

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
✍️Essay on Natural Resources: Samples in 100, 150 and 200 Words
- Updated on
- Nov 2, 2023

Wondering about how the resources provided by our planet Earth are depleting? Well, that’s true. We have come to the stage where we should start working towards saving our planet. We humans have used our resources in a humongous quantity. Therefore, it’s time we start working towards saving our planet for our future generations. Today we will provide you with a few samples of essay on natural resources which will help you write on this topic easily.
Table of Contents
- 1 What are Natural Resources?
- 2 Types of Natural Resources
- 3 Essay on Natural Resources in 100 Words
- 4 Essay on Natural Resources in 150 Words
- 5 Essay on Natural Resources in 200 Words
What are Natural Resources?
Natural Resources are resources which are present in nature independent of human actions.
These are the resources that are created naturally by the environment, without any help from humans. Soil, stone, sunlight, air, plants, animals, fossil fuels, etc. are all natural resources.
In simple language, natural resources are naturally occurring materials which are useful to humankind. They can also be useful in a variety of ways such as in technological, economic or social contexts. These resources include building, clothing materials, food, water, fertilisers and geothermal energy. Natural resources were traditionally within the purview of the natural sciences.
Also Read: Essay on Save Environment: Samples in 100, 200, 300 Words
Types of Natural Resources
Speaking of the type of natural resources, there are mainly two types of natural resources. These include Renewable and Non-renewable resources.
Renewable Resources: These are those resources which are endlessly available to humans for several uses. These resources are trees, wind, and water.
Non-Renewable Resources: These resources are available to humans in infinite quantities as they are not renewable and their supply may eventually run out. Minerals and fossil fuels are a few examples.
Also Read: Essay on the Importance of the English Language for Students
Essay on Natural Resources in 100 Words
Natural resources are parts of the natural world that are useful to humans. Renewable resources are those that can be swiftly replenished, these include soil, water, and air., Non-renewable resources are those that need time to recover, such as minerals, oil, natural gas, etc.
One should note that the survival of all life on Earth depends on natural resources. However, the usage of natural resources in excess use can cause ecosystem disruption. Many nations are taking action these days to protect their natural resources. Natural resources shouldn’t be used for purposes outside our needs. In order to preserve non-renewable resources, we should utilise renewable resources more frequently than non-renewable ones.
Essay on Natural Resources in 150 Words
The organic aspects of nature that contribute to our way of life are known as natural resources. For survival, we rely on natural resources. Natural resources include things like air, water, soil, minerals, crops, etc. Resources like minerals, oil, and other resources are found in non-living organisms and take eons to regenerate.
The distribution of natural resources is not even. Resources like these are also the primary driver of international trade relations for many nations. However, with time, these natural resources have now been overused by the human mankind beyond their limits.
However, the unrestricted exploitation of natural resources is a challenge for all nations these days. To control this, a lot of nations are emphasising garbage recycling and employing more renewable resources than non-renewable ones.
Sustainable development is the use of natural resources for current requirements without wasting them while keeping an eye on the future. It refers to the wise use of natural resources without sacrificing what coming generations will need.
Also Read: Essay on Unity in Diversity in 100 to 200 Words
Essay on Natural Resources in 200 Words
Natural resources are materials found in the environment that humans use to survive. From the very start, humans have been dependent on these resources. While some of these resources can be restored more rapidly than others, some require more time. Resources like sunlight, water, air, and other renewable resources are readily available and have higher recovery rates than consumption rates.
On the other hand, the formation and processing of non-renewable resources, such as minerals, oil, and natural gas, take a long time. Even the usage rate of these non-renewable resources is higher as compared to the renewable resources. While some natural resources are used immediately, others must first undergo processing.
Even while renewable resources are available in huge quantities, they should also be used responsibly. Both renewable and non-renewable resources require time to be created and processed. Therefore, it is very important for humans to use these resources in a limited quantity and leave some for future generations.
With time, humans are using these resources excessively. With the ever-increasing population, humans have already created a huge impact on the environment. To begin, humans are continuously polluting the air, water and noise. Buildings are being constructed on more land. The land is becoming less valuable in this way. Humans are soon becoming the biggest reason behind depleting natural resources, such as land, water, and air.
Therefore, we mustn’t undervalue these resources. The moment has come for us to recognise the importance of using these resources sustainably.
Related Articles
Natural Resources are substances which are naturally obtained from nature. Here are the 5 natural resources: Coal, Oil, Natural Gas, Sand, Gems, and Metals.
Renewable resources are natural resources that can be replenished or regenerated at a rate comparable to the rate at which they are consumed or harvested. For example: Solar energy, Wind energy, Biomass, Geothermal energy, etc.
Conserving and saving natural resources is essential for sustainable development and the preservation of the environment. Here are some easy tips to save natural resources: Implementing the 3Rs in daily life; Adopting energy-efficient practices such as using energy-saving appliances; Reducing water wastage by fixing leaks, using water-efficient appliances, and practising mindful water usage in daily activities, etc.
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our essay-writing page and follow Leverage Edu !
Malvika Chawla
Malvika is a content writer cum news freak who comes with a strong background in Journalism and has worked with renowned news websites such as News 9 and The Financial Express to name a few. When not writing, she can be found bringing life to the canvasses by painting on them.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
- CBSE Class 10th
- CBSE Class 12th
- UP Board 10th
- UP Board 12th
- Bihar Board 10th
- Bihar Board 12th
- Top Schools in India
- Top Schools in Delhi
- Top Schools in Mumbai
- Top Schools in Chennai
- Top Schools in Hyderabad
- Top Schools in Kolkata
- Top Schools in Pune
- Top Schools in Bangalore
Products & Resources
- JEE Main Knockout April
- Free Sample Papers
- Free Ebooks
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Syllabus
- NCERT Books
- RD Sharma Solutions
- Navodaya Vidyalaya Admission 2024-25
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT solutions for Class 10
- NCERT solutions for Class 9
- NCERT solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- JEE Main 2024
- MHT CET 2024
- JEE Advanced 2024
- BITSAT 2024
- View All Engineering Exams
- Colleges Accepting B.Tech Applications
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in India
- Engineering Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Engineering Colleges Accepting JEE Main
- Top IITs in India
- Top NITs in India
- Top IIITs in India
- JEE Main College Predictor
- JEE Main Rank Predictor
- MHT CET College Predictor
- AP EAMCET College Predictor
- GATE College Predictor
- KCET College Predictor
- JEE Advanced College Predictor
- View All College Predictors
- JEE Main Question Paper
- JEE Main Cutoff
- JEE Main Answer Key
- JEE Main Result
- Download E-Books and Sample Papers
- Compare Colleges
- B.Tech College Applications
- JEE Advanced Registration
- MAH MBA CET Exam
- View All Management Exams
Colleges & Courses
- MBA College Admissions
- MBA Colleges in India
- Top IIMs Colleges in India
- Top Online MBA Colleges in India
- MBA Colleges Accepting XAT Score
- BBA Colleges in India
- XAT College Predictor 2024
- SNAP College Predictor
- NMAT College Predictor
- MAT College Predictor 2024
- CMAT College Predictor 2024
- CAT Percentile Predictor 2023
- CAT 2023 College Predictor
- CMAT 2024 Registration
- TS ICET 2024 Registration
- CMAT Exam Date 2024
- MAH MBA CET Cutoff 2024
- Download Helpful Ebooks
- List of Popular Branches
- QnA - Get answers to your doubts
- IIM Fees Structure
- AIIMS Nursing
- Top Medical Colleges in India
- Top Medical Colleges in India accepting NEET Score
- Medical Colleges accepting NEET
- List of Medical Colleges in India
- List of AIIMS Colleges In India
- Medical Colleges in Maharashtra
- Medical Colleges in India Accepting NEET PG
- NEET College Predictor
- NEET PG College Predictor
- NEET MDS College Predictor
- DNB CET College Predictor
- DNB PDCET College Predictor
- NEET Application Form 2024
- NEET PG Application Form 2024
- NEET Cut off
- NEET Online Preparation
- Download Helpful E-books
- LSAT India 2024
- Colleges Accepting Admissions
- Top Law Colleges in India
- Law College Accepting CLAT Score
- List of Law Colleges in India
- Top Law Colleges in Delhi
- Top Law Collages in Indore
- Top Law Colleges in Chandigarh
- Top Law Collages in Lucknow
Predictors & E-Books
- CLAT College Predictor
- MHCET Law ( 5 Year L.L.B) College Predictor
- AILET College Predictor
- Sample Papers
- Compare Law Collages
- Careers360 Youtube Channel
- CLAT Syllabus 2025
- CLAT Previous Year Question Paper
- AIBE 18 Result 2023
- NID DAT Exam
- Pearl Academy Exam
Animation Courses
- Animation Courses in India
- Animation Courses in Bangalore
- Animation Courses in Mumbai
- Animation Courses in Pune
- Animation Courses in Chennai
- Animation Courses in Hyderabad
- Design Colleges in India
- Fashion Design Colleges in Bangalore
- Fashion Design Colleges in Mumbai
- Fashion Design Colleges in Pune
- Fashion Design Colleges in Delhi
- Fashion Design Colleges in Hyderabad
- Fashion Design Colleges in India
- Top Design Colleges in India
- Free Design E-books
- List of Branches
- Careers360 Youtube channel
- NIFT College Predictor
- UCEED College Predictor
- NID DAT College Predictor
- IPU CET BJMC
- JMI Mass Communication Entrance Exam
- IIMC Entrance Exam
- Media & Journalism colleges in Delhi
- Media & Journalism colleges in Bangalore
- Media & Journalism colleges in Mumbai
- List of Media & Journalism Colleges in India
- CA Intermediate
- CA Foundation
- CS Executive
- CS Professional
- Difference between CA and CS
- Difference between CA and CMA
- CA Full form
- CMA Full form
- CS Full form
- CA Salary In India
Top Courses & Careers
- Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com)
- Master of Commerce (M.Com)
- Company Secretary
- Cost Accountant
- Charted Accountant
- Credit Manager
- Financial Advisor
- Top Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Government Commerce Colleges in India
- Top Private Commerce Colleges in India
- Top M.Com Colleges in Mumbai
- Top B.Com Colleges in India
- IT Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- IT Colleges in Uttar Pradesh
- MCA Colleges in India
- BCA Colleges in India
Quick Links
- Information Technology Courses
- Programming Courses
- Web Development Courses
- Data Analytics Courses
- Big Data Analytics Courses
- RUHS Pharmacy Admission Test
- Top Pharmacy Colleges in India
- Pharmacy Colleges in Pune
- Pharmacy Colleges in Mumbai
- Colleges Accepting GPAT Score
- Pharmacy Colleges in Lucknow
- List of Pharmacy Colleges in Nagpur
- GPAT Result
- GPAT 2024 Admit Card
- GPAT Question Papers
- NCHMCT JEE 2024
- Mah BHMCT CET
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Delhi
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Hyderabad
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Mumbai
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Tamil Nadu
- Top Hotel Management Colleges in Maharashtra
- B.Sc Hotel Management
- Hotel Management
- Diploma in Hotel Management and Catering Technology
Diploma Colleges
- Top Diploma Colleges in Maharashtra
- UPSC IAS 2024
- SSC CGL 2024
- IBPS RRB 2024
- Previous Year Sample Papers
- Free Competition E-books
- Sarkari Result
- QnA- Get your doubts answered
- UPSC Previous Year Sample Papers
- CTET Previous Year Sample Papers
- SBI Clerk Previous Year Sample Papers
- NDA Previous Year Sample Papers
Upcoming Events
- NDA Application Form 2024
- UPSC IAS Application Form 2024
- CDS Application Form 2024
- CTET Admit card 2024
- HP TET Result 2023
- SSC GD Constable Admit Card 2024
- UPTET Notification 2024
- SBI Clerk Result 2024
Other Exams
- SSC CHSL 2024
- UP PCS 2024
- UGC NET 2024
- RRB NTPC 2024
- IBPS PO 2024
- IBPS Clerk 2024
- IBPS SO 2024
- Top University in USA
- Top University in Canada
- Top University in Ireland
- Top Universities in UK
- Top Universities in Australia
- Best MBA Colleges in Abroad
- Business Management Studies Colleges
Top Countries
- Study in USA
- Study in UK
- Study in Canada
- Study in Australia
- Study in Ireland
- Study in Germany
- Study in China
- Study in Europe
Student Visas
- Student Visa Canada
- Student Visa UK
- Student Visa USA
- Student Visa Australia
- Student Visa Germany
- Student Visa New Zealand
- Student Visa Ireland
- CUET PG 2024
- IGNOU B.Ed Admission 2024
- DU Admission
- UP B.Ed JEE 2024
- DDU Entrance Exam
- IIT JAM 2024
- IGNOU Online Admission 2024
- Universities in India
- Top Universities in India 2024
- Top Colleges in India
- Top Universities in Uttar Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Bihar
- Top Universities in Madhya Pradesh 2024
- Top Universities in Tamil Nadu 2024
- Central Universities in India
- CUET PG Admit Card 2024
- IGNOU Date Sheet
- CUET Mock Test 2024
- CUET Application Form 2024
- CUET PG Syllabus 2024
- CUET Participating Universities 2024
- CUET Previous Year Question Paper
- CUET Syllabus 2024 for Science Students
- E-Books and Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Pattern 2024
- CUET Exam Date 2024
- CUET Syllabus 2024
- IGNOU Exam Form 2024
- IGNOU Result
- CUET PG Courses 2024
Engineering Preparation
- Knockout JEE Main 2024
- Test Series JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main 2024 Rank Booster
Medical Preparation
- Knockout NEET 2024
- Test Series NEET 2024
- Rank Booster NEET 2024
Online Courses
- JEE Main One Month Course
- NEET One Month Course
- IBSAT Free Mock Tests
- IIT JEE Foundation Course
- Knockout BITSAT 2024
- Career Guidance Tool
Top Streams
- IT & Software Certification Courses
- Engineering and Architecture Certification Courses
- Programming And Development Certification Courses
- Business and Management Certification Courses
- Marketing Certification Courses
- Health and Fitness Certification Courses
- Design Certification Courses
Specializations
- Digital Marketing Certification Courses
- Cyber Security Certification Courses
- Artificial Intelligence Certification Courses
- Business Analytics Certification Courses
- Data Science Certification Courses
- Cloud Computing Certification Courses
- Machine Learning Certification Courses
- View All Certification Courses
- UG Degree Courses
- PG Degree Courses
- Short Term Courses
- Free Courses
- Online Degrees and Diplomas
- Compare Courses
Top Providers
- Coursera Courses
- Udemy Courses
- Edx Courses
- Swayam Courses
- upGrad Courses
- Simplilearn Courses
- Great Learning Courses
Access premium articles, webinars, resources to make the best decisions for career, course, exams, scholarships, study abroad and much more with
Plan, Prepare & Make the Best Career Choices
Natural Resources Essay
Resources are necessary for humans and other organisms to survive. The most fundamental source of all our resources is nature, and these resources are termed natural resources. If we look around, we can list many of them, like water, sunlight, flora and fauna, air etc., and we can't think of a world without these resources. Here are some sample essays on natural resources.

100 Word Essay On Natural Resources
Every living thing in the world needs resources to thrive, and nature is itself the epicentre of these resources. These gifts from nature make life on earth easy and comfortable. Centuries back, we humans were on the track of development and are still developing. We have found many hidden natural resources through this journey and used them widely. Today the population is many times more than the previous centuries, and our consumption has increased.
It is interesting to note that natural resources are divided into two, namely renewable and non-renewable. Renewable resources, for example, sunlight and wind, get renewed as they are consumed. On the other hand, non-renewable resources, for instance, coal and petroleum, take more time to replenish. So we need to use the resources wisely.
200 Word Essay On Natural Resources
No one can deny that we all depend on the resources around us. We breathe the air around us, plants use sunlight to make their supplements, and animals consume food from the forest. These all show how living organisms are so dependent on natural resources. Most natural resources are found on the earth's surface, and as civilisations grew, they explored the land and discovered resources hidden inside the planet. Since then, we have used many resources like Coal, Gold, Natural gas, uranium etc. And today, we are not using them but are rapidly exploiting them.
Types Of Resources
Some resources are abundantly found on earth, like water and air. These resources can be accessed when needed and are primarily available, called renewable resources. These resources are less likely to be depleted but can be contaminated, making them less favourable to consumption.
Another type of resource, which is available on earth in limited quantities, is termed non-renewable resources. These resources are limited and tend to exhaust over time.
Another resource category is Biotic and Abiotic resources, which means resources from living and non-living elements.
The current resource consumption rate is alarming, and if it is continuous, the world may run out of resources in the coming centuries.
500 Word Essay On Natural Resources
A natural resource is not anything complicated. Simply put, everything taken from the Earth is considered a natural resource. Sunlight, water, coal, natural gas, minerals, and even air play a role. Everything included here is regarded as a natural resource. These resources are necessary for the survival of life on earth. Energy is one of the most important products of resources and we humans extract energy from almost all of the available resources to meet our demands. Solar energy, wind energy, and hydro energy are some of them.
Types Of Natural Resources
While each natural resource has unique classifications and applications, they may be roughly divided into two groups: renewable and nonrenewable.
Renewable | Those natural resources are considered renewable if they can be readily replenished and there is an abundance of them. Sunlight, water, air, soil, biomass, and wood are all examples of such things. However, some of these resources, such as wood and mud, need more time to replenish than others.
Further, they originate from both living and nonliving sources. Renewable resources may be either organic (obtained from living organisms) or inorganic (obtained from nonliving materials).
Nonrenewable | The term "nonrenewable natural resources" refers to resources that cannot be replenished as readily as renewable ones. Not only that, but their regeneration process is prolonged and may take years. Coal, oil, gas, and other similar materials fall under this category.
Moreover, we divided everything into the organic and inorganic classes. Fossil fuel is an example of the nonrenewable organic resources that arise from the decaying remains of formerly living beings. On the other hand, non-living entities like wind, minerals, soil, and land are responsible for forming nonrenewable inorganic resources.
Distribution Of Natural Resources
There is a significant disparity in the world's natural resource distribution. In addition, several minerals and other natural resources may be abundant over the surface. Even though some places get sun, others get hardly any at all. In a similarity, certain areas are abundant in the water while others have plenty of minerals.
Climate and terrain have a pivotal role in determining resource distribution. This asymmetry is the lifeblood of international commerce, serving as the primary connection between nations. Even worse, it has unintended consequences since nations well-endowed with fossil fuels dominate the market and exploit others dependent on them for their energy needs. As a result, affluent countries are expanding their wealth while impoverished nations are sinking further into poverty.
Example Of Natural Resource
Fatu-Hiva rainforest on the Marquesas Islands is an example of an unspoiled natural resource. The forest supplies people with wood, food, water, and shelter for flora and fauna, tribes, and animals. The nutrient cycle between organisms forms food chains and promotes species diversification.
Earth is endowed with abundant natural resources. We can easily conserve them and the world if we utilise them responsibly until we transition entirely to renewable energy sources. Thus, we will use fewer nonrenewable resources. Not to mention, we cannot survive without them, making them quite crucial. In addition, we need to make good use of them and avoid wasting them in any way.
Explore Career Options (By Industry)
- Construction
- Entertainment
- Manufacturing
- Information Technology
Data Administrator
Database professionals use software to store and organise data such as financial information, and customer shipping records. Individuals who opt for a career as data administrators ensure that data is available for users and secured from unauthorised sales. DB administrators may work in various types of industries. It may involve computer systems design, service firms, insurance companies, banks and hospitals.
Bio Medical Engineer
The field of biomedical engineering opens up a universe of expert chances. An Individual in the biomedical engineering career path work in the field of engineering as well as medicine, in order to find out solutions to common problems of the two fields. The biomedical engineering job opportunities are to collaborate with doctors and researchers to develop medical systems, equipment, or devices that can solve clinical problems. Here we will be discussing jobs after biomedical engineering, how to get a job in biomedical engineering, biomedical engineering scope, and salary.
Ethical Hacker
A career as ethical hacker involves various challenges and provides lucrative opportunities in the digital era where every giant business and startup owns its cyberspace on the world wide web. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path try to find the vulnerabilities in the cyber system to get its authority. If he or she succeeds in it then he or she gets its illegal authority. Individuals in the ethical hacker career path then steal information or delete the file that could affect the business, functioning, or services of the organization.
GIS officer work on various GIS software to conduct a study and gather spatial and non-spatial information. GIS experts update the GIS data and maintain it. The databases include aerial or satellite imagery, latitudinal and longitudinal coordinates, and manually digitized images of maps. In a career as GIS expert, one is responsible for creating online and mobile maps.
Data Analyst
The invention of the database has given fresh breath to the people involved in the data analytics career path. Analysis refers to splitting up a whole into its individual components for individual analysis. Data analysis is a method through which raw data are processed and transformed into information that would be beneficial for user strategic thinking.
Data are collected and examined to respond to questions, evaluate hypotheses or contradict theories. It is a tool for analyzing, transforming, modeling, and arranging data with useful knowledge, to assist in decision-making and methods, encompassing various strategies, and is used in different fields of business, research, and social science.
Geothermal Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as geothermal engineers are the professionals involved in the processing of geothermal energy. The responsibilities of geothermal engineers may vary depending on the workplace location. Those who work in fields design facilities to process and distribute geothermal energy. They oversee the functioning of machinery used in the field.
Database Architect
If you are intrigued by the programming world and are interested in developing communications networks then a career as database architect may be a good option for you. Data architect roles and responsibilities include building design models for data communication networks. Wide Area Networks (WANs), local area networks (LANs), and intranets are included in the database networks. It is expected that database architects will have in-depth knowledge of a company's business to develop a network to fulfil the requirements of the organisation. Stay tuned as we look at the larger picture and give you more information on what is db architecture, why you should pursue database architecture, what to expect from such a degree and what your job opportunities will be after graduation. Here, we will be discussing how to become a data architect. Students can visit NIT Trichy , IIT Kharagpur , JMI New Delhi .
Remote Sensing Technician
Individuals who opt for a career as a remote sensing technician possess unique personalities. Remote sensing analysts seem to be rational human beings, they are strong, independent, persistent, sincere, realistic and resourceful. Some of them are analytical as well, which means they are intelligent, introspective and inquisitive.
Remote sensing scientists use remote sensing technology to support scientists in fields such as community planning, flight planning or the management of natural resources. Analysing data collected from aircraft, satellites or ground-based platforms using statistical analysis software, image analysis software or Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a significant part of their work. Do you want to learn how to become remote sensing technician? There's no need to be concerned; we've devised a simple remote sensing technician career path for you. Scroll through the pages and read.
Budget Analyst
Budget analysis, in a nutshell, entails thoroughly analyzing the details of a financial budget. The budget analysis aims to better understand and manage revenue. Budget analysts assist in the achievement of financial targets, the preservation of profitability, and the pursuit of long-term growth for a business. Budget analysts generally have a bachelor's degree in accounting, finance, economics, or a closely related field. Knowledge of Financial Management is of prime importance in this career.
Underwriter
An underwriter is a person who assesses and evaluates the risk of insurance in his or her field like mortgage, loan, health policy, investment, and so on and so forth. The underwriter career path does involve risks as analysing the risks means finding out if there is a way for the insurance underwriter jobs to recover the money from its clients. If the risk turns out to be too much for the company then in the future it is an underwriter who will be held accountable for it. Therefore, one must carry out his or her job with a lot of attention and diligence.
Finance Executive
Product manager.
A Product Manager is a professional responsible for product planning and marketing. He or she manages the product throughout the Product Life Cycle, gathering and prioritising the product. A product manager job description includes defining the product vision and working closely with team members of other departments to deliver winning products.
Operations Manager
Individuals in the operations manager jobs are responsible for ensuring the efficiency of each department to acquire its optimal goal. They plan the use of resources and distribution of materials. The operations manager's job description includes managing budgets, negotiating contracts, and performing administrative tasks.
Stock Analyst
Individuals who opt for a career as a stock analyst examine the company's investments makes decisions and keep track of financial securities. The nature of such investments will differ from one business to the next. Individuals in the stock analyst career use data mining to forecast a company's profits and revenues, advise clients on whether to buy or sell, participate in seminars, and discussing financial matters with executives and evaluate annual reports.
A Researcher is a professional who is responsible for collecting data and information by reviewing the literature and conducting experiments and surveys. He or she uses various methodological processes to provide accurate data and information that is utilised by academicians and other industry professionals. Here, we will discuss what is a researcher, the researcher's salary, types of researchers.
Welding Engineer
Welding Engineer Job Description: A Welding Engineer work involves managing welding projects and supervising welding teams. He or she is responsible for reviewing welding procedures, processes and documentation. A career as Welding Engineer involves conducting failure analyses and causes on welding issues.
Transportation Planner
A career as Transportation Planner requires technical application of science and technology in engineering, particularly the concepts, equipment and technologies involved in the production of products and services. In fields like land use, infrastructure review, ecological standards and street design, he or she considers issues of health, environment and performance. A Transportation Planner assigns resources for implementing and designing programmes. He or she is responsible for assessing needs, preparing plans and forecasts and compliance with regulations.
Environmental Engineer
Individuals who opt for a career as an environmental engineer are construction professionals who utilise the skills and knowledge of biology, soil science, chemistry and the concept of engineering to design and develop projects that serve as solutions to various environmental problems.
Safety Manager
A Safety Manager is a professional responsible for employee’s safety at work. He or she plans, implements and oversees the company’s employee safety. A Safety Manager ensures compliance and adherence to Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) guidelines.
Conservation Architect
A Conservation Architect is a professional responsible for conserving and restoring buildings or monuments having a historic value. He or she applies techniques to document and stabilise the object’s state without any further damage. A Conservation Architect restores the monuments and heritage buildings to bring them back to their original state.
Structural Engineer
A Structural Engineer designs buildings, bridges, and other related structures. He or she analyzes the structures and makes sure the structures are strong enough to be used by the people. A career as a Structural Engineer requires working in the construction process. It comes under the civil engineering discipline. A Structure Engineer creates structural models with the help of computer-aided design software.
Highway Engineer
Highway Engineer Job Description: A Highway Engineer is a civil engineer who specialises in planning and building thousands of miles of roads that support connectivity and allow transportation across the country. He or she ensures that traffic management schemes are effectively planned concerning economic sustainability and successful implementation.
Field Surveyor
Are you searching for a Field Surveyor Job Description? A Field Surveyor is a professional responsible for conducting field surveys for various places or geographical conditions. He or she collects the required data and information as per the instructions given by senior officials.
Orthotist and Prosthetist
Orthotists and Prosthetists are professionals who provide aid to patients with disabilities. They fix them to artificial limbs (prosthetics) and help them to regain stability. There are times when people lose their limbs in an accident. In some other occasions, they are born without a limb or orthopaedic impairment. Orthotists and prosthetists play a crucial role in their lives with fixing them to assistive devices and provide mobility.
Pathologist
A career in pathology in India is filled with several responsibilities as it is a medical branch and affects human lives. The demand for pathologists has been increasing over the past few years as people are getting more aware of different diseases. Not only that, but an increase in population and lifestyle changes have also contributed to the increase in a pathologist’s demand. The pathology careers provide an extremely huge number of opportunities and if you want to be a part of the medical field you can consider being a pathologist. If you want to know more about a career in pathology in India then continue reading this article.
Veterinary Doctor
Speech therapist, gynaecologist.
Gynaecology can be defined as the study of the female body. The job outlook for gynaecology is excellent since there is evergreen demand for one because of their responsibility of dealing with not only women’s health but also fertility and pregnancy issues. Although most women prefer to have a women obstetrician gynaecologist as their doctor, men also explore a career as a gynaecologist and there are ample amounts of male doctors in the field who are gynaecologists and aid women during delivery and childbirth.
Audiologist
The audiologist career involves audiology professionals who are responsible to treat hearing loss and proactively preventing the relevant damage. Individuals who opt for a career as an audiologist use various testing strategies with the aim to determine if someone has a normal sensitivity to sounds or not. After the identification of hearing loss, a hearing doctor is required to determine which sections of the hearing are affected, to what extent they are affected, and where the wound causing the hearing loss is found. As soon as the hearing loss is identified, the patients are provided with recommendations for interventions and rehabilitation such as hearing aids, cochlear implants, and appropriate medical referrals. While audiology is a branch of science that studies and researches hearing, balance, and related disorders.
An oncologist is a specialised doctor responsible for providing medical care to patients diagnosed with cancer. He or she uses several therapies to control the cancer and its effect on the human body such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiation therapy and biopsy. An oncologist designs a treatment plan based on a pathology report after diagnosing the type of cancer and where it is spreading inside the body.
Are you searching for an ‘Anatomist job description’? An Anatomist is a research professional who applies the laws of biological science to determine the ability of bodies of various living organisms including animals and humans to regenerate the damaged or destroyed organs. If you want to know what does an anatomist do, then read the entire article, where we will answer all your questions.
For an individual who opts for a career as an actor, the primary responsibility is to completely speak to the character he or she is playing and to persuade the crowd that the character is genuine by connecting with them and bringing them into the story. This applies to significant roles and littler parts, as all roles join to make an effective creation. Here in this article, we will discuss how to become an actor in India, actor exams, actor salary in India, and actor jobs.
Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats create and direct original routines for themselves, in addition to developing interpretations of existing routines. The work of circus acrobats can be seen in a variety of performance settings, including circus, reality shows, sports events like the Olympics, movies and commercials. Individuals who opt for a career as acrobats must be prepared to face rejections and intermittent periods of work. The creativity of acrobats may extend to other aspects of the performance. For example, acrobats in the circus may work with gym trainers, celebrities or collaborate with other professionals to enhance such performance elements as costume and or maybe at the teaching end of the career.
Video Game Designer
Career as a video game designer is filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. A video game designer is someone who is involved in the process of creating a game from day one. He or she is responsible for fulfilling duties like designing the character of the game, the several levels involved, plot, art and similar other elements. Individuals who opt for a career as a video game designer may also write the codes for the game using different programming languages.
Depending on the video game designer job description and experience they may also have to lead a team and do the early testing of the game in order to suggest changes and find loopholes.
Radio Jockey
Radio Jockey is an exciting, promising career and a great challenge for music lovers. If you are really interested in a career as radio jockey, then it is very important for an RJ to have an automatic, fun, and friendly personality. If you want to get a job done in this field, a strong command of the language and a good voice are always good things. Apart from this, in order to be a good radio jockey, you will also listen to good radio jockeys so that you can understand their style and later make your own by practicing.
A career as radio jockey has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. If you want to know more about a career as radio jockey, and how to become a radio jockey then continue reading the article.
Choreographer
The word “choreography" actually comes from Greek words that mean “dance writing." Individuals who opt for a career as a choreographer create and direct original dances, in addition to developing interpretations of existing dances. A Choreographer dances and utilises his or her creativity in other aspects of dance performance. For example, he or she may work with the music director to select music or collaborate with other famous choreographers to enhance such performance elements as lighting, costume and set design.
Social Media Manager
A career as social media manager involves implementing the company’s or brand’s marketing plan across all social media channels. Social media managers help in building or improving a brand’s or a company’s website traffic, build brand awareness, create and implement marketing and brand strategy. Social media managers are key to important social communication as well.
Photographer
Photography is considered both a science and an art, an artistic means of expression in which the camera replaces the pen. In a career as a photographer, an individual is hired to capture the moments of public and private events, such as press conferences or weddings, or may also work inside a studio, where people go to get their picture clicked. Photography is divided into many streams each generating numerous career opportunities in photography. With the boom in advertising, media, and the fashion industry, photography has emerged as a lucrative and thrilling career option for many Indian youths.
An individual who is pursuing a career as a producer is responsible for managing the business aspects of production. They are involved in each aspect of production from its inception to deception. Famous movie producers review the script, recommend changes and visualise the story.
They are responsible for overseeing the finance involved in the project and distributing the film for broadcasting on various platforms. A career as a producer is quite fulfilling as well as exhaustive in terms of playing different roles in order for a production to be successful. Famous movie producers are responsible for hiring creative and technical personnel on contract basis.
Copy Writer
In a career as a copywriter, one has to consult with the client and understand the brief well. A career as a copywriter has a lot to offer to deserving candidates. Several new mediums of advertising are opening therefore making it a lucrative career choice. Students can pursue various copywriter courses such as Journalism , Advertising , Marketing Management . Here, we have discussed how to become a freelance copywriter, copywriter career path, how to become a copywriter in India, and copywriting career outlook.
In a career as a vlogger, one generally works for himself or herself. However, once an individual has gained viewership there are several brands and companies that approach them for paid collaboration. It is one of those fields where an individual can earn well while following his or her passion.
Ever since internet costs got reduced the viewership for these types of content has increased on a large scale. Therefore, a career as a vlogger has a lot to offer. If you want to know more about the Vlogger eligibility, roles and responsibilities then continue reading the article.
For publishing books, newspapers, magazines and digital material, editorial and commercial strategies are set by publishers. Individuals in publishing career paths make choices about the markets their businesses will reach and the type of content that their audience will be served. Individuals in book publisher careers collaborate with editorial staff, designers, authors, and freelance contributors who develop and manage the creation of content.
Careers in journalism are filled with excitement as well as responsibilities. One cannot afford to miss out on the details. As it is the small details that provide insights into a story. Depending on those insights a journalist goes about writing a news article. A journalism career can be stressful at times but if you are someone who is passionate about it then it is the right choice for you. If you want to know more about the media field and journalist career then continue reading this article.
Individuals in the editor career path is an unsung hero of the news industry who polishes the language of the news stories provided by stringers, reporters, copywriters and content writers and also news agencies. Individuals who opt for a career as an editor make it more persuasive, concise and clear for readers. In this article, we will discuss the details of the editor's career path such as how to become an editor in India, editor salary in India and editor skills and qualities.
Individuals who opt for a career as a reporter may often be at work on national holidays and festivities. He or she pitches various story ideas and covers news stories in risky situations. Students can pursue a BMC (Bachelor of Mass Communication) , B.M.M. (Bachelor of Mass Media) , or MAJMC (MA in Journalism and Mass Communication) to become a reporter. While we sit at home reporters travel to locations to collect information that carries a news value.
Corporate Executive
Are you searching for a Corporate Executive job description? A Corporate Executive role comes with administrative duties. He or she provides support to the leadership of the organisation. A Corporate Executive fulfils the business purpose and ensures its financial stability. In this article, we are going to discuss how to become corporate executive.
Multimedia Specialist
A multimedia specialist is a media professional who creates, audio, videos, graphic image files, computer animations for multimedia applications. He or she is responsible for planning, producing, and maintaining websites and applications.
Quality Controller
A quality controller plays a crucial role in an organisation. He or she is responsible for performing quality checks on manufactured products. He or she identifies the defects in a product and rejects the product.
A quality controller records detailed information about products with defects and sends it to the supervisor or plant manager to take necessary actions to improve the production process.
Production Manager
A QA Lead is in charge of the QA Team. The role of QA Lead comes with the responsibility of assessing services and products in order to determine that he or she meets the quality standards. He or she develops, implements and manages test plans.
Process Development Engineer
The Process Development Engineers design, implement, manufacture, mine, and other production systems using technical knowledge and expertise in the industry. They use computer modeling software to test technologies and machinery. An individual who is opting career as Process Development Engineer is responsible for developing cost-effective and efficient processes. They also monitor the production process and ensure it functions smoothly and efficiently.
AWS Solution Architect
An AWS Solution Architect is someone who specializes in developing and implementing cloud computing systems. He or she has a good understanding of the various aspects of cloud computing and can confidently deploy and manage their systems. He or she troubleshoots the issues and evaluates the risk from the third party.
Azure Administrator
An Azure Administrator is a professional responsible for implementing, monitoring, and maintaining Azure Solutions. He or she manages cloud infrastructure service instances and various cloud servers as well as sets up public and private cloud systems.
Computer Programmer
Careers in computer programming primarily refer to the systematic act of writing code and moreover include wider computer science areas. The word 'programmer' or 'coder' has entered into practice with the growing number of newly self-taught tech enthusiasts. Computer programming careers involve the use of designs created by software developers and engineers and transforming them into commands that can be implemented by computers. These commands result in regular usage of social media sites, word-processing applications and browsers.
Information Security Manager
Individuals in the information security manager career path involves in overseeing and controlling all aspects of computer security. The IT security manager job description includes planning and carrying out security measures to protect the business data and information from corruption, theft, unauthorised access, and deliberate attack
ITSM Manager
Automation test engineer.
An Automation Test Engineer job involves executing automated test scripts. He or she identifies the project’s problems and troubleshoots them. The role involves documenting the defect using management tools. He or she works with the application team in order to resolve any issues arising during the testing process.
Applications for Admissions are open.

Aakash iACST Scholarship Test 2024
Get up to 90% scholarship on NEET, JEE & Foundation courses

SAT® | CollegeBoard
Registeration closing on 19th Apr for SAT® | One Test-Many Universities | 90% discount on registrations fee | Free Practice | Multiple Attempts | no penalty for guessing

JEE Main Important Chemistry formulas
As per latest 2024 syllabus. Chemistry formulas, equations, & laws of class 11 & 12th chapters

TOEFL ® Registrations 2024
Thinking of Studying Abroad? Think the TOEFL® test. Register now & Save 10% on English Proficiency Tests with Gift Cards

Resonance Coaching
Enroll in Resonance Coaching for success in JEE/NEET exams

NEET 2024 Most scoring concepts
Just Study 32% of the NEET syllabus and Score upto 100% marks
Everything about Education
Latest updates, Exclusive Content, Webinars and more.
Download Careers360 App's
Regular exam updates, QnA, Predictors, College Applications & E-books now on your Mobile
Cetifications

We Appeared in

Notes of Ch 14 Natural Resources| Class 9th Science
Study material and notes of ch 14 natural resources class 9th science.

Contact Form

Essay on Natural Resources
Natural resources are the treasures that Mother Earth has bestowed upon us. They include water, air, soil, minerals, and all living things. In this essay, we will delve into the importance of these resources, their sustainable use, and the vital role they play in our lives and the health of our planet.
let’s talk about the importance of natural resources
Our lives depend on these resources more than we realize. For example, fresh water is essential for drinking, agriculture, and industry. According to statistics, 2.2 billion people lack access to safe drinking water, highlighting the critical need for its preservation.
Natural resources fuel our economy
Many industries, such as agriculture, mining, and forestry, rely on natural resources to thrive. Experts emphasize the importance of sustainable practices in these industries to ensure the long-term availability of resources.
Biodiversity is a natural resource
Our ecosystems, which include plants, animals, and microorganisms, provide us with food, medicine, and clean air. The loss of biodiversity can have devastating effects, as experts warn of the potential consequences for our health and well-being.
Natural resources support renewable energy
The sun, wind, and water are valuable sources of renewable energy that reduce our dependence on fossil fuels. By harnessing these resources, we can combat climate change and protect our environment.
Soil is a crucial natural resource
It is the foundation of agriculture, providing nutrients for crops. Soil erosion, often caused by unsustainable farming practices, threatens our ability to grow food. Sustainable farming is essential to protecting this vital resource.
The air we breathe is a natural resource
Clean air is essential for our health, and pollution poses a significant threat. Experts stress the importance of reducing emissions and protecting our atmosphere for future generations.
Minerals are essential for modern life.
They are used in everything from construction to technology. Mining, however, can have environmental impacts, making it crucial to balance resource extraction with conservation efforts.
Forests are a valuable natural resource
They provide habitat for wildlife, absorb carbon dioxide, and offer recreational opportunities. Sustainable forestry practices are necessary to ensure the health of our forests.
The oceans are rich natural resources.
They provide food and support biodiversity. However, overfishing and pollution endanger marine ecosystems. Experts call for responsible fishing and marine conservation efforts.
The importance of conserving natural resources cannot be overstated.
Sustainable practices, such as reducing waste and conserving energy, are crucial to protecting our environment. Every individual can make a difference by adopting eco-friendly habits.
Conclusion of Essay on Natural Resources
In conclusion, natural resources are the lifeblood of our planet, supporting our existence, economy, and well-being. It is our responsibility to use these resources wisely and sustainably, ensuring they are available for future generations. By valuing and conserving our natural resources, we can secure a brighter and healthier future for ourselves and the Earth we call home.
Also Check: List of 500+ Topics for Writing Essay
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 - Natural Resources
- NCERT Solutions

Remembering all the science concepts can be tricky for many. It calls for the need for regular revision. Professional teachers at Vedantu provide you with NCERT solutions class 9 science chapter 14 in a comprehensive format making the revision process quicker and easier for all the students. The class 9 science chapter 14 notes and solutions are designed based on the CBSE format and syllabus. You can also download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.These are concisely curated and are available in PDF format for easy downloads.

Access NCERT Solutions for Biology Chapter 14 - Natural Resources
1. How is Our Atmosphere Different from the Atmospheres on Venus and Mars?
Ans: The composition of Earth's atmosphere differs from that of Venus and Mars. The atmosphere of the Earth is composed of nitrogen, oxygen, a trace of carbon dioxide, water vapour, and other gases. This allows for the existence of life on Earth. However, carbon dioxide makes up the majority of the atmosphere on Venus and Mars, which could range between 95 to 97 per cent.
2. How Does the Atmosphere Act as a Blanket?
Ans: The atmosphere keeps the temperature of the Earth constant. It avoids a sudden increase in the temperature during the daytime due to the sun. It blocks or slows down the escape of heat from the Earth into outer space during the night- time.
3. What Causes Winds?
Ans: The uneven heating of the Earth's surface causes winds. When air is heated, it becomes lighter and rises in the atmosphere. As a consequence, a low-pressure area is formed. The air then travels from a high-pressure area to a low-pressure area, creating wind.
4. How are Clouds Formed?
Ans: Due to the heat of the sun, a huge volume of water evaporates from various water bodies during the day and rises into the air. The air in the atmosphere heats up as a result of this. When water vapour-carrying air rises, it expands and cools. Water droplets develop as a result of the condensation of water vapour. Clouds arise as a result of the production of water droplets.
5. List Any Three Human Activities That You Think Would Lead to Air Pollution.
Ans: Three human activities that would lead to air pollution are deforestation, automobile emissions, and industrialisation all contribute to the combustion of fossil fuels.
6. Why Do Organisms Need Water?
Ans: Organisms need water as all the cellular processes need water as a medium. Also, the transportation of substances require water.
7. What is the Major Source of Fresh Water in the City/town/village Where You Live?
Ans: The major source of fresh water in the city/town/village is the River.
8. Do You Know of Any Activity Which May be Polluting This Water Source?
Ans: Discharge of wastewater from houses, industries, hospitals, etc. pollutes freshwater sources.
9. How is Soil Formed?
Ans: Various processes and factors help in the formation of the soil. The major plays by the sun, water, wind, and living organisms in soil formation.
Sun: During the day, the sun warms rocks, causing them to expand. These rocks cool and contract throughout the night. Since all parts of the rock do not expand and contract at the same rate, this causes the formation of cracks which lead to the breaking up of huge rocks into smaller pieces.
Water: Water contributes to soil formation in two ways. Water pours through the cracks in the rocks caused by the sun's heat. When this water freezes, it increases in volume. As a result, the size of the holes grows as well. The weathering of rocks is helped by this. Hard rocks are worn away over time by flowing water. Large and tiny rock fragments are frequently carried downstream by fast-moving water. These rocks scrape against one other, causing the rocks to crumble. Running water carries these smaller particles away and deposits them along its course.
Wind: Strong winds move rocks away, causing them to rub together. As a consequence, rocks are broken down into smaller and smaller bits.
Living Organisms: Some organisms, temperature rise, too, for example, Lichens, help in the development of soil. Lichens can also be found on rocks. Lichens emit specific chemicals during their development, which cause the rock surface to powder down, creating a thin coating of soil. Other tiny plants, such as moss, can now grow on this surface, causing the rock to break apart even further. The roots of large trees can occasionally become caught in cracks in the rocks, and as the roots get larger, the crack expands.
10. What is Soil Erosion?
Ans: Soil erosion is defined as when the top layer of soil is washed away from the ground surface by wind or water.
11. What are the Methods of Preventing or Reducing Soil Erosion?
Ans: Soil erosion can be avoided by afforestation, various agricultural practices that prevent topsoil removal, and grass overgrazing, among other things.
12. What are the Different States in Which Water is Found During the Water Cycle?
Ans: During the water cycle, water is found in solid-state as snow, ice, etc., in a liquid state as groundwater, river water, etc., and in a gaseous state as water vapour.
13. Name Two Biologically Important Compounds That Contain Both Oxygen and Nitrogen.
Ans: Amino acids DNA and RNA are two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen.
14. List Any Three Human Activities Which Would Lead to an Increase in the Carbon Dioxide Content of the Air.
Ans: Three activities that increase the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere are:
Emission from the vehicles
Burning of fossil fuels
Forest fires due to human activities, deforestation.
What is the greenhouse effect?
Ans: A rise in the amount of methane, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide etc. in the atmosphere would cause the average temperature to increase on a global level. This is called the greenhouse effect.
15. What are the Two Forms of Oxygen Found in the Atmosphere?
Ans: A diatomic molecular form (O2) and a triatomic molecular form (O3) of oxygen are present in the environment (O3 known as ozone).
16. Why is the Atmosphere Essential for Life?
Ans: The atmosphere maintains the Earth's average temperature fairly constant throughout the day and even throughout the year. During daytime hours, the atmosphere prevents a rapid rise in temperature. It reduces the amount of heat that escapes into space throughout the night. The atmosphere is necessary for life for all of these reasons.
17. Why is Water Essential for Life?
Ans: In a water medium, all cellular activities take place. All of the processes that occur within our bodies and cells take place between chemicals that are dissolved in water. Dissolved substances are transferred from one region of the body to another. As a result, organisms must maintain a constant amount of water within their bodies in order to survive.
18. How are Living Organisms Dependent on the Soil? Are Organisms That Live in Water Totally Independent of Soil as a Resource?
Ans: All living organisms are dependent on soil. Certain organisms rely on each other directly, while others rely on each other indirectly. Plants require soil to acquire nutrients and support. On the other hand, organisms depend on plants for food which is essential for life. Carnivores feed on animals, which in turn rely on plants for food, whereas herbivores feed on plants directly. As a result, they are indirectly dependent on soil. Water-dwelling organisms are not dependent on the soil as a source of food. Minerals are required for the survival of aquatic plants. Rivers, rains, and other natural processes transport these minerals from the soil to aquatic bodies. Aquatic life is hard to envisage without the flow of minerals from the land to the water bodies.
19. You Have Seen Weather Reports on Television and in Newspapers. How Do You Think We Can Predict the Weather?
Ans: Temperature, humidity, rainfall, wind speed, and other weather variables are collected by the meteorological department. These data are collected using various instruments. A thermometer known as a maximum-minimum thermometer is used to determine the day's maximum and lowest temperatures. The rain gauge is a device that measures the amount of rain that falls. Anemometers are used to measure wind speed. Humidity is measured using a variety of devices.
20. We Know That Many Human Activities Lead to Increasing Levels of Pollution of the Air, Water- Bodies and Soil. Do You Think That Isolating These Activities to Specific and Limited Areas Would Help in Reducing Pollution?
Ans: Yes, limiting human activity to restricted regions will undoubtedly aid in pollution reduction. For instance, Industries that are set up in the isolated regions will not contaminate the water resource, fertile land and agricultural land. To some extent, these methods will reduce pollution.
21. Write a Note on How Forests Influence the Quality of Our Air, Soil and Water Resources.
Ans: Forests have a variety of effects on all-natural resources. The below are a few examples. They keep the quantity of $$CO_2$$ and oxygen in the atmosphere in check. Forests help to minimize soil erosion by retaining the fertile soil in place with their roots. Forests contribute to the recovery of water supplies. Plants lose water through transpiration, which then condenses to produce clouds. These clouds produce rain, which replenishes water bodies.
Topics Covered in the Chapter
The following are the important topics that are discussed in chapter 14, natural resources for class 9 students.
Introduction to natural resources
Introduction to air
Introduction to air pollution
Ozone layer and its depletion
Water: A Wonder Liquid
Water pollution
Mineral Riches in the Soil
Biogeochemical Cycles: Carbon cycle and nitrogen cycle.
Key Points at a Glance
The following are the important points that are discussed throughout chapter 14.
Resources are defined as the biotic and abiotic component that helps in the sustenance of life.
Soil, water, and air are the planet's resources. Energy sources, light, air, and minerals, are examples of many other resources.
The earth's atmosphere is defined as a gaseous layer that surrounds it.
By volume, atmospheric air contains 78 per cent nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% additional gases.
Air pollution is defined as the addition of contaminats in the air.
The ozone layer is defined as a thin layer of the atmosphere that forms a protective shield over the stratosphere and filters most ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
Water pollution is the polluting of fresh and clean water bodies as a result of contaminants being discharged directly or indirectly into them without being properly treated.
The constant passage of water from the earth's surface to the atmosphere and again back to the ground is known as the water cycle, this is also known as the hydrologic cycle.
Soil pollution is characterized by the accumulation of toxic and hazardous contaminants to the soil that renders it barren. Fertilizers, pesticides, industrial wastes, oil spills, acid rain, and other pollutants are the primary sources of soil pollution.
The natural cycle or paths via which necessary substance is transported across an ecosphere biotic and abiotic components.
The carbon cycle is the movement and change of carbon among biotic components and the ecosystem.
The nitrogen cycle is the process of reusing and repurposing nitrogen in different forms in order to meet the needs of diverse environmental activities.
Chapter 14 Class 9 Science PDF Download
We provide you with NCERT class 9 science chapter 14 solutions in the PDF downloadable version as well. This provides the students with the freedom to study and prepare for their examinations from wherever they want. Alongside, they can also get the hardcopy class 9 natural resources NCERT solutions printed easily.
You can opt for Chapter 14 - Natural Resources NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science PDF for Upcoming Exams and also You can Find the Solutions of All the Maths Chapters below.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science
Chapter 1 - Matter in Our Surroundings
Chapter 2 - Is Matter Around us Pure
Chapter 3 - Atoms and Molecules
Chapter 4 - Structure of Atom
Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life
Chapter 6 - Tissues
Chapter 7 - Diversity in Living Organisms
Chapter 8 - Motion
Chapter 9 - Force and Laws of Motion
Chapter 10 - Gravitation
Chapter 11 - Work and Energy
Chapter 12 - Sound
Chapter 13 - Why do We Fall ill
Chapter 14 - Natural Resources
Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources
Along with this, students can also view additional study materials provided by Vedantu, for Class 9
NCERT Solutions For Class 9
Revision Notes for Class 9
CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
NCERT Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Solutions- Natural Resources
Introduction.
Earth is the only planet where life is found. This life exists because of its resources which include the land, water and air. There are several other resources on which life forms are reliable. Alongside, it also comprises the biotic and abiotic components of life.
14.1 The Breath of Life: Air
The atmosphere is a composition of several gases which include nitrogen, carbon, oxygen, water vapours, etc. Atmosphere covers the earth like a blanket keeping the temperature steady. It also plays a key role in reducing the amount of heat escaping into outer space.
Air Pollution
It is caused because of the harmful and toxic elements present in the atmosphere, some of which include pollutants and organic molecules. The causes of air pollution are mostly because of human-made sources which include fuel combustion, smoke, etc. The other natural causes include forest fires, etc. The air pollution has several negative effects on the atmosphere, which include global warming, acid rain, respiratory diseases, etc.
14.2 Water: A Wonder Liquid
Under this section, we talk of water which is among the most important resources. Only 3% of water available on earth is freshwater, the remaining 97% of which is covered by oceans.
Water Pollution
It happens when water is contaminated due to excessive pollutants being discharged in the water bodies without adequate treatment. Some of the causes of water pollution include:
Agriculture
Urbanisation
Transpiration
It is the process in which the water is lost in the atmosphere from parts of a plant called stomata.
Evaporation
It is the process through which water is lost in the atmosphere in the form of vapours.
14.3 Mineral Riches in The Soil
This section talks about soil, its importance and its components. It is the uppermost layer of the earth’s crust. Soil is formed due to continuous weathering of the mountains. The factors which lead to soil formation include:
Parent material
Organisms present in the soil
Composition of Soil
Soil is made of organic matter, the basic components of which include water, air, and other inorganic matter as well. There are various types of soils across different regions.
Soil Pollution
Soil pollution is defined as the addition of harmful substances to the soil, which makes it unproductive. Some of the pollutants include acid rain, industrial wastes, etc.
Soil Erosion
It is yet another form of soil degradation. The prime agents which lead to soil erosion include rainwater, wind, flowing water, etc. Soil erosion leads to a loss of topsoil, which further reduces the potential for crop production.
14.4 Biogeochemical Cycles
These are defined as the biological cycles in which natural elements are circulated through both biotic and abiotic parts in the ecosystem.
There are Mainly Three Biogeochemical Cycles Which Include:
Carbon cycle
Nitrogen cycle
Oxygen cycle
14.5 Ozone Layer
It is defined as a thin layer which acts as a shield for the earth, protecting it from the injurious radiation of the sun. It mainly consists of high concentrations of ozone.

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 - Natural Resources
1. What is the ozone layer depletion?
According to chapter 14 science class 9, it is defined as the reduction of ozone in the stratosphere. This leads to harmful UV radiations entering the earth’s atmosphere.
2. What is the greenhouse effect?
The greenhouse effect is referred to as the trapping of solar radiation in the earth’s atmosphere. It is a natural phenomenon. Some of the greenhouse gases include ozone, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapour, chlorofluorocarbon, etc.
3. How do forests influence the quality of water, air and soil resources?
Forests play a significant role in influencing the quality of natural resources and do so in multiple ways. Some of these include:
By maintaining the balance between carbon dioxide and oxygen in the atmosphere
Prevention of soil erosion by holding the soil intact with its roots and maintaining its fertility
Restoring water resources. Water evaporates through plants by transpiration and water bodies by evaporation, and condenses to form clouds. These clouds further discharge the water in the form of rainfall.
4. Is Chapter 14 important in Class 9 Science?
For you to score good grades, each chapter is important. Chapter ‘Natural Resources’ is as important as other chapters. The total weightage of this Chapter is also high. You can expect a few questions from this chapter for your final exam. Therefore, it is important that you prepare well. You can also visit Vedantu website and mobile app for free NCERT Solutions to help you understand the chapter better.
5. Are NCERT Solutions for Chapter 14 of Class 9 Science enough for exam preparation?
Vedantu provides NCERT solutions according to the CBSE marking scheme and the answers are provided from NCERT Book itself and in a student-friendly language. Nonetheless, it is important to go through the NCERT Book yourself and read all the chapters thoroughly. Followed by a thorough revision, you are good to go for the examination.
6. How long does it take to learn Chapter 14 of Class 9 Science from NCERT Book?
Natural Resources is not a very big chapter as compared to other chapters in the book. The concepts explained are easy to understand. The chapter contains a few new concepts that might take a little longer to understand and learn than others. The concept of understanding and learning is however subjective. Therefore, some may finish it in half a day while some may require a whole day.
7. Is Chapter 14 of Class 9 Science easy?
Yes, the chapter is easy and also very interesting as students learn a lot about the environment and the resources in use. If you are confused or stuck in between, you can always use NCERT Solutions from Vedantu to make sure you are able to understand the chapter easily. The solutions available on Vedantu are according to the CBSE curriculum and are updated according to the latest syllabus.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9
- CBSE- Natural Resources
- Sample Papers
Natural Resources-Sample Papers
- STUDY MATERIAL FOR CBSE CLASS 9 BIOLOGY
- Chapter 1 - Diversity in Living Organisms
- Chapter 2 - Improvement in Food Resources
- Chapter 3 - Natural Resources
- Chapter 4 - Why do we fall ill
- Chapter 5 - The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Chapter 6 - Tissues
- Toggle navigation

- CREST Mathematics Olympiad (CMO)
- CREST Science Olympiad (CSO)
- CREST English Olympiad (CEO)
- CREST Reasoning Olympiad (CRO)
- CREST Cyber Olympiad (CCO)
- CREST Mental Maths Olympiad (CMMO)
- International Green Warrior Olympiad (IGWO)
- CREST International Drawing Olympiad (CIDO)
- CREST International Spell Bee Summer (CSB)
- CREST International Spell Bee Winter (CSBW)
- International Teacher Olympiads
- Teacher Mathematics Olympiad
- Teacher Science Olympiad
- Teacher English Olympiad
- Exam Syllabus
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Papers
- Marking Scheme
- Cut-Offs & Ranking Criteria
- Awards & Recognition
- Subject Rankers
- Subject Cut-Off
- Zone Definition
- Green Warrior Initiatives
- Rankholder's Gallery
- Testimonials
- Olympiad Exam Blog
- WhatsApp Channel
- Olympiad Books
- Live Classes
- Mental Mathematics Olympiad (CMMO)
- Green Warrior Olympiad (IGWO)
- Country Wise Olympiads
- Student Registration
- Teacher Registration
- School Registration
- Become a Coordinator
- Special Needs Kids
- CMO arrow_drop_down
- CSO arrow_drop_down
- CEO arrow_drop_down
- CRO arrow_drop_down
- CCO arrow_drop_down
- CMMO arrow_drop_down
- IGWO arrow_drop_down
- CIDO arrow_drop_down
- CSB arrow_drop_down
- CSBW arrow_drop_down
- Individual Registration
- Register Your School
- Exam Schedule
- Ranking Criteria
- Become a Co-ordinator
- assignment_ind
- account_balance
Natural Resources
- About Topic
- Practice Questions
- More Topics
- Register for CREST Olympiads
- Online Classes
Natural Resources - Class 9 Science
Types of natural resources, air pollution, rainwater harvesting, soil erosion, soil pollution, biotic resources.
- Solved Questions on Natural Resources
Natural resources are the materials and components that occur naturally in the environment and are utilised by humans for various purposes. These resources are essential for sustaining life, supporting economic activities, and maintaining ecosystems. Natural resources can be broadly categorised into two main types: renewable and non-renewable resources.
1. Inexhaustible Natural Resources
These resources are abundant and not likely to be depleted despite continuous use.
Examples include:
- Air: The Earth's atmosphere, composed mainly of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide, is an inexhaustible resource.
- Water: Oceans, rivers, lakes, and groundwater provide a constant supply of water.
- Solar Energy: The sun's energy is an ongoing source of power that can be harnessed using solar panels.
2. Exhaustible Natural Resources
These resources are available in limited quantities and can be depleted with continuous and unchecked use. Exhaustible resources are further divided into two categories:
a) Renewable Resources: These resources can replenish themselves naturally over time, given responsible use.
- Forests: Trees can regrow and renew themselves through reproduction, making them a renewable resource.
- Wildlife: Populations of various animal species can reproduce and sustain themselves if conservation efforts are in place.
- Soil: Proper soil management practices can allow soil to regenerate and remain fertile.
- Underground Water: Responsible water usage and management can ensure a sustainable supply of underground water.
b) Non-renewable Resources: These resources cannot naturally replenish themselves in human timescales. Once they are depleted, they are gone.
- Minerals: Elements like iron, copper, and aluminium are finite in supply and cannot be regenerated within human lifetimes.
- Fossil Fuels: Coal, oil, and natural gas are formed over millions of years and cannot be renewed in a short time. Once extracted and used, they are gone.
Air is a mixture of gases that surrounds the Earth. It is composed of various gases, with nitrogen and oxygen being the most abundant. Other gases, such as carbon dioxide, argon, and trace amounts of other gases, also contribute to the composition of air. Air is essential for sustaining life on Earth and plays a crucial role in many natural processes.
The atmosphere is the layer of gases that surrounds the Earth and is held in place by gravity. It is divided into different layers based on altitude, each with distinct characteristics. The main layers, from lowest to highest, are the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere, and exosphere. The atmosphere serves several important functions:
- Protection: The atmosphere acts as a protective shield, absorbing and scattering harmful solar radiation (UV rays) and cosmic rays. It prevents these radiations from reaching the Earth's surface and causing damage to living organisms.
- Climate Regulation: The atmosphere plays a vital role in regulating the Earth's temperature. Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and water vapour, trap heat and maintain the planet's temperature within a habitable range. This phenomenon is known as the greenhouse effect.
- Weather Patterns: The movement of air masses and the distribution of heat contribute to the formation of weather patterns. The atmosphere carries moisture, which condenses to form clouds and precipitation. Wind patterns are influenced by differences in temperature and pressure.
- Oxygen Supply: Oxygen, present in the atmosphere, is essential for the respiration of humans, animals, and most organisms. It supports cellular processes and energy production.
- Carbon Cycle: The atmosphere is involved in the carbon cycle, where carbon dioxide is exchanged between the atmosphere, oceans, and land through processes like photosynthesis and respiration.
Wind: Causes and Patterns
Air movement, known as wind, is a fundamental aspect of our atmosphere, influencing our daily experiences and weather patterns. The intricate dance of wind is driven by various factors, including temperature differentials, pressure variations, and Earth's rotation.
- Causes of Air Movement: The primary driver of air movement is the uneven heating of the Earth's surface by solar radiation. This process creates variations in temperature and pressure, prompting air to flow from areas of high pressure to those of low pressure. These movements give rise to the diverse wind patterns we observe.
- Temperature and Pressure Gradients: The intensity and character of wind, whether a gentle breeze or a powerful storm, depend on the degree of temperature and pressure differences between regions. Regions receiving more sunlight become warmer, leading to the expansion of air and lower pressure. Conversely, cooler regions experience denser air and higher pressure. This contrast in pressure propels the air, creating wind currents.
- Diurnal Air Movement: Coastal areas exhibit distinct air movement patterns due to the uneven heating of land and water. During the day, land heats up more quickly than water, causing cooler air from the sea to flow toward the warmer land. It is known as the sea breeze. At night, the land cools rapidly, leading to a reversal in air flow as cooler air from the land moves toward the warmer sea. This is known as a land breeze. These shifts are driven by the variations in heating rates between land and water.
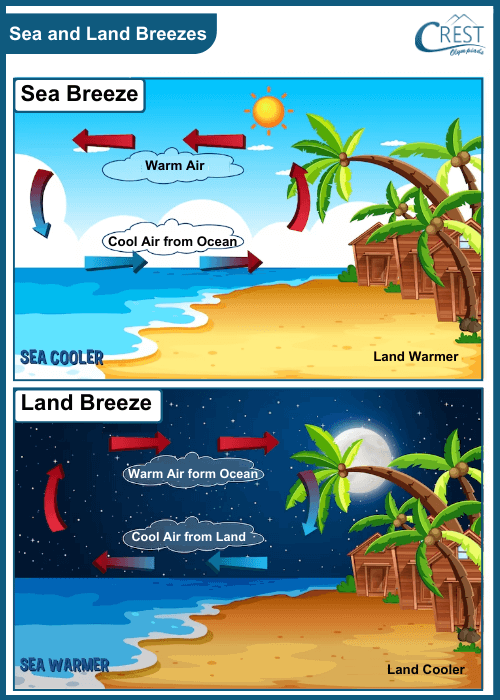
- Vertical Air Movement and Fronts: The interplay of temperature and pressure gradients also leads to vertical air movement. Warmer air near the surface, being lighter, rises, creating a low-pressure area. This uplift can lead to cloud formation and precipitation. Additionally, the collision of warm and cold air masses generates fronts and depressions, contributing to the complexity of Earth's atmospheric dynamics.
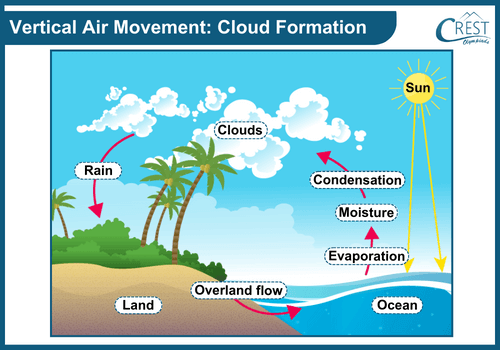
- The Coriolis Effect: The Coriolis Effect is a phenomenon that occurs due to the Earth's rotation. When objects, like air or water, move across the Earth's surface, they appear to be deflected to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere. This deflection happens because the Earth is rotating beneath these moving objects.
Imagine you're standing on a spinning carousel, and you throw a ball to someone across from you. To you, the ball appears to curve as it travels, even though you threw it in a straight line. This is similar to how the Coriolis Effect works. The Earth is like that spinning carousel, and anything that moves across its surface, like air masses or ocean currents, seems to curve due to the Earth's rotation.
The Coriolis Effect has a significant impact on various phenomena, especially large-scale movements like global wind patterns and ocean currents. It influences the way weather systems, like hurricanes, rotate and move. This effect is essential for understanding Earth's dynamic systems and how they interact with its rotation.
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the air that can have adverse effects on human health, the environment, and ecosystems. These pollutants can originate from natural sources, such as volcanic eruptions and wildfires, or human activities, such as industrial processes, transportation, and burning of fossil fuels.
Common Air pollutants
- Particulate matter (PM): Tiny solid particles or liquid droplets suspended in the air.
- Ground-level ozone (O 3 ): A component of smog formed by the reaction of pollutants in the presence of sunlight.
- Nitrogen oxides (NOx): Gases produced from combustion processes, contributing to smog and acid rain.
- Sulphur dioxide (SO 2 ): A gas produced from burning fossil fuels and industrial processes, leading to acid rain.
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): Gases emitted from vehicles, industrial processes, and solvents.
- Carbon monoxide (CO): A colourless, odourless gas produced by incomplete combustion.
Effects of Air Pollution
Air pollution can have a range of negative effects on human health, the environment, and the atmosphere:
- Health Impacts: Air pollutants can cause respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, aggravate asthma, and lead to premature death. Long-term exposure to polluted air is linked to chronic health conditions.
- Environmental Impact: Air pollution can harm plant life, damage crops, and acidify soils. It can also affect aquatic ecosystems by contaminating water bodies through deposition.
- Smog Formation: High levels of air pollutants can lead to the formation of smog, a type of air pollution characterised by a hazy appearance and poor visibility.
- Global Warming: Some air pollutants, such as carbon dioxide and methane, contribute to global warming by enhancing the greenhouse effect and causing temperature rise.
- Ozone Depletion: Certain pollutants can lead to the depletion of the ozone layer, allowing harmful UV radiation to reach the Earth's surface, increasing the risk of skin cancer and other health issues.
- Acid Rain: Pollutants like sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides can combine with water vapour in the atmosphere to form acid rain. Acid rain damages vegetation, aquatic ecosystems, and buildings.
Water is a colourless, odourless, and tasteless substance that covers about 71% of Earth's surface. It exists in various forms – solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (water vapour) – and plays a fundamental role in supporting life on our planet. Water is a universal solvent, meaning it can dissolve a wide variety of substances, making it essential for many biochemical processes. It is also a major component of all living organisms.
Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere refers to the total amount of water on Earth's surface, including oceans, rivers, lakes, glaciers, groundwater, and even water vapour in the atmosphere. It's a dynamic system where water constantly moves and cycles through different forms and locations.
Water Pollution
Water pollution refers to the contamination of water bodies – including rivers, lakes, oceans, and groundwater – by harmful substances. Pollutants can originate from various sources and have detrimental effects on aquatic ecosystems, human health, and the environment.
Sources of Water Pollution
a) Point Sources of Water Pollution: Point sources are pollution discharge points that have a specific and identifiable location from which pollutants are directly released into water bodies. These sources are usually well-defined and relatively easier to monitor and regulate. Because point sources have a fixed location, it is often possible to implement pollution control measures, such as installing treatment systems, before the pollutants are discharged into water bodies. Regulations and permits can be issued to ensure that the released pollutants meet acceptable standards.
Some examples of point sources include:
- Factories and industrial facilities that release wastewater containing chemicals, heavy metals, and other pollutants.
- Power plants that discharge heated water into water bodies.
- Sewage treatment plants that release treated or untreated wastewater.
- Underground coal mines and oil wells may release pollutants into groundwater.
b) Non-point Sources of Water Pollution: Non-point sources are diffuse and scattered pollution inputs that do not have a specific discharge point. They result from the runoff of pollutants from various land surfaces, making them more challenging to identify and control.
Some examples of non-point sources include:
- Runoff from agricultural fields carrying fertilisers, pesticides, and soil particles.
- Urban runoff from roads, streets, and parking lots carrying oil, chemicals, and litter.
- Runoff from lawns and gardens containing fertilisers and pesticides.
- Erosion from construction sites, logging areas, and disturbed land.
Causes of Water Pollution
- Industrial Discharges: Factories and industries release various chemicals, heavy metals, and pollutants into water bodies through their wastewater.
- Agricultural Runoff: Excessive use of fertilisers, pesticides, and herbicides in agriculture can lead to runoff that carries these chemicals into water bodies.
- Sewage and Wastewater: Improperly treated or untreated sewage and wastewater release harmful pathogens and pollutants into water bodies.
- Oil Spills: Accidental or intentional release of oil into water bodies can harm aquatic life and degrade water quality.
- Plastic and Trash: Improper disposal of plastic waste and other debris can accumulate in water bodies, harming marine life and ecosystems.
- Mining Activities: Mining operations can release heavy metals and toxic substances into nearby water bodies.
Effects of Water Pollution
- Impact on Human Health: Contaminated water sources can lead to various waterborne diseases, including cholera, typhoid, dysentery, hepatitis, and gastrointestinal infections. Pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and parasites present in polluted water can cause severe illnesses and even death, particularly in areas with inadequate sanitation and water treatment facilities.
- Aquatic Ecosystem Damage: Pollutants can disrupt aquatic ecosystems, killing aquatic organisms, disrupting food chains, and reducing biodiversity.
- Loss of Biodiversity: Water pollution can harm aquatic plants and animals, leading to habitat destruction and a loss of biodiversity. Many species of fish, amphibians, and invertebrates are sensitive to changes in water quality and can be severely impacted by pollution. This can disrupt entire food chains and ecological relationships.
- Depletion of Oxygen: Organic pollutants from sewage and industrial waste can lead to increased microbial activity during decomposition. As microorganisms break down these pollutants, they consume oxygen from the water, leading to reduced oxygen levels. Low oxygen levels (hypoxia) can cause "dead zones" where aquatic life cannot survive.
- Economic Impact: Industries that rely on clean water, like fishing and tourism, can suffer economic losses due to polluted water bodies.
- Food Chain Contamination: Pollutants can accumulate in the food chain, affecting both aquatic and human organisms that rely on contaminated sources.
- Eutrophication: Eutrophication is a process that occurs when water bodies, such as lakes, rivers, and ponds, become enriched with excess nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. These nutrients often come from sources like agricultural runoff, sewage discharge, and industrial effluents. The excessive nutrients cause rapid growth of algae and aquatic plants, leading to a series of detrimental effects.
Preventing Water Pollution
Efforts to prevent water pollution include:
- Regulations: Governments enact laws and regulations to limit pollutant discharges and protect water quality.
- Wastewater Treatment: Industries and municipalities treat their wastewater before releasing it into water bodies.
- Waste Management: Proper disposal and recycling of waste, especially plastics, can prevent pollutants from entering water bodies.
- Conservation Practices: Implementing sustainable agriculture practices, reducing fertiliser use, and promoting responsible waste disposal can help prevent pollution.
- Public Awareness: Educating individuals about the importance of clean water and responsible behaviour can lead to more conscious water use and pollution prevention.
Rainwater harvesting is a technique used to collect and store rainwater for various purposes. It involves the capture of rainwater from surfaces like rooftops, which is then stored in tanks or underground reservoirs. Rainwater harvesting can provide a sustainable source of fresh water in areas with low rainfall or limited access to surface or groundwater. It has several benefits:
- Water Conservation: Harvesting rainwater reduces the demand for other water sources, easing pressure on freshwater supplies.
- Reduced Flooding: Collecting rainwater reduces surface runoff, which can help mitigate flooding during heavy rainfall.
- Groundwater Recharge: By infiltrating into the ground, harvested rainwater can replenish underground aquifers and maintain groundwater levels.
- Cost Savings: Rainwater harvesting can reduce the cost of water bills, especially for non-potable uses like irrigation and toilet flushing.
Soil is a complex mixture of minerals, organic matter, water, air, and living organisms that covers the Earth's land surface. It plays a crucial role in supporting plant growth, providing nutrients to organisms, filtering and storing water, and serving as a habitat for various organisms. Soil is formed through the process of weathering of rocks and the accumulation of organic material over time.
Formation of Soil
Soil formation is a gradual process influenced by various factors, including climate, parent material (rock from which soil forms), topography, organisms, and time. The process involves physical, chemical, and biological interactions:
- Weathering: Weathering is the initial step where rocks are broken down into smaller particles. Physical weathering involves processes like freezing and thawing that break rocks apart. Chemical weathering involves reactions with water, gases, and minerals, leading to rock decomposition.
- Organic Matter Accumulation: As plants and animals decay, they contribute organic matter to the soil. This organic matter enriches the soil's fertility by providing nutrients and creating a better environment for organisms.
- Leaching: Water moving through the soil can carry dissolved minerals and nutrients from the upper layers down to the lower layers. Leaching plays a crucial role in redistributing nutrients within the soil profile.
- Mineralization: Organic matter present in the soil decomposes over time through microbial activity. This decomposition releases nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, into the soil.
- Humus Formation: Partially decomposed organic matter accumulates as dark, nutrient-rich humus. Humus enhances soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient retention.
- Soil Horizons: Over time, distinct layers or horizons form within the soil profile. Each horizon has its own unique characteristics, including texture, colour, and nutrient content. The different horizons are labelled as O, A, B, C, and sometimes even deeper layers.
Composition of Soil
Soil is a complex mixture of various components, each contributing to its overall characteristics and properties. The composition of soil includes:
- Mineral Particles: Soil is primarily composed of mineral particles, which are categorised based on their size: sand, silt, and clay. Sand particles are the largest, followed by silt particles, and clay particles are the smallest. The relative proportions of these particles determine the soil's texture. Sandy soils have larger particles, allowing for good drainage but lower water-holding capacity. Clay soils have small particles, leading to higher water retention but poor drainage. Silt falls between these two extremes.
- Organic Matter: Organic matter in the soil consists of decomposed plant and animal materials. It plays a crucial role in soil fertility, structure, and nutrient availability. Organic matter improves soil's water-holding capacity, aeration, and nutrient-holding capacity. It also provides a habitat for beneficial soil organisms.
- Water: Water is present in the spaces between soil particles. It is essential for plant growth and nutrient transportation within the soil. The amount of water soil can hold depends on its texture and structure.
- Air: Air also occupies the spaces between soil particles. Adequate air circulation in the soil is crucial for root respiration and the survival of soil organisms.
The relative proportions of these components influence soil properties such as drainage, water-holding capacity, aeration, fertility, and suitability for plant growth.
Types of Soil
Soils are categorised based on their particle size and properties:
- Clay Soil: This type of soil has fine particles and retains water well. It can become easily compacted, leading to drainage issues and poor aeration.
- Sandy Soil: Sandy soil has larger particles and doesn't retain water well. It provides good drainage and aeration but may lack essential nutrients.
- Silt Soil: Silt soil contains fine particles that are smaller than sand but larger than clay. It has good water retention and drainage properties and is fertile.
- Loam Soil: Loam soil is a balanced mixture of sand, silt, and clay. It has good water-holding capacity, and proper drainage, and is considered ideal for plant growth.
- Peat Soil: Peat soil is rich in organic matter and retains a lot of moisture. It's often found in wetlands and can be fertile but requires careful management.
Effect of Minerals on Soil Fertility
- Limestone: Limestone is calcium carbonate and can neutralise acidic soils, raising pH. It enhances fertility by improving nutrient availability in slightly acidic soils.
- Phosphate Minerals: Minerals like apatite provide phosphorus, a crucial nutrient for plant growth. Adding phosphate-rich minerals or fertilisers enhances soil fertility.
- Potassium Minerals: Minerals like feldspar release potassium as the weather. Potassium is essential for root development and overall plant health.
- Organic Matter: Adding materials like compost, manure, and plant residues improves soil structure, water retention, and nutrient availability, thus boosting fertility.
- Micronutrient-Bearing Minerals: Minerals containing micronutrients like iron, zinc, and copper contribute to soil fertility by providing essential trace elements for plants.
Soil erosion is the process of detachment and movement of soil particles from their original location by agents like water, wind, and human activities.
Causes of Soil Erosion
- Water Erosion: This type of erosion occurs due to the impact of rainfall, surface runoff, and water currents. Raindrops dislodge soil particles, which can be transported by flowing water. Streams, rivers, and even ocean currents can carry away eroded soil. Water erosion is particularly prominent on sloped landscapes.
- Wind Erosion: Wind erosion is common in arid and semi-arid regions with sparse vegetation cover. Strong winds lift and carry loose soil particles, causing them to collide with other surfaces or drop in different areas. This process is most likely to happen when the soil is dry and lacks vegetation to anchor it.
- Human Activities: Human-induced factors can greatly accelerate soil erosion:
- Deforestation: Removing trees and plants exposes soil to the impact of raindrops and reduces root systems that help hold soil in place.
- Construction: Grading and construction activities disturb the soil's natural structure and increase its vulnerability to erosion.
- Overgrazing: Continuous grazing by livestock removes vegetation cover, leaving the soil exposed to erosive forces.
Improper Agricultural Practices: Practices like ploughing along slopes, leaving fields bare between crops, and not implementing proper soil conservation measures can lead to soil erosion.
Effects of Soil Erosion
Soil erosion can have significant and far-reaching impacts on both the environment and human activities. Some of the key effects of soil erosion include:
- Loss of Fertility: Eroded topsoil contains valuable nutrients and organic matter essential for plant growth. As this nutrient-rich layer is carried away, the remaining soil becomes less fertile, leading to decreased agricultural productivity.
- Reduced Agricultural Productivity: The loss of fertile topsoil directly affects crop yields and agricultural productivity. Farmers may experience lower harvests and struggle to grow healthy crops.
- Sedimentation: Eroded soil particles can be transported by water runoff into rivers, lakes, and other water bodies. This sedimentation not only reduces the water-holding capacity of these bodies but also degrades water quality by carrying pollutants and nutrients. Aquatic habitats and ecosystems can suffer as a result.
- Landslide Risk: Soil erosion weakens the stability of slopes and hillsides. As the protective topsoil layer is eroded, the underlying soil becomes more prone to landslides, especially during heavy rainfall or other erosive events. Landslides can damage infrastructure, disrupt communities, and pose safety risks.
- Impact on Infrastructure: Eroded soil can accumulate in areas such as roads, ditches, and drainage systems, causing blockages and reducing the efficiency of these structures. This can lead to increased maintenance costs and disruptions to transportation.
- Desertification: In severe cases, continuous soil erosion can lead to the expansion of desert-like conditions, where fertile land turns into unproductive arid landscapes. This process, known as desertification, has serious consequences for local communities and ecosystems.
- Economic Consequences: The negative effects of soil erosion can result in economic losses for agricultural sectors, increased expenses for sediment cleanup in water bodies, and the need for soil conservation efforts. These economic impacts can ripple through communities and regions.
Prevention of Soil Erosion
Implementing effective soil erosion prevention measures is crucial for maintaining soil health and sustainability. Some key strategies for preventing soil erosion include:
- Plant Vegetative Cover: Planting and maintaining vegetation, such as grasses, shrubs, and trees, provides natural protection against soil erosion. The vegetation acts as a barrier, reducing the impact of raindrops and wind on the soil surface, and preventing detachment and erosion.
- Terracing: Constructing terraces on slopes involves creating level platforms with short vertical slopes. Terracing slows down the flow of water down the slope, allowing more time for water to infiltrate the soil. This helps to reduce erosion and retain moisture.
- Contour Farming: Ploughing and planting crops perpendicular to the slope contour rather than following the slope helps to slow down water runoff. This method reduces the speed at which water flows across the land, minimising erosion and allowing water to infiltrate the soil more effectively.
- Cover Crops: Planting cover crops, also known as green manure, between main crops, helps protect the soil from erosion during periods when the main crops are not growing. Cover crops improve soil structure, reduce surface runoff, and prevent soil from being exposed to erosive forces.
- Mulching: Applying a layer of organic or synthetic materials, such as straw, wood chips, or plastic, to the soil surface helps to reduce erosion by creating a protective barrier. Mulch slows down water flow, prevents soil splashing, and promotes water infiltration.
- Windbreaks: Planting rows of trees or shrubs along the edges of fields helps reduce wind erosion by acting as a wind barrier. Windbreaks also provide habitat for wildlife and can have multiple benefits beyond erosion prevention.
- Erosion-Control Structures: Installing physical structures like silt fences, check dams, and sediment ponds in areas prone to erosion can capture sediment and prevent it from entering water bodies.
- Sustainable Land Management: Adopting integrated land management practices that take into account soil health, water management, and crop selection can contribute to long-term erosion prevention.
Soil pollution refers to the contamination of soil with pollutants such as chemicals, heavy metals, pesticides, industrial waste, and sewage.
Causes of Soil Pollution
Soil pollution occurs due to various human activities that introduce harmful substances into the soil, affecting its quality and fertility. Some key causes of soil pollution include:
- Industrial Activities: Industries release pollutants and hazardous chemicals into the environment. These pollutants can find their way into the soil through various pathways, contaminating it with heavy metals, toxins, and synthetic chemicals.
- Agricultural Chemicals: The excessive use of pesticides, herbicides, and synthetic fertilisers in agriculture can lead to the accumulation of toxic chemicals in the soil. These chemicals can disrupt soil ecosystems and impact both soil and water quality.
- Improper Waste Disposal: The improper disposal of various types of waste, including untreated sewage, household waste, and electronic waste, can contaminate the soil. Toxic substances from these wastes can leach into the soil, posing risks to human health and the environment.
- Mining Activities: Mining operations can release heavy metals, toxic chemicals, and acidic substances into the soil. These contaminants can persist in the soil for long periods, affecting soil structure and fertility.
- Urbanization: The expansion of urban areas brings increased construction activities, vehicle emissions, and waste generation. Urban waste disposal, improper management of construction materials, and vehicle-related pollutants can all contribute to soil pollution.
- Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture or development exposes the soil to erosion and degradation. Soil in deforested areas is more vulnerable to pollution from other sources due to reduced vegetation cover.
- Contaminated Water Irrigation: Using contaminated water for irrigation can introduce pollutants and toxins into the soil. Irrigation with untreated or polluted water can lead to the accumulation of salts, heavy metals, and pathogens in the soil.
- Atmospheric Deposition: Airborne pollutants, such as heavy metals, can be deposited onto the soil through rain, dust, and industrial emissions. These pollutants can accumulate in the soil over time.
- Chemical Spills and Accidents: Accidental spills of chemicals, oil, or hazardous substances can lead to immediate soil contamination. These spills can impact the soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties.
- Landfill Leachate: Leachate from landfills contains a mixture of pollutants that can seep into the surrounding soil, contaminating it with a range of hazardous substances.
Effects of Soil Pollution
Soil pollution has far-reaching consequences for the environment, human health, and ecosystems. Some of the key effects of soil pollution include:
- Reduced Soil Fertility: Pollutants in the soil can disrupt the natural nutrient balance, making essential nutrients less available to plants. This results in reduced crop yields and overall plant growth, impacting agricultural productivity.
- Contaminated Food Chain: Pollutants present in the soil can be taken up by plants and subsequently transferred to animals and humans through the food chain. This can lead to the accumulation of harmful substances in edible parts of plants and animals, posing risks to human health.
- Groundwater Contamination: Pollutants from the soil can leach into groundwater, which is a vital source of drinking water for many communities. Contaminated groundwater can carry toxic substances, heavy metals, and chemicals, affecting drinking water quality and endangering public health.
- Negative Impact on Biodiversity: Soil pollution can harm soil-dwelling organisms such as earthworms, bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that play crucial roles in nutrient cycling and maintaining soil structure. The disruption of soil ecosystems can have cascading effects on higher trophic levels, impacting biodiversity.
- Ecosystem Disruption: Polluted soil can disrupt entire ecosystems by affecting the health and vitality of plants, animals, and microorganisms. Soil pollution can alter the composition of plant communities, leading to changes in animal populations and overall ecosystem dynamics.
- Soil Structure Degradation: Pollutants can alter the physical properties of soil, causing compaction, reduced water-holding capacity, and decreased soil porosity. These changes can negatively impact plant root growth and water infiltration.
- Air Quality Impacts: Some pollutants in contaminated soil can become airborne through processes like volatilization or wind erosion. These airborne pollutants can contribute to poor air quality and may have additional negative impacts on human health.
- Health Risks to Humans: Direct exposure to polluted soil can lead to various health risks for humans, such as skin diseases, respiratory issues, and the absorption of toxic substances. Consuming crops grown in polluted soil can also pose health hazards.
- Economic Losses: Soil pollution can lead to economic losses in agriculture due to reduced crop yields, increased input costs, and the need for soil remediation measures. It can also impact tourism and property values in contaminated areas.
Prevention and Mitigation of Soil Pollution
- Proper Waste Management: Effective disposal and treatment of industrial, household, and electronic waste prevent harmful substances from leaching into the soil. Safe waste disposal facilities, recycling, and proper hazardous waste management minimise the introduction of pollutants into the environment.
- Integrated Pest Management: By reducing reliance on chemical pesticides and incorporating practices like crop rotation, biological control, and using pest-resistant crop varieties, agricultural pollution from excessive pesticide use can be minimised.
- Soil Testing: Regular soil testing allows farmers, landowners, and authorities to monitor soil quality, identify potential contamination, and take corrective measures to maintain healthy soil conditions.
- Bioremediation: This technique utilises the natural abilities of certain plants and microorganisms to break down or remove pollutants from the soil. Plants may absorb and accumulate contaminants, while microorganisms can break down pollutants through biological processes.
- Reforestation: Planting trees and restoring vegetation cover helps prevent soil erosion by stabilising the soil with their root systems. Trees also play a role in absorbing pollutants and promoting healthy soil microbial communities.
- Regulation and Legislation: Enforcing strict environmental regulations and policies establishes guidelines for industries, agriculture, and individuals to follow responsible practices and reduce pollution.
- Contaminated Site Remediation: In cases where soil pollution has already occurred, various techniques such as soil excavation, soil washing, and soil vapour extraction can be employed to remove or treat contaminants and restore soil quality.
- Public Awareness and Education: Educating communities about the importance of responsible soil management practices, waste reduction, and pollution prevention raises awareness and encourages collective efforts to safeguard soil health.
- Green Infrastructure: Designing urban spaces with green roofs, permeable pavements, and vegetation helps manage stormwater runoff, prevent soil erosion, and mitigate pollution by providing natural filtration.
- Industrial Best Practices: Industries can adopt cleaner production methods, reduce emissions, and implement proper waste disposal systems to minimise the release of pollutants into the environment.
- Wastewater Treatment: Treating industrial and domestic wastewater before it is discharged into the environment prevents harmful chemicals and contaminants from infiltrating the soil and groundwater.
Biotic resources, also known as biological resources, are living organisms and organic materials that are derived from living organisms. These resources play a vital role in supporting life on Earth and provide various goods and services essential for human well-being. Biotic resources include a wide range of living organisms, from microorganisms to plants and animals.
Biotic resources can be broadly categorised into two main types:
Flora (Plants)
Flora refers to the plant life found in a particular region or ecosystem. Plants are essential components of ecosystems, providing a multitude of resources and services to humans and other organisms.
Some key biotic resources derived from plants include:
- Timber: Trees provide wood for construction, furniture, paper, and other products.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Plants yield various edible fruits, vegetables, and nuts that are important for human nutrition.
- Medicinal Plants: Many plants have medicinal properties and are used to make traditional and modern medicines.
- Fibre: Plants like cotton and jute provide fibres used for textiles and other materials.
- Rubber and Latex: Rubber trees are tapped for latex, which is used to make rubber products.
- Biofuel Crops: Certain plants are cultivated for biofuel production, such as bioethanol and biodiesel.
Fauna (Animals)
Fauna refers to the animal life in a particular region or ecosystem. Animals provide a wide range of resources and services to humans and ecosystems.
Some important biotic resources derived from animals include:
- Livestock: Domesticated animals like cattle, poultry, and goats provide meat, milk, eggs, leather, and wool.
- Fish and Seafood: Aquatic animals are an important source of protein for many people around the world.
- Honey and Beeswax: Bees produce honey, beeswax, and other products with various uses.
- Silk: Silkworms produce silk, which is used to make textiles and fabrics.
- Leather and Fur: Animal hides are used to make leather products, and fur is used for clothing.
- Labour and Transportation: Some animals are used for labour in agriculture and transportation.
Importance of Biotic Resources
Biotic resources are essential for ecosystem services that contribute to environmental stability and human well-being.
These services include:
- Biodiversity: Biotic resources contribute to the diversity of species, which is crucial for ecosystem resilience and adaptation.
- Pollination: Insects, birds, and other animals facilitate the pollination of plants, ensuring the reproduction of many crops.
- Nutrient Cycling: The decomposition of organic matter by organisms contributes to nutrient cycling and soil fertility.
- Carbon Sequestration: Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and store carbon in their biomass, contributing to climate regulation.

Share Your Feedback
CREST Olympiads has launched this initiative to provide free reading and practice material. In order to make this content more useful, we solicit your feedback.
Do share improvements at [email protected]. Please mention the URL of the page and topic name with improvements needed. You may include screenshots, URLs of other sites, etc. which can help our Subject Experts to understand your suggestions easily.
Other Science Related Topics Class 9
- Force and Laws of Motion
- Classification of Kingdom Animalia
- Diversity, Hierarchy, and Classification of Kingdom Plantae
- Animal Tissues
- Plant Tissues
- Cell-The Fundamental Unit of Life
- Structure of the Atom
- Atoms and Molecules
- Is Matter Around Us Pure?
- Change in the State of Matter
- Physical Nature of Matter
- Biogeochemical Cycles
- Improvement in Food Resources
- Gravitation
- Work, Energy and Power
- Why do We Fall Ill?


Natural Resources Notes for Class 9 Science (PDF)
Natural Resources Notes for Class 9 Science are here. You can download the Natural Resources Notes PDF to study all the topics in this chapter. Moreover the class 9 Science notes include chapter summary, definitions, examples, and key pointers for Natural Resources . Thus if you are studying 9th class Science, then the Natural Resources notes will help you easily understand the topic and ace it.
Natural Resources Notes for Class 9 Science
Natural Resources is a critical part in the study of Science . In India, it is taught in 9th class. Therefore the class 9 Notes for Science topic Natural Resources have been compiled by teachers and field experts. They explain the complete chapter of Natural Resources in one-shot . Whether you are studying the topic Natural Resources to complete your 9th class syllabus, or for any competitive exam like JEE, NEET, UPSC, you can simply refer these notes to complete the chapter in one-shot!
Natural Resources Notes Download Link – Click Here to Download PDF
Natural Resources Notes for Class 9 Science PDF
The PDF of Natural Resources class 9 notes is as follows. You can view the document here and also download it to use it anytime for future reference whenever you want to brush up your concepts of Science.

Class 9 Notes for Science – All Chapters
If you are studying Natural Resources, then chances are that you will study the other chapters in class 9 Science. Therefore we have listed all the notes here in one place, as follows.
- Atoms And Molecules
- Diversity In Living Organism
- Force And Laws Of Motion
- Fundamental Unit Of Life – Cell
- Gravitation
- Improvement In Food Resources
- Is Matter Around Us Pure
- Matter In Our Surrounding
- Natural Resources
- Structure Of The Atom
- Why Do We Fall Ill
- Work And Energy
Class 9 Notes for All Subjects
- Class 9 English Notes
- Class 9 Maths Notes
- Class 9 Science Notes
- Class 9 Social Science Notes
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Natural Resources
The Natural Resources notes here help you solve the questions and answers . Also, you can complete the class 9 Natural Resources worksheet using the same. In addition you will also tackle CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions with these class 9 notes .
However if you still need help, then you can use the NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Natural Resources to get all the answers. Natural Resources solutions contain questions, answers, and steps to solve all questions.
Notes for All Classes

Natural Resources Notes for Class 9 Science – An Overview
Class 9 natural resources notes for all boards.
You can use the class 9 Science notes of Natural Resources for all boards.
The education boards in India for which Natural Resources notes are relevant are – CBSE, CISCE, SEBA, BSE Odisha, CGBSE, HBSE, HPBOSE, KSEEB, MSBSHSE, PSEB, RBSE, TBSE, UPMSP, UBSE, BSEAP, BSEB, GBSHSE, GSEB, JAC, JKBOSE, KBPE, MBOSE, MBSE, MPBSE, NBSE, DGE TN, BSE Telangana, BOSEM, WBBSE .
Therefore you can refer to these notes as CBSE, CISCE, SEBA, BSE Odisha, CGBSE, HBSE, HPBOSE, KSEEB, MSBSHSE, PSEB, RBSE, TBSE, UPMSP, UBSE, BSEAP, BSEB, GBSHSE, GSEB, JAC, JKBOSE, KBPE, MBOSE, MBSE, MPBSE, NBSE, DGE TN, BSE Telangana, BOSEM, WBBSE notes for class Class 9 / Class 9th / IX Science for the topic Natural Resources.
Share this:
Leave a reply cancel reply, discover more from oneedu24.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

Essay on Natural Resources for Children and Students

Table of Contents
Natural resources are commonly referred to the resources that are a gift of nature. They are produced naturally without the intervention of human beings. Sunlight, water, soil and air are some of the examples of natural resources. These are available in abundance in nature. However, there are various other natural resources also that are not found as easily. These include minerals and fossil fuels. Here are essays on natural resources of varying word lengths to help you with the same in your exam. You can select any natural resources essay as per your need:
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Long and Short Essay on Natural Resources in English
Natural resources essay – 1 (200 words).
Natural resources are the resources that are available naturally on our planet. We do not require any human intervention to derive them. These resources are essential for the survival of living beings. While some of the natural resources such as air, water and sunlight are used directly; others serve as raw material to produce various items of necessity.
Many of the natural resources are present in abundance and are renewable. This means that these can be recycled and reused. However, there are many others that are non-renewable or take thousands of years to replenish. Many natural resources are depleting fast. This is owing to several reasons. One of the main reasons is the growth in population. The consumption of natural resources is on an increase continually owing to the rapid population growth.
Deforestation is another cause for the depletion of natural resources. Land is being used for urbanization. This has led to the loss of wildlife and trees. The raw material derived from them is thus decreasing by the day. The growing pollution is affecting the water bodies negatively. The coming generations may have to face scarcity of water that was once available in abundance.
It is high time we humans must stop wasting the natural resources and use them wisely.

Natural Resources Essay – 2 (300 words)
Introduction
Natural resources are the resources that are made available by nature. Man does not have to work to derive these resources. Some of the examples of natural resources include water, air, sunlight, wood, minerals and natural gases. While many of the natural resources are available abundantly in nature others take time to form and are not available as freely.
Types of Natural Resources
While the characteristics and use of each natural resource is different from the other, these have broadly been classified in two categories. These are the renewable natural resources and non-renewable natural resources. Here is a look at these in detail:
- Renewable Natural Resources : Renewable natural resources, as the name suggests are the ones that can be renewed naturally and used over and over again. Water, solar energy, wood, biomass, air and soil fall under this category. While many of these resources such as water, air and sunlight is easily renewable it takes time to renew natural resources such as wood and soil. Renewable resources are further categorized into organic and non-organic.
When renewable resources are derived from living things like animals and plants these are termed as organic renewable resources. When renewable resources are derived from non-living things, they are termed as inorganic renewable resources.
- Non-Renewable Natural Resources : These are the resources that cannot be renewed or recycled or take a very long time to form again. Coal, oil, minerals and natural gases are examples of non renewable natural resources. While these form naturally without any human intervention, non-renewable natural resources such as minerals may take thousands of years to form. These are also divided into two categories – Organic and Non-organic.
Non-renewable natural resources derived from living organisms are called organic natural resources. One of the examples of this can be fossil fuel.
Non-renewable natural resources derived from non-living things such as wind, minerals, land and soil are known as inorganic natural resources.
Natural resources, especially the non-renewable resources, must be used wisely so that these are not depleted from nature.
Natural Resources Essay – 3 (400 words)
Natural Resources are the resources that have been available in nature since the beginning of the time. These resources make life possible on earth. Life on our planet would not have been possible without natural resources such as air, sunlight and water. Other natural resources are also as important and have become an integral part of our life.
Natural Resources Employed to Different Uses
While natural resources fulfil the basic necessities of man and other living beings on earth, they also form the basis for deriving various things. These things make life easier and comfortable. Today, man cannot imagine his life without most of these. Here is a look at the various ways in which natural resources are used:
- Sunlight : It is used to generate solar power which is used in various appliances. Sunlight also enables the process of photosynthesis.
- Air : Air is used to generate wind energy. Wind mills are employed to generate the same. It is used for various purposes such as grinding grains and pumping water.
- Water : Water is used to generate hydroelectric energy. It is also used for various cleaning tasks and cooking.
- Minerals : Minerals are used for generating several items that are used in our day to day lives. Wires, aluminium cans and parts of automobiles are among some of the things that are made with different kinds of minerals. Minerals such as gold and silver are used to craft jewellery.
- Natural gases : These are used to generate electricity. These are also used in the kitchen for the purpose of heating.
- Coal : This is another natural resource which is used for the purpose of generating electricity.
- Plants : Plants offer a number of natural resources such as wood, fruits and vegetables. While fruits and vegetables are essential to keep the living beings alive, wood is used to manufacture various pieces of furniture, paper and other products.
- Animals : Animals also provide numerous natural resources. They provide milk which is used to produce curd, cheese, butter and many other dairy products. Animal fur and skin are also used to derive various clothing items and other things of necessity. Woollen sweaters and caps, leather belts and bags, silk saris and bed linens are among some of the things made with the natural resources derived from animals.
Thus, natural resources are not only useful in their raw form but are also useful when they are employed to generate other stuff. Man has certainly made use of these resources in the best possible ways to make life better.
Natural Resources Essay – 4 (500 words)
Natural resources are a gift of the nature. These are consumed by the living organisms directly as well as indirectly. Direct consumption of natural resources implies using these resources in their pure form. The best examples of these can be sunlight and oxygen. Indirect consumption of natural resources means using them by modifying them or by generating other goods and services with their help. For instance, minerals, wood and many other natural resources are crafted into different materials before putting them to use.
Uses of Different Natural Resources
Natural Resources offer several uses. Without these, life would not be possible on earth. As per a survey, the developed countries use greater amount of natural resources compared to under-developed countries. Here is how these are used for various purposes:
Natural resources produced by animals are the kind of natural resources that are much in demand. This is because they provide us food which is essential for the survival of the living beings. Animals are tamed and reared to fetch organic natural resources from them. Milk and other dairy products that provide essential nutrients to the living beings are derived from animals. Fossil fuels derived from animal wastes are also employed for various tasks such as heating, running vehicles and generating electricity. Animal fur and skin is used for manufacturing clothes, bags, shoes, belts and other such items.
Plants provide us with fruits and vegetables that are essential for the survival of the living beings. Various medicines for curing different illnesses are also produced from these natural resources. Plants also provide us oxygen and absorb the harmful and toxic gases such as carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. This functions naturally without any human interaction. Besides, plant waste also contributes in producing fossil fuels which are used in various ways.
Apart from this, trees provide wood that is used for various purposes such as constructing houses, crafting furniture, making paper and producing various other big and small things that we cannot do without.
- Minerals and Metals
Metals and minerals are also used for different purposes. All of these have their unique properties and are useful in their own way. Some of the uses of minerals and metals include creating batteries, manufacturing medical equipments, manufacturing automobile parts, crafting jewellery, constructing buildings and manufacturing utensils. These resources are limited and fall under the non-renewable natural resources category.
- Sunlight, Air and Water
The importance and use of these natural resources is known to all. These are available in abundance in the atmosphere and are used directly in their pure unadulterated form by the living beings. These are also modified and used to run various processes. Fortunately, these are renewable natural resources and are replenished and replaced easily.
We consume a good amount of natural resources on a daily basis knowingly or unknowingly. While some of these are abundantly available in the atmosphere, most of these are fast depleting from earth. It is essential to use the natural resources wisely and stop any kind of wastage to ensure that these are available for our coming generations too. The government of every country must keep a check on the consumption of these resources and take measures to reduce wastage.

Natural Resources Essay – 5 (600 words)
Natural Resources are bliss for the mankind as well as other living organisms. These form an essential part of our lives. In fact, life on earth wouldn’t be possible without most of these natural resources.
Distribution of Natural Resources
Natural resources are distributed unevenly on Earth. Different parts of the planet are rich in different kinds of natural resources. While some places receive abundance of sunlight others remain devoid of the same for most part of the year. Similarly, while certain places have numerous water bodies others have rich mineral fields. There are many factors that influence uneven distribution of natural resources. Climate and land type are among the main factors.
Countries that boast of rich reserves of natural resources include China, Iraq, Venezuela, Russia, Saudi Arabia, United States of America, Canada and Brazil. Here is a look at the natural resources these countries are rich in:
Russia ranks number one when it comes to natural resources. The country boasts of abundance of timber, oil, natural gas, coal and gold. One of the main reasons of its economic growth is export of these valuable natural resources.
China has a rich reserve of coal, timber and various metals. It supplies these resources to various parts of the world.
Iraq is known to have a whopping 9% of the total world’s oil deposits. Besides oil, it is also rich in phosphate rock.
The country is rich in natural resources such as natural gas, iron and oil. It ranks six worldwide when it comes to oil reserves. It exports oil to many countries around the world.
- Saudi Arabia
The country encompasses the fifth largest natural gas reserve. Timber is also found in abundance in Saudi Arabia.
- United States
The United States comes on the second position when it comes to the availability of natural resources. It is known for its coal, natural gas and oil reserves and gold and copper deposits.
Canada comes on number four when it comes to the availability of natural resources. It is known for its oil deposits. It supplies oil to various countries worldwide. It is also known for its uranium, phosphate and natural gas reserves and timber production.
Brazil is the world’s second largest iron producer. It also generates a good amount of timber which is supplied to various countries worldwide. Besides, Brazil is known for its deposits of uranium and gold.
Similarly, different regions grow different kinds of fruits and vegetables and export them to other places. Same is the case with animals. All kinds of animals are not available everywhere. The raw materials they produce are thus exchanged between countries.
Impact of Uneven Distribution of Natural Resources
This uneven distribution of natural resources gives way to international trades which promotes businesses and boasts the economic growth of various countries around the world. However, it also has a downside to it. It has led to power play among the countries. Countries that have higher deposits of oil, natural gases, minerals and other natural resources control and exploit those that have fewer resources. Due to this the rich and developed countries are getting richer and the poor are getting poorer.
While natural resources are essential for us so much so that our life on earth is not possible without the existence of these resources, human beings are using these without any inhibition. They do not realise the fact that most of these resources are non-renewable and many others take thousands of years to renew. We must use natural resources wisely and avoid any kind of wastage to help our future generations enjoy the kind of comfort and luxury we enjoy.
Related Information:
Slogans on Nature
Conservation of Nature Essay
Essay on Natural Resources Depletion
Essay on Forest
Essay on Water
Speech on Nature
Speech on Natural Resources
Paragraph on Nature
Paragraph on Natural Resources
Speech on Depletion of Natural Resources in India
Essay on Conservation of Natural Resources
Essay on Renewable Energy
Related content
Talk to our academic expert!
Language --- English Hindi Marathi Tamil Telugu Malayalam
Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
- CBSE Revision Notes
- Chapter 14: Natural Resources
Revision Notes For Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Revision notes for class 9 chapter 14 natural resources is given here. Revision is one of the most important parts of the study. Revising the chapter will help the students to recollect the concepts what they have learned so far. Educational experts advise students to revise the topics before a night of exam so that they can develop a confidence when they will be going to write the exam. The chapter natural resources make students familiar with the various types of natural resources present in our environments like the water, the air, trees and many more.
CBSE Class 9 Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Frequently asked questions on cbse class 9 science notes chapter 14: natural resources, what is ‘acid rain’.
Any form of precipitation with acidic components, such as sulfuric or nitric acid that fall to the ground from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms is called ‘Acid rain’.
What are the ways to prevent ‘Air pollution’?
1. Reduce unnecesary usage of vehicles.2. Elimate fireplaces in houses.3. Avoid burning of lawn, leaves and use other methods for cleaning.
What is ‘Water pollution’?
Water pollution is the contamination of water sources by substances which make the water unusable for drinking, cooking, cleaning, swimming and other activities.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Nature Essay for Students and Children
500+ words nature essay.
Nature is an important and integral part of mankind. It is one of the greatest blessings for human life; however, nowadays humans fail to recognize it as one. Nature has been an inspiration for numerous poets, writers, artists and more of yesteryears. This remarkable creation inspired them to write poems and stories in the glory of it. They truly valued nature which reflects in their works even today. Essentially, nature is everything we are surrounded by like the water we drink, the air we breathe, the sun we soak in, the birds we hear chirping, the moon we gaze at and more. Above all, it is rich and vibrant and consists of both living and non-living things. Therefore, people of the modern age should also learn something from people of yesteryear and start valuing nature before it gets too late.

Significance of Nature
Nature has been in existence long before humans and ever since it has taken care of mankind and nourished it forever. In other words, it offers us a protective layer which guards us against all kinds of damages and harms. Survival of mankind without nature is impossible and humans need to understand that.
If nature has the ability to protect us, it is also powerful enough to destroy the entire mankind. Every form of nature, for instance, the plants , animals , rivers, mountains, moon, and more holds equal significance for us. Absence of one element is enough to cause a catastrophe in the functioning of human life.
We fulfill our healthy lifestyle by eating and drinking healthy, which nature gives us. Similarly, it provides us with water and food that enables us to do so. Rainfall and sunshine, the two most important elements to survive are derived from nature itself.
Further, the air we breathe and the wood we use for various purposes are a gift of nature only. But, with technological advancements, people are not paying attention to nature. The need to conserve and balance the natural assets is rising day by day which requires immediate attention.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Conservation of Nature
In order to conserve nature, we must take drastic steps right away to prevent any further damage. The most important step is to prevent deforestation at all levels. Cutting down of trees has serious consequences in different spheres. It can cause soil erosion easily and also bring a decline in rainfall on a major level.

Polluting ocean water must be strictly prohibited by all industries straightaway as it causes a lot of water shortage. The excessive use of automobiles, AC’s and ovens emit a lot of Chlorofluorocarbons’ which depletes the ozone layer. This, in turn, causes global warming which causes thermal expansion and melting of glaciers.
Therefore, we should avoid personal use of the vehicle when we can, switch to public transport and carpooling. We must invest in solar energy giving a chance for the natural resources to replenish.
In conclusion, nature has a powerful transformative power which is responsible for the functioning of life on earth. It is essential for mankind to flourish so it is our duty to conserve it for our future generations. We must stop the selfish activities and try our best to preserve the natural resources so life can forever be nourished on earth.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [ { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “Why is nature important?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Nature is an essential part of our lives. It is important as it helps in the functioning of human life and gives us natural resources to lead a healthy life.” } }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “How can we conserve nature?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “We can take different steps to conserve nature like stopping the cutting down of trees. We must not use automobiles excessively and take public transport instead. Further, we must not pollute our ocean and river water.” } } ] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Short Essay on Natural Resources 150 words in English. Natural resources are the blessings of nature to its children, living beings that have not only made our survival possible but also made our life comfortable and nourished. Some examples of natural resources are sunlight, air, timber, coal, plants, food, animals, water, natural gases, etc.
2. Abiotic - These resources include non-living natural resources such as air, water, ground, soil, minerals, and metals. Both Renewable and Non-Renewable resources are used for various purposes: Wind energy is produced by the movement of air. Water is used for drinking and hydroelectric energy production.
Essay on Natural Resources in 150 Words. The organic aspects of nature that contribute to our way of life are known as natural resources. For survival, we rely on natural resources. Natural resources include things like air, water, soil, minerals, crops, etc. Resources like minerals, oil, and other resources are found in non-living organisms ...
Natural Resources Class 9 CBSE Notes - Chapter 14. Introduction to Natural Resources Air and Air Pollution Water A natural resource Water cycle Soil Bio geo chemical cycle Carbon cycle Nitrogen Cycle Oxygen Cycle. According to the CBSE Syllabus 2023-24, this chapter has been removed from NCERT Class 9 Science textbook.
Renewable Natural Resources - These are those natural resources that are present in abundance and also renew easily. These include sunlight, water, air, soil, biomass, and wood. But among them, some resources take time to renew like the wood and soil. In addition, they are derived from living things as well as non-living things.
Simply put, everything taken from the Earth is considered a natural resource. Sunlight, water, coal, natural gas, minerals, and even air play a role. Everything included here is regarded as a natural resource. These resources are necessary for the survival of life on earth. Energy is one of the most important products of resources and we humans ...
Class 9. Overview. Learn Videos. Existence of Life on Earth. 7 mins. Study Materials Natural Resources Essay for Students and Children | 500+ Words Essay Natural Resources in Process of Development & Environment Degradation Essay on Conservation of Natural Resources for Students in 500 Words. Quick summary with Stories.
Study Material and Notes of Ch 14 Natural Resources Class 9th Science. → Life on earth depends on resources like soil, water, air and energy from sun. → Uneven heating of air over land and water-bodies causes winds. → Evaporation of water from water-bodies and subsequent condensation give us rain. → Pollution of air, water and soil ...
Essay on Natural Resources. Natural resources are the treasures that Mother Earth has bestowed upon us. They include water, air, soil, minerals, and all living things. In this essay, we will delve into the importance of these resources, their sustainable use, and the vital role they play in our lives and the health of our planet.
Therefore, types of natural resources according to Class 9 Science Chapter 14 notes are forest, minerals, animals, air, soil, water and soil. Download the free PDF now. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. They can download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise ...
The following are the important topics that are discussed in chapter 14, natural resources for class 9 students. Introduction to natural resources. Introduction to air. Introduction to air pollution. Ozone layer and its depletion. Water: A Wonder Liquid. Water pollution. Mineral Riches in the Soil. Biogeochemical Cycles: Carbon cycle and ...
Define the Conservation of Nature. Natural resources on Earth include minerals, air, water, soil and wildlife. It contains genes, ecosystems, diversity of species and functions of the environment. It is impossible to exist on this planet without these natural resources. Conservation of nature means taking care of and protecting these resources ...
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources: Natural Resources. The Breath of Life: Air. Water: A Wonder Liquid. Mineral Riches in the Soil. Biogeochemical Cycles. Ozone Layer. These solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science. Here we have given Class 9 NCERT Science Textbook Solutions for Chapter 14 ...
Natural Resources is one of the most important chapters in today's time in class 9. It is so because the deteriorating condition of our planet earth needs awareness. This chapter does exactly the same. In other words, it makes students aware of the importance of natural resources on earth. This way, we will be able to produce more conscious ...
8. Explain the physical, chemical and biological factors which lead to the formation of soil. (4) Download free CBSE Sample paper for Class 9, Biology. A collection of questions on CBSE- Natural Resources with solutions created by best teachers are available as a PDF download.
Conservation of nature means the preservation of forests, land, water bodies, and minerals, fuels, natural gases, etc. And to make sure that all these continue to be available in abundance. Thus all these natural resources make life worth living on Earth. Life would not be imaginable without air, water, sunlight as well as other natural ...
The Class 9 Science Notes for Natural Resources include concept mapping and revision notes for all topics taught in the class 9 Science textbook in this particular unit. In addition there are important questions for class 9 Science Natural Resources - very short, short, long answer type for you to practise.
Types of Natural Resources. 1. Inexhaustible Natural Resources. These resources are abundant and not likely to be depleted despite continuous use. Examples include: Air: The Earth's atmosphere, composed mainly of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide, is an inexhaustible resource.
Natural resources, the abundant treasures bestowed upon our planet, encompass everything from air and water to minerals and biodiversity. These resources, essential for sustaining life, economic development, and environmental balance, face unprecedented threats. The unrelenting pace of exploitation and the onslaught of pollution have raised ...
Thus if you are studying 9th class Science, then the Natural Resources notes will help you easily understand the topic and ace it. Natural Resources Notes for Class 9 Science. Natural Resources is a critical part in the study of Science. In India, it is taught in 9th class.
Natural Resources Essay - 2 (300 words) Introduction. Natural resources are the resources that are made available by nature. Man does not have to work to derive these resources. Some of the examples of natural resources include water, air, sunlight, wood, minerals and natural gases.
Revision notes for class 9 chapter 14 natural resources is given here. Revision is one of the most important parts of the study. Revising the chapter will help the students to recollect the concepts what they have learned so far. Educational experts advise students to revise the topics before a night of exam so that they can develop a ...
500+ Words Nature Essay. Nature is an important and integral part of mankind. It is one of the greatest blessings for human life; however, nowadays humans fail to recognize it as one. Nature has been an inspiration for numerous poets, writers, artists and more of yesteryears. This remarkable creation inspired them to write poems and stories in ...