How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.

What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures, ethics in science: importance, principles & guidelines , jenni ai review: top features, pricing, and alternatives, 8 most effective ways to increase motivation for....
Research Question 101 📖
Everything you need to know to write a high-quality research question
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2023
If you’ve landed on this page, you’re probably asking yourself, “ What is a research question? ”. Well, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll explain what a research question is , how it’s differen t from a research aim, and how to craft a high-quality research question that sets you up for success.
Research Question 101
What is a research question.
- Research questions vs research aims
- The 4 types of research questions
- How to write a research question
- Frequently asked questions
- Examples of research questions
As the name suggests, the research question is the core question (or set of questions) that your study will (attempt to) answer .
In many ways, a research question is akin to a target in archery . Without a clear target, you won’t know where to concentrate your efforts and focus. Essentially, your research question acts as the guiding light throughout your project and informs every choice you make along the way.
Let’s look at some examples:
What impact does social media usage have on the mental health of teenagers in New York?
How does the introduction of a minimum wage affect employment levels in small businesses in outer London?
How does the portrayal of women in 19th-century American literature reflect the societal attitudes of the time?
What are the long-term effects of intermittent fasting on heart health in adults?
As you can see in these examples, research questions are clear, specific questions that can be feasibly answered within a study. These are important attributes and we’ll discuss each of them in more detail a little later . If you’d like to see more examples of research questions, you can find our RQ mega-list here .

Research Questions vs Research Aims
At this point, you might be asking yourself, “ How is a research question different from a research aim? ”. Within any given study, the research aim and research question (or questions) are tightly intertwined , but they are separate things . Let’s unpack that a little.
A research aim is typically broader in nature and outlines what you hope to achieve with your research. It doesn’t ask a specific question but rather gives a summary of what you intend to explore.
The research question, on the other hand, is much more focused . It’s the specific query you’re setting out to answer. It narrows down the research aim into a detailed, researchable question that will guide your study’s methods and analysis.
Let’s look at an example:
Research Aim: To explore the effects of climate change on marine life in Southern Africa.
Research Question: How does ocean acidification caused by climate change affect the reproduction rates of coral reefs?
As you can see, the research aim gives you a general focus , while the research question details exactly what you want to find out.
Need a helping hand?
Types of research questions
Now that we’ve defined what a research question is, let’s look at the different types of research questions that you might come across. Broadly speaking, there are (at least) four different types of research questions – descriptive , comparative , relational , and explanatory .
Descriptive questions ask what is happening. In other words, they seek to describe a phenomena or situation . An example of a descriptive research question could be something like “What types of exercise do high-performing UK executives engage in?”. This would likely be a bit too basic to form an interesting study, but as you can see, the research question is just focused on the what – in other words, it just describes the situation.
Comparative research questions , on the other hand, look to understand the way in which two or more things differ , or how they’re similar. An example of a comparative research question might be something like “How do exercise preferences vary between middle-aged men across three American cities?”. As you can see, this question seeks to compare the differences (or similarities) in behaviour between different groups.
Next up, we’ve got exploratory research questions , which ask why or how is something happening. While the other types of questions we looked at focused on the what, exploratory research questions are interested in the why and how . As an example, an exploratory research question might ask something like “Why have bee populations declined in Germany over the last 5 years?”. As you can, this question is aimed squarely at the why, rather than the what.
Last but not least, we have relational research questions . As the name suggests, these types of research questions seek to explore the relationships between variables . Here, an example could be something like “What is the relationship between X and Y” or “Does A have an impact on B”. As you can see, these types of research questions are interested in understanding how constructs or variables are connected , and perhaps, whether one thing causes another.
Of course, depending on how fine-grained you want to get, you can argue that there are many more types of research questions , but these four categories give you a broad idea of the different flavours that exist out there. It’s also worth pointing out that a research question doesn’t need to fit perfectly into one category – in many cases, a research question might overlap into more than just one category and that’s okay.
The key takeaway here is that research questions can take many different forms , and it’s useful to understand the nature of your research question so that you can align your research methodology accordingly.

How To Write A Research Question
As we alluded earlier, a well-crafted research question needs to possess very specific attributes, including focus , clarity and feasibility . But that’s not all – a rock-solid research question also needs to be rooted and aligned . Let’s look at each of these.
A strong research question typically has a single focus. So, don’t try to cram multiple questions into one research question; rather split them up into separate questions (or even subquestions), each with their own specific focus. As a rule of thumb, narrow beats broad when it comes to research questions.
Clear and specific
A good research question is clear and specific, not vague and broad. State clearly exactly what you want to find out so that any reader can quickly understand what you’re looking to achieve with your study. Along the same vein, try to avoid using bulky language and jargon – aim for clarity.
Unfortunately, even a super tantalising and thought-provoking research question has little value if you cannot feasibly answer it. So, think about the methodological implications of your research question while you’re crafting it. Most importantly, make sure that you know exactly what data you’ll need (primary or secondary) and how you’ll analyse that data.
A good research question (and a research topic, more broadly) should be rooted in a clear research gap and research problem . Without a well-defined research gap, you risk wasting your effort pursuing a question that’s already been adequately answered (and agreed upon) by the research community. A well-argued research gap lays at the heart of a valuable study, so make sure you have your gap clearly articulated and that your research question directly links to it.
As we mentioned earlier, your research aim and research question are (or at least, should be) tightly linked. So, make sure that your research question (or set of questions) aligns with your research aim . If not, you’ll need to revise one of the two to achieve this.
FAQ: Research Questions
Research question faqs, how many research questions should i have, what should i avoid when writing a research question, can a research question be a statement.
Typically, a research question is phrased as a question, not a statement. A question clearly indicates what you’re setting out to discover.
Can a research question be too broad or too narrow?
Yes. A question that’s too broad makes your research unfocused, while a question that’s too narrow limits the scope of your study.
Here’s an example of a research question that’s too broad:
“Why is mental health important?”
Conversely, here’s an example of a research question that’s likely too narrow:
“What is the impact of sleep deprivation on the exam scores of 19-year-old males in London studying maths at The Open University?”
Can I change my research question during the research process?
How do i know if my research question is good.
A good research question is focused, specific, practical, rooted in a research gap, and aligned with the research aim. If your question meets these criteria, it’s likely a strong question.
Is a research question similar to a hypothesis?
Not quite. A hypothesis is a testable statement that predicts an outcome, while a research question is a query that you’re trying to answer through your study. Naturally, there can be linkages between a study’s research questions and hypothesis, but they serve different functions.
How are research questions and research objectives related?
The research question is a focused and specific query that your study aims to answer. It’s the central issue you’re investigating. The research objective, on the other hand, outlines the steps you’ll take to answer your research question. Research objectives are often more action-oriented and can be broken down into smaller tasks that guide your research process. In a sense, they’re something of a roadmap that helps you answer your research question.
Need some inspiration?
If you’d like to see more examples of research questions, check out our research question mega list here . Alternatively, if you’d like 1-on-1 help developing a high-quality research question, consider our private coaching service .

Psst… there’s more (for free)
This post is part of our dissertation mini-course, which covers everything you need to get started with your dissertation, thesis or research project.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Developing a Research Question
by acburton | Mar 22, 2024 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources
Selecting your research question and creating a clear goal and structure for your writing can be challenging – whether you are doing it for the first time or if you’ve done it many times before. It can be especially difficult when your research question starts to look and feel a little different somewhere between your first and final draft. Don’t panic! It’s normal for your research question to change a little (or even quite a bit) as you move through and engage with the writing process. Anticipating this can remind you to stay on track while you work and that it’ll be okay even if the literature takes you in a different direction.
What Makes an Effective Research Question?
The most effective research question will usually be a critical thinking question and should use “how” or “why” to ensure it can move beyond a yes/no or one-word type of answer. Consider how your research question can aim to reveal something new, fill in a gap, even if small, and contribute to the field in a meaningful way; How might the proposed project move knowledge forward about a particular place or process? This should be specific and achievable!
The CEWC’s Grad Writing Consultant Tariq says, “I definitely concentrated on those aspects of what I saw in the field where I believed there was an opportunity to move the discipline forward.”
General Tips
Do your research.
Utilize the librarians at your university and take the time to research your topic first. Try looking at very general sources to get an idea of what could be interesting to you before you move to more academic articles that support your rough idea of the topic. It is important that research is grounded in what you see or experience regarding the topic you have chosen and what is already known in the literature. Spend time researching articles, books, etc. that supports your thesis. Once you have a number of sources that you know support what you want to write about, formulate a research question that serves as the interrogative form of your thesis statement.
Grad Writing Consultant Deni advises, “Delineate your intervention in the literature (i.e., be strategic about the literature you discuss and clear about your contributions to it).”
Start Broadly…. then Narrow Your Topic Down to Something Manageable
When brainstorming your research question, let your mind veer toward connections or associations that you might have already considered or that seem to make sense and consider if new research terms, language or concepts come to mind that may be interesting or exciting for you as a researcher. Sometimes testing out a research question while doing some preliminary researching is also useful to see if the language you are using or the direction you are heading toward is fruitful when trying to search strategically in academic databases. Be prepared to focus on a specific area of a broad topic.
Writing Consultant Jessie recommends outlining: “I think some rough outlining with a research question in mind can be helpful for me. I’ll have a research question and maybe a working thesis that I feel may be my claim to the research question based on some preliminary materials, brainstorming, etc.” — Jessie, CEWC Writing Consultant
Try an Exercise
In the earliest phase of brainstorming, try an exercise suggested by CEWC Writing Specialist, Percival! While it is normally used in classroom or workshop settings, this exercise can easily be modified for someone working alone. The flow of the activity, if done within a group setting, is 1) someone starts with an idea, 2) three other people share their idea, and 3) the starting person picks two of these new ideas they like best and combines their original idea with those. The activity then begins again with the idea that was not chosen. The solo version of this exercise substitutes a ‘word bank,’ created using words, topics, or ideas similar to your broad, overarching theme. Pick two words or phrases from your word bank, combine it with your original idea or topic, and ‘start again’ with two different words. This serves as a replacement for different people’s suggestions. Ideas for your ‘word bank’ can range from vague prompts about mapping or webbing (e.g., where your topic falls within the discipline and others like it), to more specific concepts that come from tracing the history of an idea (its past, present, future) or mapping the idea’s related ideas, influences, etc. Care for a physics analogy? There is a particle (your topic) that you can describe, a wave that the particle traces, and a field that the particle is mapped on.
Get Feedback and Affirm Your Confidence!
Creating a few different versions of your research question (they may be the same topic/issue/theme or differ slightly) can be useful during this process. Sharing these with trusted friends, colleagues, mentors, (or tutors!) and having conversations about your questions and ideas with other people can help you decide which version you may feel most confident or interested in. Ask colleagues and mentors to share their research questions with you to get a lot of examples. Once you have done the work of developing an effective research question, do not forget to affirm your confidence! Based on your working thesis, think about how you might organize your chapters or paragraphs and what resources you have for supporting this structure and organization. This can help boost your confidence that the research question you have created is effective and fruitful.
Be Open to Change
Remember, your research question may change from your first to final draft. For questions along the way, make an appointment with the Writing Center. We are here to help you develop an effective and engaging research question and build the foundation for a solid research paper!
Example 1: In my field developing a research question involves navigating the relationship between 1) what one sees/experiences at their field site and 2) what is already known in the literature. During my preliminary research, I found that the financial value of land was often a matter of precisely these cultural factors. So, my research question ended up being: How do the social and material qualities of land entangle with processes of financialization in the city of Lahore. Regarding point #1, this question was absolutely informed by what I saw in the field. But regarding point #2, the question was also heavily shaped by the literature. – Tariq
Example 2: A research question should not be a yes/no question like “Is pollution bad?”; but an open-ended question where the answer has to be supported with reasons and explanation. The question also has to be narrowed down to a specific topic—using the same example as before—”Is pollution bad?” can be revised to “How does pollution affect people?” I would encourage students to be more specific then; e.g., what area of pollution do you want to talk about: water, air, plastic, climate change… what type of people or demographic can we focus on? …how does this affect marginalized communities, minorities, or specific areas in California? After researching and deciding on a focus, your question might sound something like: How does government policy affect water pollution and how does it affect the marginalized communities in the state of California? -Janella
Our Newest Resources!
- Transitioning to Long-form Writing
- Integrating Direct Quotations into Your Writing
- Nurturing a Growth Mindset to Overcome Writing Challenges and Develop Confidence in College Level Writing
- An Introduction to Paraphrasing, Summarizing, and Quoting
Additional Resources
- Graduate Writing Consultants
- Instructor Resources
- Student Resources
- Quick Guides and Handouts
- Self-Guided and Directed Learning Activities
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write a Research Question

Academic writing and research require a distinct focus and direction. A well-designed research question gives purpose and clarity to your research. In addition, it helps your readers understand the issue you are trying to address and explore.
Every time you want to know more about a subject, you will pose a question. The same idea is used in research as well. You must pose a question in order to effectively address a research problem. That's why the research question is an integral part of the research process. Additionally, it offers the author writing and reading guidelines, be it qualitative research or quantitative research.
In your research paper , you must single out just one issue or problem. The specific issue or claim you wish to address should be included in your thesis statement in order to clarify your main argument.
A good research question must have the following characteristics.

- Should include only one problem in the research question
- Should be able to find the answer using primary data and secondary data sources
- Should be possible to resolve within the given time and other constraints
- Detailed and in-depth results should be achievable
- Should be relevant and realistic.
- It should relate to your chosen area of research
While a larger project, like a thesis, might have several research questions to address, each one should be directed at your main area of study. Of course, you can use different research designs and research methods (qualitative research or quantitative research) to address various research questions. However, they must all be pertinent to the study's objectives.
What is a Research Question?

A research question is an inquiry that the research attempts to answer. It is the heart of the systematic investigation. Research questions are the most important step in any research project. In essence, it initiates the research project and establishes the pace for the specific research A research question is:
- Clear : It provides enough detail that the audience understands its purpose without any additional explanation.
- Focused : It is so specific that it can be addressed within the time constraints of the writing task.
- Succinct: It is written in the shortest possible words.
- Complex : It is not possible to answer it with a "yes" or "no", but requires analysis and synthesis of ideas before somebody can create a solution.
- Argumental : Its potential answers are open for debate rather than accepted facts.
A good research question usually focuses on the research and determines the research design, methodology, and hypothesis. It guides all phases of inquiry, data collection, analysis, and reporting. You should gather valuable information by asking the right questions.
Why are Research Questions so important?
Regardless of whether it is a qualitative research or quantitative research project, research questions provide writers and their audience with a way to navigate the writing and research process. Writers can avoid "all-about" papers by asking straightforward and specific research questions that help them focus on their research and support a specific thesis.
Types of Research Questions

There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research . There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection.
The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused research question.
Below is a list of common research questions that can be used in a dissertation. Keep in mind that these are merely illustrations of typical research questions used in dissertation projects. The real research questions themselves might be more difficult.
Example Research Questions

The following are a few examples of research questions and research problems to help you understand how research questions can be created for a particular research problem.
Steps to Write Research Questions

You can focus on the issue or research gaps you're attempting to solve by using the research questions as a direction.
If you're unsure how to go about writing a good research question, these are the steps to follow in the process:
- Select an interesting topic Always choose a topic that interests you. Because if your curiosity isn’t aroused by a subject, you’ll have a hard time conducting research around it. Alos, it’s better that you pick something that’s neither too narrow or too broad.
- Do preliminary research on the topic Search for relevant literature to gauge what problems have already been tackled by scholars. You can do that conveniently through repositories like Scispace , where you’ll find millions of papers in one place. Once you do find the papers you’re looking for, try our reading assistant, SciSpace Copilot to get simple explanations for the paper . You’ll be able to quickly understand the abstract, find the key takeaways, and the main arguments presented in the paper. This will give you a more contextual understanding of your subject and you’ll have an easier time identifying knowledge gaps in your discipline.
Also: ChatPDF vs. SciSpace Copilot: Unveiling the best tool for your research
- Consider your audience It is essential to understand your audience to develop focused research questions for essays or dissertations. When narrowing down your topic, you can identify aspects that might interest your audience.
- Ask questions Asking questions will give you a deeper understanding of the topic. Evaluate your question through the What, Why, When, How, and other open-ended questions assessment.
- Assess your question Once you have created a research question, assess its effectiveness to determine if it is useful for the purpose. Refine and revise the dissertation research question multiple times.
Additionally, use this list of questions as a guide when formulating your research question.
Are you able to answer a specific research question? After identifying a gap in research, it would be helpful to formulate the research question. And this will allow the research to solve a part of the problem. Is your research question clear and centered on the main topic? It is important that your research question should be specific and related to your central goal. Are you tackling a difficult research question? It is not possible to answer the research question with a simple yes or no. The problem requires in-depth analysis. It is often started with "How" and "Why."
Start your research Once you have completed your dissertation research questions, it is time to review the literature on similar topics to discover different perspectives.
Strong Research Question Samples
Uncertain: How should social networking sites work on the hatred that flows through their platform?
Certain: What should social media sites like Twitter or Facebook do to address the harm they are causing?
This unclear question does not specify the social networking sites that are being used or what harm they might be causing. In addition, this question assumes that the "harm" has been proven and/or accepted. This version is more specific and identifies the sites (Twitter, Facebook), the type and extent of harm (privacy concerns), and who might be suffering from that harm (users). Effective research questions should not be ambiguous or interpreted.
Unfocused: What are the effects of global warming on the environment?
Focused: What are the most important effects of glacial melting in Antarctica on penguins' lives?
This broad research question cannot be addressed in a book, let alone a college-level paper. Focused research targets a specific effect of global heating (glacial melting), an area (Antarctica), or a specific animal (penguins). The writer must also decide which effect will have the greatest impact on the animals affected. If in doubt, narrow down your research question to the most specific possible.
Too Simple: What are the U.S. doctors doing to treat diabetes?
Appropriately complex: Which factors, if any, are most likely to predict a person's risk of developing diabetes?
This simple version can be found online. It is easy to answer with a few facts. The second, more complicated version of this question is divided into two parts. It is thought-provoking and requires extensive investigation as well as evaluation by the author. So, ensure that a quick Google search should not answer your research question.
How to write a strong Research Question?

The foundation of all research is the research question. You should therefore spend as much time as necessary to refine your research question based on various data.
You can conduct your research more efficiently and analyze your results better if you have great research questions for your dissertation, research paper , or essay .
The following criteria can help you evaluate the strength and importance of your research question and can be used to determine the strength of your research question:
- Researchable
- It should only cover one issue.
- A subjective judgment should not be included in the question.
- It can be answered with data analysis and research.
- Specific and Practical
- It should not contain a plan of action, policy, or solution.
- It should be clearly defined
- Within research limits
- Complex and Arguable
- It shouldn't be difficult to answer.
- To find the truth, you need in-depth knowledge
- Allows for discussion and deliberation
- Original and Relevant
- It should be in your area of study
- Its results should be measurable
- It should be original
Conclusion - How to write Research Questions?
Research questions provide a clear guideline for research. One research question may be part of a larger project, such as a dissertation. However, each question should only focus on one topic.
Research questions must be answerable, practical, specific, and applicable to your field. The research type that you use to base your research questions on will determine the research topic. You can start by selecting an interesting topic and doing preliminary research. Then, you can begin asking questions, evaluating your questions, and start your research.
Now it's easier than ever to streamline your research workflow with SciSpace ResearchGPT . Its integrated, comprehensive end-to-end platform for research allows scholars to easily discover, read, write and publish their research and fosters collaboration.
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Good Research Question (w/ Examples)
What is a Research Question?
A research question is the main question that your study sought or is seeking to answer. A clear research question guides your research paper or thesis and states exactly what you want to find out, giving your work a focus and objective. Learning how to write a hypothesis or research question is the start to composing any thesis, dissertation, or research paper. It is also one of the most important sections of a research proposal .
A good research question not only clarifies the writing in your study; it provides your readers with a clear focus and facilitates their understanding of your research topic, as well as outlining your study’s objectives. Before drafting the paper and receiving research paper editing (and usually before performing your study), you should write a concise statement of what this study intends to accomplish or reveal.
Research Question Writing Tips
Listed below are the important characteristics of a good research question:
A good research question should:
- Be clear and provide specific information so readers can easily understand the purpose.
- Be focused in its scope and narrow enough to be addressed in the space allowed by your paper
- Be relevant and concise and express your main ideas in as few words as possible, like a hypothesis.
- Be precise and complex enough that it does not simply answer a closed “yes or no” question, but requires an analysis of arguments and literature prior to its being considered acceptable.
- Be arguable or testable so that answers to the research question are open to scrutiny and specific questions and counterarguments.
Some of these characteristics might be difficult to understand in the form of a list. Let’s go into more detail about what a research question must do and look at some examples of research questions.
The research question should be specific and focused
Research questions that are too broad are not suitable to be addressed in a single study. One reason for this can be if there are many factors or variables to consider. In addition, a sample data set that is too large or an experimental timeline that is too long may suggest that the research question is not focused enough.
A specific research question means that the collective data and observations come together to either confirm or deny the chosen hypothesis in a clear manner. If a research question is too vague, then the data might end up creating an alternate research problem or hypothesis that you haven’t addressed in your Introduction section .
The research question should be based on the literature
An effective research question should be answerable and verifiable based on prior research because an effective scientific study must be placed in the context of a wider academic consensus. This means that conspiracy or fringe theories are not good research paper topics.
Instead, a good research question must extend, examine, and verify the context of your research field. It should fit naturally within the literature and be searchable by other research authors.
References to the literature can be in different citation styles and must be properly formatted according to the guidelines set forth by the publishing journal, university, or academic institution. This includes in-text citations as well as the Reference section .
The research question should be realistic in time, scope, and budget
There are two main constraints to the research process: timeframe and budget.
A proper research question will include study or experimental procedures that can be executed within a feasible time frame, typically by a graduate doctoral or master’s student or lab technician. Research that requires future technology, expensive resources, or follow-up procedures is problematic.
A researcher’s budget is also a major constraint to performing timely research. Research at many large universities or institutions is publicly funded and is thus accountable to funding restrictions.
The research question should be in-depth
Research papers, dissertations and theses , and academic journal articles are usually dozens if not hundreds of pages in length.
A good research question or thesis statement must be sufficiently complex to warrant such a length, as it must stand up to the scrutiny of peer review and be reproducible by other scientists and researchers.
Research Question Types
Qualitative and quantitative research are the two major types of research, and it is essential to develop research questions for each type of study.
Quantitative Research Questions
Quantitative research questions are specific. A typical research question involves the population to be studied, dependent and independent variables, and the research design.
In addition, quantitative research questions connect the research question and the research design. In addition, it is not possible to answer these questions definitively with a “yes” or “no” response. For example, scientific fields such as biology, physics, and chemistry often deal with “states,” in which different quantities, amounts, or velocities drastically alter the relevance of the research.
As a consequence, quantitative research questions do not contain qualitative, categorical, or ordinal qualifiers such as “is,” “are,” “does,” or “does not.”
Categories of quantitative research questions
Qualitative research questions.
In quantitative research, research questions have the potential to relate to broad research areas as well as more specific areas of study. Qualitative research questions are less directional, more flexible, and adaptable compared with their quantitative counterparts. Thus, studies based on these questions tend to focus on “discovering,” “explaining,” “elucidating,” and “exploring.”
Categories of qualitative research questions
Quantitative and qualitative research question examples.

Good and Bad Research Question Examples
Below are some good (and not-so-good) examples of research questions that researchers can use to guide them in crafting their own research questions.
Research Question Example 1
The first research question is too vague in both its independent and dependent variables. There is no specific information on what “exposure” means. Does this refer to comments, likes, engagement, or just how much time is spent on the social media platform?
Second, there is no useful information on what exactly “affected” means. Does the subject’s behavior change in some measurable way? Or does this term refer to another factor such as the user’s emotions?
Research Question Example 2
In this research question, the first example is too simple and not sufficiently complex, making it difficult to assess whether the study answered the question. The author could really only answer this question with a simple “yes” or “no.” Further, the presence of data would not help answer this question more deeply, which is a sure sign of a poorly constructed research topic.
The second research question is specific, complex, and empirically verifiable. One can measure program effectiveness based on metrics such as attendance or grades. Further, “bullying” is made into an empirical, quantitative measurement in the form of recorded disciplinary actions.
Steps for Writing a Research Question
Good research questions are relevant, focused, and meaningful. It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier.
1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic
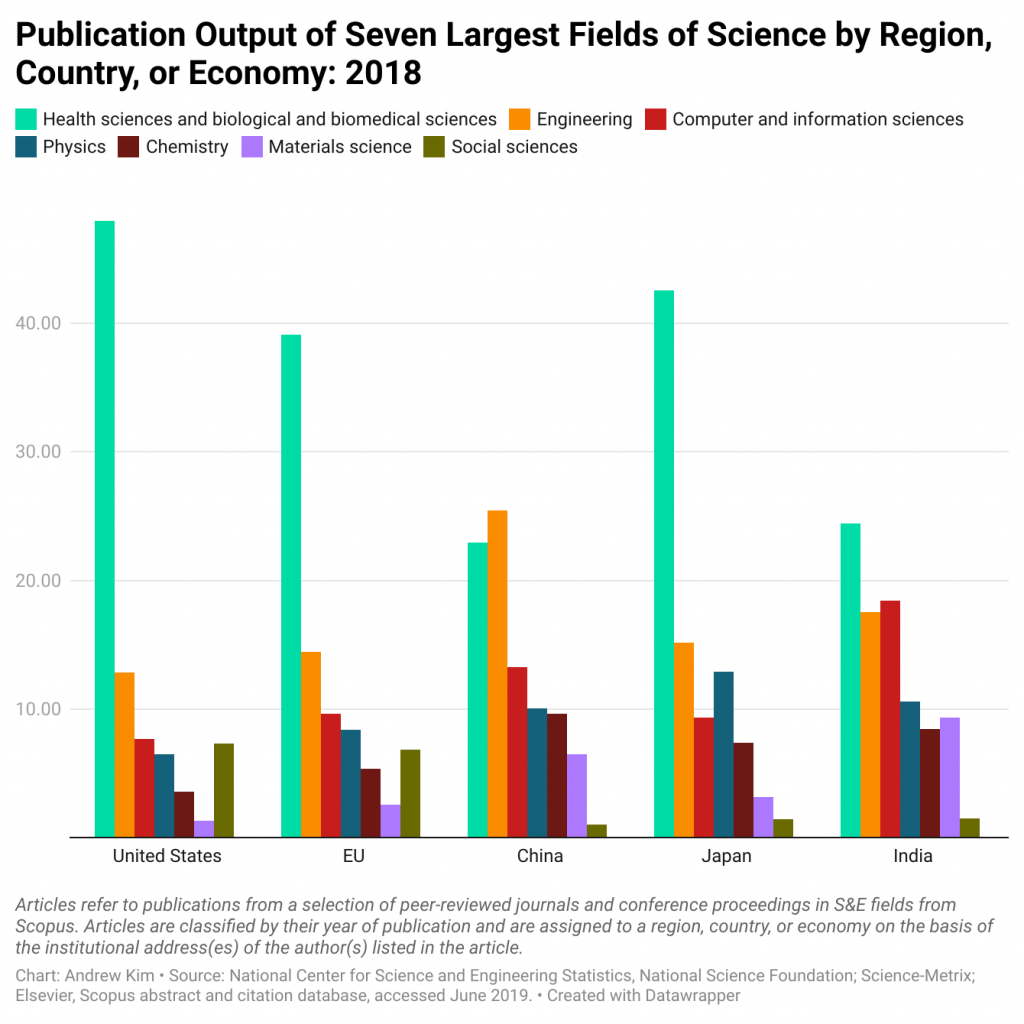
Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country’s culture or your university’s capabilities. Popular academic topics include healthcare and medical-related research. However, if you are attending an engineering school or humanities program, you should obviously choose a research question that pertains to your specific study and major.
Below is an embedded graph of the most popular research fields of study based on publication output according to region. As you can see, healthcare and the basic sciences receive the most funding and earn the highest number of publications.
2. Do preliminary research
You can begin doing preliminary research once you have chosen a research topic. Two objectives should be accomplished during this first phase of research. First, you should undertake a preliminary review of related literature to discover issues that scholars and peers are currently discussing. With this method, you show that you are informed about the latest developments in the field.
Secondly, identify knowledge gaps or limitations in your topic by conducting a preliminary literature review . It is possible to later use these gaps to focus your research question after a certain amount of fine-tuning.
3. Narrow your research to determine specific research questions
You can focus on a more specific area of study once you have a good handle on the topic you want to explore. Focusing on recent literature or knowledge gaps is one good option.
By identifying study limitations in the literature and overlooked areas of study, an author can carve out a good research question. The same is true for choosing research questions that extend or complement existing literature.
4. Evaluate your research question
Make sure you evaluate the research question by asking the following questions:
Is my research question clear?
The resulting data and observations that your study produces should be clear. For quantitative studies, data must be empirical and measurable. For qualitative, the observations should be clearly delineable across categories.
Is my research question focused and specific?
A strong research question should be specific enough that your methodology or testing procedure produces an objective result, not one left to subjective interpretation. Open-ended research questions or those relating to general topics can create ambiguous connections between the results and the aims of the study.
Is my research question sufficiently complex?
The result of your research should be consequential and substantial (and fall sufficiently within the context of your field) to warrant an academic study. Simply reinforcing or supporting a scientific consensus is superfluous and will likely not be well received by most journal editors.

Editing Your Research Question
Your research question should be fully formulated well before you begin drafting your research paper. However, you can receive English paper editing and proofreading services at any point in the drafting process. Language editors with expertise in your academic field can assist you with the content and language in your Introduction section or other manuscript sections. And if you need further assistance or information regarding paper compositions, in the meantime, check out our academic resources , which provide dozens of articles and videos on a variety of academic writing and publication topics.
Not sure how to log in to access library resources? Click here to learn how!
Guess what? We're open! Click here for our new hours
Library Home
- Library Website
- Research Basics
Developing a Research Question
- Introduction
- The Research Process
- Scholarly & Peer-Reviewed
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources
- Quantitative vs. Qualitative
- Evaluating Sources
What is a research question?
A research question is an essential tool to help guide your research paper, project, or thesis. It poses a specific question that you are seeking to answer in your paper. Research questions can be broad or narrow, and can change throughout the research process.
A good research question should be:
- Focused on a single issue
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly in your paper
- Feasible to answer within the length of your paper
- Researchable using the resources available to you
- Relevant to your field of study and/or to society at large
The length of your paper and the research you're able to locate will help to shape your research question. A longer paper, like a thesis or dissertation, may require multiple research questions.
The answer to your research question develops into your thesis statement .
Writing Your Research Question
Chose a Topic
You should choose a research topic that is interesting to you. This will make the research and writing process much more bearable.
A good way to begin brainstorming research questions is to list all the questions you would like to see answered, or topics you would like to learn more about. You may have been provided a list of potential topics by your professor, if none are interesting to you ask if you can develop your own.
It is better to start broad and narrow down your focus as you go.
Do Preliminary Research

Reference materials like encyclopedias can also be good for this purpose.
Narrow Your Topic
Now that you have a basic idea of what research exists on your topic, you can begin to narrow your focus.
Make sure that your question is specific enough that it can be answered thoroughly in the length of your paper.
Developing a Research Question Video Tutorial
Using Keywords Video Tutorial
- << Previous: Introduction
- Next: The Research Process >>
- Last Updated: Aug 15, 2023 3:47 PM
- URL: https://library.ndnu.edu/researchbasics
Academic Success Center
Emergency Information

© 2023 Notre Dame de Namur University. All rights reserved.
Notre Dame de Namur University 1500 Ralston Avenue Belmont, CA 94002 Map
Writing Studio
Formulating your research question (rq).
In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. Download this page as a PDF: Formulating Your Research Question Return to Writing Studio Handouts
In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will develop an engaging research question. Merely presenting a topic in the form of a question does not transform it into a good research question.
Research Topic Versus Research Question Examples
1. broad topic versus narrow question, 1a. broad topic.
“What forces affect race relations in America?”
1b. NARROWER QUESTION
“How do corporate hiring practices affect race relations in Nashville?”
The question “What is the percentage of racial minorities holding management positions in corporate offices in Nashville?” is much too specific and would yield, at best, a statistic that could become part of a larger argument.
2. Neutral Topic Versus Argumentative Question
2a. neutral topic.
“How does KFC market its low-fat food offerings?”
2b. Argumentative question
“Does KFC put more money into marketing its high-fat food offerings than its lower-fat ones?”
The latter question is somewhat better, since it may lead you to take a stance or formulate an argument about consumer awareness or benefit.
3. Objective Topic Versus Subjective Question
Objective subjects are factual and do not have sides to be argued. Subjective subjects are those about which you can take a side.
3a. Objective topic
“How much time do youth between the ages of 10 and 15 spend playing video games?”
3b. Subjective Question
“What are the effects of video-gaming on the attention spans of youth between the ages of 10 and 15?”
The first question is likely to lead to some data, though not necessarily to an argument or issue. The second question is somewhat better, since it might lead you to formulate an argument for or against time spent playing video games.
4. Open-Ended Topic Versus Direct Question
4a. open-ended topic.
“Does the author of this text use allusion?”
4b. Direct question (gives direction to research)
“Does the ironic use of allusion in this text reveal anything about the author’s unwillingness to divulge his political commitments?”
The second question gives focus by putting the use of allusion into the specific context of a question about the author’s political commitments and perhaps also about the circumstances under which the text was produced.
Research Question (RQ) Checklist
- Is my RQ something that I am curious about and that others might care about? Does it present an issue on which I can take a stand?
- Does my RQ put a new spin on an old issue, or does it try to solve a problem?
- Is my RQ too broad, too narrow, or OK?
- within the time frame of the assignment?
- given the resources available at my location?
- Is my RQ measurable? What type of information do I need? Can I find actual data to support or contradict a position?
- What sources will have the type of information that I need to answer my RQ (journals, books, internet resources, government documents, interviews with people)?
Final Thoughts
The answer to a good research question will often be the THESIS of your research paper! And the results of your research may not always be what you expected them to be. Not only is this ok, it can be an indication that you are doing careful work!
Adapted from an online tutorial at Empire State College: http://www.esc.edu/htmlpages/writerold/menus.htm#develop (broken link)
Last revised: November 2022 | Adapted for web delivery: November 2022
In order to access certain content on this page, you may need to download Adobe Acrobat Reader or an equivalent PDF viewer software.

How to Develop a Good Research Question? — Types & Examples
Cecilia is living through a tough situation in her research life. Figuring out where to begin, how to start her research study, and how to pose the right question for her research quest, is driving her insane. Well, questions, if not asked correctly, have a tendency to spiral us!
Image Source: https://phdcomics.com/
Questions lead everyone to answers. Research is a quest to find answers. Not the vague questions that Cecilia means to answer, but definitely more focused questions that define your research. Therefore, asking appropriate question becomes an important matter of discussion.
A well begun research process requires a strong research question. It directs the research investigation and provides a clear goal to focus on. Understanding the characteristics of comprising a good research question will generate new ideas and help you discover new methods in research.
In this article, we are aiming to help researchers understand what is a research question and how to write one with examples.
Table of Contents
What Is a Research Question?
A good research question defines your study and helps you seek an answer to your research. Moreover, a clear research question guides the research paper or thesis to define exactly what you want to find out, giving your work its objective. Learning to write a research question is the beginning to any thesis, dissertation , or research paper. Furthermore, the question addresses issues or problems which is answered through analysis and interpretation of data.
Why Is a Research Question Important?
A strong research question guides the design of a study. Moreover, it helps determine the type of research and identify specific objectives. Research questions state the specific issue you are addressing and focus on outcomes of the research for individuals to learn. Therefore, it helps break up the study into easy steps to complete the objectives and answer the initial question.
Types of Research Questions
Research questions can be categorized into different types, depending on the type of research you want to undergo. Furthermore, knowing the type of research will help a researcher determine the best type of research question to use.
1. Qualitative Research Question
Qualitative questions concern broad areas or more specific areas of research. However, unlike quantitative questions, qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional and more flexible. Qualitative research question focus on discovering, explaining, elucidating, and exploring.
i. Exploratory Questions
This form of question looks to understand something without influencing the results. The objective of exploratory questions is to learn more about a topic without attributing bias or preconceived notions to it.
Research Question Example: Asking how a chemical is used or perceptions around a certain topic.
ii. Predictive Questions
Predictive research questions are defined as survey questions that automatically predict the best possible response options based on text of the question. Moreover, these questions seek to understand the intent or future outcome surrounding a topic.
Research Question Example: Asking why a consumer behaves in a certain way or chooses a certain option over other.
iii. Interpretive Questions
This type of research question allows the study of people in the natural setting. The questions help understand how a group makes sense of shared experiences with regards to various phenomena. These studies gather feedback on a group’s behavior without affecting the outcome.
Research Question Example: How do you feel about AI assisting publishing process in your research?
2. Quantitative Research Question
Quantitative questions prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis through descriptions, comparisons, and relationships. These questions are beneficial when choosing a research topic or when posing follow-up questions that garner more information.
i. Descriptive Questions
It is the most basic type of quantitative research question and it seeks to explain when, where, why, or how something occurred. Moreover, they use data and statistics to describe an event or phenomenon.
Research Question Example: How many generations of genes influence a future generation?
ii. Comparative Questions
Sometimes it’s beneficial to compare one occurrence with another. Therefore, comparative questions are helpful when studying groups with dependent variables.
Example: Do men and women have comparable metabolisms?
iii. Relationship-Based Questions
This type of research question answers influence of one variable on another. Therefore, experimental studies use this type of research questions are majorly.
Example: How is drought condition affect a region’s probability for wildfires.
How to Write a Good Research Question?

1. Select a Topic
The first step towards writing a good research question is to choose a broad topic of research. You could choose a research topic that interests you, because the complete research will progress further from the research question. Therefore, make sure to choose a topic that you are passionate about, to make your research study more enjoyable.
2. Conduct Preliminary Research
After finalizing the topic, read and know about what research studies are conducted in the field so far. Furthermore, this will help you find articles that talk about the topics that are yet to be explored. You could explore the topics that the earlier research has not studied.
3. Consider Your Audience
The most important aspect of writing a good research question is to find out if there is audience interested to know the answer to the question you are proposing. Moreover, determining your audience will assist you in refining your research question, and focus on aspects that relate to defined groups.
4. Generate Potential Questions
The best way to generate potential questions is to ask open ended questions. Questioning broader topics will allow you to narrow down to specific questions. Identifying the gaps in literature could also give you topics to write the research question. Moreover, you could also challenge the existing assumptions or use personal experiences to redefine issues in research.
5. Review Your Questions
Once you have listed few of your questions, evaluate them to find out if they are effective research questions. Moreover while reviewing, go through the finer details of the question and its probable outcome, and find out if the question meets the research question criteria.
6. Construct Your Research Question
There are two frameworks to construct your research question. The first one being PICOT framework , which stands for:
- Population or problem
- Intervention or indicator being studied
- Comparison group
- Outcome of interest
- Time frame of the study.
The second framework is PEO , which stands for:
- Population being studied
- Exposure to preexisting conditions
- Outcome of interest.
Research Question Examples
- How might the discovery of a genetic basis for alcoholism impact triage processes in medical facilities?
- How do ecological systems respond to chronic anthropological disturbance?
- What are demographic consequences of ecological interactions?
- What roles do fungi play in wildfire recovery?
- How do feedbacks reinforce patterns of genetic divergence on the landscape?
- What educational strategies help encourage safe driving in young adults?
- What makes a grocery store easy for shoppers to navigate?
- What genetic factors predict if someone will develop hypothyroidism?
- Does contemporary evolution along the gradients of global change alter ecosystems function?
How did you write your first research question ? What were the steps you followed to create a strong research question? Do write to us or comment below.
Frequently Asked Questions
Research questions guide the focus and direction of a research study. Here are common types of research questions: 1. Qualitative research question: Qualitative questions concern broad areas or more specific areas of research. However, unlike quantitative questions, qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional and more flexible. Different types of qualitative research questions are: i. Exploratory questions ii. Predictive questions iii. Interpretive questions 2. Quantitative Research Question: Quantitative questions prove or disprove a researcher’s hypothesis through descriptions, comparisons, and relationships. These questions are beneficial when choosing a research topic or when posing follow-up questions that garner more information. Different types of quantitative research questions are: i. Descriptive questions ii. Comparative questions iii. Relationship-based questions
Qualitative research questions aim to explore the richness and depth of participants' experiences and perspectives. They should guide your research and allow for in-depth exploration of the phenomenon under investigation. After identifying the research topic and the purpose of your research: • Begin with Broad Inquiry: Start with a general research question that captures the main focus of your study. This question should be open-ended and allow for exploration. • Break Down the Main Question: Identify specific aspects or dimensions related to the main research question that you want to investigate. • Formulate Sub-questions: Create sub-questions that delve deeper into each specific aspect or dimension identified in the previous step. • Ensure Open-endedness: Make sure your research questions are open-ended and allow for varied responses and perspectives. Avoid questions that can be answered with a simple "yes" or "no." Encourage participants to share their experiences, opinions, and perceptions in their own words. • Refine and Review: Review your research questions to ensure they align with your research purpose, topic, and objectives. Seek feedback from your research advisor or peers to refine and improve your research questions.
Developing research questions requires careful consideration of the research topic, objectives, and the type of study you intend to conduct. Here are the steps to help you develop effective research questions: 1. Select a Topic 2. Conduct Preliminary Research 3. Consider Your Audience 4. Generate Potential Questions 5. Review Your Questions 6. Construct Your Research Question Based on PICOT or PEO Framework
There are two frameworks to construct your research question. The first one being PICOT framework, which stands for: • Population or problem • Intervention or indicator being studied • Comparison group • Outcome of interest • Time frame of the study The second framework is PEO, which stands for: • Population being studied • Exposure to preexisting conditions • Outcome of interest
A tad helpful
Had trouble coming up with a good research question for my MSc proposal. This is very much helpful.
This is a well elaborated writing on research questions development. I found it very helpful.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Publishing Research
- Reporting Research
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
For researchers across disciplines, the path to uncovering novel findings and insights is often filled…

- Industry News
- Trending Now

Breaking Barriers: Sony and Nature unveil “Women in Technology Award”
Sony Group Corporation and the prestigious scientific journal Nature have collaborated to launch the inaugural…

Achieving Research Excellence: Checklist for good research practices
Academia is built on the foundation of trustworthy and high-quality research, supported by the pillars…

- Diversity and Inclusion
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…
Setting Rationale in Research: Cracking the code for excelling at research
Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
Experimental Research Design — 6 mistakes you should never make!

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Introduction
Why are research questions so important?
Research question examples, types of qualitative research questions, writing a good research question, guiding your research through research questions.
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Research questions
The research question plays a critical role in the research process, as it guides the study design, data collection , analysis , and interpretation of the findings.
A research paper relies on a research question to inform readers of the research topic and the research problem being addressed. Without such a question, your audience may have trouble understanding the rationale for your research project.

People can take for granted the research question as an essential part of a research project. However, explicitly detailing why researchers need a research question can help lend clarity to the research project. Here are some of the key roles that the research question plays in the research process:
Defines the scope and focus of the study
The research question helps to define the scope and focus of the study. It identifies the specific topic or issue that the researcher wants to investigate, and it sets the boundaries for the study. A research question can also help you determine if your study primarily contributes to theory or is more applied in nature. Clinical research and public health research, for example, may be more concerned with research questions that contribute to practice, while a research question focused on cognitive linguistics are aimed at developing theory.
Provides a rationale for the study
The research question provides a rationale for the study by identifying a gap or problem in existing literature or practice that the researcher wants to address. It articulates the purpose and significance of the study, and it explains why the study is important and worth conducting.
Guides the study design
The research question guides the study design by helping the researcher select appropriate research methods , sampling strategies, and data collection tools. It also helps to determine the types of data that need to be collected and the best ways to analyze and interpret the data because the principal aim of the study is to provide an answer to that research question.

Shapes the data analysis and interpretation
The research question shapes the data analysis and interpretation by guiding the selection of appropriate analytical methods and by focusing the interpretation of the findings. It helps to identify which patterns and themes in the data are more relevant and worth digging into, and it guides the development of conclusions and recommendations based on the findings.
Generates new knowledge
The research question is the starting point for generating new knowledge. By answering the research question, the researcher contributes to the body of knowledge in the field and helps to advance the understanding of the topic or issue under investigation.
Overall, the research question is a critical component of the research process, as it guides the study from start to finish and provides a foundation for generating new knowledge.
Supports the thesis statement
The thesis statement or main assertion in any research paper stems from the answers to the research question. As a result, you can think of a focused research question as a preview of what the study aims to present as a new contribution to existing knowledge.
Here area few examples of focused research questions that can help set the stage for explaining different types of research questions in qualitative research . These questions touch upon various fields and subjects, showcasing the versatility and depth of research.
- What factors contribute to the job satisfaction of remote workers in the technology industry?
- How do teachers perceive the implementation of technology in the classroom, and what challenges do they face?
- What coping strategies do refugees use to deal with the challenges of resettlement in a new country?
- How does gentrification impact the sense of community and identity among long-term residents in urban neighborhoods?
- In what ways do social media platforms influence body image and self-esteem among adolescents?
- How do family dynamics and communication patterns affect the management of type 2 diabetes in adult patients?
- What is the role of mentorship in the professional development and career success of early-career academics?
- How do patients with chronic illnesses experience and navigate the healthcare system, and what barriers do they encounter?
- What are the motivations and experiences of volunteers in disaster relief efforts, and how do these experiences impact their future involvement in humanitarian work?
- How do cultural beliefs and values shape the consumer preferences and purchasing behavior of young adults in a globalized market?
- How do individuals whose genetic factors predict a high risk for developing a specific medical condition perceive, cope with, and make lifestyle choices based on this information?
These example research questions highlight the different kinds of inquiries common to qualitative research. They also demonstrate how qualitative research can address a wide range of topics, from understanding the experiences of specific populations to examining the impact of broader social and cultural phenomena.
Also, notice that these types of research questions tend to be geared towards inductive analyses that describe a concept in depth or develop new theory. As such, qualitative research questions tend to ask "what," "why," or "how" types of questions. This contrasts with quantitative research questions that typically aim to verify an existing theory. and tend to ask "when," "how much," and "why" types of questions to nail down causal mechanisms and generalizable findings.
Whatever your research inquiry, turn to ATLAS.ti
Powerful tools to help turn your research question into meaningful analysis, starting with a free trial.
As you can see above, the research questions you ask play a critical role in shaping the direction and depth of your study. These questions are designed to explore, understand, and interpret social phenomena, rather than testing a hypothesis or quantifying data like in quantitative research. In this section, we will discuss the various types of research questions typically found in qualitative research, making it easier for you to craft appropriate questions for your study.
Descriptive questions
Descriptive research questions aim to provide a detailed account of the phenomenon being studied. These questions usually begin with "what" or "how" and seek to understand the nature, characteristics, or functions of a subject. For example, "What are the experiences of first-generation college students?" or "How do small business owners adapt to economic downturns?"
Comparative questions
Comparative questions seek to examine the similarities and differences between two or more groups, cases, or phenomena. These questions often include the words "compare," "contrast," or "differences." For example, "How do parenting practices differ between single-parent and two-parent families?" or "What are the similarities and differences in leadership styles among successful female entrepreneurs?"
Exploratory questions
Exploratory research questions are open-ended and intended to investigate new or understudied areas. These questions aim to identify patterns, relationships, or themes that may warrant further investigation. For example, "How do teenagers use social media to construct their identities?" or "What factors influence the adoption of renewable energy technologies in rural communities?"
Explanatory questions
Explanatory research questions delve deeper into the reasons or explanations behind a particular phenomenon or behavior. They often start with "why" or "how" and aim to uncover underlying motivations, beliefs, or processes. For example, "Why do some employees resist organizational change?" or "How do cultural factors influence decision-making in international business negotiations?"
Evaluative questions
Evaluative questions assess the effectiveness, impact, or outcomes of a particular intervention, program, or policy. They seek to understand the value or significance of an initiative by examining its successes, challenges, or unintended consequences. For example, "How effective is the school's anti-bullying program in reducing incidents of bullying?" or "What are the long-term impacts of a community-based health promotion campaign on residents' well-being?"
Interpretive questions
Interpretive questions focus on understanding how individuals or groups make sense of their experiences, actions, or social contexts. These questions often involve the analysis of language, symbols, or narratives to uncover the meanings and perspectives that shape human behavior. For example, "How do cancer survivors make sense of their illness journey?" or "What meanings do members of a religious community attach to their rituals and practices?"
There are mainly two overarching ways to think about how to devise a research question. Many studies are built on existing research, but others can be founded on personal experiences or pilot research.
Using the literature review
Within scholarly research, the research question is often built from your literature review . An analysis of the relevant literature reporting previous studies should allow you to identify contextual, theoretical, or methodological gaps that can be addressed in future research.

A compelling research question built on a robust literature review ultimately illustrates to your audience what is novel about your study's objectives.
Conducting pilot research
Researchers may conduct preliminary research or pilot research when they are interested in a particular topic but don't yet have a basis for forming a research question on that topic. A pilot study is a small-scale, preliminary study that is conducted in order to test the feasibility of a research design, methods, and procedures. It can help identify unresolved puzzles that merit further investigation, and pilot studies can draw attention to potential issues or problems that may arise in the full study.
One potential benefit of conducting a pilot study in qualitative research is that it can help the researcher to refine their research question. By collecting and analyzing a small amount of data, the researcher can get a better sense of the phenomenon under investigation and can develop a more focused and refined research question for the full study. The pilot study can also help the researcher to identify key themes, concepts, or variables that should be included in the research question.
In addition to helping to refine the research question, a pilot study can also help the researcher to develop a more effective data collection and analysis plan. The researcher can test different methods for collecting and analyzing data, and can make adjustments based on the results of the pilot study. This can help to ensure that the full study is conducted in the most effective and efficient manner possible.
Overall, conducting a pilot study in qualitative research can be a valuable tool for refining the research question and developing a more effective research design, methods, and procedures. It can help to ensure that the full study is conducted in a rigorous and effective manner, and can increase the likelihood of generating meaningful and useful findings.
When you write a research question for your qualitative study, consider which type of question best aligns with your research objectives and the nature of the phenomenon you are investigating. Remember, qualitative research questions should be open-ended, allowing for a range of perspectives and insights to emerge. As you progress in your research, these questions may evolve or be refined based on the data you collect, helping to guide your analysis and deepen your understanding of the topic.

Use ATLAS.ti for every step of your research project
From the research question to the key insights, ATLAS.ti is there for you. See how with a free trial.
- UConn Library
- Research Now
- Get Started
- Forming a Research Question
Get Started — Forming a Research Question
- Reading (and Understanding) Your Assignment
- Background Research
- Initial Searching
- Help & Other Resources
- Research Now Homepage
Writing out your research question will help you articulate (to yourself and others) the direction of your research – what you need to be looking for as you prepare to gather specific information.
Forming the Research Question
Performing Background Research and Initial Searching develops your general area of interest so that you can form a more focused topic.
As you review the information you've found from these steps and the ideas you've encountered, these questions may help you to form a focus for your research:
- What am I trying to accomplish?
- How interested am I in this idea?
- How much time do I have?
- What information and resources are available?
(From Guided Inquiry: Learning in the 21st Century by Carol Kuhlthau, Leslie Maniotes, and Ann Caspari)
Your Research Log helps you to keep track of and think about your research. Look back through your log and consider:
What have you found? How does the information and ideas you've encountered fit together? What themes have emerged ? What important question do you want to develop from the ideas and information you have found? What do you want to explore in more detail? What do you want your research to focus on?
And - does your research question answer the assignment?
You'll want to make sure that you're not trying to answer too many questions - think about the time you have available. You'll want to focus on one aspect of your topic.
- Research Questions - The Good and the Not So Good
(Credit: William Badke)
How do I Know if My Topic is Sustainable?
You will not really know if your topic will work until you start searching for information. The information you found while exploring your topic doing background research should give you an idea of whether or not your topic is sustainable.
Test your topic in a few databases by searching for the key concepts or terms.
- Are you finding too much information? Perhaps your topic is too general . Add a few more terms to your search and explore (for example, you might feel like you're finding too much on "College Students." Looking for information about "Freshmen," though, will give you fewer and more specific results).
- Are you finding too little information? Perhaps your topic is too specific . Try searching again using broader synonyms for your search terms (for example, you might not find much on the topic "UConn Students." "College Students" will give you more information).
As you develop your research question, you might find that you need to ask a broader or narrower question, depending upon the resources available and the time you have to complete your assignment.
Sometimes it's hard to determine if a topic is too broad or specific. Try checking in with your instructor (who has a good idea of the field of research!) or a librarian (who has a good idea of the available resources!).
- Ask a Librarian Chat with a UConn librarian.
Developing a Research Question
(Credit: Wilfrid Laurier University Library)
Now apply what you've learned! These tools will help you write out your research question.
- Research Question Generator Worksheet A tool to help you develop your research question.

Test Your Knowledge: Forming a Research Question
- Test your knowledge: Too Broad, Too Narrow Get some practice evaluating a research question.
Does Your Research Question Actually Answer a Question?
Sometimes this is referred to as the "so what" - what makes your project interesting and important.
What makes your question important? What makes your question interesting or exciting? Does your question require anything more of you than just repeating the information you've found? (If you find you're just repeating the information found, you probably don't have a very good question).
- << Previous: Initial Searching
- Next: Help & Other Resources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 27, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/getstarted

Starting your research
- Starting Your Research
- Refine your topic
- Background information & facts
What Is a research question?
Steps to developing a research question, sample research questions.
- Other information sources
- What databases should I use?
- Boolean: AND & OR
- Truncation (stemming & wildcards)
- Phrases (quotation marks)
- Database limiters
- Subjects vs. Keywords
- I found a good source. How do I get to it?
- What do I cite? (avoiding plagiarism)
- Citation style guides
- Citation Tools
- Research checklist
A research question is the question around which you center your inquiry and write your paper. It helps focus your research by providing a path through the research and writing process, and also helps you create a paper that supports a single, arguable thesis. Your research question should be:
- Clear: providing enough specifics that your audience can easily understand its purpose without needing additional explanation.
- Focused: narrow enough that it can be answered thoroughly within the length of your paper.
- Concise: expressed in the fewest possible words.
- Complex: cannot be answered through just a "yes" or "no," but requires synthesis and analysis of ideas and sources prior to the composition of an answer.
- Arguable : potential answers are open to debate rather than simple statement of facts.
As mentioned in the previous tab, it's important to select a topic you are passionate about or interested in. You will spend a lot of time with this topic, including hours of research, reading, and writing, so make sure it's something that speaks to you.
1. Choose an interesting general topic: Start with a broad topic about which you're genuinely interested. An example of a general topic might be "the Underground Railroad" or "Films of the 1930s."
2. Do some preliminary research on that general topic: Conduct quick searches in current periodicals or journals, reference books like encyclopedias (which can be found in the library's first floor reference section), or even Wikipedia, to see what's already been done and to help you narrow your focus. What issues are scholars and researchers discussing when it comes to your topic? What questions occurred to you as you've read these sources?
3. Consider your audience: For most of your papers, your audience will be academic (specifically, the professor who assigned this project), but always keep your audience in mind when narrowing your topic and devising your research question. Would that particular audience be interested in the question you've come up with?
4. Start asking questions: Now that you have a bit of a foundation laid, start asking some open-ended "how" and "why" questions about your general topic. For example, "Why was New York's Hudson Valley such a center of the Underground Railroad?" or "How was the Great Depression reflected in Hollywood films of the 1930s?"
5. Evaluate your question: Once you've come up with some possible research questions, evaluate them to determine whether they would be effective for your project, or whether they require additional revising and refining.
- Is your research question clear? Having a clear research question will help guide and direct your research, and will make it easier for you to develop your argument as you write your paper.
- Is your research question focused? You want to be sure your question is focused enough that you can deal with the topic within the length and confines of your paper. Choose too broad a topic, and you won't be able to answer it completely before you run out of room.
- Is your research question complex? Your question shouldn't be answerable with just a simple "yes" or "no," or by easily-found facts. Instead, it should require both research and analysis on your part. Often, research questions begin with "how" or "why."
- Begin your research. After you've come up with your research question, think about the possible paths your research might take you. What sources should you look for? What research process will ensure that you find a variety of perspectives and responses to your question? Lucky for you, the following tabs on this guide will help you through this process.
Unclear: How should social media sites address the harm they cause?
Clear: What action should social media sites like Twitter and Facebook take to reduce the spread of disinformation in users' newsfeeds?
The unclear version of this question doesn't specify which social media sites the writer is focusing on, or suggest what kind of harm they might be causing. It also assumes that this "harm" is proven and/or accepted. The clearer version specifies sites (Twitter and Facebook), the type of potential harm (the spread of disinformation), and who might be experiencing that harm (users). A strong research question should never leave room for ambiguity or interpretation.
Unfocused: What is the effect on the environment from global warming?
Focused: What is the most significant effect of the melting of polar ice caps on the lives of polar bears in the Arctic?
The unfocused research question is so broad that it could never be properly addressed in an entire book, much less a standard college-level research paper. The focused version narrows down to a specific effect of global warming (the melting of polar ice caps), a specific place (the Arctic), and a specific population that is affected (polar bears). It also requires the writer to take a stance on which effect has the greatest impact on the affected animal. When in doubt, make a research question as narrow and focused as possible.
Too simple: How are doctors addressing diabetes in the U.S.?
Appropriately complex: What main environmental, behavioral, and genetic factors predict whether Americans will develop diabetes, and how can these commonalities be used to aid the medical community in prevention of the disease?
The simple version of this question can be looked up online and answered in a few factual sentences; it leaves no room for analysis. The more complex version is written in two parts; it is thought provoking and requires both significant investigation and evaluation from the writer. As a general rule, if a quick Google search can answer a research question, it's likely not very effective. This guide is heavily based upon How to Write a Research Question by George Mason University's Writing Center.
- << Previous: Background information & facts
- Next: What types of sources do I need? >>
- Last Updated: Aug 25, 2023 4:01 PM
- URL: https://library.potsdam.edu/start
Crumb Library: 315-267-2485 Crane Library: 315-267-2451 [email protected] Text Us!: 315-277-3730
Accessibility
Social media, college libraries.
SUNY Potsdam College Libraries 44 Pierrepont Ave Potsdam, NY 13676
- EXPLORE Random Article
How to Write a Research Question
Last Updated: April 20, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD and by wikiHow staff writer, Danielle Blinka, MA, MPA . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 75,817 times.
A research question helps you narrow your research and write a clear, arguable thesis. Your research question needs to be concise, arguable, and focused on your particular topic. Before writing your research question, narrow down your topic and brainstorm possible questions. Then, select the best question and craft it into a good research question. As another option, choose the type of research question that fits your purpose and format your question to fit that style.
Research Questions

Narrowing Your Topic

- When you decide on a research question for your work, it's best to run it by your instructor.

- For instance, great topics for a high school paper might include family dynamics during the civil war, body image among teens, or type 2 diabetes.
- If you're doing a college-level project, a good topic might be the environment's influence on human development, cultural influences on a poet's work, or the ethics of technological advancements.
- In some cases, your topic may be provided to you, such as when you're writing a paper for a class. You can still use the same process for narrowing your topic and selecting a research question.

- The purpose of this research is to learn more, not gather sources. That means it's okay to check sites like Wikipedia, which aren't typically considered reliable sources.

- What, why, and how questions make the best research questions.
- Write down the first questions that come to mind without worrying if they'll make a good research question. You can always revise your question later to make it better.
- For example, let's say you chose body image among teens as your topic. You might write questions like, “How does social media impact body image?” “How does the amount of time spent on Instagram relate to a teen's sense of self-worth?” “Are peers or family members a bigger influence on body image in teens?” and “What factors make teens more likely to have a poor body image?”
- Similarly, you might write a college paper about the ethics of technological advancements. Questions you might ask include, "How is social media altering the culture of society?" "How does screen time alter the brain's neural processing?" and "How might current advancements affect society over the next 25 years?"
Tip: If you find yourself drawn to a particular question, don't keep brainstorming potential questions. Instead, start evaluating the question that interests you to figure out if it might be right for your research project.
Crafting an Effective Research Question

- As an example, the question "What jobs will humans lose to robots over the next 50 years?" may be too difficult to answer. Instead, you might ask, "How has the field of robotics changed the manufacturing industry?"
Tip: When choosing your question, consider your skill level and purpose. If you're doing this project for a class, how will it be graded? What are your instructor's expectations? Additionally, make sure your question fits the scope of the assignment.

- Is this question clear enough to guide my research?
- Is this question specific?
- Does this question allow for research and analysis?
- Can I answer this question based on current research? If so, could I easily find the answer by looking at basic reference works (which means the question is too easy to answer), or will it require more in-depth analysis using multiple sources?
- Has this question already been answered?
- Can I answer the question in an objective manner, based on evidence?
- Can I answer this question in the time I have allotted for this project?

- “What factors cause teens to have poor body image?” is better stated “What environmental and social factors contribute to poor body image in teens?”
- “How does T.S. Elliot use symbolism?” becomes “Why does T.S. Elliot use tea as a symbol in 'The Lovesong of J. Alfred Prufrock?'”
- “What happened to family dynamics during the civil war?” can be narrowed to “How did the fracturing of families during the civil war affect society?”
- "How does screen time alter the brain's neural processing?" might be narrowed to "How does spending 2 hours a day on social media impact neural processing in preteens?"

- For instance, questions like, "What season of the year do parrots typically breed?" or "What era did William Wordsworth write?" are not great research questions because they are too easy to answer.
- The research question “Are peers or family members a bigger influence on body image in teens?” is arguable because you could make a case for either peers or family members having a greater influence on teenagers. Similarly, “Why does T.S. Elliot use tea as a symbol in 'The Lovesong of J. Alfred Prufrock?'” is arguable because different critics may have varying interpretations of the poem.
- As another example, "How does spending 2 hours a day on social media impact neural processing in preteens?" is debatable because you can focus on different effects. It's possible to interpret these effects differently, depending on your stance on the issue.
Tip: Research your question and see what comes up. If you feel like the search results effectively cover what you want to say, then you might want to pick a different question.
Choosing a Type of Research Question

- "What environmental factors cause birds to move nests?"
- "What changes to the habitat can encourage parrots to mate?"
- "What political conditions contributed to the start of the War of 1812?"
- "What symbols does T.S. Elliot use in 'The Lovesong of J. Alfred Prufrock?'”

- "If two different plants are both provided the same amount of sunlight and fertilizer, will they grow at the same rate?"
- "If two identical solutions are exposed to different quantities of an element, will they show equal or different reactions?"
- "If two test subjects are asked to perform a task alone and then together, how will collaboration affect their outcome?"

- "Will the introduction of a new plant to a biodome affect the ecosystem?"
- "Does changing team assignments cause workers to lose morale?"
- "Do metered ramps on highways change driver behavior?"
Community Q&A
- Make sure your research question is narrow enough to write a specific paper. If it's too broad, your paper will be too general and vague to make a clear point. A narrow research question will help you write a focused paper. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 0
- A clear, specific research question will help you create a good thesis for your paper. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- If you're doing your research as part of a class assignment, talk to your instructor if you're having trouble writing your research question. Tell them what you're considering and ask them for guidance. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libraries.indiana.edu/sites/default/files/Develop_a_Research_Question.pdf
- ↑ https://www.pewresearch.org/our-methods/u-s-surveys/writing-survey-questions/
- ↑ https://cirt.gcu.edu/research/develop/tutorials/question
- ↑ https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/how-to-write-a-research-question
About this article

To write a research question, start by writing a list of open-ended questions that relate to the topic you're researching. For example, if your topic was social media, your questions might look something like "How does social media impact body image?" or "What impact does social media have on our culture?" Next, choose the question that interests you the most, and try to make it as specific as possible. Also, make sure it can't be easily answered since you want a topic that you can thoroughly examine. For more advice, like how to choose a topic to research, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
Reader Success Stories
Apr 7, 2022
Did this article help you?
- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
- Research Paper Guides
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- How to Write a Research Question: Types & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Essay Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write a Research Question: Types & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A research question is the main query that researchers seek to answer in their study. It serves as the basis for a scholarly project such as research paper, thesis or dissertation. A good research question should be clear, relevant and specific enough to guide the research process. It should also be open-ended, meaning that it allows for multiple possible answers or interpretations.
If you have located your general subject and main sources but still aren’t quite sure about the exact research questions for your paper, this guide will help you out. First, we will explore the concept of it together, so you could answer it in your work. Then some simple steps on composing your inquiry will be suggested. In the end, we will draw your attention to some specific details which can make your work good or bad. Sometimes it’s just easier to delegate all challenging tasks to a reliable research paper service . StudyCrumb is a trustable network of qualified writers ready to efficiently solve students’ challenges.
What Is a Good Research Question: Full Definition
Good research questions provide a concise definition of a problem. As a scholar, your main goal at the beginning is to select the main focus. It should be narrow enough so you could examine it within your deadline. Your work should be focused on something specific. Otherwise, it will require too much work and might not produce clear answers. At the same time your answer should be arguable and supported by data you’ve collected. Take a look at this example:

How to Write a Research Question: Step-By-Step Guide
In this section we will examine the process of developing a research question. We will guide you through it, step by step. Keep in mind that your subject should be important for your audience. So it requires some preliminary study and brainstorming. Let’s take a closer look at the main steps.
Step 1. Choose a Broad Topic for Your Research Paper Question
First, you need to decide on your general direction. When trying to identify your research paper questions, it is better to choose an area you are really interested in. You should be able to obtain enough data to write something about this topic. Therefore, do not choose something out of your reach. At the same time, your broad topic should not be too simple. Research paper questions that can be answered without any study would hardly make any sense for your project.
Step 2. Do Preliminary Reading Before Starting Your Research Question
Next, it is time we explore the context of the selected topic. You wouldn’t want to choose research questions that have already been examined and answered in detail. On the other hand, choosing a topic that is a complete ‘terra incognita’ might be a bridge too far for your project. Browse through available sources that are related to this topic. You should try and find out what has been discovered about it before. Do you see a gap that you can fill with your study? You can proceed with developing your exact inquiry! Have no time for in-depth topic exploration? Leave this task to professionals. Entrust your “ write my research paper ” order to StudyCrumb and get a top-notch work.
Step 3. Consider an Audience for Your Research Question
It is good to know your reader well to be able to convey your ideas and results to them in the best possible way. Before writing research questions for your projects, you might need to perform a brief analysis of your audience. That's how you'll be able to understand what is interesting for them and what is not. This will allow you to make better decisions when narrowing your broad topic down. Select a topic that is interesting for your reader! This would contribute much to the success for writing a research paper .
Step 4. Start Asking a Good Research Question
After you have considered your options, go ahead and compose the primary subject of your paper. What makes a good research question? It should highlight some problematic and relevant aspects of the general topic. So, after it is answered, you should have obtained some new valuable knowledge about the subject. Typically scholars start narrowing down their general topic by asking ‘how’, ‘why’ or ‘what’s next’ questions. This approach might help you come up with a great idea quickly.
Step 5. Evaluate Your Research Question
Finally, after you have composed a research paper question, you should take a second look at it and see if it is good enough for your paper. It would be useful to analyze it from the following sides:
- Is it clear for your audience?
- Is it complex enough to require significant study?
- Is it focused on a certain aspect of your general topic?
You might use the help of your peers or your friends at this step. You can also show it to your tutor and ask for their opinion.
Types of Research Questions: Which to Choose
A number of research questions types are available for use in a paper. They are divided into two main groups:
Qualitative questions:
- Explanatory
- Ethnographic
Quantitative questions:
- Descriptive
- Comparative
- Relationship based.
Selecting a certain type would impact the course of your study. We suggest you think about it carefully. Below you can find a few words about each type. Also, you can seek proficient help from academic experts. Buy a research paper from real pros and forget about stress once and for all.
Qualitative Research Questions: Definition With Example
When doing qualitative research, you are expected to aim to understand the different aspects and qualities of your target problem. Therefore, your thesis should focus on analyzing people’s experience, ideas and reflections rather than on obtaining some statistical data and calculating trends. Thus, this inquiry typically requires observing people’s behavior, interacting with them and learning how they interpret your target problem. Let’s illustrate this with an example:

What Is Contextual Research Questions
Contextual research revolves around examining your subject in its natural, everyday environment. It may be watching animals living in their usual habitats or people doing their normal activities in their familiar surroundings (at home, at school or at office). This academic approach helps to understand the role of the context. You'll be able to better explain connections between your problem, its environment and outcomes. This type of inquiry ought to be narrow enough. You shouldn’t have to examine each and every aspect of the selected problem in your paper. Consider this example:

Definition and Sample of Evaluative Research Questions
Evaluative research is performed in order to carefully assess the qualities of a selected object, individual, group, system or concept. It typically serves the purpose of collecting evidence that supports or contradicts solutions for a problem. This type of inquiry should focus on how useful a certain quality is for solving the problem. To conduct such study, you need to examine selected qualities in detail. Then, you should assume whether they match necessary criteria. It might include some quantitative methods such as collecting statistics. Although, the most important part is analyzing the qualities. If you need some examples, here’s one for you:

Explanatory Research Questions: Definition With Example
Your paper can be dedicated to explaining a certain phenomenon, finding its reasons and important relationships between it and other important things. Your explanatory research question should aim to highlight issues, uncertainties and problematic aspects of your subject. So, your study should bring clarity about these qualities. It should show how and why they have developed this way. An explanation may include showing causes and effects of issues in question, comparing the selected phenomenon to other similar types and showing whether the selected qualities match some predefined criteria. If you need some examples, check this one:

Generative Research Questions
This type of research is conducted in order to better understand the subject. With its help, you can find some new solutions or opportunities for improvement. Therefore, its main purpose is to develop a theoretical basis for further actions. You need to compose your generative research questions in a way that facilitates obtaining new ideas. It would help to begin with asking ‘why’, ‘what is the relationship between the subject and the problems X, Y, and Z’, ‘what can be improved here’, ‘how we can prevent it’ and so on. Need relevant examples? We’ve got one for you:

Ethnographic Research Question
Ethnography research is focused on a particular group of people. The aim is to study their behavior, typical reactions to certain events or information, needs, preferences or habits. Important parameters of this group which are most relevant to your general subject are taken into consideration. These are age, sex, language, religion, ethnicity, social status and so on. Main method in this case is first-hand observation of people from the selected group during an extended period of time. If you need strong examples, here’s one:

Quantitative Research Questions: Full Definition With Examples
Quantitative research deals with data – first of all, it is numeric data. It involves mathematical calculations and statistical analysis. It helps to obtain knowledge which is mostly expressed in numbers, graphs and tables. Unlike the qualitative type, the purpose of quantitative research is finding patterns, calculating probabilities, testing causal relationships and making predictions. It is focused on testing theories and hypotheses. (We have the whole blog on what is a hypothesis .) It is mostly used in natural and social sciences. These are: chemistry, biology, psychology, economics, sociology, marketing, etc. Here are a couple of examples:

Descriptive Research Questions: Definition With Example
This is probably the most widespread type of quantitative research question. Such inquiries seek to explain when, where, why, or how something occurred. They describe it accurately and systematically. These inquiries typically start with ‘what’. You are expected to use various methods to investigate one or more variables and determine their dependencies. Note, however, that you cannot control or manipulate any of these variables. You can only observe and measure them. Looking for some interesting examples? Here is one:

Definition of Comparative Research Questions
Comparative research question is used to highlight different variables and provide numerical evidence. This type is based on comparing one object, parameter or issue with another one of a similar kind. It can help to discover the differences between two or more groups by examining their outcome variables. Take a look at these two examples:

Relationship Research Questions
We conduct this type of research when we need to make it clear whether one parameter of a selected object causes another one. A relationship based quantitative research question should help us to explore and define trends and interactions between two or more variables. Are these two things mutually dependent? What kind of dependence is it? How has it developed? And what are possible outcomes of this connection? Here is an example of relationship-based quantitative research questions:

Research Questions Examples: Free
This section contains a number of helpful examples of research questions. Feel free to use them as inspiration to create your own questions and conduct productive study. Let’s start with two simple ones:

Are you interested in well written and inspiring questions? Do you want to learn what to avoid in your study? Just stay with us – there will be more of them below.
Examples of Good and Bad Research Questions
Everyone is interested in getting the best possible appraisal for their study. Choosing a topic which doesn't suit your specific situation may be discouraging. Thus, the quality of your paper might get affected by a poor choice. We have put together some good and bad examples so that you could avoid such mistakes.
Good Research Questions Examples
It is important to include clear terms into your questions. Otherwise, it would be difficult for you to plan your investigation properly. Also, they must be focused on a certain subject, not multiple ones. And finally, it should be possible to answer them. Let’s review several good examples:

Examples of Bad Research Questions
It is difficult to evaluate qualities of objects, individuals or groups if your purpose is not clear. This is why you shouldn’t create unclear research questions or try to focus on many problems at once. Some preliminary study might help to understand what you should focus on. Here are several bad examples:

In case you may need some information about the discussion section of a research paper example , find it in our blog.
Final Thoughts on Research Questions
In this article we have made a detailed review of the most popular types of research questions. We described peculiarities. We also provided some tips on conducting various kinds of study. Besides, a number of useful examples have been given for each category of questions.
Feel free to check out essay writing services. We have experienced writers who can help you compose your paper in time. They will absolutely ensure the high quality of your text.
Frequently Asked Questions About Research Questions
1. what is an example of a weak research question.
Here is an example of the weakest research question:
An answer would be simply making a list of species that inhabit the country. This subject does not require any actual study to be conducted. There is nothing to calculate or analyze here.
2. What is the most effective type of research question?
Most effective type of research question is the one that doesn't have a single correct answer. However, you should also pay close attention to your audience. If you need to create a strong effect, better choose a topic which is relevant for them.
3. What is a good nursing research question?
If you need an idea for a nursing research question, here are a few helpful examples you could use as a reference:
4. What are some sociological research questions?
Sociological questions are the ones that examine the social patterns or a meaning of a social phenomenon. They could be qualitative or quantitative. They should target groups of people with certain parameters, such as age or income level. Keep in mind that type of study usually requires collecting numerous data about your target groups.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

Research Essentials
Background sources, selecting and narrowing a topic, from topic to research question, sample research questions.
- Identify Keywords
- Search Tips
- Too Few/Many Results?
- Use Sources
- Scholarly vs Popular
- Thesis Statements
- Cite Sources
- Find Articles
- Primary Sources
Developing a Research Question
For more information on developing a research question, check out this video from the Laurier Library.
Reference sources like dictionaries and encyclopedias provide general information about various subjects. They offer background that can be a springboard for more in-depth research.
Choose an area of interest to explore.
For you to successfully finish a research project, it is important to choose a research topic that is relevant to your field of study and piques your curiosity. The flip side is that curiosity can take you down long and winding paths, so you also need to consider scope in how to effectively cover the topic in the space that you have available. If there's an idea or concept you've recently learned that's stuck with you, that might be a good place to start !
Gather background information.
You may not know right away what your research question is - that's okay! Start out with a broad topic, and see what information is out there through cursory background research. This will help you explore possibilities and narrow your topic to something manageable. Do a few quick searches in OneSearch@IU or in other relevant sources. See what other researchers have already written to help narrow your focus.
Narrow your topic.
Once you have a sense of how other researchers are talking about the topics you’re interested, narrow down your topic by asking the 5 Ws
- Who – population or group (e.g., working class, college students, Native Americans)
- What – discipline or focus (e.g., anthropological or art history)
- Where – geographic location (e.g., United States; universities; small towns; Standing Rock)
- When – time period or era (17 th century; contemporary; 2017)
- Why – why is the topic important? (to the class, to the field, or to you)
Broad topic: Native American representations in museums
Narrowed topic: Museum efforts to adhere to NAGPRA
Adapted from: University of Michigan. (2023 Finding and Exploring your topic. Retrieved from https://guides.lib.umich.edu/c.php?g=283095&p=1886086
So, you have done some background research and narrowed down your topic. Now what? Start to turn that topic into a series of questions that you will attempt to answer the course of your research. Keep in mind that you will probably end up changing and adjusting the question(s) you have as you gather more information and synthesize it in your writing. However, having a clear line of inquiry can help you maintain a sense of your direction, which will then in turn help you evaluate sources and identify relevant information throughout your research process.
Exploratory questions.
These are the questions that comes from a genuine curiosity about your topic. When narrowing down your topic, you got a good sense of the Who, What, When, and Where of things. Now it’s time to consider
- Asking open-ended “how” and “why” questions about your general topic, which can lead you to better explanations about a phenomenon or concept
- Consider the “so what?” of your topic. Why does this topic matter to you? Why should it matter to others? What are the implications of the information you’re discovering through the search process to the Who and the What of your topic?
Evaluate your research question.
Use the following to determine if any of the questions you generated would be appropriate and workable for your assignment.
- Is your question clear ? Do you have a specific aspect of your general topic that you are going to explore further? Will the reader of your research be able to keep it in mind?
- Is your question focused? Will you be able to cover the topic adequately in the space available? Are you able to concisely ask the question?
- Is your question and arguable ? If it can be answered with a simple Yes or No, then dig deeper. Once you get to “it depends on X, Y, and Z” then you might be getting on the right track.
Hypothesize.
Once you have developed your research question, consider how you will attempt to answer or address it.
- What connections can you make between the research you’ve read and your research question? Why do those connections matter?
- What other kinds of sources will you need in order to support your argument?
- If someone refutes the answer to your research question, what is your argument to back up your conclusion?
- How might others challenge your argument? Why do those challenges ultimately not hold water?
Adapted from: George Mason University Writing Center. (2018). How to write a research question. Retrieved from https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/writing-resources/research-based-writing/how-to-write-a-research-question
A good research question is clear, focused, and has an appropriate level of complexity. Developing a strong question is a process, so you will likely refine your question as you continue to research and to develop your ideas.
Unclear : Why are social networking sites harmful?
Clear: How are online users experiencing or addressing privacy issues on such social networking sites as Facebook and TikTok?
Unfocused: What is the effect on the environment from global warming?
Focused: How is glacial melting affecting penguins in Antarctica?
Simple vs Complex
Too simple: How are doctors addressing diabetes in the U.S.?
Appropriately Complex: What are common traits of those suffering from diabetes in America, and how can these commonalities be used to aid the medical community in prevention of the disease?
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Identify Keywords >>
- Last Updated: Nov 13, 2023 10:40 AM
- URL: https://guides.libraries.indiana.edu/essentials
Social media
- Instagram for Herman B Wells Library
- Facebook for IU Libraries
Additional resources
Featured databases.
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) OneSearch@IU
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Academic Search (EBSCO)
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) ERIC (EBSCO)
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Nexis Uni
- Resource available without restriction HathiTrust Digital Library
- Databases A-Z
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Google Scholar
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) JSTOR
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Web of Science
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) Scopus
- Resource available to authorized IU Bloomington users (on or off campus) WorldCat
IU Libraries
- Diversity Resources
- About IU Libraries
- Alumni & Friends
- Departments & Staff
- Jobs & Libraries HR
- Intranet (Staff)
- IUL site admin

Blackboard Calendar Locations Student Email Moodle my.WakeTech WebAdvisor
- Research Guides
How to Conduct Research and Write Your Paper
- Develop Your Topic and Research Question
- Find Evidence and Evaluate Sources
- Take Notes and Annotate
- Library Resources
- Write Your Paper
- What is Plagiarism?
- Citation Video Tutorials
- Writing and Citation Help
- Ask a Librarian
Develop Your Topic
What are you interested in? Start by brainstorming topics of interest. Once you’ve landed on a few, do some critical background research. What questions does your reading raise?
Once you’ve done a little digging, write down everything you know about your potential topic. Then, write down the questions you thought of while reading. Can you answer these questions easily, using only the background research you’ve done?
If so, then do some more digging, and write probing questions, beginning with “Why…? What if…? How…?” The goal is to have detailed answers, not a simple yes or no.
Sample Topic and Probing Questions
Undergraduate class: POL 370--Political Violence
Topic of interest: terrorism
Background information: “ Terrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition. Common definitions of terrorism refer only to those violent acts which are intended to create fear (terror), are perpetrated for a religious, political or ideological goal, and deliberately target or disregard the safety of non-combatants (civilians).”
My questions upon reading the background information:
- What motivates someone to engage in terrorist activity?
- How can we find out what motivates people to engage in terrorist activity?
Develop Your Research Question
It’s time to move beyond background research into the literature. Start by first identifying the key scholars within your topic area, and read what they have to say. What questions do they have? How do they go about answering them?
Go back to your original questions and add to them or refine them based on the latest research you’ve done. Write down some persuasive claims that you’d like to make about your topic. Keep in mind that a good research question will have more than one possible answer. Be careful not to ask the exact same questions or statements as the scholars you’ve read; you want to take an original stance on the topic.
Bad Sample Question: What motivates terrorists to engage in terrorist activity? (too broad)
Good Sample Question: Why did the Northern Irish who joined the IRA during the Troubles choose to employ terrorist tactics in their fight for independence? (narrow enough, places the topic in context)
Useful Links
- Writing Strong Research Questions (opens in a new window)
- Generate Topic Ideas (opens in a new window)
- Last Updated: Mar 27, 2024 2:11 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.waketech.edu/claireresearchguide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
How to Write a Research Paper | A Beginner's Guide
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research.
Research papers are similar to academic essays , but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research. Writing a research paper requires you to demonstrate a strong knowledge of your topic, engage with a variety of sources, and make an original contribution to the debate.
This step-by-step guide takes you through the entire writing process, from understanding your assignment to proofreading your final draft.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Understand the assignment, choose a research paper topic, conduct preliminary research, develop a thesis statement, create a research paper outline, write a first draft of the research paper, write the introduction, write a compelling body of text, write the conclusion, the second draft, the revision process, research paper checklist, free lecture slides.
Completing a research paper successfully means accomplishing the specific tasks set out for you. Before you start, make sure you thoroughly understanding the assignment task sheet:
- Read it carefully, looking for anything confusing you might need to clarify with your professor.
- Identify the assignment goal, deadline, length specifications, formatting, and submission method.
- Make a bulleted list of the key points, then go back and cross completed items off as you’re writing.
Carefully consider your timeframe and word limit: be realistic, and plan enough time to research, write, and edit.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
There are many ways to generate an idea for a research paper, from brainstorming with pen and paper to talking it through with a fellow student or professor.
You can try free writing, which involves taking a broad topic and writing continuously for two or three minutes to identify absolutely anything relevant that could be interesting.
You can also gain inspiration from other research. The discussion or recommendations sections of research papers often include ideas for other specific topics that require further examination.
Once you have a broad subject area, narrow it down to choose a topic that interests you, m eets the criteria of your assignment, and i s possible to research. Aim for ideas that are both original and specific:
- A paper following the chronology of World War II would not be original or specific enough.
- A paper on the experience of Danish citizens living close to the German border during World War II would be specific and could be original enough.
Note any discussions that seem important to the topic, and try to find an issue that you can focus your paper around. Use a variety of sources , including journals, books, and reliable websites, to ensure you do not miss anything glaring.
Do not only verify the ideas you have in mind, but look for sources that contradict your point of view.
- Is there anything people seem to overlook in the sources you research?
- Are there any heated debates you can address?
- Do you have a unique take on your topic?
- Have there been some recent developments that build on the extant research?
In this stage, you might find it helpful to formulate some research questions to help guide you. To write research questions, try to finish the following sentence: “I want to know how/what/why…”
A thesis statement is a statement of your central argument — it establishes the purpose and position of your paper. If you started with a research question, the thesis statement should answer it. It should also show what evidence and reasoning you’ll use to support that answer.
The thesis statement should be concise, contentious, and coherent. That means it should briefly summarize your argument in a sentence or two, make a claim that requires further evidence or analysis, and make a coherent point that relates to every part of the paper.
You will probably revise and refine the thesis statement as you do more research, but it can serve as a guide throughout the writing process. Every paragraph should aim to support and develop this central claim.
A research paper outline is essentially a list of the key topics, arguments, and evidence you want to include, divided into sections with headings so that you know roughly what the paper will look like before you start writing.
A structure outline can help make the writing process much more efficient, so it’s worth dedicating some time to create one.
Your first draft won’t be perfect — you can polish later on. Your priorities at this stage are as follows:
- Maintaining forward momentum — write now, perfect later.
- Paying attention to clear organization and logical ordering of paragraphs and sentences, which will help when you come to the second draft.
- Expressing your ideas as clearly as possible, so you know what you were trying to say when you come back to the text.
You do not need to start by writing the introduction. Begin where it feels most natural for you — some prefer to finish the most difficult sections first, while others choose to start with the easiest part. If you created an outline, use it as a map while you work.
Do not delete large sections of text. If you begin to dislike something you have written or find it doesn’t quite fit, move it to a different document, but don’t lose it completely — you never know if it might come in useful later.
Paragraph structure
Paragraphs are the basic building blocks of research papers. Each one should focus on a single claim or idea that helps to establish the overall argument or purpose of the paper.
Example paragraph
George Orwell’s 1946 essay “Politics and the English Language” has had an enduring impact on thought about the relationship between politics and language. This impact is particularly obvious in light of the various critical review articles that have recently referenced the essay. For example, consider Mark Falcoff’s 2009 article in The National Review Online, “The Perversion of Language; or, Orwell Revisited,” in which he analyzes several common words (“activist,” “civil-rights leader,” “diversity,” and more). Falcoff’s close analysis of the ambiguity built into political language intentionally mirrors Orwell’s own point-by-point analysis of the political language of his day. Even 63 years after its publication, Orwell’s essay is emulated by contemporary thinkers.
Citing sources
It’s also important to keep track of citations at this stage to avoid accidental plagiarism . Each time you use a source, make sure to take note of where the information came from.
You can use our free citation generators to automatically create citations and save your reference list as you go.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
The research paper introduction should address three questions: What, why, and how? After finishing the introduction, the reader should know what the paper is about, why it is worth reading, and how you’ll build your arguments.
What? Be specific about the topic of the paper, introduce the background, and define key terms or concepts.
Why? This is the most important, but also the most difficult, part of the introduction. Try to provide brief answers to the following questions: What new material or insight are you offering? What important issues does your essay help define or answer?
How? To let the reader know what to expect from the rest of the paper, the introduction should include a “map” of what will be discussed, briefly presenting the key elements of the paper in chronological order.
The major struggle faced by most writers is how to organize the information presented in the paper, which is one reason an outline is so useful. However, remember that the outline is only a guide and, when writing, you can be flexible with the order in which the information and arguments are presented.
One way to stay on track is to use your thesis statement and topic sentences . Check:
- topic sentences against the thesis statement;
- topic sentences against each other, for similarities and logical ordering;
- and each sentence against the topic sentence of that paragraph.
Be aware of paragraphs that seem to cover the same things. If two paragraphs discuss something similar, they must approach that topic in different ways. Aim to create smooth transitions between sentences, paragraphs, and sections.
The research paper conclusion is designed to help your reader out of the paper’s argument, giving them a sense of finality.
Trace the course of the paper, emphasizing how it all comes together to prove your thesis statement. Give the paper a sense of finality by making sure the reader understands how you’ve settled the issues raised in the introduction.
You might also discuss the more general consequences of the argument, outline what the paper offers to future students of the topic, and suggest any questions the paper’s argument raises but cannot or does not try to answer.
You should not :
- Offer new arguments or essential information
- Take up any more space than necessary
- Begin with stock phrases that signal you are ending the paper (e.g. “In conclusion”)
There are four main considerations when it comes to the second draft.
- Check how your vision of the paper lines up with the first draft and, more importantly, that your paper still answers the assignment.
- Identify any assumptions that might require (more substantial) justification, keeping your reader’s perspective foremost in mind. Remove these points if you cannot substantiate them further.
- Be open to rearranging your ideas. Check whether any sections feel out of place and whether your ideas could be better organized.
- If you find that old ideas do not fit as well as you anticipated, you should cut them out or condense them. You might also find that new and well-suited ideas occurred to you during the writing of the first draft — now is the time to make them part of the paper.
The goal during the revision and proofreading process is to ensure you have completed all the necessary tasks and that the paper is as well-articulated as possible. You can speed up the proofreading process by using the AI proofreader .
Global concerns
- Confirm that your paper completes every task specified in your assignment sheet.
- Check for logical organization and flow of paragraphs.
- Check paragraphs against the introduction and thesis statement.
Fine-grained details
Check the content of each paragraph, making sure that:
- each sentence helps support the topic sentence.
- no unnecessary or irrelevant information is present.
- all technical terms your audience might not know are identified.
Next, think about sentence structure , grammatical errors, and formatting . Check that you have correctly used transition words and phrases to show the connections between your ideas. Look for typos, cut unnecessary words, and check for consistency in aspects such as heading formatting and spellings .
Finally, you need to make sure your paper is correctly formatted according to the rules of the citation style you are using. For example, you might need to include an MLA heading or create an APA title page .
Scribbr’s professional editors can help with the revision process with our award-winning proofreading services.
Discover our paper editing service
Checklist: Research paper
I have followed all instructions in the assignment sheet.
My introduction presents my topic in an engaging way and provides necessary background information.
My introduction presents a clear, focused research problem and/or thesis statement .
My paper is logically organized using paragraphs and (if relevant) section headings .
Each paragraph is clearly focused on one central idea, expressed in a clear topic sentence .
Each paragraph is relevant to my research problem or thesis statement.
I have used appropriate transitions to clarify the connections between sections, paragraphs, and sentences.
My conclusion provides a concise answer to the research question or emphasizes how the thesis has been supported.
My conclusion shows how my research has contributed to knowledge or understanding of my topic.
My conclusion does not present any new points or information essential to my argument.
I have provided an in-text citation every time I refer to ideas or information from a source.
I have included a reference list at the end of my paper, consistently formatted according to a specific citation style .
I have thoroughly revised my paper and addressed any feedback from my professor or supervisor.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (page numbers, headers, spacing, etc.).
You've written a great paper. Make sure it's perfect with the help of a Scribbr editor!
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
- Writing a Research Paper Conclusion | Step-by-Step Guide
- Research Paper Format | APA, MLA, & Chicago Templates
More interesting articles
- Academic Paragraph Structure | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Checklist: Writing a Great Research Paper
- How to Create a Structured Research Paper Outline | Example
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- How to Write Topic Sentences | 4 Steps, Examples & Purpose
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Research Paper Damage Control | Managing a Broken Argument
- What Is a Theoretical Framework? | Guide to Organizing
Unlimited Academic AI-Proofreading
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Greater Jakarta
- BINUS @Greater Jakarta
- BINUS @Bekasi
- BINUS @Bandung
- BINUS @Malang
- BINUS @Semarang
- BINUS ComDev
- Research Products
- Important Links
- BINUS Journal
- Research Repository
- RTT Profile (PDF)
- SIMLITBINUS
- Social Media
- Book Publication List
- Achievements
- Artificial Intelligence in Geospatial Economics (Geo-Eco AI)
- Consumer Behavior and Digital Ethics
- Digital Language and Behavior (D-LAB)
- Education Technology
- Photonics and Computer Systems
- Small Medium Enterprise,Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Quantitative and Decision Sciences (Q&DS)
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bioinformatics and Data Science
- Food Biotechnology
- E-PDP and Scopus Apps
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Simlitbinus
- Meet the Team
- Check My Publication KPI
Visiting Professor How to Write a Paper from Case Study
On the 26th of February 2024, BINUS University hosted an insightful workshop aimed at enhancing the academic writing skills of its faculty members. Titled “How to Write a Paper from Case Study/Business Report,” the workshop featured Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nanthakumar Loganathan from Universiti Teknologi Malaysia as the distinguished speaker. The event held at Bandung Campus, provided an invaluable opportunity for faculty members to delve into the intricacies of crafting scholarly papers, drawing from real-world case studies and business reports. With an emphasis on practical strategies and methodologies, the workshop aimed to equip participants with the necessary tools to produce high-quality academic literature.
Following the enriching workshop, BINUS University continued its academic endeavors with a public lecture on international research experiences, specifically tailored for its student body. The event welcomed Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nanthakumar Loganathan once again as the esteemed speaker. The lecture commenced with an opening speech delivered by Prof. Dr. Tirta N. Mursitama, Ph.D., Vice Rector Collaboration and Global Engagement, BINUS University, setting the tone for an engaging discourse on research practices and opportunities on the global stage. Attended by BINUS students eager to explore international research avenues, the lecture provided valuable insights into the significance of cross-cultural collaboration and exposure in the realm of academic inquiry.
Both events underscored BINUS University’s commitment to fostering a vibrant academic environment conducive to knowledge exchange and scholarly growth. With distinguished speakers and active participation from faculty members and students alike, the workshops and lectures served as catalysts for intellectual engagement and professional development within the university community. As BINUS continues to uphold its dedication to academic excellence, such initiatives play a pivotal role in nurturing a generation of researchers and scholars poised to make meaningful contributions to their respective fields and beyond.
#BINUSUniversity #AcademicWriting #FacultyDevelopment #ResearchSkills #InternationalExperience #ScholarlyGrowth #CrossCulturalCollaboration #GlobalEngagement #ProfessionalDevelopment #StudentResearch #KnowledgeExchange

Last updated : April 01, 2024 00:00

Your browser is not fully compatible with the features of our website.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
1. Start with a broad topic. A broad topic provides writers with plenty of avenues to explore in their search for a viable research question. Techniques to help you develop a topic into subtopics and potential research questions include brainstorming and concept mapping.
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Research questions should not be answerable with a simple "yes" or "no" or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with "How" or "Why.". Begin your research. After you've come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research ...
As the name suggests, these types of research questions seek to explore the relationships between variables. Here, an example could be something like "What is the relationship between X and Y" or "Does A have an impact on B". As you can see, these types of research questions are interested in understanding how constructs or variables ...
Selecting your research question and creating a clear goal and structure for your writing can be challenging - whether you are doing it for the first time or if you've done it many times before. It can be especially difficult when your research question starts to look and feel a little different somewhere between your first and final draft.
There are two types of research: Qualitative research and Quantitative research. There must be research questions for every type of research. Your research question will be based on the type of research you want to conduct and the type of data collection. The first step in designing research involves identifying a gap and creating a focused ...
Specificity: A strong research question should be specific about the main focus of your study, enabling you to gather precise data and draw accurate conclusions. It clearly defines the variables, participants, and context involved, leaving no room for ambiguity. Clarity: A good research question is clear and easily understood, so articulate the ...
Follow these steps when writing a research question: 1. Select a general topic. The first step to writing a research question is to choose a broad topic for your question. This can be something like "1920s novels" or "effects of technology." It's helpful to select something you are interested in and want to know more about, which can make ...
It can be difficult to come up with a good research question, but there are a few steps you can follow to make it a bit easier. 1. Start with an interesting and relevant topic. Choose a research topic that is interesting but also relevant and aligned with your own country's culture or your university's capabilities.
A good research question should be: Focused on a single issue. Specific enough to answer thoroughly in your paper. Feasible to answer within the length of your paper. Researchable using the resources available to you. Relevant to your field of study and/or to society at large. The length of your paper and the research you're able to locate will ...
Formulating Your Research Question (RQ) In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic.
A good research question defines your study and helps you seek an answer to your research. Moreover, a clear research question guides the research paper or thesis to define exactly what you want to find out, giving your work its objective. Learning to write a research question is the beginning to any thesis, dissertation, or research paper ...
The research question helps to define the scope and focus of the study. It identifies the specific topic or issue that the researcher wants to investigate, and it sets the boundaries for the study. A research question can also help you determine if your study primarily contributes to theory or is more applied in nature.
In essence, the research question that guides the sciences and social sciences should do the following three things:2. 1) Post a problem. 2) Shape the problem into a testable hypothesis. 3) Report the results of the tested hypothesis. There are two types of data that can help shape research questions in the sciences and social sciences ...
As you develop your research question, you might find that you need to ask a broader or narrower question, depending upon the resources available and the time you have to complete your assignment. Sometimes it's hard to determine if a topic is too broad or specific. Try checking in with your instructor (who has a good idea of the field of ...
1. Choose an interesting general topic: Start with a broad topic about which you're genuinely interested.An example of a general topic might be "the Underground Railroad" or "Films of the 1930s." 2. Do some preliminary research on that general topic: Conduct quick searches in current periodicals or journals, reference books like encyclopedias (which can be found in the library's first floor ...
The purpose of this research is to learn more, not gather sources. That means it's okay to check sites like Wikipedia, which aren't typically considered reliable sources. 4. Write a list of open-ended questions about your topic. Do a brainstorming session to generate questions you may have based on your research.
Check for free. A research question is the main query that researchers seek to answer in their study. It serves as the basis for a scholarly project such as research paper, thesis or dissertation. A good research question should be clear, relevant and specific enough to guide the research process.
Start to turn that topic into a series of questions that you will attempt to answer the course of your research. Keep in mind that you will probably end up changing and adjusting the question (s) you have as you gather more information and synthesize it in your writing. However, having a clear line of inquiry can help you maintain a sense of ...
What questions do they have? How do they go about answering them? Go back to your original questions and add to them or refine them based on the latest research you've done. Write down some persuasive claims that you'd like to make about your topic. Keep in mind that a good research question will have more than one possible answer.
Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist.
Clark led with three tips: 1) Be as "natural and authoritative as you can be," which includes finding a time and space in which you're most comfortable for an interview; 2) Consolidate research materials into bullet points; and 3) "Take responsibility for what you say because you will be quoted.".
On the 26th of February 2024, BINUS University hosted an insightful workshop aimed at enhancing the academic writing skills of its faculty members. Titled "How to Write a Paper from Case Study/Business Report," the workshop featured Assoc. Prof. Dr. Nanthakumar Loganathan from Universiti Teknologi Malaysia as the distinguished speaker. The event held at Bandung Campus, […]