

Flipkart Case Study: The Rise Of Indian E-commerce Giant
Supti Nandi
Updated on: April 8, 2024

When it comes to success stories, the Flipkart Case Study has been the most anticipated one! Reason? A company from its humble beginnings rose to fame so immensely that now it has become synonymous with online shopping. Just like Google is synonymous with search engines and Paytm is synonymous with online payment in India!

Let me tell you that when a brand becomes synonymous with a process, then that’s solid evidence of success.
Coming back to the point, Flipkart, the Indian e-commerce giant changed how you shop online. From its start, facing challenges, to becoming a big player in online retail, Flipkart’s journey is fascinating.
In this Flipkart Case Study, we will look at its early days, growth strategies, and the impact it had on how Indians shop. Also, its key moments include its joining forces with Walmart and still, it continues to evolve.
So, without any delay, let’s go through the Flipkart Case Study to understand Flipkart’s rise and how it shaped the e-commerce landscape in India.
(A) What is Flipkart? A Brief Overview

Flipkart Private Limited, an Indian multinational e-commerce giant, has its headquarters in Bangalore and is incorporated as a private limited company in Singapore. The company’s journey began with a primary focus on online book sales. However, as it evolved, Flipkart expanded its product range to include diverse categories such as consumer electronics, fashion, home essentials, groceries, and lifestyle products.
In the competitive landscape of the Indian e-commerce industry, Flipkart is a key player, directly competing with major entities like Amazon India and local rival Snapdeal.
Note: We have already explained “ Why did Snapdeal fail? Complete Snapdeal Case Study ” in detail. Check out the article for depth information.
As of March 2023, Flipkart held a significant market share, boasting 51% dominance in the country’s e-commerce sector.
One notable aspect contributing to Flipkart’s success is its strategic acquisition of Myntra, which has solidified its position in the apparel segment. This move has been pivotal in establishing Flipkart as a dominant force in the online fashion market.
Moreover, Flipkart has successfully positioned itself as a strong contender against Amazon in the sale of electronics and mobile phones, showcasing its versatility and adaptability in catering to diverse consumer needs.
We will explain it in more detail in the upcoming sections.
For now, let’s have a look at Flipkart’s profile-
In essence, Flipkart’s trajectory from an online book retailer to a multifaceted e-commerce giant is marked by strategic expansions, key acquisitions, and robust competition in the dynamic Indian market.
(B) History of Flipkart
Flipkart’s foundation in India was laid in October 2007 by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal, both alumni of IIT Delhi and former employees of Amazon. The duo initiated their venture from a modest two-bedroom apartment in Koramangala, Bangalore.
Fueled by their vision to revolutionize online retail, the initial investment of INR 2 lakh from each founder’s family set the stage for what would become a transformative journey.
Starting as an online bookstore with a nationwide shipping approach, Flipkart strategically focused on the sale of books. The company gradually gained prominence, processing 100 orders per day by 2008. This early success laid the groundwork for Flipkart’s expansion beyond books into diverse product categories.
Now, let’s briefly look at the history of Flipkart-
The journey from a small startup to an e-commerce giant included significant milestones such as the acquisition of We Read in 2010, further diversifying Flipkart’s offerings. This period marked the foundation of Flipkart’s presence in the Indian market, and its commitment to customer satisfaction and innovation paved the way for its subsequent growth, mergers, and acquisitions in the years to come.
(C) Growth Strategies: How did Flipkart rise in the Indian e-commerce market?
Flipkart rose in the Indian market by opting for numerous effective strategies. Go through the following table and you will get to know it-
Imagine a journey that begins with a small team, determined to redefine how people shop online. That’s the story of Flipkart, and it’s a tale filled with strategic moves and innovative thinking.
From the outset, customer satisfaction was at the forefront of Flipkart’s strategy. They understood the importance of competitive pricing, a user-friendly interface, and reliable delivery to win over the hearts of Indian shoppers. Introducing the “Cash on Delivery” option addressed trust concerns in a market where online payments were met with skepticism.
But Flipkart didn’t stop there.
They introduced groundbreaking events like “Big Billion Days,” turning ordinary shopping into a festival of massive discounts. Recognizing the shift towards mobile internet usage, they optimized their platform for mobile devices, making shopping accessible to millions on the go.
Building a robust logistics network became a cornerstone for Flipkart. Timely delivery, coupled with innovative programs like “Flipkart Assured,” ensured quality products reached customers swiftly. The transition from an inventory-based model to a marketplace allowed third-party sellers to join in, expanding Flipkart’s product catalog without huge inventory investments.
Strategic acquisitions, including Myntra, Jabong, and PhonePe, strengthened their position in fashion and digital payments. Partnerships for exclusive smartphone launches boosted their visibility while securing funding from investors like Tiger Global and SoftBank fueled their growth, enabling them to compete globally.
However, every story has its challenges. Flipkart faced setbacks from competition, changing regulations, and allegations of unfair practices. Regulatory scrutiny became a part of their narrative as the government examined their business model.
In a pivotal moment, Walmart stepped into the story, acquiring a majority stake in Flipkart for $16 billion in 2018. This move not only injected additional resources but also brought global expertise to Flipkart’s journey.
From adapting to changing trends, embracing new technologies, and facing challenges head-on, to the transformative Walmart acquisition – Flipkart’s story is a testament to resilience, innovation, and the pursuit of customer satisfaction in the ever-evolving landscape of e-commerce.
(D) Impact of Flipkart on Indian Retail: How has it disrupted the traditional retail models?
Flipkart has significantly disrupted traditional retail models in India, reshaping the landscape and transforming how consumers shop. You have witnessed it too! Let’s look at the impact of Flipkart on the retail landscape of India-
The Confederation of All India Traders (CAIT) contends that Flipkart’s practices have adversely affected small retailers. Many traditional retail businesses have struggled to compete, resulting in job losses and a decline in the sector.
The Competition Commission of India (CCI) is currently investigating the allegations against Flipkart. If found guilty, fines or changes in business practices may be imposed. The government is also considering new regulations to promote fair competition in the e-commerce sector.
(E) Business Review: How Flipkart is Performing Businesswise?
Why do we always analyze the companies from a business perspective? You may wonder! Well, this is a crucial aspect of the case studies. It immensely helps investors, stakeholders, and decision-makers.
Looking at Flipkart’s conditions from a business perspective offers insights into its strategies, financial stability, market presence, and customer service approaches.
So, let’s look at the business aspects of Flipkart-
From the table, it’s evident that Flipkart holds a substantial market valuation of $37.6 billion, boasting a dominant 51% market share in India. The major shareholder is Walmart, holding an 80.5% stake.
Despite a significant revenue increase from Rs.51,176 crore (FY22) to Rs.56,013 crore (FY23), expenses also escalated from Rs.54,580 crore to Rs.60,858.5 crore.
The company reported losses of Rs.3,371.2 crore (FY22) and Rs.4,890.6 crore (FY23). This data provides a snapshot of Flipkart’s financial landscape, showcasing its valuation, market share, shareholder structure, revenue, expenses, and losses in the specified fiscal years.
(F) Competitive Landscape of Flipkart
Flipkart operates in a highly competitive e-commerce landscape in India facing fierce competition from various players. The key rivals include-
- Amazon India: One of the major competitors, Amazon has a substantial presence in India, offering a diverse range of products and services. The battle for market share between Flipkart and Amazon is a defining aspect of the e-commerce landscape. We have thoroughly explained Amazon vs Flipkart . You can check that article for detailed information.
- Snapdeal: Though not as dominant as Flipkart and Amazon, Snapdeal remains a significant player, especially in certain product categories. The competition with Snapdeal adds to the dynamic nature of the market.
- New Entrants: The e-commerce sector in India has witnessed the entry of new players, both domestic and international, intensifying the rivalry and driving innovation in the industry.
Every year, Flipkart hosts a huge event called the “Big Billion Days” where they offer big discounts and special deals to attract lots of shoppers.
Flipkart’s focus is on making customers happy. They keep prices low, make the website easy to use, and deliver orders reliably.
One smart move they made was changing how they sell things – instead of owning all the products, they let other sellers join their platform, giving customers more choices without needing a huge warehouse.
Along the way, Flipkart made important friends by acquiring companies like Myntra, Jabong, and PhonePe. These additions helped Flipkart become better in fashion and digital payments.

To keep up in this fast-changing world, Flipkart also uses technology well, especially on mobile phones. They invest a lot in making sure orders reach customers on time. Despite facing challenges,
Flipkart’s story shows how they adapt and compete, making them a big player in India’s online shopping tale!
(G) Challenges Faced by Flipkart
Here are some of the tough challenges that Flipkart faced while commencing its operations in India-
These challenges reflect the dynamic nature of the e-commerce industry and the need for strategic agility by Flipkart.
(H) Post-Acquisition Developments of Flipkart

Let’s go through the post-acquisition developments of Flipkart following Walmart’s acquisition-
Thus, Walmart’s acquisition of Flipkart brought both opportunities and challenges. Simultaneously, it immensely helped in shaping the e-commerce ecosystem in India and impacted millions of consumers.
(I) Wrapping Up the Flipkart Case Study

In a nutshell, Flipkart’s journey from a small startup in 2007 to an Indian e-commerce giant is marked by strategic innovation, customer-centricity, and adaptability. Pioneering events like “Big Billion Days,” embracing a marketplace model, and strategic acquisitions have been pivotal.
The company’s commitment to customer satisfaction, technological integration, and expansion into diverse segments showcase its resilience . The acquisition by Walmart in 2018 added global expertise, propelling Flipkart to a $37.6 billion valuation.
As it ventures into new territories, Flipkart’s story remains a testament to its impact on India’s retail landscape and its ability to evolve with changing times!
Related Posts:
Contact Info: Axponent Media Pvt Ltd, 706-707 , 7th Floor Tower A , Iris Tech Park, Sector 48, Sohna Road, Gurugram, India, Pin - 122018
© The Business Rule 2024
TheBigMarketing.com
Flipkart Marketing Strategy 2024: A Case Study
Flipkart stands out in India’s e-commerce market, thanks to its top-notch marketing. In this case study, we’ll look closely at its ads and how it uses digital marketing to beat rivals. We’ll see what makes Flipkart’s promotions shine. We’ll also understand how it keeps winning online.
Key Takeaways:
- Flipkart’s marketing strategies have positioned it as a market leader in the e-commerce industry.
- The brand’s innovative advertising campaigns and promotional tactics have been key factors in its success.
- Market analysis and customer engagement play a crucial role in Flipkart’s marketing approach.
- Flipkart’s focus on digital marketing , including SEO and paid advertising, has contributed to its competitive edge.
- The case study of Flipkart’s marketing strategies highlights the potential for the future of e-commerce.
About Flipkart: History and Leadership
Flipkart is a top online marketplace in India with a fascinating history. It was started in 2007 by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal. These founders made it a strong e-commerce player. Now, Walmart owns the majority of Flipkart. CEO Kalyan Krishnamurthy has greatly changed how we shop online in India and other places.
The Beginning: Flipkart’s Founders
Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal once worked at Amazon. They saw a need for an online platform for Indian shoppers. With just a little money, they began. They focused on cash-on-delivery, which was a hit in cash-based India. This choice helped Flipkart grow quickly and become known as trustworthy and focused on customers.
Walmart’s Investment: A Game-Changing Move
In 2018, Walmart bought a 77% part of Flipkart for $16 billion. Walmart’s money and retail knowledge have helped Flipkart grow. Now, Flipkart can reach more customers in India, thanks to Walmart’s support and its own hard work.
Leadership in the Digital Era: Kalyan Krishnamurthy
Kalyan Krishnamurthy became Flipkart’s CEO in 2017. He has a lot of experience in e-commerce and leadership. Krishnamurthy has brought new ideas to Flipkart. His focus on customers helped make Flipkart a top name in India’s tough e-commerce market.
Understanding Flipkart’s past and its leaders is key. It helps us see how Flipkart grows and comes up with new strategies. Flipkart is always creating and offering new things because of its history and leadership team.
Flipkart Kids Ad Campaigns
Flipkart’s ads have always been known for being creative and effective. Their Kids Ad Campaigns stand out especially. These ads feature children, using their charm to create trust and a bond with viewers.
Adding kids to their ads has caught consumers’ eyes and hearts. Children in ads make the brand seem more friendly and trustworthy.
The Kids Ad Campaigns make Flipkart stand out from other e-commerce companies. This strategy has become a key part of Flipkart’s marketing, building its identity and consumer loyalty.
Flipkart appears as a brand for the whole family, attracting both parents and kids who have a say in shopping. Kids in ads make the brand feel genuine and close to its audience.
Flipkart’s storytelling through kids evokes emotions and makes memorable experiences. The children’s innocence and joy link positive feelings to Flipkart, enhancing its bond with customers.
The Flipkart Kids Ad Campaigns showcase the brand’s innovative approach to connect deeply with people. The fresh perspective of children in ads leaves a strong impression.
Flipkart’s Big Billion-Day Marketing Strategy
Flipkart’s Big Billion-Day sale is huge for its marketing. It boosts sales and helps get new customers. It does this by selling products at big discounts, which draws a lot of people. This move creates a lot of buzz.
The sale helps Flipkart reach more people and strengthen its online retail spot. It makes shoppers buy quickly before time runs out. This approach spikes sales and builds loyalty among customers.
Flipkart’s sale also makes it cheaper to get new customers. By throwing this big sale, it attracts people who haven’t shopped with them before. The big discounts and special deals not only bring in new shoppers but also make them check out more products on Flipkart.
This yearly sale is now a big deal for online shopping. As people look forward to the sale, Flipkart keeps improving its products. This event is good for both customers and Flipkart. It lets Flipkart show off what it has to offer.
The Big Billion-Day sale has really helped Flipkart grow. It gets people excited and talking about Flipkart, bringing in sales and new customers. This sale is a key part of Flipkart’s marketing and helps it grow big.
Flipkart SmartBuy Marketing Strategy
Flipkart’s SmartBuy brand shows their dedication to offering top products at good prices. They never let go of quality. This approach has built a strong customer base. It also gives Flipkart an edge in the competitive market.
The SmartBuy range includes a host of exclusive products found only at Flipkart. They offer items in electronics, home appliances, fashion, and more. Flipkart focuses on best-selling products. This ensures customers find what they’re looking for.
The SmartBuy line is known for being affordable. Flipkart works closely with makers and suppliers to keep prices low. This means more people can buy quality items without spending a lot.
Quality is key for Flipkart’s SmartBuy. Each item is checked to make sure it meets high standards. This focus on quality makes customers feel good about their purchase. They know they’re getting items that are reliable and will last.
Customers have reacted positively to the SmartBuy marketing strategy. They love the value and quality they get. This has led to high sales and good reviews for Flipkart.
Flipkart’s SmartBuy strategy is about giving the best to their customers. They offer popular products at great prices without cutting corners on quality. This has made Flipkart a brand people trust and rely on.
Social Media Marketing Strategy of Flipkart
Flipkart uses social media a lot as part of its broad marketing strategy. It knows that social media is crucial today and uses Twitter, YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram. The goal is to connect with people and make its brand more known.
Twitter: Direct Communication and Customer Engagement
Twitter is important to Flipkart’s marketing. It lets Flipkart talk directly to customers, help them, and share news quickly. By talking to people on Twitter, Flipkart builds trust and makes customers happier.
YouTube: Impactful Video Marketing
Flipkart uses YouTube to reach and interact with its audience well. The company makes catchy videos, like fashion shows and product ads. This way, Flipkart uses stories in videos to promote its items and get people involved.
Facebook and Instagram: Relatable Content and Interactive Campaigns
Flipkart is busy on both Facebook and Instagram. It posts content people can relate to and has interactive campaigns. The company shows its products, offers deals, and runs contests to get people involved. Flipkart knows it’s important to fit its content to each social media, so it connects well with its audience everywhere.
This image shows how Flipkart markets on social media. It highlights how active Flipkart is on different platforms.
SEO Strategies of Flipkart
Flipkart leads the e-commerce world, using smart SEO to draw more visitors. With Flipkart SEO strategies , it ranks high in search results. This helps it find the right people and boost its online look.
Long-Tail Keywords
Flipkart bets on long-tail keywords . These are longer, more precise phrases about what’s for sale. They use these in content and descriptions to pull in the right visitors. This way, they turn curious lookers into potential buyers.
Website Optimization
For Flipkart, a smooth website is key. They work on making their site quick, mobile-ready, and easy to use. This makes visitors happy and more likely to stay.
They also make sure their products and site details match popular search words. This helps them appear higher in search results.
Remarketing Techniques
Flipkart’s smart in using remarketing techniques . This re-engages people who’ve shown interest before. By showing them ads on various platforms, they’re more likely to come back and buy. This strategy promotes repeat visits and builds a strong brand.
Leveraging Backlinks
Backlinks are crucial for Flipkart. Getting links from trusted sites boosts their website’s trust with search engines. It not only lifts their ranking but also brings more visitors from those sites. This expands Flipkart’s customer reach significantly.
Paid Advertising by Flipkart
Flipkart uses paid advertising as a major part of its marketing plan . It uses Google Adwords for display, search, and commerce ads. This helps make sure Flipkart’s offers are seen in search results and online.
Flipkart also runs an affiliate program, beyond Google Adwords. This program lets others advertise Flipkart’s products. In return, they get a part of the profits. It helps Flipkart reach more customers and gives affiliates a way to earn online.
Flipkart’s Market Analysis and Customer Engagement
Market analysis is key in Flipkart’s marketing plan. By studying buyer behavior and likes, they gain useful insights. These insights help them grasp their target market and craft strategies to connect with customers well.
Flipkart spots trends, buyer habits, and changing needs through market research . This lets them update their products and promotions to suit customer needs. They aim to stay ahead in the game to serve their customers better.
Understanding Shopper Behavior
Flipkart dives deep into online shopping behavior. Understanding how people shop on their site helps better user experiences. They look at what influences buying decisions, like price, variety, and the user interface.
They analyze the shopping journey to find key customer touchpoints. Optimizing these points ensures a smooth and fun shopping journey from start to end.
Targeted Marketing Strategies
Market analysis helps Flipkart pinpoint their audience. By dividing their customers, they can make more focused marketing plans. These plans speak directly to different groups, offering personalized content and deals.
Flipkart uses data to find where their target shoppers spend time online. This guides them in using resources wisely and reaching out on platforms their audience prefers. These can be social media, emails, or other digital channels.
Customer Engagement and Loyalty
Customer engagement is vital to Flipkart’s strategy. Focusing on satisfaction, they build trust and long-lasting relationships. They use personalized communication, fast support, and valuable marketing to do this.
Market insights help them make engagement campaigns that truly speak to customers. Flipkart works to make shopping personal by suggesting products and offering special discounts. This customer-first approach helps increase loyalty and engagement.
Visualizing the Market Analysis
Flipkart’s market analysis and engagement strategies have been key to their success. They continuously study shopper behavior and focus on their audience. Through understanding and loyalty, they stand strong in the digital market.
Flipkart’s rise in e-commerce is due to smart ad campaigns and savvy use of social media. They also excel in SEO and use paid ads well. This has given Flipkart a leg up, making it a reliable brand. Their marketing story is a beacon for the growth of e-commerce.
Flipkart connects with customers through unique ads, building loyalty. By focusing on what customers like, they create tailored strategies. This has made Flipkart a top name in e-commerce.
Digital marketing is always changing, and Flipkart’s story highlights why staying updated is key. With forward-thinking marketing and new tech, brands can stand out in online shopping. Flipkart shows the huge promise e-commerce holds for the future.
What is the history of Flipkart and who are its leaders?
How does flipkart utilize children in its advertising campaigns, what is flipkart’s big billion-day sale, what is flipkart’s smartbuy marketing strategy, how does flipkart leverage social media for its marketing strategies, what seo strategies does flipkart implement, how does flipkart use paid advertising, how does flipkart conduct market analysis and engage customers, what is the significance of flipkart’s marketing strategies in the e-commerce industry, related posts.

Editorial Team
Fitbit marketing strategy 2024: a case study, foodpanda marketing strategy 2024: a case study.

Flipkart - The Journey of India's Leading E-Commerce Website

Rishabh Rathi , Manisha Mishra
Company Profile is an initiative by StartupTalky to publish verified information on different startups and organizations.
Don’t you think online buying and selling have become an essential part of our lives? It was youth and adults who initially relied on the Internet to buy products at affordable prices with amazing return policies and guarantees; it was a trend back then.
Nowadays, eCommerce websites have made online shopping a common practice for people of all ages. Flipkart is India's most popular e-commerce website, known for its innovative business model.
Flipkart is the leading Indian eCommerce website founded by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal in 2007 . The company is headquartered in Bengaluru , India. This Indian eCommerce store has brought a revolution to the Indian e-retail industry.
Let's now delve into the success story of Flipkart and learn about Flipkart's founders, subsidiaries, owners, business and revenue model, and more.
Flipkart: Company Highlights
Flipkart - About Flipkart - Industry and Target Market Size Flipkart - Founders and Team Flipkart - Startup Story Flipkart - Mission Flipkart - Name, Tagline, and Logo Flipkart - Parent Organization Flipkart - Subsidiaries Flipkart - Business Model and Revenue Model Flipkart - Partnerships Flipkart - Funding and Investors Flipkart - ESOPs Flipkart - Growth and Revenues Flipkart - Product And Service Flipkart - Investments Flipkart - Mergers and Acquisitions Flipkart - Challenges Flipkart - Competitors Flipkart - Future Plans
Flipkart - About
Flipkart, an Indian eCommerce company founded in 2007 by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal, has become a household name. Based in Bengaluru, India, Flipkart has been selling a vast range of products online, similar to Amazon.
Its phenomenal marketing strategies have attracted the attention of retail giant Walmart, which acquired Flipkart for $16 billion in May 2018.
Along with the imposing worldwide market share that Walmart has in the retail industry, the Sam Walton -founded company is also famous for its inspirational business model.
In the initial years, Flipkart focused on selling books, but today the catalog covers categories like electronics, fashion, home essentials, groceries, and lifestyle products. More than 1 billion people have shopped on Flipkart, making the e-commerce giant the leading e-retailer in India.
Flipkart also has subsidiaries like Myntra , eBay, Ekart, Jeeves, and more. Flipkart also launched Shopsy on July 2, 2021, which is designed to behave like an app that will encourage the nation's entrepreneurs to reap all the benefits of digital eCommerce that come their way without investments.
Today, Flipkart has over 100 million registered users, 100+ thousand sellers, and 21+ state-of-the-art warehouses.
It also boasts about 10+ million daily page visits and over 8 million shipments per month. Flipkart currently works as a subsidiary of Walmart .
The current CEO of Flipkart Group is Kalyan Krishnamurthy .
Flipkart acquired a 100% stake in Walmart India, which operates the Best Price cash-and-carry business.
Thus, we are launching Flipkart Wholesale. This step helped Flipkart strengthen its hold on the grocery, food, and fashion businesses, which are stated to be highly competitive in this dynamic environment.
The launch of Flipkart Wholesale will be initiated in August, thus piloting the services for the grocery and fashion categories.

"The Best Price operation will continue to run as it is. In terms of legal structure, currently, Walmart India is a separate entity within the Flipkart Group", Said Sameer Aggarwal, CEO, Walmart India.
The role of Kirana Stores and MSMEs in India's retail ecosystem is vital. With a focus on meeting their needs, Flipkart Wholesale is all set to widen opportunities at a significant value. By leveraging their expertise and knowledge, the team is breaking new norms and helping Indian businesses grow and succeed.
Earlier in 2018, Flipkart was acquired by Walmart for $16 billion , which was the largest online e-commerce acquisition in the world to the present. Flipkart launched its wholesale unit with a presence in the fashion and grocery categories.
“With the launch of Flipkart Wholesale , we will now extend our capabilities across technology, logistics and finance to small businesses across the country,” Said Kalyan Krishnamurthy , CEO, Flipkart Group
At present, Flipkart Wholesale will be headed by Adarsh Menon (a veteran at Flipkart). In order to ensure smooth functioning and transition, Sameer Aggarwal (CEO, Walmart India) will remain with the company for a while.
Flipkart - Industry and Target Market Size
Flipkart uses an undifferentiated targeting strategy since people of all demographies purchase items online, which are available to everyone where delivery is possible.
National and multinational e-commerce companies are giving neck-to-neck competition to each other, due to which their positioning is very important. Flipkart has positioned itself as a trustworthy and customer-friendly eCommerce brand.
The online retail industry market is of a size of around $60 billion . It is expected to reach $200 billion by the year 2026. The Indian and global e-commerce industry is on the verge of exponential growth, and the introduction of high-speed internet has fueled the process across the nation.
Before the pandemic, India was one of the most attractive eCommerce markets globally, expected to deliver a 30% CAGR over a six-year time horizon, according to a report by RedSeer Consulting.
Flipkart - Founders and Team
Flipkart was founded by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal in May 2007.

Kalyan Krishnamurthy is the CEO of the company. He was appointed CEO of the company in January 2017, when he replaced Binny Bansal.
Sachin Bansal
Sachin Bansal is the co-founder of Flipkart. After obtaining a Bachelor's Degree in Computer Science from IIT Delhi, Sachin started with Amazon as a Senior Software Engineer after a brief stint at Techspan. He then left his job at Amazon and co-founded Flipkart.
At Flipkart, he managed the positions of CEO and Chairman before resigning in 2018 following Walmart's major acquisition of Flipkart, where the American multinational company acquired around 77% stakes in the Indian e-commerce company. Bansal eventually started Navi with Ankit Agarwal and is currently serving as Chairman at Navi. The net worth of Sachin Bansal is currently at $1.30 billion, as of the Forbes report of 2022.
Binny Bansal
An IIT Delhi alumnus, much like Sachin, Binny completed his Bachelor's in Computer Science and Engineering, after which he co-founded Flipkart. Binny Bansal was the COO and CEO of Flipkart.
Sachin was the CEO since the inception of Flipkart,, and in 2016, Binny Bansal took over as CEO while Sachin Bansal became the executive chairman of the company. However, Binny also resigned from Flipkart in 2018 due to personal misconduct allegations against Flipkart.
Bansal also served as the group CEO of the organization. Moreover, Binny has also served as a board advisor at Acko, Blackbuck, GreyOrange, Udhyam Learning, and more such companies. Binny Bansal is currently serving as a co-founder and executive chairman at xto10x Technologies.
The net worth of Binny Bansal is also $1.30 billion, as reported by Forbes in 2022. Apart from serving in the SaaS consulting startup, Bansal was also on the Board of Directors of PhonePe.
Binny Bansal sold stakes worth $264 million (nearly Rs 2,060 crore) to Tencent, as per official documents checked out on June 13, 2022.
The documents revealed that the transaction had already been done in October 2021 and was shared only at the start of FY22.
At the end of the transaction, Binny Bansal was holding around 1.84% of the stakes, while Tencent was currently holding 0.72%. The Chinese tech giant is holding around 4-5% stakes in Flipkart Pte, which is the Singapore-based parent of Flipkart.
Binny Bansal has a history of selling stakes. He had previously sold stakes worth $90 million in 2019 to Tiger Global across two deals. Bansal also sold shares worth $76 million to FIT Holdings SARL, the Luxembourg entity that is owned and operated by Walmart, in the same year.
Flipkart's SVP, Growth and Monetisation, and Shopsy Head, Prakash Sikaria, are exiting after the festival sales, as per reports dated July 22, 2022. Sikaria also headed other verticals like recommerce and travel, which will now be taken over by Adarsh Menon.
On the other hand, Flipkart Wholesale, the B2B e-commerce business of Flipkart, will be headed by Koteshwar LN. However, Flipkart has yet to decide who to appoint for the other functions that Sikaria handled.
Flipkart currently operates with an employee strength of 33,000+ employees.

Flaunt your startup with StartupTalky
800+ stories, thousands of founders, and millions of visitors. Want to be the next?
StartupTalky is where founders, entrepreneurs, startups and businesses hang out and look up to for inspiration. If you have the means, we have the medium! Inviting founders and startups who are building sustainable solutions from ground zero! Startups who run the show, StartupTalky will let the world know!
Flipkart - Startup Story
The IIT-Delhi graduates, Sachin and Binny Bansal, were employees at Amazon when they began thinking of building their own company in India.
Though Sachin was an employee working with Amazon for some time, Binny was referred to join the company by Sachin, and the former appeared to be quite bored with the company.
It was like a "12 to 3 job or something" for Binny Bansal, who decided to quit the company as soon as Sachin and he emerged with the idea of establishing an eCommerce business.
Sachin and Binny started Flipkart as an online book store from a two-bedroom apartment in Bengaluru’s Koramangala area. They initially started with funding of Rs 4,00,000 from their own pockets.
When Sachin and Binny received a positive response and success in selling books back in 2007, they planned to expand to electronics as well, and by 2014, the company had become one of India’s most valuable startups by reaching a valuation of $1 billion.
When the duo founded Flipkart, online shopping in India was even a distant dream for them, but the hard work and consistency paid off and made Sachin and Binny into widely successful entrepreneurs, which placed them quite ahead in the list of the successful Indian entrepreneurs .
Flipkart - Mission
Flipkart's mission is to provide a delightful customer experience by being the partner of choice for Indians and to create India's most customer-centric company.
Flipkart - Name, Tagline, and Logo

The founders of Flipkart, Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal, wanted a name that could speak beyond books .
Furthermore, they also wanted to name their company in such a way that it would be suitable for a wide range of product categories that could also be expanded in the future.
Flipkart means ‘ flipping things into a shopping cart ’.
The logo of Flipkart was changed twice. There have been several taglines that the company has gone through on different occasions. Some of the popular taglines are:
- Ab Har Wish Hogi Poori
- Abhi Nahi To Kabhi Nahi
- If it's trendy, it is on Flipkart
- Be Trendy, Always
- Itne mein, Itnaaaa Milega
- Shopping ka naya address
- Ab Mehengaayi Giregi
Flipkart - Parent Organization
In August 2018, U.S.-based retail chain Walmart acquired a 77% controlling stake in Flipkart for $16 billion, valuing the company at $20 billion.
With this acquisition, Walmart claimed that the omnichannel retail sector has a huge potential for future growth.
Speaking at Retail India Summit and Expo, Walmart India President and CEO Krish Iyer claimed that
"$16 billion deal to acquire Flipkart has attracted foreign and domestic investors in country's retail and omni-channel space. The recent investment in Flipkart shows Walmart is committed to the country. We do see a great value in terms of an omnichannel play in the whole process"
Owing to the demonetization, he said that it played a crucial role in the growth of the retail sector by structuring the economy along with the implementation of the GST.
These stakes were further increased to 81.3% towards the end of the same year. Soon after the acquisition, one of the founders of Flipkart, Sachin Bansal,,, left the company.
This year, Walmart invested $3.5 billion to boost its ownership of Flipkart to 80.5%. Notably, some of Flipkart's early investors, such as Tiger Global and Accel, divested their stakes by selling them to Walmart.
Walmart Inc. is an American multinational retail corporation that operates a chain of hypermarkets, discount department stores, and grocery stores.
Flipkart - Subsidiaries
The subsidiaries of Flipkart are Myntra, Mallers, eBay, Ekart, Jeeves, Mech Mocha, Upstream Commerce, Ugenie, DSYN Technologies, AdIQuity Technologies, Jabong, ClearTrip, Shopsy, Yaantra, Liv.Ai, F1 Info Solutions and Services, Fx Mart, Appiterate, ngpay, Mime360, WeRead, Chakpak, and Sasta Sundar.
In 2016, Flipkart Group acquired PhonePe . However, in December 2022, Walmart-owned Flipkart and PhonePe declared a full ownership separation, with Flipkart no longer holding any stake in the payments firm PhonePe.
Flipkart - Business Model and Revenue Model
Flipkart works on a B2C business model i.e., a business-to-consumer model. The company initially began with a direct-consumer model, wherein it sold books and some other products.
Today, it has become a marketplace with a huge catalog of products—right from FMCG to electronics and books.
Flipkart claims it has over 80 categories and over a million sellers on board from all across India.
It is an omni-channel service provider that leveraged the same model after the Walmart acquisition of Flipkart. The company earns almost all of its operating revenues from the sale of goods.
At Recode’s Code Commerce conference, Binny Bansal, who co-founded Flipkart along with Sachin Bansal, said:
“Sometime in the future, especially with some categories, omnichannel would make a ton of sense. It is definitely something which would be there in the future.
Flipkart - Partnerships
Flipkart has seen a wide range of partnerships throughout the years it has been active. Some of the most prominent of its partnerships are:
Adani Group
The Indian eCommerce marketplace announced a strategic and commercial partnership with the Adani Group on April 12, 2021, to enhance its supply chain and logistics infrastructure.
IIM Sambalpur
The eCommerce major partnered with the Indian Institute of Management, Sambalpur in August 2021, with the aim of supporting and promoting small businesses.
Flipkart partnered with Urbanic on September 8, 2021, to target young consumers across India.
Flipkart started collaborating with the leading Indian kids' fashion brand, Hopscotch on November 25, 2021, to strengthen its kids' fashion segment.
The popular audio streaming service, Pocket FM, has partnered with Flipkart on July 26, 2022, which will be a tie-up for its distribution via the famous e-commerce marketplace.

Flipkart - Funding and Investors
Flipkart has raised $14.3 billion in funding in 27 rounds.
Below are some of the funding details:
Flipkart's valuation exceeded $40 billion in 2022, and it was preparing for its upcoming public listing.
Flipkart - ESOPs
Flipkart Singapore has expanded its ESOP trust. According to the reports dated March 31, 2022, the company has allotted 21,370 equity shares, the total worth of which is reported to be around $4.4 million (Rs 30.71 crore) to the ESOP trust.
The Indian e-commerce giant already boasts of having the largest ESOP pool among startups of Indian origin.
A recent Longhouse Consulting report claims that Flipkart's ESOP pool is worth around $2.26 billion (Rs 17,000 crore). It is followed by OYO with a $1 billion pool, Zomato with $745 million, and Paytm with a $604 million ESOP pool.
Amidst a significant development, Flipkart has commenced an impressive ESOP (Employee Stock Ownership Plan) payout amounting to $700 million in July 2023, benefiting around 19,000 of its current and former employees. This move follows Flipkart's decision to separate full ownership of PhonePe, the Indian digital payments and financial services company. Defying the trend in the current challenging funding landscape for startups, Flipkart's generous payout demonstrates its commitment to recognizing and rewarding its workforce while also aiming to retain top talent in a fiercely competitive market.
Flipkart - Growth and Revenues
From its bootstrapped beginnings to the success Flipkart is witnessing today, it proudly talks about its success.
Though the company looked a bit shaky with the arrival of US-based Amazon in the Indian markets, the danger is no longer looming today with the assertion of Kalyan Krishnamurthy as the group CEO and the acquisition of Walmart of Flipkart.
Flipkart India is currently the leading eCommerce site in India.
The Walmart-owned Indian eCommerce company also clocked an impressive 64% market share when last recorded during the festive sales in October 2021.
2Gud RoadMap for Refurbished Products
Flipkart-owned 2Gud for the refurbished market will play a major role in driving budget shoppers to premium products. Although, with its great accreditation for shopping experience refurbished market will gain trust quickly among budget buyers and refurbished sellers.
Moreover, Flipkart will also keep a strict quality check on refurbished items so that the buyers use their products hassle-free.
However, its 10-day easy return policy will be super beneficial for the refurbished shopping market. Initially, 2Gud started the refurbished market with mobiles, laptops, tablets, smart watches, and accessories and plans to introduce 40+ categories in the giant refurbished market “2Gud”.
2GUD has expanded its category offerings to cater to style-conscious Indians who are looking for value in 2019. Targeted at Tier II and Tier III markets, 2GUD plans to evolve from a refurbished-only platform to a complete customer offering with categories such as affordable fashion, accessories, and home.
As part of a larger strategy to expand the benefits of e-commerce to the next 200 million customers, 2GUD, which is present across 40+ categories, will now expand to 150+ categories. 2GUD is focusing on making the latest trends across fashion, home, decor, kids, and other categories affordable for the Indian consumer.
2GUD predicts that the refurbished goods market, on gaining the trust of users, would go on to become a 20 billion dollar industry in the next half-decade. To be a leader in this segment of e-commerce in India is not an easy task, given the “trust issues” that continue to persist in this part of the pie.
Recently, 2GUD upgraded its m-site, making it available as a mobile app as it looks to cater to a larger set of audiences and shoppers. 2GUD has served close to a million customers from over 3,000 cities across India and has over 1,000 registered sellers.
Officially, eBay.in ended operations on August 14th, 2018. In the meantime, eBay is all set to relaunch its platform with cross-border trade offers exclusively. The Walmart-owned company has enormous growth prospects and has been doing great in its own way.
Flipkart - Big Billion Sale Success
The delivery of around 1 crore shipments within 5 days of the Big Billion Day sale has created a lasting mark on the eCommerce industry. Flipkart has seen a 10X growth from the last festive Big Billion sale. Out of the 1 crore, around 35 lakh deliveries were via Kirana Partners.
The number of crorepati sellers went up by 1.5 times, and the number of lakhpati sellers rose by 1.7 times.
In the Big Billion Days sale of 2021, over 3.75 lakh sellers joined hands to offer the best products online to their customers via Flipkart. This helped the customers save a whopping Rs 11500 crore during the “biggest Indian sale ever. The platform witnessed around 110 orders placed per second that varied across various products, including electronics, fashion, books, furnishing, etc., in its Big Billion sale of 2020.
Furthermore, the company is also seeing around 100x week-on-week growth on its social commerce model, which helps in assisted shopping and charges commission from advertisements and sellers working through its platform. This is why the company is striving to get a bigger share of the grocery ecosystem in the upcoming months.
Here are some growth highlights of the brand at a glance:
- Flipkart's valuation is $35 million as of January 31, 2024.
- Flipkart is a market leader.
- It is one of the pioneering ecommerce marketplaces in the country.
- Flipkart is known as the highest-valued among the unicorn companies in India .
- Flipkart presently boasts of having more than 375K sellers/resellers.
- The company is serving 160 million+ users in the country.
Flipkart Financials
Based on data received by business intelligence platform Tofler, Flipkart India recorded a 45% increase in net loss for 2022–2023 to Rs 4,890.6 crore in FY23 from Rs 3,371.2 crore in FY22. Consolidated sales for the Walmart-owned business in 2022–2023 were Rs 56,013 crore, a 9% increase over the prior fiscal year FY22.
The company's reported expenses for the fiscal year were Rs 60,858 crore in FY23, up 11.5% from Rs 54,580 crore in FY22. This covered expenses for things like buying trade shares, paying employee benefits, and financing-related fees.
The company started a unique feature of the value proposition by offering 24 x 7 support to the customer . Flipkart charges a certain amount or percentage of commission from the sellers, which varies depending on the type of product and the kind of sales. This may range from 5% to 20%, excluding taxes and discounts.
Flipkart - Product And Service
Flipkart some of the prominent products and services are mentioned below:
Flipkart Same Day Delivery Service
Over the past two months, Flipkart has shortened their delivery times in response to growing consumer demand for quick delivery in non-metropolitan areas and greater competition from quick commerce companies like Blinkit and Zepto.
Furthermore, Flipkart has started offering free same-day delivery of goods in 20 locations across a variety of categories, as per a news report from March 11, 2024.
Flipkart Labs
Flipkart Labs is one of the latest initiatives launched by Flipkart on April 28, 2022, with a view to foraying into the Web3 and Metaverse. Based in Bengaluru, Flipkart Labs aims to build an in-house innovation capability to fuel and shape the future of customer-centric e-commerce in India.
Flipkart Health+ App
Flipkart launched its new Health+ App, which will focus on empowering users with easy access to medicines, healthcare products, and services across India, on April 6, 2022.
Flipkart Launches Spoyl app-in-app fashion Vertical
Flipkart, the renowned e-commerce platform, has introduced an app-in-app fashion segment called SPOYL on August 17, 2023, with a specific focus on catering to the preferences of Gen Z consumers. This dedicated vertical within the Flipkart app will showcase an extensive selection of over 40,000 products spanning various categories, including western wear, accessories, and footwear.
Flipkart - Investments
Being a pioneering eCommerce business that is hailed as a fast-growing company, Flipkart has seen numerous investments. Flipkart has made 35 investments, of which 30 are lead investments. The most recent investment was made on April 4, 2023, when Flipkart Marketplace raised $358.2 million.
Here's a look at the most recent investments by Flipkart:
Flipkart - Mergers and Acquisitions
Flipkart has acquired 18 companies to date, as of March 2022. ANS Commerce was the latest company that Flipkart acquired in an undisclosed deal on April 19, 2022, in order to strengthen its eCommerce ecosystem.
From having @Flipkart as our seed investor along with Blume to now joining hands to build entertainment at scale for India - it's been a quite a full circle. Feeling immense gratitude towards all @MechMocha team members, investors, advisors and partners. https://t.co/77bhfReGKN — Arpita Kapoor (@Arpita_Kapoor) November 3, 2020
Here's a look at the 11 acquisitions by Flipkart:
Flipkart has exited from three companies:
- Aditya Birla Fashion and Retail
Flipkart - Challenges
Challenges have always been face-to-face with India's most popular e-commerce player, but Flipkart has always come out victorious. One recent update has it that Flipkart and its archrival, Amazon, have been involved in alleged cases of competition law violations.
This is why CCI or the Competition Commission of India, raided a few seller offices of both Flipkart and Amazon to probe into the same after the Supreme Court gave its nod for it. The Walmart-owned company as well as that founded by Bezos were linked with multiple incidents of favoring their preferred sellers on their respective platforms.
Sushant Singh T-shirts Sales Controversy
Boycott Flipkart went trending on Twitter on July 26, 2022, after numerous Flipkart users allegedly accused Flipkart of "Cheap marketing", when they found tees containing the image of Sushant Singh Rajput with a message that read "Depression is like drowning".
According to these users, who were Sushant fans, these t-shirts with the message indicated that Sushant Singh died by suicide, while this has not been clearly identified. Some others also identified this thing as a "smear campaign" against the late actor.
Flipkart Subsidiary Cleartrip's Data Breach
Cleartrip, which is owned by Flipkart now, has experienced data breaches. The company confirmed on July 18, 2022, in an email sent to its customers that the information of some of the customers was compromised, but no sensitive information was leaked.
Flipkart-owned Cleartrip has already reached out to proper authorities and would resort to appropriate legal action systematically. The acquisition of Cleartrip was via a distress sale after the startup's growth plummeted to astonishing levels as the COVID-19 pandemic broke out. The company had earlier thrived another data breach in 2017 when a group called Turtle Squad defaced it for a few minutes.
Flipkart - Competitors
Flipkart India competes primarily with Amazon's Indian subsidiary and the domestic rival Snapdeal. In FY23, Flipkart showcased resilience among e-commerce leaders, securing a substantial 48% market share and effectively protecting its position.
Flipkart is significantly dominant in the sale of apparel (a position that was bolstered by its acquisitions of Myntra) and was described as being "neck and neck" with Amazon in the sale of electronics and mobile phones.
To list some of Flipkart's competitors, they would be:
Flipkart - Future Plans
Currently, both the founders, Sachin and Binny Bansal don’t serve Flipkart anymore but the brand continues to stand tall despite all the challenges. Flipkart has been one of the most prominent faces in the Indian startup ecosystem.
Flipkart has never been afraid of taking risks, and that is one of its key advantages. From books to electronics and household products and whatnot, it has evolved a lot in the past years and will continue to expand irrespective of the change in shareholders or competitors.
Walmart's major investment in Flipkart means better service and market presence for the latter. Advancements in eCommerce, a wider range of products, better products, and upgraded integrations with small businesses are just a small chunk of the innovations we can expect from Flipkart in the coming time.
Flipkart plans to launch its IPO at a substantial valuation of $60–70 billion, with intentions to list on U.S. stock exchanges as part of its ambitious future plans in 2023.

Is Flipkart the first online shopping company in India?
No, Flipkart is one of the first online shopping companies in India but not the first online shopping company in India. It was Fabmart.com, founded in 1999 by K Vaitheeswaran, which was India's first online shopping company.
Who is the owner of Flipkart?
Walmart, an American multinational retail corporation is the Parent Organisation of Flipkart. Flipkart was founded by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal in 2007.
Who are the founders of Flipkart?
Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal founded Flipkart in May 2007 in Bengaluru, India.
What is the Flipkart CEO's name?
The name of the Flipkart CEO is Kalyan Krishnamurthy.
What is the origin country of Flipkart?
Flipkart was founded by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal and is headquartered in Bengaluru, India.
When was Flipkart founded?
Flipkart was founded in October 2007 by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal.
Is Flipkart a product based company?
Though Flipkart was earlier solely a product-based company, it is now operating as a product and services-based company.
What is the tagline of Flipkart?
"Ab Har Wish Hogi Poori" is the tagline of Flipkart.
Where is the headquarters of Flipkart located?
The Flipkart headquarters is in Bangalore, India.
What are Flipkart products and services?
Flipkart was earlier solely an eCommerce operator that offered a wide array of products from home essentials to electronic gadgets to groceries and more. However, with the latest introduction of the cleaning and repairing services, Flipkart has already started its foray into the at-home services segment, to rival Urban Company.
Who are the Flipkart competitors in India?
Flipkart competitors in India include:
Must have tools for startups - Recommended by StartupTalky
- Convert Visitors into Leads- SeizeLead
- Payment Gateway- Razorpay
- Spy on your Competitors- Adspyder
- Manage your business smoothly- Google Workspace
Dubai Defies Nature's Fury: Global AI and Blockchain Shows Shine Through Adverse Weather
Dubai, April 19, 2024: Following a resounding success, VAP Group is thrilled to announce the triumphant conclusion of the inaugural editions of the Global AI Show and the Global Blockchain Show, held on April 16 and 17, 2024, at Grand Hyatt, Dubai. The heavy rainfall that hit Dubai on Tuesday
A Complete Guide for How to Make Money on Reddit
Making money on Reddit without spending a dime is possible with the right strategy. The key to making money is to build a user base, create high-quality content, and take advantage of Reddit's features like 'Karma' points and advertising. Additionally, you can join relevant subreddits that allow members to post
The Art of Artificial Intelligence: Top 10 AI Art Curators
When most people think of art, images of a great craftsman creating a work of beauty out of clay or stone or a talented artist painting or sketching stunning scenes on canvas come to mind. They take a lot of time and a lot of human intervention, but the finished
Mitgo Ventures Invests In Qoala Cashback Service As A Part Of $20 Million Publisher Investments Program
16th April, 2024, New Delhi, India - Mitgo Ventures, an investment arm of one of the world's leading MarTech companies, Mitgo Group, has invested in Spanish next-generation cashback service Qoala. It is a browser extension that allows users to get cashback and automatically apply coupons in over 4,000 stores.
Now, Flipkart functions entirely in India, with headquarters in Bangalore, Karnataka and earning 4500 crores annually. In no time, Flipkart also started offering other products like electronic goods, stationery supplies, fashion, home essentials and groceries.
The company now gives employment to around 5000 people. It has a consumer base of approximately 2 billion people and the company claims to deliver more than thirty thousand parcels per day.
Currently, Flipkart stores its products in its warehouses across the country. They have a delivery network across 27 cities. It helps the company to deliver orders to their customer within an appropriate time.
With passing time, internet penetration has grown across the world, hence it also acts as a booster for e-commerce platforms as it provides a secure payment option to customers.
What led to the growth of Flipkart was increasing internet connectivity in rural and urban areas.
Availability of a wide range of products from anywhere and that too at the customer’s doorstep with feasible and affordable prices.
Equipped work schedules of the young population led to more online and indoor shopping which eventually helped Flipkart grow at a faster pace.
Though, Flipkart currently faces tough competition from Amazon, what remains is the main objective is to create a unique image in the consumer’s mind.
After having an idea about the company’s evolution and how it created its own space in the Indian e-commerce markets, let’s dive deep into what are the marketing strategies that Flipkart adopted.
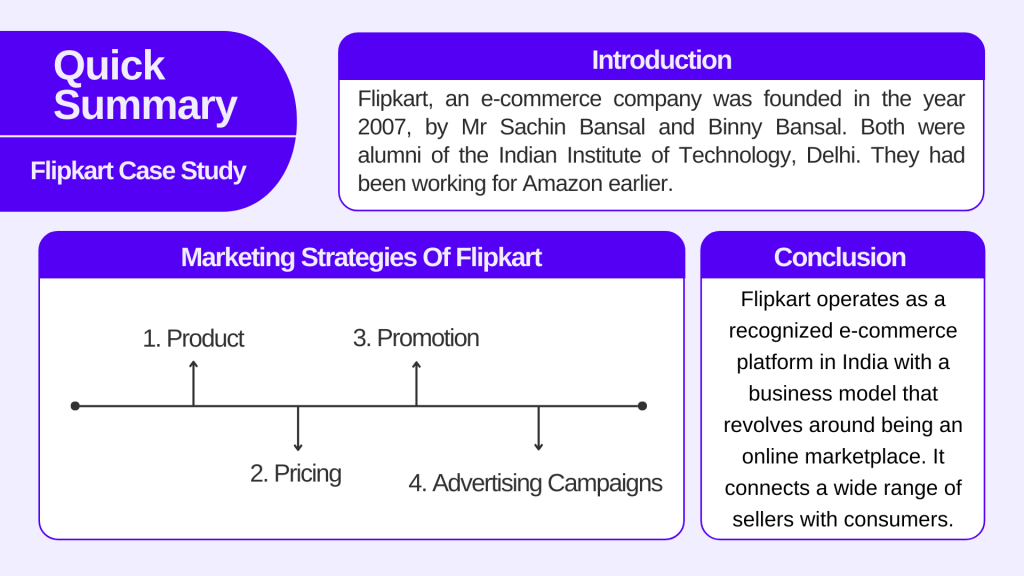
Marketing strategies of Flipkart
1 . product:.

The company generally offers its customers with wide range of products. It deals in almost all segments except for automobiles. Flipkart has recently started a grocery store to increase its market share.
The major reason Flipkart for being the most used app for online shopping is that the app is user-friendly which gives the user a phenomenal experience while browsing.
2. Pricing:

The company provides several filters for the products as per the price range selected by the customer, and easy payment options. Flipkart was the first company to provide. cash on delivery option to its users in the year 2010. The products are delivered on time and are of good quality since they are packed with utmost care to avoid any sort of damage.
The 15-day exchange policy of the company gains consumers’ confidence in buying products. Recently launched pay later option with a minor convenience fee, helps the customer to easily convert their buying into EMIs. The company also offers exclusive discounts and price drops on the occasion of Indian festivals and sales.
3. Promotion:

Flipkart can target every age group of audience irrespective of what product they are looking for online. The smart marketing strategy of Flipkart grabs the attention of its viewers who hold the power to buy and are aware that online shopping is better than offline shopping since it provides them with much better options to explore than any retailer would ever give them.
You must have heard about the term SEO; it stands for search engine optimisation.
Now what exactly is SEO It is a set of strategies and practices used to improve a website’s visibility in search engine results pages like Google, Bing, and Yahoo. The primary goal of SEO is to increase non-paid traffic to a website and boost its overall online presence.
As per the latest findings, Flipkart tops the online search results with a total of 55.6 million searches, out of which 11.3 million were mobile searches and 44.3 million were desktop searches. Also, when it comes to SEO, the loading speed of the site plays an important part since it will decide if the users will visit your site or not. Flipkart does this job great. It just takes 2 seconds for the site to load the content for its consumers.
To promote the app Flipkart has also collaborated with various Indian celebs who act as influencers for people who search for online products.
4. Advertising campaigns launched by Flipkart

One of Flipkart’s most significant annual sales events is the “Big Billion Days.” Flipkart runs wide-ranging marketing campaigns, offering discounts and deals across various product categories. These campaigns feature engaging advertisements to build eagerness and attract customers.
Flipkart ran an advertising campaign centred around our toddlers and teenagers —a voice search for kids. The campaign showcased how kids could use their voices to search for toys and other products on the app, making it easier for parents to shop for their children.
Flipkart often runs campaigns emphasizing mobile phone exchange offers, encouraging customers to upgrade their phones by exchanging their old ones. These campaigns ensure that consumers should get cost-efficient and best deals.
Flipkart introduced “Flipkart Plus,” a loyalty program offering benefits such as free and faster delivery, early access to sales, and reward points for regular customers.
Flipkart’s marketing team has a great quality of analysing consumer behaviour and based on this, they started a sort of advertising campaign which you guys must have seen while scrolling through the app, “Frequently Bought Together”. In this Flipkart suggests the buyer the product which is frequently bought by the audience.
There are various other marketing strategies that Flipkar̥t tries to implement to promote the app globally.
By now our readers must have got an idea why Flipkart holds an essential place in the market and gives tough competition to Amazon.
Flipkart’s business model depends on simplifying transactions between buyers and sellers, charging fees for various services, and constantly inventing to improve the customer experience and seller support.
Flipkart operates as a recognized e-commerce platform in India with a business model that revolves around being an online marketplace. It connects a wide range of sellers with consumers, offering diverse products and services. Flipkart’s marketing strategy is essential in establishing its brand, attracting customers, and maintaining a competitive edge in the e-commerce industry.
Divulge the amazing story of Coca-Cola .
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
- When was Flipkart founded? Flipkart was founded in the year 2007.
- Who founded Flipkart? Sachin Bansal & Binny Bansal founded Flipkart.
- Is Flipkart an Indian company? Yes, Flipkart is an Indian company with its headquarters in Bangalore. Later it was acquired by Walmart in 2018 taking over 80% stake in the company.
- What is the current annual revenue of Flipkart? The current annual revenue of Flipkart is 4500 crore.
- Which is the biggest sale of Flipkart? BIG BILLION DAYS is the biggest sale of Flipkart.
Related Posts

Grasim Industries Case Study: Subsidiaries, Products, Financials, and SWOT Analysis

HCL Technologies Case Study: Financials, KPIs, And SWOT Analysis

Varun Beverages Case Study: Business Model, Financials, and SWOT Analysis
We are a concern of pace group. pocketful is an investing platform that helps people be better investors. pocketful unlocks the discoverability of new investment and trading ideas., quick links.
- Open an Account
- Pocketful Web
- Pocketful App
- Investment Tool
- Trading Tool
- Support Portal
- Referral Program
- Calculators
- Stocks Pages
- Government Schemes
- Index Heat Map
- Stock Screener
- Mutual Funds
- Terms & Conditions
- Policies & Procedures
- Privacy Policy
- Press & Media
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >
18 Never Flip Our Cart—We Are ‘Flipkart’: A Case Study on E-commerce Giant Flipkart
- Published: August 2022
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Flipkart is not an Indian company since it is registered in Singapore and majority of its shareholders are foreigners. Because foreign companies are not allowed to do multi-brand e-retailing in India, Flipkart sells goods in India through a company called WS Retail. Other third-party sellers or companies can also sell goods through the Flipkart platform. Flipkart now employs more than 15,000 people. Flipkart allows payment methods such as cash on delivery, credit or debit card transactions, net banking, e-gift voucher, and card swipe on delivery. On 15 September 2007, Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal (not related) started Flipkart as an online bookstore. The two had known each other since 2005 when they attended the Indian Institute of Technology Delhi (IIT-Delhi) together and were colleagues at Amazon briefly. Eleven years later, the world’s largest retailer, Walmart, has agreed to buy a controlling stake in the company, Softbank chief executive officer Masayoshi Son said today (09 May). Flipkart’s journey has been nothing short of a roller-coaster ride. The company went from record-breaking investments and an acquisition spree to failed business experiments and devaluations—only to bounce back.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.

Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

Flipkart Success Story and Case Study

In this article, we will take a detailed look at the case study and success story of e-commerce giant Flipkart , which has inspired thousands of budding entrepreneurs to go after their dreams even if the path is full of problems, obstacles and initial disappointments.
Table of Contents
Table of Contents :
How was flipkart founded.
- Flipkart founders Sachin and Binny are not brothers
Flipkart Strategic Expansion
- Cashing on the COD payment option
- The challenges faced by Flipkart
- Changes in leadership
Flipkart Acquisitions
- Flipkart Reward Program
Flipkart Failures
The founders of Flipkart – Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal – are former IIT Delhi graduates. They left their lucrative jobs at Amazon to achi eve their entrepreneurial dreams. As a result, Flipkart was launched in October of 2007, with the aim of selling books online.
The plan was simple – c ustomers would place an order for books through Flipkart and get them delivered right at their doorstep. They started their journey from a 2-bedroom apartment and made just 20 shipments in its debut year. Reportedly, the company was set up with just 4 lakh rupees and now its valuation has been estimated to be roughly $24.9 billion .
No, F lipkart f ounders Sachin and Binny are not brothers
Although the two founders share the same last name, they are not related. Also, both of them have done their graduation from the same college but they were a batch apart and weren’t classmat es. Their first meeting happened at the common Amazon office , which was running a technology development centre in the southern city since 2004 .
Sachin was the one who came up with big ideas and a long-term vision while Binny took care of the implementation part. Together, they were bound for glory which they eventually received before parting ways in 2018 .
Flipkart opened up its first office in Bengaluru in the year 2008. This was followed by new offic es in Delhi and Mumbai in 2009 . The same year the ambitious startup got its first capital investment of $1 million from Accel Partners , a well-known investment firm. By the end of 2009 , the company had nearly 150 employees .
Here’ s a timeline of the flow of funds that helped Flipkart grow:

2012: Flipkart announced a $150 million funding round led by South Africa-based tech majors named Naspers . By this time Flipkart had a valuation of $1 billion, thus becoming a part of the Unicorn startup club!
2013 : The company again raised a sum of $ 20 0 million from its existing investors. Another $160 million was raised from Sofina, Morgan Stanley, Dragoneer and Vulcan capital. In this period, Flipkart had an estimated valuation of nearly $1.6 billion.
2014 : Flipkart acquired Myntra for nearly $280 million. It then raised $210 million from DST Global. The valuation was recorded at $2.6 billion.
2014 : The same year Flipkart witnessed a $1 billion funding round from GIC Singapore. As a result, the company valuation shot up to $7 billion within 3 months.
2014 : In another round, the company raised as many as $700 million from hedge funds such as Steadview Capital, Greenoaks , sovereign wealth fund Qatar I nvestment Authority, T Rowe Price. The valuation at this point stood at an enormous $11 billion.
2015: Flipkart reached a landmark valuation at $15.5 billion. It again raised roughly $700 million from its investors.
2016: Flipkart would like to forget this year as the company witnessed the first big markdown by a Mutual Fund (Morgan Stanley). The valuation came down to $11 billion.
2016: Flipkart kept receiving continuous markdowns by a number of mutual fund investors such as T Rowe Price, Vanguard and Fidelity.
2016: A Morgan Stanley Mutual Fund made a significant cut to the value of its Flipkart shares. As a result, the valuation wit nessed a further drop to $5.6 billion.
2018: Walmart acquired 77% stake in Flipkart for $16 billion .
Cashin g on the Cash On Delivery Payment (COD) option
Flipkart was among the first major e-commerce players in India to introduce the cash on delivery option for its customers in 2010. There are many reasons as to why cash on delivery plays an important role in the e-commerce sector. For instance:
Helps develop a sense of trust
When Flipkart started operating in the country, it knew that people will be doubtful about any kind of scam or loss if they stuck to prepaid orders. So they introduced cash on delivery (COD) payment option so that people can place orders with trust, without any fear of losing money.
No dependency on payment cards This point is especially valid for deliveries in rural or sub-urban areas, where people still rely heavily on cash for any kind of transaction.
Allows some time to gather money for payment Sometimes e-commerce companies like Flipkart launch exciting offers which are very hard to ignore for people fond of online shopping. Choosing cash on delivery gives them some time to gather cash so that they do not miss out on the limited-time offer.
The Challenges faced by Flipkart
The term e-commerce was almost unknown when Flipkart launched its ambitious startup. Many market experts dismissed online shopping as a western concept, stating that Indian customers wanted to ‘ touch and feel’ whatever they buy . Here are a number of challenges that the company came across in its long journey:
Supply Chain and Logistics
In order to procure products from thousands of sellers, maintain inventory and ensure timely delivery, an effective supply chain and logistics network was the first challenge that Flipkart had to endure.
Reverse logistics is still a major issue for the company as more than 15% of shipments are returned by customers for a number of reasons. These bring huge losses to the company.
Managing Inventory
Flipkart has major warehouses across many cities, especially metropolitan areas , such as Bengaluru, Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, Delhi, Noida, and many other cities. Furthermore, they have small regional distribution centres in over 600 locations. With Flipkart’s “F-Assured” program, you can expect to get quality products delivered as the company practices strict quality checks before shipping any item from its warehouse.
Cash On Delivery Issues
COD does have many benefits for customers, but it indeed puts burden on e-commerce firms such as Flipkart. Many customers return the product without paying; and the company ends up losing all the money spent on procuring, storing and shipping the product. That is why prepaid payment options are always favourite among sellers listed on Flipkart.
Managing vendors and Logistics Provider
Managing lakhs of sellers on a platform is a herculean task in itself. Added to that is the issue of managing all logistics service providers (LSPs), if the company is dependent on 3 rd party services. Flipkart, however, has its in-house logistics company, named E k art, which ensures smooth and on-time deliveries.
Funding Issues
For any startup to prosper, a continuous flow of funds is a must. These funds not only aid improving existing services and facilities but also help the companies to bring ne w, innovative ideas to reality. Fortunately for Flipkart, there hasn’t been any shortage of funds, as seen in the timeline mentioned above.
Tough Competition from rival Amazon India
When Amazon entered the online shopping market in India in 2013, many exp erts feared that it may attract Flipkart’s loyal customers with great service, offers, international brand value , video streaming services and no shortage of funds. However, despite Amazon being a threat, Flipkart is still the largest online retailer in India as of 2019 with a market share of 31.9%, while Amazon India is following closely with a share of 31.2%.
The festive season in India often becomes a hot battleground for these two giants as they offer great deals to customers in the form of Flipkart Big Billion Days and Amazon Great Indian Festival.
Changes in Leadership
Co-Founder Sachin Bansal quit as the CEO of Flipkart in 2016, presumably due to performance-oriented issues. He was succeeded by Binny Bansal as the former took over the position of Executive Chairman.
In the year 2017, Kalyan Krishnamurthy took charge as the new CEO of Flipkart. He was previously an executive in Flipkart investor, Tiger Global. Upon Krishnamurthy’s appointment, Binny Bansal became CEO of the entire group which includes portals such as Myntra-Jabong, PhonePe and logistics company Ekart.
Flipkart bought online apparel portal Myntra for roughly $300 million in the year 2014. Two years later, they acquired online fashion retailer Jabong in a deal worth $70 million.
The same year Flipkart acquired digital payments startup PhonePe. It also acquired Ebay India in exchange for an equity stake . Ebay also agreed to make a $500 million investment in its business before handing it over to Flipkart in 2017.
The Flipkart reward program – Flipkart Plus
Whenever you shop on Flipkart, the company rewards you with 2 Super Coins for every 100 rupees spent. As soon as you collect 200 Super Coins, you can use them to become a plus member – and the best part is that the coins will not be deducted. You can use these coins to get heavy discounts on Flipkart products and other products and services offered by partner companies. With Flipkart Plus membership, the company offers you the following benefits:
- Free and Fast Delivery
- Early access to big billion day sales
- Redeem coins for rewards
- Superior customer support
Failures are meant for growth. If a company does not embrace its failures as much as its successes, they are bound for long-term loss. Flipkart too has had its fair share of failures, which have been listed below:
Flipkart tried to get into the online music streaming business in 2011. For this purpose, they acquired a digital content platform named Mime360. Flyte was launched in the year 20 12; however, with tough competition from existing portals offering free services and the problem posed by piracy, Flyte had to shut down in 2013.
Before Flipkart acquired PhonePe, it tried experimenting with a payment gat eway named PayZippy in 2013. The project failed miserably as the payment gateway was unable to bring merchants on-board. It was shut in 2014.
Going A pp-only for mobile users
In order to push mobile users to download their apps, Flipkart blocked them from accessing their website and prompted them to download the app. The move was apparently backfiring and therefore Flipkart had to reinstate the mobile website.
If you look closely at the journey of India’s home-grown e-commerce giant Flipkart , you will see that the company never lost faith in its investors and customers. Despite tough competition from arch rivals Amazon, the company has been going strong despite many major changes in leadership in the past few years.

E-commerce has become a huge part of our daily lives. Owing to the number of job opportunities and huge business scope that the sector provides, every individual should take up a course in e-commerce marketing .
Thanks for reading 🙂

For Queries, Feedback & Assistance
Ciim online support, 9:00am - 7:00pm, for admissions & career counselling, call back request.

- Our Trainers
- Student Reviews
- Online Payment
- Online Registration
- Get A Free Class
- Placements Gallery
- Life at CIIM
- Apply for Franchise
- Hire From Us
- Become Trainer
- Scholarships
Refer & Earn
- For Students
- For Teachers
- For Individual
Digital Marketing Courses
- Master in Digital Marketing
- Diploma in Digital Marketing
- Advanced Digital Marketing Certification
- Digital Marketing Foundation Course
- Online Advanced Digital Marketing Certification
- All Courses
Short Courses
- Paid Ads (Google, Facebook) Specialist
- Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) Specialist
- Social Media Marketing Specialist
- Ecommerce Marketing Specialist
- YouTube Marketing Specialist
- Affiliate Marketing Specialist
- Email Marketing Specialist
- Content Writing Specialist
- Google Adsense Specialist
- Amazon Marketing Course
Digital Marketing Courses Across India
- Himachal Pradesh
- Kurukshetra
- Yamunanagar
- Dharamshala
- Bahadurgarh
Digital Marketing Courses Across World
- Umm Al Quwain
- Ras Al Khaimah
Corporate Training Courses
- Corporate Training
- Educational Institutions
Quick Links
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Get Direction

Apply Before April 27, 2024
To get scholarship of up to.

- Pre-Recorded Courses
- URL Shortener Tool

Case Study: Flipkart’s Digital Marketing Strategies [Download PDF]
- February 20, 2024

Table of Contents
Flipkart is a leading e-commerce business that has become one of the known names in Indian households.
They have a strong hold on their marketing strategies and are an example for many marketers.
Flipkart case study will focus on its digital marketing strategies and how they have been effective in increasing its sales and customer base.
The company’s history, website, social media, SEO and other strategies will be discussed in detail.
About Flipkart
The history of Flipkart is a fascinating one. The company was founded in 2007 by two former Amazon employees, Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal .

The company was started with the aim of providing a better online shopping experience to Indian consumers.
The company has since then overgrown and is now one of the leading e-commerce companies in India.
It is an Indian private limited company with its headquarters in Bangalore and Singapore incorporation.
Before branching out into other product categories like consumer electronics, fashion, household staples, food, and lifestyle goods, the company initially concentrated on online book sales.
Flipkart: Brand Overview
Why should marketers study flipkart’s digital marketing strategies.
Flipkart can be considered one of the leading e-commerce platforms in India.
While digital marketing is crucial for every business – it is of even more importance for eCommerce brands.
Flipkart has its A-game in almost every field of digital marketing.
Here are some things special to Flipkart that marketers can take inspiration from .
We are all gradually integrating virtual and augmented reality into our lives, and we have already observed the influence and application of filters by businesses on Instagram Stories.
When it comes to embracing new technologies, Flipkart is constantly prepared. By including VR in the Big Billion Sale Campaign, Flipkart found the ideal time window to capitalize on the technology.
Undoubtedly, the Big Billion Day campaign significantly contributed to Flipkart’s marketing success, and they used cutting-edge VR technology to achieve the aim far more successfully.
The promotion was started as Full Moon Day drew near because it is considered auspicious and intimately related to the Indian holiday calendar.

The audience was impressed and fascinated by this campaign because it was unlike anything they had ever seen before. It brought Flipkart 5 million views and a CTR of 2%.
Celebrity endorsements
Flipkart is renowned for its partnerships with other businesses. Additionally, it frequently uses well-known people and celebrities for its promotion.
Every year, Flipkart continues to collaborate with various well-known public figures from around the globe.
Their most well-known endorsement campaign to date was centred around Ranbir Kapoor and Alia Bhatt and was dubbed “IndiaKaFashionCapital.”

Relevant and Relatable.
With a variety of entertaining activities, Flipkart keeps its audience interested. However, they also make sure to sprinkle in a few current trends.
For instance, numerous items have trended and became popular during this lockdown, and they went on with the trend to stay relevant and relatable.
Flipkart’s Digital Marketing Strategies & Case Study
Flipkart’s social media marketing strategies , flipkart’s instagram marketing strategies.
Flipkart has over 3.3 million followers on its page and has posted 4,260 posts to date (as of November 2022). On average, they post up to three times every day.

Their Instagram content is majorly for engagement (through posts and majorly reels) , and has occasional posts centring around their products. The product-related posts don’t sell their products directly but are rather subtle.
Here are a few examples of their product-related posts

Here is one of their engagement posts that takes up most of the space on their feed
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Flipkart (@flipkart)
They even post contests periodically to get more engagement and increase their followers.
Finally, they constantly post relatable, funny or trendy reels to garner more engagement.

Flipkart’s Instagram engagement rate
Flipkart’s Instagram engagement rate is 0.04%, with an average of 1,289 likes and 52 posts as of November 2022.

Flipkart’s Facebook Marketing Strategies
Flipkart’s Facebook account has over 10 million followers and more than 9 million likes.

Flipkart has separate category-focused Facebook pages for each category, like books, fashion, games, and so on. These pages are mostly used for building engagement with their fans. Flipkart also uses Facebook as a way to acquire customers by promoting their deals and offers.
These are the Highlights of Flipkart’s Facebook Account
- Posts are based on the seasons, holidays, or birthdays.
- Enquiries from customers and updates on new products.
- Customer complaints receive an average and inconsistent response.
- They conduct competitions and gamification.
- They also have a separate dedicated customer assistance tab.
- The acquisition and engagement of customers are emphasised.
Overall, Flipkart posts the same content as it does on Instagram.
Flipkart’s Twitter Marketing Strategies
Flipkart has over 2.8 million followers on its Twitter as of November 2022.

These are the Highlights of Flipkart’s Twitter Handle
- They post updates using eye-catching videos and images of new products, deals, and discounts.
- Exclusive channel for tech news at Flipkart.
- Running a contest centred on products or services, such as Flipkart First or AcerA1
- On average, 2-3 products are launched or offered every day.
- Exclusive Channel for Support from Flipkart.com.
- Flipkart provides channel-based exclusive offers.
- 24-hour customer service line
- Instantaneous Connect.
- The inquiry has a real-time response.
Flipkart’s Twitter Engagement Rate
Flipkart’s Twitter engagement rate is 0.02%, receiving an average of 407 likes and 237 retweets per tweet as of November 2022.

Flipkart’s SEO strategies
Flipkart uses a mix of organic and paid means to get more traffic to its website and increase its ranking to visible.
Here are the different SEO strategies it uses and the success it has achieved using the methods strategically.
Flipkart, no doubt, is in the front seat regarding SEO. They have an “amazing” score for all the different factors that affect the website’s ranking.
Flipkart has over 22,811,205 organic keywords , 236,950,566 of just organically monthly traffic , a domain authority of 90 , and 70,895,150 backlinks .

www.flipkart.com
Obtaining such huge numbers is not an easy task, which is why marketers can learn a lot from how Flipkart’s strategies and optimise its website.
Flipkart’s Traffic and Engagement Analysis
With a total visit of over 237.4 million, traffic has decreased by 17.87% in October compared to last month (Desktop).

These are the different ways through which Flipkart is on its best game
- In order to ensure that the proper audience sees their advertisement, Flipkart’s SEO approach focuses on long-tail keywords or phrases rather than single words.
- Flipkart’s SEO methods aim to build a user- and mobile-friendly website .
- Flipkart looks at users’ most popular queries, picks the top ones, and turns them into URLs for web pages . To ensure that their website ranks, Flipkart uses a pretty effective method.
- The speed of the website is a crucial component of search engine optimization. Your SEO health depends on your website’s speed. The percentage of visitors leaving your site dramatically rises for every additional 0.5 seconds it takes to load.
- Flipkart offers a high-return affiliate program for its users to promote its products through unique referral links. It’s an amazing money-making opportunity to turn your influence into income with every purchase made through your recommendations.
Paid search
In order to ensure that the proper audience sees their advertisement, Flipkart’s SEO approach focuses on long-tail keywords or phrases rather than single words. Simply said, Flipkart’s SEO methods aim to build a user-friendly and mobile-friendly website.
These are some of Flipkart’s recent ads targeting different categories & relevant audiences.

Google Ads are a tool used by e-commerce platforms to draw traffic to their site by showing up in other platforms’ search results.
Getting your Google ad text is essential, with Amazon providing neck-to-neck competition.
In order to remarket to customers who add items to their carts or just wish lists, Flipkart employs third-party platforms to run adverts and advertise on other websites.
The top publishers sending traffic to flipkart.com.
Currently, there are 180 publishers referring visitors. That’s the result of a proper advertising strategy.

Flipkart uses the Pixel s to retarget users who have clicked on one of its Google ads across various social media platforms.
Flipkart’s Target Audience and Remarketing Strategy
Any marketing and advertising method known as “remarketing” involves reconnecting with potential customers who have already visited a retailer’s website.
Remarketing already existed before the invention of the Internet, but its application has moved from offline to online, where it is much more advantageous and inbound.
In most cases, people who visit internet portals do not finish their purchases.
Remarketing involves showing these potential customers advertisements that encourage them to buy across several digital channels.
Flipkart’s audience is 66.98% male and 33.02% female. The largest age group of visitors are 25-34 years old.

A sizable portion of Flipkart’s consumer base browses the products and checks the product details. However, not every product that customers view ends up being purchased.
Even hours after first viewing some products, shoppers frequently return to them. When shoppers leave items in the shopping basket, it shows a strong intent to purchase.
According to a survey, 30 of 100 online shoppers add items to their shopping carts.
That is 30% of customers who are considering making a purchase. That is a substantial sum. However, just 3% of these customers ultimately purchase the product.
About 27% of these customers simply stop using the merchandise. Remarketing is used to reach this audience with advertisements.
Flipkart’s Top Digital Marketing Campaigns
Flipkart has repeatedly rolled out digital marketing strategies that have impressed us all. Let’s discuss a few of their strategies that impressed us the most.
1. #LeadLikeHer
Flipkart launched a campaign to stand by what it believes – Fashion should be affordable and accessible to all.
The 10-week campaign features ads on Television, YouTube and social media platforms to reach a wider audience of all age groups.
Through this campaign, Flipkart establishes itself as a brand for everyone and the perfect destination for all with a love of fashion.
This campaign was an extension of their previous campaign that went by the name ‘Be trendy, always.’
A distinctive factor of their recent campaign is how they have featured kids in their advertisements.
2. #IndiaKaFashionCapital
One of its most recent campaigns, #IndiaKaFashionCapital, features Alia Bhatt and Ranbir Kapoor, assuring their customers that Flipkart is the best place for shopping.
Over the years, Flipkart has served customers with best-in-class services thanks to its deep understanding of their needs. They promise their customers to offer a fashionable lifestyle that is easily accessible and value-driven.
3. #BigBillionDays
The #BigBillionDays is one of the most successful campaigns introduced by Flipkart.
During the Big Billion Days sale, Flipkart received over 666 million visits, with over 52% of those coming from Tier III and higher locations.
The Filpkart #BigBillionDay ad in 2014
The Filpkart #BigBillionDay ad in 2021
The Filpkart #BigBillionDay ad in 2022
Amazing 110 orders were placed each second on the platform.
Flipkart saw 1.5 times as many sellers engage in transactions as it did the previous year, and over 35% of sellers experienced 3 times as much growth in sales.
Conclusion
As you can see, Flipkart has a website to advertise its products and brand. Want to create similarly successful plans?
Learn how to develop powerful digital marketing strategies for your company by enrolling in the online digital marketing course powered by AI & dual certification provided by Digital Scholar.
Enrolling in this course is a good idea if you want to learn everything there is to know about digital marketing and how to use it for your own company. Visit their website at www.digitalscholar.in to learn more about them.
Are you prepared to improve your company’s reputation? Now is the perfect time to enrol in an online digital marketing program!
Which Flipkart advertising effort do you prefer? Enter your feedback in the field provided here.
Q. What are the key elements of an effective ecommerce marketing strategy?
Ecommerce marketing strategy is a collection of steps for creating and carrying out an online selling plan. The strategy searches for and attracts clients who fit a specified demographic and persuades them to make purchases. It has a psychological and demographic focus.
Q. What are the strategies used by Flipkart?
Flipkart uses multiple channels for its marketing campaign, its major traffic comes from targeting its competitors & retargeting. Flipkart does not miss any special moment & comes with special offers & sales to attract a new set of audience.
Q. What are the top 7 most effective e-commerce strategies?
The top 7 e-commerce strategies that are the most effective way to drive conversions include offering free shipping, offering a return policy, advertising, creating landing pages, retargeting, customer support, secure checkout process.
Written By Digital Scholar
Digital Scholar is a premier agency-styled digital marketing institute in India. Which offers an online digital marketing course and a free digital marketing course worldwide to elevate their digital skills and become industry experts. Digital Scholar is headed by Sorav Jain and co-founder Rishi Jain, who are pioneers in the field of digital marketing. Digital Scholar’s blogs touch upon numerous aspects of digital marketing and help you get intensive ideas of different domains of digital marketing.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts

10 Best SEO Competitor Analysis Tools To Improve Your Traffic in 2024 [Free & Paid]

What is LinkedIn Pulse? A Complete Guide

Top 10 Pros and Cons of Digital Marketing in 2024

20 Best Income Opportunities in The World To Try in 2023
- Español – América Latina
- Português – Brasil
- Tiếng Việt
Flipkart triples time-on-site with Progressive Web App

Flipkart, India’s largest e-commerce site, decided to combine their web presence and native app into a Progressive Web Application that has resulted in a 70% increase in conversions.
In 2015, Flipkart, India’s largest e-commerce site, adopted an app-only strategy and temporarily shut down their mobile website. The company found it harder and harder to provide a user experience that was as fast and engaging as that of their mobile app. But then, Flipkart decided to rethink their development approach. They were drawn back to the mobile web by the introduction of features that made the mobile web run instantly, work offline, and re-engage users.
Key insights
- Users time on site with Flipkart lite vs. previous mobile experience: 3.5 minutes vs 70 seconds .
- 3x more time spent on site
- 40% higher re-engagement rate
- 70% greater conversion rate among those arriving via Add to Homescreen
- 3x lower data usage
Download PDF Case study
Flipkart Lite
They soon began building Flipkart Lite, a Progressive Web App that combines the best of the web and the best of the Flipkart native app. It leverages new, open web APIs to offer a mobile web experience that loads fast, uses less data than before, and re-engages users in multiple ways. Users visit via their browser and find a fast app-like user experience. When they come back, it loads nearly instantly, even on flaky networks. Users can choose to add the site to their homescreen with just two taps, making it easier for them to come back. Amar Nagaram, an Engineering Director at Flipkart shares, "We know that everyone needs to build mobile-first experiences. With Flipkart Lite, we've developed a powerful, technically-advanced web app that performs as well as our native app. We now feel we have the best of both worlds."
A fast and streamlined site
With 63% of Flipkart Lite users reaching the site via a 2G network, a fast user experience was essential. To decrease load times, Flipkart added service workers and streamlined the site to help consumers quickly reach the product they are looking for. Users can even continue to browse categories, review previous searches, and view product pages—all while offline.
Taking advantage of the web's low friction
Reaching a broad set of users is important for Flipkart. With Flipkart Lite, users are one click away from accessing content and many new users are first-time internet users. In addition to easy access, Flipkart Lite requires less data. A key metric for Flipkart is tracking data usage to complete first transaction: when comparing Flipkart Lite to the native app, Flipkart Lite uses 3x less data. Nagaram continues, "Having a strong and engaging mobile website means we’re no longer turning away potential shoppers who don’t want to use data or space to download an app."
Bringing users back with home screen icon
Flipkart wanted to be able to re-engage with mobile web users just as they would with mobile app users.
The company implemented an "Add to Home Screen" prompt. Now, 60% of all visits to Flipkart Lite come from people launching the site from the homescreen icon. Add to Home Screen also delivers high-quality visits, with customers converting 70% more than average users.
These two activities alone resulted in engagement numbers that were 40% higher than before.
Building for future success for the evolving online shopper
Flipkart will continue using progressive web technology to reach their evolving online shoppers. Nagaram concludes, "Flipkart Lite has enabled us to find some of our highest-value customers. We will continue to expand progressive web app technology across all of our platforms, investing significant resources to maximize the potential scale. We truly believe that this is a new way to experience mobile and we’re just getting started."
Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License , and code samples are licensed under the Apache 2.0 License . For details, see the Google Developers Site Policies . Java is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Last updated 2016-03-28 UTC.

- Development
- Digital Marketing
Flipkart Case Study: Marketing and Advertising Campaigns
Flipkart is an e-commerce Indian-based online marketplace, founded in 2007 by two friends Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal . The fact is that Binny Bansal is a former employee of Amazon. Sachin had referred Binny to Amazon, which till then had been working in the company for more than a year.
When Flipkart was launched, it was initially aimed at selling books before expanding into other product categories such as consumer electronics, fashion, home essentials and groceries, and lifestyle products.
According to Redseer, in October 2023, Flipkart had a 64% market share of India’s e-commerce industry.
Flipkart, currently with a strength of 33,000 employees, has 295 million registered users and over 12 million daily visits. Flipkart’s technology has enabled it to deliver 8.5 million shipments per month – and that number is increasing year on year.
According to Crunchbase, The total funding amount to be received by Flipkart by 2023 is US$ 12.9 billion.
On This Page:
Flipkart: Warehousing & Shipments
Logistics is one of the most important aspects of any successful e-commerce platform. Flipkart ships more than 100000 items in a day which makes managing the logistics an overwhelming task for the company.
Also, the cost of delivery is paid by the company itself, making logistics a financially complicated issue. Hence in order to successfully manage the logistics. Flipkart uses its in-house logistics known as eKart‟ (EKL).
The e-commerce company created E-Cart as a personal brand in April 2009 to serve the B2C side of WS-Retail, Flipkart and currently reaches consumers in around 150 cities.
eKart currently provides services like Delivery Logistics, Reverse Logistics and cash on Delivery. It also provides customer support and technology integration for order tracking, customer notifications, and reporting.
Digital Marketing Strategies
Let’s look at how Flipkart used digital marketing to promote its products and services.
Flipkart mostly targets Indians who use the internet and don’t have time to visit offline shopping stores. Although its target audience is scattered across different market segments as consumers of all demographic backgrounds can find products of interest to them, 85% of its audience is between the age group of 16 to 55 years.
Search Engine Optimization
If we talk about organic traffic, Flipkart has achieved tremendous results through search engine optimization.
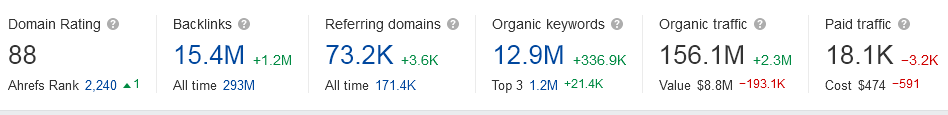
Flipkart is India’s largest online retailer and has worked hard to optimise its website for search engines. Flipkart appears in the top 5 results for every product search, and this is possible because Flipkart has invested heavily in SEO.
Social Media Marketing
Flipkart continues to win over the audience on social media, duly manned by celebrity influencers apart from its roster of brand ambassadors from time to time. They often run campaigns for specific sales, opportunities, and brands.
- Flipkart gets 79.08% of website visits from Youtube.
- From Facebook 7.71%.
- 3.99% of People prefer to share Flipkart products on WhatsApp with friends and relatives. which is a sign of brand management and trust in Flipkart.
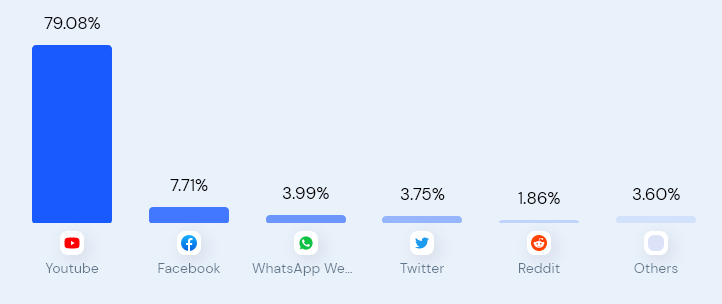
Video Advertisement on YouTube
As the data mentioned above shows that Flipkart gets the most traffic from YouTube. So now have to look at and understand the Flipkart video advertising strategy.
Celebrities Marketing Campaign
Flipkart is known for its collaborations. It also makes particular investments in star power and celebrity marketing. Flipkart keeps on collaborating with various famous personalities year after year.
One of the memorable and recent collaborations was with Ranbir Kapoor and Alia Bhatt on “#IndiaKaFashionCapital”.
Television Ads
Flipkart and its subsidiaries – Myntra and PhonePe – have seen a significant increase in their television commercials since August, when they were acquired by US retail giant Walmart. The last time Flipkart launched a branding campaign with the tagline ‘Ab Har Vish Hogi Puri’ was when it spent massive marketing dollars to create brand awareness.
Affiliate Marketing
Affiliate marketing is commission-based marketing by which a person can earn rewards in the form of commission for marketing the products of another person or company.
Flipkart undertakes the responsibility of marketing its products to third parties known as affiliates and shares a portion of the profit on the sale of the products.
Affiliate programs of e-commerce portals like Flipkart and Amazon are some of the legitimate ways to earn money online in 2022. The Flipkart portal provides almost everything needed for a common man.
From beauty to baby care products to fashion to electronics and from beauty to baby care products, everything can be found on this online portal. All you need is good traffic to your website or blog.
Flipkart vs Amazon
The presence of two of the biggest brands in the Indian market has made the industry highly competitive. Since both have entered the private-label business to increase sales. Both introduced unique features and value-added services and expanded into specific areas to compete with their businesses.
Although Amazon is a world-recognized brand but in India, Flipkart is always 1 step ahead of Amazon.
SWOT Analysis: Flipkart
- The supply chain
- Strong brand value and brand awareness
- Advertising and promotion
- Strategy acquisition
- late delivery
- IT Infrastructure
Business Model of Flipkart
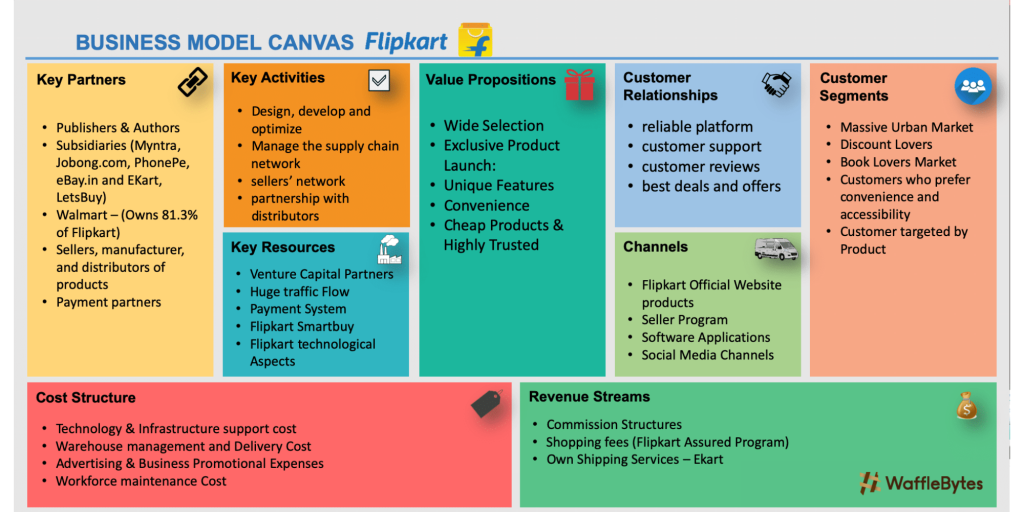
Flipkart, which has redefined shopping in India, operates on a B2C (business-to-consumer model). Flipkart started with a direct-to-consumer model selling books and some other products, before turning to a marketplace model that connects sellers and buyers and expands its catalogue.
Today, it sells everything from smartphones to clothes to furniture to refrigerators to FMCG accessories – and yes, books too.
Flipkart claims to have millions of sellers from across India who list their products in over 80 categories. The average consumer may not care about who the seller is and the relationship he has with Flipkart. Whereas the seller who hasn’t exactly reached out to the customer can now do so thanks to Flipkart’s platform. To facilitate this transaction and fulfil the order, Flipkart charges different percentages as the commission fees from the seller.
List of Flipkart Subsidiaries
Here is the list of 10 Flipkart subsidiaries with a short description and the date of acquiring these companies.
- Myntra – It’s another ecommerce online store acquired by Flipkart in May 2014.
- PhonePe – is an Indian digital payment and financial technology company that Flipkart acquired in April 2016.
- Cleartrip – This is a travel booking search engine globally famous for its incredible service. Flipkart acquired 100 per cent of Cleartrip’s shareholding in April 2021.
- Flipkart Health – This is an online pharmacy, also known as SastaSundar. Flipkart acquired SastaSundar in December 2021.
- Ekart – is a logistics company that delivers 10 million orders per month. Flipkart acquired eKart in 2015.
- Shopsy – Like Flipkart, shopsy is another ecommerce platform that Flipkart acquired in July 2021.
- Flipkart Wholesale – This platform mainly focuses on B2B, in other words, WS retail. We have yet to learn the old name of this company, but Flipkart acquired it in 2012.
- Jeeves-F1 – Jeeves & F1, both part of the Flipkart Group of companies, are among India’s most prominent third-party neutral service providers offering comprehensive lifecycle management for various categories, including Mobility Consumer Electronics, Home Appliances, Furniture, IT & IT Peripherals, AV & Enterprise Solutions.
- Yaantra – is a single window stopover that caters to all smartphone queries, such as broken glass, water damage, software problem, power issue etc. with the best in the industry services. Flipkart Group acquired electronics ecommerce firm Yaantra in January 2022.
- ANS Commerce – is India’s #1 full-stack e-commerce enabler helping brands sell online. Flipkart acquired ANS Commerce in June 2022 to strengthen its e-commerce system via technological innovation.
In Conclusion
However, the situation is not as dire as it may seem. Flipkart’s magical Bansal touch may have disappeared, but its collective expertise and experience to deal with the Indian audience live on. The quick solution to tackle COVID-19 and offering essential items to the cities by Flipkart is commendable. However, e-retailers should seek to gain their market share by winning the trust of their customers rather than money.
Thanks for visiting Waffle Bytes Blog !
Waffle Bytes
Ecommerce website development cost in india: a reality check, 8 tips for getting 100k views on reels., you may also like, canva business model: how canva makes money., candy crush: marketing strategy with psychological appeal, dream11 business model: revenue and operations, leave a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
WhatsApp us
- Deutschland
- Asia, Australia & New Zealand
- Europe, Middle East & Africa
- United States & Canada
- Latinoamérica
How Flipkart pioneered a new digital approach to position itself as “India Ka Fashion Capital”
To quickly resonate among shoppers as one of India’s premier online fashion destinations, Flipkart went beyond its usual even-paced strategy to reach a wide audience. The brand took a YouTube-led approach to make an immediate impact online, resulting in 100M users reached in the first 10 days of the campaign and a near 10% lift in consideration by the end.
Last year, if you’d asked most Indian consumers about Flipkart , they’d likely have told you about its broad array of consumer electronics at competitive prices. Behind the scenes, however, fashion was actually one of Flipkart’s best-performing categories. In 2018, the brand set its sights on matching up reality with perception by aligning Flipkart Fashion as India’s online fashion capital. This was no easy task given the highly competitive market, but the brand recognized an opportunity ripe for the taking.
To establish its identity as “India Ka Fashion Capital,” Flipkart knew it needed to grab the attention of new fashion shoppers before their go-to stores were set in stone.
How ripe? By 2020, online sales for products including apparel and accessories in India is estimated to reach $40-45 billion . Improved infrastructure across India's non-metro cities has opened Flipkart’s doors to a wider audience of online shoppers. But the brand was still challenged by a fundamental shopping behavior: frequent shoppers typically buy from their favorite retailers. To establish its identity as “India Ka Fashion Capital,” Flipkart knew it needed to grab the attention of new fashion shoppers before their go-to stores were set in stone.
Flipkart is known to take experimental approaches to its campaigns , and this time was no different. Rather than steadily building up its reach over time, the brand quickly cast a wide net online from day one of the campaign, focusing on Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities where consumer growth was strong and steady. Along with immediately boosting awareness, this strategy gave Flipkart early insights from digital that helped personalize its approach in the following weeks. With Flipkart Fashion fresh on consumers’ minds, the rest of the campaign eventually drove impressive lifts in consideration and interest.
Using digital to reach and nurture a wider audience
Flipkart kicked off its “India Ka Fashion Capital” campaign with a bang: the brand complemented its TV spot with a variety of YouTube ads to maximize its reach while running search and dynamic display ads in support. This ensured that Flipkart Fashion would be visible to consumers across multiple touchpoints, and using audience insights garnered in the first two weeks helped the brand hone its messaging to be more relevant at each stage of the journey.
Flipkart’s video creative played off its previous “kidults” (kids as adults) campaign with a twist: the first ads teased the addition of two leading Bollywood celebrities, Shraddha Kapoor and Ranbir Kapoor .
On YouTube, Flipkart was able to use affinity audiences to reach shoppers interested in fashion apparel and then follow up with bumper ads (featuring both Shraddha and Ranbir ) on fashion-related content. After the 10-day blast period, the brand tailored its search and dynamic display ads throughout the rest of the campaign to reconnect with consumers who showed interest in Flipkart Fashion.
Striving for early impact to make a lasting impression
Flipkart’s front-loaded media strategy helped the brand reach more than 100 million users on YouTube alone in the first 10 days, whereas the brand’s previous Flipkart Fashion campaign took a month to do the same.
Comparing cumulative reach over time
Digital blast strategy
Traditional strategy
Think with Google
Share this page.
But the best result wasn’t just reaching millions of shoppers. By making an early connection, the brand was in a better position to develop meaningful, long-term relationships with its audience. And once the full campaign had finished, it had clearly resonated beyond initial awareness: Brand Lift studies showed results that exceeded Flipkart’s past campaigns across the board.
Flipkart revealed that brands that go heavy on digital to make an early impression on a wide audience can drive even more impact with their campaigns down the line. Best of all, it showed how better results can arise from achieving the same online reach in a shorter period of time. “When we experiment and break barriers with our marketing, we’ve always seen great results,” said Kunal Dubey, Flipkart’s director of marketing. “This year’s Flipkart Fashion campaign was no different. Frontloading our digital spend and using our audience signals to optimize over time turned out to be more effective than we could’ve ever imagined.”
Others are viewing
Marketers who view this are also viewing
How Nestlé Taiwan used data-driven attribution to reach moms-to-be
The philippines' summit media achieves 7x roas for airline advertiser through premium content and travel audience insights, how idom tailored its campaigns to reach high-value car buyers in japan, what brands can learn from india on personalized storytelling, how online video is empowering consumers in india to take action, youtube advertisers, focus on these 4 key drivers of roi, roohneet kaur, sources (1).
1 ComScore Video Multi-Platform, India, June 2018, 18+ population.
Others are viewing Looking for something else?
Complete login.
To explore this content and receive communications from Google, please sign in with an existing Google account.

Downloads > Case Studies
Case Studies
- Download 1080
- File Size 2.93 MB
- File Count 2
- Create Date May 26, 2022
- Last Updated March 21, 2023
The Economic Times daily newspaper is available online now.
Flipkart’s majority stake order drops out of zepto cart.
Ecommerce major Flipkart held talks with Zepto for a potential deal but the discussions fell through and are unlikely to be revived, said two people in the know of the matter.

Why is India no longer the top importer of Russian oil?

As crude prices rise, should we worry about India’s strategic oil buffer?

How this Advent PE-backed Indian firm is prepping to take on Chinese big pharma

When an INR5,000 crore corpus isn’t enough to refund Sahara investors their money

What Boeing’s long, choppy flight into whistleblower hell means for passenger safety

Twin tailwinds: Banning of Russian metal and Chinese revival, 5 metal stocks with an upside potential of up to 23%
Find this comment offensive?
Choose your reason below and click on the Report button. This will alert our moderators to take action
Reason for reporting:
Your Reason has been Reported to the admin.

To post this comment you must
Log In/Connect with:
Fill in your details:
Will be displayed
Will not be displayed
Share this Comment:
Uh-oh this is an exclusive story available for selected readers only..
Worry not. You’re just a step away.

Prime Account Detected!
It seems like you're already an ETPrime member with
Login using your ET Prime credentials to enjoy all member benefits
Log out of your current logged-in account and log in again using your ET Prime credentials to enjoy all member benefits.
You’re reading this story from ET newspaper.
Unlock epaper & other members-only benefits with etprime., new financial year offer: flat 20% off, enjoy reading for special offer, your current plan does not offer access to newspaper articles, upgrade to unlock complete access to exclusive stories, epaper & all market tools..
Exclusive Economic Times Stories, Editorials & Expert opinion across 20+ sectors
Stock analysis. Market Research. Industry Trends on 4000+ Stocks
Get 1 Year Complimentary Subscription of TOI+ worth Rs.799/-
Stories you might be interested in

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In 2018, Walmart acquired a 77% stake in Flipkart for approximately $16 billion. This deal valued the 11-year-old Indian e-commerce firm at $20.8 billion. Immediate Impact. The acquisition provided SoftBank Vision Fund with a profitable exit, as they had previously invested heavily in Flipkart.
The case study of Flipkart's marketing strategies highlights the potential for the future of e-commerce. About Flipkart: History and Leadership. Flipkart is a top online marketplace in India with a fascinating history. It was started in 2007 by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal. These founders made it a strong e-commerce player.
Equally giant competitors might threaten Flipkart's business but it will definitely continue to rule the E-commerce industry for decades to come. All this is because of the brilliant marketing strategy of Flipkart. If you liked this case study, on the marketing strategy of Flipkart then do share it with your friends.
This concludes the case study on the Business Model of Flipkart, now let's go through the final points of Flipkart. Conclusion Being India's largest e-commerce platform it operates on a B2C business model by providing services related to the online book store and some other products.
Abstract. Flipkart was launched in 2007 as an online platform for selling books by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal. Ten years later, the e-commerce company had 54 million active users and 100,000 ...
Two young alumni of IIT Delhi—Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal (not related)—while working at Amazon conceived of an electronic bookstore and ventured a start-up under the name of Flipkart with modest facilities of an office in a 2-Bed-room-Hall-Kitchen (2 BHK) residential apartment in Koramangala in Bangalore with just two computers and an overall investment of ₹400,000.
Flipkart is India's most popular e-commerce website, known for its innovative business model. Flipkart is the leading Indian eCommerce website founded by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal in 2007. The company is headquartered in Bengaluru, India. This Indian eCommerce store has brought a revolution to the Indian e-retail industry.
Flipkart was launched in 2007 as an online platform for selling books by Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal. Ten years later, the e-commerce company had 54 million active users and 100,000 plus sellers and had sold 261 million units. The founders had taken several steps to garner this growth, by making investments in technology, undertaking high ...
Mobiles. Flipkart Ads x realme 11 Pro: A Case Study in Precision Marketing. 04 JAN 2024. The mobile phone industry is a beacon of continuous evolution and innovation.
Flipkart Case Study- Business Model and Marketing Strategy. Welcome to our yet another blog, today we bring you yet another success story of a startup. When it comes to online shopping or e-commerce businesses, in recent years various platforms have evolved. Some of the most widely used sites for online shopping are Amazon, Flipkart, Myntra etc.
This case study examines the journey, strategies, and impact of Flipkart on the Indian market. Background: In the early 2000s, e-commerce was a nascent industry in India, with limited internet ...
Abstract. Flipkart is not an Indian company since it is registered in Singapore and majority of its shareholders are foreigners. Because foreign companies are not allowed to do multi-brand e-retailing in India, Flipkart sells goods in India through a company called WS Retail.
Helpline073473 92745. Flipkart Success Story and Case Study. Flipkart Success Story and Case Study - Launching a startup is perhaps every youth's dream these days, but only a few possess the right mindset, strength and courage to do so. If we ask you to name a few successful startup stories, we are sure that the names 'Flipkart ...
Read the case study of Flipkart's Digital Marketing Strategies and download pdf of amazing stats. It also makes significant investments in influencer marketing and celebrity endorsements. Bollywood is extremely popular in India, and Flipkart exploits this to promote its services and brand. February 20, 2024. 9,134 Views.
Download PDF Case study. Flipkart Lite. They soon began building Flipkart Lite, a Progressive Web App that combines the best of the web and the best of the Flipkart native app. It leverages new, open web APIs to offer a mobile web experience that loads fast, uses less data than before, and re-engages users in multiple ways.
Flipkart Case Study: Marketing and Advertising Campaigns. Flipkart is an e-commerce Indian-based online marketplace, founded in 2007 by two friends Sachin Bansal and Binny Bansal. The fact is that Binny Bansal is a former employee of Amazon. Sachin had referred Binny to Amazon, which till then had been working in the company for more than a year.
All events are going to explore this in this Flipkart Case Study Article. About Flipkart. Flipkart is the first Indian e-commerce company established in 2007 in Banglore by Sachin Bansal and Binny ...
By Team Flipkart Stories / February 15, 2022. WWF India's case study identifies Flipkart's practical solutions — sustainable packaging designs that led to a transformation in the Indian e-commerce ecosystem — and urges greater participation by private stakeholders and other members of the value chain to build a holistic, circular ...
By Team Flipkart Stories / April 26, 2022. In a case study documenting Flipkart's electric mobility journey, the World Business Council for Sustainable Development highlights the steps and possibilities for other e-commerce companies to adopt and scale electric mobility, stressing the commercial and technical viability of complete ...
Using digital to reach and nurture a wider audience. Flipkart kicked off its "India Ka Fashion Capital" campaign with a bang: the brand complemented its TV spot with a variety of YouTube ads to maximize its reach while running search and dynamic display ads in support. This ensured that Flipkart Fashion would be visible to consumers across ...
Oct 18, 2023. Introduction. This UX case study examines the user experiences of two leading e-commerce platforms, Amazon and Flipkart. Both platforms offer a wide range of products and services ...
File Action; Flipkart-WBCSD-Study.pdf: Download: WWF-Case-Study-on-Flipkart-Group.pdf: Download
A report by the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD), revealed that 100% electrification of e-commerce delivery fleets is possible in India. This report — 'Advancing electrification of e-commerce deliveries in India - A Flipkart case study' — recognizes Flipkart Group as an electric mobility trendsetter in India.
Ecommerce major Flipkart held talks with Zepto for a potential deal but the discussions fell through and are unlikely to be revived, said two people in the know of the matter. Zepto, a top player in the fast-growing quick commerce segment, is understood to have opted for a financial round over a strategic sale, these people said on condition of anonymity as the talks were private.