statement should follow the KISS rule (Keep It Simple, Stupid). For example, Shopify’s mission statement is “Make commerce better for everyone.”
When describing your company’s history, make it simple and avoid the temptation of tying it to a defensive narrative. Write it in the manner you would a profile. Your company’s history should include the following information:
- Founding Date
- Major Milestones
- Location(s)
- Flagship Products or Services
- Number of Employees
- Executive Leadership Roles
When you fill in this information, you use it to write one or two paragraphs about your company’s history.
Business Objectives
Your business objective must be SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.) Failure to clearly identify your business objectives does not inspire confidence and makes it hard for your team members to work towards a common purpose.
3. Perform Market and Competitive Analyses to Proof a Big Enough Business Opportunity
The third step in writing a business plan is the market and competitive analysis section. Every business, no matter the size, needs to perform comprehensive market and competitive analyses before it enters into a market.
Performing market and competitive analyses are critical for the success of your business. It helps you avoid entering the right market with the wrong product, or vice versa. Anyone reading your business plans, especially financiers and financial institutions will want to see proof that there is a big enough business opportunity you are targeting.
This section is where you describe the market and industry you want to operate in and show the big opportunities in the market that your business can leverage to make a profit. If you noticed any unique trends when doing your research, show them in this section.
Market analysis alone is not enough, you have to add competitive analysis to strengthen this section. There are already businesses in the industry or market, how do you plan to take a share of the market from them?
You have to clearly illustrate the competitive landscape in your business plan. Are there areas your competitors are doing well? Are there areas where they are not doing so well? Show it.
Make it clear in this section why you are moving into the industry and what weaknesses are present there that you plan to explain. How are your competitors going to react to your market entry? How do you plan to get customers? Do you plan on taking your competitors' competitors, tap into other sources for customers, or both?
Illustrate the competitive landscape as well. What are your competitors doing well and not so well?
Answering these questions and thoughts will aid your market and competitive analysis of the opportunities in your space. Depending on how sophisticated your industry is, or the expectations of your financiers, you may need to carry out a more comprehensive market and competitive analysis to prove that big business opportunity.
Instead of looking at the market and competitive analyses as one entity, separating them will make the research even more comprehensive.
Market Analysis
Market analysis, boarding speaking, refers to research a business carried out on its industry, market, and competitors. It helps businesses gain a good understanding of their target market and the outlook of their industry. Before starting a company, it is vital to carry out market research to find out if the market is viable.

The market analysis section is a key part of the business plan. It is the section where you identify who your best clients or customers are. You cannot omit this section, without it your business plan is incomplete.
A good market analysis will tell your readers how you fit into the existing market and what makes you stand out. This section requires in-depth research, it will probably be the most time-consuming part of the business plan to write.
- Market Research
To create a compelling market analysis that will win over investors and financial institutions, you have to carry out thorough market research . Your market research should be targeted at your primary target market for your products or services. Here is what you want to find out about your target market.
- Your target market’s needs or pain points
- The existing solutions for their pain points
- Geographic Location
- Demographics
The purpose of carrying out a marketing analysis is to get all the information you need to show that you have a solid and thorough understanding of your target audience.
Only after you have fully understood the people you plan to sell your products or services to, can you evaluate correctly if your target market will be interested in your products or services.
You can easily convince interested parties to invest in your business if you can show them you thoroughly understand the market and show them that there is a market for your products or services.
How to Quantify Your Target Market
One of the goals of your marketing research is to understand who your ideal customers are and their purchasing power. To quantify your target market, you have to determine the following:
- Your Potential Customers: They are the people you plan to target. For example, if you sell accounting software for small businesses , then anyone who runs an enterprise or large business is unlikely to be your customers. Also, individuals who do not have a business will most likely not be interested in your product.
- Total Households: If you are selling household products such as heating and air conditioning systems, determining the number of total households is more important than finding out the total population in the area you want to sell to. The logic is simple, people buy the product but it is the household that uses it.
- Median Income: You need to know the median income of your target market. If you target a market that cannot afford to buy your products and services, your business will not last long.
- Income by Demographics: If your potential customers belong to a certain age group or gender, determining income levels by demographics is necessary. For example, if you sell men's clothes, your target audience is men.
What Does a Good Market Analysis Entail?
Your business does not exist on its own, it can only flourish within an industry and alongside competitors. Market analysis takes into consideration your industry, target market, and competitors. Understanding these three entities will drastically improve your company’s chances of success.

You can view your market analysis as an examination of the market you want to break into and an education on the emerging trends and themes in that market. Good market analyses include the following:
- Industry Description. You find out about the history of your industry, the current and future market size, and who the largest players/companies are in your industry.
- Overview of Target Market. You research your target market and its characteristics. Who are you targeting? Note, it cannot be everyone, it has to be a specific group. You also have to find out all information possible about your customers that can help you understand how and why they make buying decisions.
- Size of Target Market: You need to know the size of your target market, how frequently they buy, and the expected quantity they buy so you do not risk overproducing and having lots of bad inventory. Researching the size of your target market will help you determine if it is big enough for sustained business or not.
- Growth Potential: Before picking a target market, you want to be sure there are lots of potential for future growth. You want to avoid going for an industry that is declining slowly or rapidly with almost zero growth potential.
- Market Share Potential: Does your business stand a good chance of taking a good share of the market?
- Market Pricing and Promotional Strategies: Your market analysis should give you an idea of the price point you can expect to charge for your products and services. Researching your target market will also give you ideas of pricing strategies you can implement to break into the market or to enjoy maximum profits.
- Potential Barriers to Entry: One of the biggest benefits of conducting market analysis is that it shows you every potential barrier to entry your business will likely encounter. It is a good idea to discuss potential barriers to entry such as changing technology. It informs readers of your business plan that you understand the market.
- Research on Competitors: You need to know the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors and how you can exploit them for the benefit of your business. Find patterns and trends among your competitors that make them successful, discover what works and what doesn’t, and see what you can do better.
The market analysis section is not just for talking about your target market, industry, and competitors. You also have to explain how your company can fill the hole you have identified in the market.
Here are some questions you can answer that can help you position your product or service in a positive light to your readers.
- Is your product or service of superior quality?
- What additional features do you offer that your competitors do not offer?
- Are you targeting a ‘new’ market?
Basically, your market analysis should include an analysis of what already exists in the market and an explanation of how your company fits into the market.
Competitive Analysis
In the competitive analysis section, y ou have to understand who your direct and indirect competitions are, and how successful they are in the marketplace. It is the section where you assess the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, the advantage(s) they possess in the market and show the unique features or qualities that make you different from your competitors.

Many businesses do market analysis and competitive analysis together. However, to fully understand what the competitive analysis entails, it is essential to separate it from the market analysis.
Competitive analysis for your business can also include analysis on how to overcome barriers to entry in your target market.
The primary goal of conducting a competitive analysis is to distinguish your business from your competitors. A strong competitive analysis is essential if you want to convince potential funding sources to invest in your business. You have to show potential investors and lenders that your business has what it takes to compete in the marketplace successfully.
Competitive analysis will s how you what the strengths of your competition are and what they are doing to maintain that advantage.
When doing your competitive research, you first have to identify your competitor and then get all the information you can about them. The idea of spending time to identify your competitor and learn everything about them may seem daunting but it is well worth it.
Find answers to the following questions after you have identified who your competitors are.
- What are your successful competitors doing?
- Why is what they are doing working?
- Can your business do it better?
- What are the weaknesses of your successful competitors?
- What are they not doing well?
- Can your business turn its weaknesses into strengths?
- How good is your competitors’ customer service?
- Where do your competitors invest in advertising?
- What sales and pricing strategies are they using?
- What marketing strategies are they using?
- What kind of press coverage do they get?
- What are their customers saying about your competitors (both the positive and negative)?
If your competitors have a website, it is a good idea to visit their websites for more competitors’ research. Check their “About Us” page for more information.

If you are presenting your business plan to investors, you need to clearly distinguish yourself from your competitors. Investors can easily tell when you have not properly researched your competitors.
Take time to think about what unique qualities or features set you apart from your competitors. If you do not have any direct competition offering your product to the market, it does not mean you leave out the competitor analysis section blank. Instead research on other companies that are providing a similar product, or whose product is solving the problem your product solves.
The next step is to create a table listing the top competitors you want to include in your business plan. Ensure you list your business as the last and on the right. What you just created is known as the competitor analysis table.
Direct vs Indirect Competition
You cannot know if your product or service will be a fit for your target market if you have not understood your business and the competitive landscape.
There is no market you want to target where you will not encounter competition, even if your product is innovative. Including competitive analysis in your business plan is essential.
If you are entering an established market, you need to explain how you plan to differentiate your products from the available options in the market. Also, include a list of few companies that you view as your direct competitors The competition you face in an established market is your direct competition.
In situations where you are entering a market with no direct competition, it does not mean there is no competition there. Consider your indirect competition that offers substitutes for the products or services you offer.
For example, if you sell an innovative SaaS product, let us say a project management software , a company offering time management software is your indirect competition.
There is an easy way to find out who your indirect competitors are in the absence of no direct competitors. You simply have to research how your potential customers are solving the problems that your product or service seeks to solve. That is your direct competition.
Factors that Differentiate Your Business from the Competition
There are three main factors that any business can use to differentiate itself from its competition. They are cost leadership, product differentiation, and market segmentation.
1. Cost Leadership
A strategy you can impose to maximize your profits and gain an edge over your competitors. It involves offering lower prices than what the majority of your competitors are offering.
A common practice among businesses looking to enter into a market where there are dominant players is to use free trials or pricing to attract as many customers as possible to their offer.
2. Product Differentiation
Your product or service should have a unique selling proposition (USP) that your competitors do not have or do not stress in their marketing.
Part of the marketing strategy should involve making your products unique and different from your competitors. It does not have to be different from your competitors, it can be the addition to a feature or benefit that your competitors do not currently have.
3. Market Segmentation
As a new business seeking to break into an industry, you will gain more success from focusing on a specific niche or target market, and not the whole industry.
If your competitors are focused on a general need or target market, you can differentiate yourself from them by having a small and hyper-targeted audience. For example, if your competitors are selling men’s clothes in their online stores , you can sell hoodies for men.
4. Define Your Business and Management Structure
The next step in your business plan is your business and management structure. It is the section where you describe the legal structure of your business and the team running it.
Your business is only as good as the management team that runs it, while the management team can only strive when there is a proper business and management structure in place.
If your company is a sole proprietor or a limited liability company (LLC), a general or limited partnership, or a C or an S corporation, state it clearly in this section.
Use an organizational chart to show the management structure in your business. Clearly show who is in charge of what area in your company. It is where you show how each key manager or team leader’s unique experience can contribute immensely to the success of your company. You can also opt to add the resumes and CVs of the key players in your company.
The business and management structure section should show who the owner is, and other owners of the businesses (if the business has other owners). For businesses or companies with multiple owners, include the percent ownership of the various owners and clearly show the extent of each others’ involvement in the company.
Investors want to know who is behind the company and the team running it to determine if it has the right management to achieve its set goals.
Management Team
The management team section is where you show that you have the right team in place to successfully execute the business operations and ideas. Take time to create the management structure for your business. Think about all the important roles and responsibilities that you need managers for to grow your business.
Include brief bios of each key team member and ensure you highlight only the relevant information that is needed. If your team members have background industry experience or have held top positions for other companies and achieved success while filling that role, highlight it in this section.

A common mistake that many startups make is assigning C-level titles such as (CMO and CEO) to everyone on their team. It is unrealistic for a small business to have those titles. While it may look good on paper for the ego of your team members, it can prevent investors from investing in your business.
Instead of building an unrealistic management structure that does not fit your business reality, it is best to allow business titles to grow as the business grows. Starting everyone at the top leaves no room for future change or growth, which is bad for productivity.
Your management team does not have to be complete before you start writing your business plan. You can have a complete business plan even when there are managerial positions that are empty and need filling.
If you have management gaps in your team, simply show the gaps and indicate you are searching for the right candidates for the role(s). Investors do not expect you to have a full management team when you are just starting your business.
Key Questions to Answer When Structuring Your Management Team
- Who are the key leaders?
- What experiences, skills, and educational backgrounds do you expect your key leaders to have?
- Do your key leaders have industry experience?
- What positions will they fill and what duties will they perform in those positions?
- What level of authority do the key leaders have and what are their responsibilities?
- What is the salary for the various management positions that will attract the ideal candidates?
Additional Tips for Writing the Management Structure Section
1. Avoid Adding ‘Ghost’ Names to Your Management Team
There is always that temptation to include a ‘ghost’ name to your management team to attract and influence investors to invest in your business. Although the presence of these celebrity management team members may attract the attention of investors, it can cause your business to lose any credibility if you get found out.
Seasoned investors will investigate further the members of your management team before committing fully to your business If they find out that the celebrity name used does not play any actual role in your business, they will not invest and may write you off as dishonest.
2. Focus on Credentials But Pay Extra Attention to the Roles
Investors want to know the experience that your key team members have to determine if they can successfully reach the company’s growth and financial goals.
While it is an excellent boost for your key management team to have the right credentials, you also want to pay extra attention to the roles they will play in your company.
Organizational Chart

Adding an organizational chart in this section of your business plan is not necessary, you can do it in your business plan’s appendix.
If you are exploring funding options, it is not uncommon to get asked for your organizational chart. The function of an organizational chart goes beyond raising money, you can also use it as a useful planning tool for your business.
An organizational chart can help you identify how best to structure your management team for maximum productivity and point you towards key roles you need to fill in the future.
You can use the organizational chart to show your company’s internal management structure such as the roles and responsibilities of your management team, and relationships that exist between them.
5. Describe Your Product and Service Offering
In your business plan, you have to describe what you sell or the service you plan to offer. It is the next step after defining your business and management structure. The products and services section is where you sell the benefits of your business.
Here you have to explain how your product or service will benefit your customers and describe your product lifecycle. It is also the section where you write down your plans for intellectual property like patent filings and copyrighting.
The research and development that you are undertaking for your product or service need to be explained in detail in this section. However, do not get too technical, sell the general idea and its benefits.
If you have any diagrams or intricate designs of your product or service, do not include them in the products and services section. Instead, leave them for the addendum page. Also, if you are leaving out diagrams or designs for the addendum, ensure you add this phrase “For more detail, visit the addendum Page #.”
Your product and service section in your business plan should include the following:
- A detailed explanation that clearly shows how your product or service works.
- The pricing model for your product or service.
- Your business’ sales and distribution strategy.
- The ideal customers that want your product or service.
- The benefits of your products and services.
- Reason(s) why your product or service is a better alternative to what your competitors are currently offering in the market.
- Plans for filling the orders you receive
- If you have current or pending patents, copyrights, and trademarks for your product or service, you can also discuss them in this section.
What to Focus On When Describing the Benefits, Lifecycle, and Production Process of Your Products or Services
In the products and services section, you have to distill the benefits, lifecycle, and production process of your products and services.
When describing the benefits of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Unique features
- Translating the unique features into benefits
- The emotional, psychological, and practical payoffs to attract customers
- Intellectual property rights or any patents
When describing the product life cycle of your products or services, here are some key factors to focus on.
- Upsells, cross-sells, and down-sells
- Time between purchases
- Plans for research and development.
When describing the production process for your products or services, you need to think about the following:
- The creation of new or existing products and services.
- The sources for the raw materials or components you need for production.
- Assembling the products
- Maintaining quality control
- Supply-chain logistics (receiving the raw materials and delivering the finished products)
- The day-to-day management of the production processes, bookkeeping, and inventory.
Tips for Writing the Products or Services Section of Your Business Plan
1. Avoid Technical Descriptions and Industry Buzzwords
The products and services section of your business plan should clearly describe the products and services that your company provides. However, it is not a section to include technical jargons that anyone outside your industry will not understand.
A good practice is to remove highly detailed or technical descriptions in favor of simple terms. Industry buzzwords are not necessary, if there are simpler terms you can use, then use them. If you plan to use your business plan to source funds, making the product or service section so technical will do you no favors.
2. Describe How Your Products or Services Differ from Your Competitors
When potential investors look at your business plan, they want to know how the products and services you are offering differ from that of your competition. Differentiating your products or services from your competition in a way that makes your solution more attractive is critical.
If you are going the innovative path and there is no market currently for your product or service, you need to describe in this section why the market needs your product or service.
For example, overnight delivery was a niche business that only a few companies were participating in. Federal Express (FedEx) had to show in its business plan that there was a large opportunity for that service and they justified why the market needed that service.
3. Long or Short Products or Services Section
Should your products or services section be short? Does the long products or services section attract more investors?
There are no straightforward answers to these questions. Whether your products or services section should be long or relatively short depends on the nature of your business.
If your business is product-focused, then automatically you need to use more space to describe the details of your products. However, if the product your business sells is a commodity item that relies on competitive pricing or other pricing strategies, you do not have to use up so much space to provide significant details about the product.
Likewise, if you are selling a commodity that is available in numerous outlets, then you do not have to spend time on writing a long products or services section.
The key to the success of your business is most likely the effectiveness of your marketing strategies compared to your competitors. Use more space to address that section.
If you are creating a new product or service that the market does not know about, your products or services section can be lengthy. The reason why is because you need to explain everything about the product or service such as the nature of the product, its use case, and values.
A short products or services section for an innovative product or service will not give the readers enough information to properly evaluate your business.
4. Describe Your Relationships with Vendors or Suppliers
Your business will rely on vendors or suppliers to supply raw materials or the components needed to make your products. In your products and services section, describe your relationships with your vendors and suppliers fully.
Avoid the mistake of relying on only one supplier or vendor. If that supplier or vendor fails to supply or goes out of business, you can easily face supply problems and struggle to meet your demands. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships for better business stability.
5. Your Primary Goal Is to Convince Your Readers
The primary goal of your business plan is to convince your readers that your business is viable and to create a guide for your business to follow. It applies to the products and services section.
When drafting this section, think like the reader. See your reader as someone who has no idea about your products and services. You are using the products and services section to provide the needed information to help your reader understand your products and services. As a result, you have to be clear and to the point.
While you want to educate your readers about your products or services, you also do not want to bore them with lots of technical details. Show your products and services and not your fancy choice of words.
Your products and services section should provide the answer to the “what” question for your business. You and your management team may run the business, but it is your products and services that are the lifeblood of the business.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing your Products and Services Section
Answering these questions can help you write your products and services section quickly and in a way that will appeal to your readers.
- Are your products existing on the market or are they still in the development stage?
- What is your timeline for adding new products and services to the market?
- What are the positives that make your products and services different from your competitors?
- Do your products and services have any competitive advantage that your competitors’ products and services do not currently have?
- Do your products or services have any competitive disadvantages that you need to overcome to compete with your competitors? If your answer is yes, state how you plan to overcome them,
- How much does it cost to produce your products or services? How much do you plan to sell it for?
- What is the price for your products and services compared to your competitors? Is pricing an issue?
- What are your operating costs and will it be low enough for you to compete with your competitors and still take home a reasonable profit margin?
- What is your plan for acquiring your products? Are you involved in the production of your products or services?
- Are you the manufacturer and produce all the components you need to create your products? Do you assemble your products by using components supplied by other manufacturers? Do you purchase your products directly from suppliers or wholesalers?
- Do you have a steady supply of products that you need to start your business? (If your business is yet to kick-off)
- How do you plan to distribute your products or services to the market?
You can also hint at the marketing or promotion plans you have for your products or services such as how you plan to build awareness or retain customers. The next section is where you can go fully into details about your business’s marketing and sales plan.
6. Show and Explain Your Marketing and Sales Plan
Providing great products and services is wonderful, but it means nothing if you do not have a marketing and sales plan to inform your customers about them. Your marketing and sales plan is critical to the success of your business.
The sales and marketing section is where you show and offer a detailed explanation of your marketing and sales plan and how you plan to execute it. It covers your pricing plan, proposed advertising and promotion activities, activities and partnerships you need to make your business a success, and the benefits of your products and services.
There are several ways you can approach your marketing and sales strategy. Ideally, your marketing and sales strategy has to fit the unique needs of your business.
In this section, you describe how the plans your business has for attracting and retaining customers, and the exact process for making a sale happen. It is essential to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales plans because you are still going to reference this section when you are making financial projections for your business.
Outline Your Business’ Unique Selling Proposition (USP)

The sales and marketing section is where you outline your business’s unique selling proposition (USP). When you are developing your unique selling proposition, think about the strongest reasons why people should buy from you over your competition. That reason(s) is most likely a good fit to serve as your unique selling proposition (USP).
Target Market and Target Audience
Plans on how to get your products or services to your target market and how to get your target audience to buy them go into this section. You also highlight the strengths of your business here, particularly what sets them apart from your competition.

Before you start writing your marketing and sales plan, you need to have properly defined your target audience and fleshed out your buyer persona. If you do not first understand the individual you are marketing to, your marketing and sales plan will lack any substance and easily fall.
Creating a Smart Marketing and Sales Plan
Marketing your products and services is an investment that requires you to spend money. Like any other investment, you have to generate a good return on investment (ROI) to justify using that marketing and sales plan. Good marketing and sales plans bring in high sales and profits to your company.
Avoid spending money on unproductive marketing channels. Do your research and find out the best marketing and sales plan that works best for your company.
Your marketing and sales plan can be broken into different parts: your positioning statement, pricing, promotion, packaging, advertising, public relations, content marketing, social media, and strategic alliances.
Your Positioning Statement
Your positioning statement is the first part of your marketing and sales plan. It refers to the way you present your company to your customers.
Are you the premium solution, the low-price solution, or are you the intermediary between the two extremes in the market? What do you offer that your competitors do not that can give you leverage in the market?
Before you start writing your positioning statement, you need to spend some time evaluating the current market conditions. Here are some questions that can help you to evaluate the market
- What are the unique features or benefits that you offer that your competitors lack?
- What are your customers’ primary needs and wants?
- Why should a customer choose you over your competition? How do you plan to differentiate yourself from the competition?
- How does your company’s solution compare with other solutions in the market?
After answering these questions, then you can start writing your positioning statement. Your positioning statement does not have to be in-depth or too long.
All you need to explain with your positioning statement are two focus areas. The first is the position of your company within the competitive landscape. The other focus area is the core value proposition that sets your company apart from other alternatives that your ideal customer might consider.
Here is a simple template you can use to develop a positioning statement.
For [description of target market] who [need of target market], [product or service] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [top competition], it [most essential distinguishing feature].
For example, let’s create the positioning statement for fictional accounting software and QuickBooks alternative , TBooks.
“For small business owners who need accounting services, TBooks is an accounting software that helps small businesses handle their small business bookkeeping basics quickly and easily. Unlike Wave, TBooks gives small businesses access to live sessions with top accountants.”
You can edit this positioning statement sample and fill it with your business details.
After writing your positioning statement, the next step is the pricing of your offerings. The overall positioning strategy you set in your positioning statement will often determine how you price your products or services.
Pricing is a powerful tool that sends a strong message to your customers. Failure to get your pricing strategy right can make or mar your business. If you are targeting a low-income audience, setting a premium price can result in low sales.
You can use pricing to communicate your positioning to your customers. For example, if you are offering a product at a premium price, you are sending a message to your customers that the product belongs to the premium category.
Basic Rules to Follow When Pricing Your Offering
Setting a price for your offering involves more than just putting a price tag on it. Deciding on the right pricing for your offering requires following some basic rules. They include covering your costs, primary and secondary profit center pricing, and matching the market rate.
- Covering Your Costs: The price you set for your products or service should be more than it costs you to produce and deliver them. Every business has the same goal, to make a profit. Depending on the strategy you want to use, there are exceptions to this rule. However, the vast majority of businesses follow this rule.
- Primary and Secondary Profit Center Pricing: When a company sets its price above the cost of production, it is making that product its primary profit center. A company can also decide not to make its initial price its primary profit center by selling below or at even with its production cost. It rather depends on the support product or even maintenance that is associated with the initial purchase to make its profit. The initial price thus became its secondary profit center.
- Matching the Market Rate: A good rule to follow when pricing your products or services is to match your pricing with consumer demand and expectations. If you price your products or services beyond the price your customer perceives as the ideal price range, you may end up with no customers. Pricing your products too low below what your customer perceives as the ideal price range may lead to them undervaluing your offering.
Pricing Strategy
Your pricing strategy influences the price of your offering. There are several pricing strategies available for you to choose from when examining the right pricing strategy for your business. They include cost-plus pricing, market-based pricing, value pricing, and more.

- Cost-plus Pricing: This strategy is one of the simplest and oldest pricing strategies. Here you consider the cost of producing a unit of your product and then add a profit to it to arrive at your market price. It is an effective pricing strategy for manufacturers because it helps them cover their initial costs. Another name for the cost-plus pricing strategy is the markup pricing strategy.
- Market-based Pricing: This pricing strategy analyses the market including competitors’ pricing and then sets a price based on what the market is expecting. With this pricing strategy, you can either set your price at the low-end or high-end of the market.
- Value Pricing: This pricing strategy involves setting a price based on the value you are providing to your customer. When adopting a value-based pricing strategy, you have to set a price that your customers are willing to pay. Service-based businesses such as small business insurance providers , luxury goods sellers, and the fashion industry use this pricing strategy.
After carefully sorting out your positioning statement and pricing, the next item to look at is your promotional strategy. Your promotional strategy explains how you plan on communicating with your customers and prospects.
As a business, you must measure all your costs, including the cost of your promotions. You also want to measure how much sales your promotions bring for your business to determine its usefulness. Promotional strategies or programs that do not lead to profit need to be removed.
There are different types of promotional strategies you can adopt for your business, they include advertising, public relations, and content marketing.
Advertising
Your business plan should include your advertising plan which can be found in the marketing and sales plan section. You need to include an overview of your advertising plans such as the areas you plan to spend money on to advertise your business and offers.
Ensure that you make it clear in this section if your business will be advertising online or using the more traditional offline media, or the combination of both online and offline media. You can also include the advertising medium you want to use to raise awareness about your business and offers.
Some common online advertising mediums you can use include social media ads, landing pages, sales pages, SEO, Pay-Per-Click, emails, Google Ads, and others. Some common traditional and offline advertising mediums include word of mouth, radios, direct mail, televisions, flyers, billboards, posters, and others.
A key component of your advertising strategy is how you plan to measure the effectiveness and success of your advertising campaign. There is no point in sticking with an advertising plan or medium that does not produce results for your business in the long run.
Public Relations
A great way to reach your customers is to get the media to cover your business or product. Publicity, especially good ones, should be a part of your marketing and sales plan. In this section, show your plans for getting prominent reviews of your product from reputable publications and sources.
Your business needs that exposure to grow. If public relations is a crucial part of your promotional strategy, provide details about your public relations plan here.
Content Marketing
Content marketing is a popular promotional strategy used by businesses to inform and attract their customers. It is about teaching and educating your prospects on various topics of interest in your niche, it does not just involve informing them about the benefits and features of the products and services you have,

Businesses publish content usually for free where they provide useful information, tips, and advice so that their target market can be made aware of the importance of their products and services. Content marketing strategies seek to nurture prospects into buyers over time by simply providing value.
Your company can create a blog where it will be publishing content for its target market. You will need to use the best website builder such as Wix and Squarespace and the best web hosting services such as Bluehost, Hostinger, and other Bluehost alternatives to create a functional blog or website.
If content marketing is a crucial part of your promotional strategy (as it should be), detail your plans under promotions.
Including high-quality images of the packaging of your product in your business plan is a lovely idea. You can add the images of the packaging of that product in the marketing and sales plan section. If you are not selling a product, then you do not need to include any worry about the physical packaging of your product.
When organizing the packaging section of your business plan, you can answer the following questions to make maximum use of this section.
- Is your choice of packaging consistent with your positioning strategy?
- What key value proposition does your packaging communicate? (It should reflect the key value proposition of your business)
- How does your packaging compare to that of your competitors?
Social Media
Your 21st-century business needs to have a good social media presence. Not having one is leaving out opportunities for growth and reaching out to your prospect.
You do not have to join the thousands of social media platforms out there. What you need to do is join the ones that your customers are active on and be active there.

Businesses use social media to provide information about their products such as promotions, discounts, the benefits of their products, and content on their blogs.
Social media is also a platform for engaging with your customers and getting feedback about your products or services. Make no mistake, more and more of your prospects are using social media channels to find more information about companies.
You need to consider the social media channels you want to prioritize your business (prioritize the ones your customers are active in) and your branding plans in this section.

Strategic Alliances
If your company plans to work closely with other companies as part of your sales and marketing plan, include it in this section. Prove details about those partnerships in your business plan if you have already established them.
Strategic alliances can be beneficial for all parties involved including your company. Working closely with another company in the form of a partnership can provide access to a different target market segment for your company.
The company you are partnering with may also gain access to your target market or simply offer a new product or service (that of your company) to its customers.
Mutually beneficial partnerships can cover the weaknesses of one company with the strength of another. You should consider strategic alliances with companies that sell complimentary products to yours. For example, if you provide printers, you can partner with a company that produces ink since the customers that buy printers from you will also need inks for printing.
Steps Involved in Creating a Marketing and Sales Plan
1. Focus on Your Target Market
Identify who your customers are, the market you want to target. Then determine the best ways to get your products or services to your potential customers.
2. Evaluate Your Competition
One of the goals of having a marketing plan is to distinguish yourself from your competition. You cannot stand out from them without first knowing them in and out.
You can know your competitors by gathering information about their products, pricing, service, and advertising campaigns.
These questions can help you know your competition.
- What makes your competition successful?
- What are their weaknesses?
- What are customers saying about your competition?
3. Consider Your Brand
Customers' perception of your brand has a strong impact on your sales. Your marketing and sales plan should seek to bolster the image of your brand. Before you start marketing your business, think about the message you want to pass across about your business and your products and services.
4. Focus on Benefits
The majority of your customers do not view your product in terms of features, what they want to know is the benefits and solutions your product offers. Think about the problems your product solves and the benefits it delivers, and use it to create the right sales and marketing message.
Your marketing plan should focus on what you want your customer to get instead of what you provide. Identify those benefits in your marketing and sales plan.
5. Focus on Differentiation
Your marketing and sales plan should look for a unique angle they can take that differentiates your business from the competition, even if the products offered are similar. Some good areas of differentiation you can use are your benefits, pricing, and features.
Key Questions to Answer When Writing Your Marketing and Sales Plan
- What is your company’s budget for sales and marketing campaigns?
- What key metrics will you use to determine if your marketing plans are successful?
- What are your alternatives if your initial marketing efforts do not succeed?
- Who are the sales representatives you need to promote your products or services?
- What are the marketing and sales channels you plan to use? How do you plan to get your products in front of your ideal customers?
- Where will you sell your products?
You may want to include samples of marketing materials you plan to use such as print ads, website descriptions, and social media ads. While it is not compulsory to include these samples, it can help you better communicate your marketing and sales plan and objectives.
The purpose of the marketing and sales section is to answer this question “How will you reach your customers?” If you cannot convincingly provide an answer to this question, you need to rework your marketing and sales section.
7. Clearly Show Your Funding Request
If you are writing your business plan to ask for funding from investors or financial institutions, the funding request section is where you will outline your funding requirements. The funding request section should answer the question ‘How much money will your business need in the near future (3 to 5 years)?’
A good funding request section will clearly outline and explain the amount of funding your business needs over the next five years. You need to know the amount of money your business needs to make an accurate funding request.
Also, when writing your funding request, provide details of how the funds will be used over the period. Specify if you want to use the funds to buy raw materials or machinery, pay salaries, pay for advertisements, and cover specific bills such as rent and electricity.
In addition to explaining what you want to use the funds requested for, you need to clearly state the projected return on investment (ROI) . Investors and creditors want to know if your business can generate profit for them if they put funds into it.
Ensure you do not inflate the figures and stay as realistic as possible. Investors and financial institutions you are seeking funds from will do their research before investing money in your business.
If you are not sure of an exact number to request from, you can use some range of numbers as rough estimates. Add a best-case scenario and a work-case scenario to your funding request. Also, include a description of your strategic future financial plans such as selling your business or paying off debts.
Funding Request: Debt or Equity?
When making your funding request, specify the type of funding you want. Do you want debt or equity? Draw out the terms that will be applicable for the funding, and the length of time the funding request will cover.
Case for Equity
If your new business has not yet started generating profits, you are most likely preparing to sell equity in your business to raise capital at the early stage. Equity here refers to ownership. In this case, you are selling a portion of your company to raise capital.
Although this method of raising capital for your business does not put your business in debt, keep in mind that an equity owner may expect to play a key role in company decisions even if he does not hold a major stake in the company.
Most equity sales for startups are usually private transactions . If you are making a funding request by offering equity in exchange for funding, let the investor know that they will be paid a dividend (a share of the company’s profit). Also, let the investor know the process for selling their equity in your business.
Case for Debt
You may decide not to offer equity in exchange for funds, instead, you make a funding request with the promise to pay back the money borrowed at the agreed time frame.
When making a funding request with an agreement to pay back, note that you will have to repay your creditors both the principal amount borrowed and the interest on it. Financial institutions offer this type of funding for businesses.
Large companies combine both equity and debt in their capital structure. When drafting your business plan, decide if you want to offer both or one over the other.
Before you sell equity in exchange for funding in your business, consider if you are willing to accept not being in total control of your business. Also, before you seek loans in your funding request section, ensure that the terms of repayment are favorable.
You should set a clear timeline in your funding request so that potential investors and creditors can know what you are expecting. Some investors and creditors may agree to your funding request and then delay payment for longer than 30 days, meanwhile, your business needs an immediate cash injection to operate efficiently.
Additional Tips for Writing the Funding Request Section of your Business Plan
The funding request section is not necessary for every business, it is only needed by businesses who plan to use their business plan to secure funding.
If you are adding the funding request section to your business plan, provide an itemized summary of how you plan to use the funds requested. Hiring a lawyer, accountant, or other professionals may be necessary for the proper development of this section.
You should also gather and use financial statements that add credibility and support to your funding requests. Ensure that the financial statements you use should include your projected financial data such as projected cash flows, forecast statements, and expenditure budgets.
If you are an existing business, include all historical financial statements such as cash flow statements, balance sheets and income statements .
Provide monthly and quarterly financial statements for a year. If your business has records that date back beyond the one-year mark, add the yearly statements of those years. These documents are for the appendix section of your business plan.
8. Detail Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projections
If you used the funding request section in your business plan, supplement it with a financial plan, metrics, and projections. This section paints a picture of the past performance of your business and then goes ahead to make an informed projection about its future.
The goal of this section is to convince readers that your business is going to be a financial success. It outlines your business plan to generate enough profit to repay the loan (with interest if applicable) and to generate a decent return on investment for investors.
If you have an existing business already in operation, use this section to demonstrate stability through finance. This section should include your cash flow statements, balance sheets, and income statements covering the last three to five years. If your business has some acceptable collateral that you can use to acquire loans, list it in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
Apart from current financial statements, this section should also contain a prospective financial outlook that spans the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, and capital expenditure budget.
If your business is new and is not yet generating profit, use clear and realistic projections to show the potentials of your business.
When drafting this section, research industry norms and the performance of comparable businesses. Your financial projections should cover at least five years. State the logic behind your financial projections. Remember you can always make adjustments to this section as the variables change.
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section create a baseline which your business can either exceed or fail to reach. If your business fails to reach your projections in this section, you need to understand why it failed.
Investors and loan managers spend a lot of time going through the financial plan, metrics, and projection section compared to other parts of the business plan. Ensure you spend time creating credible financial analyses for your business in this section.
Many entrepreneurs find this section daunting to write. You do not need a business degree to create a solid financial forecast for your business. Business finances, especially for startups, are not as complicated as they seem. There are several online tools and templates that make writing this section so much easier.
Use Graphs and Charts
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business. Charts and images make it easier to communicate your finances.
Accuracy in this section is key, ensure you carefully analyze your past financial statements properly before making financial projects.
Address the Risk Factors and Show Realistic Financial Projections
Keep your financial plan, metrics, and projection realistic. It is okay to be optimistic in your financial projection, however, you have to justify it.
You should also address the various risk factors associated with your business in this section. Investors want to know the potential risks involved, show them. You should also show your plans for mitigating those risks.
What You Should In The Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection Section of Your Business Plan
The financial plan, metrics, and projection section of your business plan should have monthly sales and revenue forecasts for the first year. It should also include annual projections that cover 3 to 5 years.
A three-year projection is a basic requirement to have in your business plan. However, some investors may request a five-year forecast.
Your business plan should include the following financial statements: sales forecast, personnel plan, income statement, income statement, cash flow statement, balance sheet, and an exit strategy.
1. Sales Forecast
Sales forecast refers to your projections about the number of sales your business is going to record over the next few years. It is typically broken into several rows, with each row assigned to a core product or service that your business is offering.
One common mistake people make in their business plan is to break down the sales forecast section into long details. A sales forecast should forecast the high-level details.
For example, if you are forecasting sales for a payroll software provider, you could break down your forecast into target market segments or subscription categories.

Your sales forecast section should also have a corresponding row for each sales row to cover the direct cost or Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). The objective of these rows is to show the expenses that your business incurs in making and delivering your product or service.
Note that your Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) should only cover those direct costs incurred when making your products. Other indirect expenses such as insurance, salaries, payroll tax, and rent should not be included.
For example, the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) for a restaurant is the cost of ingredients while for a consulting company it will be the cost of paper and other presentation materials.

2. Personnel Plan
The personnel plan section is where you provide details about the payment plan for your employees. For a small business, you can easily list every position in your company and how much you plan to pay in the personnel plan.
However, for larger businesses, you have to break the personnel plan into functional groups such as sales and marketing.
The personnel plan will also include the cost of an employee beyond salary, commonly referred to as the employee burden. These costs include insurance, payroll taxes , and other essential costs incurred monthly as a result of having employees on your payroll.

3. Income Statement
The income statement section shows if your business is making a profit or taking a loss. Another name for the income statement is the profit and loss (P&L). It takes data from your sales forecast and personnel plan and adds other ongoing expenses you incur while running your business.

Every business plan should have an income statement. It subtracts your business expenses from its earnings to show if your business is generating profit or incurring losses.
The income statement has the following items: sales, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), gross margin, operating expenses, total operating expenses, operating income , total expenses, and net profit.
- Sales refer to the revenue your business generates from selling its products or services. Other names for sales are income or revenue.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) refers to the total cost of selling your products. Other names for COGS are direct costs or cost of sales. Manufacturing businesses use the Costs of Goods Manufactured (COGM) .
- Gross Margin is the figure you get when you subtract your COGS from your sales. In your income statement, you can express it as a percentage of total sales (Gross margin / Sales = Gross Margin Percent).
- Operating Expenses refer to all the expenses you incur from running your business. It exempts the COGS because it stands alone as a core part of your income statement. You also have to exclude taxes, depreciation, and amortization. Your operating expenses include salaries, marketing expenses, research and development (R&D) expenses, and other expenses.
- Total Operating Expenses refers to the sum of all your operating expenses including those exemptions named above under operating expenses.
- Operating Income refers to earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. It is simply known as the acronym EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization). Calculating your operating income is simple, all you need to do is to subtract your COGS and total operating expenses from your sales.
- Total Expenses refer to the sum of your operating expenses and your business’ interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization.
- Net profit shows whether your business has made a profit or taken a loss during a given timeframe.
4. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement tracks the money you have in the bank at any given point. It is often confused with the income statement or the profit and loss statement. They are both different types of financial statements. The income statement calculates your profits and losses while the cash flow statement shows you how much you have in the bank.

5. Balance Sheet
The balance sheet is a financial statement that provides an overview of the financial health of your business. It contains information about the assets and liabilities of your company, and owner’s or shareholders’ equity.
You can get the net worth of your company by subtracting your company’s liabilities from its assets.

6. Exit Strategy
The exit strategy refers to a probable plan for selling your business either to the public in an IPO or to another company. It is the last thing you include in the financial plan, metrics, and projection section.
You can choose to omit the exit strategy from your business plan if you plan to maintain full ownership of your business and do not plan on seeking angel investment or virtual capitalist (VC) funding.
Investors may want to know what your exit plan is. They invest in your business to get a good return on investment.
Your exit strategy does not have to include long and boring details. Ensure you identify some interested parties who may be interested in buying the company if it becomes a success.

Key Questions to Answer with Your Financial Plan, Metrics, and Projection
Your financial plan, metrics, and projection section helps investors, creditors, or your internal managers to understand what your expenses are, the amount of cash you need, and what it takes to make your company profitable. It also shows what you will be doing with any funding.
You do not need to show actual financial data if you do not have one. Adding forecasts and projections to your financial statements is added proof that your strategy is feasible and shows investors you have planned properly.
Here are some key questions to answer to help you develop this section.
- What is your sales forecast for the next year?
- When will your company achieve a positive cash flow?
- What are the core expenses you need to operate?
- How much money do you need upfront to operate or grow your company?
- How will you use the loans or investments?
9. Add an Appendix to Your Business Plan
Adding an appendix to your business plan is optional. It is a useful place to put any charts, tables, legal notes, definitions, permits, résumés, and other critical information that do not fit into other sections of your business plan.
The appendix section is where you would want to include details of a patent or patent-pending if you have one. You can always add illustrations or images of your products here. It is the last section of your business plan.
When writing your business plan, there are details you cut short or remove to prevent the entire section from becoming too lengthy. There are also details you want to include in the business plan but are not a good fit for any of the previous sections. You can add that additional information to the appendix section.
Businesses also use the appendix section to include supporting documents or other materials specially requested by investors or lenders.
You can include just about any information that supports the assumptions and statements you made in the business plan under the appendix. It is the one place in the business plan where unrelated data and information can coexist amicably.
If your appendix section is lengthy, try organizing it by adding a table of contents at the beginning of the appendix section. It is also advisable to group similar information to make it easier for the reader to access them.
A well-organized appendix section makes it easier to share your information clearly and concisely. Add footnotes throughout the rest of the business plan or make references in the plan to the documents in the appendix.
The appendix section is usually only necessary if you are seeking funding from investors or lenders, or hoping to attract partners.
People reading business plans do not want to spend time going through a heap of backup information, numbers, and charts. Keep these documents or information in the Appendix section in case the reader wants to dig deeper.
Common Items to Include in the Appendix Section of Your Business Plan
The appendix section includes documents that supplement or support the information or claims given in other sections of the business plans. Common items you can include in the appendix section include:
- Additional data about the process of manufacturing or creation
- Additional description of products or services such as product schematics
- Additional financial documents or projections
- Articles of incorporation and status
- Backup for market research or competitive analysis
- Bank statements
- Business registries
- Client testimonials (if your business is already running)
- Copies of insurances
- Credit histories (personal or/and business)
- Deeds and permits
- Equipment leases
- Examples of marketing and advertising collateral
- Industry associations and memberships
- Images of product
- Intellectual property
- Key customer contracts
- Legal documents and other contracts
- Letters of reference
- Links to references
- Market research data
- Organizational charts
- Photographs of potential facilities
- Professional licenses pertaining to your legal structure or type of business
- Purchase orders
- Resumes of the founder(s) and key managers
- State and federal identification numbers or codes
- Trademarks or patents’ registrations
Avoid using the appendix section as a place to dump any document or information you feel like adding. Only add documents or information that you support or increase the credibility of your business plan.
Tips and Strategies for Writing a Convincing Business Plan
To achieve a perfect business plan, you need to consider some key tips and strategies. These tips will raise the efficiency of your business plan above average.
1. Know Your Audience
When writing a business plan, you need to know your audience . Business owners write business plans for different reasons. Your business plan has to be specific. For example, you can write business plans to potential investors, banks, and even fellow board members of the company.
The audience you are writing to determines the structure of the business plan. As a business owner, you have to know your audience. Not everyone will be your audience. Knowing your audience will help you to narrow the scope of your business plan.
Consider what your audience wants to see in your projects, the likely questions they might ask, and what interests them.
- A business plan used to address a company's board members will center on its employment schemes, internal affairs, projects, stakeholders, etc.
- A business plan for financial institutions will talk about the size of your market and the chances for you to pay back any loans you demand.
- A business plan for investors will show proof that you can return the investment capital within a specific time. In addition, it discusses your financial projections, tractions, and market size.
2. Get Inspiration from People
Writing a business plan from scratch as an entrepreneur can be daunting. That is why you need the right inspiration to push you to write one. You can gain inspiration from the successful business plans of other businesses. Look at their business plans, the style they use, the structure of the project, etc.
To make your business plan easier to create, search companies related to your business to get an exact copy of what you need to create an effective business plan. You can also make references while citing examples in your business plans.
When drafting your business plan, get as much help from others as you possibly can. By getting inspiration from people, you can create something better than what they have.
3. Avoid Being Over Optimistic
Many business owners make use of strong adjectives to qualify their content. One of the big mistakes entrepreneurs make when preparing a business plan is promising too much.
The use of superlatives and over-optimistic claims can prepare the audience for more than you can offer. In the end, you disappoint the confidence they have in you.
In most cases, the best option is to be realistic with your claims and statistics. Most of the investors can sense a bit of incompetency from the overuse of superlatives. As a new entrepreneur, do not be tempted to over-promise to get the interests of investors.
The concept of entrepreneurship centers on risks, nothing is certain when you make future analyses. What separates the best is the ability to do careful research and work towards achieving that, not promising more than you can achieve.
To make an excellent first impression as an entrepreneur, replace superlatives with compelling data-driven content. In this way, you are more specific than someone promising a huge ROI from an investment.
4. Keep it Simple and Short
When writing business plans, ensure you keep them simple throughout. Irrespective of the purpose of the business plan, your goal is to convince the audience.
One way to achieve this goal is to make them understand your proposal. Therefore, it would be best if you avoid the use of complex grammar to express yourself. It would be a huge turn-off if the people you want to convince are not familiar with your use of words.
Another thing to note is the length of your business plan. It would be best if you made it as brief as possible.
You hardly see investors or agencies that read through an extremely long document. In that case, if your first few pages can’t convince them, then you have lost it. The more pages you write, the higher the chances of you derailing from the essential contents.
To ensure your business plan has a high conversion rate, you need to dispose of every unnecessary information. For example, if you have a strategy that you are not sure of, it would be best to leave it out of the plan.
5. Make an Outline and Follow Through
A perfect business plan must have touched every part needed to convince the audience. Business owners get easily tempted to concentrate more on their products than on other sections. Doing this can be detrimental to the efficiency of the business plan.
For example, imagine you talking about a product but omitting or providing very little information about the target audience. You will leave your clients confused.
To ensure that your business plan communicates your full business model to readers, you have to input all the necessary information in it. One of the best ways to achieve this is to design a structure and stick to it.
This structure is what guides you throughout the writing. To make your work easier, you can assign an estimated word count or page limit to every section to avoid making it too bulky for easy reading. As a guide, the necessary things your business plan must contain are:
- Table of contents
- Introduction
- Product or service description
- Target audience
- Market size
- Competition analysis
- Financial projections
Some specific businesses can include some other essential sections, but these are the key sections that must be in every business plan.
6. Ask a Professional to Proofread
When writing a business plan, you must tie all loose ends to get a perfect result. When you are done with writing, call a professional to go through the document for you. You are bound to make mistakes, and the way to correct them is to get external help.
You should get a professional in your field who can relate to every section of your business plan. It would be easier for the professional to notice the inner flaws in the document than an editor with no knowledge of your business.
In addition to getting a professional to proofread, get an editor to proofread and edit your document. The editor will help you identify grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and inappropriate writing styles.
Writing a business plan can be daunting, but you can surmount that obstacle and get the best out of it with these tips.
Business Plan Examples and Templates That’ll Save You Tons of Time
1. hubspot's one-page business plan.

The one-page business plan template by HubSpot is the perfect guide for businesses of any size, irrespective of their business strategy. Although the template is condensed into a page, your final business plan should not be a page long! The template is designed to ask helpful questions that can help you develop your business plan.
Hubspot’s one-page business plan template is divided into nine fields:
- Business opportunity
- Company description
- Industry analysis
- Target market
- Implementation timeline
- Marketing plan
- Financial summary
- Funding required
2. Bplan’s Free Business Plan Template

Bplans' free business plan template is investor-approved. It is a rich template used by prestigious educational institutions such as Babson College and Princeton University to teach entrepreneurs how to create a business plan.
The template has six sections: the executive summary, opportunity, execution, company, financial plan, and appendix. There is a step-by-step guide for writing every little detail in the business plan. Follow the instructions each step of the way and you will create a business plan that impresses investors or lenders easily.
3. HubSpot's Downloadable Business Plan Template

HubSpot’s downloadable business plan template is a more comprehensive option compared to the one-page business template by HubSpot. This free and downloadable business plan template is designed for entrepreneurs.
The template is a comprehensive guide and checklist for business owners just starting their businesses. It tells you everything you need to fill in each section of the business plan and how to do it.
There are nine sections in this business plan template: an executive summary, company and business description, product and services line, market analysis, marketing plan, sales plan, legal notes, financial considerations, and appendix.
4. Business Plan by My Own Business Institute

My Own Business Institute (MOBI) which is a part of Santa Clara University's Center for Innovation and Entrepreneurship offers a free business plan template. You can either copy the free business template from the link provided above or download it as a Word document.
The comprehensive template consists of a whopping 15 sections.
- The Business Profile
- The Vision and the People
- Home-Based Business and Freelance Business Opportunities
- Organization
- Licenses and Permits
- Business Insurance
- Communication Tools
- Acquisitions
- Location and Leasing
- Accounting and Cash Flow
- Opening and Marketing
- Managing Employees
- Expanding and Handling Problems
There are lots of helpful tips on how to fill each section in the free business plan template by MOBI.
5. Score's Business Plan Template for Startups

Score is an American nonprofit organization that helps entrepreneurs build successful companies. This business plan template for startups by Score is available for free download. The business plan template asks a whooping 150 generic questions that help entrepreneurs from different fields to set up the perfect business plan.
The business plan template for startups contains clear instructions and worksheets, all you have to do is answer the questions and fill the worksheets.
There are nine sections in the business plan template: executive summary, company description, products and services, marketing plan, operational plan, management and organization, startup expenses and capitalization, financial plan, and appendices.
The ‘refining the plan’ resource contains instructions that help you modify your business plan to suit your specific needs, industry, and target audience. After you have completed Score’s business plan template, you can work with a SCORE mentor for expert advice in business planning.
6. Minimalist Architecture Business Plan Template by Venngage

The minimalist architecture business plan template is a simple template by Venngage that you can customize to suit your business needs .
There are five sections in the template: an executive summary, statement of problem, approach and methodology, qualifications, and schedule and benchmark. The business plan template has instructions that guide users on what to fill in each section.
7. Small Business Administration Free Business Plan Template

The Small Business Administration (SBA) offers two free business plan templates, filled with practical real-life examples that you can model to create your business plan. Both free business plan templates are written by fictional business owners: Rebecca who owns a consulting firm, and Andrew who owns a toy company.
There are five sections in the two SBA’s free business plan templates.
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Service Line
- Marketing and Sales
8. The $100 Startup's One-Page Business Plan

The one-page business plan by the $100 startup is a simple business plan template for entrepreneurs who do not want to create a long and complicated plan . You can include more details in the appendices for funders who want more information beyond what you can put in the one-page business plan.
There are five sections in the one-page business plan such as overview, ka-ching, hustling, success, and obstacles or challenges or open questions. You can answer all the questions using one or two sentences.
9. PandaDoc’s Free Business Plan Template

The free business plan template by PandaDoc is a comprehensive 15-page document that describes the information you should include in every section.
There are 11 sections in PandaDoc’s free business plan template.
- Executive summary
- Business description
- Products and services
- Operations plan
- Management organization
- Financial plan
- Conclusion / Call to action
- Confidentiality statement
You have to sign up for its 14-day free trial to access the template. You will find different business plan templates on PandaDoc once you sign up (including templates for general businesses and specific businesses such as bakeries, startups, restaurants, salons, hotels, and coffee shops)
PandaDoc allows you to customize its business plan templates to fit the needs of your business. After editing the template, you can send it to interested parties and track opens and views through PandaDoc.
10. Invoiceberry Templates for Word, Open Office, Excel, or PPT

InvoiceBerry is a U.K based online invoicing and tracking platform that offers free business plan templates in .docx, .odt, .xlsx, and .pptx formats for freelancers and small businesses.
Before you can download the free business plan template, it will ask you to give it your email address. After you complete the little task, it will send the download link to your inbox for you to download. It also provides a business plan checklist in .xlsx file format that ensures you add the right information to the business plan.
Alternatives to the Traditional Business Plan
A business plan is very important in mapping out how one expects their business to grow over a set number of years, particularly when they need external investment in their business. However, many investors do not have the time to watch you present your business plan. It is a long and boring read.
Luckily, there are three alternatives to the traditional business plan (the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck). These alternatives are less laborious and easier and quicker to present to investors.
Business Model Canvas (BMC)
The business model canvas is a business tool used to present all the important components of setting up a business, such as customers, route to market, value proposition, and finance in a single sheet. It provides a very focused blueprint that defines your business initially which you can later expand on if needed.

The sheet is divided mainly into company, industry, and consumer models that are interconnected in how they find problems and proffer solutions.
Segments of the Business Model Canvas
The business model canvas was developed by founder Alexander Osterwalder to answer important business questions. It contains nine segments.

- Key Partners: Who will be occupying important executive positions in your business? What do they bring to the table? Will there be a third party involved with the company?
- Key Activities: What important activities will production entail? What activities will be carried out to ensure the smooth running of the company?
- The Product’s Value Propositions: What does your product do? How will it be different from other products?
- Customer Segments: What demography of consumers are you targeting? What are the habits of these consumers? Who are the MVPs of your target consumers?
- Customer Relationships: How will the team support and work with its customer base? How do you intend to build and maintain trust with the customer?
- Key Resources: What type of personnel and tools will be needed? What size of the budget will they need access to?
- Channels: How do you plan to create awareness of your products? How do you intend to transport your product to the customer?
- Cost Structure: What is the estimated cost of production? How much will distribution cost?
- Revenue Streams: For what value are customers willing to pay? How do they prefer to pay for the product? Are there any external revenues attached apart from the main source? How do the revenue streams contribute to the overall revenue?
Lean Canvas
The lean canvas is a problem-oriented alternative to the standard business model canvas. It was proposed by Ash Maurya, creator of Lean Stack as a development of the business model generation. It uses a more problem-focused approach and it majorly targets entrepreneurs and startup businesses.

Lean Canvas uses the same 9 blocks concept as the business model canvas, however, they have been modified slightly to suit the needs and purpose of a small startup. The key partners, key activities, customer relationships, and key resources are replaced by new segments which are:
- Problem: Simple and straightforward number of problems you have identified, ideally three.
- Solution: The solutions to each problem.
- Unfair Advantage: Something you possess that can't be easily bought or replicated.
- Key Metrics: Important numbers that will tell how your business is doing.
Startup Pitch Deck
While the business model canvas compresses into a factual sheet, startup pitch decks expand flamboyantly.
Pitch decks, through slides, convey your business plan, often through graphs and images used to emphasize estimations and observations in your presentation. Entrepreneurs often use pitch decks to fully convince their target audience of their plans before discussing funding arrangements.

Considering the likelihood of it being used in a small time frame, a good startup pitch deck should ideally contain 20 slides or less to have enough time to answer questions from the audience.
Unlike the standard and lean business model canvases, a pitch deck doesn't have a set template on how to present your business plan but there are still important components to it. These components often mirror those of the business model canvas except that they are in slide form and contain more details.

Using Airbnb (one of the most successful start-ups in recent history) for reference, the important components of a good slide are listed below.
- Cover/Introduction Slide: Here, you should include your company's name and mission statement. Your mission statement should be a very catchy tagline. Also, include personal information and contact details to provide an easy link for potential investors.
- Problem Slide: This slide requires you to create a connection with the audience or the investor that you are pitching. For example in their pitch, Airbnb summarized the most important problems it would solve in three brief points – pricing of hotels, disconnection from city culture, and connection problems for local bookings.
- Solution Slide: This slide includes your core value proposition. List simple and direct solutions to the problems you have mentioned
- Customer Analysis: Here you will provide information on the customers you will be offering your service to. The identity of your customers plays an important part in fundraising as well as the long-run viability of the business.
- Market Validation: Use competitive analysis to show numbers that prove the presence of a market for your product, industry behavior in the present and the long run, as well as the percentage of the market you aim to attract. It shows that you understand your competitors and customers and convinces investors of the opportunities presented in the market.
- Business Model: Your business model is the hook of your presentation. It may vary in complexity but it should generally include a pricing system informed by your market analysis. The goal of the slide is to confirm your business model is easy to implement.
- Marketing Strategy: This slide should summarize a few customer acquisition methods that you plan to use to grow the business.
- Competitive Advantage: What this slide will do is provide information on what will set you apart and make you a more attractive option to customers. It could be the possession of technology that is not widely known in the market.
- Team Slide: Here you will give a brief description of your team. Include your key management personnel here and their specific roles in the company. Include their educational background, job history, and skillsets. Also, talk about their accomplishments in their careers so far to build investors' confidence in members of your team.
- Traction Slide: This validates the company’s business model by showing growth through early sales and support. The slide aims to reduce any lingering fears in potential investors by showing realistic periodic milestones and profit margins. It can include current sales, growth, valuable customers, pre-orders, or data from surveys outlining current consumer interest.
- Funding Slide: This slide is popularly referred to as ‘the ask'. Here you will include important details like how much is needed to get your business off the ground and how the funding will be spent to help the company reach its goals.
- Appendix Slides: Your pitch deck appendix should always be included alongside a standard pitch presentation. It consists of additional slides you could not show in the pitch deck but you need to complement your presentation.
It is important to support your calculations with pictorial renditions. Infographics, such as pie charts or bar graphs, will be more effective in presenting the information than just listing numbers. For example, a six-month graph that shows rising profit margins will easily look more impressive than merely writing it.
Lastly, since a pitch deck is primarily used to secure meetings and you may be sharing your pitch with several investors, it is advisable to keep a separate public version that doesn't include financials. Only disclose the one with projections once you have secured a link with an investor.
Advantages of the Business Model Canvas, Lean Canvas, and Startup Pitch Deck over the Traditional Business Plan
- Time-Saving: Writing a detailed traditional business plan could take weeks or months. On the other hand, all three alternatives can be done in a few days or even one night of brainstorming if you have a comprehensive understanding of your business.
- Easier to Understand: Since the information presented is almost entirely factual, it puts focus on what is most important in running the business. They cut away the excess pages of fillers in a traditional business plan and allow investors to see what is driving the business and what is getting in the way.
- Easy to Update: Businesses typically present their business plans to many potential investors before they secure funding. What this means is that you may regularly have to amend your presentation to update statistics or adjust to audience-specific needs. For a traditional business plan, this could mean rewriting a whole section of your plan. For the three alternatives, updating is much easier because they are not voluminous.
- Guide for a More In-depth Business Plan: All three alternatives have the added benefit of being able to double as a sketch of your business plan if the need to create one arises in the future.
Business Plan FAQ
Business plans are important for any entrepreneur who is looking for a framework to run their company over some time or seeking external support. Although they are essential for new businesses, every company should ideally have a business plan to track their growth from time to time. They can be used by startups seeking investments or loans to convey their business ideas or an employee to convince his boss of the feasibility of starting a new project. They can also be used by companies seeking to recruit high-profile employee targets into key positions or trying to secure partnerships with other firms.
Business plans often vary depending on your target audience, the scope, and the goals for the plan. Startup plans are the most common among the different types of business plans. A start-up plan is used by a new business to present all the necessary information to help get the business up and running. They are usually used by entrepreneurs who are seeking funding from investors or bank loans. The established company alternative to a start-up plan is a feasibility plan. A feasibility plan is often used by an established company looking for new business opportunities. They are used to show the upsides of creating a new product for a consumer base. Because the audience is usually company people, it requires less company analysis. The third type of business plan is the lean business plan. A lean business plan is a brief, straight-to-the-point breakdown of your ideas and analysis for your business. It does not contain details of your proposal and can be written on one page. Finally, you have the what-if plan. As it implies, a what-if plan is a preparation for the worst-case scenario. You must always be prepared for the possibility of your original plan being rejected. A good what-if plan will serve as a good plan B to the original.
A good business plan has 10 key components. They include an executive plan, product analysis, desired customer base, company analysis, industry analysis, marketing strategy, sales strategy, financial projection, funding, and appendix. Executive Plan Your business should begin with your executive plan. An executive plan will provide early insight into what you are planning to achieve with your business. It should include your mission statement and highlight some of the important points which you will explain later. Product Analysis The next component of your business plan is your product analysis. A key part of this section is explaining the type of item or service you are going to offer as well as the market problems your product will solve. Desired Consumer Base Your product analysis should be supplemented with a detailed breakdown of your desired consumer base. Investors are always interested in knowing the economic power of your market as well as potential MVP customers. Company Analysis The next component of your business plan is your company analysis. Here, you explain how you want to run your business. It will include your operational strategy, an insight into the workforce needed to keep the company running, and important executive positions. It will also provide a calculation of expected operational costs. Industry Analysis A good business plan should also contain well laid out industry analysis. It is important to convince potential investors you know the companies you will be competing with, as well as your plans to gain an edge on the competition. Marketing Strategy Your business plan should also include your marketing strategy. This is how you intend to spread awareness of your product. It should include a detailed explanation of the company brand as well as your advertising methods. Sales Strategy Your sales strategy comes after the market strategy. Here you give an overview of your company's pricing strategy and how you aim to maximize profits. You can also explain how your prices will adapt to market behaviors. Financial Projection The financial projection is the next component of your business plan. It explains your company's expected running cost and revenue earned during the tenure of the business plan. Financial projection gives a clear idea of how your company will develop in the future. Funding The next component of your business plan is funding. You have to detail how much external investment you need to get your business idea off the ground here. Appendix The last component of your plan is the appendix. This is where you put licenses, graphs, or key information that does not fit in any of the other components.
The business model canvas is a business management tool used to quickly define your business idea and model. It is often used when investors need you to pitch your business idea during a brief window.
A pitch deck is similar to a business model canvas except that it makes use of slides in its presentation. A pitch is not primarily used to secure funding, rather its main purpose is to entice potential investors by selling a very optimistic outlook on the business.
Business plan competitions help you evaluate the strength of your business plan. By participating in business plan competitions, you are improving your experience. The experience provides you with a degree of validation while practicing important skills. The main motivation for entering into the competitions is often to secure funding by finishing in podium positions. There is also the chance that you may catch the eye of a casual observer outside of the competition. These competitions also provide good networking opportunities. You could meet mentors who will take a keen interest in guiding you in your business journey. You also have the opportunity to meet other entrepreneurs whose ideas can complement yours.
Exlore Further
- 12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
- 13 Sources of Business Finance For Companies & Sole Traders
- 5 Common Types of Business Structures (+ Pros & Cons)
- How to Buy a Business in 8 Steps (+ Due Diligence Checklist)
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1222648303-e00f14f235ba4c63aa222a87f430e345.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

The 12 Key Components of a Business Plan
There are 12 components of a business plan entrepreneurs must know as they lay out how their business will work.

Entrepreneurs who create business plans are more likely to succeed than those who don’t.
Not only can a sound plan help your business access investment capital but—as the study found—it can even determine the success or failure of your venture.
Here are the critical components of a business plan to help you craft your own.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document outlining your business goals and your strategies for achieving them. It might include your company’s mission statement , details about your products or services, how you plan to bring them to market, and how much time and money you need to execute the plan.
For a thorough explanation of how to write a business plan, refer to Shopify’s guide .

12 components of a business plan
Business plans vary depending on the product or service. Some entrepreneurs choose to use diagrams and charts, while others rely on text alone. Regardless of how you go about it, good business plans tend to include the following elements:
- Executive summary
- Company description
- Market analysis
- Marketing plan
- Competitive analysis
- Organizational structure
- Products and services
- Operating plan
- Financial plan
- Funding sources
1. Executive summary
The executive summary briefly explains your business’s products or services and why it has the potential to be profitable. You may also include basic information about your company, such as its location and the number of employees.
2. Company description
The company description helps customers, lenders, and potential investors gain a deeper understanding of your product or service. It provides detailed descriptions of your supply chains and explains how your company plans to bring its products or services to market.
3. Market analysis
The market analysis section outlines your plans to reach your target audience . It usually includes an estimate of the potential demand for the product or service and a summary of market research .
The market analysis also includes information about marketing strategies, advertising ideas, or other ways of attracting customers.
Another component of this section is a detailed breakdown of target customers. Many businesses find it helpful to analyze their target market using customer segments , often with demographic data such as age or income. This way, you can customize your marketing plans to reach different groups of customers.
4. Marketing plan
The marketing plan section details how you plan to attract and retain customers. It covers the marketing mix: product, price, place, and promotion. It shows you understand your market and have clear, measurable goals to guide your marketing strategy.
For example, a fashion retail store might focus on online sales channels, competitive pricing strategies, high-quality products, and aggressive social media promotion.
5. Sales plan
This section focuses on the actions you’ll take to achieve sales targets and drive revenue. It’s different from a marketing plan because it’s more about the direct process of selling the product to your customer. It looks at the methods used from lead generation to closing the sale, as well as revenue targets.
An ecommerce sales strategy might involve optimizing your online shopping experience, using targeted digital marketing to drive traffic, and employing tactics like flash sales , personalized email marketing, or loyalty programs to boost sales.
6. Competitive analysis
It’s essential that you understand your competitors and distinguish your business. There are two main types of competitors: direct and indirect competitors.
- Direct competitors. Direct competitors offer the same or similar products and services. For example, the underwear brand Skims is a direct competitor with Spanx .
- Indirect competitors. Indirect competitors, on the other hand, offer different products and services that may satisfy the same customer needs. For example, cable television is an indirect competitor to Netflix.
A competitive analysis explains your business’s unique strengths that give it a competitive advantage over other businesses.
7. Organizational structure
The organizational structure explains your company’s legal structure and provides information about the management team. It also describes the business’s operating plan and details who is responsible for which aspects of the company.
8. Products and services
This component goes in-depth on what you’re actually selling and why it’s valuable to customers. It’ll provide a description of your products and services with all their features, benefits, and unique selling points. It may also discuss the current development stage of your products and plans for the future.
The products and services section also looks at pricing strategy , intellectual property (IP) rights, and any key supplier information. For example, in an ecommerce business plan focusing on eco-friendly home products, this section would detail the range of products, explain how they are environmentally friendly, outline sourcing and production practices, discuss pricing, and highlight any certifications or eco-labels the products have received.
9. Operating plan
Here is where you explain the day-to-day operations of the business. Your operating plan will cover aspects from production or service delivery to human and resource management. It shows readers how you plan to deliver on your promises.
For example, in a business plan for a startup selling artisanal crafts, this section would include details on how artisans are sourced, how products are cataloged and stored, the ecommerce platform used for sales, and the logistics for packaging and shipping orders worldwide.
10. Financial plan
The financial plan is one of the most critical parts of the business plan, especially for companies seeking outside funding.
A plan often includes capital expenditure budgets, forecasted income statements , and cash flow statements , which can help predict when your company will become profitable and how it expects to survive in the meantime.
If your business is already profitable, your financial plan can help with convincing investors of future growth. At the end of the financial section, you may also include a value proposition , which estimates the value of your business.
11. Funding sources
Some businesses planning to expand or to seek funds from venture capitalists may include a section devoted to their long-term growth strategy, including ways to broaden product offerings and penetrate new markets.
12. Appendix
The final component of a business plan is the appendix. Here, you may include additional documents cited in other sections or requested by readers. These might be résumés, financial statements, product pictures, patent approvals, and legal records.
Components of a business plan FAQ
What are 8 common parts of a good business plan.
Some of the most common components of a business plan are an executive summary, a company description, a marketing analysis, a competitive analysis, an organization description, a summary of growth strategies, a financial plan, and an appendix.
What is a business plan format?
A business plan format is a way of structuring a business plan. Shopify offers a free business plan template for startups that you can use to format your business plan.
What are the 5 functions of a business plan?
A business plan explains your company’s products or services, how you expect to make money, the reliability of supply chains, and factors that might affect demand.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 1, 2024
Jul 31, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.
Table of Contents
What is a business plan, the advantages of having a business plan, the types of business plans, the key elements of a business plan, best business plan software, common challenges of writing a business plan, become an expert business planner, business planning: it’s importance, types and key elements.

Every year, thousands of new businesses see the light of the day. One look at the World Bank's Entrepreneurship Survey and database shows the mind-boggling rate of new business registrations. However, sadly, only a tiny percentage of them have a chance of survival.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, about 20% of small businesses fail in their first year, about 50% in their fifth year.
Research from the University of Tennessee found that 44% of businesses fail within the first three years. Among those that operate within specific sectors, like information (which includes most tech firms), 63% shut shop within three years.
Several other statistics expose the abysmal rates of business failure. But why are so many businesses bound to fail? Most studies mention "lack of business planning" as one of the reasons.
This isn’t surprising at all.
Running a business without a plan is like riding a motorcycle up a craggy cliff blindfolded. Yet, way too many firms ( a whopping 67%) don't have a formal business plan in place.
It doesn't matter if you're a startup with a great idea or a business with an excellent product. You can only go so far without a roadmap — a business plan. Only, a business plan is so much more than just a roadmap. A solid plan allows a business to weather market challenges and pivot quickly in the face of crisis, like the one global businesses are struggling with right now, in the post-pandemic world.
But before you can go ahead and develop a great business plan, you need to know the basics. In this article, we'll discuss the fundamentals of business planning to help you plan effectively for 2021.
Now before we begin with the details of business planning, let us understand what it is.
No two businesses have an identical business plan, even if they operate within the same industry. So one business plan can look entirely different from another one. Still, for the sake of simplicity, a business plan can be defined as a guide for a company to operate and achieve its goals.
More specifically, it's a document in writing that outlines the goals, objectives, and purpose of a business while laying out the blueprint for its day-to-day operations and key functions such as marketing, finance, and expansion.
A good business plan can be a game-changer for startups that are looking to raise funds to grow and scale. It convinces prospective investors that the venture will be profitable and provides a realistic outlook on how much profit is on the cards and by when it will be attained.
However, it's not only new businesses that greatly benefit from a business plan. Well-established companies and large conglomerates also need to tweak their business plans to adapt to new business environments and unpredictable market changes.
Before getting into learning more about business planning, let us learn the advantages of having one.
Since a detailed business plan offers a birds-eye view of the entire framework of an establishment, it has several benefits that make it an important part of any organization. Here are few ways a business plan can offer significant competitive edge.
- Sets objectives and benchmarks: Proper planning helps a business set realistic objectives and assign stipulated time for those goals to be met. This results in long-term profitability. It also lets a company set benchmarks and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) necessary to reach its goals.
- Maximizes resource allocation: A good business plan helps to effectively organize and allocate the company’s resources. It provides an understanding of the result of actions, such as, opening new offices, recruiting fresh staff, change in production, and so on. It also helps the business estimate the financial impact of such actions.
- Enhances viability: A plan greatly contributes towards turning concepts into reality. Though business plans vary from company to company, the blueprints of successful companies often serve as an excellent guide for nascent-stage start-ups and new entrepreneurs. It also helps existing firms to market, advertise, and promote new products and services into the market.
- Aids in decision making: Running a business involves a lot of decision making: where to pitch, where to locate, what to sell, what to charge — the list goes on. A well thought-out business plan provides an organization the ability to anticipate the curveballs that the future could throw at them. It allows them to come up with answers and solutions to these issues well in advance.
- Fix past mistakes: When businesses create plans keeping in mind the flaws and failures of the past and what worked for them and what didn’t, it can help them save time, money, and resources. Such plans that reflects the lessons learnt from the past offers businesses an opportunity to avoid future pitfalls.
- Attracts investors: A business plan gives investors an in-depth idea about the objectives, structure, and validity of a firm. It helps to secure their confidence and encourages them to invest.
Now let's look at the various types involved in business planning.
Become a Business and Leadership Professional
- Top 10 skills in demand Business Analysis As A Skill In 2020
- 14% Growth in Jobs Of Business Analysis Profile By 2028
Business Analyst
- Industry-recognized certifications from IBM and Simplilearn
- Masterclasses from IBM experts
Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis
- Get mentored and network with industry experts from Amazon, Microsoft, and Google
- Access Harvard Business Publishing case studies of Pearson, CarMax, EvCard, etc
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Assistant Consultant at Tata Consultancy Services , Tata Consultancy Services
My experience with Simplilearn has been great till now. They have good materials to start with, and a wide range of courses. I have signed up for two courses with Simplilearn over the past 6 months, Data Scientist and Agile and Scrum. My experience with both is good. One unique feature I liked about Simplilearn is that they give pre-requisites that you should complete, before a live class, so that you go there fully prepared. Secondly, there support staff is superb. I believe there are two teams, to cater to the Indian and US time zones. Simplilearn gives you the most methodical and easy way to up-skill yourself. Also, when you compare the data analytics courses across the market that offer web-based tutorials, Simplilearn, scores over the rest in my opinion. Great job, Simplilearn!
I was keenly looking for a change in my domain from business consultancy to IT(Business Analytics). This Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis course helped me achieve the same. I am proficient in business analysis now and am looking for job profiles that suit my skill set.
Business plans are formulated according to the needs of a business. It can be a simple one-page document or an elaborate 40-page affair, or anything in between. While there’s no rule set in stone as to what exactly a business plan can or can’t contain, there are a few common types of business plan that nearly all businesses in existence use.
Here’s an overview of a few fundamental types of business plans.
- Start-up plan: As the name suggests, this is a documentation of the plans, structure, and objections of a new business establishments. It describes the products and services that are to be produced by the firm, the staff management, and market analysis of their production. Often, a detailed finance spreadsheet is also attached to this document for investors to determine the viability of the new business set-up.
- Feasibility plan: A feasibility plan evaluates the prospective customers of the products or services that are to be produced by a company. It also estimates the possibility of a profit or a loss of a venture. It helps to forecast how well a product will sell at the market, the duration it will require to yield results, and the profit margin that it will secure on investments.
- Expansion Plan: This kind of plan is primarily framed when a company decided to expand in terms of production or structure. It lays down the fundamental steps and guidelines with regards to internal or external growth. It helps the firm to analyze the activities like resource allocation for increased production, financial investments, employment of extra staff, and much more.
- Operations Plan: An operational plan is also called an annual plan. This details the day-to-day activities and strategies that a business needs to follow in order to materialize its targets. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of the managing body, the various departments, and the company’s employees for the holistic success of the firm.
- Strategic Plan: This document caters to the internal strategies of the company and is a part of the foundational grounds of the establishments. It can be accurately drafted with the help of a SWOT analysis through which the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats can be categorized and evaluated so that to develop means for optimizing profits.
There is some preliminary work that’s required before you actually sit down to write a plan for your business. Knowing what goes into a business plan is one of them.
Here are the key elements of a good business plan:
- Executive Summary: An executive summary gives a clear picture of the strategies and goals of your business right at the outset. Though its value is often understated, it can be extremely helpful in creating the readers’ first impression of your business. As such, it could define the opinions of customers and investors from the get-go.
- Business Description: A thorough business description removes room for any ambiguity from your processes. An excellent business description will explain the size and structure of the firm as well as its position in the market. It also describes the kind of products and services that the company offers. It even states as to whether the company is old and established or new and aspiring. Most importantly, it highlights the USP of the products or services as compared to your competitors in the market.
- Market Analysis: A systematic market analysis helps to determine the current position of a business and analyzes its scope for future expansions. This can help in evaluating investments, promotions, marketing, and distribution of products. In-depth market understanding also helps a business combat competition and make plans for long-term success.
- Operations and Management: Much like a statement of purpose, this allows an enterprise to explain its uniqueness to its readers and customers. It showcases the ways in which the firm can deliver greater and superior products at cheaper rates and in relatively less time.
- Financial Plan: This is the most important element of a business plan and is primarily addressed to investors and sponsors. It requires a firm to reveal its financial policies and market analysis. At times, a 5-year financial report is also required to be included to show past performances and profits. The financial plan draws out the current business strategies, future projections, and the total estimated worth of the firm.
The importance of business planning is it simplifies the planning of your company's finances to present this information to a bank or investors. Here are the best business plan software providers available right now:
- Business Sorter
The importance of business planning cannot be emphasized enough, but it can be challenging to write a business plan. Here are a few issues to consider before you start your business planning:
- Create a business plan to determine your company's direction, obtain financing, and attract investors.
- Identifying financial, demographic, and achievable goals is a common challenge when writing a business plan.
- Some entrepreneurs struggle to write a business plan that is concise, interesting, and informative enough to demonstrate the viability of their business idea.
- You can streamline your business planning process by conducting research, speaking with experts and peers, and working with a business consultant.
Whether you’re running your own business or in-charge of ensuring strategic performance and growth for your employer or clients, knowing the ins and outs of business planning can set you up for success.
Be it the launch of a new and exciting product or an expansion of operations, business planning is the necessity of all large and small companies. Which is why the need for professionals with superior business planning skills will never die out. In fact, their demand is on the rise with global firms putting emphasis on business analysis and planning to cope with cut-throat competition and market uncertainties.
While some are natural-born planners, most people have to work to develop this important skill. Plus, business planning requires you to understand the fundamentals of business management and be familiar with business analysis techniques . It also requires you to have a working knowledge of data visualization, project management, and monitoring tools commonly used by businesses today.
Simpliearn’s Executive Certificate Program in General Management will help you develop and hone the required skills to become an extraordinary business planner. This comprehensive general management program by IIM Indore can serve as a career catalyst, equipping professionals with a competitive edge in the ever-evolving business environment.
What Is Meant by Business Planning?
Business planning is developing a company's mission or goals and defining the strategies you will use to achieve those goals or tasks. The process can be extensive, encompassing all aspects of the operation, or it can be concrete, focusing on specific functions within the overall corporate structure.
What Are the 4 Types of Business Plans?
The following are the four types of business plans:
Operational Planning
This type of planning typically describes the company's day-to-day operations. Single-use plans are developed for events and activities that occur only once (such as a single marketing campaign). Ongoing plans include problem-solving policies, rules for specific regulations, and procedures for a step-by-step process for achieving particular goals.
Strategic Planning
Strategic plans are all about why things must occur. A high-level overview of the entire business is included in strategic planning. It is the organization's foundation and will dictate long-term decisions.
Tactical Planning
Tactical plans are about what will happen. Strategic planning is aided by tactical planning. It outlines the tactics the organization intends to employ to achieve the goals outlined in the strategic plan.
Contingency Planning
When something unexpected occurs or something needs to be changed, contingency plans are created. In situations where a change is required, contingency planning can be beneficial.

What Are the 7 Steps of a Business Plan?
The following are the seven steps required for a business plan:
Conduct Research
If your company is to run a viable business plan and attract investors, your information must be of the highest quality.
Have a Goal
The goal must be unambiguous. You will waste your time if you don't know why you're writing a business plan. Knowing also implies having a target audience for when the plan is expected to get completed.
Create a Company Profile
Some refer to it as a company profile, while others refer to it as a snapshot. It's designed to be mentally quick and digestible because it needs to stick in the reader's mind quickly since more information is provided later in the plan.
Describe the Company in Detail
Explain the company's current situation, both good and bad. Details should also include patents, licenses, copyrights, and unique strengths that no one else has.
Create a marketing plan ahead of time.
A strategic marketing plan is required because it outlines how your product or service will be communicated, delivered, and sold to customers.
Be Willing to Change Your Plan for the Sake of Your Audience
Another standard error is that people only write one business plan. Startups have several versions, just as candidates have numerous resumes for various potential employers.
Incorporate Your Motivation
Your motivation must be a compelling reason for people to believe your company will succeed in all circumstances. A mission should drive a business, not just selling, to make money. That mission is defined by your motivation as specified in your business plan.
What Are the Basic Steps in Business Planning?
These are the basic steps in business planning:
Summary and Objectives
Briefly describe your company, its objectives, and your plan to keep it running.
Services and Products
Add specifics to your detailed description of the product or service you intend to offer. Where, why, and how much you plan to sell your product or service and any special offers.
Conduct research on your industry and the ideal customers to whom you want to sell. Identify the issues you want to solve for your customers.
Operations are the process of running your business, including the people, skills, and experience required to make it successful.
How are you going to reach your target audience? How you intend to sell to them may include positioning, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
Consider funding costs, operating expenses, and projected income. Include your financial objectives and a breakdown of what it takes to make your company profitable. With proper business planning through the help of support, system, and mentorship, it is easy to start a business.
Our Business And Leadership Courses Duration And Fees
Business And Leadership Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
| Program Name | Duration | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort Starts: | 6 Months | € 1,990 |
| Cohort Starts: | 5 months | € 4,500 |
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 2,499 |
| 11 Months | € 1,299 |
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Business and Leadership
Business Analysis Basics
Data Science & Business Analytics
Business Intelligence Fundamentals
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
Career Masterclass: AI UI/UX Designer: The New Job on the Rise in 2024
Career Information Session: Find Out How to Become a Business Analyst with IIT Roorkee
Industry Trends: Unleash the AI Gateway for Advancing Your UI/UX Design Career in 2024
Recommended Reads
Business Intelligence Career Guide: Your Complete Guide to Becoming a Business Analyst
Corporate Succession Planning: How to Create Leaders According to the Business Need
Top Business Analyst Skills
Business Analytics Basics: A Beginner’s Guide
Financial Planning for Businesses Across the Globe
How to Become a Business Analyst
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

The ultimate guide to business planning (with template)
November 19, 2020 by MindManager Blog
By: Jill Huettich
If you could do something to double the success of your business, would you do it? Of course you would! Happily, that’s not pie-in-the-sky kind of talk either. There is something you can do to increase your likelihood of business success by a whopping 200%. That something is business planning. Time and time again, business planning has been shown to have a huge impact on business growth.
Take, for instance, the results of a survey completed by 2,877 business owners. After analyzing respondents’ answers, the Oregon Department of Economics concluded that business planning correlates with success in multiple areas, including: obtaining a loan, getting investment capital, making a major purchase, recruiting a new team member, thinking more strategically, and growing a company.
Mind you, those results were “regardless of the type of company, the growth stage of the company, and the intent of the business plan.” Clearly, business planning works!
In this guide to business planning, we’ll cover everything you need to know about business plans, their benefits and importance, what does into one, and will provide a template for you to get started. Jump ahead using the links below.
What is business planning?
The importance of business planning, how to write a business plan, sample business plan template.
- Downloadable MindManager template
[Free eBook] How Visualization Builds Better Strategic Plans
Business planning refers to the process of determining a company’s objectives, strategies, and projected actions to reach certain goals within a specific time fame. Typically, business planning focuses on two key areas: making profits and mitigating risks.
When companies engage in business planning, it’s with the objective of creating a business plan. A business plan is a written document that contains: the company’s vision, a description of the company, information about its products and services, marketing research, sales strategies, financial projections, competitor analysis, and financial records.
The purpose of a business plan is to act as a road map of sorts, providing a company with the direction, focus, and clarity it needs to achieve its goals.
Business planning vs. strategic planning
Now that you know what business planning is, you may be wondering if it’s any different from strategic planning, and if so, how? That’s what we’ll go over in this section.
As we mentioned before, business planning provides a detailed overview of a company. Usually, this is undertaken with the goal of building revenue and support for a startup. In other words, a business plan tests the proposition that a “particular undertaking—program, partnership, new venture, growth strategy, or entity as a whole—is economically or operationally viable.”
By contrast, a strategic plan is a high-level document that creates a vision for an established company. From that vision, broadly defined objectives are outlined.
Because strategic plans define companies’ most important objectives, they’re used to align department goals, build consensus among stakeholders, and prioritize company spending.
Another difference between these two types of plans is the length of time they cover. A strategic plan typically looks at a period of 3-5 years, whereas a business plan usually just looks at a year.
Additionally, business plans are primarily written to raise money, so their audience is external. Strategic plans are internal documents, created for people within the company.
The importance of business planning cannot be overstated. In particular, businesses do it for the following reasons :
1. To obtain loans or investments
It would be virtually impossible for a startup to secure capital without a business plan—they’re considered that essential.
That’s because business plans establish the viability of a business, which is something any bank or venture capitalist needs to be convinced of before funding a venture.
2. To prevent mistakes
Unfortunately, most startups don’t even last 5 years. There are a number of different reasons for this, but some of the main ones include: tough competition, low demand for what they’re selling, a poor pricing model, an inadequate team, and an inability to secure that all-important funding we just mentioned.
A good business plan helps companies anticipate these types of problems, so they can prevent them.
3. To examine viability
The idea for a startup is often met with a lot of enthusiasm. That vending machine featuring high-end desserts and pastries? Brilliant!
However, sometimes that enthusiasm needs to be tempered by reality. A business plan offers a great opportunity to do that, because it gets entrepreneurs to think through the answers to questions they may never have even considered, like “Is there a demand in this neighborhood for desserts?” and “How many businesses are already selling desserts in this location?
4. To reduce risk
Flying by the seat of your pants in the business world is not the best idea. A business plan clearly lays out a company’s objectives, as well as the landscape of the market.
As a result, business leaders know which challenges to expect. With that knowledge in hand, they can take proactive steps to mitigate their risks.
5. To accelerate growth
Quite simply, business planning works. In fact, according to one study, companies that plan grow 30% faster than those who don’t. And, interestingly enough, another study found that 71% of fast-growing companies (those defined as having 92% growth in sales from one year to the next) have business plans.
6. To identify problems with cash flow
Business plans contain 3 financial statements: a balance sheet, an income statement, and a cash flow statement. For startups, these numbers are projected.
When entrepreneurs have these numbers to refer to, they can more easily monitor cash flow, comparing reality to their projections. This gives them the opportunity to quickly deal with cash flow challenges, should any arise.
7. To make decisions
When faced with tough business decisions, it can be difficult to know which path to choose. However, with a business plan in hand, entrepreneurs can make well-thought-out decisions based on the analysis they’ve already performed.
As you can see, there are tons of great reasons to create a business plan, particularly for start-ups and other new businesses. However, even well-established businesses can benefit from a business plan.
Not only does a business plan provide a valuable overview of an entire company, but it’s also an excellent tool for pinpointing potential challenges, so they can be proactively addressed and resolved.
There may be nothing more critical to your company’s success than a business plan. That’s why it’s so important to understand how to write a business plan, and to devote time and effort to creating a solid, well-researched one.
The elements of a business plan are fairly straightforward. While no two business plans are identical, most of them rely on the following structure:
1. Executive summary
Business plans typically run dozens of pages long. While, ideally, you’d like to think that people will read your entire plan, there’s no guarantee of that—which is why the executive summary is the most important part of your business plan.
In the summary, you’ll want to provide readers with a quick synapsis that explains what your company is and why it’ll be successful.
This summary should include your company’s mission statement and a description of the product or service you provide. You’ll also want to briefly touch on the company’s founders, employees, location, and financial growth.
Aim to make your executive summary about 4 pages max , and don’t write it until you’ve completed the rest of your business plan. That’ll make it easier to summarize all the information your plan contains.
2. Company description
This detailed overview of your company includes such things as the problems your business solves, as well as the customers it serves. You should view this section as your opportunity to shine by also explaining your business’ competitive advantages.
3. Market analysis
What’s the outlook of the industry you’re in? Who’s your target market and how do you plan to reach the people in it? These are the types of questions you’ll answer in this section of your business plan.
Additionally, you’ll want to use the Market Analysis section to perform a competitor analysis, identifying who the major players are in your industry, as well as their strengths and weaknesses.
By understanding what’s working well for your competitors—and what isn’t—you’ll be better able to determine how you can grab some of their market share.
4. Organization & management
How will your business be structured—as a sole proprietorship, corporation, partnership, or LLC? Include that information in this section, as well as an organization chart showing who’s heading up your company. You may also want to include resumes or CVs for key team members here too.
5. Service or product line
This section should explain what you sell, how it helps customers, and what the product lifecycle looks like. This is where you’ll also want to mention any patents or copyrights.
6. Marketing & sales
How do you intend to attract customers? What marketing channels will you use? What’s your strategy for growth? Think carefully about your answers to these questions, because later, you’ll use this information to make your financial projections.
7. Funding request
If one of the objectives of your business plan is to obtain funding, this section should be included in your plan. When you write your funding request, you’ll want to explain what your funding requirements are over the next 5 years and how those funds will be used.
Additionally, this section should specify , “whether you want debt or equity, the terms you’d like applied, and the length of time your request will cover.”
8. Financial projections
Financial projections are a key part of your plan, particularly if you’re seeking funding. In this section, you’ll want to include financial projections for the next five years, as well as explain how you came up with those figures.
Your projections should include cash flow statements, balance sheets, income statements, and capital expenditure budgets. If your business is operational already, you’ll also want to include the past 3-5 years of those same documents.
9. Appendix
Think of this section as your final opportunity to convince readers of your business’ success. So, this is where you can include supporting documentation, like product pictures, reference letters, permits, patents, legal documents, contracts, credit histories, etc.
And there you have it! Once you’ve finished the analysis required for each of these elements—and typed your findings into a well-formatted document–your business plan will be complete.
Understanding the business planning cycle
After you’ve completed the business planning process, your work—while not over—gets easier. Your job now is to review the business plan periodically to see how well your company is achieving its objectives.
Did you meet your financial projections? In what areas is your company doing well? How is it falling short? Are there any new opportunities for your organization?
During this period of analysis, you’ll ideally want to set 1-year and 3-year goals , as well as key performance indicators (KPIs). These will help you track on a quarterly, or even monthly, basis how well your company’s meeting its objectives.
Most businesses engage in business planning on an annual or quarterly basis. Truly, it depends on how much time your organization has to devote to the task, as well as the industry you’re in.
For smaller businesses, a good aim is to perform the business planning process once a year. For larger companies—or ones where the market changes frequently—you may want to “plan to plan” every quarter.
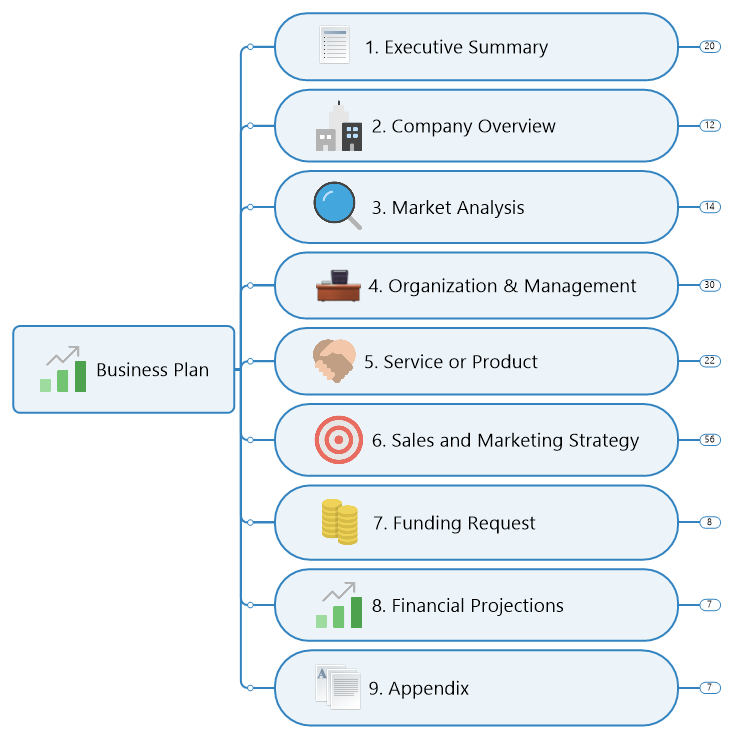
Generally speaking, most business plan templates will include the following key elements and information. We’ve provided a downloadable MindManager template below that you can use to create your own business plan.
Section 1: Executive summary
The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, so you’ll really want to put time and effort into getting it just right.
Make sure to include the following elements :
- Explain the mission of your company – what is the reason for your company?
- Describe your product or service – what types of products and services will you offer customers?
- Introduce the company founders – who are your company’s founders, and what roles will they play within your organization?
- Briefly provide information about your customer base – which customers will your business target, and how will your company serve them?
- Provide an overview of your competitors – explain why your business will succeed by identifying your competitive advantage and describing how you’ll get market share.
- Summarize your financial projections – what financial growth do you expect your company to achieve over the next few years?
- Mention financing requirements – if your business is a start-up seeking financing, briefly mention those financial requirements here.
If you want a good idea of what your completed executive summary should look like, you can check out an example of one here.
Section 2: Company overview
In this section, you’ll want to go into greater detail than you did in the executive summary, explaining which problems your business solves, who its customers are, and what competitive advantages your company has.
Here are the important elements you’ll want to include :
- Provide an overview of your company – what’s its mission, vision, and purpose?
- Give background about the formation of your company – when did your company form?
- Explain who your company’s founders are – what backgrounds do they have that make them uniquely qualified to run your business successfully?
- Provide geographic information – where is your business located and in which markets do you have a presence?
- Describe your company’s competitive advantages – while this was briefly touched upon in the executive summary, you’ll want to provide more information here about why your company will be successful.
Section 3: Market analysis
In this section, you want to prove the viability of your business by providing solid market research about your industry.
To achieve this goal, you’ll want to include the following in this section:
- Identify your target market – who are you trying to sell your products and services to?
- Describe the need for your products or services – why do you anticipate demand for your company’s offerings?
- Give information about the overall market size – how big is the market? How much do you expect your company to sell? Are there any demographic or geographic factors that might impact your sales projections?
- Identify the competition – who are your company’s main competitors? What advantages and disadvantages do they have? What’s their percentage of market share? How much do they sell annually?
- Perform a SWOT analysis – identify your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and strengths.
For help writing this section, you may find it useful to look at this marketing analysis example .
For the competitor and SWOT analyses, we recommend an information visualization software, like MindManager. View the SWOT analysis template at the end of this article.
Section 4: Organization & management
In this section, you want to give readers a solid overview of how your company will be structured. To do that, you’ll want to answer the following questions :
- Describe the legal structure of your business – is it a sole proprietorship, corporation, partnership, or LLC?
- Identify your management team – name the key roles within your organization, identify who will fulfill them, and explain how those individuals will be compensated. You may want to include an organization chart here too, as well as brief resumes or CVs for key team members.
Section 5: Service or product line
In this portion of the business plan, you’ll want to provide more information about the product or service you provide. So, make sure to include these elements here :
- Describe the product or service you sell – what are you offering and how does it help customers?
- Explain the product lifecycle – how long does it take to bring new products/services to market?
- Provide pricing information – how will you price your products or services? What will your operating costs be?
- Describe how you’ll acquire products – are you the manufacturer? If not, who is? Are you working directly with a manufacturer or are you going through a wholesaler? If product demand suddenly increases, what’s the likelihood you’ll experience supply problems?
Section 6: Sales and marketing strategy
Your customer acquisition strategy is especially important to potential investors, so you’ll definitely want to be thorough here. Plus, later you’ll be using this information to make financial projections, so take your time when writing this part of your plan.
- Describe the customer acquisition process – how will you find and attract customers? For instance, will you use salespeople, call centers, social media ads, etc.?
- Explain any promotional methods you plan on using – will you offer free samples or perform product demonstrations?
- Provide information about the marketing materials you intend to use – like brochures, flyers, trade show booths, etc.
- Estimate your advertising budget – how much will you have to spend to achieve your marketing objectives?
Section 7 – Funding request
This section is only necessary if you’re seeking business funding. If you are, you’ll want to include the following information in your business plan:
- Identify your funding requirements – how much money are you requesting and how will those funds be used?
- Describe the terms you’re seeking – do you want debt or equity? Which terms do you want applied? What length of time does your request cover?
Section 8 – Financial projections
As you might imagine, financial projections are a key part of your plan, especially if you’re seeking funding. So, in this section, you’ll want to make sure you include :
- 5 years of projected cash flow statements, balance sheets, income statements, and capital expenditure budgets – these documents should also explain how you came up with the figures you’re using.
- If your business is already up and running, you’ll also want to include the past 3-5 years of those same documents.
Of course to create these financial projections, you’ll need to have the right software. Two good ones to check out are ProjectionHub and PlanGuru .
These forecasting software packages make it easy to create the kinds of financial statements you’ll want to include in your business plan.
Section 9 – Appendix
This is your last chance to convince readers your business will be a success. So, if you have additional information to give your business plan more weight, you’ll want to incorporate it here. Consider including the following in this section:
- Product pictures
- Reference letters
- Legal documents
- Credit histories
And that’s it! After you’ve completed these sections, just assemble them into a single document, format everything neatly, add a table of contents, and your business plan will be complete.
Afterwards, you can use it to obtain loans, determine viability, reduce risk, assess cash flow problems, make decisions, and accelerate business growth—making it well-worth the time and effort it takes to write your plan.

How Visualization Leads to Better Strategic Plans
Download this free eBook to learn: how visualization builds a better plan, 5 proven visualization methods, and a deep dive into the business benefits of visualization.
Write your business plans in MindManager
Download the business planning and SWOT analysis templates below by clicking Menu > Download. You can then open the templates in MindManager.
Don’t have a copy of MindManager yet? Try it free for 30 days.
Business plan template in MindManager
Swot analysis template in mindmanager, ready to take the next step.
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager
Do you REALLY need a business plan?
The top three questions that I get asked most frequently as a professional business plan writer will probably not surprise you:
- What is the purpose of a business plan – why is it really required?
- How is it going to benefit my business if I write a business plan?
- Is a business plan really that important – how can I actually use it?
Keep reading to get my take on what the most essential advantages of preparing a business plan are—and why you may (not) need to prepare one.
The importance, purpose and benefit of a business plan is in that it enables you to validate a business idea, secure funding, set strategic goals – and then take organized action on those goals by making decisions, managing resources, risk and change, while effectively communicating with stakeholders.
Let’s take a closer look at how each of the important business planning benefits can catapult your business forward:
1. Validate Your Business Idea
The process of writing your business plan will force you to ask the difficult questions about the major components of your business, including:
- External: industry, target market of prospective customers, competitive landscape
- Internal: business model, unique selling proposition, operations, marketing, finance
Business planning connects the dots to draw a big picture of the entire business.
And imagine how much time and money you would save if working through a business plan revealed that your business idea is untenable. You would be surprised how often that happens – an idea that once sounded so very promising may easily fall apart after you actually write down all the facts, details and numbers.
While you may be tempted to jump directly into start-up mode, writing a business plan is an essential first step to check the feasibility of a business before investing too much time and money into it. Business plans help to confirm that the idea you are so passionate and convinced about is solid from business point of view.
Take the time to do the necessary research and work through a proper business plan. The more you know, the higher the likelihood that your business will succeed.
2. Set and Track Goals
Successful businesses are dynamic and continuously evolve. And so are good business plans that allow you to:
- Priorities: Regularly set goals, targets (e.g., sales revenues reached), milestones (e.g. number of employees hired), performance indicators and metrics for short, mid and long term
- Accountability: Track your progress toward goals and benchmarks
- Course-correction: make changes to your business as you learn more about your market and what works and what does not
- Mission: Refer to a clear set of values to help steer your business through any times of trouble
Essentially, business plan is a blueprint and an important strategic tool that keeps you focused, motivated and accountable to keep your business on track. When used properly and consulted regularly, it can help you measure and manage what you are working so hard to create – your long-term vision.
As humans, we work better when we have clear goals we can work towards. The everyday business hustle makes it challenging to keep an eye on the strategic priorities. The business planning process serves as a useful reminder.
3. Take Action
A business plan is also a plan of action . At its core, your plan identifies where you are now, where you want your business to go, and how you will get there.
Planning out exactly how you are going to turn your vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between an idea and reality. Success comes not only from having a vision but working towards that vision in a systematic and organized way.
A good business plan clearly outlines specific steps necessary to turn the business objectives into reality. Think of it as a roadmap to success. The strategy and tactics need to be in alignment to make sure that your day-to-day activities lead to the achievement of your business goals.
4. Manage Resources
A business plan also provides insight on how resources required for achieving your business goals will be structured and allocated according to their strategic priority. For example:
Large Spending Decisions
- Assets: When and in what amount will the business commit resources to buy/lease new assets, such as computers or vehicles.
- Human Resources: Objectives for hiring new employees, including not only their pay but how they will help the business grow and flourish.
- Business Space: Information on costs of renting/buying space for offices, retail, manufacturing or other operations, for example when expanding to a new location.
Cash Flow It is essential that a business carefully plans and manages cash flows to ensure that there are optimal levels of cash in the bank at all times and avoid situations where the business could run out of cash and could not afford to pay its bills.
Revenues v. Expenses In addition, your business plan will compare your revenue forecasts to the budgeted costs to make sure that your financials are healthy and the business is set up for success.
5. Make Decisions
Whether you are starting a small business or expanding an existing one, a business plan is an important tool to help guide your decisions:
Sound decisions Gathering information for the business plan boosts your knowledge across many important areas of the business:
- Industry, market, customers and competitors
- Financial projections (e.g., revenue, expenses, assets, cash flow)
- Operations, technology and logistics
- Human resources (management and staff)
- Creating value for your customer through products and services
Decision-making skills The business planning process involves thorough research and critical thinking about many intertwined and complex business issues. As a result, it solidifies the decision-making skills of the business owner and builds a solid foundation for strategic planning , prioritization and sound decision making in your business. The more you understand, the better your decisions will be.
Planning Thorough planning allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time , prepare for anticipate problems before they arise, and ensure that any tactical solutions are in line with the overall strategy and goals.
If you do not take time to plan, you risk becoming overwhelmed by countless options and conflicting directions because you are not unclear about the mission , vision and strategy for your business.
6. Manage Risk
Some level of uncertainty is inherent in every business, but there is a lot you can do to reduce and manage the risk, starting with a business plan to uncover your weak spots.
You will need to take a realistic and pragmatic look at the hard facts and identify:
- Major risks , challenges and obstacles that you can expect on the way – so you can prepare to deal with them.
- Weaknesses in your business idea, business model and strategy – so you can fix them.
- Critical mistakes before they arise – so you can avoid them.
Essentially, the business plan is your safety net . Naturally, business plan cannot entirely eliminate risk, but it can significantly reduce it and prepare you for any challenges you may encounter.
7. Communicate Internally
Attract talent For a business to succeed, attracting talented workers and partners is of vital importance.
A business plan can be used as a communication tool to attract the right talent at all levels, from skilled staff to executive management, to work for your business by explaining the direction and growth potential of the business in a presentable format.
Align performance Sharing your business plan with all team members helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page when it comes to the long-term vision and strategy.
You need their buy-in from the beginning, because aligning your team with your priorities will increase the efficiency of your business as everyone is working towards a common goal .
If everyone on your team understands that their piece of work matters and how it fits into the big picture, they are more invested in achieving the objectives of the business.
It also makes it easier to track and communicate on your progress.
Share and explain business objectives with your management team, employees and new hires. Make selected portions of your business plan part of your new employee training.
8. Communicate Externally
Alliances If you are interested in partnerships or joint ventures, you may share selected sections of your plan with the potential business partners in order to develop new alliances.
Suppliers A business plan can play a part in attracting reliable suppliers and getting approved for business credit from suppliers. Suppliers who feel confident that your business will succeed (e.g., sales projections) will be much more likely to extend credit.
In addition, suppliers may want to ensure their products are being represented in the right way .
Professional Services Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, including attorneys, accountants, and other professional consultants as needed, to make sure that everyone is on the same page.
Advisors Share the plan with experts and professionals who are in a position to give you valuable advice.
Landlord Some landlords and property managers require businesses to submit a business plan to be considered for a lease to prove that your business will have sufficient cash flows to pay the rent.
Customers The business plan may also function as a prospectus for potential customers, especially when it comes to large corporate accounts and exclusive customer relationships.
9. Secure Funding
If you intend to seek outside financing for your business, you are likely going to need a business plan.
Whether you are seeking debt financing (e.g. loan or credit line) from a lender (e.g., bank or financial institution) or equity capital financing from investors (e.g., venture or angel capital), a business plan can make the difference between whether or not – and how much – someone decides to invest.
Investors and financiers are always looking at the risk of default and the earning potential based on facts and figures. Understandably, anyone who is interested in supporting your business will want to check that you know what you are doing, that their money is in good hands, and that the venture is viable in the long run.
Business plans tend to be the most effective ways of proving that. A presentation may pique their interest , but they will most probably request a well-written document they can study in detail before they will be prepared to make any financial commitment.
That is why a business plan can often be the single most important document you can present to potential investors/financiers that will provide the structure and confidence that they need to make decisions about funding and supporting your company.
Be prepared to have your business plan scrutinized . Investors and financiers will conduct extensive checks and analyses to be certain that what is written in your business plan faithful representation of the truth.
10. Grow and Change
It is a very common misconception that a business plan is a static document that a new business prepares once in the start-up phase and then happily forgets about.
But businesses are not static. And neither are business plans. The business plan for any business will change over time as the company evolves and expands .
In the growth phase, an updated business plan is particularly useful for:
Raising additional capital for expansion
- Seeking financing for new assets , such as equipment or property
- Securing financing to support steady cash flows (e.g., seasonality, market downturns, timing of sale/purchase invoices)
- Forecasting to allocate resources according to strategic priority and operational needs
- Valuation (e.g., mergers & acquisitions, tax issues, transactions related to divorce, inheritance, estate planning)
Keeping the business plan updated gives established businesses better chance of getting the money they need to grow or even keep operating.
Business plan is also an excellent tool for planning an exit as it would include the strategy and timelines for a transfer to new ownership or dissolution of the company.
Also, if you ever make the decision to sell your business or position yourself for a merger or an acquisition , a strong business plan in hand is going to help you to maximize the business valuation.
Valuation is the process of establishing the worth of a business by a valuation expert who will draw on professional experience as well as a business plan that will outline what you have, what it’s worth now and how much will it likely produce in the future.
Your business is likely to be worth more to a buyer if they clearly understand your business model, your market, your assets and your overall potential to grow and scale .
Related Questions
Business plan purpose: what is the purpose of a business plan.
The purpose of a business plan is to articulate a strategy for starting a new business or growing an existing one by identifying where the business is going and how it will get there to test the viability of a business idea and maximize the chances of securing funding and achieving business goals and success.
Business Plan Benefits: What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan benefits businesses by serving as a strategic tool outlining the steps and resources required to achieve goals and make business ideas succeed, as well as a communication tool allowing businesses to articulate their strategy to stakeholders that support the business.
Business Plan Importance: Why is business plan important?
The importance of a business plan lies in it being a roadmap that guides the decisions of a business on the road to success, providing clarity on all aspects of its operations. This blueprint outlines the goals of the business and what exactly is needed to achieve them through effective management.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
Sign up for our newsletter for product updates, new blog posts, and the chance to be featured in our Small Business Spotlight!

The importance of a business plan

Business plans are like road maps: it’s possible to travel without one, but that will only increase the odds of getting lost along the way.
Owners with a business plan see growth 30% faster than those without one, and 71% of the fast-growing companies have business plans . Before we get into the thick of it, let’s define and go over what a business plan actually is.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a 15-20 page document that outlines how you will achieve your business objectives and includes information about your product, marketing strategies, and finances. You should create one when you’re starting a new business and keep updating it as your business grows.
Rather than putting yourself in a position where you may have to stop and ask for directions or even circle back and start over, small business owners often use business plans to help guide them. That’s because they help them see the bigger picture, plan ahead, make important decisions, and improve the overall likelihood of success.
Why is a business plan important?
A well-written business plan is an important tool because it gives entrepreneurs and small business owners, as well as their employees, the ability to lay out their goals and track their progress as their business begins to grow. Business planning should be the first thing done when starting a new business. Business plans are also important for attracting investors so they can determine if your business is on the right path and worth putting money into.
Business plans typically include detailed information that can help improve your business’s chances of success, like:
- A market analysis : gathering information about factors and conditions that affect your industry
- Competitive analysis : evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors
- Customer segmentation : divide your customers into different groups based on specific characteristics to improve your marketing
- Marketing: using your research to advertise your business
- Logistics and operations plans : planning and executing the most efficient production process
- Cash flow projection : being prepared for how much money is going into and out of your business
- An overall path to long-term growth
What is the purpose of a business plan?
A business plan is like a map for small business owners, showing them where to go and how to get there. Its main purposes are to help you avoid risks, keep everyone on the same page, plan finances, check if your business idea is good, make operations smoother, and adapt to changes. It's a way for small business owners to plan, communicate, and stay on track toward their goals.
10 reasons why you need a business plan
I know what you’re thinking: “Do I really need a business plan? It sounds like a lot of work, plus I heard they’re outdated and I like figuring things out as I go...”.
The answer is: yes, you really do need a business plan! As entrepreneur Kevin J. Donaldson said, “Going into business without a business plan is like going on a mountain trek without a map or GPS support—you’ll eventually get lost and starve! Though it may sound tedious and time-consuming, business plans are critical to starting your business and setting yourself up for success.
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business.
1. To help you with critical decisions
The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and crisis management. Sitting down and considering all the ramifications of any given decision is a luxury that small businesses can’t always afford. That’s where a business plan comes in.
Building a business plan allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time.
Creating a robust business plan is a forcing function—you have to sit down and think about major components of your business before you get started, like your marketing strategy and what products you’ll sell. You answer many tough questions before they arise. And thinking deeply about your core strategies can also help you understand how those decisions will impact your broader strategy.
Send invoices, estimates, and other docs:
- via links or PDFs
- automatically, via Wave
*While subscribed to Wave’s Pro Plan, get 2.9% + $0 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0 (Amex) per transaction for the first 10 transactions of each month of your subscription, then 2.9% + $0.60 (Visa, Mastercard, Discover) and 3.4% + $0.60 (Amex) per transaction. Discover processing is only available to US customers. See full terms and conditions for the US and Canada . See Wave’s Terms of Service for more information.
Send invoices, get paid, track expenses, pay your team, and balance your books with our financial management software.
2. To iron out the kinks
Putting together a business plan requires entrepreneurs to ask themselves a lot of hard questions and take the time to come up with well-researched and insightful answers. Even if the document itself were to disappear as soon as it’s completed, the practice of writing it helps to articulate your vision in realistic terms and better determine if there are any gaps in your strategy.
3. To avoid the big mistakes
Only about half of small businesses are still around to celebrate their fifth birthday . While there are many reasons why small businesses fail, many of the most common are purposefully addressed in business plans.
According to data from CB Insights , some of the most common reasons businesses fail include:
- No market need : No one wants what you’re selling.
- Lack of capital : Cash flow issues or businesses simply run out of money.
- Inadequate team : This underscores the importance of hiring the right people to help you run your business.
- Stiff competition : It’s tough to generate a steady profit when you have a lot of competitors in your space.
- Pricing : Some entrepreneurs price their products or services too high or too low—both scenarios can be a recipe for disaster.
The exercise of creating a business plan can help you avoid these major mistakes. Whether it’s cash flow forecasts or a product-market fit analysis , every piece of a business plan can help spot some of those potentially critical mistakes before they arise. For example, don’t be afraid to scrap an idea you really loved if it turns out there’s no market need. Be honest with yourself!
Get a jumpstart on your business plan by creating your own cash flow projection .
4. To prove the viability of the business
Many businesses are created out of passion, and while passion can be a great motivator, it’s not a great proof point.
Planning out exactly how you’re going to turn that vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between concept and reality. Business plans can help you confirm that your grand idea makes sound business sense.

A critical component of your business plan is the market research section. Market research can offer deep insight into your customers, your competitors, and your chosen industry. Not only can it enlighten entrepreneurs who are starting up a new business, but it can also better inform existing businesses on activities like marketing, advertising, and releasing new products or services.
Want to prove there’s a market gap? Here’s how you can get started with market research.
5. To set better objectives and benchmarks
Without a business plan, objectives often become arbitrary, without much rhyme or reason behind them. Having a business plan can help make those benchmarks more intentional and consequential. They can also help keep you accountable to your long-term vision and strategy, and gain insights into how your strategy is (or isn’t) coming together over time.
6. To communicate objectives and benchmarks
Whether you’re managing a team of 100 or a team of two, you can’t always be there to make every decision yourself. Think of the business plan like a substitute teacher, ready to answer questions any time there’s an absence. Let your staff know that when in doubt, they can always consult the business plan to understand the next steps in the event that they can’t get an answer from you directly.
Sharing your business plan with team members also helps ensure that all members are aligned with what you’re doing, why, and share the same understanding of long-term objectives.
7. To provide a guide for service providers
Small businesses typically employ contractors , freelancers, and other professionals to help them with tasks like accounting , marketing, legal assistance, and as consultants. Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, while ensuring everyone is on the same page.
8. To secure financing
Did you know you’re 2.5x more likely to get funded if you have a business plan?If you’re planning on pitching to venture capitalists, borrowing from a bank, or are considering selling your company in the future, you’re likely going to need a business plan. After all, anyone that’s interested in putting money into your company is going to want to know it’s in good hands and that it’s viable in the long run. Business plans are the most effective ways of proving that and are typically a requirement for anyone seeking outside financing.
Learn what you need to get a small business loan.
9. To better understand the broader landscape
No business is an island, and while you might have a strong handle on everything happening under your own roof, it’s equally important to understand the market terrain as well. Writing a business plan can go a long way in helping you better understand your competition and the market you’re operating in more broadly, illuminate consumer trends and preferences, potential disruptions and other insights that aren’t always plainly visible.
10. To reduce risk
Entrepreneurship is a risky business, but that risk becomes significantly more manageable once tested against a well-crafted business plan. Drawing up revenue and expense projections, devising logistics and operational plans, and understanding the market and competitive landscape can all help reduce the risk factor from an inherently precarious way to make a living. Having a business plan allows you to leave less up to chance, make better decisions, and enjoy the clearest possible view of the future of your company.
Business plan FAQs
How does having a business plan help small business owners make better decisions.
Having a business plan supports small business owners in making smarter decisions by providing a structured framework to assess all parts of their businesses. It helps you foresee potential challenges, identify opportunities, and set clear objectives. Business plans help you make decisions across the board, including market strategies, financial management, resource allocation, and growth planning.
What industry-specific issues can business plans help tackle?
Business plans can address industry-specific challenges like regulatory compliance, technological advancements, market trends, and competitive landscape. For instance, in highly regulated industries like healthcare or finance, a comprehensive business plan can outline compliance measures and risk management strategies.
How can small business owners use their business plans to pitch investors or apply for loans?
In addition to attracting investors and securing financing, small business owners can leverage their business plans during pitches or loan applications by focusing on key elements that resonate with potential stakeholders. This includes highlighting market analysis, competitive advantages, revenue projections, and scalability plans. Presenting a well-researched and data-driven business plan demonstrates credibility and makes investors or lenders feel confident about your business’s potential health and growth.
Understanding the importance of a business plan
Now that you have a solid grasp on the “why” behind business plans, you can confidently move forward with creating your own.
Remember that a business plan will grow and evolve along with your business, so it’s an important part of your whole journey—not just the beginning.
Related Posts
Now that you’ve read up on the purpose of a business plan, check out our guide to help you get started.
The information and tips shared on this blog are meant to be used as learning and personal development tools as you launch, run and grow your business. While a good place to start, these articles should not take the place of personalized advice from professionals. As our lawyers would say: “All content on Wave’s blog is intended for informational purposes only. It should not be considered legal or financial advice.” Additionally, Wave is the legal copyright holder of all materials on the blog, and others cannot re-use or publish it without our written consent.

Business Plan Example and Template
Learn how to create a business plan
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that contains the operational and financial plan of a business, and details how its objectives will be achieved. It serves as a road map for the business and can be used when pitching investors or financial institutions for debt or equity financing .

A business plan should follow a standard format and contain all the important business plan elements. Typically, it should present whatever information an investor or financial institution expects to see before providing financing to a business.
Contents of a Business Plan
A business plan should be structured in a way that it contains all the important information that investors are looking for. Here are the main sections of a business plan:
1. Title Page
The title page captures the legal information of the business, which includes the registered business name, physical address, phone number, email address, date, and the company logo.
2. Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most important section because it is the first section that investors and bankers see when they open the business plan. It provides a summary of the entire business plan. It should be written last to ensure that you don’t leave any details out. It must be short and to the point, and it should capture the reader’s attention. The executive summary should not exceed two pages.
3. Industry Overview
The industry overview section provides information about the specific industry that the business operates in. Some of the information provided in this section includes major competitors, industry trends, and estimated revenues. It also shows the company’s position in the industry and how it will compete in the market against other major players.
4. Market Analysis and Competition
The market analysis section details the target market for the company’s product offerings. This section confirms that the company understands the market and that it has already analyzed the existing market to determine that there is adequate demand to support its proposed business model.
Market analysis includes information about the target market’s demographics , geographical location, consumer behavior, and market needs. The company can present numbers and sources to give an overview of the target market size.
A business can choose to consolidate the market analysis and competition analysis into one section or present them as two separate sections.
5. Sales and Marketing Plan
The sales and marketing plan details how the company plans to sell its products to the target market. It attempts to present the business’s unique selling proposition and the channels it will use to sell its goods and services. It details the company’s advertising and promotion activities, pricing strategy, sales and distribution methods, and after-sales support.
6. Management Plan
The management plan provides an outline of the company’s legal structure, its management team, and internal and external human resource requirements. It should list the number of employees that will be needed and the remuneration to be paid to each of the employees.
Any external professionals, such as lawyers, valuers, architects, and consultants, that the company will need should also be included. If the company intends to use the business plan to source funding from investors, it should list the members of the executive team, as well as the members of the advisory board.
7. Operating Plan
The operating plan provides an overview of the company’s physical requirements, such as office space, machinery, labor, supplies, and inventory . For a business that requires custom warehouses and specialized equipment, the operating plan will be more detailed, as compared to, say, a home-based consulting business. If the business plan is for a manufacturing company, it will include information on raw material requirements and the supply chain.
8. Financial Plan
The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations. Some of the information contained in the financial plan includes a projected income statement , balance sheet, and cash flow.
9. Appendices and Exhibits
The appendices and exhibits part is the last section of a business plan. It includes any additional information that banks and investors may be interested in or that adds credibility to the business. Some of the information that may be included in the appendices section includes office/building plans, detailed market research , products/services offering information, marketing brochures, and credit histories of the promoters.
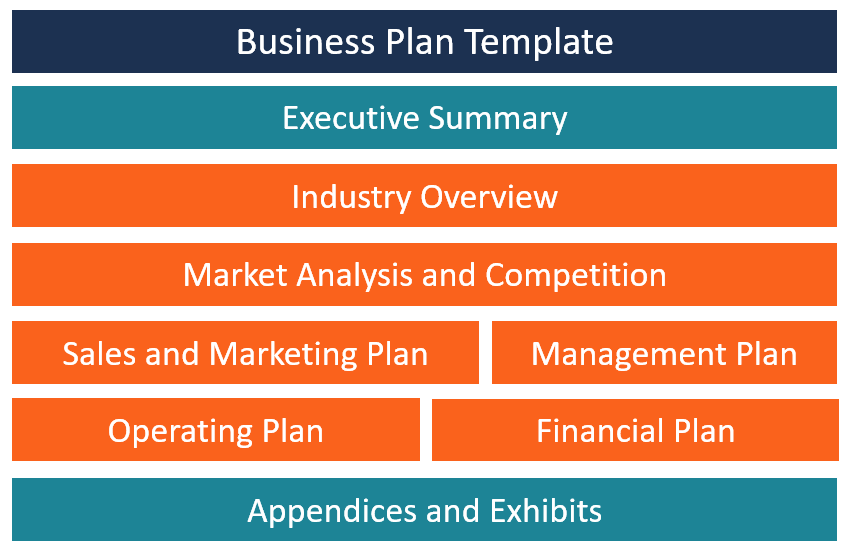
Business Plan Template
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan:
Section 1: Executive Summary
- Present the company’s mission.
- Describe the company’s product and/or service offerings.
- Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
- Summarize the industry competition and how the company will capture a share of the available market.
- Give a summary of the operational plan, such as inventory, office and labor, and equipment requirements.
Section 2: Industry Overview
- Describe the company’s position in the industry.
- Describe the existing competition and the major players in the industry.
- Provide information about the industry that the business will operate in, estimated revenues, industry trends, government influences, as well as the demographics of the target market.
Section 3: Market Analysis and Competition
- Define your target market, their needs, and their geographical location.
- Describe the size of the market, the units of the company’s products that potential customers may buy, and the market changes that may occur due to overall economic changes.
- Give an overview of the estimated sales volume vis-à-vis what competitors sell.
- Give a plan on how the company plans to combat the existing competition to gain and retain market share.
Section 4: Sales and Marketing Plan
- Describe the products that the company will offer for sale and its unique selling proposition.
- List the different advertising platforms that the business will use to get its message to customers.
- Describe how the business plans to price its products in a way that allows it to make a profit.
- Give details on how the company’s products will be distributed to the target market and the shipping method.
Section 5: Management Plan
- Describe the organizational structure of the company.
- List the owners of the company and their ownership percentages.
- List the key executives, their roles, and remuneration.
- List any internal and external professionals that the company plans to hire, and how they will be compensated.
- Include a list of the members of the advisory board, if available.
Section 6: Operating Plan
- Describe the location of the business, including office and warehouse requirements.
- Describe the labor requirement of the company. Outline the number of staff that the company needs, their roles, skills training needed, and employee tenures (full-time or part-time).
- Describe the manufacturing process, and the time it will take to produce one unit of a product.
- Describe the equipment and machinery requirements, and if the company will lease or purchase equipment and machinery, and the related costs that the company estimates it will incur.
- Provide a list of raw material requirements, how they will be sourced, and the main suppliers that will supply the required inputs.
Section 7: Financial Plan
- Describe the financial projections of the company, by including the projected income statement, projected cash flow statement, and the balance sheet projection.
Section 8: Appendices and Exhibits
- Quotes of building and machinery leases
- Proposed office and warehouse plan
- Market research and a summary of the target market
- Credit information of the owners
- List of product and/or services
Related Readings
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Business Plans. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful:
- Corporate Structure
- Three Financial Statements
- Business Model Canvas Examples
- See all management & strategy resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
More From Forbes
Why your business-planning process is more important than the plan itself.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Shane Jackson, President of Jackson Healthcare , a $1.5 billion healthcare staffing and technology company built on a values-led culture
There is an old adage that no battle plan survives contact with the enemy. Or, as Mike Tyson is famously known to have said, “Everybody has a game plan until they get punched in the face.”
I don’t know about you, but I feel like all my plans for the past two years were punched. It’s that time of year again where so many businesses are kicking off the New Year with fresh plans and budgets. I have written a lot of business plans over the years and created many, many financial forecasts. There was one thing that was consistent about all of them: They were all wrong.
Here’s the thing: Plans are based on assumptions. I make plans for dinner based on the assumption that my family will eat with me. Then I learn my teenage kids have made other plans to hang out with their friends. I made an incorrect assumption. Now, what do I do with all these groceries?
Business leaders have never faced as many unknowns as they have during the pandemic. Just when we think we are starting to get some certainty back, we add inflation, supply chain issues and Covid-19 variants. As a result, planning is harder than ever.
You might be tempted, as I have been lately, to just throw planning out the window completely. Why take the time to do a financial forecast when changes in the pandemic could make it irrelevant in 30 days?
Best Travel Insurance Companies
Best covid-19 travel insurance plans.
But I would argue the answer is not to stop planning; it is to do more planning.
Put aside for a moment that plans and budgets can be necessary for pesky things like resource allocation. The real value of planning lies in the questions you must consider when creating the plan. Who is your customer? What are their needs? How can you best solve their problems? What should you be paying attention to in the market? What can you learn from your latest successes and failures?
The business plans I’ve written in the past weren’t wrong because I’m not good at my job or because I had bad ideas or reached bad conclusions. They were wrong because the information I had when creating the plan was limited and sometimes incorrect. I had hypotheses about how the market would react but not proof. I made an assumption that the way a small group of customers behaved was representative of the way the rest of the market would behave. I thought I could hire people with certain skills at a specific time but had not yet done so.
As leaders, we are sometimes lulled by the notion that we can run our businesses as though we can forecast the year ahead with complete accuracy. We create business plans assuming we know everything about the market, exactly what the solutions are to the market problem we want to solve, and exactly how our people and processes will act in delivering those solutions. Then we take this plan and put it on a shelf to collect dust until perhaps we pull it out to reference in next year’s plan. Or, worse, we actually operate the company using it.
Perhaps you’ve had a conversation that goes something like this: “Hey, we’ve got this great new product that will really boost sales. Can we hire this person to help us get it to market faster?” And you find the answer is, “No, sorry; we created a budget 14 months ago and that position isn’t in there. Wait another three months for your meeting with the CFO, and maybe you can get it approved.”
I believe the most important part of writing a business plan is the process, not the plan itself. Planning shouldn’t happen once a year; it should happen all year long. The questions one attempts to answer in strategic planning should be asked and answered as often as you have new information.
A big part of leaders' job is to build a rhythm of learning in their organizations. Make sure you are instilling disciplines that force you to regularly work on the business — versus working in the business — in a way that helps you identify and challenge the assumptions behind your decisions. What has changed in the market or in your ability to deliver? You built this plan thinking one thing, but then discovered that something else actually happened. Now, how do you react?
The ripple effect of the pandemic has created an environment that forced all of us to become more agile. Let’s codify that agility into our businesses and all become better planners, all year long.
Forbes Business Council is the foremost growth and networking organization for business owners and leaders. Do I qualify?

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
Businessing Magazine
Strategizing Logan March 5, 2019 6 min read
10 Important Aspects of a Successful Business Plan
Every business needs to have a business plan, no matter the size. The main reason so many startups don’t survive past the first five years is because they didn’t set a strong business plan. You may have a great business idea, but then after setting out a plan and crunching the numbers, you find out it’s not such a great idea.
Your business plan is the roadmap for your business; it’ll contain future milestones, your budget and finances, marketing and sales strategy, and will help you overcome future obstacles. Whether your business plan is for bankers, venture capitalists, or just your employees, there are main elements set by the Small Business Administration ( www.sba.gov ) that should be included in every business plan.
What Are the Elements of a Business Plan?
- The Executive Summary This is the first section of the business plan. It can be from 1 to 5 pages. It serves as the table of content for your plan.
- Company Profile In this section, you explain what your business is, what your goals are, your vision, and mission, why you’re special and unique. Some companies mention the management and team members with short descriptions.
- Market Analysis Before starting a business, you need to learn about the market. Study your competitors. Find out their profit range, what they’re known for, and what technologies are used in the industry. Every detail matters and can give you an advantage in your business.
- Product/ Service Explain your products, different types or packages, your selling points, and answer all the questions a customer/ investor may have. Whoever reads your business plan should fully understand what you’re offering.
- Marketing and Sales Strategy The best product in the world wouldn’t sell if it has a poor marketing plan. Get into detail with how you’ll advertise your product. Detail your target audience, prices, and any promotional discounts.
- Funding This is the most important section in your plan because it states your initial budget, the funds you’ll need for the next five years, what you plan on doing with the funds, the creditors’ or investors’ return, and all business expenses such as salaries and equipment.
- Financial Forecast If you’re using your business plan for a loan or funds, you need to have the documents to back up your claim. You need to include all your financial statements and balance sheets, and any sources of income from the past few years.
- Business Overview Give a general overview of your business with info like the legal structure, operations plan, business address , whether it’s an online or physical business, number of employees, specific roles, etc.
What Are the Aspects of a Successful Business Plan?
Now that we’ve stated the main elements that should be included in a business plan, let’s get to the points you should focus on to create a successful business plan and not just a boring, lengthy one.
Use a Template or Hire Someone with Experience
You can write your business plan yourself, but with all the elements that need to be added, it can get complicated. If your business plan is short, then you might not need a template. If your plan is lengthy, you can find templates with a prepared structure online. In order to have a professional, well-written business plan, you can look into hiring someone with experience to get the job done. They would be able to better structure your plan and add charts and graphs when needed.
Do Your Research
Before jumping into writing your business plan, you need to ensure you’ve done an efficient amount of research. It’s your responsibility to have the answers to the questions that creditors or investors would ask. Whether it’s researching the market, competitors, or the industry, you need to know every small detail that can be an advantage or disadvantage to your business.
Define the Purpose of Your Business Plan
Your business plan will be your guide throughout the years, working as your roadmap, but you need to define why you’re creating it from the start. For example, are you making a plan for personal needs, as a guide for your employees, or are you planning on using it for investors and funding? If for funding, you’ll need to be very precise and clear with your targets and overall writing.
A Modified Business Plan
Your business plan is going to be read by various types of people from bankers, investors, and venture capitalists, to employees and yourself. Each audience type has certain points they’re looking for in your plan and you need to address those points accordingly. Make sure your plan can easily be modified according to your target audience. For example, banks would focus on balance sheets and statements while your employees will be focused on business goals or market research. You need to be able to make small alterations to serve different purposes.
Don’t Make It Too Long
The truth is no one is actually going to read your whole business plan. An executive summary is important so readers can easily find the sections they need. A typical business plan usually ranges from 20 to 50 pages. For example, venture capitalists are usually time restricted, so they’d want to find things like the financial forecast and investors’ return quickly. Knowing this, you should place this information in the beginning.
Regularly Update Your Business Plan
Your business plan needs to be updated as your business evolves and grows. Not all the sections will need updating, but the objectives set at the start of your business will change and your financial records will need to be up-to-date, especially if you’re still looking for funding. As mentioned before, your business plan is your roadmap, so don’t neglect it down the line.
Stand Out, but Don’t Overdo It
Your business plan is mostly stating the facts about your business but you need to capture the reader’s attention, mention why you’re different from your competitors, what makes you better. But sometimes businesses tend to oversell themselves, explain your passion, how much you care for your business, and the problems you want to solve but without unnecessary exaggeration.
Don’t Undersell Your Competitors
Every business has competitors and you need to clearly acknowledge these competitors in your business plan. Some startups think that not mentioning their competitors or underselling them helps their case, when in fact, it does the complete opposite.
You need to highlight what your competitors are good at, and state how you can do better. This will give you an edge with investors. Never talk bad about competitors or imply they’re not worthy of mentioning, this will lessen your credibility and make you look unprofessional.
Set Long-term and Short-term Goals
Every business plan should include five-year goals, but most importantly, it should include short-term goals such as annual and quarterly goals. It’s great to know where you want your business to be in the future, but investors need to know you have a clear plan to get there.
Back Up Your Plan with Documents, Charts, or Graphs
A business plan shouldn’t just be blocks of text; you need to make your plan appealing by adding images, charts, or graphs whenever possible. It won’t only improve your overall design; it can simplify and explain complicated sections. In order to strengthen your plan, you need to add supporting documents like articles about your business, financial statements, or contracts.
These were 10 important aspects that will help you create a successful and polished business plan. A great business plan from the start can change the trajectory of your whole business so giving it the right amount of work, focus, and dedication is vital for your business.
Logan is a passionate content creator, specializing in the business solutions sector. He loves to share his experience about technology, startups, entrepreneurs, and business-related updates.
Related Articles
Entrepreneuring
Strategizing
Official Supporters
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
12 Reasons You Need a Business Plan In the new book "Write Your Own Business Plan," business expert Eric Butow breaks down how a solid business plan can save your startup during those tough early days.
By Dan Bova Sep 19, 2023
Running a business can be unpredictable, which is why having a solid business plan as a foundation is vital to surviving and thriving in the early days of your startup. Eric Butow, CEO of online marketing ROI improvement firm Butow Communications Group, has teamed up with Entrepreneur Media to write the second edition of our best-selling book Write Your Business Plan , providing you with a roadmap for success.
In the following excerpt, Butow explains how a well-thought-out plan can power your startup and help your vision come to life.
Business plans could be considered cheap insurance. Just as many people don't buy fire insurance on their homes and rely on good fortune to protect their investments, many successful business owners do not rely on written business plans but trust their own instincts. However, your business plan is more than insurance. It reflects your ideas, intuitions, instincts, and insights about your business and its future—and provides the cheap insurance of testing them out before you are committed to a course of action. There are so many reasons to create a business plan, and chances are that more than one of the following will apply to your business.
1. A plan helps you set specific objectives for managers.
Good management requires setting specific objectives and then tracking and following up. As your business grows, you want to organize, plan, and communicate your business priorities better to your team and to you. Writing a plan gets everything clear in your head before you talk about it with your team.
2. You can share your strategy, priorities, and plans with your spouse or partner.
People in your personal life intersect with your business life, so shouldn't they know what's supposed to be happening?

Order Write Your Own Business Plan Now and Get 1 Month of Free Access to Business Planning Software Liveplan Premium
- Easy step-by-step business plan generator
- Built-in financial c alculators
- 500+ sample plans and templates
3. Use the plan to explain your displacement.
A short definition of displacement is, "Whatever you do is something else you don't do." Your plan will explain why you're doing what you've decided to do in your business.
4. A plan helps you figure out whether or not to rent or buy new space.
Do your growth prospects and plans justify taking on an increased fixed cost of new space?
5. You can explain your strategy for hiring new people.
How will new people help your business grow and prosper? What exactly are they going to do?
6. A plan helps you decide whether or not to bring on new assets.
How many new assets do you need, and will you buy or lease them? Use your business plan to help decide what's going to happen in the long term and how long important purchases, such as computer equipment, will last in your plan.
7. Share your plan with your team.
Explain the business objectives in your plan with your leadership team, employees, and new hires. What's more, make selected portions of your plan part of your new employee training.
8. Share parts of your plan with new allies to bring them aboard.
Use your plan to set targets for new alliances with complementary businesses and also disclose selected portions of your plan with those businesses as you negotiate an alliance.
9. Use your plan when you deal with professionals.
Share selected parts of your plan with your attorneys and accountants, as well as consultants if necessary.
Write Your Own Business Plan is available now at Entrepreneur Bookstore | Barnes & Noble | Amazon
10. Have all the information in your plan when you're ready to sell.
Sell your business when it's time to put it on the market so you can help buyers understand what you have, what it's worth, and why they want it.
11. A plan helps you set the valuation of the business.
Valuation means how much your business is worth, and it applies to formal transactions related to divorce, inheritance, estate planning, and tax issues. Usually, that takes a business plan as well as a professional with experience. The plan tells the valuation expert what your business is doing, when it's doing (or will do) certain things, why those things are being done, how much that work will cost, and the benefits that work will produce.
12. You can use information in the plan when you need cash.
Seek investment for a business no matter what stage of growth the business finds itself in. Investors need to see a business plan before they decide whether or not to invest. They'll expect the plan to cover all the main points.
To dig deeper, buy Write Your Own Business Plan and get 1 month of free access to business planning software Liveplan Premium.
Entrepreneur Staff
VP of Special Projects
Dan Bova is the VP of Special Projects at Entrepreneur.com. He previously worked at Jimmy Kimmel Live, Maxim, and Spy magazine. His latest books for kids include This Day in History , Car and Driver's Trivia Zone , Road & Track Crew's Big & Fast Cars , The Big Little Book of Awesome Stuff , and Wendell the Werewolf .
Read his humor column This Should Be Fun if you want to feel better about yourself.
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- Jake Paul Has Made Millions Using This Mindset Hack — and It Will Help Him Fight Mike Tyson, Too: 'Let It Fuel You'
- Lock How to Tell You're About to Get Fired — Plus 4 'Typical' Reasons for It, From a Career Expert
- They Showed Up to Apple With a Product They Built in Their Dorm Room. Now These Entrepreneurs Are on the Way to Changing the Way Fans Watch Sports.
- Got Some Bad Press? 5 Tactics to Reclaim Your Reputation — and Your Google Search Ranking
- You Can Earn Full-Time Profits With This Part-Time Work — Just Don't Call It a Side Hustle
- Lock 4 Not-So-Obvious Signs That Your Company Culture Is Becoming Toxic
Most Popular Red Arrow
How to find the right programmers: a brief guideline for startup founders.
For startup founders under a plethora of challenges like timing, investors and changing market demand, it is extremely hard to hire programmers who can deliver.
How to Transform Public Services With Innovative Digital Solutions
Digital transformation of public services is not merely a trend; it is a necessity. However, getting a contract can be a challenging task for companies. Why do governments sometimes hesitate to invest in digitalization, and how can businesses overcome this challenge? Let's figure it out.
These Grandparents Make $10,000 a Month on Their Delivery Side Hustle, With Free Workcations — 'We Hit a Hotel With a Pool'
These seniors started driving for Instacart and Doordash, then added apps from there. Within a few months, the "Giggin' Grandparents" had turned a part-time delivery gig into a comfortable living.
Don't Follow Your Passion to Build Wealth, Do This Instead, Says Scott Galloway
Galloway says the relationship between mastery and passion matters — and can lead to more money.
A Survey Asked Small Business Owners What They Really Care About in the 2024 Election — The Results Were Surprising
Small business organization, National Write Your Congressman (NWYC), released its Q2 2024 Index measuring how business owners feel about Congress, the 2024 presidential election and the direction of the U.S. economy.
The Benefits and Risks of Franchising Your Business
The flexibility, speed-of-growth and payoff possibilities of this sector are more robust than ever, but there are also pitfalls to consider: How to know if becoming a franchisor is the right move.
Successfully copied link
Social Security
What important things to consider when planning for retirement ( en español ).
What Is The Best Age To Start Your Benefits?
There is no "best age" for everyone. Ultimately, it is your choice. You should make an informed decision about when to apply for benefits based on your personal situation.
Your monthly benefit amount can differ greatly based on the age at which you start receiving benefits . If you decide to start benefits:
- Before your full retirement age , your benefit will be smaller but you will receive it for a longer period.
- At your full retirement age or later, you will receive a larger monthly benefit for a shorter period.
The benefit amount you first receive sets the base for the amount you will receive the rest of your life.
You may want to consider the following when deciding:
If you plan to continue working while receiving benefits , there are limits on how much you can earn each year between age 62 and full retirement age and still get all of your benefits.
Once you reach full retirement age, your earnings do not affect your benefits.
- After you reach full retirement age, we recalculate your benefit amount to give you credit for any months you did not receive a benefit because of your earnings.
- When additional earnings appear on your record, we check to see if they will increase your monthly benefit. If they do, we will send you a letter with the information about your new benefit amount.
- You can apply for just Medicare at age 65 and start receiving retirement benefits later.
When you think about retirement, be sure to plan for the long term.
As you plan for your retirement, it is important to know the approximate amount you will receive in benefits and your life expectancy. Since Social Security first began paying monthly Social Security benefits in 1940, life expectancies have changed. The life expectancy for men reaching age 65 on April 1, 2024, is age 84.2. For women reaching age 65 on April 1, 2024, life expectancy is now 86.8.
How long do you expect to live?
You must consider your family history and your lifestyle when estimating your life expectancy. If you come from a family with long-life expectancies, you may need extra money in later years. This is particularly important as you may outlive your pensions or annuities, especially any with limits on how long they are paid.
Your life expectancy affects your retirement planning decisions. Knowing this, helps you determine whether you should start receiving your benefits at age 62, or wait until age 70 to receive a higher payment.
If you stop working, not only will you lose your paycheck, but you may also lose employer-provided health insurance. Although there are exceptions , most people will not be covered by Medicare until they reach age 65.
Your employer should be able to tell you if you will have health insurance benefits after you retire or if you are eligible for temporary continuation of health coverage . If your spouse is employed, you may be able to switch to their health insurance.
Should I apply for Medicare?
Remember, Medicare usually starts when you reach age 65 .
If you decide to delay starting your benefits past age 65, be sure to go online and file for Medicare.
You will need to apply for Original Medicare (Part A and Part B) 3 months before you turn age 65. If you don’t sign up for Medicare Part B when you’re first eligible at age 65, you may have to pay a late enrollment penalty for as long as you have Medicare coverage.
Even if you have health insurance through a current or former employer or as part of your severance package, you should contact them to find out if you need to sign up for Medicare. Some health insurance plans change automatically at age 65.
Please read the general and special enrollment period information in our Medicare booklet to find out what may happen if you delay.
If you are eligible on another record , you may have additional options:
- If you are eligible for benefits as a surviving spouse or surviving divorced spouse on another record, you may choose to apply for survivors benefits now and delay your retirement benefit until later.
If you delay receiving your retirement benefit until your full retirement age or later, your retirement benefit will be higher.
- If you were born before January 2, 1954, and have already reached your full retirement age , and are eligible for a spouse’s or divorced-spouse’s benefit and your own retirement benefit, you can choose to receive only the spouse’s benefit. You can delay receiving your retirement benefit until a later date. If you were born on January 2, 1954, or later, the option to take only one benefit at full retirement age no longer exists. If you file for one benefit, you will be effectively filing for all retirement or spousal benefits.
If you don't need your benefits now, you may decide to:
- Wait beyond full retirement age to receive delayed retirement credits .
- Choose early retirement and increase the value of your benefits by investing them instead of spending them.
Reminder: If you're receiving early retirement from your employer, keep in mind that some company pensions include a Social Security-equivalent supplement that stops automatically at age 62.
The supplement stops because they assume you will apply for your retirement benefits at age 62.
When you start receiving Social Security retirement benefits, some members of your family also may be eligible to receive benefits on your record.
If they are eligible, your spouse or child may receive a monthly payment of up to one-half of your full retirement benefit amount. These payments will not decrease your retirement benefit.
Get personalized retirement benefit estimates
Choosing when to retire is an important decision. The best way to start planning for your future is by creating a personal my Social Security account . If you have an account, you can get an estimate of your personal retirement benefits and see the effects of different ages to begin receiving retirement benefits.
Get expert insights delivered straight to your inbox.
The Most Important Types of Business Meetings Your Company Needs
10 Min Read | Jul 29, 2024
Another meeting? Really?
Let’s be honest—we've all silently groaned at the thought of adding another meeting to our already jam-packed work schedules. That’s often because we’ve been in too many unproductive meetings that have sucked away precious time (and a piece of our soul, if we’re being real). When are we supposed to run our business and keep everyone on track— and get the work done we’re meeting about, right?
But here’s the thing: Business meetings don't have to be the enemy. In fact, the right meetings happening in the right cadences, or rhythms, will help you develop stronger communication, healthier teams and a thriving company culture. The key is to figure out what meetings actually move your company forward. Then it’s up to you to make these meetings part of the regular rhythm of your business operations.
Here are seven essential types of meetings to keep your team moving in the same direction as your business grows:
Weekly Staff Meetings
Weekly one-on-ones, weekly leader meetings, quarterly and annual strategic planning meetings, daily stand-ups, monthly leadership training, annual reviews.
Now, let's dive into more about why regular business meetings matter and which ones to add to your communication rhythms.
Why Business Meetings Are Important
Every business—yep, yours included—should have certain standing meetings that only move when there’s an emergency or a major conflict. Why? Because purposeful business meetings give you and your team a chance to share important information, make decisions, and build relationships. (We’ll talk about the types of business meetings you need in just a minute.) Without the right meetings in place, things fall apart fast. But with them, you and your team members become stronger in these areas:
- Communication that aligns everyone with the company’s goals, provides clarity on tasks, and provides space to talk openly about wins and challenges
- Accountability at work on progress, which keeps team members on track
- Collaboration that brings different perspectives and leads to more creative, effective solutions
- Culture-building that prioritizes team bonding and rapport and reinforces company values
Types of Business Meetings
The dream is to have meetings that benefit your whole team and move your business forward. With that vision to inspire you, let’s talk about what types of business meetings are most important to have regularly.
First, a few housekeeping notes:
- If you’re a small company, you won’t need every meeting right away. Your top priority is making payday by Friday, not annual planning—we get it. So adjust your meetings to what works best now for professional accountability and team alignment. Then add more in or change the cadences to help you stay connected and accountable as your team grows. (If you’re looking for a way to grow your business more efficiently, the first four meetings are an essential part of the EntreLeadership System —the road map that takes the guesswork out of your business’s growth.)
- It will take a few months to find your meeting groove, and that’s totally normal. Introduce new meetings just a few at a time and stick with them. Thousands of thriving EntreLeadership business leaders confirm these meetings have turned their business operations around. How? Instead of managing by the seat of their pants, they’re tackling issues proactively—through recurring meetings.
- Remember—these standing meetings shouldn’t be moved unless there’s an emergency . . . or a holiday (no one needs to be in a meeting on Christmas day). Over time, they create a rhythm that helps everyone stay organized, productive and connected.
Every week, gather your entire team for a 30- to 60-minute staff meeting. This doesn’t need to be a fancy or overly produced gathering. Simply focus on these main goals:
1. Beat the drum on company vision and culture. Lead with purpose , teaching on your vision or one of your core values to remind everyone who you are as a company and why the work you do matters. When you do this, adding in stories about the company and real customers whose lives you’ve made better, you keep your mission front and center and inspire your team.
2. Give general announcements . Introduce new team members, mourn losses, and give revenue and project updates. This is also where you’ll remind everyone about progress toward company-wide goals.
3. Celebrate individual, team and business wins. If a customer brags on your business or a team member, pass it on . You can also share work anniversaries and birthdays and shout out accomplishments.
All-staff meetings are a time for transparency and unity, reminding everyone they’re part of something bigger.
Stop winging it and start winning.
The EntreLeadership System is the small-business road map that takes the guesswork out of growing your business. To get the most out of the system, download the easy-to-follow Getting Started Guide.
Wondering which meeting you can’t do without for long-term success? Wonder no more. It’s weekly one-on-ones between leaders and their direct reports—100 percent. Why? Because, done well, one-on-ones show you care about your team members and give them space to discuss challenges, goals and where they need extra support. This translates into more engaged teams, lower turnover, and a lot more trust and fun together!
Plan anywhere from 30 to 60 minutes every week or two with each person you lead. After a quick catch-up on life, use your time to hit on one or two of these key areas based on your team member’s needs:
1. Accountability: Professional accountability ensures your team member feels responsible for their work and owns how their role helps the company move forward..
2. Clearing blockers: You want your team members to win, so help them overcome setbacks and reach their goals. Whatever the challenge, let them know you’ve got their back.
3. Coaching: Even if you’re leading someone with more experience in their discipline than you, you can offer valuable leadership perspective. Listen well, ask good questions, and show them you’re there for them. If you’re not sure how to get started, ask this simple question: What’s on your mind right now? You’ll be amazed by what you learn—maybe they’ve got a big trip coming up, a baby on the way, or another personal milestone worth celebrating. This question also opens an opportunity to coach your team member through a tough issue like how to deal with a difficult coworker or personal loss. Never take lightly the privilege of speaking into others’ leadership growth, work and lives.
Pro tip: If adding in one-on-one meetings seems like a lot to bite off, you might need others to help you carry the load. Learn how to develop other leaders and then delegate well .
Weekly leader meetings are where your key leadership team gathers for tactical, working sessions to solve problems and drive your business forward. Together you’ll make strategic decisions for the week ahead and ensure your leaders stay aligned on the company’s vision and goals.
Develop a list of issues, opportunities and topics you want to address, including actions like budget review, goal setting, strategic planning and team changes. Encourage your leaders to bring any challenges they see too. Sometimes you’ll knock out issues in minutes, but other times you’ll need a few sessions to clear the path toward your vision.
Finding time to work on your business, not just in it , is hard—really hard sometimes. But the only way to move through the Stages of Business is to get above your company and plan your path forward. In other words, you’ve got to set aside time for quarterly and annual strategic planning.
What exactly is quarterly planning? It’s time (usually a half to full day) dedicated to planning next steps and setting goals for the upcoming three months. You’ll also look at your progress toward existing goals and adjust strategies and objectives as you need to.
Your annual strategic planning meeting is a lot like your quarterly meetings, but you're looking further out. During annual planning, you'll create a desired future statement to guide your business decisions for the coming year. What does a desired future statement do? It brings clarity and alignment on where your business is headed and what winning looks like for your company. And it keeps you on the straight and narrow path toward your priorities, or key results.
Both quarterly and annual planning meetings are critical times for reflection and forward thinking. So even if you don't have a leadership team yet, use the time to review where you’re winning, losing and primed for growth.
These quick meetings are perfect for specific discipline teams, like your sales or customer service teams. If your team is small and wearing lots of hats, just gather everyone for a quick connect. Hint : Actually stand up at these meetings instead of sitting down around a conference table to keep them short and to the point.
Stand-ups happen early in the workday and last just 5 or 10 minutes. The point is for everyone to share what they’re working on today and any blockers they’re facing. Daily stand-ups anchor everyone to action. If something’s in the way of achieving a goal, the team looks for ways to clear obstacles so they can go faster.
Leaders aren’t born, they’re built. So set aside an hour or more each month to help your leaders own your company values and develop skills from building relationships and casting vision to making decisions and driving results. This training gives your leaders a shared language and a chance to connect on their pain points and wins.
Pro tip: If you’re an EntreLeadership Elite member, use Elite’s video courses and eCoaching videos to align and inspire your leaders during your monthly training sessions.
Annual reviews (also called annual check-ins) shouldn’t be scary, uncertain or bomb-drop events for team members. They’re a review of a year’s worth of work accomplished by each team member and should be extensions of the one-on-one meetings you’ve been doing all year, just longer and often with a pay raise for work well done.
Take an hour or more to grab a coffee or lunch and talk with your team member about their major milestones and honor their wins. Next, review how they’ve met their Key Results Areas , then challenge them with one major growth area based on the potential you see in them. Annual check-ins are a special chance to pour into every team member’s personal and career development.
Business Meetings in Different Work Environments
Businesses today work in all kinds of ways. Your team may be all in one office, out in the field, or spread across the country or world. You may have team members on-site, online or a hybrid of both. Whatever your makeup, think outside the box on how to prioritize real human-to-human connections, and make these meeting rhythms work for you. For remote teams, leverage tools and technology like Zoom, Slack or Microsoft Teams, and ensure everyone has a chance to participate. The key is consistency and creativity.
Prioritize the right communication rhythms to drive your company forward. Remember, the goal of business communication strategies isn’t to fill calendars with meetings and suck souls. None of that, please. It’s to use meetings strategically to build a stronger, more connected and more effective team.
Next Step: Find the Rhythm of Success
Communication rhythms are just one part of the EntreLeadership System—your road map to taking the guesswork out of business growth. Get your free EntreLeadership System guide to learn about the full system and access tools and resources that will help you build a business you love to ru
Did you find this article helpful? Share it!
About the author
EntreLeadership
EntreLeadership is the part of Ramsey Solutions that exists to help small-business owners thrive by mastering themselves, rallying their teams, and imposing their will on the marketplace. Thousands of leaders use our proven EntreLeadership System and resources to develop as leaders and grow their businesses. These resources include The EntreLeadership Podcast , EntreLeadership Elite digital membership , books, live events, coaching sessions and business workshops. Learn More.
How to Create an Onboarding Plan Your New Employees Will Love
Without a great onboarding plan in place, you’re setting your new hire up to fail before they start. Learn how to onboard team members the right way so they stay energized, enthused and ready to succeed.
How to Choose a Financial Wellness Program for Your Employees
Knowing how to choose a financial wellness program for your employees can be tough. Here’s what you need to know to start your search and get your employees a benefit that can change their lives.
You're reading a free article with opinions that may differ from The Motley Fool's Premium Investing Services. Become a Motley Fool member today to get instant access to our top analyst recommendations, in-depth research, investing resources, and more. Learn More
This Undervalued Stock Could Join Alphabet in the $2 Trillion Club
- Averaging just above 8.5% annual returns could get TSMC in the $2 trillion club.
- TSMC's business segment, which contains its AI-related revenue, increased 28% from the previous quarter.
- TSMC plans to increase capital expenditures to meet the demand for AI semiconductors.
- Motley Fool Issues Rare “All In” Buy Alert
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing

With fresh growth prospects and a potential rebound in one of its most important businesses, TSMC could hit the $2 trillion mark sooner than expected.
The trillion-dollar market cap club is exclusive. As it stands, there are only seven companies in the world that have passed that mark. Apple , Microsoft , and Nvidia reign supreme, sitting in the illustrious $3 trillion club, but Alphabet is the lonely company in the $2 trillion club -- for now.
With a market cap of just over $880 billion, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing ( TSM -4.60% ) (TSMC) still has a ways to go to reach $2 trillion, but the milestone is well within its reach. And it might not take too long, either.
Since it became listed on the New York stock exchange in October 1997, TSMC has averaged around 13.5% annual returns. In the past decade, it's been even more impressive, averaging over 23% annual returns. A lot of that can be attributed to the 61% it's up in the past 12 months, but even much more modest returns can get TSMC into the $2 trillion club.
It would take just over 8.5 years to go from a $880 billion market cap to a $2 trillion market cap, averaging 10% annual returns. With TSMC's growth prospects, I believe this is doable.
TSMC is an important player in the tech ecosystem
TSMC is the largest and most important semiconductor company in the world. It established the foundry model, where instead of making semiconductors for general sale, it makes semiconductors for a company's specific needs.
This model and the quality of TSMC's semiconductors have made it the go-to for some of the world's best companies, including Apple, Nvidia, and Tesla . Semiconductors are the foundation for many electronics and applications we use today. They're in iPhones, graphic processing units ( GPUs ), cars, and even medical devices.
You could make a strong case that without TSMC, many of these items and applications we enjoy would take a quality hit. This is why it's continued to be the top choice despite other companies like Intel embracing the same foundry model.
TSMC is on the early end of an AI-fueled revenue boost
For a while, TSMC's financial performance relied on its smartphone business, and that caused it to hit a rough spot as global smartphone sales slowed down. Smartphones will continue to be an important part of TSMC's business, but it's getting help from its high-performance computing (HPC) segment, which includes artificial intelligence (AI)-related revenue.
In the second quarter, TSMC's revenue grew nearly 33% year over year to $20.8 billion, with HPC accounting for 52% of it. This continues a trend that's taken place over the past few quarters:
| Quarter | Percentage of Revenue from HPU | Percentage of Revenue From Smartphones |
|---|---|---|
| Q2 2024 | 52% | 33% |
| Q1 2024 | 46% | 38% |
| Q4 2023 | 43% | 43% |
Data source: TSMC.
TSMC's semiconductors are important to the GPUs that power most data centers. Without these data centers, it'd be virtually impossible to store and transport the data needed to train the AI applications that have become prominent in the past couple of years. So, it all begins with TSMC's semiconductors.
The success of its second quarter caused TSMC to raise its full-year revenue guidance to right above the mid-20 percentage range. It also expects its capital expenditures to be between $30 billion and $32 billion after previously estimating it to be between $28 billion to $32 billion. This potential increase in investments will help better position it to handle the increased demand cause by the AI surge.

TSM Capital Expenditures (Annual) data by YCharts
TSMC's valuation makes it an attractive option
Despite surging over 57% this year, TSMC's stock is still valued at a reasonable level. Its forward price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio is around 20.5, well below the 23.7 P/E ratio it has averaged over the past five years.

TSM PE Ratio (Forward 1y) data by YCharts
TSMC could face some geopolitical headwinds, as it potentially gets caught up in U.S.-China trade tensions and export restrictions, but these are issues TSMC's CEO has reassured won't stop the company's growth and expansion plan.
Given expected growth from AI demand and additional revenue that could come from a rebound in the smartphone market (especially as Apple iPhone sales are expected to rebound with the addition of Apple Intelligence in its next generation models), there's reason to think TSMC can join the $2 trillion club within the next decade.
Suzanne Frey, an executive at Alphabet, is a member of The Motley Fool's board of directors. Stefon Walters has positions in Apple and Microsoft. The Motley Fool has positions in and recommends Alphabet, Apple, Microsoft, Nvidia, Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing, and Tesla. The Motley Fool recommends the following options: long January 2026 $395 calls on Microsoft and short January 2026 $405 calls on Microsoft. The Motley Fool has a disclosure policy .
Related Articles

Premium Investing Services
Invest better with The Motley Fool. Get stock recommendations, portfolio guidance, and more from The Motley Fool's premium services.
- How to budget your money
1. Examine your income
- 2. Choose your budgeting strategy
- 3. Reduce spending
4. Automate savings and investments
- 5. Track your progress
- How to budget on a low income
Why is budgeting important?
How to budget: tips, tools, and techniques.
Affiliate links for the products on this page are from partners that compensate us and terms apply to offers listed (see our advertiser disclosure with our list of partners for more details). However, our opinions are our own. See how we rate banking products to write unbiased product reviews.
- A budget can help you stay on top of expenses, pay off debts, and achieve your financial goals.
- There are several strategies for budgeting. Each has its own unique pros and cons.
- Checking in on your budget, adjusting it, and analyzing your spending habits regularly is critical.
A budget is, at its simplest, a plan for how you'll spend your earnings. It ensures you have the funds to cover your essentials — like housing, groceries, utilities, and your monthly debt payments — while also working toward other financial and savings goals .
In short: Budgets allow you to get the most out of your paycheck. Without one, there's a chance you could run out of money before your next pay date.
How to budget your money
Budgeting is critical if you want to stay on top of bills, pay off debts , or save for the future, and there are several ways to go about it.
"Building a budget doesn't have to be overly complicated or time-consuming," says Brittany Castro, former in-house CFP for Mint. "It's actually the first step in putting yourself in control of your finances because it means you know where your money goes each month."
How to plan a budget
Budgeting as a beginner can be daunting. Use these steps when making a personal finance budget for the first time:
- Examine your income and expenses so that you can understand how much you're making, how much you're using, and if you're spending more than you're making
- Choose your approach to budgeting, such as the 50/30/20 rule or the envelope system, when determining how much to save each month
- Figure out where you can cut back on spending — and make strategies to help you stick to those cutbacks
- Automate your savings and investments so you can continue to make money off of your extra income without too much effort
- Find ways of tracking your budgeting process that work for you, such as using budgeting apps and/or creating a budgeting spreadsheet
To start budgeting, you first need a good pulse on your monthly income — more specifically, how much you take home each after taxes. If you're unsure what your net income (your income after taxes) looks like off the top of your head, you can typically use pay stubs or bank statements to get these numbers.
Once you have your income estimated, you'll also need to estimate your monthly expenses — things like your rent or mortgage, utility costs, groceries, insurance, and gas. If you have debts (like credit cards or personal loans ), add these in as well. Then compare the two numbers.
"If your expected expenses are greater than your expected income, you will need to earn additional income, cut out some purchases, go into debt, or do a combination of these three," says Todd Christensen, an accredited financial counselor and education manager at Money Fit.
If your income outweighs your expenses, though, that means you have extra cash to put in savings, add to an emergency fund , or put toward other financial goals.
2. Choose your budgeting strategy
The next step is to create your budget — a specific plan for how you'll use your earnings each month and eventually achieve your financial goals.
There are several strategies for doing this, each with its own pros and cons. Here are a few of the options you might consider:
50/30/20 rule
According to Christensen, the 50/30/20 rule has become increasingly popular in the last 20 years. "It suggests you live on 50% of your income — housing, transportation, cell phone, utilities — enjoy 30% with dining out, recreation, or travel, and save and invest 20%."
The benefit here is that it's a simple, easy-to-learn approach, and it doesn't force you to account for every single purchase or expenditure. On the downside, it doesn't take into account your circumstances and may not work in every scenario. (If you live in a high-cost housing market, for example, adhering to that 50% rule may be unrealistic.)
70/20/10 rule
The 70/20/10 rule is similar to the 50/30/20 rule in that it has a loose budgeting structure. The categories for this budgeting strategy are: 70% goes to wants and needs, 20% goes toward savings and investments, and 10% goes toward debt payments or donations.
Zero-balance or traditional budget
With a zero-balance budget, you're trying to get your income minus your expenses to equal zero. That means you use all your income each month — first, toward your essentials, and then, toward your wants and financial goals. Under this strategy, if you were to find yourself with an unspent $300 at the end of the month, you'd put that money in savings, make an extra loan payment, or make some other use of it.
The advantage of a zero-balance budget is that it accounts for every dollar, ensuring you make the absolute most of your earnings. The main drawback is that it's time-consuming. Tracking each expenditure and every dollar you earn can be tiresome. It's also difficult to use on unpredictable incomes (you never know how much you can allot for each expense).
Pay yourself first budget
The pay yourself first strategy starts with your financial goals and works backward. So, say you know you want to put $500 toward your mortgage and $500 into savings each month. You'd start by subtracting that $1,000 from your monthly take-home pay (for example, $4,000 - $1,000), and then use that number ($3,000) for your monthly bills and expenses.
This strategy's big perk is that it prioritizes your goals and allows flexibility in spending. On the downside, it may create stress if you leave yourself with too little to cover your monthly costs.
The envelope budget
The envelope system is a monthly budgeting method created by financial author Dave Ramsey. It requires putting cash into individual envelopes for each expense or category of expenses (e.g., housing, utilities, food, and entertainment). You then pull cash out of the envelopes as costs arise during the month.
If you run out of money in an envelope, it's a sign you overspent or need to allot more to that category. If you have lots left over, you can adjust the budget for the next month and put those funds elsewhere.
The benefit of this method is that it's visual and tangible, making it easy to understand your budget and how you can improve it. Unfortunately, it's also time-consuming, and cash isn't always accepted — especially in today's digital economy.
3. Reduce spending
While you go about creating a budget, it's important to fully analyze your expenses. You should ask yourself: Are those expenses necessary? If so, are there ways to reduce them or make them more affordable? This might mean renegotiating your pricing, switching service providers, or looking for coupons or special deals.
Here are some budgeting tips to cut down what you spend:
- Increase friction: Friction is when something like spending money becomes a little more difficult. An example of adding friction when spending would be removing your saved credit card information from your favorite site so that you have to manually re-add it in every time. This is a great way to make it harder for you to spend easily.
- Wait before buying something: Set a 48-hour waiting rule for your purchases. If there's something you'd like to buy, sleep on it. If it still seems like a good idea in two days, then make the purchase. This helps you steer clear of unnecessary impulse buys.
- Audit your monthly subscription services: There are so many subscription services these days, and it's easy to lose track of just how much you're spending. Take a hard look at your subscriptions and consider cutting any you're not actively using. Look at streaming services, apps, subscription boxes, and even Subscribe and Save subscriptions on Amazon.
- Refinance any loans to get lower rates: You'll be surprised how much interest adds up on any loans you have. Refinancing your mortgage , car loan, and sometimes even your student loans could reduce your interest rate, monthly payment, or both, freeing up cash flow that you can put toward your budget for other, more important, expenses. Make sure to shop around with several lenders if you're considering this route.
- Meal plan: Planning your meals ahead of time helps you stay on track at the grocery store and avoid eating out in a pinch. You'll want a plan for every day of the week, including breakfasts, lunches, dinners, and snacks.
Cutting back even slightly could free up more cash for paying down debts, achieving your financial goals, or just reducing overall financial stress.
No matter which budgeting method you choose, it's important to make saving a part of your plan. Typically, the best option is an automated deposit into your savings account, as this reduces hassle and keeps your goals on track. To maximize your savings, you might consider a high-yield savings account , which earns money at a higher rate than other options.
Once you've automated your savings, you can also think about investing any income you might have left over. If this is something you're interested in, consider talking to a certified financial planner before diving in. They can help you choose the best investments for your goals.
5. Track your progress
Budgets are ever-evolving tools, and you'll need to track your progress, adjust, and recalibrate often — especially in the beginning. You'll also need to adjust your spending habits as you go.
"The key is to identify your spending trends and ensure they match up with your spending priorities," Christensen says. "If you're spending $50 a week on soft drinks, but you would rather prioritize the purchase of a new gaming console, then it's time to change your soft-drink purchasing behavior."
Though you can certainly manually check in on your budget, Christensen recommends using a budgeting app that connects to your bank account, as these can streamline the process. For example, Rocket Money is an app that helps you create a budget, negotiate your bills, and reduce your spending — and it has a free plan.
Some budgeting apps offer credit monitoring services , as well. Consider tracking your credit score and credit card use when you're tracking your budget to better understand all of your financial needs.
You can also create an expense tracking spreadsheet in Excel, ask for receipts for every purchase, and total them up at the end of each week or month.
How to budget on a low income
If you're struggling financially, budgeting is particularly important. As Lisa Fischer, chief growth and lending officer at Mission Lane , explains, "Keeping a close eye on spending is crucial for all consumers, but especially those who may be living paycheck to paycheck."
Not only can budgeting help you monitor your spending habits and stay on track with bills and expenses, but it can also ensure you prioritize saving, which should improve your financial outlook down the line.
In addition to budgeting, you can consider applying for rental or housing payment assistance, food pantries, and health care sharing plans to reduce your costs. Financial, debt, or credit counseling might be helpful as well. If this is something you're interested in, the nonprofit National Foundation for Credit Counseling is a good place to start.
If you want to make the most of your income while also achieving your long-term financial goals, having a budget is crucial. As Castro explains, "You need a solid budget and financial plan in order to set yourself up for long-term financial wellness, avoid running into problems such as racking up credit card debt, and build your net worth over time."
There are many ways to go about budgeting, and you may need to try a few before you find the right fit. You can also speak to a financial advisor for help choosing the best budgeting route for your household.
How to budget: FAQs
The best way to start a budget is to figure out how much you're making and compare it to what you're spending. Then you can figure out what budgeting method you want to use.
Cash stuffing is a budgeting technique that involves assigning monthly spending and saving categories to different envelopes. Then you put the amount of money you want to spend on those categories into the envelopes.
The 50/30/20 rule is a budgeting technique in which you assign 50% of your income to living expenses (such as rent and utilities), 30% of your income to non-necessary expenses (such as concerts or travel), and 20% to savings and investments.
- Bank accounts
- Savings and CD rate trends
- How banks operate
- Real estate
- Certificates of deposit
- Savings accounts
- Checking accounts
- Bank reviews
- Main content

- The Star ePaper
- Subscriptions
- Manage Profile
- Change Password
- Manage Logins
- Manage Subscription
- Transaction History
- Manage Billing Info
- Manage For You
- Manage Bookmarks
- Package & Pricing
Australia to tighten mining exploration rules
Friday, 02 Aug 2024
Related News

Major South-East Asia economies to see promising growth in 10 years: Report
Roundup: indicators show strong going for cyprus' economy despite adverse environment, korean air cuts hot cup noodles in economy class.
“It puts the handbrake on companies making up their own terminology and definitions,” Steve Hunt, JORC committee chair said. — Bloomberg
MELBOURNE: Australia – one of the world’s most important mining nations – is planning to tighten up rules that govern how companies announce their exploration results, with a revised code for listed companies including industry leaders BHP Group Ltd and Rio Tinto Group.
A draft of the new code published yesterday would impose new environmental requirements, plus a need for qualified experts to sign off on estimates of minerals and metals to be mined.
The tweaked JORC Code – or Australasian Code for Reporting of Exploration Results, Mineral Resources and Ore Reserves – will require ministerial approval before coming into force.
“It puts the handbrake on companies making up their own terminology and definitions,” Steve Hunt, JORC committee chair told Bloomberg. “There’s always a tendency for companies to talk up, as best as they can, their investment opportunities. This code provides technical guardrails.”
Australia has a vast mining industry, with players large and small seeking to exploit the nation’s trove of mineral resources including iron ore, gold, and copper, as well materials central to new-energy technology such as lithium.
The JORC Code has its roots in the 1970s, when thousands of investors lost billions after a mining company falsified exploration results, then collapsed. It was first published in 1989 and last updated more than a decade ago.
Under the planned changes – which, when adopted, will apply to all locally-listed miners – a company will need to acknowledge publicly any environmental risks to their projects. In addition, a qualified professional, with experience in mining, is required for the technical sign off on a project, and must now display their credentials publically.
“To the extent that any proposals impact on the listing rules and our guidance, our main interest will be that the changes continue to encourage strong and consistent disclosure on our market of mining exploration results and estimates of resources and reserves,” an Australian Securities Exchange (ASX) spokesperson told Bloomberg.
No mining entity listed on the ASX will be exempt from the changes, which are expected to take effect next year. — Bloomberg
Tags / Keywords: MiningRegulations , JORCCode , AustraliaMining , EnvironmentalCompliance , ResourceReporting , MineralExploration
Found a mistake in this article?
Report it to us.
Thank you for your report!

A commitment to community wellbeing
Next in business news.

Trending in Business
Air pollutant index, highest api readings, select state and location to view the latest api reading.
- Select Location
Source: Department of Environment, Malaysia
Others Also Read
Best viewed on Chrome browsers.

We would love to keep you posted on the latest promotion. Kindly fill the form below
Thank you for downloading.
We hope you enjoy this feature!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
There's no right or wrong way to write a business plan. What's important is that your plan meets your needs. Most business plans fall into one of two common categories: traditional or lean startup. Traditional business plans are more common, use a standard structure, and encourage you to go into detail in each section. They tend to require ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Step #3: Conduct Your Market Analysis. Step #4: Research Your Competition. Step #5: Outline Your Products or Services. Step #6: Summarize Your Financial Plan. Step #7: Determine Your Marketing Strategy. Step #8: Showcase Your Organizational Chart. 14 Business Plan Templates to Help You Get Started.
Build a strategy. 4. Crafts a roadmap to achieve important milestones. A business plan is like a roadmap for your business. It helps you set, track and reach business milestones. For your plan to function in this way, your business plan should first outline your company's short- and long-term goals.
Here's why I think a business plan is important: 1. Securing Financing From Investors. Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break-even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
1. Create Your Executive Summary. The executive summary is a snapshot of your business or a high-level overview of your business purposes and plans. Although the executive summary is the first section in your business plan, most people write it last. The length of the executive summary is not more than two pages.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
That's where your business plan comes in. It provides investors, lenders and potential partners with an understanding of your company's structure and goals. If you want to gain the financial autonomy to run a business or become an entrepreneur, a financial advisor can help align your finances. 1. Executive Summary.
4. Marketing plan. The marketing plan section details how you plan to attract and retain customers. It covers the marketing mix: product, price, place, and promotion. It shows you understand your market and have clear, measurable goals to guide your marketing strategy.
1. Executive summary. This is one of the shortest components of a business plan, but the one you should spend the most time working on. Whether your business plan is 5 or 30 pages, an executive summary section must recap all of the material in your plan in only two pages.
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
Financial Plan: This is the most important element of a business plan and is primarily addressed to investors and sponsors. It requires a firm to reveal its financial policies and market analysis. At times, a 5-year financial report is also required to be included to show past performances and profits. The financial plan draws out the current ...
A business plan clearly lays out a company's objectives, as well as the landscape of the market. As a result, business leaders know which challenges to expect. With that knowledge in hand, they can take proactive steps to mitigate their risks. 5. To accelerate growth. Quite simply, business planning works.
Let's take a closer look at how each of the important business planning benefits can catapult your business forward: 1. Validate Your Business Idea. The process of writing your business plan will force you to ask the difficult questions about the major components of your business, including: External: industry, target market of prospective ...
To outline the importance of business plans and make the process sound less daunting, here are 10 reasons why you need one for your small business. 1. To help you with critical decisions. The primary importance of a business plan is that they help you make better decisions. Entrepreneurship is often an endless exercise in decision making and ...
The financial plan is an important section that will often determine whether the business will obtain required financing from financial institutions, investors, or venture capitalists. It should demonstrate that the proposed business is viable and will return enough revenues to be able to meet its financial obligations.
Wait another three months for your meeting with the CFO, and maybe you can get it approved.". I believe the most important part of writing a business plan is the process, not the plan itself ...
Product/ Service Explain your products, different types or packages, your selling points, and answer all the questions a customer/ investor may have. Whoever reads your business plan should fully understand what you're offering. Marketing and Sales Strategy The best product in the world wouldn't sell if it has a poor marketing plan.
A business plan is an executive document that acts as a blueprint or roadmap for a business. It is quite necessary for new ventures seeking capital, expansion activities, or projects requiring additional capital. It is also important to remind the management, employees, and partners of what they represent. You are free to use this image on your ...
10. Have all the information in your plan when you're ready to sell. Sell your business when it's time to put it on the market so you can help buyers understand what you have, what it's worth, and ...
5. There's no wrong way to write a business plan. There is no right or wrong way to write a business plan. You can pick a plan format that works best for you. What's important is that your business plan meets your needs. Most business plans fall into one of two common categories: traditional or lean startup.
1. Know your competition. You need to name them and point out what makes you different from (and better than) each of them. But do not disparage your competition.
As you plan for your retirement, it is important to know the approximate amount you will receive in benefits and your life expectancy. Since Social Security first began paying monthly Social Security benefits in 1940, life expectancies have changed. The life expectancy for men reaching age 65 on April 1, 2024, is age 84.2.
1. Beat the drum on company vision and culture. Lead with purpose, teaching on your vision or one of your core values to remind everyone who you are as a company and why the work you do matters. When you do this, adding in stories about the company and real customers whose lives you've made better, you keep your mission front and center and inspire your team.
With fresh growth prospects and a potential rebound in one of its most important businesses, TSMC could hit the $2 trillion mark sooner than expected. The trillion-dollar market cap club is exclusive.
Mark Zuckerberg said the ability to think critically and "go deep and do one thing really well" is the most important trait. Menu icon A vertical stack of three evenly spaced horizontal lines.
Meal plan: Planning your meals ahead of time helps you stay on track at the grocery store and avoid eating out in a pinch. You'll want a plan for every day of the week, including breakfasts ...
Australia - one of the world's most important mining nations - is planning to tighten up rules that govern how companies announce their exploration results, with a revised code for listed ...